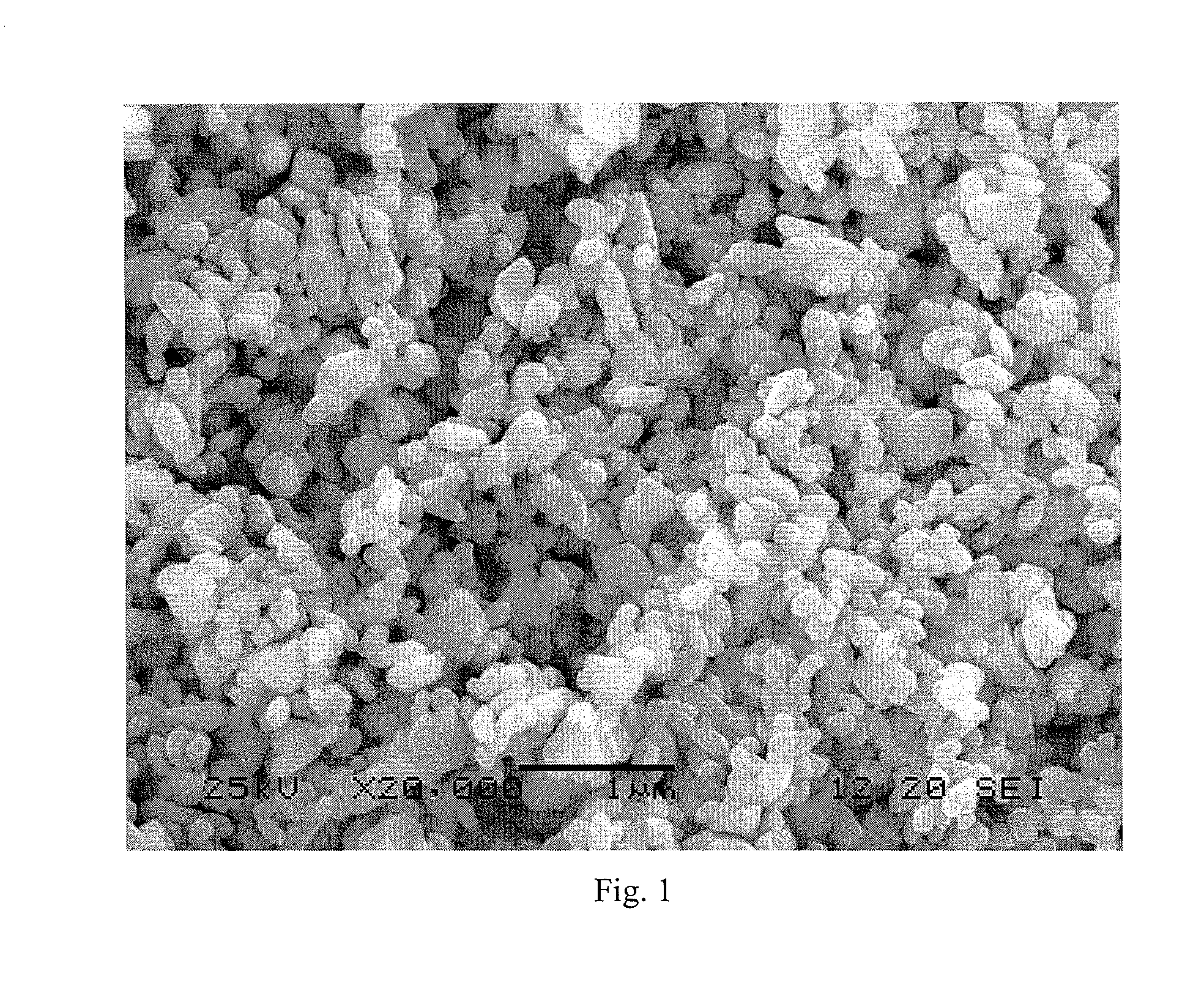
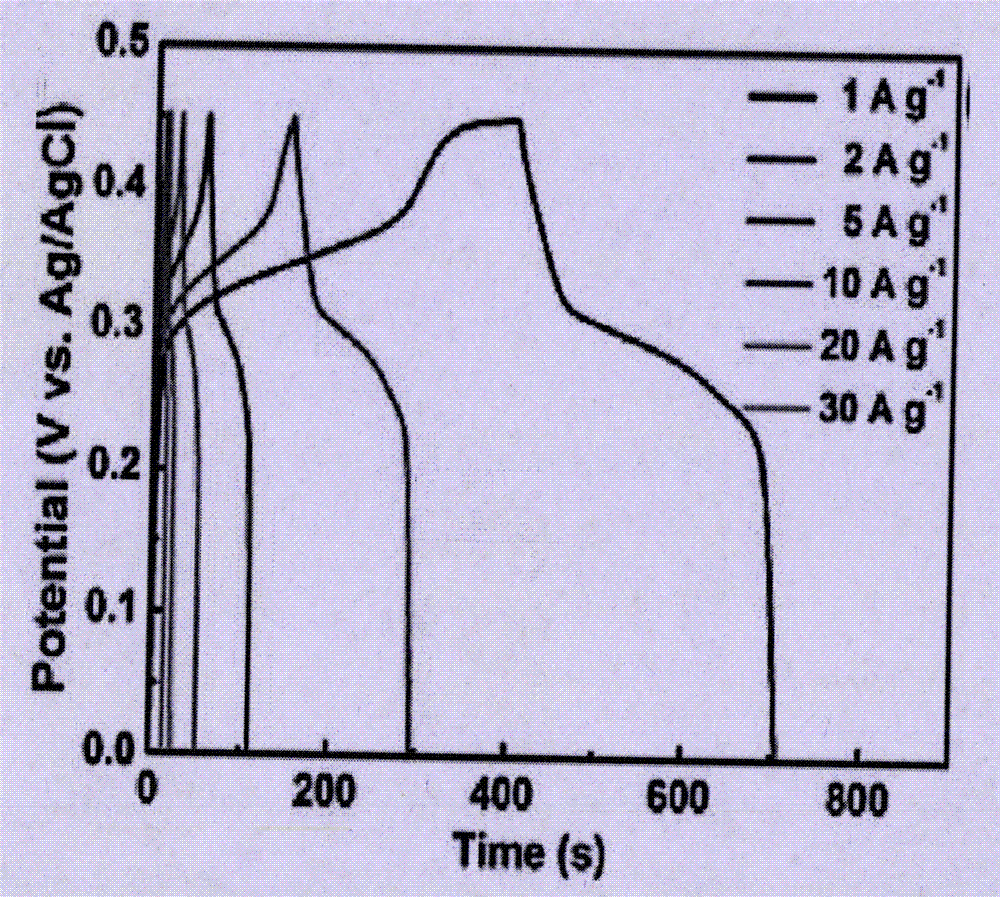
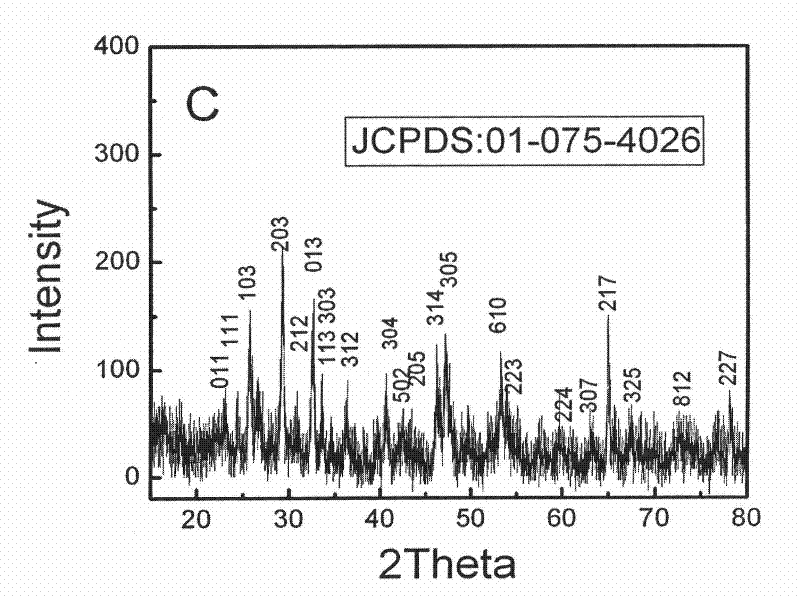
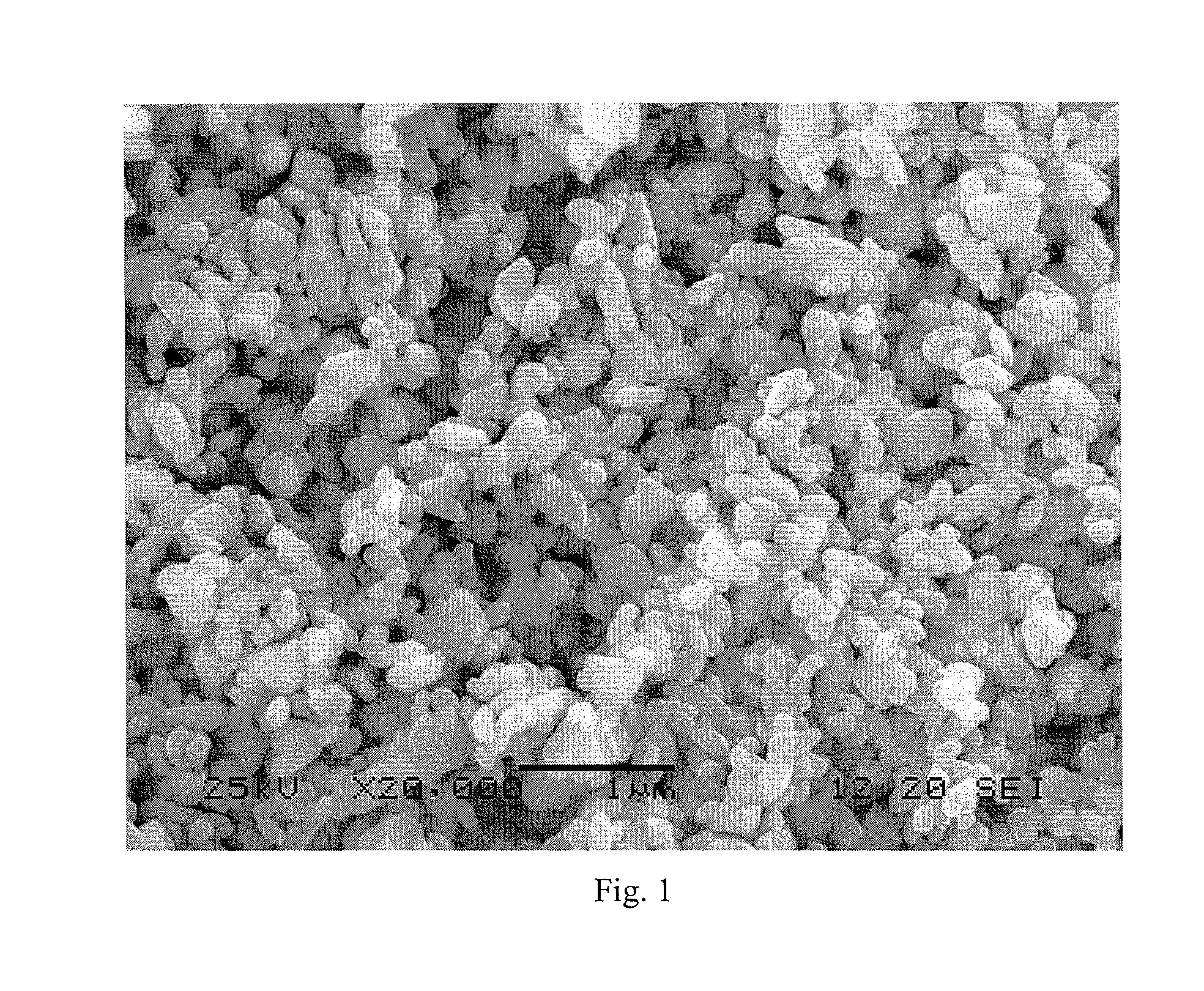
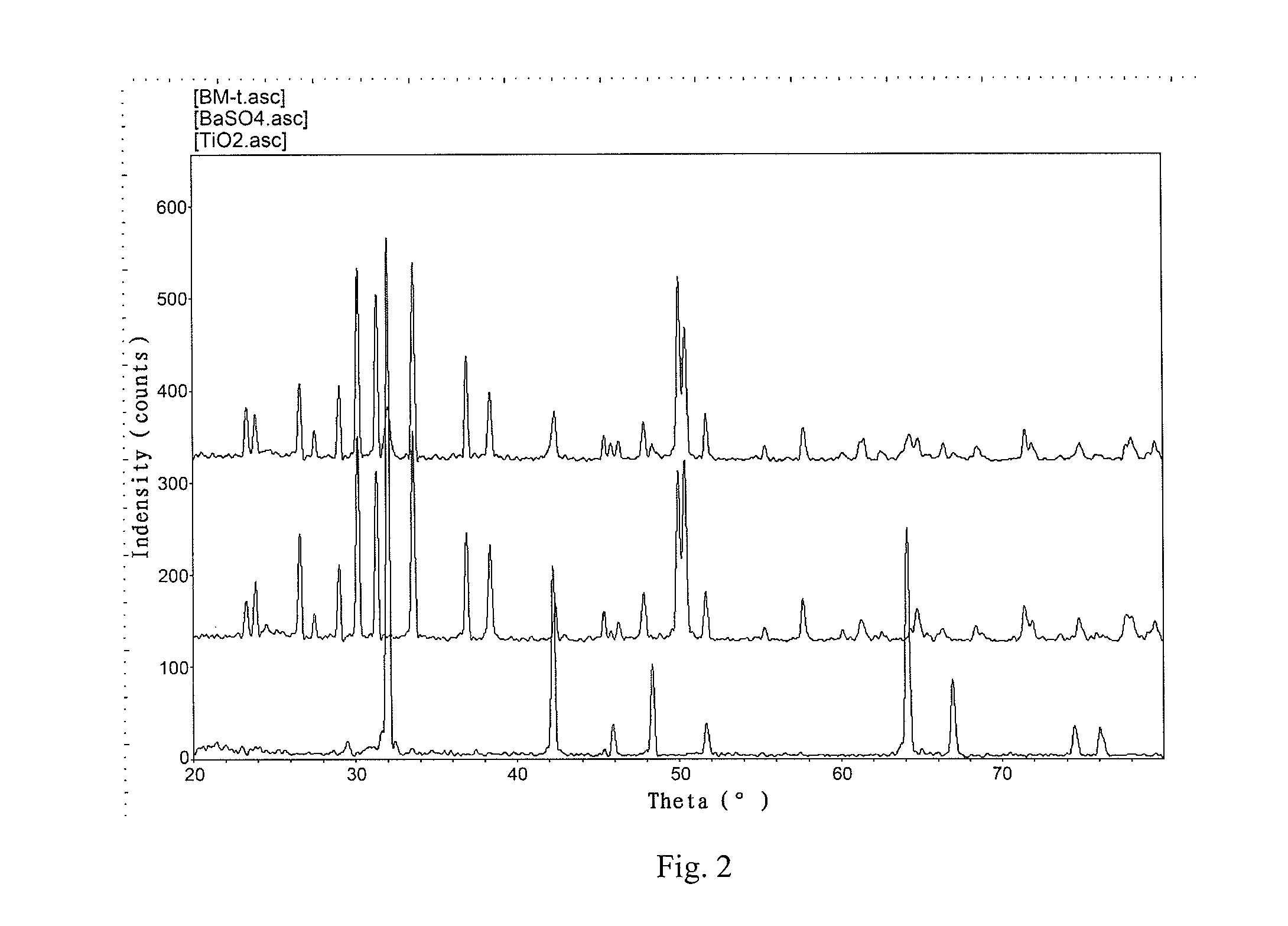
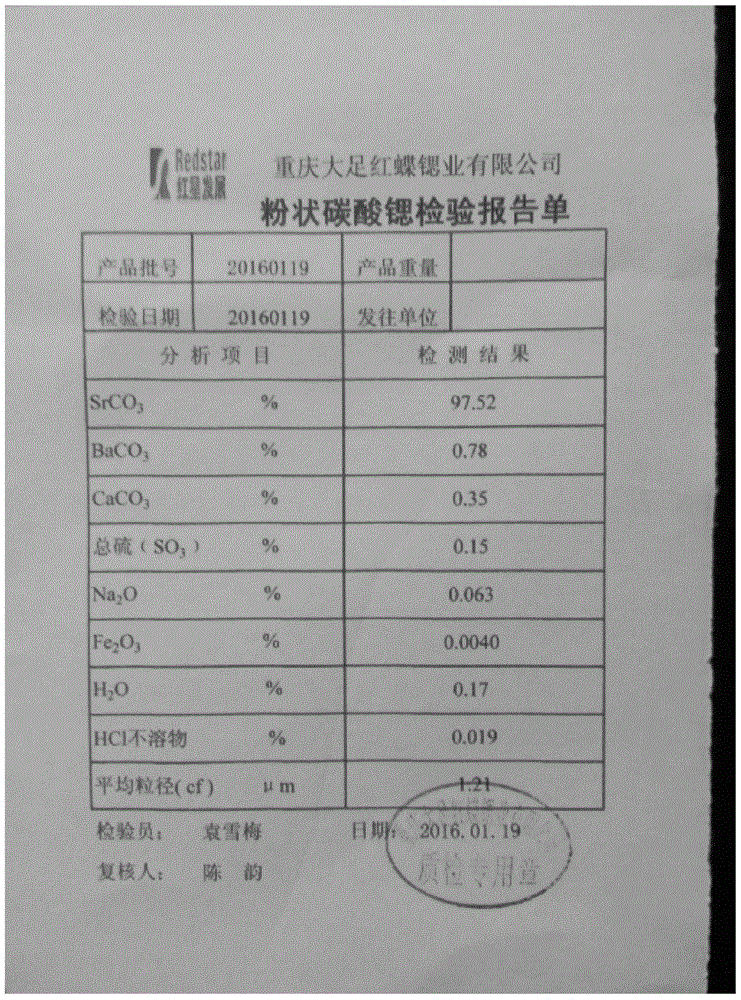
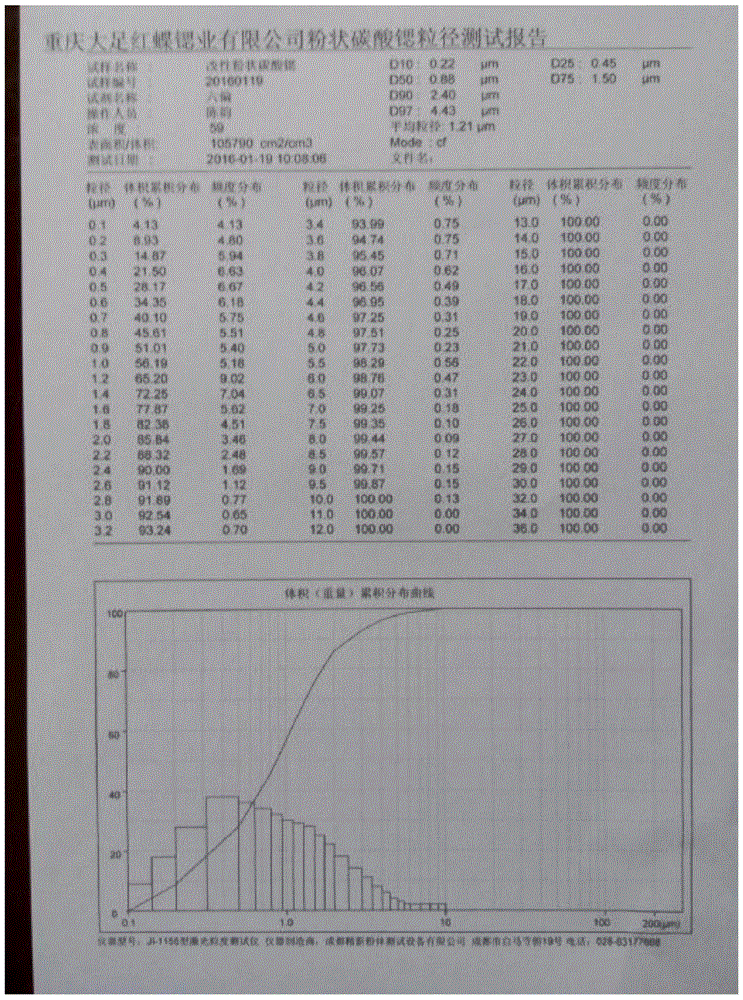
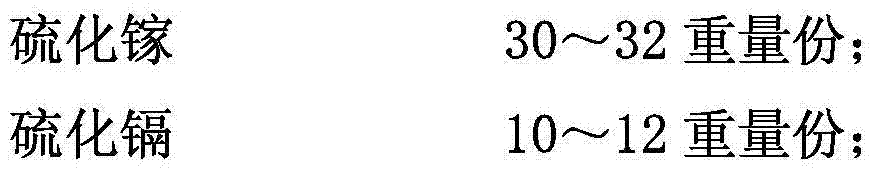Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Strontium sulfide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Strontium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula SrS. It is a white solid. The compound is an intermediate in the conversion of strontium sulfate, the main strontium ore called celestite, to other more useful compounds.
