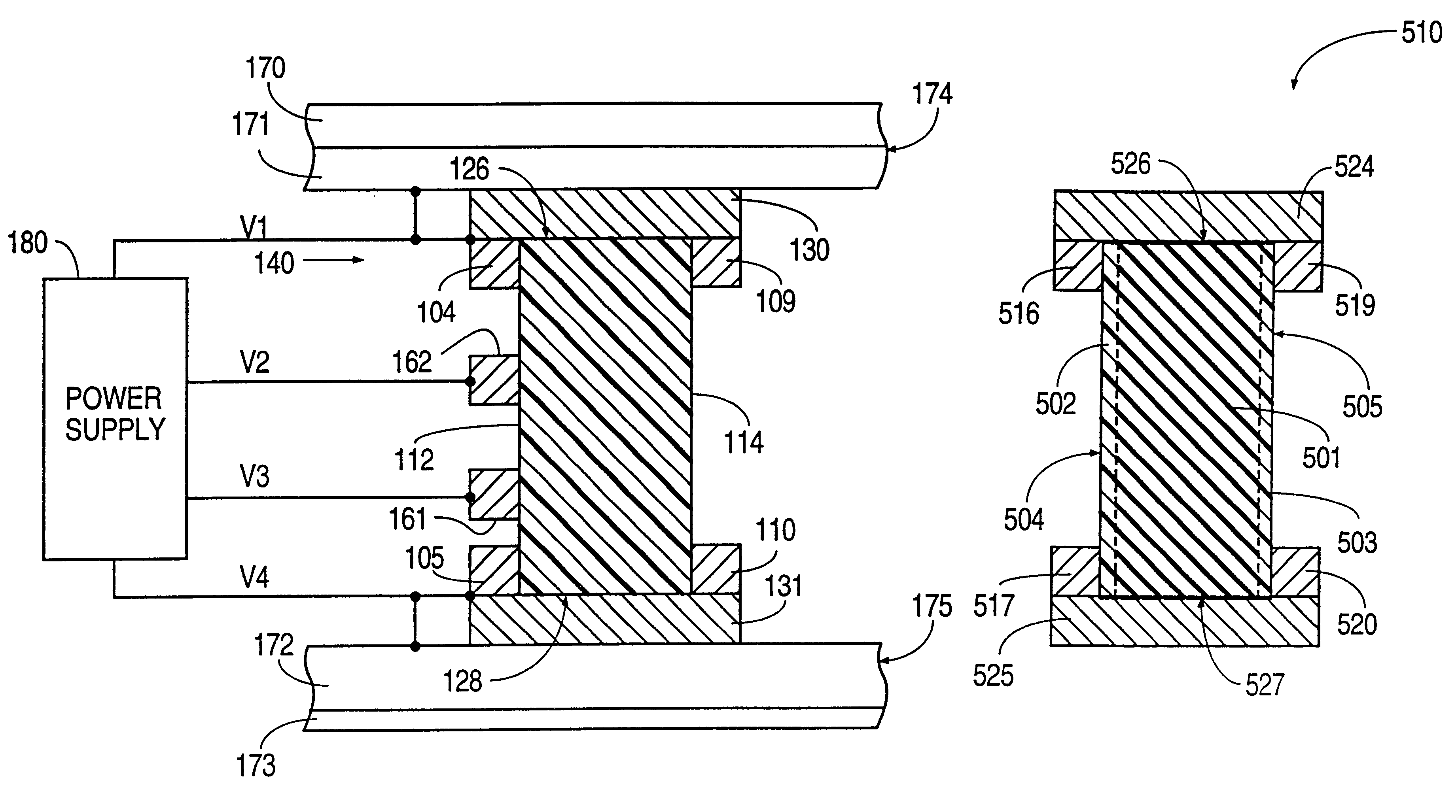
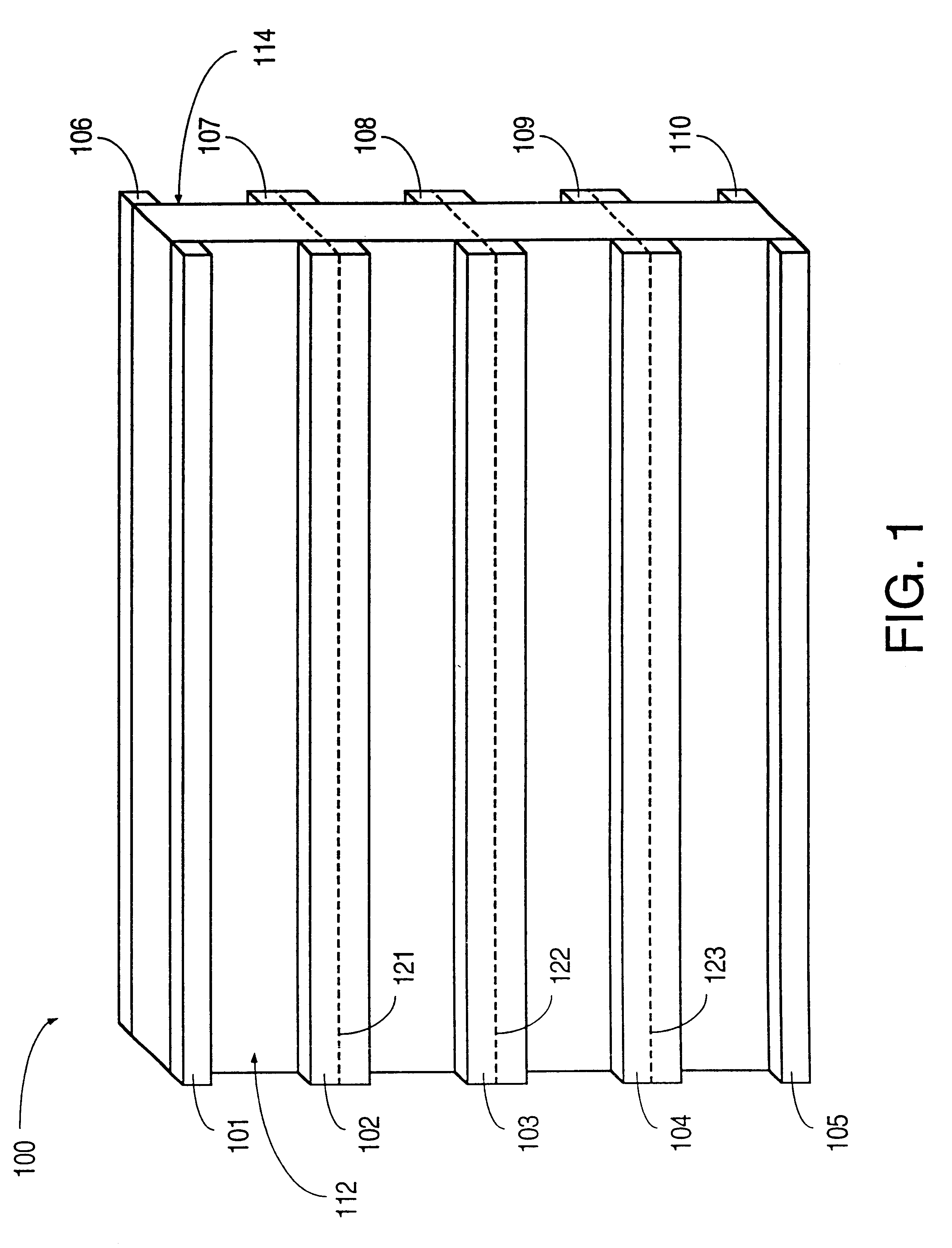
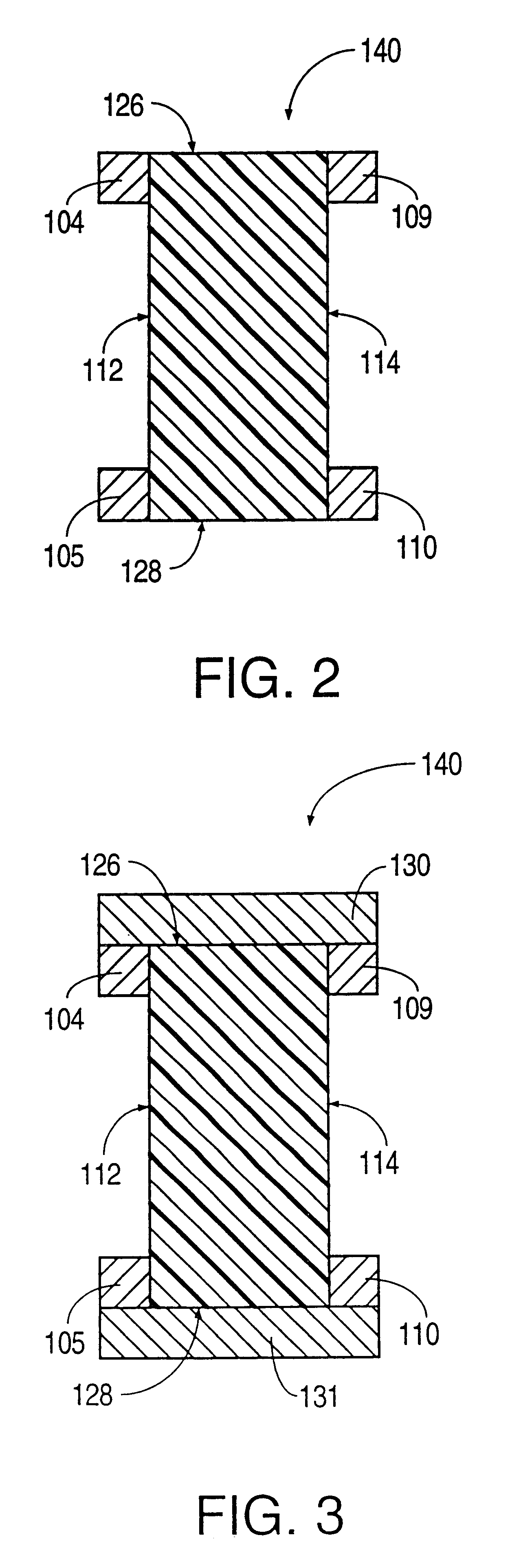
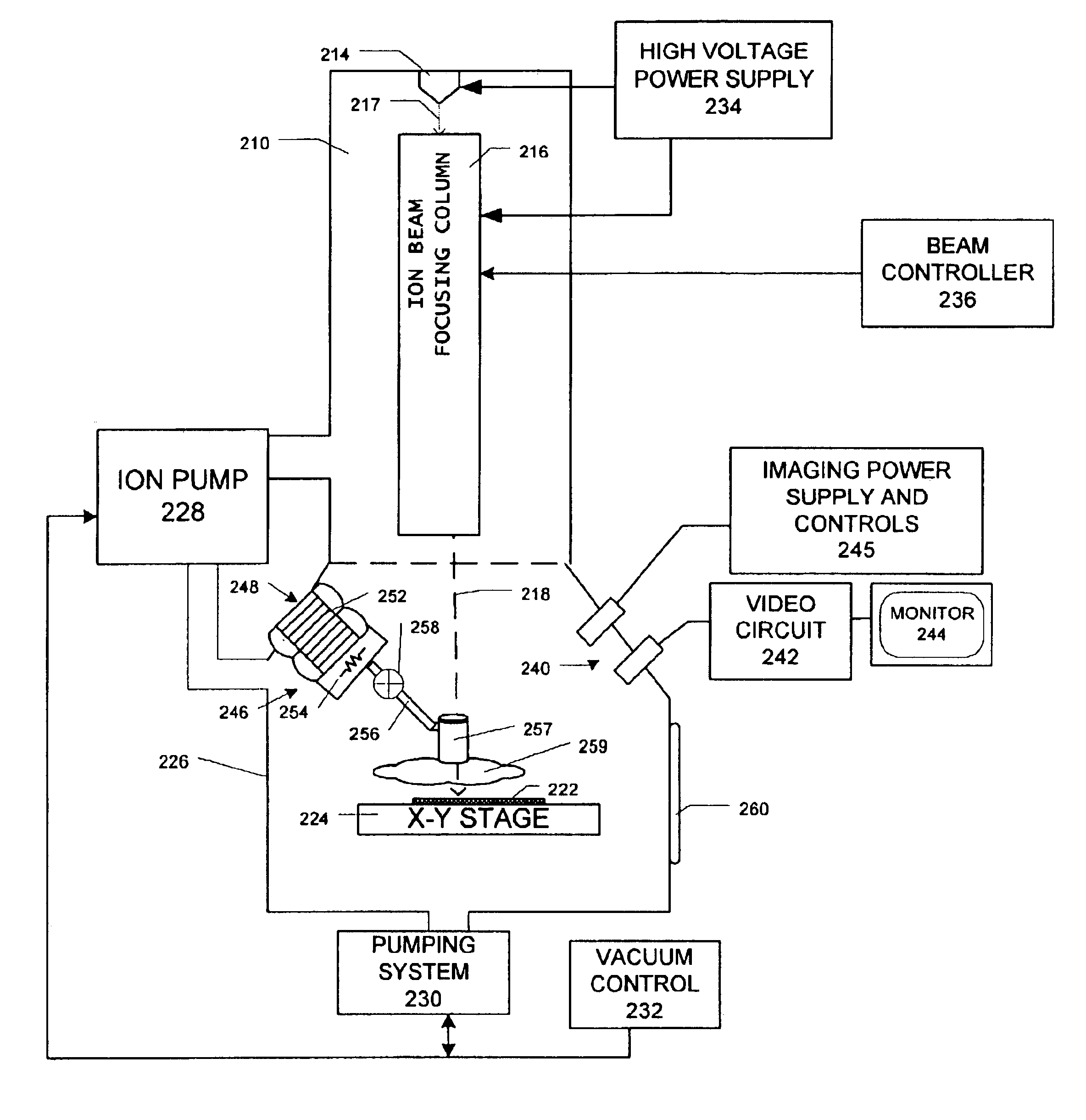
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
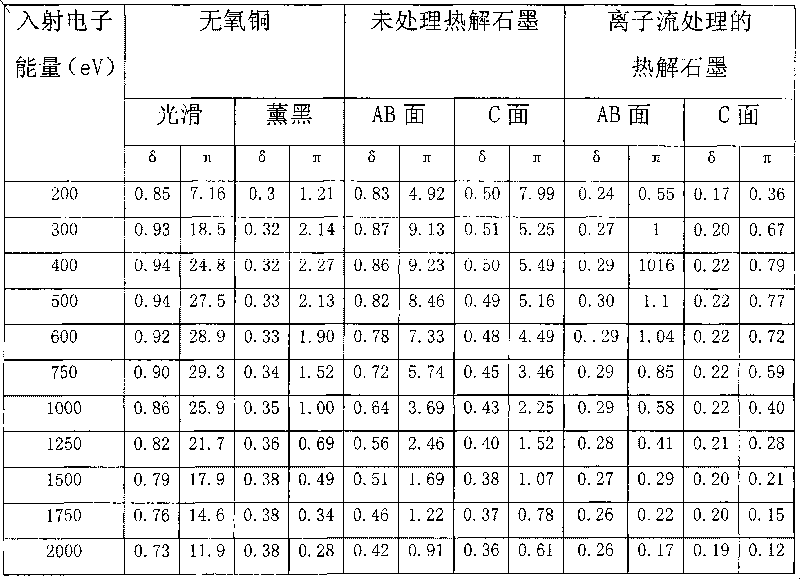
198 results about "Secondary electron emission coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
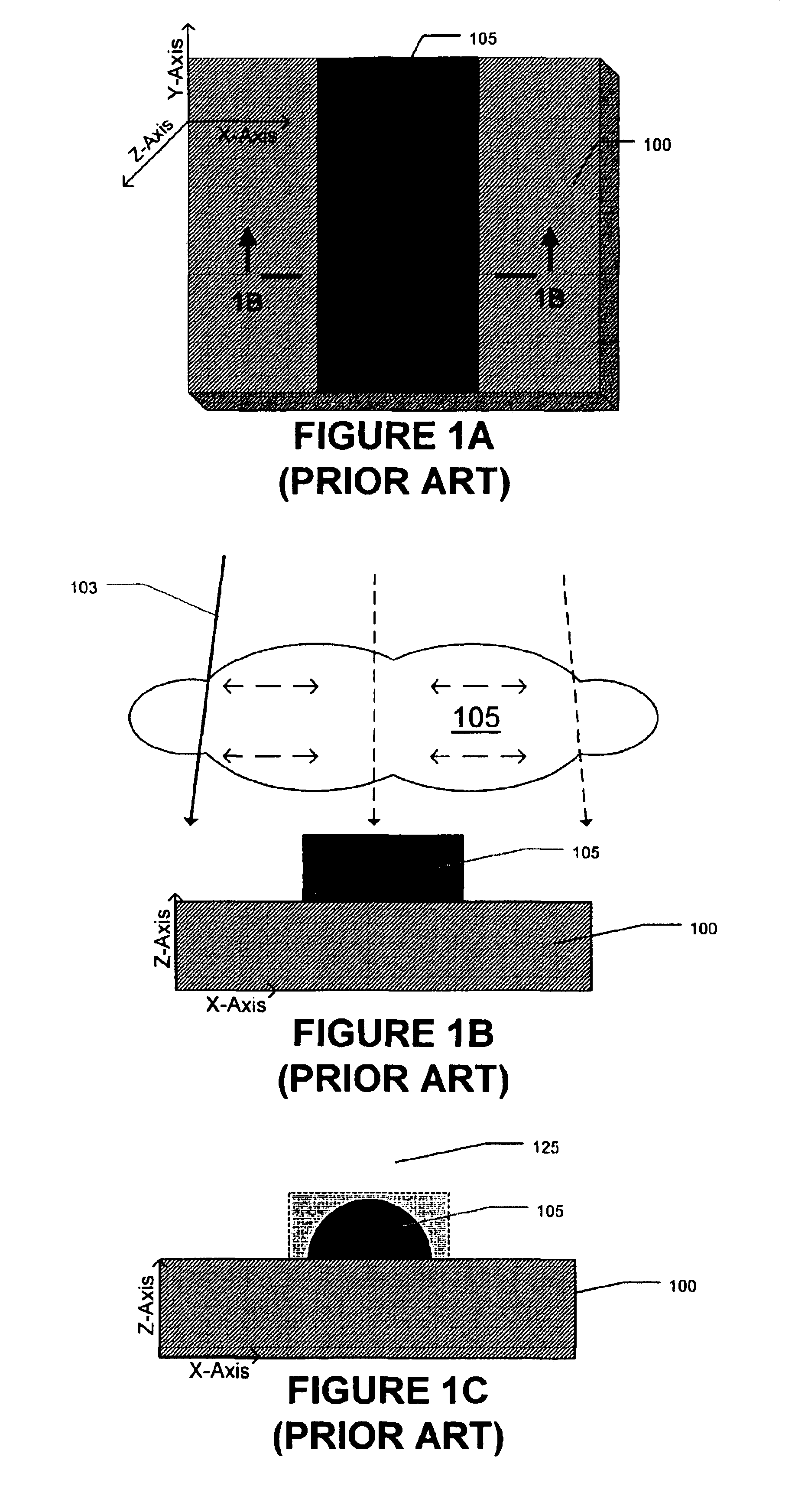
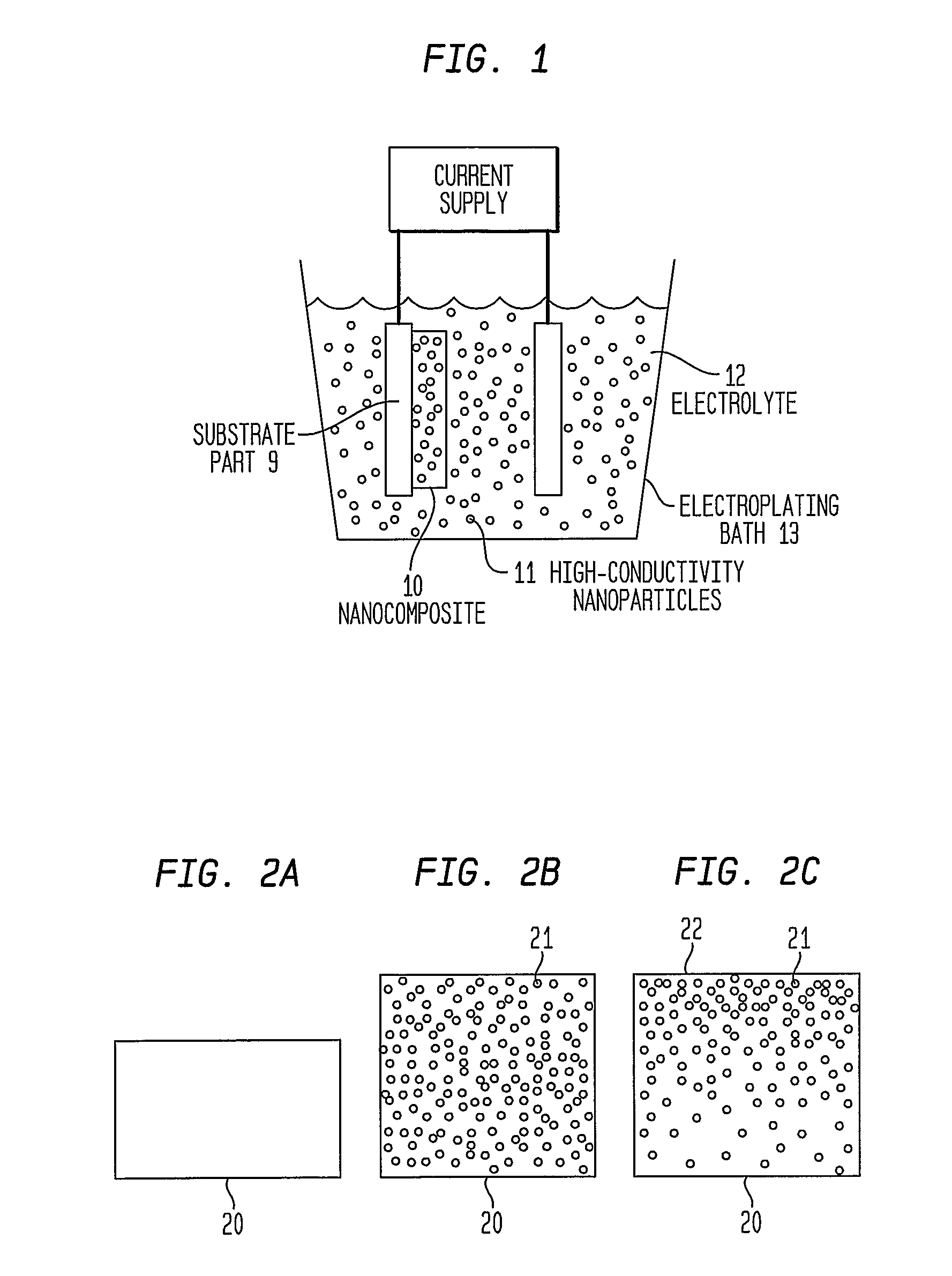
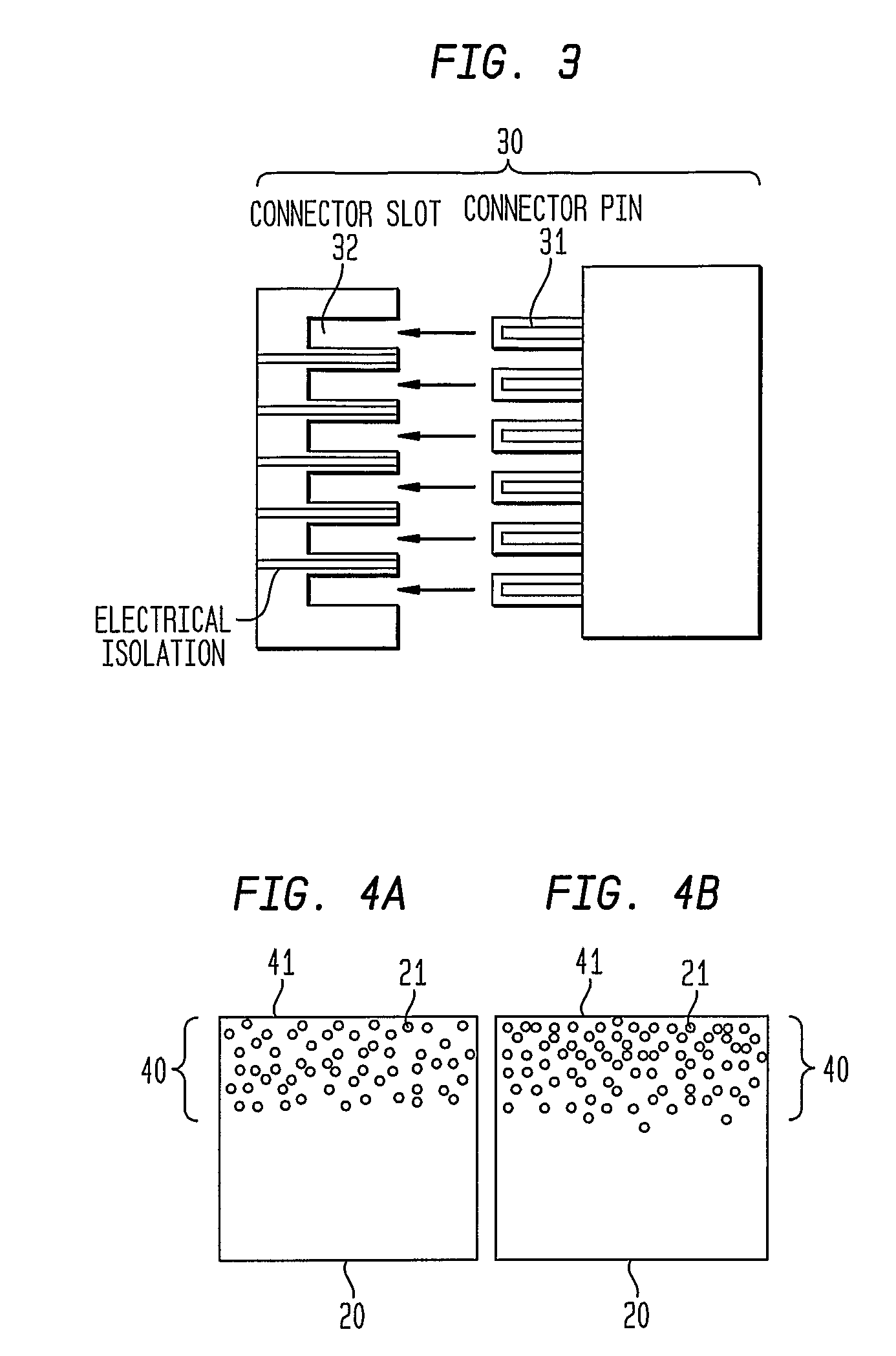
Articles Comprising High-Electrical-Conductivity Nanocomposite Material and Method for Fabricating Same
InactiveUS20080044685A1Minimize field enhancementImprove thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsManufacturing technologyElectron multiplication
This invention discloses novel nanocomposite material structures which are strong, highly conductive, and fatigue-resistant. It also discloses novel fabrication techniques to obtain such structures. The new nanocomposite materials comprise a high-conductivity base metal, such as copper, incorporating high-conductivity dispersoid particles that simultaneously minimize field enhancements, maintain good thermal conductivity, and enhance mechanical strength. The use of metal nanoparticles with electrical conductivity comparable to that of the base automatically removes the regions of higher RF field and enhanced current density. Additionally, conductive nanoparticles will reduce the surface's sensitivity to arc or sputtering damage. If the surface is sputtered away to uncover the nanoparticles, their properties will not be dramatically different from the base surface. Most importantly, the secondary electron emission coefficients of all materials in the nanocomposite are small and close to unity, whereas the previously used insulating particles can produce significant and undesirable electron multiplication.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
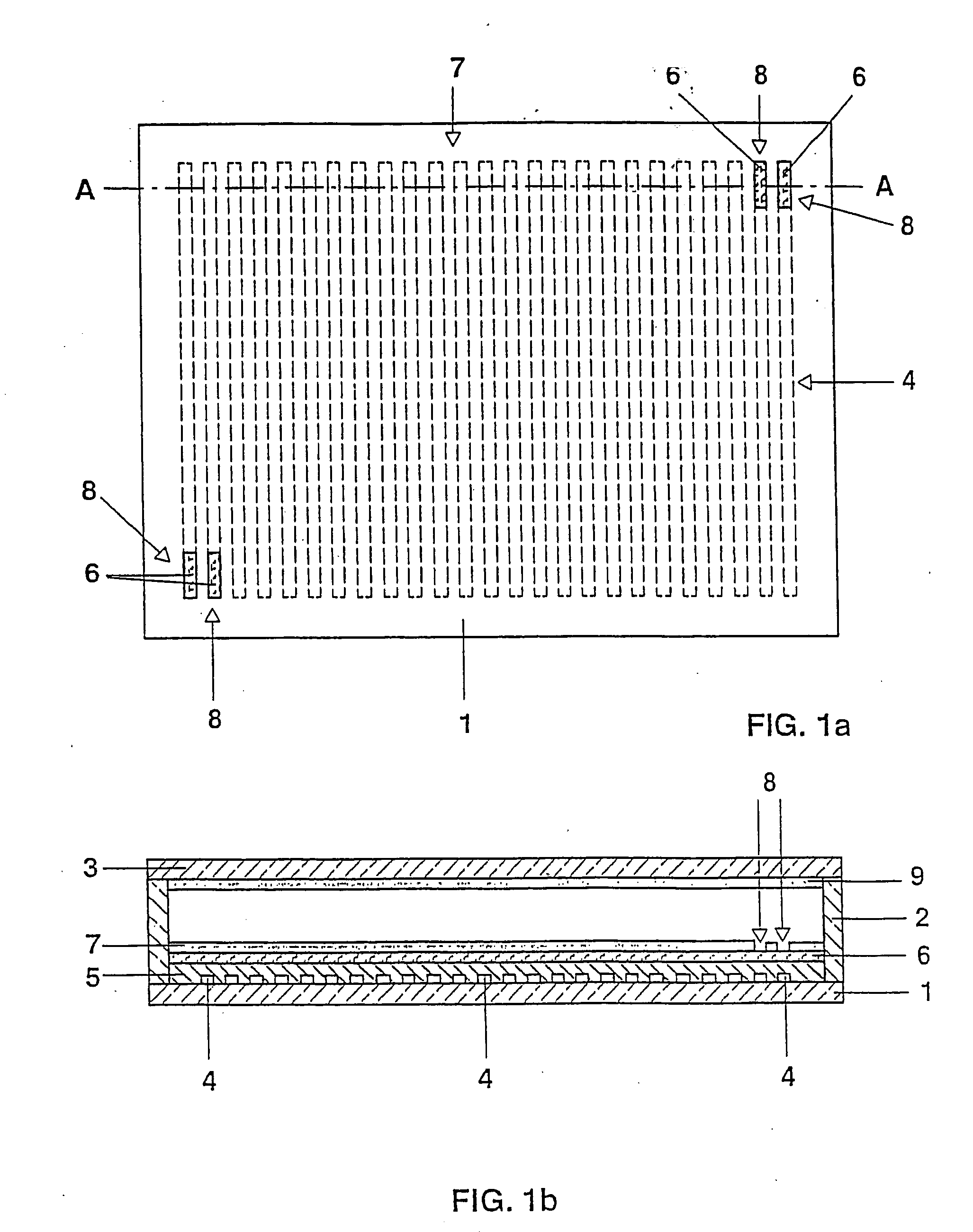
Spacer suitable for use in flat panel display
