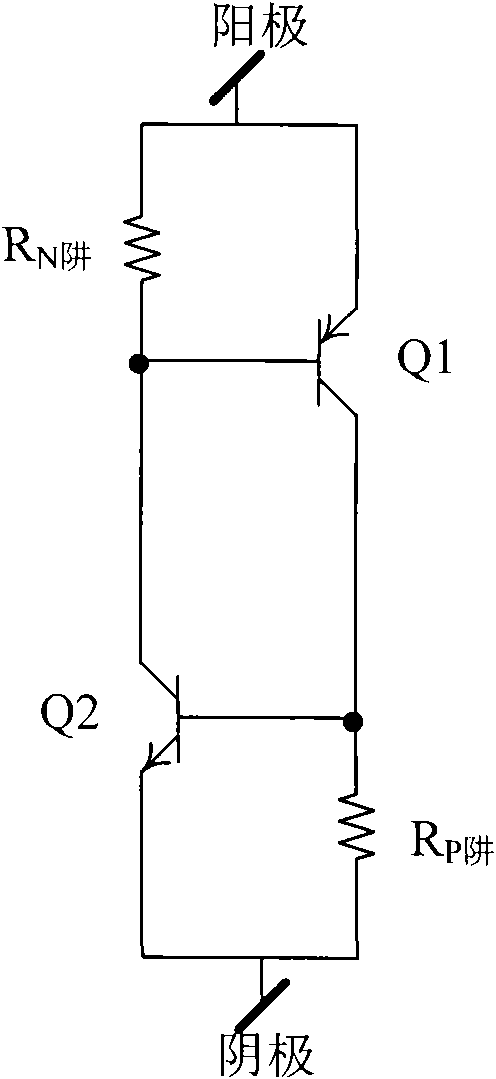
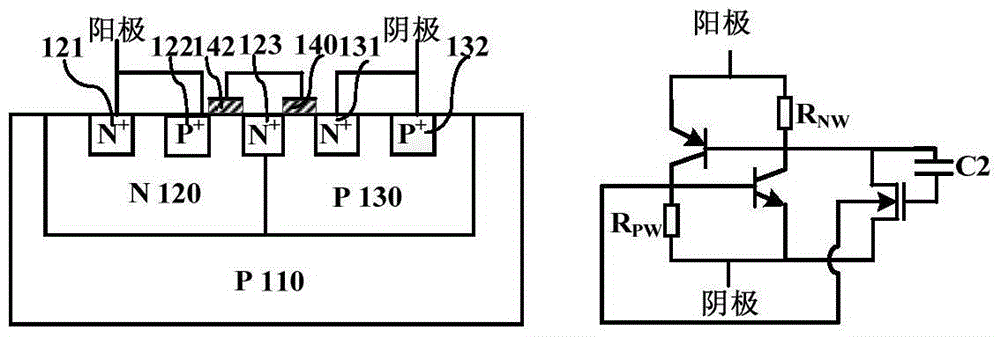
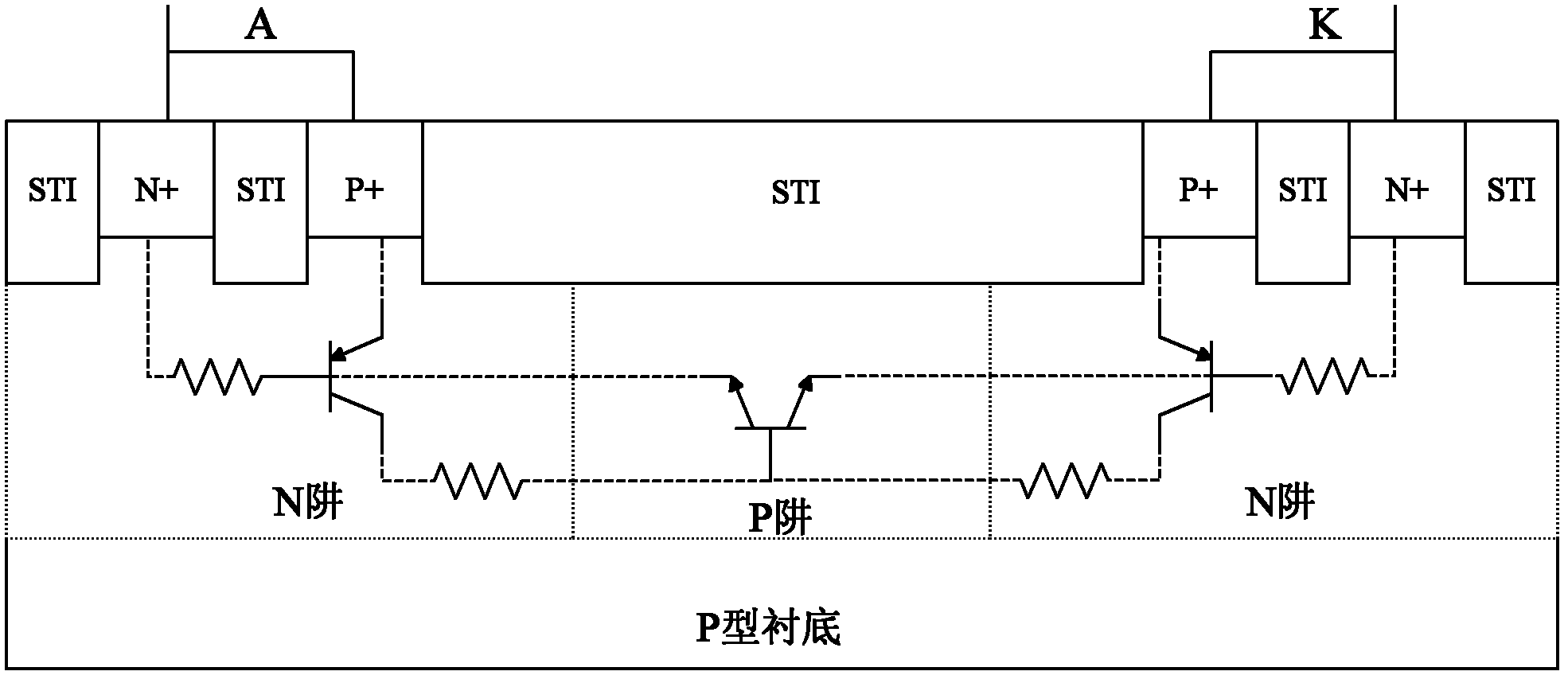
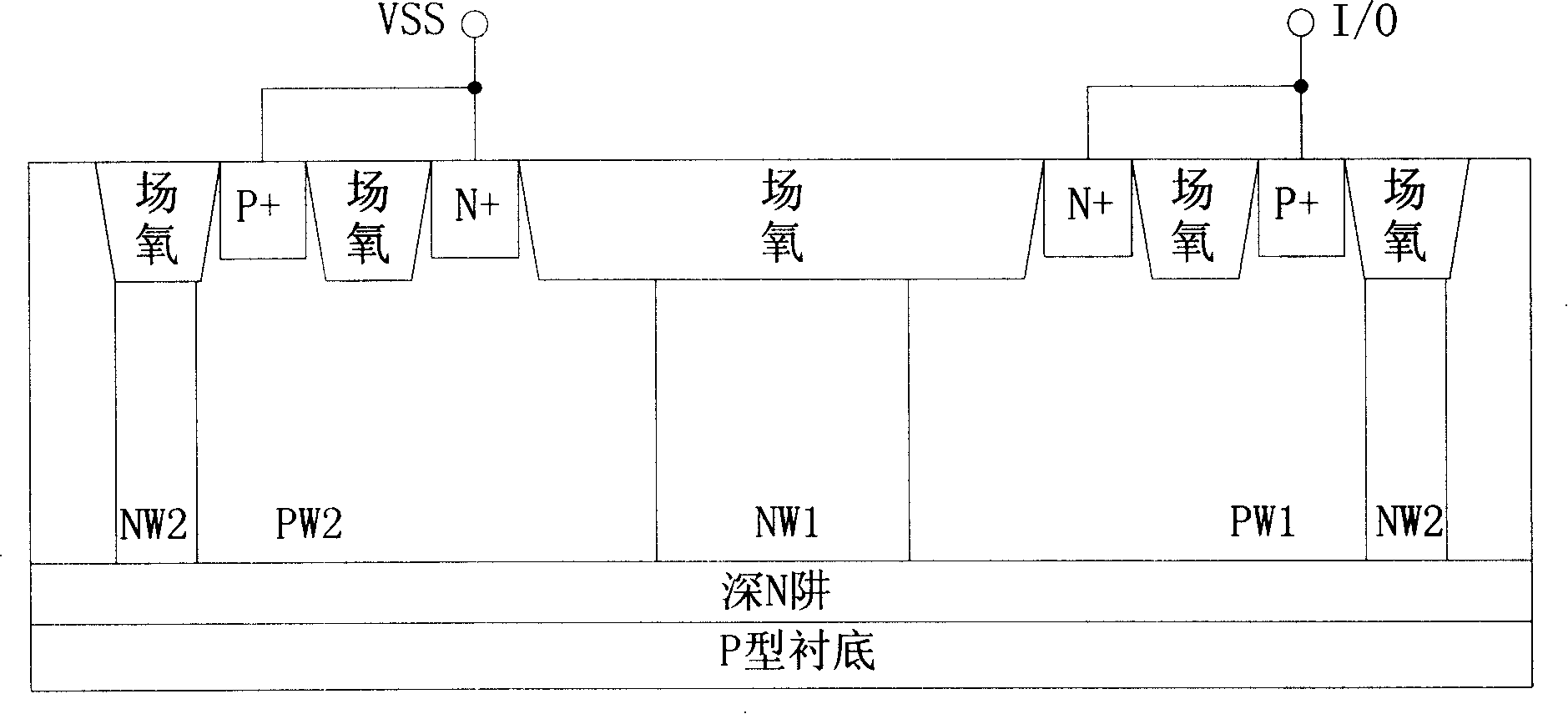
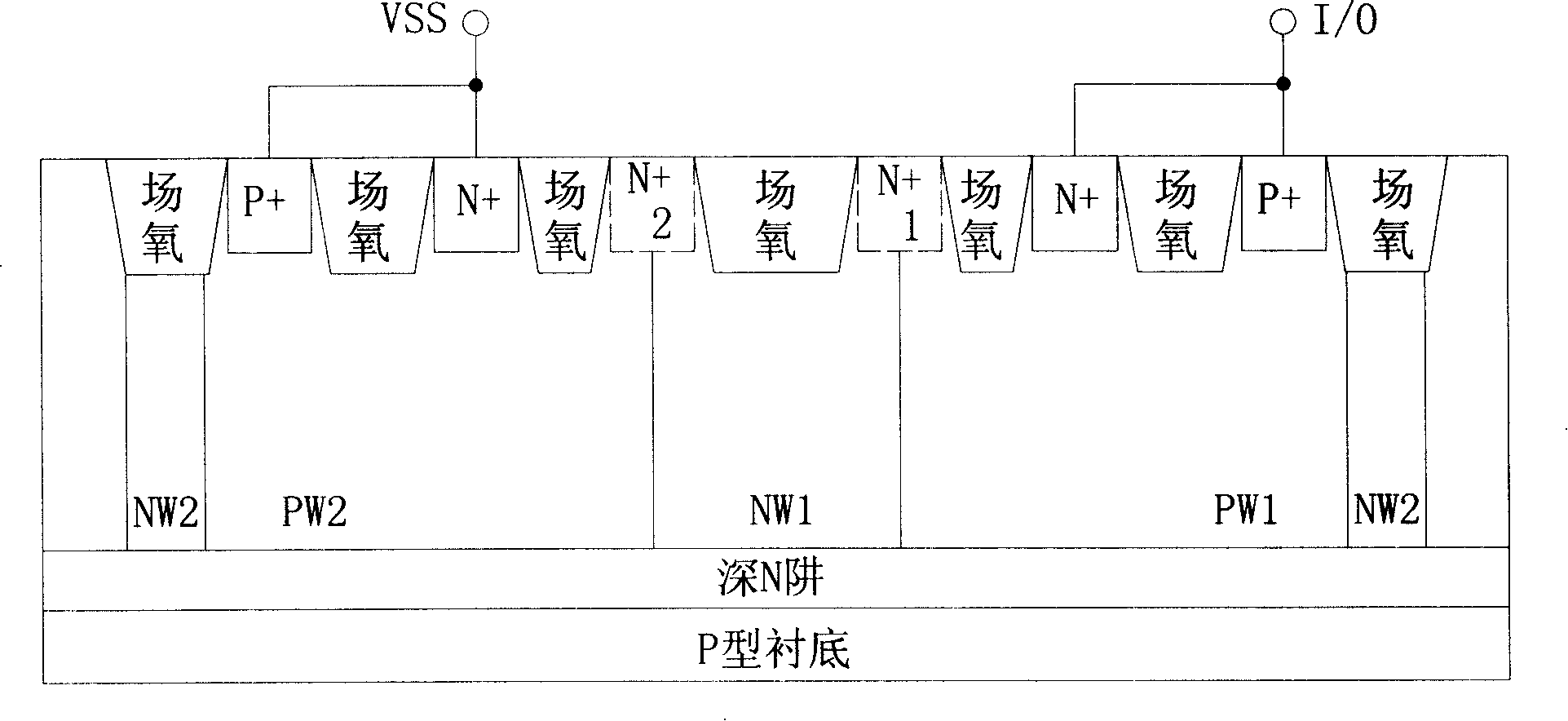
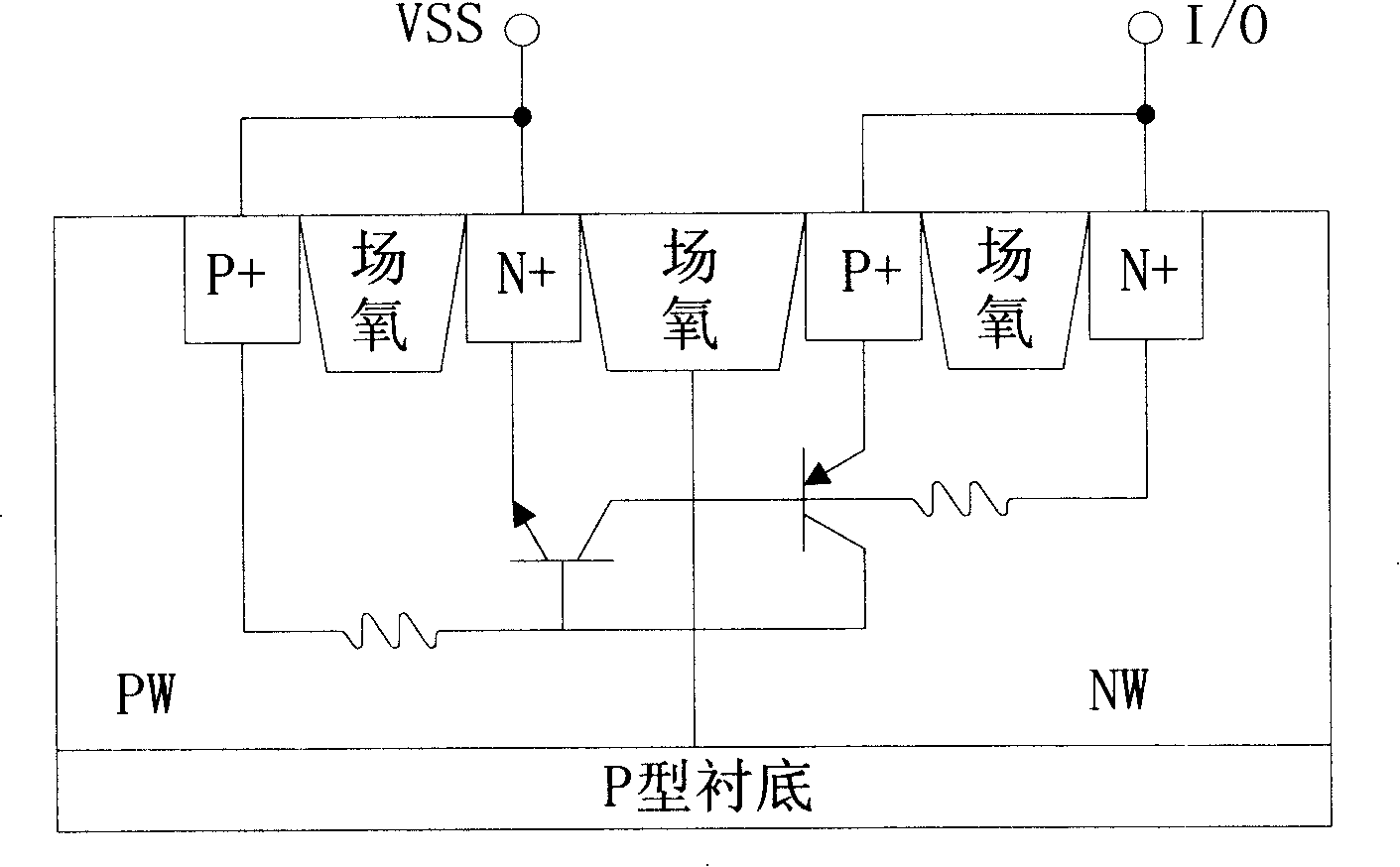
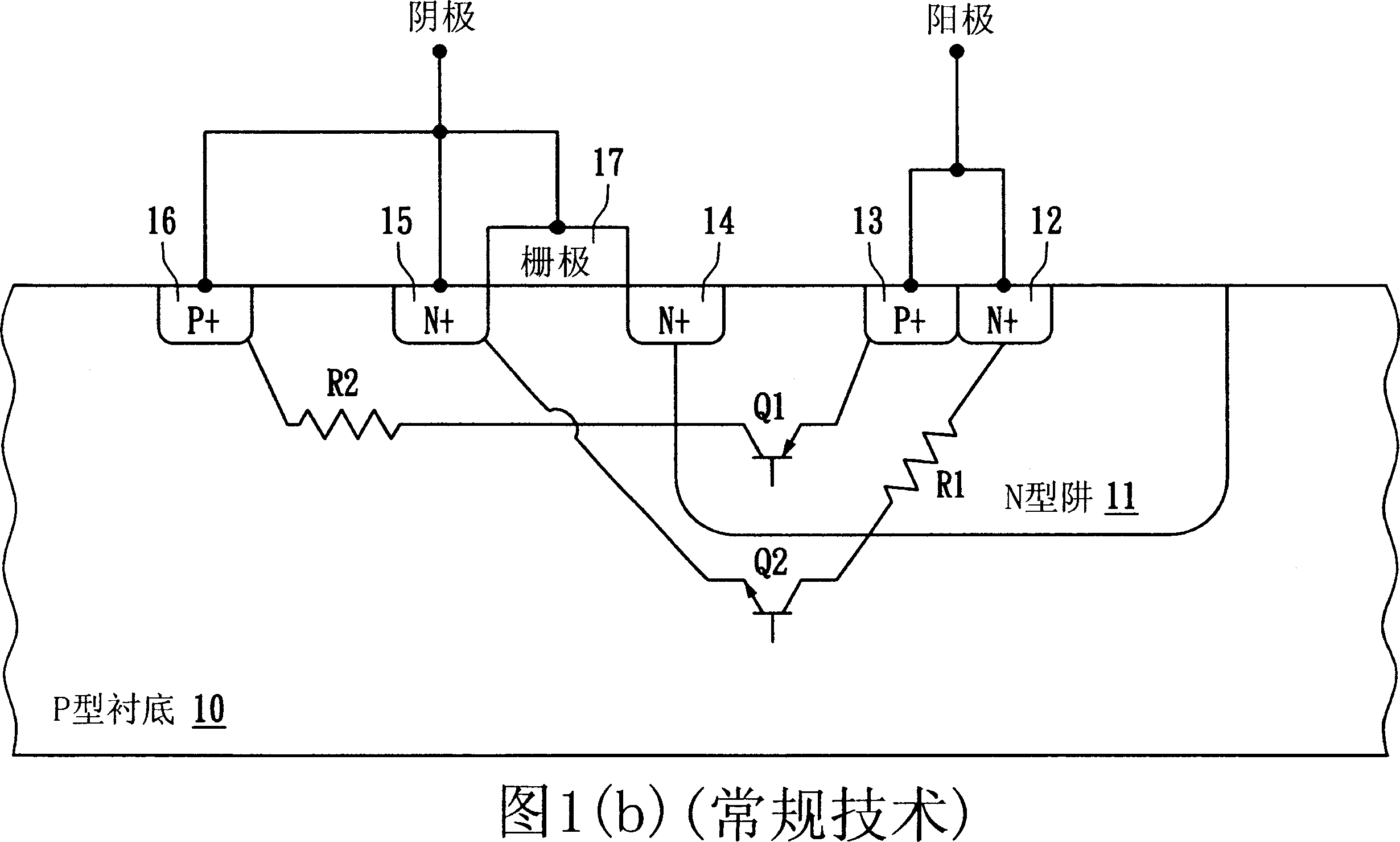
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
352results about How to "Lower the trigger voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
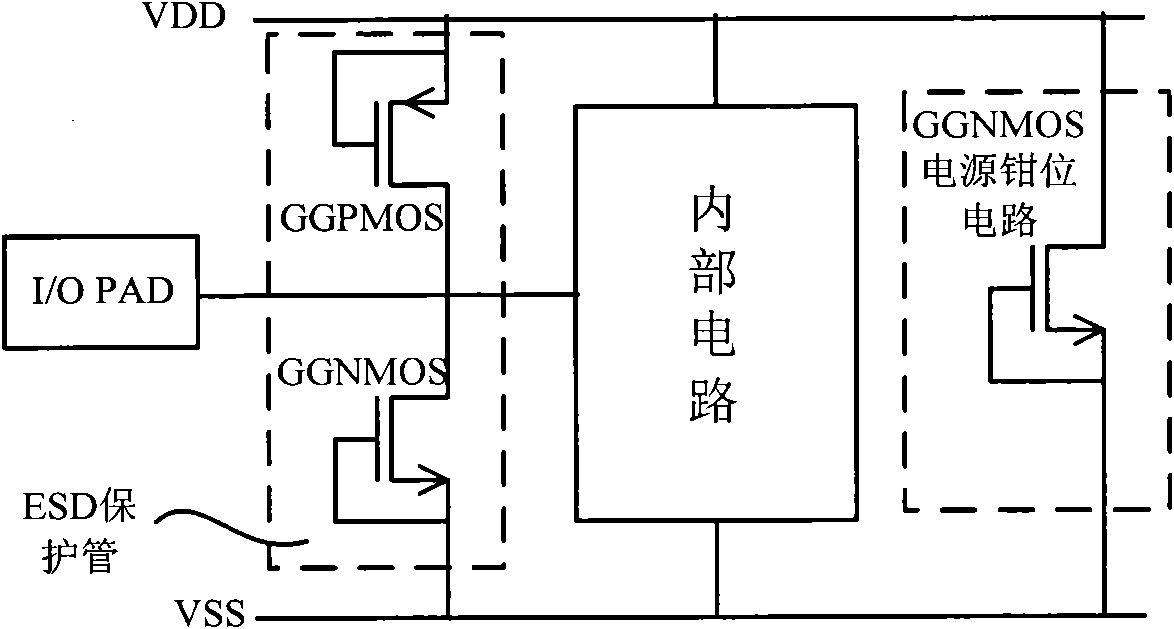
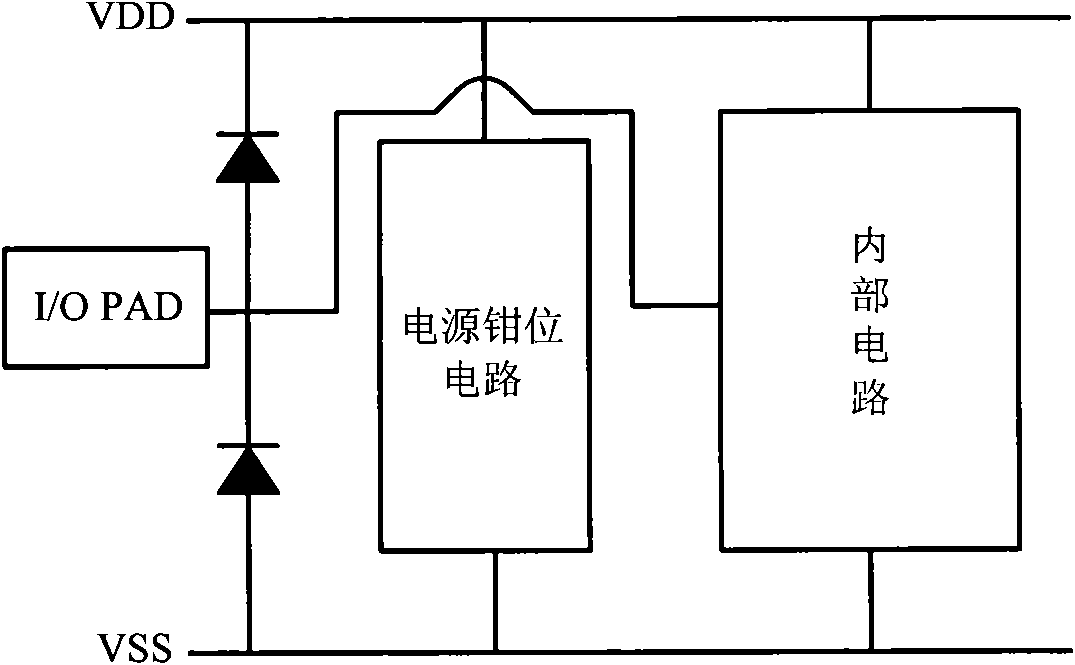
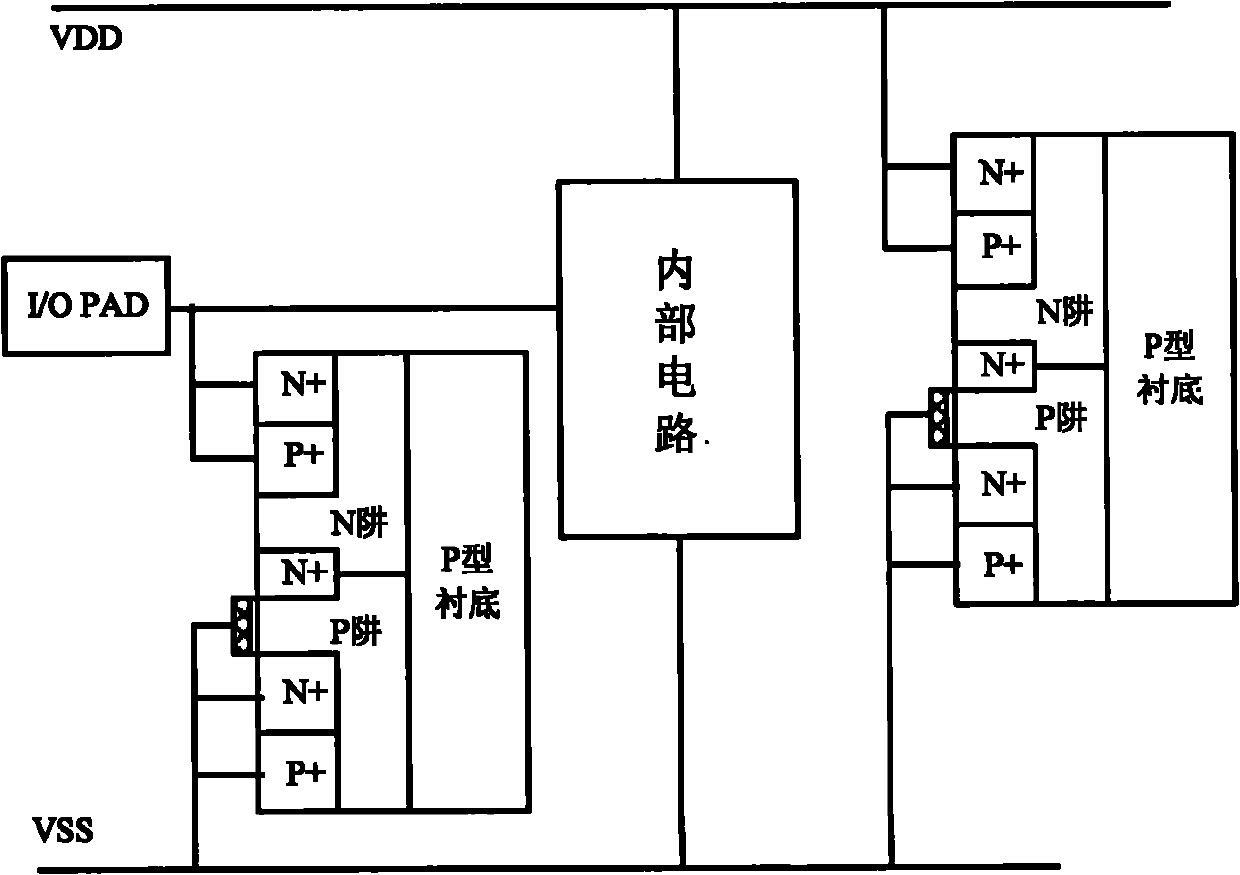
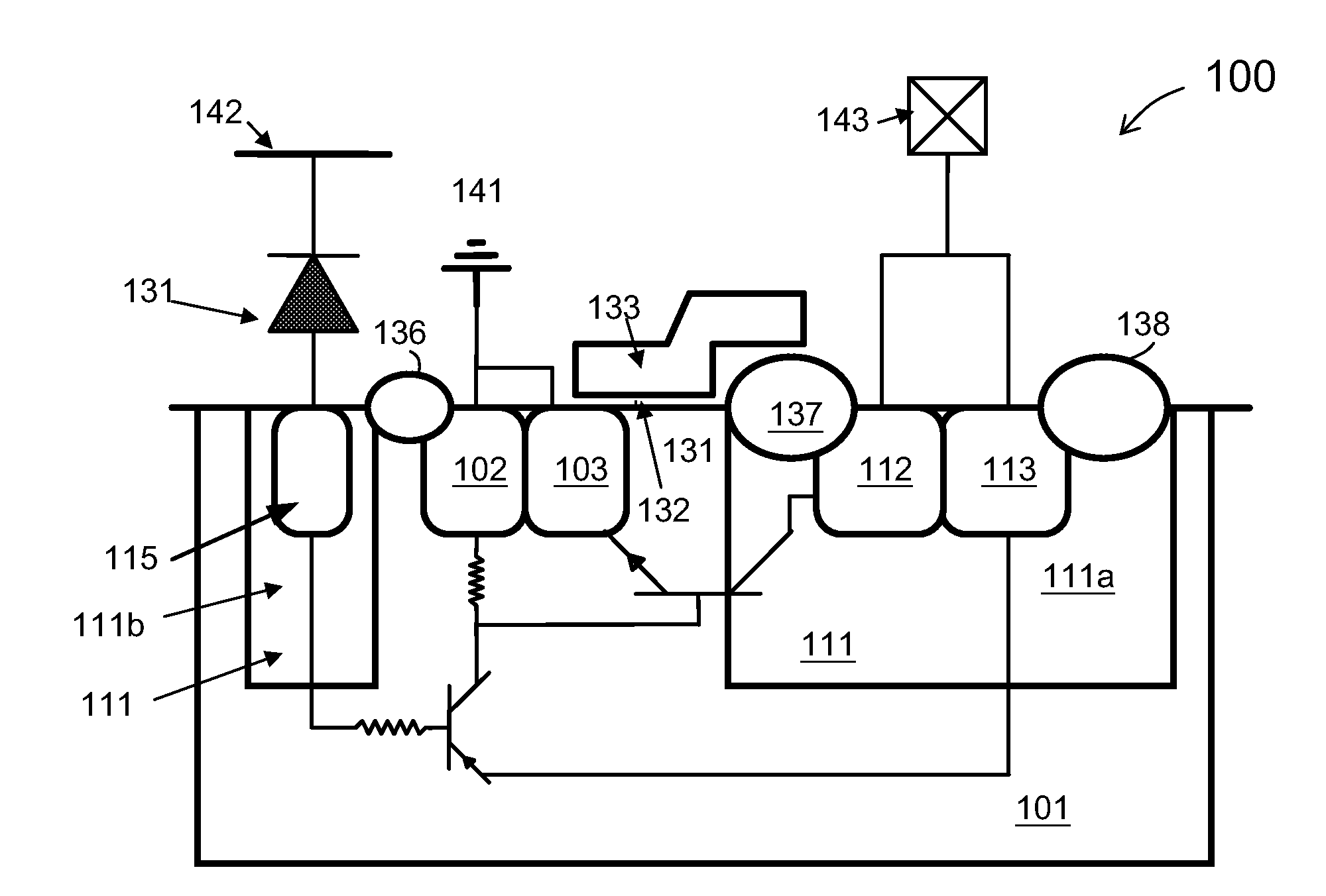
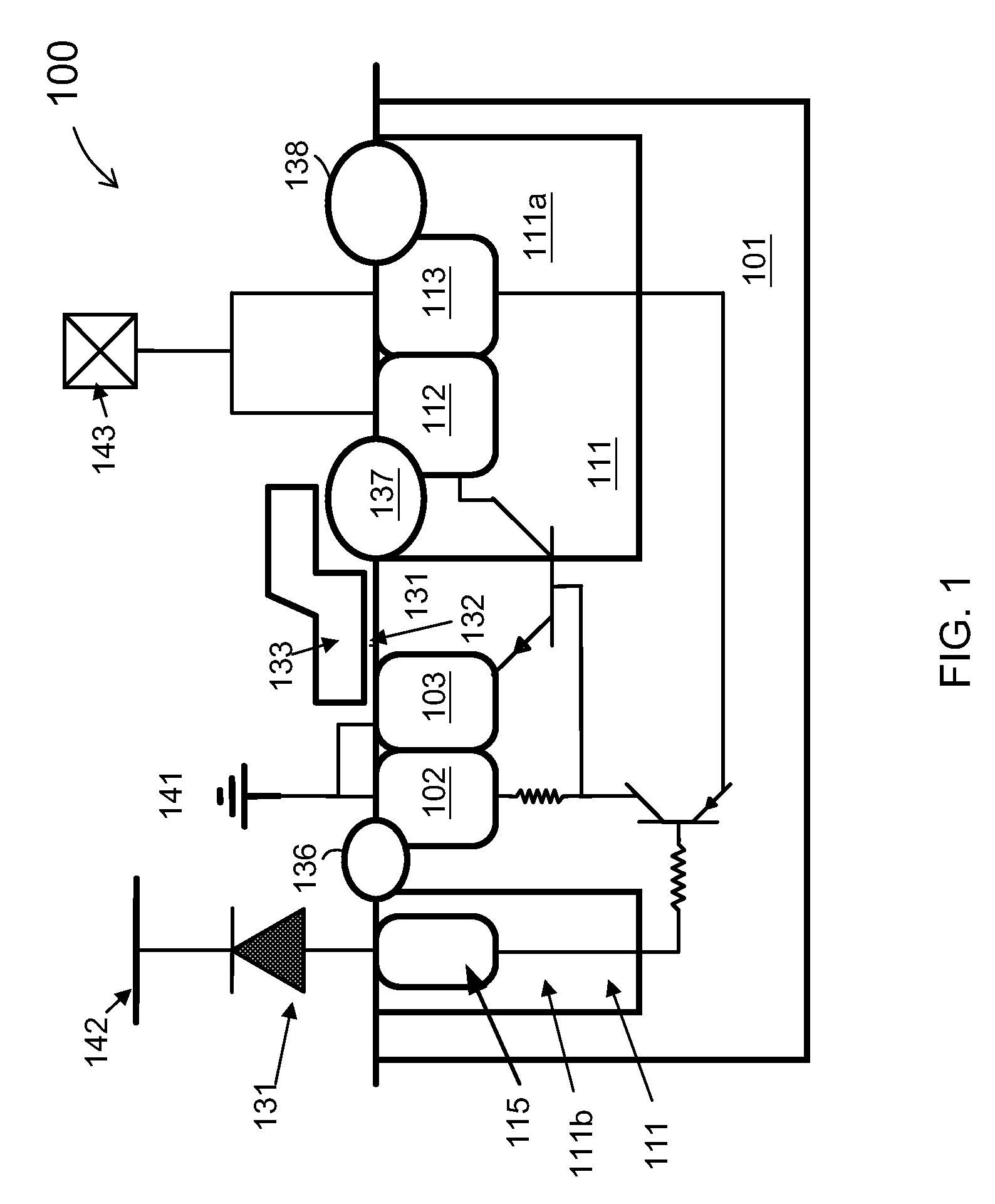