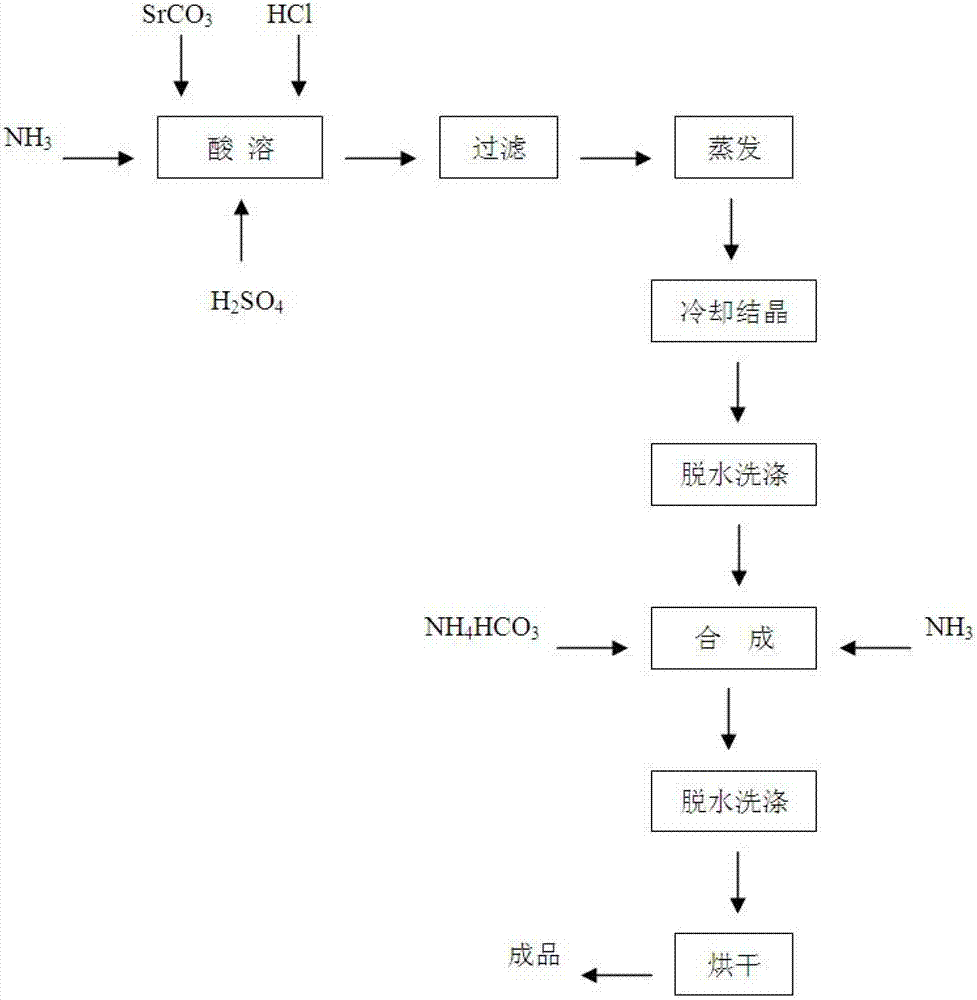
Preparation method of platy strontium carbonate particles
InactiveCN101559964AIncrease profitFully contactedCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesNanostructure manufactureCarbonizationStrontium chloride
The invention provides a preparation method of platy strontium carbonate particles. The steps include using reduced coal dust to roast reduced celestite ore at high temperature and prepare chamotte containing strontium sulfide; leaching the chamotte by hydrothermal to obtain strontium sulfide solution and simultaneously removing calcium, barium and other foreign ions from the strontium-containing solution; then carrying out oxidation treatment on the strontium-containing solution under the action of a catalyst and recovering sulphur side product and obtaining clean strontium solution; and finally preparing the strontium carbonate product with special platy structure by strictly controlling the carbonizing treatment condition of the strontium solution. The platy strontium carbonate product has uniform particles, high purity, and excellent flow property, dispersion property and fusion property with other materials. The preparation method avoids generating sulfureted hydrogen gas in carbonization process, thoroughly gets rid of sulfureted hydrogen pollution in the production process and can simultaneously separate solid sulphur to be beneficial to the strict control over the index of total sulphur in the product.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation of red strontium sulphide long afterglow material
InactiveCN101328405AEasy to controlWell mixedLuminescent compositionsSolubilitySurface-active agents
The invention discloses a method for preparing a red strontium sulphide long afterglow material, comprising a hydrothermal coprecipitation method which comprises the following steps that: (a) water-solubility strontium salt, water-solubility europium salt, water-solubility dysprosium salt, carbamide and water are weight according to the mol ratio of 1: between 0.01 and 0.05: between 0.01 and 0.05: between 4 and 6: between 28 and 32 and are put inside a container to be stirred and dissolved, the mixture is insulated in a sealing state at a temperature of between 80 and 160 DEG C for 5 to 24 hours so that a precursor is obtained; (b) the precursor is subject to filtering and annealing at a temperature of between 900 and 1200 DEG C in the reaction environment for 0. 5 to 2 hours so that the red strontium sulphide long afterglow material is prepared; the water-solubility strontium salt is strontium nitrate or strontium chloride or strontium acetate, the water-solubility europium salt is europium nitrate, europium chloride or polyimide, the water-solubility dysprosium salt is dysprosium nitrate or dysprosium chloride or dysprosium acetate, and a surface active agent is added according to the mol ratio of the water-solubility strontium salt to the surface active agent of 1: between 0.0001 and 0.0003. The method is widely applied to the fields such as building decoration, traffic transportation, military facilities, fire emergency service and goods for everyday consumption.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
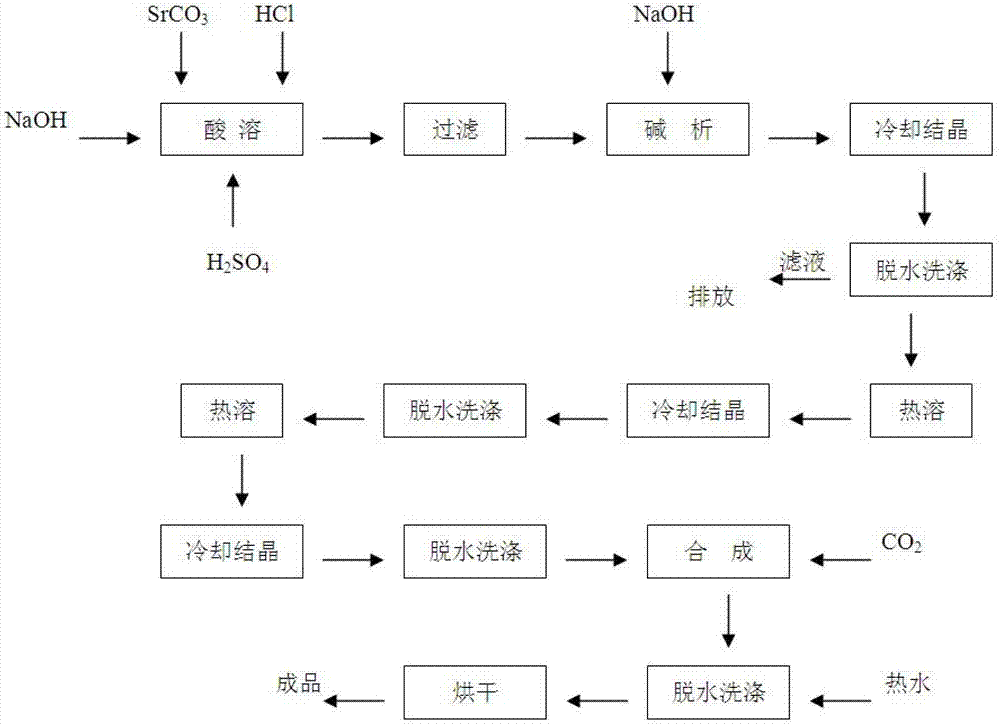
Process for preparing high purity strontium carbonate
InactiveCN1699178AImprove recovery rateImprove one-time yieldCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium sulfideStrontium carbonate
Disclosed is a process for preparing high purity strontium carbonate, which comprises mixing celestite, anthracite coal, calcium chloride as catalyst, high-temperature roasting for deacidizing strontium sulfide, filtering strontium monosulfide through heat leaching, charging sodium-hydroxide and strontium monosulfide to result in alkali analysis reaction, producing strontium hydroxide crystalline body, the purifying strontium hydroxide through recrystallization process, finally reacting pure strontium hydroxide solution with let-in carbon dioxide at the presence of ultrasonic wave action, thus producing high purity strontium carbonate powder, and reacting lime cream with strontium monosulfide to obtain sodium-hydroxide and strontium monosulfide precipitate, wherein sodium-hydroxide can be circulated in the alkali analysis reaction.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Process for producing superfine barium carbonate and strontium carbonate
InactiveCN1504411ALow costIncrease productivityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium carbonateStrontium sulfide
A novel process for preparing ultra-fine barium carbonate and strontium carbonate, wherein barium sulphide solution or barium hydrate solution are used as raw material to be carbonized by carbon dioxide in helical channel type revolving bed, obtaining precipitate, then ultramicro fine barium carbonate is obtained through washing, dewatering and drying, and strontium sulfide solution or strontium hydroxide solution are used as raw material to be carbonized by carbon dioxide in helical channel type revolving bed, obtaining precipitate, then ultramicro fine strontium carbonate is obtained through washing, dewatering and drying.
