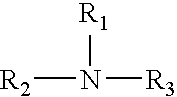Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
271 results about "Tungsten Compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inorganic compounds that contain tungsten as an integral part of the molecule.
Infrared shielding material microparticle dispersion infrared shield, process for producing infrared shield material microparticle and infrared shielding material microparticle
ActiveUS20060178254A1Improve featuresEffective shieldingPigmenting treatmentTungsten oxides/hydroxidesArgon atmosphereRoom temperature
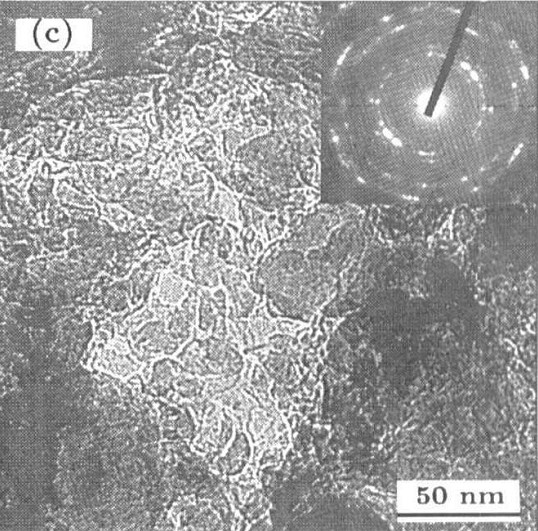
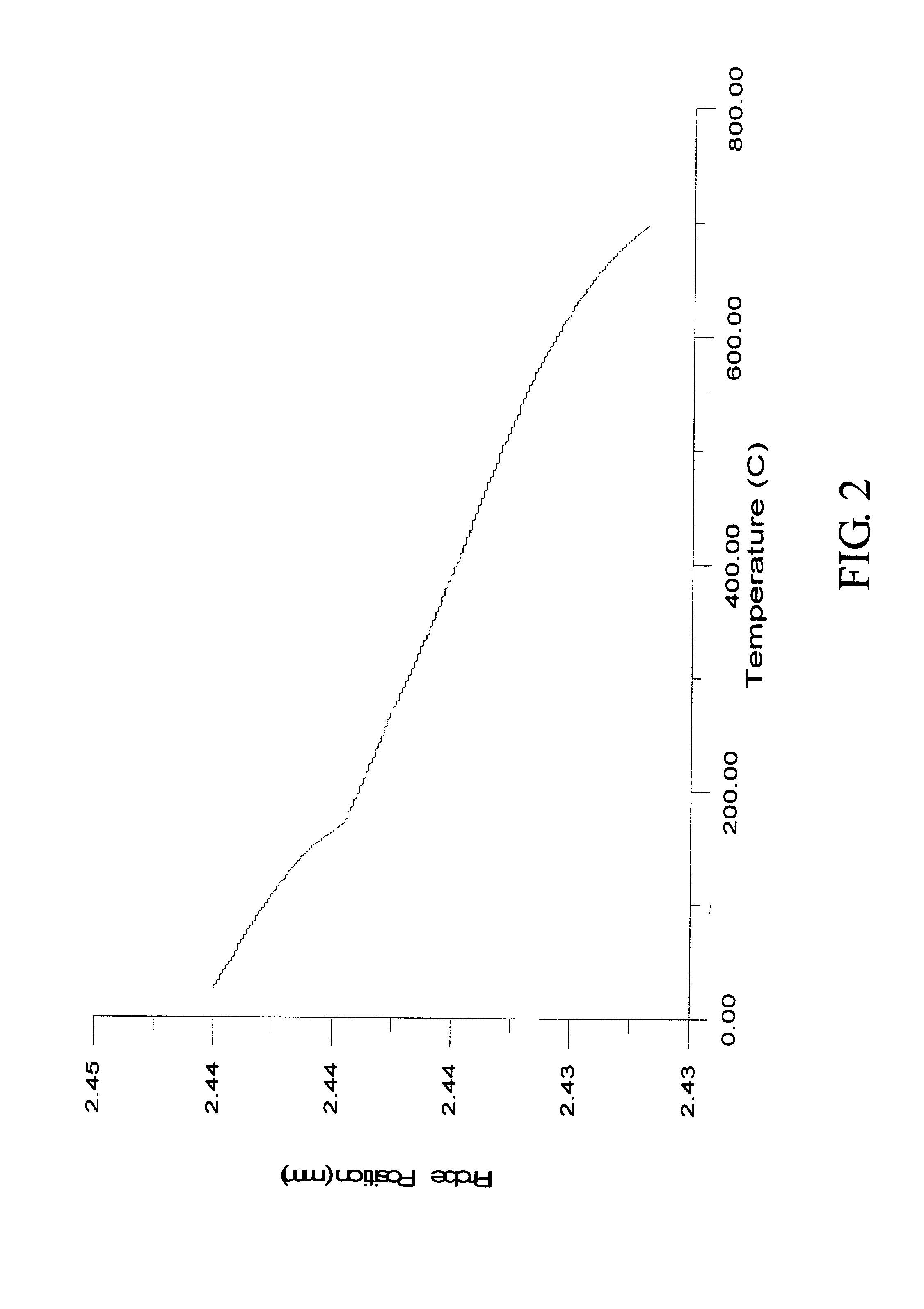
To provide an infrared-shielding body sufficiently transmitting visible rays, having no half-mirror shaped appearance, requiring no large-scale apparatus when forming a film on a substrate, efficiently shutting invisible near-infrared rays with wavelength range of 780 nm or more, while eliminating a heat treatment at high temperature after film formation, and having a spectral characteristic such as transparency with no change of color tone. The starting material, which is a mixture containing a predetermined amount of a tungsten compound, is heated at 550° C. in a reductive atmosphere for 1 hour, then cooled to room temperature once in an argon atmosphere, thus producing powder of W18O49. Then, the powder, the solvent, and the dispersant are mixed, then subjected to dispersion treatment to obtain a dispersion solution. The dispersion solution and a UV-curable hardcoat resin are mixed to obtain a solution of fine particle dispersion of infrared-shielding material. The solution of the fine particle dispersion of infrared-shielding material is applied on a PET resin film to form a film, which is then cured, and an infrared-shielding film having a transmission profile shown in the figure is thereby obtained.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
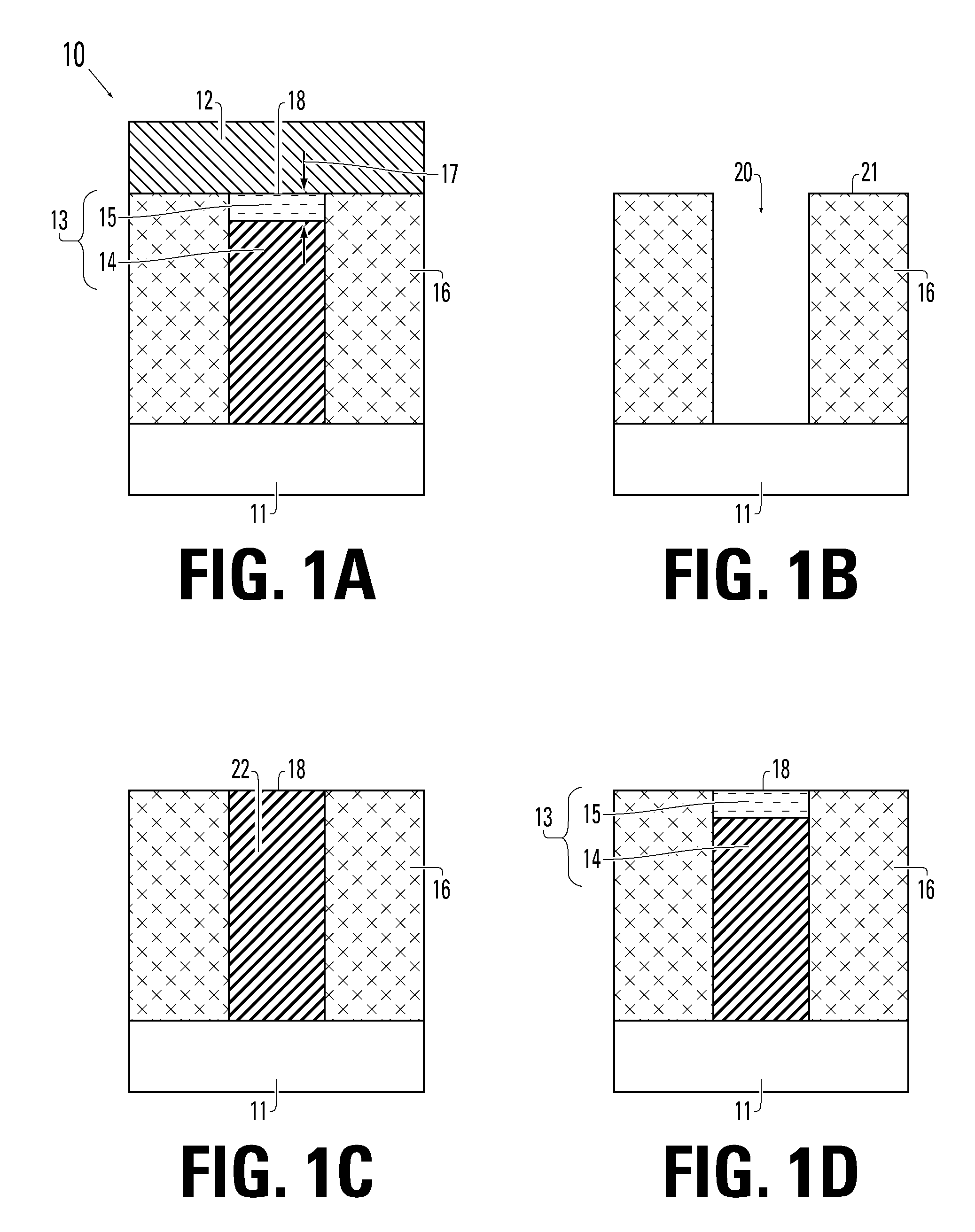
Resistance memory with tungsten compound and manufacturing
Memory devices based on tungsten-oxide memory regions are described, along with methods for manufacturing and methods for programming such devices. The tungsten-oxide memory region can be formed by oxidation of tungsten material using a non-critical mask, or even no mask at all in some embodiments. A memory device described herein includes a bottom electrode and a memory element on the bottom electrode. The memory element comprises at least one tungsten-oxygen compound and is programmable to at least two resistance states. A top electrode comprising a barrier material is on the memory element, the barrier material preventing movement of metal-ions from the top electrode into the memory element.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
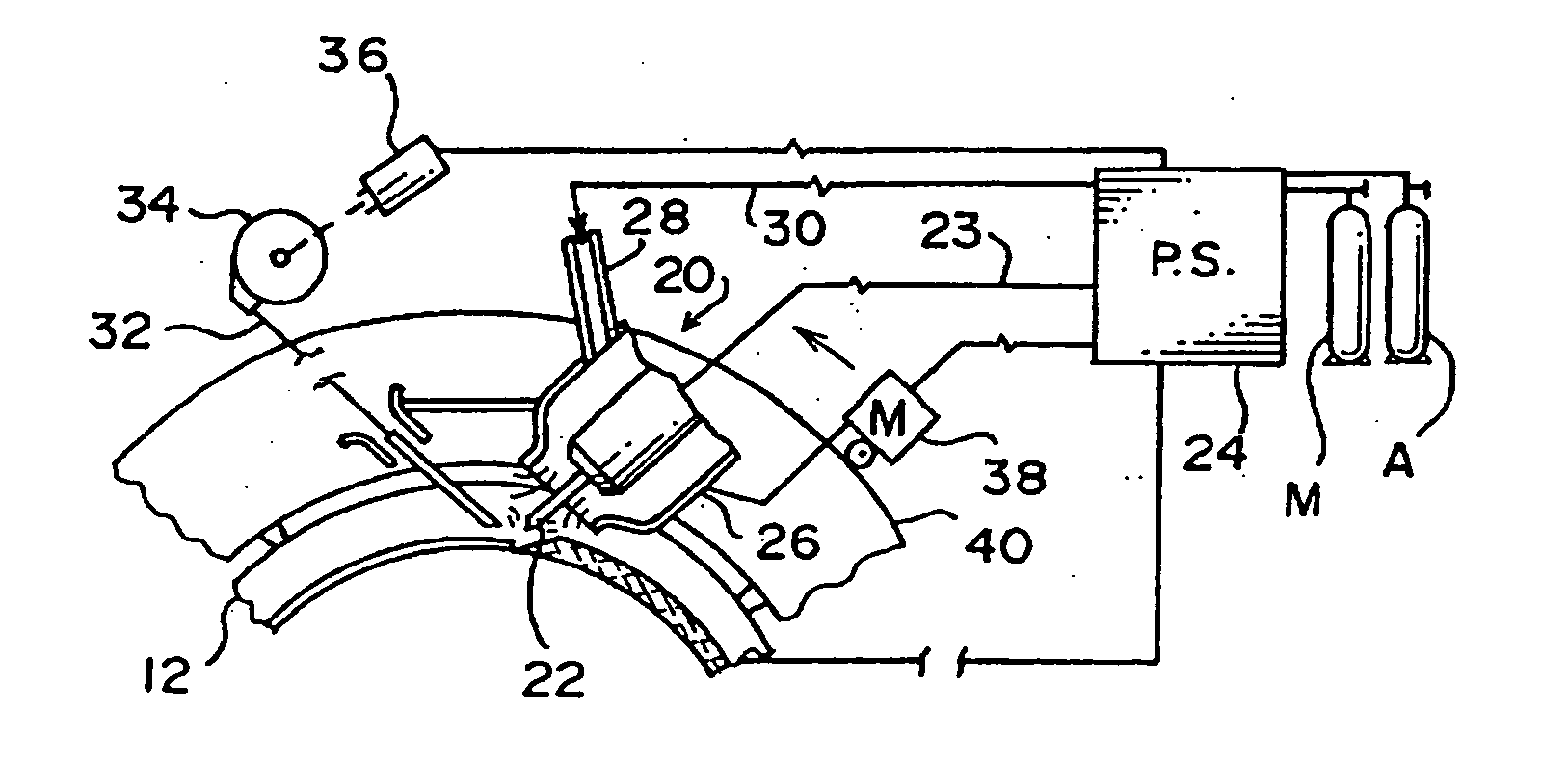
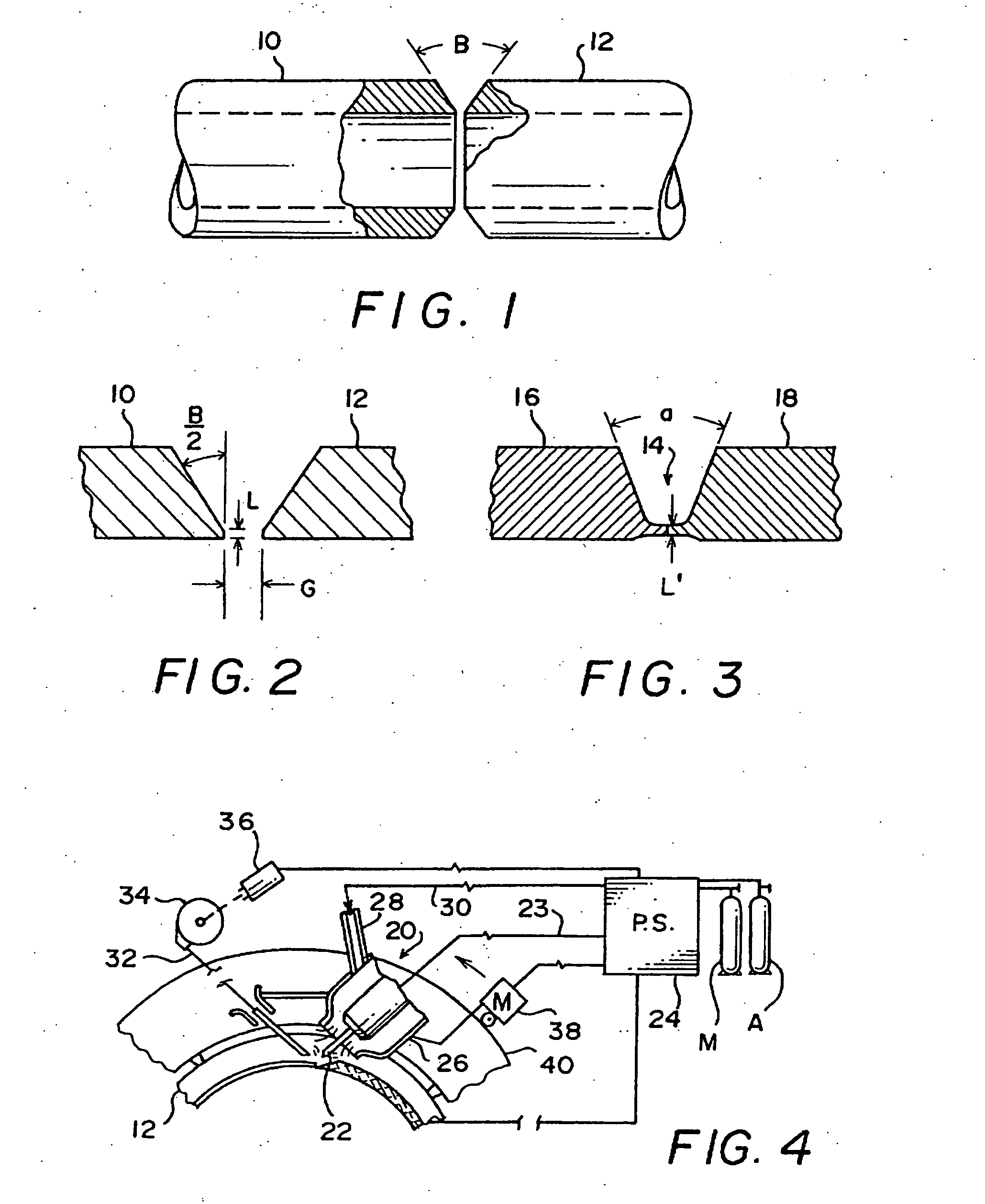
Process for welding
InactiveUS7170032B2Long electrode lifeEvacuating shieldingWelding/cutting media/materialsElastomerShielding gas
A welding process for non-stainless steel workpieces using GTAW equipment and hydrogen containing shield gas on a first root pass is improved by using a shield gas delivery system comprising hoses or conduits made of elastomeric material having a moisture permeability coefficient of less that 275, preferably less than 100, and using a tungsten electrode composition comprising at least tungsten and lanthanum oxide, and preferably tungsten, lanthanum oxide, yttrium oxide and zirconium oxide. Preventing moisture permeation through the elastomeric hoses delivering hydrogen containing shield gas eliminates expulsion of fused weld metal during second pass filler welding over the root pass weld. Electrode life is enhanced using the tungsten compounds.
