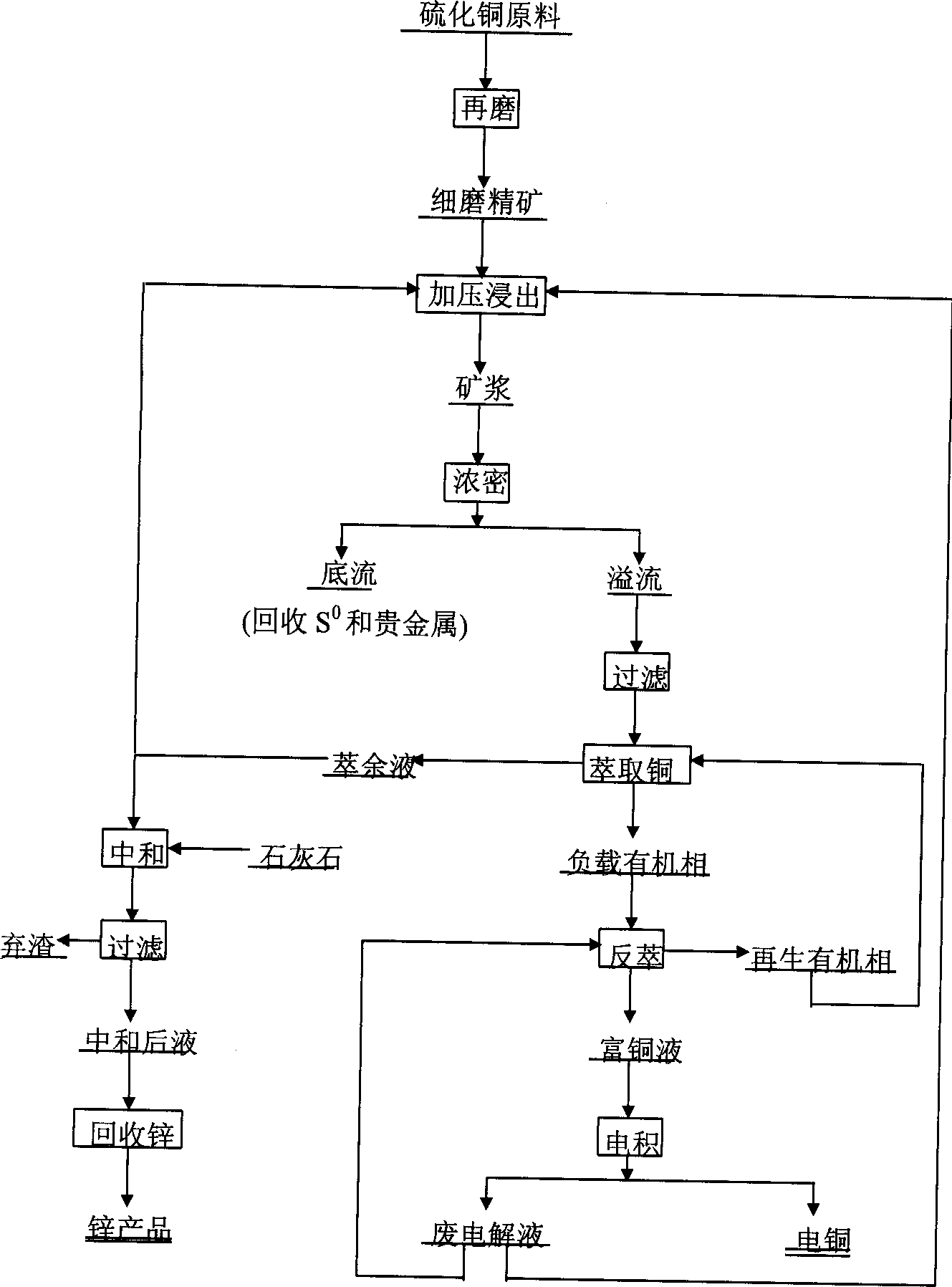
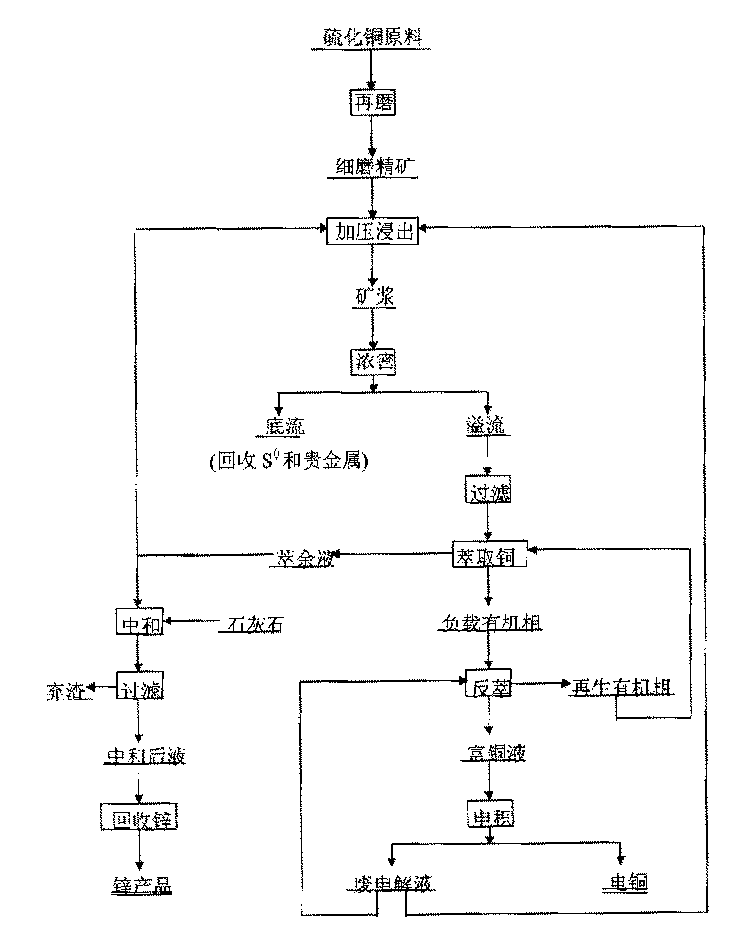
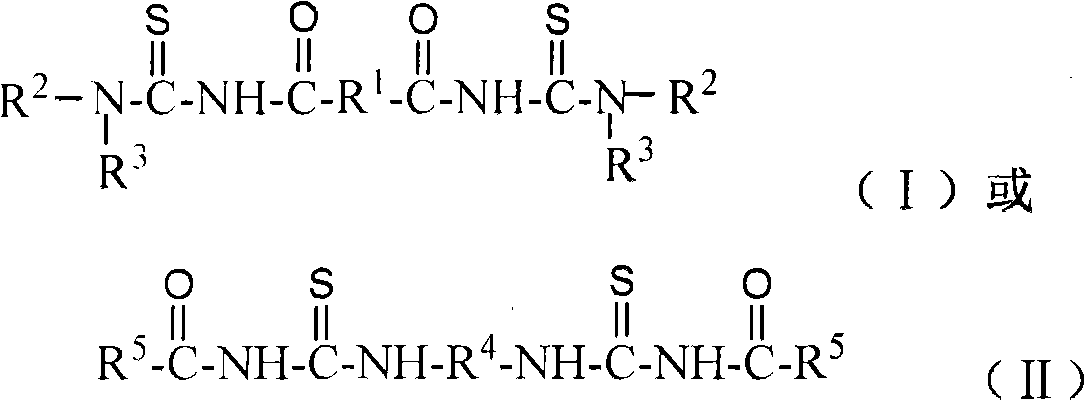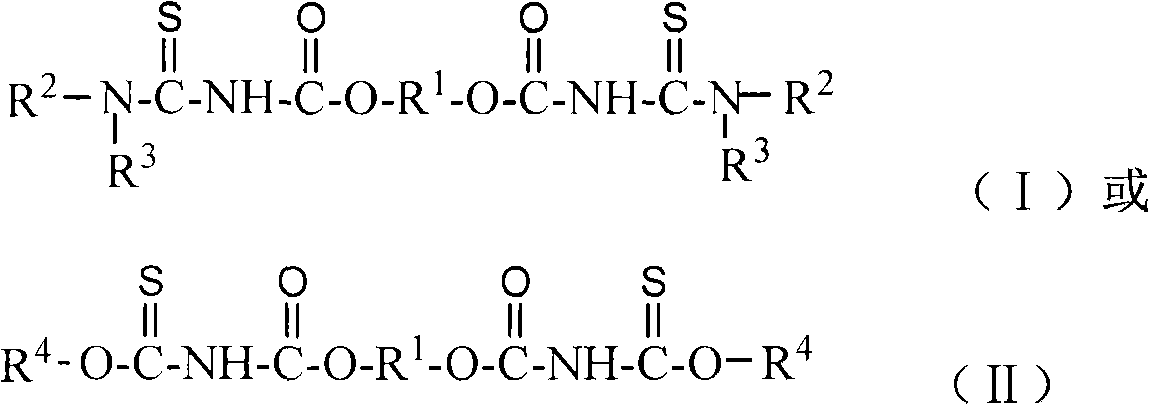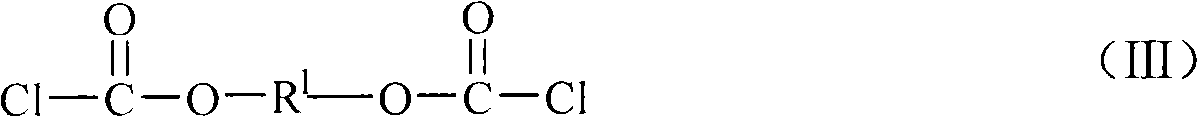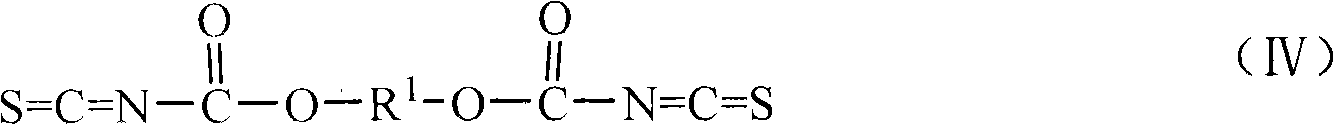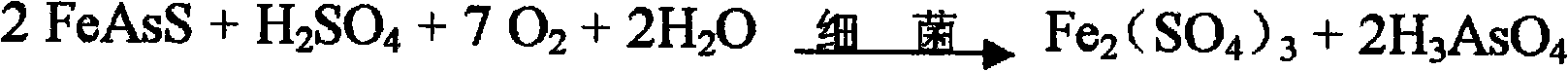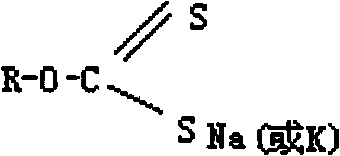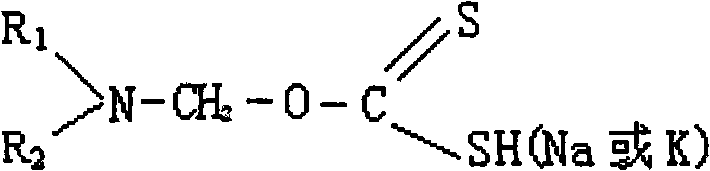Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
295 results about "Sulfide minerals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
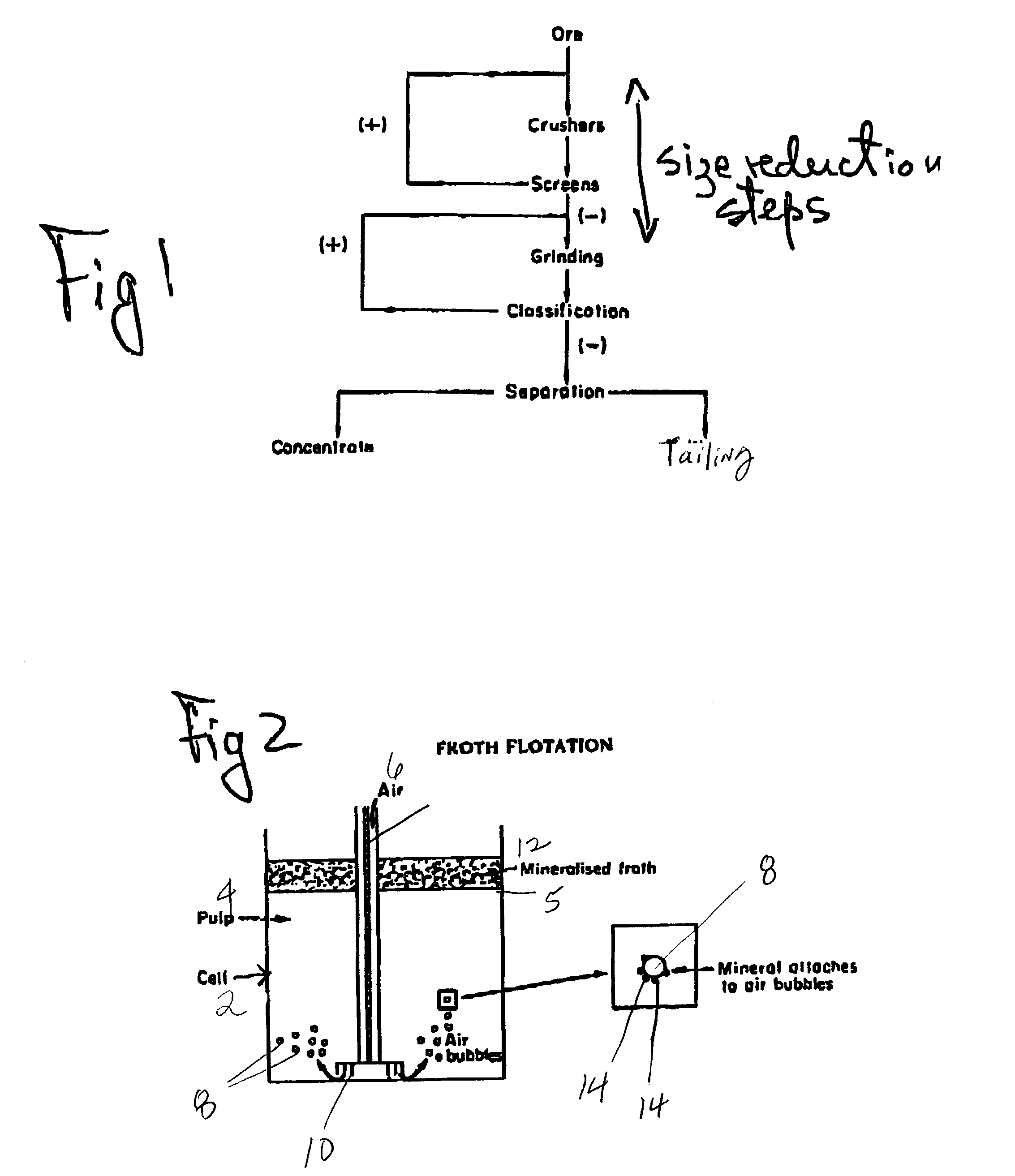
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S²⁻) or persulfide (S₂²⁻) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the arsenides, the antimonides, the bismuthinides, the sulfarsenides and the sulfosalts. Sulfide minerals are inorganic compounds.
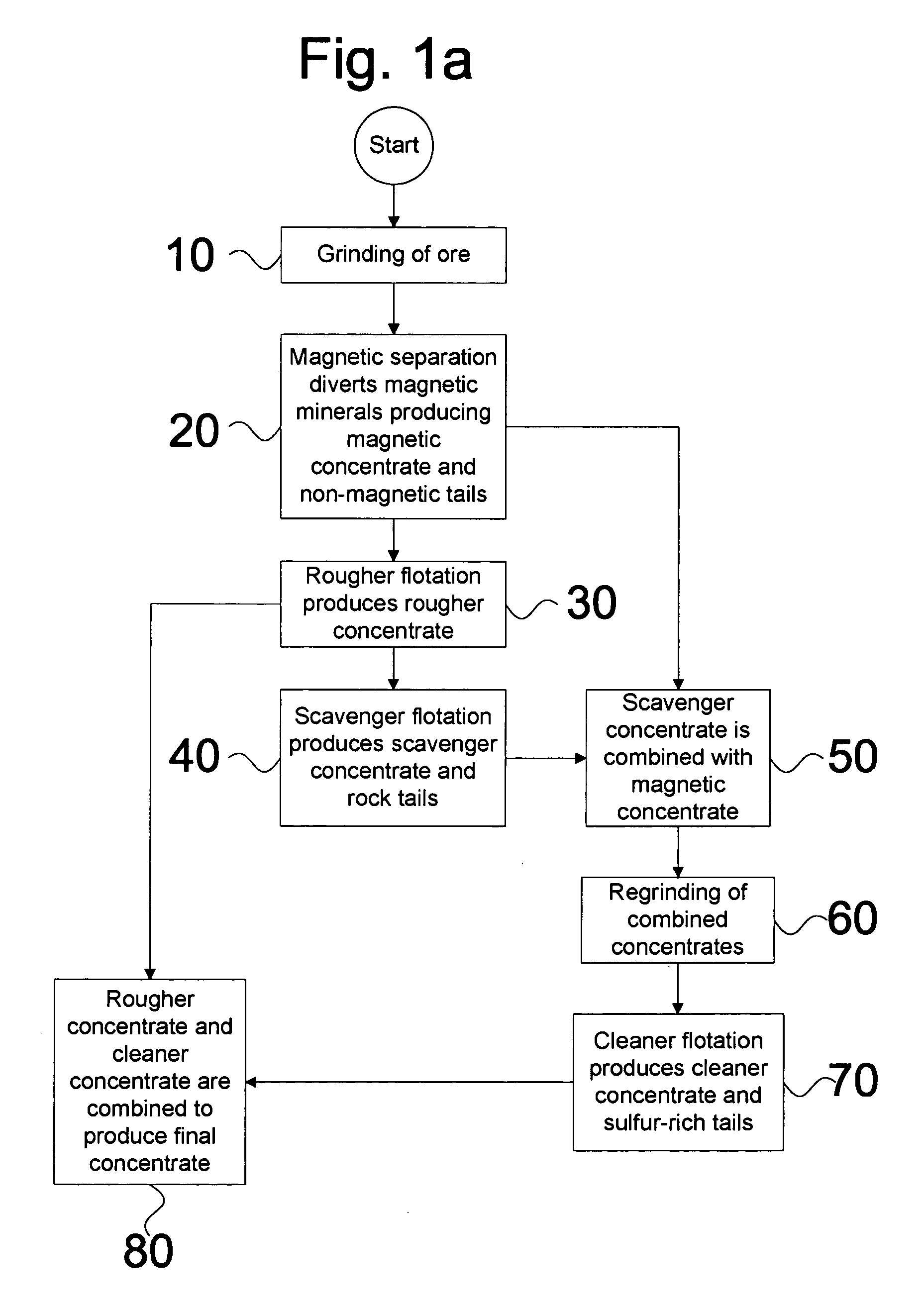
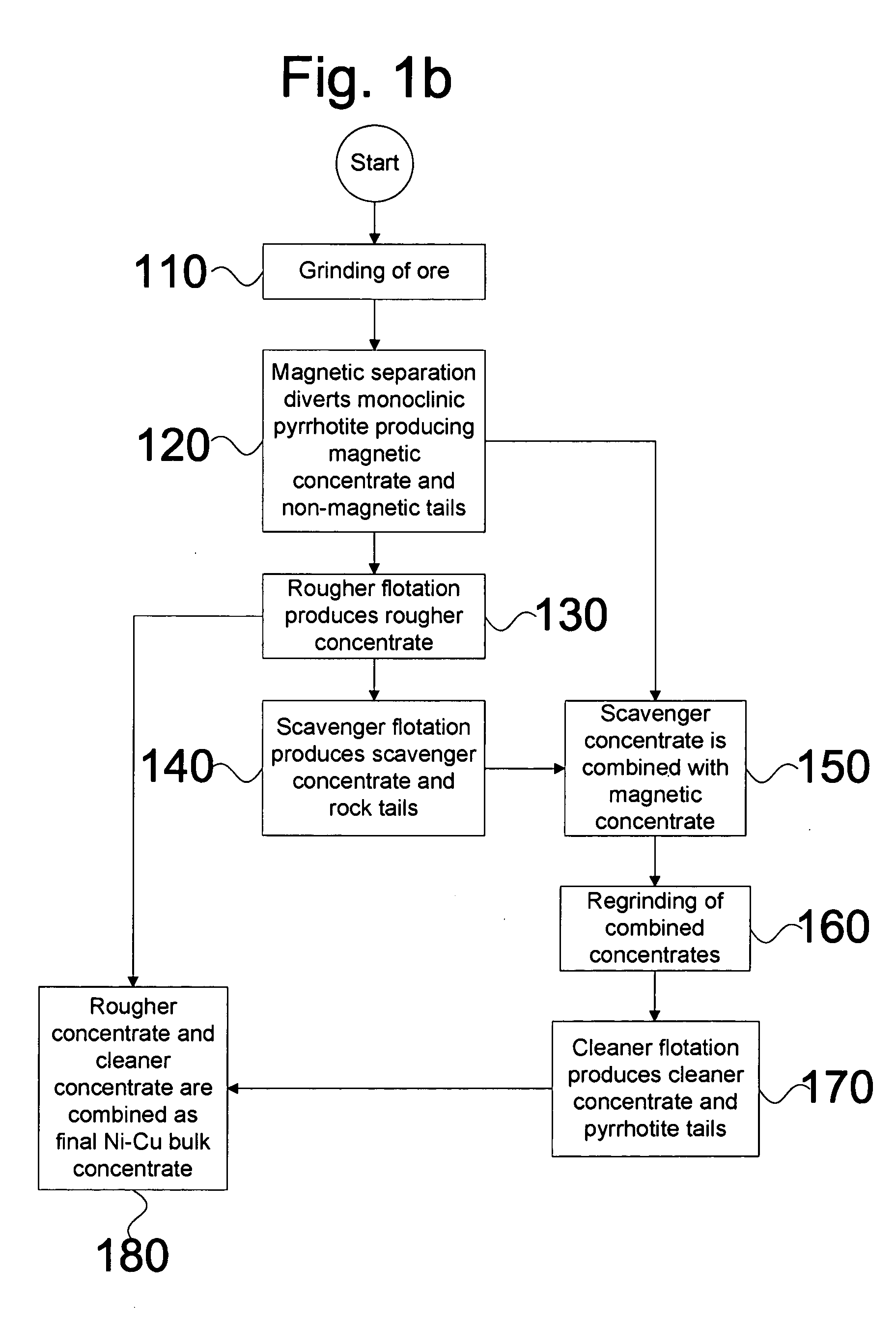
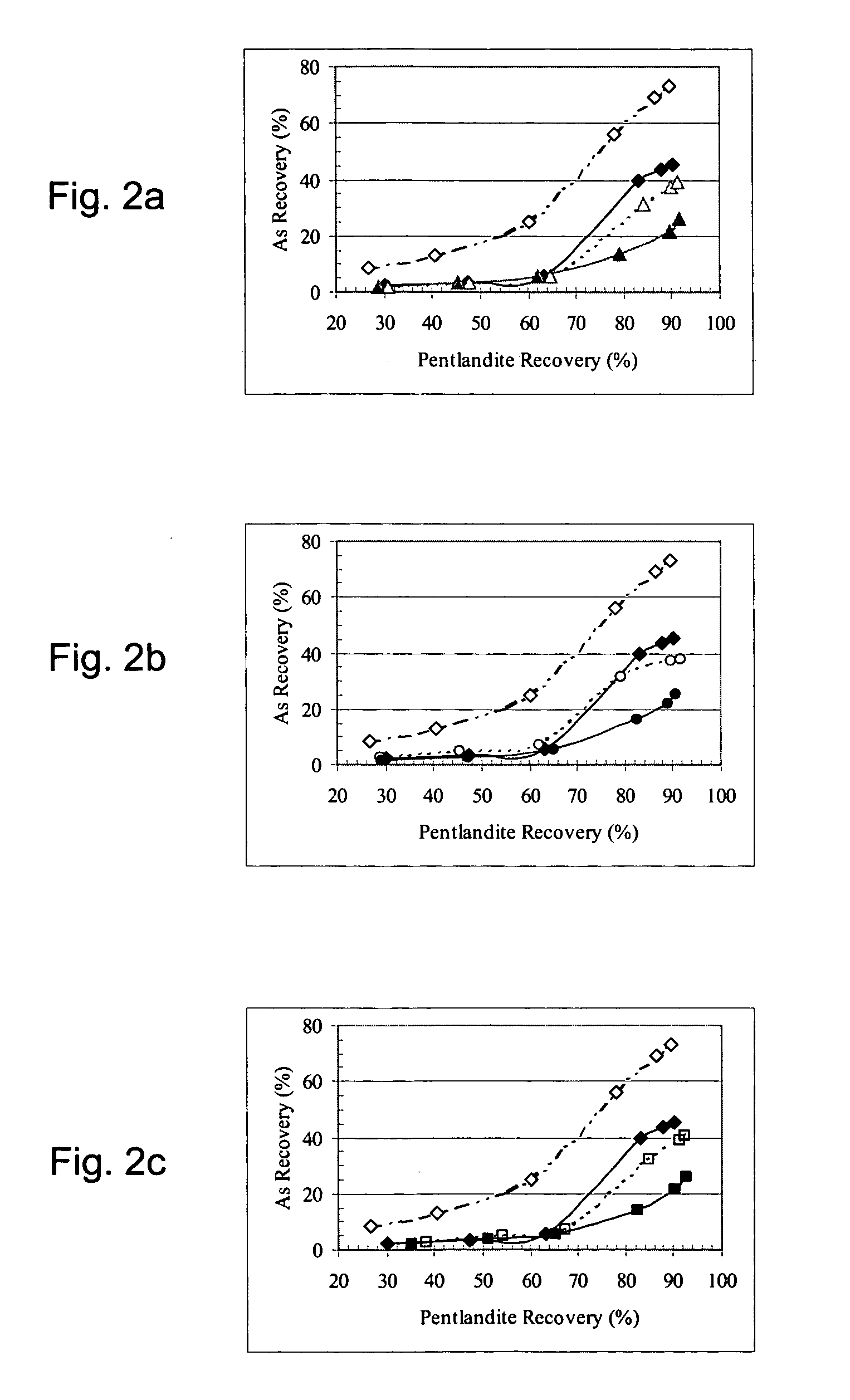
Arsenide depression in flotation of multi-sulfide minerals
A mineral separation process includes wet-grinding the ore to liberation of minerals, oxidizing the slurry using air, hydrogen peroxide or other oxidants and floating the valuable minerals at a pH between about 9.0 and 10.0 with a xanthate as collector, and a combination of a polyamine and a sulfur containing species as depressants for arsenide minerals. This depressant suite effectively depresses the flotation of arsenide minerals with no effect on the flotation of the valuable minerals.
