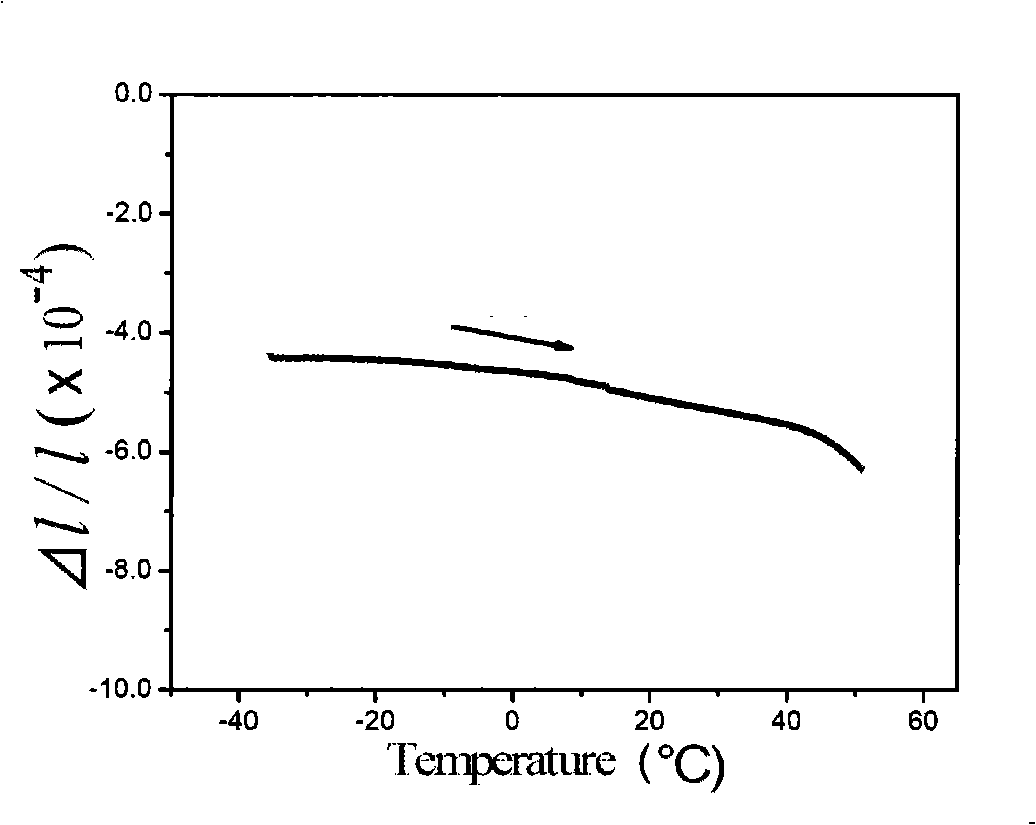
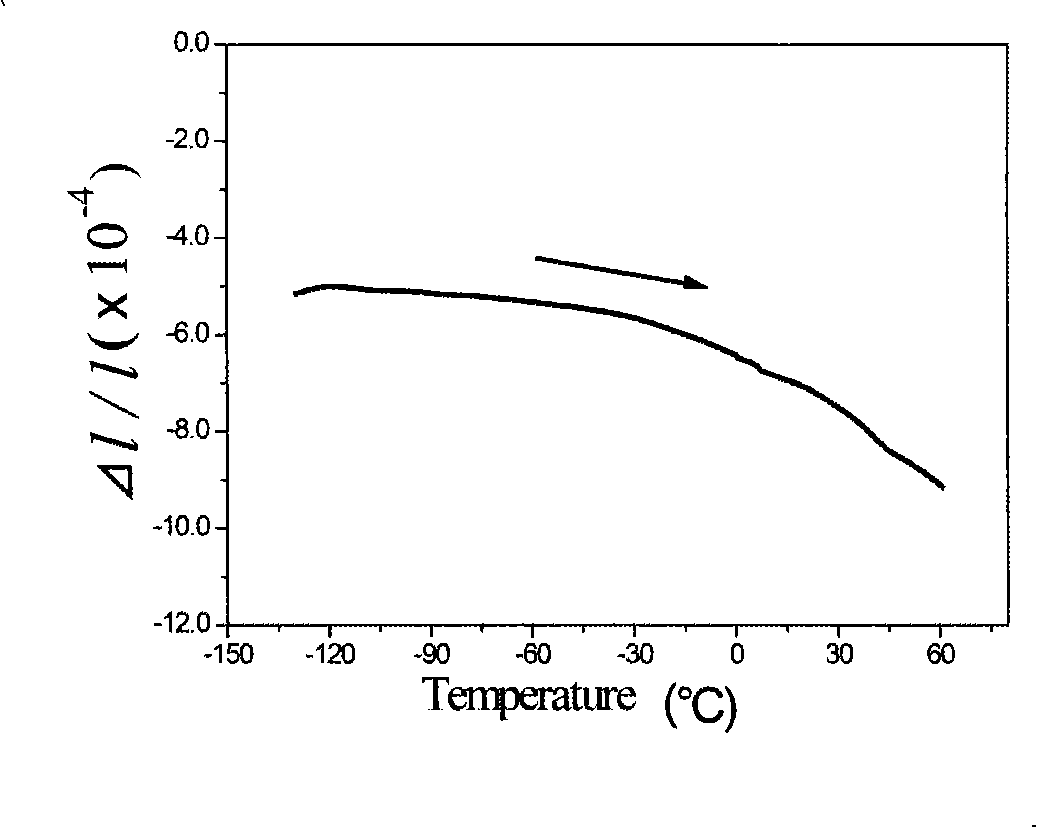
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
415 results about "Negative thermal expansion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Negative thermal expansion (NTE) is an unusual physicochemical process in which some materials contract upon heating, rather than expand as most other materials do. Materials which undergo NTE have a range of potential engineering, photonic, electronic, and structural applications. For example, if one were to mix a negative thermal expansion material with a "normal" material which expands on heating, it could be possible to make a zero expansion composite material.
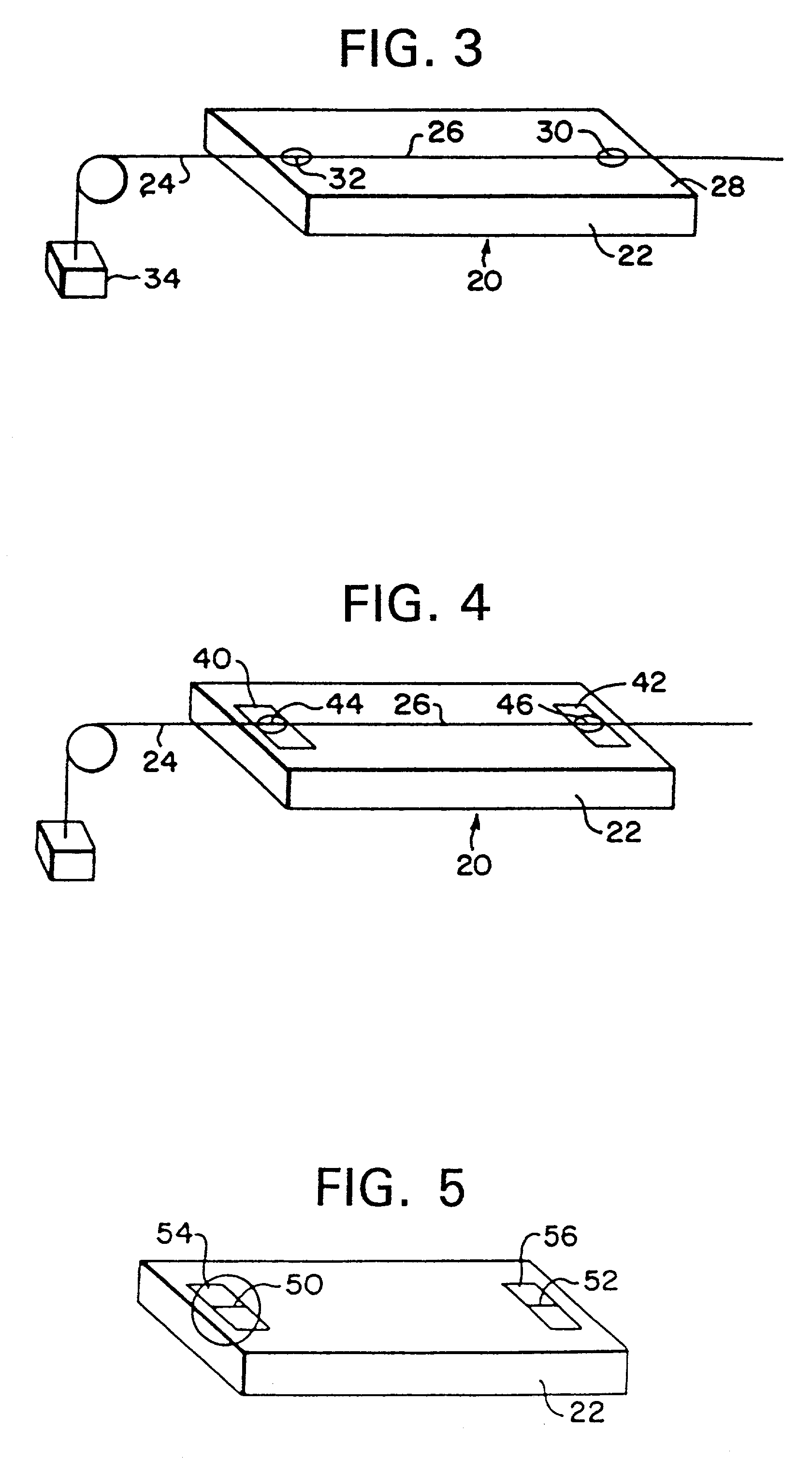
Optical fiber diffraction grating, a method of fabricating thereof and a laser light source
InactiveUS6067392ACanceled outPositive linear thermal expansion coefficientOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesPolyesterLaser light
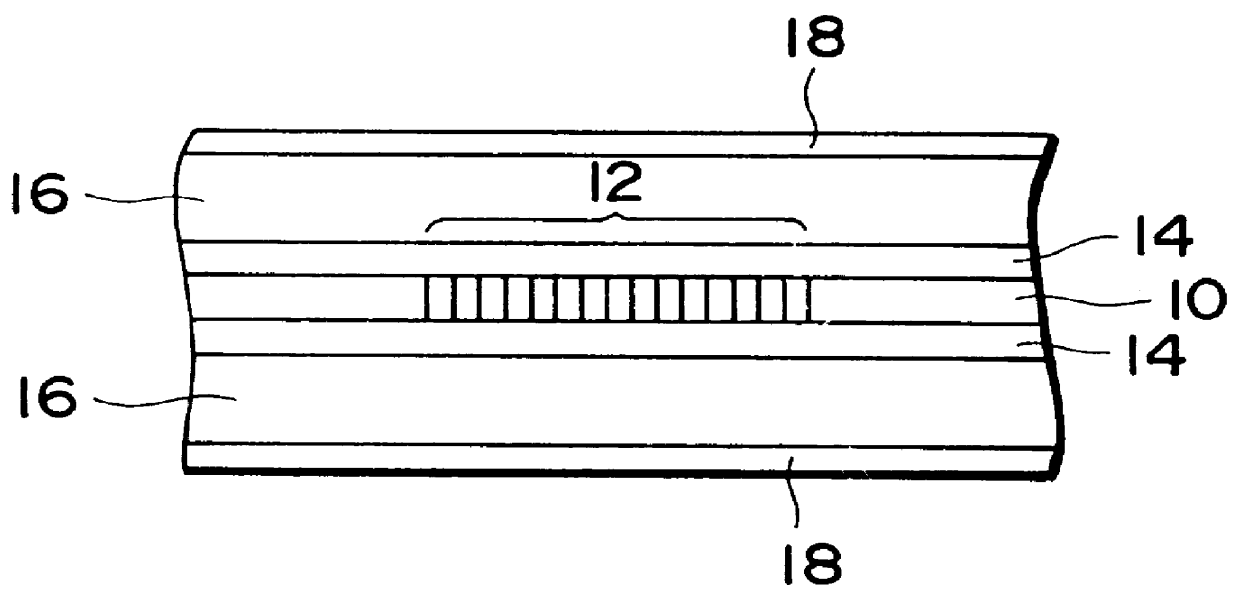
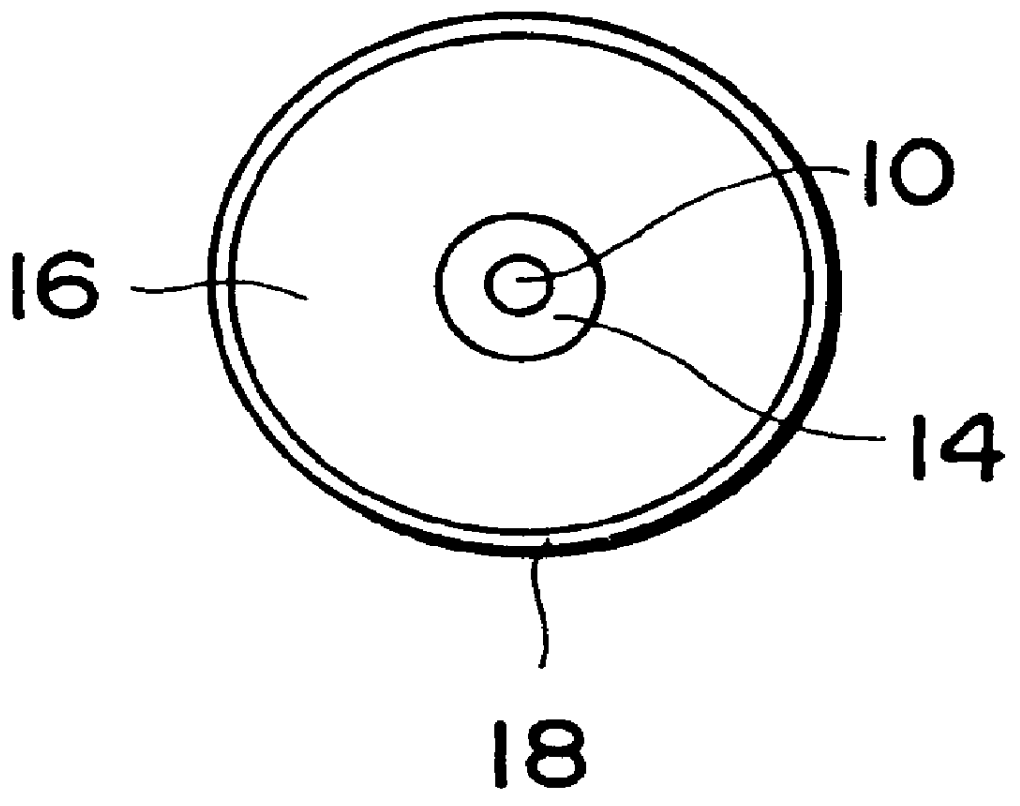
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 03000 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 16, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 16, 1997 PCT Filed Oct. 16, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 14983 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 24, 1997A diffraction grating portion (12) is formed in an optical fiber (10), having a diameter of 125 mu m and serving to transmit light, along its optical axis. The optical fiber is concentrically surrounded by a lower coating portion (14) having an outer diameter of 300 mu m and consisting of a