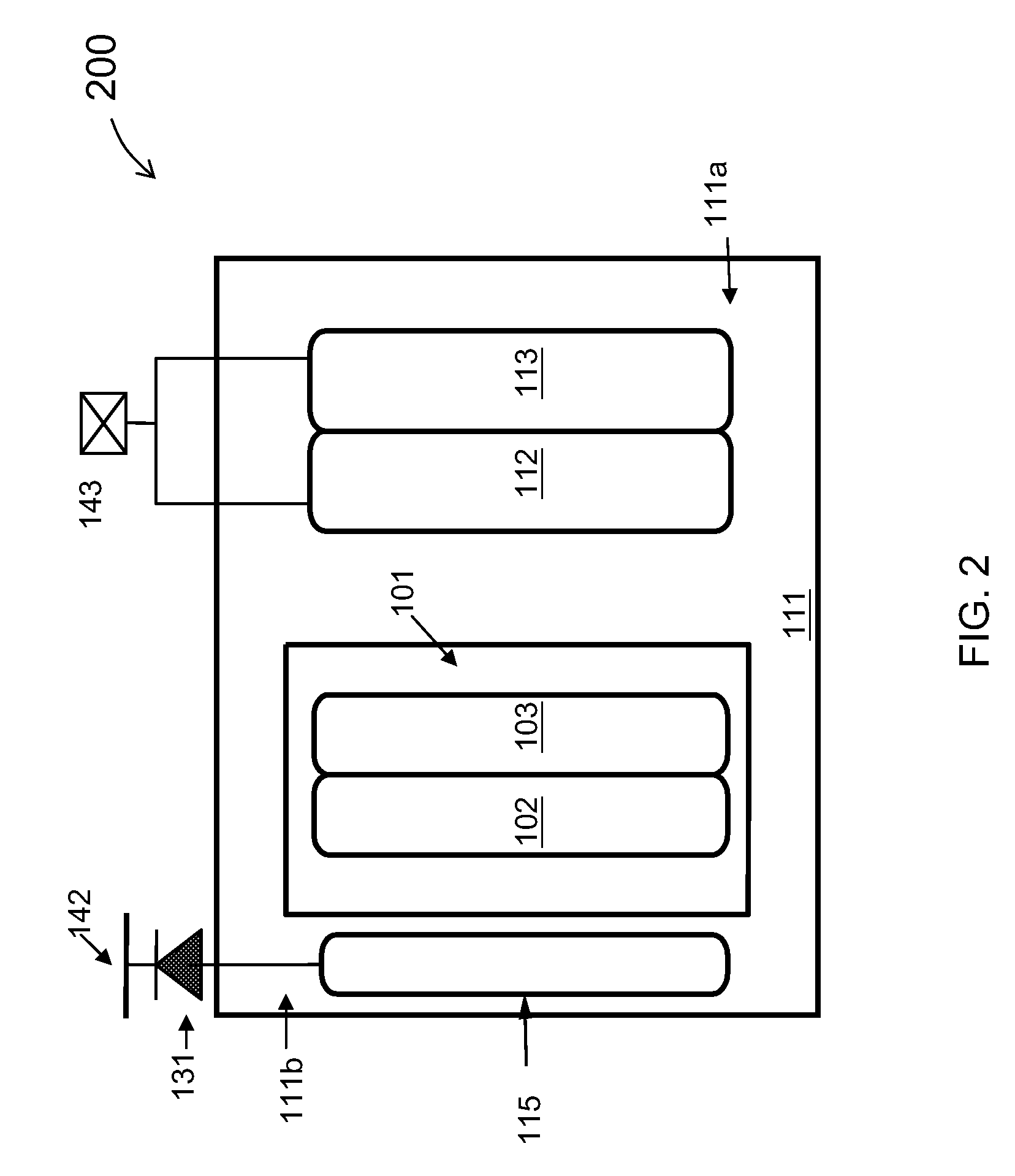
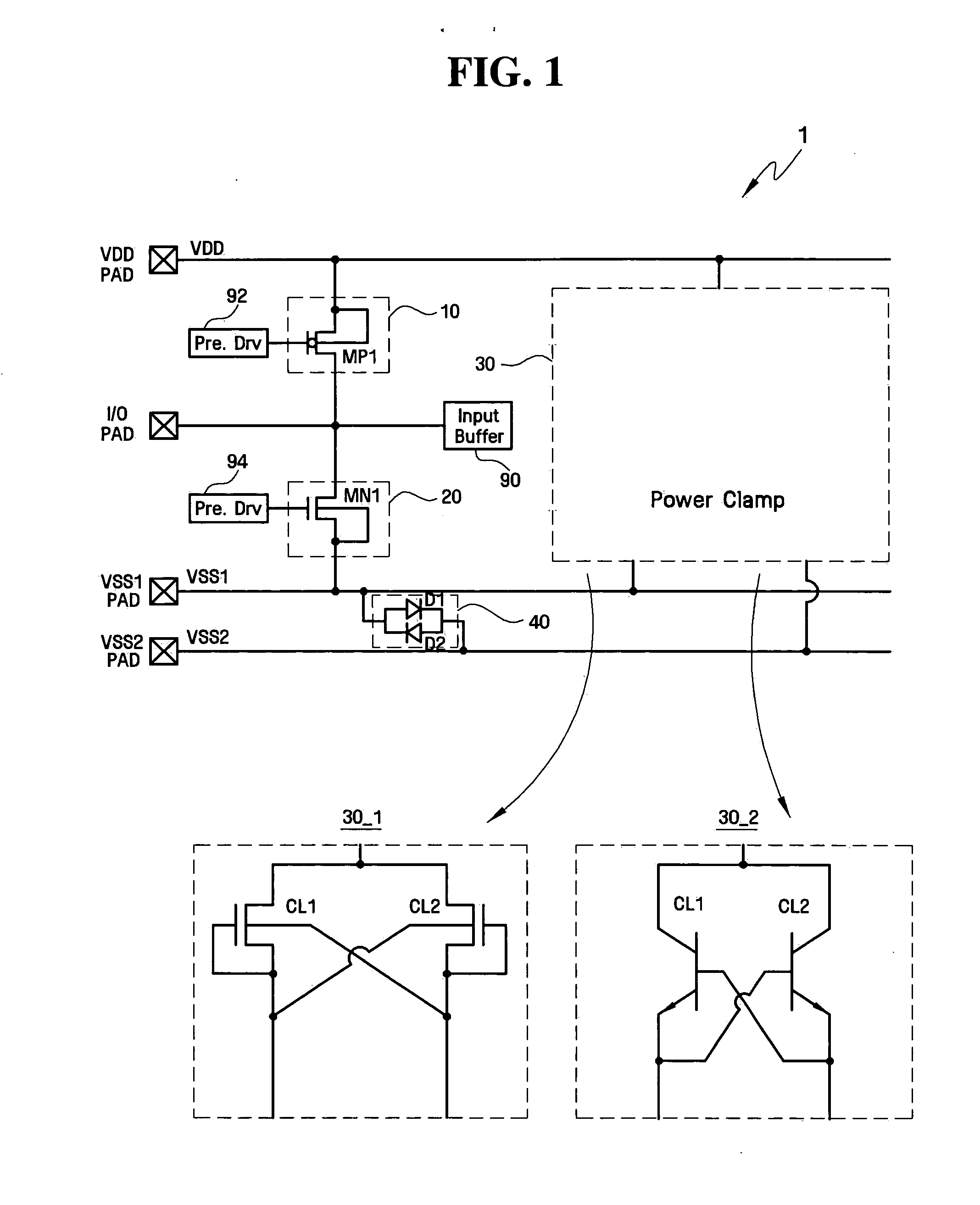
ESD protection devices and methods for reducing trigger voltage
InactiveUS7009252B2Quicker trigger mechanismBetter ESD protection levelTransistorThyristorP–n junctionBreakdown voltage
ESD protection devices and methods to form them are provided in this invention. By employing the thin gate oxide fabricated by a dual gate oxide process, ESD protection devices with a lower trigger voltage are provided. The NMOS for ESD protection according to the present invention has islands with thin gate oxides and a control gate with a thick gate oxide. These islands overlap the drain region of the NMOS to reduce the breakdown voltage of the PN junction in the drain region, thereby reducing the ESD trigger voltage and improving the ESD protection level of the NMOS. Furthermore, the invention is applicable to general integrated-circuit processes as well as various ESD protection devices.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Material of over voltage protection device, over voltage protection device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20080079533A1Lower the trigger voltageEasy to useCurrent responsive resistorsVaristor coresAdhesiveEngineering
The present invention relates to a material of an over voltage protection device and an over voltage protection device manufactured by the material. The material comprises a non-conductive powder, a metal conductive powder, and an adhesive. The over voltage protection device comprises a first electrode, a second electrode, and a porous structure connected between the first electrode and the second electrode. The present invention also relates to a method for manufacturing the over voltage protection device. The present invention also relates to a method of adjusting the breakdown voltage of an over voltage protection device.