Owner:JV IND CO LLC
Process for welding
InactiveUS20050109735A1Long electrode lifeEvacuating shieldingWelding/cutting media/materialsElastomerShielding gas
A welding process for non-stainless steel workpieces using GTAW equipment and hydrogen containing shield gas on a first root pass is improved by using a shield gas delivery system comprising hoses or conduits made of elastomeric material having a moisture permeability coefficient of less that 275, preferably less than 100, and using a tungsten electrode composition comprising at least tungsten and lanthanum oxide, and preferably tungsten, lanthanum oxide, yttrium oxide and zirconium oxide. Preventing moisture permeation through the elastomeric hoses delivering hydrogen containing shield gas eliminates expulsion of fused weld metal during second pass filler welding over the root pass weld. Electrode life is enhanced using the tungsten compounds.
Owner:JV IND CO LLC
Polymerizable composition, and photosensitive layer, permanent pattern, wafer-level lens, solid-state imaging device and pattern forming method each using the composition
InactiveUS20120068292A1Efficient processIncreased durabilityPhotosensitive materialsLayered productsAcetophenonePolymerization
A polymerizable composition contains (A) a polymerization initiator that is an acetophenone-based compound or an acylphosphine oxide-based compound, (B) a polymerizable compound, (C) at least either a tungsten compound or a metal boride, and (D) an alkali-soluble binder.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
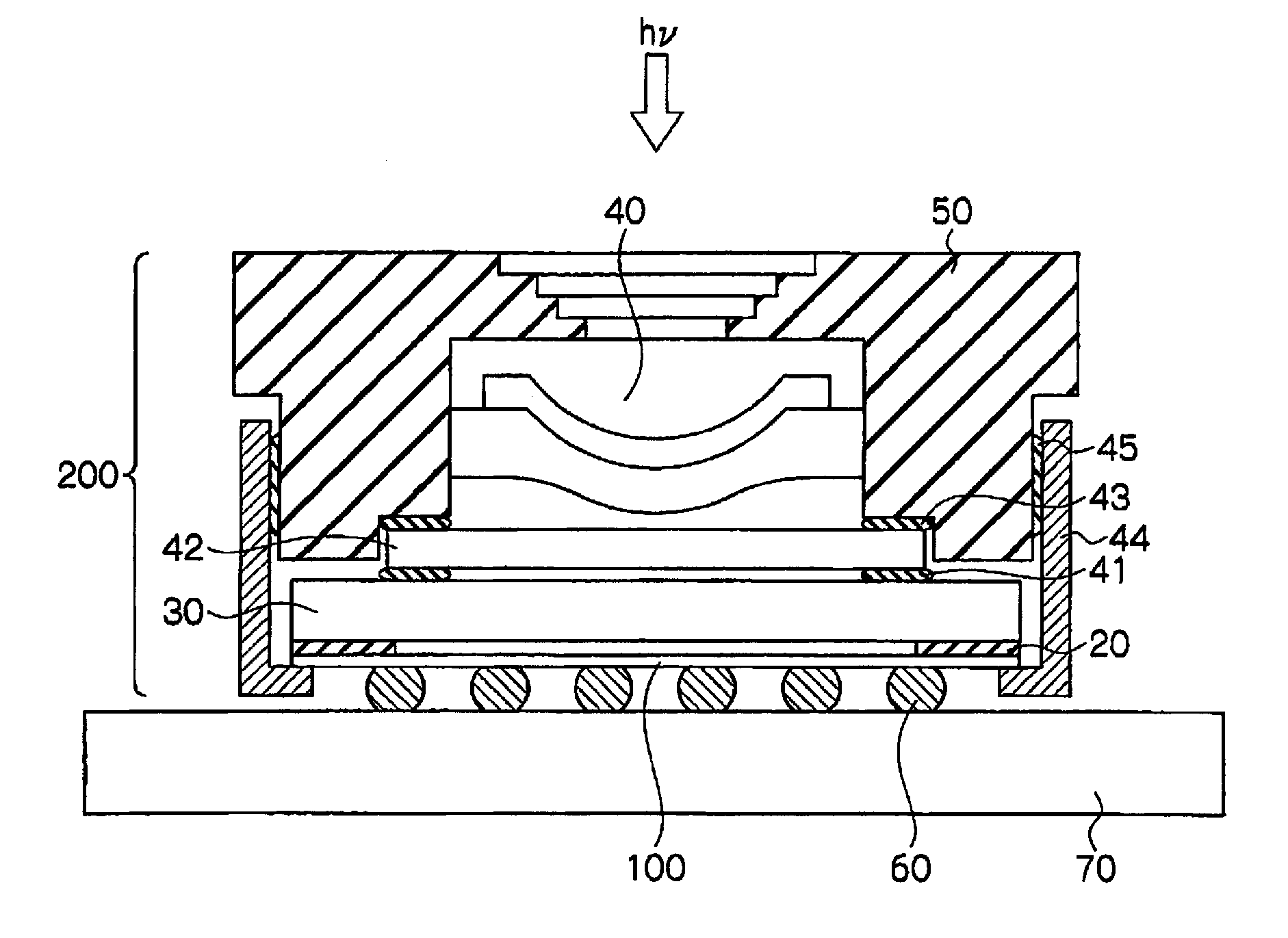
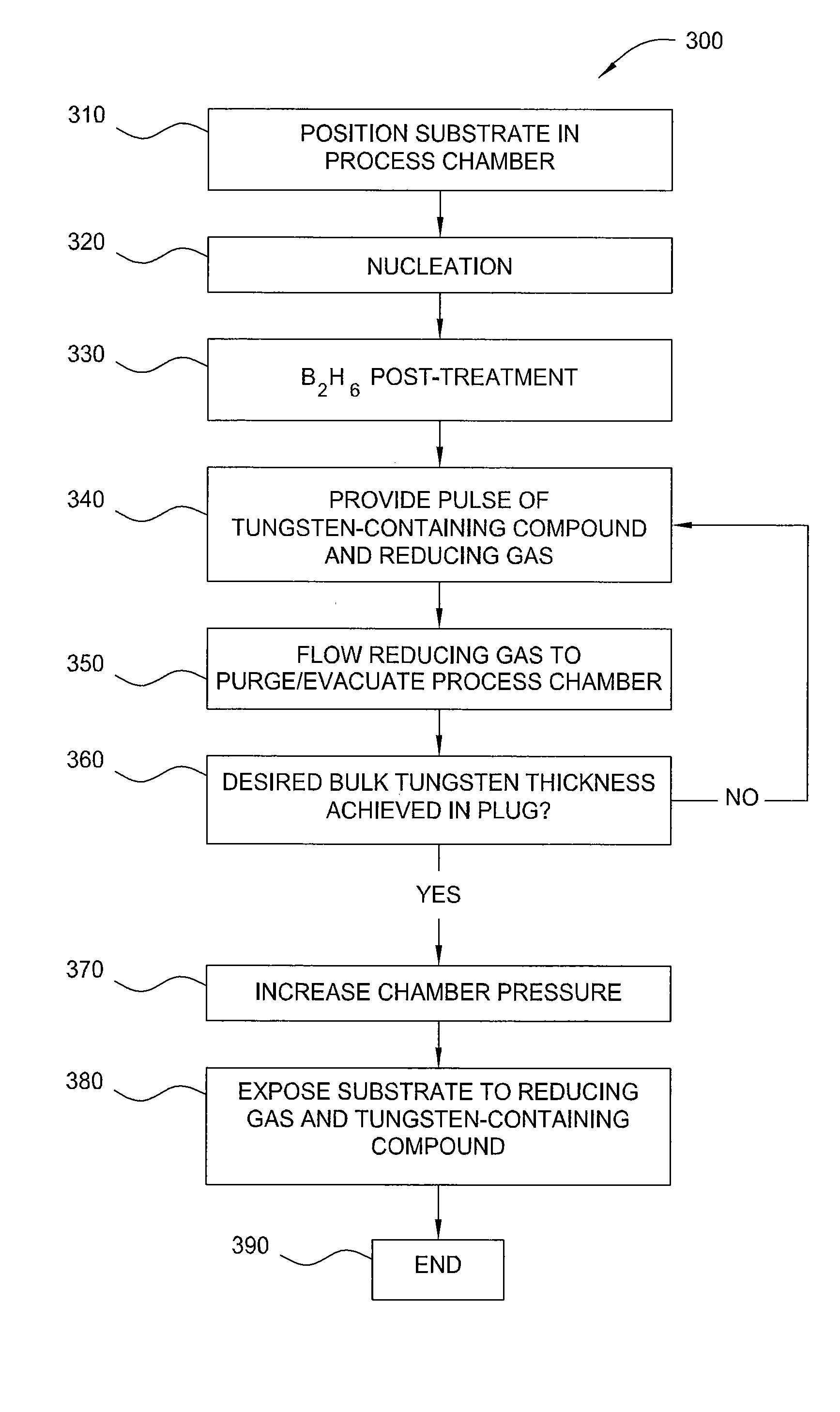
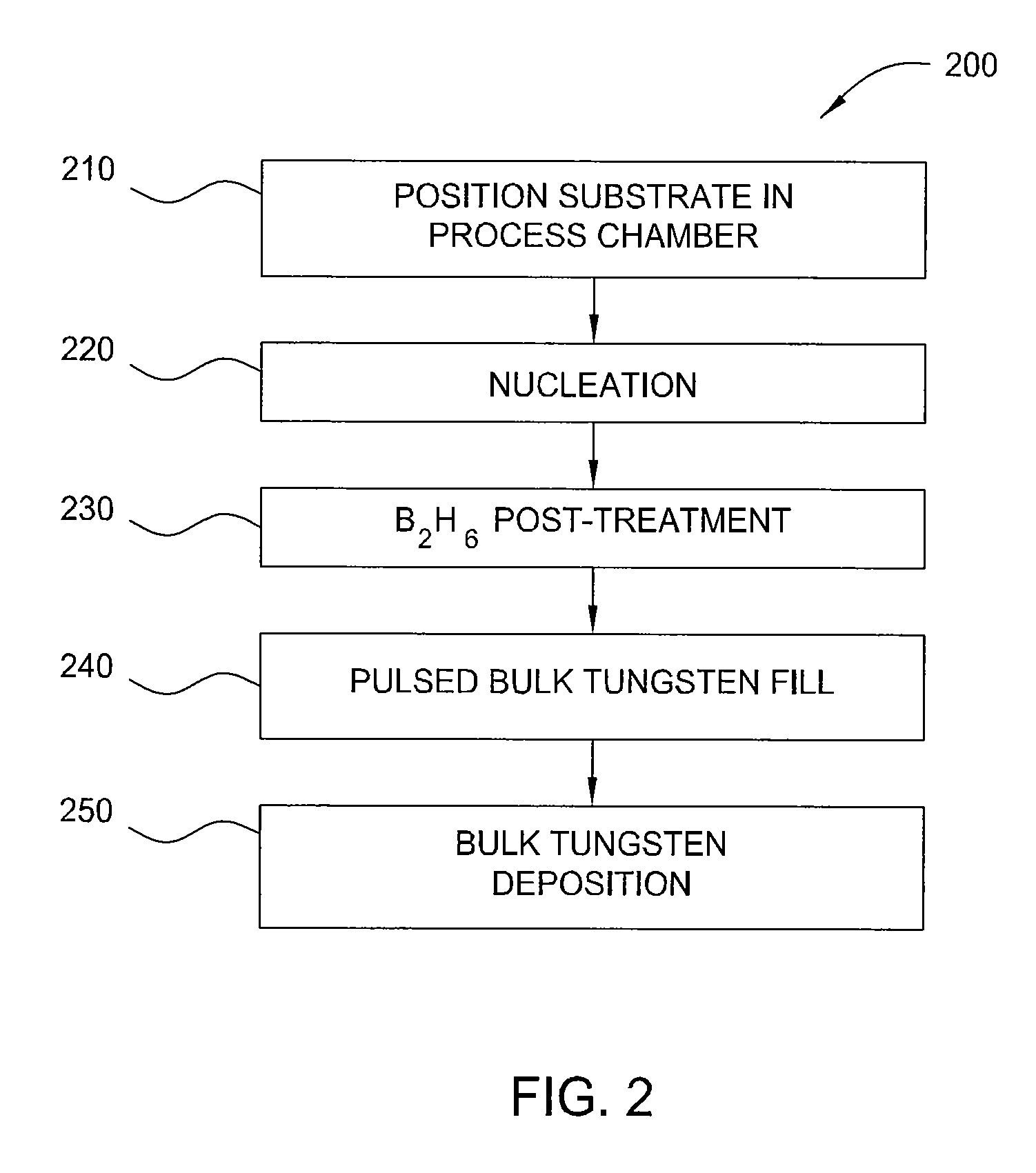
Method of depositing tungsten film with reduced resistivity and improved surface morphology
InactiveUS20100167527A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingContinuous flowSubstrate surface
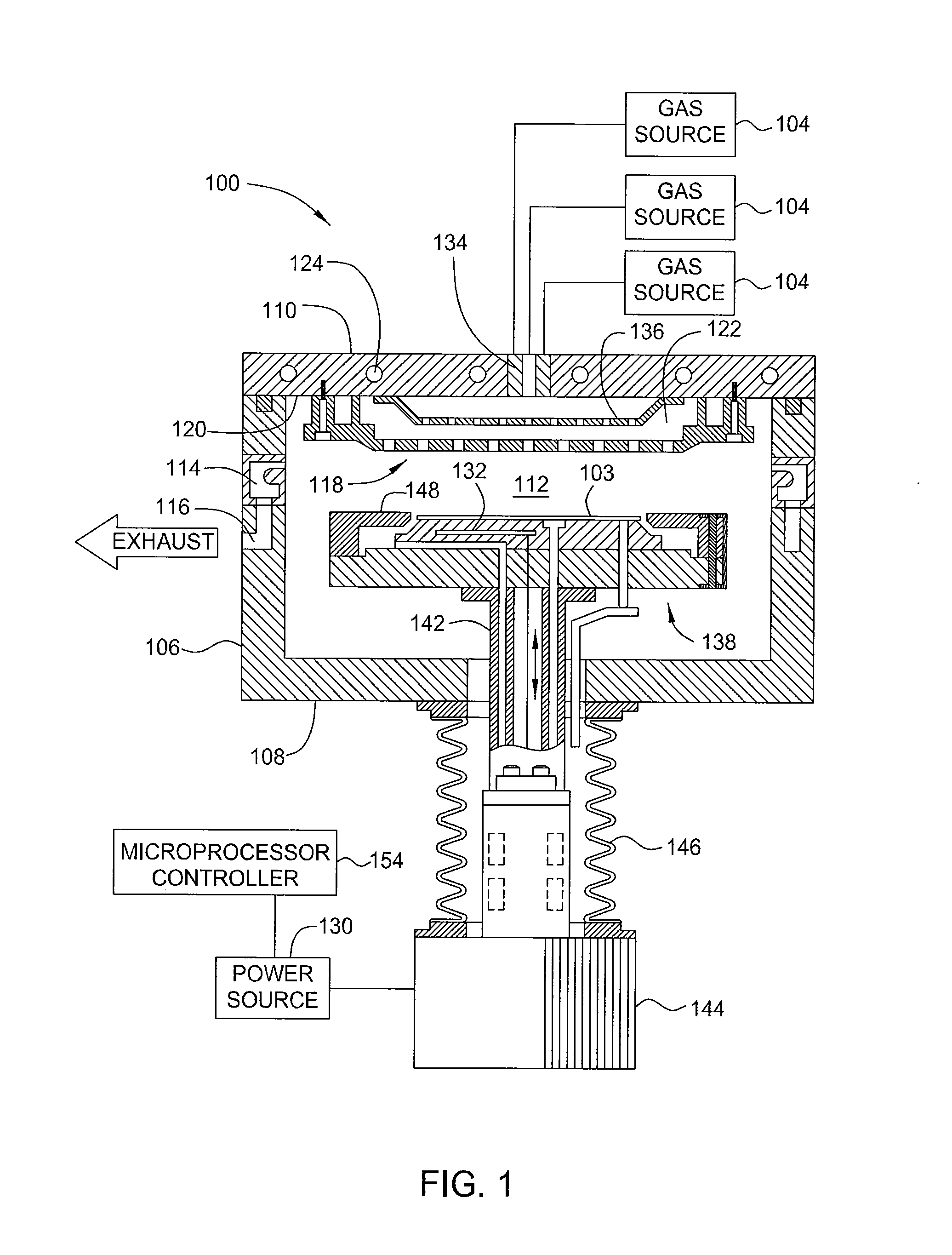
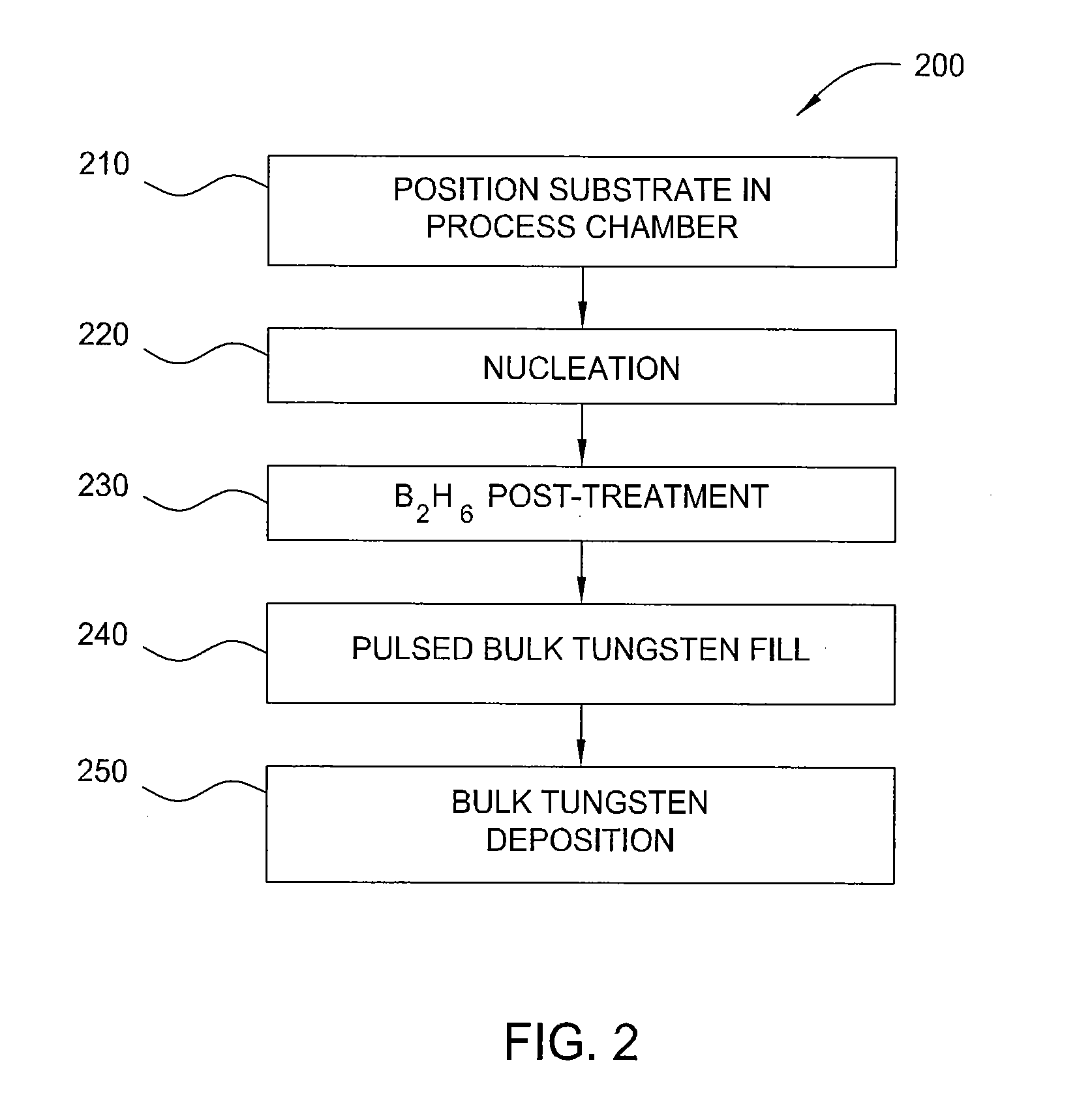
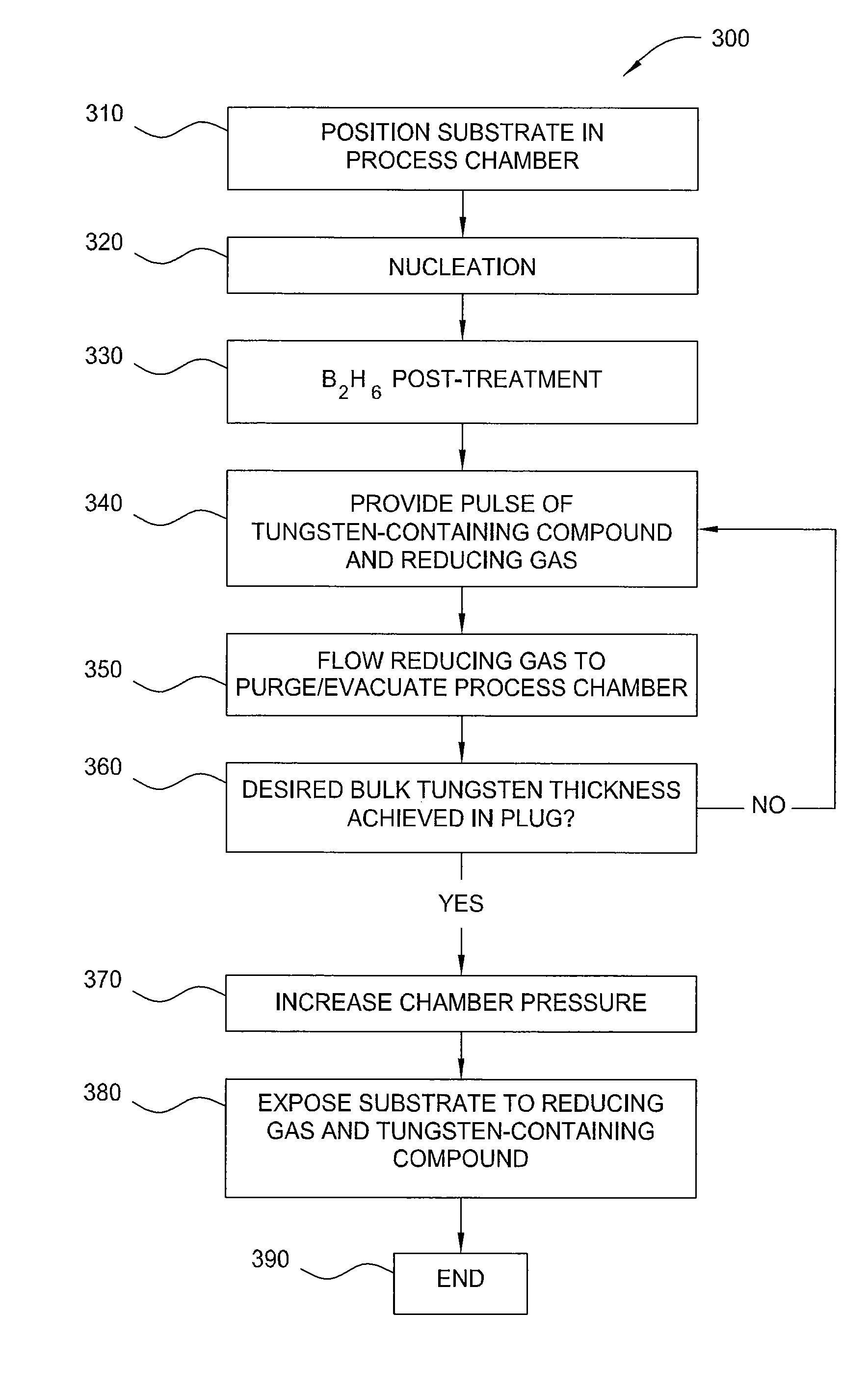
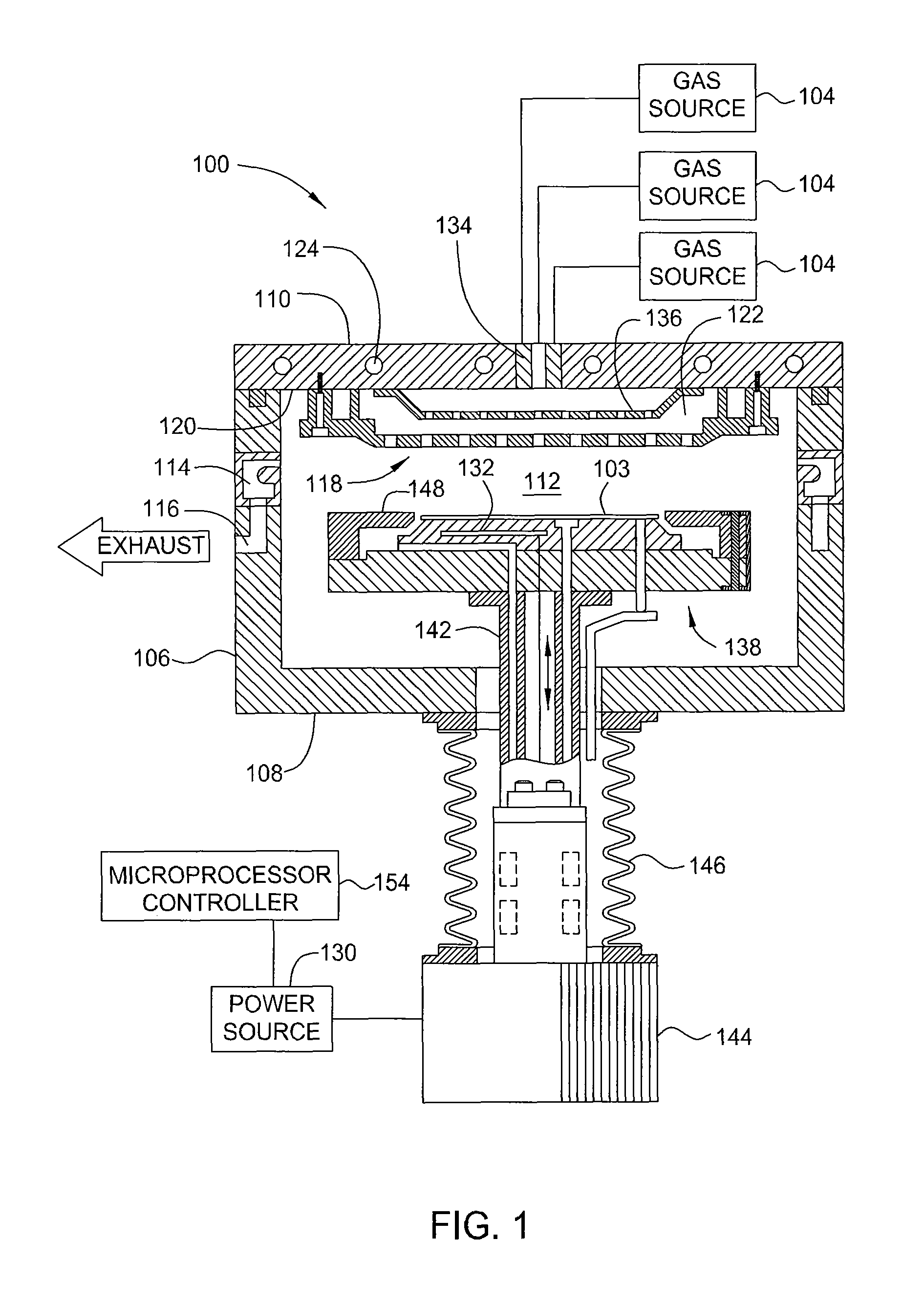
A method of controlling the resistivity and morphology of a tungsten film is provided, comprising depositing a first film of a bulk tungsten layer on a substrate during a first deposition stage by (i) introducing a continuous flow of a reducing gas and a pulsed flow of a tungsten-containing compound to a process chamber to deposit tungsten on a surface of the substrate, (ii) flowing the reducing gas without flowing the tungsten-containing compound into the chamber to purge the chamber, and repeating steps (i) through (ii) until the first film fills vias in the substrate surface, increasing the pressure in the process chamber, and during a second deposition stage after the first deposition stage, depositing a second film of the bulk tungsten layer by providing a flow of reducing gas and tungsten-containing compound to the process chamber until a second desired thickness is deposited.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Process for regenerating a catalyst
InactiveUS20080214384A1Reduced activityIncreased space-time yieldInorganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsAcroleinGlycerol
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Solution composition and method for electroless deposition of coatings free of alkali metals