silicone resin. The lower coating portion is concentrically surrounded by a coating portion (16) having an outer diameter of 900 mu m and consisting of a liquid crystal polymer, e.g., polyester amide. The coating portion is further surrounded by an outermost coating portion (18) having an outer diameter of 1 mm and consisting of a UV curing resin colored for identification. Both the optical fiber (10) and the lower coating portion (14) have positive thermal expansion coefficients. In contrast to this, the coating portion (16) consisting of the liquid crystal polymer has a negative thermal expansion coefficient.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Negative thermal expansion materials including method of preparation and uses therefor
InactiveUS6187700B1Avoid microcracksRelieve pressureCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideGratingMaterials science
Negative thermal expansion materials, methods of preparation and uses therefor are disclosed. The materials are useful for negative thermal expansion substrates, such as those used for optical fiber gratings.
Owner:CORNING INC
Semiconductor transformers
ActiveUS8049301B2Improve conductivityHigh coefficient of thermal expansionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesSalicideElectricity
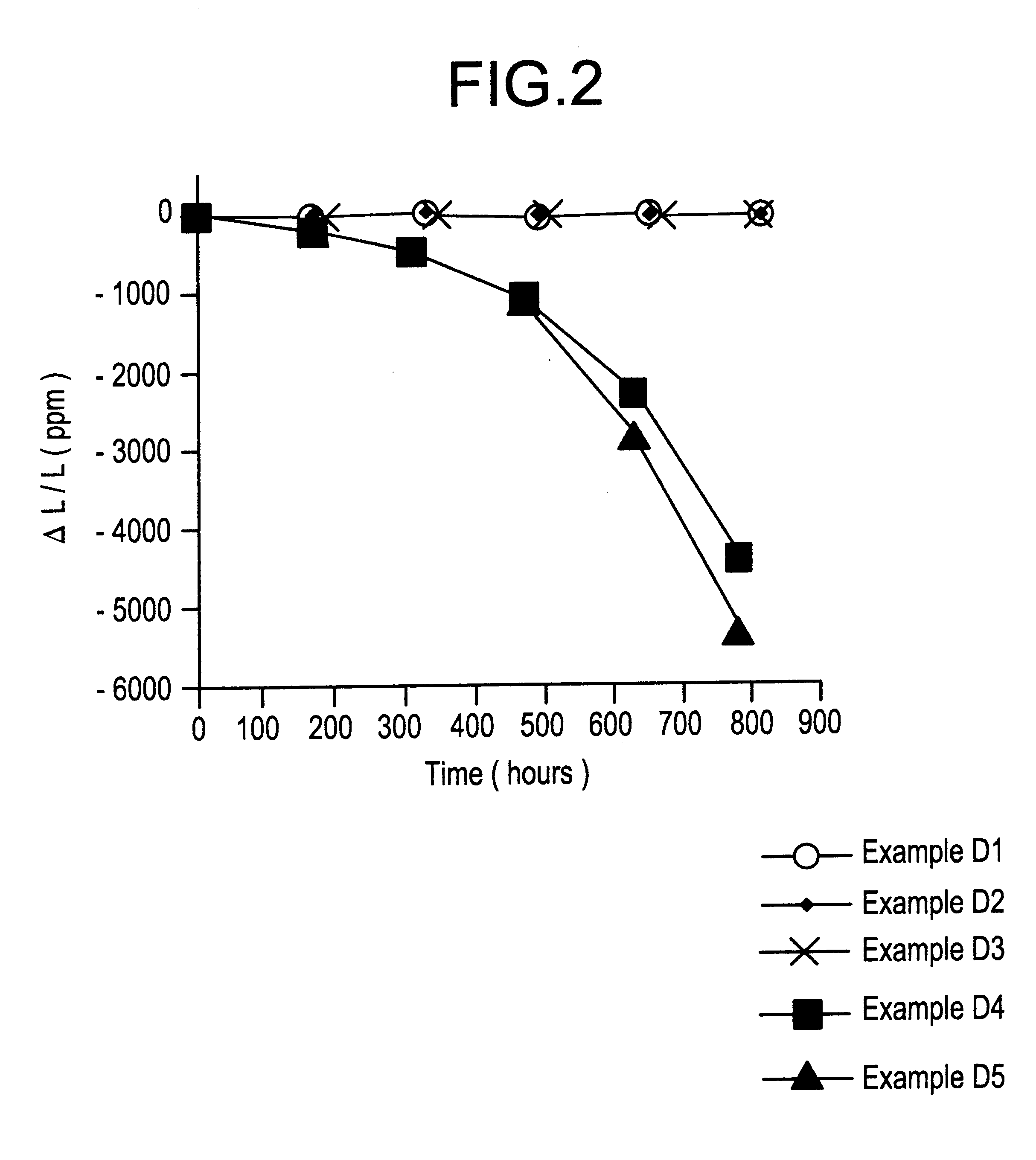
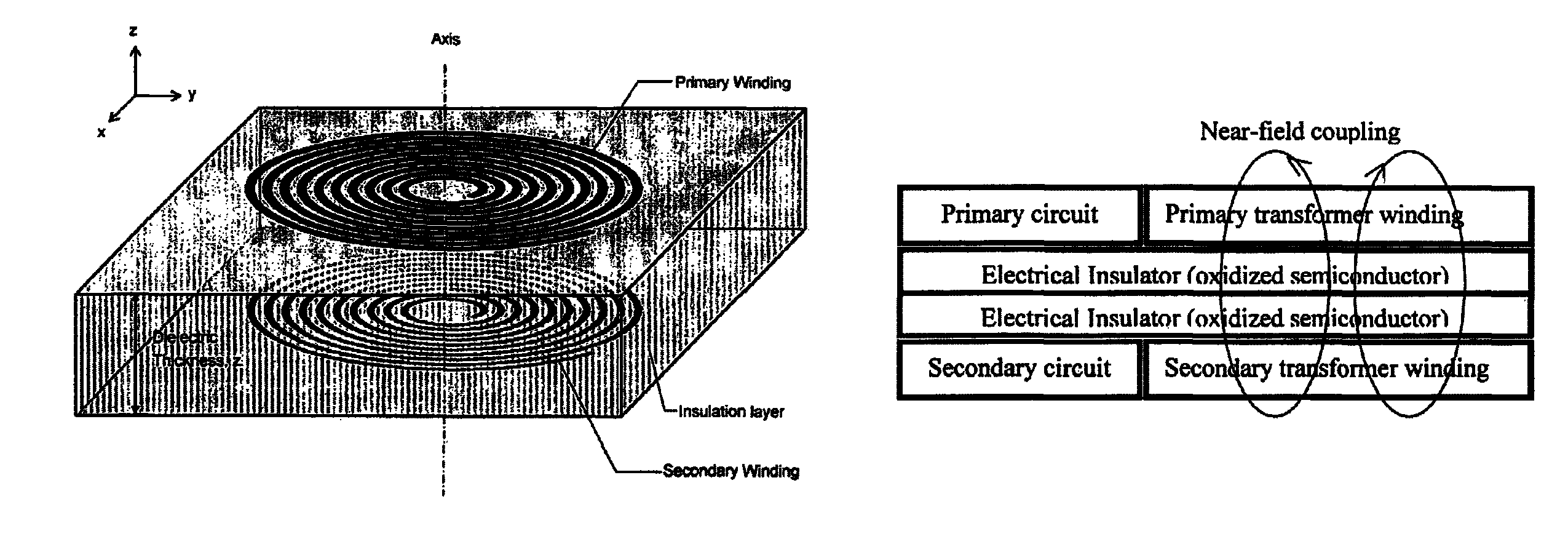
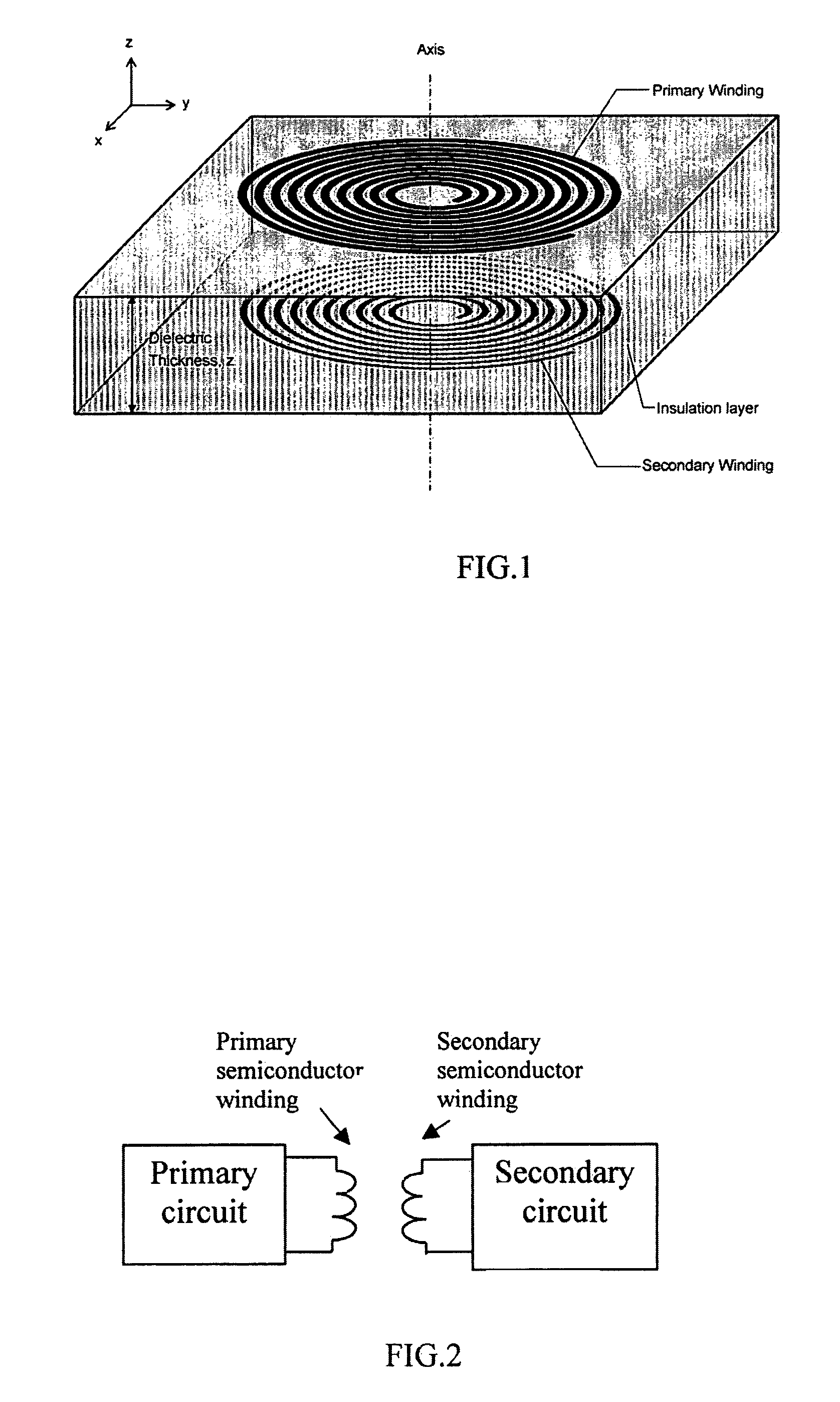
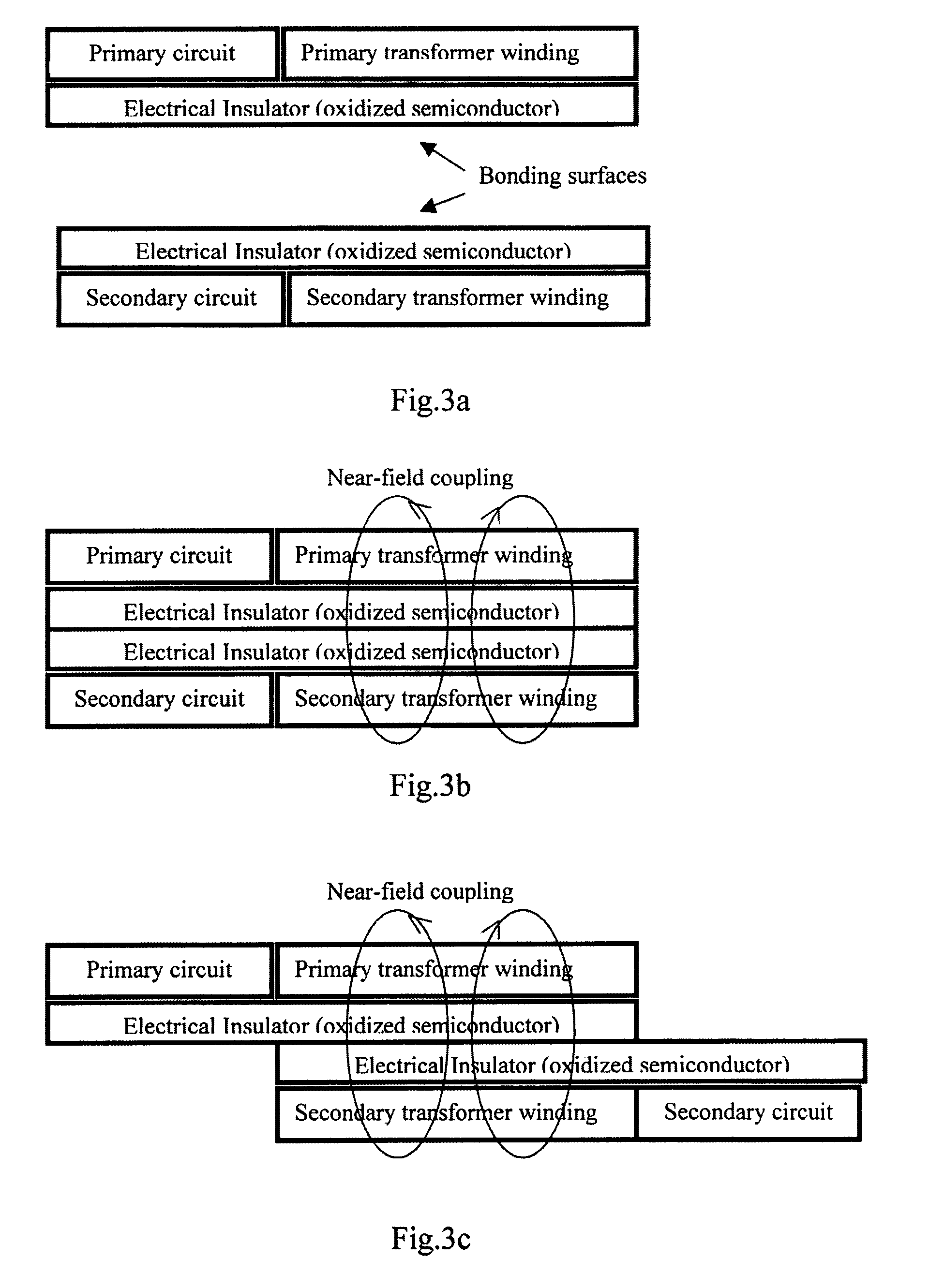
