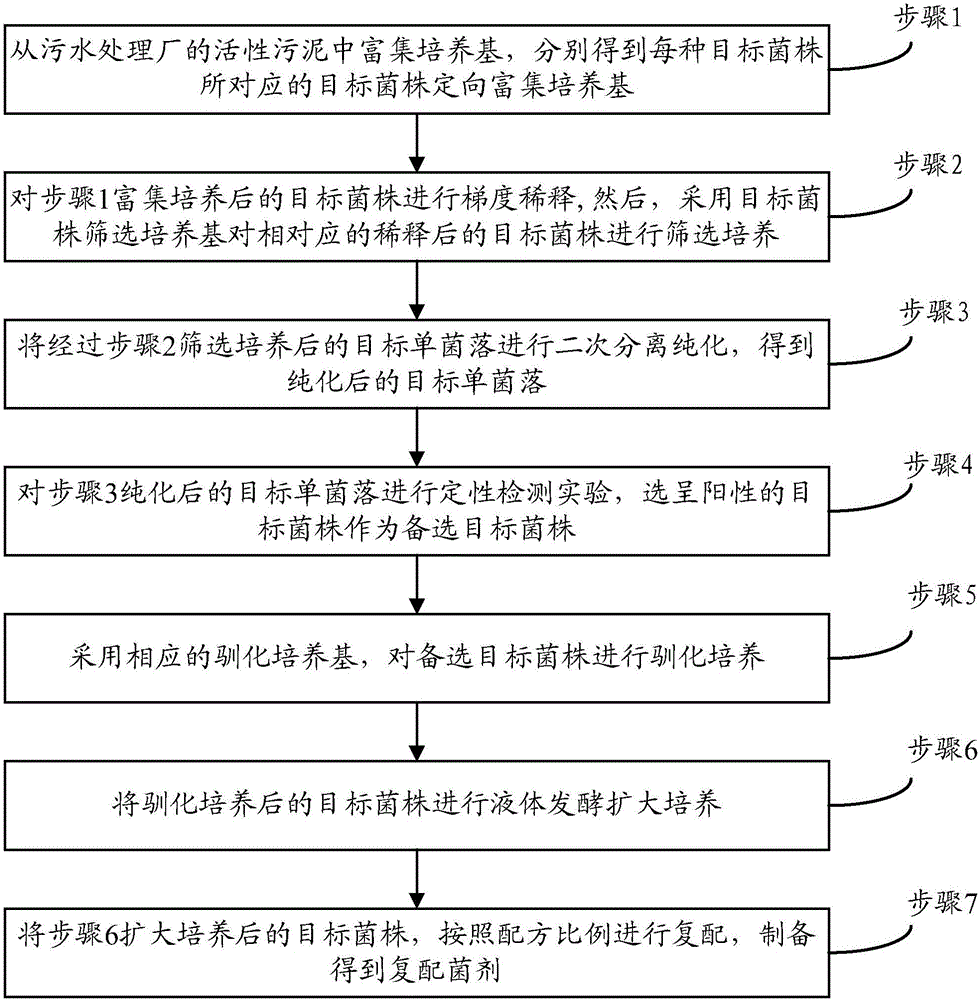
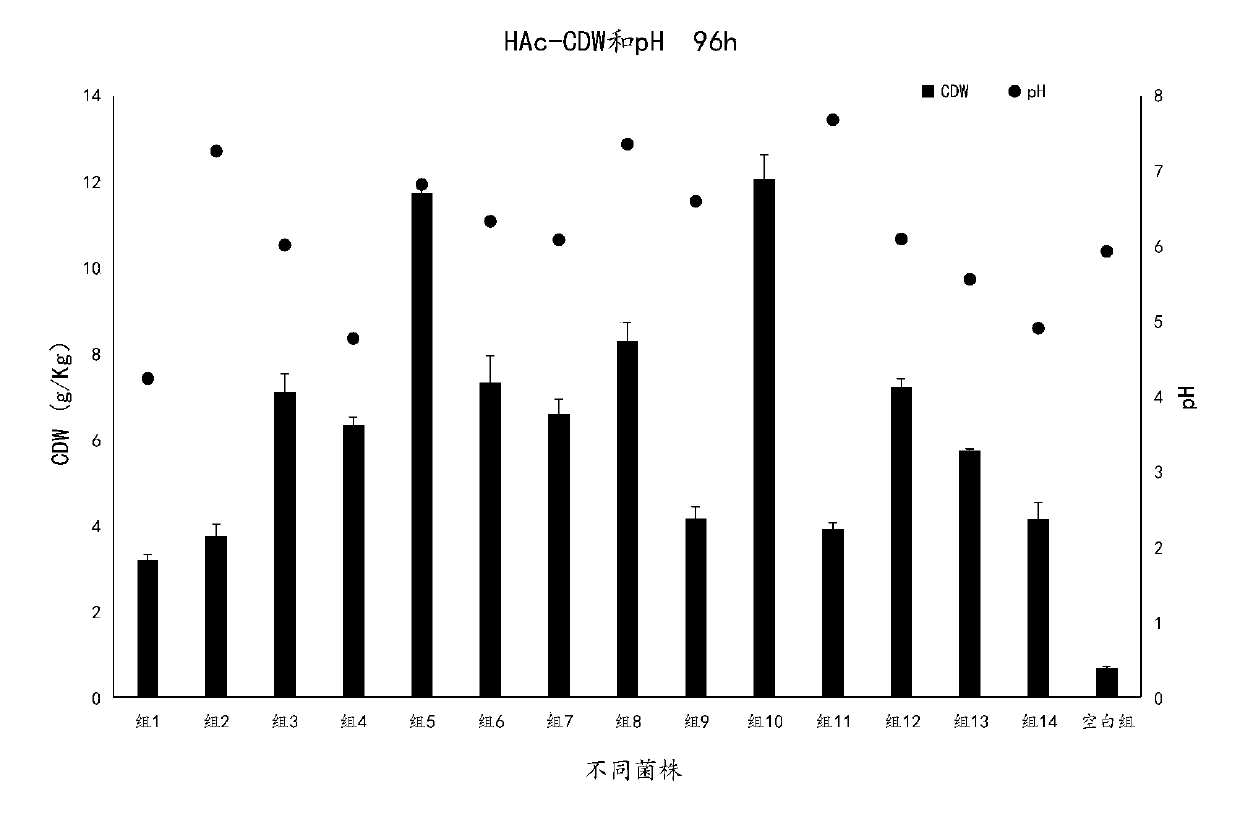
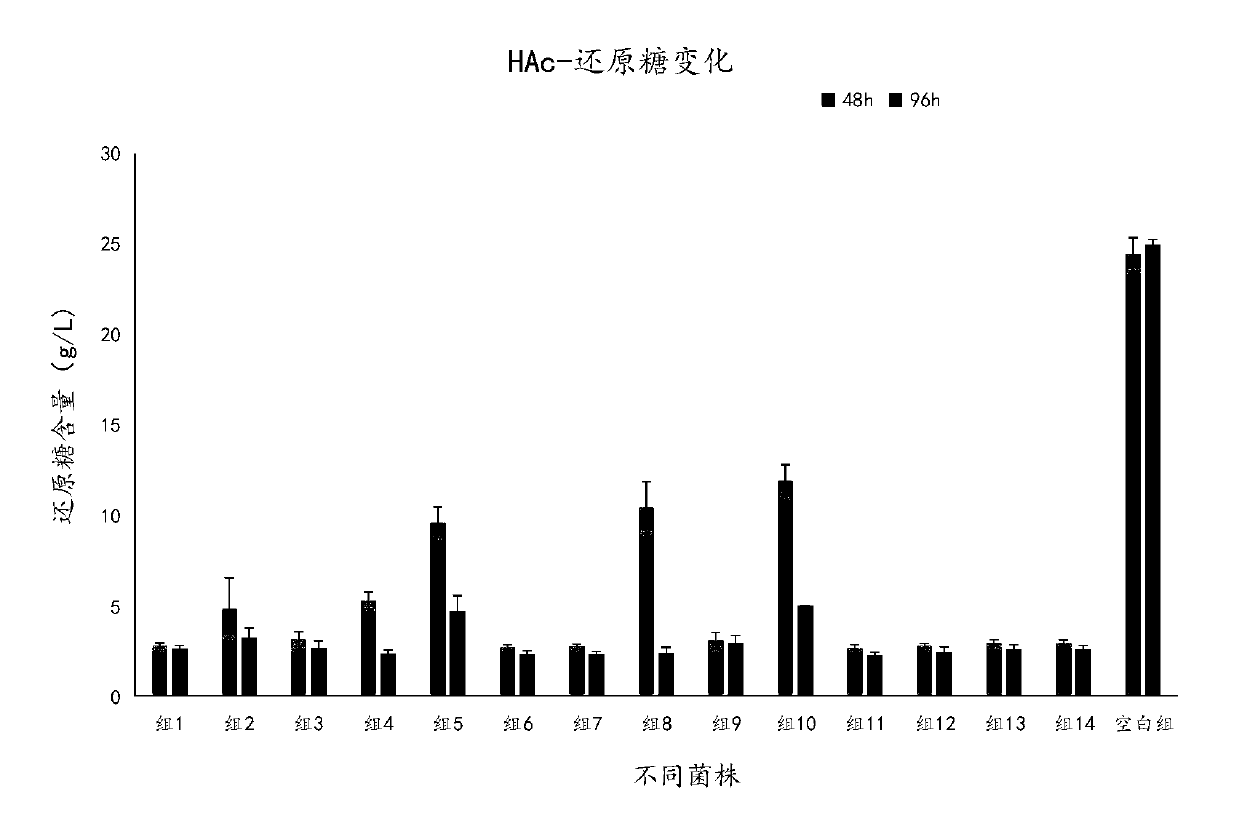
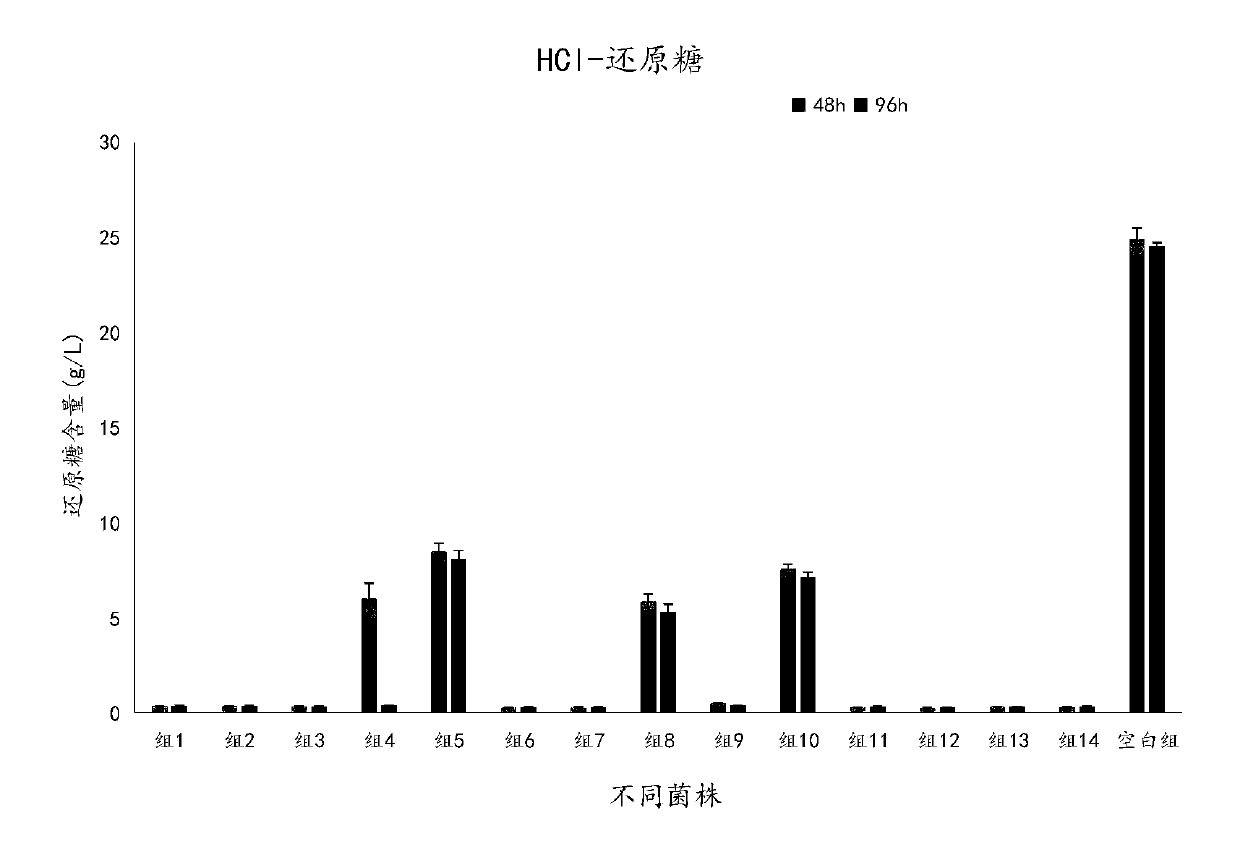
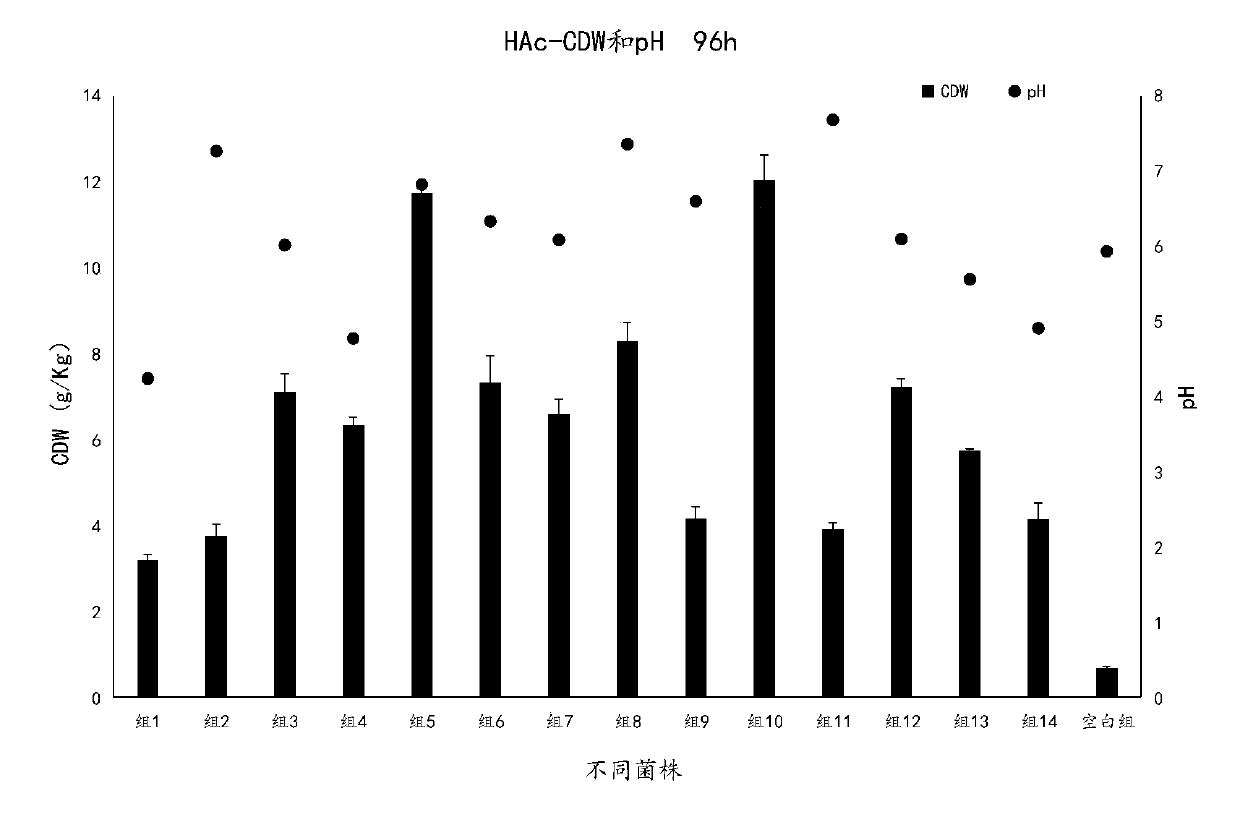
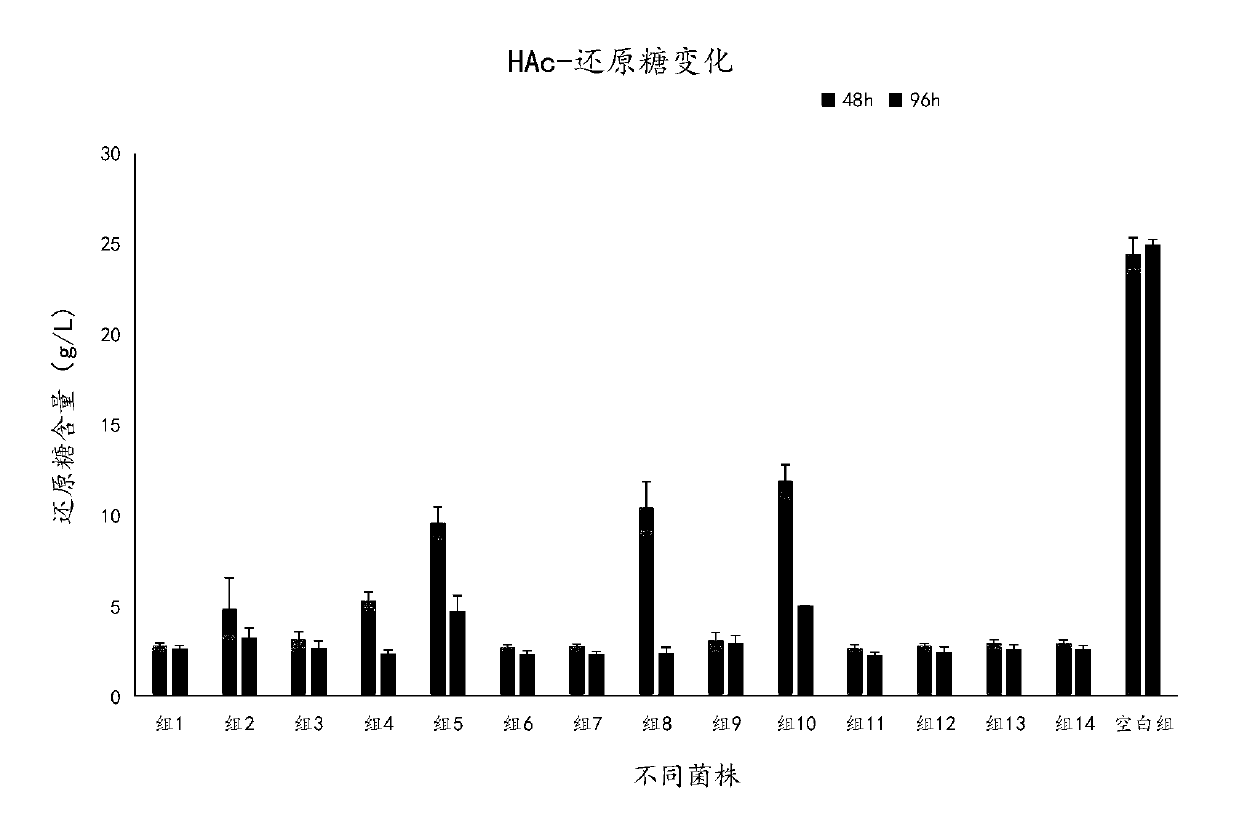
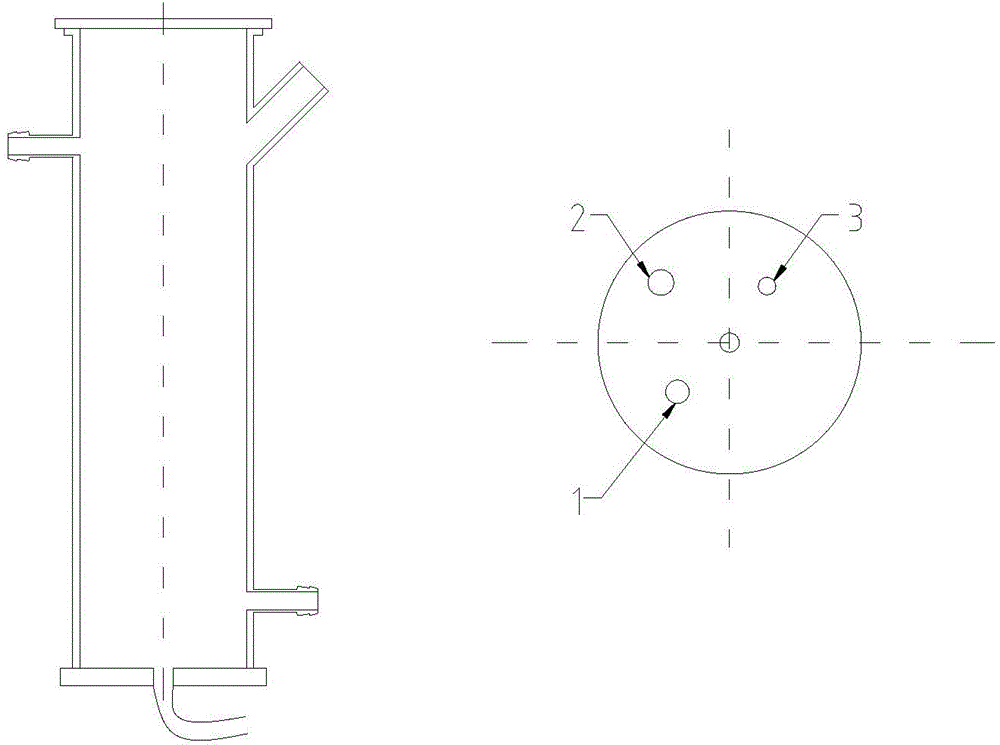
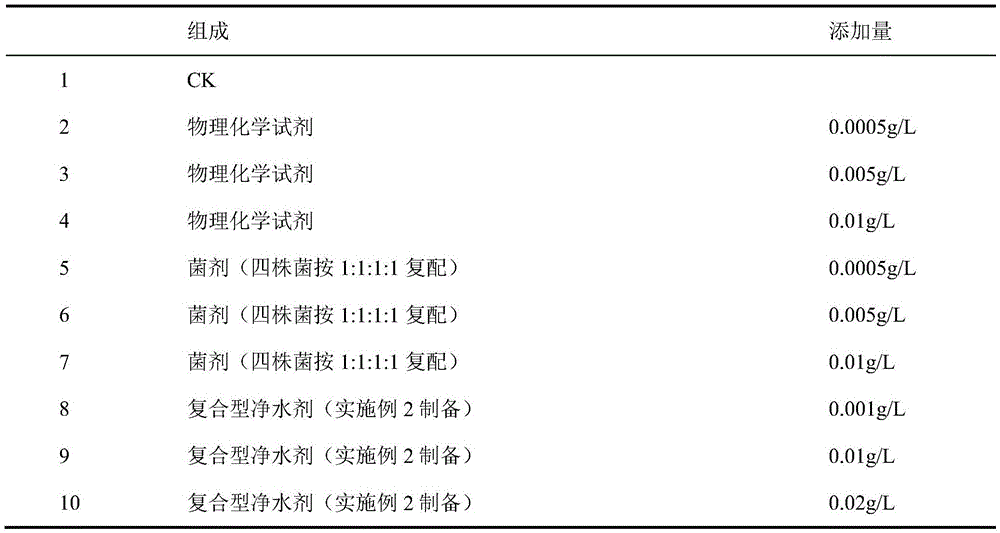
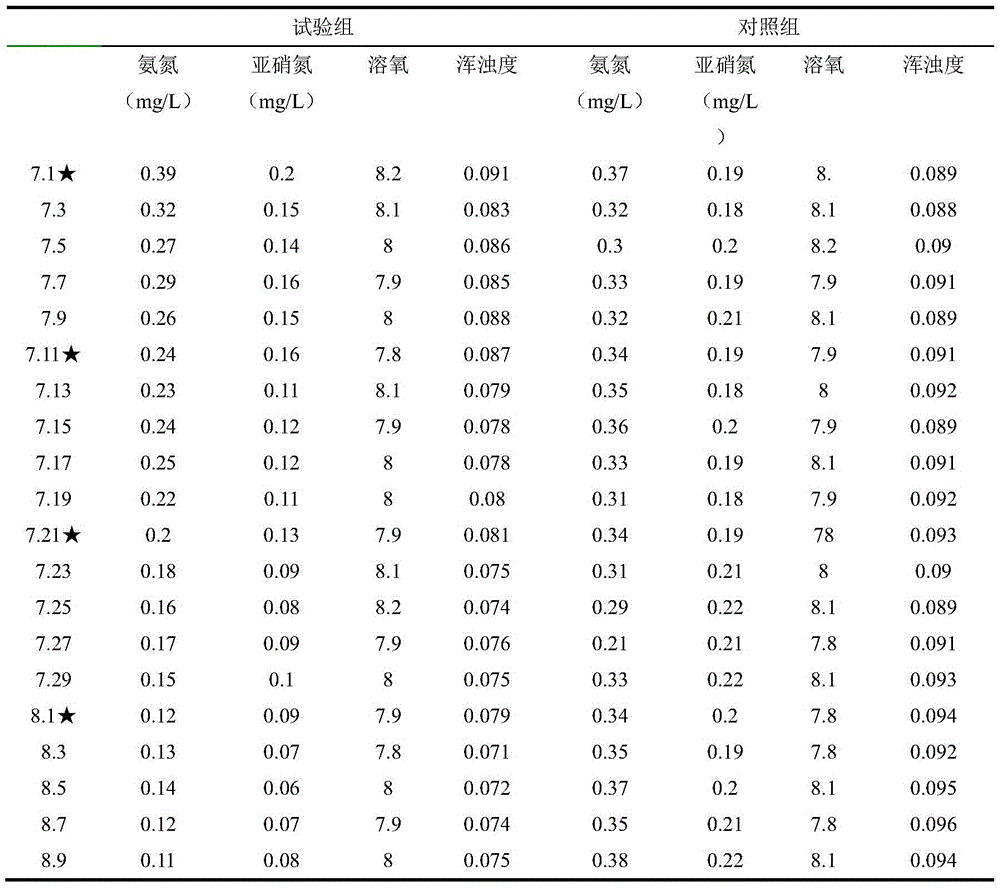