InactiveUS6489718B1Pigmenting treatmentCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersElectrical resistance and conductanceDisplay device
A spacer (140) suitable for use in a flat panel display is formed with ceramic, transition metal, and oxygen. At least part of the oxygen is bonded to the transition metal or / and constituents of the ceramic to form a uniform electrically resistive material having a resistivity of 105-1010 ohm-cm and a secondary electron emission coefficient of less than 2 at 2 kilovolts.
Owner:CANON KK
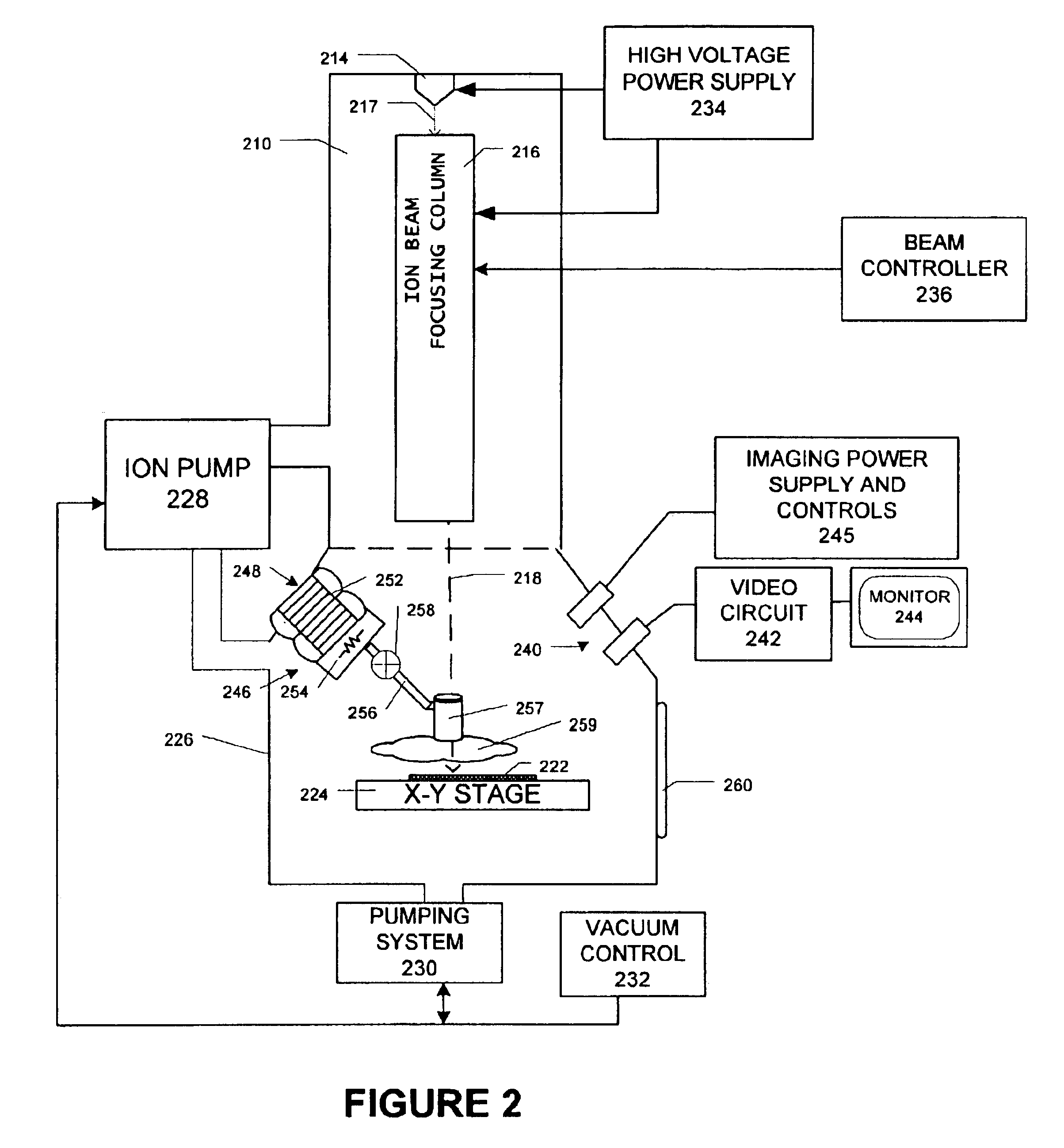
Proximity deposition
InactiveUS6926935B2Accurate measurementIncrease chanceElectric discharge heatingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementTarget surfaceHigh rate
The present invention provides methods for achieving substantially damage-free material deposition using charged particle (e.g., ion, electron) or light beams for generating secondary electrons to induce deposition in a gas deposition material. Among other things, some of the methods can be used to deposit, with satisfactory throughput, a protective layer over a semiconductor feature without significantly altering the feature thereby preserving it for accurate measurement. In one embodiment, the beam is directed onto an electron-source surface next to the target surface but not within it. The beam is scanned on the electron-source surface causing secondary electrons to be emitted from the electron-source surface and enter the region over the target surface to interact with deposition gas for depositing a desired amount of material onto the target surface. In this way, materials can be deposited onto a the target surface at a suitably high rate without having to expose the target surface, itself, to the beam being used to perform the material deposition. In another embodiment, the beam is directed onto a separate electron generating surface (preferably one that has a relatively high secondary electron emission coefficient) proximal to the target surface for generating the electrons to deposit the deposition material onto the target surface.