Owner:HENGYANG JINYUAN NANO TECH
Method of forming a thick film dielectric layer in an electroluminescent laminate
InactiveUS20050202157A1Reduce porosityReduce thicknessElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPorosityOxygen
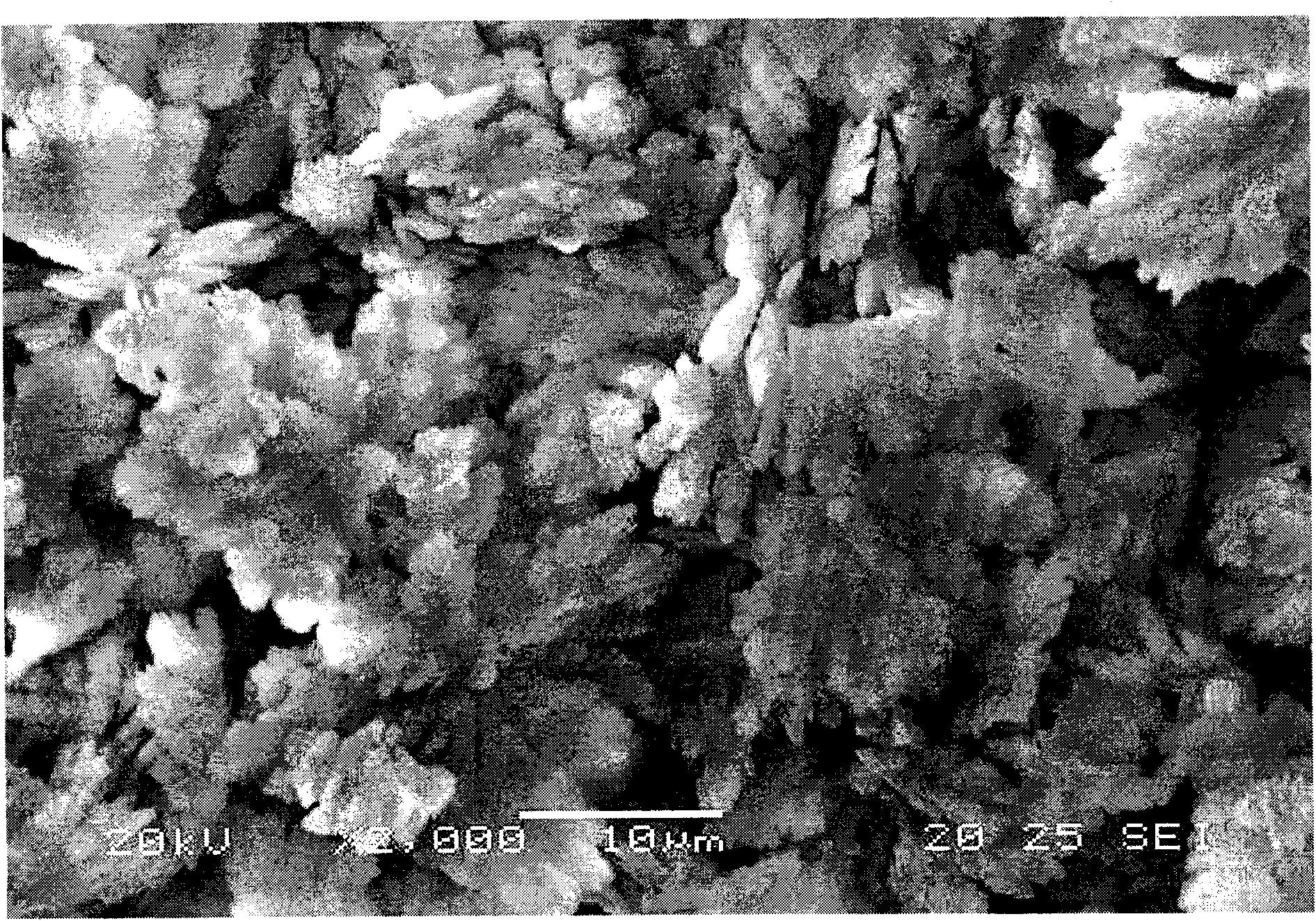
A patterned phosphor structure, and EL laminate containing same, forming red, green and blue sub-pixel phosphor elements for an AC electroluminescent display. The patterned phosphor structure includes at least a first and a second phosphor emitting light in different ranges of the visible spectrum, but with combined emission spectra contains red, green and blue light, the first and second phosphors being in a layer, arranged in adjacent, repeating relationship to each other to provide a plurality of repeating first and second phosphor deposits. The phosphor structure also includes one or more means associated with one or more of the first and second phosphor deposits, and which together with the first and second phosphor deposits, form the red, green and blue sub-pixel phosphor elements, for setting and equalizing the threshold voltages of the red, green and blue sub-pixel phosphor elements, and for setting the relative luminosities of the red, green and blue sub-pixel phosphor elements so that they bear set ratios to one another at each operating modulation voltage used to generate the desired luminosities for red, green and blue. Photolithographic methods for producing the patterned phosphor structure are also provided. Also provided is an improved dielectric layer for use in an EL laminate, including a pressed, sintered ceramic material having, compared to an unpressed, sintered dielectric layer of the same composition, improved dielectric strength, reduced porosity and uniform luminosity in an EL laminate. Also provided are combined substrate and dielectric layer components or EL laminates containing the pressed thick film dielectric layer, and methods of forming the pressed thick film dielectric layer. A process is also provided for synthesizing strontium sulfide phosphors by providing a source of high purity strontium carbonate in a dispersed form, heating the strontium carbonate in a reactor with gradual heating up to a maximum temperature in the range of 800 to 1200° C., contacting the heated strontium carbonate with a flow of sulfur vapours formed by heating elemental sulfur in the reactor to at least 300° C. in an inert atmosphere; and terminating the reaction by stopping the flow of sulfur at a point when sulfur dioxide or carbon dioxide in the reaction gas reaches an amount which correlates with an amount of oxygen in oxygen-containing strontium compounds in the reaction product which is in the range of 1 to 10 atomic percent.
Owner:IFIRE IP CORP
Method for preparing high-quality strontium carbonate
InactiveCN101070177AReduce sulfur contentImprove qualityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium carbonateStrontium sulfide
The invention offers a new kind of method producing strontium carbonate using lazurite mineral as raw material. Mix lazurite breeze with reduced iron powders in certain proportion to get black ash, dip black ash in water of opposite flow and get strontium carbonate solution; regard calcined soda as carburizer, make them reactivate at temperature of 90-100deg.C under mixing to form slurry including deposition of strontium carbonate and sodium sulfide solution of low iron, and get deposition of strontium carbonate and sodium sulfide solution of low iron through separating solid and liquid, absterge strontium carbonate with water of opposite flow for 3-5 times, dry it and get product of strontium carbonate of high quality; Mother liquor absterging strontium carbonate for the first time mixes with centrifugal mother liquor of slurry of strontium carbonate and the mixed solution is vaporized by cold boiler which regards heat transfer oil as medium, get byproduct of sodium sulfide of low iron. The producing craft of the invention is simple, the procedure is short with low cost, the investment of equipment is small, quality of main product and byproduct is high, it has a good economical effect.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of strontium carbonate with high purity
ActiveCN102765740AIncrease profitReduce consumptionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesStrontium ranelateIon
The invention discloses a preparation method of strontium carbonate with high purity. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) cooling and crystallizing a strontium sulfide solution, and separating out crude strontium hydroxide crystals; (2) recrystallizing the crude strontium hydroxide crystals after 2-5 times to obtain pure strontium hydroxide crystals; and (3) reacting the crystals prepared in the step (2) with liquid carbon dioxide to produce strontium carbonate, and dewatering and drying to obtain the strontium carbonate with high purity. According to the invention, brine from a leaching procedure in an original strontium carbonate production process is used as a raw material to realize low preparation cost; no sodium ion or chloride ion is added during the preparation process of the strontium carbonate with high purity; the product has easily controlled quality, and is simple for washing; no acid solution is added, and no waste gas is generated in the entire production process; wastewater generated in production process all returns to an industrial production line of strontium carbonate; therefore, the production process is green and clean.
Owner:NANJING JINYAN STRONTIUM IND
Green luminescent material for infrared excitation
The invention discloses a green luminescent material for infrared excitation, which comprises a matrix material namely strontium sulfide, wherein the matrix material is added with an activator containing cerium, a co-activator containing samarium and a fluxing agent containing lithium chloride, and the mixture is sintered at a high temperature in a protective atmosphere. The prepared luminescent material, after absorbing ultraviolet light, does not have long-lasting phosphorescence, and can release green fluorescent light for a long time under the irradiation of infrared light. The green luminescent material can be used for detecting, tracking, checking and identifying invisible near infrared light, and can be widely used in the technical fields of a plurality of subjects such as near infrared laser detection, laser facula display, optical fiber communication instruction, optical information storage, X-ray image processing, infrared imaging and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI KEYAN PHOSPHOR TECH
Titania composite and preparing method thereof
InactiveUS20110253012A1Good chemical stabilityGood weather resistancePigmenting treatmentLiquid surface applicatorsBarium sulfideRutile
A titania composite and a preparing method thereof are provided. The titania composite comprises an inner core and a coating film layer, wherein the inner core is a barium sulfate crystal and / or a strontitum sulfate crystal with subsphaeroidal shape, having a particle size of less than 1 μm and whiteness of more than 98%, and the coating film layer is nano rutile titania. The preparing method thereof comprises the following steps: (a) preparing barium sulfate or strontium sulfate; (b) coating treatment; (c) subjecting the titania composite to a high-temperature heat treatment; and (d) subjecting the titania composite to a post treatment. The subsphaeroidal titania composite is obtained by chemically synthesizing a subsphaeroidal submicron barium sulfide or strontium sulfide, and then hydrolyzing and coating thereon to form a coating film layer of titania to make titania grow evenly. The particle size of the titania composite is small, and the particle size distribution range of the titania composite is controllable.