InactiveUS6911067B2Low costImprove anti-corrosion performanceAnti-corrosive paintsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroless depositionMaterials science
An electroless deposition solution of the invention for forming an alkali-metal-free coating on a substrate comprises a first-metal ion source for producing first-metal ions, a pH adjuster in the form of a hydroxide for adjusting the pH of the solution, a reducing agent, which reduces the first-metal ions into the first metal on the substrate, a complexing agent for keeping the first-metal ions in the solution, and a source of ions of a second element for generation of second-metal ions that improve the corrosion resistance of the aforementioned coating. The method of the invention consists of the following steps: preparing hydroxides of a metal such as Ni and Co by means of a complexing reaction, in which solutions of hydroxides of Ni and Co are obtained by displacing hydroxyl ions OH− beyond the external boundary of ligands of mono- or polydental complexants; preparing a complex composition based on a tungsten oxide WO3 or a phosphorous tungstic acid, such as H3[P(W3O10)4], as well as on the use of tungsten compounds for improving anti-corrosive properties of the deposited films; mixing the aforementioned solutions of salts of Co, Ni, or W and maintaining under a temperatures within the range of 20° C. to 100° C.; and carrying out deposition from the obtained mixed solution.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Method of depositing tungsten film with reduced resistivity and improved surface morphology
InactiveUS8071478B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingThin membraneElectric resistivity
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Teeth spherical heavy oil hydrotreating catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101497044AAchieve technical effectLarge specific surface areaMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrocarbon oils treatmentHydrodesulfurizationReaction temperature
The invention discloses a dentiform sphere shaped heavy oil hydrotreated catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst comprises an active composition, an addition agent and a dentiform sphere shaped aluminum oxide carrier, wherein the active composition comprises compounds of cobalt and nickel, and a compound of molybdenum or / and tungsten; the addition agent comprises a compound of phosphor, silicon, boron or halogen or compounds of any two compositions of the phosphor, the silicon, the boron and the halogen; and compositions according to gross weight of the dentiform sphere shaped heavy oil hydrotreated catalyst comprise: 2 to 6 percent of the cobalt compound, 3 to 10 percent of the nickel compound, 0 to 26 percent of the molybdenum compound, 0 to 8 percent of the tungsten compound, and 0.5 to 2 percent of the addition agent. The catalyst has the characteristics of high specific surface area, large pore volume, high strength, proper surface acid content, small bed pressure drop, low reaction temperature and high activity of hydrodesulfurization and denitrification. The preparation method comprises preparation of a precursor substance of the aluminum oxide carrier, preparation of the dentiform sphere shaped aluminum oxide carrier, preparation of a catalyst steeping fluid and preparation of the catalyst. The preparation process can be mastered and realized simply and easily.