Owner:INCO
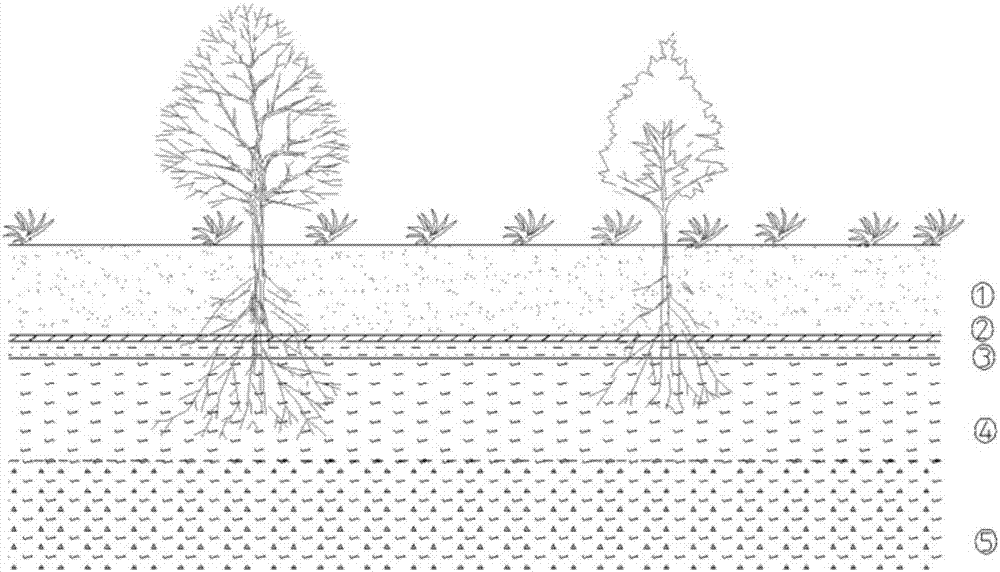
Pollution prevention and vegetation recovery method for metal sulphide ore solid waste storage yard
ActiveCN103806454APrevent oxidationReduce pollutionExcavationsHorticultureRecovery methodRevegetation
The invention relates to a pollution prevention and vegetation recovery method for a metal sulphide ore solid waste storage yard. The method comprises the following steps of conducting stabilizing treatment on side slopes of the storage yard, laying a two-way geogrid, building intercepting ditches in the slope faces of the storage yard, spraying an acidic improvement layer, laying a flexible isolating layer, laying ecological sticks, laying a two-way geogrid, spraying a base material layer, spraying a seed layer and laying a protective layer, so that plants have sufficient water and nutrition during growth. Due to the fact that the acidic improvement layer is built for neutralizing H+, the plant growth condition can be built; the flexible isolating layer and vegetation recovery are combined for preventing H2O and O2 from making contact with tailings, sulfide minerals in waste rock can be effectively prevented from being oxidized, and therefore waste water acidification and heavy metal ion leaching are prevented. According to the pollution prevention and vegetation recovery method, the problem of environmental pollution of pollutants in the metal sulphide ore solid waste storage yard can be effectively reduced, the area of green plants can be increased, and the good ecological environment is built; the pollution prevention and vegetation recovery method is simple in construction technology, easy to implement, high in efficiency and suitable for large-area application.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Sulphide ore floation collector and use method of diacyl bis-thiourea and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101337206AEasy to makeEfficient flotation separationOrganic chemistryFlotationMagmaThiourea
The invention discloses the application processes and the preparation methods of a sulphide ore flotation collector as well as a diacyl bis-thiourea. The invention relates to a novel collector used for high efficiently recycling valuable sulfide minerals from metal sulphide ores; the compositions of the sulphide ore flotation collector include diacyl bis-thiourea surface active agents; the diacyl bis-thiourea compound is shown in the constitutional formula (1) or (2). The collector has strong collecting ability to copper sulphide minerals such as chalcopyrite, etc., lead sulfide minerals or zinc sulfide minerals activated by copper ions, nickel sulfide minerals as well as noble metal minerals such as gold, silver, etc., and has good selectivity to gangue sulphide minerals such as iron pyrites, pyrrhotite, etc., thereby realizing the high efficient flotation separation of the copper sulphide minerals and ferric sulfide minerals when the pH value of ore magma is below 11, reducing the used amount of lime, and improving the comprehensive recovery of copper sulphide ores.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
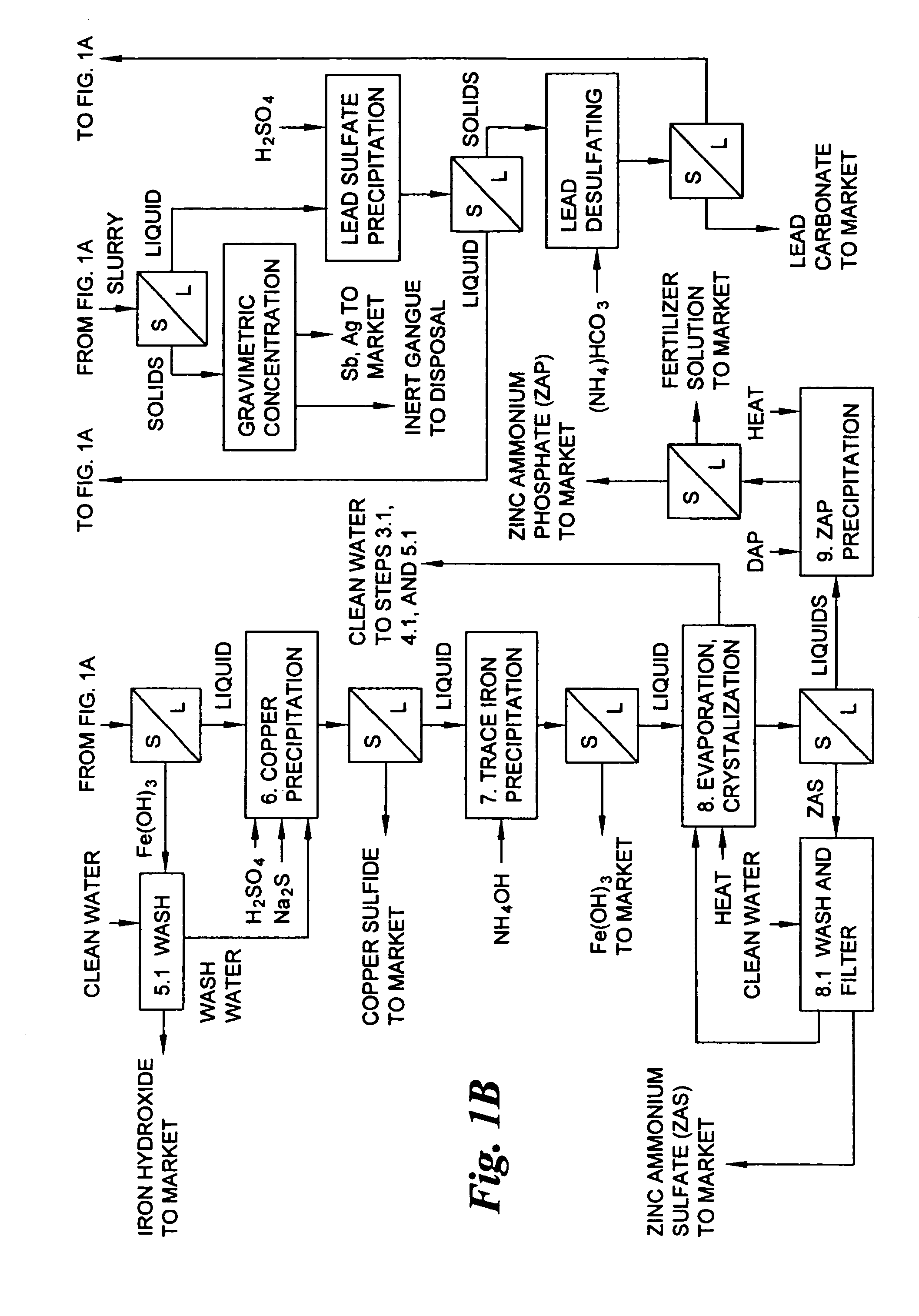
Hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of metal-bearing sulfide mineral concentrates
InactiveUS20070098609A1Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredSolvent extractionGold compoundsAmmonium compoundsMetallic sulfide
A hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of complex silver-bearing sulfide ores and concentrates that recovers substantially all silver, lead, antimony, zinc, copper and sulfur, along with the chemical reagents utilized during the process. Finely ground ores and concentrates are leached under heat and pressure with water, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, oxygen, and a catalyst, and are further treated to recover silver in the form of silver chloride; iron in the form of iron hydroxide; copper and all traces of soluble toxic metals as sulfides; zinc as zinc ammonium sulfate and specifically nitric acid, sulfuric acid, oxygen, ammonia, and ammonium compounds as valuable fertilizer products.
Owner:ROYAL SILVER PANAMA
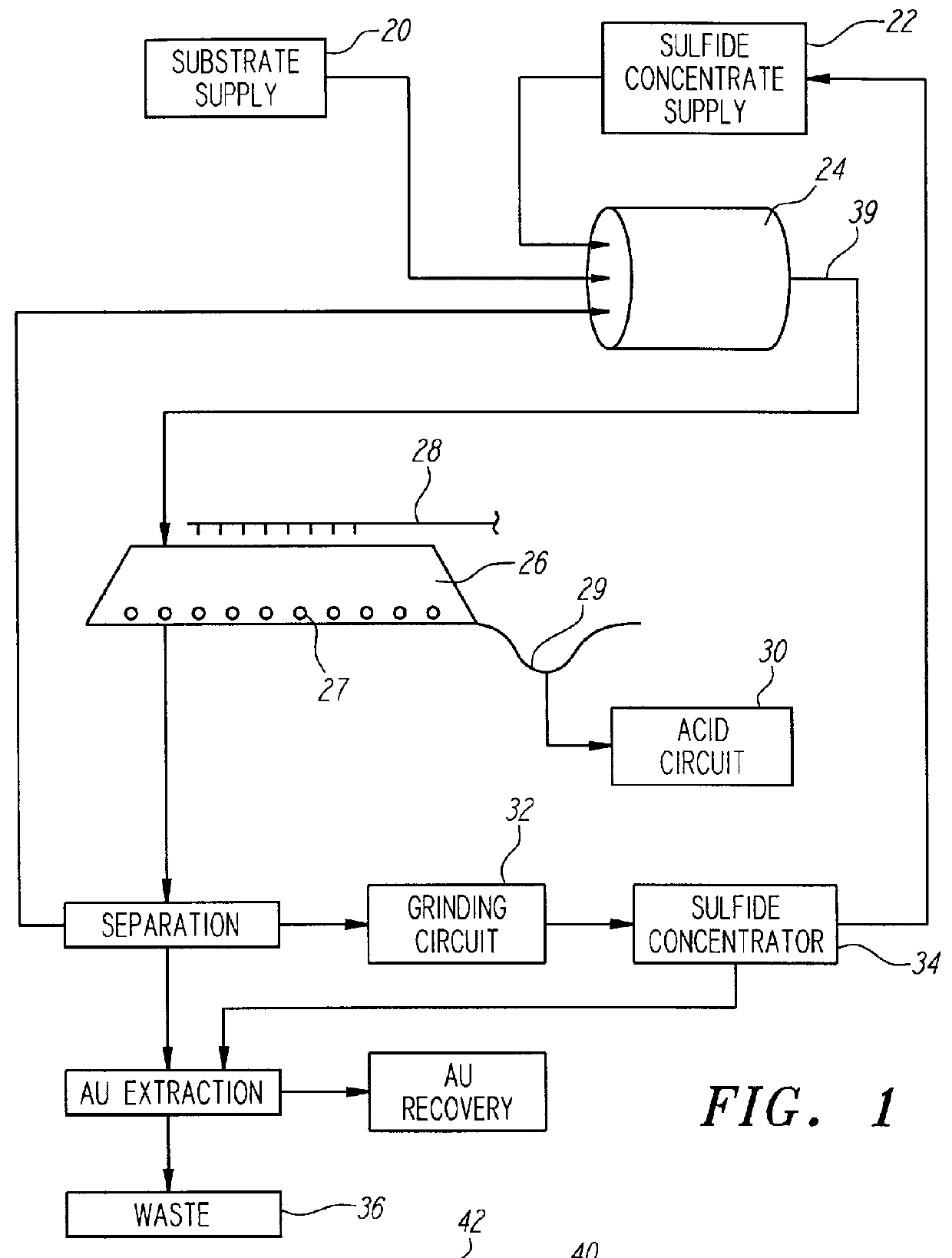
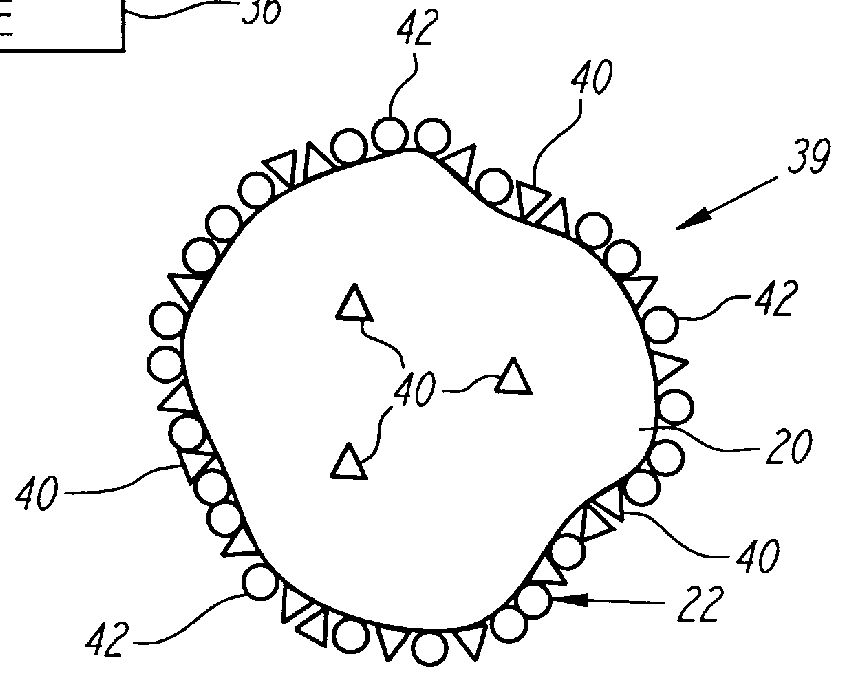
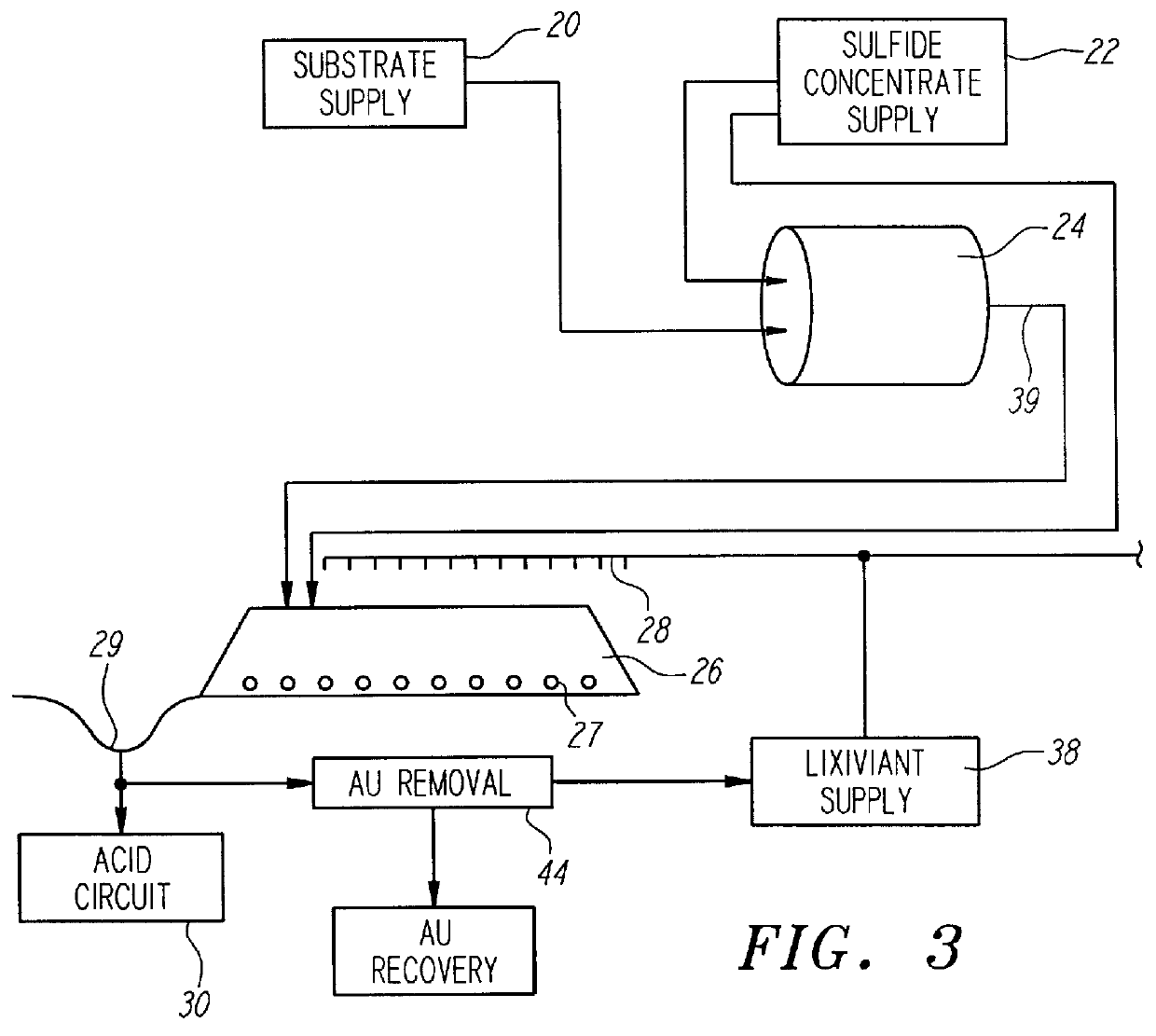
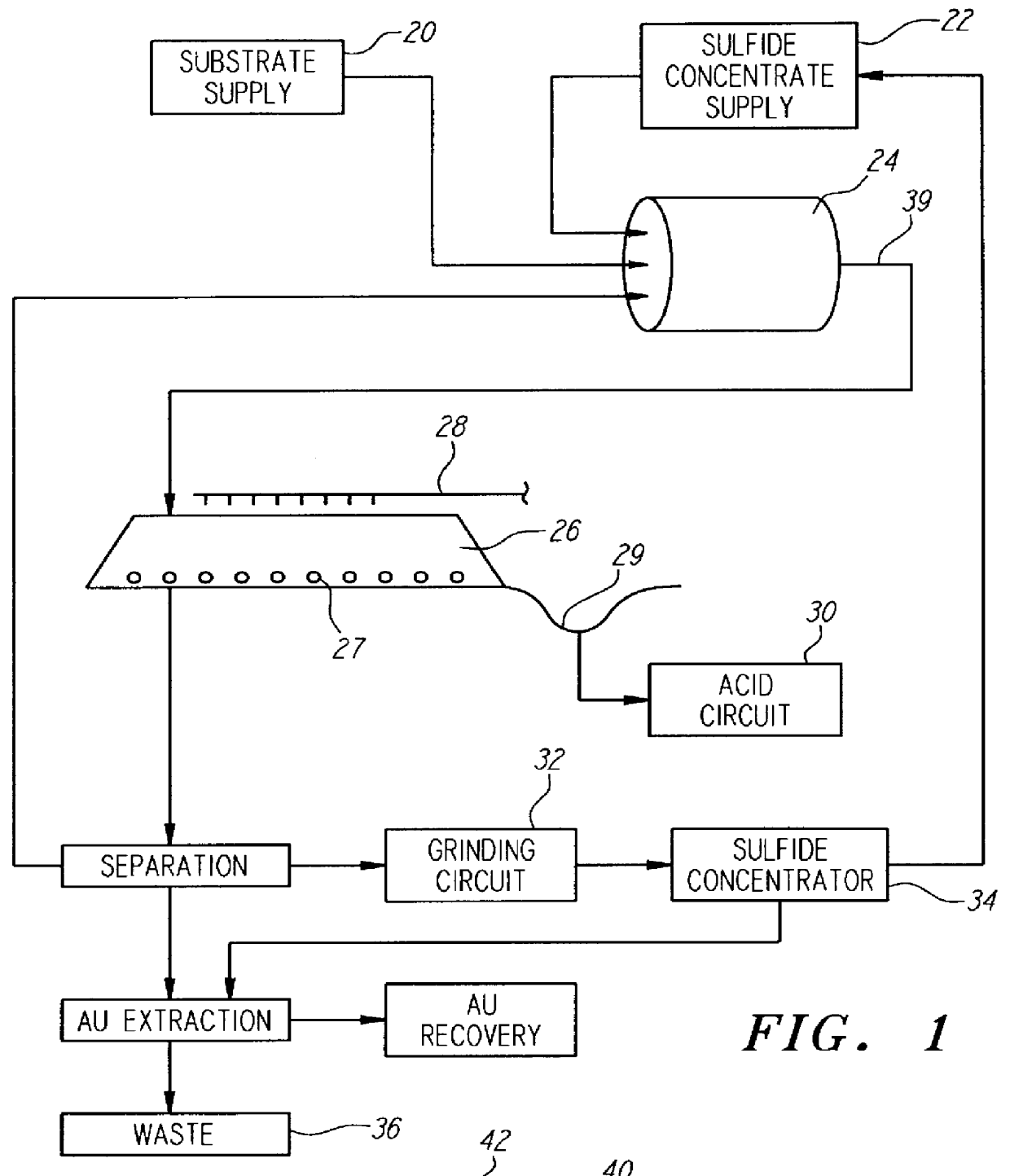
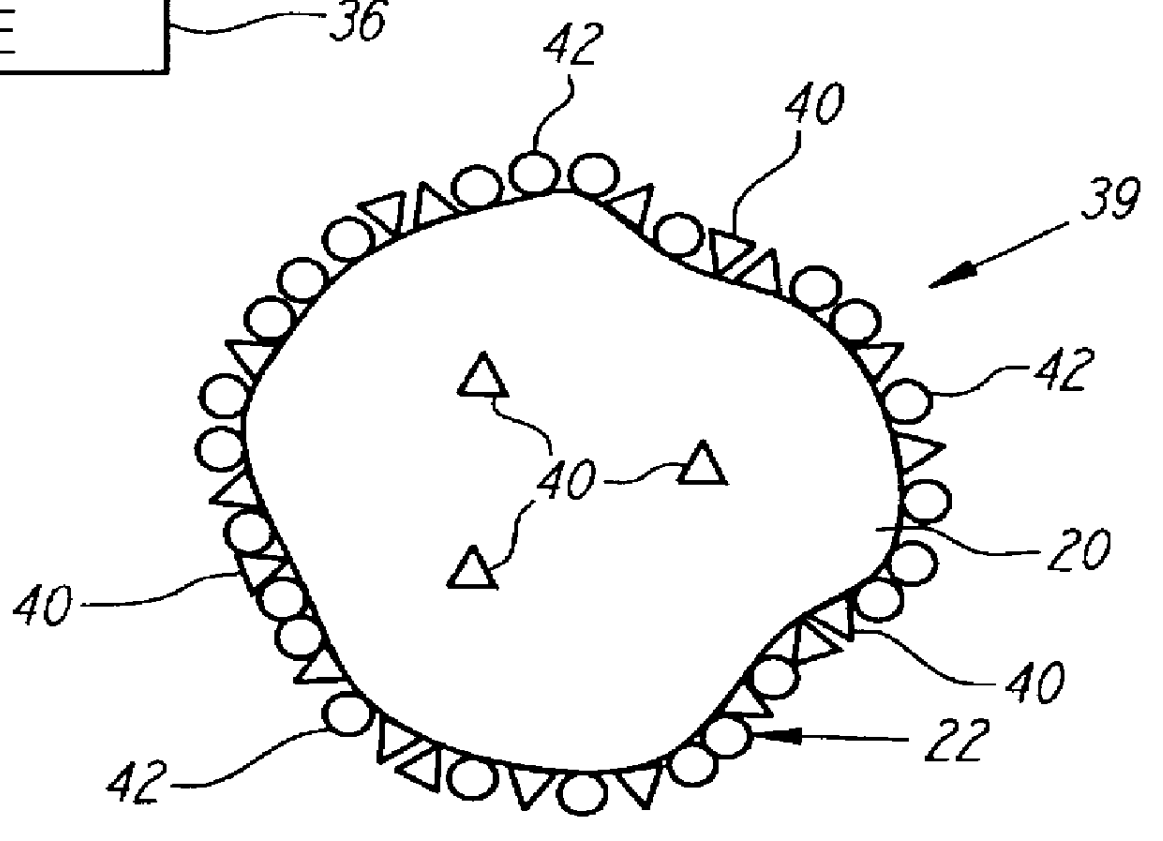
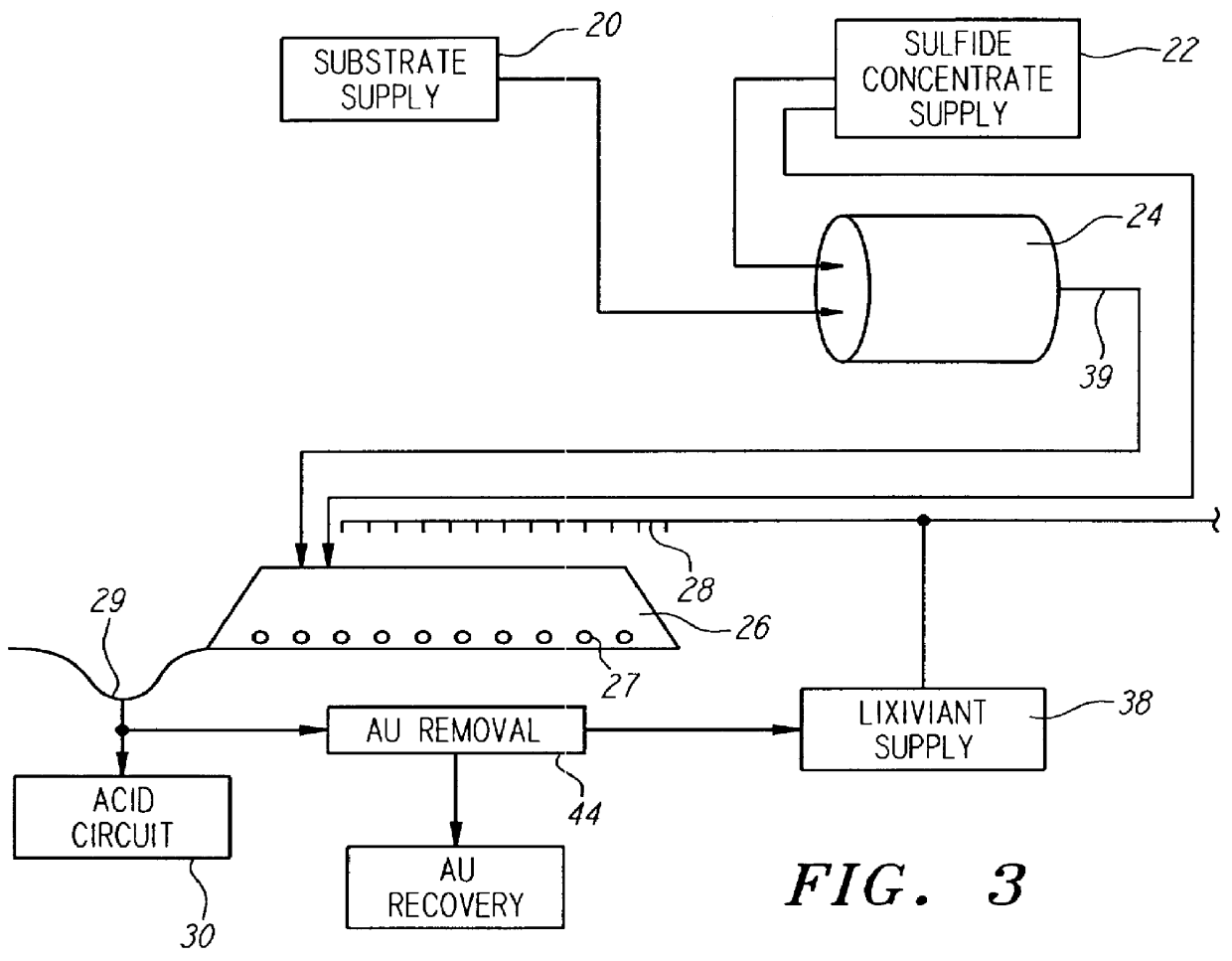
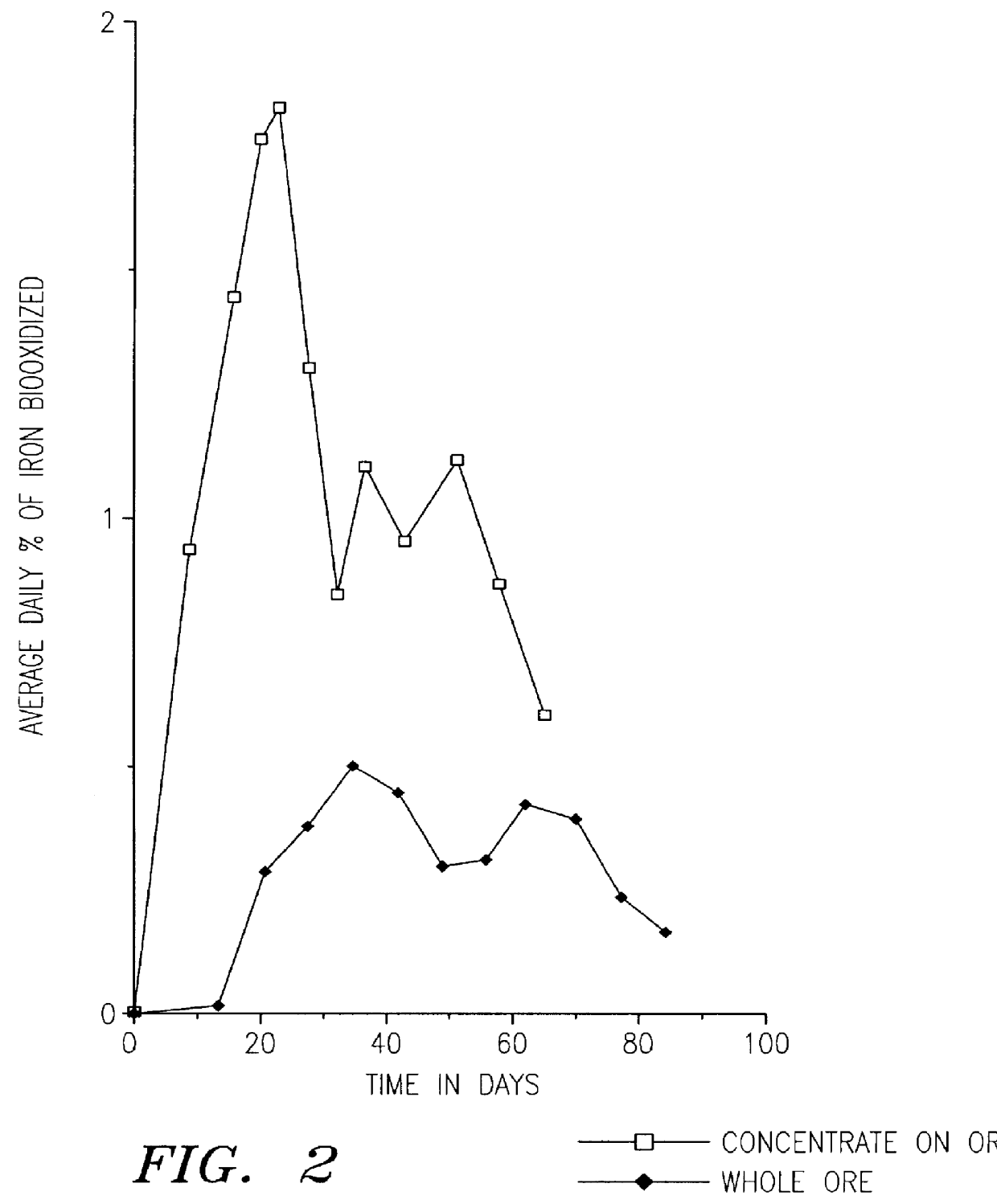
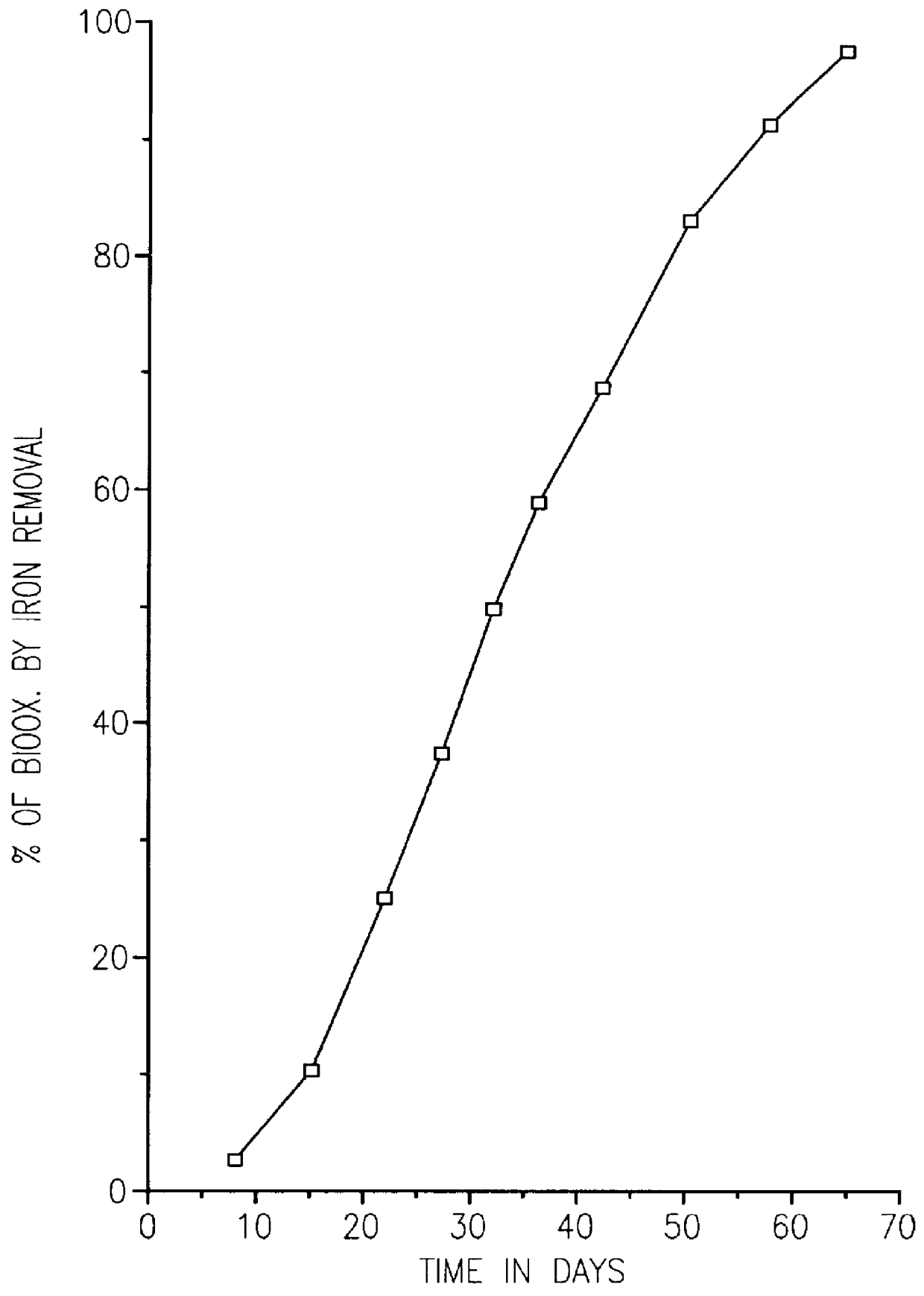
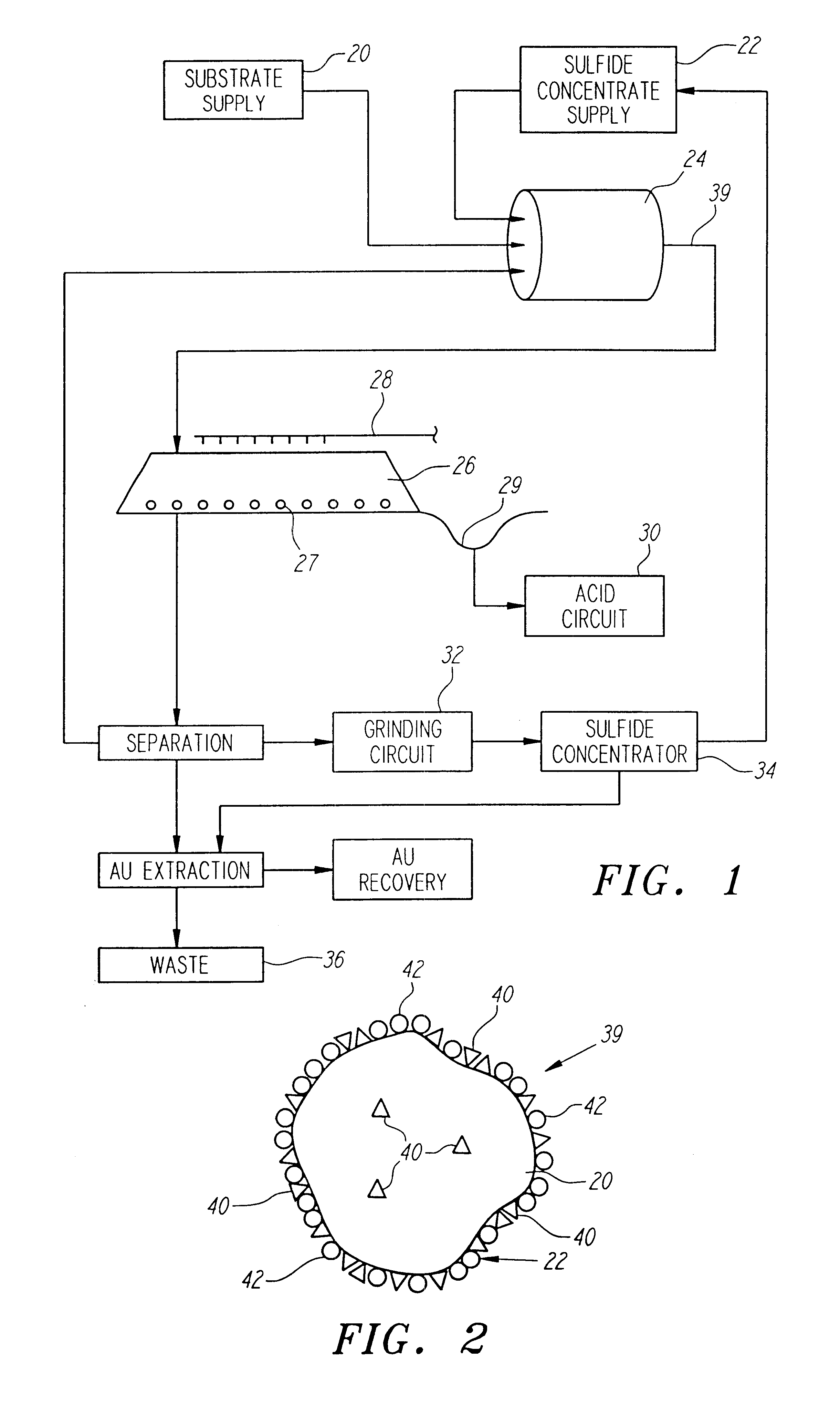
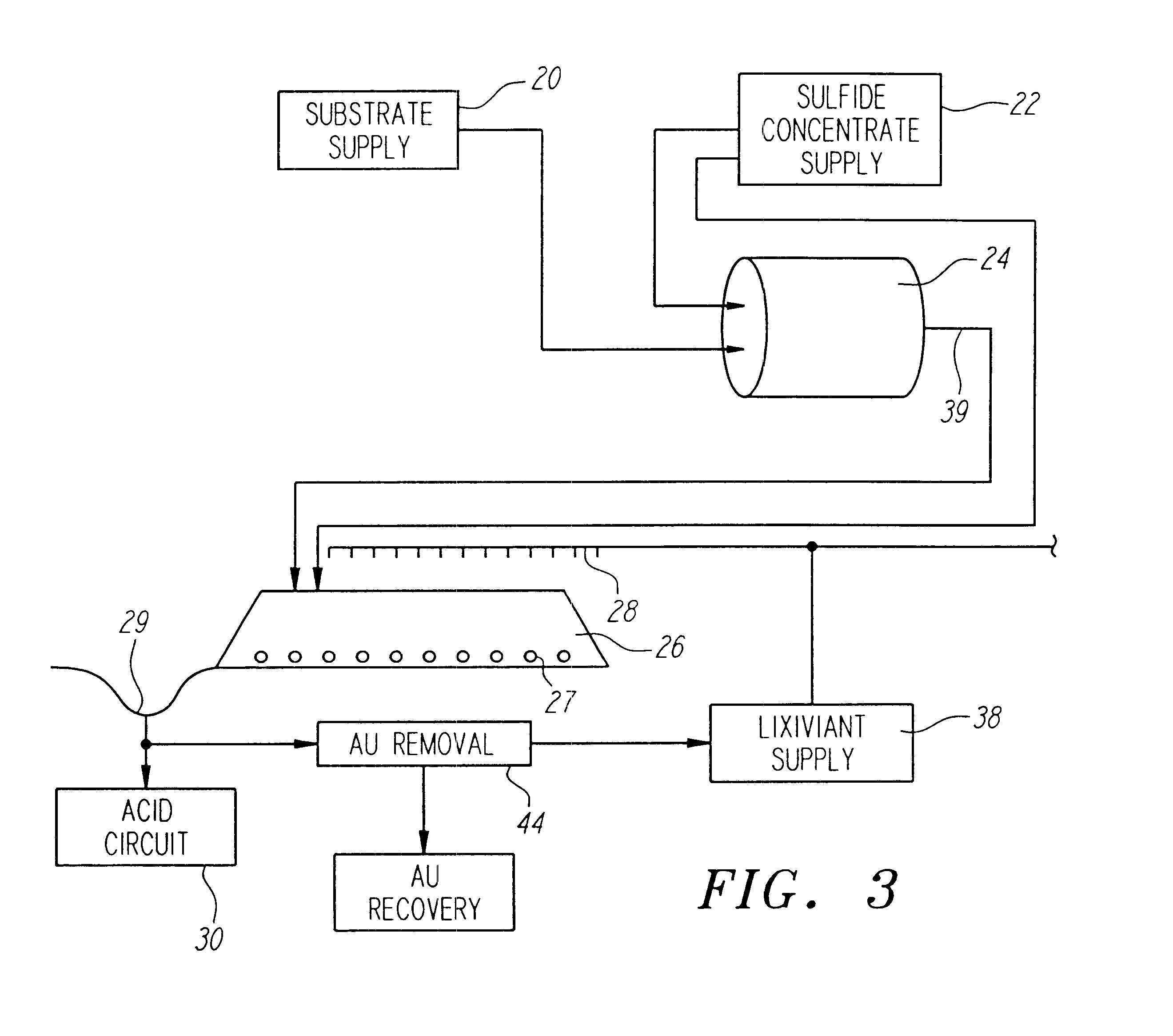
Nonstirred bioreactor for processing refractory sulfide concentrates and method for operating same
InactiveUS6083730AReduced pHIncrease equipment costSolvent extractionContaminated soil reclamationSulfide mineralsMetallic sulfide
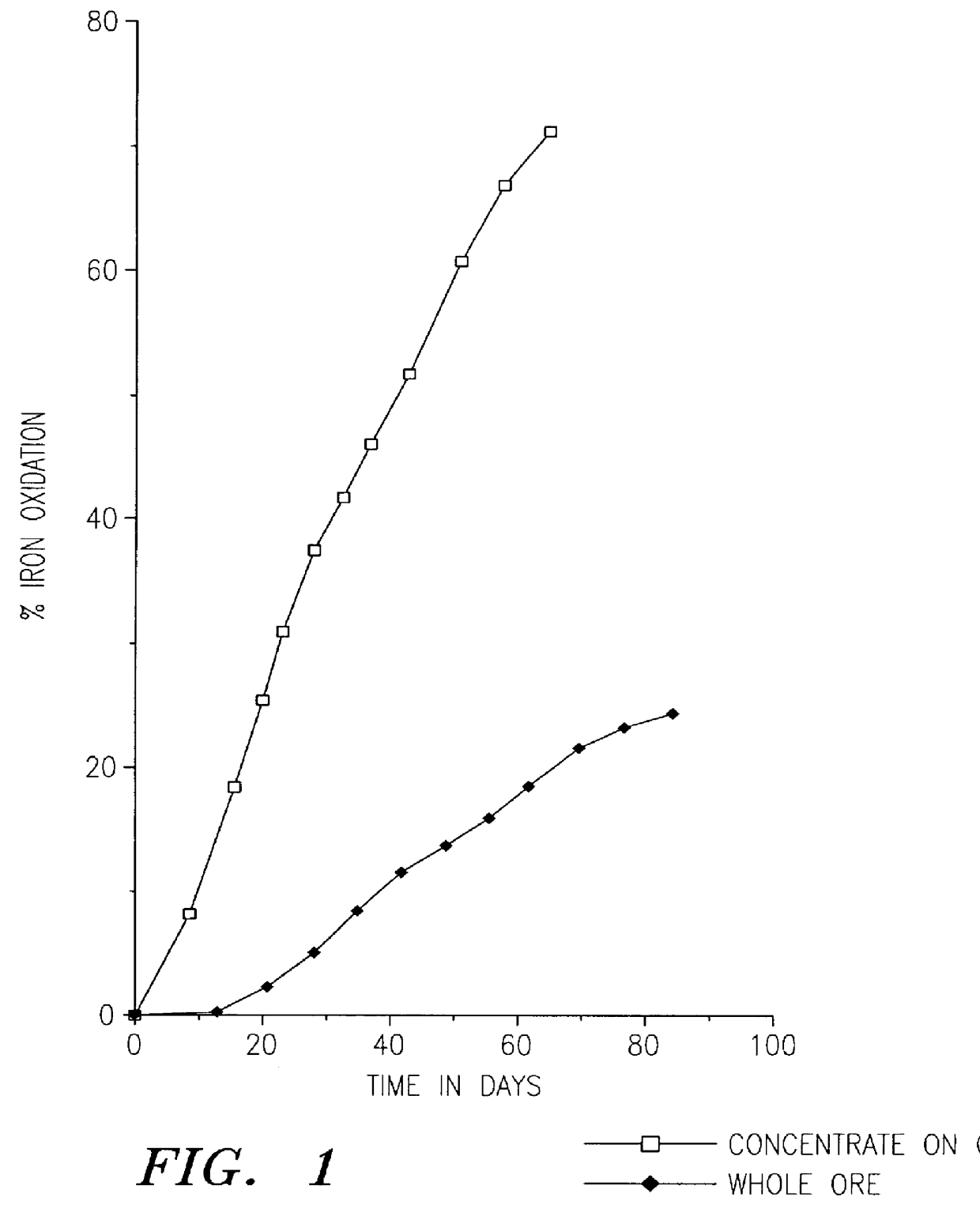
A method of biooxidizing sulfide minerals in a nonstirred bioreactor is provided. According to the disclosed method, a concentrate of sulfide minerals is coated onto a substrate, such as coarse ore particles, lava rock, gravel or rock containing mineral carbonate as a source of CO2 for the biooxidizing bacteria. After the sulfide minerals are coated onto the substrate, a heap is formed with the coated substrates or the coated substrates are placed within a tank. The sulfide minerals are then biooxidized to liberate the metal value of interest. Depending on the particular ore deposit being mined, the sulfide mineral concentrates used in the process may comprise sulfide concentrates from precious metal bearing refractory sulfide ores or they may comprise sulfide concentrates from metal sulfide type ores, such as chalcopyrite, millerite or sphalorite. The distinction being that in the former, the metal of interest is a precious metal occluded within the sulfide minerals, whereas in the latter, the metal to be recovered is copper, nickel or zinc and is present as a metal sulfide in the sulfide concentrate.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS LLC (US)
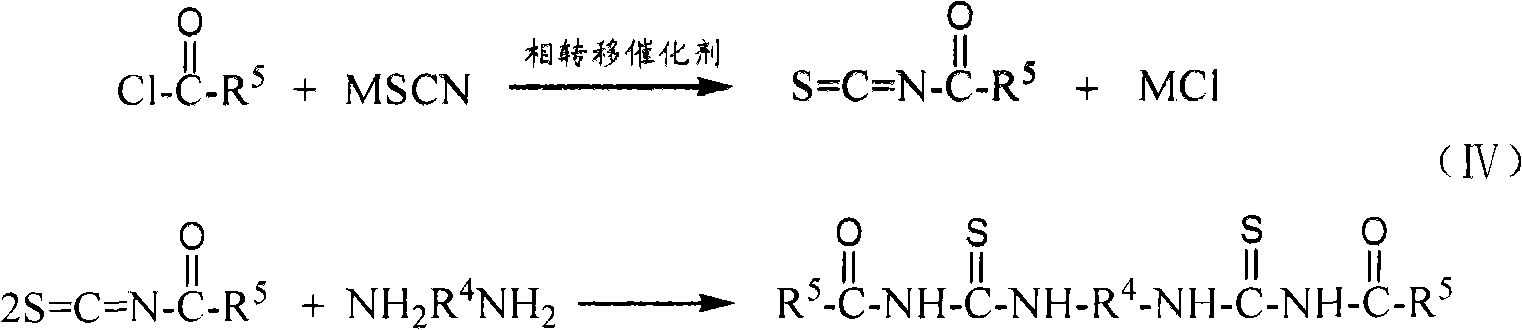
Use of diester isosulfocyanate in sulphide ore floation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101337205AEasy to makeStrong harvesting abilityOrganic chemistryFlotationMagmaSulfide minerals
The invention discloses a diester-based 2-thiocyanate ester derivate applied in sulphide flotation, and the preparation method thereof. Diester-based 2-thiourea (the formula one) or diester-based 2-ethionine ester (the formula two) is applied as a novel collector for high efficiently recycling valuable sulfide minerals from metal sulphide ores by floatation. The collector has wide pH range in ore magma, thereby having strong ability to collect copper sulphide minerals such as chalcopyrite, etc., lead sulfide minerals or zinc sulfide minerals activated by copper ions, nickel sulfide minerals as well as noble metal minerals such as gold, silver, etc., and having good selectivity to gangue sulphide minerals such as iron pyrites, pyrrhotite, etc.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