A planar transformer structure, which can be constructed in an integrated semiconductor circuit without using traditional metallic windings. To avoid large thermal expansion of metallic spiral windings and associated mechanical stress on a metal-semiconductor interface, it is suggested that highly doped semiconductor materials with or without silicides and salicides can be used to form windings or conducting paths because their thermal expansion coefficients are similar to that of semiconductor material. The planar semiconductor transformer may find application for low-power and signal transfer that needs electrical isolation.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Very low thermal expansion composite
InactiveUS20050191515A1Low thermal expansionPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyNegative coefficientOpto electronic
Disclosed are composites having very low coefficients of thermal expansion and methods of preparing the composites. Also disclosed are composites having negative coefficients of thermal expansion. Applications of the composites to a wide variety of uses, such as electronic and optoelectronic devices are also disclosed.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
Negative thermal expansion material filler for low CTE composites
InactiveUS20070135550A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPolymer scienceBi modal
The present invention relates to a filler featuring a negative coefficient of thermal expansion and a bi-modal size distribution of filler particles. In an embodiment, the filler has micron and nanometer size filler particles. The present invention also relates to a composite having a polymer and a filler with nanometer size filler particles. Additionally, the present invention discloses a method of forming an electronic package with a composite having a polymer and a filler with nanometer size filler particles.