Owner:BEIJING GAOXIN LIHUA TECH CO LTD
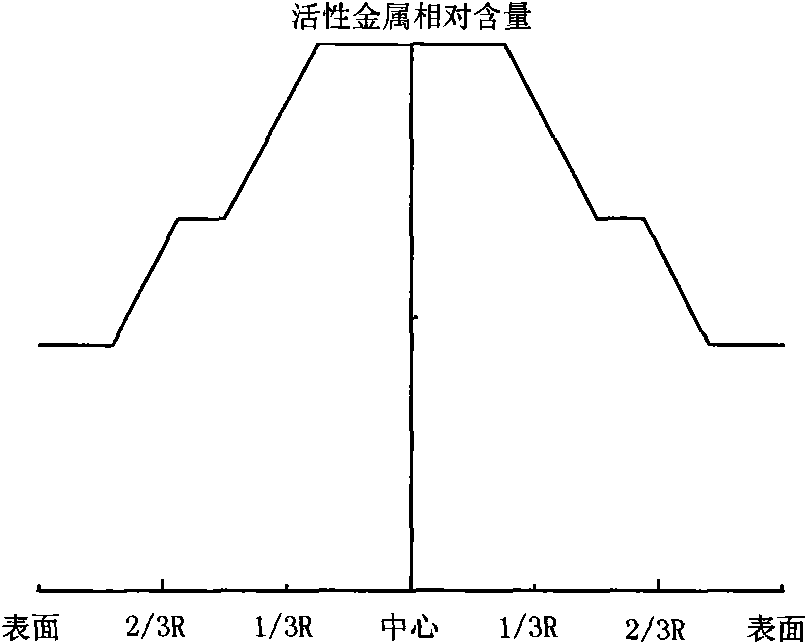
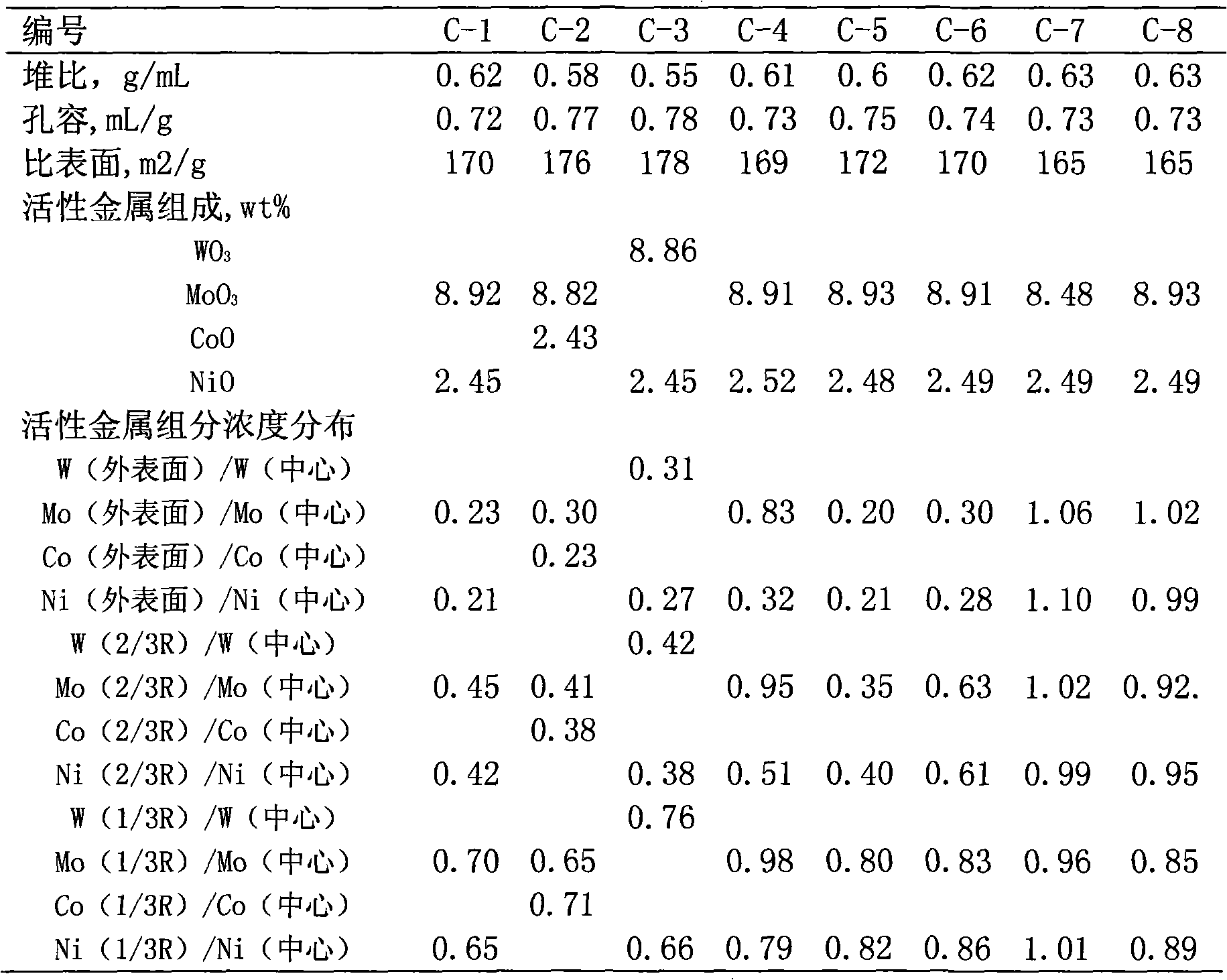
Hydrogenation catalyst with gradient-decreasing-distributed active metal constituent concentration and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101927196AGood demetallizationGood charcoal removalCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSal ammoniacAmmonia
The invention relates to a hydrogenation catalyst with gradient-decreasing-distributed active metal constituent concentration and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by using Al2O3 or Al2O3 containing SiO2, TiO2 and ZrO2 as the carrier, mixing molybdenum and / or tungsten compounds and / or nickel and / or cobalt compounds with deionized water or ammonia water to obtain a metal dipping solution; preparing a thicker metal dipping solution dipping carrier, and gradually adding deionized water or ammonia water to dilute the metal dipping solution saturated spray carrier, or preparing metal dipping solutions with at least two different concentrations; and drying at 80-150 DEG C for 1-8 hours, and roasting in the air at 300-650 DEG C for 2-6 hours. The catalyst contains 1.0-10.0 wt% of molybdenum and / or tungsten oxides and / or 0.2-5.0 wt% of cobalt and / or nickel oxides. The hydrogenation catalyst has favorable activities of demetallization, carbon residue removal, devulcanization and denitrification, has the advantages of high stability, simple preparation and low cost, and is used for hydrogenating heavy-weight oil.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
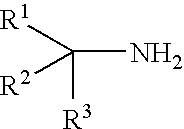
Amine Tungstates and Lubricant Compositions
ActiveUS20070042917A1Improved deposit controlPromote oxidationAdditivesMolybdenum sulfidesTungstateAntioxidant
This invention relates to lubricating oil additives, and to lubricating oil compositions, their method of preparation, and use. More specifically, this invention relates to several novel lubricating oil additives and compositions which contain a tungsten compound and an antioxidant, namely aminic antioxidants such as a secondary diarylamine or an alkylated phenothiazine. The use of the tungsten compound with the secondary diarylamine and / or the alkylated phenothiazine provides improved oxidation and deposit control to lubricating oil compositions. The lubricating oil compositions of this invention are particularly useful as crankcase and transmission lubricants, gear oils and other high performance lubricant applications.
Owner:KING INDUSTRIES INC
Resistance memory with tungsten compound and manufacturing
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Electrodeposition paint
InactiveUS20070149655A1Improve corrosion resistanceExcellent finished appearanceSurface reaction electrolytic coatingPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsBismuth hydroxideMetal
This invention provides an electrodeposition paint comprising particles of at least one metallic compound selected from bismuth hydroxide, zirconium compound and tungsten compound, said particles of the metallic compound having an average particle diameter of 1-1,000 nm. The electrodeposition paint forms coating film excelling in corrosion resistance, finished appearance, paint stability and so on.
