Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
173 results about "Anode potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
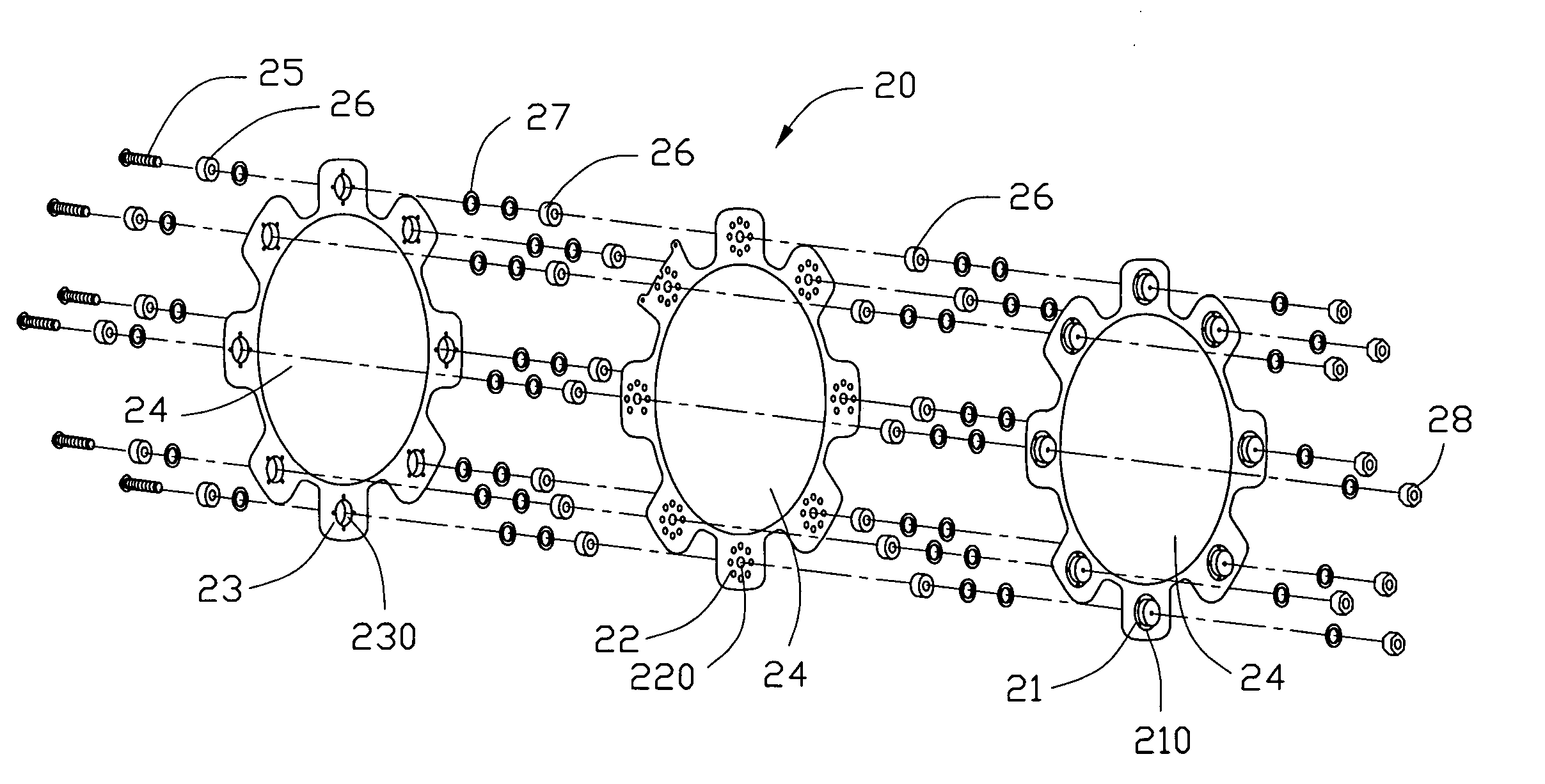
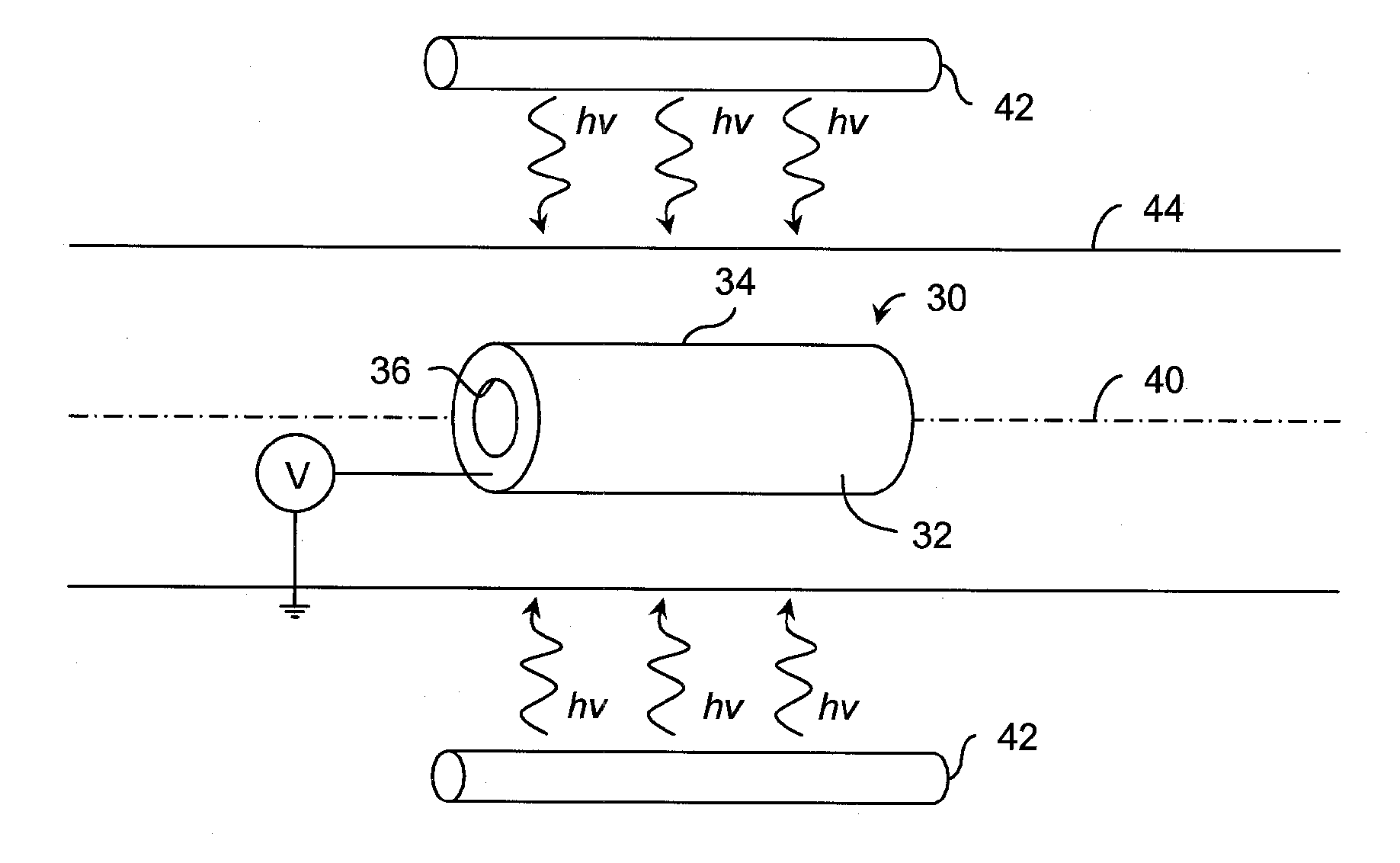
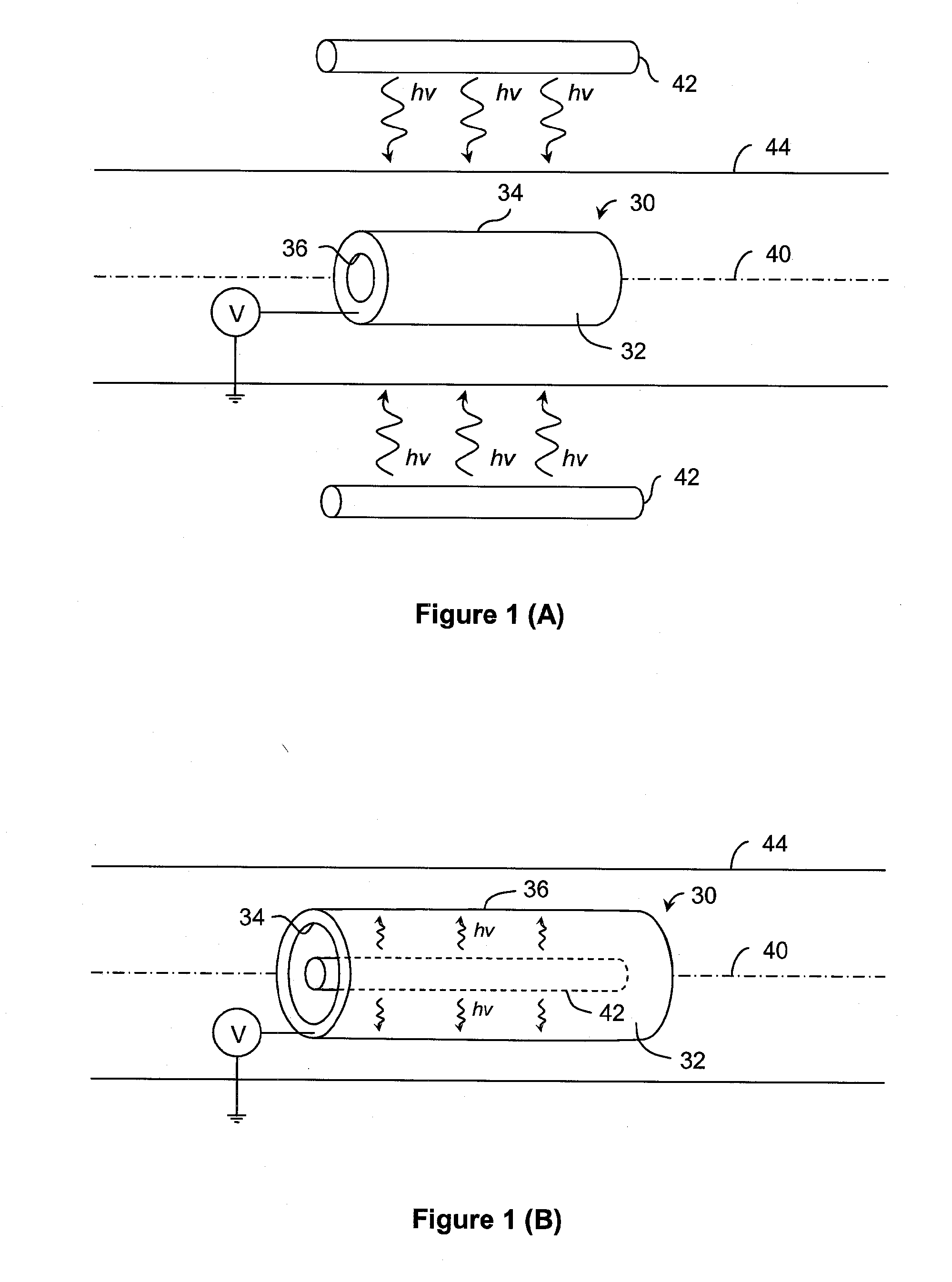
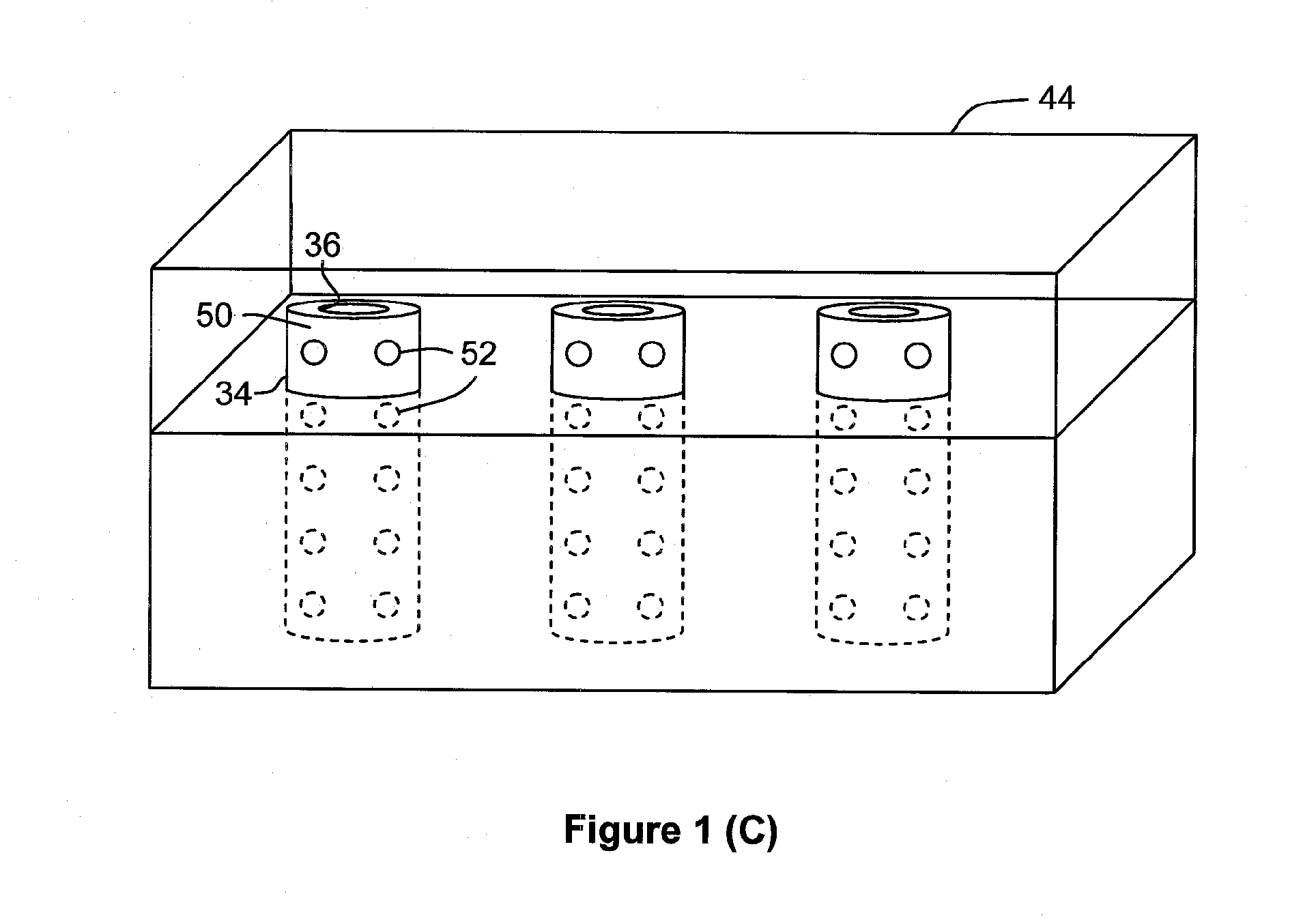
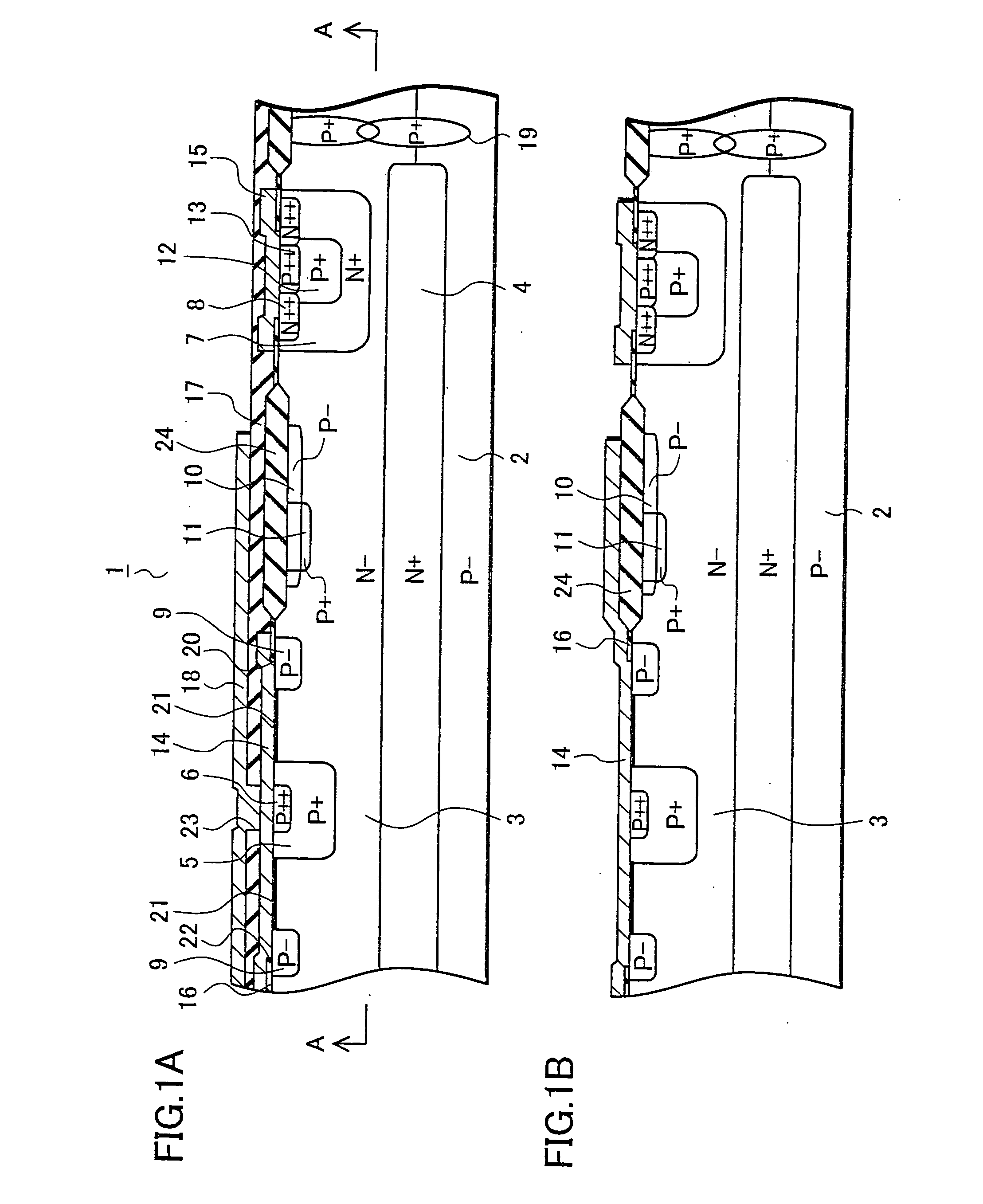
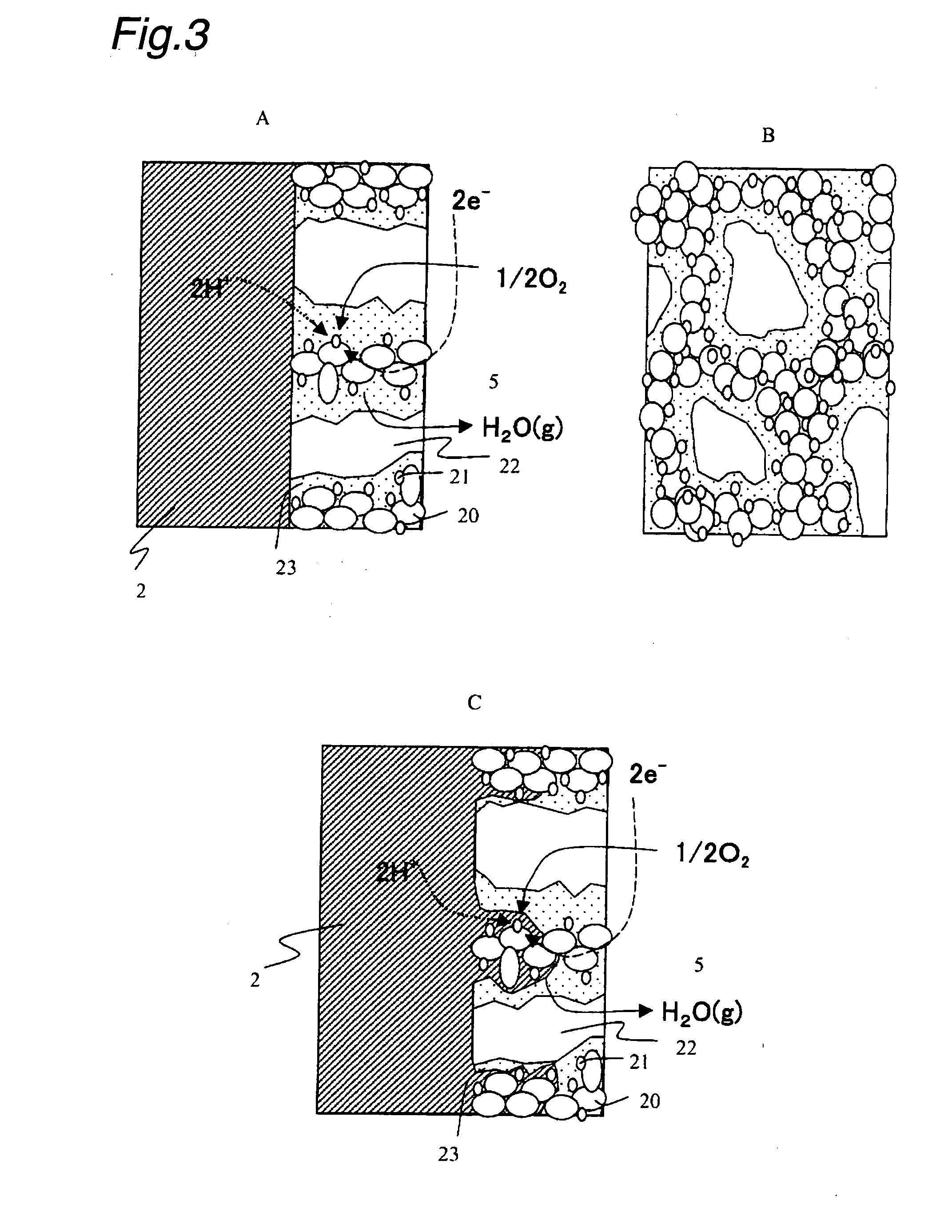
Ion source with particular grid assembly
InactiveUS20060017011A1Improving yield and throughputQuality improvementElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsMesh gridEngineering
An ion source (1) to be used in optical thin film deposition by IAD process includes a discharge chamber (10), a gas source, an actuator (11), a grid assembly (20) and an outer shell (30). The grid assembly includes a screen grid (21), an accelerator grid (22) and a decelerator grid (23). The screen grid is kept at anode potential and is disposed near the ions. The accelerator grid is kept at cathode potential and is spaced from the screen grid. The decelerator grid is equal to the ground and is disposed beyond the accelerator grid. Each grid has a curved central portion (24) defining a plurality of apertures aligned with those of the other two grids to form extraction channels for an ion beam (40). When disposing the grid assembly at one end of the discharge chamber, the curved central portions of the three grids are arranged in an inwardly curved manner toward the interior of the discharge chamber, and thus the ion beam is extracted from the grid assembly in a converged manner to have a sequentially reduced cross-sectional area.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL INT LTD
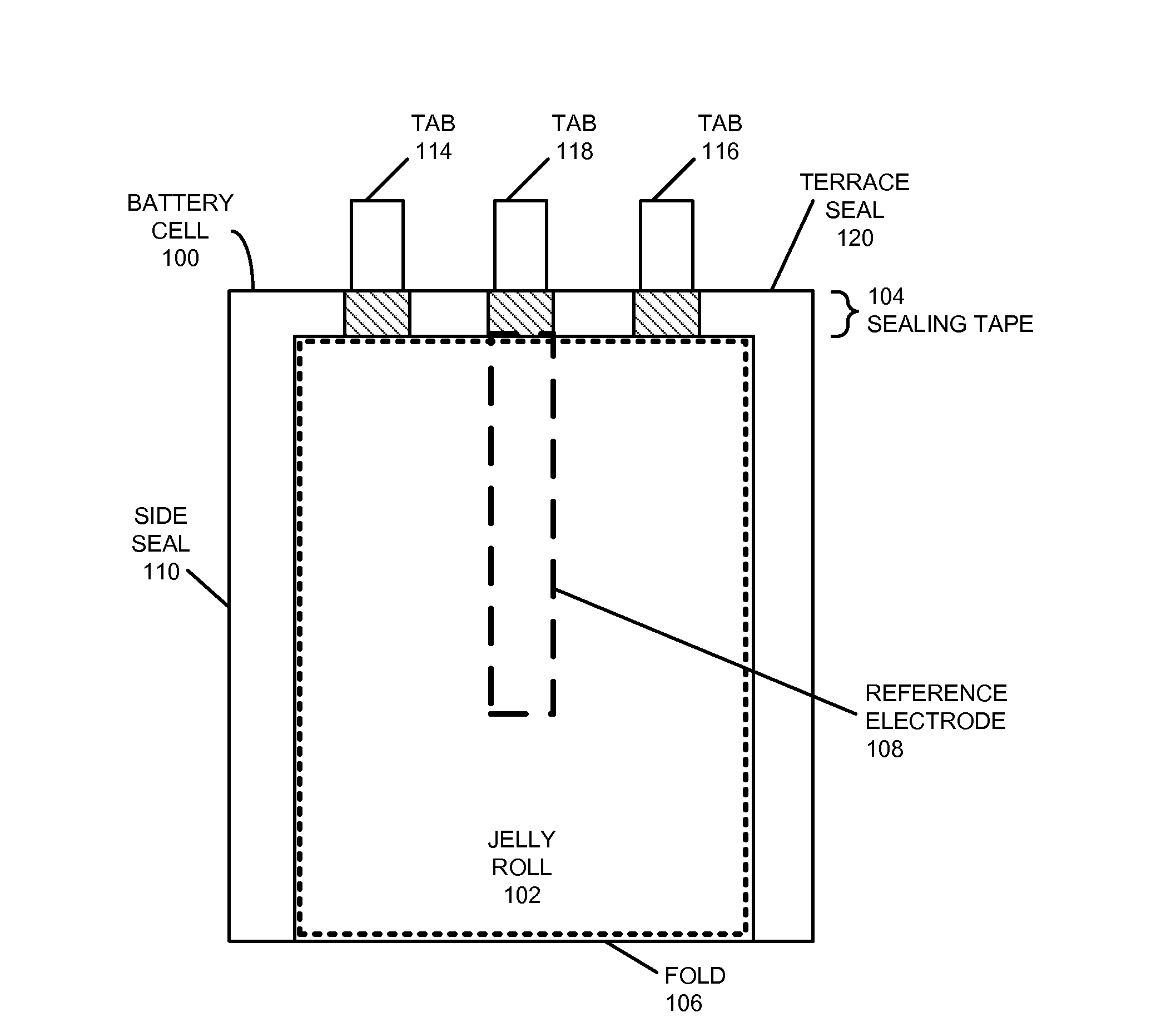
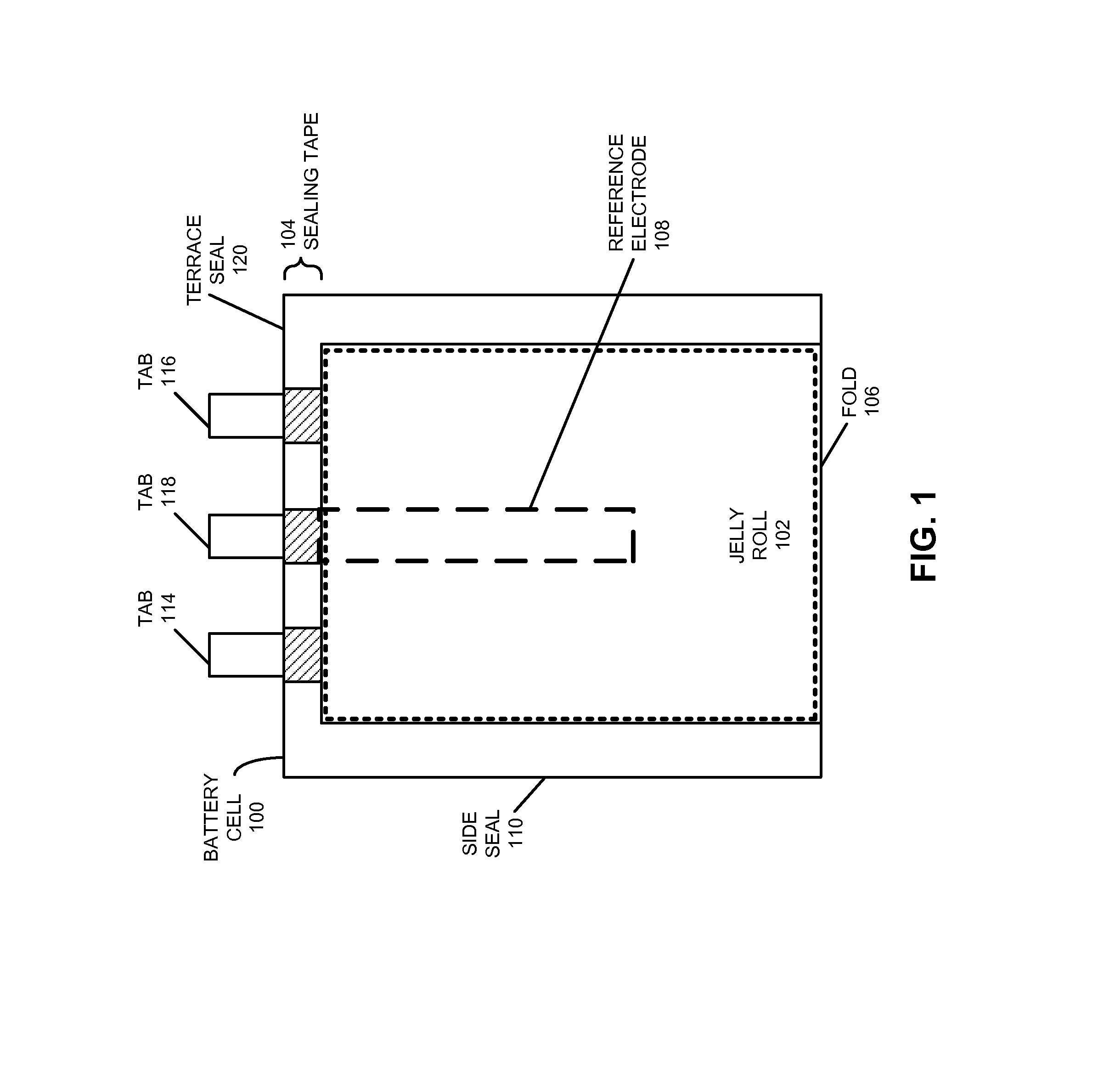
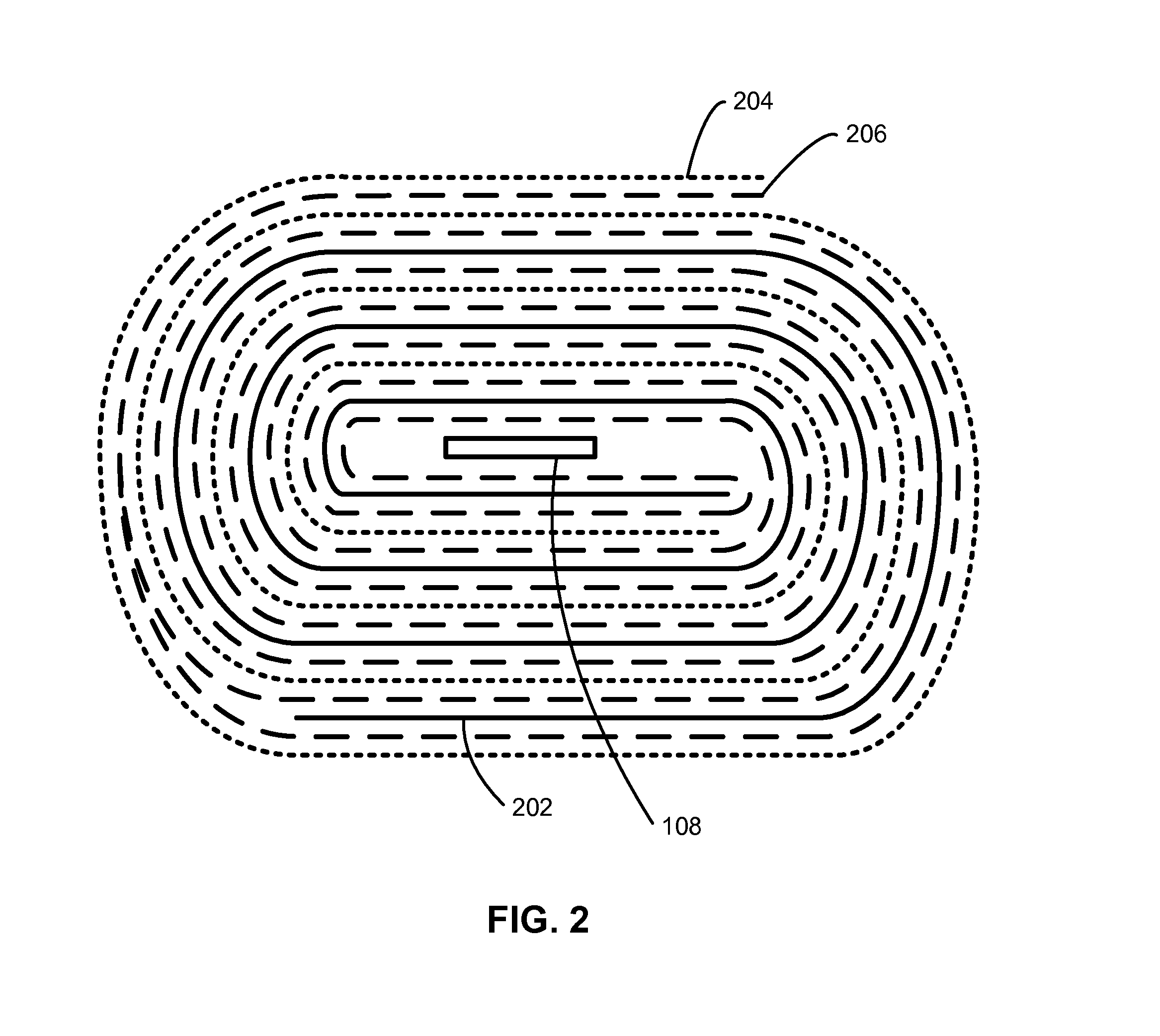
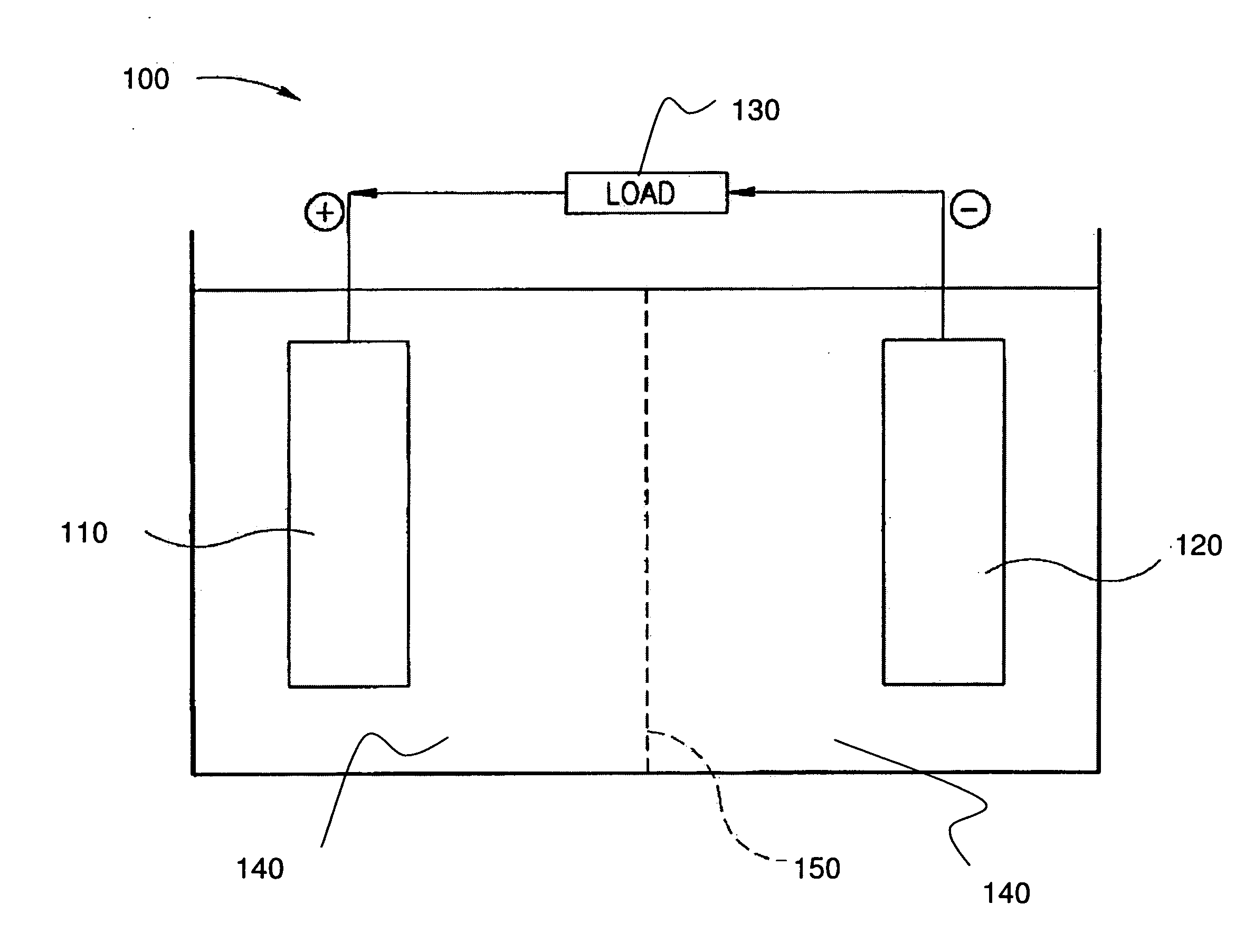
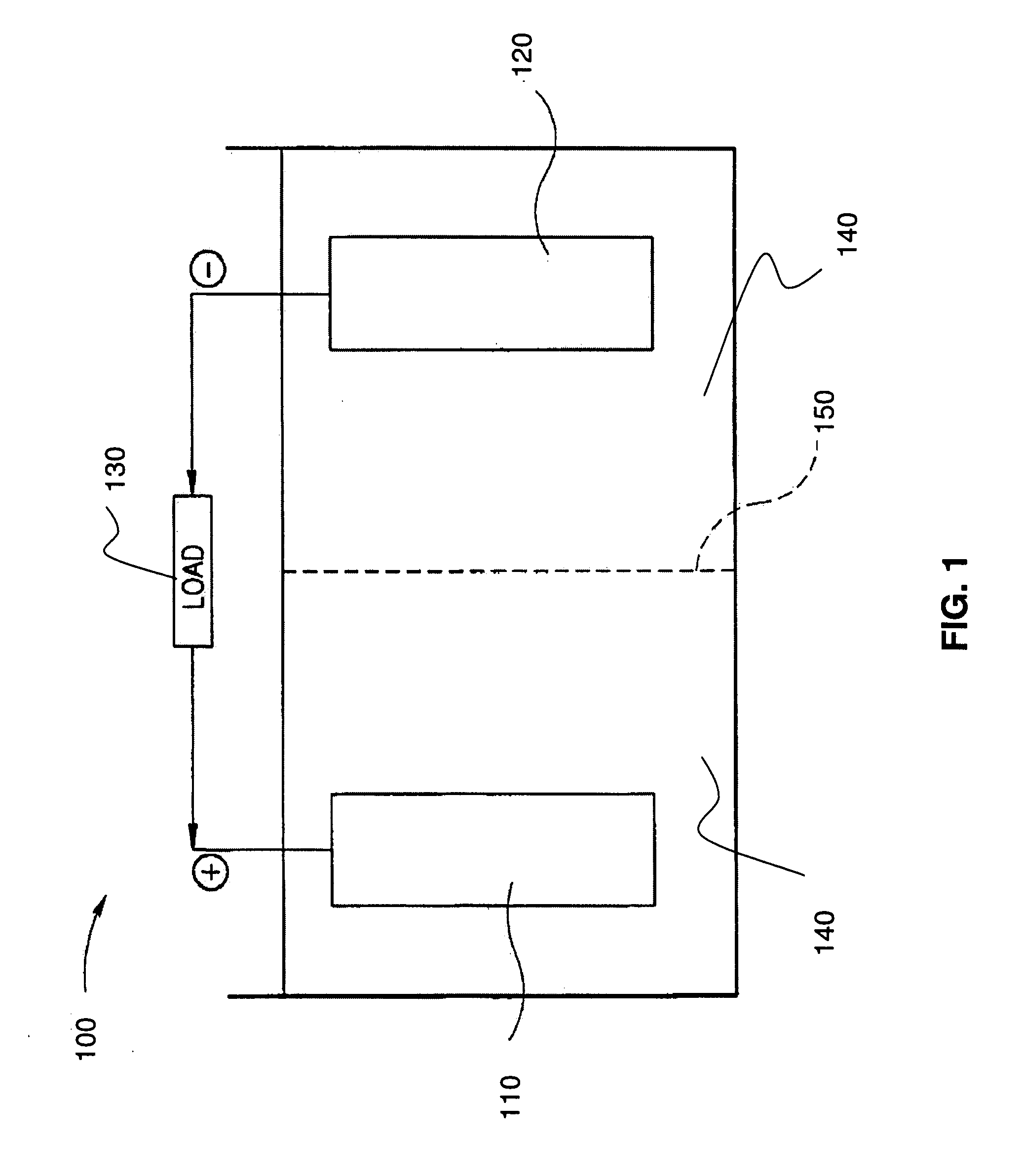
Using reference electrodes to manage batteries for portable electronic devices
ActiveUS20130009604A1Improve cycle lifeReduce charging currentBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingCharge currentElectrical battery