Owner:INPAQ TECH
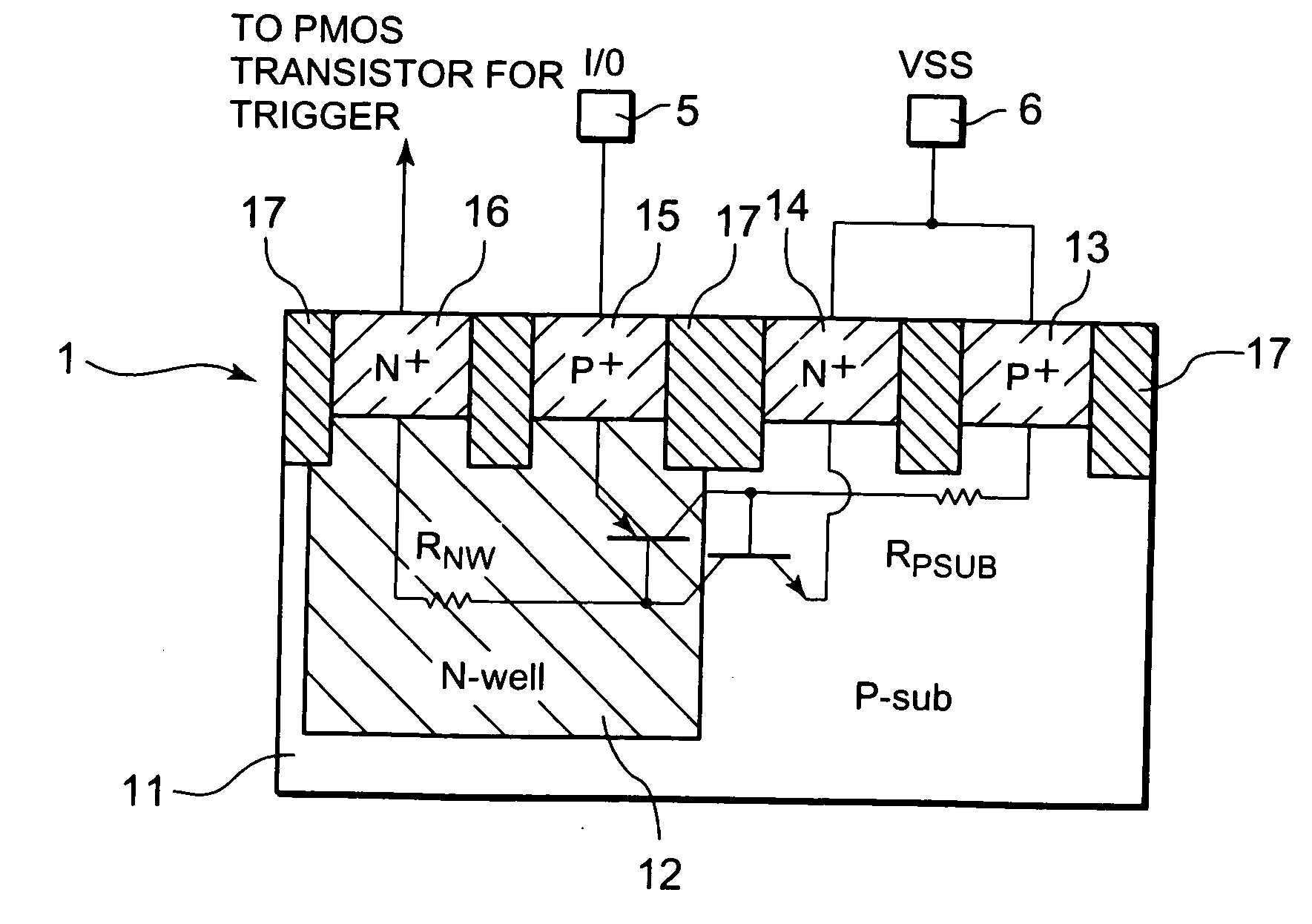
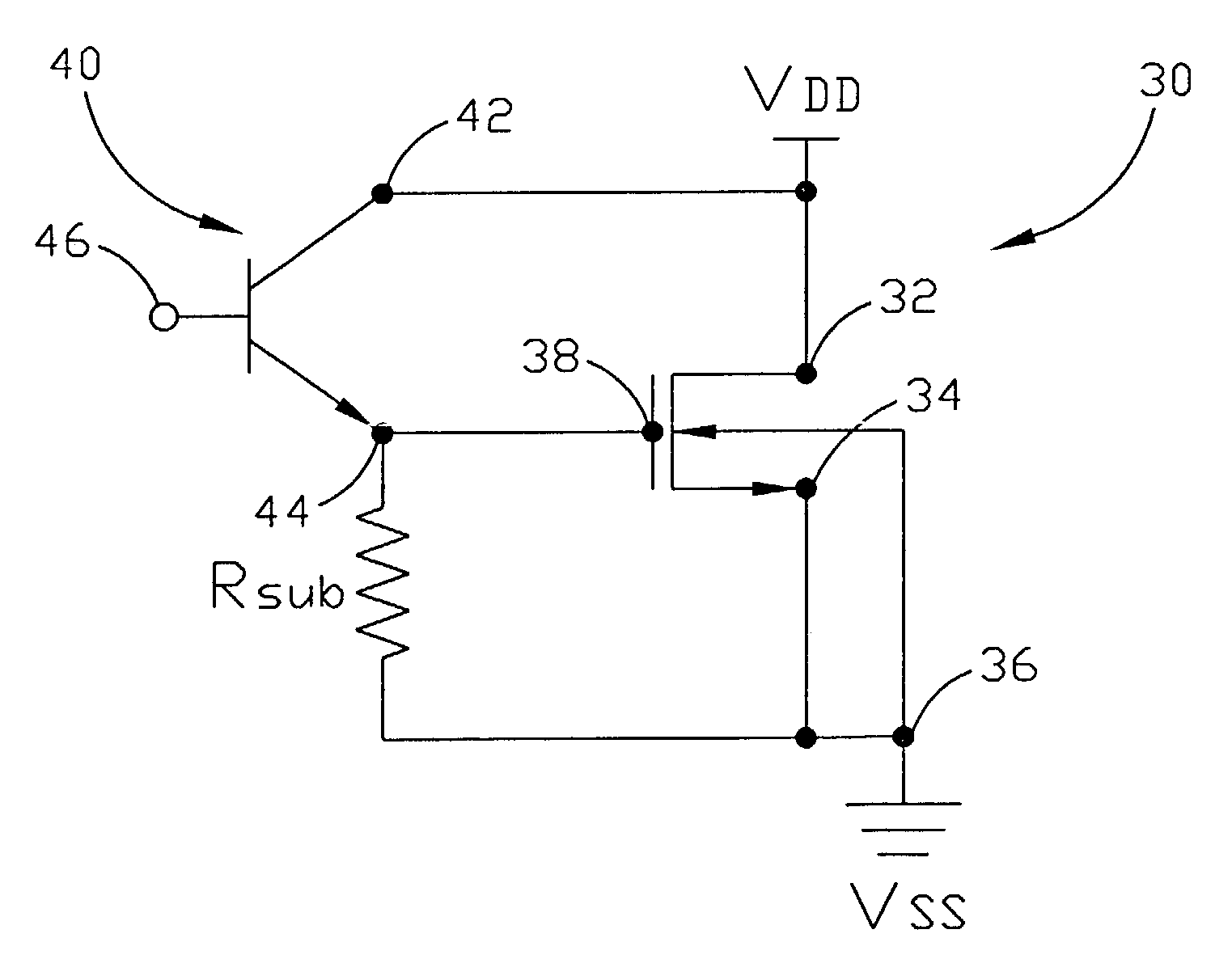
Semiconductor circuit including electrostatic discharge circuit having protection element and trigger transistor
ActiveUS20080217650A1Low trigger voltageReduce leakage currentTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectrostatic dischargeEngineering
A semiconductor circuit includes, a first pad for a first power source, a second pad for a second power source, a third pad for an input / output signal, a protection element arranged between the third pad and the second pad; and a transistor functioning as a trigger element for use in flowing a trigger current to the protection element. The transistor includes a gate and a backgate being connected to the first pad and is connected to the protection element such that a source potential of the transistor becomes lower than a potential of the third pad, based on a voltage drop caused by the protection element, when potentials of the first pad and the third pad are kept at a power supply voltage level.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
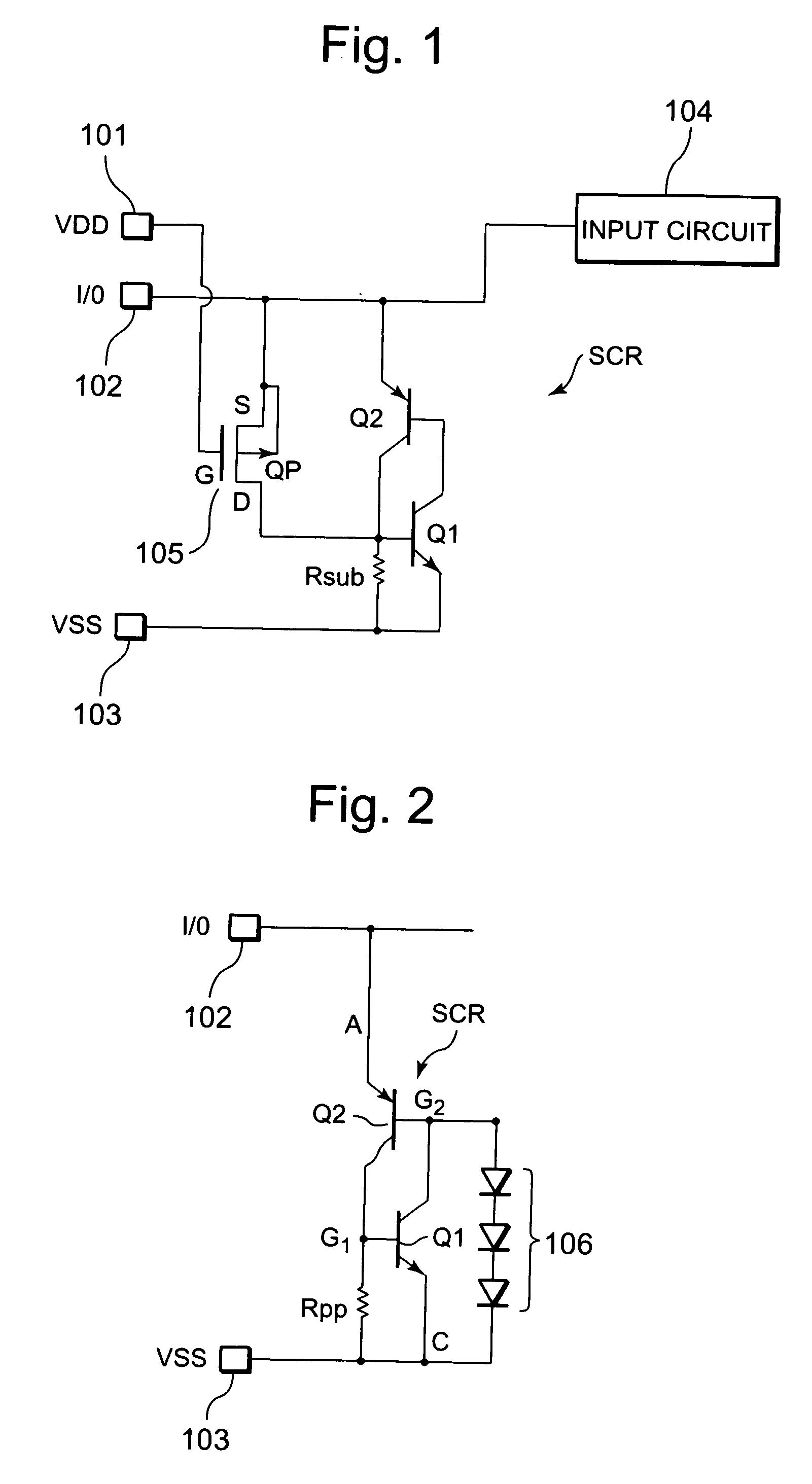