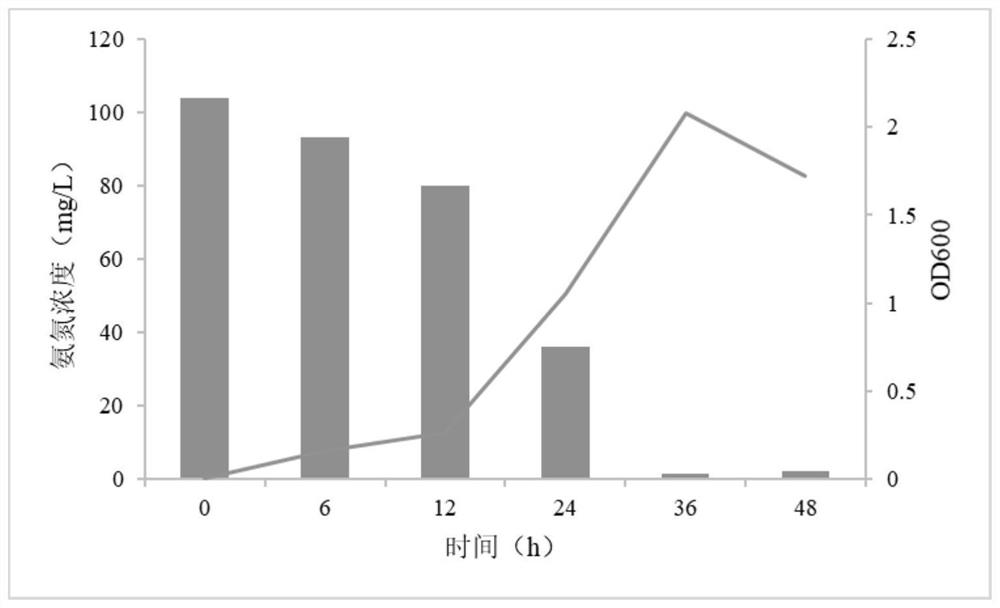
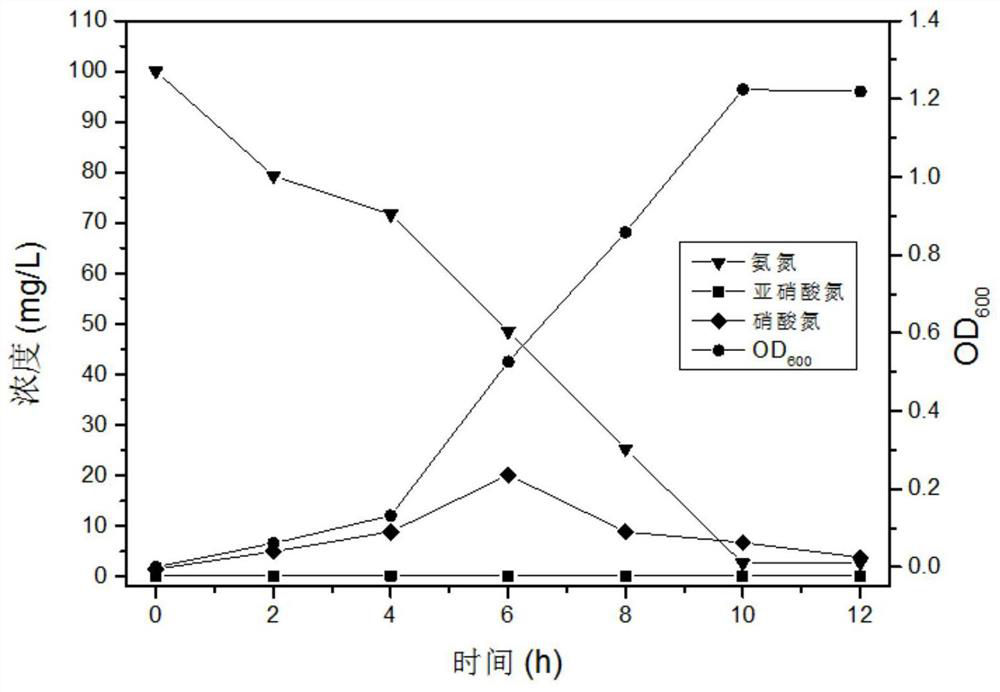
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
159 results about "Ammonia n" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ammonia is a nutrient that contains nitrogen and hydrogen. Its chemical formula is NH. 3 in the un-ionized state and NH. 4 + in the ionized form.