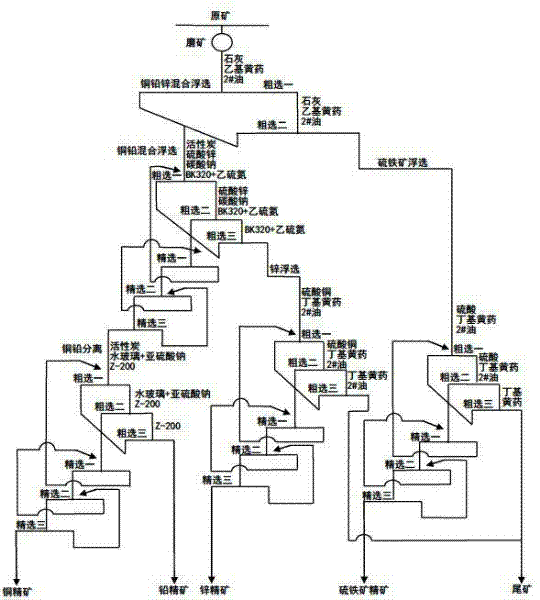
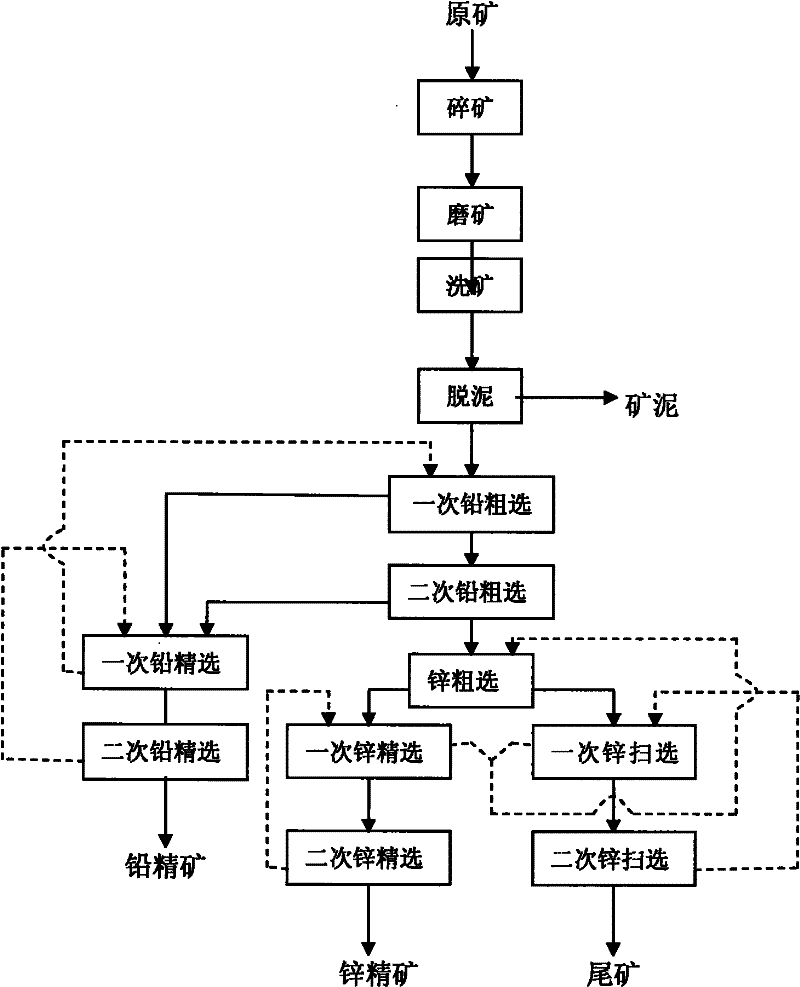
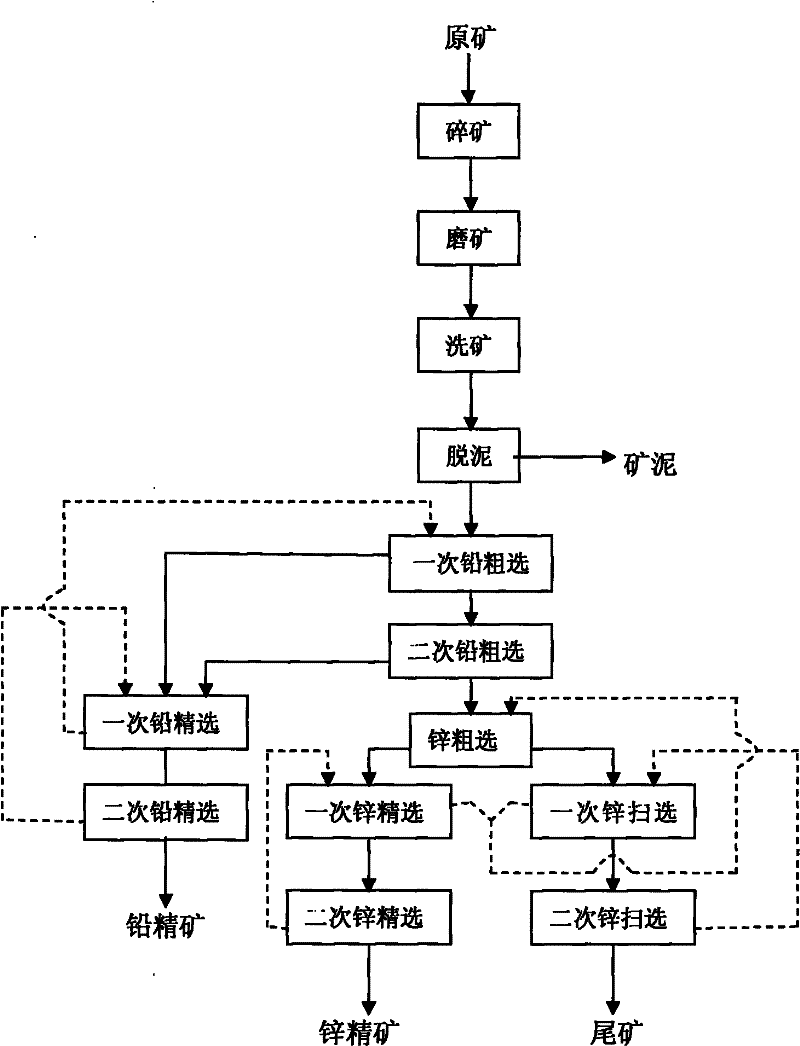
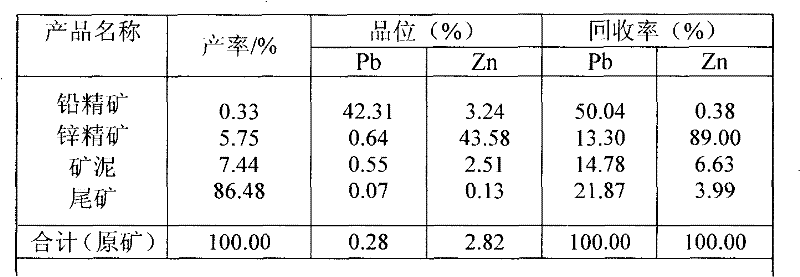
Mineral dressing method for separating Cu-Pb-Zn-Fe multi-metal sulfide mineral
The invention discloses a mineral dressing method for separating a Cu-Pb-Zn-Fe multi-metal sulfide mineral, which comprises the following steps: selecting a raw mineral, grinding the mineral, carrying out mixed flotation to Cu, Pb and Zn, carrying out mixed flotation to Cu and Pb, separating Cu and Pb, carrying out Zn flotation and pyrite flotation, and finally obtaining a Cu, Pb, Zn and pyrite concentrate. The method has the advantages of good metal sulfide mineral effect and high metal recovery rate, is simple to operate and is suitable to popularize and apply.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gold extraction process with low pollution and high recovery for refractory gold concentrate
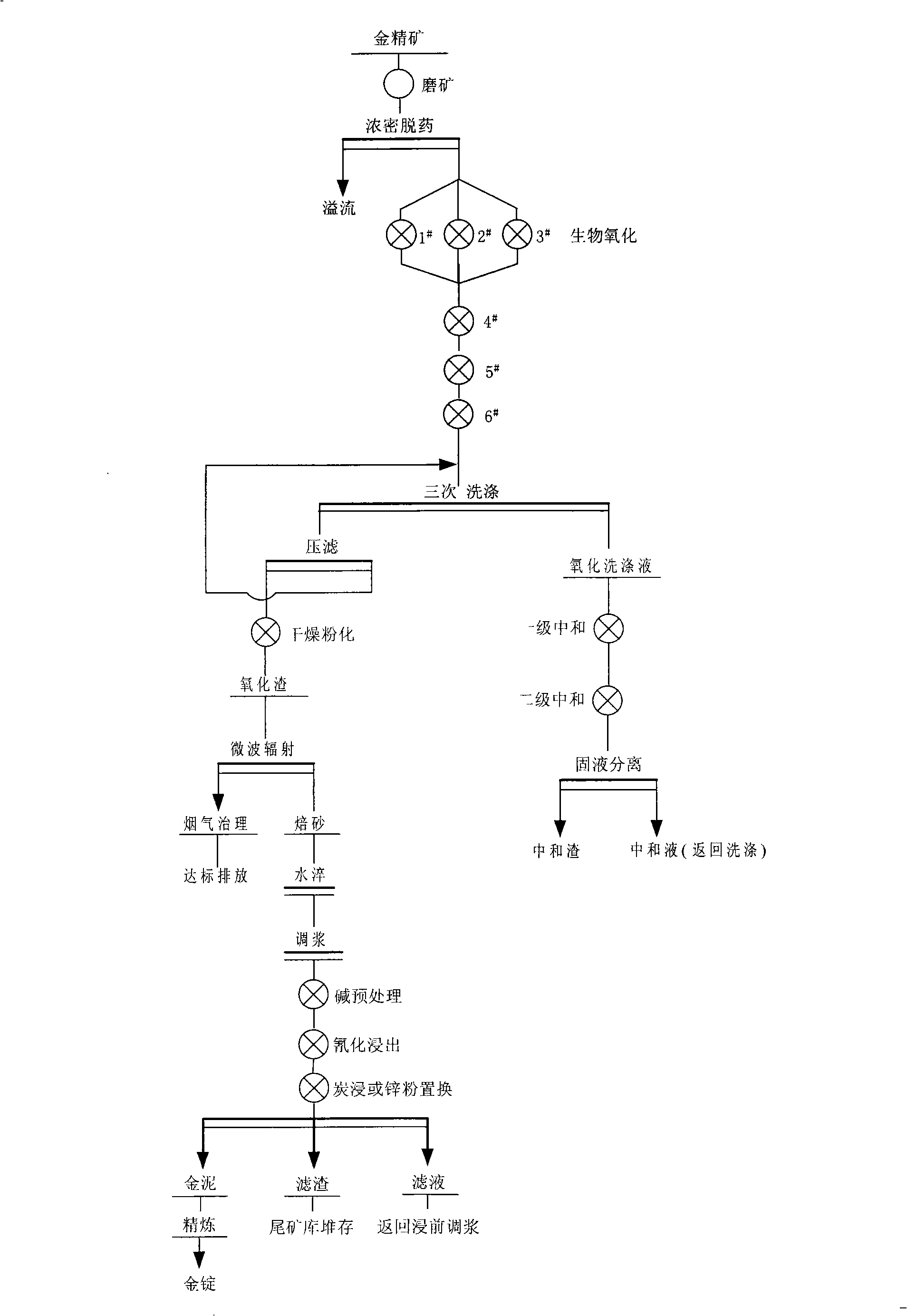
ActiveCN101285126AReduce pollutionAvoid secondary packagingProcess efficiency improvementSlagSulfide minerals
The invention relates to a process for extracting gold of refractory gold concentrates with low pollution and high recovery rate, belonging to the metallurgical process class. The process proposal which combines organically the bacterial oxidation technology with the microwave irradiation technology comprises the following steps of: oxidizing and decomposing sulfide minerals by means of the bacterial oxidation technology first; exposing and dissociating sufficiently the gold; oxidizing a large part of sulfur and arsenic to enter a liquid-phase; carrying out the neutralization treatment to the oxidizing liquid and returning to use; roasting oxidizing slag with microwave at the low temperature; and removing organic carbon in ore. The process solves completely the problem of absorbing the gold in the subsequent cyaniding gold extraction work. The process has high recovery rate of the gold and less environment pollution, is easy to automatically control and saves energy.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST +1
Separation of minerals
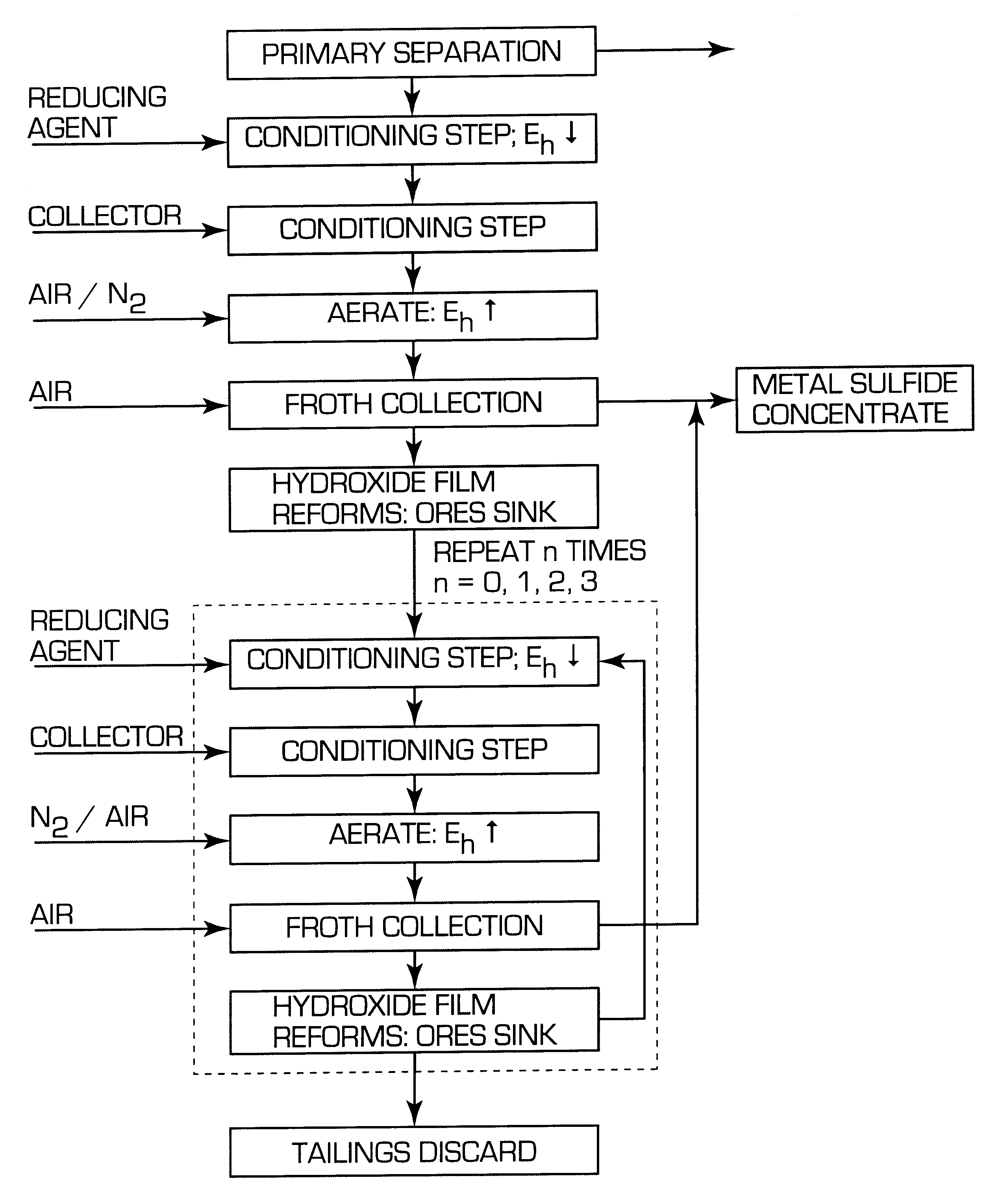
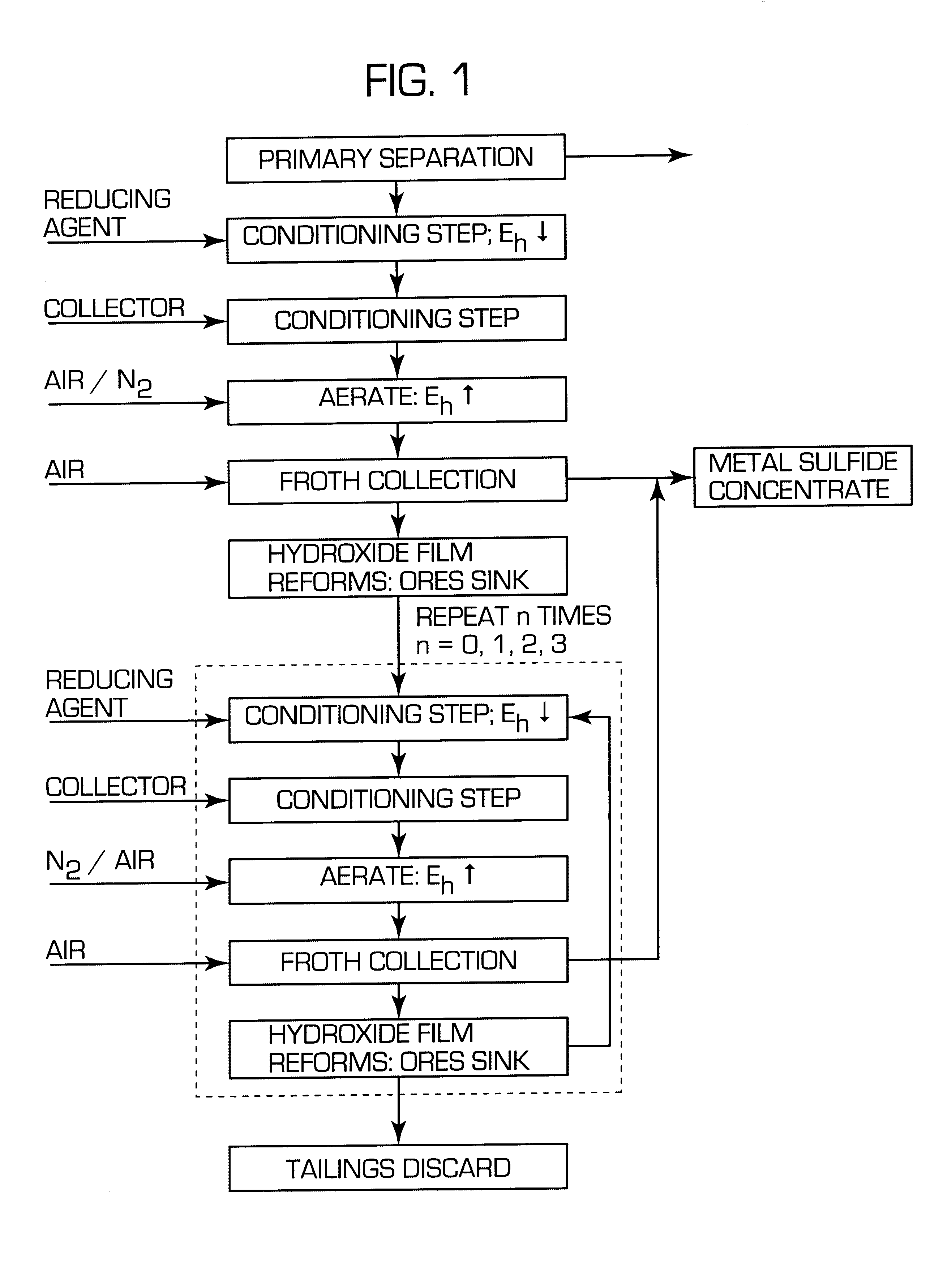
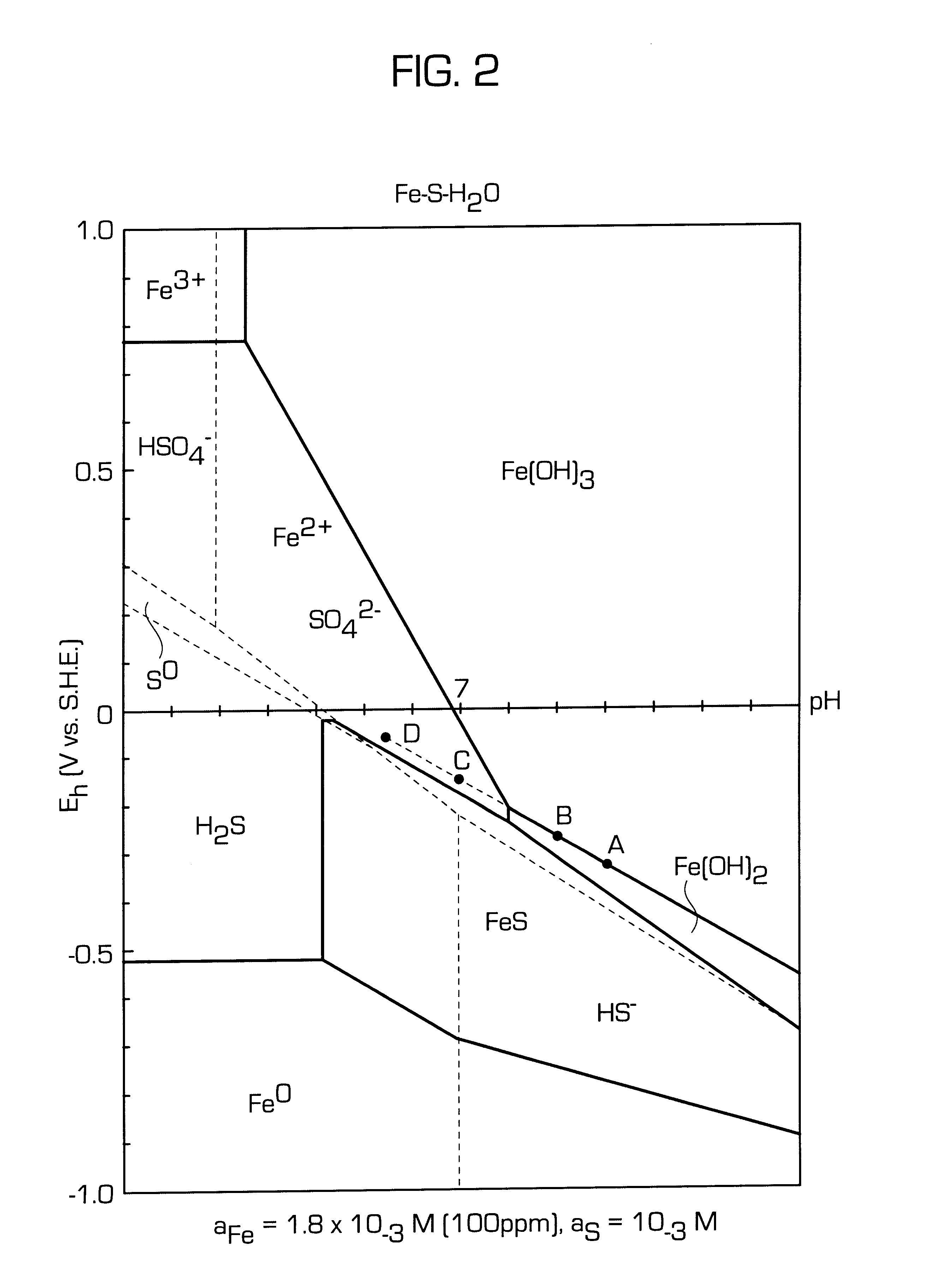
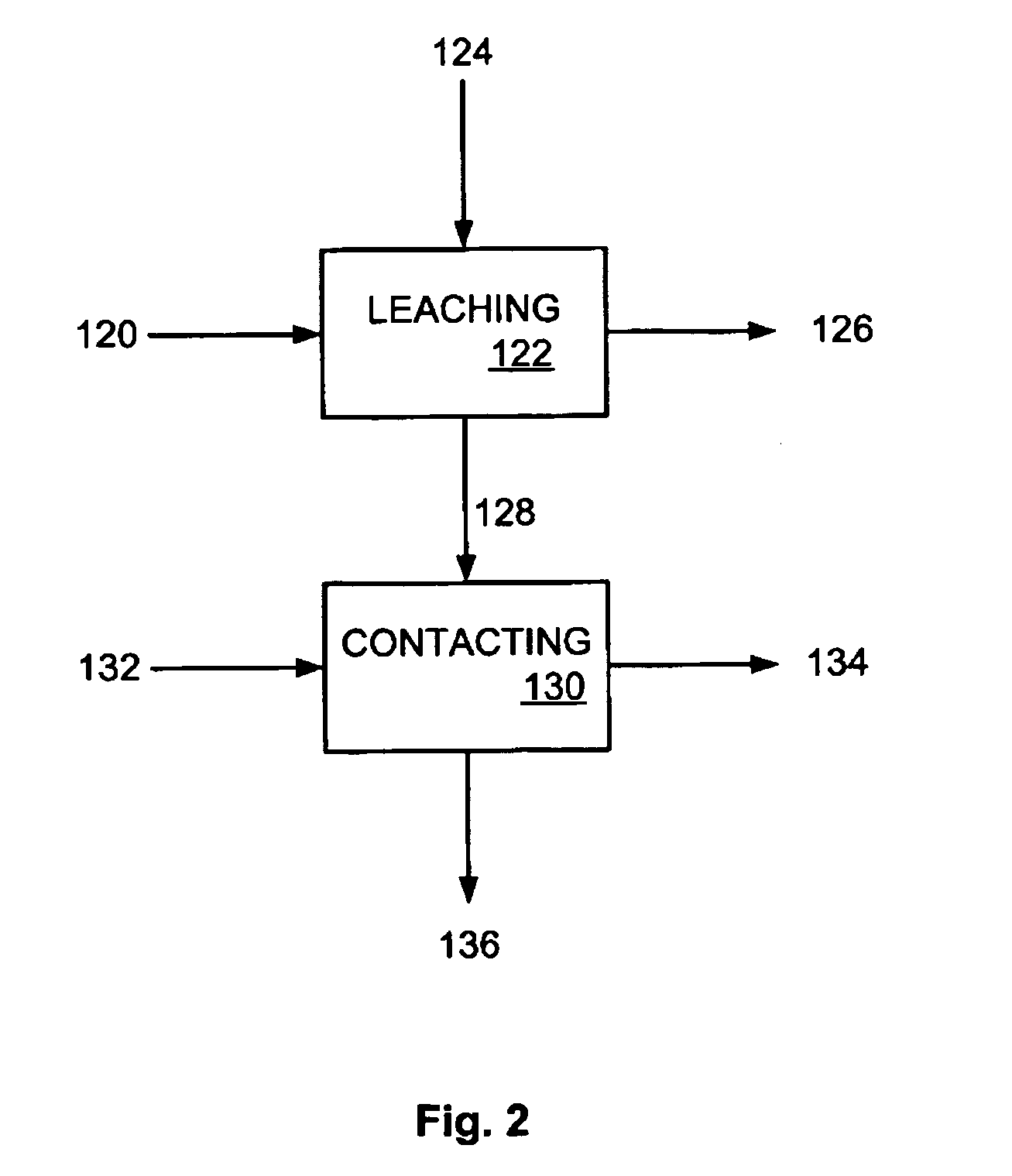
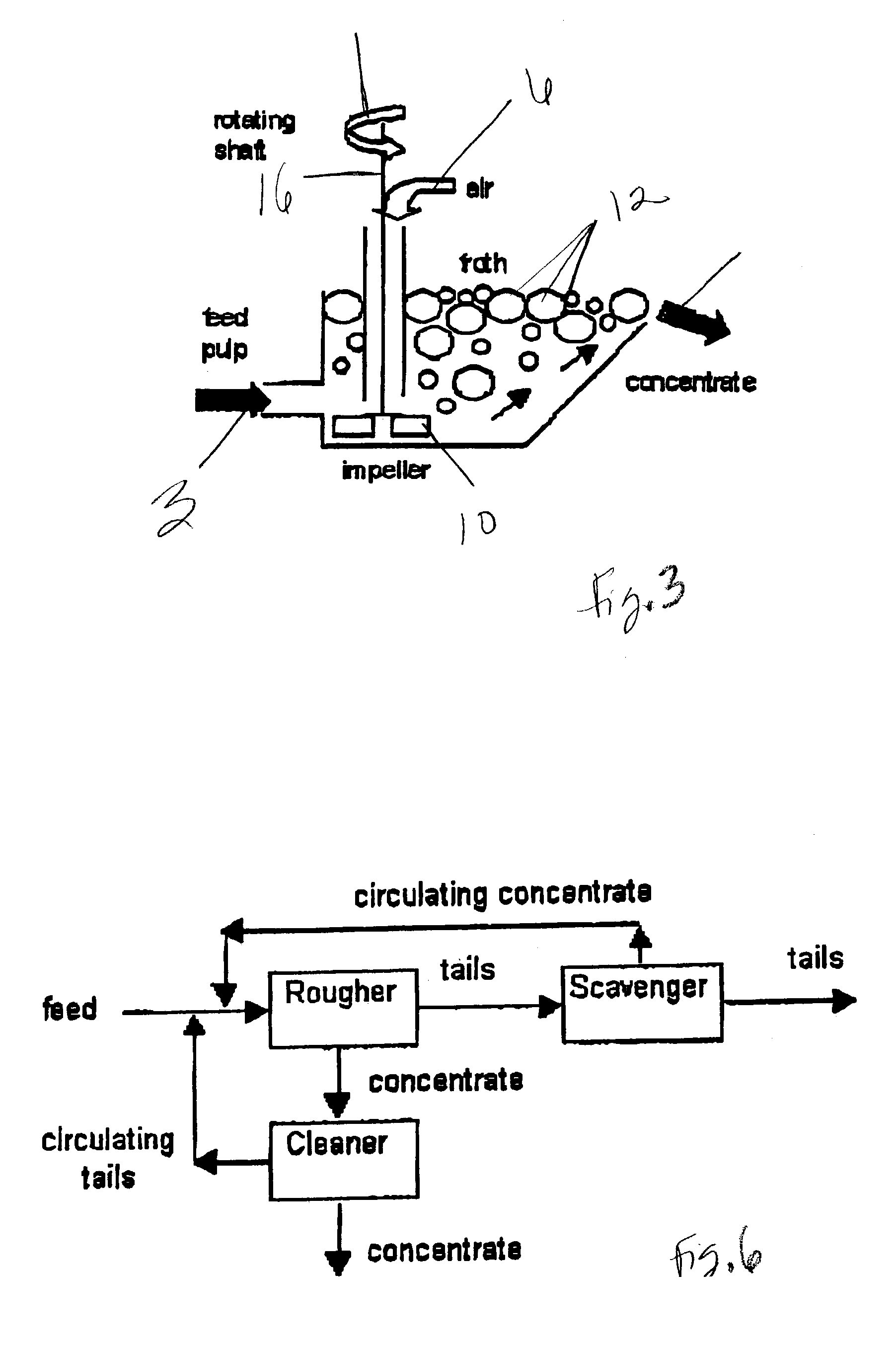
A process for floating fine particles containing metal values of an iron-bearing sulphide mineral ore including the steps of conditioning the aqueous pulp of ore at a pH of between about 7 and about 10 with a reducing agent which is preferably oxy-sulphur compound which dissociates to form oxy-sulphur ions having the general formula:where n is greater than 1; y is greater than 2; and z is the valance of the ion.A suitable collector is then added to the conditioned aqueous pulp to further condition the pulp and the pulp potential of the pulp raised to a sufficient level for the collector to adsorb onto the sulphide mineral ore. Gas is then bubbled through the aqueous pulp to subject the pulp to froth flotation. The froth from the flotation process is recovered to produce a concentrate of fine sulphide mineral and other metal values.By conditioning the aqueous pulp at a pulp potential which dissolves the iron hydroxide film from the surface of the metal sulphide inclusions in the ore and subjecting the ore to froth flotation at a suitable pulp potential before the iron hydroxide can reform, the recovery of metal values in the fine ores can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