Owner:GUIZHOU REDSTAR DEVING
Sr/ graphene composite material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106935412AImprove electrochemical performanceHigh specific capacitanceHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceStrontium sulfide
The invention provides a strontium / graphene composite material, which comprises a strontium compound and graphene, the strontium compound being selected from strontium hydroxide or strontium sulfide. The strontium / graphene composite material prepared through a hydrothermal method serves as an electrode material of a supercapacitor, and such material not only has good electrochemical performance, but also has higher specific capacitance and longer cycle life. The experiment result shows that the specific capacitance of the supercapacitor electrode material made from the strontium / graphene composite material prepared through the hydrothermal method can reach 10-1500F / g, and after constant-current charging and discharging for 3000 times, the specific capacitance thereof can still remain more than 98.5%.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method for preparing strontium chloride
InactiveCN101070179AQuality improvementAvoid corrosionCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesSocial benefitsStrontium sulfide
The invention offers a new method of strontium chloride preparation, the method uses breeze to deoxidize celestite which is dipped into hot water and get solution of strontium sulfide, put sulfureted hydrogen gas into solution of strontium sulfide to make solution of strontium hydrosulphide which reacts with magnesium chloride to get products of strontium chloride and magnesium hydrate, sulfureted hydrogen gas formed in the reaction is used to make strontium hydrosulphide, thus, it circulates like these steps above. The flow of the invention id short, it no need to consume chemical raw material, the raw material used in this invention is simple to get and is cheap, the quality of the product is high; it can get byproduct of magnesium hydrate at the same time and avoid pollution of sulfureted hydrogen, therefore, it has good economical and social benefits, and it is especially suitable for area where the sources of magnesium chloride is abundant.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing bismuth sulfide nanorod crystal material
InactiveCN101613882BLow costSimplify operating proceduresPolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsBismuth sulfideChemical reaction
The invention discloses a method for preparing bismuth sulfide nanorod crystal material, which is suitable for the preparation of sulfide nano crystal materials such as bismuth sulfide. The method is characterized in that it is synthesized by chemical reaction at normal pressure and 100-300°C with molten compound nitrate solvent, the raw materials used are soluble inorganic metal bismuth salt and sodium sulfide or sulfur powder, and the cost is low in the synthesis process , various parameters in the reaction process are easy to monitor and control, less environmental pollution, good uniformity of the reaction system, simple process, easy to scale up production; and the obtained bismuth sulfide has good crystallization, clean surface and uniform size, which is suitable for this process Research on characteristic properties and maximizing the function of nanocrystalline materials.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Process for producing strontium carbonate and barium carbonate without continuous carbonization of hydrogen sulfide gas holder
InactiveCN107140670ASubsequent production process is stableBarium carbonatesStrontium carbonatesStrontium carbonateStrontium sulfide
The application of the present invention discloses a process for continuously carbonizing strontium carbonate and barium carbonate without hydrogen sulfide gas tank, which includes the following process steps: the first step is to pass the strontium sulfide or barium sulfide liquid through the liquid feed pipe first from the first carbonization tower The upper part is sprayed down; the second step is to adjust the flow rate to maintain a stable liquid level in the first carbonization tower; the third step is to adjust the flow rate to maintain a stable liquid level in the second carbonization tower, and so on; The fourth step is to completely react carbon dioxide with strontium sulfide or barium sulfide solution, and the hydrogen sulfide gas produced is discharged from the exhaust pipe at the top of the first carbonization tower into the subsequent production process; the fifth step is to discharge strontium sulfide or barium strontium sulfide slurry , and then adjust the flow rate to maintain a stable liquid level in the last carbonization tower; the sixth step is to start the car and start continuous production according to the above process. By adopting the process of the invention, the hydrogen sulfide gas tank can be eliminated, and at the same time, the production stability of the follow-up process using hydrogen sulfide as a raw material can be guaranteed.
Owner:CHONGQING KINGLONG FINE STRONTIUM CHEM
Process for producing barium sulfate byproduct in process of removing barium from yellow water
InactiveCN102502750ASuppress generationImprove qualityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesPolyacrylamideCoal
The invention relates to a process for producing a barium sulfate byproduct in the process of removing barium from yellow water. The process comprises the following steps of: (1) obtaining the yellow water, namely calcining celestite and reducing coal to obtain black ash, and leaching the black ash by using water to obtain an aqueous solution of strontium sulfide, namely the yellow water; and performing natural sedimentation on the yellow water at the temperature of between 80 and 85 DEG C to remove impurities, namely acid-insoluble substances and calcium ions so as to obtain clear yellow water; (2) performing barium removal reaction, namely adding industrial dilute sulfuric acid into the clear yellow water, and performing barium removal reaction; and continuously stirring for 2 to 5 hours to convert barium ions into barium sulfate; (3) adding a flocculating agent, namely a polyacrylamide solution into the yellow water subjected to barium removal reaction, stirring, and filtering to obtain a filter cake and filtrate yellow water; and (4) carbonizing the filtrate yellow water by the conventional process to produce strontium carbonate; and washing the filter cake for one to two times, drying, and grinding to obtain the barium sulfate byproduct. The process is simple and low in cost, the clarity of the yellow water can be effectively improved, the content of the barium ions in the yellow water is reduced, and the environment-friendly barium sulfate byproduct is obtained.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
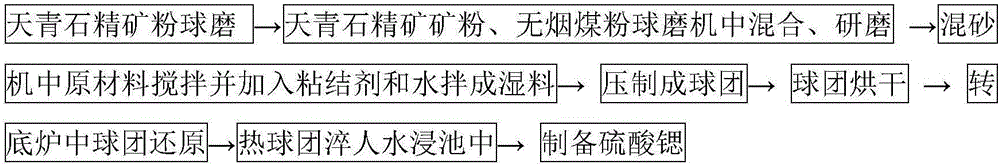
Process for reducing celestine in rotary hearth furnace to produce strontium sulfide
InactiveCN106586975AReduce manufacturing costIncrease production capacityEnergy inputMagnesium/calcium/strontium/barium sulfides/polysulfidesStrontium carbonateStrontium sulfide
The invention relates to a production process for reducing celestine concentrate pellets with carbon in a rotary hearth furnace to produce strontium sulfide. The process comprises the following steps: subjecting celestine concentrate powder and anthracite duff or petroleum coke powder, used as main raw materials, to batching according to a certain ratio, weighing and mixing, adding a binder and water and carrying out blending so as to obtain a wet material; pressing the wet material with a ball press machine to obtain cold-bonded pellets with certain sizes; drying the pellets in a chain grate, then conveying the dried pellets to the rotary hearth furnace with a highest reduction temperature of 1200 to 1300 DEG C to convert strontium sulfate in celestine into strontium sulfide; and discharging the reduced hot pellets out from the rotary hearth furnace and directly quenching the hot pellets in a water leaching pool, wherein the waste heat of the pellets can be used for increasing water temperature so as to facilitate acceleration of a series of chemical reactions for subsequent preparation of strontium carbonate. The process for production of strontium sulfide via the rotary hearth furnace has the advantages of simple operation, high efficiency, great output, low cost, no pollution, etc. Detection results show that the conversion rate of strontium sulfate in celestine reaches 95% or above through reduction of celestine with carbon in the rotary hearth furnace.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Iron-based powder metallurgy self-lubricating CNG engine valve retainer with good heat-conducting property and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106435383AHigh strengthIncrease frictionTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusAdditive ingredientNiobium
The invention discloses an iron-based powder metallurgy self-lubricating CNG engine valve retainer with a good heat-conducting property. The iron-based powder metallurgy self-lubricating CNG engine valve retainer is prepared from, by weight, 6.4-6.8 parts of chrome, 4.4-4.8 parts of cobalt, 1.1-1.5 parts of nickel, 3.4-3.8 parts of scandium, 2.1-2.4 parts of niobium, 4.3-4.7 parts of aluminum, 13-15 parts of copper, 1.2-1.5 parts of nanometer molybdenum disulfide, 0.2-0.3 part of sodium borate, 0.7-0.9 part of strontium sulfide, 1-3 parts of stainless steel powder, 0.1-0.3 part of potassium permanganate, 2-3 parts of bisphenol-A epoxy resin, 0.6-0.8 part of realgar powder and 60-64 parts of iron. The surface of the modified nanometer molybdenum disulfide is covered with a layer of copper film used as a solid lubricating agent, meanwhile, strontium sulfide, scandium, niobium, aluminum and other ingredients are added, the product prepared through sintering, infiltration and heat treatment technologies is high in strength, good in heat-conducting property and excellent in wear resistance, and the working condition requirements of a natural gas fuel engine can be met.
Owner:安徽马仪科技股份有限公司
Light sensitive energy-saving street lamp
ActiveCN104515102ALow costGood weather resistanceMechanical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsIridiumHafnium
The invention discloses a light sensitive energy-saving street lamp. A sensor is arranged at the top of the street lamp and can control on and off the street lamp according to the intensity of visible light, a light sensitive resistor is arranged in the sensor and comprises an upper electrode layer, a lower electrode layer and a middle light sensitive material layer, and the light sensitive material layer comprises gallium sulfide, cadmium sulfide, zinc sulfide, copper sulfide, beryllium sulfide, strontium sulfide, germanium oxide, niobium oxide, hafnium, iridium and Y4-x-yLuxFeyO6. A light sensitive material is low in manufacturing cost, resistant to ageing, wide in application field and beneficial to large-scale popularization and application, has excellent weather resistance and corrosion resistance and has strong compatibility with the sensor, the light sensitive energy-saving street lamp can automatically sense the visible light, can be automatically turned on and turned off according to the intensity of the visible light and conforms to the advocated trend of energy conservation and environmental protection, and resources are reasonably distributed and used.
