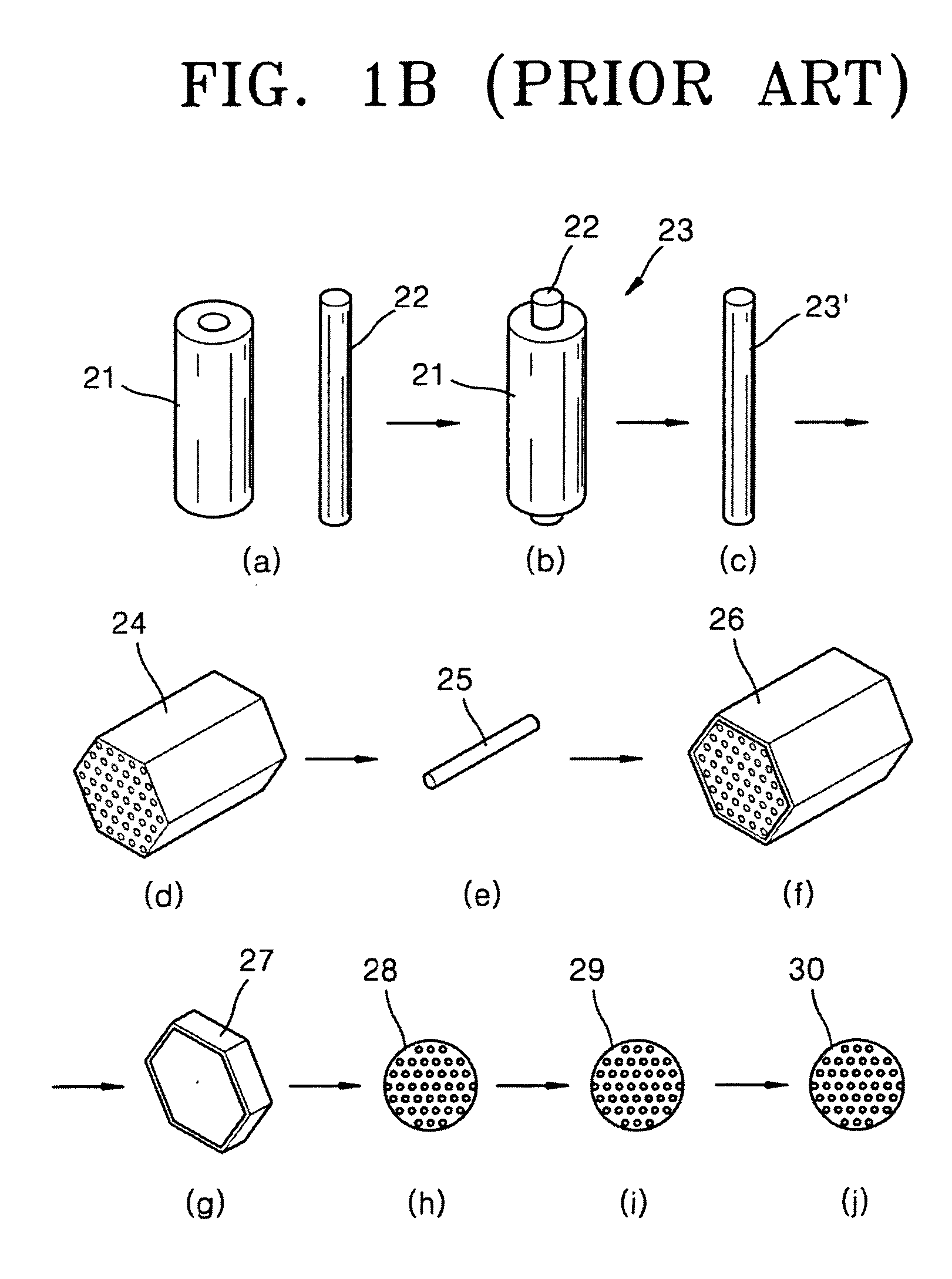
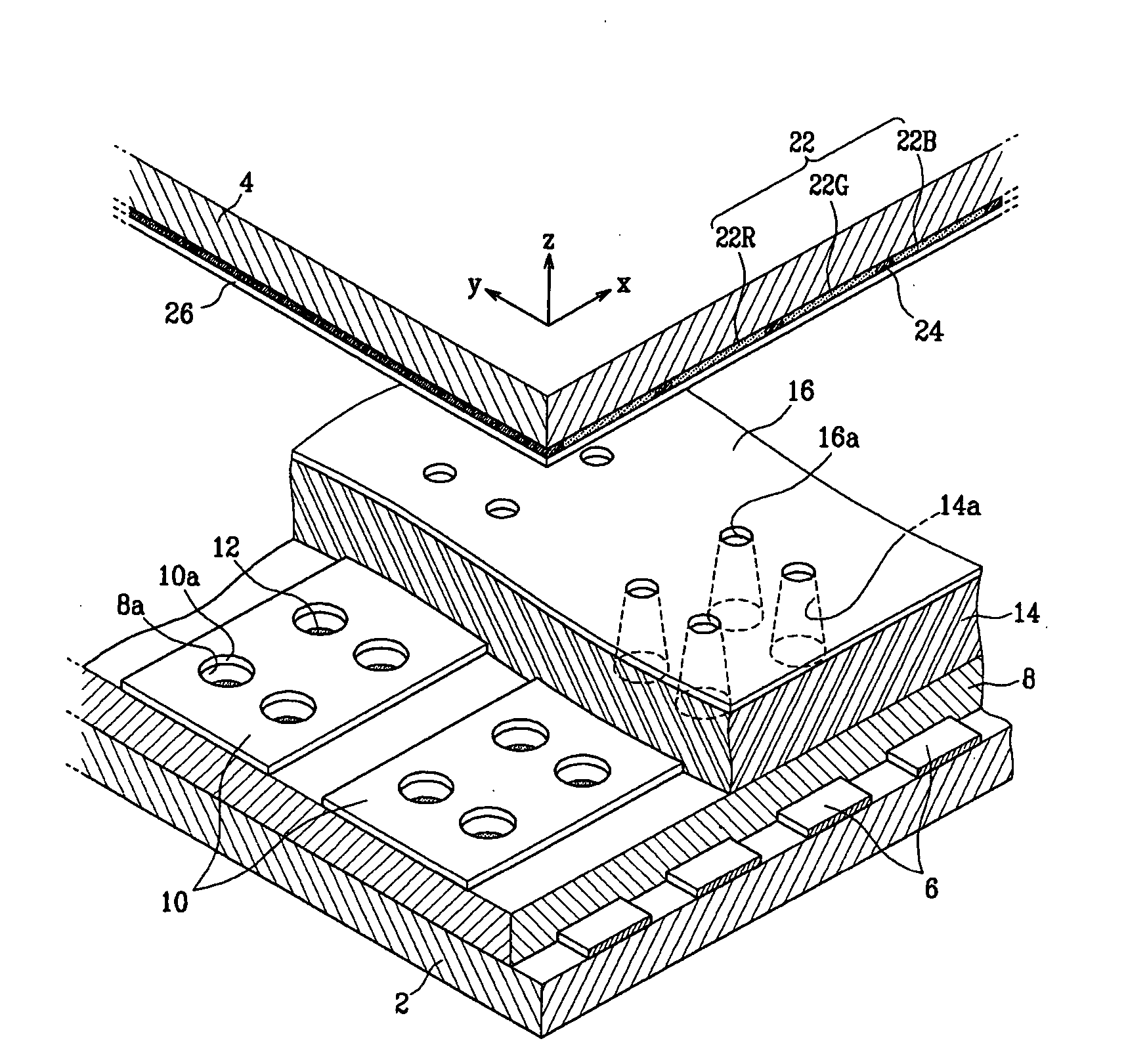
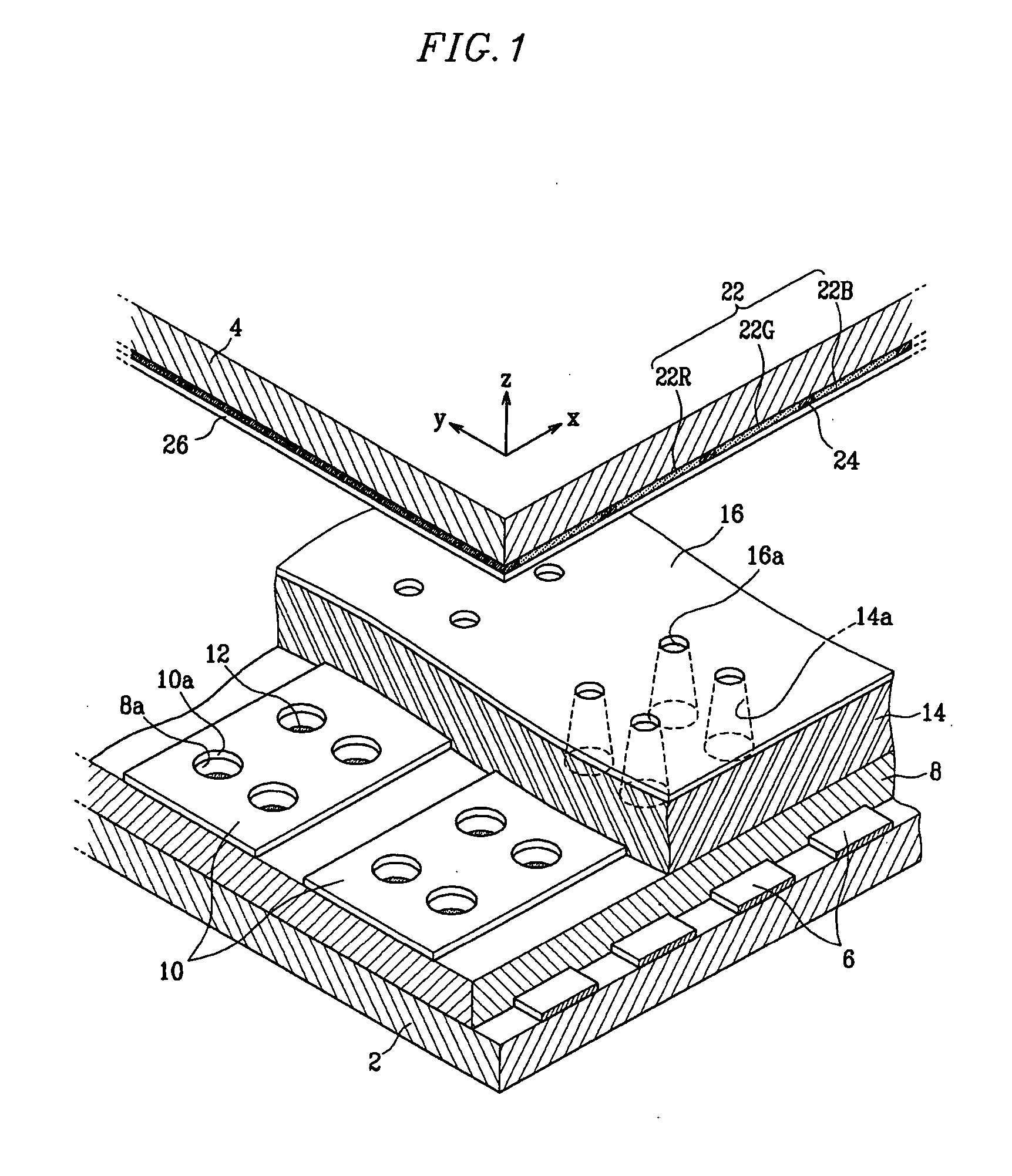
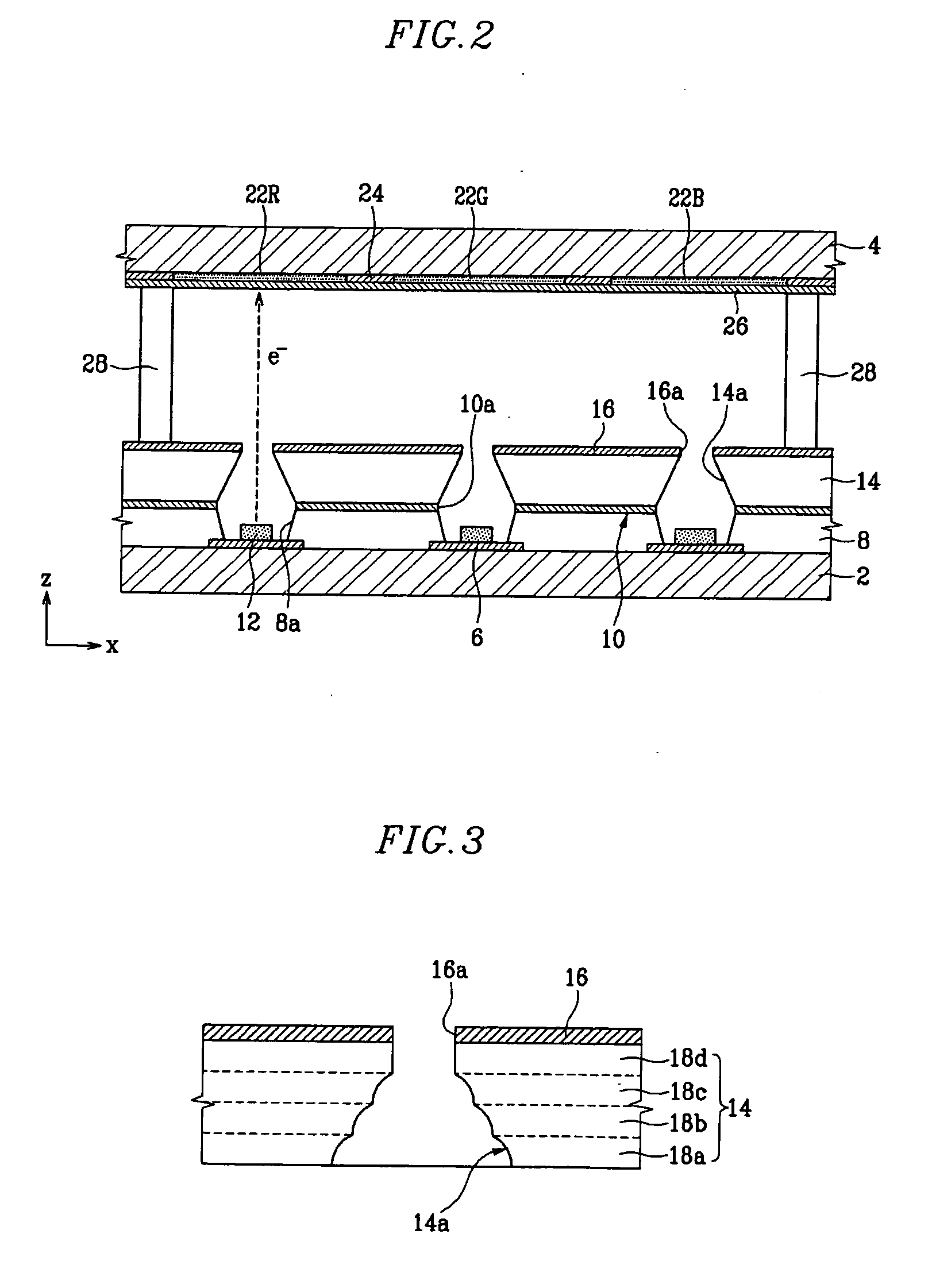
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75results about "Secondary electron emitting electrodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
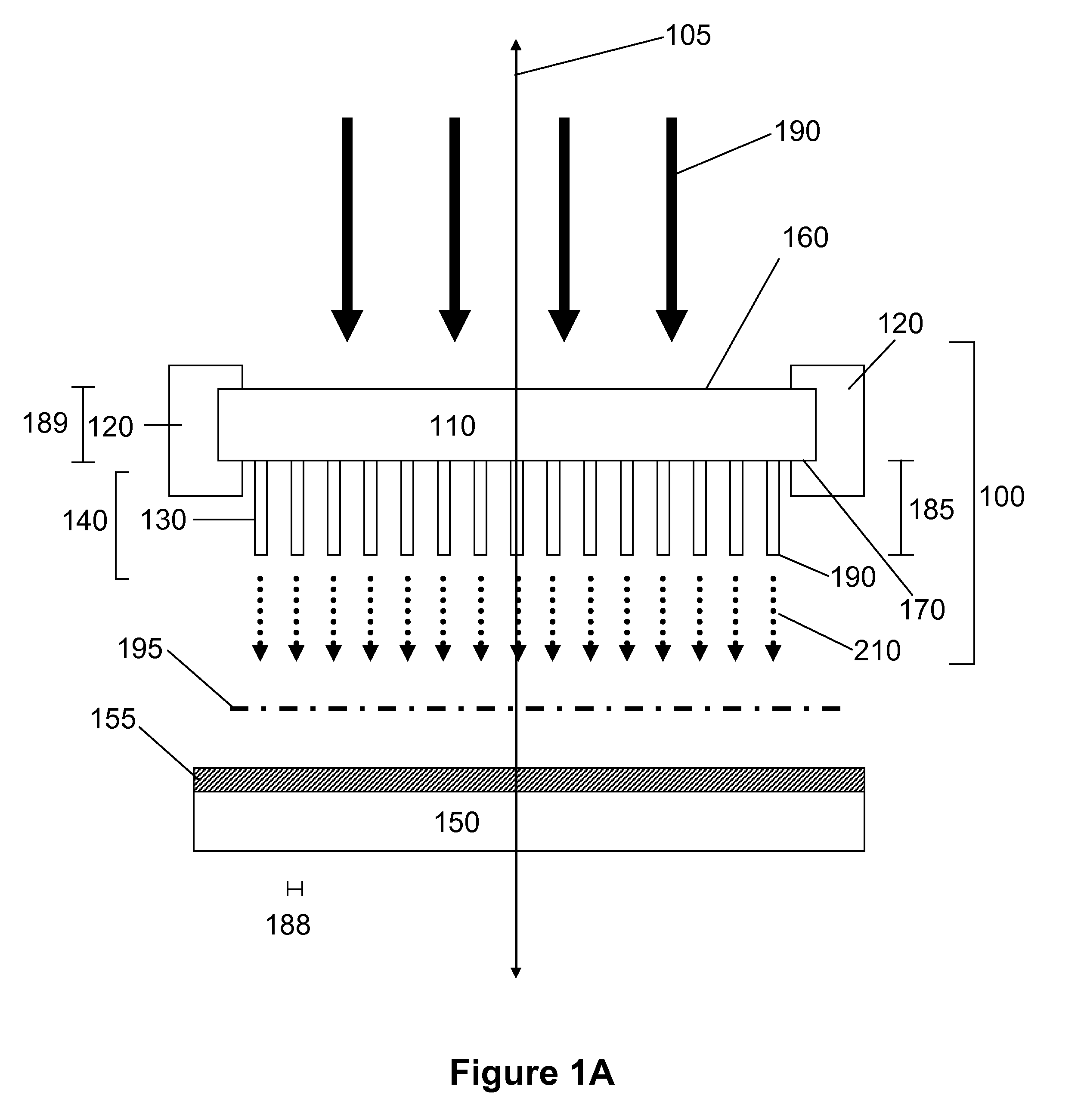
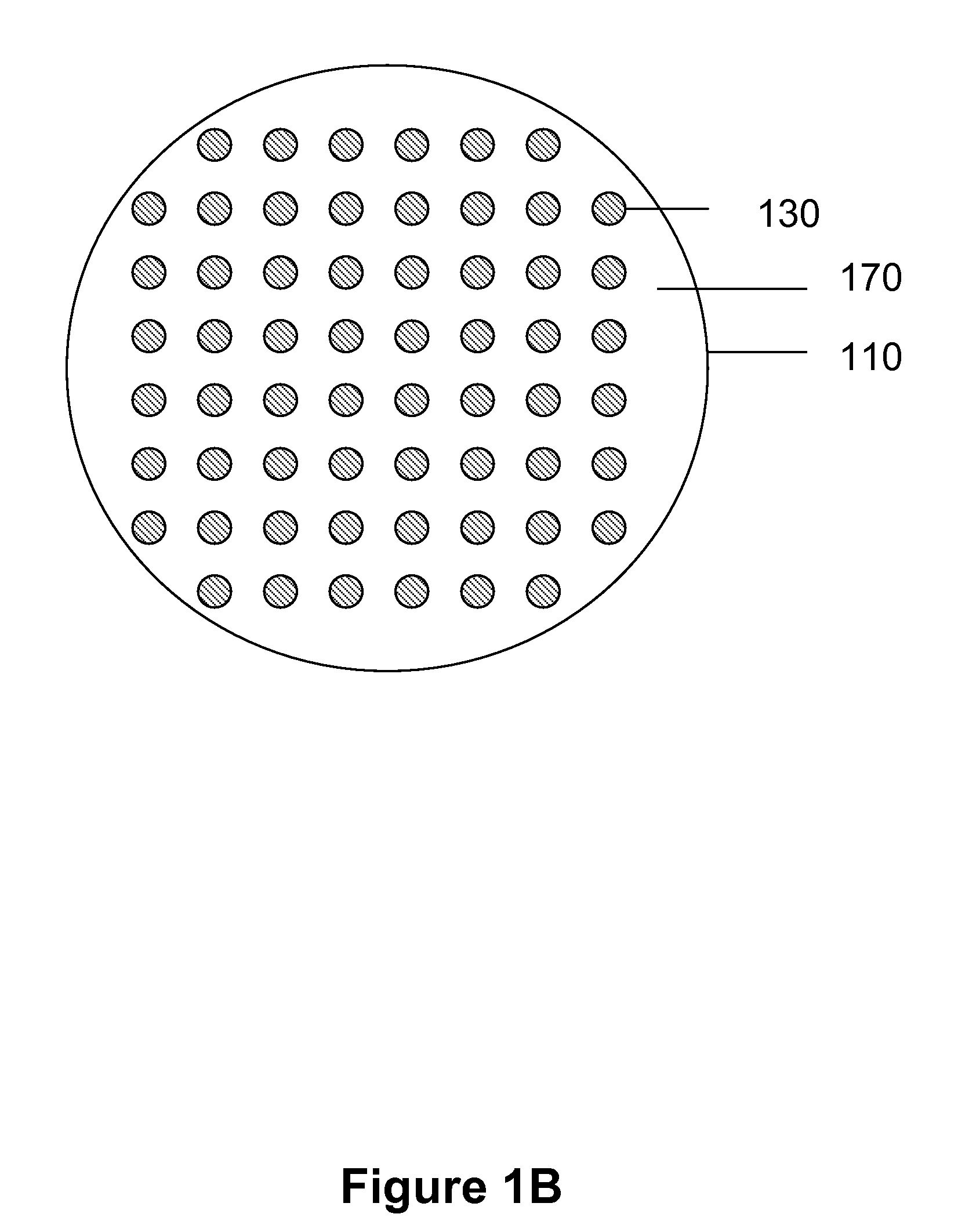
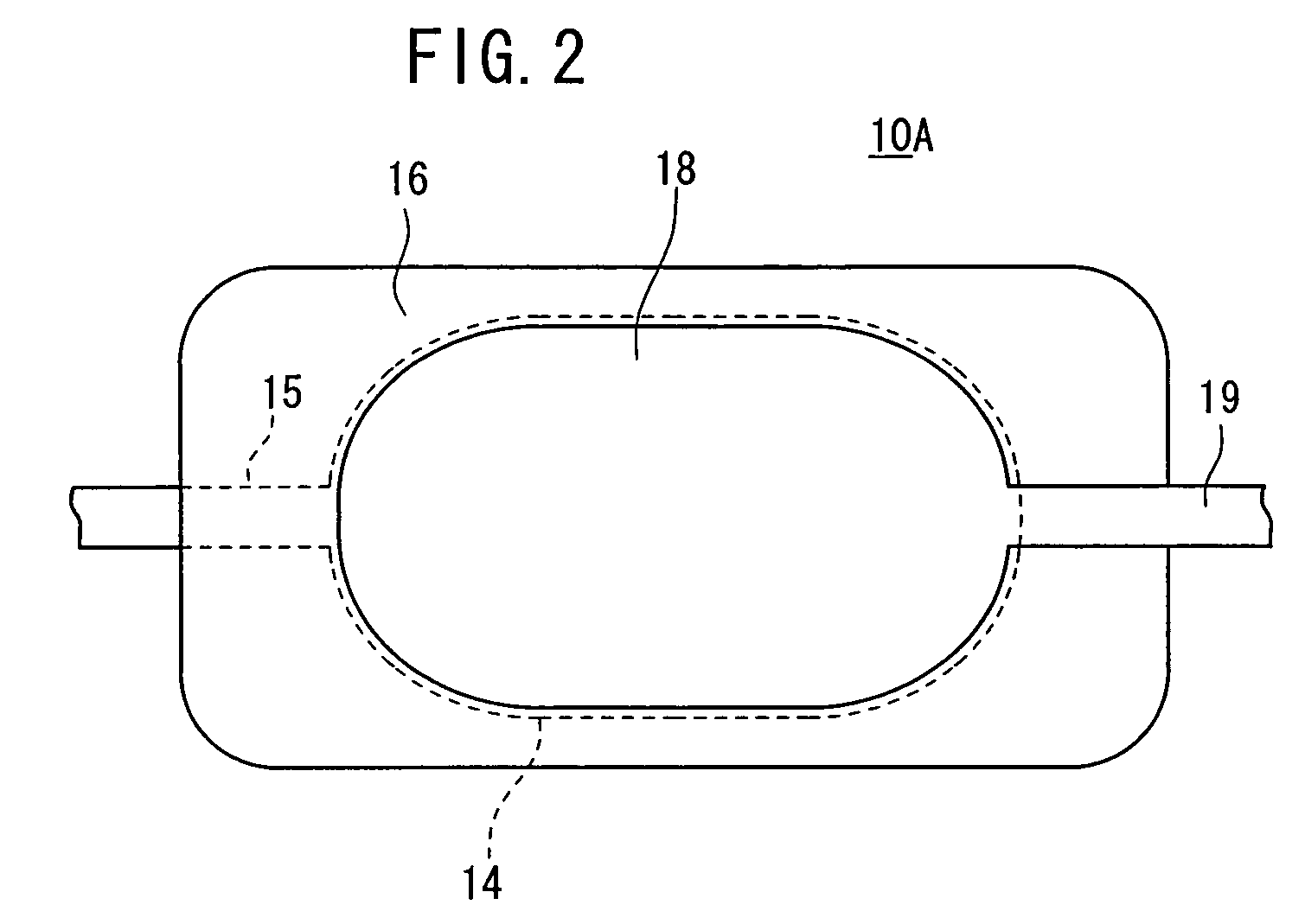
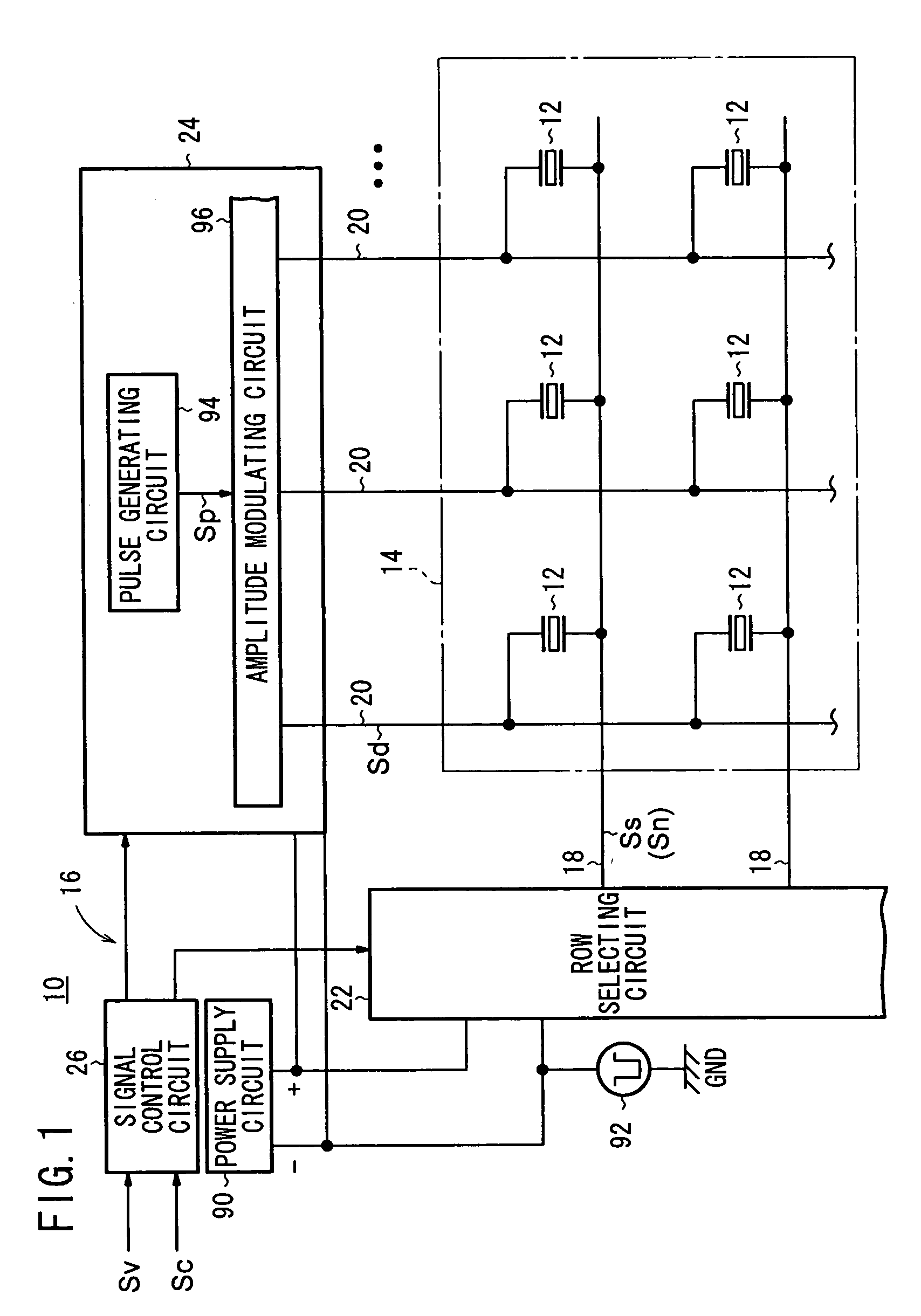
X-ray generation using secondary emission electron source
InactiveUS20080187093A1Harsh operating environmentEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingElectron currentSecondary emission
A method and apparatus are provided for generating high frequency electromagnetic energy using a secondary emission electron source. An x-ray source is therefore provided having a primary electron emitter, a secondary emission member, and an anode. The primary electron emitter provides a primary electron current directed to the secondary emission member. The secondary emission member then generates a secondary electron current which causes x-ray generation when impinging upon the anode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electron emitter and method of producing the same
InactiveUS7307383B2Improve electron emission efficiencyIncrease the number ofWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersDischarge tube luminescnet screensTriple junctionElectron
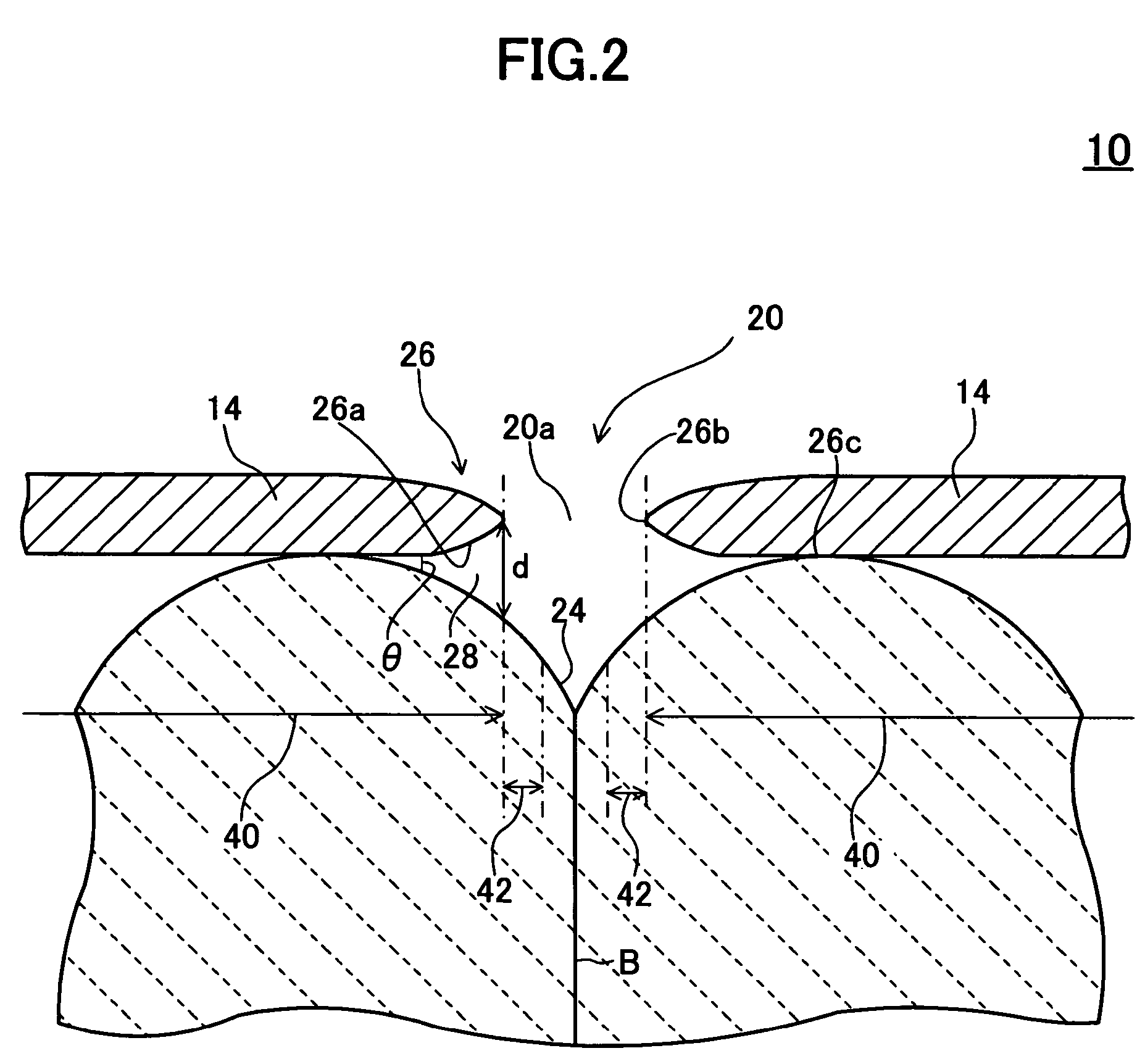
An electron emitter includes an emitter section having a plate shape, a cathode electrode formed on a front surface of the emitter section, and an anode electrode formed on a back surface of the emitter section. A gap is formed between an outer peripheral portion of the cathode electrode and the front surface of the emitter section. The front surface of the emitter section contacts a lower surface of the outer peripheral portion to form a base end as a triple junction. The gap expands from the base end toward a tip end of the outer peripheral portion.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electron emitter formed of a dielectric material characterized by having high mechanical quality factor
InactiveUS7723909B2Increase productionIncrease speedDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsThin layerElectron
A dielectric-film-type electron emitter includes an emitter section, a first electrode, and a second electrode. The emitter section is formed of a thin layer of a polycrystalline dielectric material. The dielectric material constituting the emitter section is formed of a material having high mechanical quality factor (Qm). Specifically, the dielectric material has a Qm higher than that of a so-called low-Qm material (a material having a Qm of 100 or less). The Qm of the dielectric material is preferably 300 or more, more preferably 500 or more.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Nanopillar arrays for electron emission
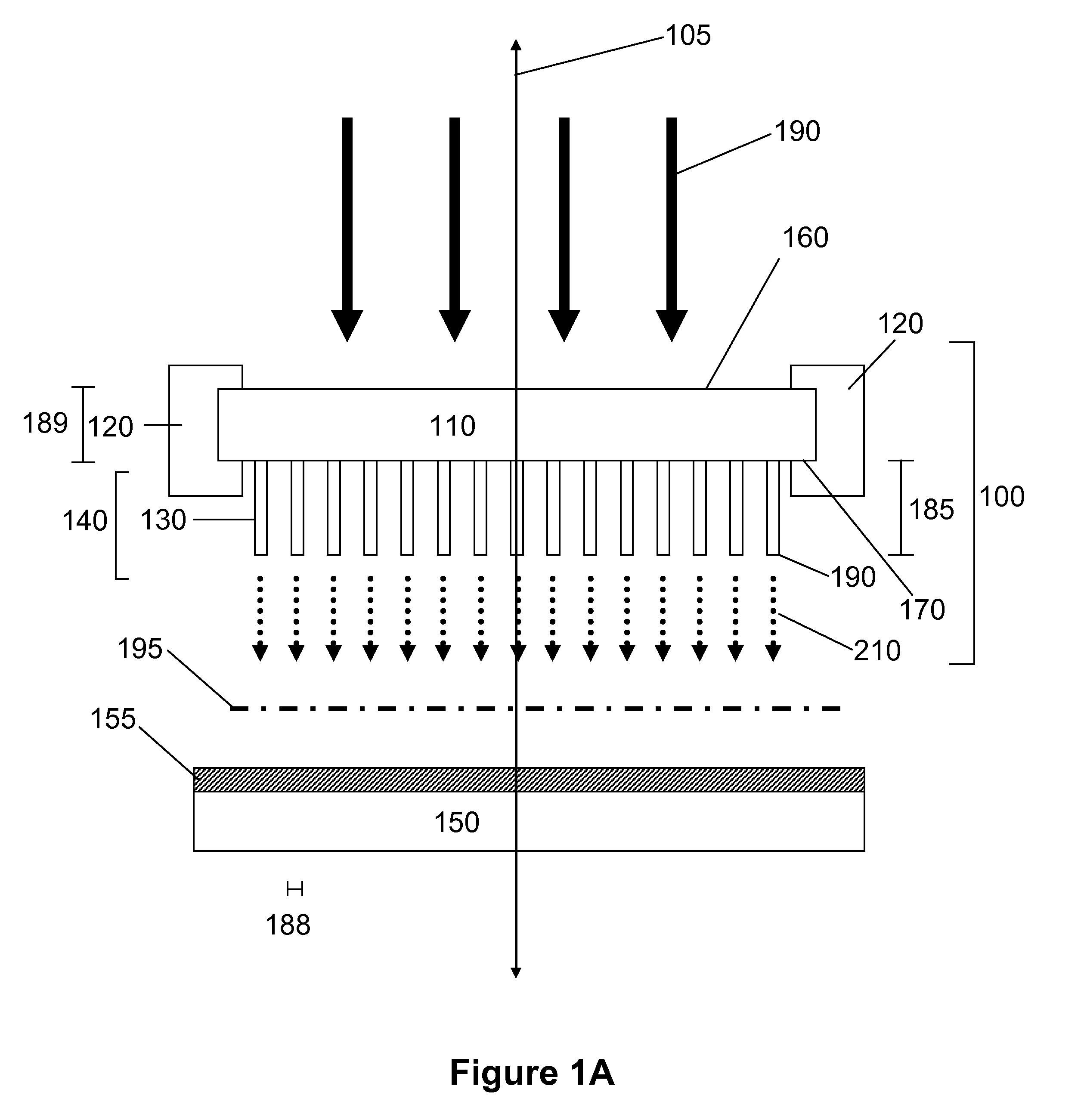
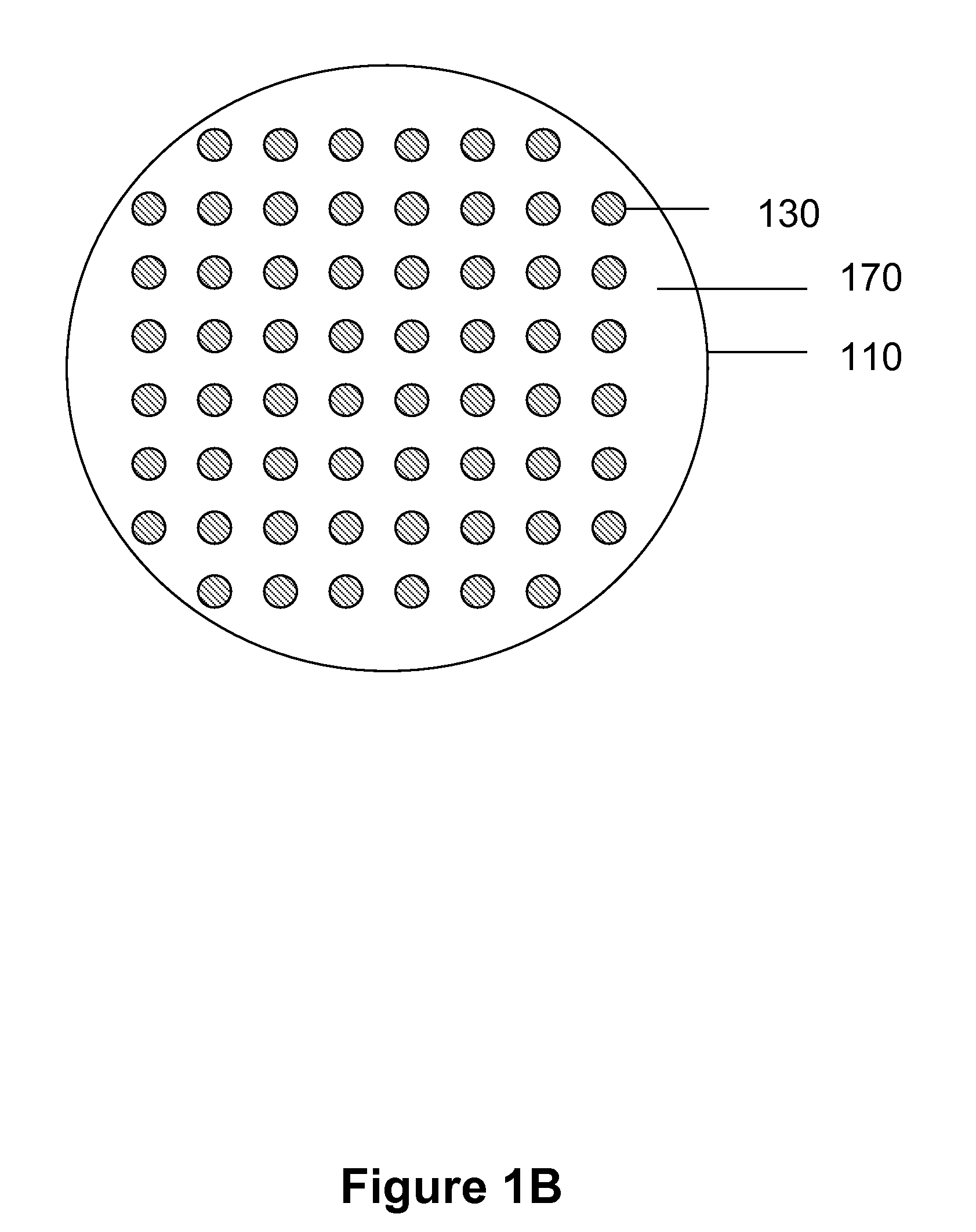
The present invention provides systems, devices, device components and structures for modulating the intensity and / or energies of electrons, including a beam of incident electrons. In some embodiments, for example, the present invention provides nano-structured semiconductor membrane structures capable of generating secondary electron emission. Nano-structured semiconductor membranes of this aspect of the present invention include membranes having an array of nanopillar structures capable of providing electron emission for amplification, filtering and / or detection of incident radiation, for example secondary electron emission and / or field emission. Nano-structured semiconductor membranes of the present invention are useful as converters wherein interaction of incident primary electrons and nanopillars of the nanopillar array generates secondary emission. Nano-structured semiconductor membranes of this aspect of the present invention are also useful as directed charge amplifiers wherein secondary emission from a nanopillar array provides gain functionality for increasing the intensity of radiation comprising incident electrons.