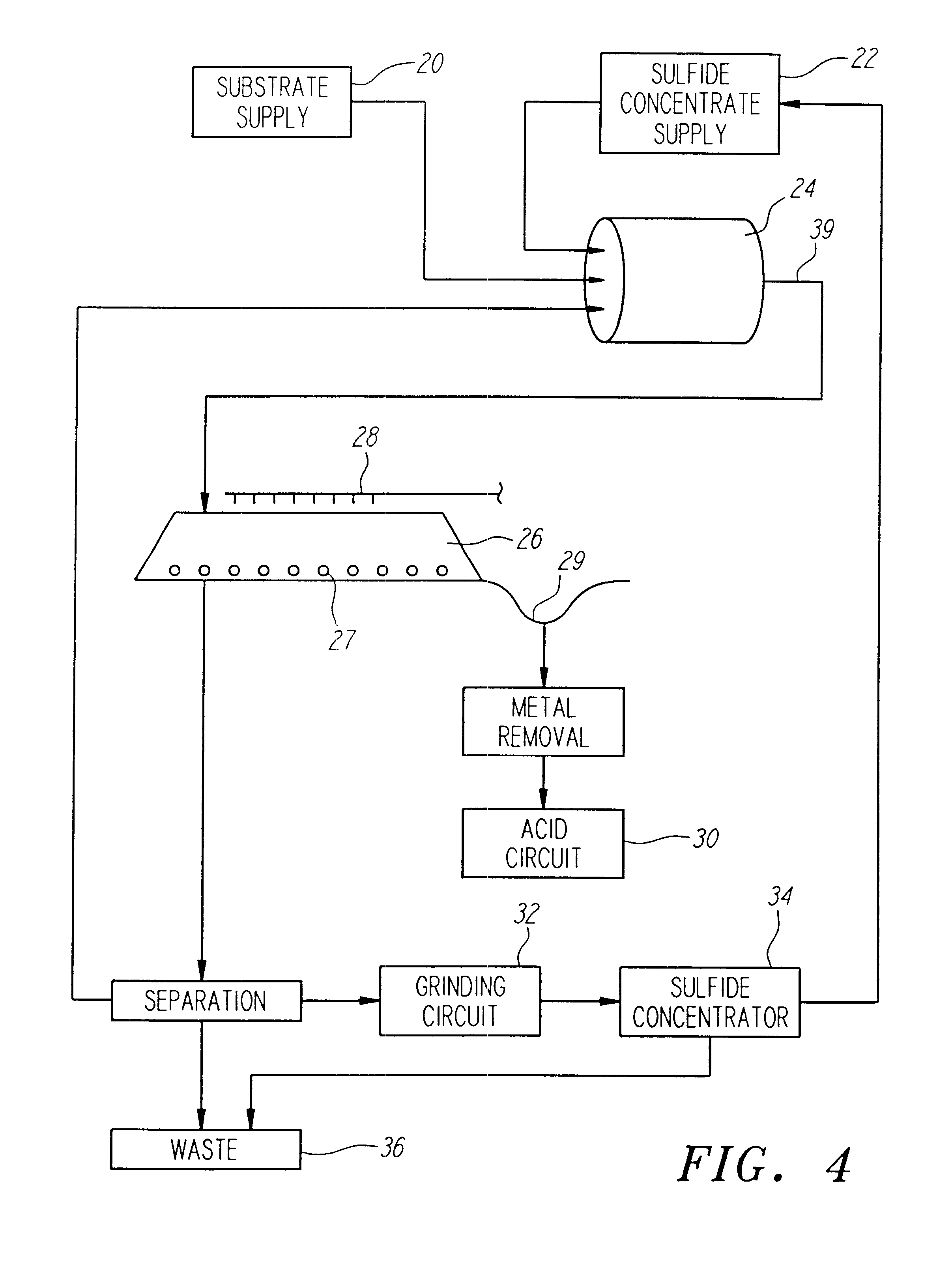
Method of biotreatment for solid materials in a nonstirred surface bioreactor
InactiveUS6159726AIncrease capacitySpeed up the processSolvent extractionSolid waste disposalMicrobial inoculationSulfide minerals
A method of biotreating a solid material to remove an undesired compound using a nonstirred surface bioreactor is provided. According to the method the surface of a plurality of coarse substrates is coated with a solid material to be biotreated to form a plurality of coated coarse substrates. The coarse substrates have a particle size greater than about 0.3 cm and the solid material to be biotreated has a particle size less than about 250 mu m. A nonstirred surface reactor is then formed by stacking the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a heap or placing the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a tank so that the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 25%. The reactor is inoculated with a microorganism capable of degrading the undesired compound in the solid material, and the solid material is then biotreated in the surface bioreactor until the undesired compound in the solid material is degraded to a desired concentration. Preferably the thickness of the solid material coating on the plurality of coarse substrates is less than about 1 mm and the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 35%. The process is useful for many different biotreatment processes, including the bioremediation of contaminated soils, the desulfurization of coal, and the biooxidation of refractory sulfide ores and concentrates. In bioremediation applications, the undesired compound is typically an organic compound. In coal desulfurization and refractory sulfide ore biooxidation applications, the undesired compound is sulfide minerals.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS LLC (US)
Five-layer coverage forced reduction in-situ mineralization restorative method
ActiveCN107363083AAvoid pollutionReduce penetrationSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationSolubilityReaction layer
The invention provides a five-layer coverage forced reduction in-situ mineralization restorative method, and belongs to the technical field of mine environment ecological restoration. A five-layer structure involved in the method particularly comprises a non-pollution new soil layer, a clay sealing layer, a biomass reduction sealing layer, a main reaction layer and an original tailing layer. The method comprises the steps that organic matter in biomass on the main reaction layer is taken as the reducing agent, arsenic in a high oxidation state is reduced into arsenic in a low oxidation state or in a reduced state under the effect of anaerobic bacteria, and sulphur in a high oxidation state is reduced into sulphur in a reduced state, so that the minerals of realgar, orpiment and the like are formed again; and meanwhile, a large amount of iron is reduced to form iron pyrite, arsenopyrite, pyrrhotite and other minerals with the low solubility, and the heavy metals of Pb<2+>, Zn<2+>, Cu<2+>, Hg<2+>, Cd<2+>, Sb<3+> and the like form galena, blende, copper pyrites, cinnabar, greenockite, stibnite and other sulfide minerals with the extremely low solubility, so that mine heavy metal pollution in-situ mineralization restoration is achieved.