Owner:FEI CO
Multistage cusped magnetic field plasma thruster segmented ceramic channel
ActiveCN103775297AReduce plume divergence angleSmall plume divergence angleMachines/enginesUsing plasmaElectron temperatureDivergence angle
The invention discloses a multistage cusped magnetic field plasma thruster segmented ceramic channel, relates to the field of plasma thrusting, and aims to solve the problems of plume concussion of an outlet area of a multistage cusped magnetic field plasma thruster, large plume divergence angle, over-high wall temperature of a ceramic channel and low ionization rate. The front section of the ceramic channel is of a baffle structure, so that corrosion of the front end face of the thruster caused by electrons is decreased, the front section of the ceramic channel and an outlet permanent magnet form a magnet loop with a certain shielding function, the magnetic field intensity of the outlet plume area is reduced, the electrons more easily enter the channel to perform ionization, potential drop is concentrated in an outlet magnetic interface, the plume divergence angle is decreased, boron nitride ceramics of a middle section has a low secondary electron emission coefficient, the electron temperature and the ionization rate are high, heat insulation ceramics close to a rear section of an anodic area reduce anodic heat absorbed by the channel, the anodic heat is conducted and dissipated by the aid of an anodic bottom surface, heat dissipation of the permanent magnet is decreased, and demagnetization of the permanent magnet due to high temperature is avoided. The multistage cusped magnetic field plasma thruster segmented ceramic channel is applicable to the field of plasma thrusting.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
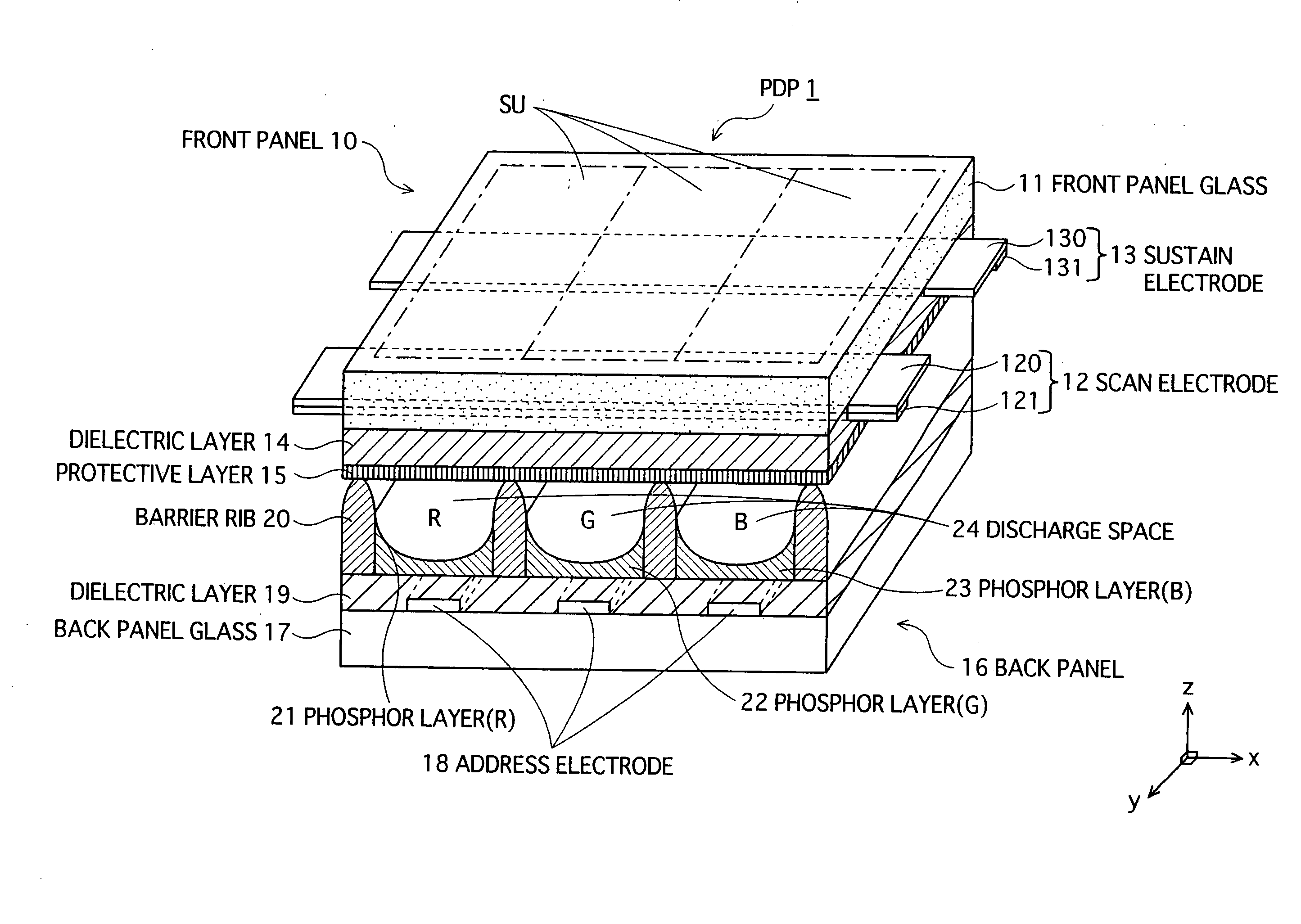
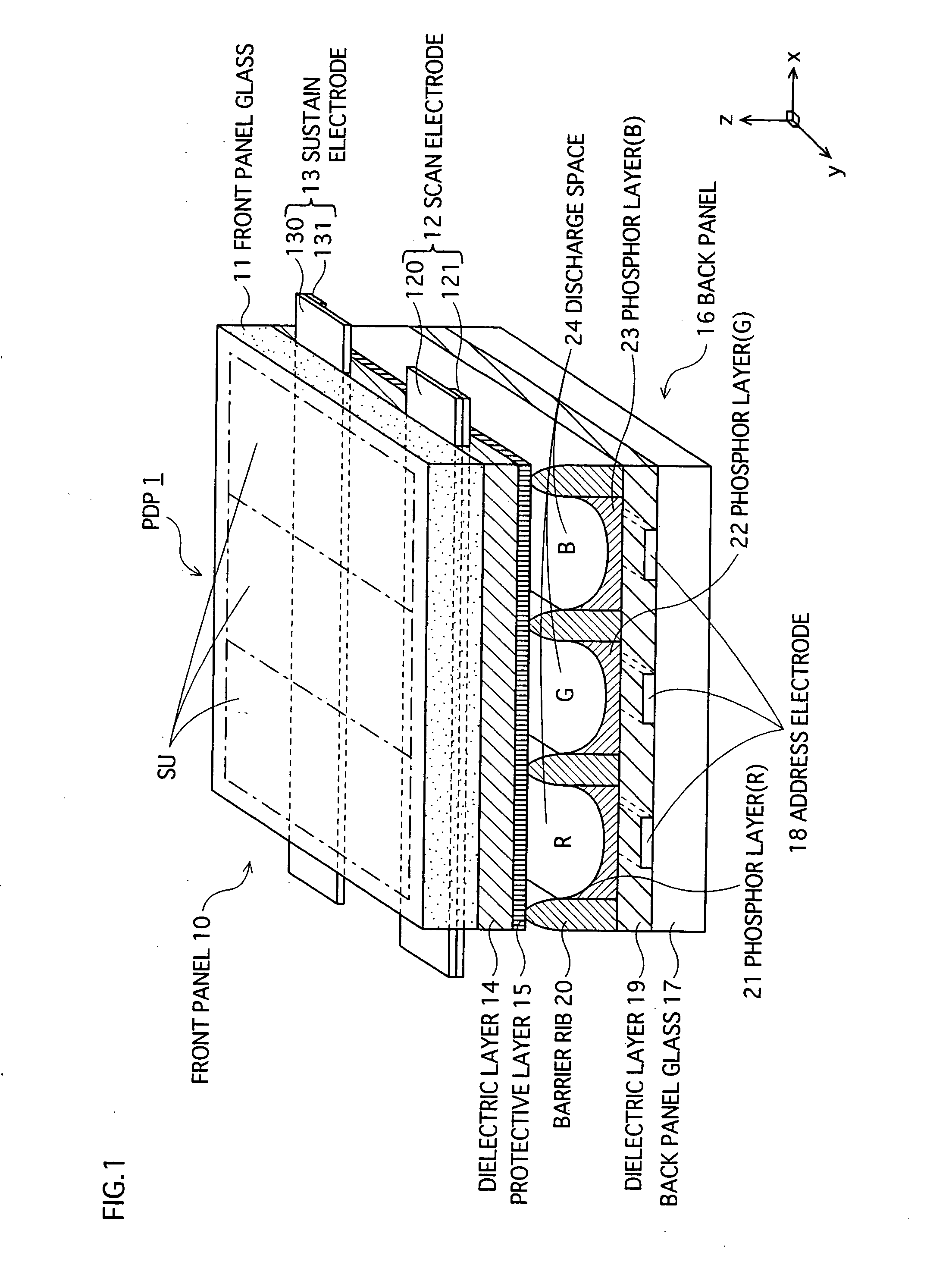
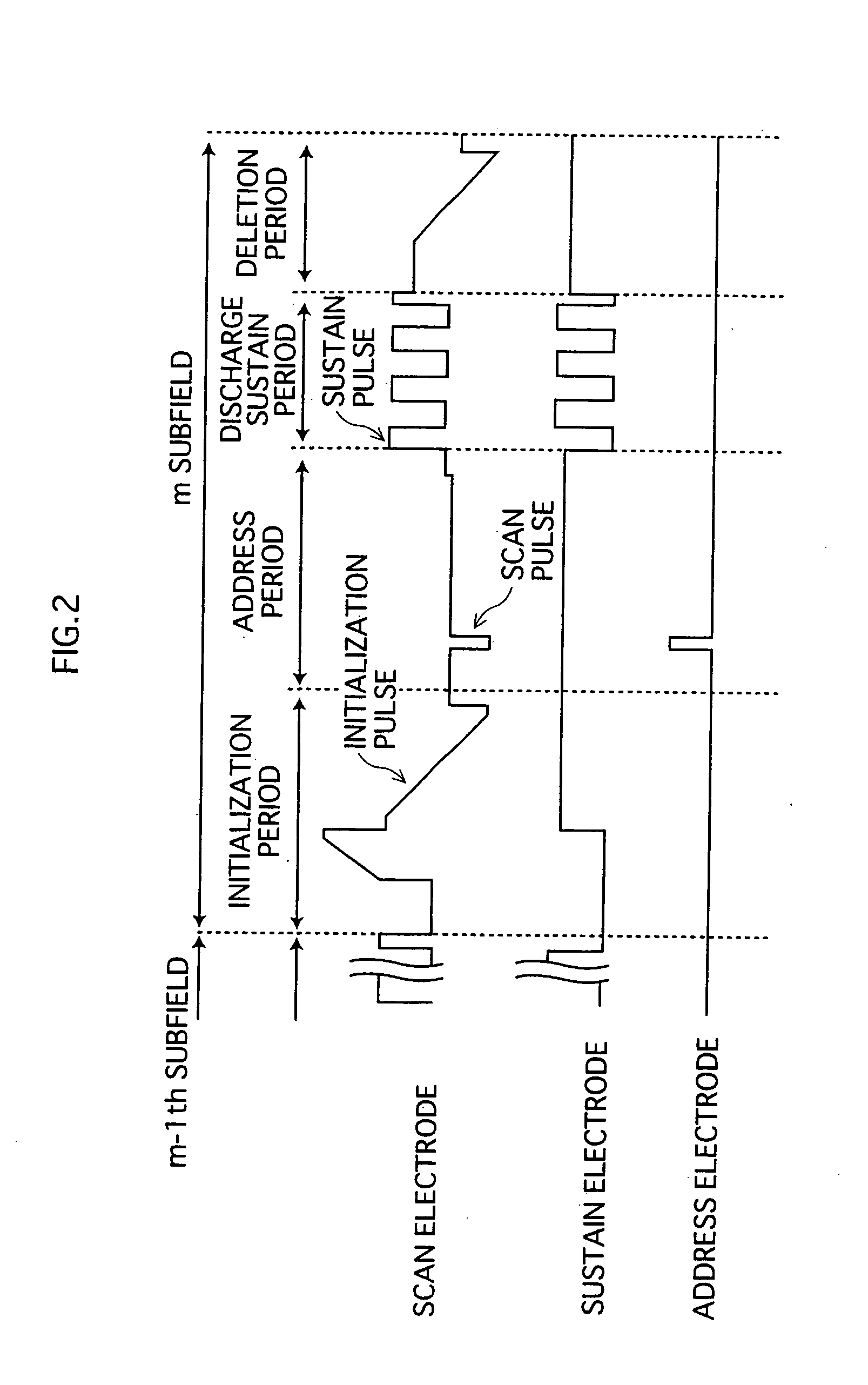
Plasma Display Panel And Production Method Therefor
InactiveUS20080061692A1Control generationReduced luminous efficiencyTube/lamp screens manufactureDischarge tube luminescnet screensImaging qualityEngineering
A PDP capable of lowering a discharge initiating voltage with a weak discharge always stabilized during an initialization period even if a Xe partial pressure ratio to a total pressure in discharge gas is increased, improving an image quality with the occurrence of an initializing bright point prevented, preventing the lowering of a light emission efficiency and brightness, and improving brightness; and a production method for simply producing the PDP. The PDP comprises a front panel and a rear panel disposed facing each other with a discharge space provided between them. A fluorescent layer is formed in the area on the discharge space side of the rear panel, and a fluorescent film as a high γ portion is formed in part of the area of its surface. The fluorescent film is formed of a material higher in secondary electron emission coefficient γ than a fluorescent material constituting the fluorescent layer. Part of the surface of the fluorescent layer is covered with the fluorescent film, with the other part facing the discharge space.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
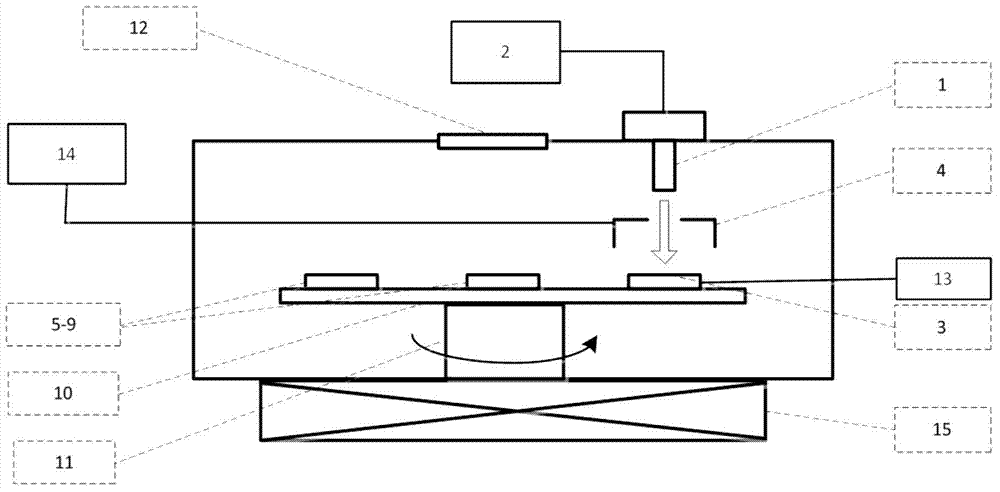
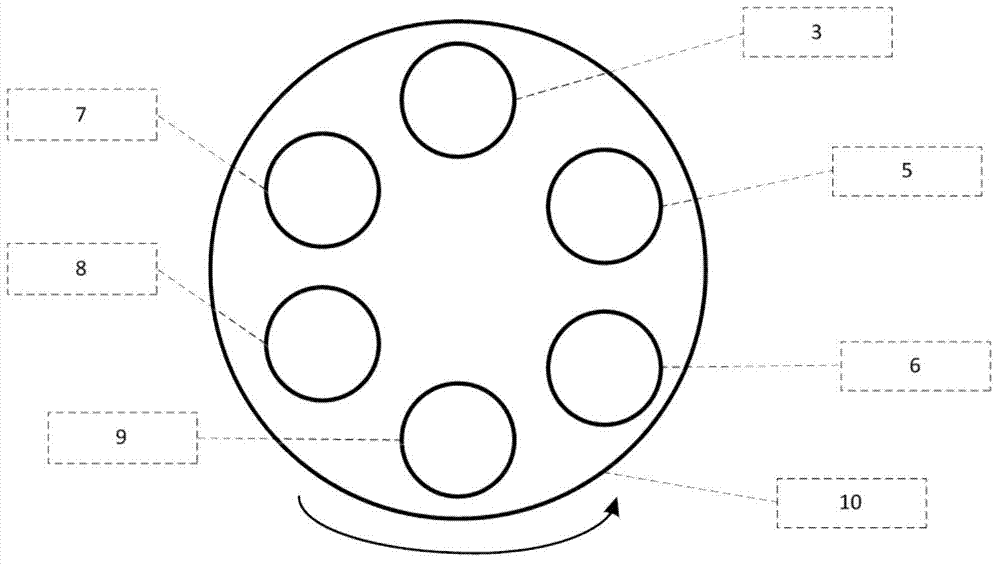
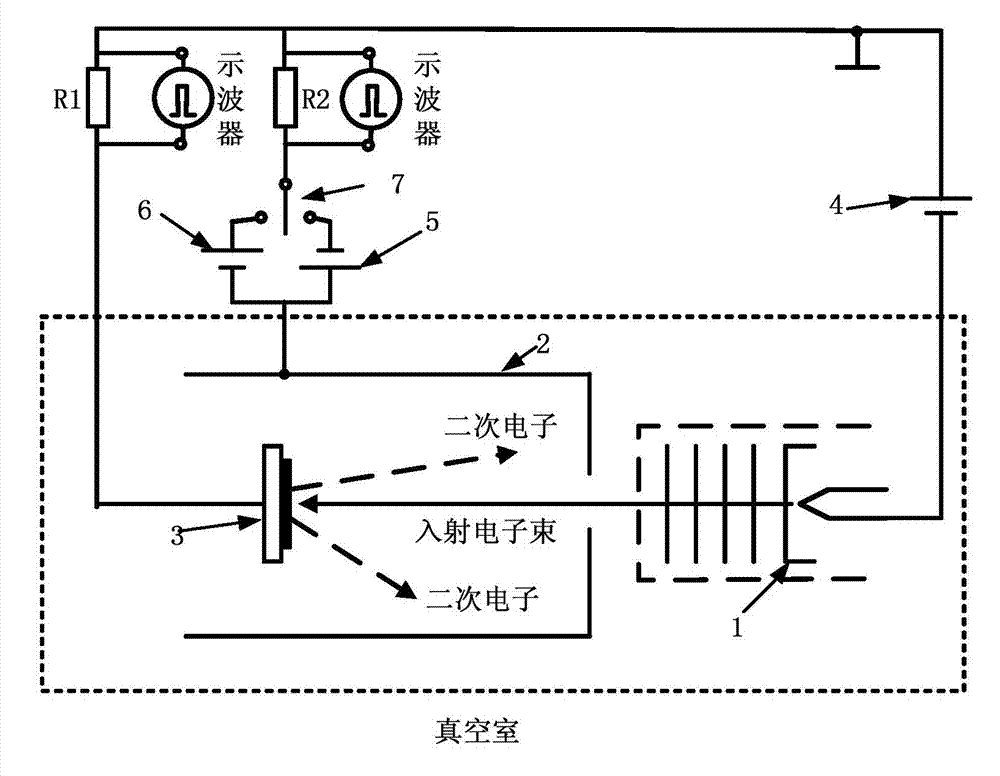
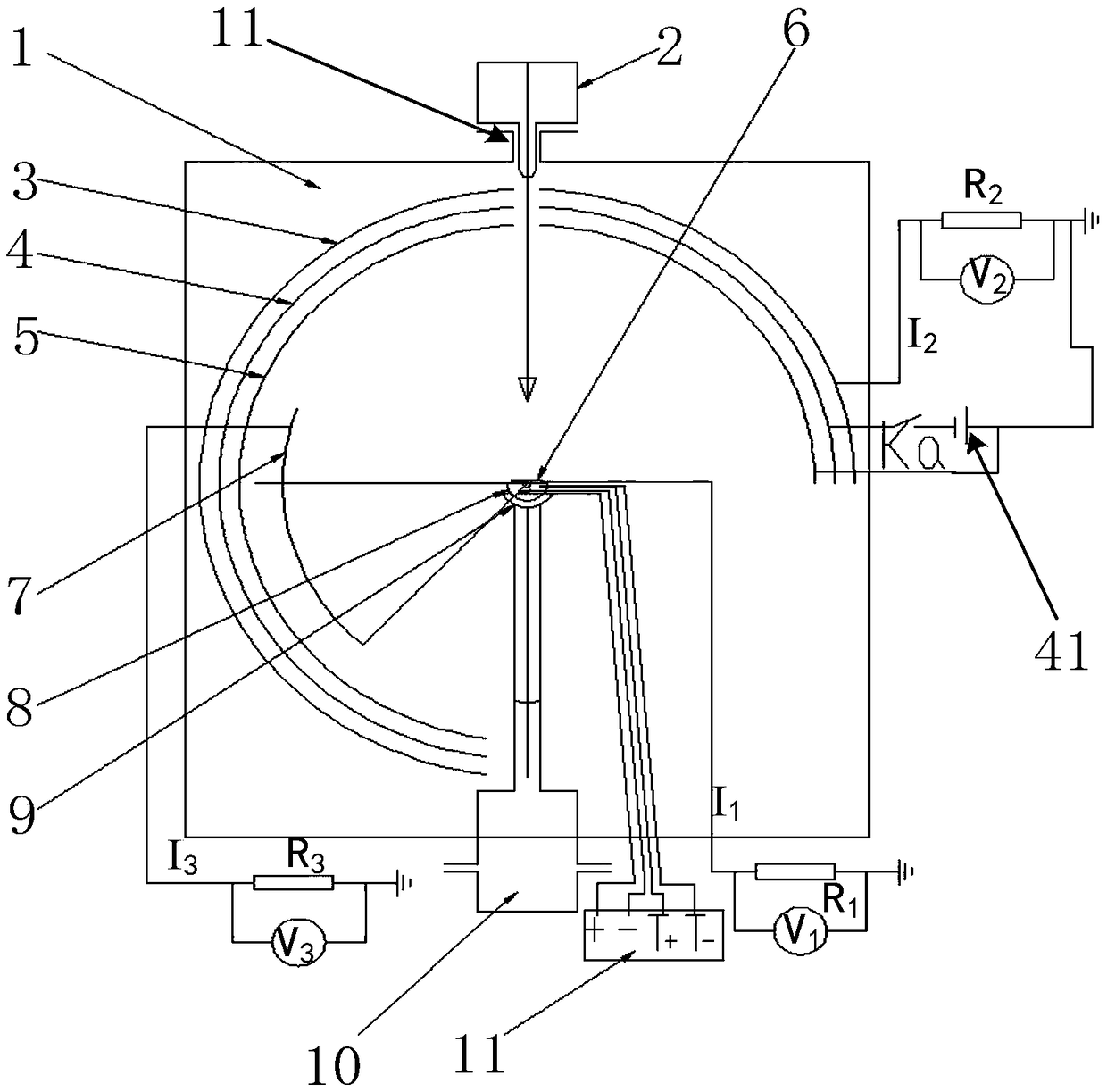
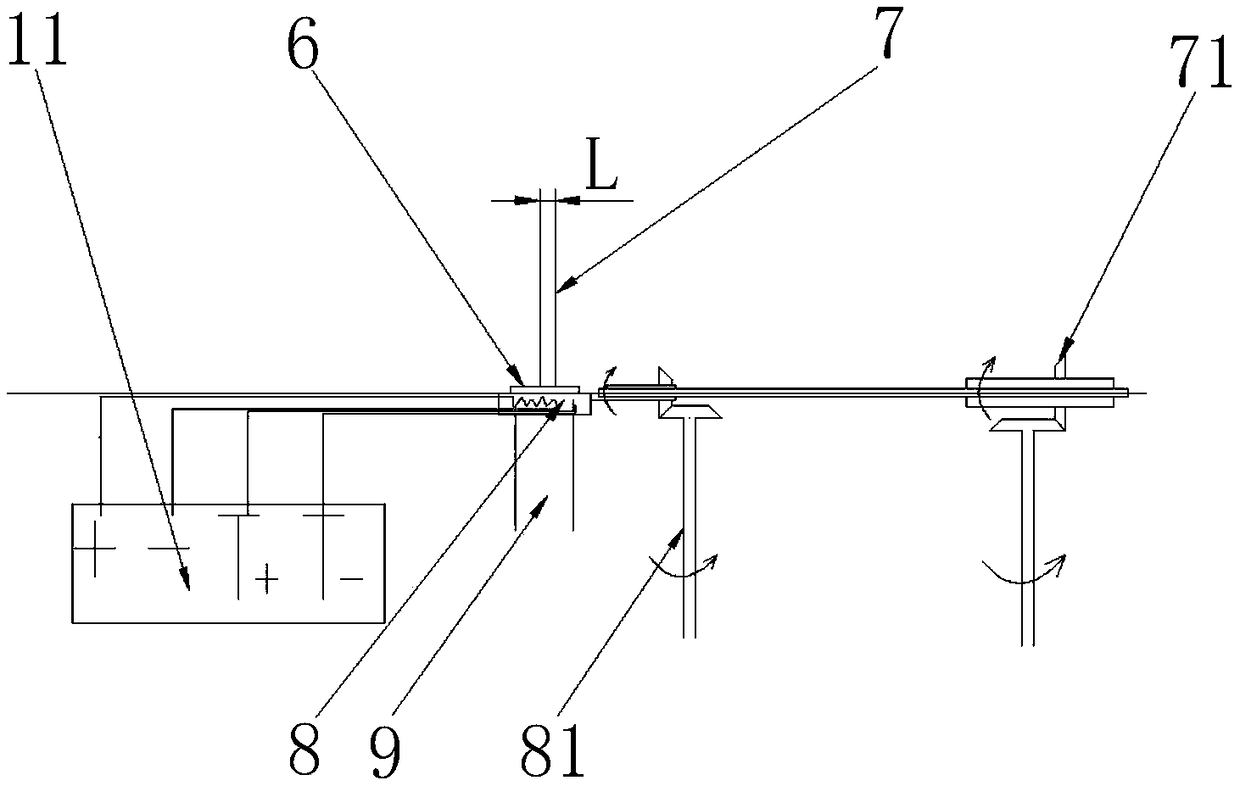
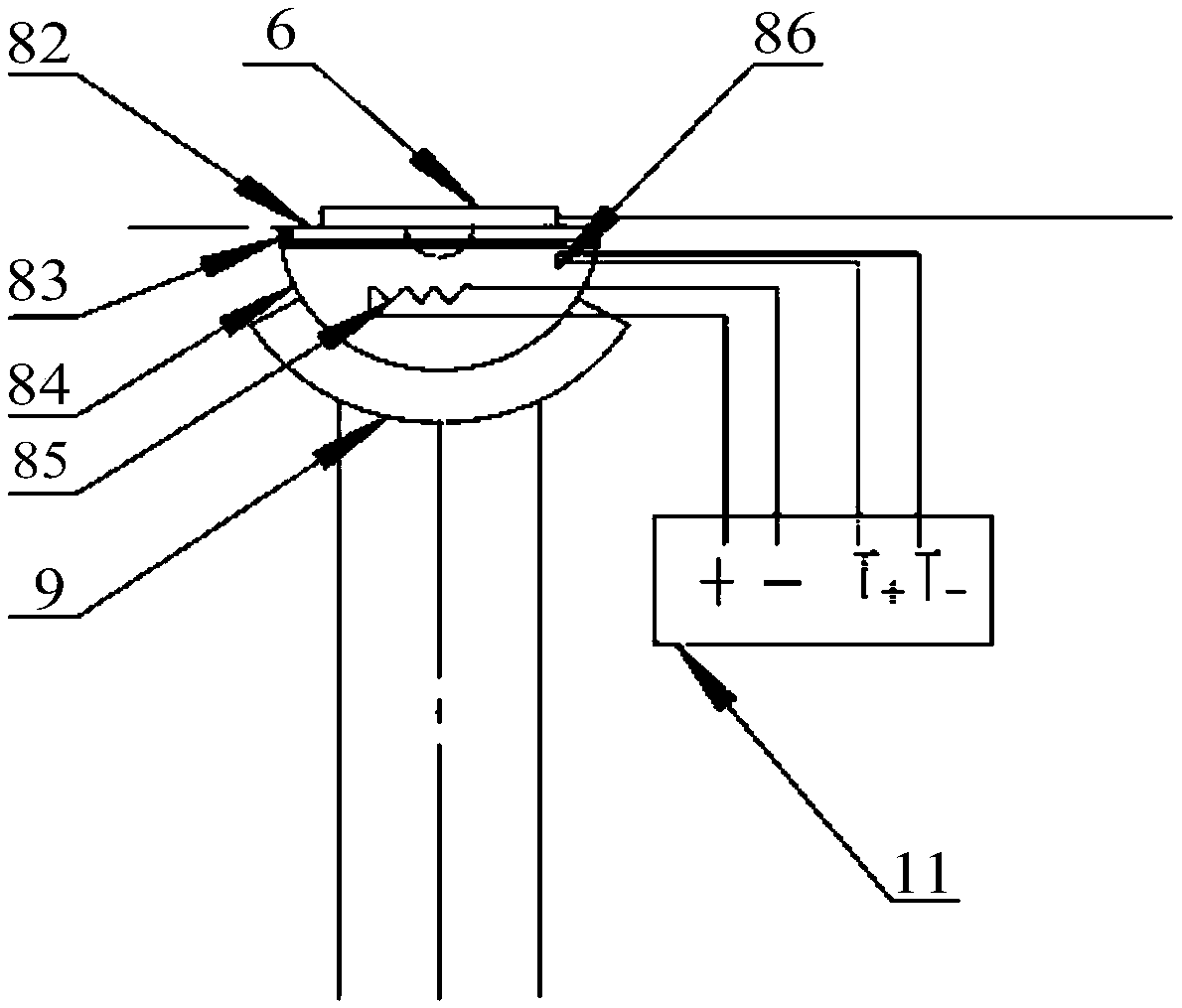
Panel type collection device and method for measuring secondary electron emission coefficient
ActiveCN103776858AEfficient collectionIntuitive and convenient adjustmentMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionTemperature controlMeasurement device
The invention discloses a panel type collection device and method for measuring a secondary electron emission coefficient. A measuring device mainly comprises a rotary platform, a sample table, a heating device, a Faraday cylinder, a current amplifier and a collection electrode, wherein the inner wall of the Faraday cylinder is plated with a layer of carbon, the Faraday cylinder is connected with a bias voltage device and the current amplifier and is used for measuring a primary incidence current; the collection electrode is in a panel structure, the upper surface of the collection electrode is coated with a layer of fluorescent powder so as to conveniently adjust and focus electron beam faculae, and the lower surface of the collection electrode is plated with a layer of carbon so as to inhibit electron multiplication phenomenon in a collection process; the collection electrode is connected with a bias voltage device and the current amplifier and is used for measuring secondary electron stream emitted by the surface of a material. By utilizing a rotary device, multiple samples can be simultaneously measured, so that the measuring time is saved; by utilizing the heating device and a temperature control device, the temperature of a sample can be accurately controlled in a range of 30-300 DEG C, and the heating device and a temperature control device are used for researching the influence of the temperature on the secondary electron emission coefficient; by providing the novel electron collection device for measuring the secondary electron emission coefficient, the measurement of the secondary electron emission coefficients under different temperatures is realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
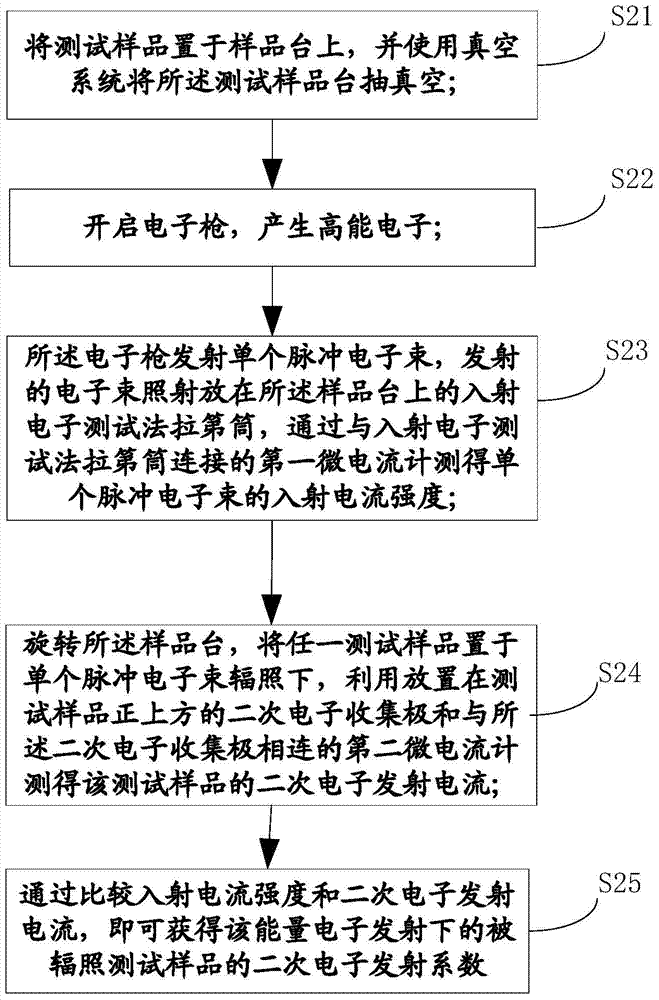
Method and system for testing secondary electron yield of star-used dielectric materials
InactiveCN103760181AReduce the impactImprove test accuracyMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionCurrent meterTest efficiency
The invention discloses a method and a system for testing secondary electron yield of star-used dielectric materials. The method comprises the following steps of placing at least one testing sample which is made of a star-used dielectric material on a sample platform, and vacuumizing the sample platform by using a vacuum system; turning on an electronic gun, launching a single pulse electron beam by the electronic gun or irradiating an incident electron testing Faraday cylinder placed on the sample platform, and testing the incident current intensity of the single pulse electron beam through a first micro-current meter; rotating the sample platform, placing any testing sample under the irradiation of the single pulse electron beam, and testing the secondary electron launching current of the testing sample by using a secondary electron collecting pole and a second micro-current meter; comparing the incident current intensity with the secondary electron launching current, thus obtaining the secondary electron yield of the sample. The method and the system provided by the invention have the advantages that after the primary high vacuum is obtained, the testing for the secondary electron yields of a plurality of testing samples can be developed, thus the testing efficiency is improved, and the testing accuracy is high.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Device and method for inhibition of charge injection under transient electric field