Owner:INTEL CORP
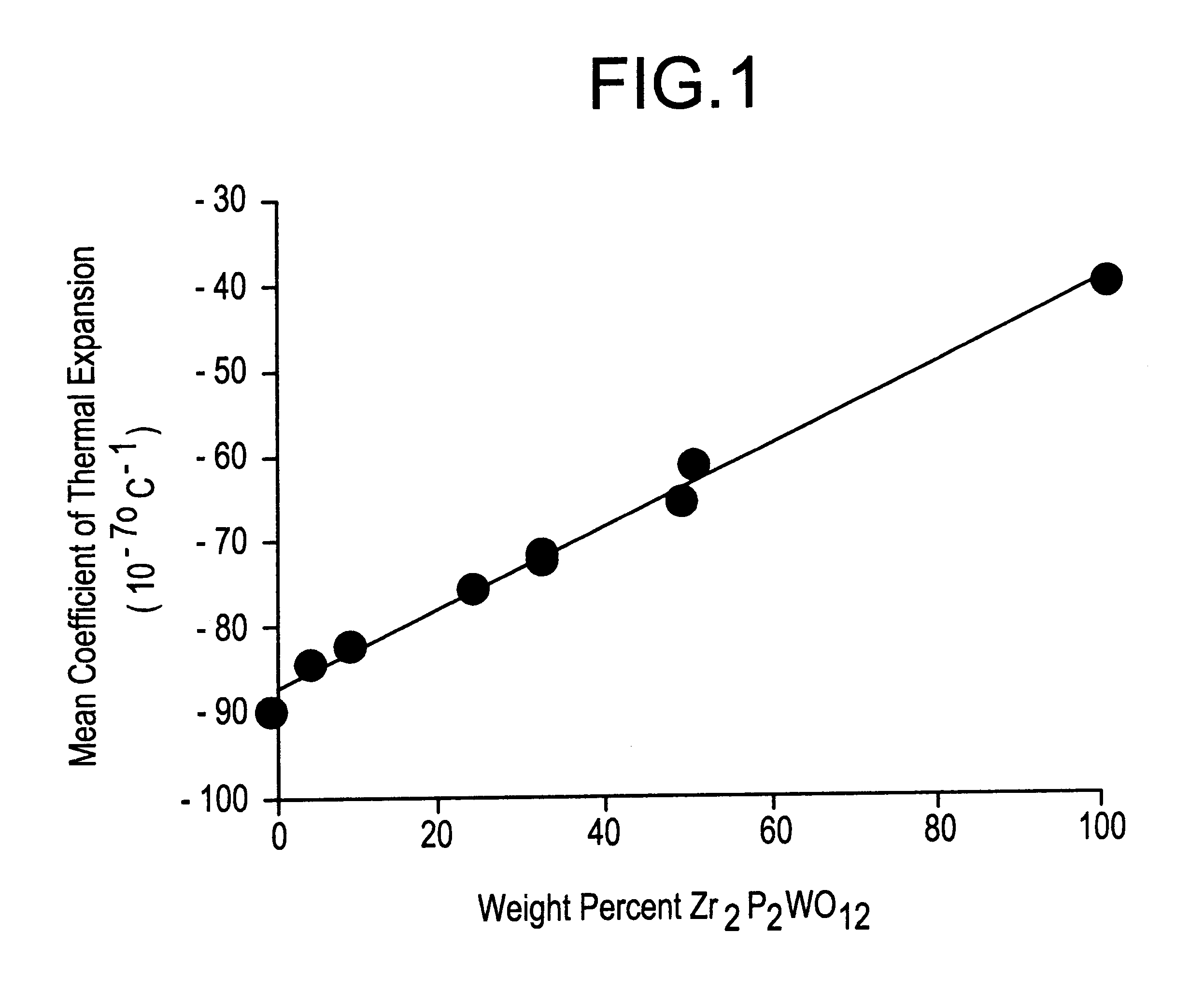
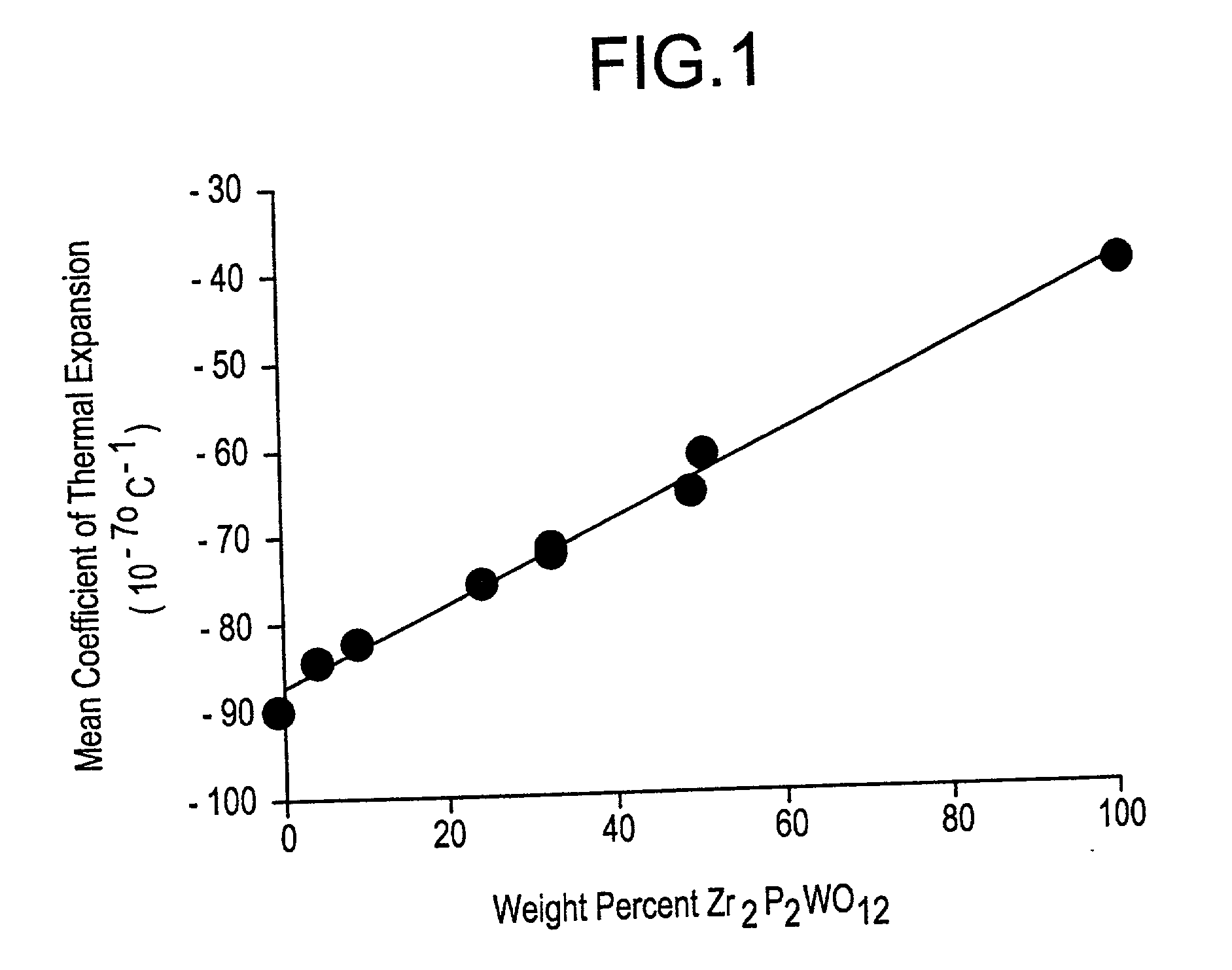
Sintering synthesis method of metal-based ceramic material Al-Zr2P2WO12 having controllable thermal expansion coefficient
The invention belongs to the field of inorganic non-metallic materials, and discloses a sintering synthesis method of a metal-based ceramic material Al-Zr2P2WO12 having a controllable thermal expansion coefficient. The sintering synthesis method utilizes ZrOCl2.8H2O, 5(NH4)2O.12WO3.5H2O and NH4H2PO4 as raw materials. The raw materials are respectively prepared into solutions. The sintering synthesis method comprises the following steps of 1, orderly and dropwisely adding a NH4H2PO4 solution and a ZrOCl2.8H2O solution into a 5(NH4)2O.12WO3.5H2O solution with stirring, wherein a mole ratio of Zr, P to W in the mixed solution is 2: 2: 1, adjusting a pH value of the mixed solution to a pH value of 8 to 10, and continuously stirring well, 2, standing for layering, removing supernatant and drying precipitates to obtain a precursor, and 3, sintering the dried precursor at a temperature of 900 to 1000 DEG C for 4 to 6 hours to obtain Zr2P2WO12 ceramic powder having a negative expansion coefficient, mixing the Zr2P2WO12 ceramic powder having a negative expansion coefficient and aluminum powder, grinding uniformly, compacting the mixture into blocks, and sintering at a temperature of 660 to 840 DEG C for 1 to 4 hours. The sintering synthesis method has simple processes, does not produce pollution, allows a low sintering temperature and a low sintering speed, and is suitable for large-scale production. Through combination of the Zr2P2WO12 ceramic powder having a negative expansion coefficient and the aluminum powder, the sintering synthesis method realizes production of the metal-based ceramic material Al-Zr2P2WO12 having a controllable thermal expansion coefficient, wherein the controllable thermal expansion coefficient can be changed in a wide range by control.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Nano rare earth zirconate ceramic powder material for high temperature heat barrier coat and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101104557ASmall particle diameterHigh coefficient of thermal expansionRare-earth elementZirconate
Disclosed are a nano-rare earth zirconate ceramic powder material for high-temperature thermal barrier coatings, and the preparation method, relating to a nano-rare earth zirconate ceramic powder material for high-temperature thermal barrier coatings, and the preparation method. The invention solves the problems that the existing ceramic materials for high-temperature thermal barrier coatings are of phase change failure, serious sintering, and too high thermal conductivity and mismatch with the matrix thermal expansion. The chemical formula of the nano-rare earth zirconate ceramic powder material for high-temperature thermal barrier coatings is Ln2Zr2O7, wherein, Ln is the combination of one or more rare earth elements among Gd, Sm, Nd or Yb. The preparation method is that rare earth oxide or soluble salt and zirconium salt containing rare earth oxides are used to respectively prepare the solution containing Ln3 + and the solution containing Zr4 +; the two solutions are mixed and added with surfactant under the ongoing mixing conditions; the mixed solution is dropped into precipitator to get sediment; after repeated washing, the sediment is dried, grinded and calcined. The invention can effectively protect high temperature alloy.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Honeycombed porous ceramic having high thermal conductivity and ultralow expansion coefficient
ActiveCN103145439AGood coating effectImprove mechanical propertiesCeramicwareCeramic moldingCrystal orientation
A honeycombed porous ceramic having a high thermal conductivity and an ultralow expansion coefficient relates to the technical field of the silicate industry. The ceramic having a low even negative thermal expansion coefficient and a high thermal conductivity is obtained through treating a rare earth mixture, potassium phosphotungstate, zirconium oxide and amorphous quartz particles as a sintering aid, and expansion coefficient and thermal conductivity adjustment agents, and the ceramic has a high-orientation sheet iolite structure and has a good catalyst coating performance and good mechanical strengths; and ethylene oxide having different molecular weights are adopted as a ceramic molding binder, rapeseed oil or peanut oil is treated as a primary molding lubrication agent, a paste goes through a high-pressure extruder orientation extruding channel, a crystal orientation carding die and a honeycombed porous die to obtain a green body having high-orientation arranged crystals, and a special sintering curve is adopted to obtain the ceramic. The above whole ceramic preparation process flow and the above formula are economic, stable and environmentally-friendly.