Owner:JIANGSU TIWIN OPTO ELECTRONICS TECH
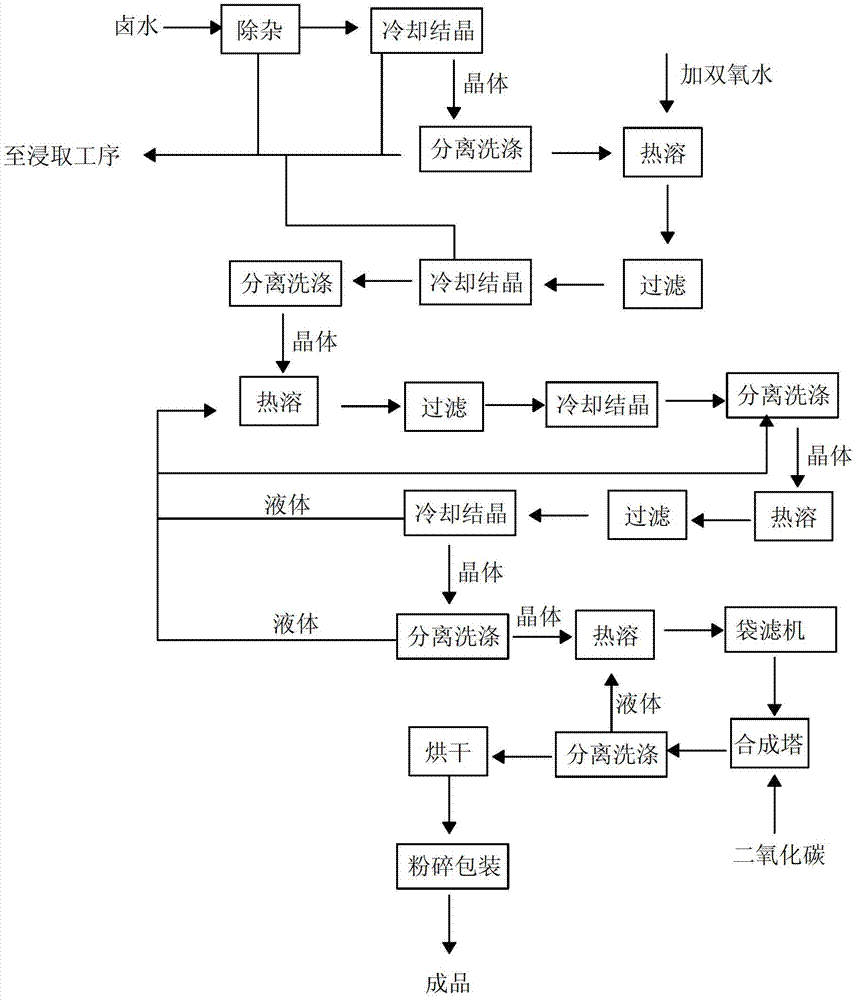
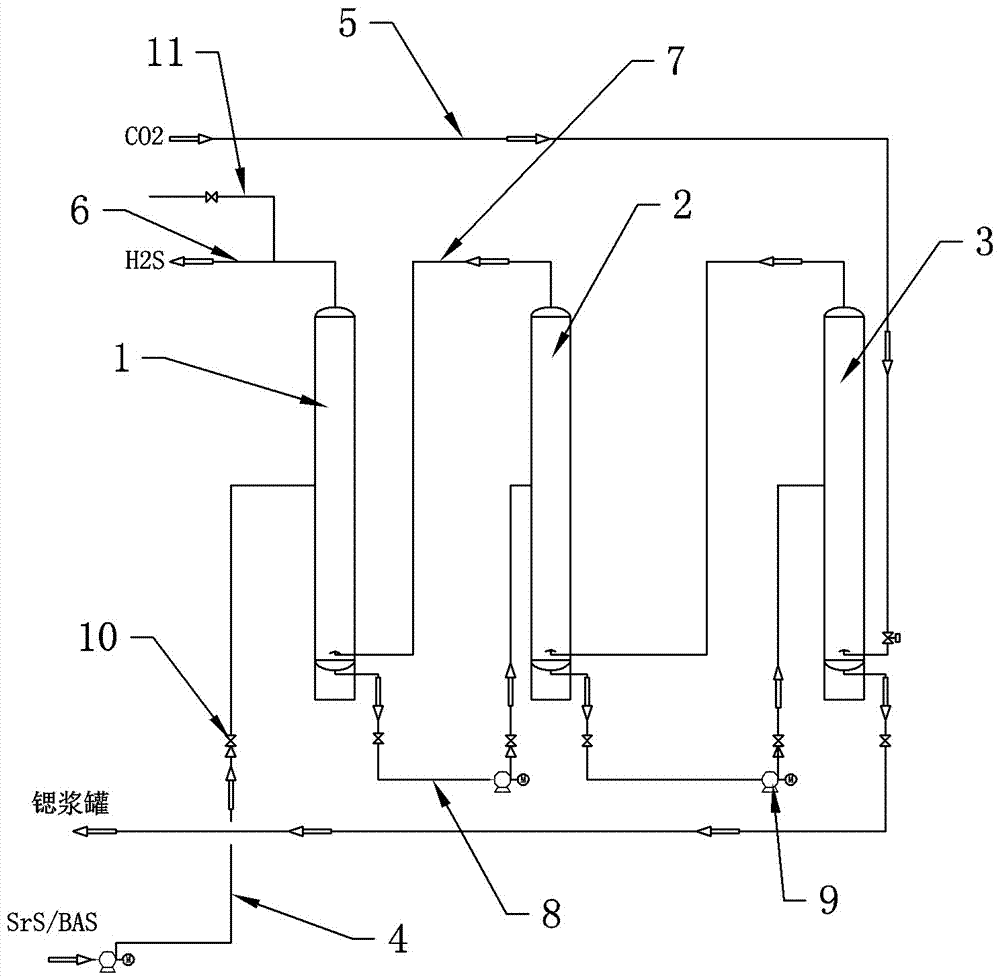
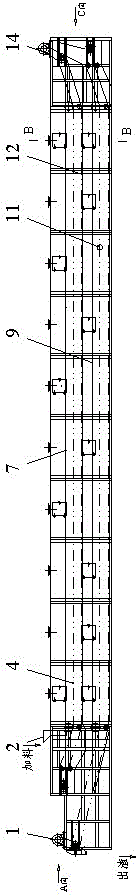
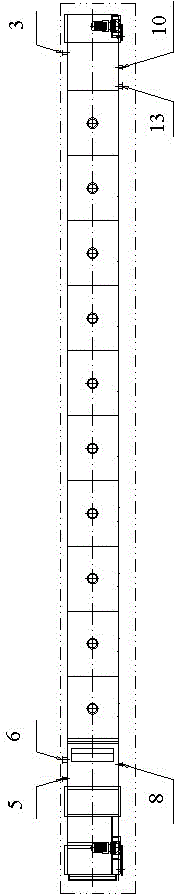
Extraction method and device for strontium sulfide
ActiveCN102718195AIncrease profitQuality improvementMagnesium/calcium/strontium/barium sulfides/polysulfidesStrontium sulfideSlag
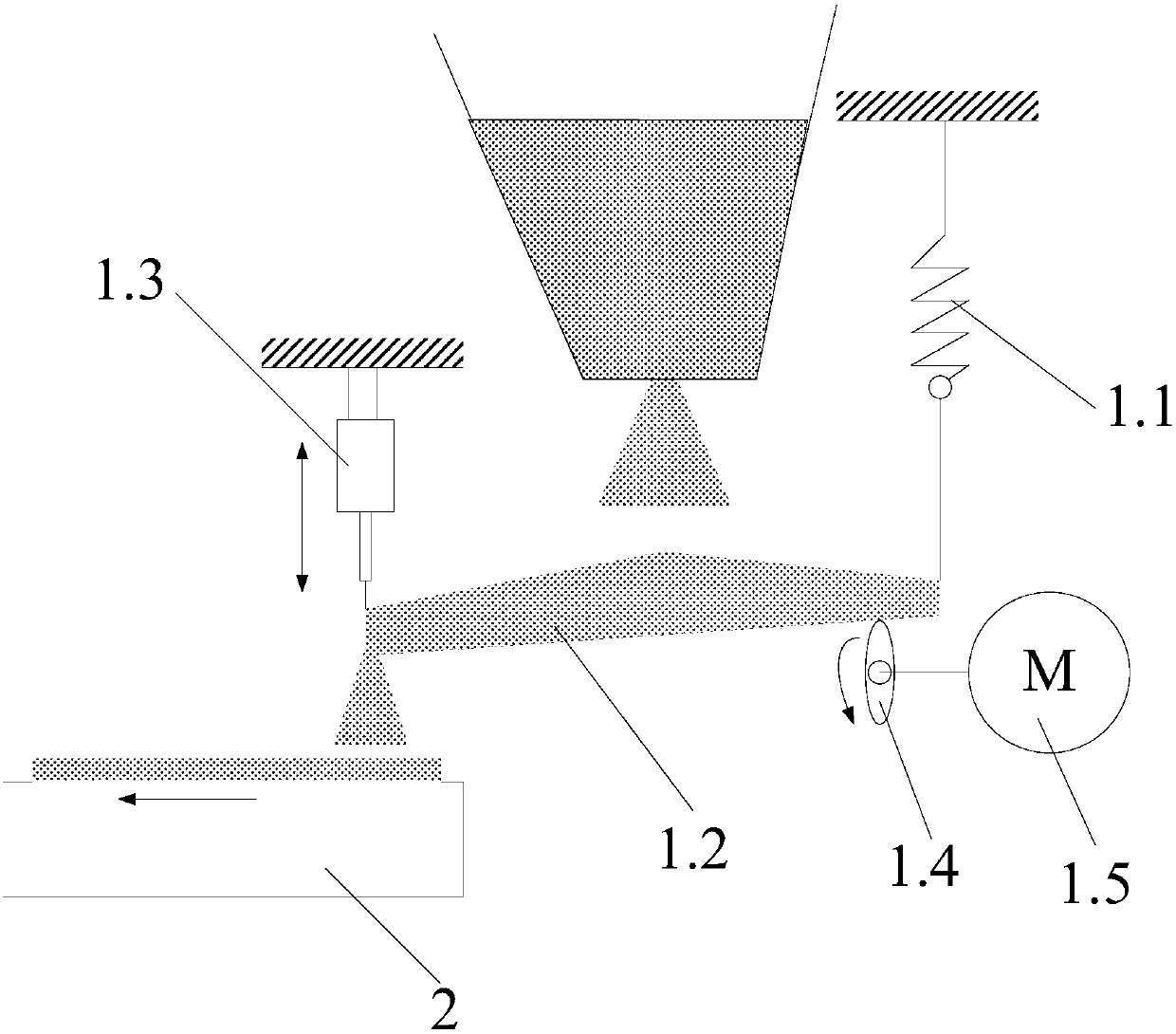
The invention discloses a continuous type extractor for strontium sulfide, which comprises a closed type hydrolyzing tank, a movable mesh belt and a transmission device, wherein the movable mesh belt is supported by bipatch big roller chain riveted seamless steel tubes, and is dragged by the transmission device to move in the hydrolyzing tank. The closed type hydrolyzing tank is also provided with a material inlet, a water inlet, a water outlet and a slag outlet. The material inlet is formed in the upper part of one end of the hydrolyzing tank, and rightly faces the movable mesh belt. A distributor is arranged at the material inlet. The water inlet is arranged at the other end of the hydrolyzing tank. The invention further discloses an extraction method of strontium sulfide. According to the invention, a dynamic continuous extraction way is adopted, so that the mechanization degree is greatly increased, and the labor intensity of the worker is relieved; and continuous production is adopted, so that the quality of extracted liquid can be increased, and the undulating range of concentration of the extracted liquid is reduced, so as to be helpful for decreasing the control difficultyof extracting production.