Latch-up-free ESD protection circuit using SCR
InactiveUS20050275984A1Improve discharge efficiencyQuick switchTransistorPulse automatic controlOvervoltageSilicon-controlled rectifier
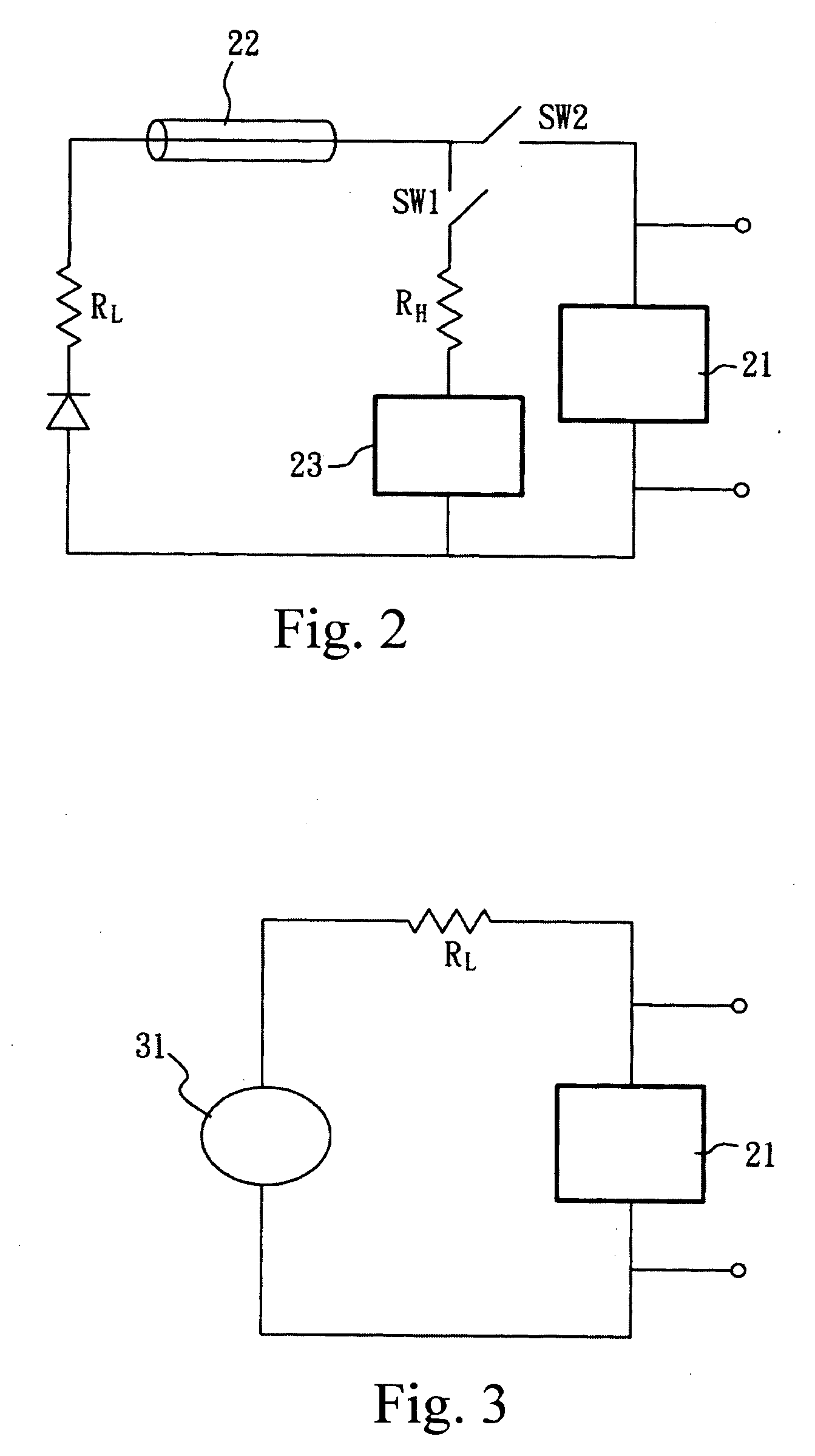
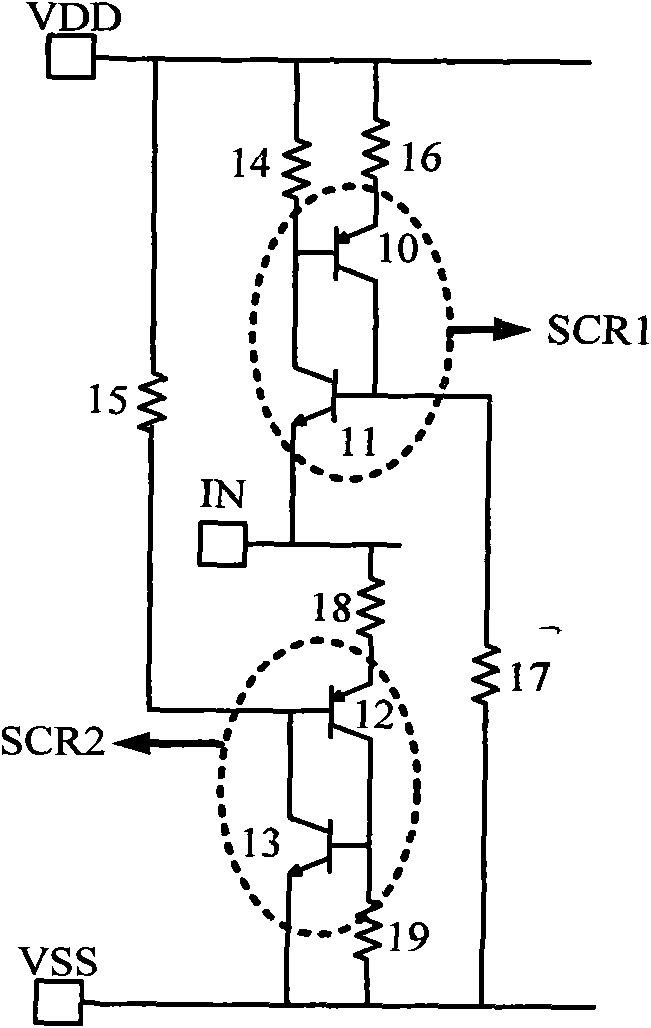
A latch-up-free ESD protection circuit using SCR is disclosed, in which an SCR is connected between the input pad and the negative power supply; a turn-on switch and a turn-off switch are connected between the positive power supply VDD (or the input pad) and the SCR; and a transistor gating circuit is connected to the turn-on switch and the turn-off switch to direct the operation of the SCR. When overvoltage stress develops over the input pad in the fast-transient mode, the turn-on switch enables the NPN transistor to switch on the SCR to form a discharging path for electrostatic discharge; and when overvoltage stress is released, the turn-off switch enables the PNP transistor to switch off the SCR, thus making it immune to any latch-up after the overvoltage stress is released, and having the advantages of fast triggering, low trigger voltage, no latch-up, and full ESD protection in the active and passive modes.