InactiveCN107578861AImprove electron work functionIncreased operating lifeWindings insulation materialWindings insulation shape/form/constructionOvervoltageEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of power transmission and distribution equipment, in particular to a device and method for inhibition of charge injection under a transient electric field.When a high-voltage electric appliance operates in a transient overvoltage waveform, a local high-voltage electric field enables charge injection into an insulating medium and enables continuous physical processes of charge injection and extraction and the like under the action of external stress, and consequently local electric field distortion is aggravated, and internal breakdown and surface flashover faults can be probably caused. The method for inhibition of charge injection under the transient electric field includes steps: selecting a magnesium oxide target material, and adopting a magnetron sputtering instrument to form a magnesium oxide film on the surface of a substrate; performing insulating coverage on a high-voltage equipment current-carrying module by the aid of the substrate. The electron work function of a metal insulating interface can be increased, the surface secondary electron emission coefficient is increased, and insulating surface flashover starting voltage under a high vacuum condition is raised.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Measurement system and measurement method for secondary electron emission coefficient of medium film
InactiveCN103713001ASimple structureLow costMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionElectrical resistance and conductanceBarrel Shaped
The invention discloses a measurement system and a measurement method for a secondary electron emission coefficient of a medium film. The system comprises an electronic gun, a barrel-shaped collection electrode, a sample holder and a general power. A round hole is arranged at the top of the barrel-shaped collection electrode. The sample holder is arranged in the barrel-shaped collection electrode. The electronic gun is arranged outside the barrel-shaped collection electrode. The sample holder, the round hole and the emission end of the electronic gun are in the same straight line. The sample holder is connected with the grounding terminal of the general power through a first resistor. The electronic gun is connected with the negative electrode of the general power. The barrel-shaped collection electrode is connected with a first power supply and a second power supply which have opposite positive and negative electrodes. Change-over switches are connected with the other ends of the first power supply and the second power supply. The change-over switches are connected with the grounding terminal of the general power through a second resistor. In the method, only one electronic gun and one collection electrode are needed, a secondary electron emission coefficient of a sample can be tested, the measuring cycle is shortened, and the efficiency is raised. The measurement system has a simple structure and low cost.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
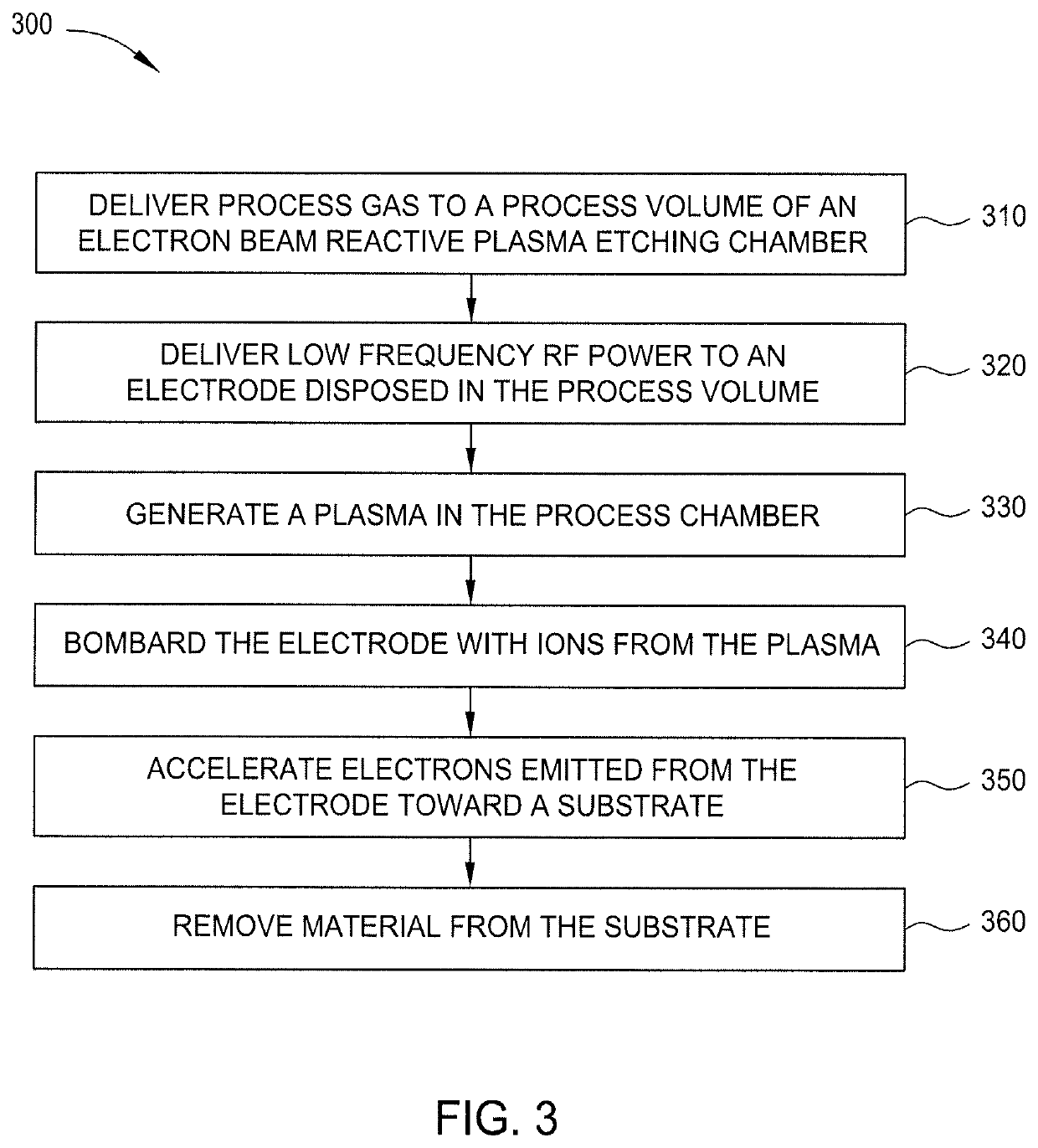
Etching methods
ActiveUS10707086B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReactive plasmaSecondary electron emission coefficient
Embodiments described herein relate to apparatus and methods for performing electron beam reactive plasma etching (EBRPE). In one embodiment, an apparatus for performing EBRPE processes includes an electrode formed from a material having a high secondary electron emission coefficient. In another embodiment, methods for etching a substrate include generating a plasma and bombarding an electrode with ions from the plasma to cause the electrode to emit electrons. The electrons are accelerated toward a substrate to induce etching of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Measuring device and method for secondary electron characteristic parameters of material in low and high-temperature environments
PendingCN109142409AReduced measurement timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMetallic materialsDistribution characteristic
The invention discloses a measuring device and method for secondary electron characteristic parameters of a material in low and high-temperature environments. A secondary electron detector in the measuring device is arranged in a vacuum chamber and comprises a spherical shell collection shell, a spherical shell grid electrode and a spherical shell grounding electrode which are arranged from outside to inside in sequence and are all greater than or equal to 3 / 4 of a sphere and insulated from one another; a sample table and a temperature adjustment system and an angle distribution measuring system thereof are also arranged in the secondary electron detector; an electron beam emitted by an electron gun run through the secondary electron detector and is injected into the sample table. The device can measure secondary electron emission coefficients, secondary electron angle distribution characteristics and secondary electron energy spectrum distributions of a metal material and a medium material under the low and high-temperature environments and can further measure the secondary electron characteristic parameters under different incident angles; charges accumulated on the surface of amedium can be effectively neutralized by quickly heating the medium material, and the measuring time is reduced; furthermore, by introducing a checking mechanism, the accuracy and the reliability of ameasuring result are guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Preparation method of secondary-electron emission thin film
InactiveCN103789730AAdvantages of preparation methodFilm forming process is flexibleVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringSecondary electrons
The invention discloses a preparation method of a secondary-electron emission thin film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) depositing a buffer layer on a metal substrate; (2) depositing a magnesium oxide and metal mixed layer on the buffer layer by sputtering a magnesium target / magnesium oxide target and sputtering other metal targets; (3) depositing a surface on the magnesium oxide and metal mixed layer. In the step (2), the two targets are used for respectively depositing magnesium oxide and other metals, the sputtering power, the sputtering time, the flow rates of working gas and reactant gas and the temperature of the substrate are individually controlled so as to prepare the magnesium oxide and metal mixed layer with proper magnesium oxide and metal grain size, magnesium oxide crystallization orientation, metal content and distribution of metal grains in a membrane layer and thickness of the membrane layer. The secondary-electron emission thin film prepared by the method has high secondary electron emission yield and good electrical conductivity, and therefore, the secondary-electron emission thin film has high secondary-electron emission stability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
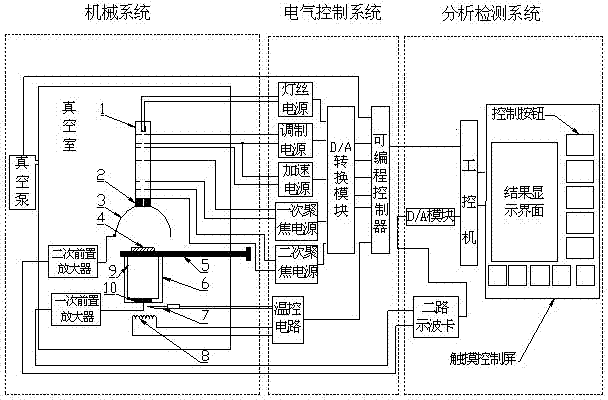
Solid material secondary electron emission coefficient testing device with intelligent measurement and control technology
InactiveCN102288628AReduce lossesAvoid compromising accuracyTube electron sourcesMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionHemt circuitsEngineering