Owner:NANJING JINYAN STRONTIUM IND
Strontium carbonate production method
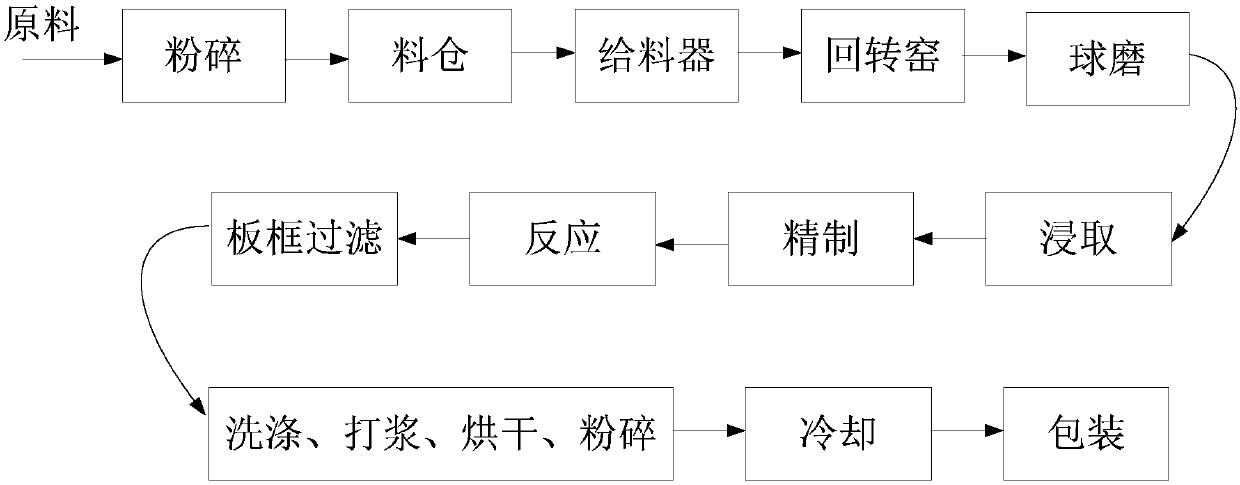
InactiveCN109574054AReduce manufacturing costLow impurity contentStrontium carbonatesEngineeringCrusher
The invention discloses a strontium carbonate production method. The strontium carbonate production method comprises the following steps: S100: after smashing celestite and raw coal via a smashing machine, feeding the smashed celestite and raw coal into a bin; S200: feeding raw materials in the bin into a rotary kiln through an oscillating feeder (1) and a conveying device (2); S300, ball-millingrough strontium sulfide into powder through a ball-miller; S400: leaching to obtain leaching liquid containing strontium ions; S500: refining; S600: carrying out chemical combination to generate a strontium carbonate precipitate and sodium sulfide mixture; S700: washing, pulping, drying and smashing sodium carbonate obtained by filtering and separating to obtain strontium carbonate particles; andS800, cooling and packing to obtain a final strontium carbonate product. The quality of the strontium carbonate product is improved, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:URUMQI VOCATIONAL UNIV
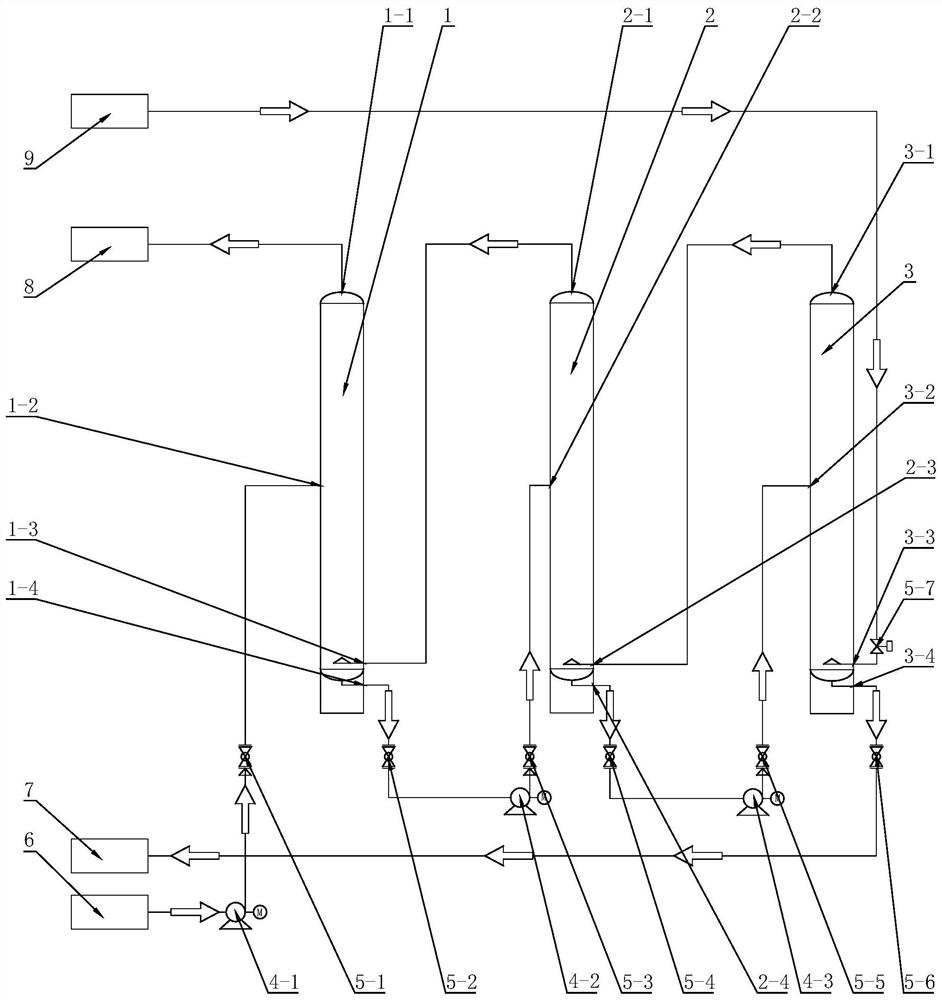
Continuous carbonization reaction system and production process for producing high-purity large-particle-size strontium carbonate
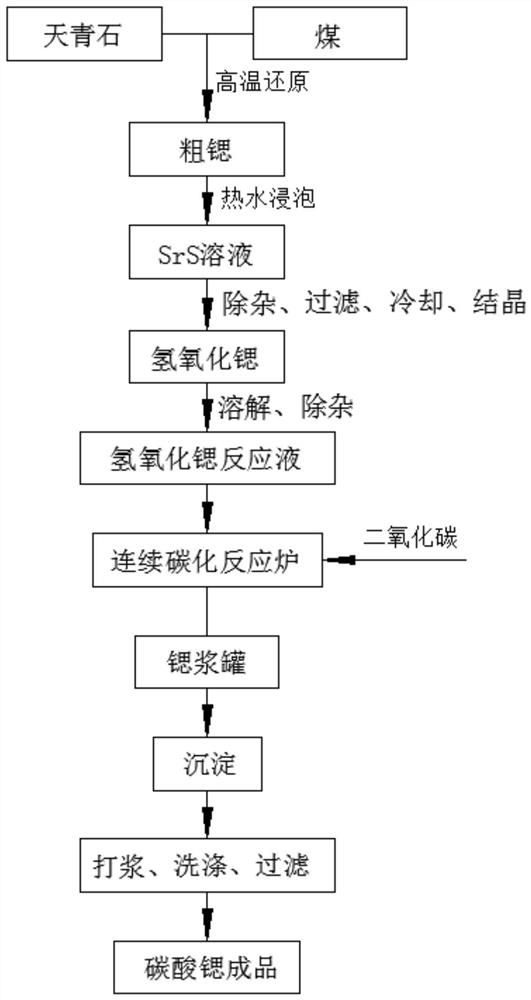
PendingCN112678859ALarge particle sizeHighly stable particle sizeCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCelestineStrontium carbonate
The invention discloses a continuous carbonization reaction system and production process for producing high-purity large-particle-size strontium carbonate. The production process comprises the following steps of: carrying out high-temperature reduction on celestite to obtain strontium sulfide; soaking the strontium sulfide in hot water; performing filtering, impurity removing, cooling and crystallizing to obtain strontium hydroxide crystals; dissolving the strontium hydroxide crystals to remove impurities, thereby obtaining a strontium hydroxide reaction solution; introducing the strontium hydroxide reaction solution into a continuous carbonization reaction tower which is provided with three reaction towers communicated with one another; introducing the strontium hydroxide reaction solution and carbon dioxide gas into the reaction towers; and keeping the liquid level of each reaction tower stable, thereby obtaining the high-purity large-particle-size strontium carbonate, The production process of the invention is simple; a continuous production mode is adopted; the strontium sulfide is directly used for producing the large-particle-size strontium carbonate, and barium hydroxide can also be used for producing barium carbonate; and high stability of the liquid level in the reaction process is guaranteed by controlling the concentration and impurity content of the reaction solution, and the produced high-purity strontium carbonate or barium carbonate product is large in particle size and stable in quality; large-scale production is facilitated.
Owner:CHONGQING KINGLONG FINE STRONTIUM CHEM
Titania composite and preparing method thereof
InactiveUS8221834B2Small particle sizeGood physical and chemical stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsFrom normal temperature solutionsChemical synthesisRutile
A titania composite and a preparing method thereof are provided. The titania composite comprises an inner core and a coating film layer, wherein the inner core is a barium sulfate crystal and / or a strontitum sulfate crystal with subsphaeroidal shape, having a particle size of less than 1 μm and whiteness of more than 98%, and the coating film layer is nano rutile titania. The preparing method thereof comprises the following steps: (a) preparing barium sulfate or strontium sulfate; (b) coating treatment; (c) subjecting the titania composite to a high-temperature heat treatment; and (d) subjecting the titania composite to a post treatment. The subsphaeroidal titania composite is obtained by chemically synthesizing a subsphaeroidal submicron barium sulfide or strontium sulfide, and then hydrolyzing and coating thereon to form a coating film layer of titania to make titania grow evenly. The particle size of the titania composite is small, and the particle size distribution range of the titania composite is controllable.