Kitchen waste degrading compound bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN107435032AHigh reduction rateImprove degradation rateBacteriaSolid waste disposalBacillus oleroniusBacillus amyloliquefaciens
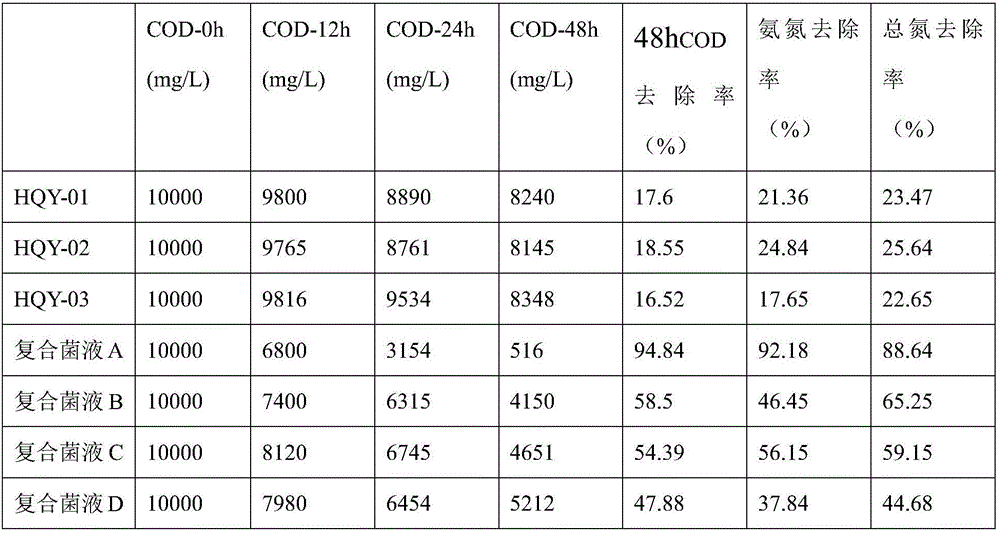
The invention discloses a kitchen waste degrading compound bacterium. The kitchen waste degrading compound bacterium is composed of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HQY-01, Bacillus oleronius HQY-02 and Bacillus tequilensis HQY-03 which are preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, on February 16, 2017, the preservation number of the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HQY-01 is CCTCC NO:M2017040, the preservation number of the Bacillus oleronius HQY-02 is CCTCC NO:M2017039, and the preservation number of the Bacillus tequilensis HQY-03 is CCTCC NO:M2017041. The kitchen waste degrading compound bacterium can be used for degrading kitchen wastes, and has the advantages of high waste weight loss rate, and high removal rate of CODs, ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAQINGYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Microorganism bacterium agent for treating leather wastewater and preparation method thereof
PendingCN106834158APromote degradationStrong resistance to changeFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a microorganism bacterium agent and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a composite bacterium agent and a preparation method thereof. The composite bacterium agent can be used for efficiently removing a large amount of COD (chemical oxygen demand), ammonia and nitrogen in leather wastewater. The composite bacterium agent is prepared from mycobacterium, microbacterium, acinetobacter, pichia pastoris, lactobacillus, klebsiella oxytoca and a liquid culture medium. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, activating the bacteria strains of raw materials; 2, enriching and culturing; 3, mixing the bacterium strains according to a weight ratio, and adding into the liquid culture medium, so as to obtain the composite bacterium agent. The composite bacterium agent has the advantages that the biological activity is high, the growth speed is high, the leather wastewater can be treated under the low temperature condition, the removal rate of organic matter can be obviously increased, the contents of COD, ammonia and nitrogen in the leather wastewater are effectively decreased, and the effect is obvious.
Owner:北京市科学技术研究院资源环境研究所
Compound bacterial agent for purifying black and odorous water body and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106148246ADegraded ammonia nitrogen contentDegradation of phosphate contentFungiBacteriaNitrifying bacteriaBacillus subtilis
The invention provides a compound bacterial agent for purifying a black and odorous water body and a preparation method thereof. The compound bacterial agent comprises the following components: actinomycetes, bacillus subtilis, nitrifying bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, candida utilis and pseudomonas aeruginosa in a weight ratio of 2:2:2:1:1:1. The invention has the following advantages: the COD content, ammonia nitrogen content and phosphate salt in the black and odorous water body can be effectively reduced, and the odor of the black and odorous water body can be eliminated; and meanwhile, by adding the ammonia nitrogen removal strain, the transparency of the water body can be gradually improved.
Owner:BIOLAND ENVIRONMENTAL TECH GRP CORP
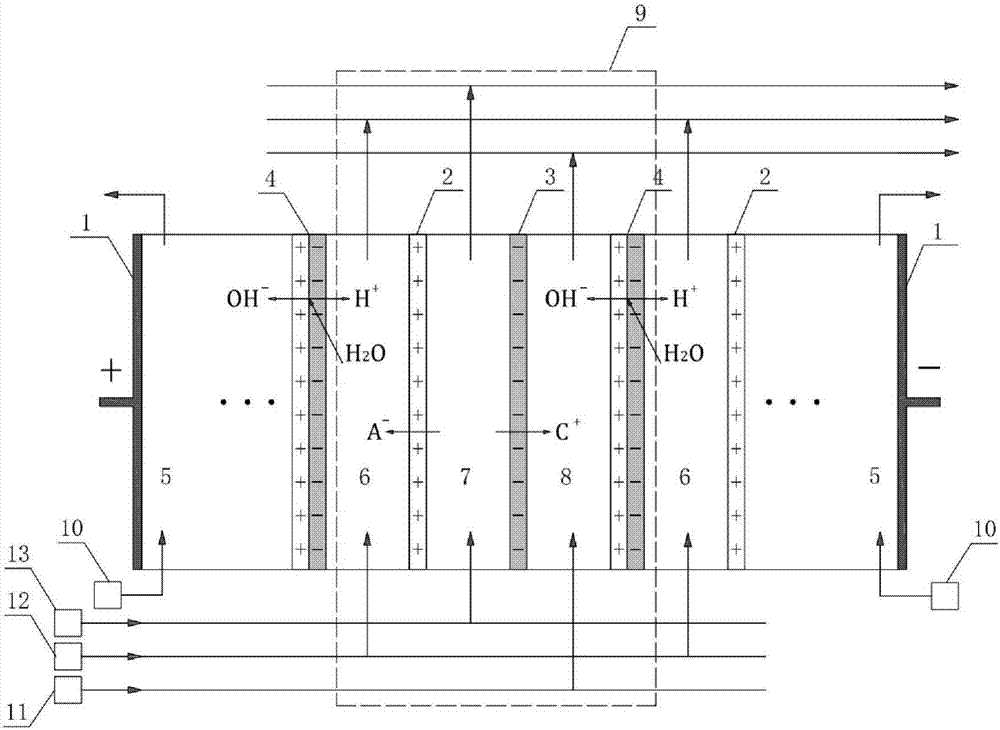
Method for recycling ammonia nitrogen, phosphorus and volatile fatty acid in livestock-poultry excrement hydrolysate by two-stage bipolar membrane electrodialysis
ActiveCN107055712AAvoid pollution lossImprove recycling efficiencyWater contaminantsDispersed particle separationIonChemistry
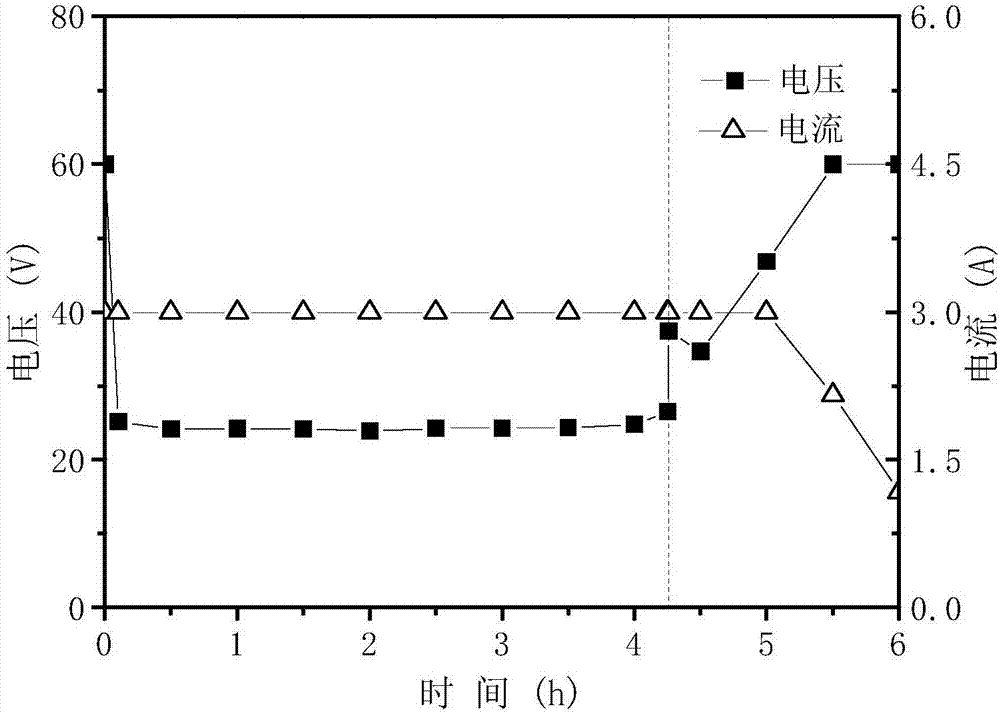
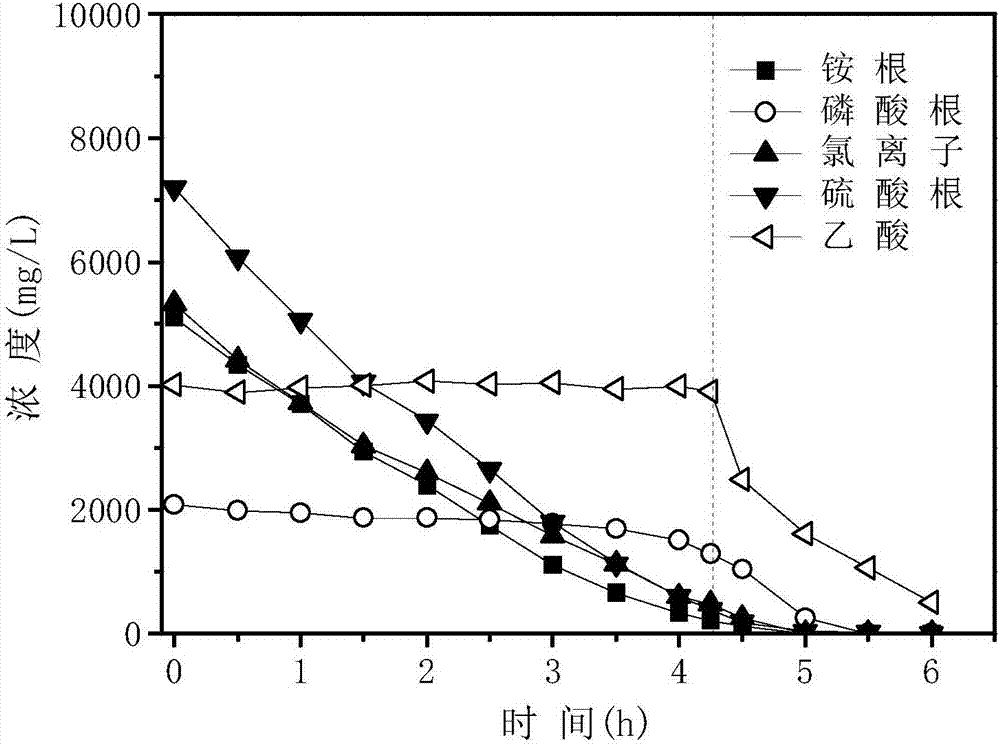
The invention discloses a method for recycling ammonia nitrogen, phosphorus and volatile fatty acid in livestock-poultry excrement hydrolysate by two-stage bipolar membrane electrodialysis; the method comprises: pretreating livestock-poultry excrement hydrolysate, adding into a bipolar membrane electrodialytic saline chamber, and extracting ions contained in the hydrolysate. The reaction process is divided into a front phase and a rear phase according to voltage changes, namely a strong electrolyte removal phase and a weak electrolyte removal phase; finally, ammonia nitrogen, chlorine ions and sulfates are removed in the first phase equivalently, while phosphates and weak acids such as VFAs (volatile fatty acids) are removed in the second phase. The produced strong acid solution is subjected to reflow for adjusting pH of the hydrolysate during pretreatment; when pH is 5, about 90% of solid phosphorus is released, and the VFAs separation efficiency is improved. The two-phase separation method according to the invention enables ions in the excrement hydrolysate to be removed and recycled in class-based form, loss of ion diffusion between adjacent compartments in late reaction is decreased, and product recycling rate is increased.