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Electron amplifier utilizing carbon nanotubes and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050200254A1Excellent secondary electron emission propertyEasy to makeNanoinformaticsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierCarbon nanotube
An electron amplifier and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. The electron amplifier includes a substrate in which a plurality of through holes are formed, a resistive layer deposited on the sidewalls of the through holes, an electron emissive layer including carbon nanotubes which is deposited on the resistive layer, and an electrode layer formed on each of the upper and lower sides of the substrate. Because the electron emissive layer of the electron amplifier is uniform and provides a high electron emission efficiency, the electron amplification efficiency is improved. The electron amplifier manufacturing method enables economical mass production of electron amplifiers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electron emission device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060208628A1Enhance electron beam focusing efficiencyHigh imagingDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesElectronCathode electrode
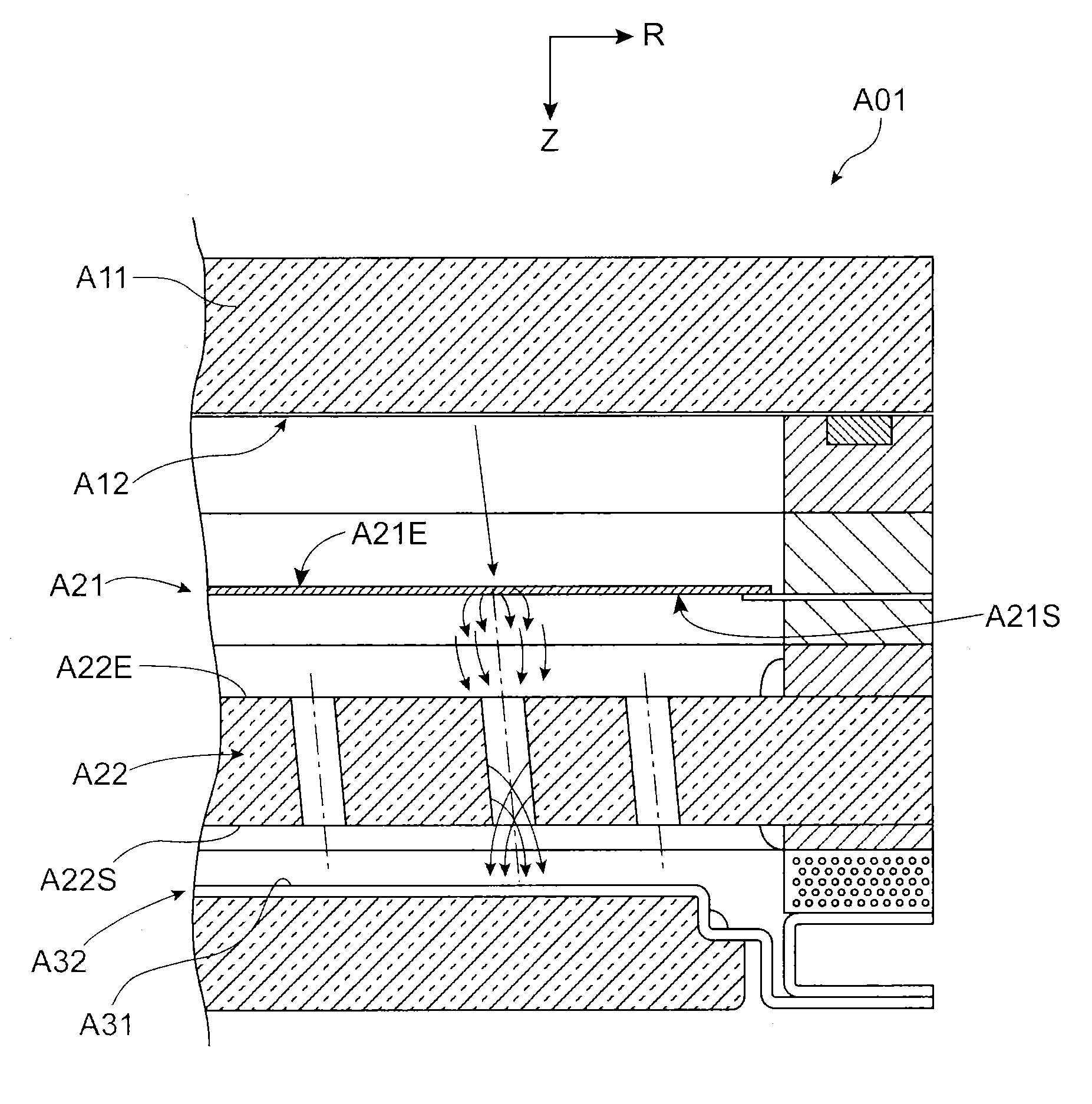
An electron emission device includes a substrate, cathode electrodes formed on the substrate, and electron emission regions electrically connected to the cathode electrodes. Gate electrodes are formed over the cathode electrodes with a first insulating layer interposed therebetween. The gate electrodes have a plurality of opening portions exposing the electron emission regions on the substrate. A focusing electrode is formed over the first insulating layer and the gate electrodes while interposing a second insulating layer. The focusing electrode has opening portions corresponding to the opening portions of the gate electrodes with a size smaller than the size of the opening portions of the gate electrodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Electron emitter and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20050073261A1Improve electron emission efficiencyImprove distributionDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesTriple junctionElectron
An electron emitter includes an emitter section having a plate shape, a cathode electrode formed on a front surface of the emitter section, and an anode electrode formed on a back surface of the emitter section. A gap is formed between an outer peripheral portion of the cathode electrode and the front surface of the emitter section. The front surface of the emitter section contacts a lower surface of the outer peripheral portion to form a base end as a triple junction. The gap expands from the base end toward a tip end of the outer peripheral portion.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electron multiplier device having a nanodiamond layer
ActiveUS20130240907A1High global gainIncrease the multiplier device's number of steps of multiplicationMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSecondary electronsElectron multiplier
An electron multiplier for a system for detecting electromagnetic radiation or an ion flow is disclosed. The multiplier includes at least one active structure intended to receive a flow of incident electrons, and to emit in response a flow of electrons called secondary electrons. The active structure includes a substrate on which is positioned a thin nanodiamond layer formed from diamond particles the average size of which is less than or equal to about 100 nm.
