Driving method of light emitting device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment mode 1
[0035] This embodiment mode describes a driving method in the case where a predetermined signal is inputted plural times.
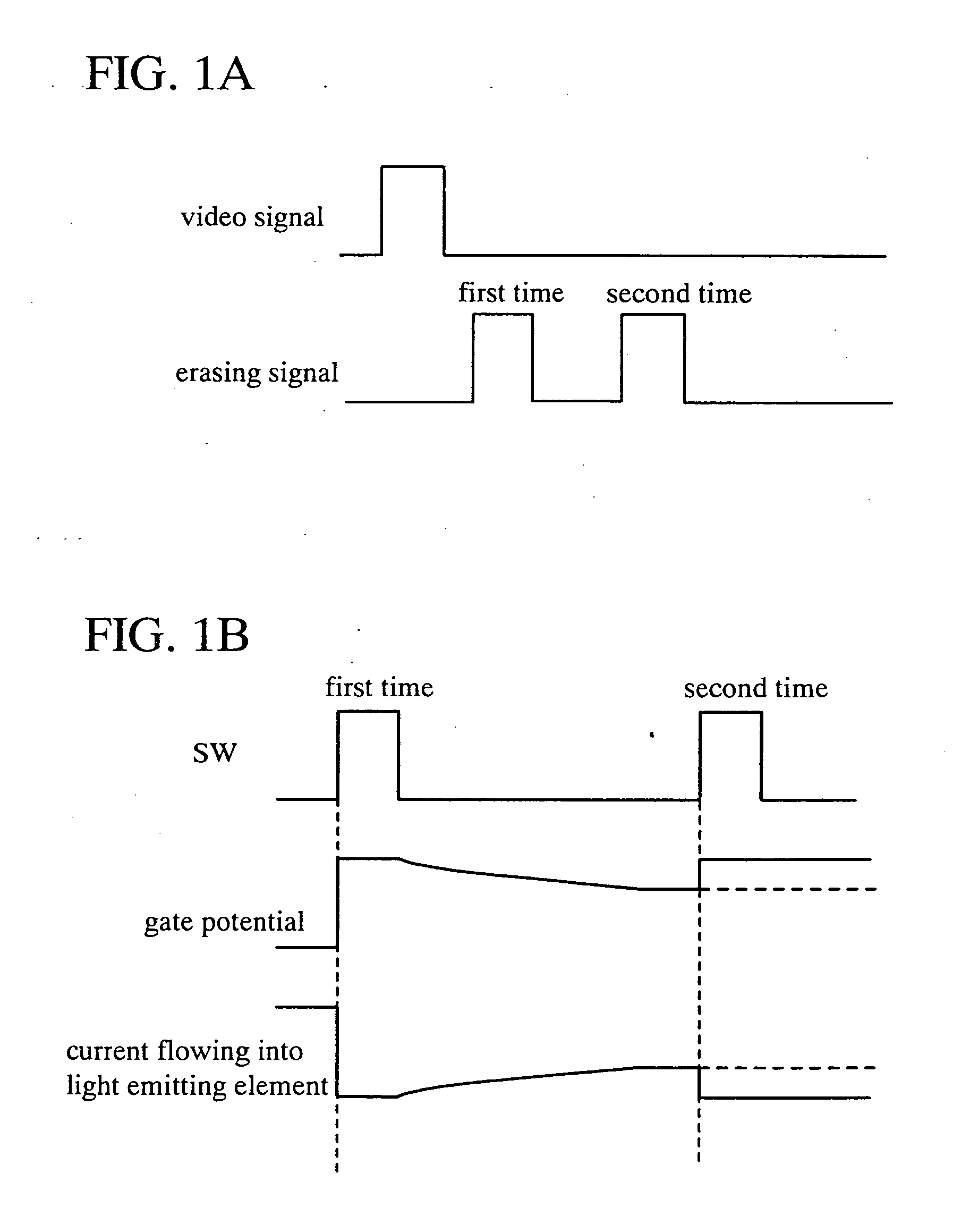
[0036] In FIG. 1A, operation in the case where an erasing signal is inputted two times in a digital gray scale method is shown. First, at a predetermined timing, a digital signal for display (a video signal) is inputted, and then a first erasing signal is inputted after a predetermined time has passed. At this time, if the capacitor (CEL) or the parasitic capacitance (CP) exists, a potential of a gate electrode (a gate potential) of a driving transistor does not relatively become 0 only by the first erasing signal so that off operation cannot be performed; as a result, it is difficult to perform accurate gray scale display and gray scale deviation occurs. In view of this, according to the invention, the erasing signal is inputted again, that is, a second erasing signal is inputted after a predetermined time has passed. Accordingly, the gate potential can be relat...
embodiment mode 2
[0043] Described in this embodiment mode is a timing chart of a digital gray scale method in the case where a period for inputting a video signal and a period for inputting an erasing signal plural times are provided.