Owner:北科蕴宏环保科技(北京)有限公司
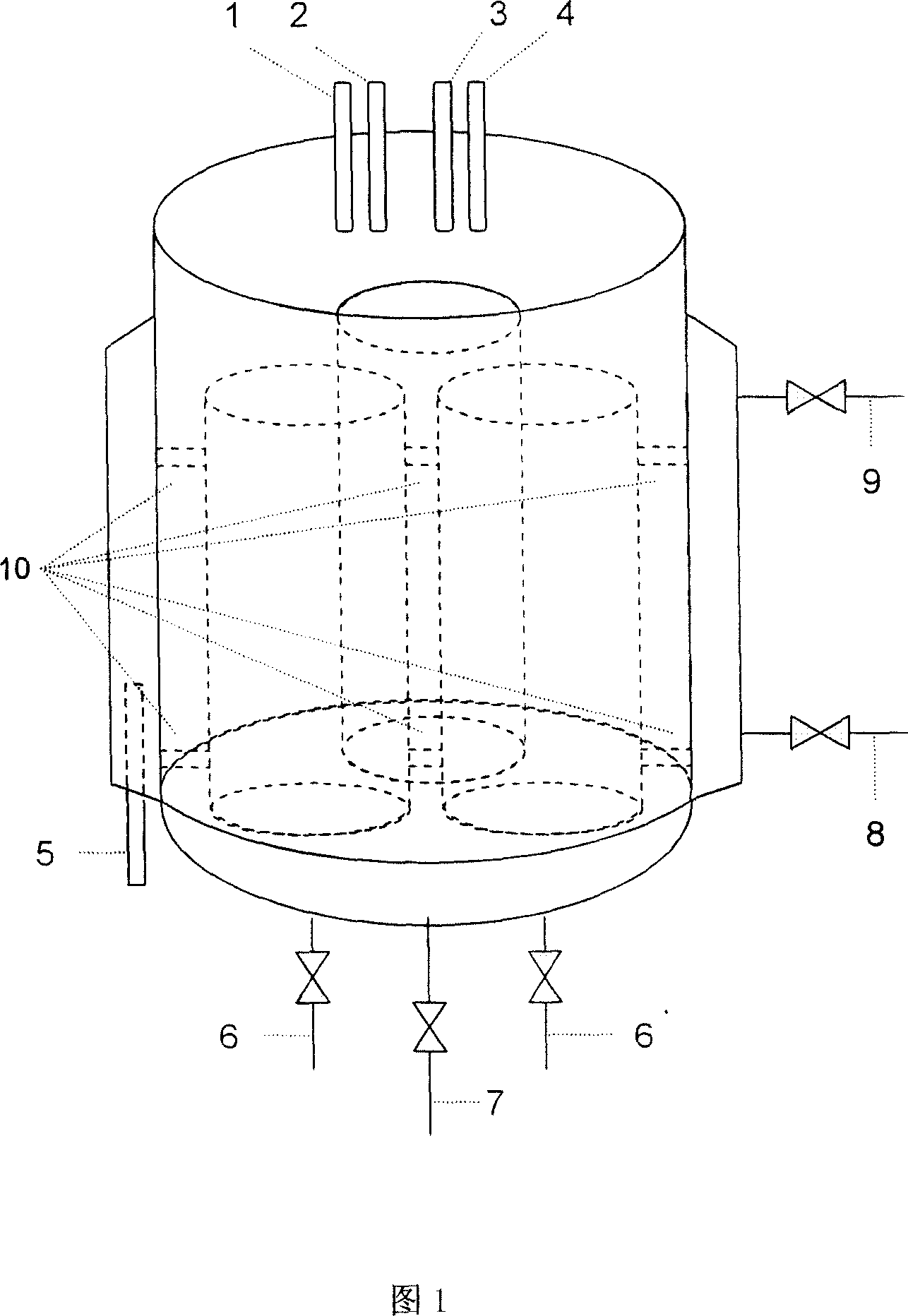
Multiple guide shell gas circulating bioreactor bacteria ore leaching and ore leaching bacteria culture
The invention discloses a new type immersion ore bioreactor to proceed biological oxidation of sulfide mineral in biological metallurgical technical domain, which is characterized by the following: adopting internal ring gas-flow elevating type reactor; using compressed air as liquid hoisting power to accelerate the macrography mixing of material and mass transfer course; and providing oxygen for growth of microbe and biological oxidation of mineral; lightening the attrition and damage of microbiological thallus caused by ore sand greatly; comparing to traditional stirring type immersion ore bioreactor; composing by cylindrical tank and bottom of tank; assembling three built-in type guild shell to decrease the height of reactor; making the high diameter ratio (H / D) reach 1-1.5 range of the reactor. This invention possesses merits of soft stirring, small hurt for cell, good mass transfer effect and simple structure, which compared to traditional method.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Iron pyrite inhibitor for use under low-alkalinity condition
The invention discloses an iron pyrite inhibitor for use under a low-alkalinity condition. The iron pyrite inhibitor consists of the following components in parts by weight: 40-50 parts of sodium thiosulfate, 40-50 parts of citric acid and 5-15 parts of polyacrylamide, wherein the polyacrylamide is hydroxyl-containing low molecular polyacrylamide of which the molecular content is 400-600. The inhibitor is prepared by using a method comprising the following steps of weighing sodium thiosulfate, citric acid and polyacrylamide; uniformly mixing to obtain 1-5 percent by weight of aqueous solution; and stirring. The iron pyrite inhibitor is used for selectively inhibiting iron sulfide minerals under a low-alkalinity condition, has good inhibition effects on minerals such as pyrite, magnetic pyrite and the like, has the advantages of stable performance, small using amount, low cost and environment friendliness, can be widely applied to sulfide ore dressing of copper, copper lead, copper zinc, lead zinc, copper lead zinc, gold and the like, and contributes to effectively increasing the scoring indexes of copper, lead, zinc, metal minerals and pyrite, effectively enhancing the flotation separation effect of multi-metal sulfide minerals and increasing the recovery rate of associated gold and silver.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
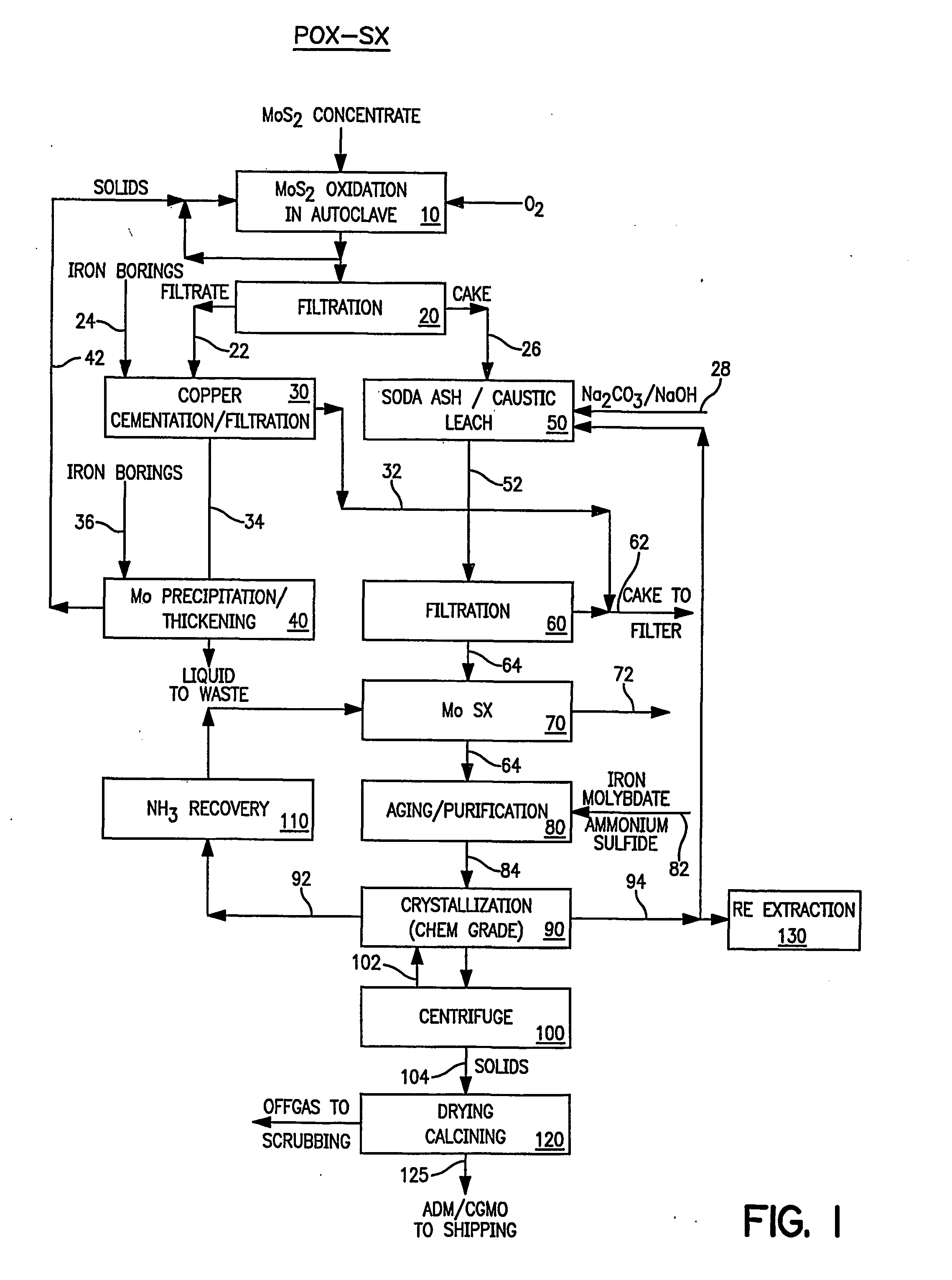
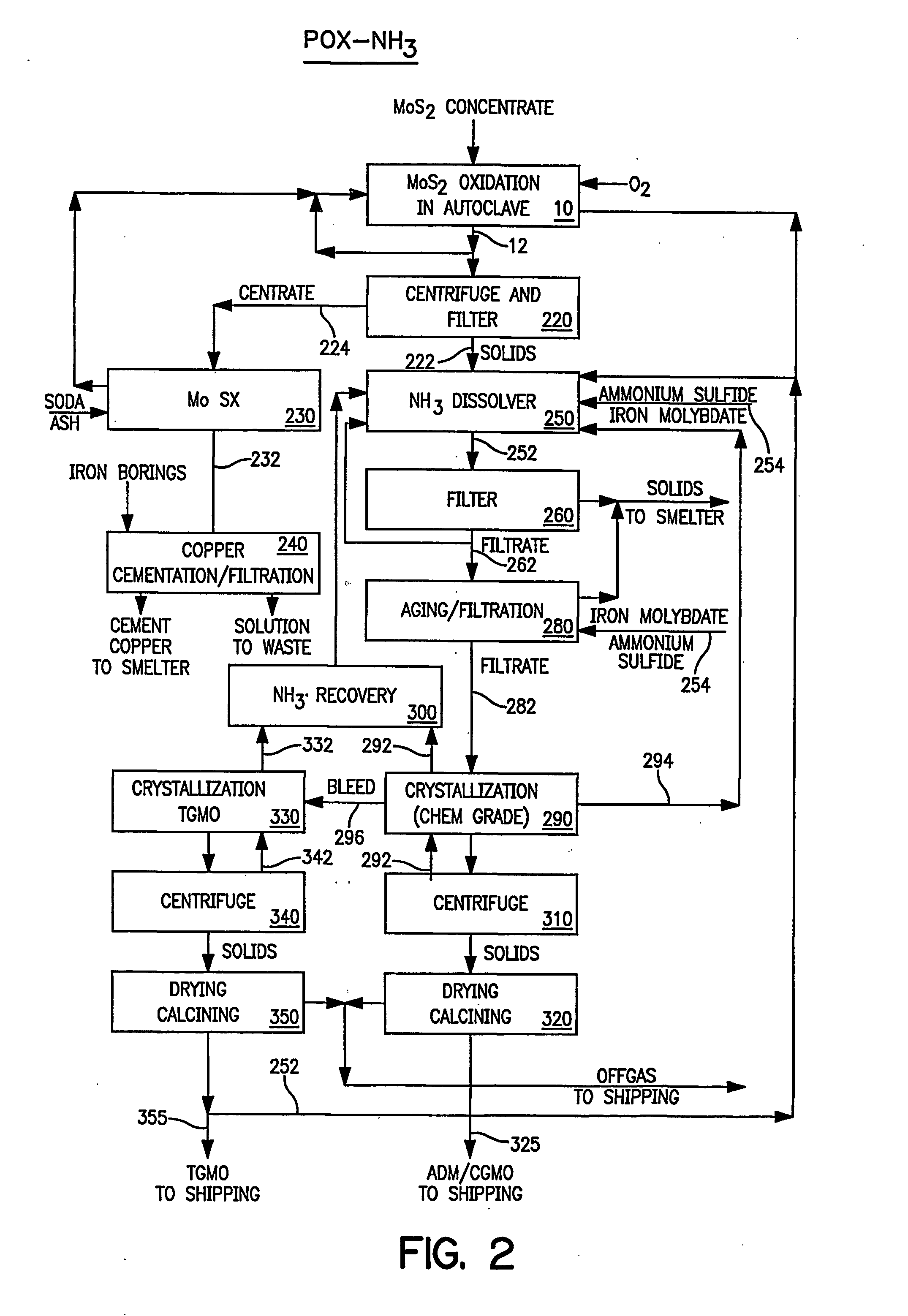
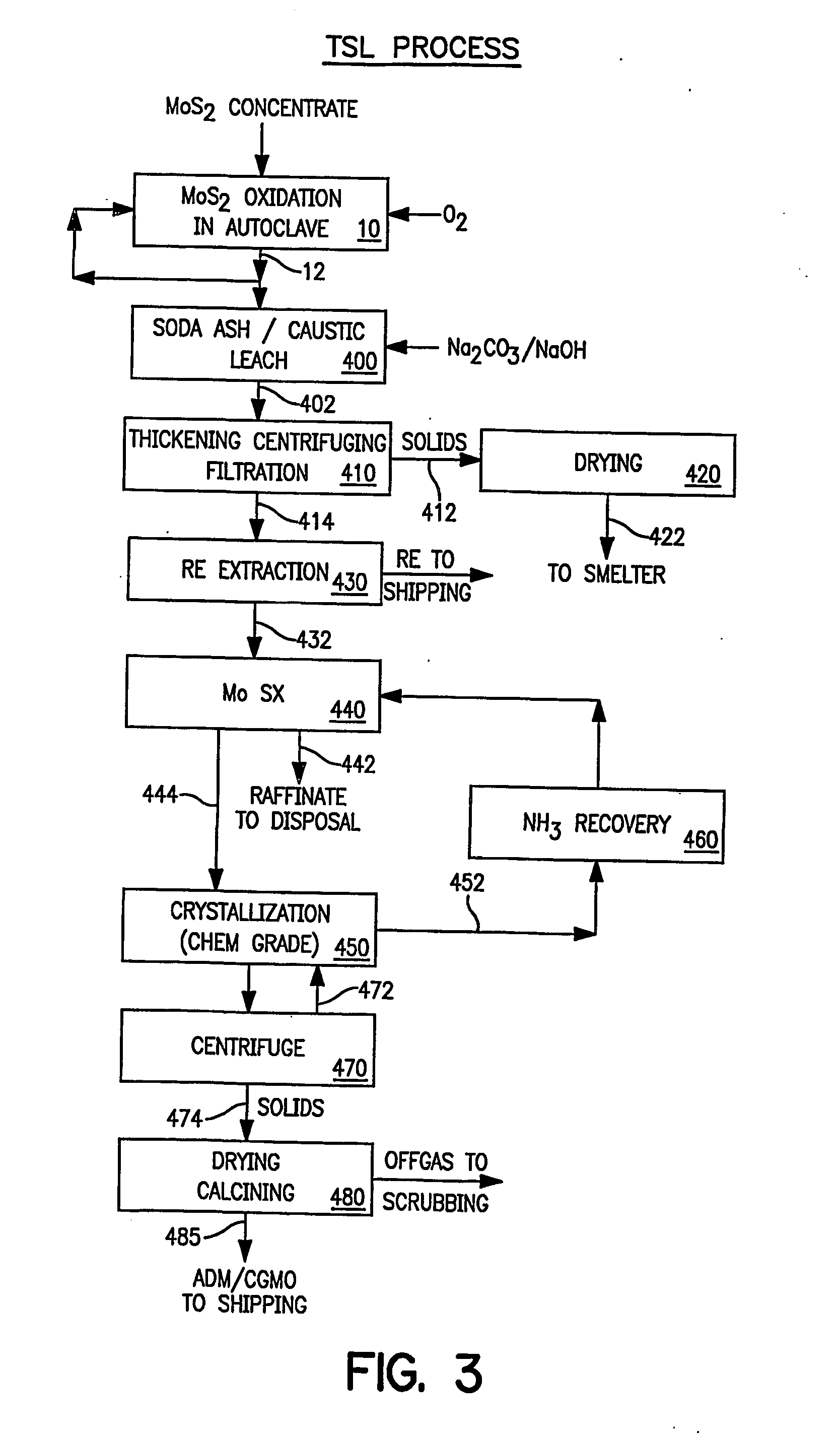
Production of pure molybdenum oxide from low grade molybdenite concentrates
InactiveUS20050019247A1High purityValue maximizationOxide/hydroxide preparationMolybdeum compounds preparationProcess chemistryFiltration
High purity ammonium dimolybdate or molybdenum oxide is produced by the pressure oxidation of low grade molybdenite concentrates or molybdenum intermediates. The process entails nearly complete oxidation of the sulfide minerals while optimizing the process chemistry and autoclave conditions to solubilize as little of the molybdenum values as possible. The autoclave discharge 12 is then subjected to a leaching step, either an alkaline leach 50, 400 or ammonium leach 250 process, before or after a liquid / solid separation step 20, 220, 410. The solution is then subjected to (a) filtration 60, 410, solvent extraction 70, 440, crystallization 90, 450, and calcination 120, 480 or (b) filtration 260, 280, crystallization 290, and calcination 320 to produce a product suitable for chemical-grade molybdenum oxide 125, 325, 485.
