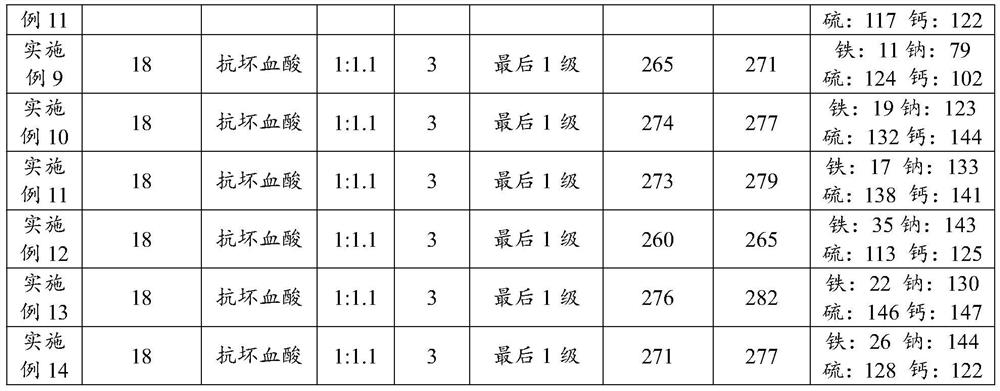
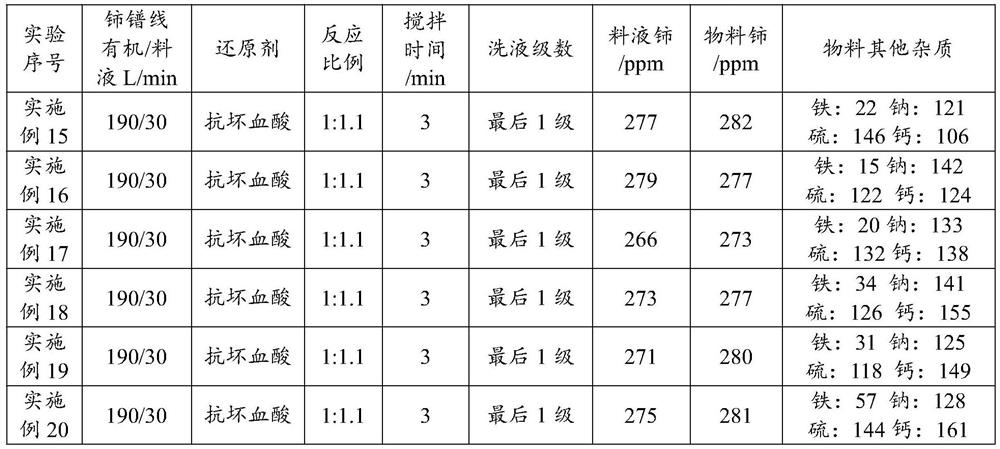
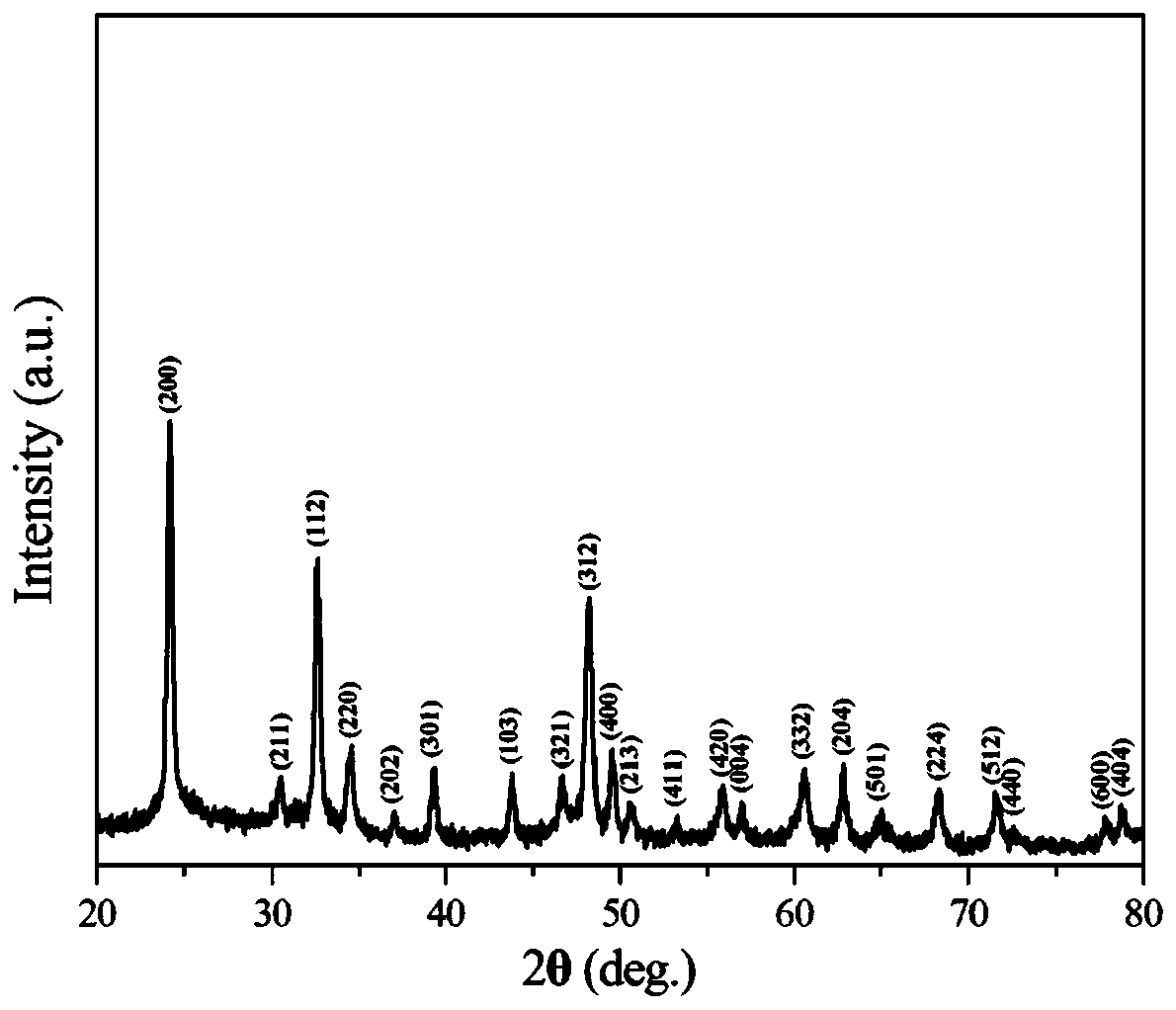
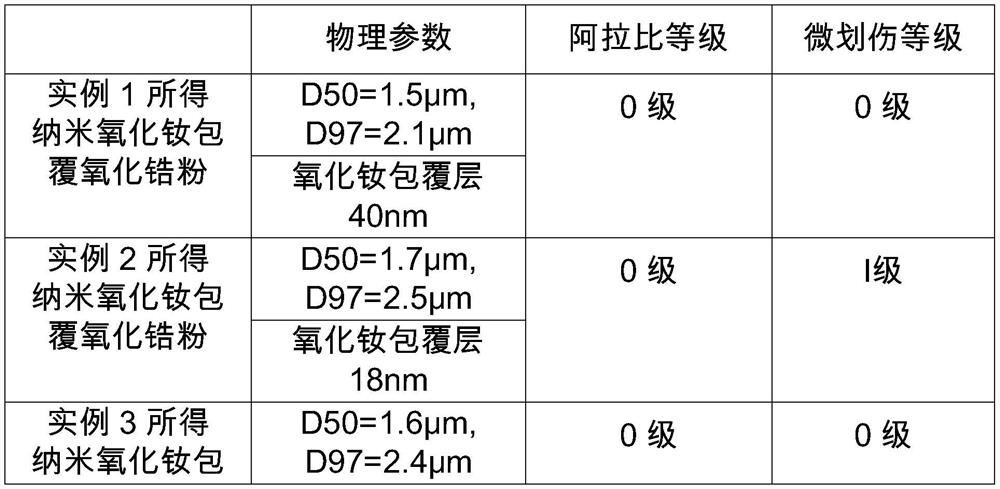
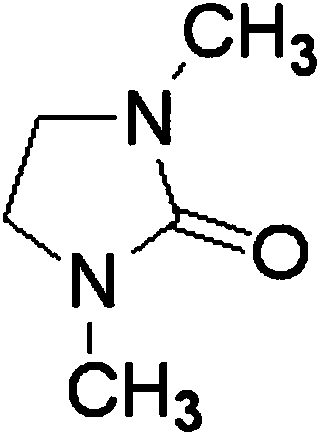
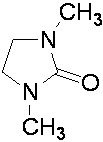
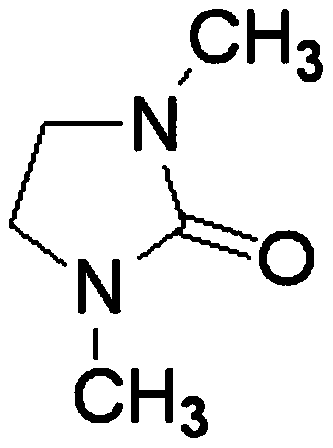
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Praseodymium(III) chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Praseodymium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula PrCl₃. It is a blue-green solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a light green heptahydrate.