Owner:安徽中鼎美达环保科技有限公司
Optical device with negative thermal expansion substrate and uses therefor
InactiveUS20010021292A1Avoid microcracksEasy to meetCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesGratingMaterials science
Negative thermal expansion materials, methods of preparation and uses therefor are disclosed. The materials are useful for negative thermal expansion substrates, such as those used for optical fiber gratings.
Owner:CORNING INC
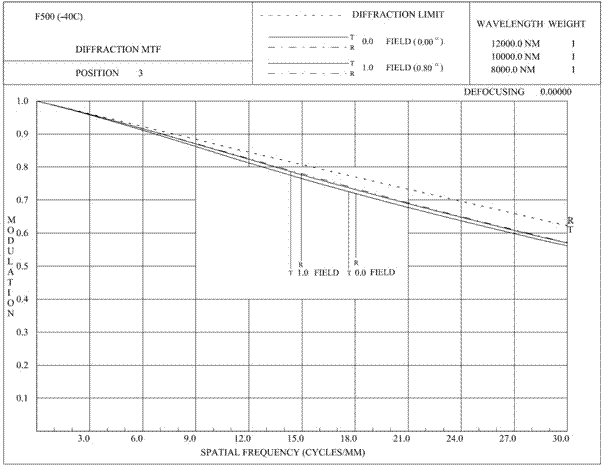
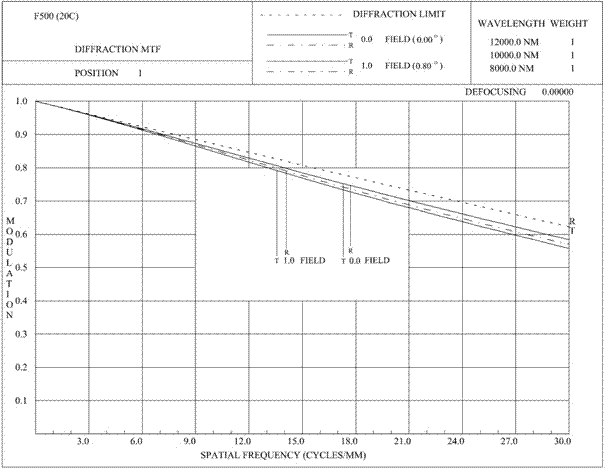
Large-relative-aperture long-focal length non-cooled infrared athermalization optical system
ActiveCN106990517ALong focal lengthIncrease the optical pathRadiation pyrometryOptical elementsImaging qualityOptoelectronics
A large-relative-aperture long-focal length non-cooled infrared athermalization optical system is arranged in front of the focal plane in the light spreading direction, and is composed of a main reflector, a secondary reflector, a first positive crescent lens, a second positive crescent lens, a reflection / diffraction mixed lens, a movable lens and a second negative crescent lens which are coaxially arranged in parallel. The system adopts a cassette system to increase the optical path by multiple reflections of light, thereby realizing the long coking of the optical system, wherein F<#> is 1; the focal length is 500mm; the center block is smaller or equal to 0.3; and the optical total length and focal length ratio is smaller than or equal to 0.64. Through the secondary imaging, the impact of stray light on the image quality of the system can be effectively inhibited. With the utilization of characteristics of negative dispersion and negative thermal expansion coefficient of the diffractive element and the reasonable distribution of the focal power of the reflection / diffraction mixed lens, the defocusing amount caused by the infrared optical system due to the temperature change is reduced, and combined with the mechanical active athermalization, the image plane defocusing compensation of the system in the temperature range of from -40 DEG C to +60 DEG C is achieved.
Owner:凯迈(洛阳)测控有限公司
Thermal expansion inhibitor, zero thermal expansion material, negative thermal expansion material, method for inhibiting thermal expansion, and method for producing thermal expansion inhibitor
InactiveCN101023147AExpanding the magnetic phase transition temperature rangeEnsuring a linear temperature profileOther chemical processesPrinted circuit aspectsNitrideMaterials science
Owner:RIKEN
TiNi alloy-based composite material with near-zero thermal expansion characteristic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102534275AAdjustable coefficient of thermal expansionAdjustable mechanicsTitaniumUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a TiNi alloy-based composite material with a near-zero thermal expansion characteristic and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing pure Ti powder and pure Ni powder according to an atomic ratio of titanium and nickel of (54-58 percent):(42-46 percent), preparing a porous TiNi alloy with negative thermal expansion and uniformly distributed pores by combining a holing technology and a unit metal powder step sintering method, and introducing a magnesium alloy with conventional positive thermal expansion into the pores of the porous TiNi alloy by using a light metal pressureless infiltration method to obtain the TiNi alloy-based composite material with the near-zero thermal expansion characteristic. The TiNi alloy-based composite material prepared by the method still has a shape memory effect and a hyperelastic behavior, is lighter than a compact TiNi alloy, has higher strength than the common porous TiNi alloy, and has the near-zero thermal expansion characteristic under certain conditions. The invention is used for preparing near-zero thermal expansion materials and controlling the thermal expansivity of the materials.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
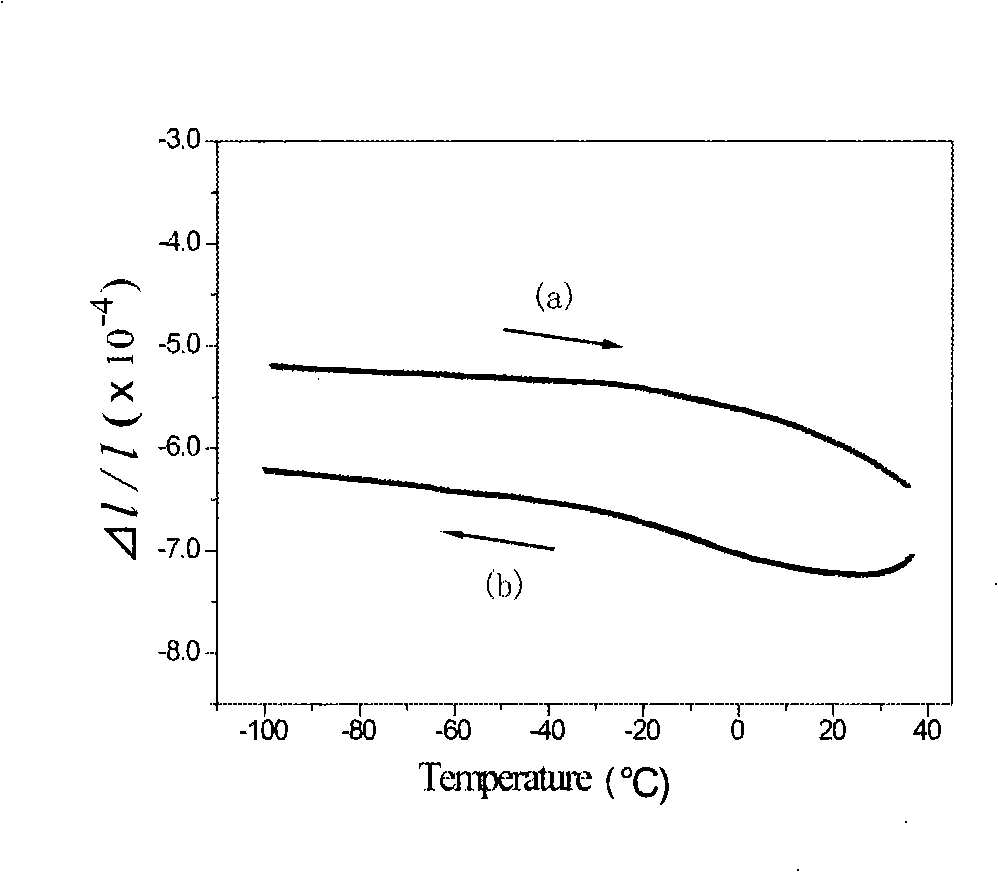
Nickel titanium niobium negative thermal expansion alloy and method of producing the same
InactiveCN101270424AHas negative thermal expansionSignificant negative thermal expansionRoll force/gap control deviceTemperature control deviceIngotTitanium
The invention discloses a negative thermal expansion alloy of Nickel-Titanium-Niobium and a preparation method thereof, relates to an alloy in particular to a negative thermal expansion alloy of Nickel-Titanium-Niobium and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides a negative thermal expansion alloy of Nickel-Titanium-Niobium which has negative thermal expansion characteristics in a wider temperature range and a preparation method. The component and the content in atom percentage is 40 to 49 percent of Nickel, 42 to 50 percent of Titanium and 1 to 18 percent of Niobium. The raw material of Nickel, Titanium and Niobium are added in furnace, the furnace is vacuumed and filled with Argon, and the Nickel-Titanium-Niobium alloy ingot is obtained after melting in 2500 to 2900 DEG C; the Nickel-Titanium-Niobium alloy ingot is hot-rolled to bulk alloy in 800 to 950 DEG C; the bulk alloy obtained is packaged in a quartz tube for heat treatment in the temperature of 800 to 950 DEG C and cooled in air. The bulk alloy after cooling is cool-rolled in 3 to 15 percent of the rolling reduction along the same direction and consequently the negative thermal expansion alloy of Nickel-Titanium-Niobium is obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Semiconductor device that is advantageous in operational environment at high temperatures
InactiveUS20070045623A1Read-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorSemiconductor
A semiconductor device comprises an N-type insulated-gate field-effect transistor including a first insulating layer that is provided along side walls of a gate electrode, has a negative thermal expansion coefficient, and applies a tensile stress to a channel region of the N-type insulated-gate field-effect transistor. The device also comprises a P-type insulated-gate field-effect transistor including a second insulating layer that is provided along side walls of a gate electrode, has a positive thermal expansion coefficient, and applies a compression stress to a channel region of the P-type insulated-gate field-effect transistor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High-performance thermoelectric device and ultrafast fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN107946452AImprove electrical output performanceImprove job stabilityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric materialsEnergy conversion efficiency
The invention discloses a high-performance thermoelectric device and an ultrafast fabrication method thereof. In the high-performance thermoelectric device, a segmented structure is employed to perform optimal matching of a thermoelectric material and a temperature difference environment, a blocking layer and a buffer stress layer are employed to reduce interface element migration and longitudinalcontact thermal expansion stress and improve bonding strength, a phonon scattering layer and a negative thermal expansion buffer layer are embedded to fix a thermoelectric leg so as to improve internal thermal resistance and horizontal thermal matching performance of the high-performance thermoelectric device, internal package and external package are employed to prevent the thermoelectric material from being oxidized and sublimed and improve external collision-resistant capability, the technical bottlenecks of low energy conversion efficiency, small specific power, poor thermal stability, poor collision performance, complicated fabrication process and the like of a traditional thermoelectric device are effectively broken through, meanwhile, the thermal stability and the mechanical structural performance of the high-performance thermoelectric device are improved to a great extent, long-term and excellent electrical output performance is guaranteed, and the working environment is expanded.