Owner:BALLIETT ROBERT W +6
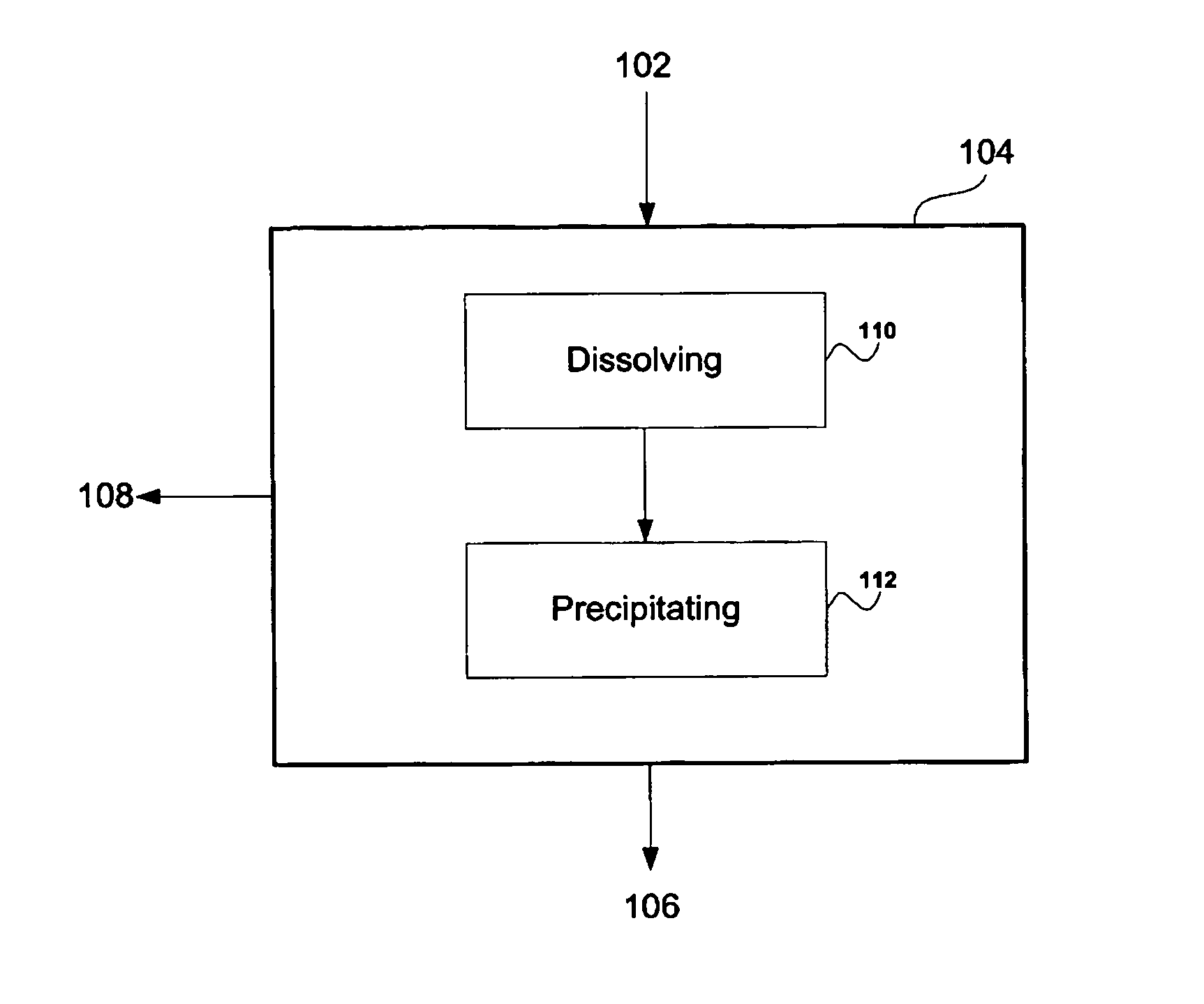
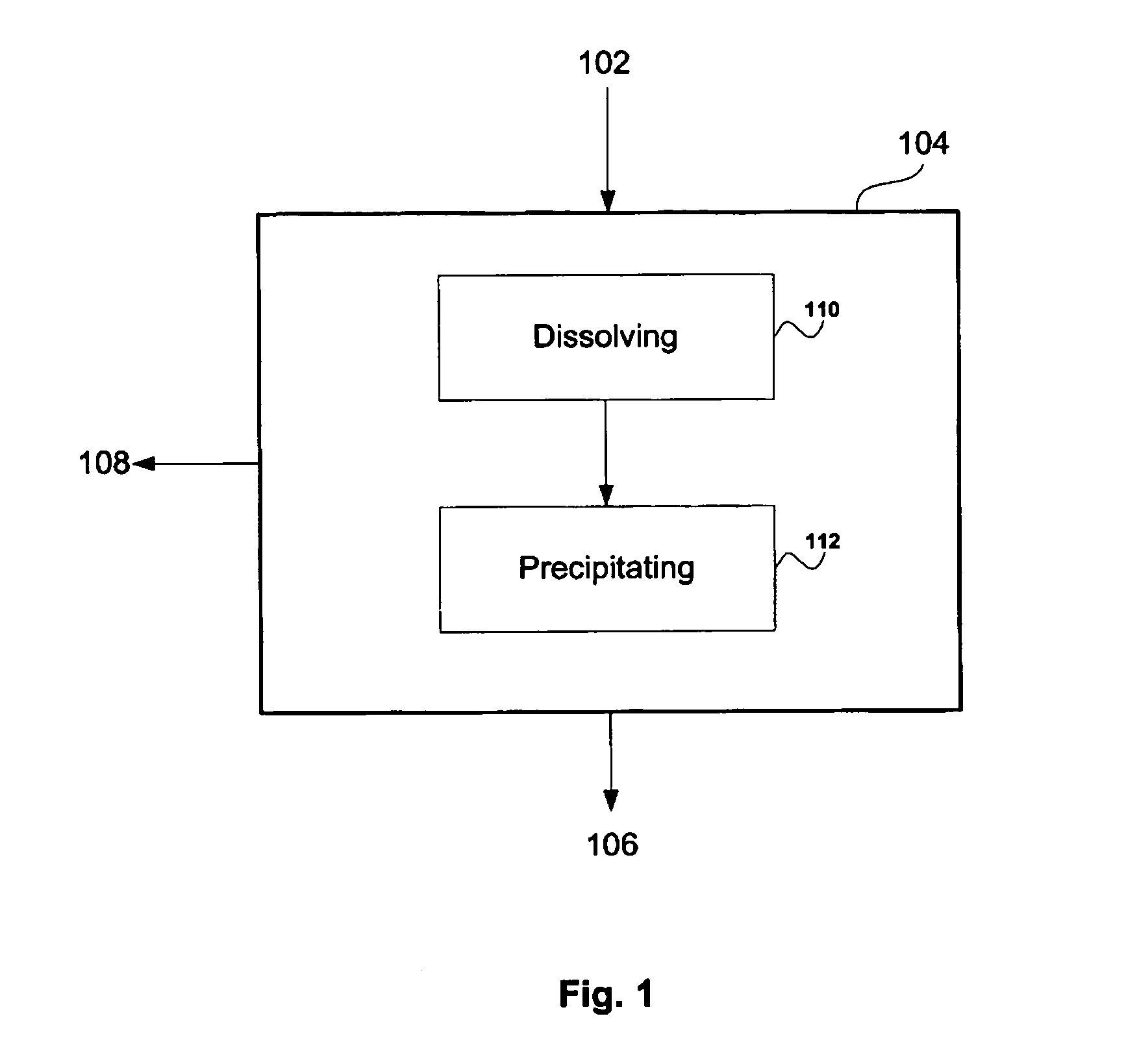
Flotation processing including recovery of soluble nonferrous base metal values
A method of flotation processing ores and other mineral materials containing soluble nonferrous base metal and sulfide minerals involves dissolving the soluble nonferrous base metal and precipitating the soluble nonferrous base metal in the form of a floatable precipitate that is collected as part of a sulfide concentrate. The use of an oxygen-deficient flotation gas, such as nitrogen gas, promotes the precipitation of the floatable precipitate. A method for removing dissolved nonferrous base metal from solution involves contacting the solution with a particulate containing sulfide minerals under conditions promoting precipitation of the nonferrous base metal onto the sulfide mineral.
Owner:NEWMOST USA
Comprehensive recovering process of multimetal sulfide mineral
ActiveCN100999782AHigh recovery rateImprove resource utilizationPhotography auxillary processesMagnetic separationResource utilizationHydrometallurgy
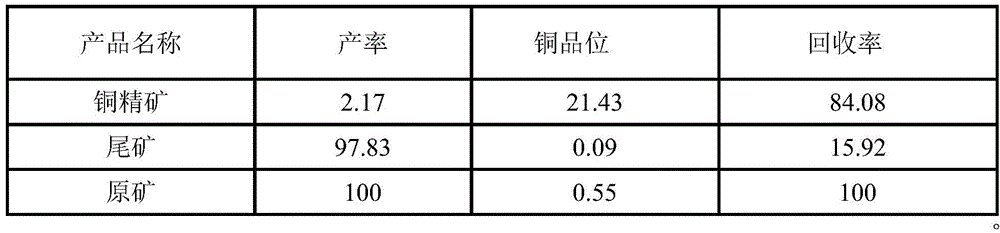
The present invention discloses one kind of comprehensive polymetal sulfide mineral recovering process. The recovering process combines a roasting process after adding proper amount of lime and potassium chloride into raw mineral and a wet metallurgical process to recover Cu, Zn, Co, S, Fe, etc from the polymetal sulfide mineral. It can obtain electrolytic copper, electrolytic zinc, electrolytic cobalt, potassium sulfate, iron ore concentrate and other products, and has Cu and Zn recovering rate over 94 % and 92 % separately, simplified production process, raised comprehensive metal recovering rate and high resource utilization rate.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
Beneficiation method of lead-zinc oxide mine difficult to beneficiate
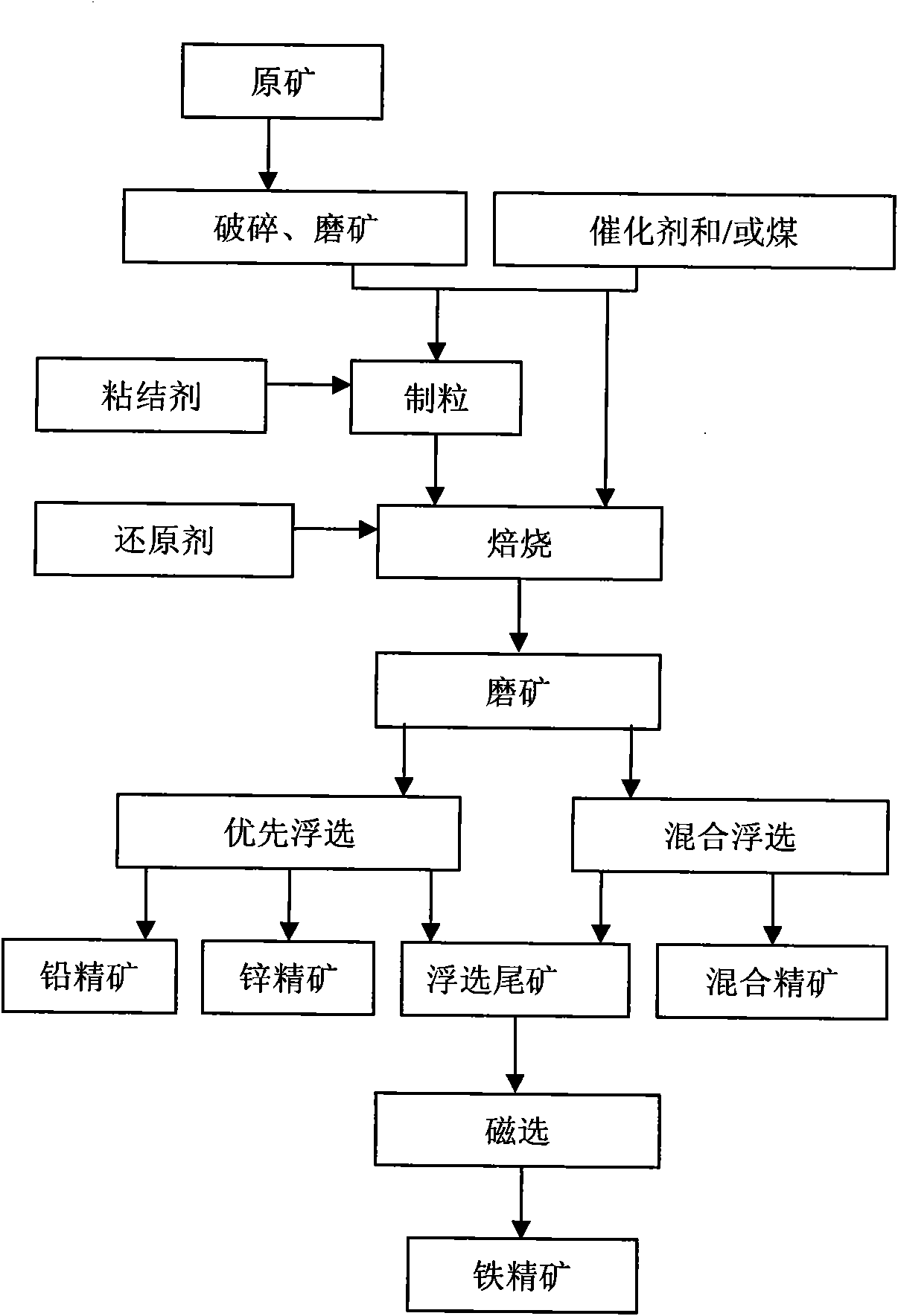
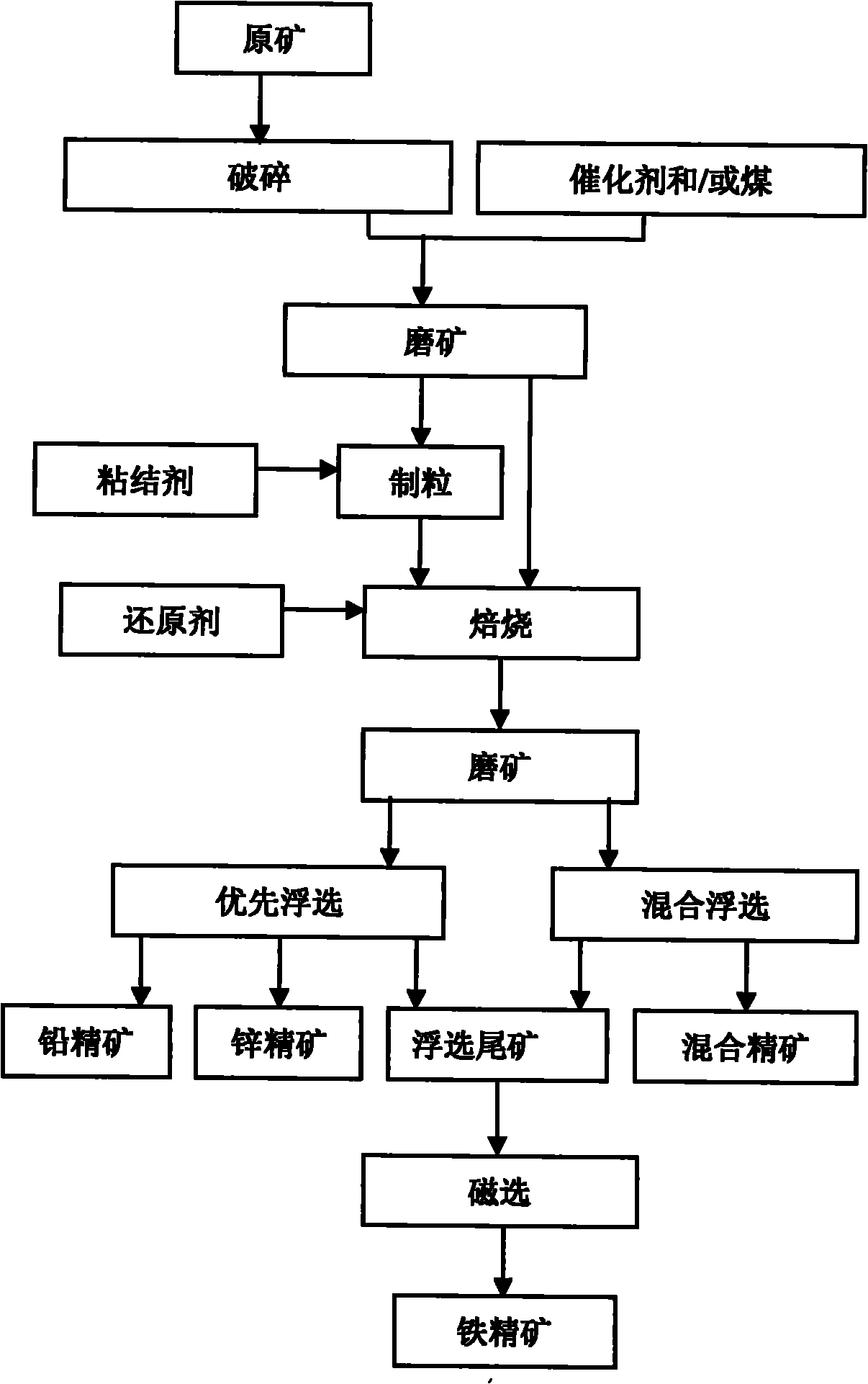
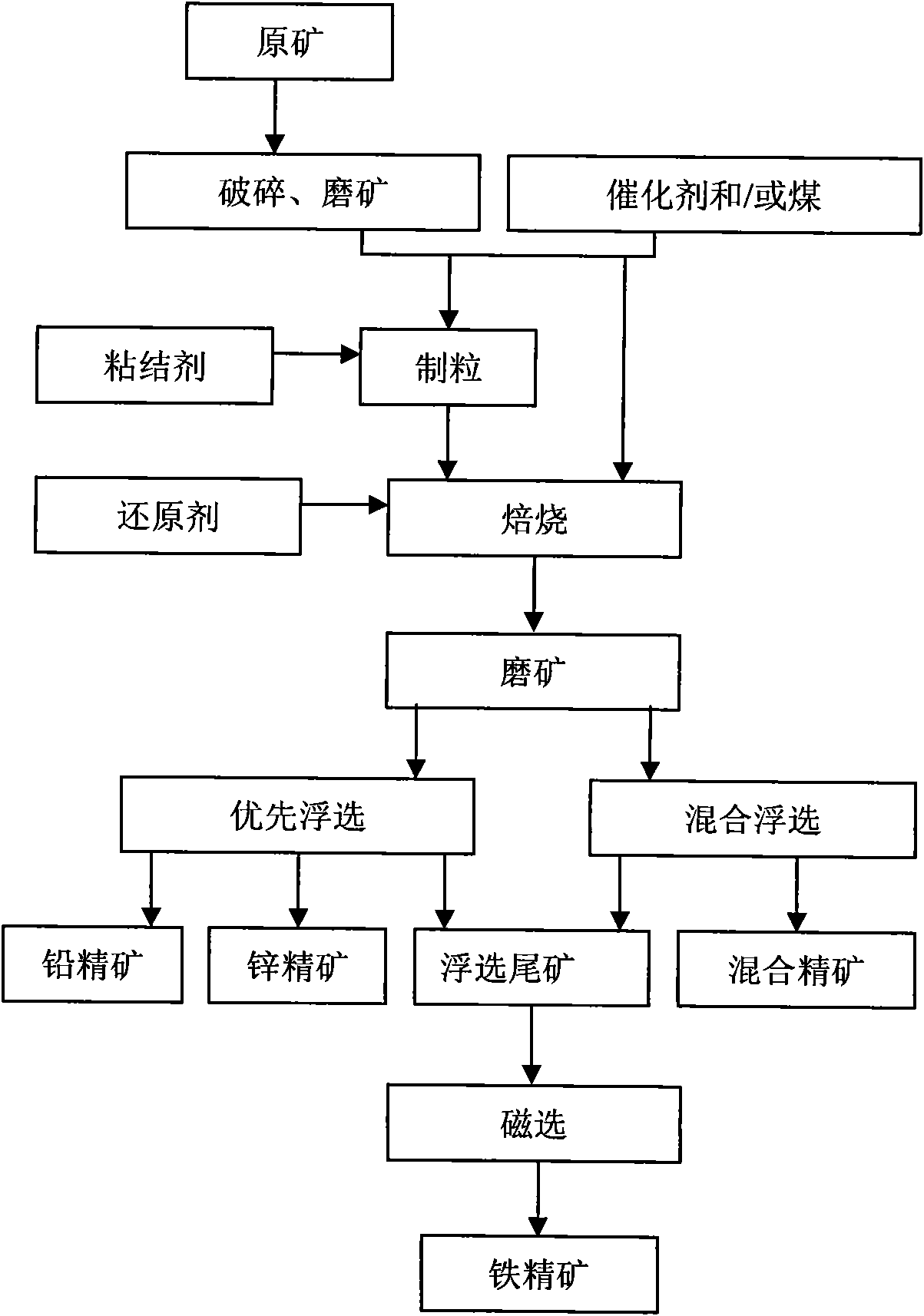
ActiveCN101934246AImprove resource utilizationSimplify subsequent processingWet separationSulfide mineralsDiiron Trioxide
The invention relates to a beneficiation method of a lead-zinc oxide mine difficult to beneficiate, which comprises the steps of crushing ores of the lead-zinc oxide mine difficult to beneficiate, grinding ores, uniformly mixing the ores, a catalyst and coal and then roasting; or crushing the ores of the lead-zinc oxide mine difficult to beneficiate, grinding the ores with the catalyst and the coal, and roasting so as to transform the lead-zinc oxide ores difficult to beneficiate into sulfide minerals easy to float as well as weak-magnetism iron trioxide minerals into strong-magnetism ferroferric oxide; floating by adopting a method for floating lead-zinc sulfate minerals to obtain lead concentrate, zinc concentrate or lead-zinc concentrate; and recovering iron ore concentrate by carrying out a magnetic method on tailings left after beneficiating lead-zinc minerals. The method can synthetically recover useful elements in the ores of the lead-zinc oxide mine difficult to beneficiate and has the characteristics of high concentrate grade and high recovery rate.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
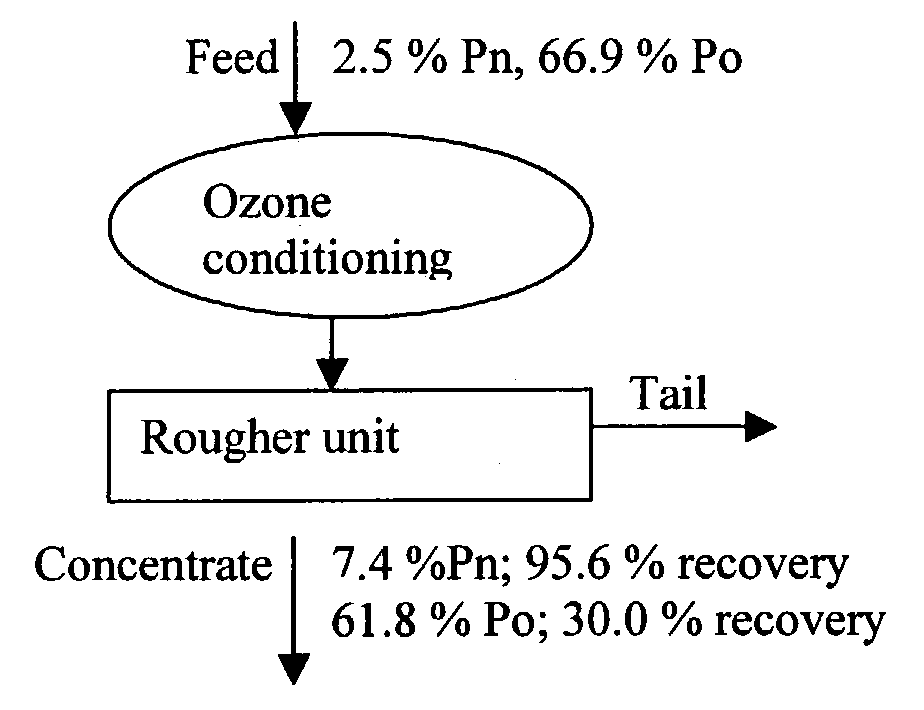
Use of ozone to increase the flotation efficiency of sulfide minerals
The use of ozone during certain stages of metal separation by flotation degrades certain collectors that are absorbed on the particle surface, as well as the collectors and frothers in the liquid slurry. As a result, the mineral particle has a fresh surface and new chemical reagent(s) can be added in the subsequent flotation step(s). Also since ozone oxidizes the iron sulfide particles faster than the other mineral particles, depending upon the duration of treatment, the ozone concentration, and the kg O3 / ton consumed by the treated ore, the surface of the iron sulfide particles may be partially or even totally oxidized, thus allowing better separation. As a consequence, the iron content is decreased, and the grade of the mineral value such as zinc, copper, and nickel increases. Also, sulfide emissions during heat treatment or further processing of the minerals are decreased due to decrease iron sulfide content.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
Beneficiation method for improving ore dressing recovery percentage of copper sulfide mineral hard to dispose
ActiveCN106269287AEfficient use ofNo pollution in the processFlotationSulfide mineralsCopper sulfide
The invention relates to a beneficiation method for improving the ore dressing recovery percentage of copper sulfide ore hard to dispose. By applying the method, flotation separation of copper sulfide mineral from hydrophobic silicate gangue talc and ferric sulfide mineral pyrite can be realized, and the preparing technical indexes of copper sulfide mineral can be improved. The method comprises the operations of ore grinding, size mixing, rougher flotation, scavenging and selection. According to the invention, a combined inhibitor TYZ01 has a selective inhibiting effect on talc and pyrite and cannot affect the flotation of copper pyrites, and a combined collecting agent TBS02 has strong collecting capability on copper pyrites; by using the two combined reagents, efficient utilization of copper sulfide mineral containing hydrophobic silicate gang and pyrite can be realized; proved by practices, by using the beneficiation method disclosed by the invention, good selection indexes can be obtained; and the adopted reagents, calcium lignosulfonate and Arabic gum, are organic macromolecule reagents, thus being easy to degrade and having no pollution to the environment.