Rare earth compound/titanate coupling agent modified ultrafine calcium carbonate filler
ActiveCN103788410ASimple production processGood dispersionPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsRare earthPolyvinyl chloride
The invention relates to a calcium carbonate filler and in particular relates to a rare earth compound / titanate coupling agent modified ultrafine calcium carbonate filler. The modified calcium carbonate is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 200 parts of ultrafine calcium carbonate, 1-2 parts of talcum powder, 1-2 parts of homo-polypropylene, 2-4 parts of jade powder, 1-2 parts of zinc sulfate, 1-2 parts of yttrium chloride, 1-2 parts of praseodymium chloride, 1-2 parts of lanthanum nitrate, 1-2 parts of titanate coupling agent TMC-TTS, 1-2 parts of graphene and 4-5 parts of accessory ingredient. According to the modified calcium carbonate powder, composite rare earth compounds such as yttrium chloride, praseodymium chloride, lanthanum nitrate and the like and the titanate coupling agent TMC-TTS are used for modifying the ultrafine calcium carbonate, so that performance indexes such as oil absorption value, viscosity and activating rate are improved; the ultrafine calcium carbonate is more easily dispersed and dissolved in high-molecular polymers; and when the ultrafine calcium carbonate is used for filling a PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) material, the mechanical property of the PVC material is effectively improved and the good effect of toughening and reinforcing is achieved.
Owner:安徽雪城超细碳酸钙有限公司
Preparation method of yellow zirconium silicate pigment for ink-jet printing and product prepared by same
InactiveCN102173427AUniform colorHigh suspension and tinting strengthSilicon compoundsChemistryVivid color
The invention relates to a preparation method of a yellow zirconium silicate pigment for ink-jet printing and a product prepared by the same. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: successively introducing gas-phase SiO2 into a ZrOCl2.8H2O solution according to the molar ratio, and adding a praseodymium chloride solution and PEG (polyethylene glycol) 1000 for reacting to obtain a colloid; regulating the pH value of the colloid to be equal to 7, and then, adding LiF powder; and calcining at 900-1000 DEG C to obtain a yellow pigment for ink-jet printing, wherein the granularity of the yellow pigment is less than 1mu m, and the service temperature of the yellow pigment is higher than 1300 DEG C. The product prepared by the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of uniform chromaticity, high suspension property and coloring power, good high-temperature stability, vivid color development, good decorative effect and the like, meets the requirement for ink-jet printing of ink, and has wide application prospects in the fields of production and the like of architectural ceramics.
Owner:JINGDEZHEN CERAMIC INSTITUTE
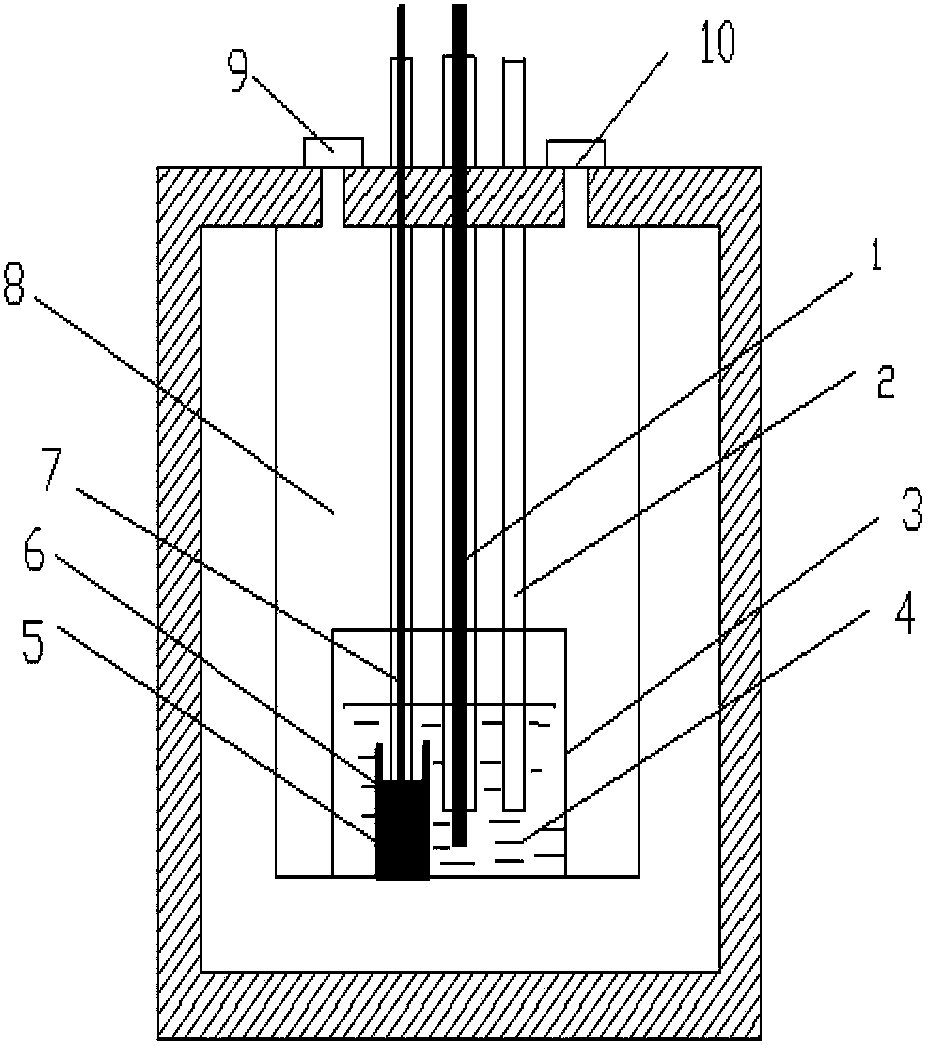
Method and device for reducing, extracting and separating rear earth through fused salt and liquid metal
The invention provides a method and a device for reducing, extracting and separating rear earth through fused salt and liquid metal. Liquid aluminum serves as a cathode, a graphite rod serves as an anode, KCl-LiCl is added into an electrolytic cell to be heated and smelted to serve as electrolyte, and lithium obtained from electrolysis at the cathode is dissolved in the liquid aluminum to obtain a liquid aluminum-lithium alloy by means of electrolysis; praseodymium chloride and samarium chloride are added into the electrolytic cell to serve as a fused salt phase, and a constant speed stirring extraction reaction is carried out in an argon atmosphere with the liquid aluminum-lithium alloy as an extraction agent; the fused salt phase is separated from a liquid metal phase, samarium is extracted into the liquid metal phase to form an aluminum-lithium-samarium alloy, and praseodymium is left in the fused salt phase so as to separate the samarium from the praseodymium. The method and the device provided by the invention are suitable for extreme conditions such as high temperature, and strong radiation; the reducing agent can be recycled to save resources; the distribution coefficient of the samarium in the alloy and the fused salt is 68.1-142.4, the distribution coefficient of the praseodymium in the alloy and the fused salt is 2.9-23.2, and the samarium-praseodymium separation coefficient is 5.0-23.3.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
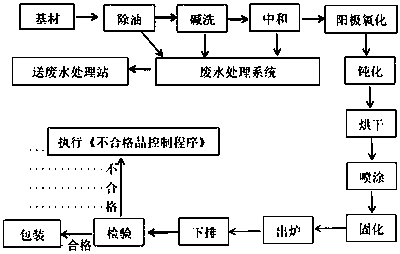
Preparation method of anticorrosive aluminum profile
InactiveCN110644030AEffective protectionStrong adhesionAnodisationAnti-corrosive paintsChemical treatmentMaterials science
The invention discloses a preparation method of an anticorrosive aluminum profile. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, degreasing; S2, alkali washing; S3, neutralization; S4, anodic oxidation; S5, passivation treatment, specifically, the aluminum alloy profile is immersed into a chemical treatment solution containing sodium fluoride with the concentration of 0.2-0.3g / L, ammonium hydrofluoric acid with the concentration of 0.4-0.6g / L, potassium permanganate with the concentration of 0.1-0.15g / L, nitrate with the concentration of 0.1-0.13g / L and praseodymium chloride with the concentration of 0.2-0.3g / L, a protective layer is formed on the surface of an anodic oxide film in the soaking process, and after soaking for 20-30min, the aluminum alloy profile is taken out and then is washed by clear water; S6, drying treatment; and S7, spraying treatment, specifically, a raw material consisting of 21-35 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, 80-90 parts of dimethylacetamide, 13-18 partsof NaH2PO4, 5-10 parts of titanium dioxide and 10-12 parts of pigment is sprayed onto the surface of the aluminum alloy profile, the spraying time is 1.0-2.0min, and the spraying pressure is 0.05-0.07MPa, so that an anticorrosive coating is formed on the surface of the protective layer. The preparation method of the anticorrosive aluminum profile has the beneficial effects that the corrosion resistance effect is better, and the adhesive force is stronger; and toxic substances harmful to the human body and the environment cannot be generated in the production and preparation process, and the environment is not polluted.