Owner:KING BILLION ELECTRONICS
Low-voltage SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) structure for ESD (Electronic Static Discharge) protection of integrated circuit chip
InactiveCN102034811AImprove protectionLower the trigger voltageSolid-state devicesDiodeSilicon-controlled rectifierLow voltage
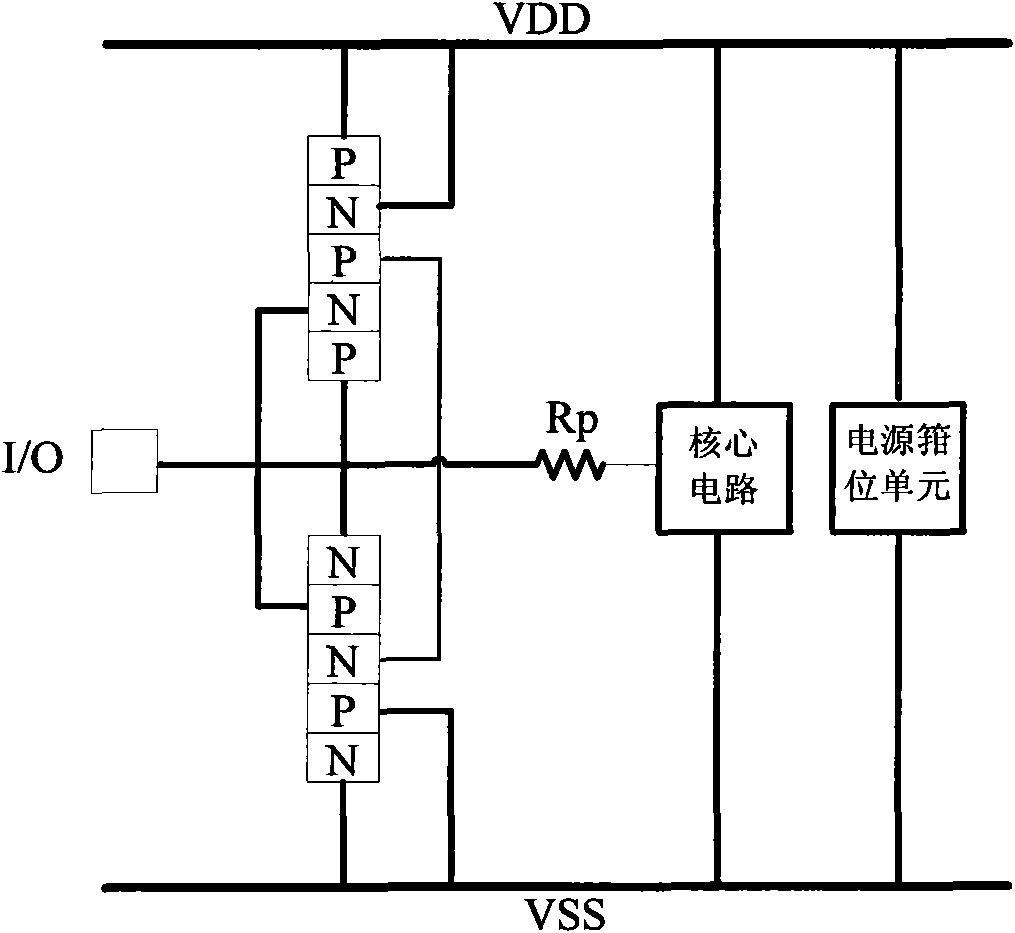
The invention relates to a low-voltage SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) structure for ESD (Electronic Static Discharge) protection of an integrated circuit chip, belonging to the technical field of electronics. The structure comprises two kinds of low-voltage SCR ESD protection devices, wherein the first kind of SCR ESD protection device integrates two N-well diodes and two NMOSs (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductors); the N-well diodes are connected between I / O (Input / Output) and a VDD (Virtual Device Driver); the NMOSs are connected between the VDD and VSS (Visual Source Safe); and the N-well diodes and the NMOSs form an SCR structure which provides ESD protection between PS and PD modes and VDD-VSS. The second kind of device integrates two P-well diodes and two PMOSs (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductors), wherein the P-well diodes are connected between the I / O and the VSS, and the PMOSs are connected between the VSS and the VDD, and the P-well diodes and the PMOSs jointly form an SCR structure which provides ESD protection between ND and NS modes and VDD-VSS. According to the invention, the chip has higher maintaining voltage and latch-up resistance effect during normal working and has lower triggering voltage and higher triggering speed during ESD; and the low-voltage SCR structure can effectively reduce the relative chip-occupying area of the protection devices and decrease parasitic capacitance at the same time of providing a plurality of modes of ESD protection functions and excellent ESD protection performance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Methods and structures for electrostatic discharge protection
ActiveUS20100109043A1Enhanced ESD protectionSimple structureTransistorReliability increasing modificationsSemiconductorCondensed matter physics
A semiconductor device includes a first well region of a first conductivity, a second well region of a second conductivity type, a source region of the second conductivity type within the first well region, and a drain region of the second conductivity type at least partially within the second well region. A well contact to the first well region is coupled to the source. A third doped region of the first conductivity type and a fourth doped region of the second conductivity type are located in the second well region. A first transistor includes the third doped region, the second well region, and the first well region. The first transistor is coupled to a switch device. A second transistor includes the second well region, the first well region, and the source region. The first and the second transistors are configured to provide a current path during an ESD event.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
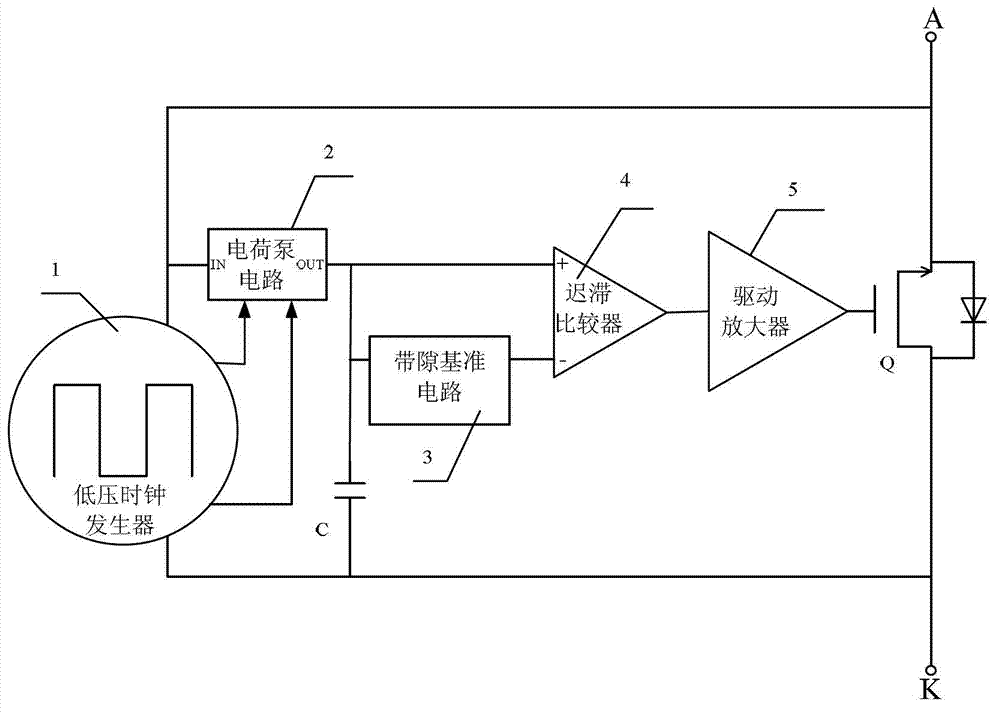
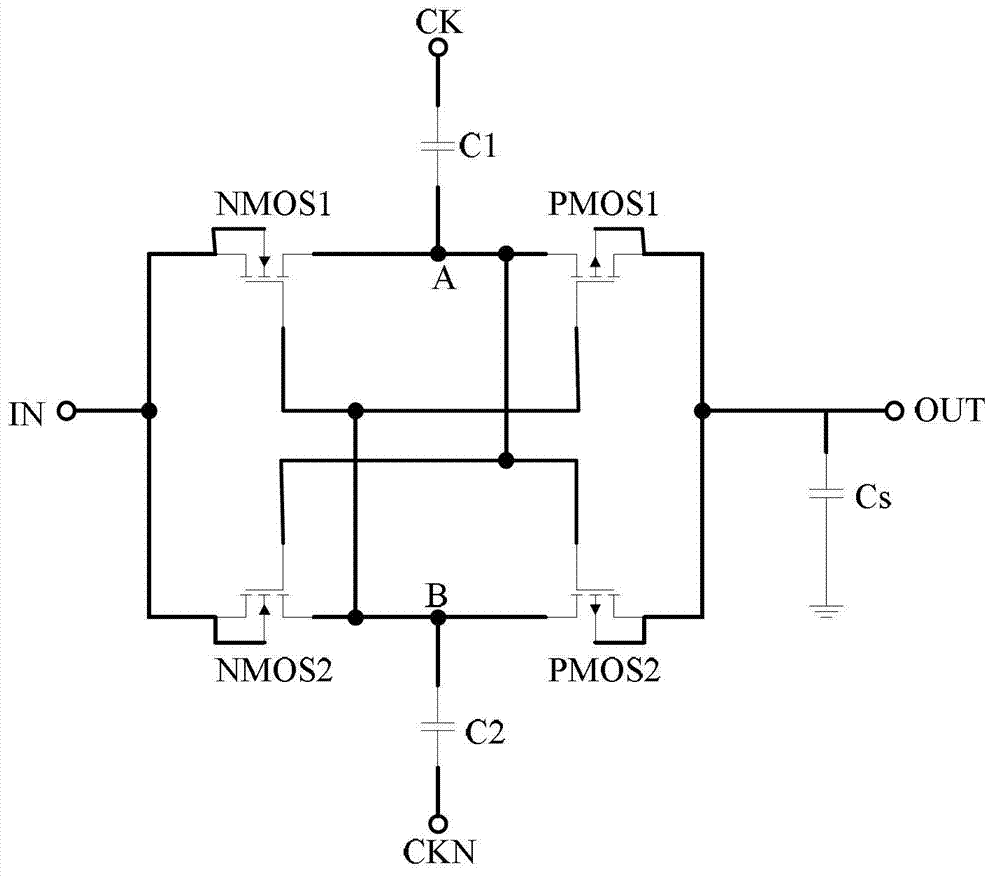
High-performance rectifier diode replaced circuit
ActiveCN102904421AReduce forward voltage dropSolve excessive power consumptionAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionAudio power amplifierLow voltage
The invention discloses a high-performance rectifier diode replaced circuit which comprises a capacitor, a low-voltage clock generator, a charge pump circuit, a band-gap reference circuit, a hysteresis comparator, a driving amplifier and a power metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) pipe and is characterized in that the low-voltage clock generator detects voltages at two ends of a diode pipe and generates clock signals to drive the charge pump circuit; the charge pump circuit detects the voltages at two ends of the diode pipe and stores the charges in the capacitor after the charges are amplified; the voltage stored on the capacitor and the standard voltage output by the band-gap reference circuit are respectively output to the hysteresis comparator for comparison; and when the voltage stored in the capacitor is larger than the standard voltage output by the band-gap reference circuit, the hysteresis comparator outputs starting signals which are amplified by the driving amplifier and then output to the power MOS pipe to drive the power MOS pipe to be conducted. The high-performance rectifier diode replaced circuit can achieve equivalent diode working characteristics through a pulse working mode and can totally replace original selective beacon radar (SBR) devices in performance and dimension.