Owner:深圳热电新能源科技有限公司
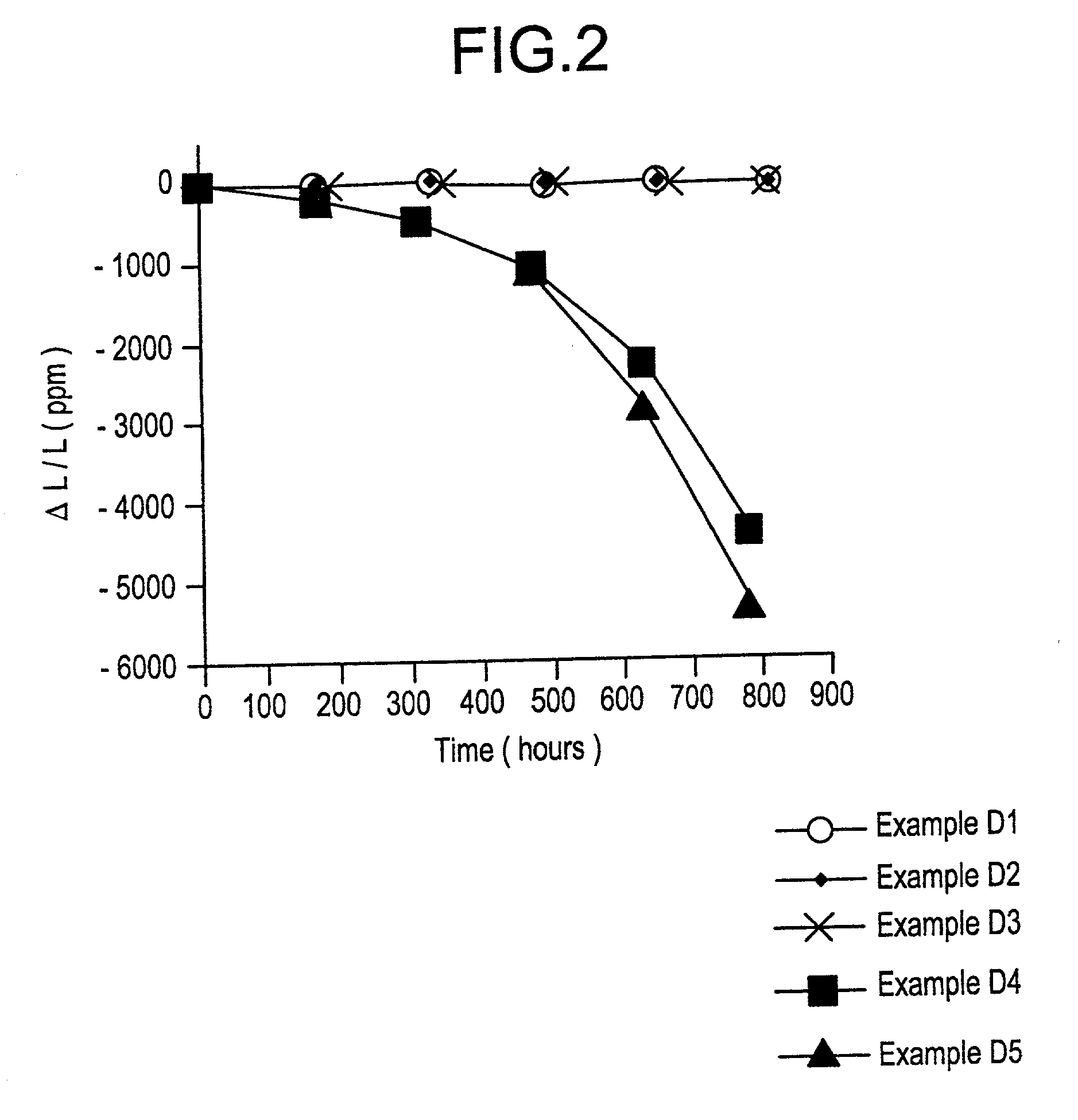
Sintering and synthesizing method of negative thermal expansion material Zr2P2MO12
The invention discloses a sintering and synthesizing method of negative thermal expansion material Zr2P2MO12, belonging to the field of inorganic nonmetallic materials. The negative thermal expansion material has a molecular formula as follows: Zr2P2MO12, wherein M is W or Mo. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: taking materials based on that a mole ratio of ZrO2 to WO3 to P2O5 or ZrO2 to MoO3 toP2O5 of 2:(1-1.2): (1-1.2), grinding and evenly mixing, and directly sintering the mixed raw materials or sintering the mixed raw materials after tabletting. The invention uses the high temperature rapid sintering and synthesizing method to prepare the negative thermal expansion material Zr2P2MO12 and takes P2O5 as the raw material, thereby avoiding discharge of redundant ammonia and reducing pollution; and the negative thermal expansion material can be sintered for one time at the same time. The invention has the advantages that the reaction process is simple, the sintering speed is rapid, and the sintering time is short; and the raw materials can fully react at high temperature, and the produced product has high purity.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN102636899AImprove box thickness uniformityWide operating temperature rangeNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayColor film
The invention discloses a liquid crystal display device, which comprises an array substrate and a color film substrate opposite to each other, wherein frame sealing glue is coated on the array substrate or the color film substrate, a display area is arranged within a frame sealing glue area, and an area between the peripheral edge of the display area and the inner side of the frame sealing glue is provided with a negative thermal expansion material. The liquid crystal display device disclosed by the invention solves the problems that low-temperature air bubbles are generated within the display area of a liquid crystal panel at a low temperature, and high-temperature vertical flows are generated at a high temperature.