Owner:PHOTONIS FRANCE
Electronic pulse generation device
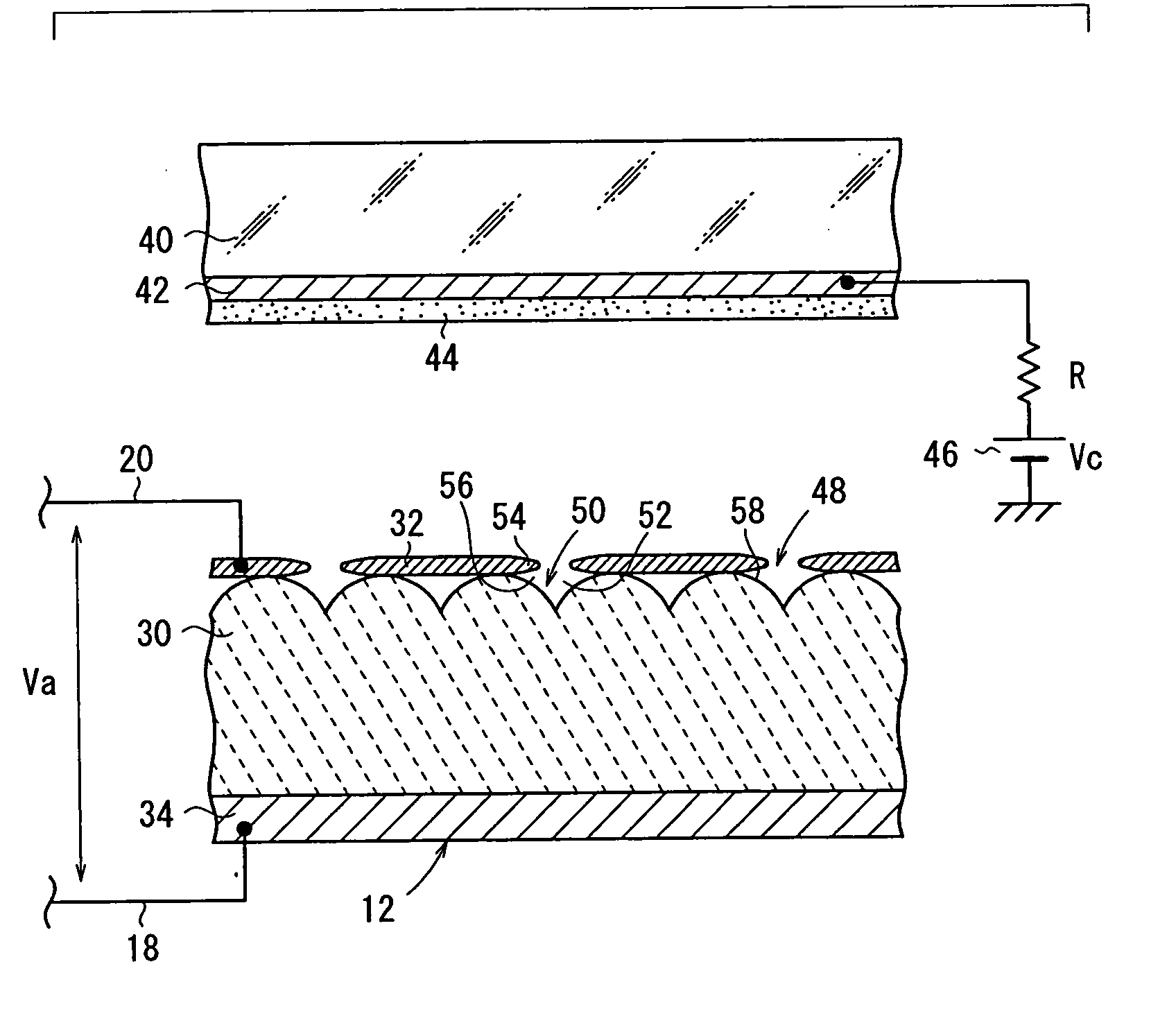
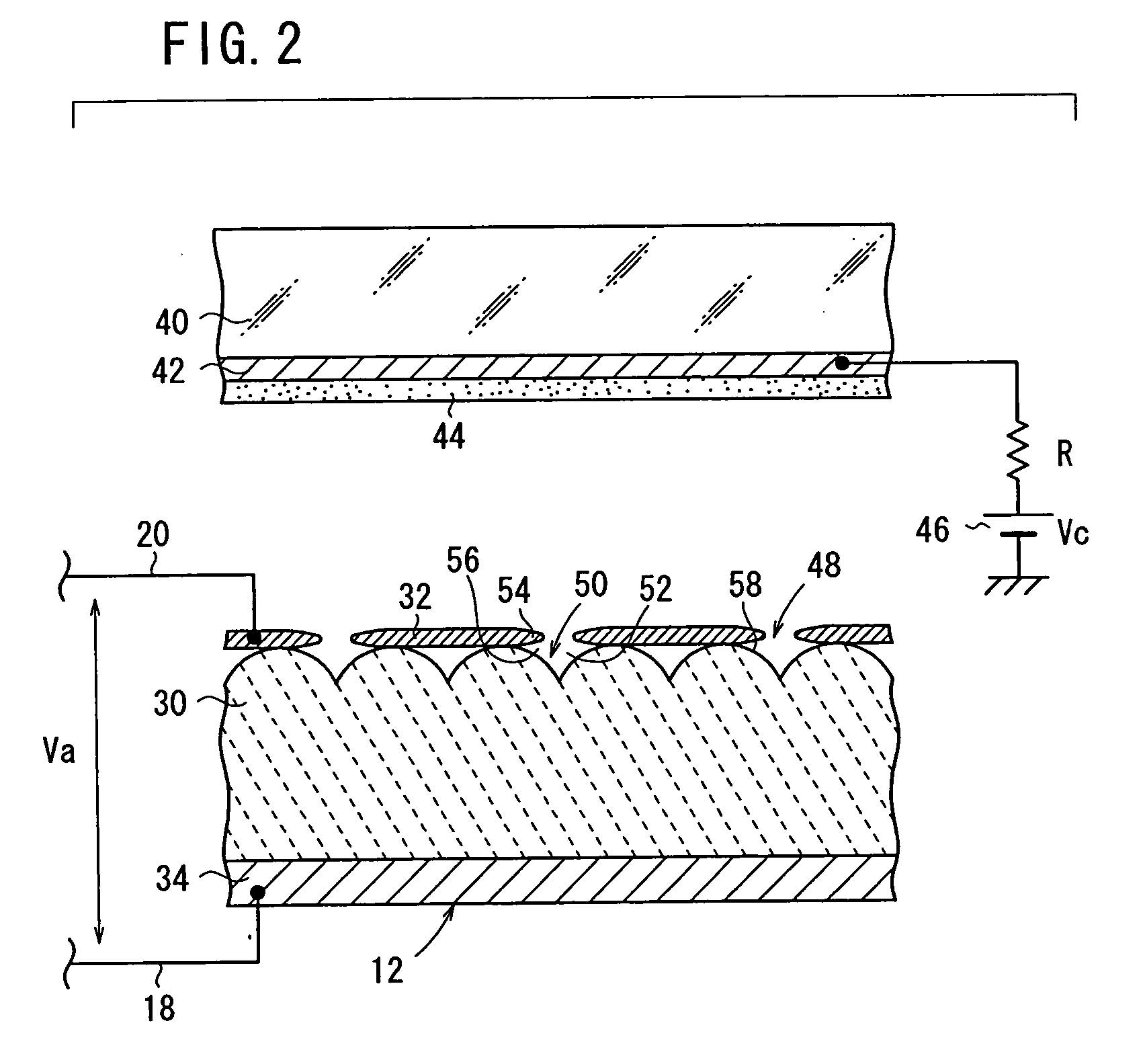
InactiveUS7071628B2Easy to controlImprove performanceControl electrodesStatic indicating devicesPhosphorElectron
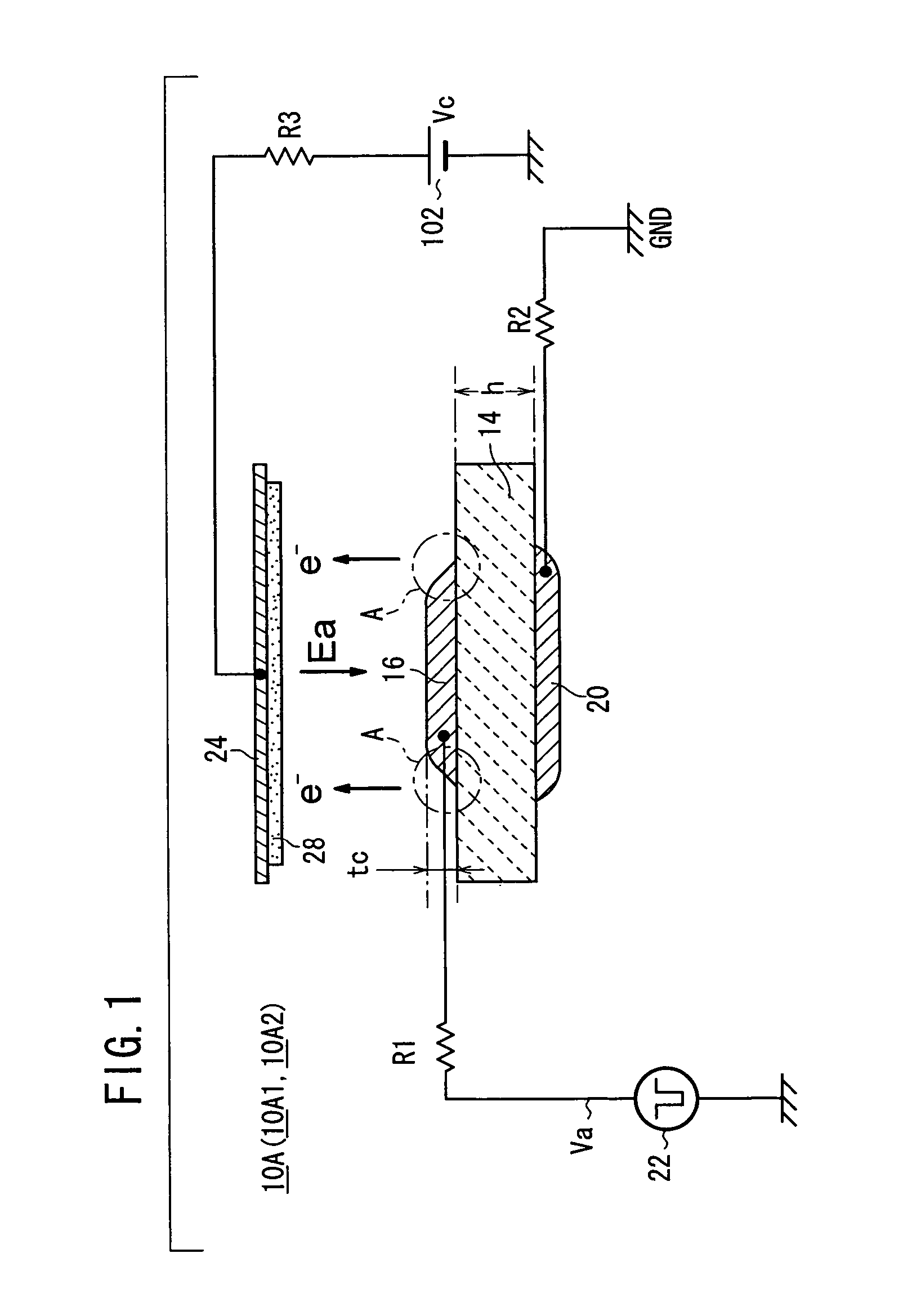
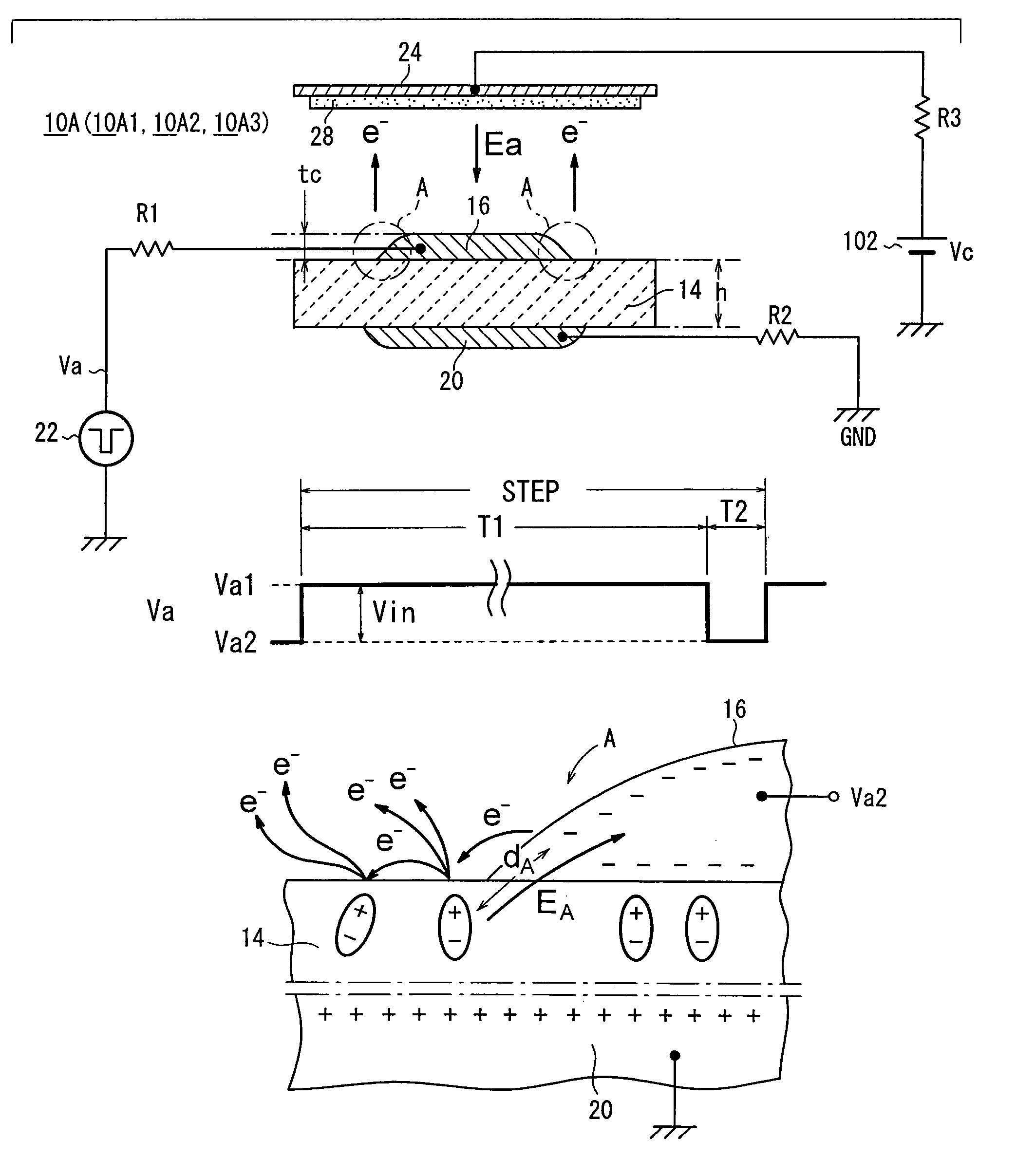
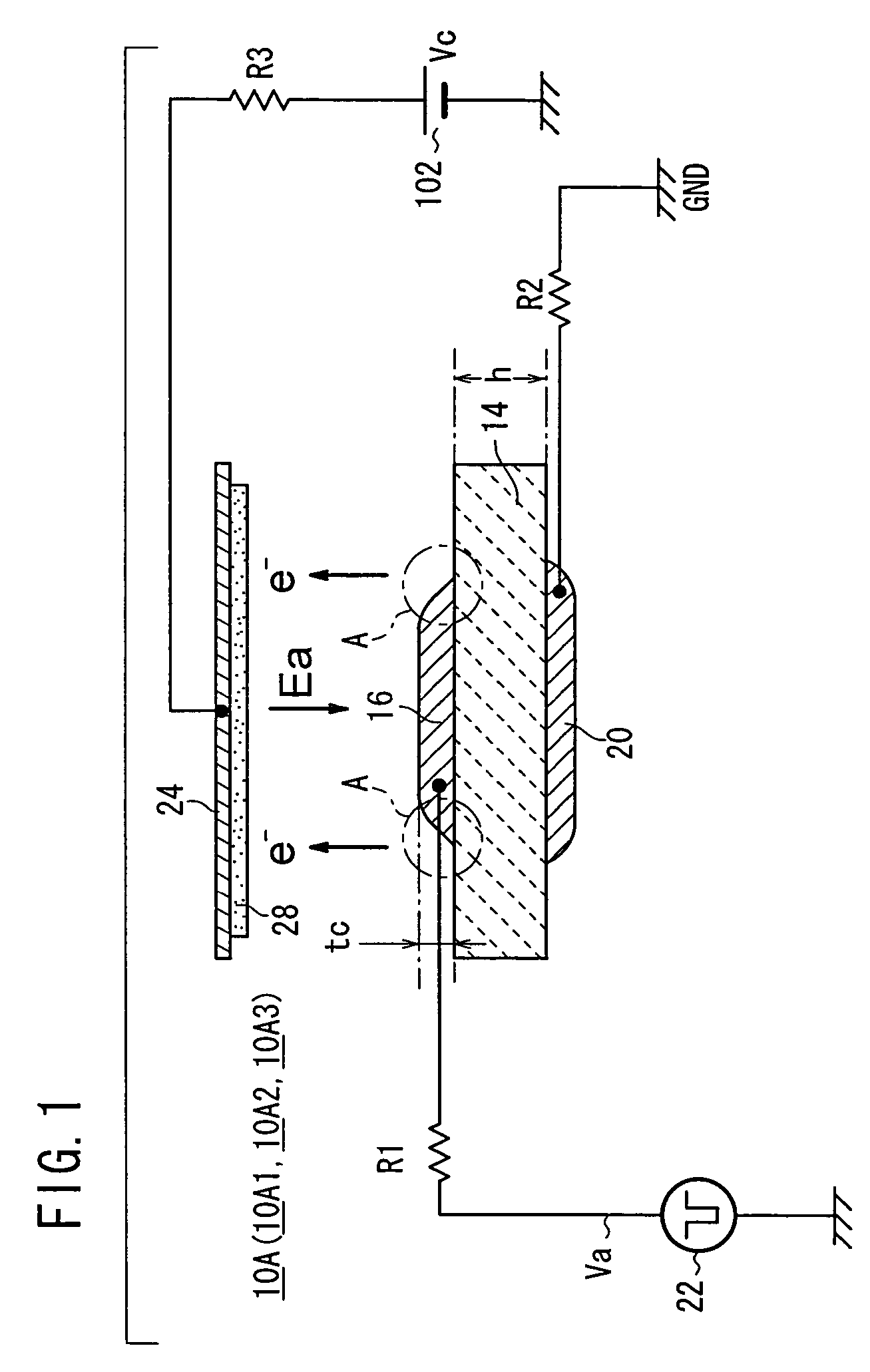
An electronic pulse generation device has an emitter section having a plate shape, a cathode electrode formed on a front surface of the emitter section, an anode electrode formed on a back surface of the emitter section, and a pulse generation source which applies a drive voltage between the cathode electrode and the anode electrode through a resistor. The anode electrode is connected to GND through another resistor. A collector electrode is provided above the cathode electrode, and the collector electrode is coated with a phosphor layer. A bias voltage is applied to the collector electrode through another resistor.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electron multiplier detector formed from a highly doped nanodiamond layer
ActiveUS20130146778A1Low mobilityRisk of defectPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSecondary electronsOutput device
A system for detecting electromagnetic radiation or an ion flow, including an input device for receiving the electronic radiation or the ion flow and emitting primary electrons in response, a multiplier of electrons in transmission, for receiving the primary electrons and emitting secondary electrons in response, and an output device for receiving the secondary electrons and emitting an output signal in response. The electron multiplier includes at least one nanocrystalline diamond layer doped with boron in a concentration of higher than 5·1019 cm−3.