Owner:CHENGDU SUNSHINE ALUMINUM
Chestnut shell active carbon and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103551109AWell-developed pore structureWell-developed structureOther chemical processesCerium nitrateHazardous substance
Chestnut shell active carbon is prepared by the following raw materials by weight: 120-140 parts of chestnut shell, 3-5 parts of zinc chloride, 4-6 parts of Arabic gum, 4-6 parts of periston, 25-30 parts of bentonite, 10-15 parts of alumina, 20-25 parts of pumice, 2-4 parts of lanthanum chloride, 2-4 parts of cerium chloride, 2-4 parts of scandium chloride, 2-4 parts of yttrium chloride, 2-4 parts of praseodymium chloride, 1-3 parts of lanthanum nitrate, 1-3 parts of cerium nitrate, 1-2 parts of scandium nitrate, 1-2 parts of yttrium nitrate, 1-2 parts of praseodymium nitrate, 4-5 parts of modified diatomite, and a proper amount of water. Chestnut shell is used as a raw material, so as that the active carbon has advantages of developed aperture structure, big specific surface area, high adsorption speed, and good adsorption capability on various solutes and dissociation gases; lanthanum chloride is used for activation so as to form active carbon, which has big gaps and strong adsorption capability, is suitable for absorbing organic matters in air and water and removing harmful substances like formaldehyde, is low in cost, and is suitable for industrialization production.
Owner:BENGBU PIONEER FILTER
Method for modifying aluminium profile for buildings
InactiveCN103820776AStable internal performanceImprove performanceMetallic material coating processesSodium sulfateMaterials science
The invention relates to modification of aluminium profiles and in particular relates to a method for modifying an aluminium profile for buildings. The method comprises the steps of smelting aluminium ingots into molten aluminium, adding mixed powder of zirconium-coated titanium dioxide and zirconium-coated silicon dioxide, maintaining the materials at a melting temperature for 3-5 hours, pouring the materials into a mold with a temperature above 600 DEG C under the pressure of 1.1-1.5MPa, and cooling and insulating so as to obtain the aluminium profile through demolding; preparing a modifying agent from 20-40 parts of sodium fluoride, 30-60 parts of ammonium bifluoride, 10-20 parts of potassium permanganate, 40-50 parts of potassium chromate, 15-25 parts of zinc phosphate, 8-18 parts of sodium nitrate, 5-12 parts of praseodymium chloride, 10-16 parts of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 7-14 parts of malic acid, 8-12 parts of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfate, 6-13 parts of nickel sulfate, 15-25 parts of triethanolamine, 5-10 parts of reducing agents containing alkali metals, 7-13 parts of chlorinated polypropylene or polyolefin substrate adhesion promoter and 500-900 parts of water by weight, and controlling the pH value to be 3-4, thus obtaining the modifying agent; dipping and drying twice to obtain a modified aluminium profile. The prepared aluminium profile is bright and soft, has excellent corrosion resistance and is safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:MERLAN INT GRP H K
Method for separating and recovering valuable components from rare earth praseodymium-neodymium fused salt electrolysis waste
ActiveCN104805292AReduce roasting processSimple processProcess efficiency improvementSolid phasesScrap
The invention discloses a separating and recovering method for separating valuable components in rare earth praseodymium-neodymium fused salt electrolysis waste into a liquid phase (praseodymium-neodymium chloride) and a solid phase (praseodymium-neodymium fluoride) by adopting leaching by low-concentration hydrochloric acid. The method is characterized by comprising steps of raw materials processing, beating and leaching to obtain filter residues containing praseodymium-neodymium fluoride and filtrate containing praseodymium-neodymium chloride; the filter residues containing praseodymium-neodymium fluoride are washed to neutral and dried at the temperature of 60-80 DEG C to obtain praseodymium-neodymium fluoride; the filtrate containing praseodymium-neodymium chloride is subjected to crystallization and precipitation with an oxalic acid method to obtain praseodymium-neodymium oxalate, and the obtained praseodymium-neodymium oxalate is burnt at the temperature of 950 DEGC and degraded to obtain praseodymium-neodymium oxide. By means of the characteristic that rare earth fluoride does not react with hydrochloric acid, the low-concentration hydrochloric acid is used for leaching soluble impurities and oxides, a rare earth fluoride structure is not required to be damaged with high-temperature strong acid or strong base, and the valuable components are recycled; compared with the traditional concentrated sulfuric acid roasting method or strong base roasting method, the method omits a roasting process, a follow-up feed liquid is not required to be subjected to an extraction process, so that the method has the characteristics of simple process, short process flow, low cost, high yield and environment-friendliness, and the fluorine element is recycled efficiently.