Owner:HUANGSHAN TIANZHIDU ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
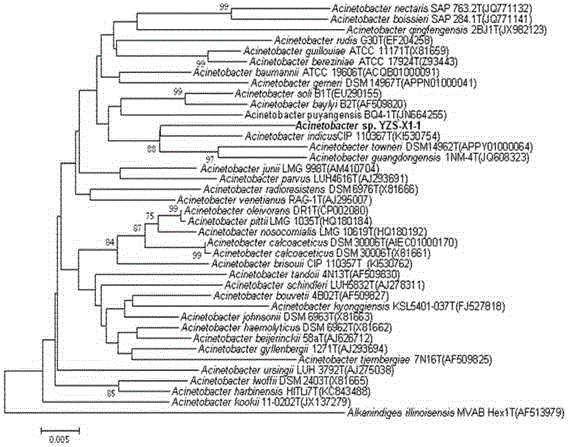
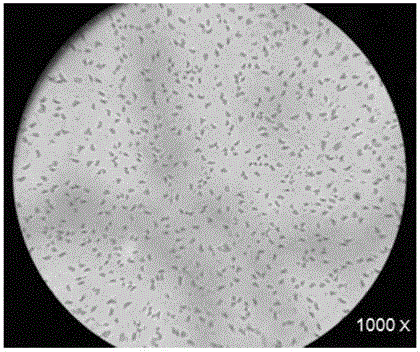
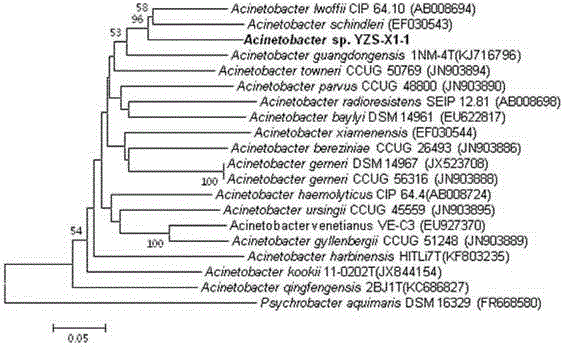
Efficient denitrification novel Acinetobacter and application thereof
ActiveCN105331552AImprove denitrification effectEfficient removalBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiochemical engineeringMicrobiology
The invention discloses an efficient denitrification novel Acinetobacter and application thereof. Acinetobacter guangzhouensis YZS-X1-1 is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on 6th August, 2014 under CCTCC NO. M2014369. The Acinetobacter has good denitrification capacity and is effective in removing ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen to protect the environment. The Acinetobacter can also be made into biological denitrification bacterial agents.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Treatment method of anaerobic fermentation biogas slurry from livestock and poultry raising
InactiveCN102701512AGood effectImprove water qualityMultistage water/sewage treatmentEnvironmental engineeringOrganic matter
The invention relates to a treatment method of anaerobic fermentation biogas slurry from livestock and poultry raising. After pH adjustment, the anaerobic fermentation biogas slurry enters an ammonia blow-off column for ammonia nitrogen pretreatment; after pH adjustment, the effluent enters a SBR pool for biochemical treatment; easily-degraded COD is removed through microbial metabolism in the SBR pool; ammonia and nitrogen are further removed through nitrification and denitrification; and total phosphorus is also removed partially; SBR effluent enters a coagulation slanting board sedimentation pool to complete removal of difficultly-degraded organic matter and residual total phosphorus. The invention provides simple, high-efficient, highly-applicable, and standard treatment technology ofanaerobic fermentation biogas slurry from livestock and poultry raising.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Micro-organism preparation for preventing and curing streptococcicosis of Tilapia mossambica as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102583777AImprove environmental qualityInhibit pathogenClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBiotechnologyInorganic salts
The invention relates to a micro-organism preparation for preventing and curing streptococcicosis of Tilapia mossambica as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The micro-organism preparation method for preventing and curing streptococcicosis of Tilapia mossambica comprises steps of compounding mixed vaccine with red Nocardia ATCC11653 and coral Nocardia ACCC40100, fermenting and cultivating the mixed vaccine with fermentation medium which is compounded of nitrogen source, carbon source and inorganic salt, and processing resultants into solid powder after the fermentation and cultivation. The micro-organism preparation for preventing and curing streptococcicosis of Tilapia mossambica, which provided by the invention, can reduce the content of ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen in the Tilapia mossambica breeding water body, antagonize the streptococcicosis of the Tilapia mossambica, reduce the accumulation of harmful substances of the middle and later breeding periods, enhance the immunity of the Tilapia mossambica,, achieve the aim of preventing and curing streptococcicosis of Tilapia mossambica, reduce the economic loss caused by diseases, and ensure the breeding output and quality of the Tilapia mossambica. The micro-organism preparation provided by the invention has advantages of convenience in use, small amount of usage and stable effect after use.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Pig feed additive with efficacies of protecting intestinal tracts and improving food calling function
ActiveCN104431560AEffectively adjust the balanceEffective regulation of antibacterial and bactericidalAnimal feeding stuffRapeseedFeed additive
The invention relates to a pig feed additive with efficacies of protecting intestinal tracts and improving a food calling function. The pig feed additive is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.5-0.9 part of glycine zinc, 0.6-1.2 parts of beta-mannase, 0.5-1 part of yeast powder, 0.5-0.8 part of bifidobacterium bifidum probiotic powder, 0.5-0.8 part of enterococcus faecalis powder, 8-12 parts of dry white wine grain stillage and 9-12 parts of a food calling composition, wherein the composition is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight in a mixing manner: 10-12 parts of robinia flowers, 9-12 parts of orange peel and 1-3 parts of rapeseeds. The additive is capable of effectively adjusting the balance of intestinal flora, increasing the palatability, improving the growth performance, restraining and sterilizing bacteria, preventing and treating diarrhea and dysentery, obviously improving the animal immunity and the production performance, and reducing the ammonia-nitrogen emission to the environment.
Owner:江苏傲农生物科技有限公司
Underflow constructed wetland ecological system for disposing rural domestic waste and disposing method
ActiveCN107686167AGuaranteed denitrification efficiencyMaintain stable operationWater contaminantsBiological treatment apparatusRoot systemEcosystem
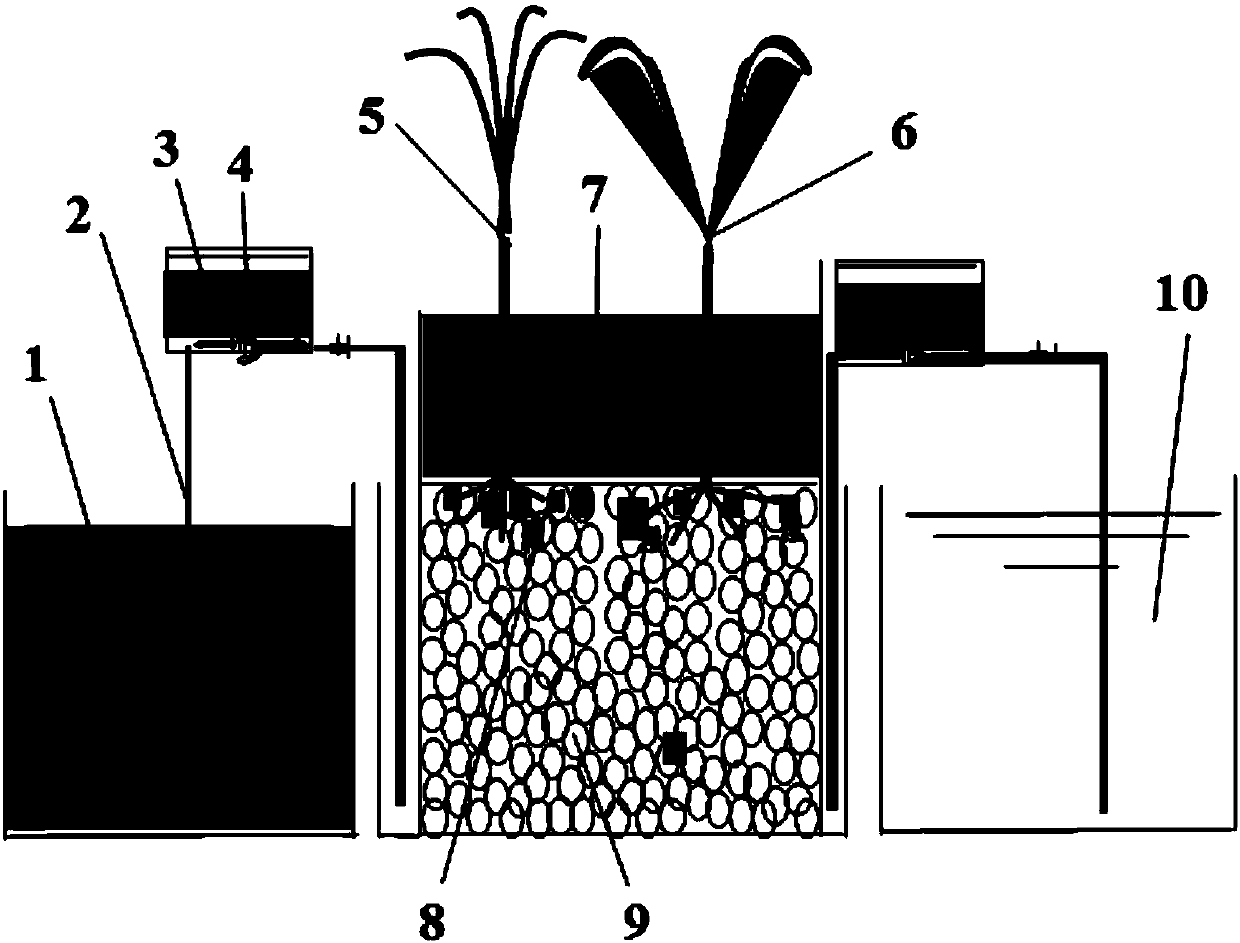
The invention discloses an underflow constructed wetland ecological system for disposing rural domestic waste and a disposing method. By adding root advantageous microorganisms in a canna water planting system, ratio of Alkaligenes, flavobacterium, lysobacter, Pseudomonas and other advantageous germs can be rapidly increased, the abundance of dioxygenase, dehydrogenase, phosphate dehydrogenase, urease, nitrate reductase, and dehydrogenase gene in catalase gene in the constructed wetland can be improved; two kinds of wetland plants can be planted in an intersecting manner, thus the different plant root secreta can be generated and a rich root microbial community structure is formed; the underflow constructed wetland ecological system can remove COD, ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus atthe same time. Then the method of alternatively running continuous water feeding-intermittent water feeding is applied, thus the nitrogen removal efficiency is promoted while the system is stably operated. The method fully applies the advantages of the constructed wetland, strengthens the rapid construction of the constructed wetland ecological system, and optimizes the wetland running mode; the underflow constructed wetland ecological system is significant in environment, economic and social values.