Owner:PHOTONIS FRANCE
Nanopillar arrays for electron emission
ActiveUS7884324B2High strengthAvoid accumulationThermometer detailsNanotechNanopillarSecondary emission
The present invention provides systems, devices, device components and structures for modulating the intensity and / or energies of electrons, including a beam of incident electrons. In some embodiments, for example, the present invention provides nano-structured semiconductor membrane structures capable of generating secondary electron emission. Nano-structured semiconductor membranes of this aspect of the present invention include membranes having an array of nanopillar structures capable of providing electron emission for amplification, filtering and / or detection of incident radiation, for example secondary electron emission and / or field emission. Nano-structured semiconductor membranes of the present invention are useful as converters wherein interaction of incident primary electrons and nanopillars of the nanopillar array generates secondary emission. Nano-structured semiconductor membranes of this aspect of the present invention are also useful as directed charge amplifiers wherein secondary emission from a nanopillar array provides gain functionality for increasing the intensity of radiation comprising incident electrons.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
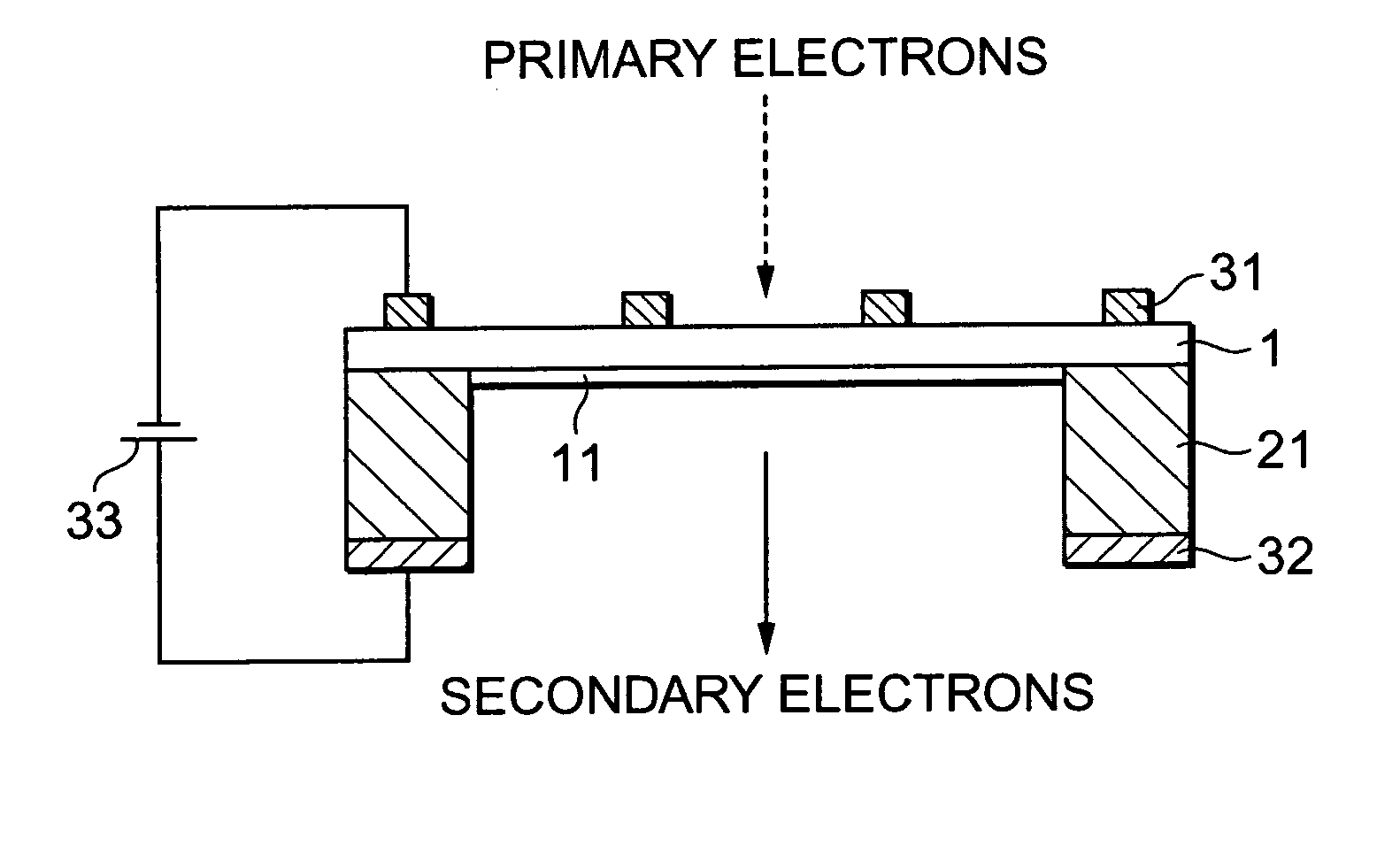
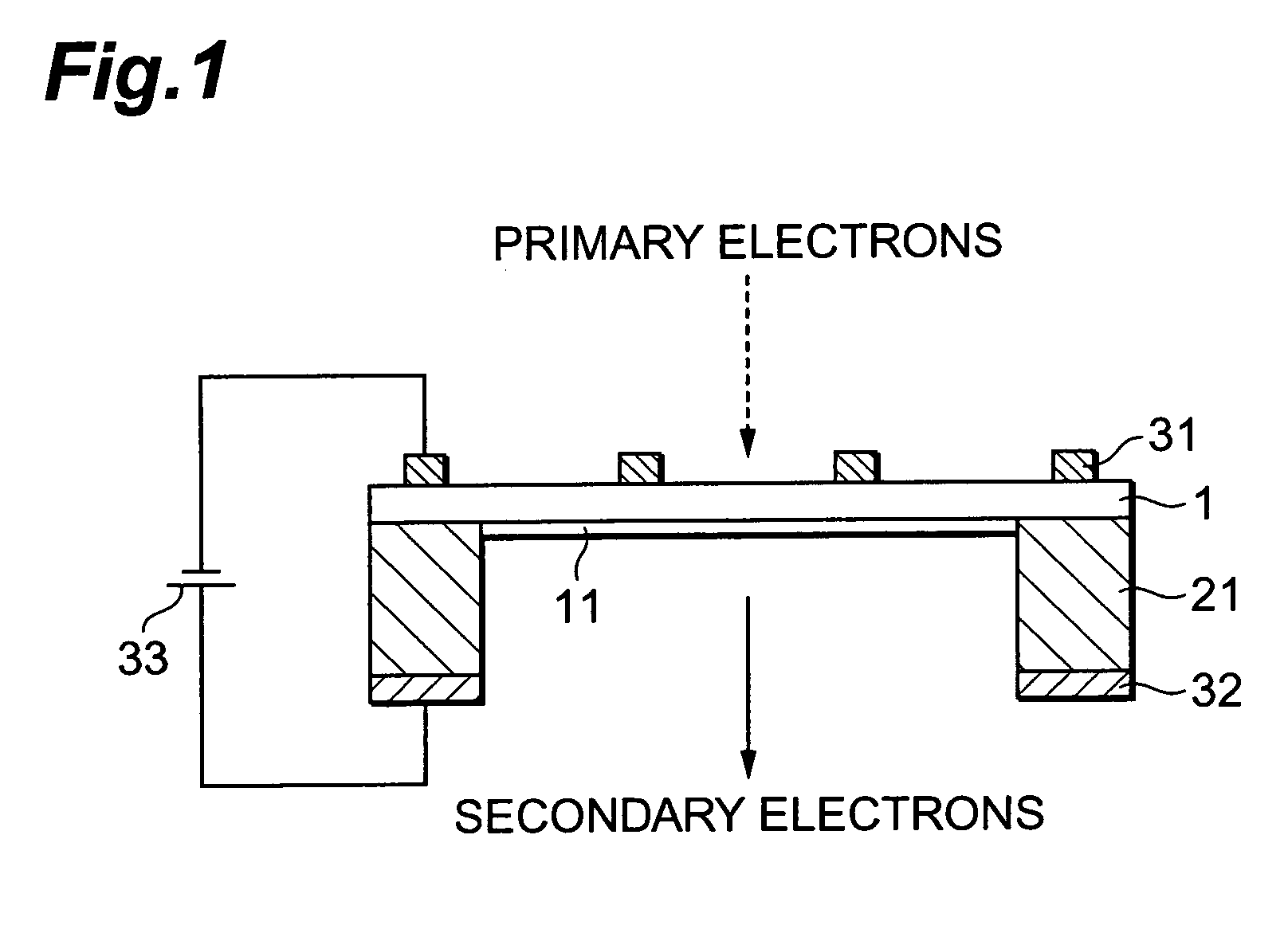
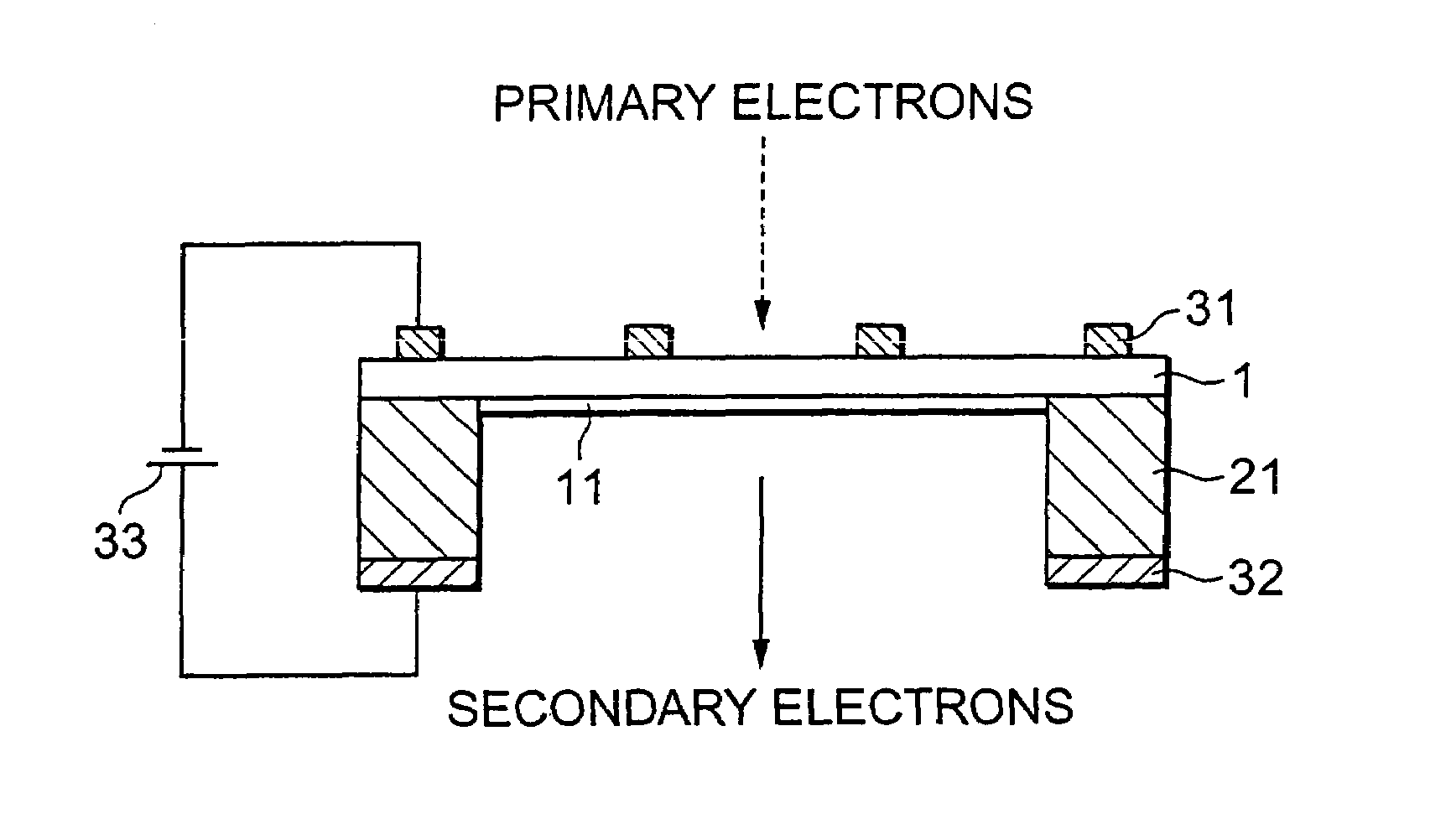
Transmitting type secondary electron surface and electron tube
InactiveUS20050104527A1Efficient emissionsLow efficiencyElectrode and associated part arrangementsImage/pattern display tubesSecondary electronsElectric field
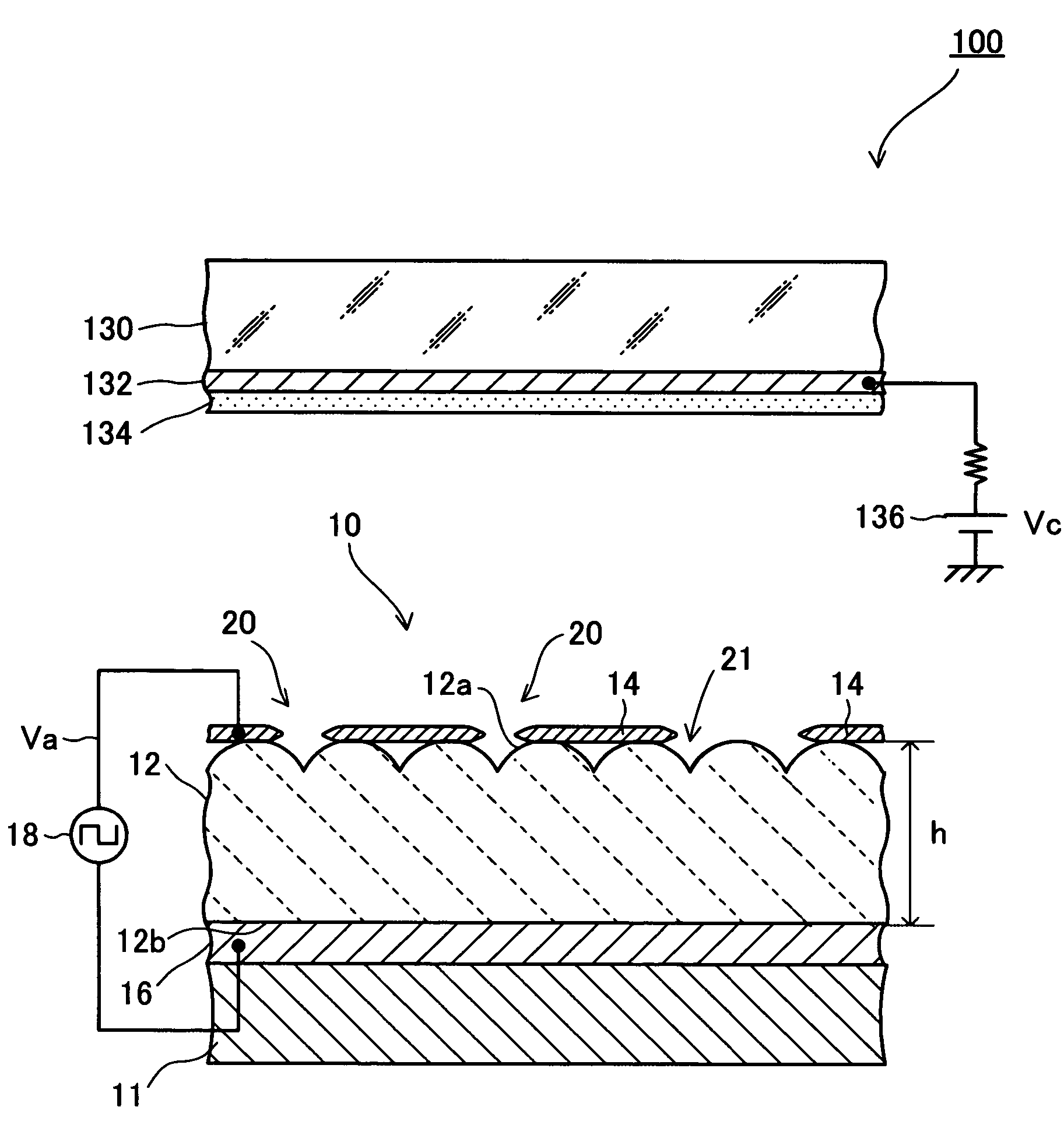
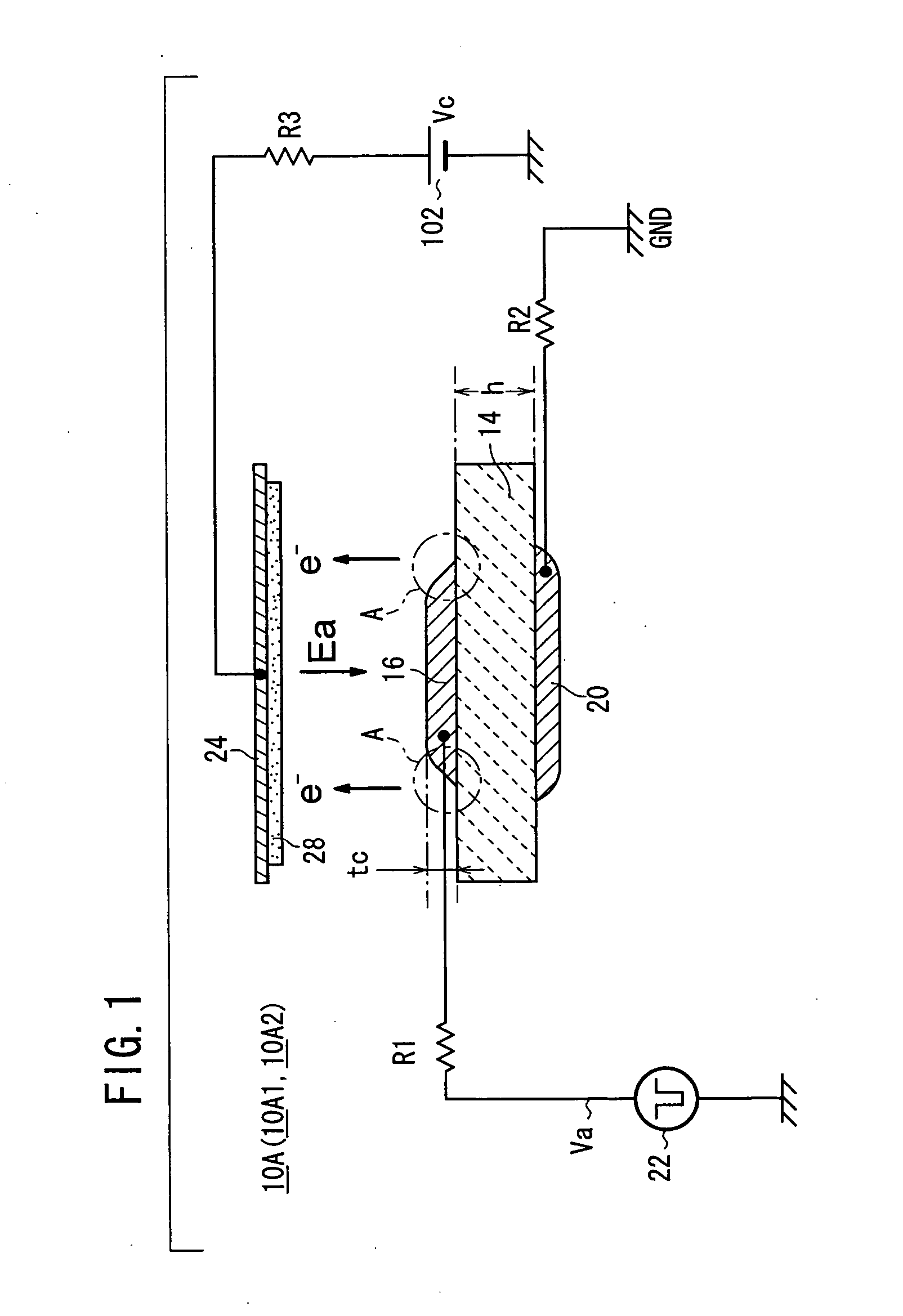
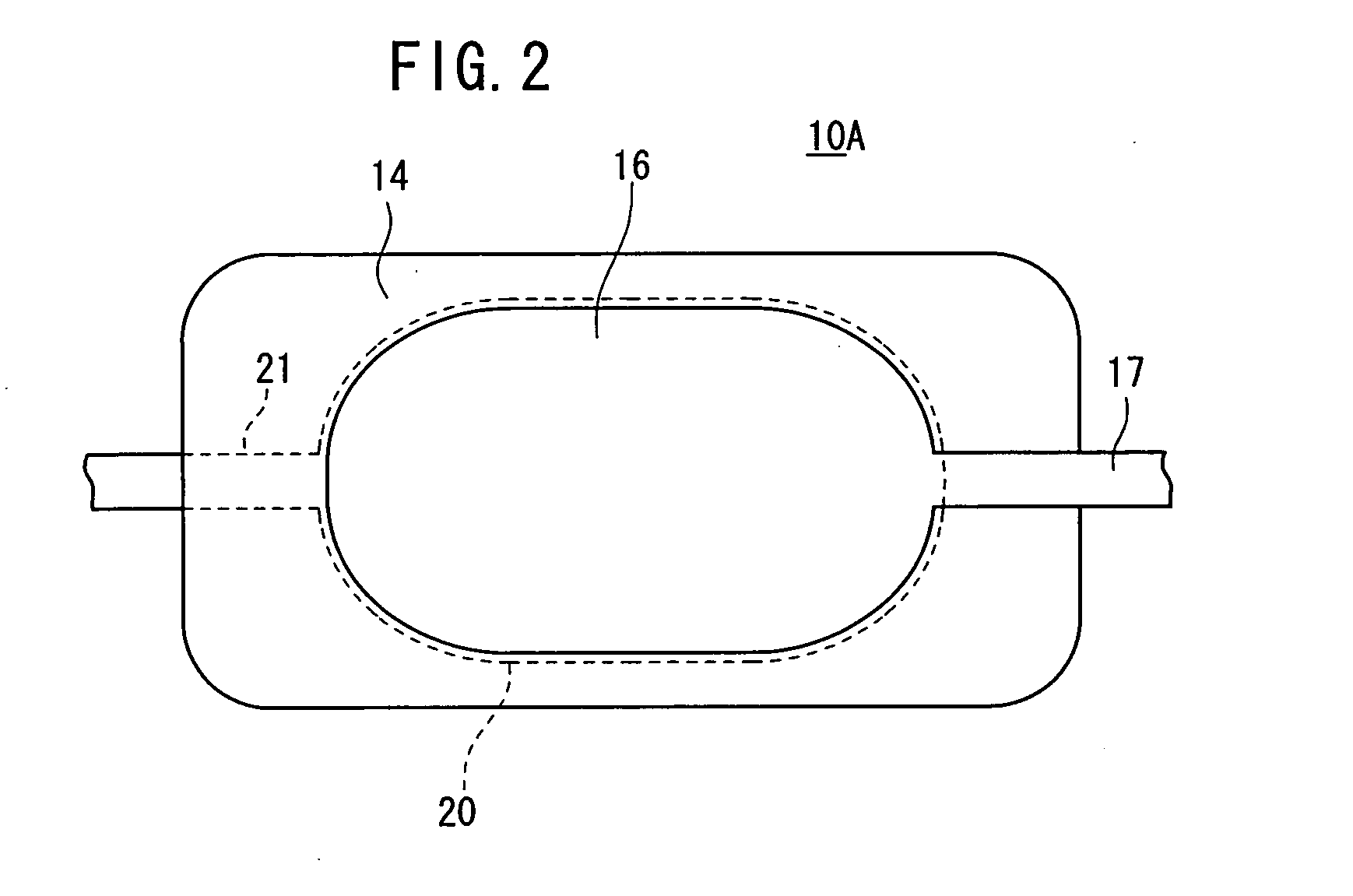
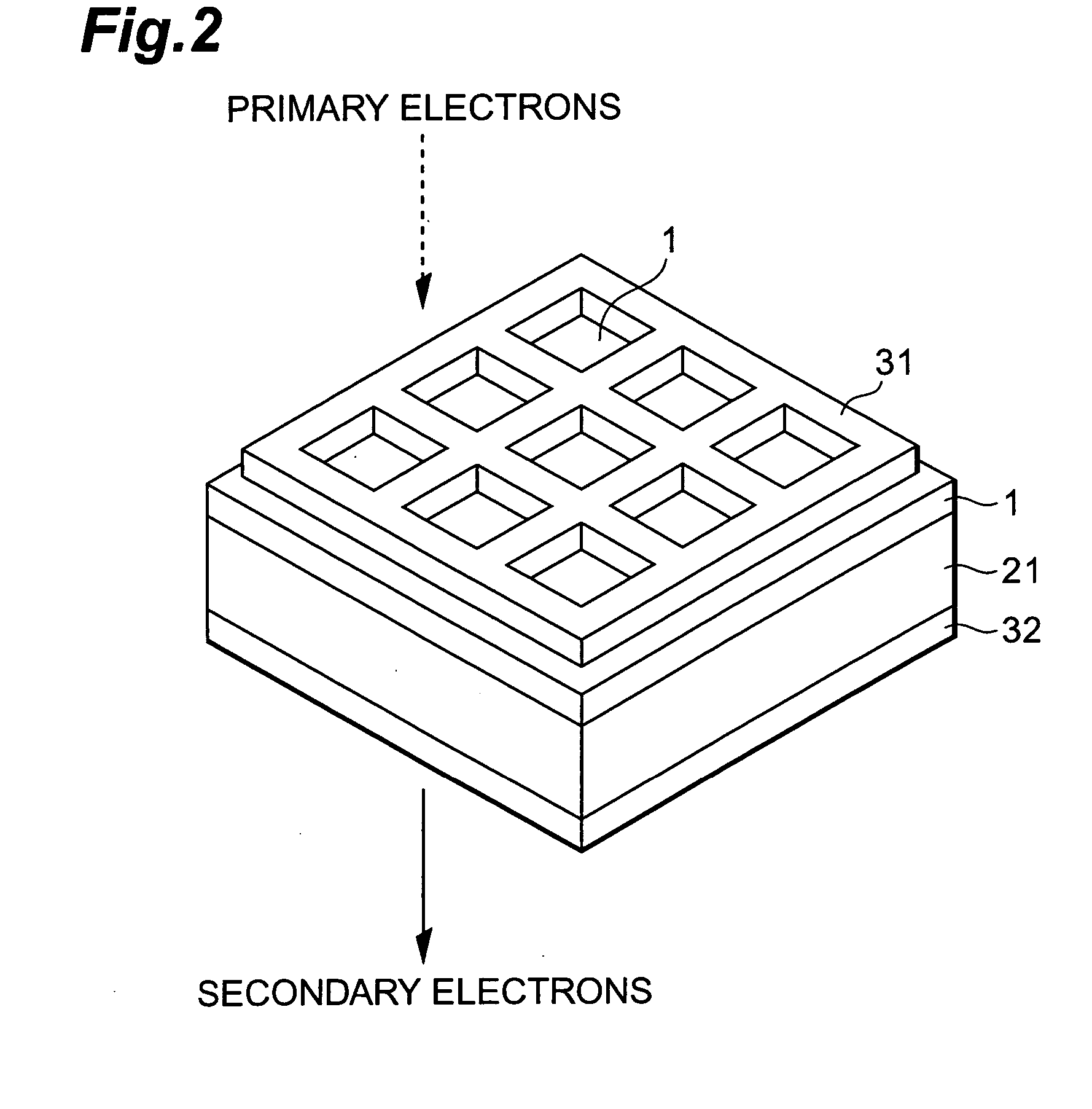
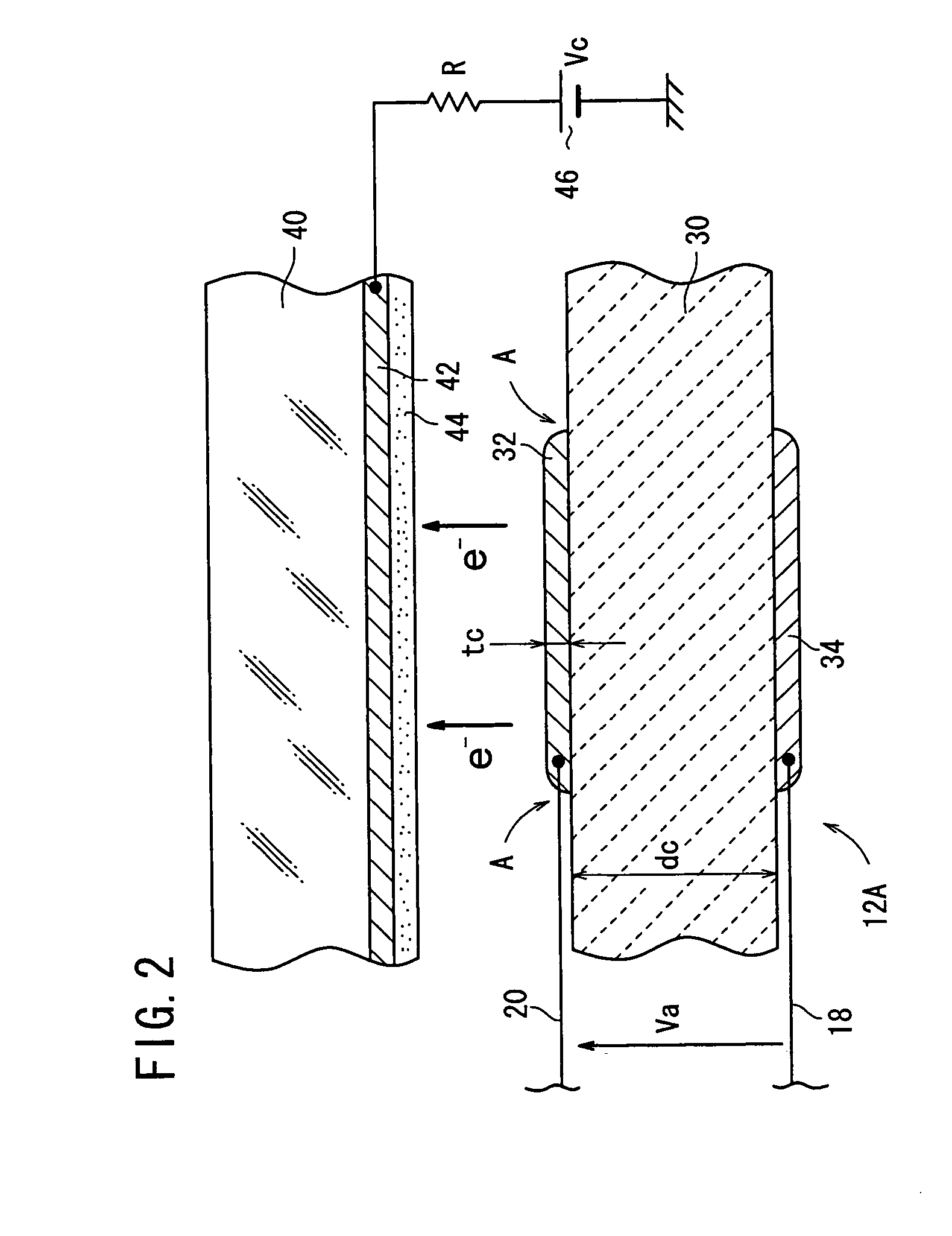
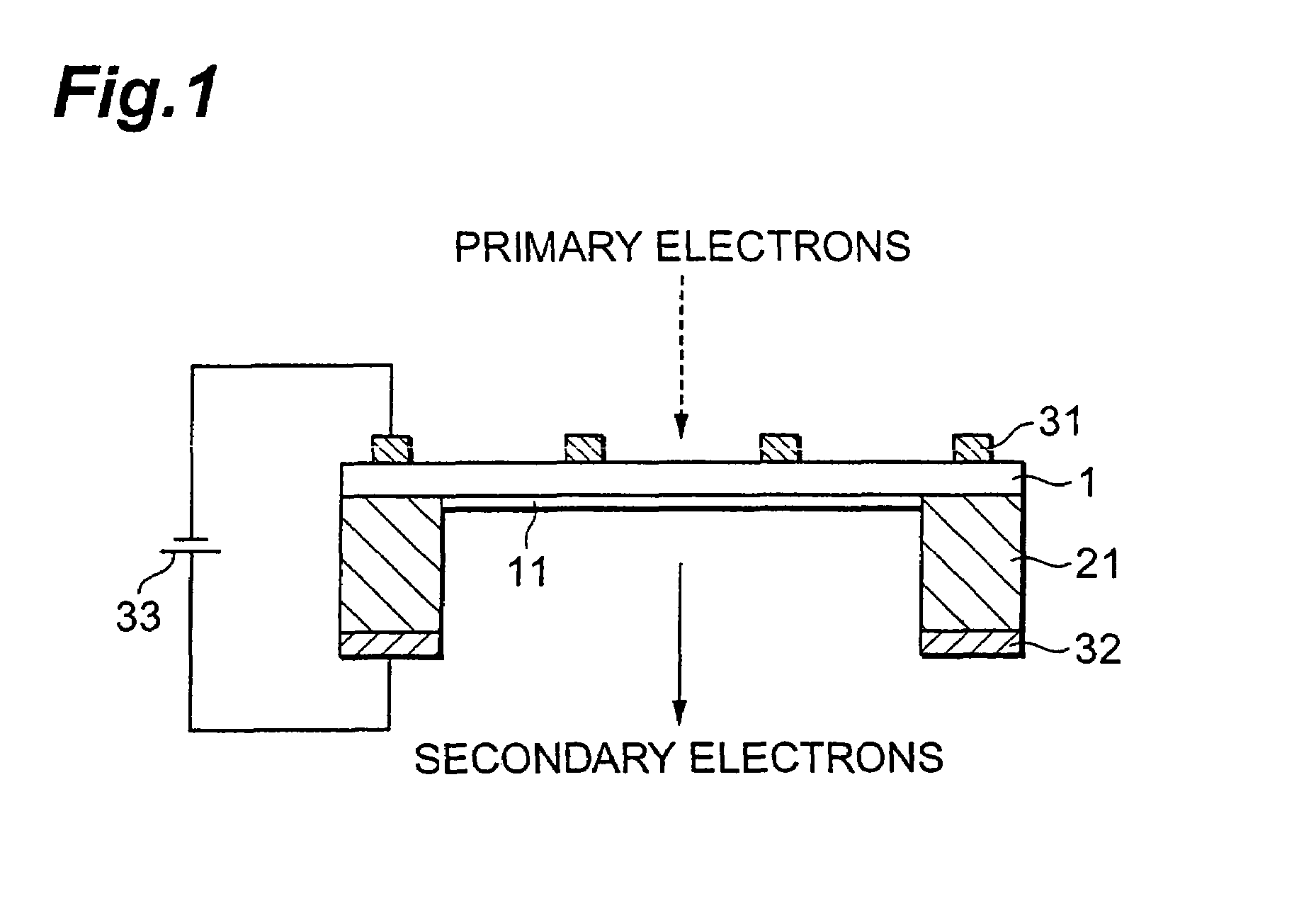
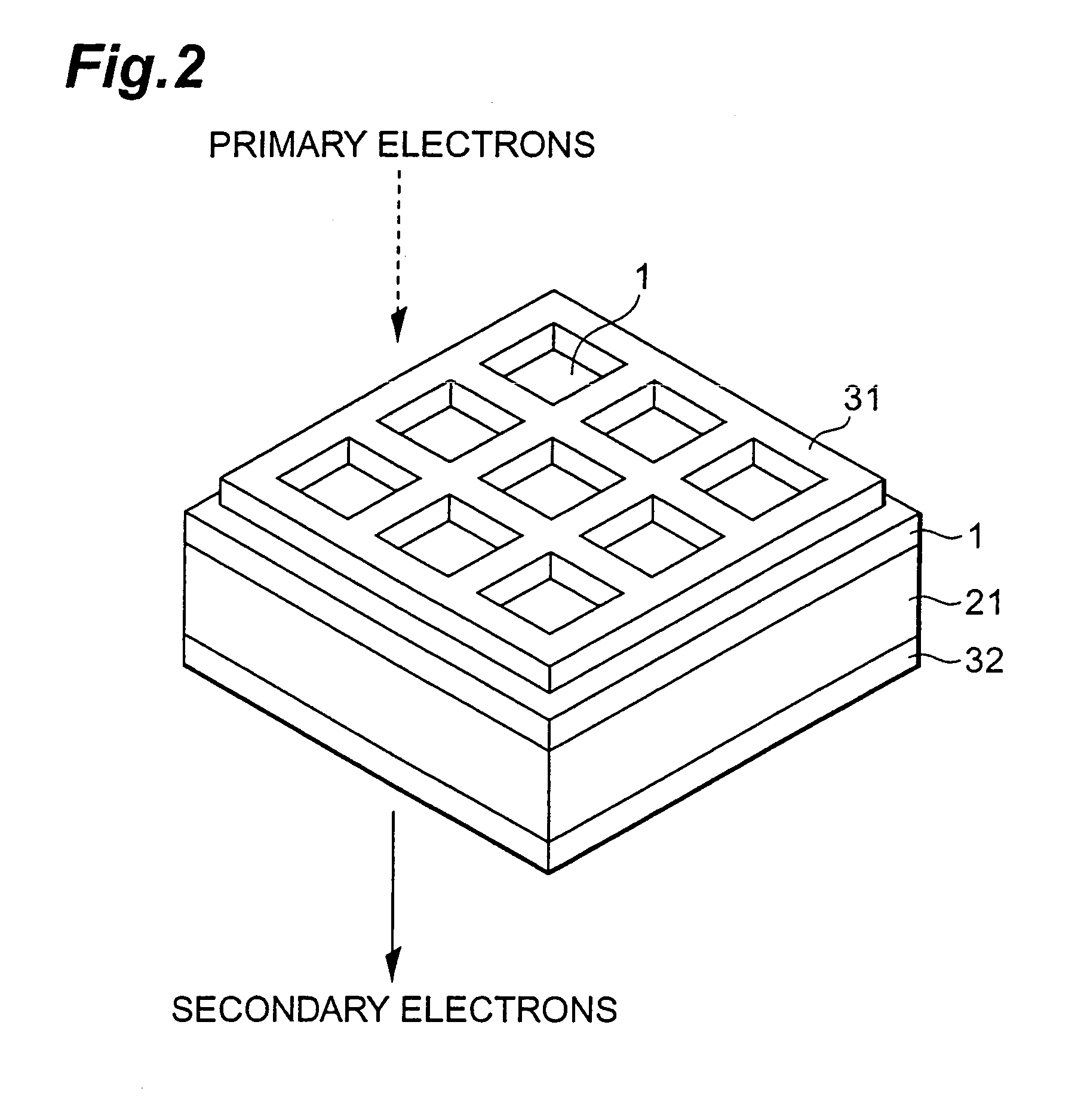