Owner:YIYANG HONGYUAN RARE EARTH
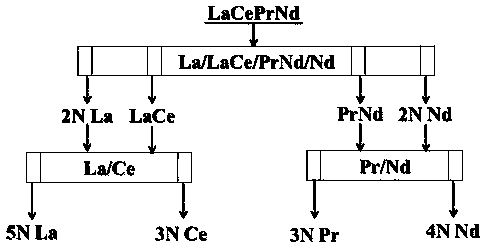
Technology for separating light rare earth from southern ion-absorbing type rare earth ore
InactiveCN110306047AHigh yieldImprove separation efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementRare earthCerium
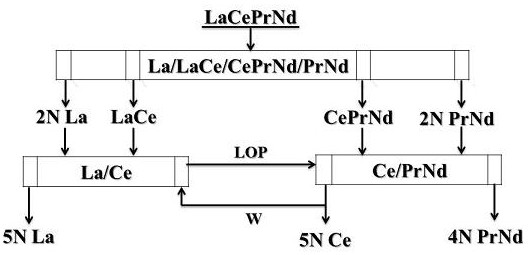
The invention provides a technology for separating light rare earth from southern ion-absorbing type rare earth ore. The technology is implemented by adopting an aqueous light rare earth chloride solution obtained by grouping separation from the southern ion-absorbing type rare earth ore as a feed liquid and P507 as an extraction agent, and comprises three fractional extraction systems, and the three fractional extraction systems comprise a La / LaCe / PrNd / Nd four-outlet fractional extraction and separation system, a La / Ce two-feed-inlet fractional extraction and separation system and a Pr / Nd two-feed-inlet fractional extraction and separation system. By means of combination of the three fractional extraction systems, four separation products including 5N-grade lanthanum chloride, 3N-grade cerium chloride, 3N-grade praseodymium chloride and 4N-grade neodymium chloride are obtained directly. The technology has the advantages of high purity of a target separation product, high yield of rareearth element, low acid-base consumption, short technological process, low separation cost and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Method for dyeing protein fiber fabric with natural blue pigment Indigoidine after color matching
InactiveCN108894014AHas antibacterial propertiesGood technical effectDyeing processIndigoidineLanthanum
The invention relates to the field of light industries, and discloses a method for dyeing protein fiber fabric with a natural blue pigment Indigoidine after color matching. The natural blue pigment Indigoidine, a monascus red pigment and / or a monascus yellow pigment are sequentially added to a solvent for color matching; and the mixture are added to water together with praseodymium chloride or lanthanum trioxide or sodium sulfonate with the mass percentage being 0.1-5 g / L, the pH value is adjusted to 2.5-6.5, the fabric is added into the dyeing liquor, the temperature is heated to 50-95 DEG Cfor dyeing, the fabric is washed with water and dried, and then the dyeing of the fabric is completed. Natural pigments do not produce toxins during fermentation. In order to achieve industrial production, strains must also be used for liquid fermentation so as to solve the shortcomings of plant dyes. Furthermore, some microbial dyes have certain antibacterial effects in addition to bright colors, which indicates that some microbial dyes also have potential application value in the functional finishing of fabric.
Owner:德清亿玛生物科技有限公司
Catalyst for production of tert-butylamine as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
ActiveCN103657691AIncrease contact areaExtended service lifePhysical/chemical process catalystsAmino compound preparation by condensation/addition reactionsWater vaporBiological activation
The invention provides a catalyst for production of tert-butylamine as well as a preparation method and an application of the catalyst. A fluorine-modified Ni-containing hydrotalcite-like compound adopting a mesoporous structure is taken as a carrier, after activation by vapor, the hydrotalcite-like compound is used for carrying gadolinium chloride and / or praseodymium chloride with a liquid phase sedimentation method, and then the catalyst product is produced through drying. The specific aperture and the shape selectivity of the catalyst product are very effective on inhibiting side reactions, and the carried gadolinium chloride / praseodymium chloride provides L acidic active sites for the catalyst. Under the low pressure condition, the higher isobutylene conversion per pass can also be maintained if the catalyst is applied to a reaction for preparing the tert-butylamine through direct amination of isobutylene and ammonia, the catalyst can still keep higher activity after long-term operations, and the service life of the catalyst can be prolonged.
Owner:NANTONG FINC PHARMA CHEM
Method for manufacturing low-expansion glass-ceramics by high silicon-iron tailings
A method for manufacturing low-expansion glass-ceramics by high silicon-iron tailings comprises the step of perparing a low-expansion glass-ceramics batch which comprises the following materials in parts by weight: 40-45 parts of 80-mesh high-silicon iron tailings, 50-55 parts of 100-mesh quartz sand, 10-15 parts of 100-mesh alumina, 10-15 parts of lithium carbonate, 3-6 parts of zinc oxide, 3-6 parts of barium selenate, 2-5 parts of rare-earth cerium oxide powder, 1-4 parts of lithium zirconate, 2-5 parts of boron nitride, 3-6 parts of praseodymium chloride, 0.2-0.5 part of beryllia, 0.5-0.9 part of bismuth subcarbonate and 0.1-0.4 part of sodium antimonate. The invention aims to provide the method for manufacturing low-expansion glass-ceramics by high silicon-iron tailings, the method can reduce environmental pollution and lower manufacturing cost, and the obtained glass-ceramics is low in thermal expansion coefficient, high in thermal stability and softening temperature and very good in thermal shock resistance.
Owner:BEIJING QING MAI HUA QING HLDG GRP CO LTD
Catalyst for production of tert-butylamine as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
ActiveCN103657691BIncrease contact areaExtended service lifePhysical/chemical process catalystsAmino compound preparation by condensation/addition reactionsWater vaporBiological activation
The invention provides a catalyst for production of tert-butylamine as well as a preparation method and an application of the catalyst. A fluorine-modified Ni-containing hydrotalcite-like compound adopting a mesoporous structure is taken as a carrier, after activation by vapor, the hydrotalcite-like compound is used for carrying gadolinium chloride and / or praseodymium chloride with a liquid phase sedimentation method, and then the catalyst product is produced through drying. The specific aperture and the shape selectivity of the catalyst product are very effective on inhibiting side reactions, and the carried gadolinium chloride / praseodymium chloride provides L acidic active sites for the catalyst. Under the low pressure condition, the higher isobutylene conversion per pass can also be maintained if the catalyst is applied to a reaction for preparing the tert-butylamine through direct amination of isobutylene and ammonia, the catalyst can still keep higher activity after long-term operations, and the service life of the catalyst can be prolonged.
Owner:NANTONG FINC PHARMA CHEM
Method for extracting praseodymium and preparing aluminum-lithium-praseodymium alloy by continuous use of molten salt electrolysis and reduction extraction
The invention provides a method for extracting praseodymium and preparing an aluminum-lithium-praseodymium alloy by continuous use of molten salt electrolysis and reduction extraction. The method comprises the following steps of: performing electrolysis by taking molten aluminum as a cathode, a graphite rod as an anode and a mixture of KCl and LiCl as an electrolyte; performing cathode electrolysis to obtain lithium; dissolving the lithium in the molten aluminum to obtain a molten aluminum-lithium alloy with lithium content of 3-5% by mass; adding praseodymium chloride as a molten salt phase into an electrolytic tank, mixing the molten aluminum-lithium alloy as a liquid metal phase with the molten salt, and performing an extraction reaction by taking the molten aluminum-lithium alloy as an extraction agent; and pouring out the molten salt to obtain the aluminum-lithium-praseodymium alloy. By adopting a molten salt / liquid metal system, the method provided by the invention is suitable for extreme conditions such as high temperature, intense radiation and the like; compared with wet-process extraction, the volume of the material extracted by use of high-temperature molten salt is small, and the miniaturization of equipment is facilitated; and a reducing agent is prepared by the molten salt electrolysis and can be recycled. The method provided by the invention adopts high-temperature chemical extraction and has broad application prospects in the field of nuclear waste after-treatment.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
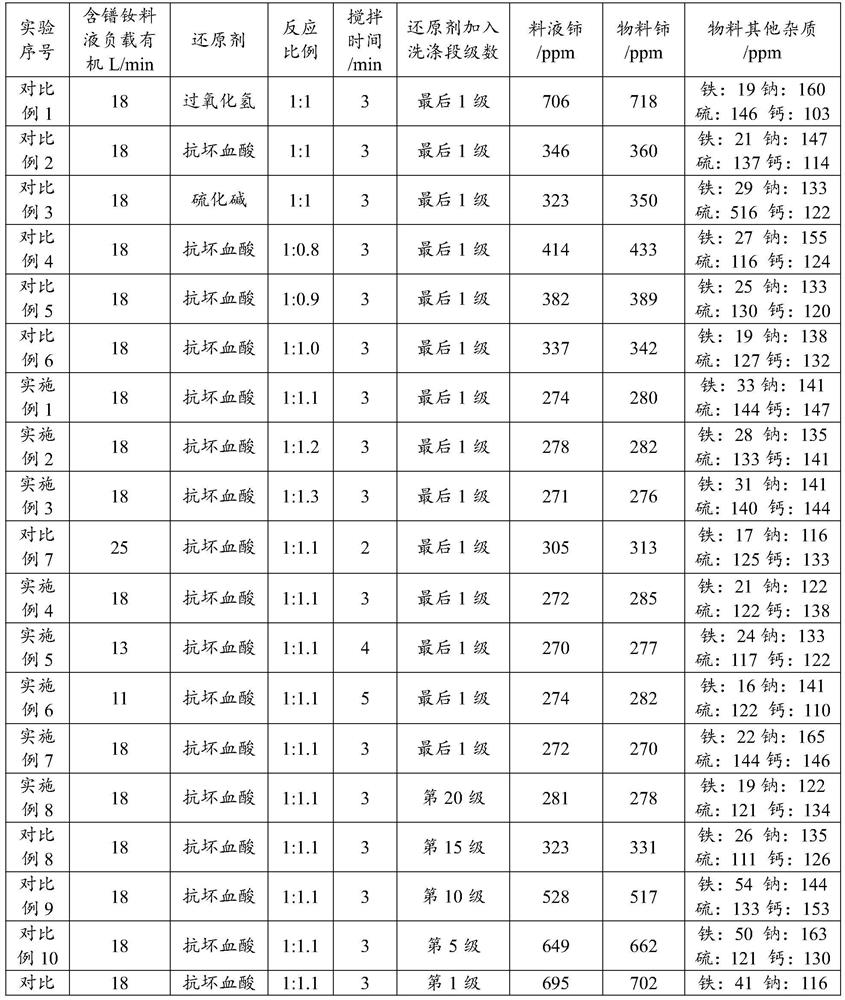
Method for reducing cerium content in praseodymium neodymium chloride and preparation method of praseodymium neodymium oxide
PendingCN114162846AReduced cerium contentReduce Ce ion contentRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesRare earth metal compounds preparation/treatmentPhysical chemistryCerium
The invention relates to the technical field of praseodymium neodymium oxide preparation, in particular to a method for reducing the content of cerium in praseodymium neodymium chloride and a preparation method of praseodymium neodymium oxide. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: carrying out multi-stage countercurrent washing on a praseodymium neodymium chloride organic phase solution and a water phase washing solution, and adding ascorbic acid during at least one stage of the multi-stage countercurrent washing. The purified praseodymium neodymium chloride organic phase solution prepared by the method provided by the invention is low in Ce ion content, so that praseodymium neodymium oxide obtained after the purified praseodymium neodymium chloride organic phase solution is sequentially subjected to multi-stage countercurrent back extraction, precipitation and roasting is low in Ce ion content.