The solid material secondary electron emission coefficient testing device with intelligent measurement and control technology of the present invention includes a mechanical system, an electrical control system and an analysis and detection system; the mechanical system includes a vacuum chamber, a vacuum pump, an electron gun, an electron collection device and a heating device, and Provide a vacuum environment, generate and collect secondary electrons; the electrical control system includes a power supply, a programmable controller and a temperature control circuit, and the programmable controller controls the power supply voltage through a digital and analog conversion module; the analysis and detection system includes an industrial computer , digital-to-analog conversion module, two-way oscilloscope card and touch control screen, and KingView is installed on the industrial computer to store, analyze and process the detected electronic signals, and display the secondary electron emission coefficient of the measured solid material The relation curve between electron energy and electron gun exiting electron energy. The invention can better meet the needs of industrial antistatic design, engineering material selection and static electricity prediction for measuring the secondary electron emission coefficient of solid materials.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
High-collecting-efficiency micro-channel plate, micro-channel plate type photomultiplier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106298427AImprove reflectivityFlat reflective surfaceMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureGlass ballElectron multiplication
The invention discloses a high-collecting-efficiency micro-channel plate, a micro-channel plate type photomultiplier and a preparation method thereof. The photomultiplier has a structure which can realize high gain, high collecting efficiency, good single photoelectron spectrum, and collecting efficiency uniformity. The photomultiplier disclosed by the invention comprises a glass ball shell, an electronic focusing barrel, a photocathode and a micro-channel plate electron multiplication system. A metal electrode surface of a first micro-channel plate in an electron incident direction of an electron multiplier of the micro-channel plate type photomultiplier disclosed by the invention and the inner wall surface of a channel are both covered with a thin film with a high secondary electron emission coefficient, so that effective multiplication of electrons can be realized and the high collecting efficiency and the collecting efficiency uniformity of the photomultiplier can be improved.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
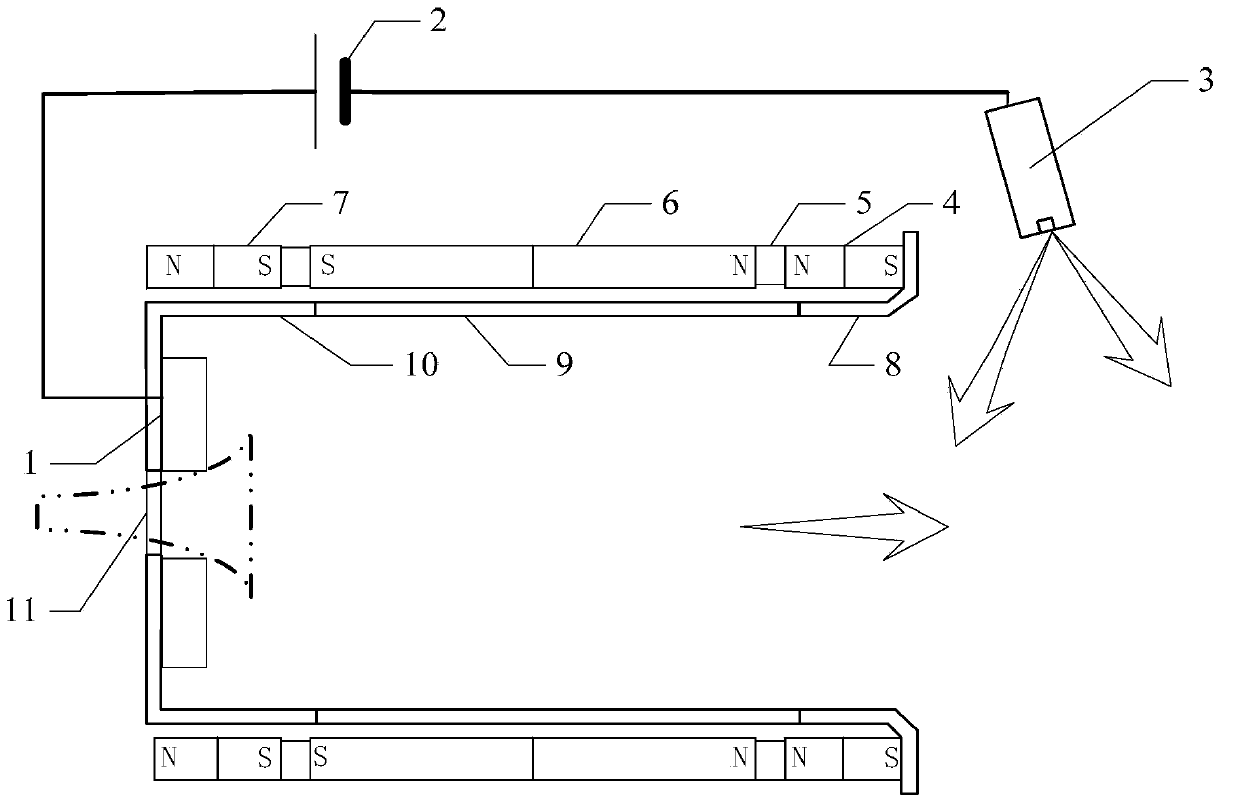
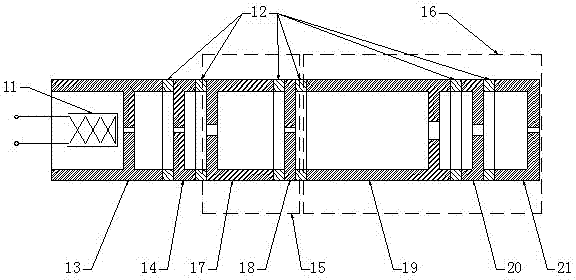
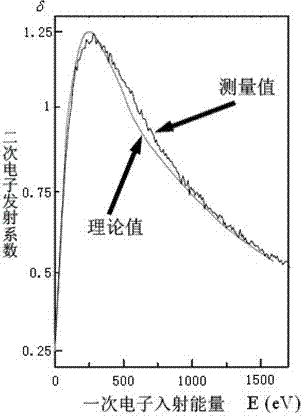
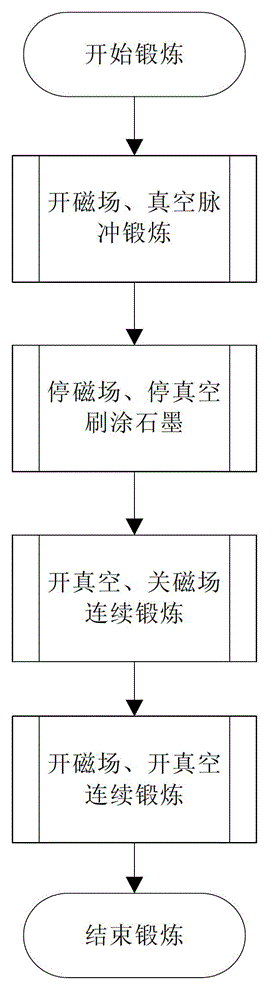
Cavity exercising method of high-current compact type editcyclotron
ActiveCN102869185AOut of breathMultiple electron multiplication effect overcomesMagnetic resonance acceleratorsElectron multiplicationMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a radio-frequency cavity exercising method of a high-current compact type editcyclotron. The method is mainly characterized in that a cavity is primarily exercised through long-cycle narrow pulses, and the range of a multi-electron multiplication effect generated voltage is judged; according to color changes of the surface of a radio-frequency cavity, a magnetic pole face or a panel of the editcyclotron in the process, a graphite material is brushed at corresponding positions so as to reduce the secondary electron emission coefficient of the region; afterwards, by means of closing a magnetic field of the editcyclotron, all multi-electron effect regions are exercised from low to high in sequence by using a continuous power increase method, when all the multi-electron effect regions are passed, power feed is tuned and maintained for a period of time to accelerate gas outlet on a surface, then, push power is reduced at fixed time interval, and all the multi-electron effect regions are exercised from high to low; and after the processes are repeated ten times, the power supply of the magnetic field is switched on, and the exercise of the radio-frequency cavity can be completed rapidly by using the same method.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Articles comprising high-electrical-conductivity nanocomposite material and method for fabricating same
InactiveUS7959830B2Avoid damageReduce sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsManufacturing technologyElectron multiplication
This invention discloses novel nanocomposite material structures which are strong, highly conductive, and fatigue-resistant. It also discloses novel fabrication techniques to obtain such structures. The new nanocomposite materials comprise a high-conductivity base metal, such as copper, incorporating high-conductivity dispersoid particles that simultaneously minimize field enhancements, maintain good thermal conductivity, and enhance mechanical strength. The use of metal nanoparticles with electrical conductivity comparable to that of the base automatically removes the regions of higher RF field and enhanced current density. Additionally, conductive nanoparticles will reduce the surface's sensitivity to arc or sputtering damage. If the surface is sputtered away to uncover the nanoparticles, their properties will not be dramatically different from the base surface. Most importantly, the secondary electron emission coefficients of all materials in the nanocomposite are small and close to unity, whereas the previously used insulating particles can produce significant and undesirable electron multiplication.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Double-layer electrode for multi-level depressed collector and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN101752168AImprove efficiencySuppress emissionTransit-tube collectorsCold cathode manufactureHigh densityGraphite
The invention discloses a double-layer electrode for a multi-level depressed collector and a preparation method thereof, and relates to vacuum device technology. The double-layer electrode comprises a metal layer and a graphite layer; opposite surfaces of the two layers are fixedly connected tightly; and the material of the graphite layer is pyrolytic graphite or high-density isotropic graphite. The electrode can ensure air-tight seal with ceramics and other metals by utilizing the outer-layer electrode; and the inner-layer pyrolytic graphite or high-density isotropic graphite has low secondary electron yield so as to facilitate improving the efficiency of the multi-level depressed collector. The preparation process adopts coating and sintering technology, and is simple and firm.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite dielectric protective film of plasma display panel (PDP) and preparation method thereof
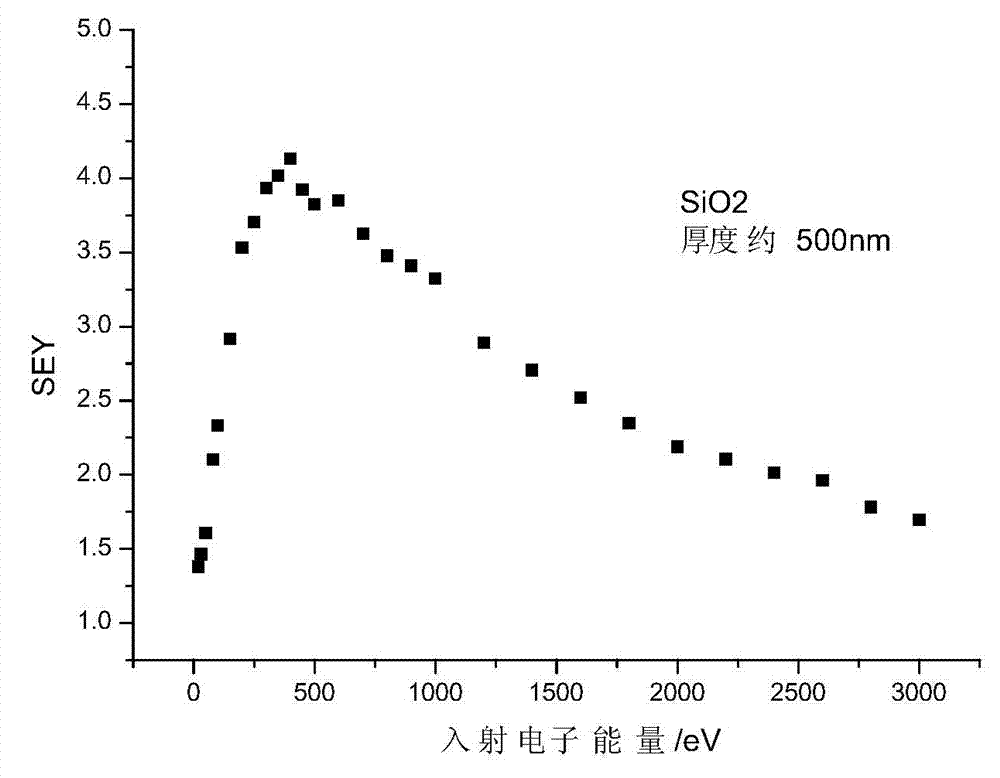
InactiveCN102087944AHigh secondary electron emission coefficientExtended service lifeTube/lamp screens manufactureSolid cathode detailsTectorial membraneSecondary electron emission coefficient
The invention discloses a composite dielectric protective film of a plasma display panel (PDP). The composite dielectric protective film on a dielectric layer on a front substrate of the PDP comprises a crystalline grain of a core-shell structure, wherein the inner-layer core of the crystalline grain is made of a material with high secondary electron emission coefficient; and the outer-layer shell of the crystalline grain is made of magnesium oxide. The composite dielectric protective film has high secondary electron emission coefficient, high lagging electron emission speed and good sputtering resistance, and can obviously reduce the ignition voltage and maintaining voltage of the PDP, shorten the addressing time and prolong the service life of the PDP. At the same time, the invention also provides a method for preparing the composite dielectric protective film of the PDP.