The transmission secondary electron emitter according to the present invention comprises a secondary electron emitting layer 1 made of diamond or a material containing diamond as a main component, a supporting frame 21 reinforcing the mechanical strength of the secondary electron emitting layer 1, a first electrode 31 formed on the surface of incidence of the secondary electron emitting layer 1, and a second electrode 32 formed on the surface of emission of the secondary electron emitting layer 1. A voltage is applied between the surfaces of the incidence and the emission of the secondary electron emitting layer 1 to form an electric field in the secondary electron emitting layer 1. When the incidence of primary electrons into the secondary electron emitting layer 1 generates secondary electrons in the secondary electron emitting layer 1, the secondary electrons are accelerated in the direction to the surface of the emission by the electric field formed in the secondary electron emitting layer 1, and emitted out of the transmission secondary electron emitter. Therefore, a transmission secondary electron emitter capable of efficiently emitting the secondary electrons by the incidence of the primary electrons, and an electron tube using the same can be achieved.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Electron multiplier device having a nanodiamond layer
ActiveCN103168339AHigh global gainMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsSecondary electronsElectron multiplier
The invention relates to an electron multiplier (1) for a system for detecting electromagnetic radiation or an ion flow. The multiplier (1) comprises at least one active structure (2) for receiving a flow of incident electrons and for emitting a flow of so-called secondary electrons in response. Said active structure (2) comprises a substrate (3) on which a thin nanodiamond layer (4) is arranged, wherein said layer consists of diamond particles, the average size of which is no greater than 100 nm.