Owner:苏尼特右旗朱日和铜业有限责任公司
Separation and extraction method for nickel and cobalt in low-grade sulfide mineral bioleaching agent through synergistic extraction
InactiveCN103184337ARealization of iron removalReduce entrainment lossProcess efficiency improvementSulfide mineralsCobalt
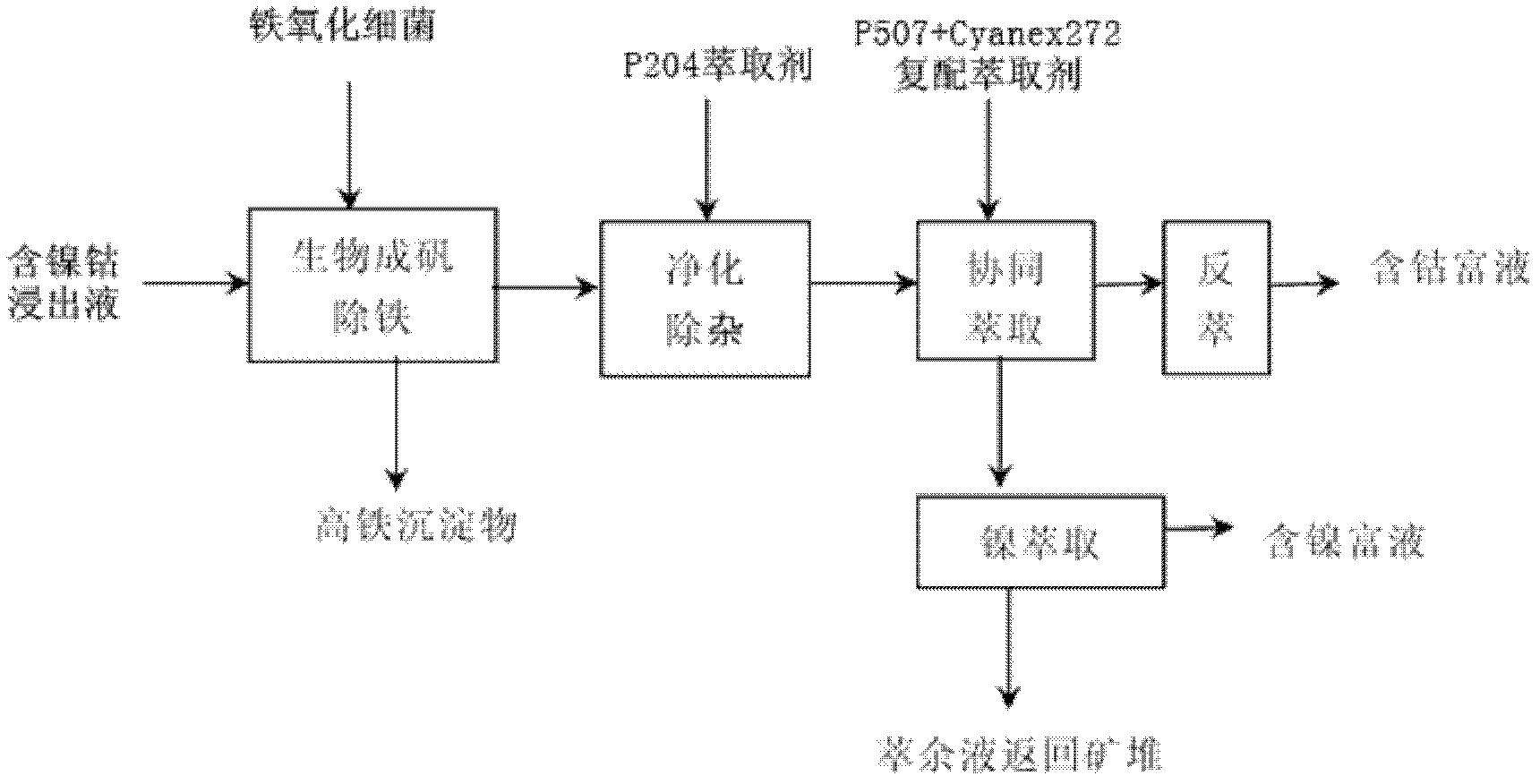
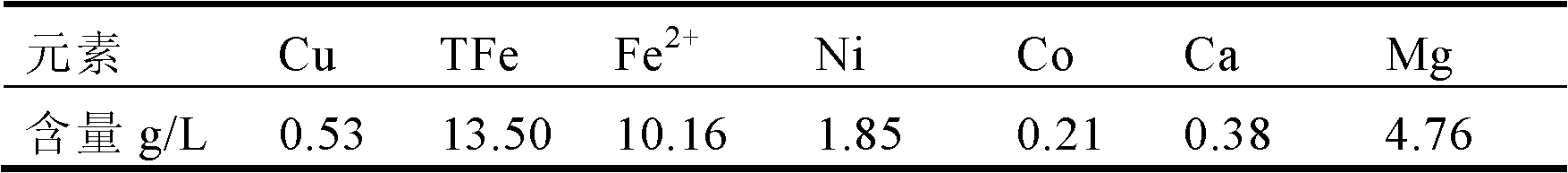
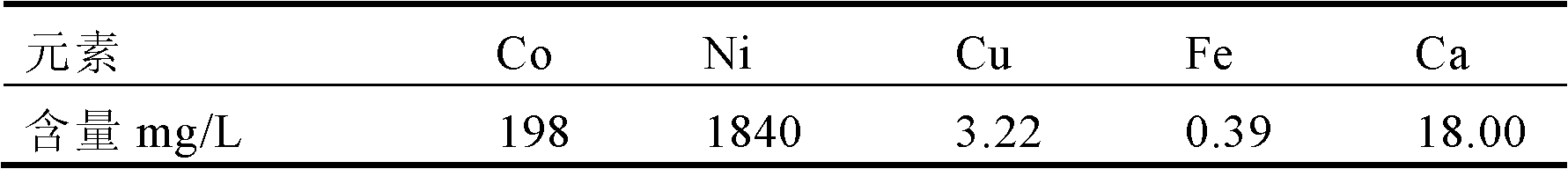
The invention provides a separation and extraction method for nickel and cobalt in a low-grade sulfide mineral bioleaching agent through synergistic extraction. The separation and extraction method comprises the following steps: adopting a biological alum precipitation method to perform iron removing on the nickel-cobalt-containing leaching agent, adding iron-oxidizing bacteria under the condition that the pH is 1.8 to 2.0, utilizing oxidation of the bacteria to oxidize ferrous ions in the leaching agent into ferric ions, and enabling the ferric iron to form jarosite-class precipitation; adopting the extraction agent P204 to perform impurity removing on the residual impurities in the leaching agent after iron removing to remove impurities including calcium, magnesium and the like; and using the compound extraction agent containing extraction agent P507 and Cynaex 272 to perform synergistic extraction on the leaching agent after impurity removing, standing for phase splitting for 30 min after extraction, and adding sulfuric acid into the organic phase and performing reverse extraction to extract out cobalt, so as to realize separation of nickel and cobalt through synergistic extraction. The method provided by the invention can reduce neutralization cost of pH value adjustment before extraction of the leaching agent, and omits the pH adjusting procedure when subsequent extraction raffinate returns back to the mineral pile, so as to simplify the technological process, and reduce the neutralization cost and nickel and cobalt entrainment losses caused in the neutralization process.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Soil improver and method for improving soil
InactiveCN105838381AAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesClay mineralsSodium Bentonite
The invention relates to a soil conditioner and a method for improving soil. The soil conditioner comprises mineral powder A, modified powder B, modified powder C and a modified solvent, wherein the mineral powder A is selected from sulfide mineral powder, oxide mineral powder, clay One or more of mineral powders; modified powder B is selected from one or more of bentonite, persulfate compound, kaolin; modified powder C is selected from red mud, DTC-chelating agent, iron manganese oxide One or more of the mineral powders, the improving solvent is selected from one or more of humic acid, organic solvents, and reactive colloids; the soil improving agent can adjust the pH value of the soil and the dissolved products of environmental mineral materials and heavy metal ions The chemical immobilization effect and the interaction with soil microorganisms permanently fix the ionic heavy metals in the soil in the newly formed soil minerals, inhibit the absorption of heavy metal ions by crops, and achieve the purpose of reducing the heavy metal content of crops.
Owner:ZHONGDA TESTING (HUNAN) CO LTD +1
Method for extracting copper for copper containing sulfurized ore
InactiveCN1358871ALow leaching temperatureRelieve pressureProcess efficiency improvementSlagSulfide minerals
The method for extracting copper from copper-bearing sulfide mineral is characterized by leaching copper-bearing mineral under the condition of introduction of oxygen and in the presence of sulfuric acid and chlorine ion, the liquid-solid ratio of leaching-out liquor is 1-8:1, primary concentration of sulfuric acid is 5-70 g / L, leaching total pressure is 200-1000 kPa, partial pressure of oxygen is 100-800 kPa, temp. is 100-130 deg.C and time is 1-4 hr. The leaching temp. and pressure of said method are low, its selectivity is good, the pyrite can not be oxidated, and the harmful impurity, for example arsenic, can be solidifed in arsenic-ion slag, so that it is a process friendly to environment.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY +1
Wet process sulfide mineral leaching-out method
InactiveCN1456692AFast leachingMild reaction conditionsProcess efficiency improvementHypochloritePerchlorate
A process for leaching sulfide ore by full-wet method includes such steps as mixing the sulfide ore with additive, adding water, reacting at 10-150 deg.C while controlling the final pH to 0-14, and oxidizing by adding oxidizing agent. Said ore is the sulfuride of Cu, Ni, Co, or Zn. Said additive is the water-soluble compound of Cu, Pb, and Co, etc. Said oxidizing agent may be air O2, H2O2, etc. Its advantage is high leaching speed.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Amino methyl xanthogenic acid cyanogen ethyl ester compound and preparation method as well as collector thereof
InactiveCN102464599ALight weightReduce solubilityOrganic chemistryFlotationSolubilityMineral flotation
The invention relates to an amino methyl xanthogenic acid cyanogen ethyl ester compound and a preparation method thereof; and the compound can serve as a metallic mineral flotation collector to be used for recycling sulphide ore or oxidized ore containing metals in foam flotation. The aim of the invention is to provide the amino methyl xanthogenic acid cyanogen ethyl ester compound and the preparation method thereof. The other aim of the invention is to provide the amino methyl xanthogenic acid cyanogen ethyl ester to serve as a new sulfide mineral or oxidized mineral flotation collector and an application method of the flotation collector so as to enrich the variety of the xanthogenic acid cyanogen methyl ester collector and enlarge the range of selection of a flotation agent. The amino mthyl xanthogenic acid cyanogen ethyl ester compound synthesized by the method is generally of oily liquid, has special smell and little solubility and is slightly lower than water in specific gravity; the product is not needed to be purified and separated; and the mixed product containing impurities has better ore dressing and collecting performance for the metallic minerals. The preparation process is simple, efficient and economic; and the crude product can be used as the flotation collector; and the conversion yield of the crude product is in the range of 65%-100%.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
Beneficiation method for improving recovery rate of low-grade zinc oxide ore
The invention relates to a beneficiation method for improving the recovery rate of low-grade zinc oxide ore, which comprises the following steps: washing ore at normal temperature to remove impurities; mixing and selecting oxide minerals and sulfide minerals; and carrying out zinc rough selection and zinc scavenging by using modified alkylamine zinc oxide chelating collector ZJ-5. The invention has the characteristics of easy purchase and low cost of the collector ZJ-5, short process flow, low cost of beneficiation cost, wire range of application, high grade and recovery rate of zinc ore concentrate and the like and is applicable to the low-grade zinc oxide ore.
Owner:新疆紫金锌业有限公司
Nonstirred bioreactor for processing refractory sulfide concentrates and method for operating same
InactiveUS6107065ASatisfies needSolvent extractionContaminated soil reclamationSulfide mineralsCarbonate
A method of biooxidizing sulfide minerals in a nonstirred bioreactor is provided. According to the disclosed method, a concentrate of sulfide minerals is coated onto a plurality of substrates, such as coarse ore particles, lava rock, gravel or rock containing a small amount of mineral carbonate as a source of CO2 for the biooxidizing bacteria. After the sulfide minerals are coated or spread onto the plurality of substrates, a heap is formed with the coated substrates or the coated substrates are placed within a tank. The sulfide minerals on the surface of the plurality of coated substrates are then biooxidized to liberate the metal value of interest. Depending on the particular ore deposit being mined, the sulfide mineral concentrates used in the process may comprise sulfide concentrates from precious metal bearing refractory sulfide ores or they may comprise sulfide concentrates from metal sulfide type ores, such as chalcopyrite, pyrite or sphalorite. The distinction being that in the former, the metal of interest is a precious metal occluded within the sulfide minerals, whereas in the latter, the metal to be recovered is copper, iron, or zinc and is present as a metal sulfide in the sulfide concentrate.
Owner:GEOBIOTICS INC
Nonferrous metal mineral flotation collector with sulfydryl-hydroxamic acidyl structure and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a nonferrous metal mineral flotation collector with a sulfydryl-hydroxamic acidyl structure and a preparation method and application thereof. The flotation collector has both sulfydryl groups and hydroxamic acidyl groups; by taking the flotation collector as a nonferrous metal mineral collector, nonferrous metal minerals in nonferrous metal ores can be efficiently recovered through flotation separation, and therefore the goal that minerals in the form of sulfide and minerals in the form of oxide in the nonferrous metal ores are recovered simultaneously by a single flotation reagent is achieved. A synergistic effect on chelate metal ions exists between the sulfydryl groups and hydroxamic acidyl groups, so adsorption on metal ions on the interfaces of sulfide minerals and the interfaces of oxide minerals in nonferrous metals can be enhanced, and the recovery rate of nonferrous metal minerals in the nonferrous metal ores is greatly increased; the nonferrous metal mineral flotation collector is especially suitable for the metal recovery of mixed minerals containing both the sulfide minerals and the oxide minerals of the nonferrous metals; the recovery process of the nonferrous metals is simple, efficient and workable, and the industrial application requirement is met.
Owner:岳阳中科华昂精细化工科技有限公司
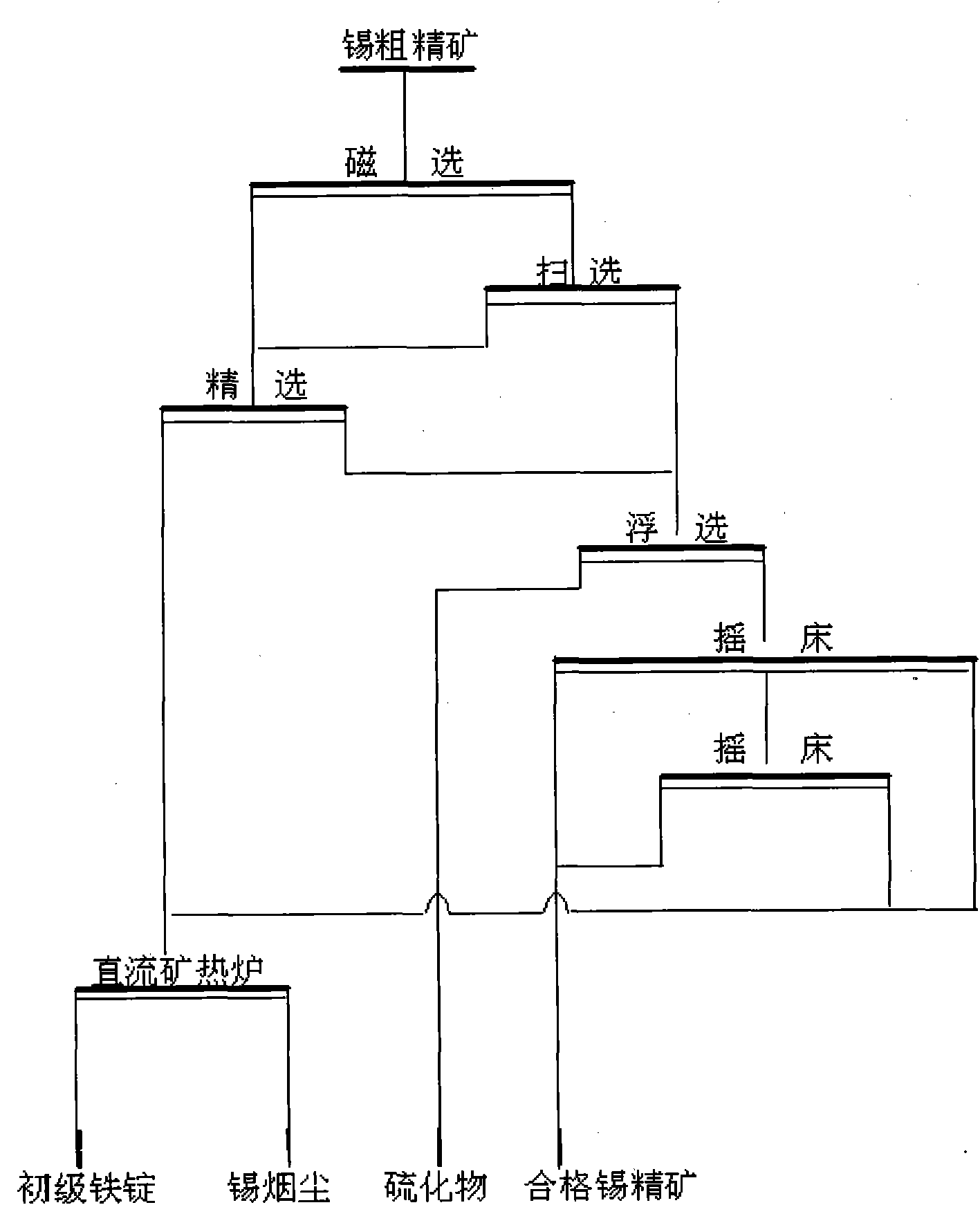
Combined flow treatment method of tin rough concentrate
ActiveCN101792867AHigh recovery rateImprove recovery indicatorsFlotationMagnetic separationTin dioxideResource utilization
The invention relates to a combined flow treatment method of tin rough concentrate, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metal ore-dressing and metallurgy. The process flow comprises the following steps: preparing pulp containing the tin rough concentrate; feeding the tin rough concentrate subjected to the pulp preparation into a magnetic separator for dressing magnetic minerals; making sulfide minerals float out of non magnetic ore by a floating operation; sorting by using a table concentrator to obtain qualified tin rough concentrate and a lean middling ore product; combining a magnetic mineral and lean middling ore obtained by magnetic separation; and treating a mixture by a direct current submerged arc furnace to obtain tin dioxide soot and primary iron ingot. By adopting an ore-dressing and metallurgy combined process flow, the method greatly simplifies the ore-dressing and concentrating process flow. Iron products are treated by the direct current submerged arc furnace, so that not only tin metals of the iron products can be recovered, but also the primary iron ingot can be obtained and iron metals can be recycled while improving the tin recovery rate; and the invention improves the resource utilization rate and has favorable application and popularization prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG
Method of biotreatment for solid materials in a nonstirred surface bioreactor
InactiveUS6410304B2Increase capacitySpeed up the processSolvent extractionSolid waste disposalMicrobial inoculationSulfide minerals
A method of biotreating a solid material to remove an undesired compound using a nonstirred surface bioreactor is provided. According to the method the surface of a plurality of coarse substrates is coated with a solid material to be biotreated to form a plurality of coated coarse substrates. The coarse substrates have a particle size greater than about 0.3 cm and the solid material to be biotreated has a particle size less than about 250 mum. A nonstirred surface reactor is then formed by stacking the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a heap or placing the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a tank so that the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 25%. The reactor is inoculated with a microorganism capable of degrading the undesired compound in the solid material, and the solid material is then biotreated in the surface bioreactor until the undesired compound in the solid material is degraded to a desired concentration. Preferably the thickness of the solid material coating on the plurality of coarse substrates is less than about 1 mm and the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 35%. The process is useful for many different biotreatment processes, including the bioremediation of contaminated soils, the desulfurization of coal, and the biooxidation of refractory sulfide ores and concentrates. In bioremediation applications, the undesired compound is typically an organic compound. In coal desulfurization and refractory sulfide ore biooxidation applications, the undesired compound is sulfide minerals.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS LLC (US)
Beneficiation method for separating copper-nickel sulfide ore from serpentine gangue
ActiveCN105413877AIncrease buoyancyWeaken heterogeneous condensationFlotationPyrophosphateSulfide minerals
The invention relates to a beneficiation method for separating copper-nickel sulfide ore from serpentine gangue. The beneficiation method comprises the following steps: when the copper-nickel sulfide ore is roughly concentrated, a polymer reagent poloxamer which can be adsorbed onto the surface of sulfide mineral through hydrophobic interaction but cannot be adsorbed onto the surface of the serpentine gangue is added; ore pulp is dispersed through the steric hindrance of the polymer reagent, the heterocoagulation of serpentine and sulfide minerals is eliminated, the inhibiting effect of serpentine on the sulfide minerals is reduced, and the recovery rate of rough concentration of the copper-nickel sulfide ore containing serpentine is increased; for rough copper-nickel sulfide concentrate obtained through rough concentration, regulators sodium pyrophosphate and carboxymethyl cellulose are added to further disperse and inhibit gangue minerals; meanwhile a collector is added before the regulators are added, so that the collector is adsorbed onto the surfaces of sulfide minerals to protect the sulfide minerals; the selective inhibition to the gangue minerals is realized, and therefore the concentrate grade is increased. The beneficiation method solves the problems that the reagent dosage is large, valuable minerals are inhibited and tailings hardly sedimentate in the traditional method.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com