The disclosed embodiments provide a system that manages use of a battery in a portable electronic device. During operation, the system uses a reference electrode in the battery to monitor an anode potential of an anode in the battery during charging of the battery in the portable electronic device. If the anode potential falls below an anode potential threshold, the system modifies a charging technique for the battery to extend a cycle life of the battery. For example, the system may reduce a charge current of the battery if the anode potential falls below the anode potential threshold to prevent degradation caused by a negative anode potential during charging of the battery.
Owner:APPLE INC
Stabilized electrodes for electrochemical cells
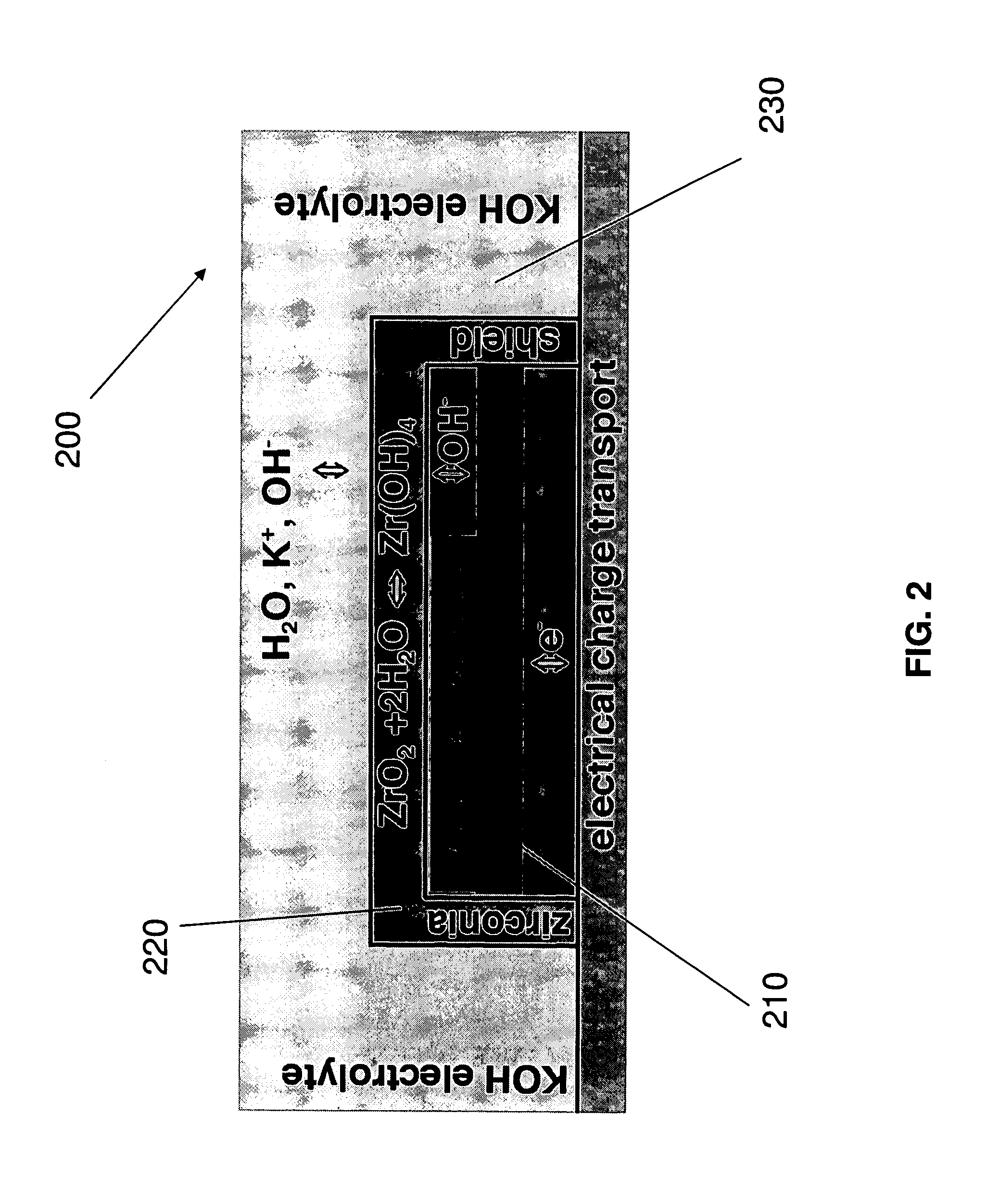
Stabilized electrodes for electrochemical cells. An electrochemical cell based on an environmentally benign zirconia stabilized Fe6+ / B2− chemistry is disclosed. An electrochemical potential is sustained compatible to the pervasive, conventional alkaline (MnO2—Zn battery), and with a much higher electrical storage capacity. Either or both the anode and cathode may be stabilized. For example, a zirconia overlayer on either TiB2 or VB2 boride anodes, and / or super-iron, K2FeO4, cathodes stabilizes the electrodes, while sustaining facile charge transfer. The energetic Fe6+ cathode elevates, and fully compensates for, the boride / zinc anode potential differential.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
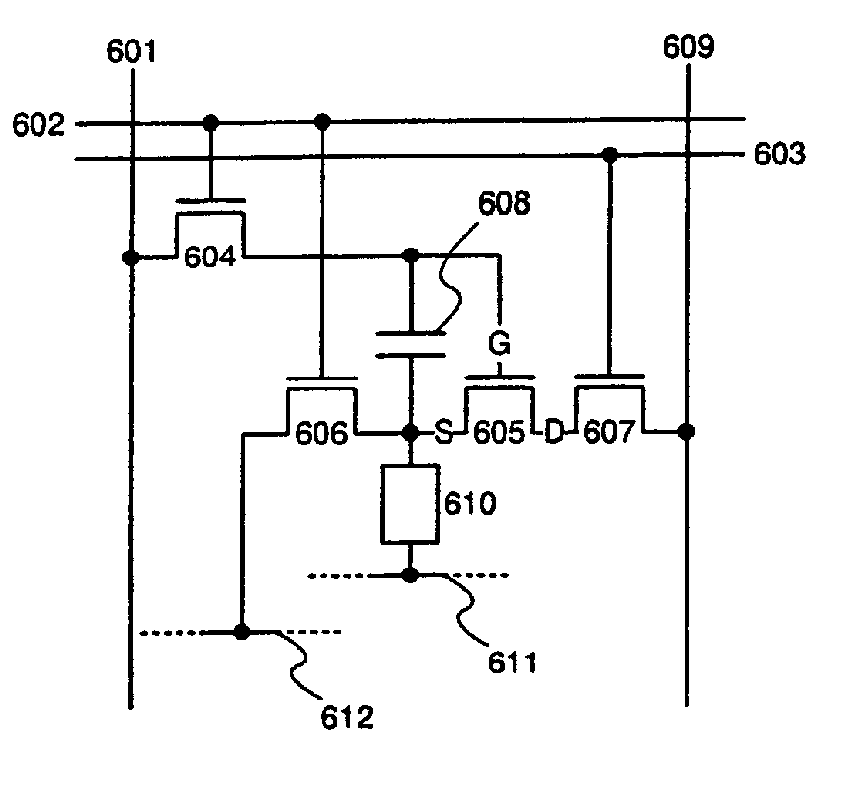
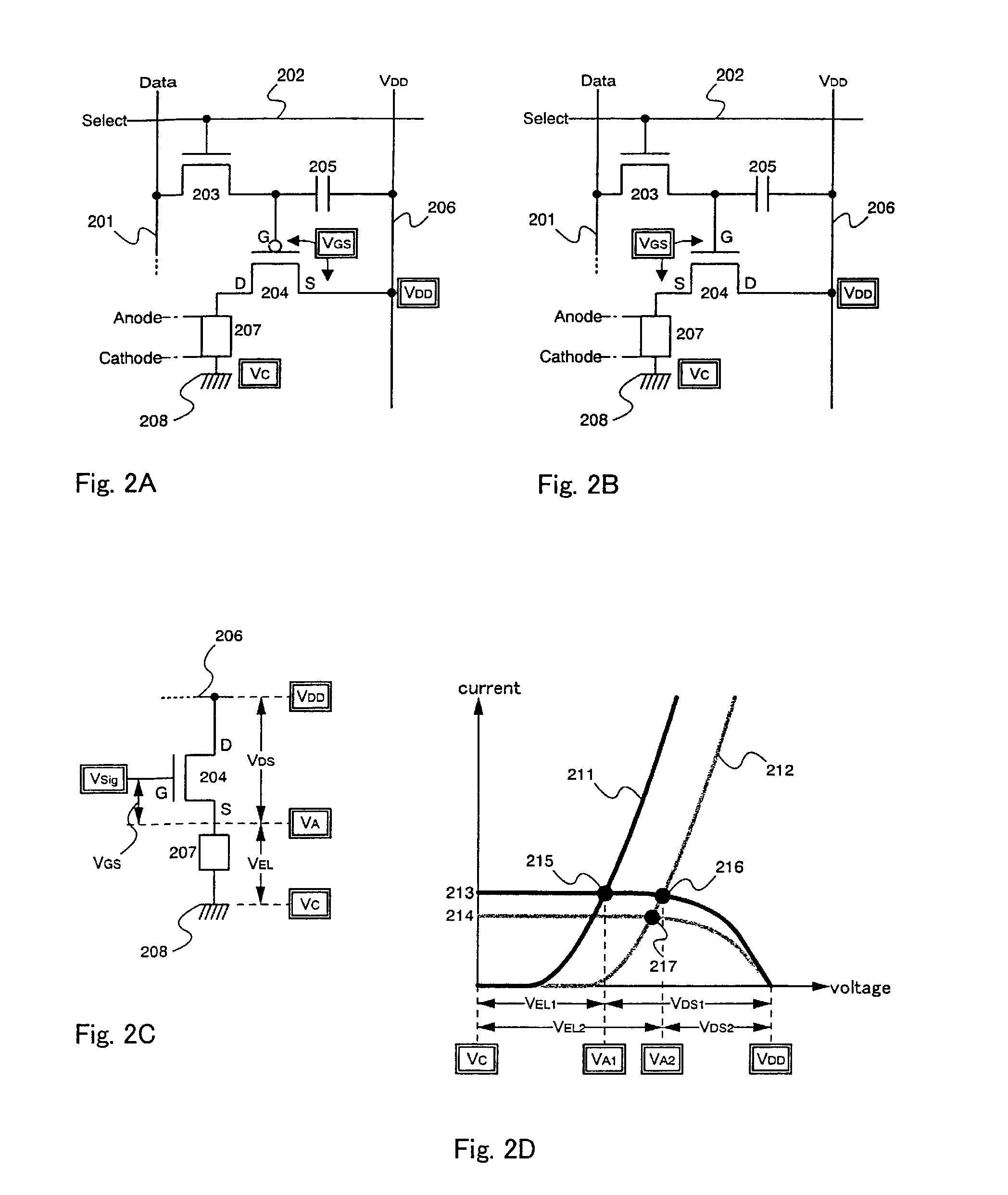
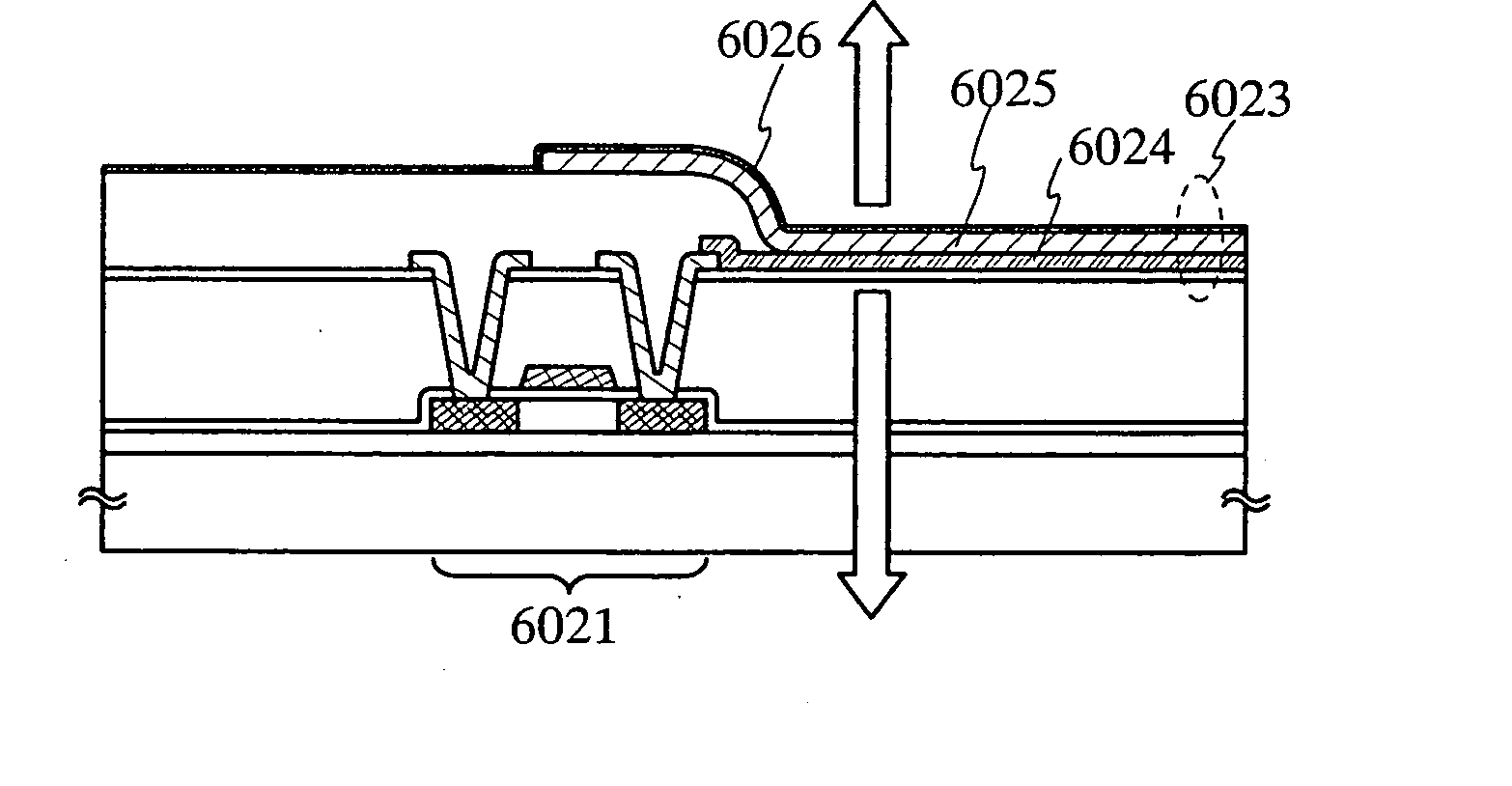
Display Device and Method for Driving the Same
ActiveUS20070210720A1Small sizeLow costPower managementStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceElectrode potential
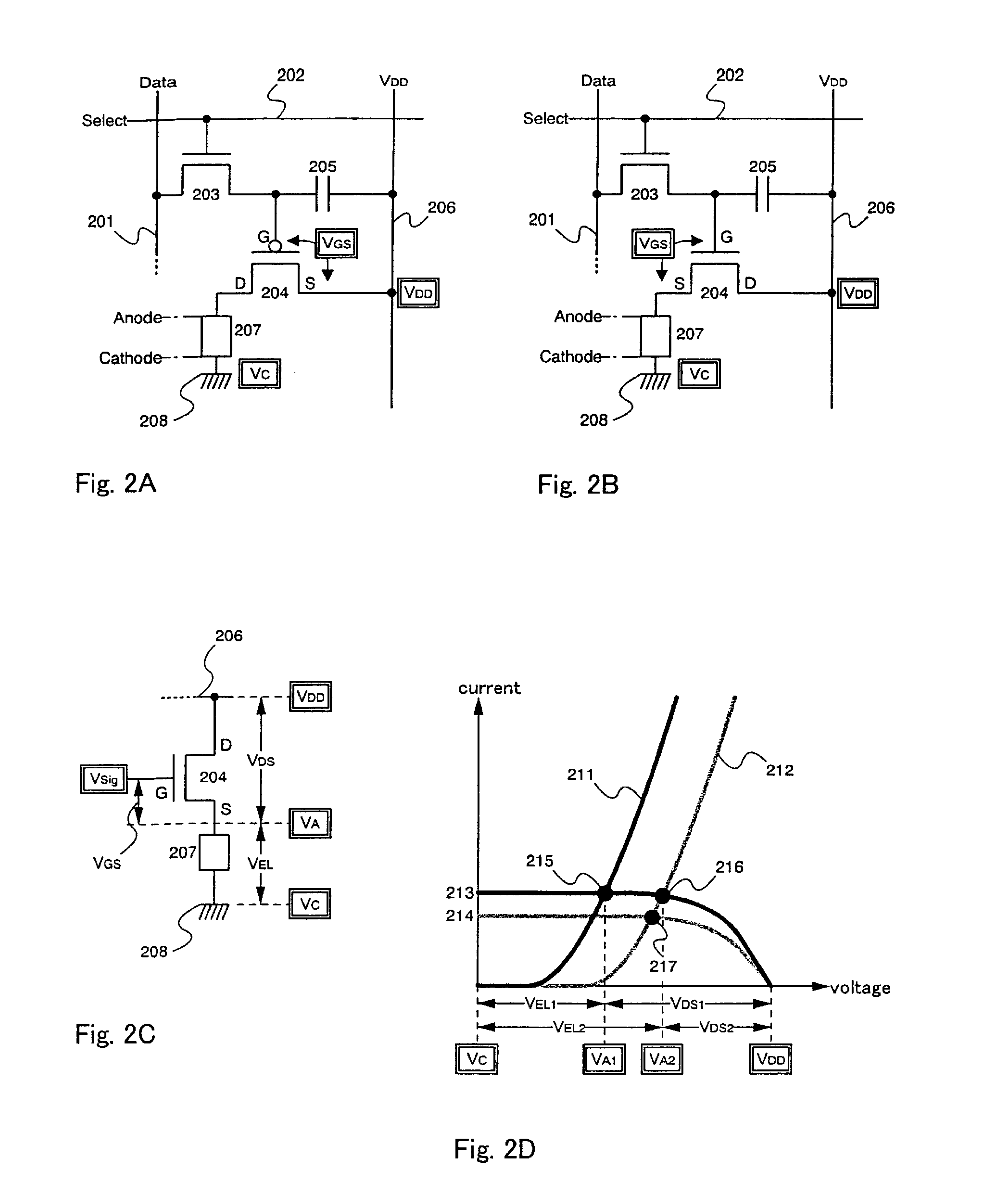
A semiconductor device having a configuration hardly generating variations in the current value due to a deteriorated EL element is to be provided. A capacitance element is disposed between the gate and the source of a driving TFT, video signals are inputted to the gate electrode, and then it is in the floating state. At this time, when the gate-source voltage of the driving TFT exceeds the threshold, the driving TFT is turned on. Suppose an EL element is deteriorated and the anode potential rises, that is, the source potential of the driving TFT rises, the potential of the gate electrode of the driving TFT, being in the floating state by coupling of the capacitance element, is to rise by the same amount. Accordingly, even when the anode potential rises due to the deteriorated EL element, the rise is added to the gate electrode potential as it is, and the gate-source voltage of the driving TFT is allowed to be constant.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