Owner:ZHEJIANG METALLURGICAL RES INST +1
Galactomyces candidum and method for treating high-ammonia-nitrogen biogas slurry by using galactomyces candidum to produce single cell protein
ActiveCN110982706ARapid productionHigh DCW concentrationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCentrifugation
The invention belongs to the field of biological fermentation, and particularly relates to a galactomyces candidum and a method for treating high-ammonia-nitrogen biogas slurry by using the galactomyces candidum to produce single cell protein. The invention has the following specific technical scheme: the galactomyces candidum has a preservation number of CGMCC No.18570. The method of fermenting the biogas slurry comprises the following steps: taking the biogas slurry, performing filtration to remove large-particle impurities, adding a carbon source, adjusting a carbon-to-nitrogen ratio to 6:1to 10:1, and adjusting the pH to 5.5-7 to obtain a fermentation substrate; inoculating the fermentation substrate with the galactomyces candidum grown to a logarithmic stage, and performing fermentation at 20-30 DEG C; and after the fermentation is completed, performing centrifugation on the fermentation liquid, and drying the precipitate obtained after centrifugation at 50-60 DEG C to a constantweight to obtain the required single cell protein. The method only needs a period of biological reaction to treat the biogas slurry, has a low running cost and convenient operation, has an excellenttreatment effect on the biogas slurry, and can provide high economic value products, thereby providing an integrated and economic solution for biogas slurry treatment.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Preparation method of magnetic biological microcapsule for processing organic matters and ammonia nitrogen in water
ActiveCN104911173AIncrease vitalityFree from damageOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierBacterial strainCulture mediums
The invention discloses a preparation method of a magnetic biological microcapsule for processing organic matters and ammonia nitrogen in water. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adding Candida yeast living cells into a disinfected YPD culture medium, culturing at 25-28DEG C under 150-200rpm for 5-6h, taking a bacterial strain liquid obtained after a logarithmic phase, carrying out low temperature drying refrigeration, centrifuging, washing, and carrying out suspension extraction by using normal saline to obtain a bacterial strain Candida yeast suspension with the OD value of 1.5-1.8; 2, mixing sodium alginate and Fe3O4 powder, adding the obtained mixture to deionized water according to the addition amount of sodium alginate of 19-21g / L and the addition amount of the Fe3O4 powder of 1.8-2.2g / L, heating until sodium alginate is completely dissolved, and cooling; and 3, uniformly mixing the yeast suspension with the obtained sodium alginate-iron powder solution according to a volume ratio of 1:9-1:11, adding the obtained solution mixture into a calcium chloride solution in a dropwise manner, curing for 30-40min, and filtering to obtain the microcapsule. The magnetic biological microcapsule prepared in the invention can efficiently degrade the organic matters and ammonia nitrogen in water, can maintain the vitality of thalli, separates the thalli from extraneous adverse environment, can be uniformly distributed in water and separated from water, and is stable in the storage and use process.
Owner:上海艾耐基科技股份有限公司
Compound feed additive for improving anti-stress ability of crucian
ActiveCN104304684ARepair damageImprove hypoxia resistanceAnimal feeding stuffAnti stressWeight gaining
The invention provides a compound feed additive for improving anti-stress ability of a crucian. The compound feed additive comprises tea polyphenol, taurine, tryptophan, organic zinc, organic selenium, mannan oligosaccharide, vitamin C and a carrier. After adding the feed additive at a weight percentage of 0.2-0.3% to basic formula feed of the crucian under severe water quality conditions with 1-3mg / L dissolved oxygen and the concentration of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite being 0.1-1.5mg / L, a survival rate and a weight gain rate of the crucian are increased, a feed coefficient is reduced at the same time, and the culture efficiency is improved.
Owner:广东海因特生物技术集团有限公司
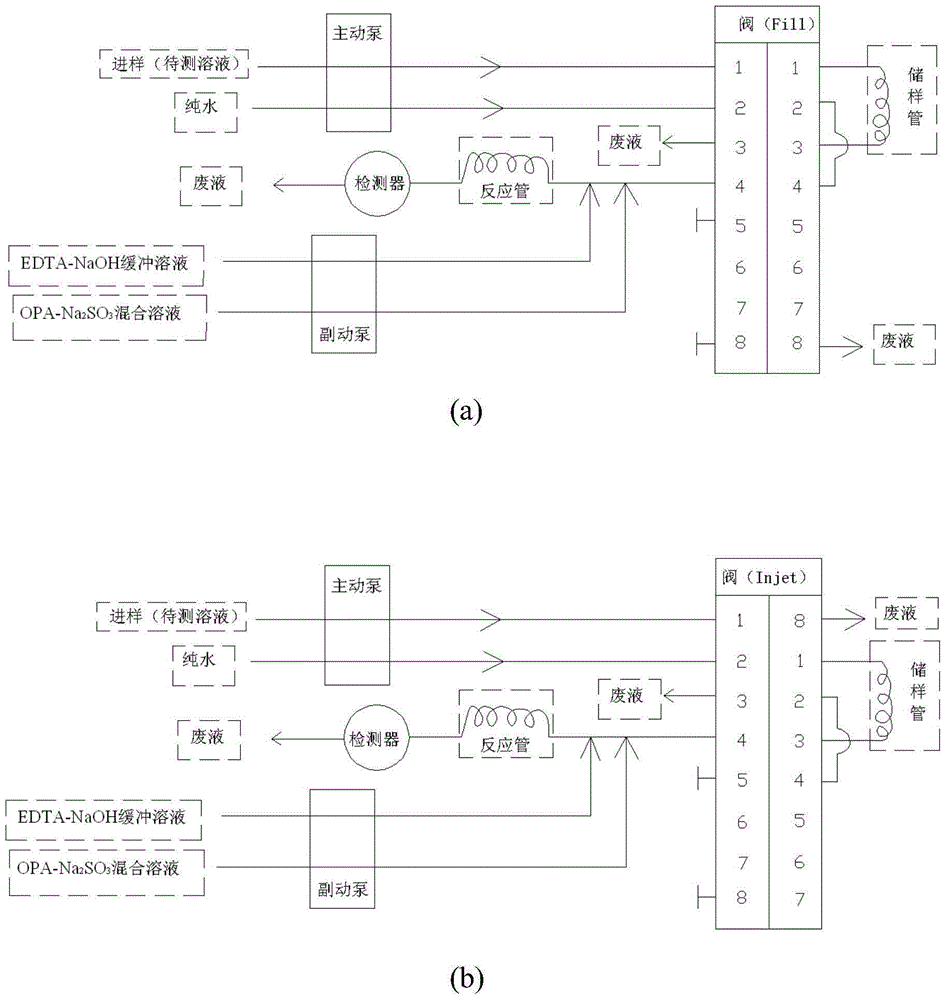
Phthalic dicarboxaldehyde-NH3-Na2SO3 reaction-based flow injection spectrophotometry method for measuring Ammonia-N in water sample
InactiveCN105203476ADetermined to meetLow detection limitColor/spectral properties measurementsSurface waterEarth surface
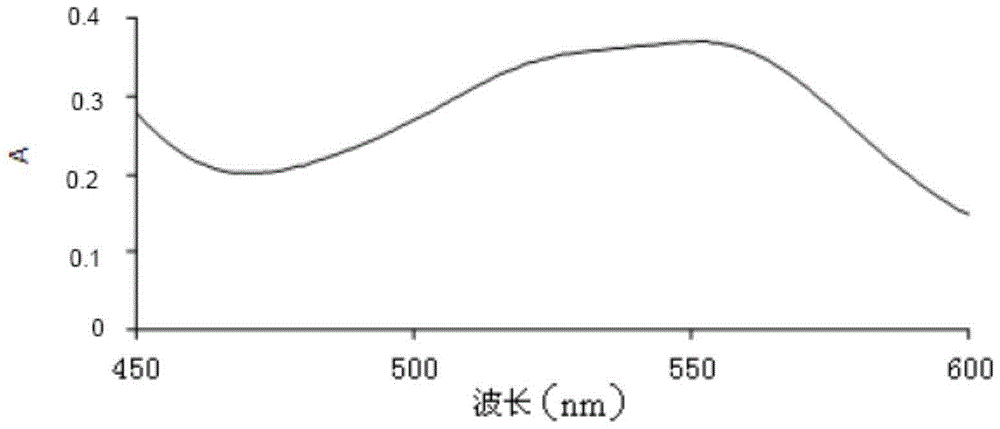
The invention discloses a phthalic dicarboxaldehyde-NH3-Na2SO3 reaction-based flow injection spectrophotometry method for measuring Ammonia-N in a water sample. The method specifically comprises the step of adopting a flow injection analyzer and an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer to jointly measure Ammonia-N content in a water sample. An amaranth complex is generated based on an OPA(O phthalic aldehyde)-NH3-Na2SO3 reaction; the complex realizes strong absorption at a 550nm position, and has an absorbance value in direct proportion to Ammonia-N concentration in the water sample, thus creating the flow injection spectrophotometry method for measuring Ammonia-N in the water sample. The detection limit of the method can be as low as 0.007mmol / L, and measuring on Ammonia-N concentrations in various surface water can be realized; average substrate adding standard recovery rates of lake water, river water and groundwater are respectively 100.4 percent, 95.2 percent and 101.7 percent; besides, the analysis speed is high, and a result is not remarkably different from that of a indophenol blue spectrophotometry method.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Process for treating high-concentration nitrate and ammonia-nitrogen wastewater by using sludge fermentation liquor as carbon source through series connection of short-cut denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation
InactiveCN113023870AAchieve reductionLow additional costWater treatment parameter controlBiological treatment regulationVolatile fatty acidsNitration
The invention discloses a process for treating high-concentration nitrate and ammonia-nitrogen wastewater by using sludge fermentation liquor as a carbon source through series connection of short-cut denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. The device comprises a sludge fermentation tank, a PD-SBR reactor, an AMX-SBR reactor and the like. The method comprises the following steps: the residual sludge is fermented under a medium-temperature alkaline anaerobic condition, and converting refractory organic matters into easily degradable organic matters; denitrifying bacteria perform short-cut denitrification by utilizing volatile fatty acid in the fermentation liquor, and nitrate is converted into nitrite; and effluent and high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater enter an anaerobic ammonium oxidation film reactor together for autotrophic nitrogen removal, and the polyurethane sponge filler is used for holding anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria. According to the method, the aeration energy consumption is reduced, the sludge fermentation liquid is used as the external carbon source, a high-quality carbon source is provided for denitrification, sludge reduction is realized, the sludge treatment cost and the external carbon source addition cost are reduced, stable nitrite accumulation is realized by short-cut denitrification, and synchronous treatment of high-nitrate wastewater and high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater is realized by combining anaerobic ammonia oxidation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing earthworm special feed from kitchen waste
InactiveCN109170234AImprove the growing environmentEasy to smokeFood processingAnimal feeding stuffMicroorganismEngineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing earthworm special feed from kitchen waste. The method comprises the following steps: collection of kitchen waste, reduction sorting, deoiling treatment,desalting treatment, crushing treatment, dewatering treatment, high-temperature curing treatment, and addition of palatable materials to form the earthworm special feed; in the high-temperature curingtreatment process, the kitchen waste subjected to the dewatering treatment is loaded into a horizontal pipeline tank with an intestine-like zigzag roundabout inner part, the materials are pushed by air pressure to operate, the temperature in the pipeline tank is 80-120 DEG C, and the kitchen waste operates in the tank for 25-35m for 10-15 minutes; and in the process of addition of palatable materials to form the earthworm special feed, the kitchen waste is added to a stirring device, a sweetening agent and a sour agent are added, stirring is performed uniformly, the addition amount of the sweetening agent is 0.2-0.6% of the kitchen waste by weight, and the addition amount of the sour agent is 0.2-0.6% of the kitchen waste by weight. The method for preparing the earthworm special feed fromkitchen waste can be used for preparing special feed easy to suck by earthworms; the earthworm special feed has high nutritional value, no harmful microorganisms, no parasitic ova, no ammonia nitrogen smell and good palatability; the earthworms like to eat the special feed and have high activity; and the produced earthworm excretion has high quality.