Owner:淄博包钢灵芝稀土高科技股份有限公司
Praseodymium vanadate nanowire electrode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110589887AEasy to makeEasy to controlNanotechnologyVanadium compoundsNanowireMaterials science
The invention discloses a praseodymium vanadate nanowire electrode material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of functional material preparation. The praseodymium vanadate nanowires are composed of tetragonal PrVO4 crystal phases; and the nanowires have diameters of 50-150 nm and a length of more than 10 [mu]m. The preparation method of the electrode material comprises the following steps: firstly fixing a copper sheet in the middle of a reaction container, then mixing praseodymium chloride, sodium vanadate and water, placing the mixture in the reaction container, performing sealing, performing heating by microwaves, and performing heat preservation to obtain a copper sheet with the surface containing a grey deposit; and placing the uniformly-mixed praseodymium chloride and sodium vanadate in a reaction vessel of a high-temperature atmosphere furnace, placing the copper sheet in a water-cooled low-temperature area of the reaction vessel, sealing the reaction vessel, performing heating on the reaction vessel, and performing heat preservation. The method adopts a two-step reaction process and has a simple preparation process, and the praseodymium vanadate nanowires are expected to be used as the electrode material, and have good application prospects in the field of sensing devices.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
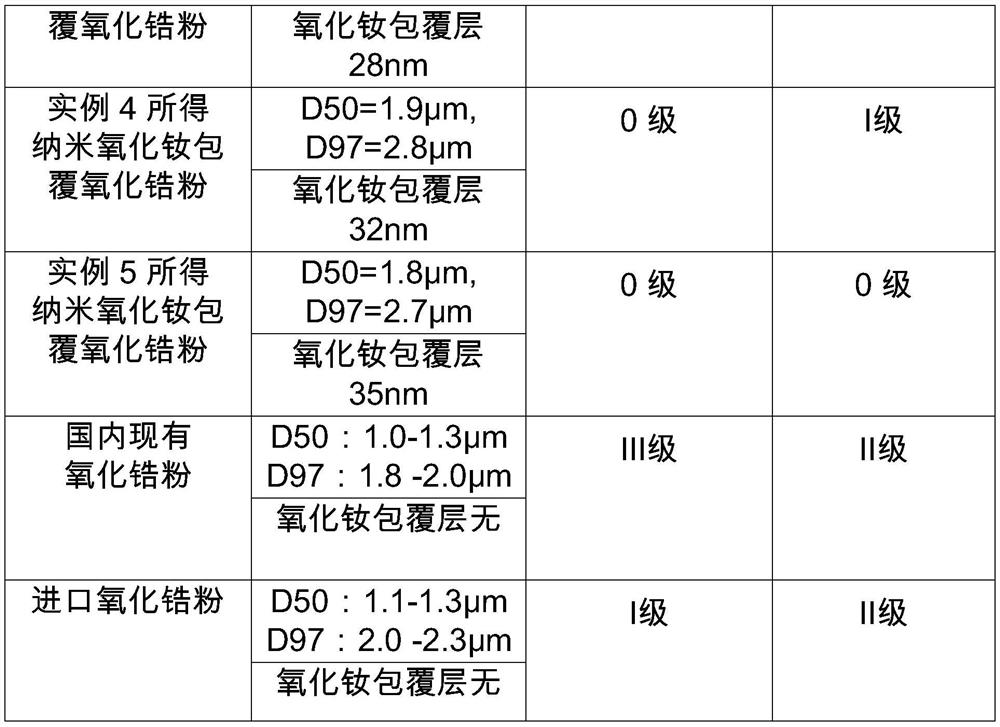
Preparation method of nano neodymium oxide coated zirconium oxide powder
ActiveCN111925732AStable generationGenerate efficientlyPolishing compositions with abrasivesPhysical chemistryNeodymium chloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of nano neodymium oxide coated zirconium oxide powder, and relates to the technical field of preparation of materials for optical glass processing and polishing. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a composite suspending agent; (2) preparing neodymium chloride and praseodymium chloride solutions; (3) preparing a precipitator; (4) preparing a mixing agent; (5) performing precipitation reaction; (6) filtering; (7) performing spray drying; and (8) calcinng. The nano neodymium oxide coated zirconium oxide powder obtainedby the preparation method has the characteristics of solving the problem of scratch of optical glass, ensuring that the glass is not corroded, solving the Arabic phenomenon commonly occurring in the polishing process of domestic products and the like, and is suitable for processing precision optical glass lenses; the method is particularly suitable for precision machining of large-caliber opticalglass lenses and optical glass made of special soft materials.
Owner:HUNAN HAOZHI TECH
Method for dyeing fabric with color-matched natural pigment
InactiveCN108755192AHas antibacterial propertiesGood technical effectDyeing processChemical industrySolvent
The invention relates to the field of light chemical industry, and discloses a method for dyeing a fabric with a color-matched natural pigment. The method comprises the following steps: respectively dissolving two or three of natural blue pigment Indigoidine, monascus red pigment and monascus yellow pigment in a solvent, and mixing the obtained pigment solutions to achieve color matching; and adding the obtained mixture into water together with praseodymium chloride and / or lanthanum trioxide and / or sodium sulfonate, adjusting the pH value of the obtained solution to 3-6, adding the fabric intothe obtained dyeing solution, raising the temperature to 60-90 DEG C, dyeing the fabric, washing the dyed fabric with water, and drying the washed dyed fabric to complete the dyeing of the fabric. The method uses the environmentally-friendly natural dyes or pigments produced by microbial fermentation to completely abandon artificially synthesized dyes or pigments in order to dye silk, wool and other protein fiber fabrics, so the fabric of the silk, wool and other protein fibers has a good color yield percentage and a good color fastness, and green and ecological printing and dyeing processingof the silk, wool and other protein fiber fabrics is achieved.