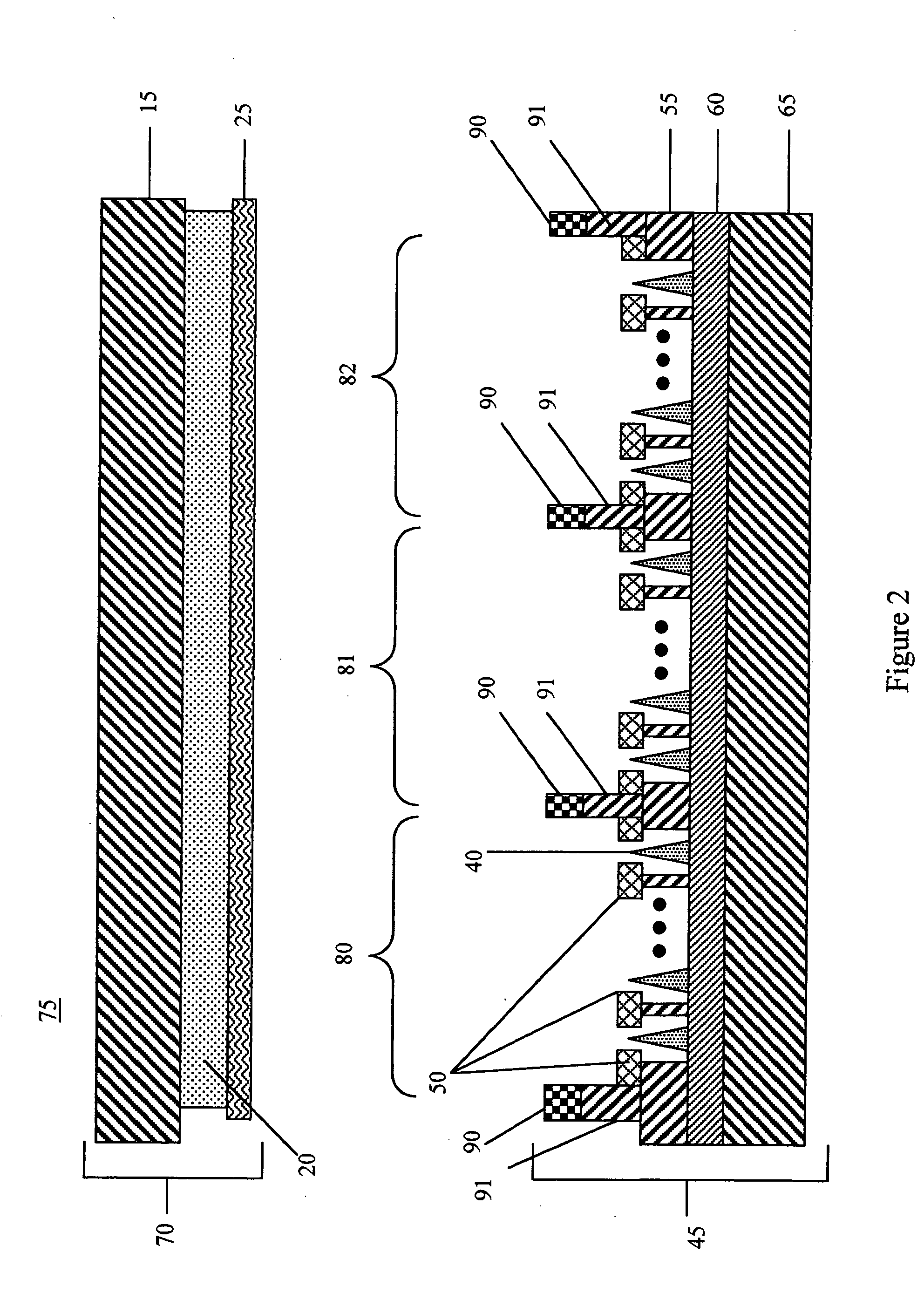
Image-forming apparatus and method of manufacturing the same
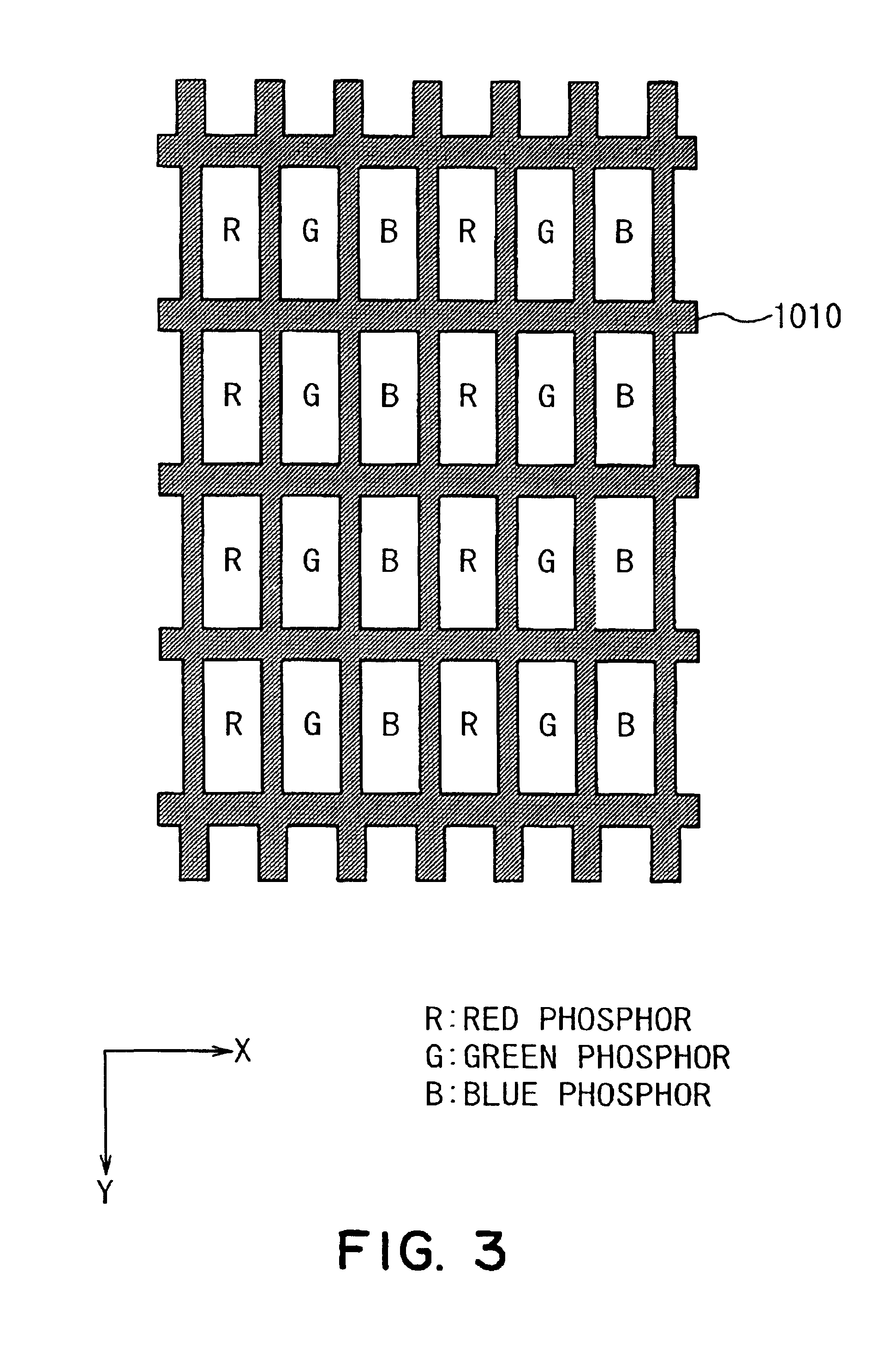
InactiveUS6509691B2Cathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrical resistance and conductanceElectron source
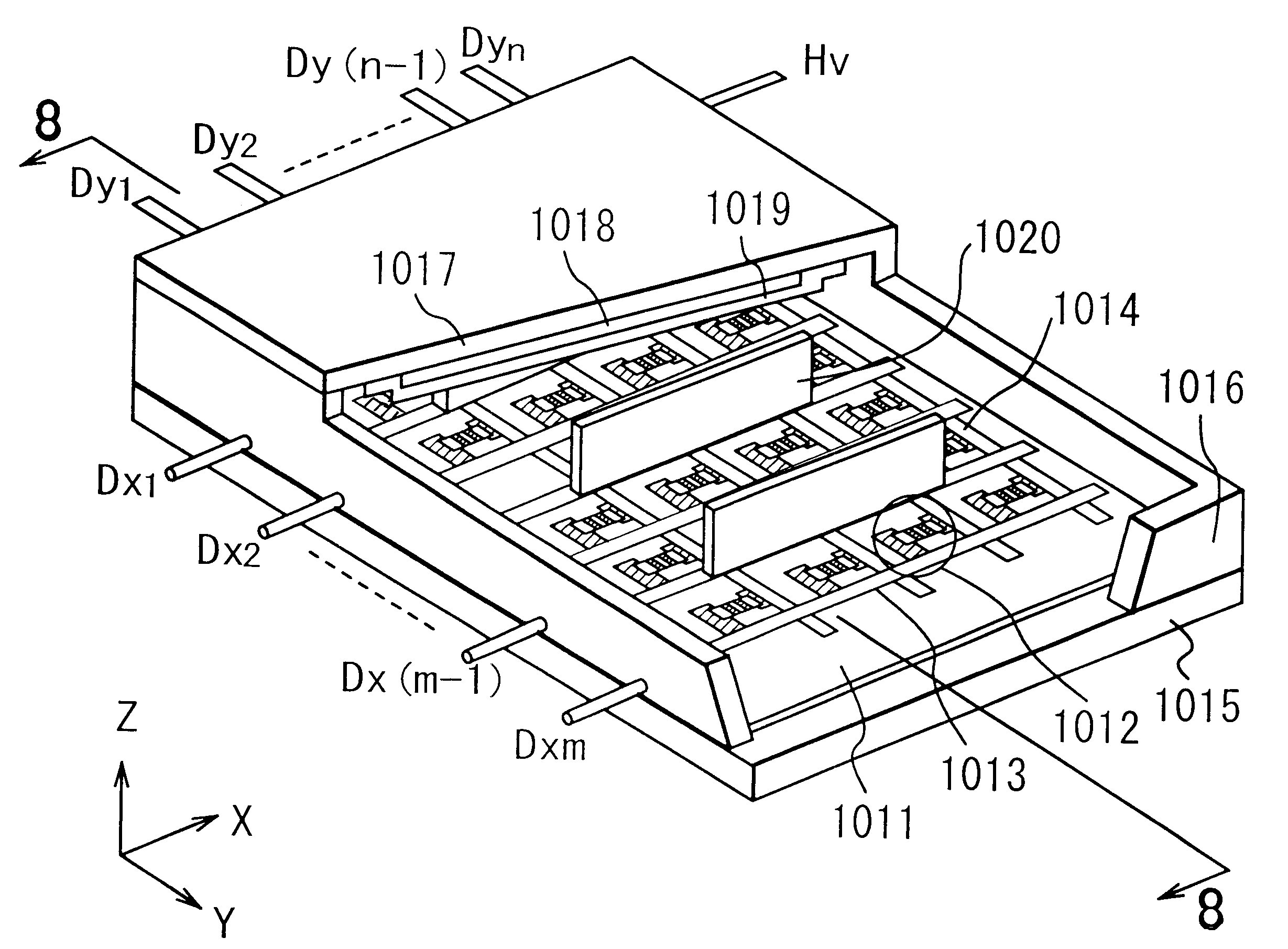
An image-forming apparatus of the present invention includes: a vacuum container constituted by disposing in opposition to each other a rear plate with an electron source formed thereon, and a face plate having an image display region provided with at least phosphors for being irradiated with electrons emitted from the electron source to form an image and anodes disposed on the phosphors; anode potential supplying means for supplying an electric potential higher than that of the electron source to the anode; at least one electroconductive member provided at a site outside of the image display region on an inner surface of the face plate; potential supplying means for supplying to the electroconductive member an electric potential at a level between a lowest electric potential of those which are applied to the electron source and an electric potential applied to the anode; first and second resistant members electrically connected between the anode and the electroconductive members, having resistances higher than that of the anode and having different resistances from each other, wherein the anode, the first resistant member, the second resistant member, and the electroconductive member are electrically connected in series.
Owner:CANON KK
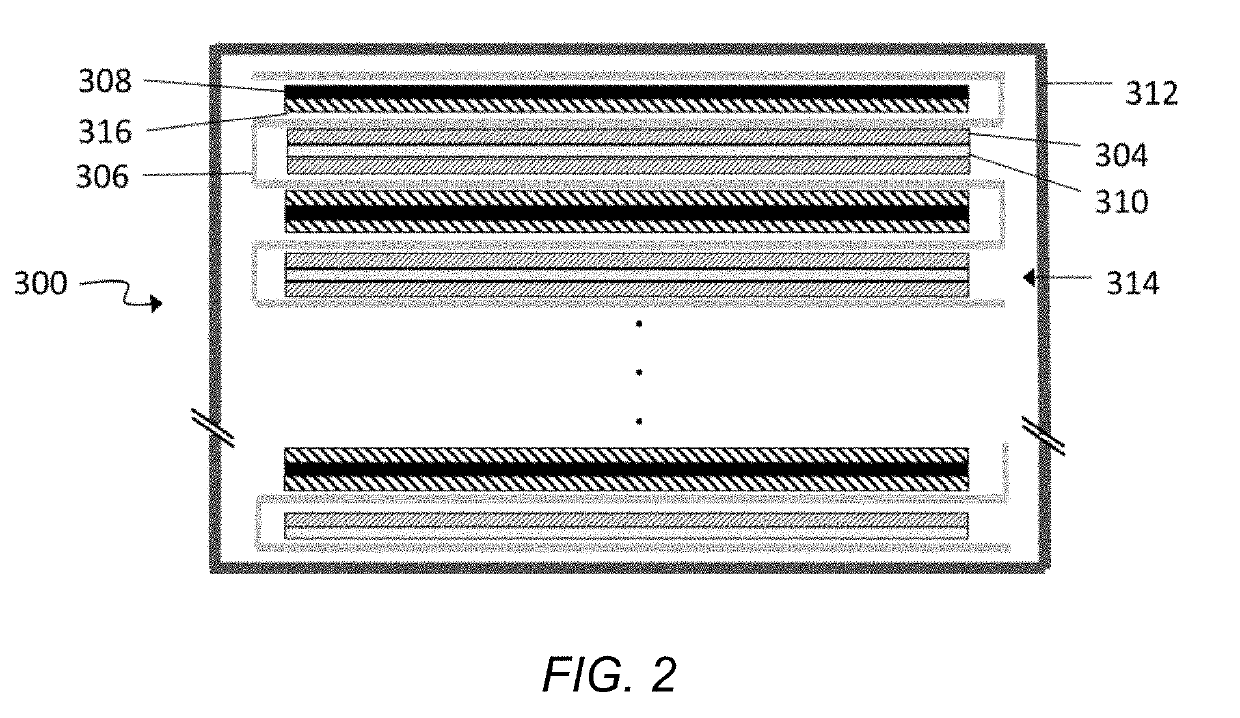
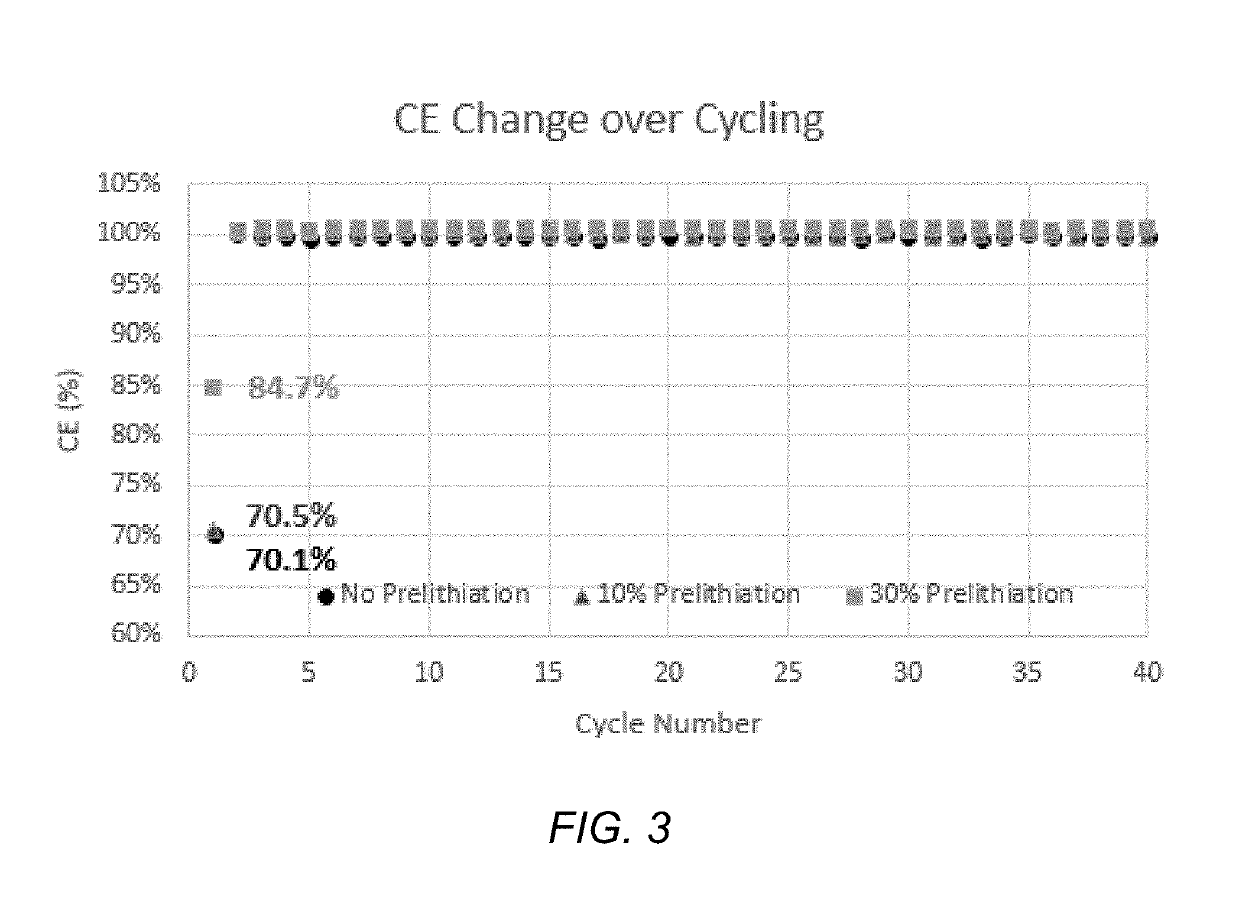
Prelithiated and methods for prelithiating an energy storage device
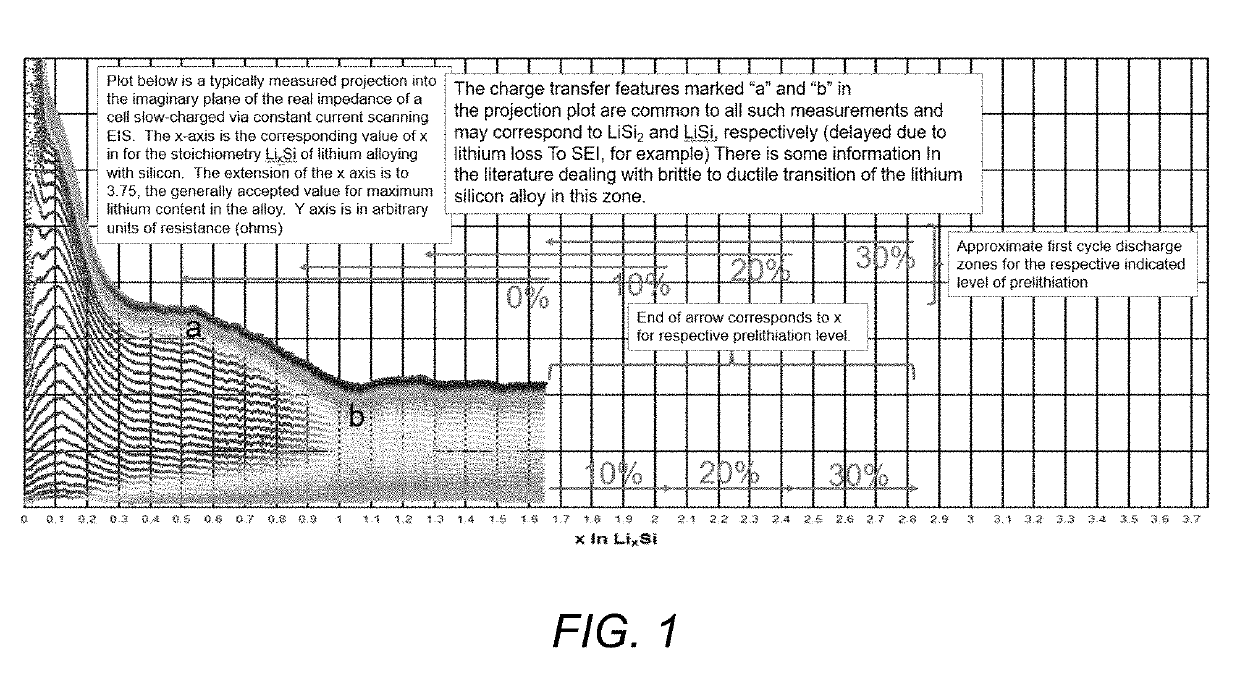
The present disclosure relates to prelithiated Si electrodes, methods of prelithiating Si electrodes, and use of prelithiated electrodes in electrochemical devices are described. There are several characteristics of electrode prelithiation that enable the superior battery performance. First, a prelithiated silicon anode is already in its expanded state during SEI formation, and therefore less of the SEI layer breaks down and reforms during cycling. Second, the prelithiated anode has a lower anode potential, which may also help the cycle performance of an electrochemical device.