Owner:FOTONIS FRANS SAS
Electron emitter comprising emitter section made of dielectric material
InactiveUS7187114B2Easy to useImprove reliabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesOptoelectronicsElectron
An electron emitter has an emitter section formed on a substrate, and a cathode electrode and an anode electrode formed on a same surface of the emitter section. A slit is formed between the cathode electrode and the anode electrode. A drive voltage from a pulse generation source is applied between the anode electrode and the cathode electrode. The anode electrode is connected to the ground. A charging film is formed on a surface of the anode electrode.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
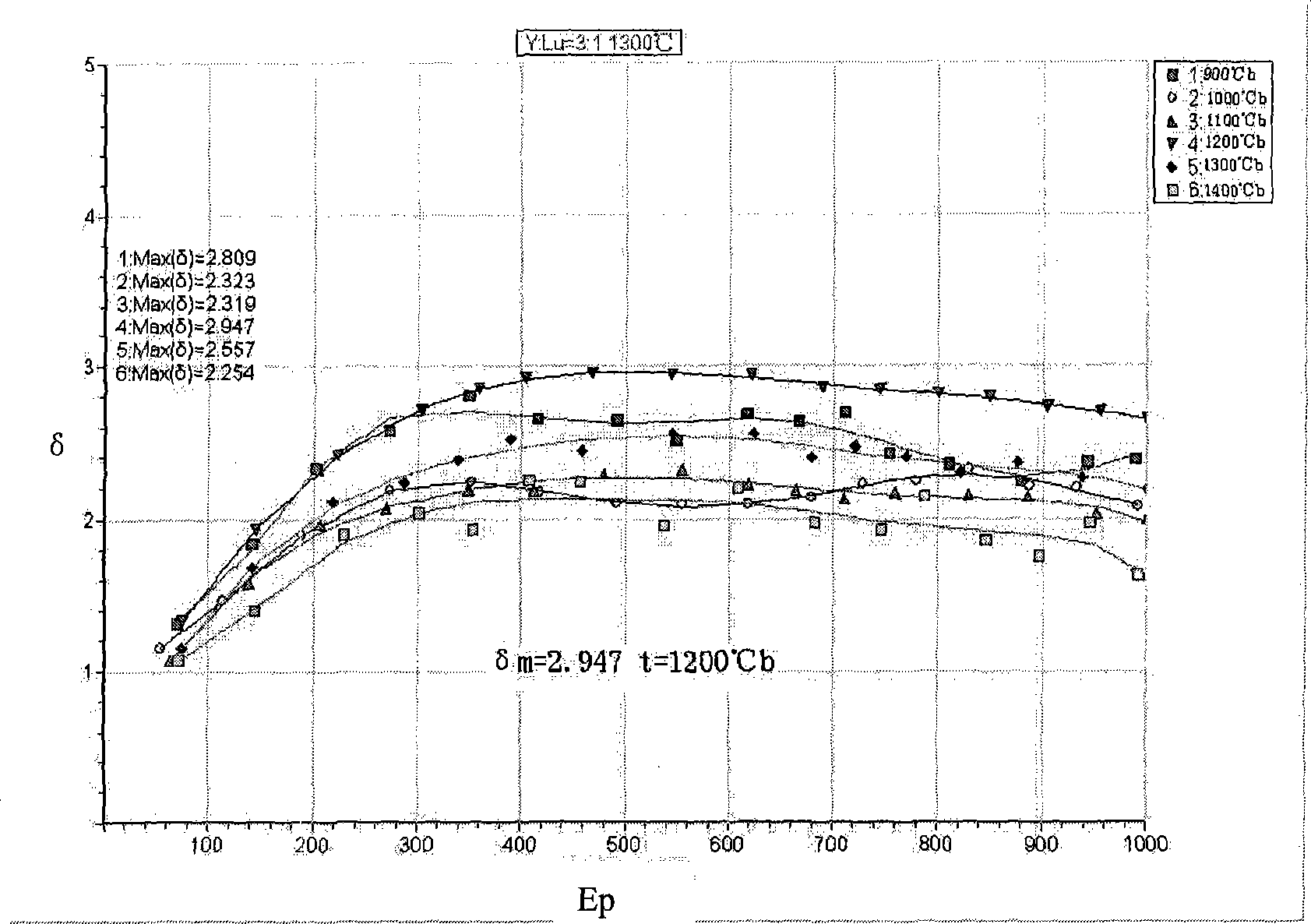
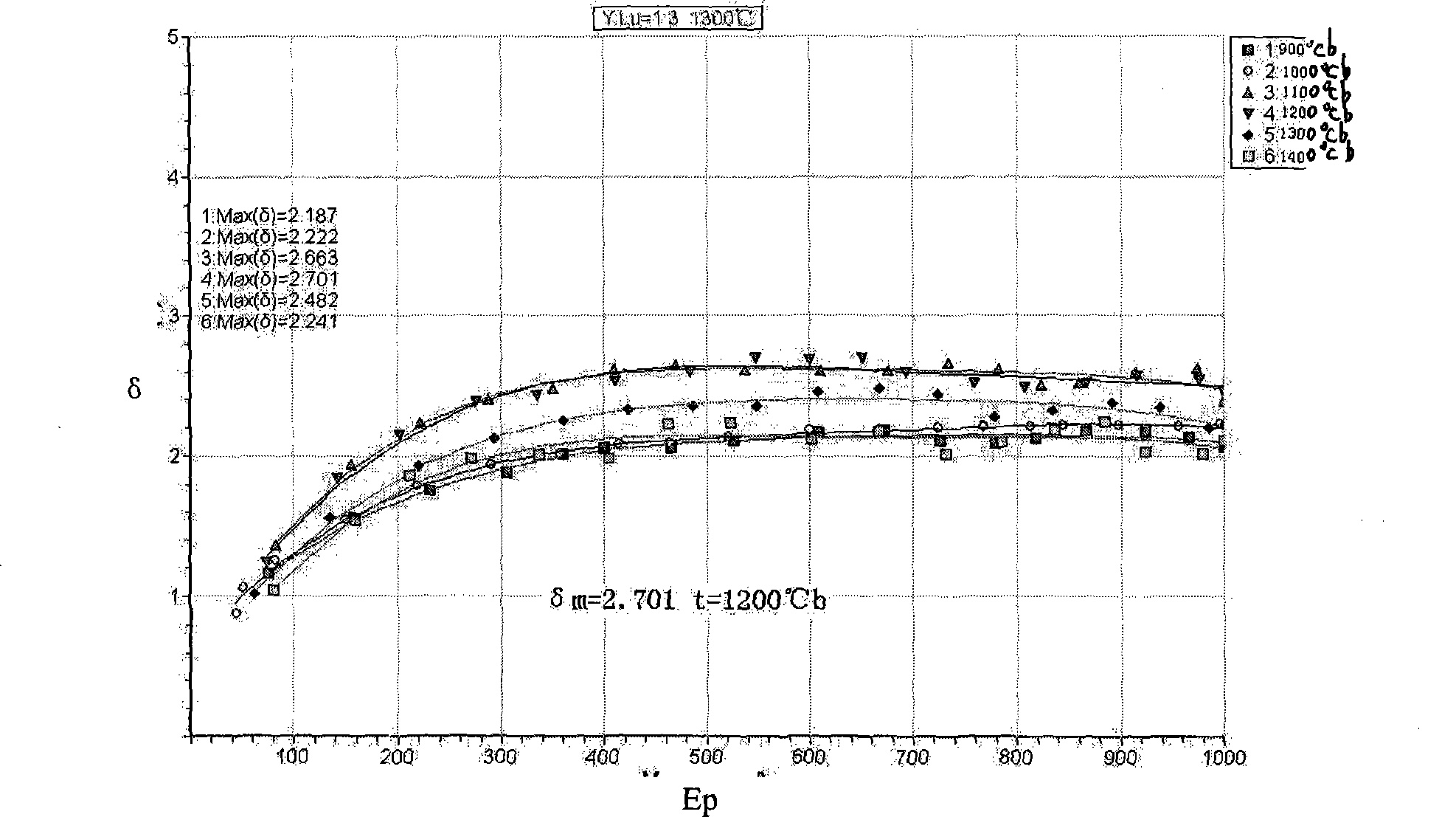
Y2O3-Lu2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101447376AEasy to processHigh secondary electron emission coefficientSecondary electron emitting electrodesPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureRare-earth elementLutetium
The invention discloses Y2O3-Lu2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of rare earth refractory metal cathode materials. The prior cathode material cannot satisfy the higher electron emission requirements. The Y2O3-Lu2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and the preparation method thereof are characterized in that yttrium and lutetium which are rare earth elements are used as additional elements, and are mixed into metal molybdenum in any proportion for the preparation of the cathode material. The material is obtained by mixing Lu2O3 and Y2O3 which are two rare earth oxides in any proportion, the mixed rare earth oxides account for 20 percent wt of the gross weight of the emission material, and others are molybdenum. The Y2O3-Lu2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material can be utilized to make rare earth-molybdenum secondary electron emission material, the secondary electron emission coefficient thereof is higher a lanthanum-containing cathode, and optimum activation temperature is less than the lanthanum-containing cathode and a cerium-containing cathode.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Light source
InactiveUS20060214557A1Increase profitHigh-luminance light emissionIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensPhosphorElectron
A light source has a transparent substrate, a fixed substrate disposed in facing relation to the transparent substrate, and a plurality of electron emitters disposed on a principal surface of the fixed substrate. A light reflecting film is disposed on a portion of the principal surface of the fixed substrate which is free of the electron emitters. An anode electrode in the form of a transparent electrode is disposed on a substantially entire reverse side of the transparent substrate. Phosphor layers are disposed on the anode electrode at respective positions facing the electron emitters.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electron amplifier utilizing carbon nanotubes and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6870308B2Excellent secondary electron emission propertyEasy to manufactureNanoinformaticsCarbon preparation/purificationAudio power amplifierCarbon nanotube
An electron amplifier and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. The electron amplifier includes a substrate in which a plurality of through holes are formed, a resistive layer deposited on the sidewalls of the through holes, an electron emissive layer including carbon nanotubes which is deposited on the resistive layer, and an electrode layer formed on each of the upper and lower sides of the substrate. Because the electron emissive layer of the electron amplifier is uniform and provides a high electron emission efficiency, the electron amplification efficiency is improved. The electron amplifier manufacturing method enables economical mass production of electron amplifiers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Plasma display panel and drive method therefor
InactiveUS20080068304A1Weak reset dischargeEnhancement in dark contrastStatic indicating devicesAlternating current plasma display panelsElectricityFluorescence
A plasma display panel and a drive method therefor, which can enhance a representation capability when displaying a dark image. The plasma display panel includes fluorophor layers containing magnesium oxide. The drive method includes a reset step to initialize all the pixel cells into states of one of a light-up mode and a light-off mode, and an address step in which the pixel cells are caused to perform address discharges selectively in accordance with pixel data, which are successively executed in each of a head subfield and a second subfield within a one-field display period. In reset step, a voltage that sets row electrodes on one side, in the row electrode pairs as an anode and sets the column electrodes set as a cathode is applied between the row electrodes on the one side and the column electrodes.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electron bombardment of wide bandgap semiconductors for generating high brightness and narrow energy spread emission electrons
InactiveUS7005795B2Small energy spreadReduce in quantityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsElectron holeElectron bombardment
A semiconductor source of emission electrons which uses a target of a wide bandgap semiconductor having a target thickness measured from an illumination surface to an emission surface. The semiconductor source is equipped with an arrangement for producing and directing a beam of seed electrons at the illumination surface and a mechanism for controlling the energy of the seed electrons such that the energy of the seed electrons is sufficient to generate electron-hole pairs in the target. A fraction of these electron-hole pairs supply the emission electrons. Furthermore, the target thickness and the energy of the seed electrons are optimized such that the emission electrons at the emission surface are substantially thermalized. The emission of electrons is further facilitated by generating negative electron affinity at the emission surface. The source of the invention can take advantage of diamond, AlN, BN, Ga1-yAlyN and (AlN)x(SiC)1-x, wherein 0≦y≦1 and 0.2≦x≦1 and other wide bandgap semiconductors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Plasma display panel