Owner:德清亿玛生物科技有限公司
Method for dyeing fabric with natural blue pigment matched monascus pigment
InactiveCN108589333AHas antibacterial propertiesGood technical effectDyeing processChemical industrySulfonate
The invention relates to the field of light chemical industry, and discloses a method for dyeing a fabric with natural blue pigment matched monascus pigment. The method comprises the following steps:mixing two or three solid powders of natural blue pigment Indigoidine, monascus red pigment and monascus yellow pigment to achieve color matching; adding the obtained mixture into water together withpraseodymium chloride and / or lanthanum trioxide and / or sodium sulfonate, adjusting the pH value of the obtained solution to 3-6, adding the fabric into the obtained dyeing solution, raising the temperature to 60-90 DEG C, dyeing the fabric, washing the dyed fabric with water, and drying the washed dyed fabric to complete the dyeing of the fabric, wherein the sum of the mass percentages of the praseodymium chloride and / or lanthanum trioxide and / or sodium sulfonate is 5-10 g / L. The method uses the environment-friendly natural dyes or pigments produced by microbial fermentation to completely replace artificially synthesized dyes or pigments in order to dye silk, wool and other protein fiber fabrics, so the fabric has a good color yield percentage and a good color fastness, and green and ecological printing and dyeing processing of the silk, wool and other protein fiber fabrics is achieved.
Owner:德清亿玛生物科技有限公司
A bright and anti-corrosion aluminum profile preparation method
InactiveCN103820775BImprove performanceBright hasMetallic material coating processesSodium sulfateAntiseptic Agent
The invention relates to the modification of aluminum profiles, in particular to a method for preparing bright and anti-corrosion aluminum profiles. It includes in turn: preparation of bright anticorrosion liquid: prepare 20-40 parts of sodium fluoride, 30-60 parts of ammonium bifluoride, 10-20 parts of potassium permanganate, 40-50 parts of potassium chromate, and 15-25 parts of zinc phosphate by weight 8-18 parts of sodium nitrate, 5-12 parts of praseodymium chloride, 10-16 parts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 7-14 parts of malic acid, 8-12 parts of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfate, 6- 13 parts, 15-25 parts of triethanolamine, 500-900 parts of water; control the pH value of 3-4 to obtain a bright anticorrosive solution; heat to 30-40 ° C, then impregnate the aluminum profile, the second impregnation, and then the first After the dipping treatment, the bright antiseptic is microwaved for 3-7 seconds, washed with flowing water, and dried. The aluminum profiles prepared by the invention are bright and soft, have excellent corrosion resistance, and are safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUA LV ALUMINUM
A method for removing aluminum ions in a praseodymium neodymium chloride feed solution
ActiveCN110184460BIncrease sedimentation rateReduce sedimentation rateProcess efficiency improvementAluminum IonPhysical chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of rare-earth separation, and particularly relates to a method for removing aluminum ions in a neodymium praseodymium chloride material liquid. Due to diversity of mineral sources, non-rare earth impurities in a mixed rare earth chloride material liquid obtained through chemical leaching are difficult to remove. According to the method, another way is opened, the hydrolytic process of the aluminum ions in the neodymium praseodymium chloride material liquid subjected to extraction separation is explored, and optimal conditions of aluminum ion hydrolysis are found out by adding an additive and used for removing the aluminum ions in the neodymium praseodymium chloride material liquid. It is shown through the experimental result that the depositionrate of the aluminum ions in the neodymium praseodymium chloride material liquid reaches 93% or above, the deposition rate of rear earth is 1.5% or below, the deposition volume rate is small, and solid-liquid separation is facilitated.
Owner:SICHUAN PROVINCE LESHAN CITY RUIFENG METALLURGY CO LTD
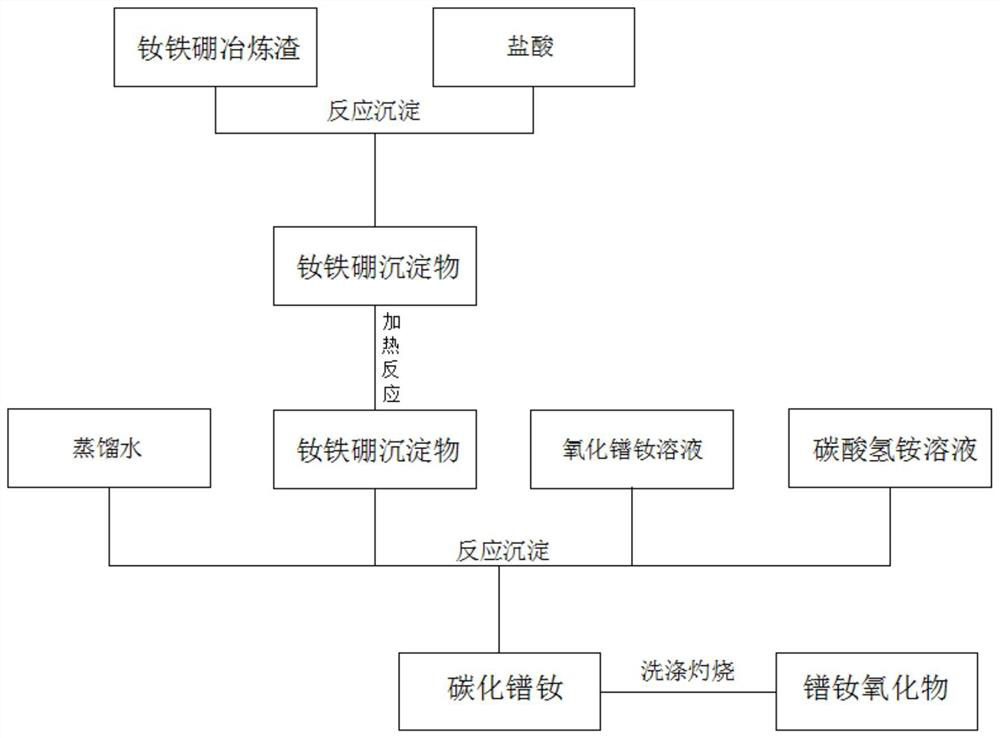
Process for producing high-purity praseodymium neodymium oxide by using neodymium iron boron smelting slag
InactiveCN113501539AReduce manufacturing costLanthanide oxides/hydroxidesChemical industryOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATESlag
The invention provides a process for producing high-purity praseodymium neodymium oxide by using neodymium iron boron smelting slag, the method comprises the following steps: taking 86 parts of neodymium iron boron smelting slag, 37 parts of hydrochloric acid, 82 parts of praseodymium neodymium chloride solution, 57 parts of ammonium bicarbonate solution and 43 parts of distilled water as raw materials, carrying out a series of process steps such as reaction treatment, heating reaction, showering and filtering, reaction precipitation, washing and firing and the like, sequentially adding a praseodymium neodymium chloride solution and an ammonium bicarbonate solution, keeping the flow rate of the praseodymium neodymium chloride solution at 0.6 mL / min for 35 minutes, then adding the filtered neodymium iron boron precipitate, precipitating for 45 minutes, washing the precipitate obtained by precipitation with hot water for three times, and firing the precipitate obtained by washing at the firing temperature of 1080 DEG C to obtain the praseodymium neodymium oxide. The neodymium iron boron smelting slag is used for producing the praseodymium neodymium oxide, the praseodymium neodymium oxide can be purified through distilled water reactive distillation and multiple times of filtering and washing, oxalic acid is not used as a precipitator, and the production cost of the praseodymium neodymium oxide is greatly reduced.