Owner:ENEVATE CORP
Display device and method for driving the same
ActiveUS8059068B2Small sizeLow costPower managementStatic indicating devicesElectrode potentialCapacitance
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electrochemical wastewater treatment method for removing salts and refractory organic matters synchronously
ActiveCN104671364AShort process flowSave spaceDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processElectricityWastewater
The invention provides an electrochemical wastewater treatment method for removing salts and refractory organic matters synchronously and is mainly applied to wastewater containing low-concentration salts and low-concentration refractory organic matters. According to the method, the salts are removed under the electro-adsorption effect of a high-specific-surface-area material on negative and positive ions, and the refractory organic matters are oxidized and removed through control on cathode and anode potential to generate reactive oxygen components and reactive chlorine components. According to the method, characteristics of electro-adsorption salt removal and electrochemical oxidation methods are combined, a cathode and an anode are fully utilized, the efficiency for removal of the salts and the refractory organic matters is high, and the removal cost is low.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image-forming apparatus and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6853148B2Improve reliabilityReduce harmCathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrical resistance and conductanceElectron source
An image-forming apparatus of the present invention includes: a vacuum container constituted by disposing in opposition to each other a rear plate with an electron source formed thereon, and a face plate having an image display region provided with at least phosphors for being irradiated with electrons emitted from the electron source to form an image and anodes disposed on the phosphors; anode potential supplying means for supplying an electric potential higher than that of the electron source to the anode; at least one electroconductive member provided at a site outside of the image display region on an inner surface of the face plate; potential supplying means for supplying to the electroconductive member an electric potential at a level between a lowest electric potential of those which are applied to the electron source and an electric potential applied to the anode; first and second resistant members electrically connected between the anode and the electroconductive members, having resistances higher than that of the anode and having different resistances from each other, wherein the anode, the first resistant member, the second resistant member, and the electroconductive member are electrically connected in series.
Owner:CANON KK
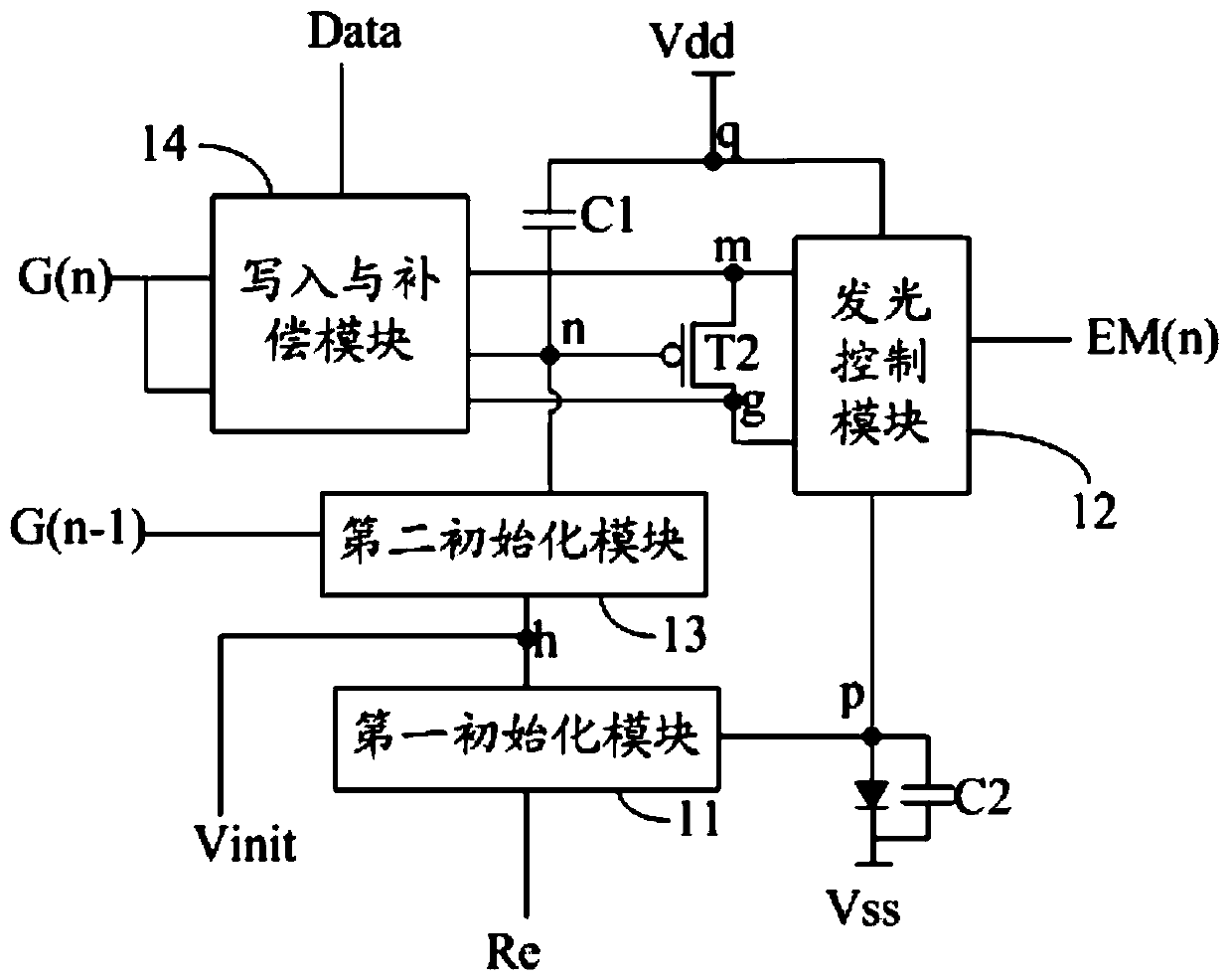
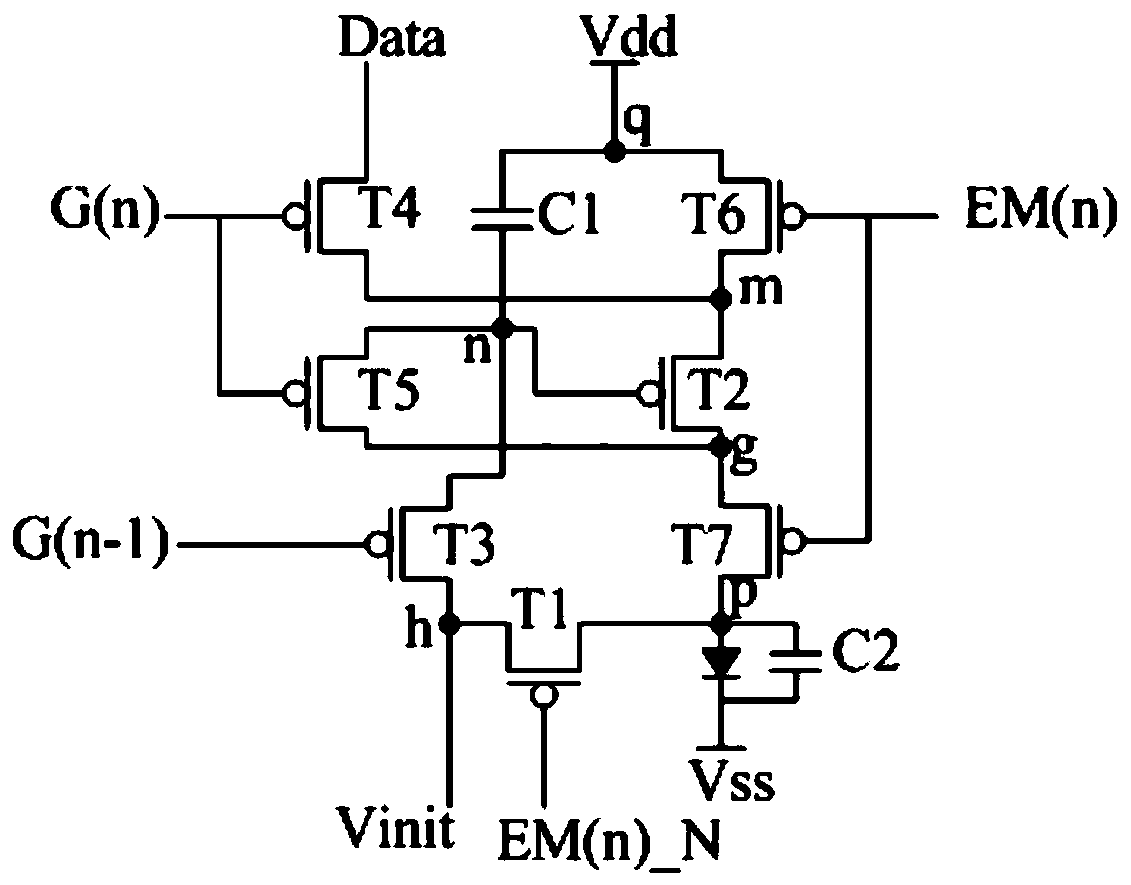
Pixel circuit and driving method thereof, display panel and display device
InactiveCN108877680AImprove luminous efficiencyExtended service lifeStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceDisplay device
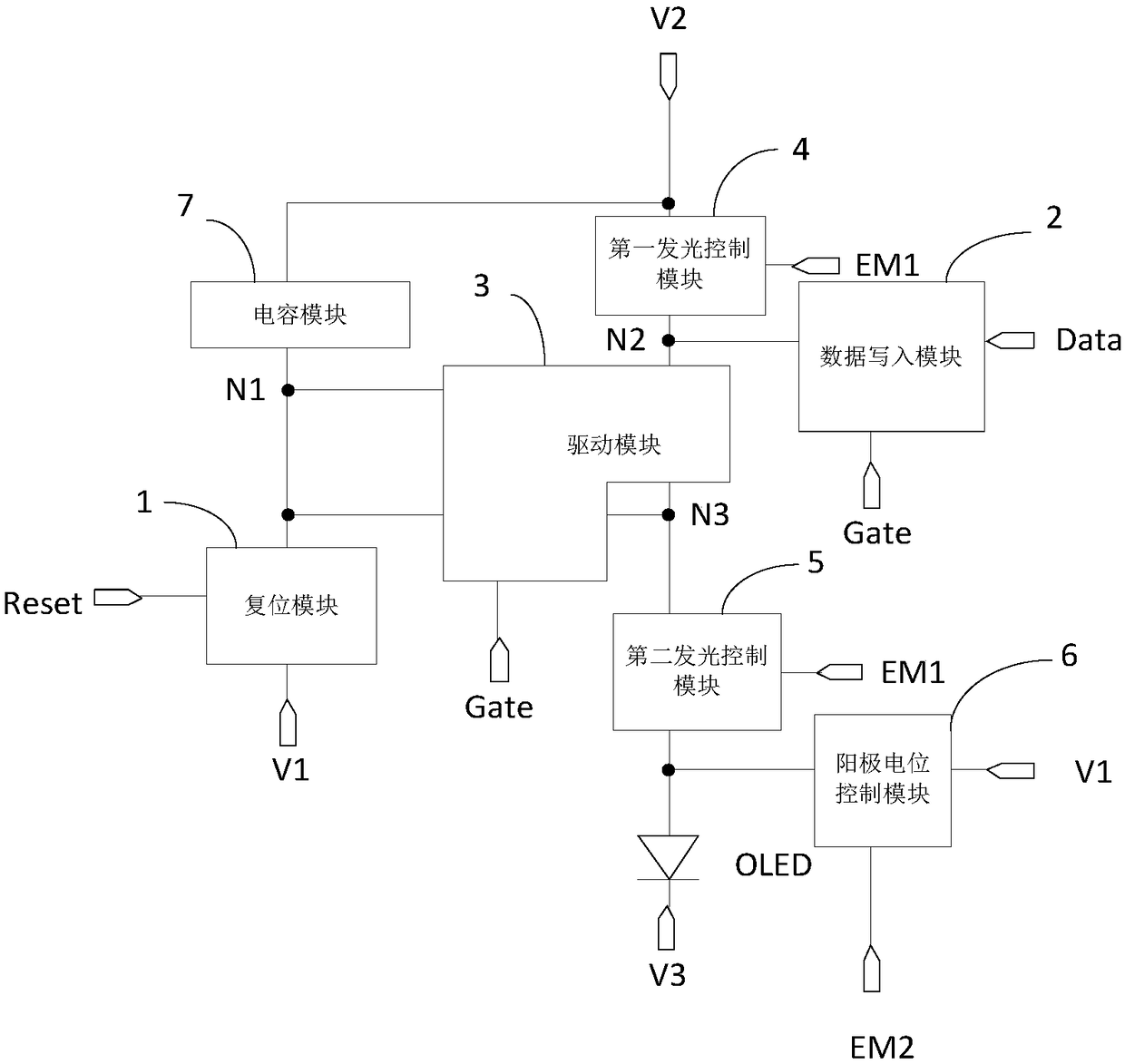
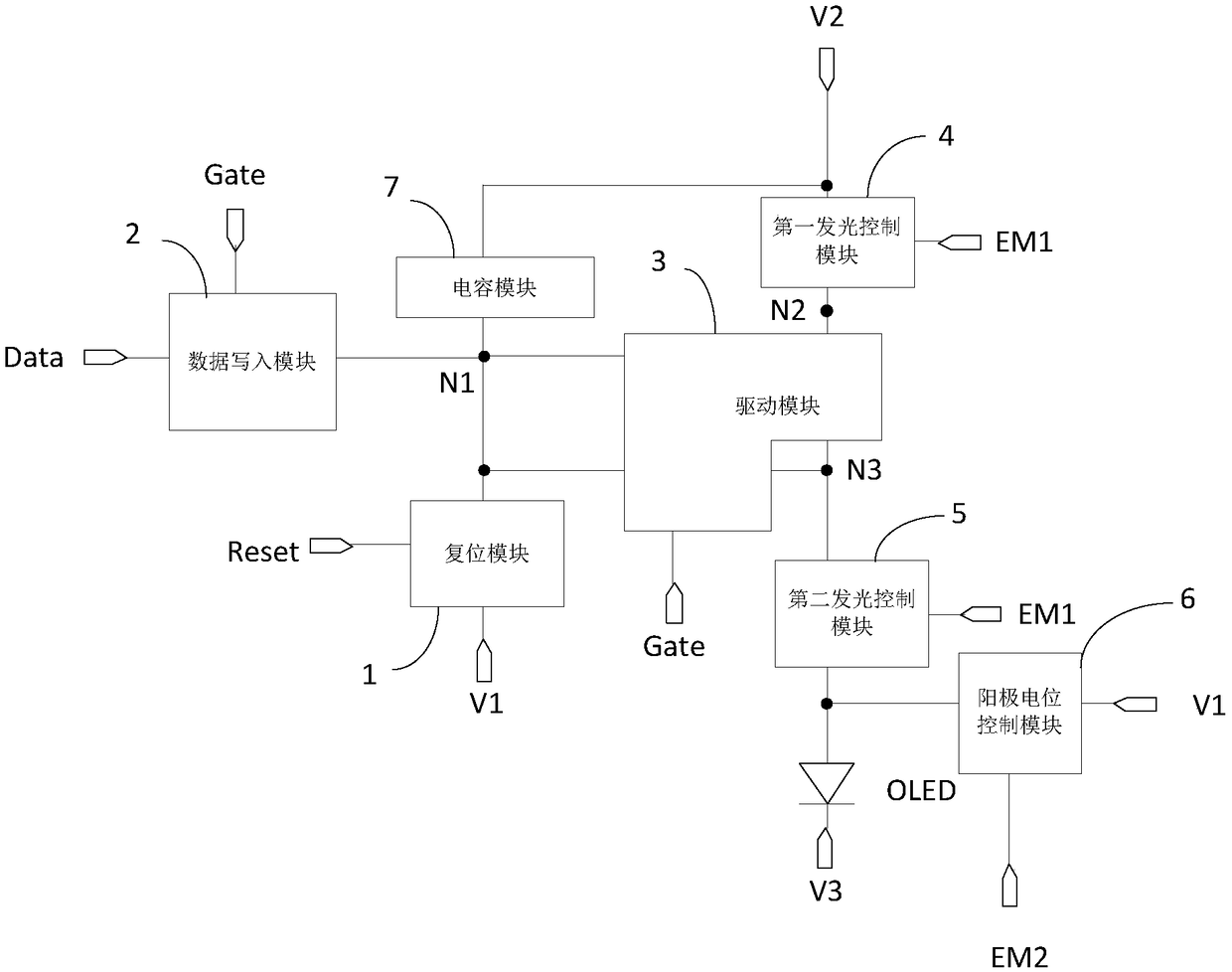
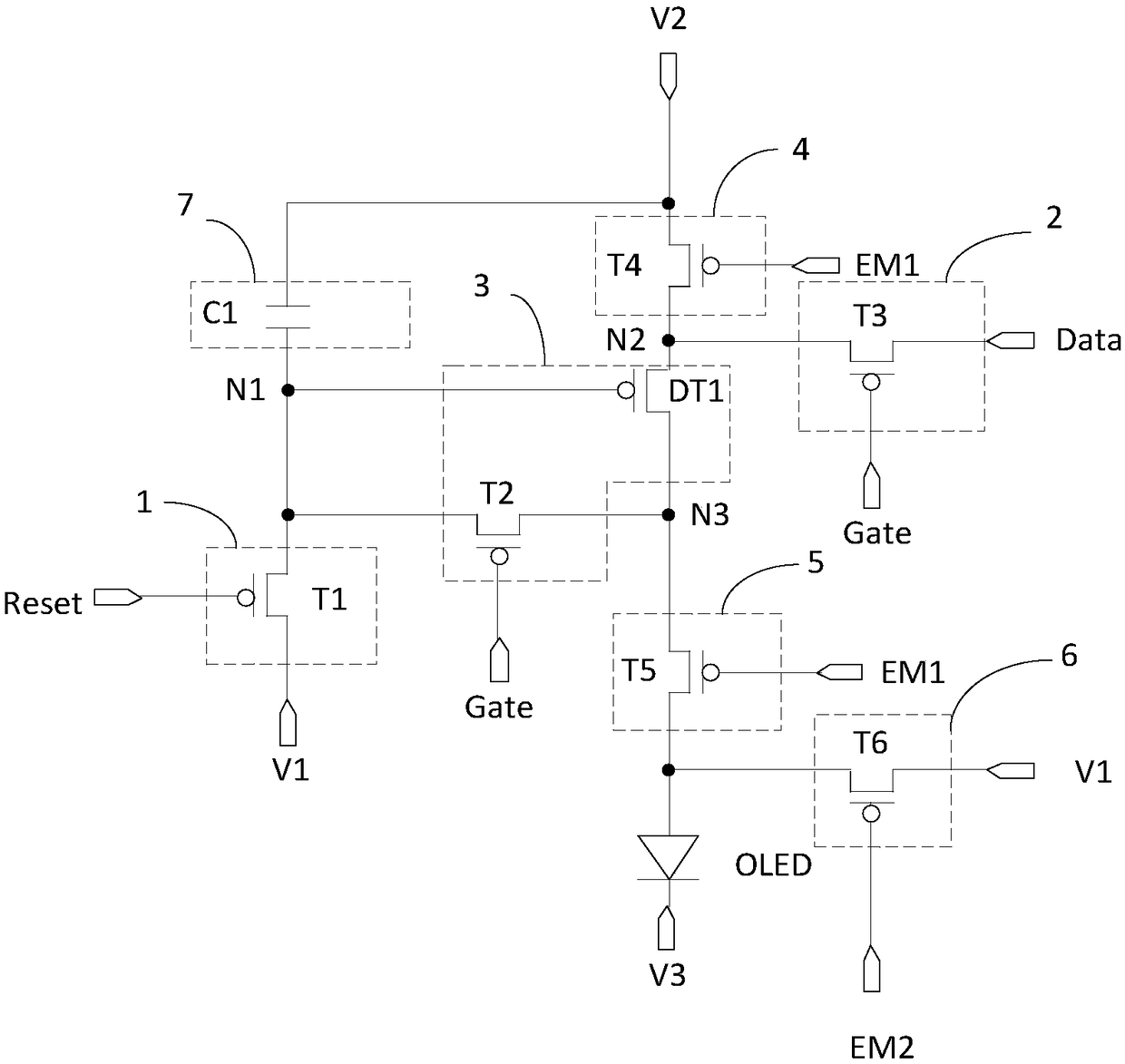
The present invention discloses a pixel circuit and a driving method thereof, a display panel and a display device. The pixel circuit comprises a reset module, a data writing-in module, a drive module, a first light-emitting control module, a second light-emitting control module, an anode potential control module, a capacitive module and a light-emitting device. Through cooperative work of the modules mentioned above, the pixel circuit drives the light-emitting device to emit light, and the second light-emitting control module supplies a voltage of an output end of the drive module to an anodeof the light-emitting device in a light-emitting stage; and the anode potential control module supplies signals of a first voltage signal terminal to the anode of the light-emitting device in a non-light-emitting stage to allow the bias voltage of the light-emitting device in the non-light-emitting stage to be opposite to the bias voltage of the light-emitting device in the light-emitting stage so as to improve the light-emitting efficiency and the service life of the light-emitting device.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Method and system for combined photocatalytic and electrochemical wastewater remediation
InactiveUS20120279872A1Improve performanceEffectively drives electrochemical oxidationCellsWater treatment compoundsElectron holeInorganic Chemical
The present invention utilizes the marriage of photocatalytic degradation and electrochemical oxidation to provide wastewater remediation and water purification based on the use of bifunctional electrodes. The bifunctional electrode provides for combined photocatalytic and electrochemical wastewater remediation for removing any one or combination of organic chemical pollutants, inorganic chemical pollutants and microorganisms. The electrode includes an electronically conducting substrate having a photocatalyst applied to a portion of the surface, the photocatalyst having a bandgap energy (Eg), and an electrocatalyst applied to another portion of the surface. Under illumination the photocatalyst produces electron-hole pairs which are separated by an anodic bias potential applied across the photocatalyst. The same bias is applied across the electrocatalyst. The application of the anodic potential bias not only greatly enhances the performance of the photocatalyst for photooxidation of pollutants at the photocatalyst, but also effectively drives electrochemical oxidation of pollutants at the electrocatalyst surface.