Owner:SICHUAN COC DISPLAY DEVICES
Method for inhibiting secondary electron emission of microwave component surface by adopting nanostructure plating layer
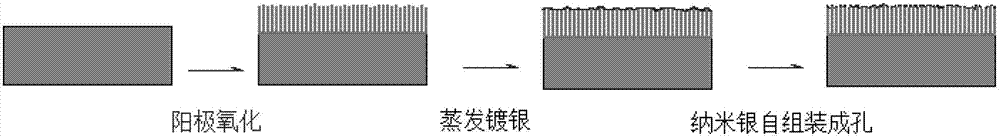
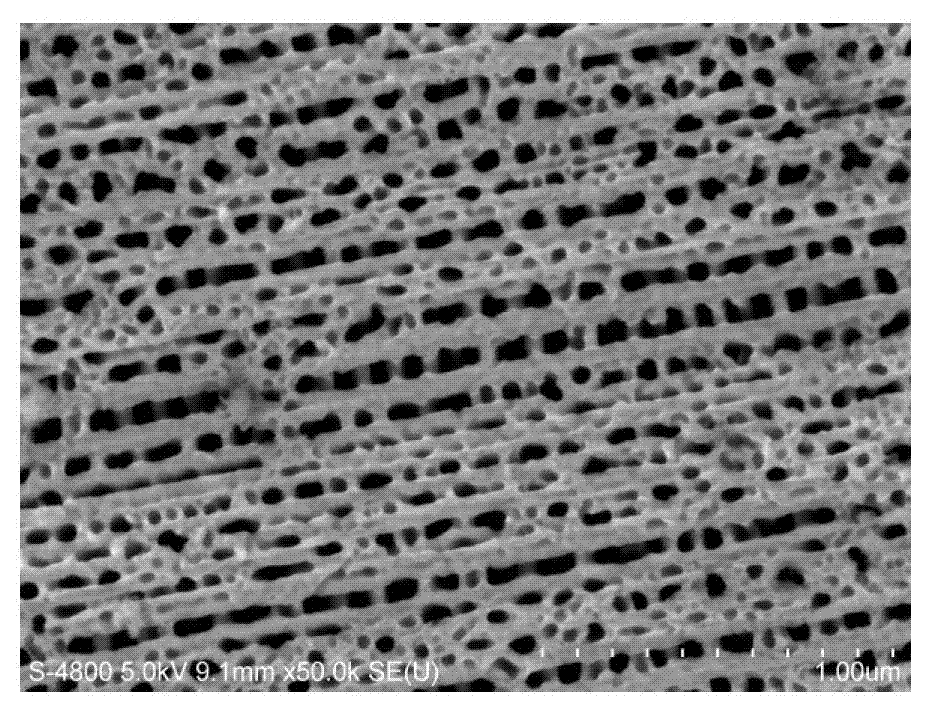
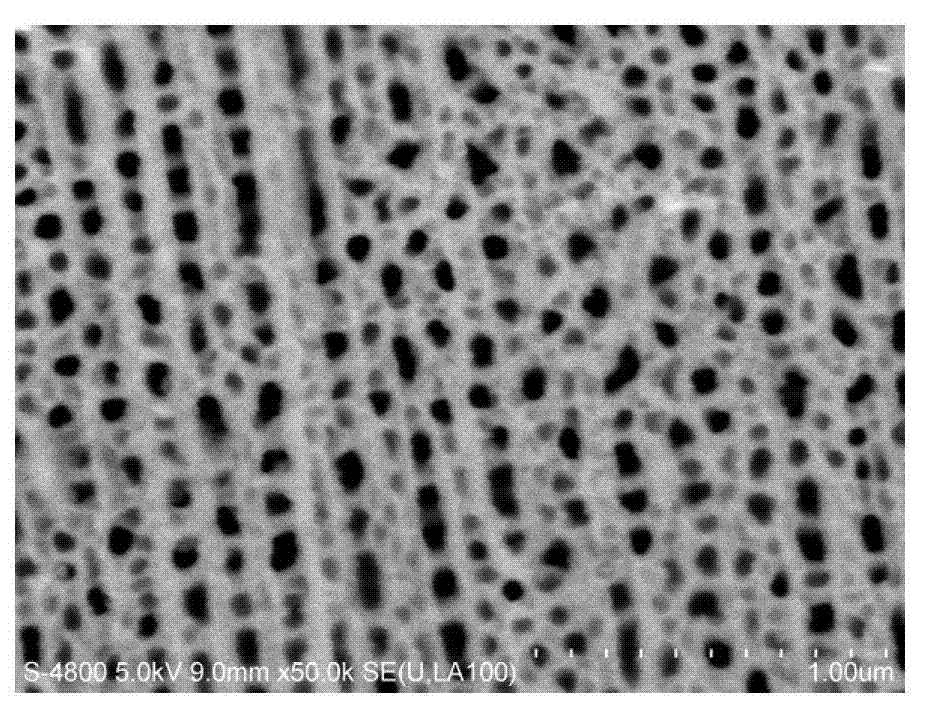
InactiveCN102732931ARaise the discharge thresholdReduced emissivityAnodisationVacuum evaporation coatingEvaporationField electron emission
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting secondary electron emission of a microwave component surface by adopting a nanostructure plating layer. According to the method, a microwave component is subjected to necessary washing, and then is coated with a protection glue to protect the surface requiring no treatment; phosphoric acid is adopted to carry out an electrochemical etching treatment, such that a porous alumina film layer with a hole size of about 100 nm and a depth-to-width ratio more than 10 is formed on the surface of an aluminum alloy; repeated washing is performed to remove the protection glue; a layer of a silver layer with a thickness of about 50 nm is plated on the oxidation film through evaporation plating; and finally a vacuum heating treatment is performed. With the treatment of the method of the present invention, binding force of the plating layer and the substrate can be improved, and the characteristic of the significantly-reduced melting point of the nano-silver is adopted, such that the nano-silver is self-assembled on the surface of the oxidation layer to form a nano-trap structure while the continuity of the silver plating layer can be maintained well; and inhibition of secondary electron emission is achieved based on assurance of a certain electrical conductivity. The method of the present invention provides good cohesion for the existing microwave component treatment process, and the secondary electron emission coefficient of the microwave component surface is significantly inhibited.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
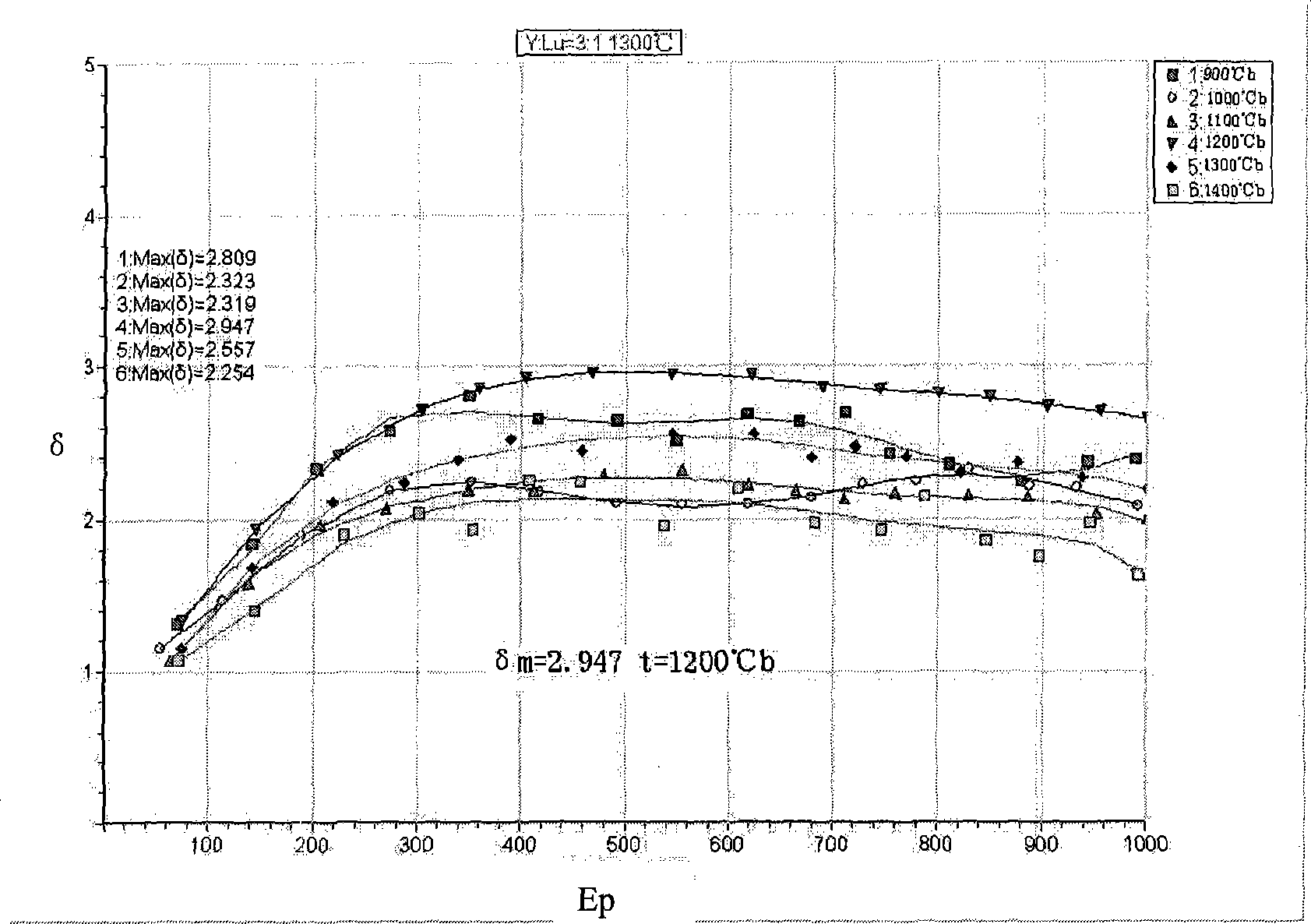
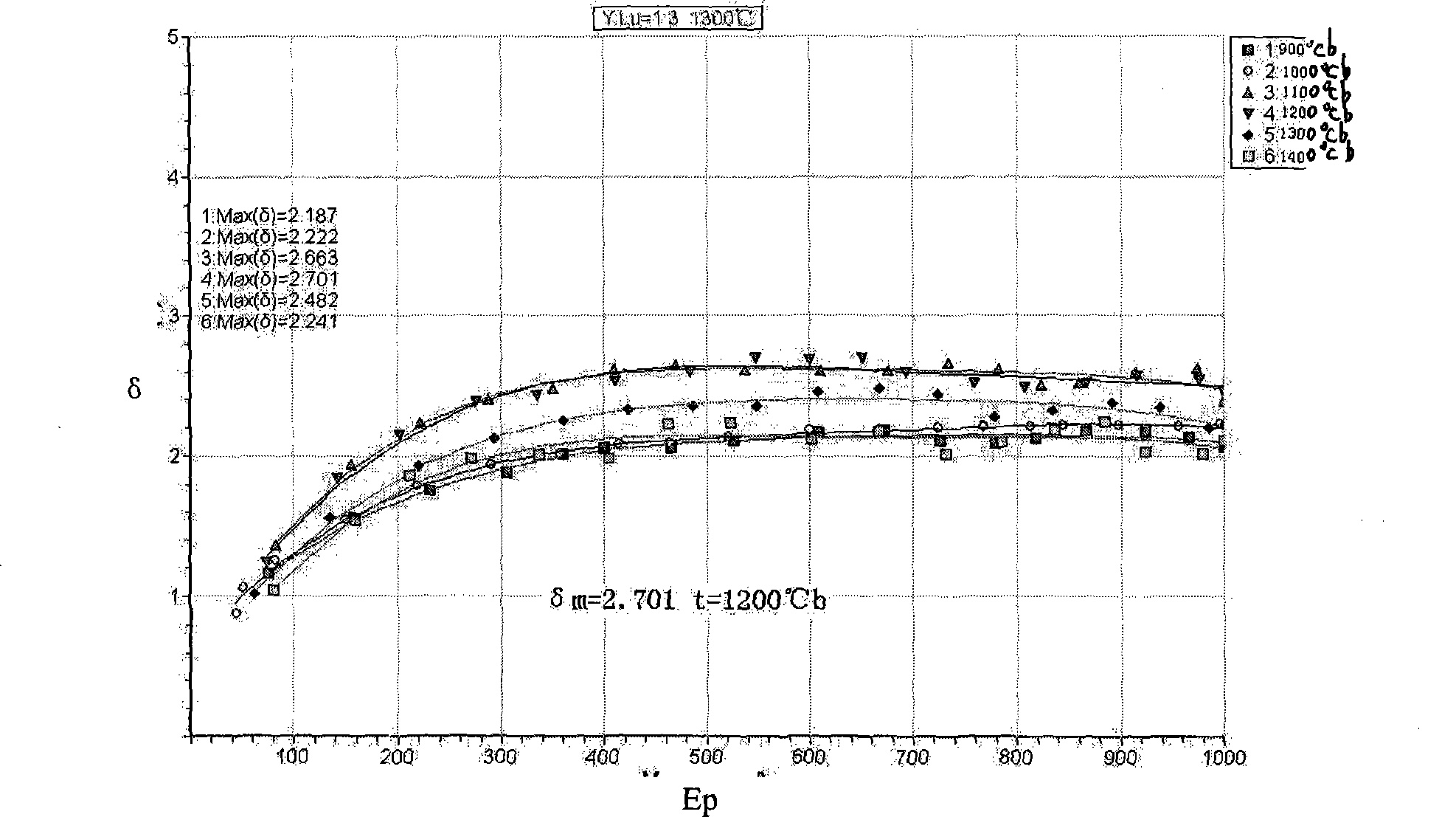
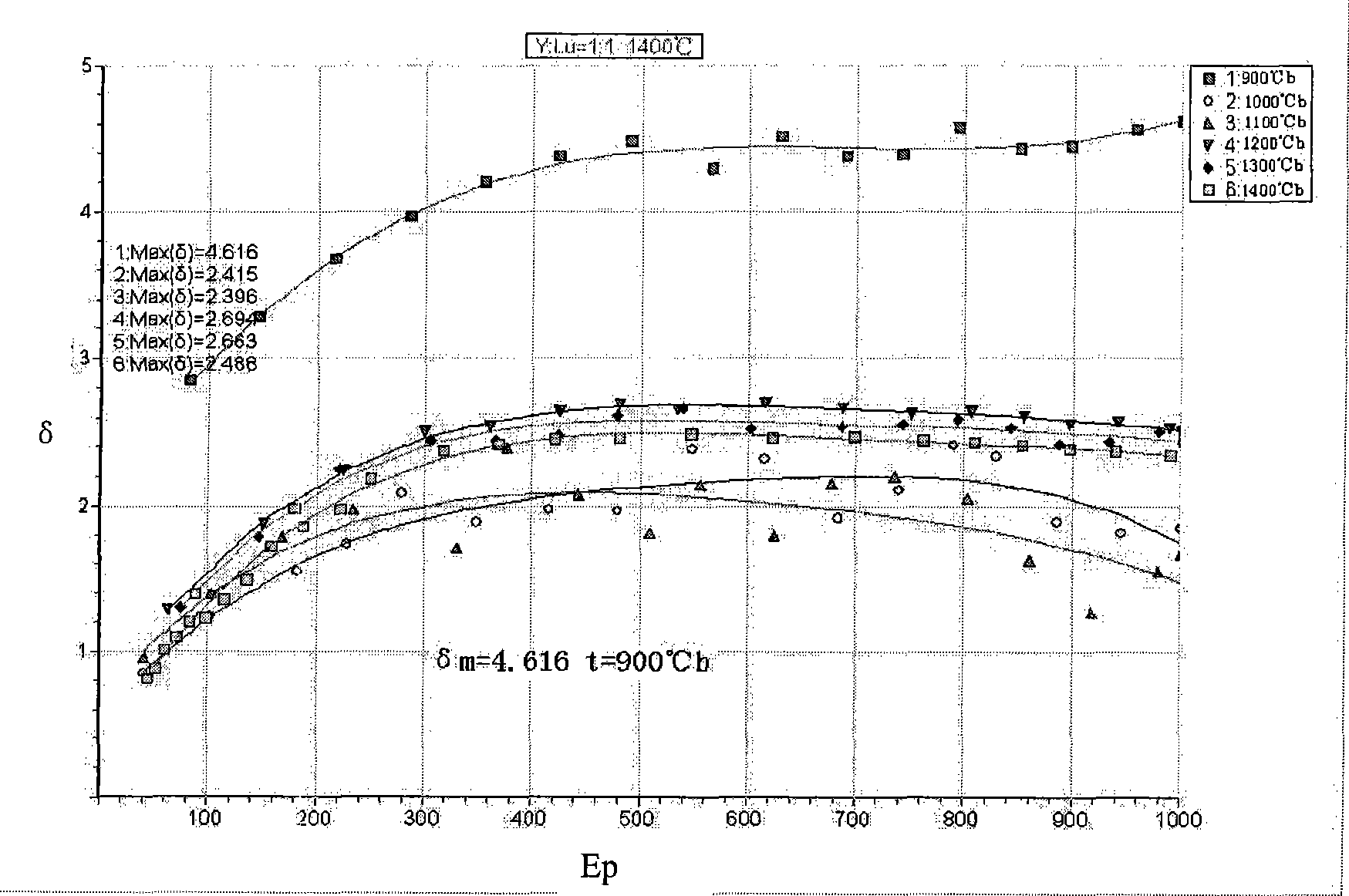
Y2O3-Lu2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101447376AEasy to processHigh secondary electron emission coefficientSecondary electron emitting electrodesPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureRare-earth elementLutetium
The invention discloses Y2O3-Lu2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of rare earth refractory metal cathode materials. The prior cathode material cannot satisfy the higher electron emission requirements. The Y2O3-Lu2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and the preparation method thereof are characterized in that yttrium and lutetium which are rare earth elements are used as additional elements, and are mixed into metal molybdenum in any proportion for the preparation of the cathode material. The material is obtained by mixing Lu2O3 and Y2O3 which are two rare earth oxides in any proportion, the mixed rare earth oxides account for 20 percent wt of the gross weight of the emission material, and others are molybdenum. The Y2O3-Lu2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material can be utilized to make rare earth-molybdenum secondary electron emission material, the secondary electron emission coefficient thereof is higher a lanthanum-containing cathode, and optimum activation temperature is less than the lanthanum-containing cathode and a cerium-containing cathode.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
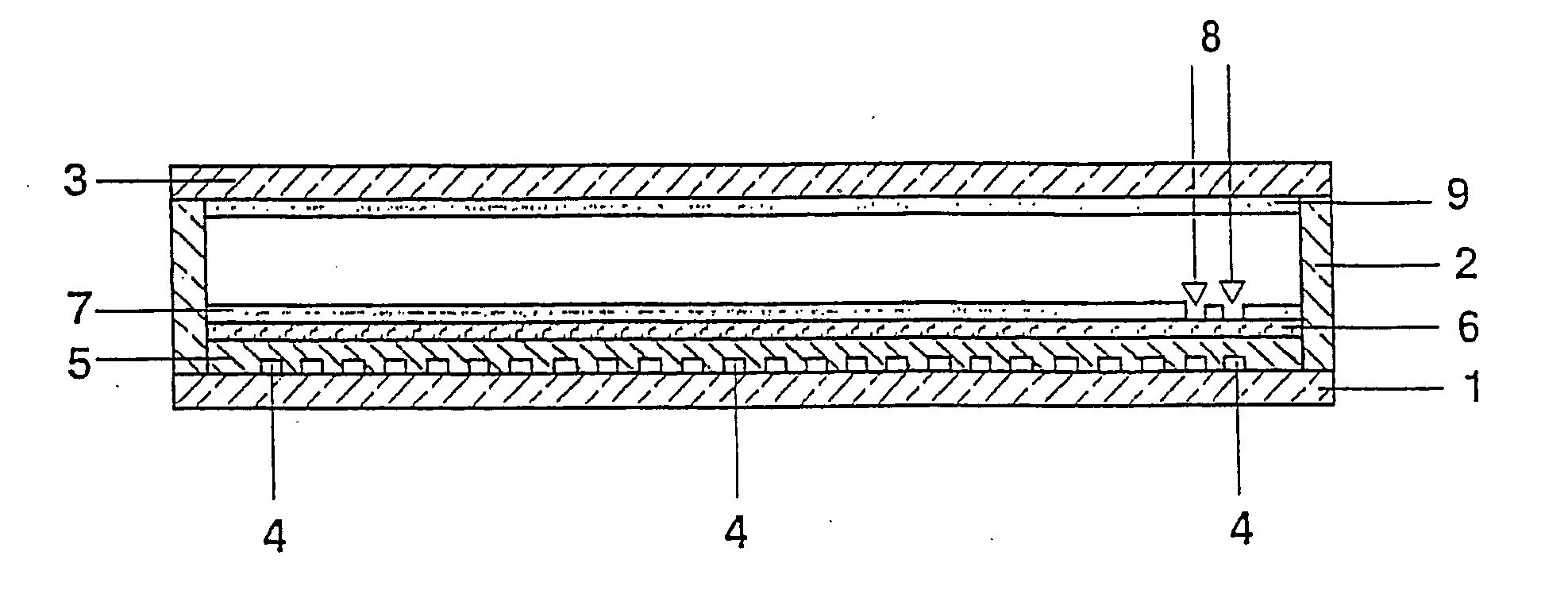
With ignition assisted discharge lamp
InactiveUS20040046490A1Gas-filled discharge tubesDischarge tube luminescnet screensGas-discharge lampSecondary electron emission coefficient
A dielectric barrier discharge lamp having electrodes arranged on the wall of the discharge vessel has a VUV / VIS reflection layer (6) made of a material with a high secondary electron emission coefficient on at least a part of the inner wall of the discharge vessel. A luminescent material layer (7) is in turn applied on the VUV / VIS reflection layer (6). Moreover, at least one partial region (8) without luminescent material is provided in the luminescent material layer (7), this at least one partial region (8) partially uncovering the underlying VUV / VIS reflection layer (6) and additionally being arranged at least in direct proximity to one or more electrodes (4) of the lamp. As a result, the ignition behavior of the lamp is improved, in particular during ignition in darkness.