Owner:江苏大硕源环保科技有限公司
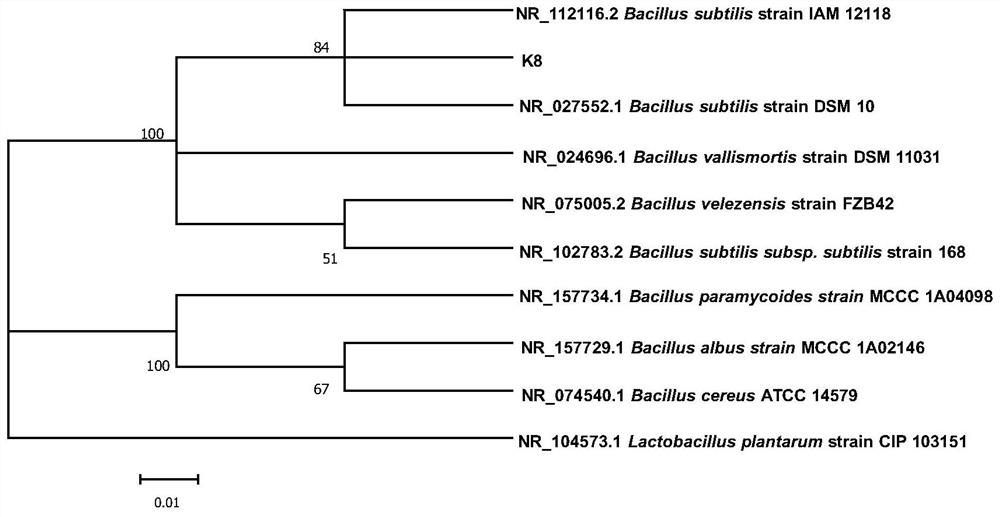
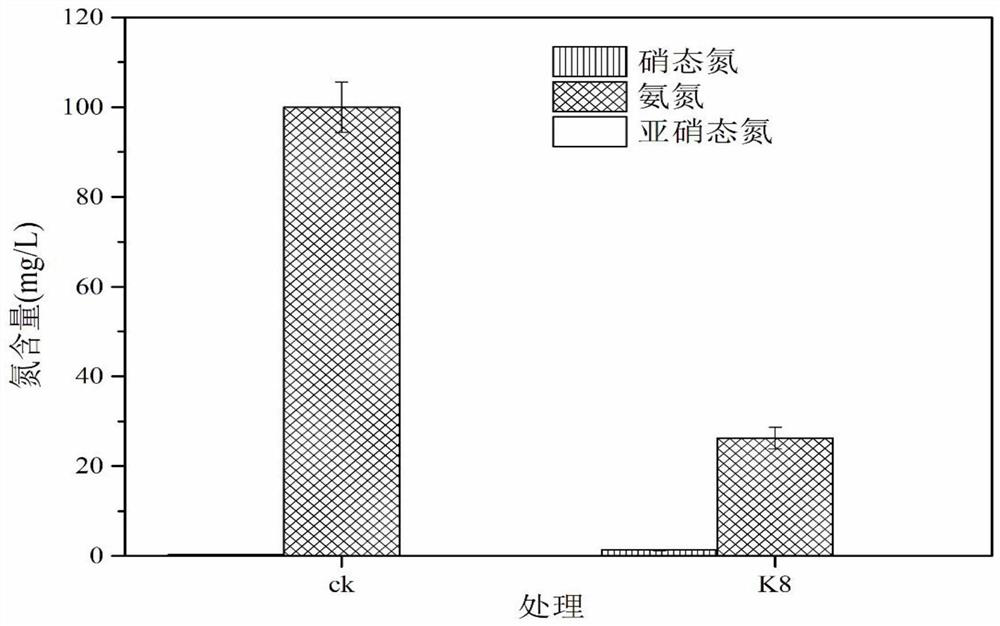
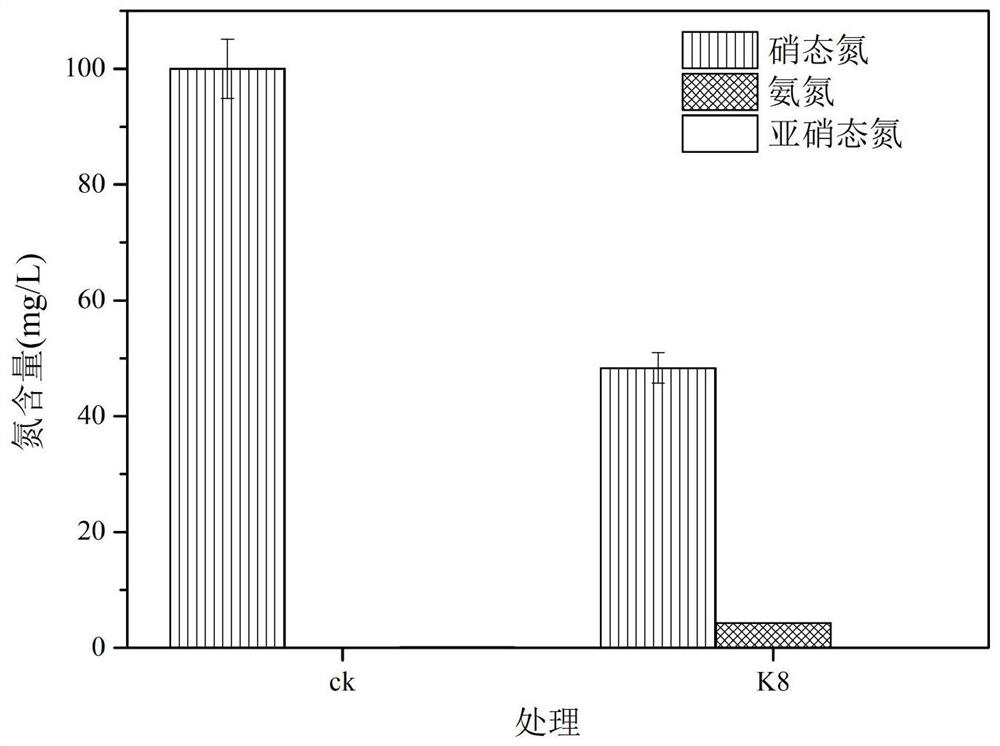
Synchronous nitrification and denitrification bacillus subtilis K8 and application thereof
ActiveCN112011486AFast denitrificationImprove nitrogen removal efficiencyFungiBacteriaAmylaseLactic bacteria
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, in particular to synchronous nitrification and denitrification bacillus subtilis K8 and application thereof. The strain obtained by screening is identified as Bacillus subtilis through physiological and ecological analysis and molecular biology. The strain can grow under the condition of taking ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen or nitrate nitrogen as a unique nitrogen source. Under a heterotrophic aerobic condition, through the synchronous nitrification and denitrification effect, the removal rates of 100 mg / L ammonia nitrogen, 100 mg / L nitrate nitrogen and 25 mg / L nitrite nitrogen reach 73.7%, 51.7% and 100% respectively in 24 h, and inorganic nitrogen is not accumulated; the removal rates of mixed nitrogen sources of 50mg / L ammonia nitrogen and 12.5 mg / L nitrite nitrogen in the water body respectively reach 89.1% and 100%, and nitrate accumulation is avoided; and a good prevention and treatment effect is achieved on blue-green algae. The strain also has relatively strong amylase and protease producing capacity, is acid-resistant and cholate-resistant, and can be compounded with saccharomycetes and lactic acid bacteria to prepare a fermented feed, so that the contents of amino acids and total proteins in the feed can be increased.
Owner:天津市农业科学院
Enrichment method of anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
ActiveCN110683643AGuaranteed long-term stabilityEliminate nitriteWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides an enrichment method of anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. According to the method, wastewater is used as an enrichment substrate and a nutrient source, and a microbial agentis added to treat the wastewater in different stages. On the one hand, the required enrichment culture conditions for anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria can be provided, so that outlet water COD and ammonia nitrogen nitrites reach requirements for enrichment of an anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing strain; and on the other hand, the synergistic domestication action of the target strain is performed during the enrichment process, the growth rate and tolerance performance of the anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria can be improved, and the enrichment effect and the total nitrogen removal rate of theanaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria are improved. Quick start of the strain and an apparatus can be ensured in a subsequent application process, and thereby a process of biological nitrogen removalby an anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing process is accelerated.
Owner:WUHAN SHUIZHIGUO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Fermentation bacterial agent for harmless treatment of solid organic matter and application method of fermentation bacterial agent
The invention relates to a fermentation bacterial agent for harmless treatment of solid organic matter and an application method of the fermentation bacterial agent. The fermentation agent is preparedfrom aspergillus oryzae, streptococcus thermophilus, bacillus thermophilus, streptococcus faecalis, bacillus mucilaginosus, biochar and auxiliary materials according to a certain proportion. Strainsused by the fermentation bacterial agent can correspondingly be obtained from separation of the natural environment, and have good symbiosis, and the antagonistic effect does not exist between the strains, functions, advantages and characteristics of each strain are fully used and applied to the harmless treatment of the solid organic matter, decomposition of feces can be accelerated, decomposition of organic matter is strengthened, pathogenic bacteria and insect eggs are killed through rapid heating, the odor of the feces is effectively eliminated, losses of ammonia nitrogen and other nutrients are reduced, fermentation time is shortened, and fermentation efficiency is improved, and products after fermentation and decomposition are high-quality raw materials for organic fertilizers; and the biochar is added on the basis of bacteria for the first time, the growth of microorganisms is greatlypromoted, and fermentation efficiency is improved.
Owner:武汉丰甜生物科技有限公司
Domestication method of ammonia nitrogen and propionic acid resisting methane production strain
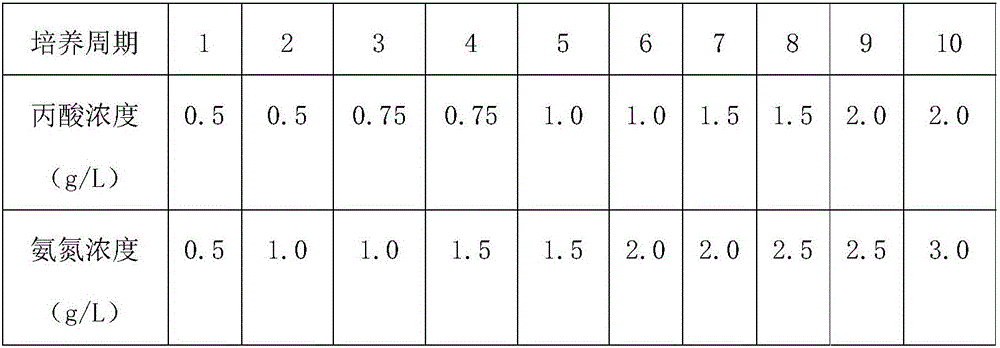
ActiveCN106754611AStrong impact resistanceHigh stability of bioaugmentationBacteriaWaste based fuelPropanoic acidFermentation
The invention discloses a domestication method of an ammonia nitrogen and propionic acid resisting methane production strain. The ammonia nitrogen and propionic acid resisting methane production strain comprises a propionic acid oxidization flora, a syntrophaceae propionic acid oxidization flora, an acetic acid cracking methane production flora, a hydrogen nutrition type methane production flora and a denitrification flora. The method takes marsh gas fermentation liquid as an inoculum, takes propionic acid as a carbon source and takes urea or NH4Cl as an ammonia nitrogen source; the marsh gas fermentation liquid is domesticated through a method for alternately improving the concentration of the propionic acid and the concentration of ammonia nitrogen, so as to obtain the ammonia nitrogen and propionic acid resisting methane production strain; the strain can stably produce gas for a long period under the conditions that the concentration of the ammonia nitrogen is more than 3.0g / L and the concentration of the propionic acid is more than 2.0g / L; the gas yield is 60 percent more than a theoretical yield; the utilization rate of the propionic acid and acetic acid is more than 90 percent; the ammonia nitrogen and propionic acid resisting methane production strain has the advantages of high impact resistance, high stability of biological enhancing effect and the like, and can be used for removing comprehensive inhibition of the ammonia nitrogen and the propionic acid in a marsh gas fermentation process and improving the fermentation performance of marsh gas.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Treatment method of high-salt and high-ammonia-nitrogen degradation-resistant organic wastewater
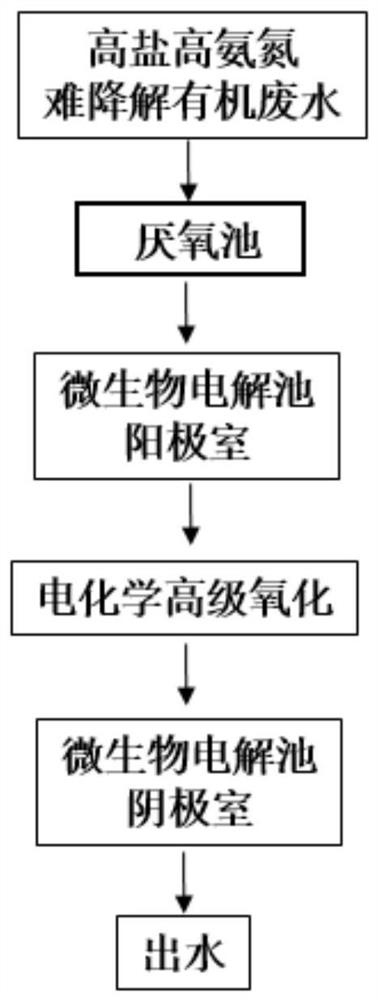
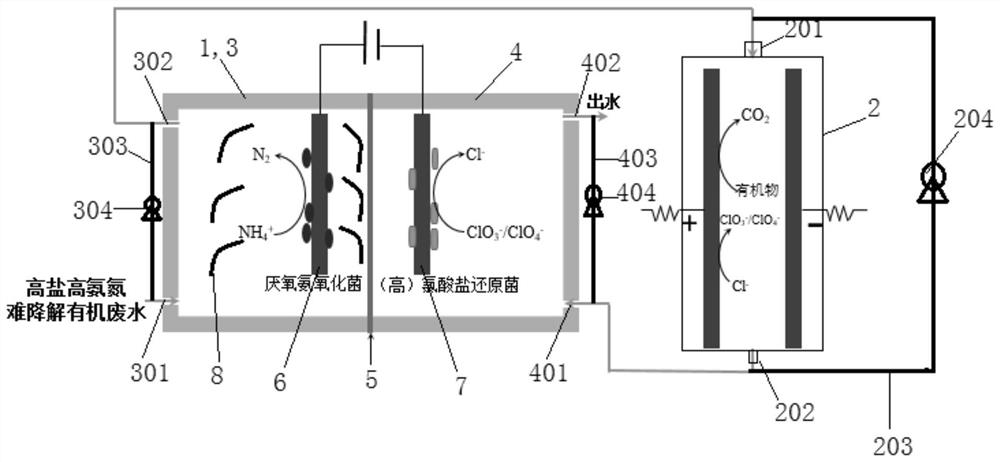
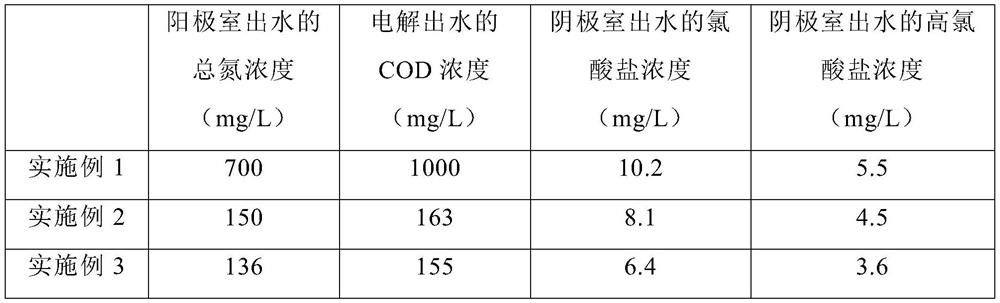
ActiveCN113072251AImprove utilization efficiencySolve pain pointsTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesBiological treatment regulationEngineeringElectrochemistry
The invention relates to a treatment method of high-salt and high-ammonia-nitrogen degradation-resistant organic wastewater. The treatment method comprises the following steps that: S100, wastewater enters an anode chamber of a microbial electrolysis cell for anaerobic ammonia oxidation autotrophic nitrogen removal; S200, the wastewater enters an electrochemical advanced oxidation unit after being subjected to denitrification treatment, and refractory organic matters are degraded; and S300, the effluent of the electrochemical advanced oxidation unit enters a cathode chamber of the microbial electrolysis cell for reduction of perchlorate and chlorate so as to reduce the concentration of chlorine by-products in the wastewater. According to the treatment method, ammonia nitrogen removal, (per) chlorate reduction and advanced oxidation of organic matters are organically coupled, a novel microbial electrolysis cell is established by utilizing the electrochemical activity of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria and chlorate reducing bacteria, autotrophic nitrogen removal by a biological anode and (per) chlorate reduction by a biological cathode are synchronously realized, a new technology for treating the high-salt and high-ammonia-nitrogen degradation-resistant organic wastewater through microbial electrolysis cell-electrochemical advanced oxidation is formed, and economic, efficient and green treatment of the wastewater is realized.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Necteromyces rattus and method for treating high-ammonia-nitrogen biogas slurry by using necteromyces rattus to produce single cell protein