Owner:LAKEHEAD UNIVERSITY
Device and method for removing polychlorinated biphenyl in bottom mud through microorganism electrolytic tank
ActiveCN104984994AAchieving Reductive RemovalImplement pollution remediationContaminated soil reclamationToxicity reductionPolychlorinated biphenyl
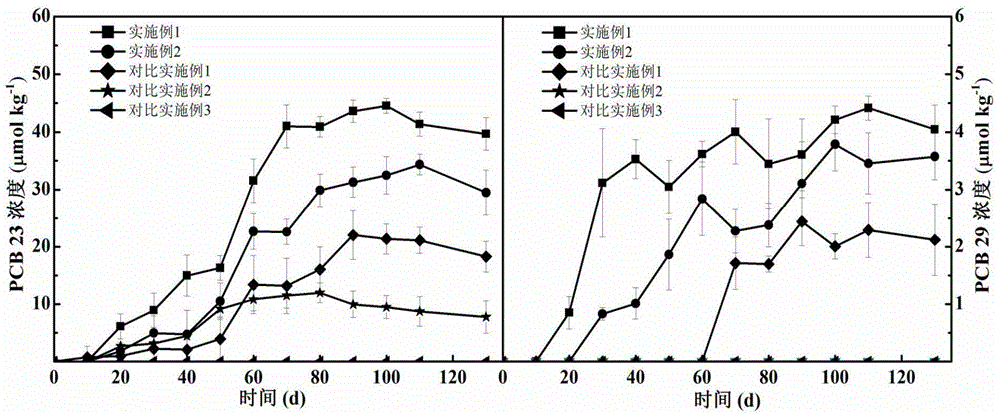
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil restoration and discloses a device and method for removing polychlorinated biphenyl in bottom mud through a microorganism electrolytic tank. The microorganism electrolytic tank is established, hybrid electrochemical activity bacteria and perchlorate domesticated bacteria are inoculated to an anode chamber, soil polluted by polychlorinated biphenyl is added, a nutrient solution is supplemented to the rest part, the water phase-bottom mud anode chamber is formed, anode potential is controlled to be kept constant through an electrochemical work station, growth and propagation of the hybrid electrochemical activity bacteria and the perchlorate domesticated bacteria can be promoted, dechloridation efficiency can be greatly improved, and constant bioelectric currents can be generated. By the adoption of the device and method, natural restoration and toxicity reduction can be conducted on the polluted soil, and good environmental protection benefits are achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation for gold electrode with nano-pore structure by electrochemistry alloying/dealloying method
InactiveCN101104940AHigh specific surface areaHigh sensitivityElectrode shape/formsMaterial electrochemical variablesMetallic electrodeAuxiliary electrode
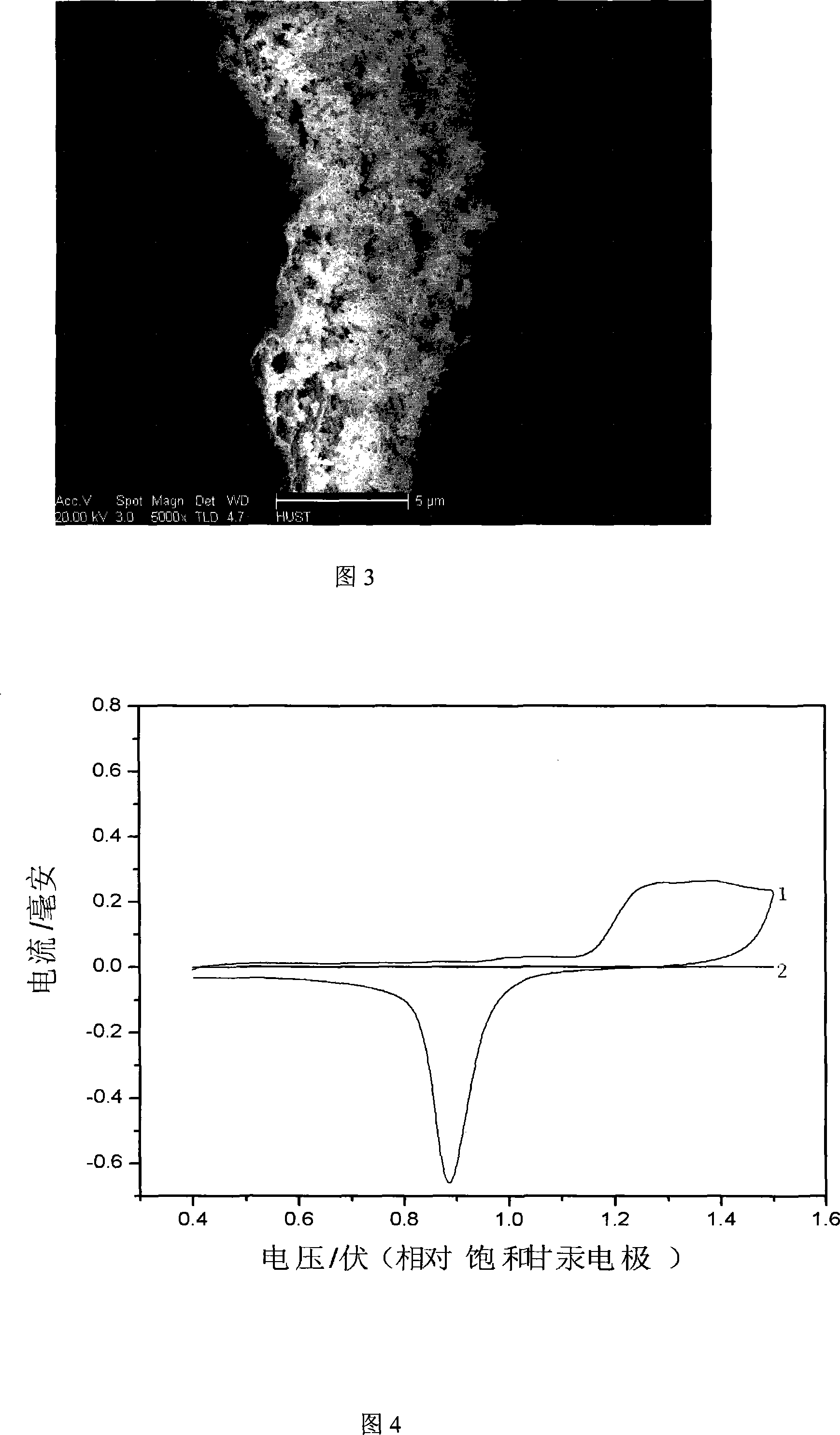
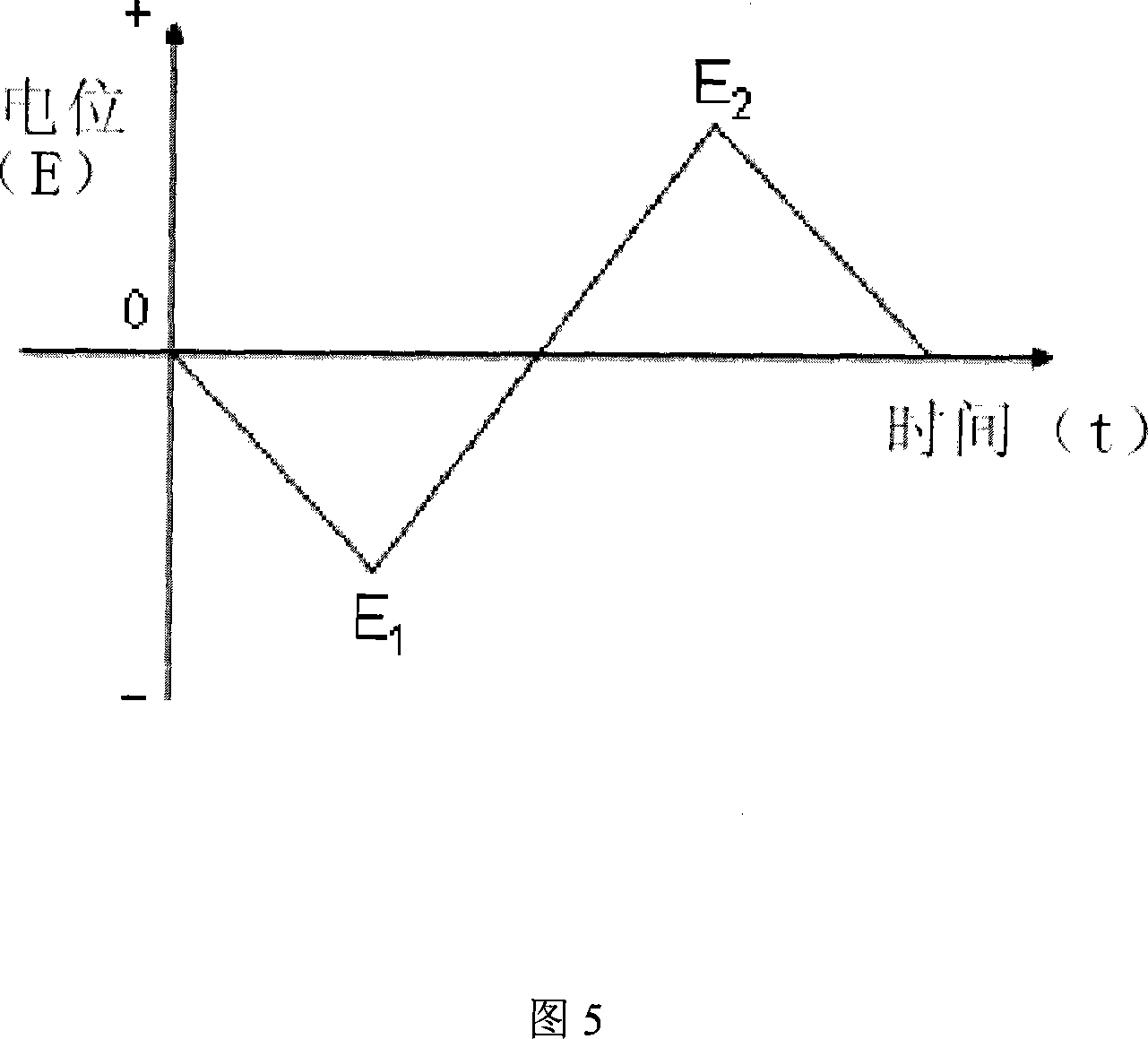
A method for preparing metallic electrode with nano-pore structure by electrochemical alloying / dealloying process is provided. The method comprises: firstly adding a zinc salt into an organic solvent and heating to allow dissolution; then inserting a metallic electrode as working electrode, a zinc sheet as auxiliary electrode and an inert metal as reference electrode; electrochemically applying a circulatory potential scanning, wherein a Zn coating is formed on the surface of Au substrate during cathode potential scanning, and the deposited Zn reacts with Au substrate to form Zn-Au alloy with the solution temperature rise during the electrogalvanizing; and finally dissolving Zn from the alloy by the anode potential scanning and dealloying. The method can produce the metallic electrode with nano-pore structure, which has extremely-high roughness after treatment, substantially increase the effective response area of metallic electrode, and greatly improve the sensitivity and catalytic efficiency of metallic electrode in application. The invention has the advantages of simple operation, easily-accessible raw material, low cost, no toxicity, and no environmental pollution; and is used in analysis, catalysis and sensor fields.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060244091A1Avoid paddingReduces change in curvatureOther printing matterWriting implementsCapacitanceSchottky barrier
In a semiconductor device of the present invention, a protection diode for protecting a device is formed on an epitaxial layer formed on a substrate. A Schottky barrier metal layer is formed on a surface of the epitaxial layer and a P-type diffusion layer is formed at a lower portion of an end portion of the Schottky barrier metal layer. Then, P-type diffusion layers are formed in a floating state closer to a cathode region side than the P-type diffusion layer, and are capacitively coupled with a metal layer to which an anode potential is applied. This structure reduces a large change in a curvature of a depletion layer, thereby improving a withstand voltage characteristic of the protection diode.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
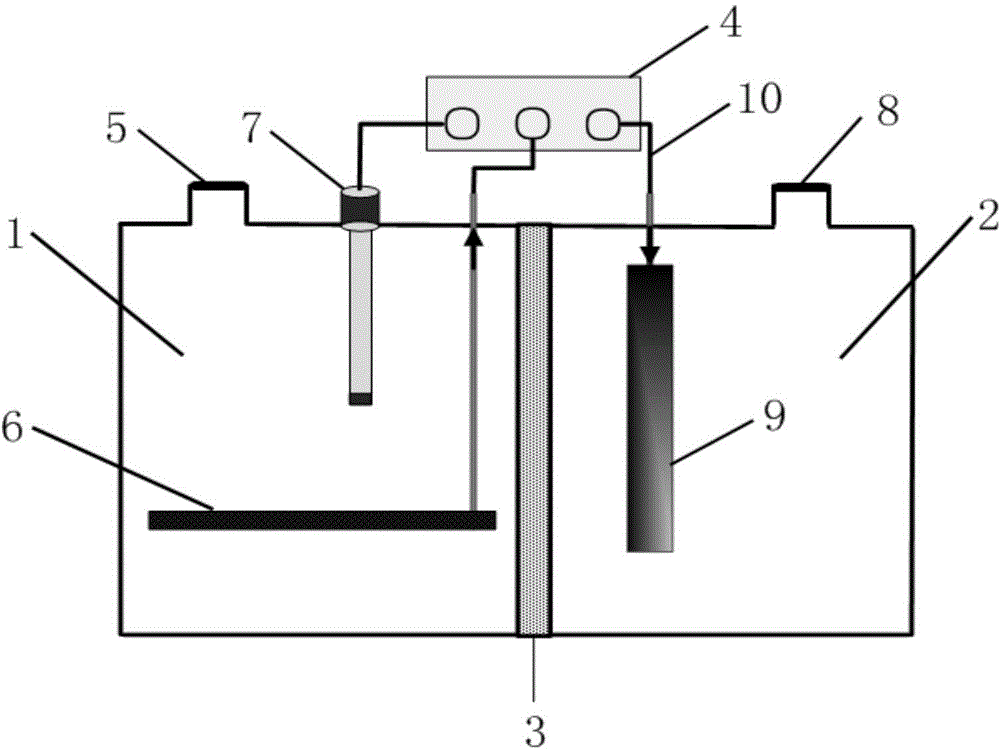
Anode for Bioelectric Power Generation And Power Generation Method And Apparatus Utilizing Same
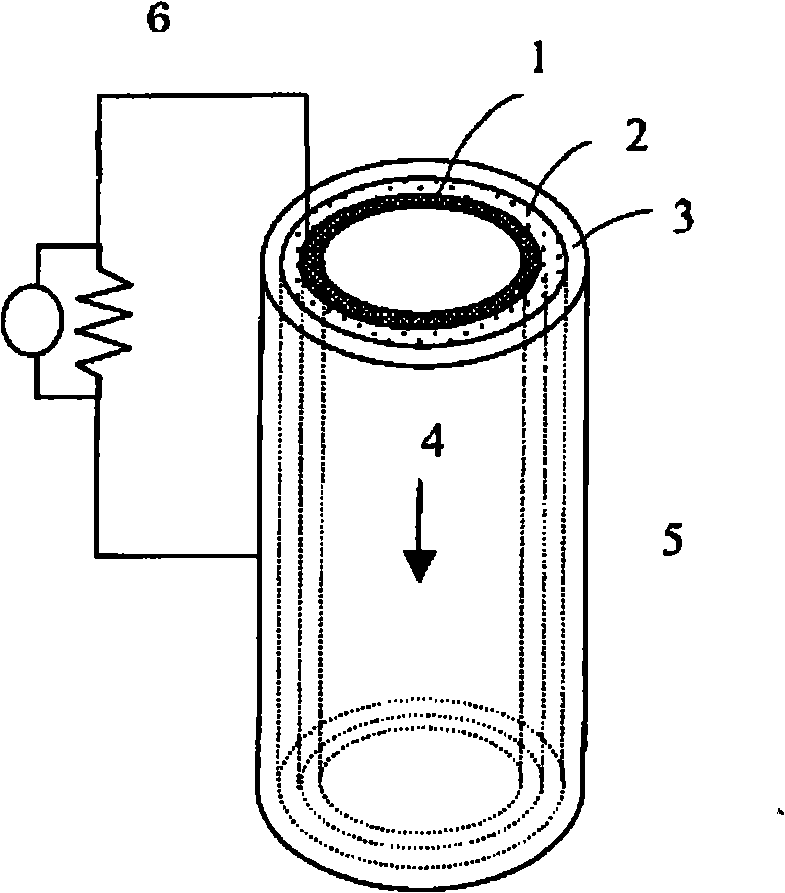
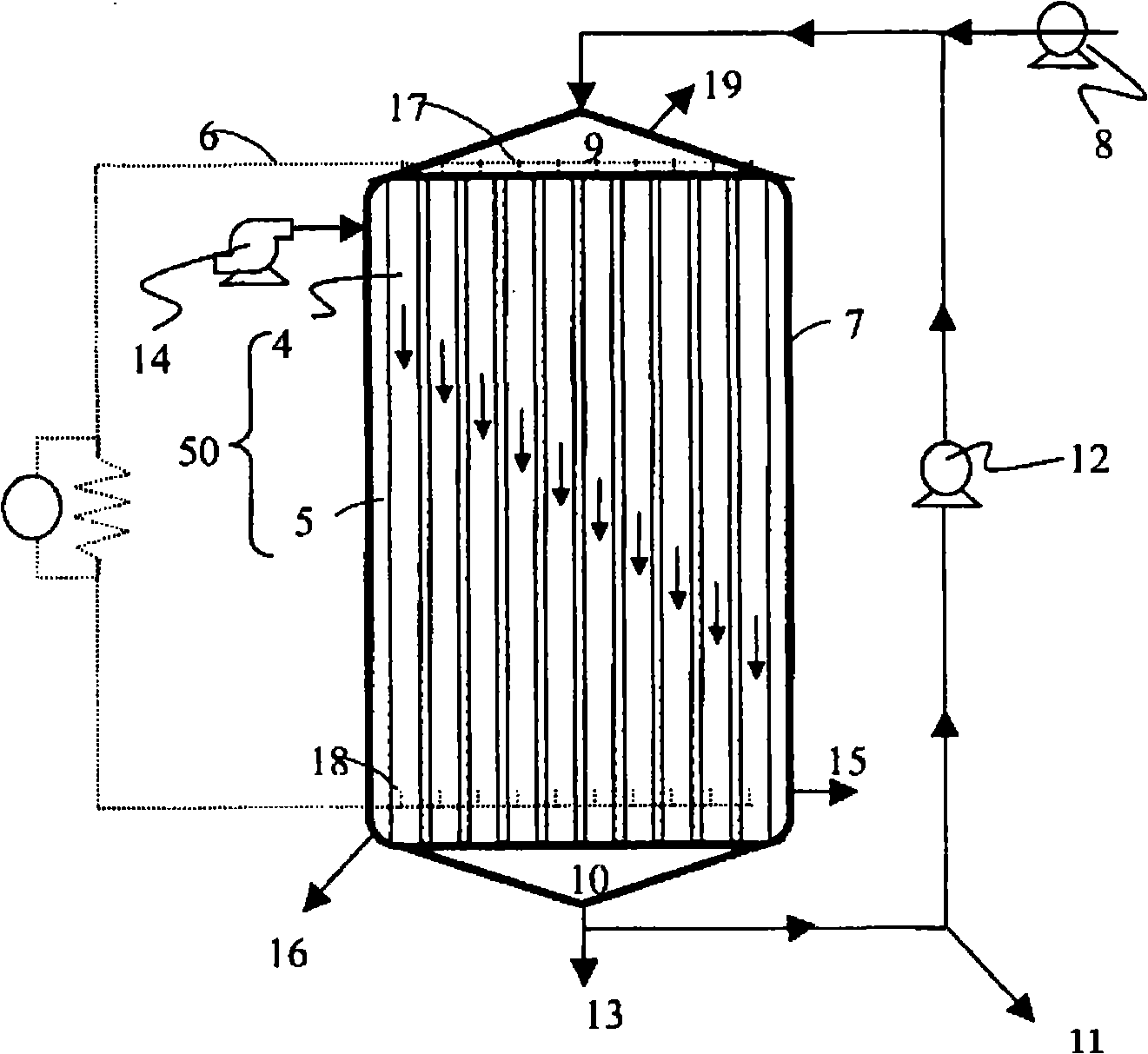
InactiveUS20090297890A1Efficient biological power generationSimple equipmentCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsOvervoltageHydrophilic polymers
A method and a device for obtaining electric energy efficiently from a hydrous organic substance by suppressing the activation overvoltage of an anode low and thereby obtaining a sufficiently low anode potential. The power generating device comprises an anaerobic region (4) including microorganisms which can grow under anaerobic conditions, solution or suspension containing an organic substance, an electron mediator and an anode (1), an aerobic region (5) including molecular oxygen and a cathode (3), and a diaphragm (2) defining the anaerobic region (4) and the aerobic region (5), wherein a closed circuit (6) is formed by connecting the anode (1) and the cathode (3) electrically with a power utilization apparatus, and oxidation reaction of microorganisms using the organic substance in the anaerobic region (4) as electron donor and a reduction reaction using oxygen in the aerobic region (5) as electron acceptor are utilized. The anode (1) includes a conductive substrate having a surface coated at least partly with a hydrophilic polymer layer, an electron mediator is introduced into the hydrophilic polymer layer with chemical bond, and the anode (1) has a standard electrode potential (E0′) at pH 7 in a range of −0.13 V to −0.28 V.
Owner:EBARA CORP
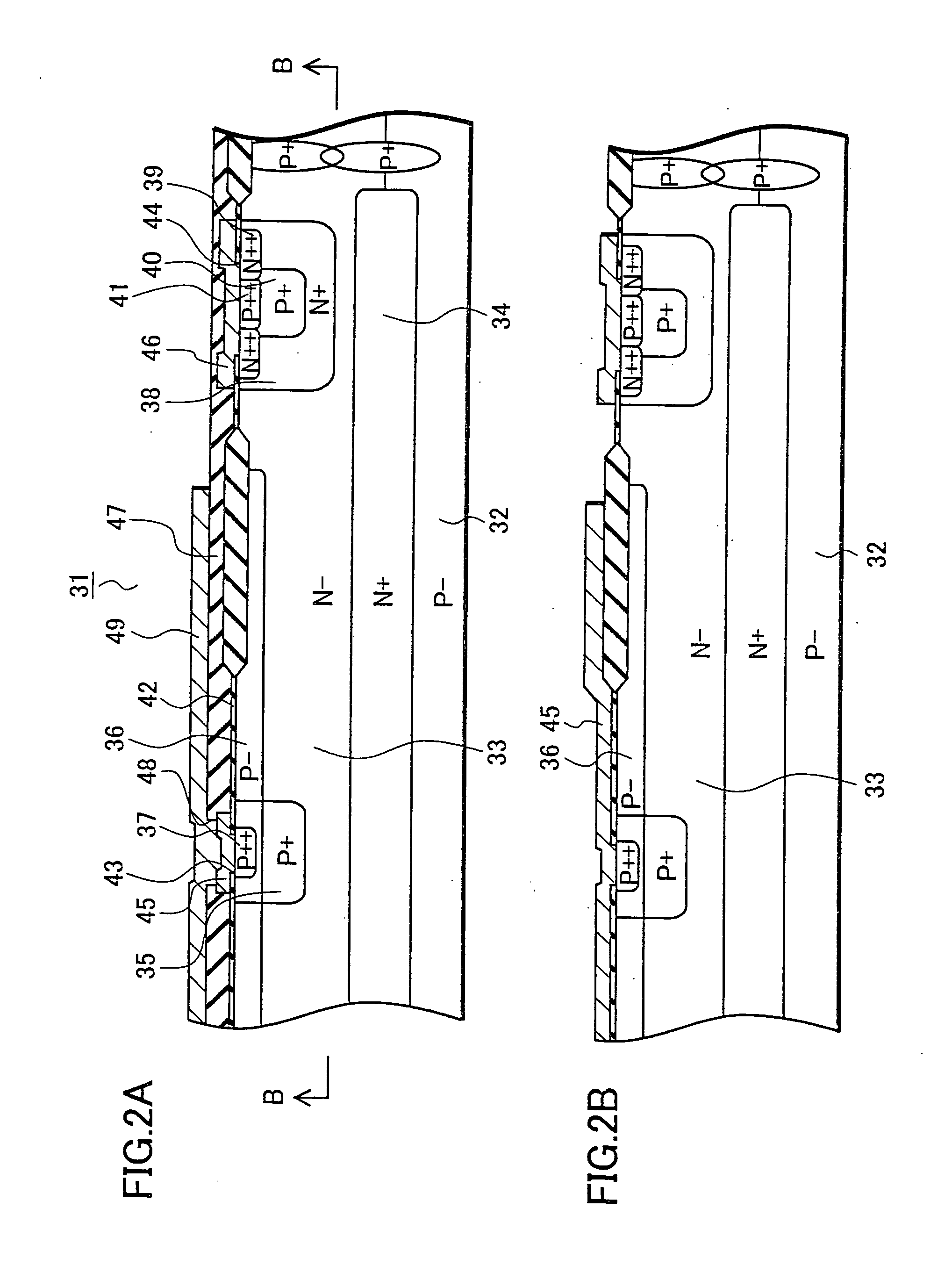
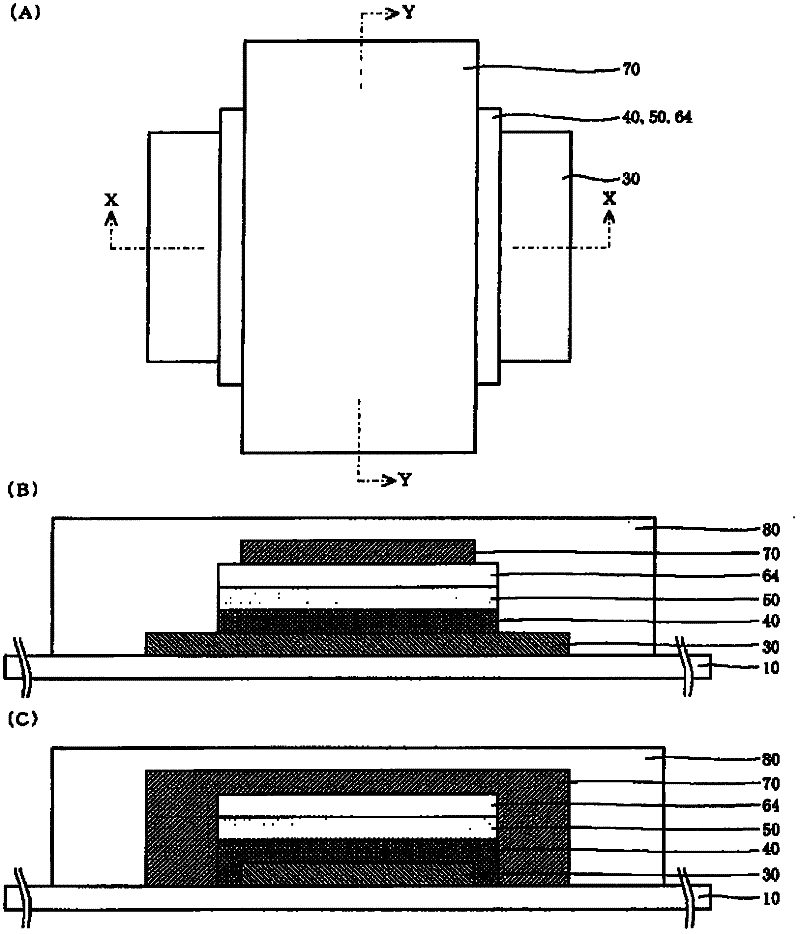
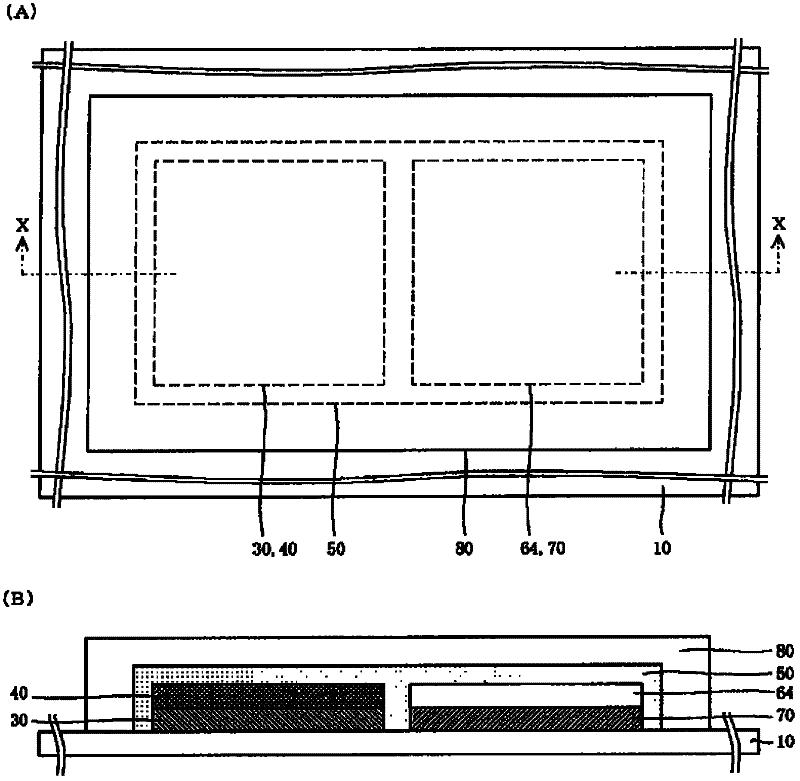
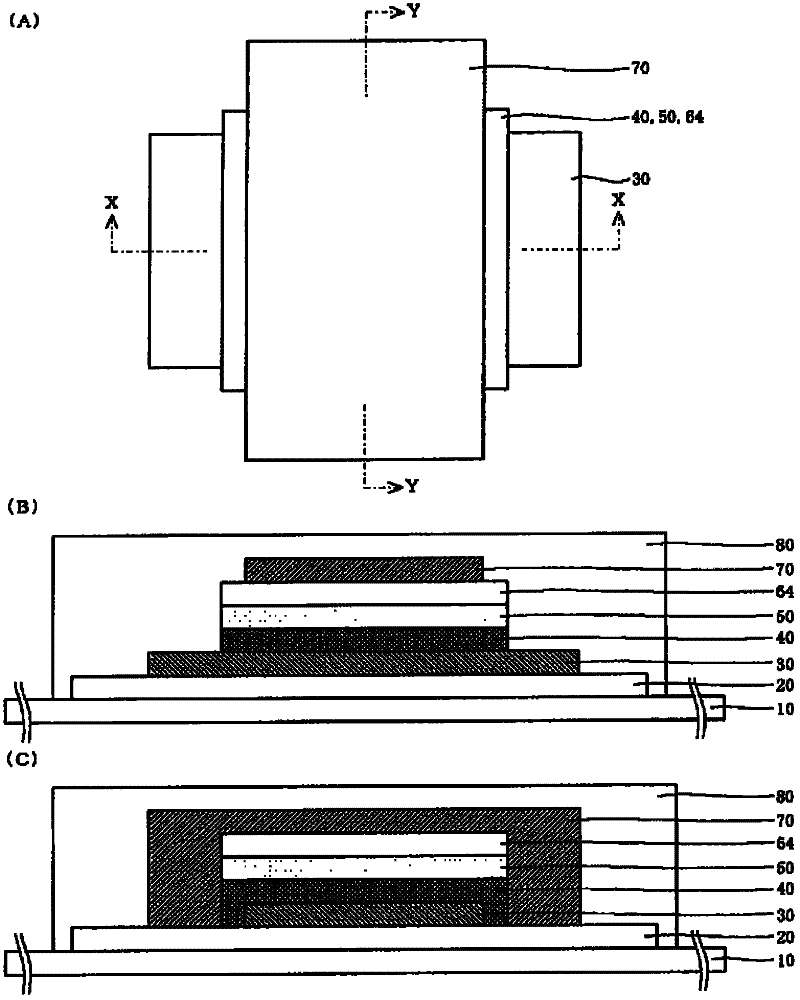
Thin film solid lithium ion secondary battery and manufacturing method thereof
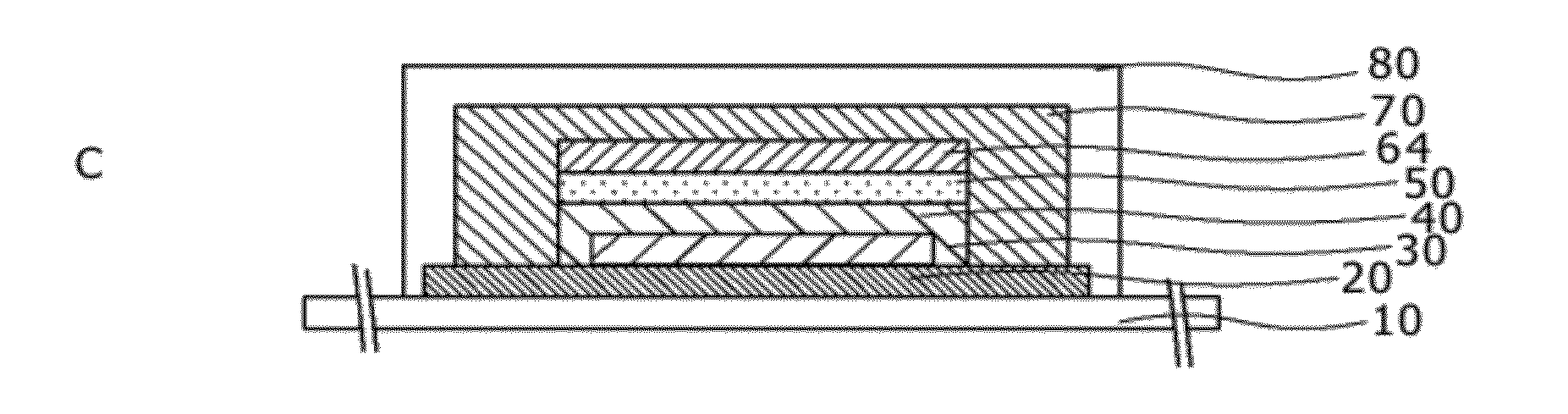
ActiveCN102301518ADrive stabilityImprove featuresFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsSolid state electrolyteEngineering
Disclosed are a high-performance, inexpensive solid state thin film lithium ion secondary battery that is able to be charged and discharged in the atmosphere and can be manufactured at good yield, and a manufacturing method therefor. A solid state thin film lithium ion secondary battery comprises an electrically insulating substrate (10) of an organic resin, an inorganic insulating film that is disposed on the surface of this substrate, a cathode side collector film (30), a cathode active material film (40), a solid state electrolyte film (50), an anode potential formation layer (64), and an anode side collector film (70), which cathode side collector film and / or anode side collector film is / are formed on the surface of the inorganic insulating film, wherein the anode potential formation layer is formed from a cathode active material that is the same or different from the cathode active material film, and is a layer that is provided to form an anode potential during discharging. The thickness of the aforementioned anode potential formation layer is 2 nm or greater and 20 nm or less, and the inorganic insulating film is not less than 5 nm and not more than 500 nm thick and contains at least one of either an oxide or nitride or sulfide containing any of Si, Al, Cr, Zr, Ta, Ti, Mn, Mg, or Zn.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Anode for biological power generation and power generation method and device utilizing it
A method and a device for obtaining electric energy efficiently from an organic substance containing water by suppressing the activation overvoltage of an anode low and thereby obtaining a sufficiently low anode potential. The power generating device comprises an anaerobic region (4) including microorganisms which can grow under anaerobic conditions, solution or suspension containing an organic substance, an electron mediator and an anode (1), an aerobic region (5) including oxygen in molecular state and a cathode (3), and a diaphragm (2) defining the anaerobic region (4) and the aerobic region (5), wherein a closed circuit (6) is formed by connecting the anode (1) and the cathode (3) electrically with a power utilization apparatus, and oxidation reaction of microorganisms using the organic substance in the anaerobic region (4) as electron donor and a reduction reaction using oxygen in the aerobic region (5) as electron receptor are utilized. The anode (1) includes a conductive substrate having a surface coated at least partially with a hydrophilic polymer layer, an electron mediator is introduced into the hydrophilic polymer layer while boded chemically, and standard electrode potential (E0') at pH7 is in the range of -0.13V to -0.28V.