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
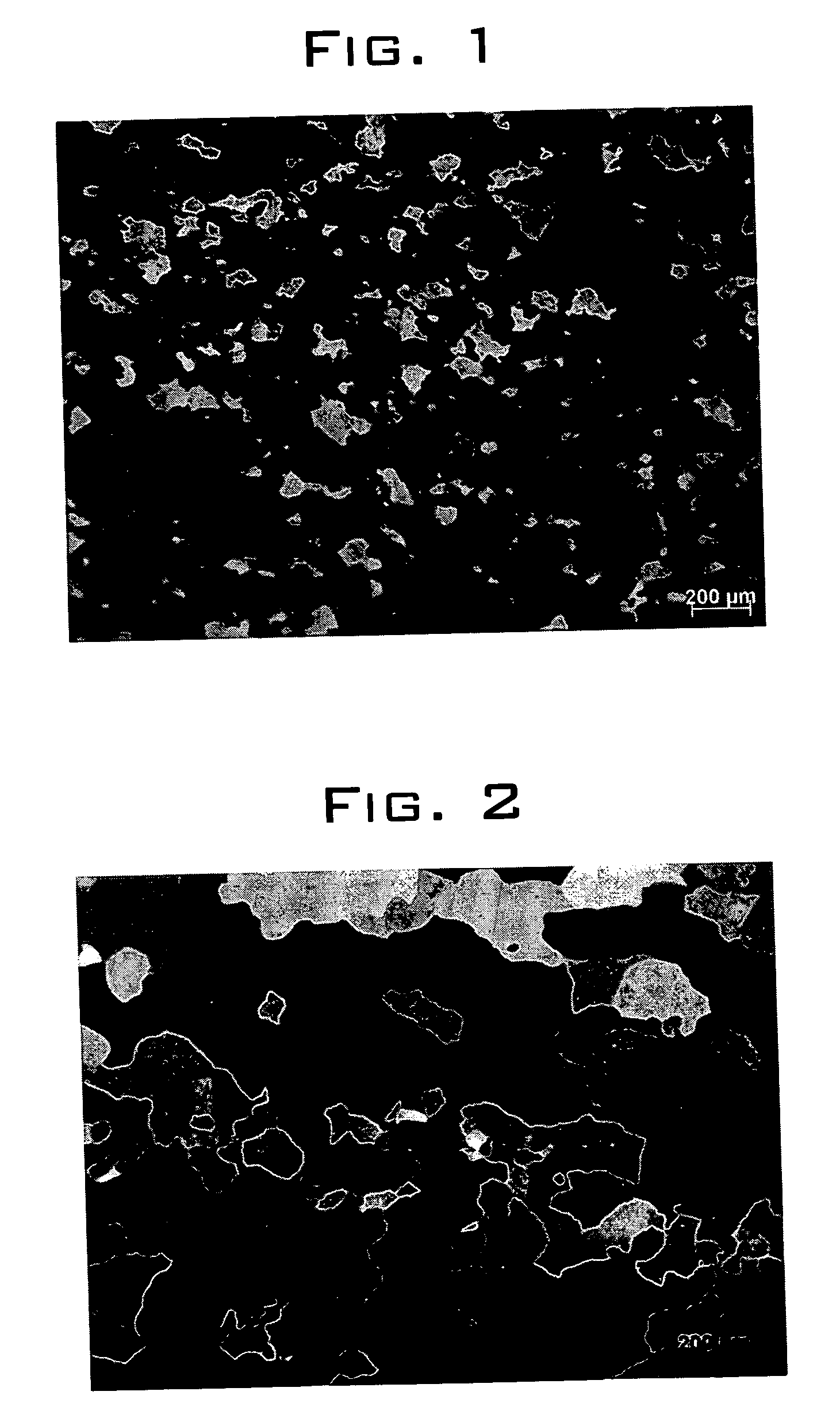
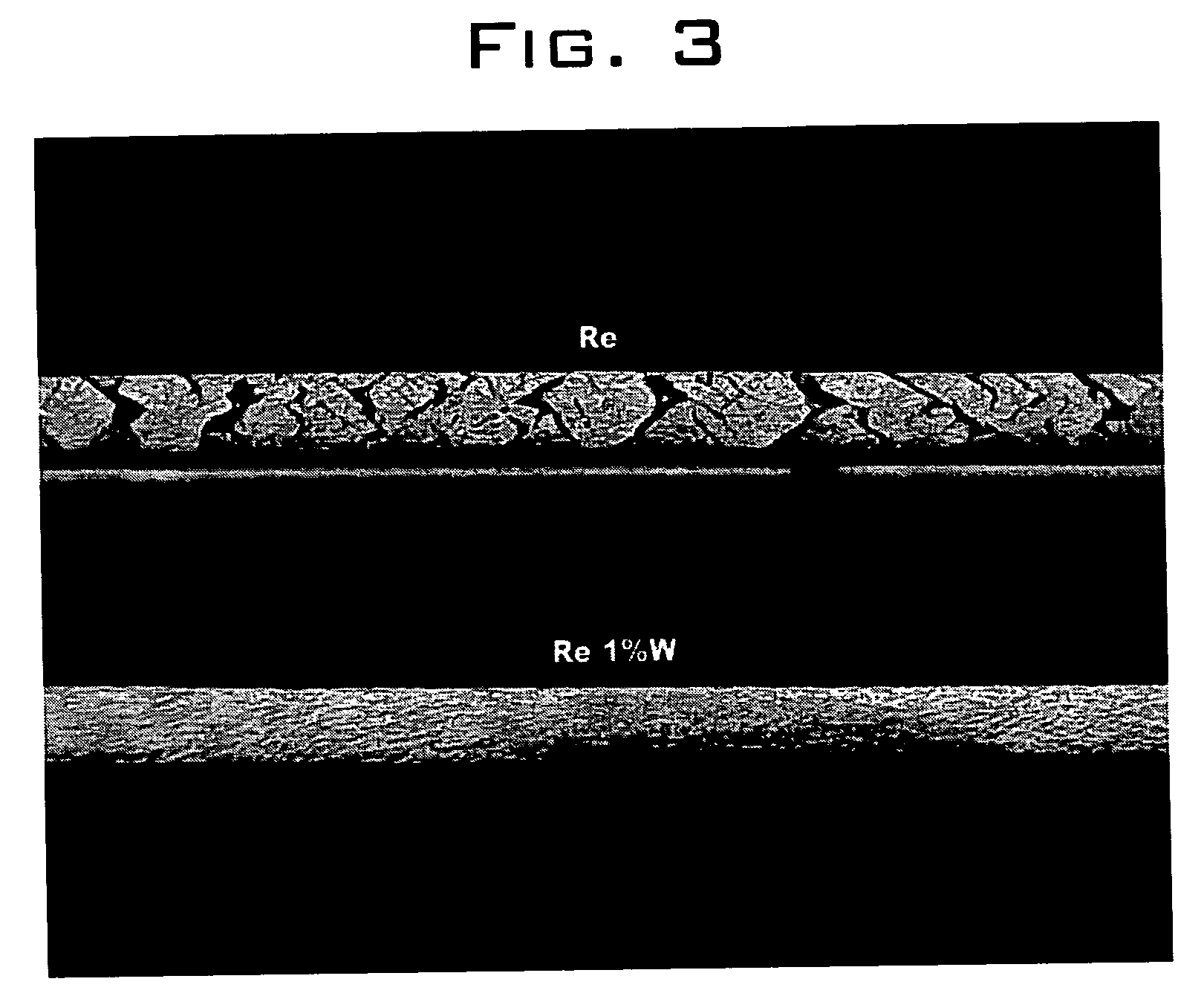
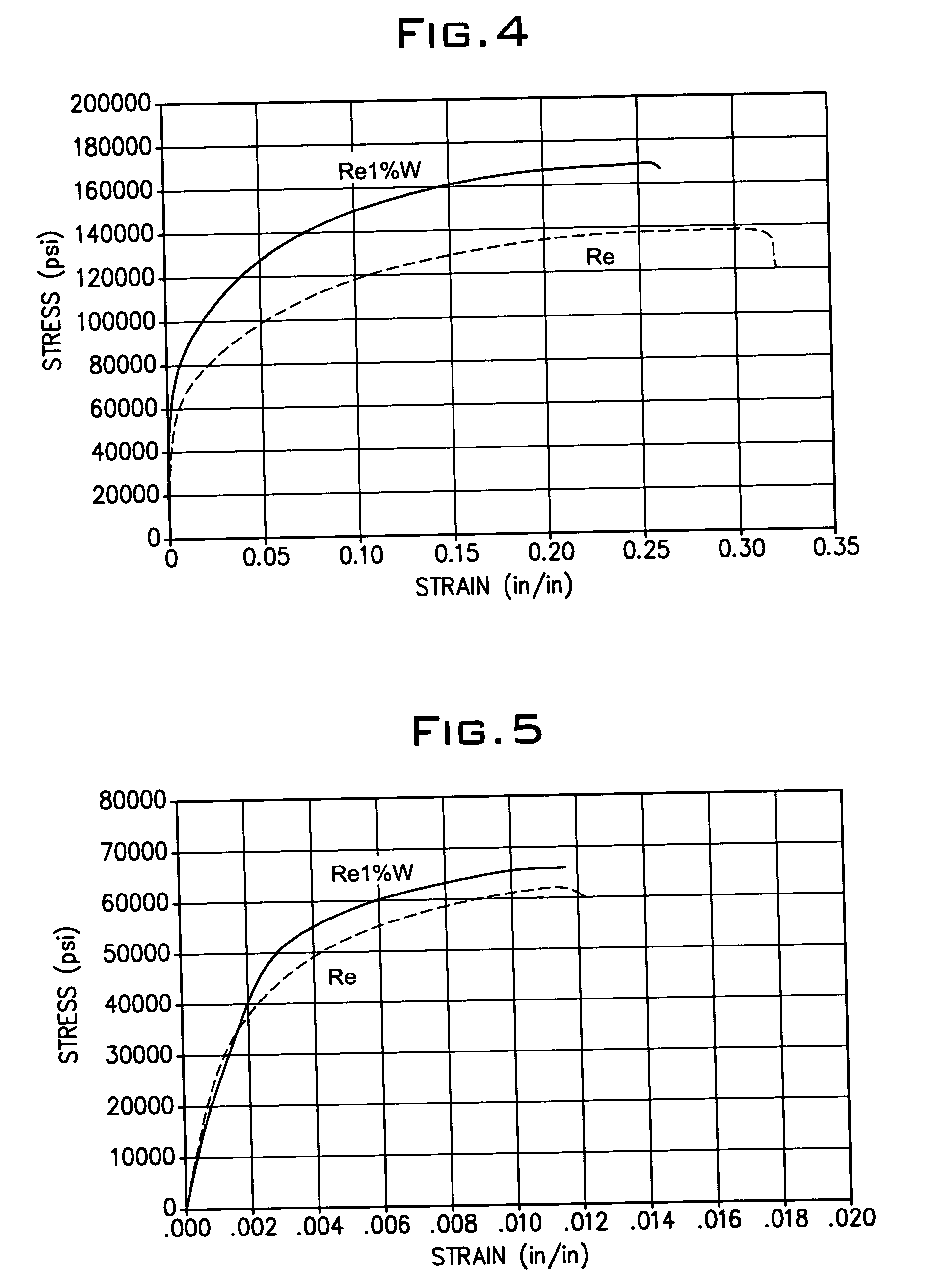
Binary rhenium alloys
InactiveUS20050238522A1Improve mechanical propertiesLoss in ductilityTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusRheniumMetal powder
Rhenium-tungsten alloys including rhenium and from about 0.025% to less than about 10% by weight tungsten. The rhenium-tungsten alloys are formed by a process that includes coating rhenium metal powders with a liquid including a tungsten compound, drying the coated rhenium powder, compressing the dried coated powder to form a compact, and then sintering the compact to form the rhenium-tungsten alloy. The rhenium-tungsten alloys according to the invention exhibit mechanical properties that are superior to high-purity rhenium metal without a loss in ductility.