InactiveUS20050264201A1Increase opening ratioAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesPhosphorFluorescence
Provided is a plasma display panel (PDP) design that results in improved light emission efficiency and improved brightness and improved opening ratio. The PDP includes a transparent upper substrate, a lower substrate oriented parallel to the upper substrate, a first discharge electrode extending in a first direction on the lower substrate, a dielectric layer that covers the first discharge electrode, a plurality of barrier ribs made of a dielectric material between the upper and lower substrates dividing a space between the upper and the lower substrate into a plurality of discharge cells, a second discharge electrode within the barrier ribs and extending in a second direction to cross the first discharge electrode, a phosphor layer located within the discharge cell, and a discharge gas located within the discharge cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
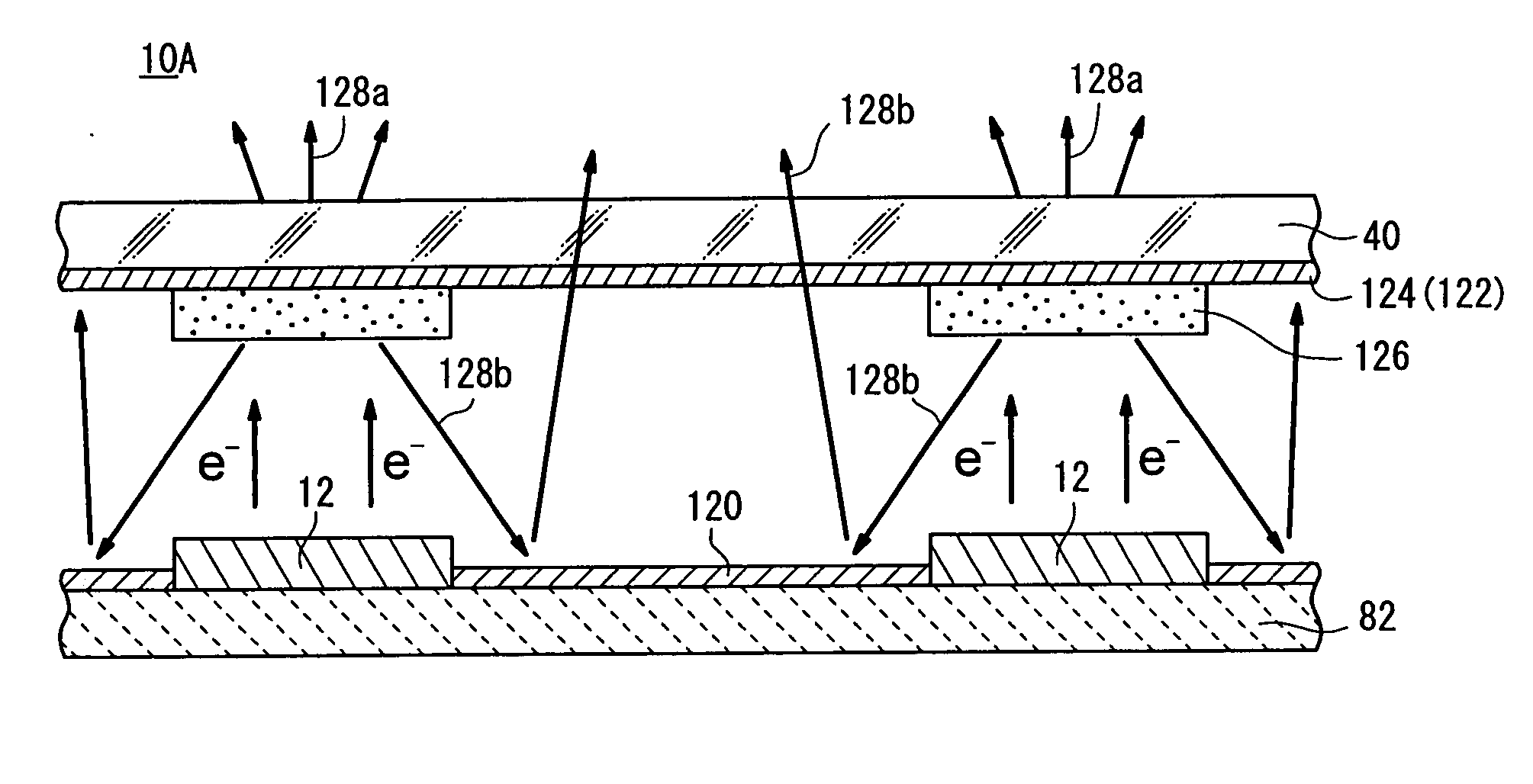
Electron emitter and light emission element
InactiveUS7288881B2Improve reliabilityExtended service lifeStatic indicating devicesNanoinformaticsSecondary electronsLight emission
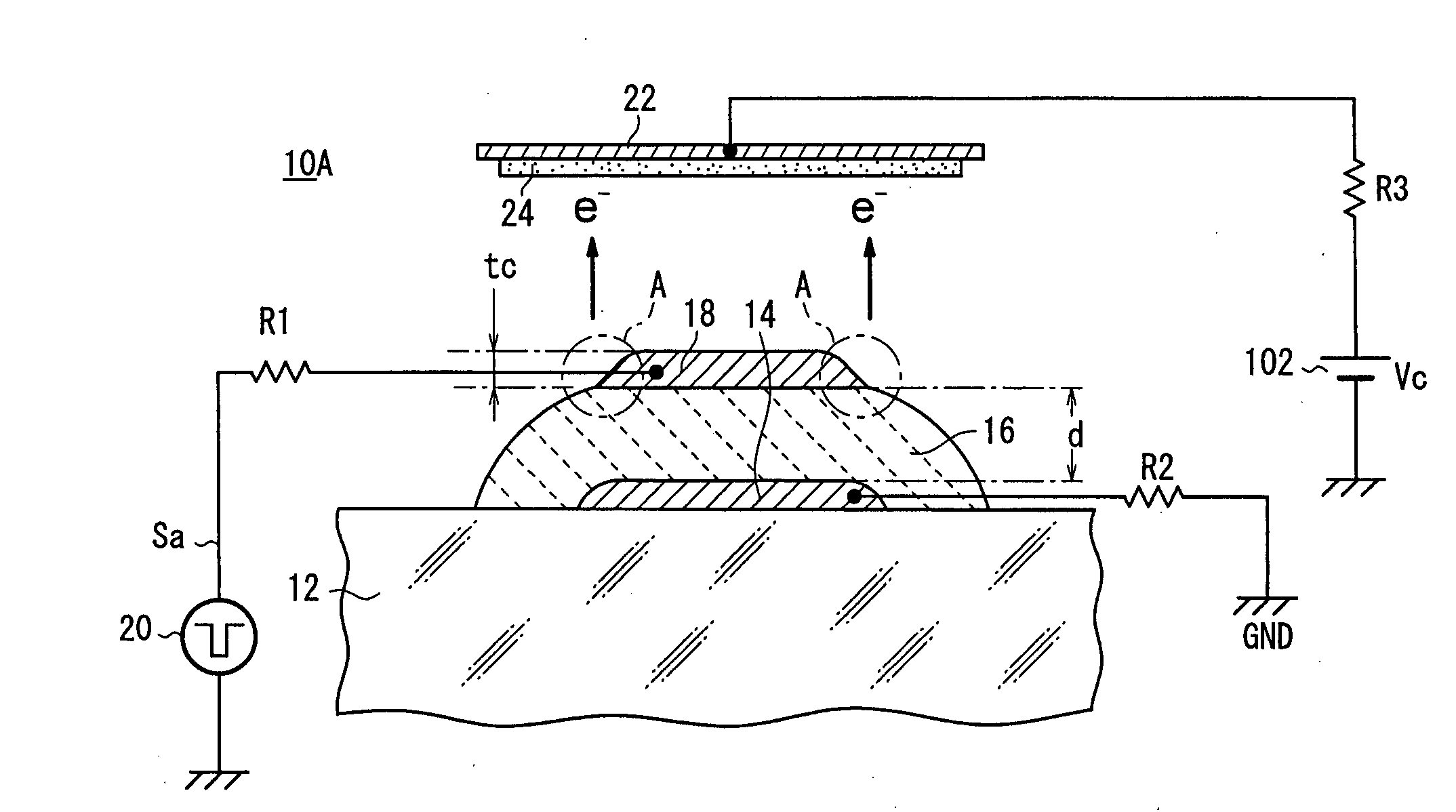
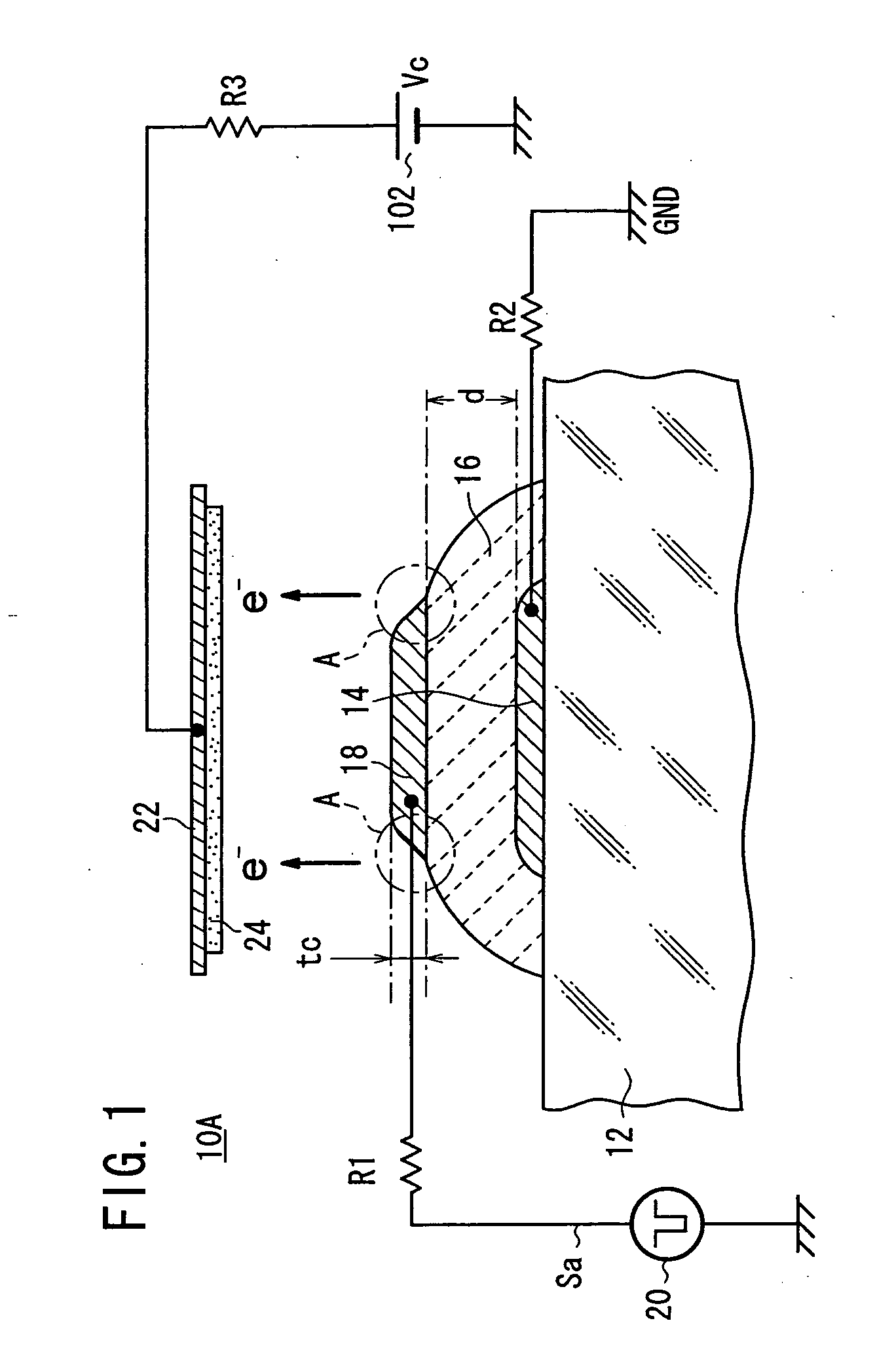
Primary electrons impinge upon an emitter section of an electron emitter for causing emission of the secondary electrons. The secondary electrons are outputted from the electron emitter. The secondary electrons emitted from the emitter section are accelerated in an electric field applied to the emitter section for generating an electron beam. The electron emitter has the emitter section having a plate shape, a cathode electrode formed on a front surface of the emitter section, an anode electrode formed on a back surface of the emitter section. A drive voltage from a pulse generation source is applied between the cathode electrode and the anode electrode through a resistor. The anode electrode is connected to GND. A collector electrode is provided above the cathode electrode. A bias voltage is applied to the collector electrode.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electron emitter and method for manufacturing electron emitter
InactiveUS20070069622A1Increase productionCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsCondensed matter physicsElectron
An electron emitter includes an emitter layer composed of a dielectric material, a first electrode disposed onto a first surface of the emitter layer, and a second electrode disposed onto the first surface, inside, or onto a second surface opposite to the first surface of the emitter layer. A microscopic recess is disposed on a surface of the first electrode. Alternatively, an opening is disposed in the first electrode, the opening exposing the first surface of the emitter layer to the outside of the electron emitter, and a plurality of microscopic protrusions are disposed along the thickness direction of the first electrode at an inner edge of the opening.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Light source
InactiveUS20060214556A1Increase profitHigh-luminance light emissionDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsPhosphorFluorescence
A light source has a transparent substrate, a fixed substrate disposed in facing relation to the transparent substrate, at least one electron emitter disposed on the fixed substrate, a phosphor layer disposed on a surface of the transparent substrate which confronts the fixed substrate, and a trajectory deflector for deflecting the trajectory of a pulsed electron flow intermittently emitted from the electron emitter. The pulsed electron flow is deflected by the trajectory deflector to two-dimensionally scan a position of the phosphor layer which is irradiated with the pulsed electron flow for thereby spreading the pulsed electron flow.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Transmitting type secondary electron surface and electron tube
InactiveUS7208874B2Efficient emissionsLow efficiencyElectrode and associated part arrangementsImage/pattern display tubesSecondary electronsElectric field
A transmission secondary electron emitter is provided which emits secondary electrons generated by the incidence of primary electrons. The transmission secondary electron emitter includes a secondary electron emitting layer which is made of diamond or a material containing diamond as a main component, and of which one surface is the surface of incidence for making the primary electrons incident thereon, and the other surface is the surface of emission for emitting the secondary electrons. Also included is a voltage applying arrangement for applying a predetermined voltage between the surfaces of the incidence and the emission of the secondary electron emitting layer to form an electric field in the secondary electron emitting layer.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
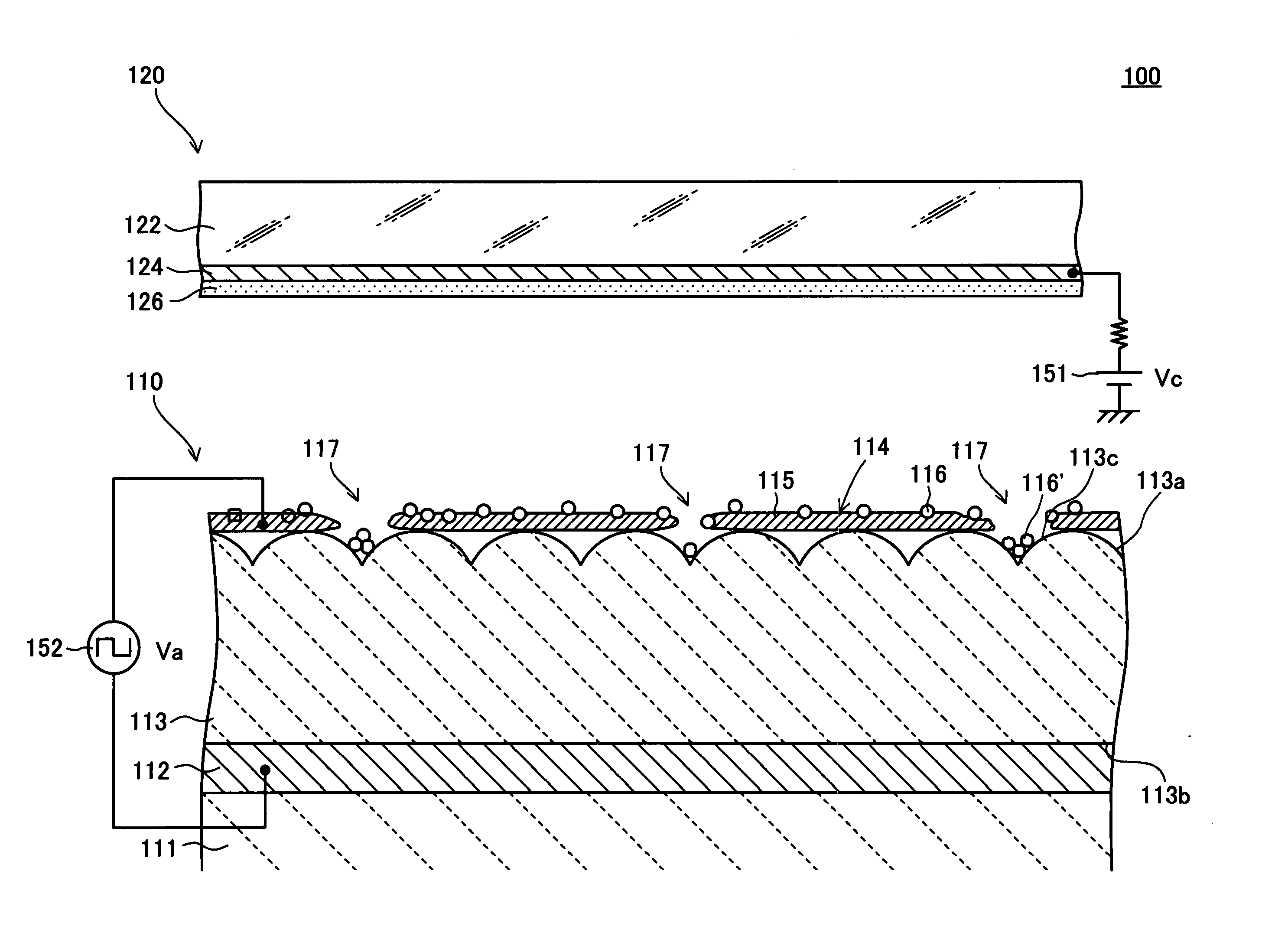
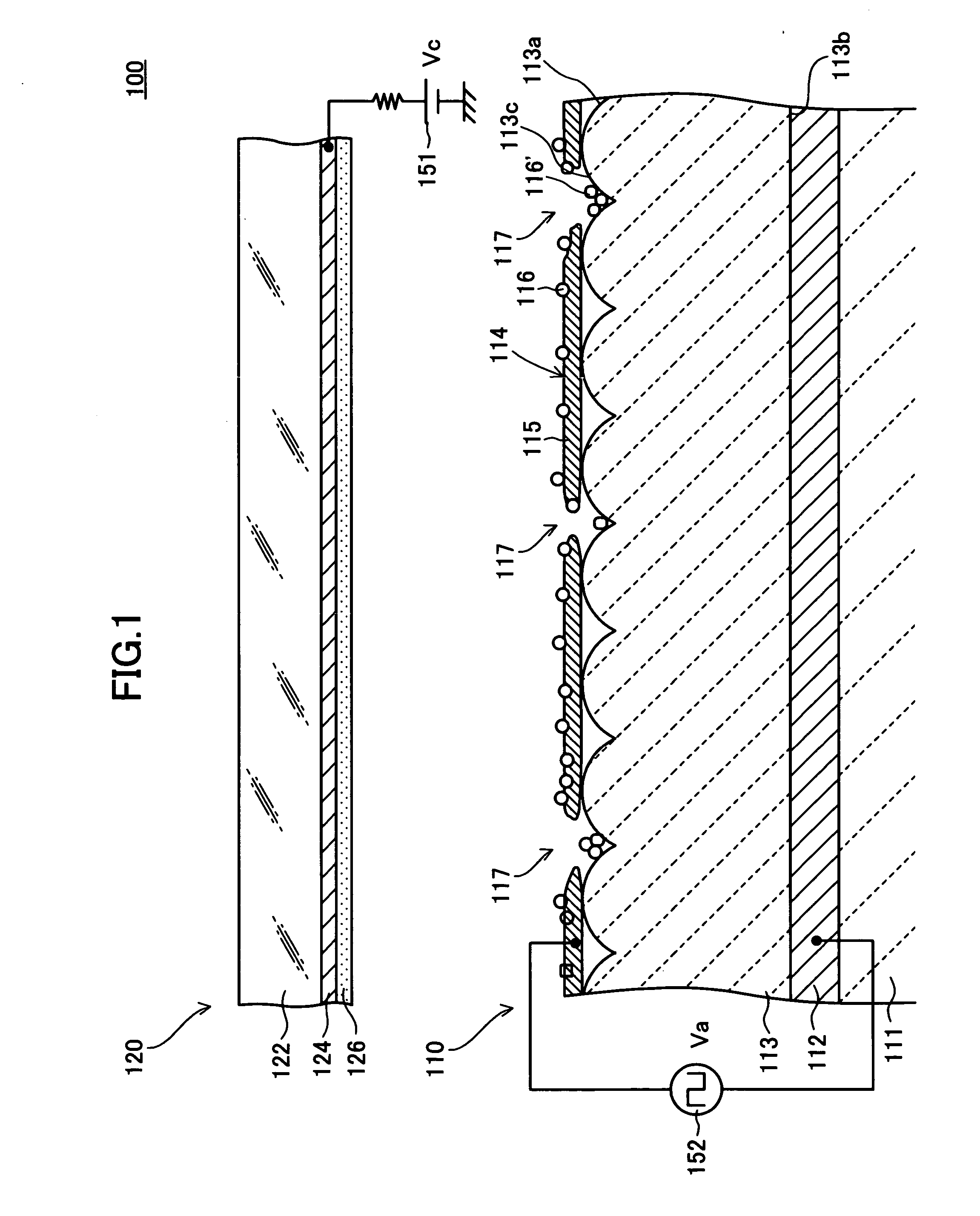
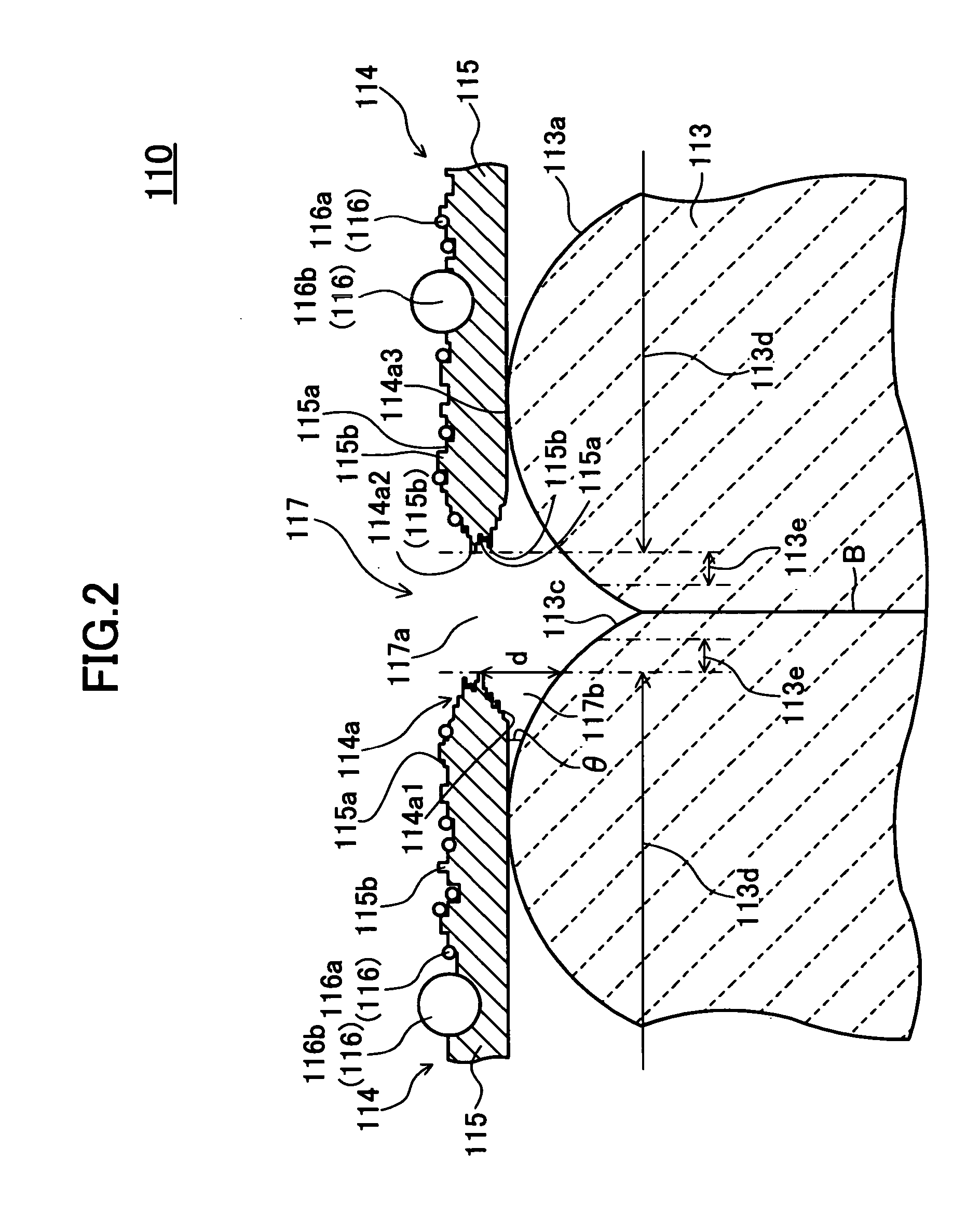
Electron emitter
InactiveUS20050062400A1Easy to useImprove reliabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsElectrode potentialElectron
An electron emitter has an anode electrode formed on a substrate, an electric field receiving member formed on the substrate to cover the anode electrode, and a cathode electrode formed on the electric field receiving member. The cathode electrode is supplied with a drive signal from a pulse generation source, and the anode electrode is connected to an anode potential generation source (GND in this example). A collector electrode is provided above the cathode electrode, and the collector electrode is coated with a fluorescent layer. The collector electrode is connected to a collector potential generation source (Vc in this example) through a resistor.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Apparatus for treating substrate