Owner:EBARA CORP
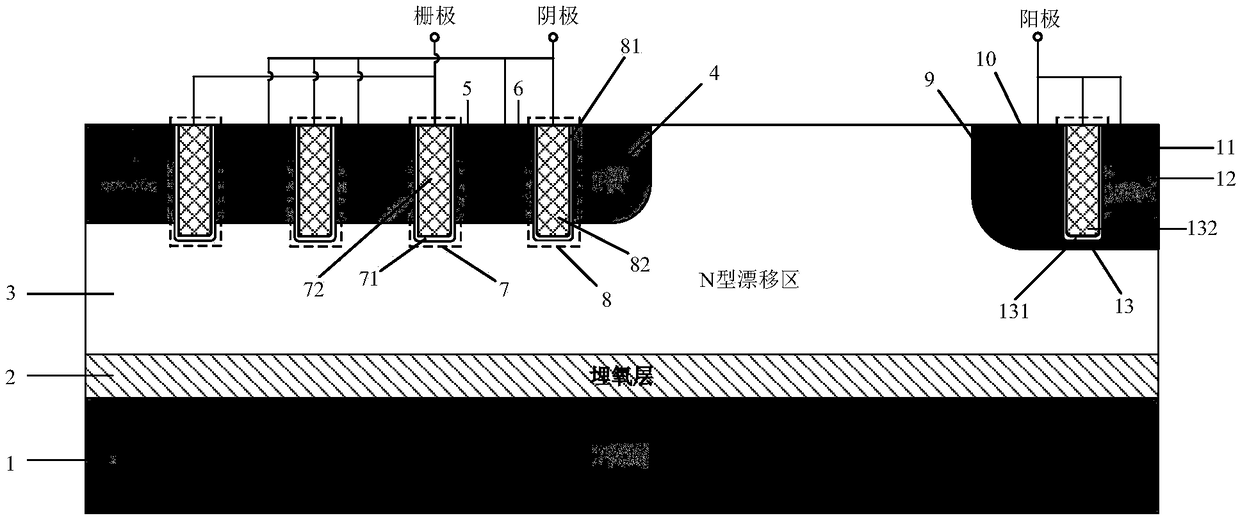
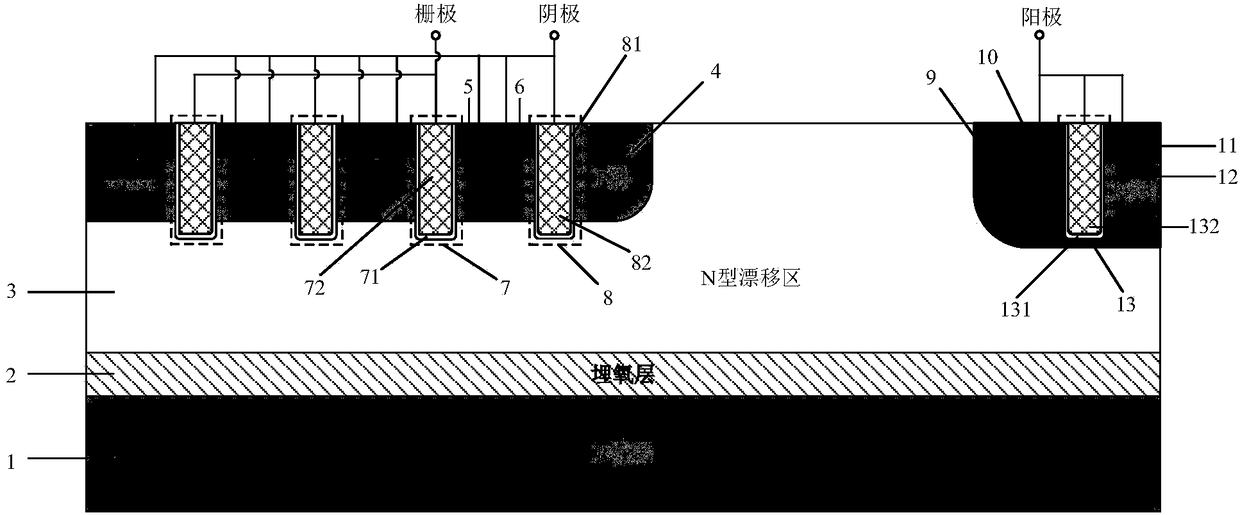
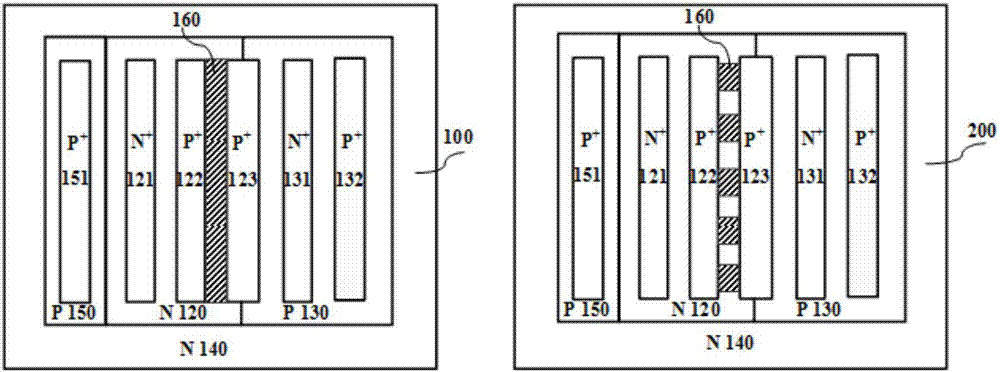
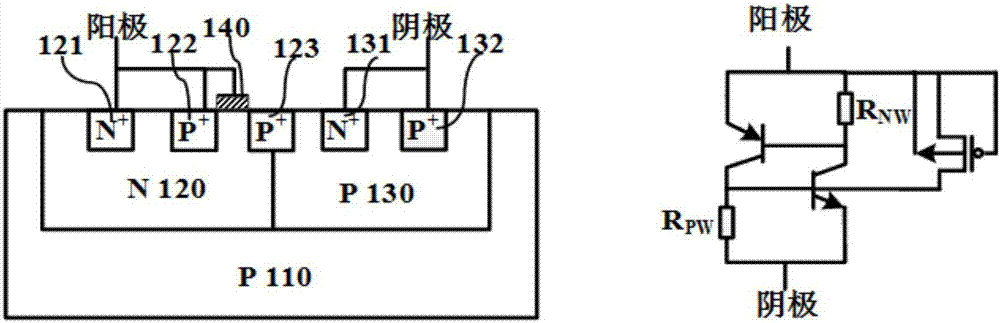
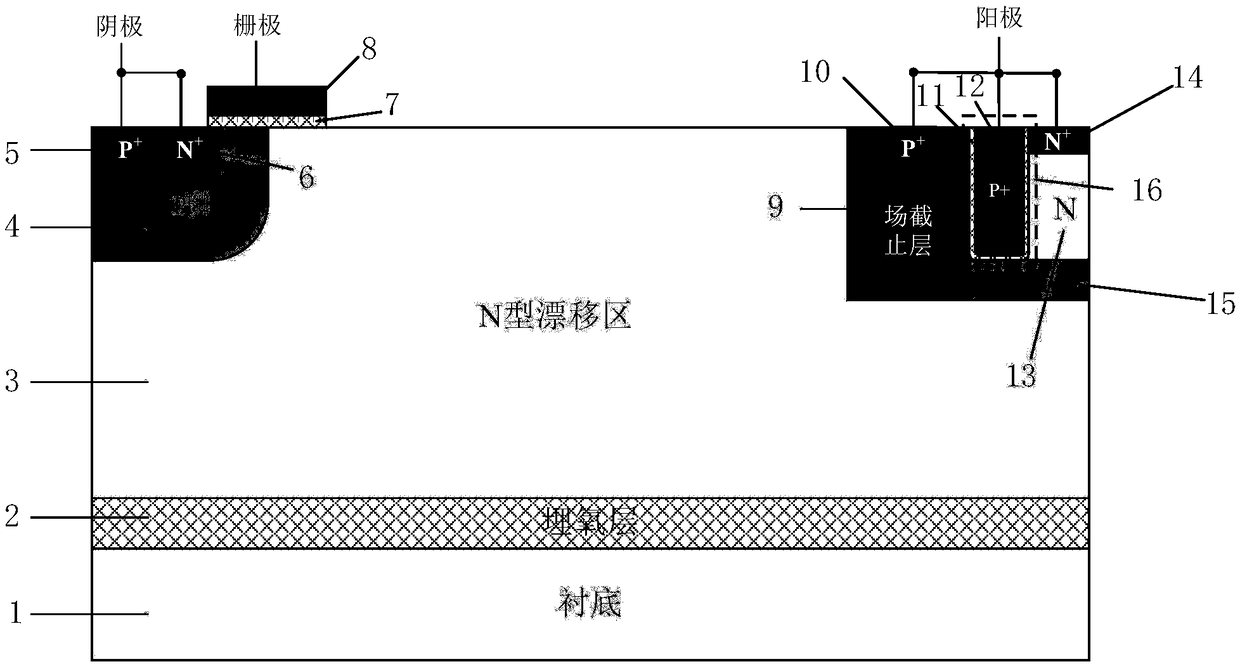
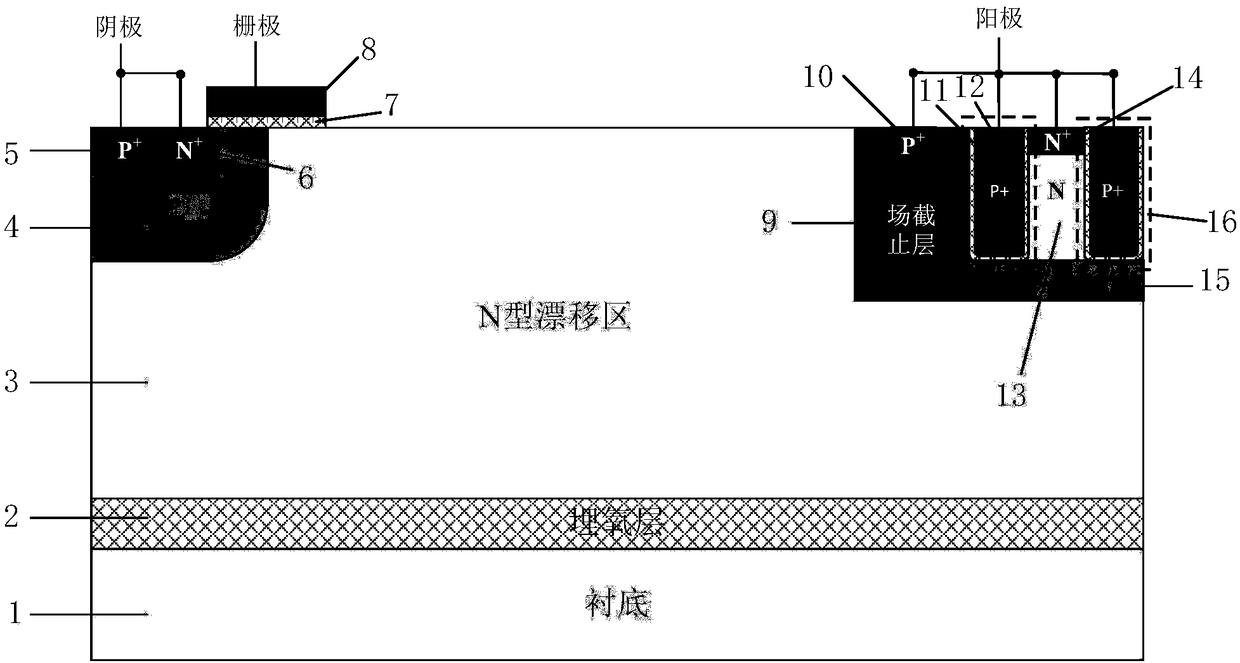
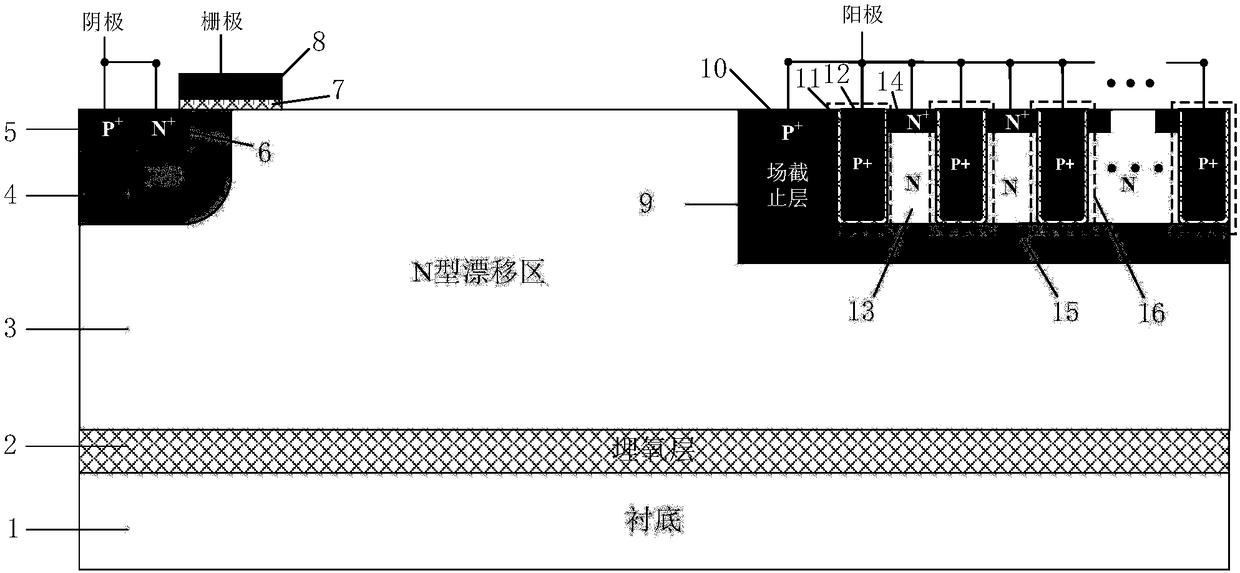
Grooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors and relates to a grooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT. In comparison with the traditional short circuit anode LIGBT, anode grooves connected to anode potential are introduced at an anode end, and a P body area is introduced right below an N+ anode area; and grooved gates and cathode grooves connected with a cathode are introduced in a cathode area. When the device is turned off, the anode groove is connected to high potential, an NMOS in the anode area is started automatically, extraction of electrons stored in a driftarea is quickened, and the turn-off time and the turn-off energy loss are reduced; when the device is in a high-voltage high-current state, the cathode groove forms a hole bypass, and happening of latch-up effects is suppressed; when the device is conducted, under blocking of an electronic barrier in the P body area, electron current in the drift region is not easy to be collected by the N+ anode,voltage reentry effects are eliminated, and as the grooved gate structures of the cathode are in parallel connection, the channel density is increased and the conduction voltage drop is reduced. Thegrooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT has the beneficial effects that in comparison with the traditional short circuit anode LIGBT, a voltage reentry phenomenon is eliminated under a smaller transverse cell size, and the conduction voltage drop is lower.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for charging a lithium ion battery
ActiveUS20170244255A1Increase ion concentrationHigh currentCell electrodesSecondary cells charging/dischargingEngineeringLithium-ion battery
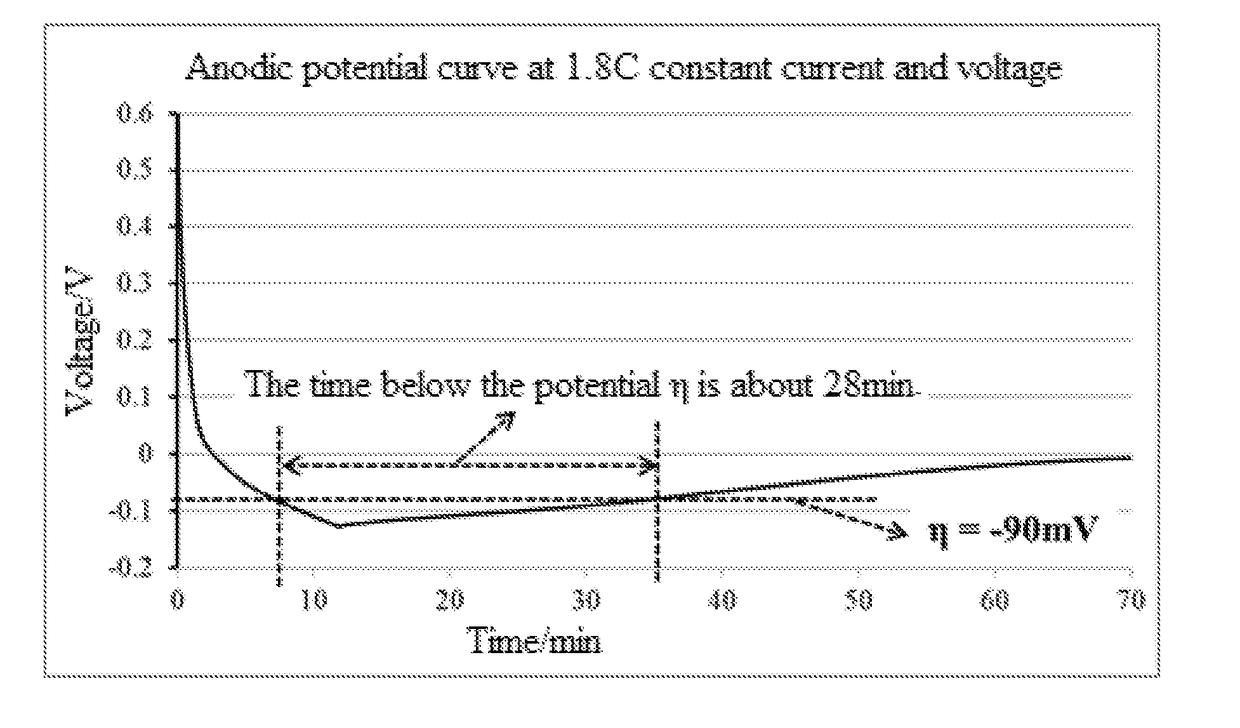
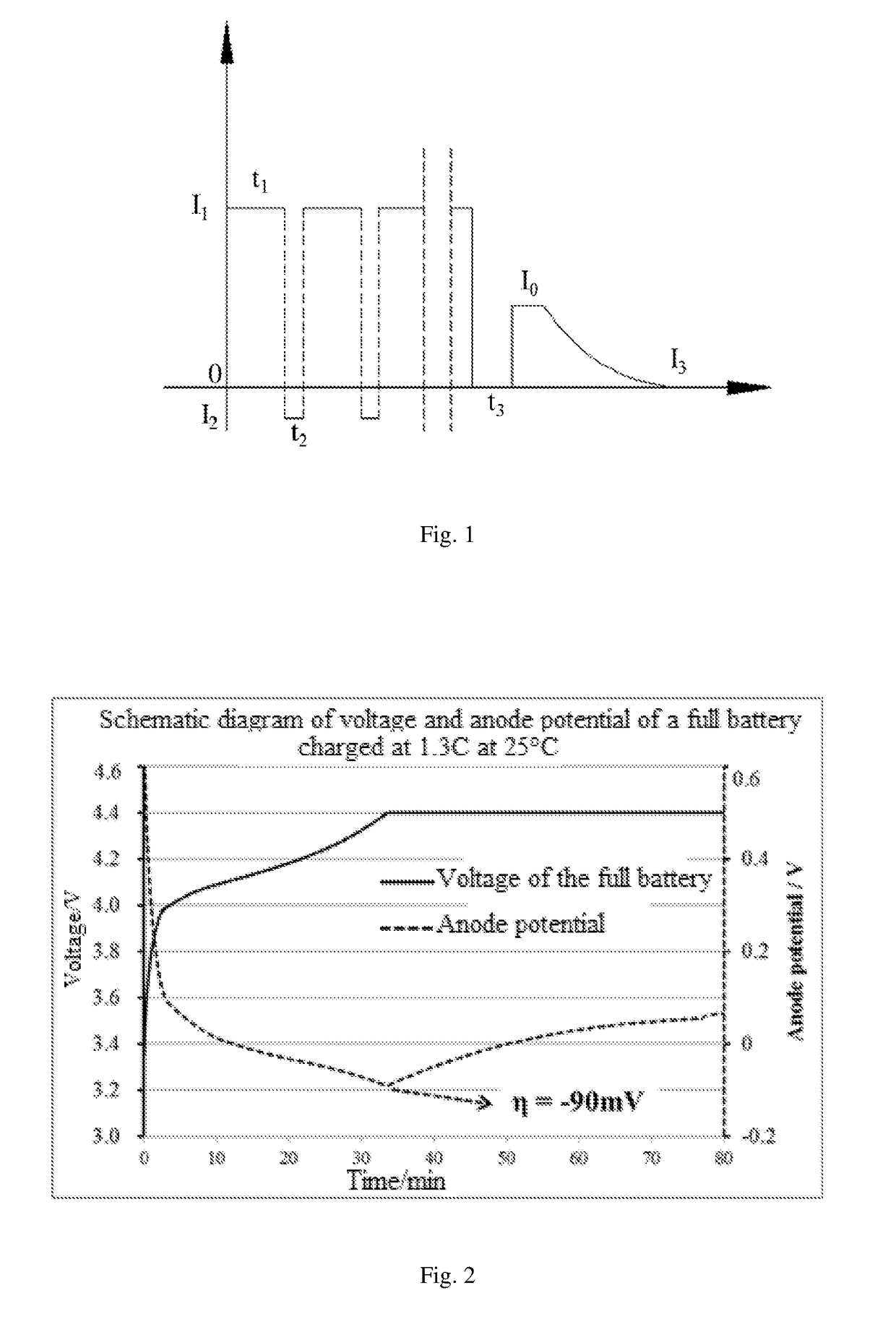
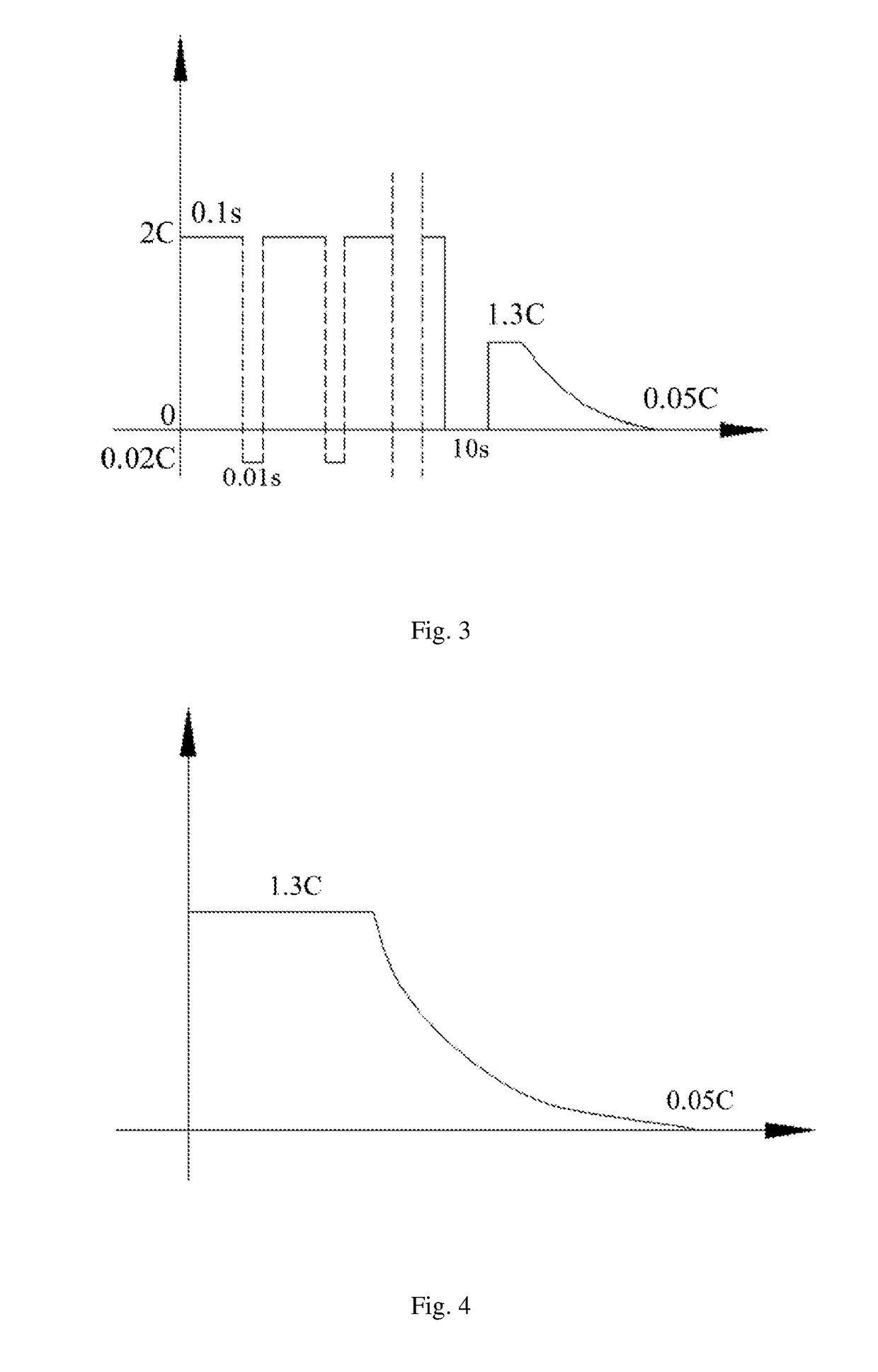
A method for charging a lithium ion battery includes the steps of: 1) determining a maximum charging current I0 and a lowest anode potential η of the lithium ion battery at which no lithium precipitation occurs; 2) charging the lithium ion battery at a constant current of I1 which is greater than I0 for a charging time t1; 3) discharging the lithium ion battery at a constant current of I2 which is less than I0 for a discharging time t2, 5≦t1 / t2≦50; 4) repeating steps 2) and 3) until a cutoff voltage of the lithium ion battery reaches V0 and standing the lithium ion battery for a standing time t3; and 5) charging the lithium ion battery at a constant current of I0 until the cutoff voltage of the lithium ion battery reaches V0 and charging the lithium ion battery to a cutoff current of I3 at a constant voltage.