ActiveCN110982717APromote growthEfficient productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCentrifugation
The invention belongs to the field of biological fermentation, and in particular relates to a necteromyces rattus and a method for treating high-ammonia-nitrogen biogas slurry by using the necteromyces rattus to produce single cell protein. The invention comprises the following specific technical scheme: the necteromyces rattus has a preservation number of CGMCC No.18371. The method of fermentingthe biogas slurry comprises the following steps: taking the biogas slurry, performing filtration to remove large-particle impurities, adding a carbon source, adjusting a carbon-to-nitrogen ratio to 6:1 to 10:1, and adjusting the pH to 5.5-7 to obtain a fermentation substrate; inoculating the fermentation substrate with the necteromyces rattus grown to a logarithmic stage, and performing fermentation at 20-30 DEG C; and after the fermentation is completed, performing centrifugation on the fermentation liquid, and drying the precipitate after centrifugation at 50-60 DEG C to a constant weight toobtain the required single cell protein. The method only needs a biological reaction to treat the biogas slurry, has a low running cost and convenient operation, has an excellent treatment effect onthe biogas slurry, and can provide high-economic-value products, thereby providing an integrated and economic solution for biogas slurry treatment.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Composite microbial remediation agent for black and odorous water body and application thereof
InactiveCN109554315ASpecific and efficient degradationFungiBacteriaPichia pastorisCandida tropicalis
The invention belongs to the technical field of black and odorous water body treatment, and provides a composite microbial remediation agent for a black and odorous water body and an application thereof. The compound microbial remediation agent for the black and odorous water body is composed of bacillus subtilis, pichia pastoris, candida tropicalis and a nitrifying bacterial agent. The weight ratio of the four bacterial agents is bacillus subtilis:pichia pastoris:candida tropicalis:nitrifying bacterial agent=(3-5):(1-3):(1-2):(1-2). The bacillus subtilis has a specific and efficient degradation effect on organic matters of black and odorous water and is compounded with specific bacterial agents, and the compound microbial remediation agent for the black and odorous water body is obtained.The compound microbial remediation agent is applied to treatment of the black and odorous water body, and has the advantages of all the bacterial agents, and degrades the black and odorous water bodyto the maximum extent. With adopting of the compound microbial remediation agent, after treatment, the odor of the water body is eliminated, the water body is clarified and transparent, and the waterquality COD and the ammonia nitrogen contents meet the V-class standard of 'environmental quality standards for surface water'.
Owner:CHAMBROAD CHEM IND RES INST CO LTD
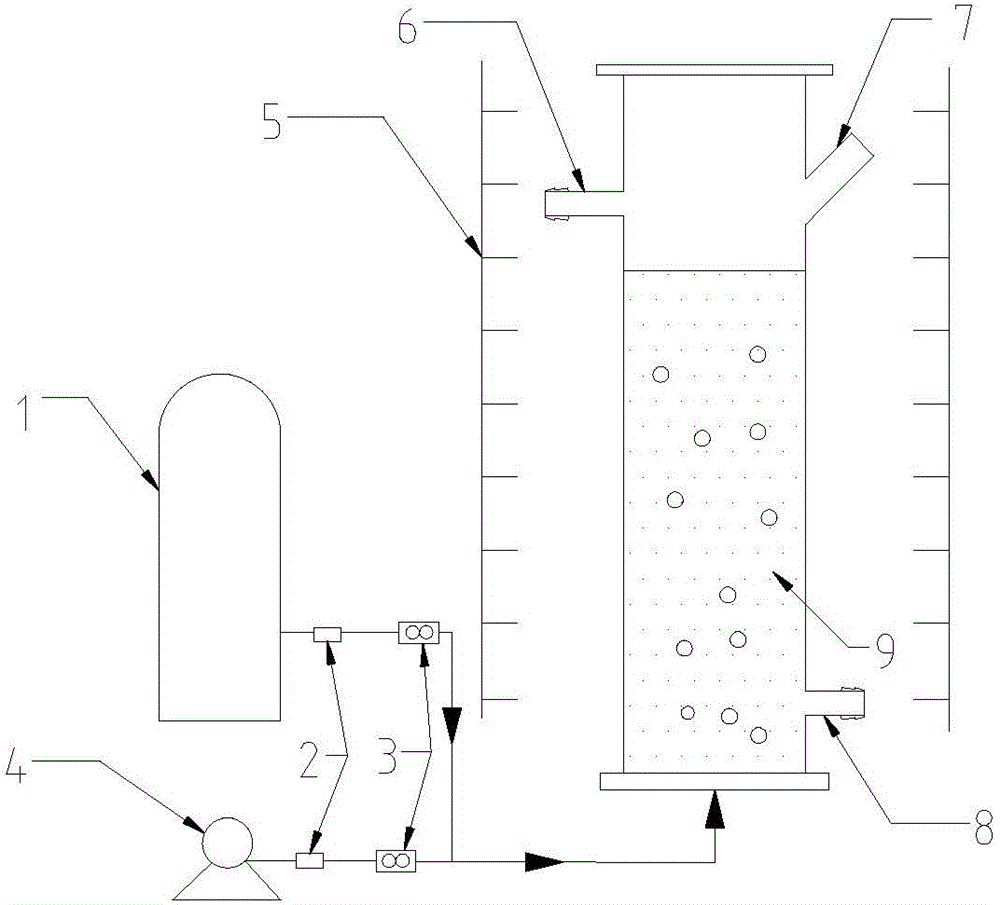
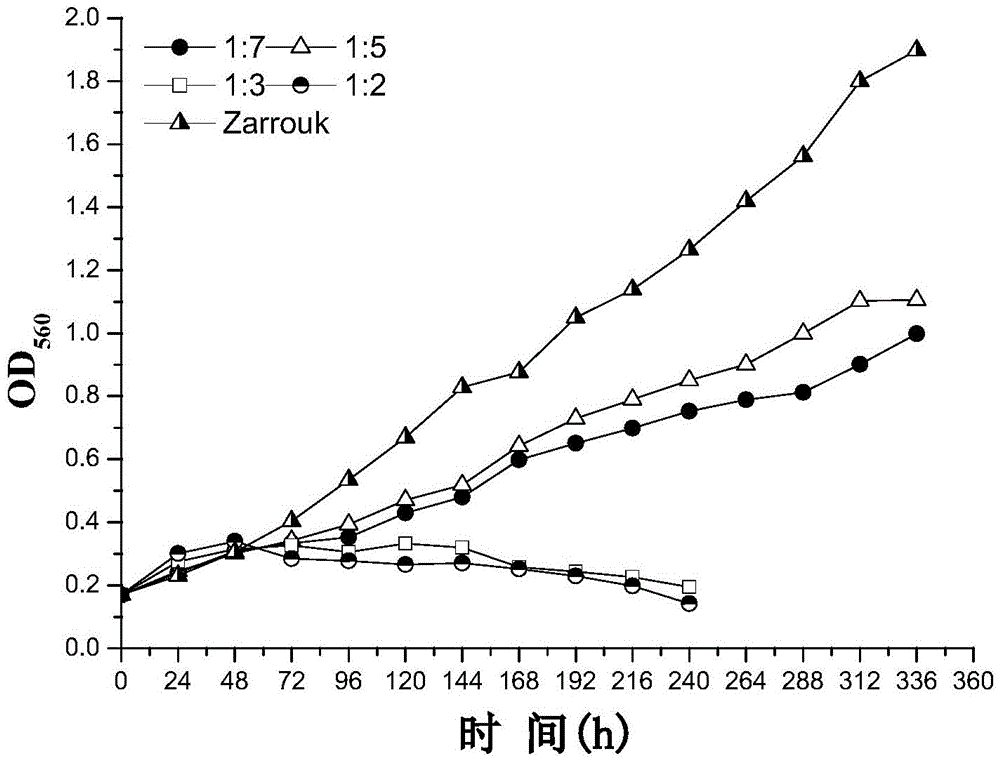
Method for culturing nitrogen fixation spirulina by using kitchen wastewater
InactiveCN104862231AReduce manufacturing costEasy to prepareBacteriaUnicellular algaeResource utilizationNitrate nitrogen
The invention discloses a method for culturing nitrogen fixation spirulina by using kitchen wastewater, and belongs to the technical fields of environment engineering and microalgae culture. According to the method, microelements are added into kitchen wastewater so as to prepare a microalgae culture medium for culturing microalgae, an effect of a Zarrouk culture medium can be generally achieved, use of chemical medicines is reduced, the environment pollution is also reduced, meanwhile the production cost of microalgae is lowered, sustainable microalgae production can be achieved, the culture medium is simple in preparation method, the kitchen wastewater can be used for culturing the microalgae without being sterilized, resource utilization of kitchen wastewater can be achieved, environment pollution can be reduced, the utilization rate of ammonia nitrogen in the kitchen wastewater can be 100%, the utilization rate of nitrous nitrogen can be up to 72.361%, the utilization rate of nitrate nitrogen is 7.849%, the utilization rate of TN is 32.035%, the absorption property of carbon sequestration spirulina on the nitrogen element is that NO2<-> -N is less than NH4<+>-N and greater than NO3<->-N, the nitrogen source in the wastewater is sufficient for spirulina to grow, and the utilization rate of TP is 59.140%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
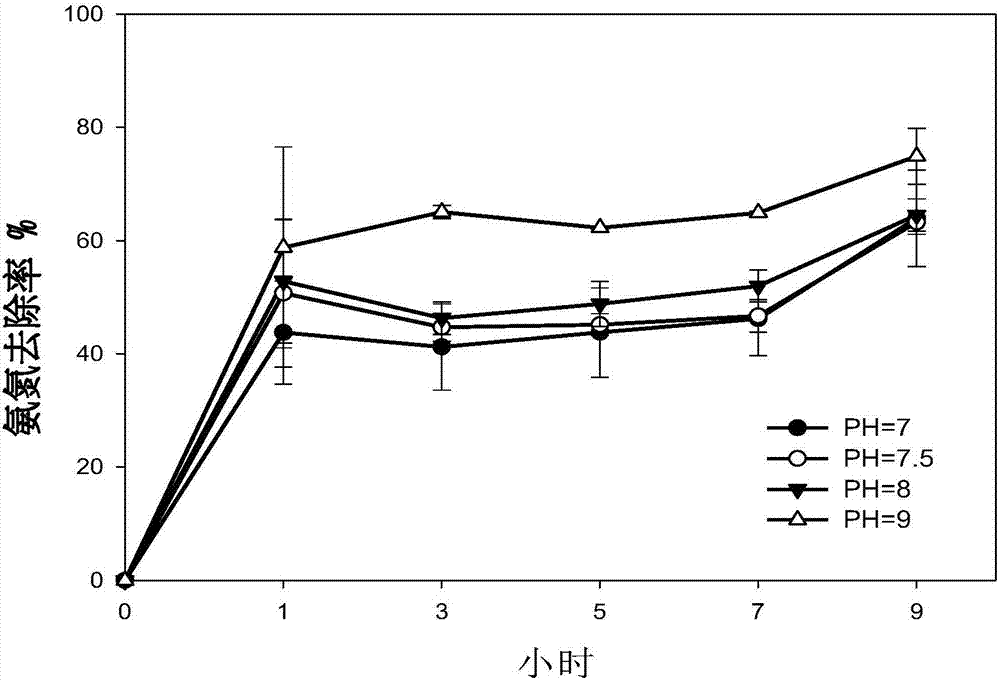
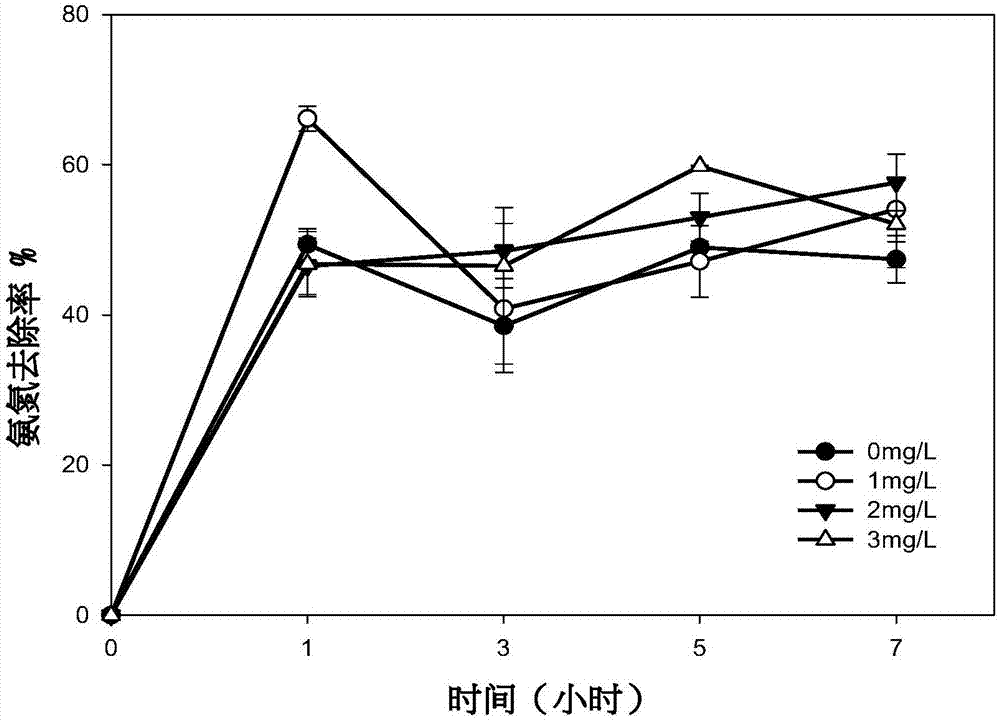
Method for eliminating ammonia inhibition in anaerobic fermentation process of livestock and poultry excrement
InactiveCN106865936AReduce consumptionRapid responseWaste water treatment from animal husbandryBiological sludge treatmentFecesVolatile fatty acids
The invention provides a method for eliminating ammonia inhibition in an anaerobic fermentation process of livestock and poultry excrement. According to the method, a struvite crystallization and sedimentation technology is used for detecting the concentration of NH<4+> in an ammonia inhibition system under the conditions that the pH value is 7-9, and the mass concentration ratio of volatile fatty acid to total inorganic carbon is less than 0.4; magnesium salt and phosphorus salt are added into a livestock and poultry excrement fermentation reaction system according to a molar ratio of the NH<4+> to Mg<2+> to PO4<3-> being equal to 1: 1: 1; the concentration of ammonia nitrogen is reduced to about a concentration value of the fermentation process without ammonia inhibition. The method for eliminating the ammonia inhibition in the anaerobic fermentation process of the livestock and poultry excrement is established by studying the influence factors of an ammonium magnesium phosphate reaction in the inner environment of an anaerobic fermentation tank and the self-limiting factors of the reaction. The method is simple in technology; furthermore, struvite precipitation produced in the reaction is slow release fertilizer, and not only can eliminate the ammonia nitrogen inhibition, but also can recover nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, so that the operating cost is lowered.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
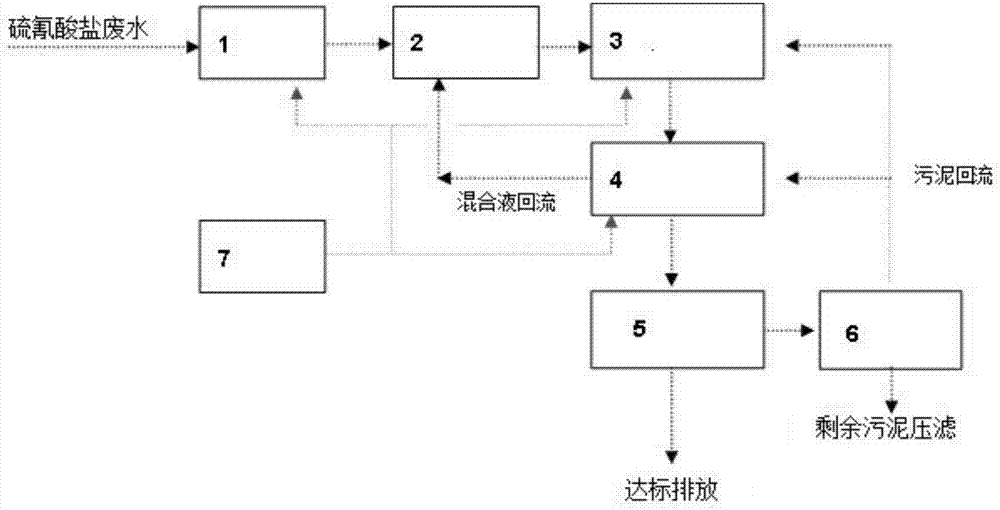
Device and method for treatment of high-concentration thiocyanate wastewater
PendingCN107963719AGood removal effectOvercome the shortcomings of incomplete degradationWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsBiotechnologyCyanide compound