Owner:RHENIUM ALLOYS
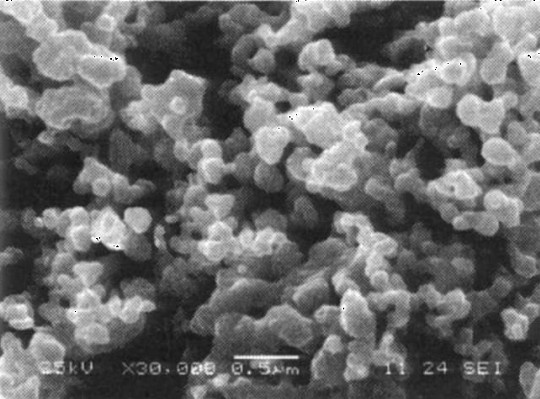
Nano-scale wolfram carbine composite powder and method of manufacturing the same
The invention provides a nanometer carbonized tungsten compound powder, which includes carbonized tungsten, vanadium carbide or / and chrome carbide, and a metallic element without binding phase exists in the compound powder. The preparation method of the nanometer carbonized tungsten compound powder is characterized in that the powdery ammonium tungstate, the carbonaceous reducing agent and the inhibitor are adopted as raw materials, the raw materials are dissolved in deionized water or distilled water and evenly stirred so as to obtain a solution, then the solution is heated and dried, the precursor powder is obtained finally, the precursor powder is put into a high-temperature reaction furnace, under the vacuum, argon or hydrogen atmosphere protection condition and the condition of 1,000 to 1,200 DEG C and 30 to 60 min, the carbonized tungsten compound powder with the average particle diameter less than 100 nm and even particle size distribution is obtained through carbonization. The method has the characteristics of low reaction temperature, short reaction time, low manufacturing cost, simple process and the like, which is suitable for the industrial production and used for the ultrafine hard alloy nanometer carbonized tungsten compound powder.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method of nano-structure WC-Co composite powder
InactiveCN102350506AWell mixedOvercoming coarse compound salt crystallizationChromium CompoundsVanadium oxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano-structure WC-Co composite powder, and belongs to the field of an alloy preparation method. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: adding a carbonic powder material which is excessive to tungsten, vanadium and chromium carbides into water-soluble saturated mixed aqueous solution of tungsten-containing compound, cobalt-containing compound, chromium-containing compound and vanadium-containing compound to adsorb the saturated composite salt solution; dehydrating and drying to form a nano-scale composite salt thin layer on the surface of the carbonic powder material; removing crystal water out of the composite salt at the temperature below 500 DEG C under a condition of isolating air, and decomposing the composite salt into composite oxide of tungsten oxide, chromium hemitrioxide, vanadium oxide and cobalt oxide, further heating, and reducing and carbonizing the composite oxide on the surface of the carbonic powder material to generate the WC-Co nano-structure composite powder at the temperature below 850 DEG C. The preparation is a simpler and more reliable novel preparation method of the nano WC-Co composite powder by a direct carbonization method.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
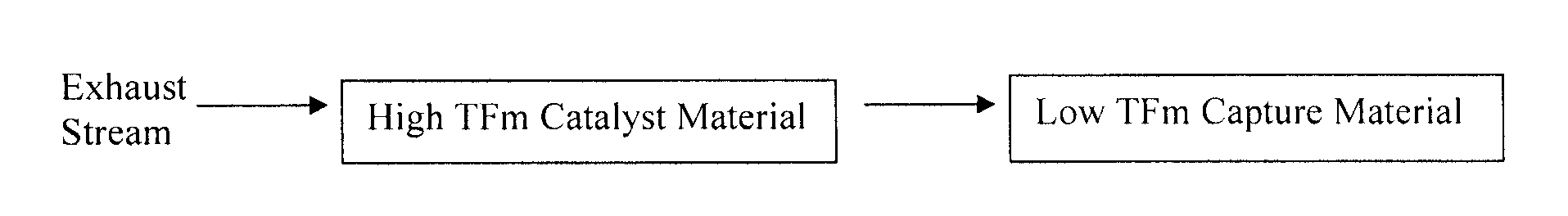
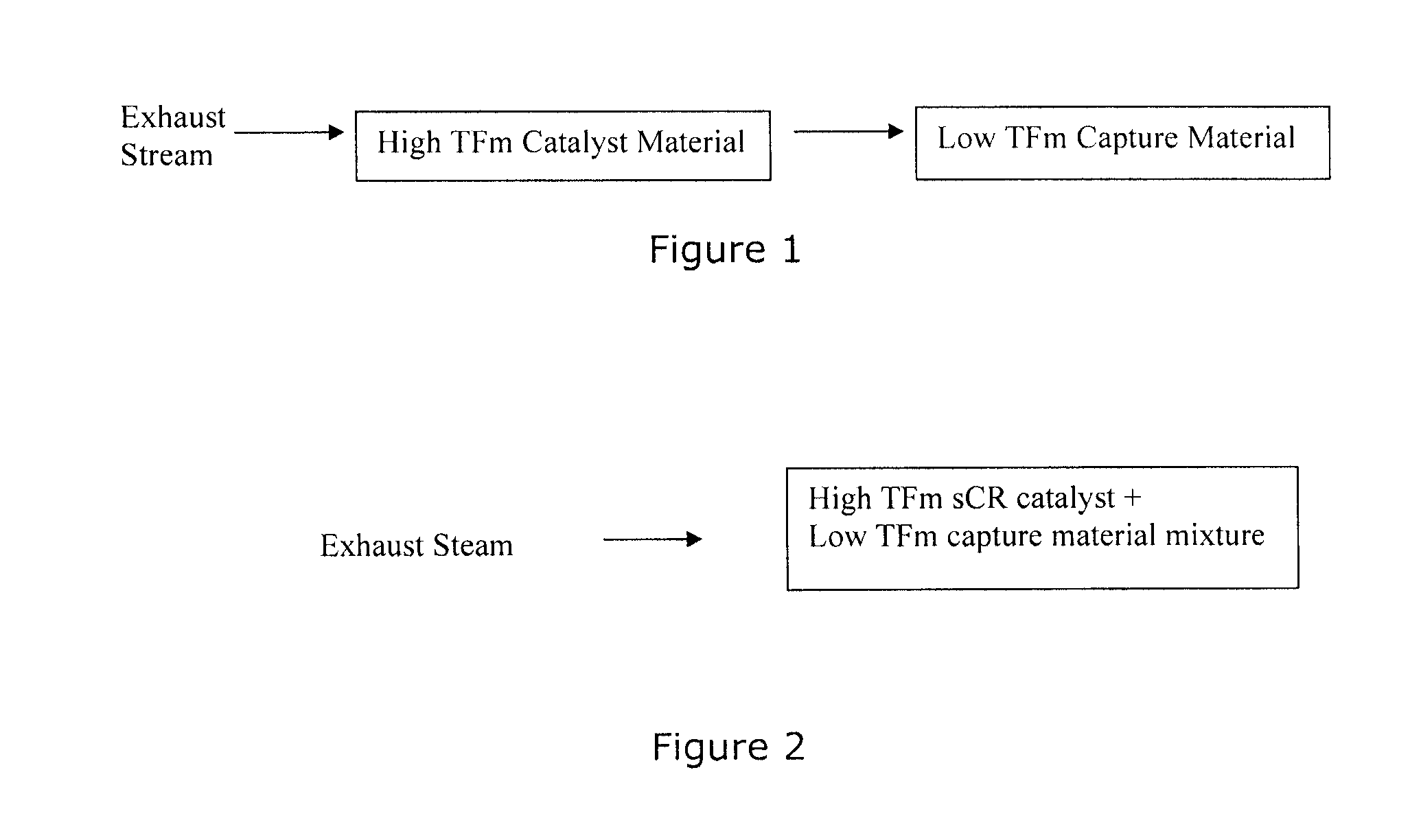
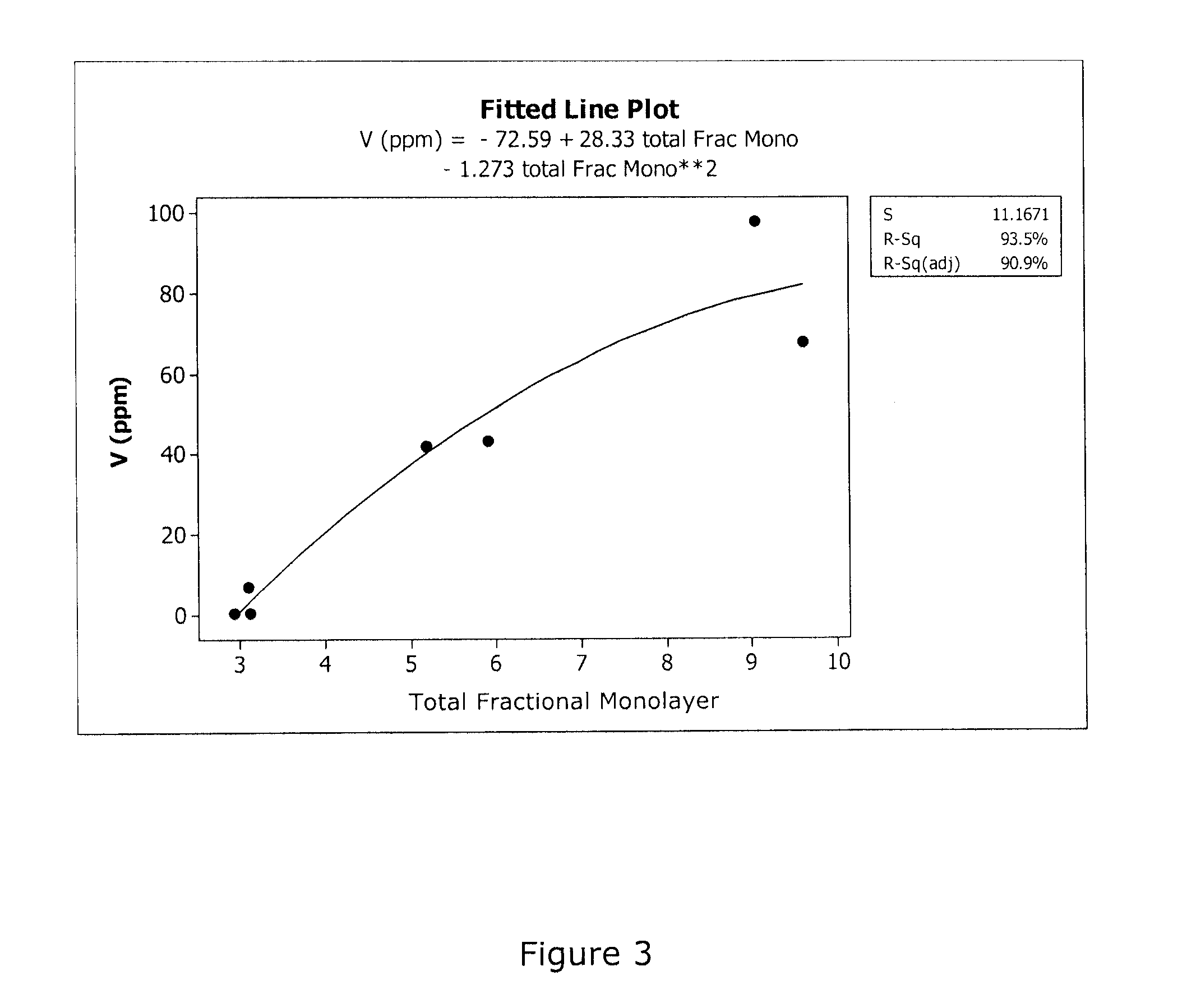
Capture of volatilized vanadium and tungsten compounds in a selective catalytic reduction system
ActiveUS20110138789A1Reduce and eliminate catalyst component volatilityReduce volatilityNitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesManganeseCerium
An apparatus and method for treating diesel exhaust gases are described. The system consists of two functionalities, the first being a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalyst system and the second being a capture material for capturing catalyst components that have appreciable volatility under extreme exposure conditions. The SCR catalyst component is typically based on a majority phase of titania, with added minority-phase catalyst components comprising of one or more of the oxides of vanadium, silicon, tungsten, molybdenum, iron, cerium, phosphorous, copper and / or manganese vanadia. The capture material typically comprises a majority phase of high surface area oxides such as silica-stabilized titania, alumina, or stabilized alumina, for example, wherein the capture material maintains a low total fractional monolayer coverage of minority phase oxides for the duration of the extreme exposure. The method involves treatment of hot exhaust streams by both the catalyst material and capture material, wherein the capture material can be in a mixture with the catalyst material, or can be located downstream thereof, or both, but still be maintained at the extreme temperatures. Volatile catalyst components such as vanadia are thus removed from the vapor phase of the exhaust gas.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
Novel catalysts and process for dehydrating glycerol
InactiveUS20080183019A1Low carbonization tendencyPromote regenerationMolecular sieve catalystsThiol preparationAcroleinGlycerol
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
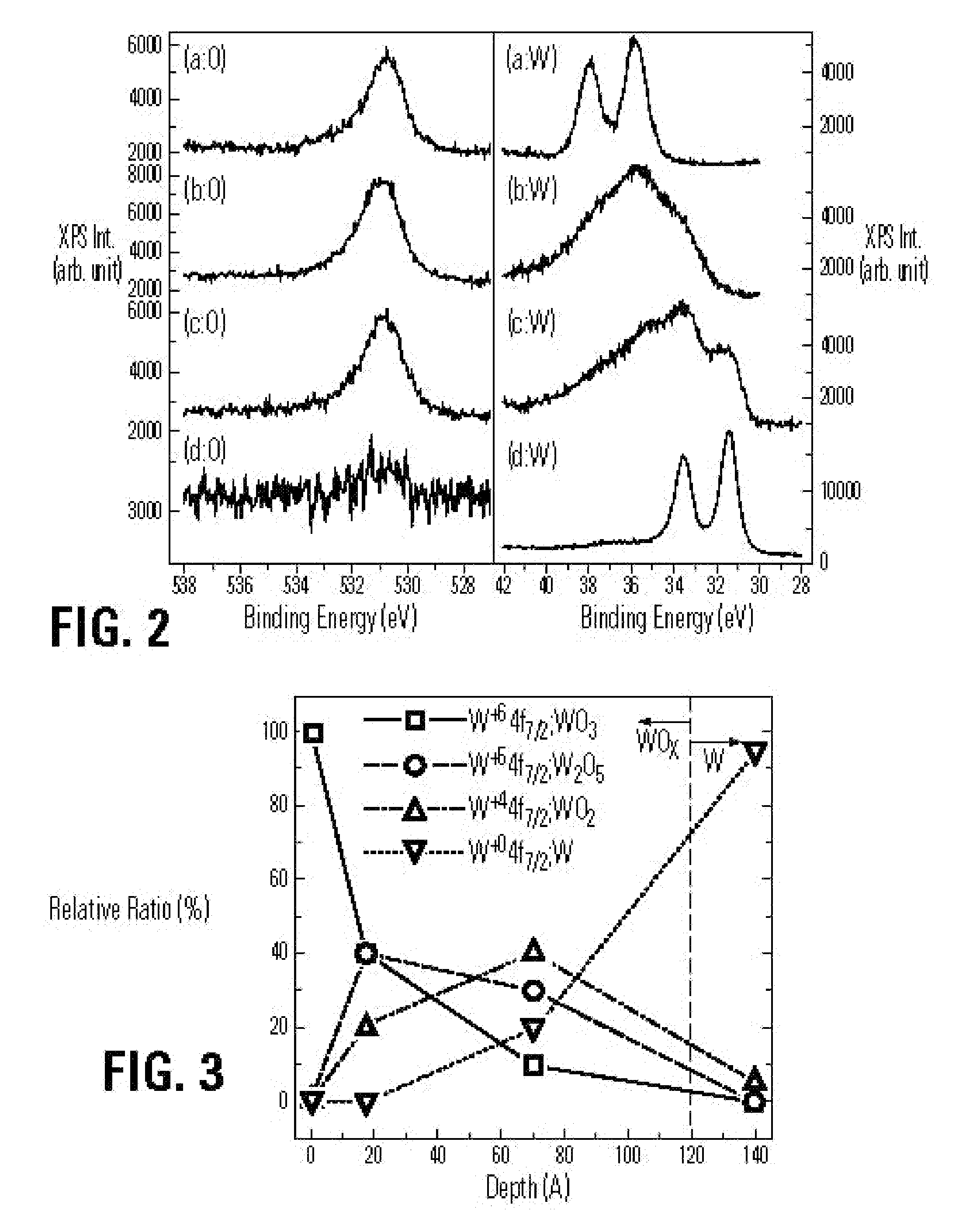
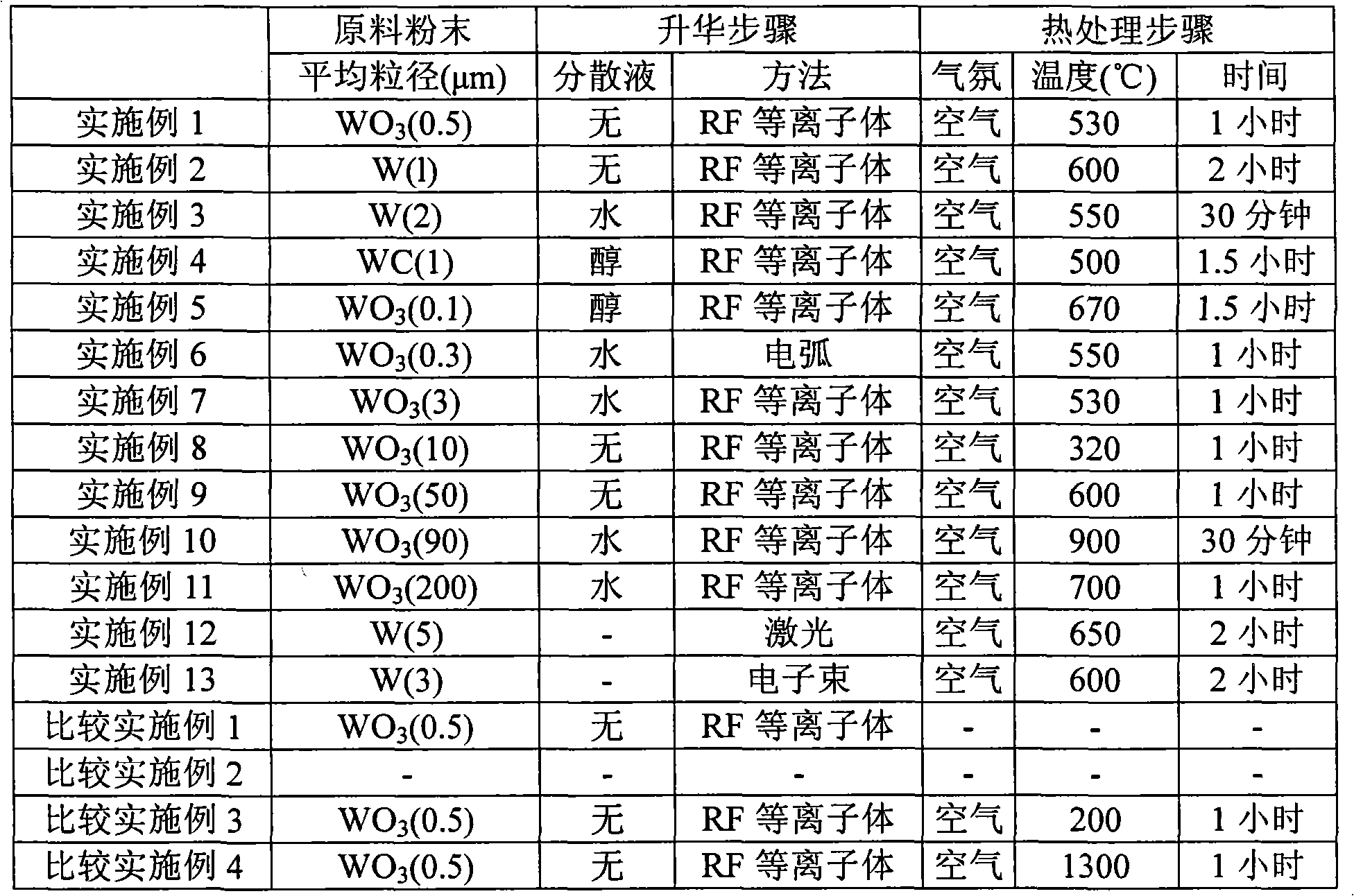
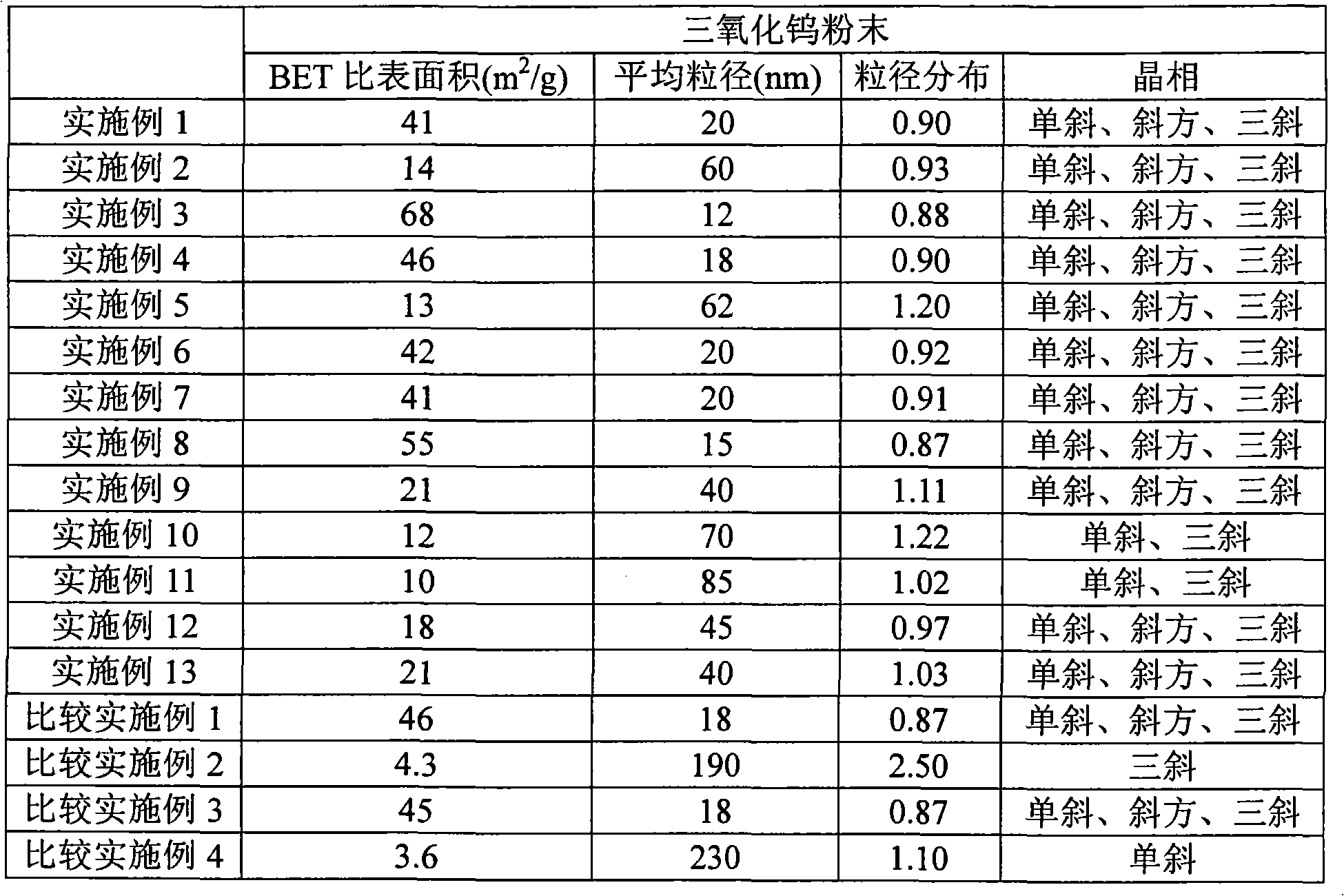
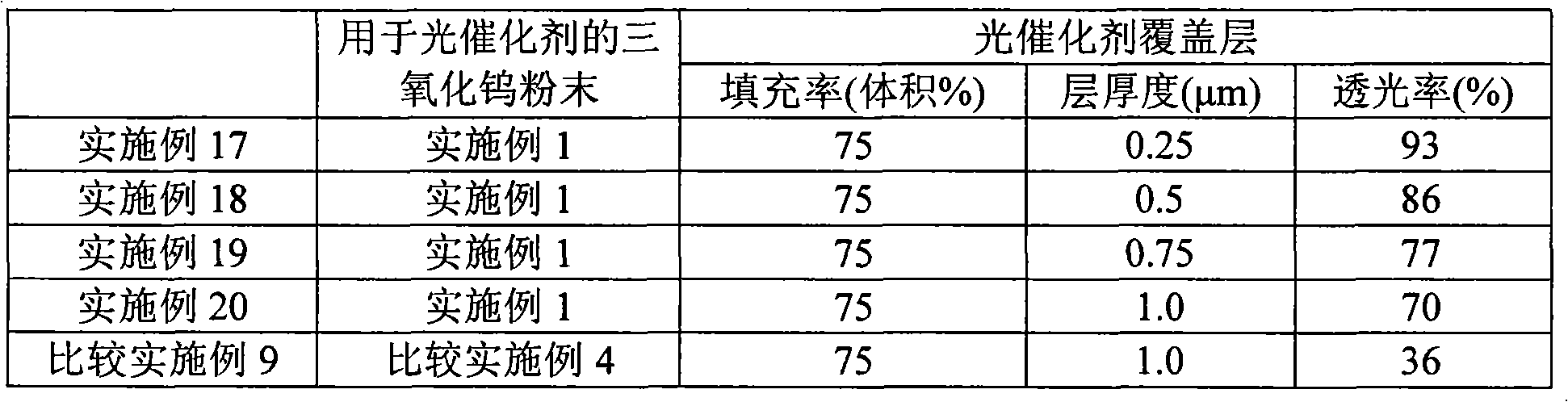
Method for producing tungsten trioxide powder for photocatalyst, tungsten trioxide powder for photocatalyst, and photocatalyst product
ActiveUS8003563B2Small particle sizeNarrow particle size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingInductively coupled plasmaTungsten trioxide
A method for producing a tungsten trioxide powder for a photocatalyst according to the present invention is characterized by comprising a sublimation step for obtaining a tungsten trioxide powder by subliming a tungsten metal powder or a tungsten compound powder by using inductively coupled plasma process in an oxygen atmosphere, and a heat treatment step for heat-treating the tungsten trioxide powder obtained in the sublimation step at 300° C. to 1000° C. for 10 minutes to 2 hours in an oxidizing atmosphere. A tungsten trioxide powder which is obtained by the method for producing a tungsten trioxide powder for a photocatalyst according to the present invention has excellent photocatalytic performance under visible light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Amine tungstates and lubricant compositions