Owner:DONGGUAN AMPEREX TECH +1
Solid-state electrolyte battery and cathode activating substance
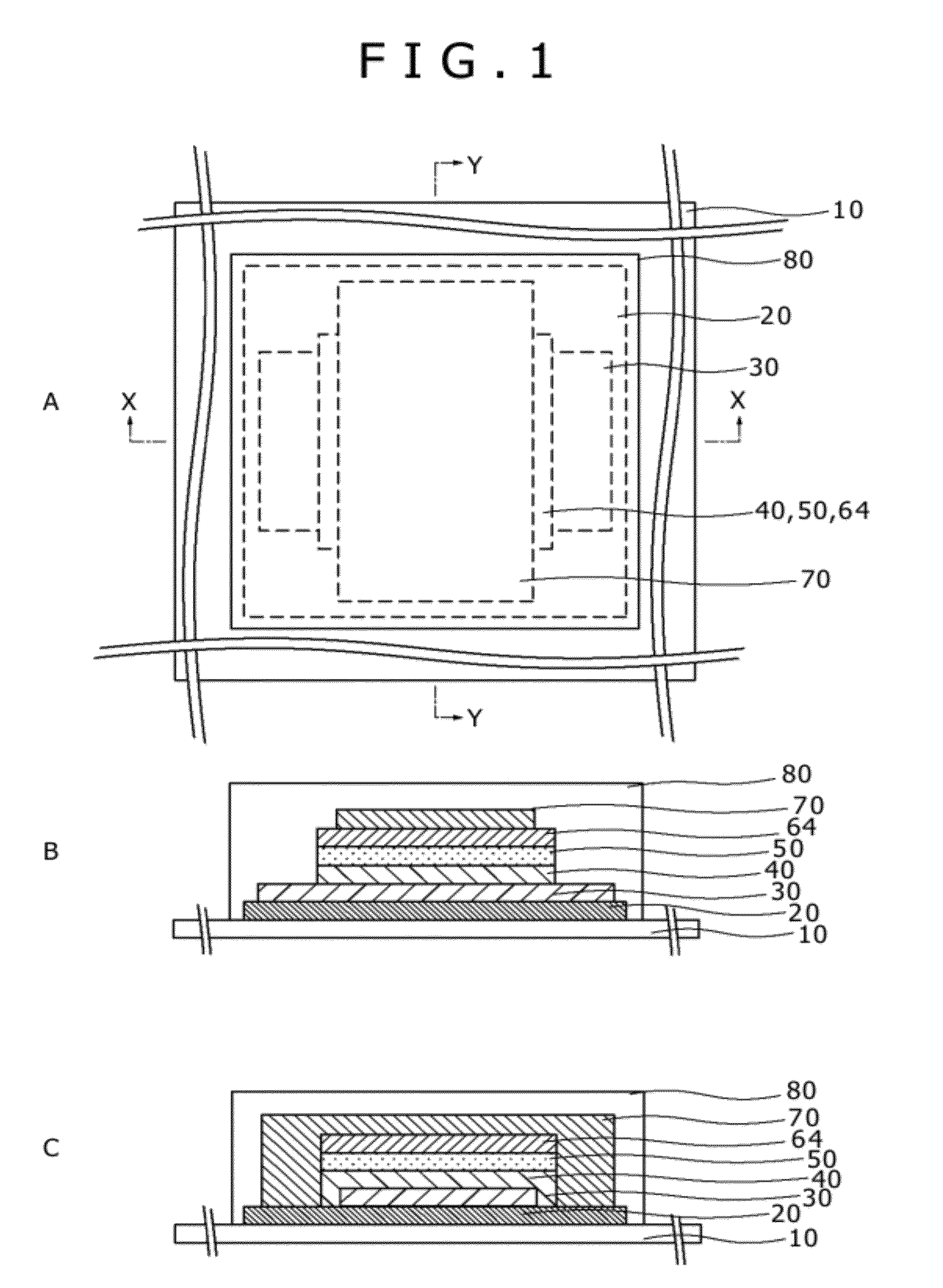
ActiveUS20120214064A1Improve ionic conductivityFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsSubstance useSolid state electrolyte
The present invention provides a solid-state electrolyte battery using a cathode activating substance which functions as such in an amorphous state and has a high ionic conductivity and provides a cathode activating substance used for the same. This solid-state electrolyte battery includes a laminated body. In the laminated body, a cathode-side current collector film, cathode activating substance film, solid-state electrolyte film, anode potential formation layer and anode-side current collector film are stacked above a substrate in this order. The cathode activating substance film is made of LixMyPO4−zNz, i.e., a lithium complex oxide in an amorphous state.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Pd-Containing Coatings for Low Chlorine Overvoltage
ActiveUS20070289865A1Reduction in operating potentialElimination of the voltage “break-inMachining electrodesCellsOvervoltageElectrolysis
The present invention relates to an electrocatalytic coating and an electrode having the coating thereon, wherein the coating is a mixed metal oxide coating, preferably platinum group metal oxides with or without valve metal oxides, and containing a transition metal component such as palladium, rhodium or cobalt. The electrocatalytic coating can be used especially as an anode component of an electrolysis cell for the electrolysis of a halogen-containing solution wherein the palladium component reduces the operating potential of the anode and eliminates the necessity of a “break-in” period to obtain the lowest anode potential.
Owner:ELTECH SYST
Low trigger voltage SCR structure based on floating trap trigger
ActiveCN107017248ATrigger voltage can be adjustedLower the trigger voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceMOSFET
The invention belongs to the electrostatic discharge protection field of an integrated circuit and especially provides a low trigger voltage SCR structure based on floating trap trigger used for ESD protection. And the structure is used for further reducing a trigger voltage of a LVTSCR device. Through an internal structure design, one floating trap structure is introduced into the device. The floating trap structure is equivalent to one diode structure, an anode is connected to a polycrystalline silicon grid electrode of a PMOS and a cathode is connected to an anode of a SCR. When an ESD pulse is coming, a potential of a floating trap is lower than an anode potential of a SCR device. A potential difference between the two is enough to make the PMOS be started. After a P channel MOSFET is started, a parasitic NPN transistor in the SCR device is triggered to be started, then a parasitic PNP transistor is triggered to be started, and finally the SCR device starts and discharges an ESD current. Therefore, a trigger voltage of the device is determined by the floating trap structure and a parasitic PMOS grid source capacitor so that a purpose of reducing a SCR device trigger voltage can be realized and the trigger voltage can be modulated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
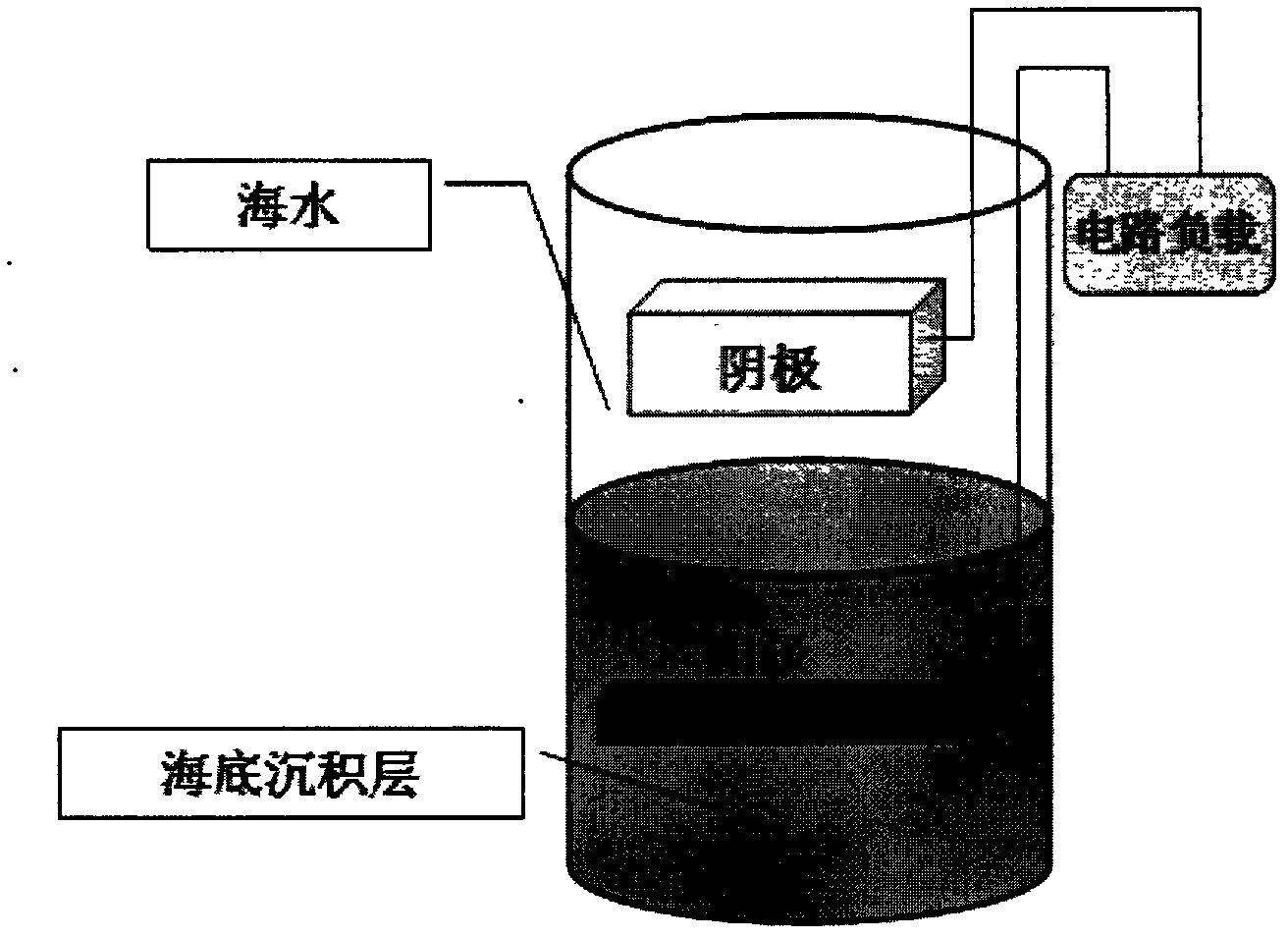
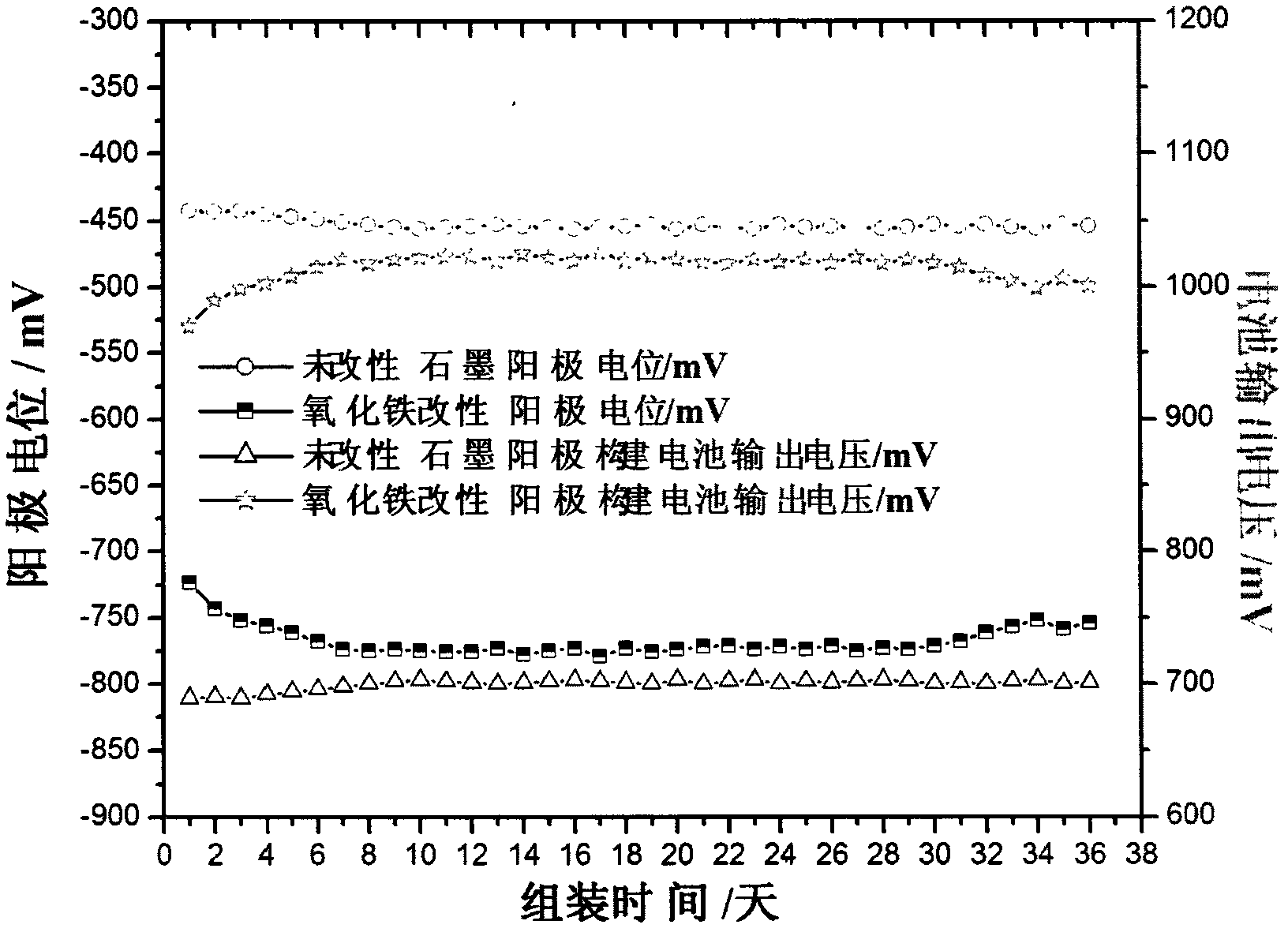
Method for constructing ocean sediment microbial fuel battery with high output voltage and high output power
InactiveCN102509809AIncrease the output voltageImprove power densityCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsElectrolysisElectrical battery
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial fuel battery, and provides a method for constructing ocean sediment microbial fuel battery with high output voltage and high output power. The high output power of the battery mainly derives from high output voltage, and the high output voltage is realized by adopting a graphite anode with ferric oxide electrolytically deposited thereon. Due to the electrolytic deposition of ferric oxide on the graphite anode, the potential of the anode modified by ferric oxide reaches -775 mV (with respect to saturated calomel electrode), and the maximum exchange current density is 0.00124 A / cm<2>. The novel ocean sediment microbial fuel battery constructed by the graphite anode has an output voltage of about 1.0 to 1.1 V, and maximum output power density of 743.7 mW / m<2>, which is 17 times that of battery assembled with unmodified anode.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Titanium-based composite anode for manganese electrolysis and preparation method of titanium-based composite anode
ActiveCN103668342AStable jobEfficient use ofPhotography auxillary processesElectrodesElectrolysisManganese
The invention relates to a titanium-based composite anode for manganese electrolysis and a preparation method of the titanium-based composite anode. According to the invention, a titanium wire mesh is used as a framework, and the titanium wire mesh is combined with titanium foam to form titanium wire mesh reinforced foamed titanium to be used as a base body, the surface of the base is coated with one or more precious metallic oxide layers, and then a manganese dioxide layer is coated through pre-electrolysis, so that composite anode is obtained. According to the invention, the preparation process is simple, the prepared titanium-based composite anode solves the difficult problems of a traditional lead silver alloy anode that the anode potential is high and an anode by-product contains lead and is hard to use repeatedly, in addition, the problem that a traditional titanium-based modified anode is easily passivated in a manganese electrolysis system is also solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Pixel driving circuit, driving method, display panel and display device
PendingCN110782838AEfficient use ofImprove the display effectStatic indicating devicesControl signalDisplay device
The invention discloses a pixel driving circuit, a driving method, a display panel and a display device. The pixel driving circuit comprises a driving transistor, a grid electrode of the driving transistor is electrically connected with a first electrode of a first storage capacitor, and the first electrode and a second electrode are electrically connected with a light-emitting control module; thelight-emitting control module is connected with a light-emitting control signal and a first power supply voltage, and under the control of the light-emitting control signal, the anode of the electroluminescent device is connected with the first power supply voltage, and the driving transistor is enabled to be in a saturated state; the first electrode of the second storage capacitor is electrically connected with the anode of the electroluminescent device, the second electrode of the second storage capacitor is electrically connected with the cathode of the electroluminescent device, and the cathode of the electroluminescent device is electrically connected with the second power supply voltage; and a first initialization module is connected with an initialization signal and an initialization voltage, and initializes the anode potential of the electroluminescent device under the control of the initialization signal, and the effective duration of the initialization signal is greater thanthe discharge duration of the second storage capacitor.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Short-circuit anode SOI LIGBT with anode pinch-off groove