Owner:BAOTOU RARE EARTH HUAXING TECH CO LTD
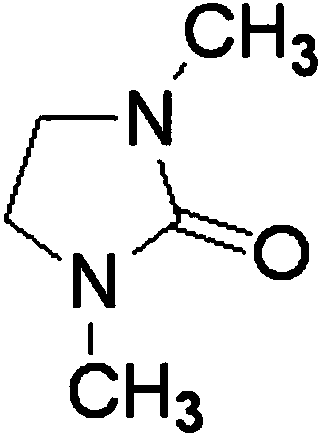
Low cost metal praseodymium preparation method through electrolysis of praseodymium chloride
ActiveCN109208033AShort processReduce production energy consumptionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementMischmetalUniform system
The invention relates to a low cost metal praseodymium preparation method through electrolysis of praseodymium chloride, and belongs to rare earth metal low temperature extraction. The method comprises following steps: at a room temperature, dissolving lithium nitrate into DMI to obtain DMI electrolyte of lithium nitrate; filling the DMI electrolyte of lithium nitrate into an electrolytic tank, adding anhydrous praseodymium chloride into the electrolytic tank, stirring and mixing the electrolyte to form a uniform system; controlling the temperature of the system in a range of 30 to 80 DEG C, controlling the electrolytic voltage in a range of -2.0 to -2.4 V vs Ag; and during the electrolysis process, adding anhydrous praseodymium chloride into the electrolytic tank at intervals so as to control the mole concentration of praseodymium chloride to be 98% to 102% of the primary concentration. The provided method can prepare rare earth metal praseodymium efficiently, and at the same time, the energy consumption and production cost are prominently reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
A method for producing metal praseodymium by electrolysis of praseodymium chloride at low cost
ActiveCN109208033BShort processReduce production energy consumptionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolytic agentPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a low-cost method for producing praseodymium metal by electrolyzing praseodymium chloride, and belongs to the field of low-temperature extraction of rare earth metals. A low-cost method for electrolyzing praseodymium chloride to produce praseodymium metal, including the following process steps: dissolving lithium nitrate in DMI at room temperature to obtain a DMI electrolyte of lithium nitrate; placing the DMI electrolyte of lithium nitrate in an electrolytic tank , then add anhydrous praseodymium chloride to it, stir and mix in the electrolytic tank to form a uniform system, control the temperature of the entire system at 30~80℃, and the electrolysis voltage range -2.0~-2.4V vs Ag; during the electrolysis process , add anhydrous praseodymium chloride to the electrolytic cell at regular intervals, and control the molar concentration of praseodymium chloride to the initial concentration ±2%. The method of the present invention can significantly reduce energy consumption and production costs while efficiently preparing rare earth metal praseodymium.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Bright anticorrosive aluminum profile for air purifier and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a bright anticorrosive aluminum profile for an air purifier. The bright anticorrosive aluminum profile is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 80 partsof an aluminum profile, 20 to 30 parts of sodium hydroxide, 20 to 30 parts of potassium permanganate, 40 to 50 parts of potassium chromate, 10 to 20 parts of zinc phosphate, 8 to 18 parts of sodium nitrate, 5 to 12 parts of praseodymium chloride, 6 to 13 parts of nickel sulfate, 15 to 25 parts of triethanolamine, and 500 to 900 parts of water; the bright anticorrosive aluminum profile is obtainedby controlling the pH value to be 3 to 4; and the acidity is regulated by a sodium hydroxide solution, which facilitates the soaking of the aluminum profile.
Owner:安徽鑫铂科技有限公司
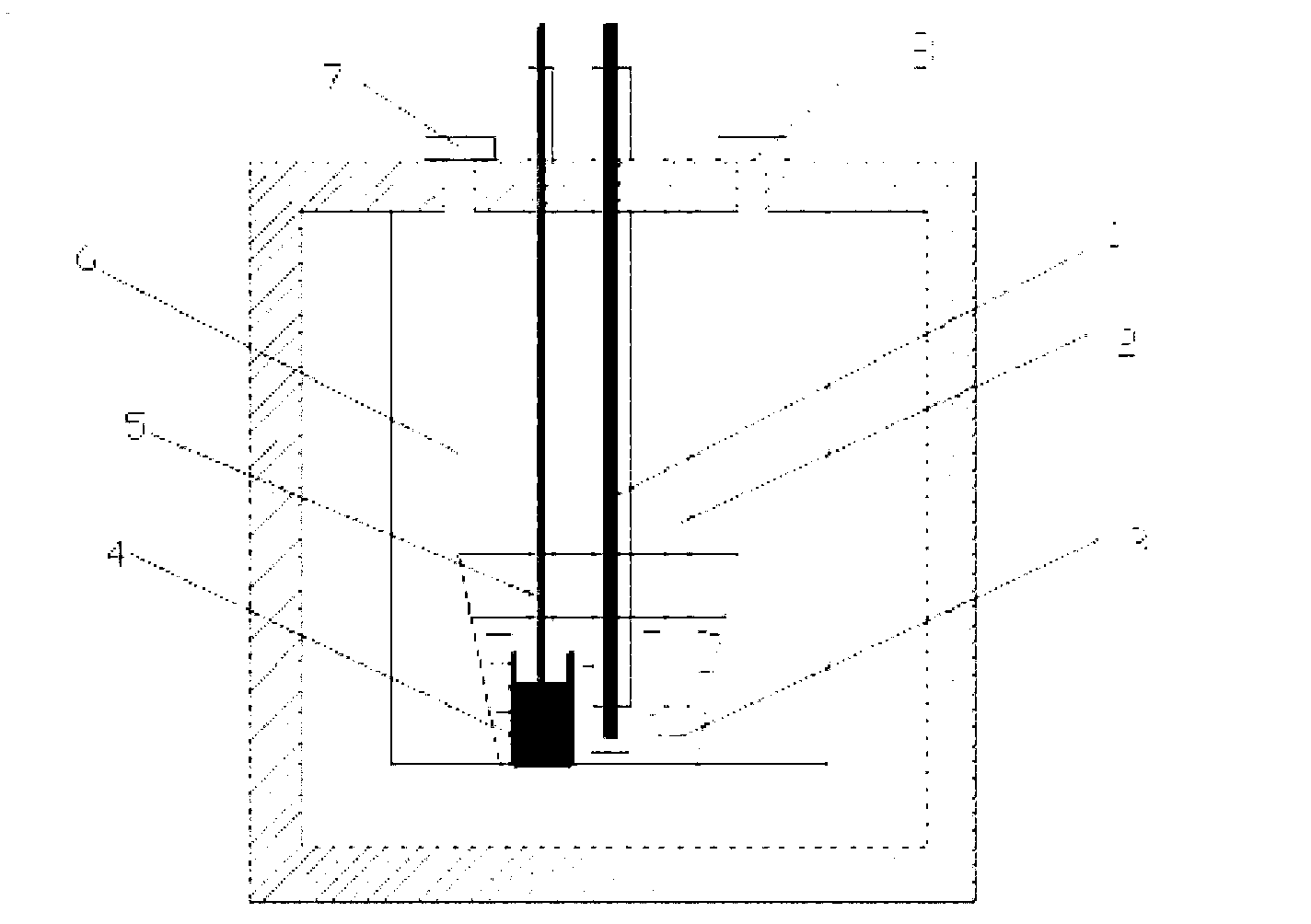
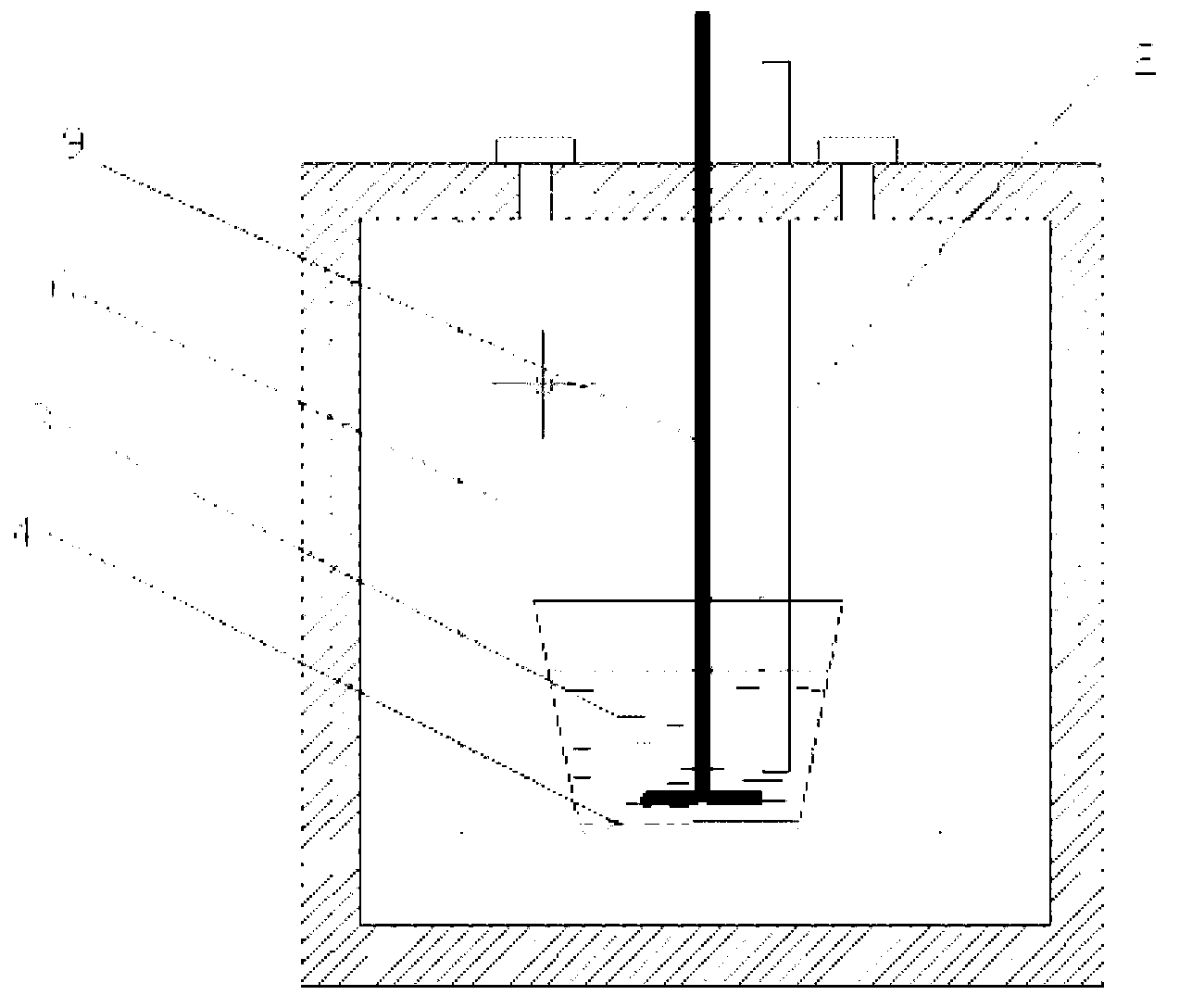
Method for preparing anhydrous praseodymium chloride on basis of spray drying-melting dehydration
InactiveCN107954461ANo pollution in the processSimple processRare earth metal chloridesMercury columnPollution
The invention discloses a method for preparing anhydrous praseodymium chloride on the basis of spray drying-melting dehydration. The method comprises the following steps: S1, a praseodymium chloride solution with concentration not lower than 200 g / L is prepared from praseodymium chloride heptahydrate; S2, the praseodymium chloride solution is subjected to spray drying at 110-120 DEG C, and praseodymium chloride trihydrate is obtained; S3, praseodymium chloride trihydrate is subjected to heating melting, and a clear melted liquid and an impurity liquid are obtained, wherein a mercury column atthe temperature of 760-1000 DEG C and the vacuum degree of 50-100 mm is adopted in the heating melting process; S4, separation and cooling are performed on the clear melted liquid, and anhydrous praseodymium chloride is obtained. According to the method, anhydrous praseodymium chloride is prepared from praseodymium chloride heptahydrate with the spray drying-melting dehydration method, the processis simple, pollution is avoided, equipment requirements are low, and industrial production is easy to realize; compared with the general dehydration method in the prior art, protective atmosphere isnot needed, introduction of organic matter or other heavy metals is not needed, and poisonous gases such as hydrogen chloride or ammonia gas and the like are not produced.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production process of low-impurity praseodymium-neodymium carbonate