Owner:PATENT TREUHAND GESELLSCHAFT FUR ELECTRIC GLUEHLAMPEN MBH
Gas Discharge Display Panel
InactiveUS20080278074A1More reliabilityReduce layeringVacuum evaporation coatingAlternating current plasma display panelsManufacturing cost reductionTectorial membrane
Provided is a gas discharge display panel that exhibits a favorable display performance by maintaining a wall charge retaining power, controlling discharge delay within a range adequate for optimal image display, and reducing the discharge starting voltage at comparatively low cost. Also provided is a PDP that exhibits more reliability with enhanced display quality by further improving the secondary electron emission factor γ compared to conventional cases and lowering the discharge starting voltage to widen the driving margin. Further provided is a manufacturing method of a gas discharge display panel, by which the manufacturing cost lowers by reduction of the exhaustion time in the sealing exhaustion process, and by which the driving circuit cost is reduced. In a gas discharge display panel of the present invention, a protective layer (15) has a first protective film (151) and a second protective film (152), the second protective film (152) is formed on at least part of a surface of the first protective film (151), and the first protective film (151) has a larger impurity content than the second protective film (152).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for restraining secondary electron emission by directly depositing nano-graphene
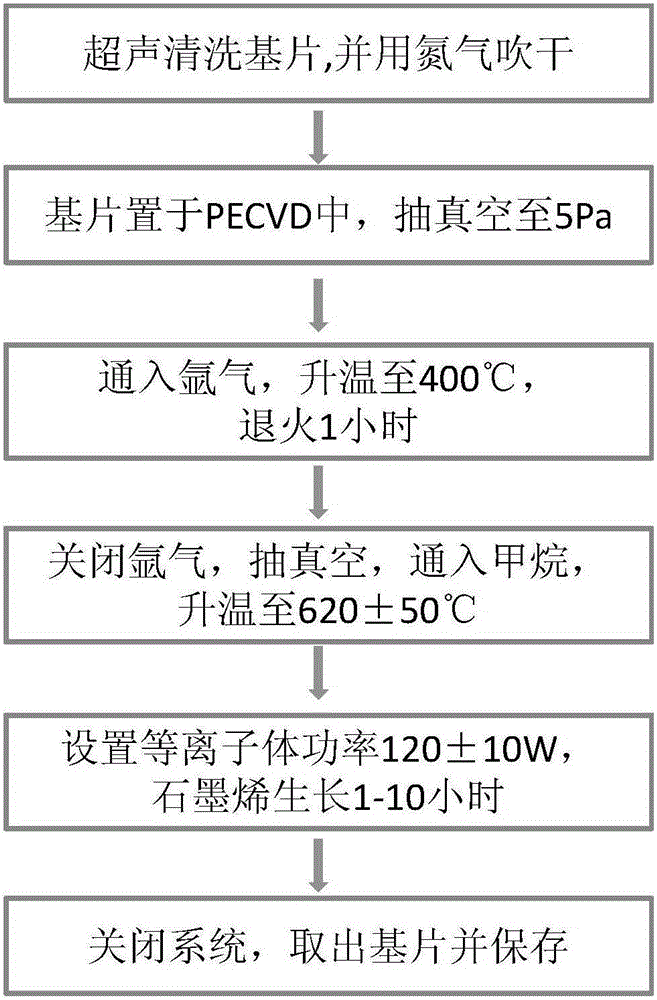
ActiveCN105200390AReduced emissivityImprove conductivityChemical vapor deposition coatingParticle acceleratorMicrowave
The invention relates to a method for restraining secondary electron emission by directly depositing nano-graphene. By means of the method, the plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition nano-graphene process technology is applied to the field of restraining secondary electron emission, thickness-controllable nano-graphene thin film growth is achieved on the surface of a metal substrate by conducting improvement and optimization design on the technological process, and the coefficient of secondary electron emission can be decreased to be smaller than 1.1; meanwhile, the process stability is high, the change of the coefficient of substrate secondary electron emission is smaller than 10% after the substrate is placed under the room-temperature atmosphere for half a year. The method has good application prospects in the aspects of solving the problems of the microwave part micro-discharge effect and the electronic cloud of particle accelerators.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
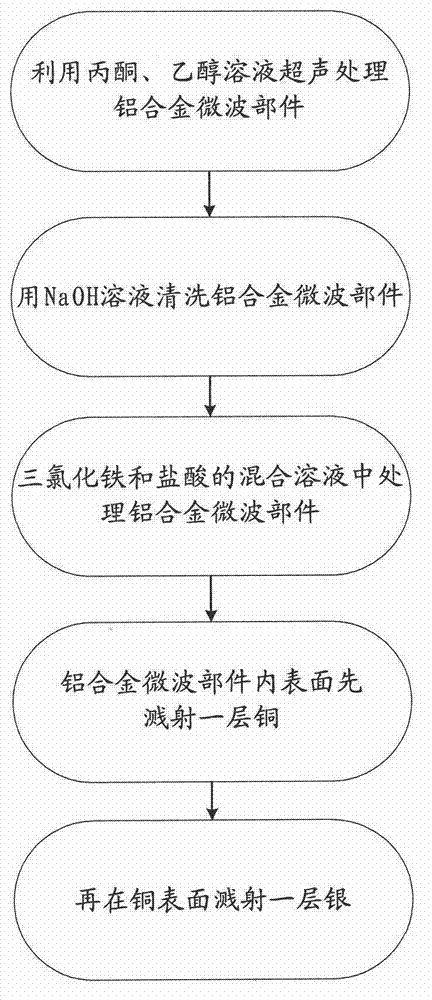
Method for reducing secondary electron emission coefficient on silver-plated surface of aluminum alloy
ActiveCN102816997ALower emissivitySmall featureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSilver plateElectron
The invention provides a method for reducing a secondary electron emission coefficient on silver-plated surface of aluminum alloy. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out ultrasonic cleaning with an acetone solution on the interior surface of an aluminum alloy microwave component for 10 min and then carrying out ultrasonic cleaning with an ethanol solution for 10 min; (2) cleaning the cleaned interior surface of the aluminum alloy microwave component with a NaOH solution having a concentration of 50 g / L and a temperature of 50 DEG C for 1 min so as to remove an oxide film on the surface of the aluminum alloy; (3) treating the aluminum alloy microwave component with ferric trichloride having a concentration of 5 g / L and a hydrochloric acid mixed solution having a concentration of 10 g / L for 3 min at a temperature of 40 DEG C; (4) sputtering a layer of copper on the interior surface of the aluminum alloy microwave component; and (5) sputtering a layer of silver on the surface of copper. The method provided by the invention can effectively reduce the secondary electron emission coefficient on the silver-plated surface of the aluminum alloy.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Ac-plasma display devices using metal nanoparticles or nanostructures and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110260602A1Excellent luminous propertiesIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsTectorial membranePhotoluminescence
The present invention provides an AC plasma display device using metal nanostructures, including: a front panel and a rear panel which are disposed in parallel to each other and at least one of which is provided with electrodes for gas discharge; an electrode layer, a front dielectric layer and a protective film which are sequentially formed on a side of the front panel which faces the rear panel; a phosphor layer which is formed on the rear panel and which is excited and simultaneously radiated by gas discharge occurring in the electrodes; and metal nanostructures included in the protective film and the phosphor layer, and provides a method of manufacturing the same. The AC plasma display device can improve a secondary electron emission coefficient and photoluminescent intensity using surface plasmon excitation because it is provided with a protective film including metal nanostructures.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
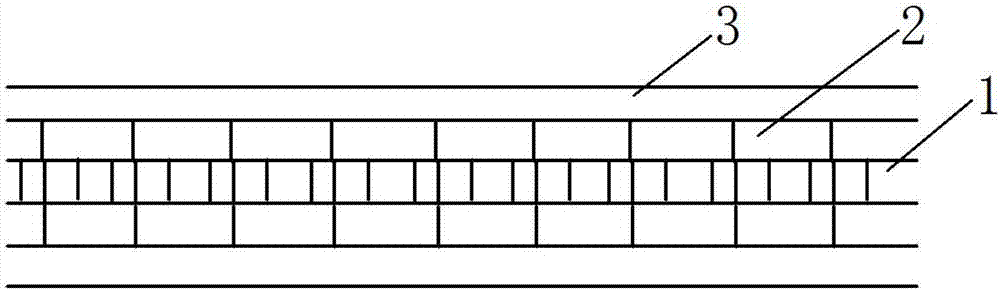
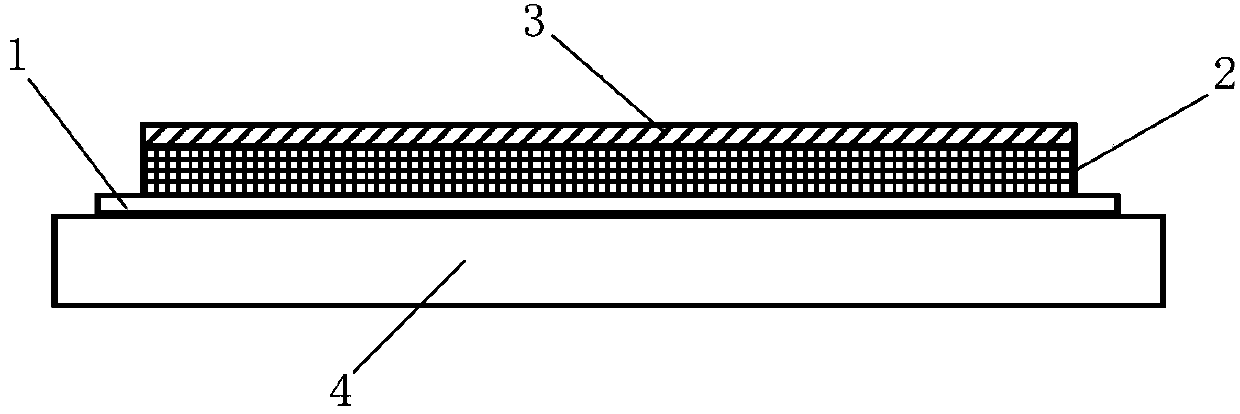
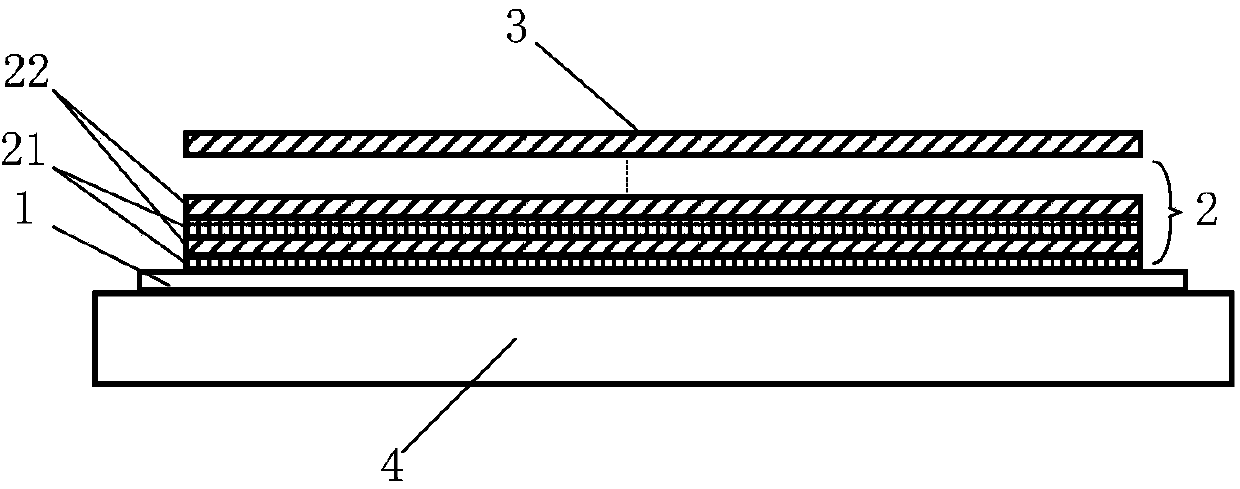
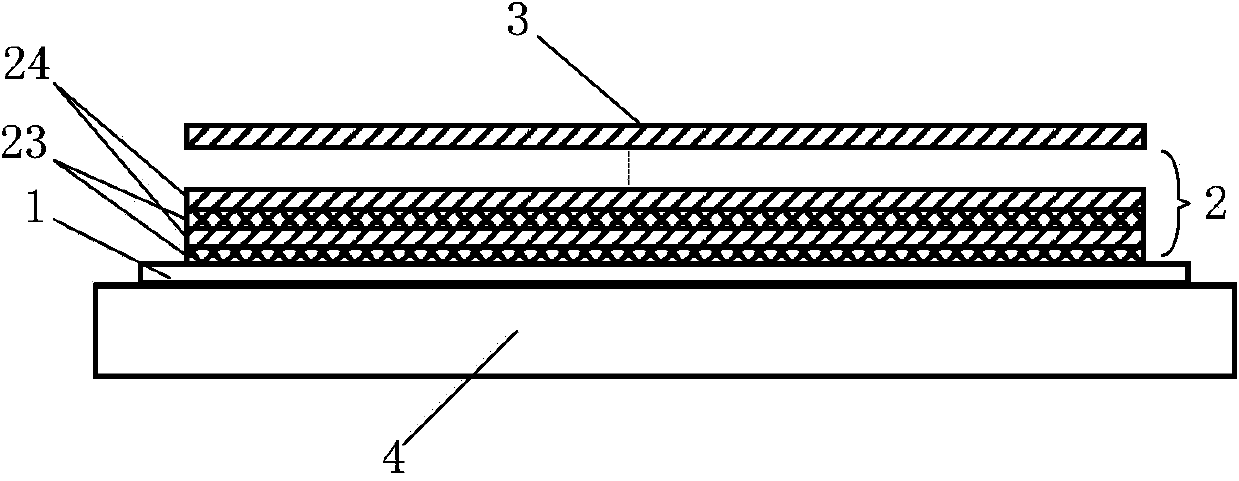
Vacuum insulation structure
InactiveCN1841572ALower secondary electron emission coefficientIncrease vacuum surface flashover voltageInsulatorsSecondary electron emission coefficientField intensity
The invention relates to a vacuum insulating structure, which especially relates to an insulating structure for impulse voltage effect in the field of vacuum impulse technique. It is characterized in that it arranges a complex film layer between the vacuum impulse voltage of the base insulating material (1) and the vacuum touched surface; the complex film layer is formed by a low second time electron sending factor insulating material film layer (2) and a mental film layer (3), wherein the insulating material film layer (2) is located on the surface of the base insulating material (1); the mental film layer (3) can be embedded into the base insulating material (1) or the insulating material film layer (2). It arranges a transient metal layer (4) between the base insulating material (1) and the insulating material film layer (2).