ActiveCN108321195AIncreased shutdown speedReduce lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationConductive materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors, and relates to a short-circuit anode SOI LIGBT (Lateral Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) with an anode pinch-off groove. Compared with the traditional short-circuit anode LIGBT, anode grooves connected with the anode potential are introduced at the anode end, a conductive material of the anode grooves comprises high-concentration P-type doping, and a low-concentration N-type doped region is introduced one side of each groove wall. When the device is turned off, the outer wall of each anode groove accumulates electrons, low-resistance channels are provided, the extractions of electrons in a drift region is accelerated, and the turn-off time and the turn-off loss are reduced. When the device is just turned on, a P-type impurity in the anode grooves enable the low-concentration N-type doped regions to be exhausted, the electrons are prevented from being extracted by the N+ anode, a voltage turning-back effect is eliminated, a conductivity modulation effect is enhanced at the same time, and the conduction voltage drop is reduced. The beneficial effects are that the short-circuit anode SOI LIGBT has high turn-off speed and lower loss compared with the traditional LIGBT; and the short-circuit anode SOI LIGBT eliminates the voltage turning-back phenomenon under a smaller transverse cell size compared with the traditional short-circuit anode LIGBT, and has lower conduction voltage drop at the same time.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for constructing electro-catalytic bacterial biofilm at anode of microbial electrochemical reactor
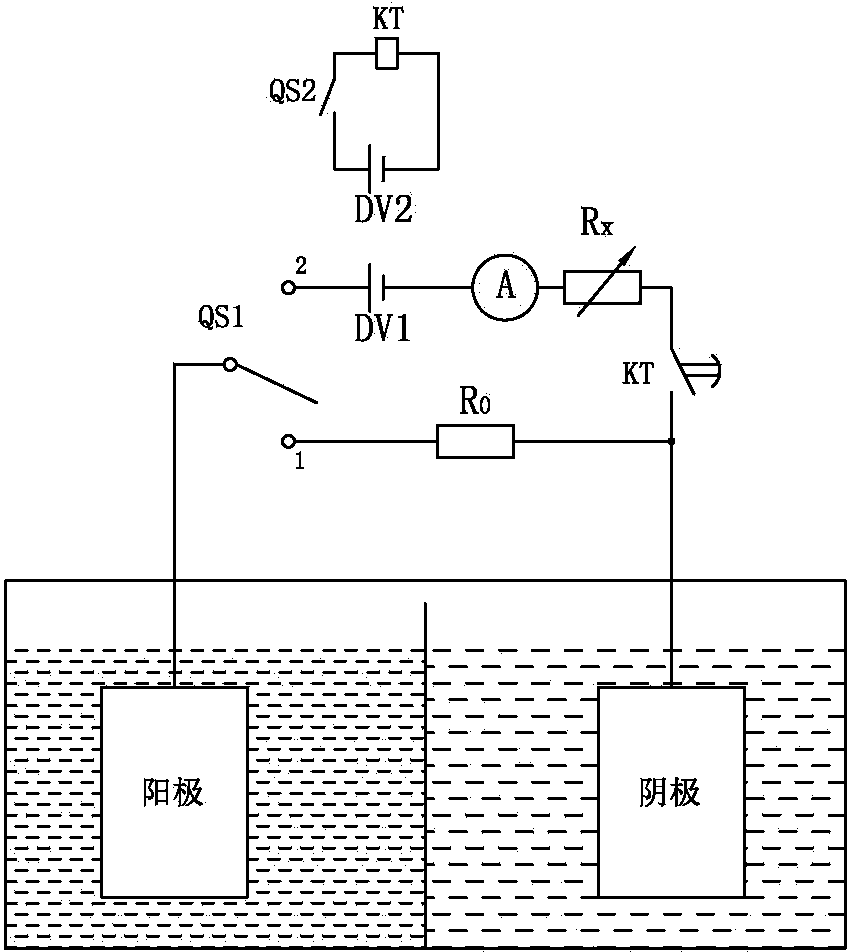
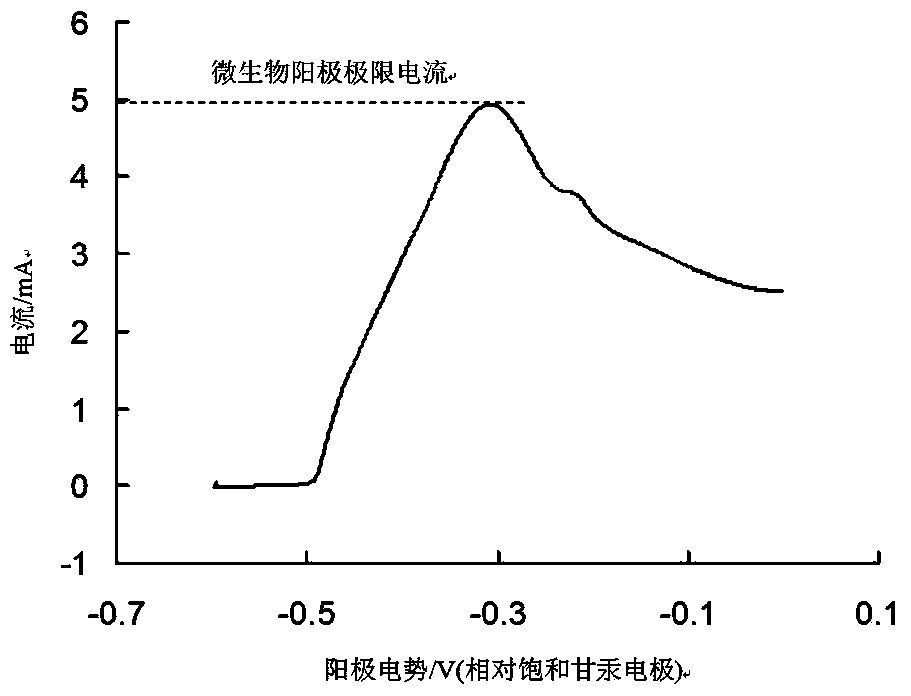
InactiveCN103952305AAvoid damageAchieve stimulationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCell electrodesAnode potentialResistor
The invention relates to a method for constructing an electro-catalytic bacterial biofilm at an anode of a microbial electrochemical reactor. The method comprises the following steps: firstly assembling the microbial electrochemical reactor and connecting with circuits, wherein the first path is formed by connecting a fixed resistor between the anode and a cathode in series, and the second path is formed by connecting a direct current stabilized power supply, an ampere meter, a variable resistor and a working contact of a cycle time relay between the anode and the cathode in series; then injecting a bacterial growth culture medium liquid into an anode chamber, inoculating a bacteria source, conducting the first path to carry out prestart on the microbial anode, measuring the anode potential change to obtain a polarization curve and determining an ultimate current value of the anode; and after electro-catalytic bacterial biofilm is stimulated by using ultimate pulse current to grow, successively obtaining a new ultimate current value again, then stimulating again under the new ultimate pulse current, repeating the steps till no significant growth of the ultimate current exists and finishing construction of the anodic electro-catalytic bacterial biofilm. The electro-catalytic bacterial biofilm can stably run under relatively high working current.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
System and method for recalibrating flat panel field emission displays
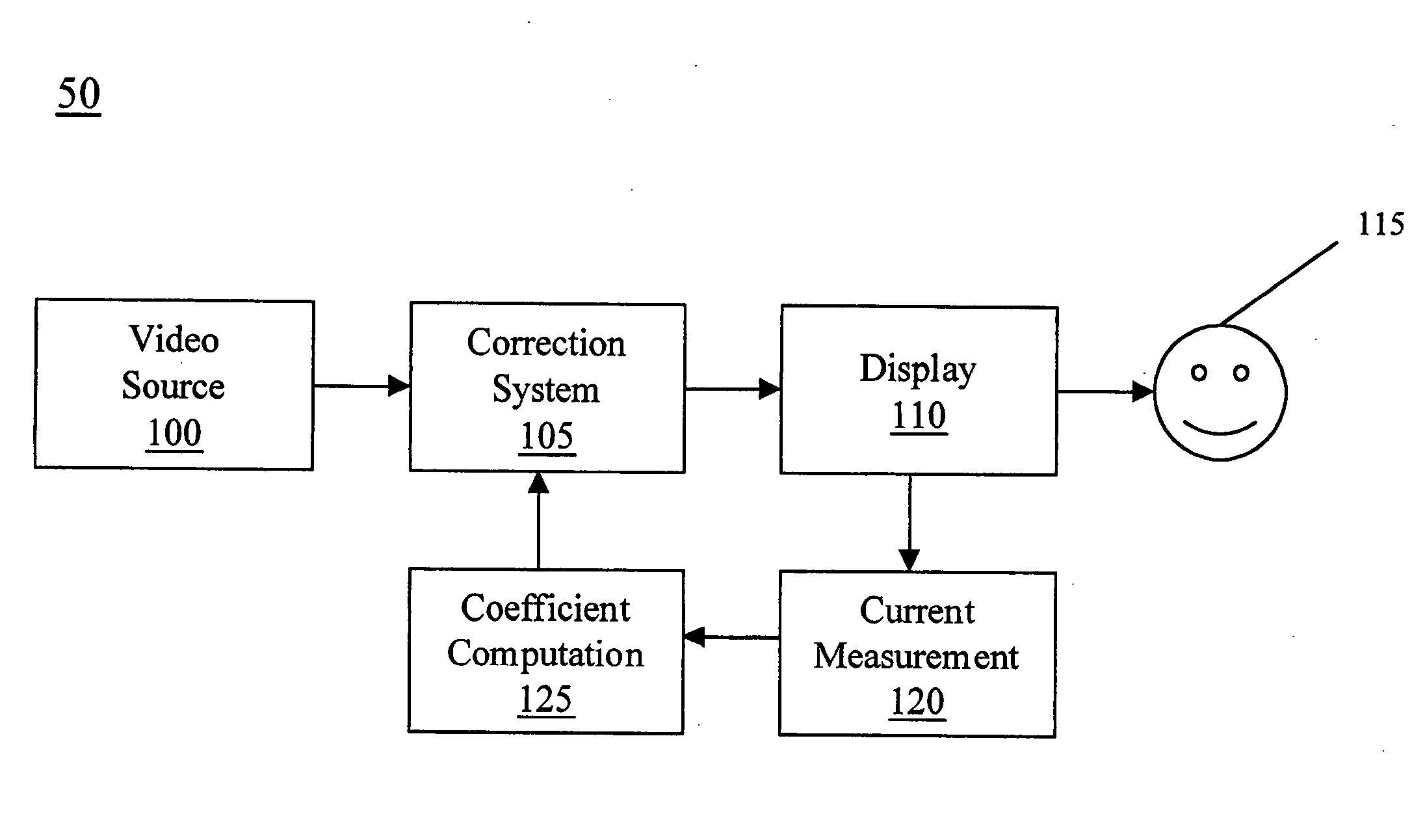
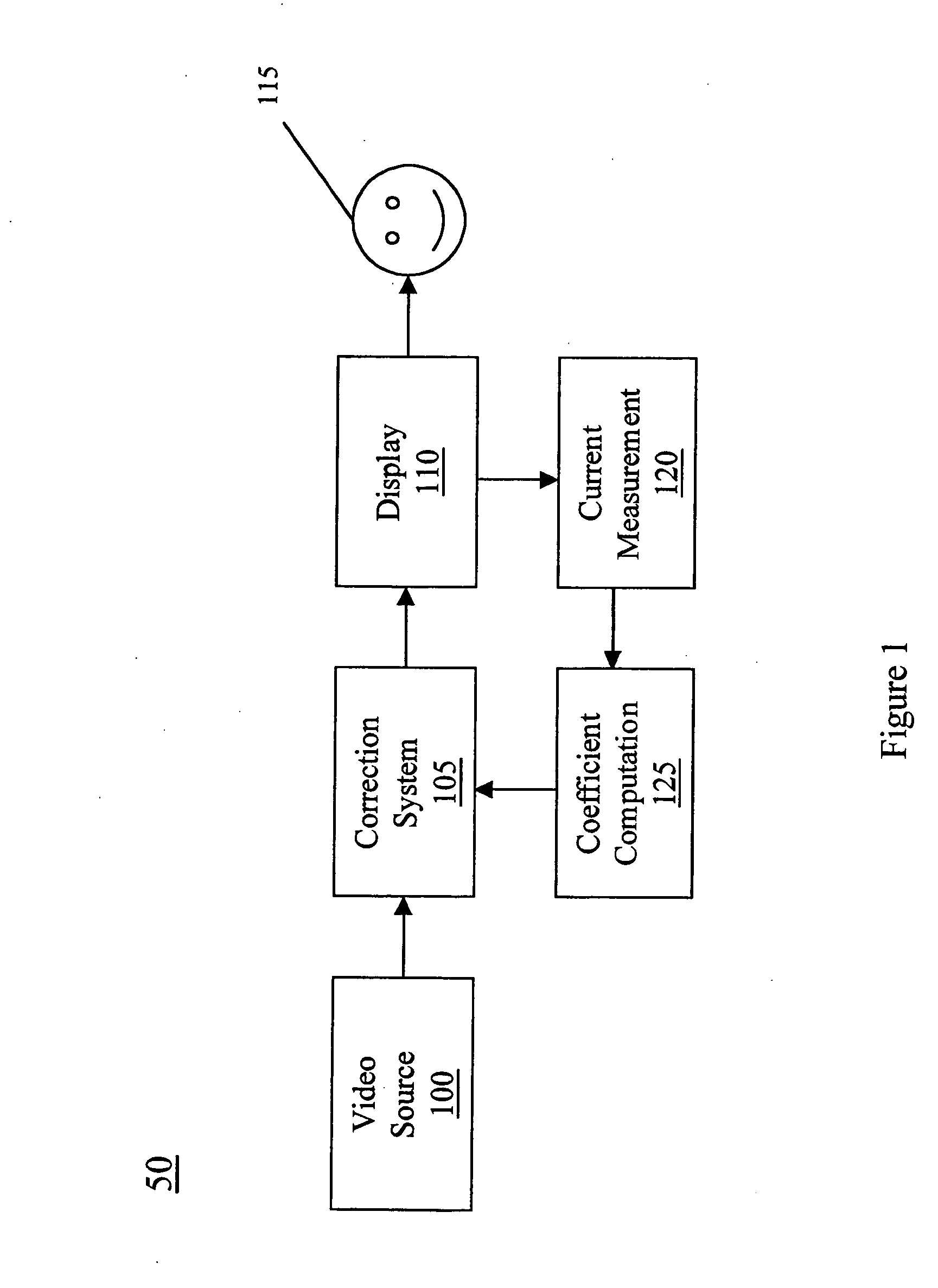
InactiveUS20060114188A1Increase working voltageTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceField emission display
A field emission display (FED) having a correction system with a correction coefficient derived from emission current is presented. Within one embodiment in accordance with the present invention, a field emission display has an anode at the faceplate and a focus structure. The anode potential is held at ground while the focus structure potential is held between, but is not limited to, 40 and 50 volts. The current flowing to the focus structure is measured and used as the basis for the correction coefficient for the field emission display.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method of improving chemical activity of carbon nano-tube
InactiveCN101108728ANo toxicityOperational securityNanostructure manufactureCarbon nanotubePt element
The invention designs a method which can change the appearance of the carbon nanotubes and the surface functional groups through electrooxidation to improve the chemical activity. By adopting the organic supporting membrane, the carbon nanotubes are prepared into membrane with thickness of 0.2mm to 5mm, which is connected with platinum wire as anode; a platinum sheet is used as cathode; chloride solution is used as electrolytic solution; a potentiostat is used to control the open potential in 1.50V to 2.5V (relative to saturated calomel electrode) to carry out constant potential electrolysis in three-electrode electrolytic cell. The electrolytic oxidation treatment process is controllable with low cost and light pollution. The invention has good purification effect on the carbon nanotubes and the chemical activity of the carbon nanotubes after oxidation treatment is obviously improved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
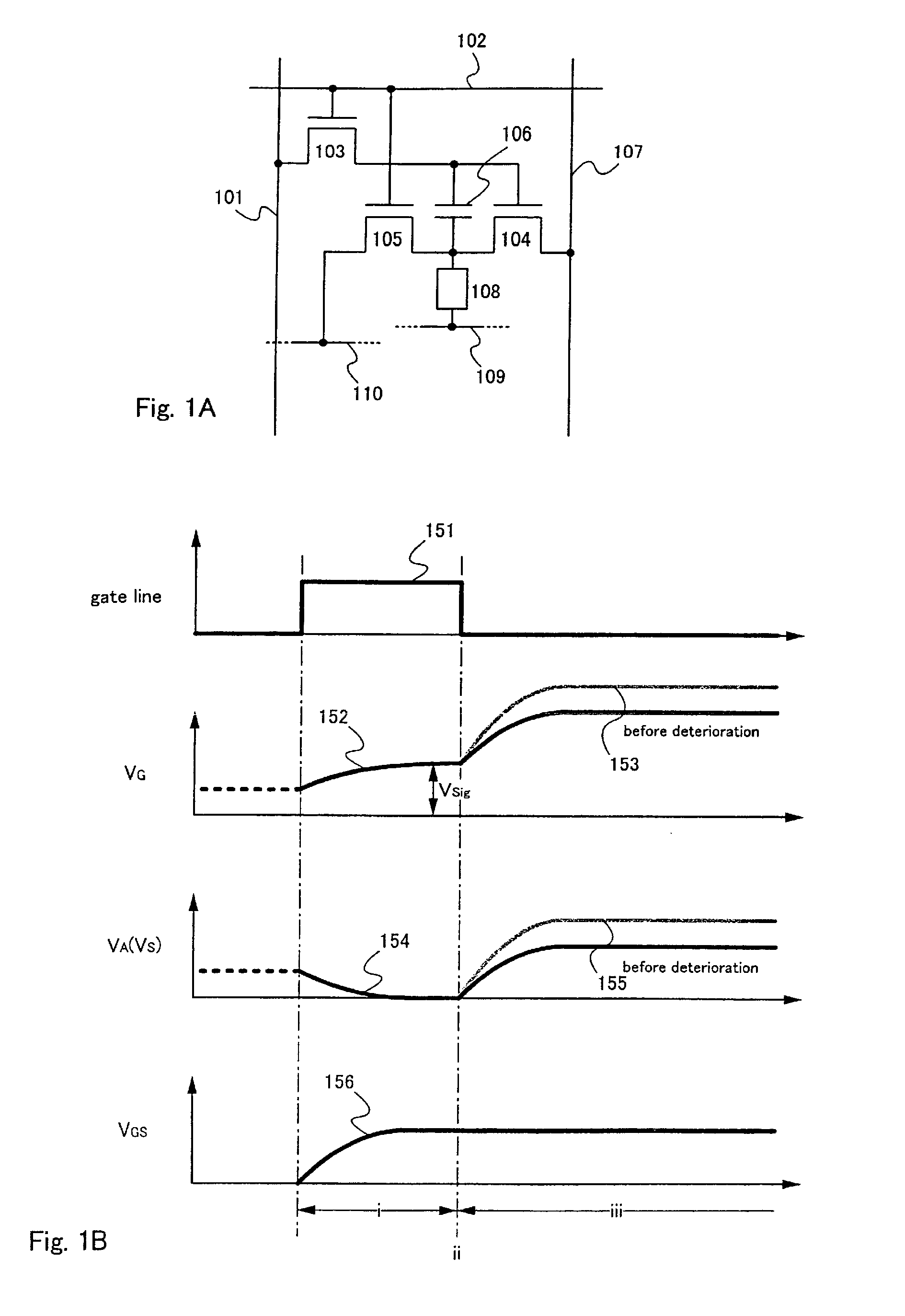
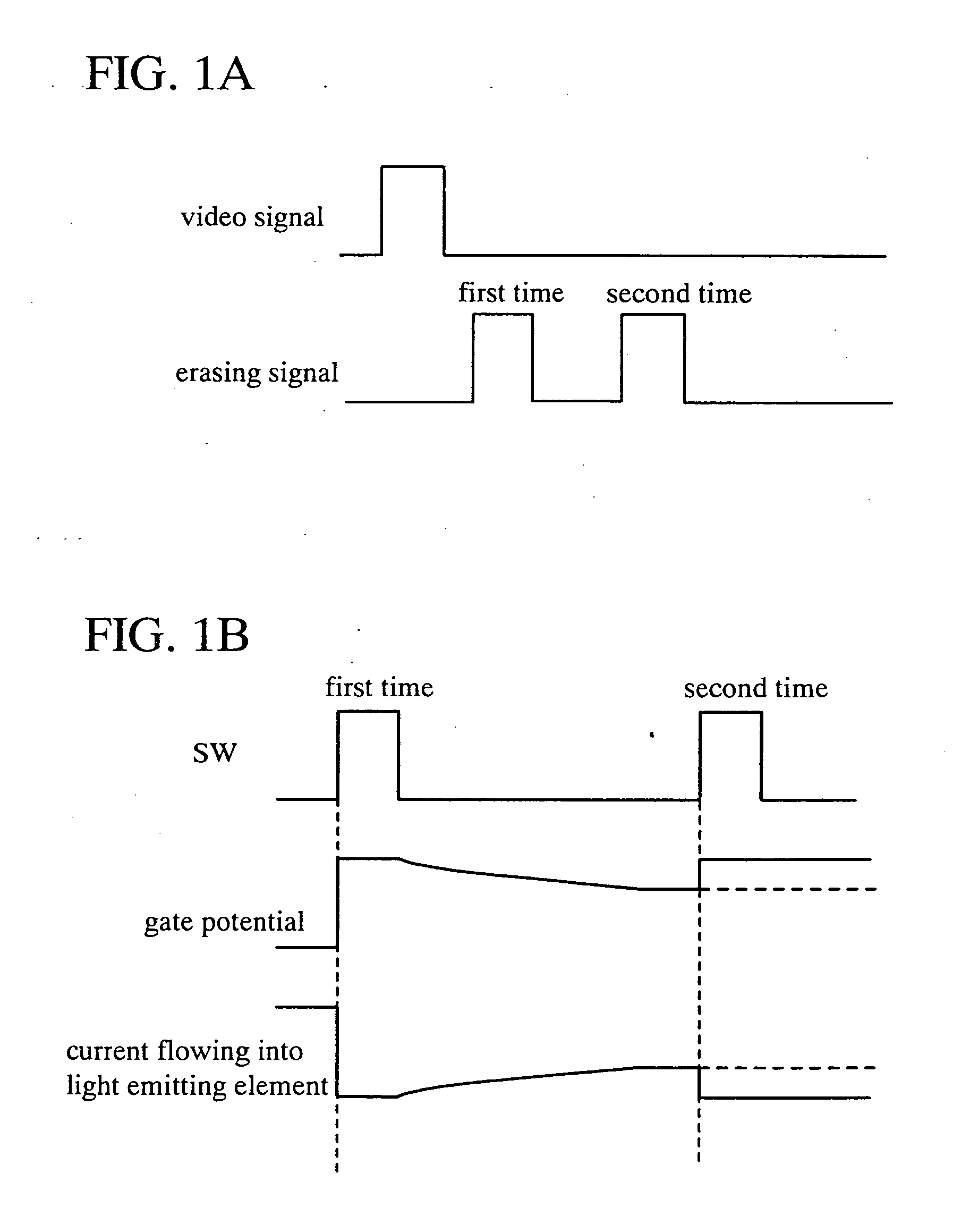
Driving method of light emitting device
InactiveUS20060076567A1Accurate gray scale displayAccurate displayStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
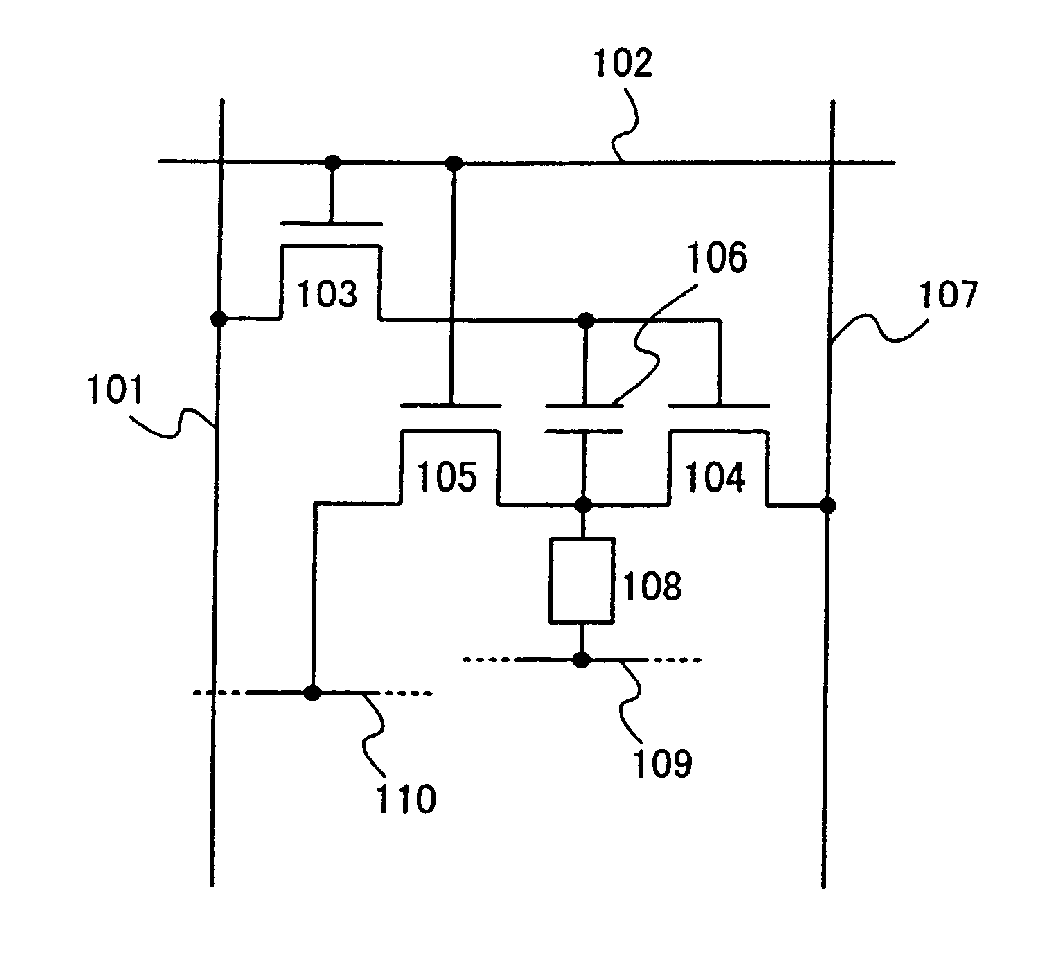
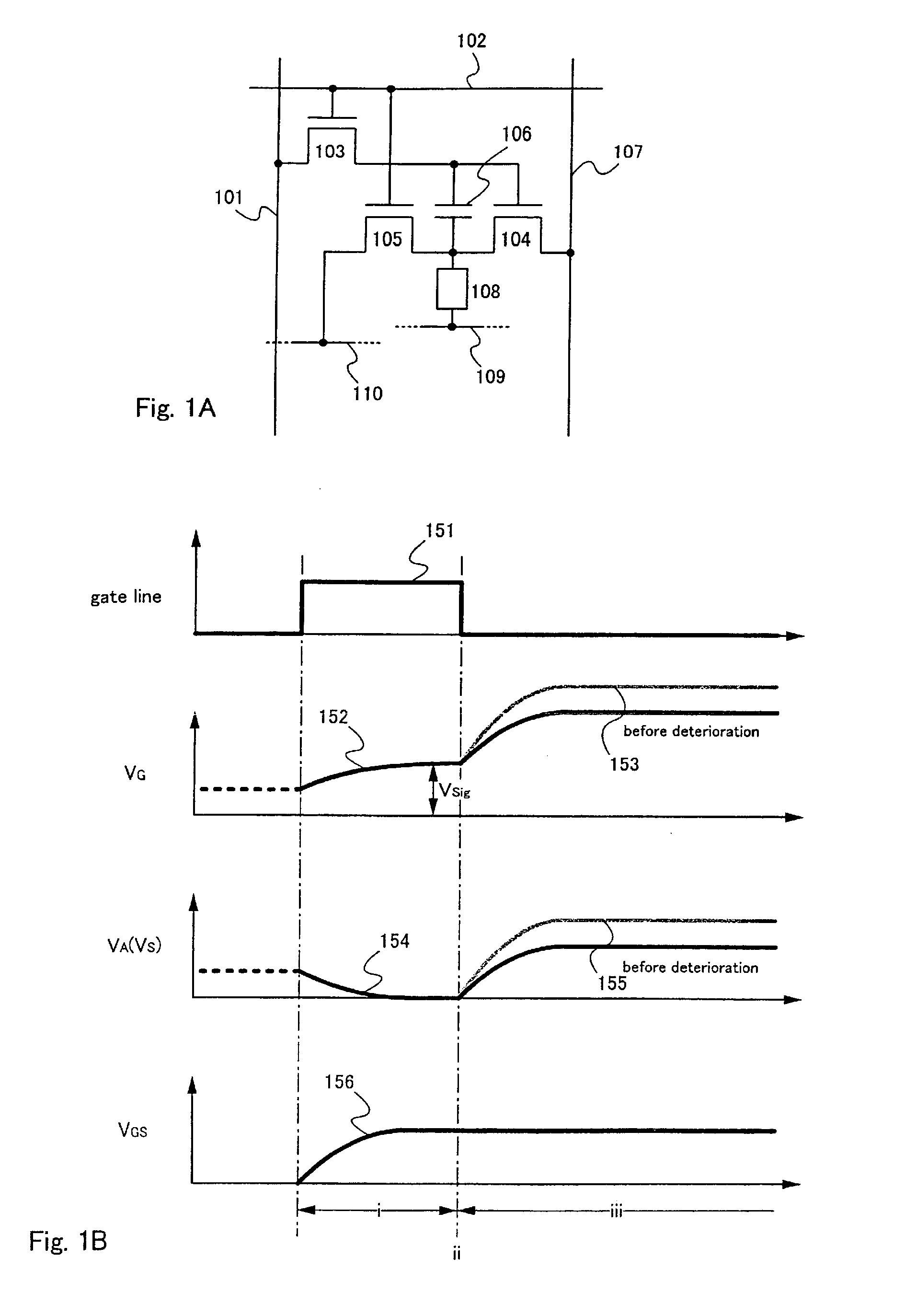
If a potential of a gate electrode of a driving transistor varies after a gray scale signal is inputted into each pixel, a current value of a current supplied to a light emitting element varies so that accurate gray scale display cannot be obtained. In particular, in the case of performing black display, current may flow, which makes clear black display difficult. Accordingly, the invention provides a light emitting device capable of performing accurate gray scale display, and a driving method thereof. According to the invention, a signal for display is inputted plural times within a predetermined timing period, or a writing operation period is lengthened. Consequently, the gate voltage of the transistor is determined after the anode potential of the light emitting element is stabilized, and therefore accurate gray scale display can be performed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com