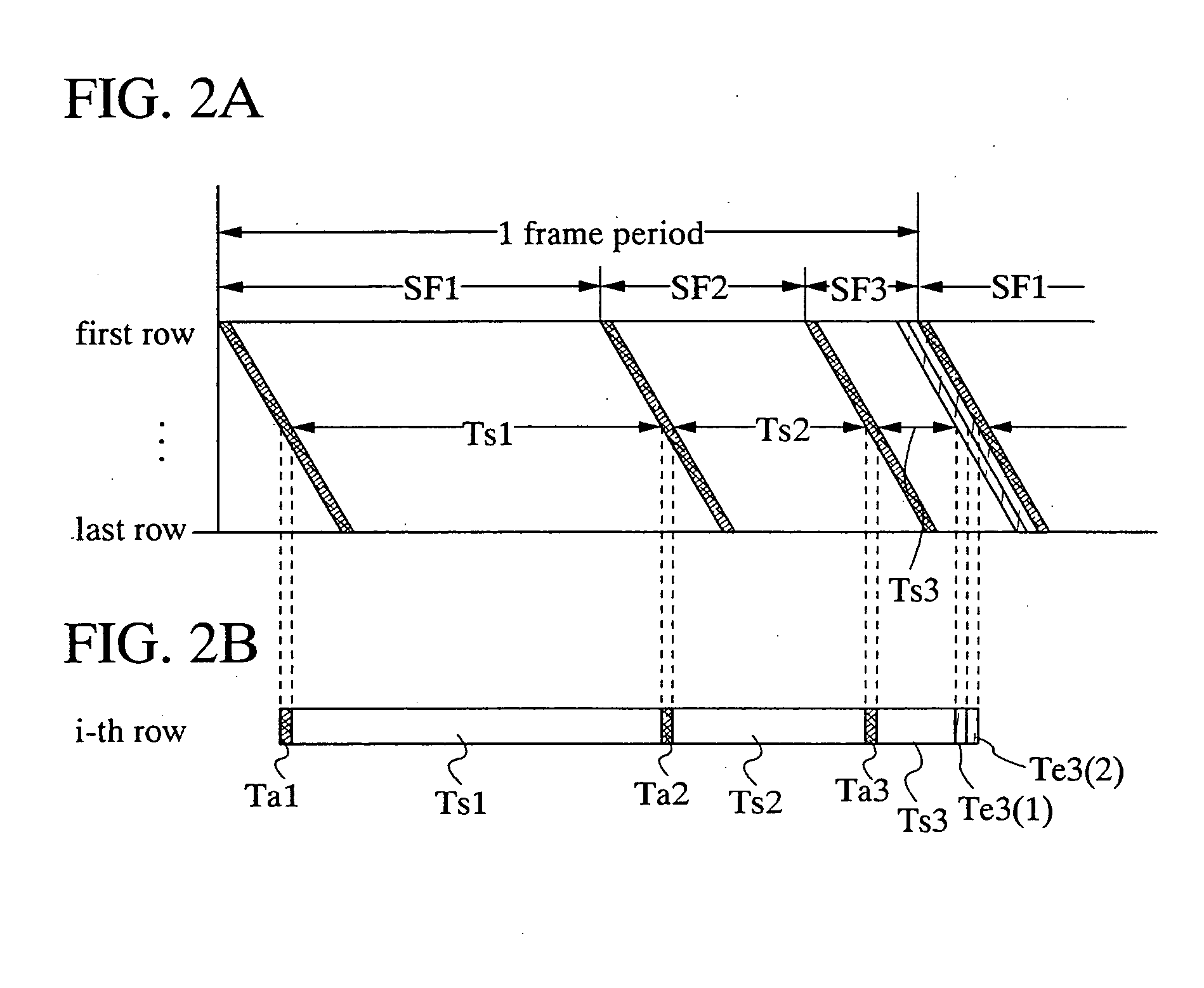
[0044] One frame period can be divided into a plurality of subframe periods SF1, SF2, . . . , and SFn (n is a positive integer). FIG. 2A is a timing chart in the case where one frame period is divided into three subframe periods (SF1, SF2, and SF3) to perform 6-gray scale display, in which an erasing signal is inputted two times in the subframe period SF3. FIG. 2B is a timing chart focusing on a scan line of the i-th row.
[0045] The subframe periods (SF1, SF2, and SF3) have writing operation periods for inputting a video signal (Ta1, Ta2, and Ta3) (also referred to as periods for inputting a writing signal) and light emitting periods for performing light emission depending on the written video signal (Ts1, Ts2, and Ts3) respectively. The length of the light emitting pe...
embodiment mode 3
[0050] Described in this embodiment mode is a timing chart of a digital gray scale method in the case where a plurality of writing operation periods (also referred to as periods for inputting a writing signal) is provided.
[0051] One frame period can be divided into a plurality of subframe periods SF1, SF2, . . . , and SFn (n is a positive integer). FIG. 3A is a timing chart in the case where one frame period is divided into three subframe periods (SF1, SF2, and SF3) to perform 6-gray scale display, in which a period for applying a reverse voltage is provided. FIG. 3B is a timing chart focusing on a scan line of the i-th row.
[0052] The subframe periods (SF1, SF2, and SF3) include writing operation periods (Ta1(W), Ta2(W), and Ta3(W)) and light emitting periods for performing light emission depending on the written signal (Ts1, Ts2, and Ts3) respectively. The length of the light emitting periods is set to satisfy Ts1:Ts2:Ts3=22:21:20. In the shortest subframe period SF3, a period fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com