Owner:GUIZHOU REDSTAR DEVING
Attapulite powdery animal depilating agent
InactiveCN101376913AEasy to useImprove adhesionPre-tanning chemical treatmentStrontium sulfideAnimal science
The invention discloses attapulgite powdery animal depilating agent. The main points of the technical proposal are as follows: the attapulgite powdery animal depilating agent is composed of purified attapulgite clay, sodium sulfide, calcium thioglycollate, strontium sulfide, sodium hydroxide and sodium dodecyl sulfate. The production method of the attapulgite powdery animal depilating agent comprises the following steps: feeding, mixing, milling and packaging into finished attapulgite powdery animal depilating agent. In the attapulgite powdery animal depilating agent, the purified attapulgite clay serves as the main raw material, and no additional thickening agent and humectant need to be added in; the purified attapulgite clay has good adhesive force and can lead the attapulgite powdery animal depilating agent to be firmly adhered to the surface of the fur, thereby increasing the contact area with the hair and improving the use effect of the depilating agent. The attapulgite powdery animal depilating agent has strong penetrability, can expand and enlarge the hair, solidify, weaken and break the hair follicle protein, and is applicable in the depilation of animals.
Owner:XUYI BOTU ATTAPULGITE CLAY HIGH TECH DEV
Attapulite powdery animal depilating agent
InactiveCN101376913BEasy to useImprove adhesionPre-tanning chemical treatmentStrontium sulfideHair follicle
Owner:XUYI BOTU ATTAPULGITE CLAY HIGH TECH DEV
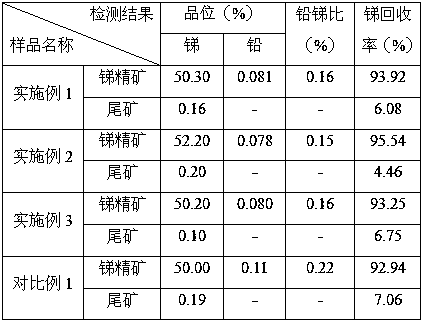
A method for treating antimony-containing sulfide ore
ActiveCN106893860BEfficient deliveryEnhanced mass transferProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSlurry
The invention discloses a method for treating antimony-bearing sulphide ore. The method comprises the steps that antimony-bearing sulphide ore slurry in the diluted hydrochloric acid system is placed in a slurry tank, a mechanical stirring paddle is arranged in the slurry tank, and the slurry is in a uniformly mixed state; and the slurry enters a swirling electrolysis system at a certain speed through a pneumatic pump, after being electrolyzed, the slurry is discharged from an electrolysis device and continuously enters the slurry tank, and antimony in ore is efficiently extracted after a certain time through the circulation, wherein the technological conditions are that the concentration of diluted hydrochloric acid in the slurry is 110 g / L to 180 g / L, the temperature is 55 DEG C to 85 DEG C, the liquid-solid ratio is (6-12) to 1, and the density of a cathode current is 100 A / m<2> to 200 A / m<2>. According to the method, process is short, reaction speed is high, mass transfer during the reaction process is uniform, and compared with a traditional method, the recovery rate of antimony is greatly increased, antimony in ore is comprehensively and efficiently extracted, and the utilization rate of antimony resources is increased.
Owner:广西自贸区西江资源循环科技产业股份有限公司
Industrial production method for strontium carbonate
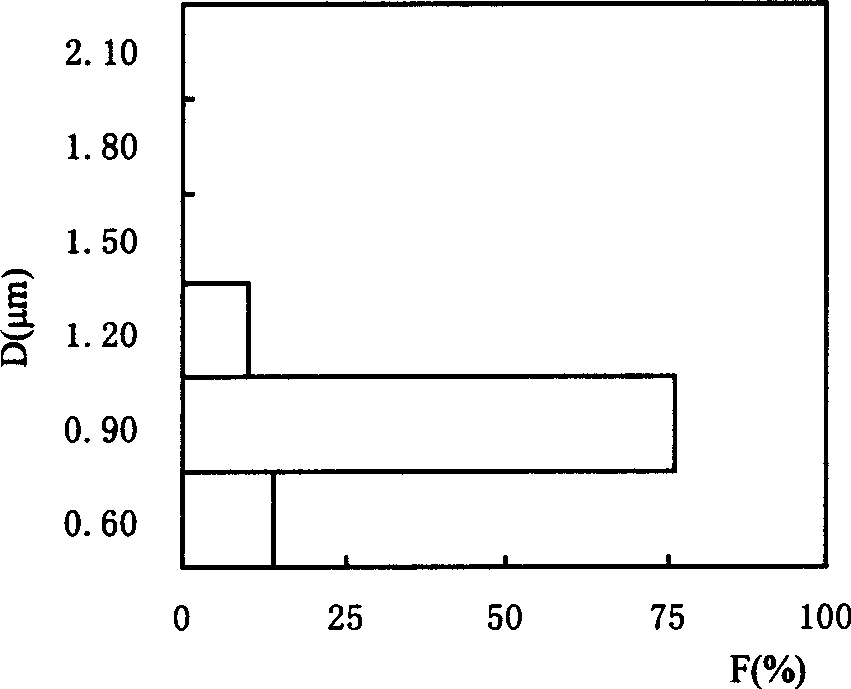
The invention discloses an industrial production method for strontium carbonate. The industrial production method comprises the following steps: soaking a material obtained by carrying out carbon reduction on celestite, with high-temperature hot water to prepare a strontium sulfide solution; introducing a sufficient amount of pure carbon dioxide gas to a carbonization tower, and pumping the strontium sulfide solution to the carbonization tower at a reaction pressure of 0.3Mpa; controlling to continuously react for 30 to 40 minutes and then discharging liquid; dehydrating the liquid, and drying till the moisture content of the product is less than 0.1 percent. According to the industrial production method for strontium carbonate, the strontium carbonate which has the advantage particle size being less than 1.5 mu m, and the total sulfur amount being less than 0.16 percent can be produced; the industrial production method is simple in process method, low in cost and high in efficient, wherein the pure carbon dioxide is adopted to overcome the defects of instable flow and instable quality of gas produced from a lime kiln; existing carbonization equipment in the company is adopted, and flexible production adjustment can be performed by adopting a single-tower or three-tower series manner in a targeted manner according to different demands of different users to physical indexes and chemical indexes of the product.
Owner:CHONGQING DAZU HONGDIE STRONTIUM IND CO LTD
Mixture for the production of an amber glass, amber glass, method for the production of tubes and blanks of tinted bulbs, and tinted bulbs obtained with said glass
ActiveCN1914127AEasy to understandBlow machinesIncadescent envelopes/vesselsThermal treatmentCadmium Cation
The invention relates to a mixture for the production of a vat-dyed amber glass; an amber glass formed from the vitrifiable mixture, based on a silico-sodo-calcic composition; and a method for the production of tubes and blanks (2) for bulbs (1) using said glass. The mixture contains 100% by weight of the following ingredients: 0.01%-1% by weight molybdenum bisulphur and 0.01%-7% strontium sulphur by weight. The glass thus obtained is devoid of harmful products such as cadmium and no additional heat treatment is required in order to obtain the desired colour thereof.
Owner:JWF公司
Process for producing superfine barium carbonate and strontium carbonate
InactiveCN100431967CLow costIncrease productivityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium sulfideStrontium carbonate
A novel process for preparing ultra-fine barium carbonate and strontium carbonate, wherein barium sulphide solution or barium hydrate solution are used as raw material to be carbonized by carbon dioxide in helical channel type revolving bed, obtaining precipitate, then ultramicro fine barium carbonate is obtained through washing, dewatering and drying, and strontium sulfide solution or strontium hydroxide solution are used as raw material to be carbonized by carbon dioxide in helical channel type revolving bed, obtaining precipitate, then ultramicro fine strontium carbonate is obtained through washing, dewatering and drying.
Owner:HENGYANG JINYUAN NANO TECH
A kind of beneficiation method of antimony sulfide ore
ActiveCN106733210BStrong flotation collection capacityImprove recycling effectFlotationLead nitrateSulfide minerals
The invention relates to a mineral processing method of antimony sulfide ore. The mineral processing method comprises the following steps: crushing raw antimony sulfide ore, carrying out ore grinding, adding water, stirring, carrying out size mixing, recycling antimony sulfide minerals by adopting a flotation method, and carrying out roughing once, scavenging for three times and concentration for three times to obtain antimony concentrate, wherein lead nitrate is taken as an activating agent, xanthogenate mixture and B sulfur nitrogen are taken as a combined collecting agent and new coniferyl oil is taken as a foaming agent during the roughing, and the lead nitrate is taken as the activating agent and the xanthogenate mixture is taken as a collecting agent during primary scavenging and secondary scavenging. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that floatation collecting capability on the antimony sulfide minerals is strong, recycling effect is good, antimony recovery rate is more than or equal to 93.2% and is increased by 0.98% compared with the prior art, lead-antimony ratio in the antimony concentrate is reduced by more than or equal to 26.8%, and antimony concentrate grade is more than or equal to 50.0%; reaction conditions of the method provided by the invention are neutral, corrosive effect on mineral processing equipment is alleviated, operation safety is improved, and production cost is reduced; and the method provided by the invention is easy to operate, efficient and environmentally friendly.
Owner:锡矿山闪星锑业有限责任公司
Bismuth sulfide electrode material with specific morphological structure and its application
ActiveCN106299357BLarge specific surface areaLower impedanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsStrontium sulfideBismuth sulfide
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing high-quality strontium carbonate
InactiveCN100560500CReduce sulfur contentImprove qualityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium carbonateStrontium sulfide
The invention offers a new kind of method producing strontium carbonate using lazurite mineral as raw material. Mix lazurite breeze with reduced iron powders in certain proportion to get black ash, dip black ash in water of opposite flow and get strontium carbonate solution; regard calcined soda as carburizer, make them reactivate at temperature of 90-100deg.C under mixing to form slurry including deposition of strontium carbonate and sodium sulfide solution of low iron, and get deposition of strontium carbonate and sodium sulfide solution of low iron through separating solid and liquid, absterge strontium carbonate with water of opposite flow for 3-5 times, dry it and get product of strontium carbonate of high quality; Mother liquor absterging strontium carbonate for the first time mixes with centrifugal mother liquor of slurry of strontium carbonate and the mixed solution is vaporized by cold boiler which regards heat transfer oil as medium, get byproduct of sodium sulfide of low iron. The producing craft of the invention is simple, the procedure is short with low cost, the investment of equipment is small, quality of main product and byproduct is high, it has a good economical effect.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com