Biological leaching process for separating out metal ions from waste battery directly
A waste battery, biological leaching technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of high processing cost, large investment, large acid consumption, etc., and achieve high metal dissolution rate, good application prospect and low processing cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Taking chemical extraction and bioleaching to compare the leaching efficiency of metals in three kinds of waste batteries (nickel-cadmium batteries, zinc-manganese batteries, and lithium-ion batteries) as an example, the specific operations are as follows:
[0033] 1) Disassemble the used battery to remove single components such as copper cap, aluminum foil, zinc foil, film, carbon rod, etc., collect the positive and negative electrode materials of the battery with complex composition and the most concentrated metal content, carefully crush them into powder, and pass through a 20-mesh sieve and bottled for later use;
[0034] 2) Prepare, inoculate, and shake several bottles of 100mL culture solution according to the conditions of the acid-producing culture solution. When the pH drops to 2.0, add 1.0g of the electrode mixture material that has been peeled off and put it into the shaker for bioleaching. Add the specified battery at the initial pH value, and then cultivate...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Taking the treatment of waste zinc-manganese batteries by bioleaching technology as an example, the specific operations are as follows:
[0039] 1) same example 1(1);
[0040] 2) Prepare, inoculate and shake several bottles of 100mL culture solution according to the conditions of the acid-producing culture solution (the concentration of sulfur powder is 2.0g / L, 3.0g / L, 4.0g / L respectively). (2.0, 3.0, 4.0), add the specified battery (0.5g, 1.0g, 1.5g), and then cultivate it at a certain temperature (27°C, 35°C, 42°C);
[0041] 3) regularly sample and measure the pH change of the solution and the metal ion concentration change in the solution;
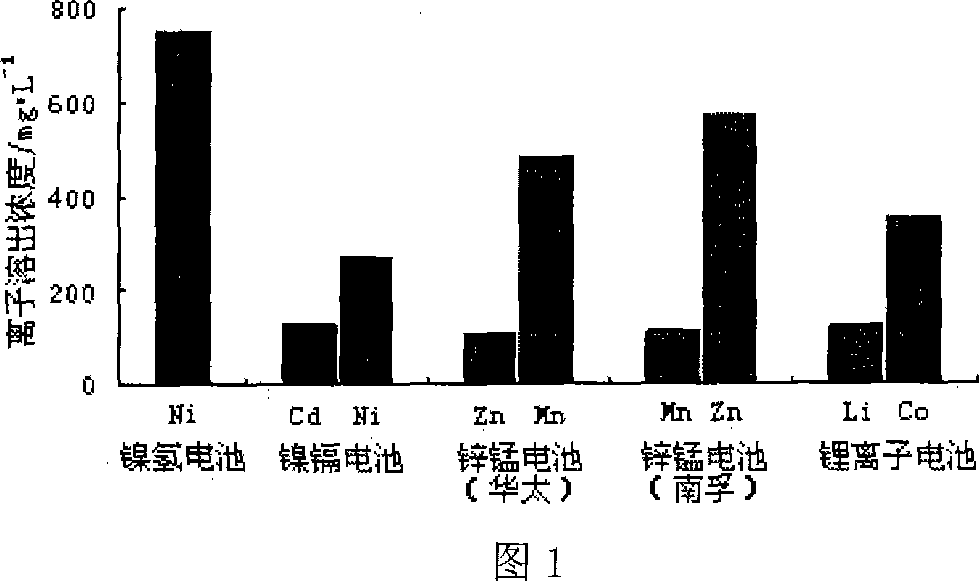
[0042] 4) The experimental results show that when the pH value is 2.0, the sulfur powder concentration is 4.0g / L, and the battery dosage is 1.0g, the dissolution concentrations of zinc and manganese ions in waste zinc-manganese batteries are 500mg / L and 800mg / L respectively. L. While at pH 1.0, the dissolution concentrations o...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Taking the use of bioleaching technology to treat waste nickel-metal hydride batteries as an example, the specific operations are as follows:
[0045] 1)-3) Same example 2(3);
[0046] 4) The results show that: when the pH value is 2.0, the sulfur powder concentration is 4.0g / L, and the battery dosage is 1.0g, the nickel dissolution concentration in the positive electrode material in the waste nickel-hydrogen battery is 1938mg / L respectively. At pH 1.0, the dissolution concentration of nickel in the positive electrode material is 4976mg / L, and the dissolution concentration of cobalt is 240mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com