InactiveUS20090029888A1Improved performance characteristicsEasy to controlAdditivesGroup 6/16 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesChemical compositionAntioxidant
This invention relates to lubricating oil additives, and to lubricating oil compositions, their method of preparation, and use. More specifically, this invention relates to several novel lubricating oil additives and compositions which contain a tungsten compound and an antioxidant, namely aminic antioxidants such as a secondary diarylamine or an alkylated phenothiazine. The use of the tungsten compound with the secondary diarylamine and / or the alkylated phenothiazine provides improved oxidation and deposit control to lubricating oil compositions. The lubricating oil compositions of this invention are particularly useful as crankcase and transmission lubricants, gear oils and other high performance lubricant applications.
Owner:KING INDUSTRIES INC
Rare-earth-based composite multi-component denitration and dioxin-removing catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104841489ASolve pollutionHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDispersed particle separationFiberCatalytic decomposition
The invention relates to a rare-earth-based composite multi-component denitration and dioxin-removing catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The rare-earth-based composite multi-component denitration and dioxin-removing catalyst takes titanium dioxide and silicon powder as carriers, and takes tungsten compounds, vanadium compounds, cerium compounds and lanthanum compounds as active components; and under the accompanying of auxiliary materials, all the raw materials are mixed, granulated, kneaded, molded, dried and roasted to prepare the catalyst, wherein the auxiliary materials comprise monoethanolamine, ammonia water, lactic acid, stearic acid, glass fibers, citric acid, PP (Propene Polymer) fibers, cellulose ether, polyoxyethylene and water. The preparation method of the rare-earth-based composite multi-component denitration and dioxin-removing catalyst has a simple process and is safe to operate, and the catalyst has a plurality of functions of denitration, dioxin removal and mercury removal; by adopting a catalytic decomposition technology, the dioxin pollution problem is solved; compared with that of active carbon, the adsorption is relatively complete; and the activity of the catalyst is extremely improved and the temperature use range is expanded.
Owner:SHANDONG AIREP ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Method for producing tungsten trioxide powder for photocatalyst, tungsten trioxide powder for photocatalyst, and photocatalyst product
ActiveUS20100113254A1Improve photocatalytic performanceSmall sizeMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingInductively coupled plasmaTungsten trioxide
A method for producing a tungsten trioxide powder for a photocatalyst according to the present invention is characterized by comprising a sublimation step for obtaining a tungsten trioxide powder by subliming a tungsten metal powder or a tungsten compound powder by using inductively coupled plasma process in an oxygen atmosphere, and a heat treatment step for heat-treating the tungsten trioxide powder obtained in the sublimation step at 300° C. to 1000° C. for 10 minutes to 2 hours in an oxidizing atmosphere. A tungsten trioxide powder which is obtained by the method for producing a tungsten trioxide powder for a photocatalyst according to the present invention has excellent photocatalytic performance under visible light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
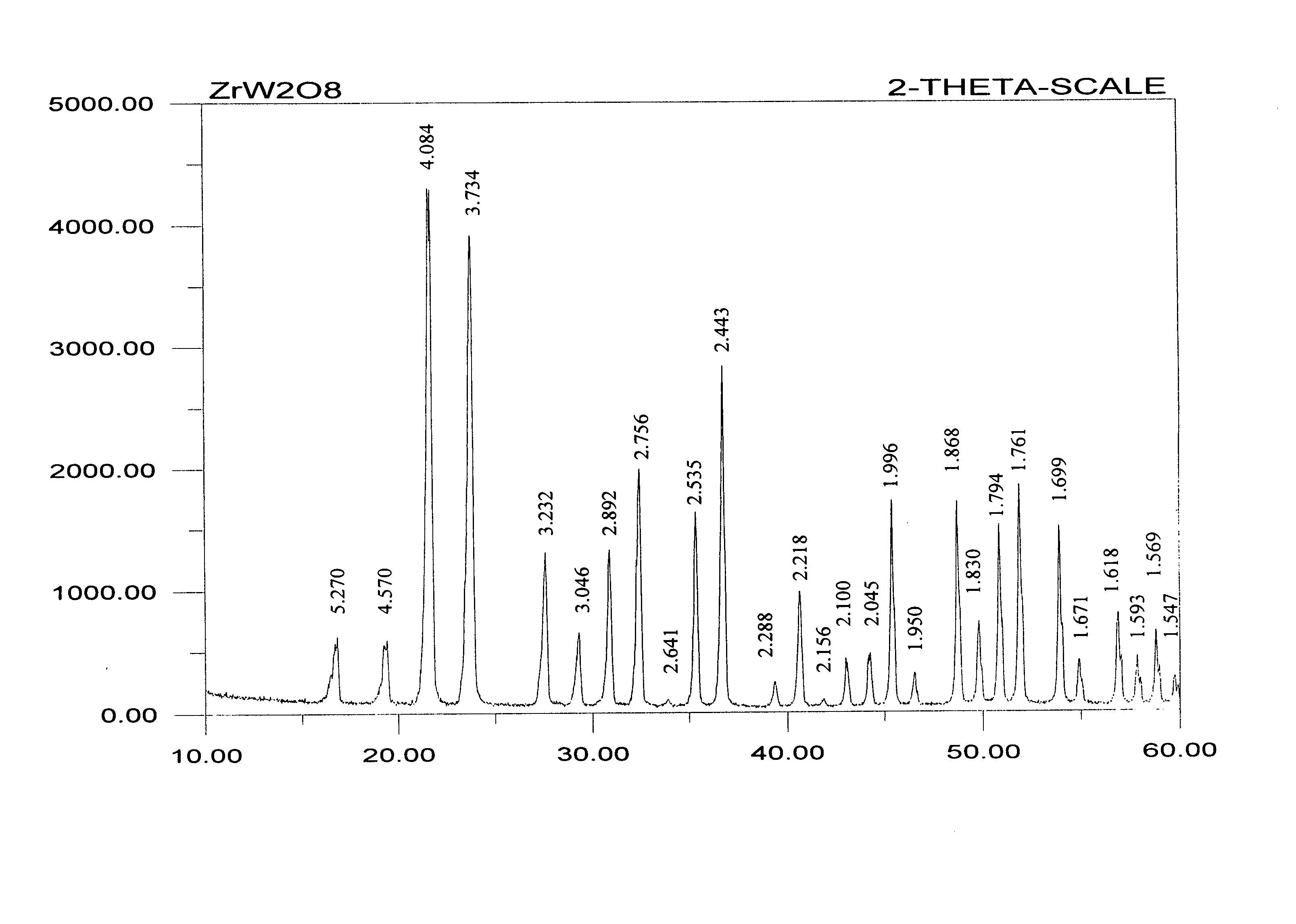
Method for making negative thermal expansion material zirconium tungstate
InactiveUS20050101133A1Low cost of reagentsSimple processFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthWater insolubleWater soluble
A method for making negative thermal expansion material zirconium tungstate (ZrW2O8) comprise: (a)forming a gel wrapped solid product comprising a water-soluble zirconium compound, preferably zirconium oxyhalides or zirconium oxynitrates and a water-insoluble tungsten compound, preferably tungsten powder or tungsten oxide powder; and (b)heating the gel wrapped solid product to a temperature sufficient to form ZrW2O8; the temperature required for forming zirconium tungstate should be at least about 1165° C.; the upper limit of the temperature should be about 1250° C., and preferably should be about 1180˜1200° C.; and the time needed for the formation of zirconium tungstate is less than about 5 hours; this method has the advantages on enhancing the selectivity of the reactants, simplifying production process, reducing the cost of reagent, and facilitating the mass production for making ZrW2O8.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Composite water treatment agent
InactiveCN103663738AImprove protectionGood corrosion and scale inhibition effectTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsCarboxylic acidCarboxylate
The invention discloses a composite water treatment agent which comprises the following components in parts by mass: 15-45 parts of sodium tungstate, 5-25 parts of polyaspartic acid, 1-5 parts of zinc salt, 2-15 parts of sodium benzoate and 2-25 parts of carboxylate, wherein sodium tungstate is a corrosion inhibitor which is non-toxic, causes no environmental hazard and can generate the synergic corrosion inhibition function with polyaspartic acid. With addition of other assistants, the composite water treatment agent becomes a green composite water treatment agent which has excellent corrosion inhibition and scale inhibition effects, lower in cost, non-phosphorus, easily biodegradable and beneficial to environmental protection. In China, tungsten reserves and yield are abundant, so that the sufficient tungsten compounds can be provided, and the cost of the treatment agent is greatly lowered.