Owner:NANJING CEC PANDA LCD TECH
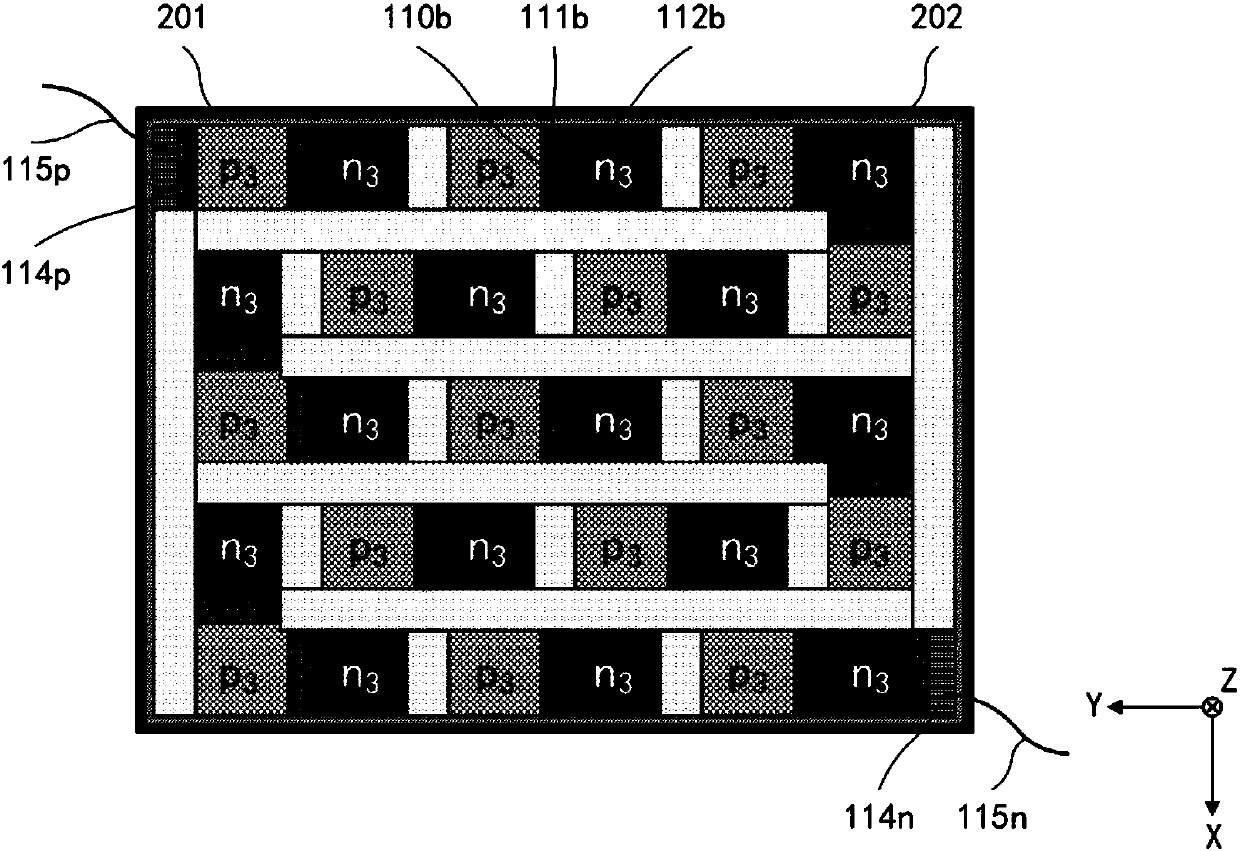
Negative thermal expansion dielectrics for thermal pole tip protrusion compensation
InactiveUS7102853B2Low deposition rateEasy to controlConstruction of head windingsHeads using thin filmsDielectricTransducer
A slider having a magnetic read / write head and including, a base coat, a reader element having a transducer, a writer element, the writer element including at least one conductive coil, the coil being electrically insulated by a composition which has a negative coefficient of thermal expansion, and an overcoat.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
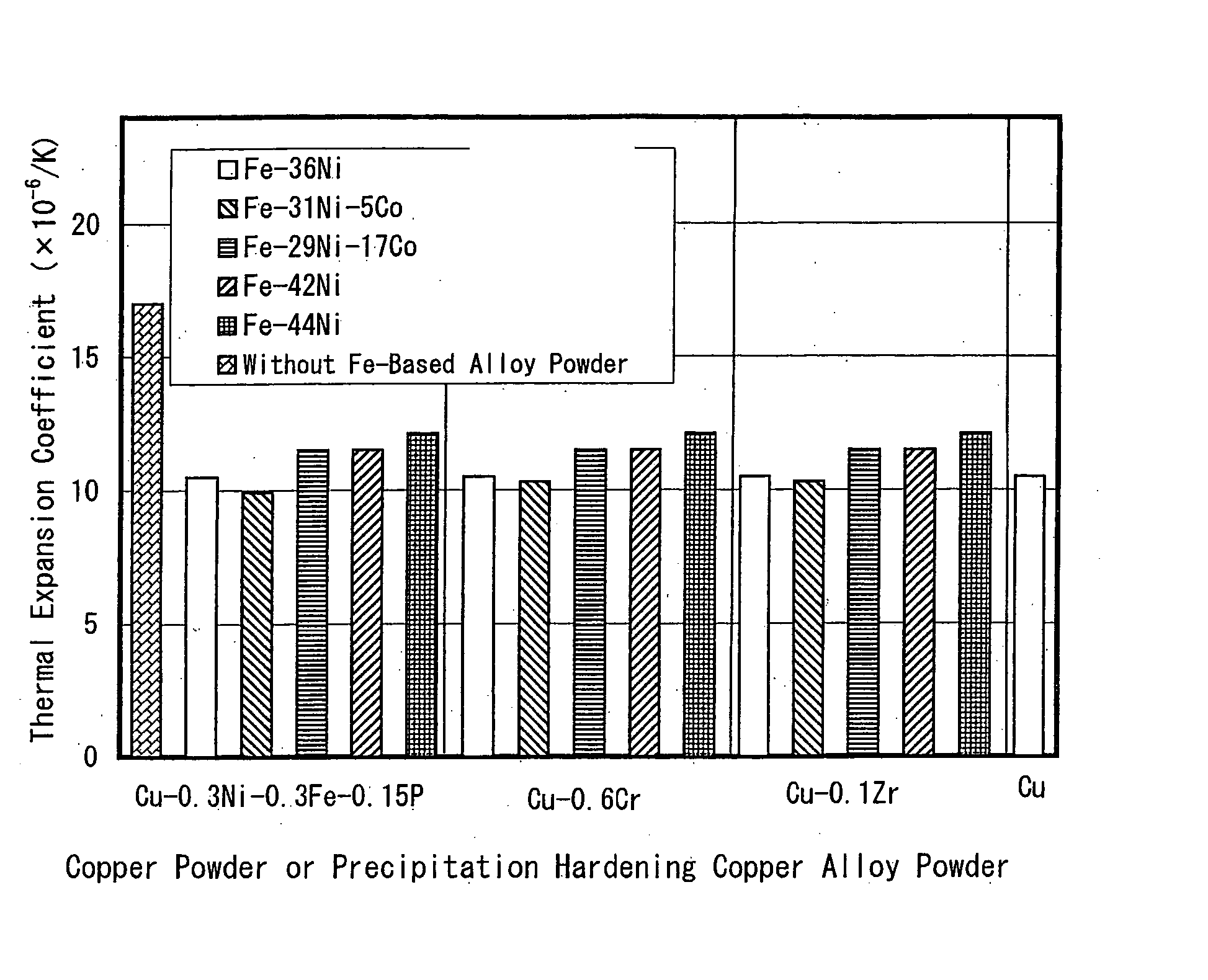
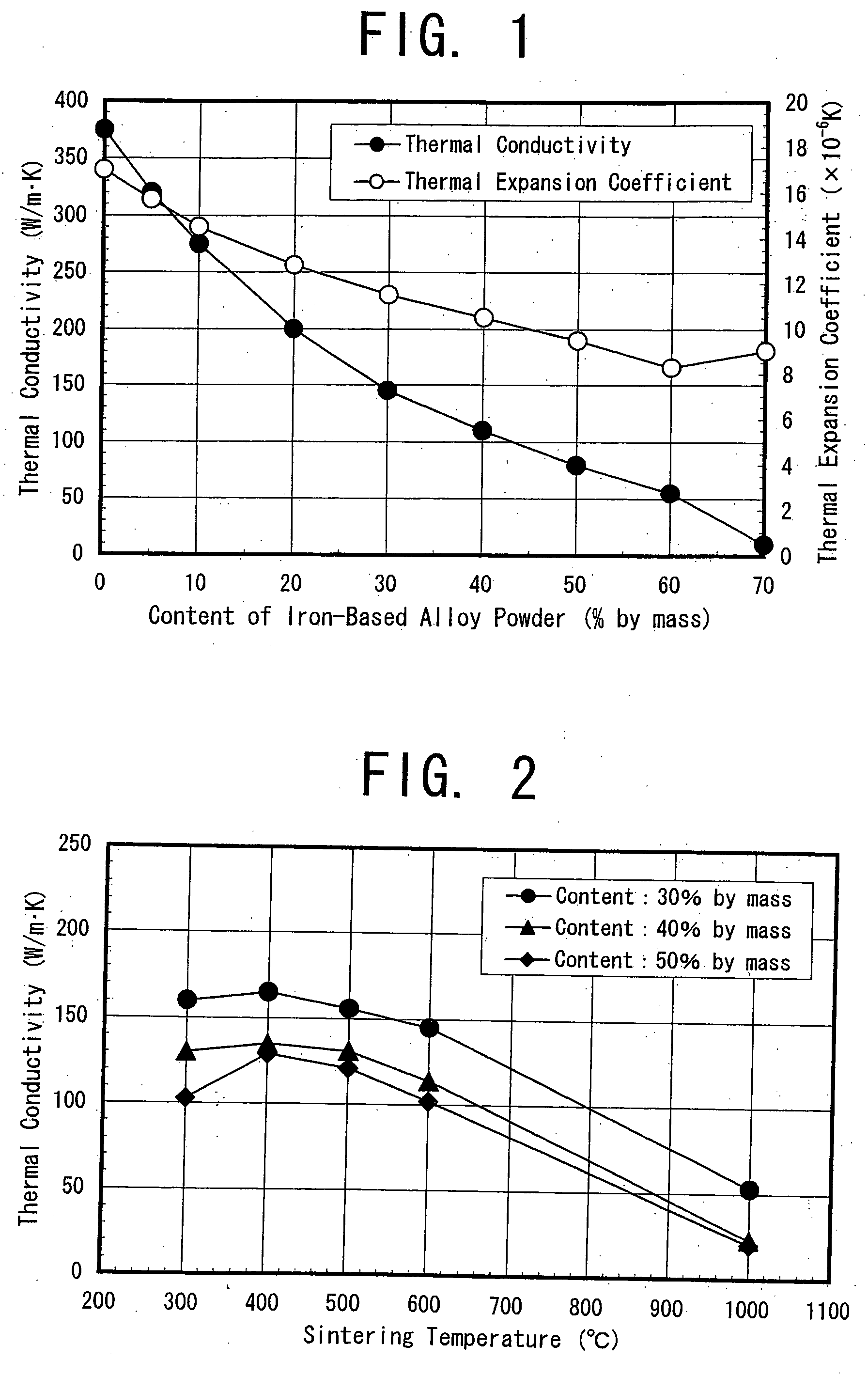
Copper based material of law thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20040213692A1Maintain good propertiesHigh production costTransportation and packagingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPowder mixtureMachinability
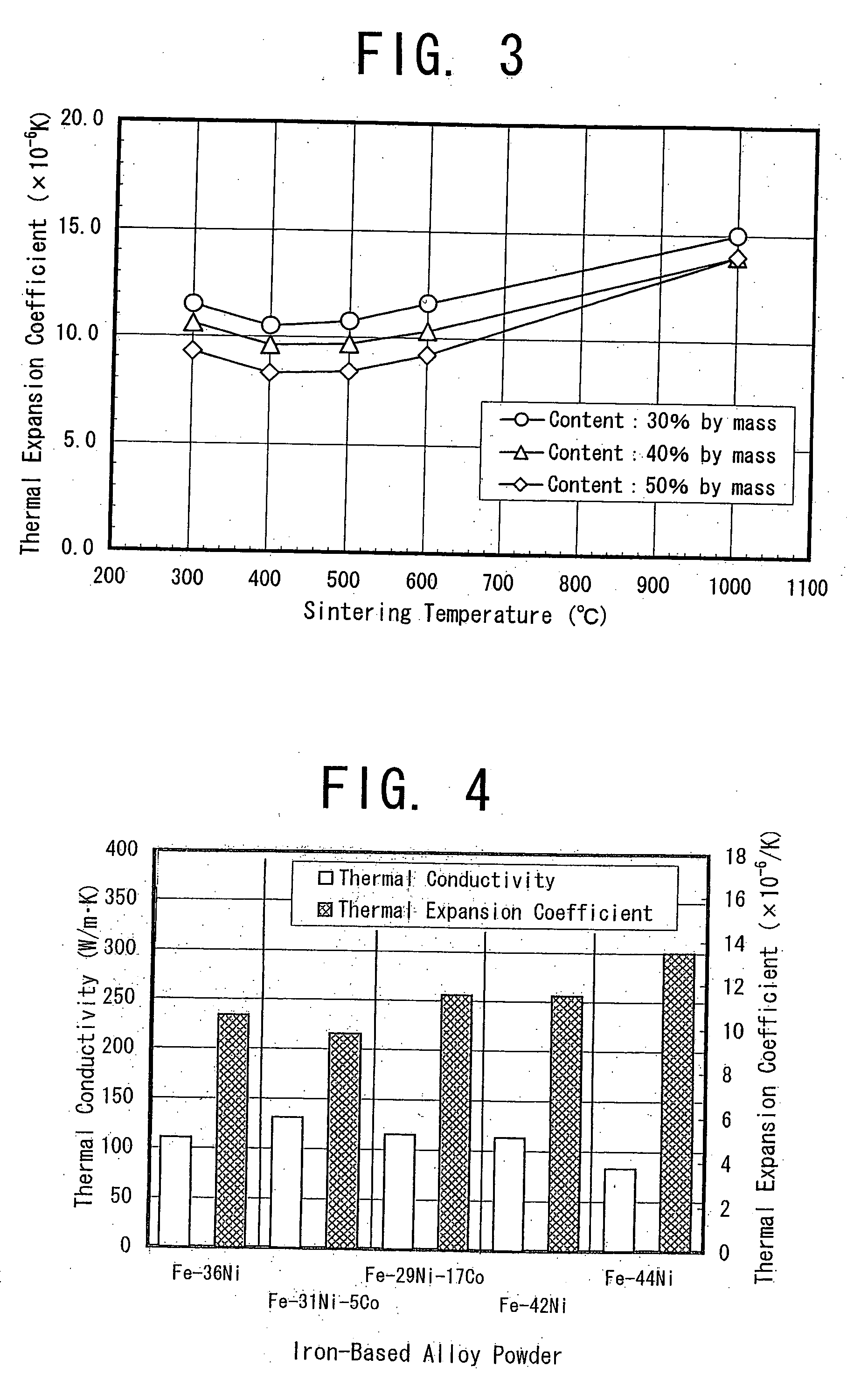
The invention proposes a copper-based material with low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity having good machinability and adaptability to nickel plating and also proposes a method for producing the same. The copper-based material is prepared through the steps of: adding 5 to 60% of iron-based alloy power having a certain value in thermal expansion coefficient into a matrix powder of pure copper phase powder and / or a precipitation hardening copper alloy powder; mixing the powders together; compacting the obtained powder mixture into a green compact and sintering it at temperatures of 400 to 600° C.