The invention discloses a device and a method for treatment of high-concentration thiocyanate wastewater. The method includes the steps of: using thiocyanate high-effective degrading bacteria and using SCN<-> as a required nutrient in growth for microbially metabolizing the thiocyanides into SO4<2->, CO2 and N2. According to the technical scheme, the thiocyanides in wastewater is high-effectivelydegraded; the degradation process is completed with a large number of microorganisms, including bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi, which degrade the cyanides and thiocyanates into ammonia, CO2 and sulfates, and all the cyanides and thiocyanates can be removed by means of combination of oxidization and adsorption with a large number of microorganisms. The microbial treatment on the thiocyanate wastewater is carried out in a special bio-oxidizing pool, wherein proper growth conditions need to be created for the microorganisms artificially in order to culture the thiocyanate high-effective degrading bacteria. The microorganisms are fully utilized to decompose the thiocyanates, thereby high-effectively purifying the wastewater. After treatment, discharged water is less than 100 mg / L in COD, less than 8 mg / L in ammonia nitrogen and less than 0.5 mg / L in CN.
Owner:GUIZHOU JINFENG MINING
Application of gamma-aminobutyric acid serving as snakehead feed additive for resisting ammonia nitrogen stress
InactiveCN105029125APromote growthTo promote metabolismOrganic active ingredientsClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention provides snakehead matching feed. The snakehead matching feed comprises, by weight, 43.50-45.50 parts of domestic fish meal, 0.35-0.37 part of aspartic acid, 1.28-1.45 parts of fish oil. 1.48-1.79 parts of peanut oil, 6.4-6.60 parts of corn, 7.90-8.10 parts of bean pulp, 6.60-8.60 parts of cottonseed meal, 5.80-10.80 parts of rapeseed meal, 3.50-6.50 parts of peanut meal, 0.94-0.96 part of vitamin premix, 10.50-14.50 parts of wheat bran, 24.50-28.50 parts of wheat middling, 2.54-2.56 parts of bentonite, 0.4-0.6 part of sodium alginate, 1.70-1.90 parts of mineral salt premix and 1.10-1.30 parts of gamma-aminobutyric acid. It is shown by experiments that growth and metabolism of snakeheads can be promoted, the feed utilization rate is increased, and the acute ammonia nitrogen stress ability is improved.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Compound water purifying agent used for aquaculture and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105481101AShort onset timeProlong the action timeWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentBacillus cereusBacillus subtilis
The invention discloses a compound water purifying agent used for aquaculture. The compound water purifying agent is prepared by mixing microorganism bacterium powder with a physical and chemical reagent in a mass ratio of (1-3) to 1, wherein the microorganism bacterium powder is prepared by mixing bacillus subtilis B7348 with ammonia nitrogen degrading capacity, bacillus subtilis N9-1-35 with ammonia nitrogen degrading capacity, bacillus cereus with acid production capacity and bacillus subtilis BLS1 with algae lysing capacity; the number of viable bacteria in the microorganism bacterium powder obtained after mixing is more than or equal to 10<8>cfu / g; the physical and chemical reagent is prepared by mixing zeolite powder, sodium thiosulfate and aluminium potassium sulfate in a mass ratio of (3-5) to (2-4) to (1-3). The compound water purifying agent has good water purifying effects, is low in use cost, is safe and effective and can meet the requirements of mass aquaculture farmers.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司 +1
Heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN113736700AImprove cleanlinessGood effect in removing ammonia nitrogenBacteriaWater contaminantsSodium acetateButanedioic acid
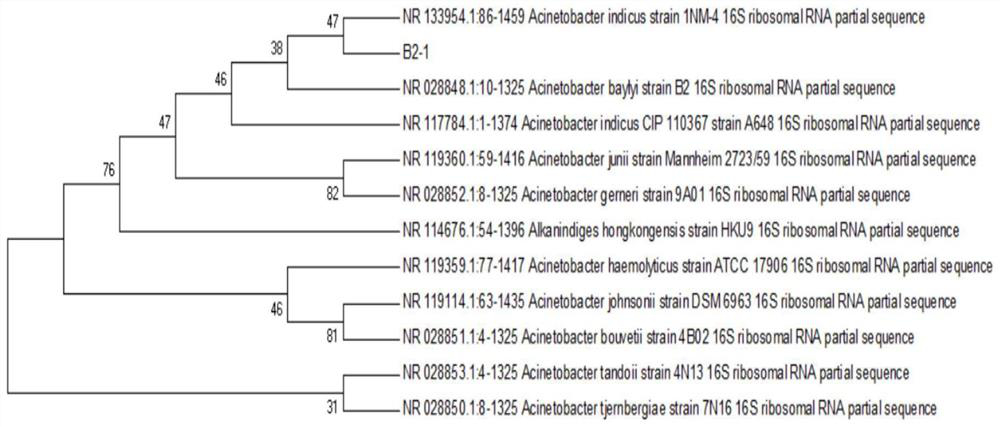
The invention discloses a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium and an application thereof. The heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the classification name is Acinetobacter indicus ZJB20129, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2020965, and the preservation date is December 24, 2020. The heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification acinetobacter indicus strain B2-1 (Acinetobacter indicus strain B2-1) ZJB20129 can utilize sodium succinate and sodium acetate as carbon sources, has the optimal ammonia nitrogen removal effect which is 99.27% when being aerobically cultured for 36 hours under the conditions that the sodium succinate is the optimal carbon source, the C / N mass ratio is 15, the pH value is 8, the temperature is 35 DEG C and the rotating speed is 160rpm. Meanwhile, the strain has a very good removal effect on nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Indigenous high-efficiency denitrification strains of Pseudomonas fulva K3 and Pseudomonas mosselii K17 in soil of rare earth leaching site and application of strains
ActiveCN111718864AEasy to removeEfficient removalTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaMicroorganismSoil science
The invention relates to indigenous high-efficiency denitrification strains of Pseudomonas fulva K3 and Pseudomonas mosselii K17 in soil of a rare earth leaching site and application of the strains. The strains are both enriched and screened from the soil of rare earth leaching site, and belong to Pseudomonas fulva and Pseudomonas mosselii respectively, both of the strains are transferred to ChinaCenter for Type Culture Collection for preservation on Decomber 16, 2019, and the corresponding deposit numbers are respectively CCTCC NO: M 20191055 and CCTCC NO: M 20191056. The two strains are both heterotrophic nitrifying-aerobic denitrifying bacteria, can quickly remove ammonia nitrogen in a leachate (initial ammonia nitrogen concentration <= 300 mg / L)from the rare earth leaching site underaerobic conditions, the denitrification rate is more than 90%, the accumulation of nitrite nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen is less than 6 mg / L, and the ammonia nitrogen concentration in the leachate after treatment reaches the national emission standard. The discovery of the strains provides a high-efficiency and environment-friendly microbial denitrification treatment method for the lechate from the rare earth leaching site, and the strains have broad application prospects.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Non-ammonia molybdenum precipitation method for sodium-modifying vanadium-rich liquor
InactiveCN111020231AAvoid emissionsNo worries about environmental protectionProcess efficiency improvementAmmonia productionPhosphine
The invention relates to a non-ammonia molybdenum precipitation method for sodium-modifying vanadium-rich liquor. The non-ammonia molybdenum precipitation method comprises the following steps: 1) regulating the pH value of the sodium-modifying vanadium-rich liquor with sulfuric acid, and adding calcium chloride and an aluminum sulfate solution to purify, remove silicon, remove phosphine and filter; 2) regulating the pH value of the obtained purified filtrate with the sulfuric acid, adding the sulfuric acid, introducing CO2 under a stirring condition, adding certain polymer polyvanadic acid asseed crystal, heating to a temperature of 90 DEG C or higher, and preserving the heat for 1-2 hours until molybdenum precipitation is complete, and filtering; 3) adding an acidic ammonium sulfate solution into obtained filter residues, introducing CO2 under the stirring condition, and heating up to a boiling point for sodium removal and filtration, adding lime to treat and filter by supplementingammonium sulfate into filtrate to circulate by certain times, returning filtrate to a fine vanadium burning furnace, and spraying and absorbing ammonia gas released by fine vanadium burning, and recycling produced ammonium sulfate for sodium removal of polymer polyvanadic acid; and 4) washing the filter residues with a sulfuric acid aqueous solution and clear water to further produce vanadium pentoxide. The non-ammonia molybdenum precipitation method has the beneficial effects of solving emission of ammonia nitrogen wastewater from the source, and being environmentally friendly.
Owner:杨秋良
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com