InactiveCN110002486AHigh purityImprove the efficiency of the reaction to form neodymium carbonateRare earth metal carbonatesRare earthChloride
The invention discloses a production process of low-impurity praseodymium-neodymium carbonate and belongs to the technical field of rare earth extraction. According to the production process disclosedby the invention, by controlling the conditions such as feeding ratio and feed liquid concentration of neodymium praseodymium chloride and ammonium bicarbonate, as well as temperature and pH value inthe reaction process, the generation efficiency of neodymium carbonate through reaction of the neodymium praseodymium chloride and the ammonium bicarbonate is greatly improved; the generation of praseodymium-neodymium carbonate double salt is avoided, crystalline neodymium carbonate with small mass fraction of chlorine root and the purity of 99.9 percent or above is obtained, rapid precipitationcrystallization is achieved, and the purity of the praseodymium-neodymium carbonate is improved.
Owner:赣州天和永磁材料有限公司
A bright and anti-corrosion aluminum profile for air purifiers and its preparation method
The invention discloses a bright anti-corrosion aluminum profile used for an air purifier. The bright anti-corrosion aluminum profile is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 80 parts of aluminum profile, 20-30 parts of sodium hydroxide, and 20 parts of potassium permanganate ‑30 parts, potassium chromate 40‑50 parts, zinc phosphate 10‑20 parts, sodium nitrate 8‑18 parts, praseodymium chloride 5‑12 parts, nickel sulfate 6‑13 parts, triethanolamine 15‑25 parts, water 500 parts -900 parts, obtained by controlling the pH value of 3-4; the acidity is adjusted through the set sodium hydroxide solution, which is convenient for the immersion of aluminum profiles.
Owner:安徽鑫铂科技有限公司
Method for producing low-expansion glass-ceramics from high-silicon iron tailings
InactiveCN105481255BImprove high temperature resistanceHigh mechanical strengthThermal dilatationFerrosilicon
Owner:BEIJING QING MAI HUA QING HLDG GRP CO LTD
A method for preparing high-purity lanthanum, high-purity cerium and high-purity praseodymium neodymium
InactiveCN110306048BHigh purityHigh yieldProcess efficiency improvementCerous chlorideNeodymium chloride
A kind of method for preparing high-purity lanthanum, high-purity cerium and high-purity praseodymium neodymium of the present invention takes light rare earth chloride aqueous solution as feed liquid, and P507 is extraction agent; It is made up of three fractionation extraction systems, respectively La / LaCe / CePrNd / PrNd four-outlet fractional extraction and separation system, La / Ce fully loaded two-inlet fractional extraction and separation system and Ce / PrNd two-inlet fractional extraction and separation system. Through the combination of three fractional distillation extraction separation systems, three separated products of 5N grade lanthanum chloride, 5N grade cerium chloride and 4N grade praseodymium neodymium chloride are directly obtained. The invention has the advantages of high product purity, high yield of rare earth elements, low acid-base consumption, short process flow, low separation cost and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Dyeing method of fabric with color matched natural blue pigment Indigoidine
InactiveCN108611873AHas antibacterial propertiesGood technical effectDyeing processChemical industryIndigoidine
Relating to the field of light chemical industry, the invention discloses a dyeing method of a fabric with a color matched natural blue pigment Indigoidine. The method is characterized by: mixing thesolid powder of natural blue pigment Indigoidine, monascus red pigment and / or monascus yellow pigment for color matching; then adding the color matched pigment and praseodymium chloride or lanthanum trioxide or sodium sulfonate with a mass percent of 0.1-5g / L into water, adjusting the pH value to 2.5-6.5, adding the fabric into the dyeing solution, performing heating to 50-95DEG C, and conductingwashing and drying, thus finishing dyeing of the fabric. The natural pigment fermentation process does not produce toxin, and in order to achieve industrial production, the strains need to be applicable to liquid fermentation, thus solving the shortcomings of plant dyes. In addition, besides bright color, some microbial dyes also have certain antibacterial effect, thereby indicating that part of microbial dyes also have potential application value in functional finishing of fabrics.
Owner:德清亿玛生物科技有限公司
Features
- Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com