A method for producing metal praseodymium by electrolysis of praseodymium chloride at low cost
A low-cost technology of praseodymium chloride, applied in the field of low-temperature extraction of rare earth metals, can solve the possibility of increasing the production cost of ionic liquids, environmental pollution, no large-scale practical application background, and reduce the green characteristics of ionic liquids, etc., to achieve good chemistry and thermal stability, excellent solubility, and the effect of improving the working environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
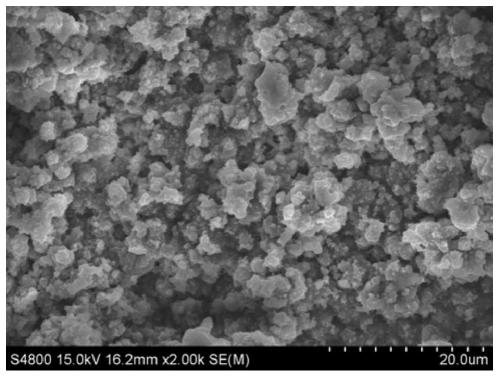
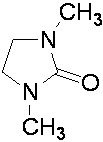
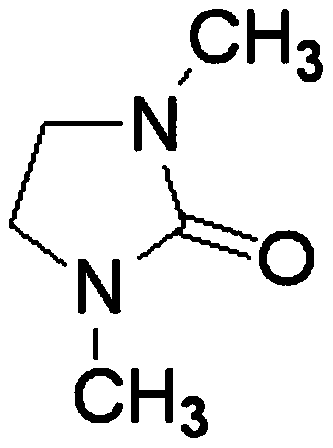
[0034] The raw materials for preparing the electrolyte are praseodymium chloride and lithium nitrate, and the solvent DMI, which are stirred and mixed in the electrolytic cell to form an electrolyte system, wherein the molar concentrations of praseodymium chloride and lithium nitrate are 0.001mol / L and 0.01mol / L, respectively. Control the constant temperature of the electrolyte system at 30°C, the electrolysis voltage is -2.0V (vs Ag), and the anode material is graphite; after 30 minutes of electrolysis, add praseodymium chloride once to make the concentration of praseodymium chloride in the system 0.001mol / L; after 60 minutes of electrolysis, the substrate The sediments on the site are collected and preserved, and the collected sediments are reprocessed according to the needs. After characterization and testing, the results show that metal praseodymium can be effectively deposited, and the total content of praseodymium elements detected by ICP is 72.32%.
Embodiment 2
[0036] The raw materials for preparing the electrolyte are praseodymium chloride and lithium nitrate, and the solvent DMI is stirred and mixed in the electrolytic cell to form an electrolyte system, wherein the molar concentrations of praseodymium chloride and lithium nitrate are 0.002mol / L and 0.02mol / L, respectively. Control the constant temperature of the electrolyte system at 45°C, the electrolysis voltage is -2.1V (vs Ag), and the anode material is a tungsten rod; after 30 minutes of electrolysis, add praseodymium chloride once to make the concentration of praseodymium chloride in the system 0.002mol / L; after 60 minutes of electrolysis, add The deposits on the substrate are collected and preserved, and the collected deposits are reprocessed as required. After characterization and testing, the results show that metal praseodymium can be effectively deposited, and the total content of praseodymium elements detected by ICP is 96.57%.
Embodiment 3
[0038]The raw materials for preparing the electrolyte are praseodymium chloride and lithium nitrate, and the solvent DMI is stirred and mixed in the electrolytic cell to form an electrolyte system, wherein the molar concentrations of praseodymium chloride and lithium nitrate are 0.01mol / L and 0.03mol / L, respectively. Control the constant temperature of the electrolyte system at 55°C, the electrolysis voltage is -2.2V (vs Ag), and the anode material is a molybdenum rod; after 30 minutes of electrolysis, add praseodymium chloride once to make the concentration of praseodymium chloride in the system 0.01mol / L; after 60 minutes of electrolysis, add The deposits on the substrate are collected and preserved, and the collected deposits are reprocessed as required. After characterization and testing, the results show that metal praseodymium can be effectively deposited, and the total content of praseodymium elements detected by ICP is 97.94%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com