Owner:QINGDAO BAIZHONG CHEM TECH
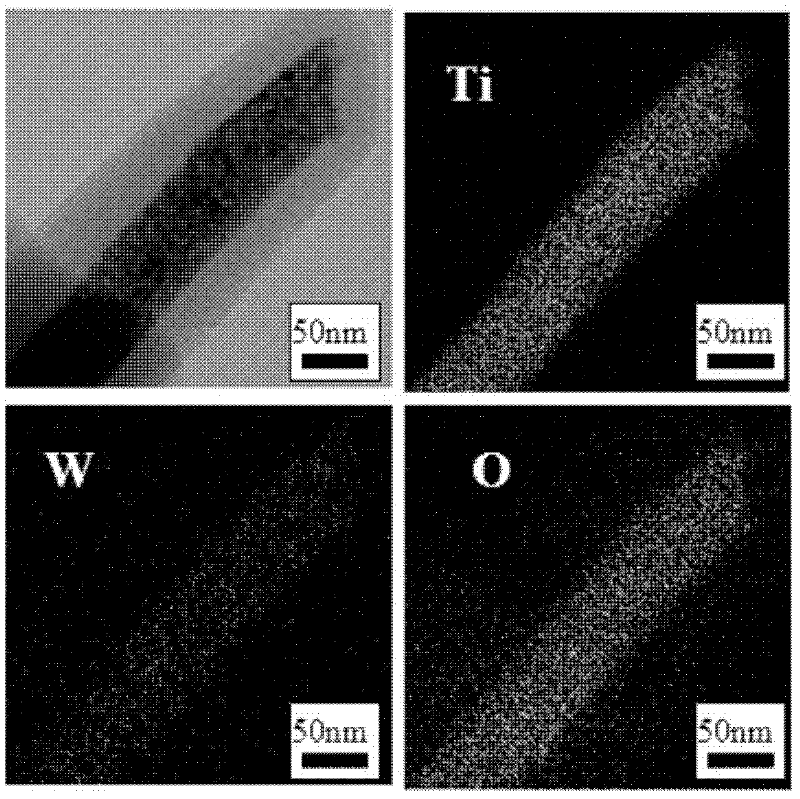
Method for preparing titanium-tungsten compound oxide nano-fiber
InactiveCN102358964AEasy to prepareEasy to controlFilament/thread formingFibre chemical featuresFiberAcetone
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
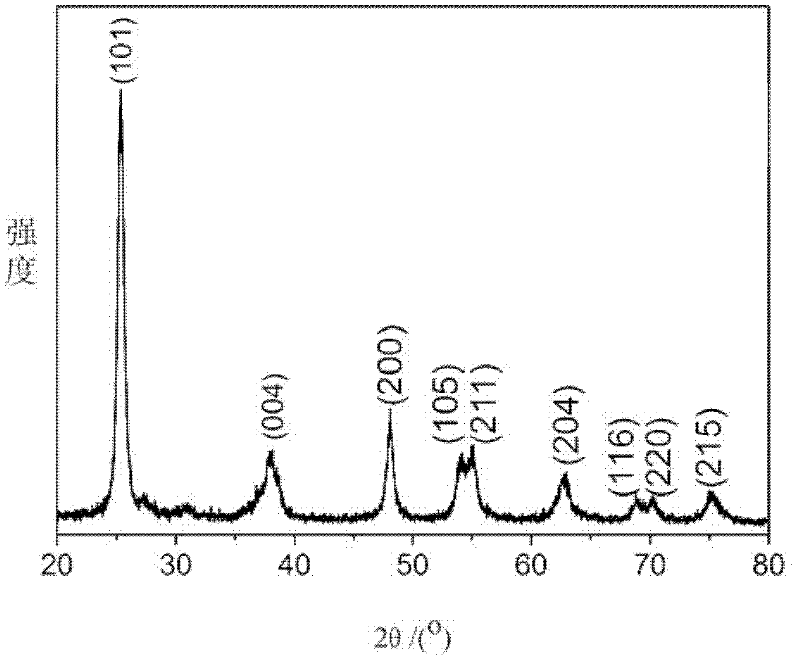
Solid-phase synthesis method for caesium tungsten bronze powder
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal oxide powder preparation and particularly relates to a solid-phase synthesis method for caesium tungsten bronze powder. The solid-phase synthesis method comprises the following steps of weighing a tungsten compound and cesium salt according to the W / Cs molar ratio (2-3.5):1, and mixing and grinding; placing the ground substance into a sealed vessel to react at the temperature of 750-800 DEG C for 1-2 hours; and ending the reaction to obtain the black blue caesium tungsten bronze powder with complete crystallinity, wherein the crystal phase comprises the component, namely Cs0.3WO3 or Cs0.32WO3. According to the solid-phase synthesis method, a solid raw material is adopted to directly react in a sealed vessel, inert gases or reducing gases are not needed to be introduced, and a gas generated by self-reaction is used as a protecting gas, so that the obtained powder is black blue, the air source is saved, and the cost is reduced; in addition, the synthesis process disclosed by the invention is simple, short in reaction period and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:烟台佳隆纳米产业有限公司
Positive electrode active material for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries, method for manufacturing the same, and nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery using said positive electrode active material
ActiveUS20150228974A1Increase productionLarge capacityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureLithium metalComposite oxide
Provided is a method for manufacturing the positive electrode active material for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries, the method comprising: a first step, wherein an alkaline solution with a tungsten compound dissolved therein is added to and mixed with a lithium metal composite oxide powder represented by a general formula LizNi1—x—yCoxMyO2 (wherein, 0.10≦x≦0.35, 0≦y≦0.35, 0.97≦Z≦1.20, and M is at least one element selected from Mn, V, Mg, Mo, Nb, Ti, and Al), including primary particles and secondary particles composed of aggregation of the primary particles, and thereby W is dispersed on a surface of the primary particles; and a second step, wherein, by heat treating the mixture of the alkaline solution with the tungsten compound dissolved therein and the lithium metal composite oxide powder, fine particles containing W and Li are formed on a surface of the primary particles.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Tungsten oxide quantum dot material and preparation method thereof
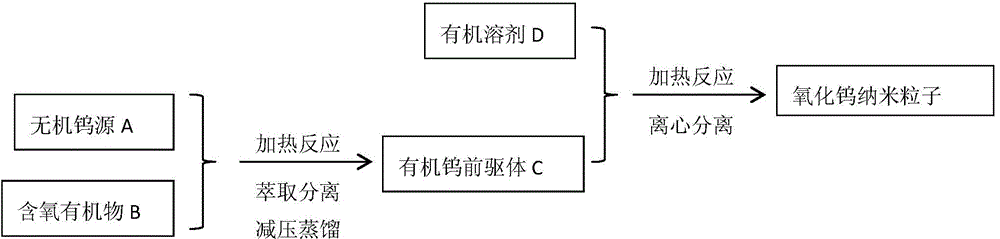
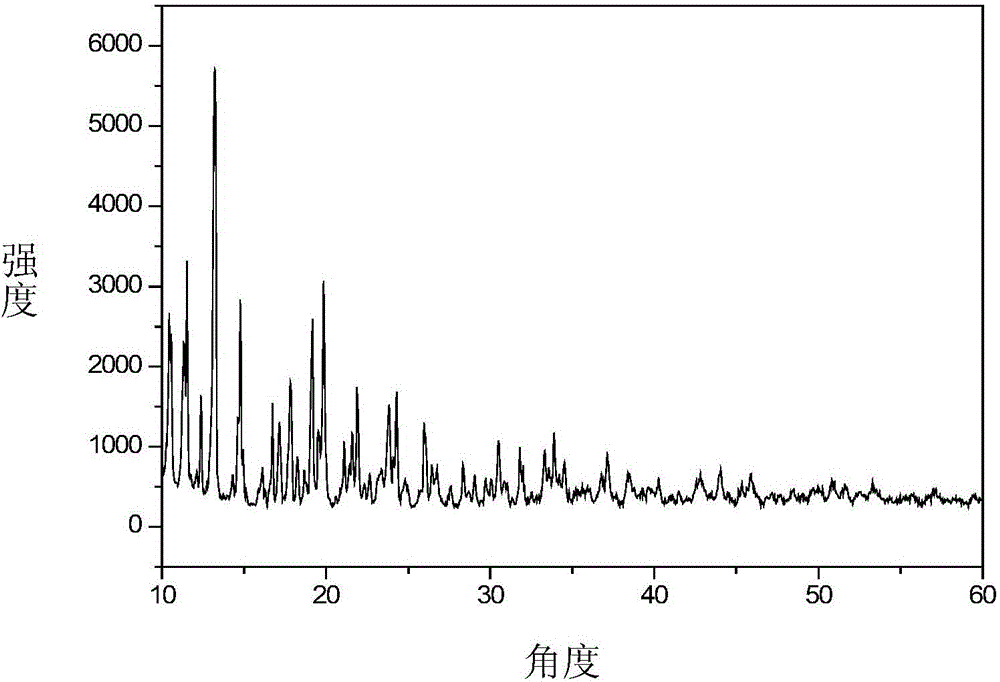
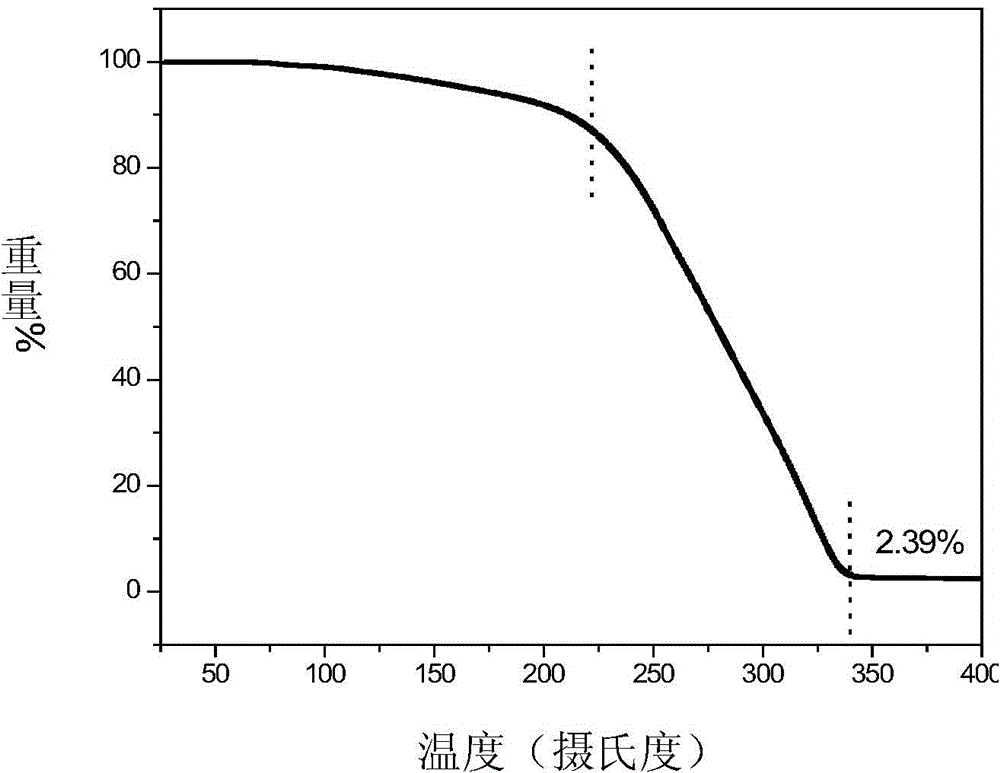
ActiveCN104789218ALow costUniform particle sizeTungsten oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyOrganic solventNanoparticle
The invention provides a tungsten oxide quantum dot material and a preparation method thereof. The tungsten oxide quantum dot material comprises tungsten oxide nanoparticles with the particle size of several nanometers to a dozen of nanometers, the particle size of the tungsten oxide nanoparticles is uniform, the surface of the nanoparticles is covered with an organic matter coating layer, and the nanoparticles can be highly dispersed in a non-polar organic solvent, and has a quantum dimension effect. Preferably, the particle size of the tungsten oxide quantum dot material is smaller than 2nm; and the tungsten oxide quantum dot material can be prepared through a liquid phase method, and is prepared through two steps of preparing an organic tungsten precursor from an easily available inorganic tungsten compound and preparing the material. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process flow, easily available raw material, good reappearance and high controllability, and the obtained tungsten oxide nanoparticles have the advantages of uniform particle size, adjustable dimension, high dispersion, obvious quantum dimension effect and wide application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method for producing tungsten trioxide powder for photocatalyst, tungsten trioxide powder for photocatalyst, and photocatalyst product
ActiveCN101641292AEfficient productionSmall particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologyTungsten oxides/hydroxidesPhysical chemistryInductively coupled plasma
Disclosed is a method for producing a tungsten trioxide powder for photocatalysts, which is characterized by comprising a sublimation step wherein a tungsten trioxide powder is obtained by subliming atungsten metal powder or a tungsten compound powder by inductively coupled plasma processing in an oxygen atmosphere, and a heat treatment step wherein the tungsten trioxide powder obtained in the sublimation step is heated at 300-1000 DEG C for 10 minutes to 2 hours in an oxidizing atmosphere. A tungsten trioxide powder obtained by such a method for producing a tungsten trioxide powder for photocatalysts has high photocatalytic activity under visible light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com