Owner:HITACHI POWDERED METALS COMPANY
Curable Resin Composition
ActiveCN104098871AHigh strengthArithmetic mean roughness is lowPrinted circuit detailsNon-metallic protective coating applicationEpoxyAnthracene
The object of the present invention is to provide a curable resin composition which is excellent in cracking elongation rate, is low in arithmetic average roughness of an insulating layer surface in a wet roughing process, is also low in root mean square roughness, can form a plated and inlaid conductor layer having enough peel strength, and is also low in coefficient of linear thermal expansion. The curable resin composition provided by the present invention comprises a phenoxy resin (A) having an anthracene structure, an epoxy resin (B) and a curing agent (C),and is characterized in that the total quantity of the phenoxy resin (A), the epoxy resin (B) and the curing agent (C) is set as 100% by mass, the above phenoxy resin (A) is 1-15% by mass, and the epoxide equivalent of the above phenoxy resin (A) is more than 5000.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Thermal switch based on negative thermal expansion
InactiveCN105304409ASimple structureLarge running strokeThermal switch detailsMaterials scienceThermal load
The invention discloses a thermal switch based on negative thermal expansion. The thermal switch comprises a negative thermal expansion element and a conductive element. The negative thermal expansion element is made of a negative thermal expansion material. The negative thermal expansion element is connected with the conductive element. When the temperature of the negative thermal expansion element is above a predetermined threshold, the conductive element and a thermal load are disconnected. When the temperature of the negative thermal expansion element is below the predetermined threshold, the conductive element and the thermal load are connected. According to the invention, the thermal switch based on negative thermal expansion is simple in structure and only has two parts; the running stroke of the thermal switch is large; a large gap caused by a large stroke can reduce an angle coefficient between two end faces of the gap; radiation heat transfer can be reduced; and disconnected thermal resistance is increased.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of synthesizing negative thermal expansion ceramics
A method of synthesizing negative-thermal-expansion ceramics of synthesizing Zr(1-x)XxW2O8 in which X represents a substituent element for zirconium Zr, and 0<=x <<1, having a negative thermal expansion coefficient, the method comprising mixing two mols of tungsten trioxide WO3 and one mol of the sum of zirconium oxide ZrO2 and a substituent element X in accordance with substitution amount x at a stoichiometrical ratio, further mixing the thus obtained starting material in a powdery form having a particle size distribution including two groups of particles comprising smaller diameter particles with a particle size of 0.1 to 1 mum and larger diameter particles with a particle size of 5 to 50 mum, and then sintering the staring powder being placed in a desired molding die whereby negative-thermal-expansion ceramics having an increased density equal with or higher than that of press molding products and of a larger size than that of the press molding products without press-molding the starting powder can be synthesized.
Owner:MORITEX CORP
Fuel injection valve
InactiveUS7032833B2Less complicated designLow thermal expansionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCombustionMagnetostrictive actuator
In a fuel injector, in particular a fuel injector for fuel-injection systems of internal combustion engines, a piezoelectric or magnetostrictive actuator is surrounded by a compensation sleeve. The compensation sleeve is made of a material exhibiting virtually no, or negative, thermal expansion, so that the thermal expansion of the compensation sleeve and that of an upper valve-body section and / or lower valve-body section essentially corresponds to the thermal expansion of the actuator and effective transmission elements to the valve-sealing seat. The compensation sleeve, radially on the outside, is enclosed by a spring sleeve, which connects the lower valve-body section to the upper valve-body section and prestresses the compensation sleeve for pressure.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Temperature-sensing switch for miniature thermal expansion fixed electrical contact
InactiveCN101226852AReduce volumeAction temperature sensitiveFire alarm electric actuationThermal switch detailsElectricityElectrical conductor
The purpose of the invention is to provide a mini-sized heat expansion temperature sensitive switch of fixing electric contacts. The electric contacts in short circuit output switch alarming signals and signals with different resistance values according to heat expansion of conducting fluid. The mini-sized heat expansion temperature sensitive switch of fixing electric contacts is small in volume, fast in response speed, high in sensitivity and wide in detecting temperature scope. The purpose of the invention is to realize the scheme as follows that a mini-sized heat expansion temperature sensitive switch of fixing electric contacts is composed of a sealing housing, heat expansion conducting fluid (which is called conducting fluid as follows) and conducting lead wires, which is characterized in that when the heat expansion conducting fluid is heat-expanded, the volume of the heat expansion conducting fluid is enlarged to reach and surpass different contact positions of the conducting lead wire to conduct the two ends of the conducting lead wire, thereby signaling short circuit signals with different temperatures. Compared with the prior art, the mini-sized heat expansion temperature sensitive switch of fixing electric contacts has the advantages that the invention has small volume, can output the switch alarming signals with different action temperatures, and is sensitive and reliable in action temperature.
Owner:张陈
Negative coefficient of thermal expansion particles and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20050100743A1Eliminate and reduce problemSimple and inexpensive methodLiquid surface applicatorsConductive materialNegative coefficientMaterials science
A negative coefficient of thermal expansion particle includes a first bilayer having a first bilayer inner layer and a first bilayer outer layer, and a second bilayer having a second bilayer inner layer and a second bilayer outer layer. The first and second bilayers are joined together along perimeters of the first and second bilayer outer layers and first and second bilayer inner layers, respectively. The first bilayer inner layer and the second bilayer inner layer are made of a first material and the first bilayer outer layer and the second bilayer outer layer are made of a second material. The first material has a greater coefficient of thermal expansion than that of the second material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Illumination system comprising a compound with low thermal expansion coefficient
InactiveUS20100181585A1Fabrication and/or setupOvercomes drawbackLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devices for light sourcesLighting systemMaterials science
The invention relates to an illumination system with a material having a low or negative thermal expansion coefficient in order to compensate for the thermal expansion of the further materials present in the illumination system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Negative thermal expansion system (NTEs) device for TCE compensation in elastomer composites and conductive elastomer interconnects in microelectronic packaging
ActiveUS7417315B2Enhancing negative coefficientLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStress conditionsElastomer composites
A Negative Thermal Expansion system (NTEs) device for TCE compensation or CTE compensation in elastomer composites and conductive elastomer interconnects in microelectronic packaging. One aspect of the present invention provides a method for fabricating micromachine devices that have negative thermal expansion coefficients that can be made into a composite for manipulation of the TCE of the material. These devices and composites made with these devices are in the categories of materials called “smart materials” or “responsive materials.” Another aspect of the present invention provides microdevices comprised of dual opposed bilayers of material where the two bilayers are attached to one another at the peripheral edges only, and where the bilayers themselves are at a minimum stress conditions at a reference temperature defined by the temperature at which the bilayers are formed. These devices have the technologically useful property of volumetrically expanding upon lowering of the device temperature below the reference or processing temperature.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Package structure and manufacturing method for the same
InactiveUS20130105852A1Avoid alignmentAlignment shiftSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound (substance)Electrical connection
A package structure and a manufacturing method for the same are provided. The package structure includes a chip, a substrate and at least one adhesive layer. The chip has at least one electrode portion. The substrate has at least one circuit portion. The adhesive layer is disposed between the electrode portion and the circuit portion to form an electrical connection therebetween. The adhesive layer is a material, which comprises a metal compound, with a Negative Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (Negative CTE). Because of the material with a Negative CTE, the alignment shift can be avoided after the chip and the substrate are adhered together.
Owner:WALSIN LIHWA
Micro-channel heat dissipation structure, manufacturing method and electronic device
ActiveCN110364501AImprove effective thermal conductivityMeet cooling needsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringNegative thermal expansion
The invention provides a micro-channel heat dissipation structure. The structure comprises at least two heat dissipation units which are stacked in sequence; each heat dissipation unit is provided with a heat dissipation channel; at least one inlet and at least one outlet, communicating with the heat dissipation channels, are formed in the heat dissipation units in contact with a chip; at least two circulation channels are formed in the other heat dissipation units, so that the heat dissipation channels in the adjacent heat dissipation units are connected; the structure also comprises negativethermal expansion bodies; each circulation channel is filled with the corresponding negative thermal expansion body; and the negative thermal expansion bodies are used for connecting or disconnectingthe heat dissipation channels of the adjacent heat dissipation units. The conduction or non-conduction of the adjacent heat dissipation units is controlled by the expansion or contraction of the negative thermal expansion bodies. Thus, the effective heat conduction coefficient of the heat dissipation structure can be improved on the whole, and the heat dissipation requirements of a high-power chip are met. The invention further provides a manufacturing method of the micro-channel heat dissipation structure and an electronic device with the micro-channel heat dissipation structure.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Insulating resin composition for printed circuit board and products manufactured by using the same
InactiveCN104559055APlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsCopperNegative coefficient
Disclosed herein are an insulating resin composition for a printed circuit board, and an insulating film, a prepreg, a copper clad laminate, or a printed circuit board manufactured by using the same. More specifically, the insulating resin composition contains an eucryptite inorganic filler having a negative coefficient of thermal expansion, such that a glass transition temperature and a coefficient of thermal expansion may be improved, and warpage of the insulating film, the prepreg, the copper clad laminate, or the printed circuit board manufactured by using the insulating resin composition for a printed circuit board may be minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com