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
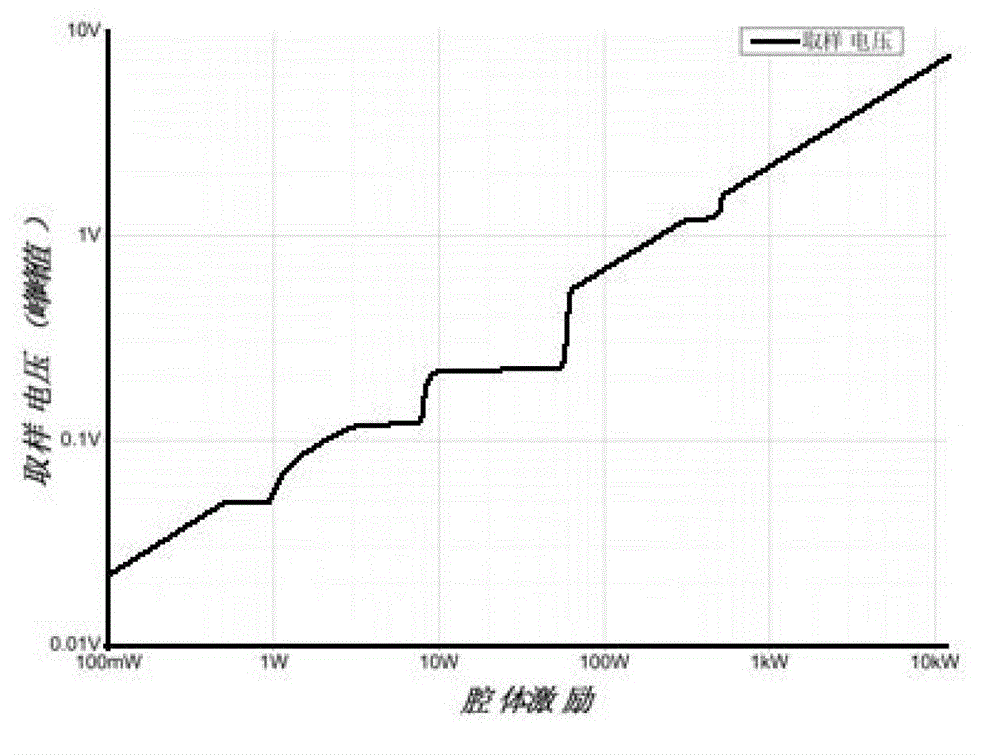
Gas pulse discharge parameter measuring method and device
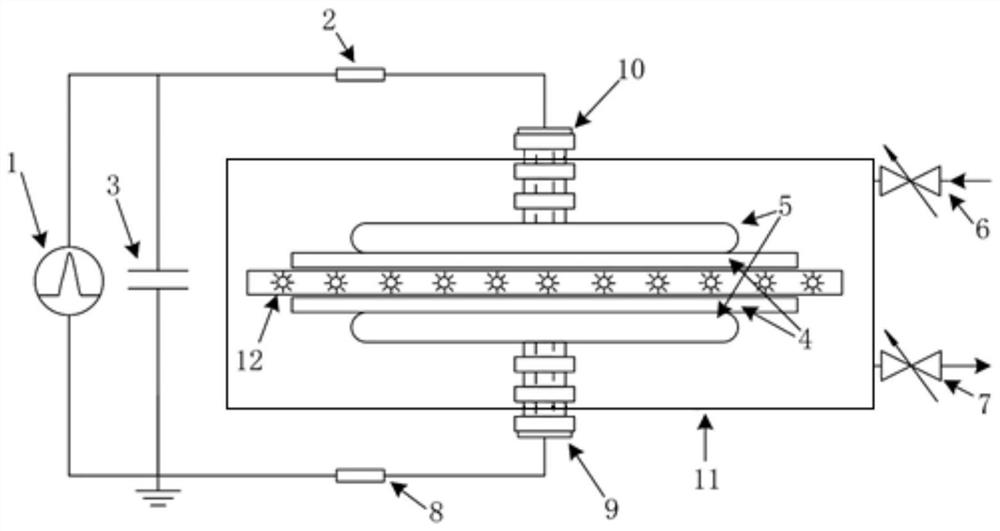
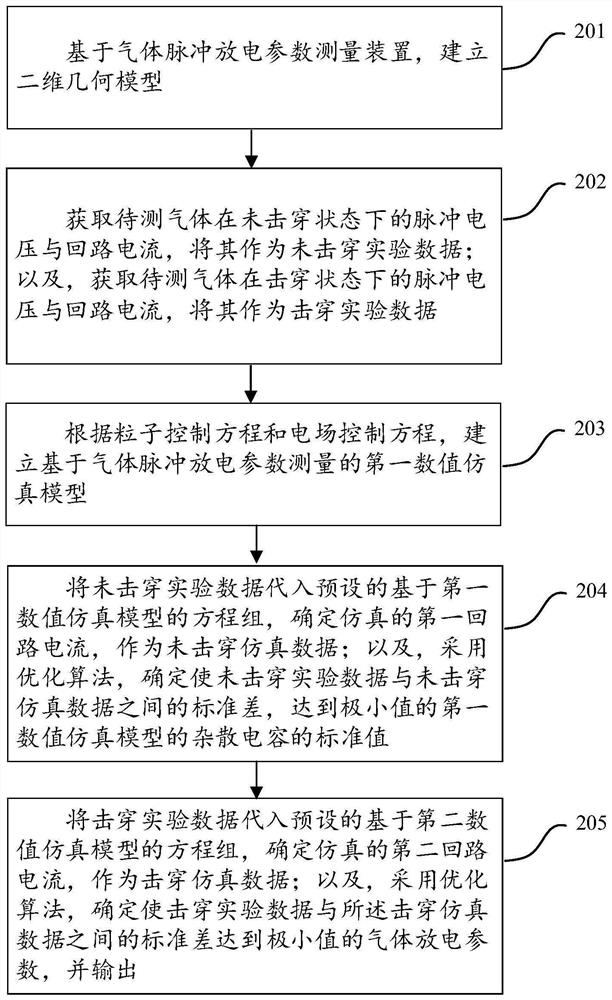
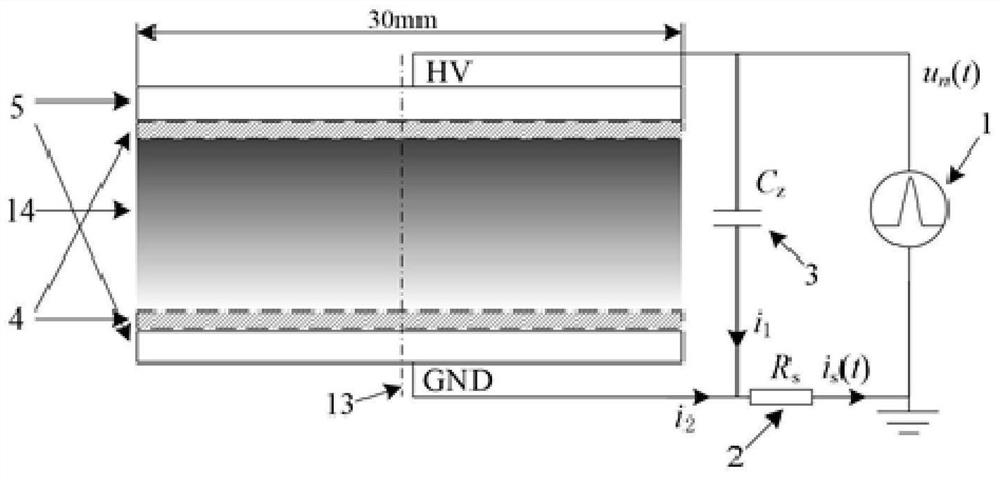
ActiveCN111880051ARealize measurementFill in the measurement gapsTesting dielectric strengthCapacitanceEngineering
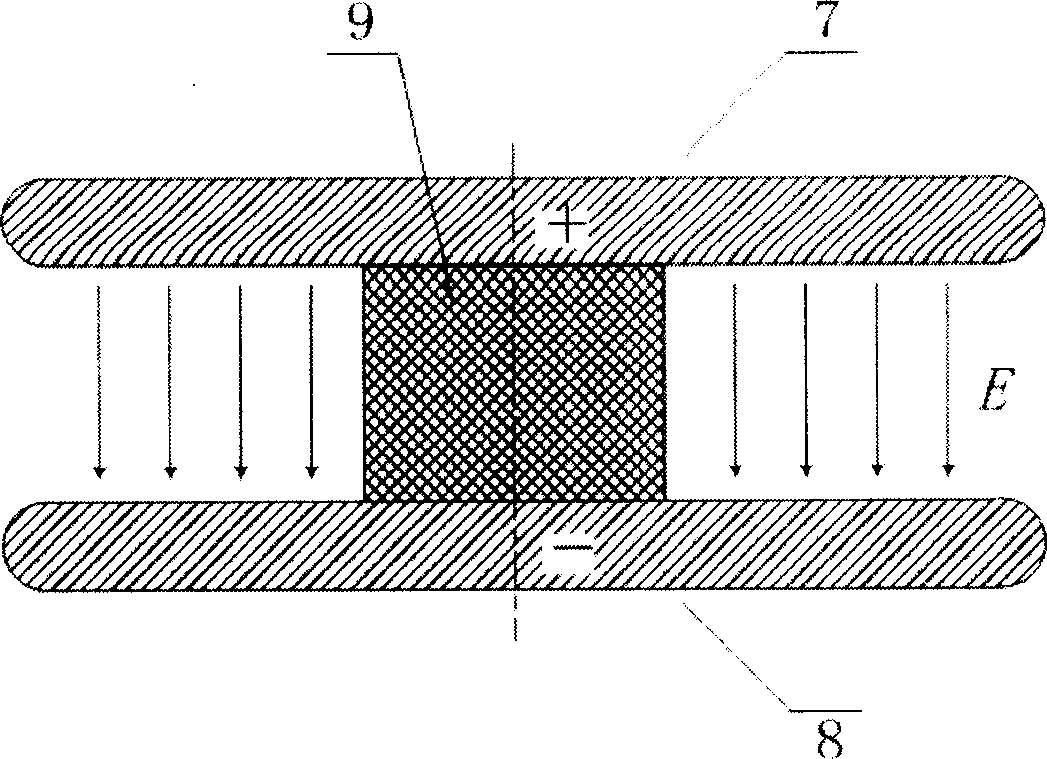
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring gas pulse discharge parameters, and the method and device are used for realizing accurate measurement of the gas pulse discharge parametersunder an atmospheric pressure condition. According to the invention, the method comprises the steps: adopting a gas pulse discharge parameter measuring device to respectively obtain a pulse voltage and a loop current of gas to be measured in a non-breakdown state and a breakdown state; establishing a numerical simulation model according to the particle control equation and the electric field control equation; according to the numerical simulation model and a preset equation set, adjusting and optimizing the stray capacitance parameter value of the numerical simulation model through the non-breakdown experiment data; according to the optimized numerical simulation model, obtaining the simulated loop current, and then determining gas discharge parameters such as a soup ionization coefficient, an electron adhesion coefficient, a secondary electron emission coefficient, a photoionization coefficient and the like which enable the breakdown experiment data and the breakdown simulation data to take minimum values by adopting a direction acceleration optimization method, and calculating the standard deviation between the breakdown experiment data and the breakdown simulation data.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation method of high beryllium copper alloy strip material short process for dynode of photomultiplier
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high beryllium copper alloy strip material short process for a dynode of a photomultiplier, and relates to a preparation method of the beryllium copper alloy strip. The problems that the mass fraction of beryllium in an existing beryllium copper strip is low, the porosity of a beryllium copper strip is large, the compactness of a structure is poor, macroscopic segregation is generated and production efficiency is low are solved; the method comprises the following steps that 1, semi-continuous preparation is carried out to prepare a blank; 2, extrusion is carried out; 3, rolling and acid pickling are carried out; and 4, finish rolling, annealing and winding are carried out to obtain the high beryllium copper alloy strip for the dynode of the photomultiplier. According to the method, a peak secondary electron emission coefficient of the high beryllium copper alloy strip for the dynode of the photomultiplier prepared by the method is 8.4-10.8, the tensile strength is 645.4 MPa-670.2 MPa, the yield strength ranges from 314.8 MPa-360.9 MPa, and the percentage elongation after fracture is 15%-19%; and the high beryllium copper alloy strip for the dynode of the photomultiplier can be obtained.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Preparation method of silver membrane trap structure for inhibiting secondary electron emission on surface of microwave part
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silver membrane trap structure for inhibiting secondary electron emission on the surface of a microwave part. The preparation method comprises the steps of promoting growth of a ZnO nano array on the surface of the microwave part, plating silver in gaps of the nano array through electrochemical deposition, and carrying out corrosion treatment on a silver-plated sample sheet through diluted hydrochloric acid, thus finally forming the silver film trap structure on the surface of the microwave part. By constructing the silver film trap structure on the surface of the microwave part, a surface porosity of the microwave part and a depth-width ratio of nano-pores are greatly increased; secondary electron emission on the surface of the microwave part is obviously inhibited; a secondary electron emission coefficient of the surface of the part is reduced to be less than 1.0.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Determination method for secondary electron emission coefficient of metal surface of microwave component
ActiveCN103196932AGuaranteed accuracySolving the Puzzle of Secondary Electron Emission CoefficientsMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionMicrowaveIncident energy
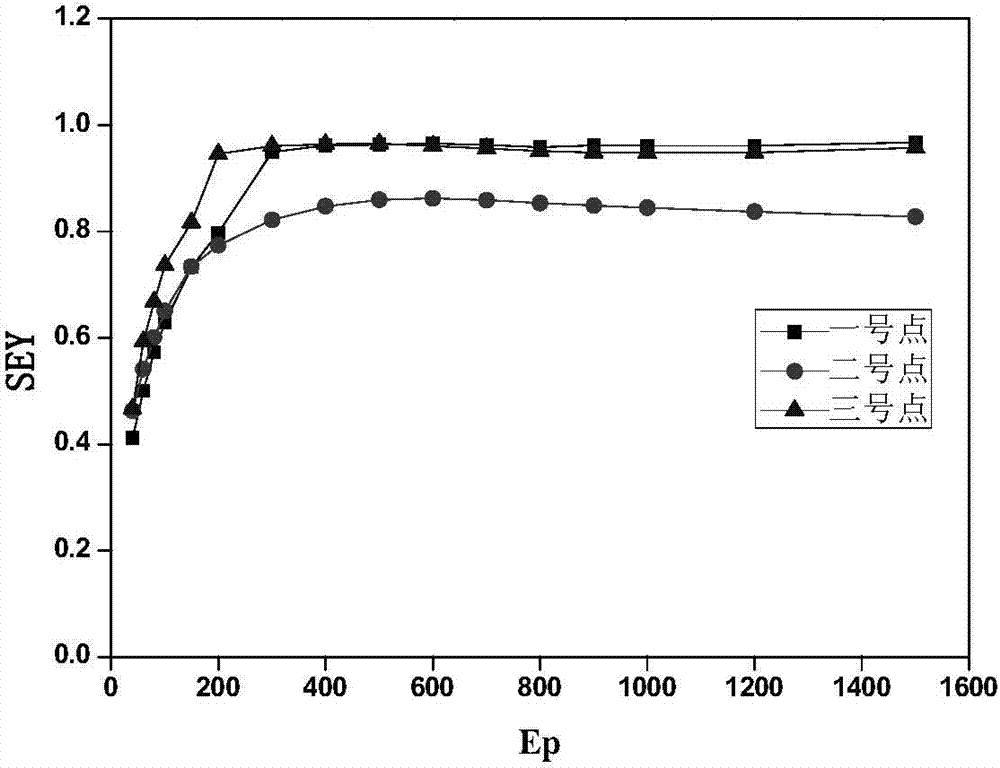
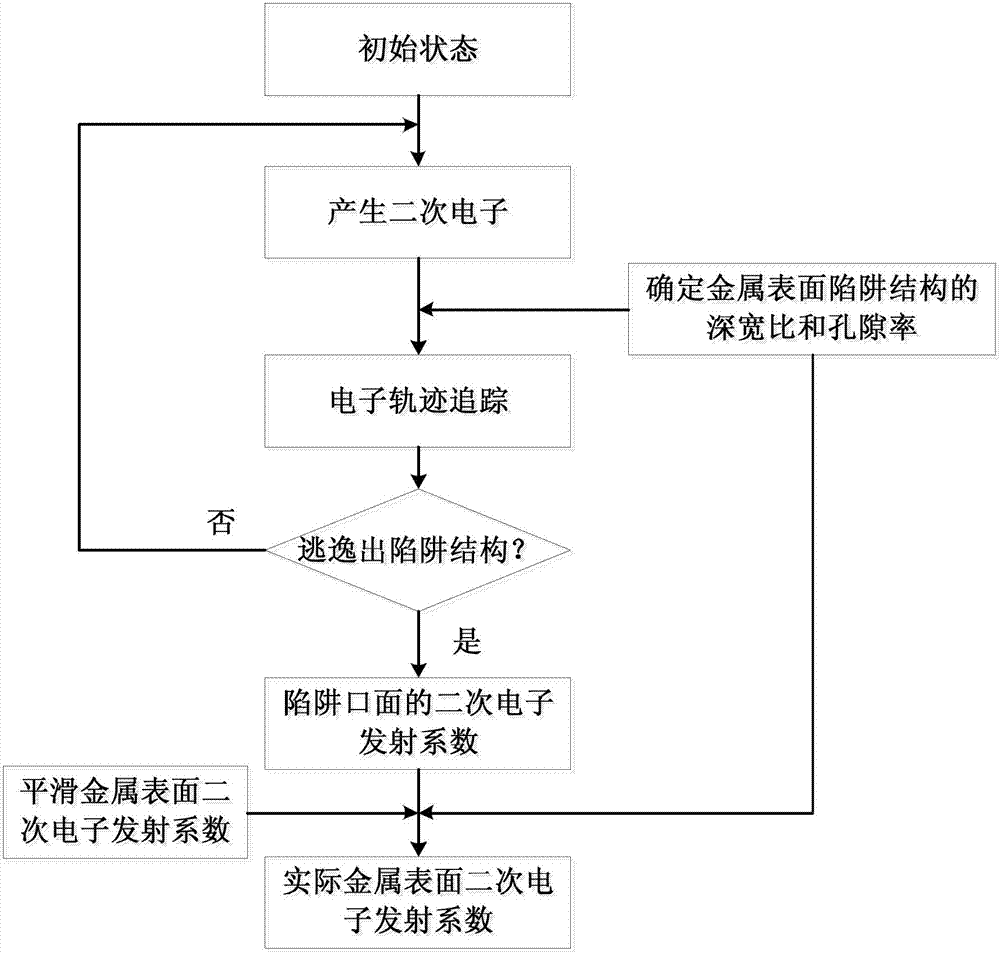
The invention provides a determination method for a secondary electron emission coefficient of the metal surface of a microwave component. The method comprises the following steps: (1) setting an initial state of an incident electron; (2) changing initial energy of the incident electron and counting the number of outgoing electrons under the conditions of different amounts of incident energy so as to obtain a secondary electron emission coefficient of a metal surface; (3) acquiring distribution density and a depth-to-width ratio of a trap structure of the metal surface based on micro-morphology of the metal surface; (4) establishing boundary conditions based on the depth-to-width ratio and an absolute depth, carrying out trajectory tracking on outgoing electrons after collision each time, determining secondary electrons which undergo collision again, are absorbed by a metal wall or escape from a trap opening and go out as the trap structure and finally carrying out counting to obtain a secondary electron emission coefficient on the surface of a trap structure opening; and (5) determining a secondary electron emission coefficient of any actual metal surface based on the distribution density of the trap structure and the secondary electron emission coefficient of the smooth metal surface.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com