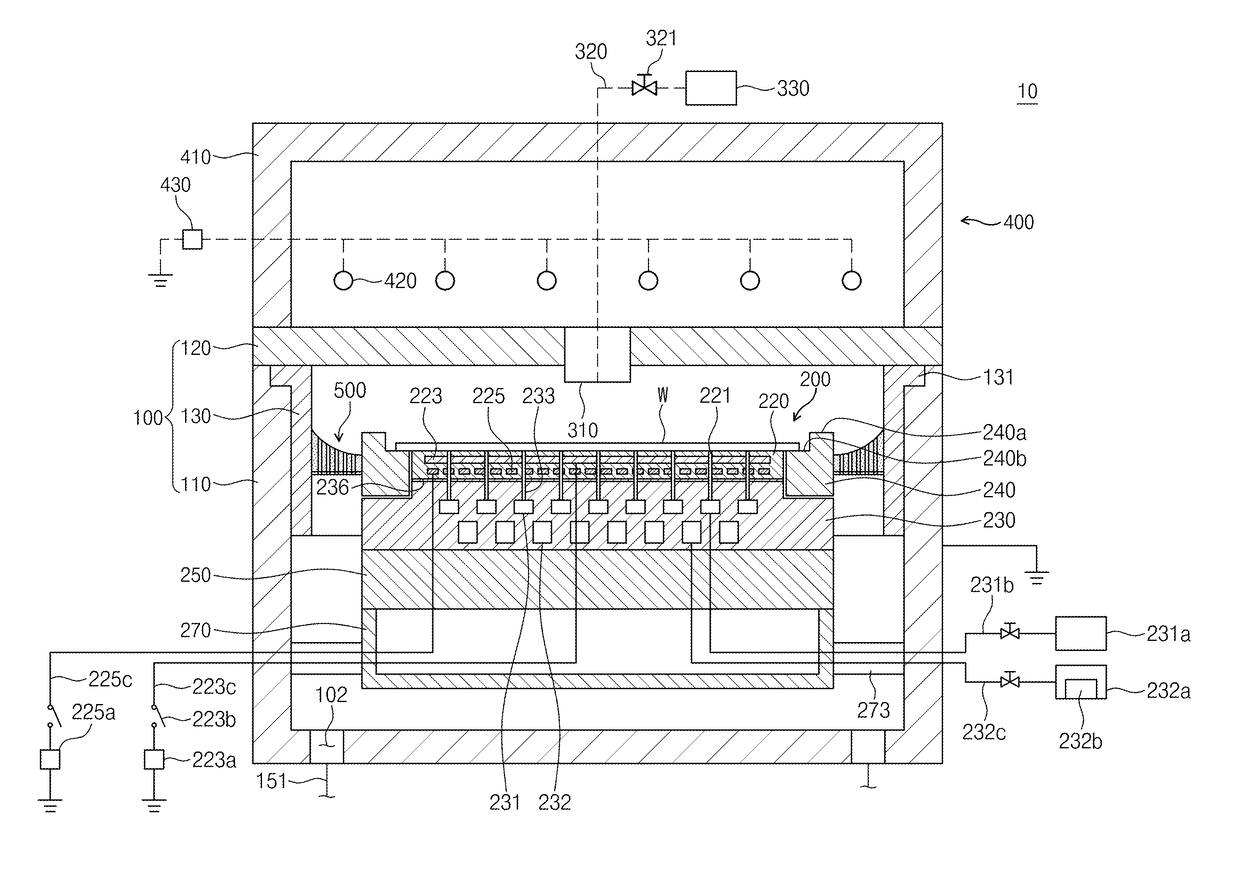
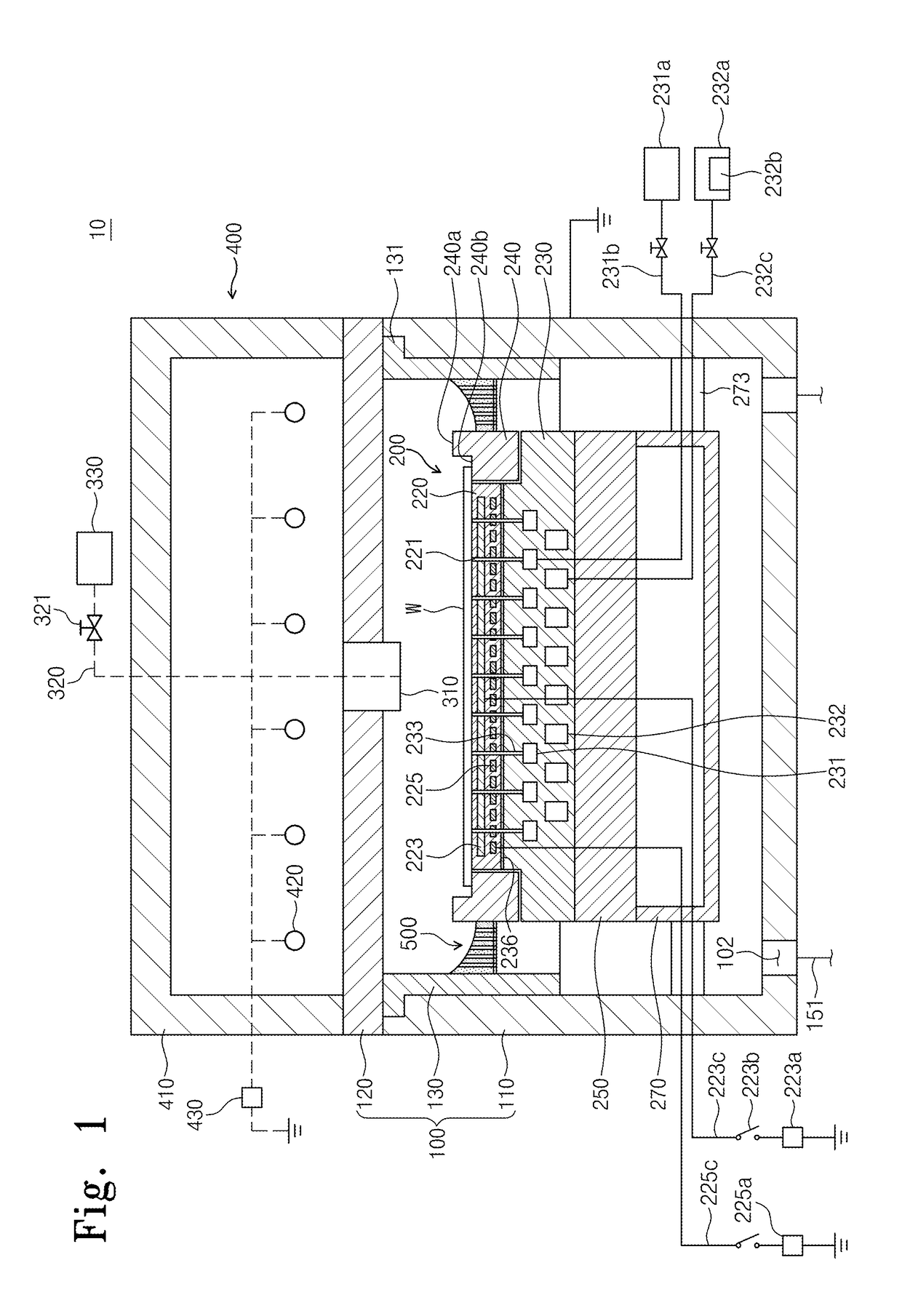
ActiveUS10103018B2Prevent archingElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic materialsEngineering
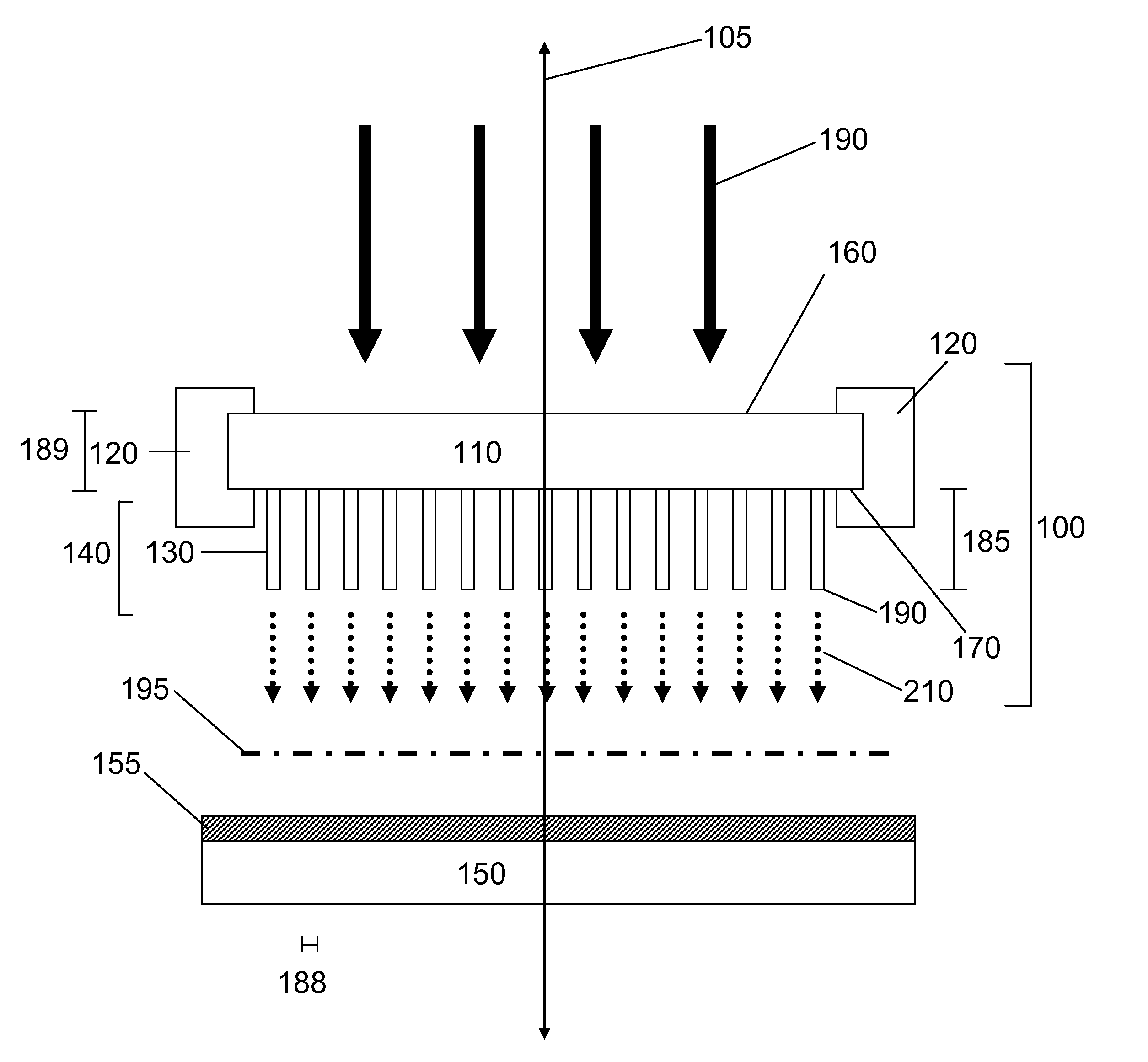
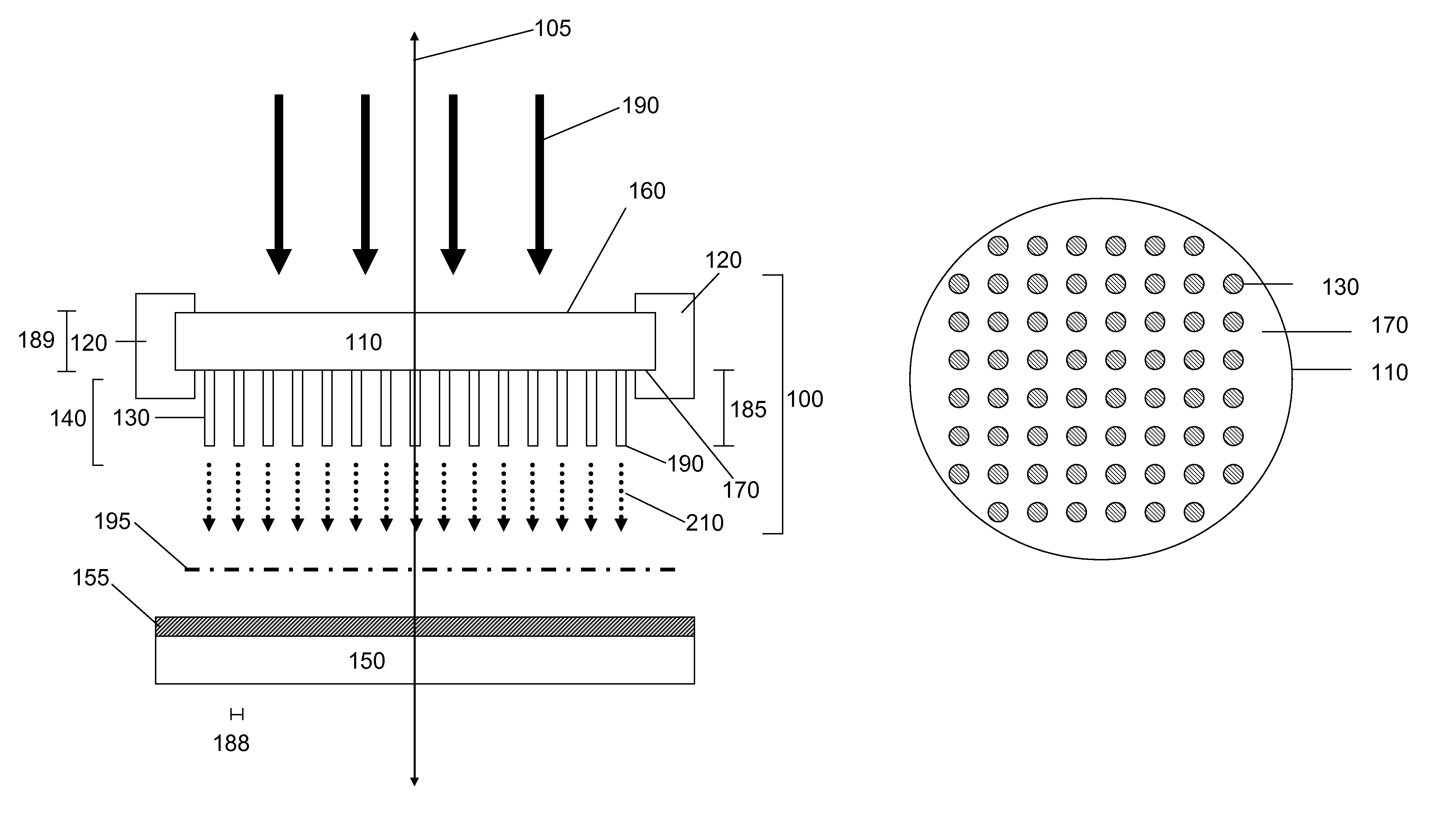
Provided is a substrate treatment apparatus using plasma. The substrate treatment apparatus includes a housing having an inner space in which a substrate is treated, a support member disposed within the housing to support the substrate, a gas supply unit supplying a gas into the housing, a plasma source generating plasma from the gas supplied into the housing, and a baffle unit disposed to surround the support member within the housing, the baffle unit including a baffle in which through holes for exhausting the gas into the inner space of the housing are defined. The baffle is divided into a plurality of areas when viewed from an upper side, and each of portions of the plurality of areas is formed of a metallic material, and each of the other portions of the plurality of areas is formed of a nonmetallic material.
Owner:SEMES CO LTD
Plasma display panel and drive method therefor
InactiveUS7990345B2Increase contrastReduce contrastStatic indicating devicesAlternating current plasma display panelsFluorescenceElectrode pair
A plasma display panel and a drive method therefor, which can enhance a representation capability when displaying a dark image. The plasma display panel includes fluorophor layers containing magnesium oxide. The drive method includes a reset step to initialize all the pixel cells into states of one of a light-up mode and a light-off mode, and an address step in which the pixel cells are caused to perform address discharges selectively in accordance with pixel data, which are successively executed in each of a head subfield and a second subfield within a one-field display period. In reset step, a voltage that sets row electrodes on one side, in the row electrode pairs as an anode and sets the column electrodes set as a cathode is applied between the row electrodes on the one side and the column electrodes.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
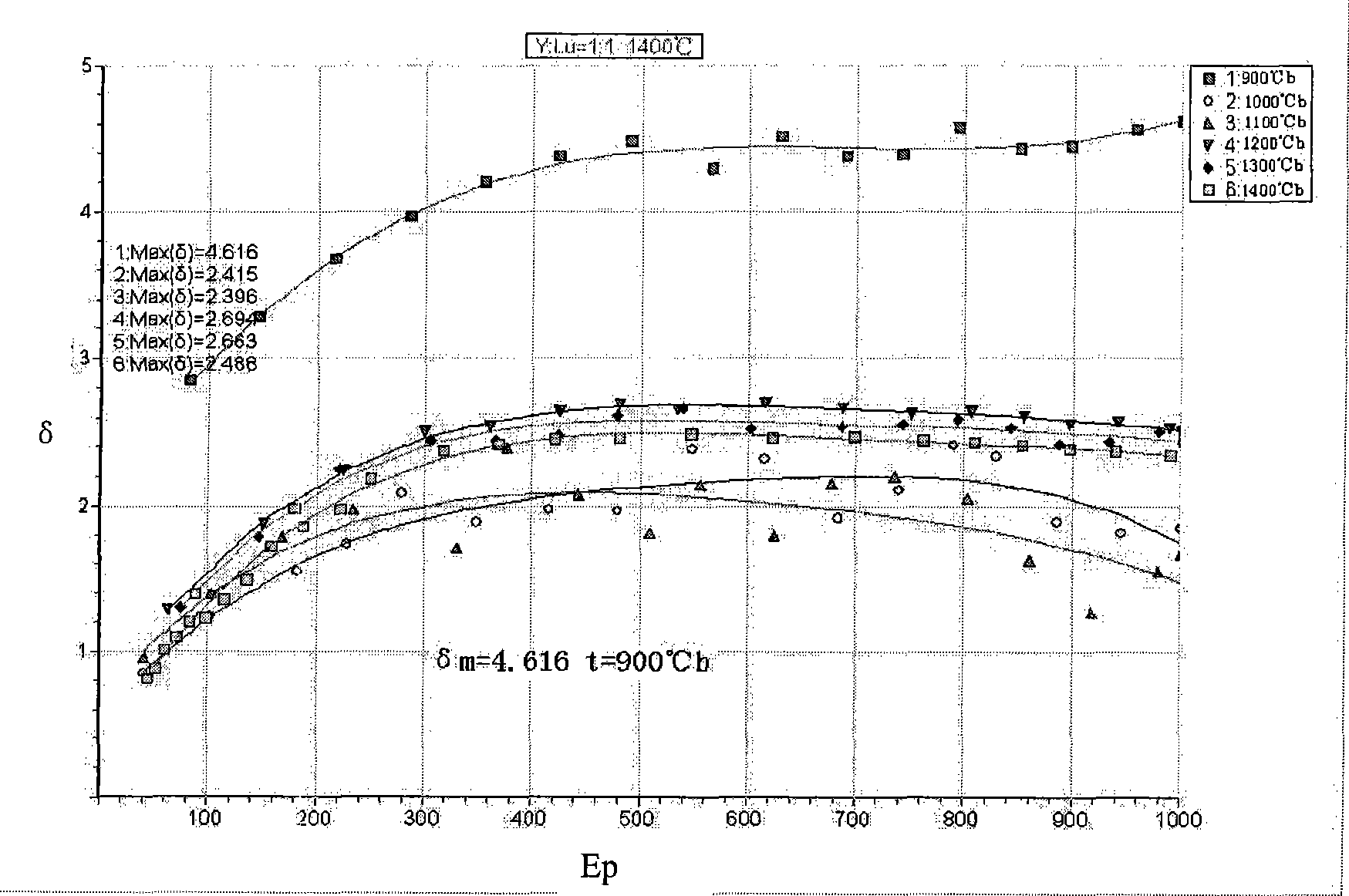
Y2O3-Gd2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101447377ALaunch bigImprove performanceSecondary electron emitting electrodesPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureRare-earth elementCerium
The invention discloses Y2O3-Gd2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of secondary electron emission materials. The prior secondary electron emission material cannot satisfy the higher electron emission requirements. The Y2O3-Gd2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material and the preparation method thereof are characterized in that yttrium and gadolinium which are rare earth elements are used as additional elements, and are mixed into metal molybdenum in different proportions for the preparation of the cathode material. The Y2O3-Gd2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material is obtained by mixing Gd2O3 and Y2O3 which are two rare earth oxides in any proportion, the mixed rare earth oxides account for 30 percent wt of the gross weight of the emission material, and others are molybdenum. The Y2O3-Gd2O3 system composite rare earth-molybdenum electron emission material can be utilized to make rare earth-molybdenum secondary electron emission material, the secondary electron emission coefficient thereof is higher a lanthanum-containing cathode, optimum activation temperature is less than the lanthanum-containing cathode, and the emission performance is stable in a larger voltage range and is superior to a cerium-containing cathode.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Electron emitter and method of fabricating electron emitter
InactiveUS7528539B2Increase the number ofExpansion quantityControl electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectric forceElectron
An electron emitter includes an emitter layer formed of a dielectric material, an upper electrode, and a lower electrode. A drive voltage is applied between the upper electrode and the lower electrode, for emitting electrons. The upper electrode is formed of scale-like conductive particles on the upper surface of the emitter layer and has a plurality of opening portions. The surfaces of overhanging portions of the opening portions that face the emitter layer are apart from the emitter layer. The overhanging portions each have such a cross-sectional shape as to be acutely pointed toward the inner edge of the opening portion, or the tip end of the overhanging portion, so that lines of electric force concentrate at the inner edge.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
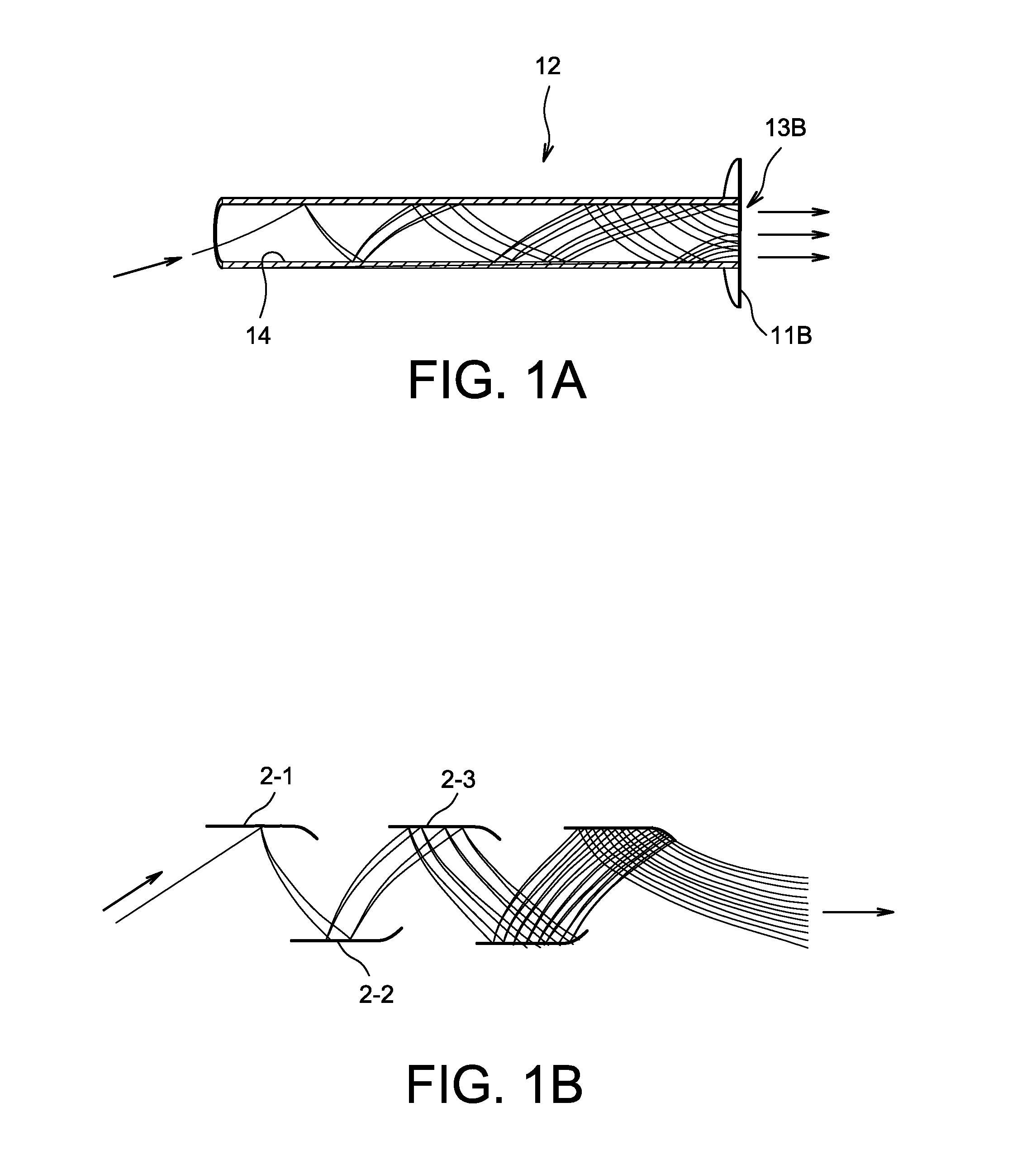
An electron multiplying structure for use in a vacuum tube using electron multiplying as well as a vacuum tube using electron multiplying provided with such an electron multiplying structure
The invention relates to an electron multiplying structure for use in a vacuum tube using electron multiplying and to an vacuum tube using electron multiplying provided with such an electron multiplying structure. According to the invention an electron multiplying structure is proposed for use in a vacuum tube using electron multiplying, the electron multiplying structure comprising an input face intended to be oriented in a facing relationship with an entrance window of the vacuum tube, an output face intended to be oriented in a facing relationship with a detection surface of the vacuum tube, wherein the electron multiplying structure at least is composed of a semi-conductor material layer adjacent the detection windows.
Owner:福托尼斯法国公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com