Owner:CHONGQING SOUTHWEST INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN
Silicon controlled rectifier electrostatic discharge protection circuit structure triggered by grid controlled diode
InactiveCN101826523AEffective protectionDimensional deviation has little effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSilicon-controlled rectifierCMOS
The invention relates to a silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection circuit structure triggered by a grid controlled diode, belonging to the technical field of electronics. Through integrating the grid controlled diode with low breakdown voltage, the trigger voltage of a conventional SCR ESD protection circuit structure is converted to the breakdown voltage of a grid controlled N+ / P well (or N well / P+) node from the breakdown voltage of a P well / N well node, thereby reducing the trigger voltage of the SCR ESD and finally well protecting a circuit in a chip. Moreover, through changing the grid controlled bias voltage of the grid controlled diode, the trigger voltage of the SCR ESD protection circuit structure can be controlled; and through simply adjusting the dimension parameters of a device, the controllable maintaining voltage of the device can be obtained. The structure is suitable for technologies such as CMOS, BiMOS, BCD, SOI and the like, can be connected between an integrated circuit and a power supply and is used as the ESD protection of a power clamp, and can also be connected between the input port and the output port of the integrated circuit and the power supply (ground) and is used as the ESD protection of the input port and the output port.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low-trigger-voltage SCR (semiconductor control rectifier) device used for ESD (electro-static discharge) protection
ActiveCN105609488ALower the trigger voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLow voltageEngineering
The invention belongs to the electro-static discharge protection field for an integrated circuit, and provides a low-trigger-voltage SCR (semiconductor control rectifier) device used for ESD (electro-static discharge) protection used for further lowering the trigger voltage of an LVTSCR (low voltage triggering semiconductor control rectifier) device. The low-trigger-voltage SCR device comprises a first conductive type silicon substrate, a second conductive type well region and a first conductive type well region formed on the silicon substrate, wherein a second conductive type heavily-doped region and a first conductive type heavily-doped region are arranged in each well region separately; the second conductive type heavily-doped region is bridge jointed between the two well regions; a gate oxide layer region is arranged on the silicon surface between the bridge jointed second conductive type heavily-doped region, and the second conductive type heavily-doped region in the first conductive type well region; and the other gate oxide layer region is further arranged on a device-free structural region on the silicon surface in the second conductive type well region; and polysilicon layers on the two gate oxide layer regions are connected through metals. According to the low-trigger-voltage SCR device used for ESD protection, an RC (resistance-capacity) access is introduced into the device, so that the trigger voltage of the SCR device can be further lowered, and in addition, the trigger voltage can be modulated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Bidirectional triode thyristor based on diode auxiliary triggering
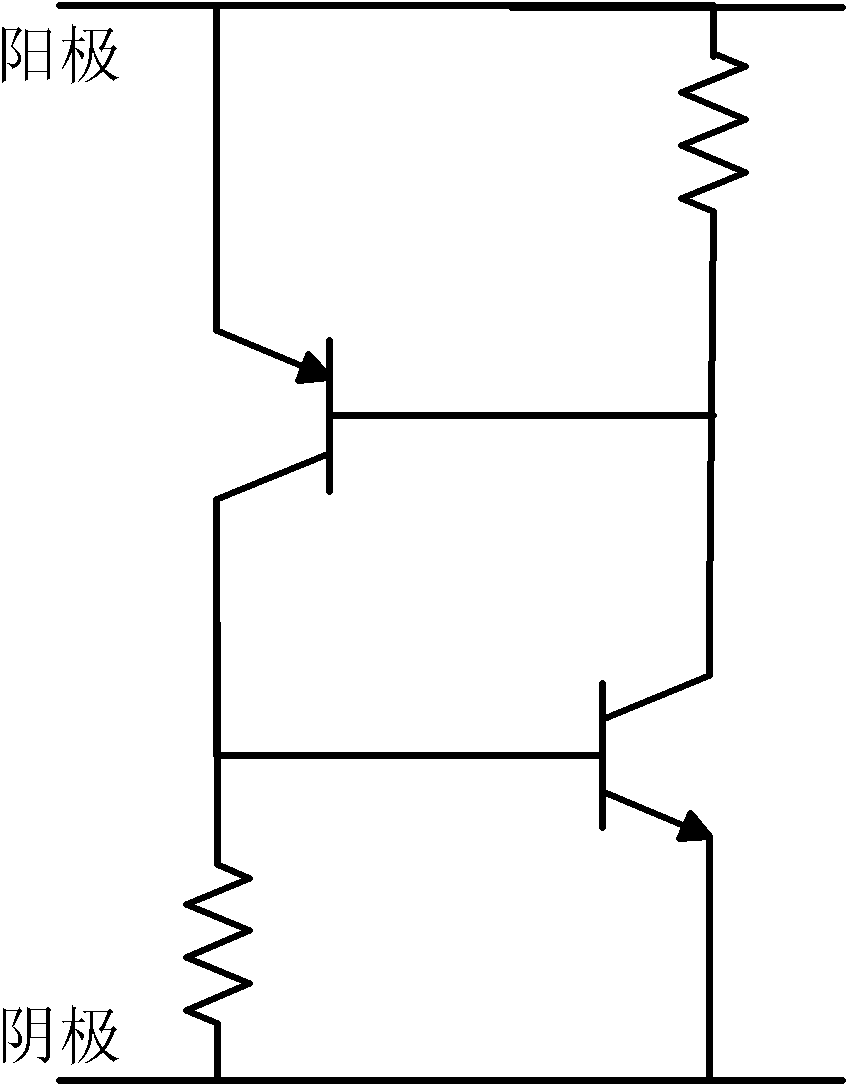
The invention discloses a bidirectional triode thyristor based on diode auxiliary triggering, which comprises a P substrate layer and two diode links, wherein a first N well, a P well and a second N well are arranged on the P substrate layer; a first N plus active implantation area, a first P plus active implantation area and a second N plus active implantation area are arranged on the first N well; a third N plus active implantation area, a second P plus active implantation area and a fourth N plus active implantation area are arranged on the second N well; and the third N plus active implantation area is connected with the anode of a first diode link, and the second N plus active implantation area is connected with the anode of a second diode link. The bidirectional triode thyristor utilizes diodes as auxiliary triggering units, so the thyristor has adjustable and lower forward and reverse breakdown voltages, can be suitable to on-chip electronic static discharge (ESD) protection in a deep sub-micron technology, and can be particularly suitable to the ESD protection and application of a plurality of mixing voltage interface circuits or different power supply areas.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Schottky junction plane explosion switch used for exploding foil initiator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103344151ASmall sizeReduce manufacturing costSpark gaps with auxillary triggeringBlasting cartridgesInsulation layerEngineering
The invention discloses a schottky junction plane explosion switch used for exploding foil initiator and a preparation method of the schottky junction plane explosion switch. The switch comprises a silica-based substrate, a SiO2 insulation layer on the silica-based substrate, a metallic copper layer and a schottky junction bridge zone layer. Compared with the prior art, the schottky junction plane explosion switch has the advantages that the switch is small in size and low in manufacturing cost, and by the utilization of a MEMS (micro electro mechanical system) technology, the switch is easy to integrate with a exploding foil initiation system to achieve microminiaturization of the exploding foil initiation system; the switch containing schottky junctions is low in trigger voltage and capable of resisting stray current and has certain safety, and the effect of controllable excitation energy is achieved through control over the number of the schottky junctions; the switch is a one-time effect device and meets the characteristics of one-time effect of the exploding foil initiation system, and in comparison with a traditional vacuum trigger switch, the usage rate of the switch is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Low trigger voltage SCR structure based on floating trap trigger
ActiveCN107017248ATrigger voltage can be adjustedLower the trigger voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceMOSFET
The invention belongs to the electrostatic discharge protection field of an integrated circuit and especially provides a low trigger voltage SCR structure based on floating trap trigger used for ESD protection. And the structure is used for further reducing a trigger voltage of a LVTSCR device. Through an internal structure design, one floating trap structure is introduced into the device. The floating trap structure is equivalent to one diode structure, an anode is connected to a polycrystalline silicon grid electrode of a PMOS and a cathode is connected to an anode of a SCR. When an ESD pulse is coming, a potential of a floating trap is lower than an anode potential of a SCR device. A potential difference between the two is enough to make the PMOS be started. After a P channel MOSFET is started, a parasitic NPN transistor in the SCR device is triggered to be started, then a parasitic PNP transistor is triggered to be started, and finally the SCR device starts and discharges an ESD current. Therefore, a trigger voltage of the device is determined by the floating trap structure and a parasitic PMOS grid source capacitor so that a purpose of reducing a SCR device trigger voltage can be realized and the trigger voltage can be modulated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
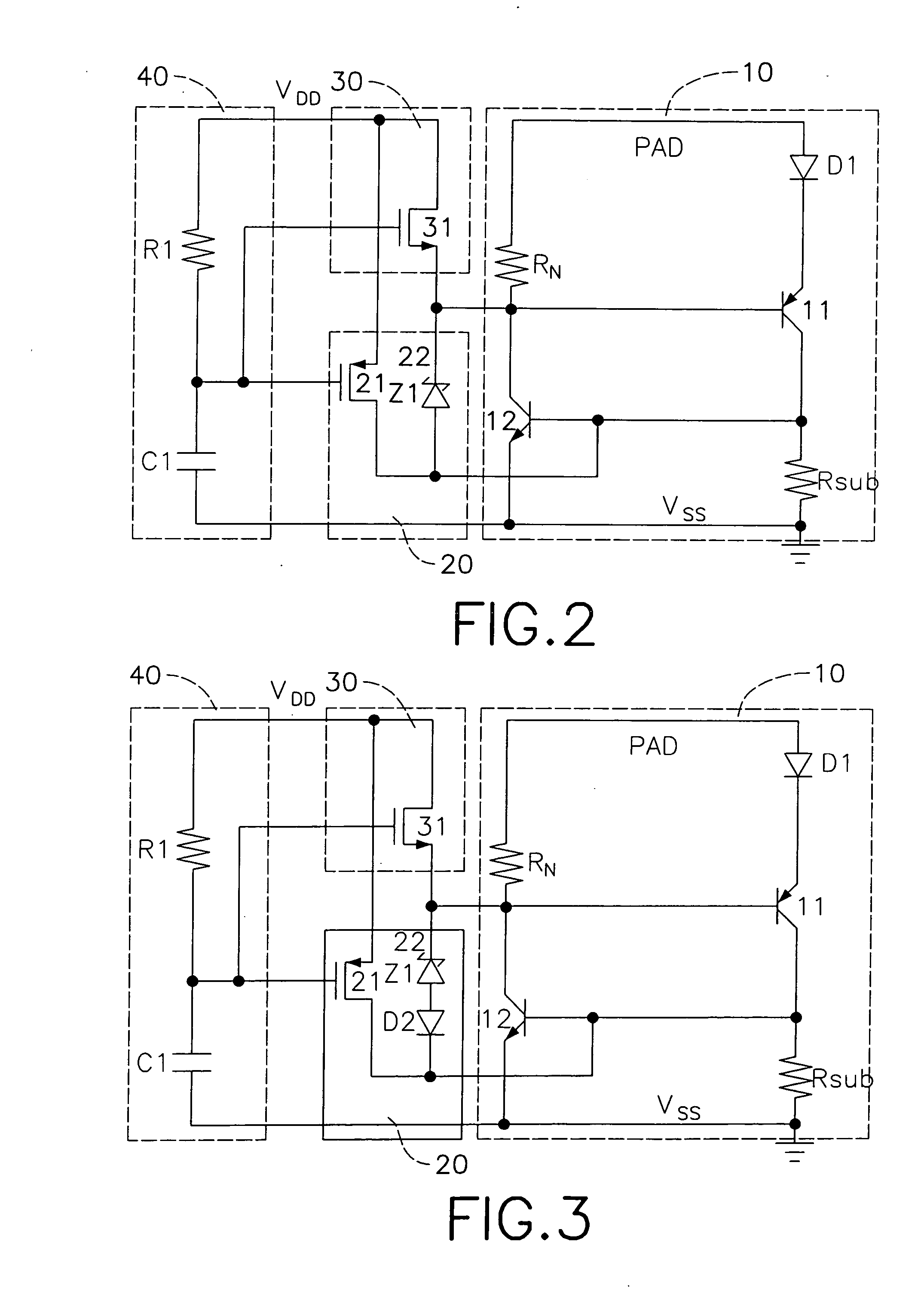
Dual-node capacitor coupled MOSFET for improving ESD performance
InactiveUSRE38319E1Lower the trigger voltageImprove uniform turn-onPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesMOSFETCapacitance
A dual-node capacitor coupling technique is used to lower the trigger voltage and to improve the uniform turn-on of a multi-finger MOSFET transistor. Preferably, each MOSFET is an NMOS device. Specifically, each NMOS device includes a capacitor that is connected between the gate of the NMOS device and the pad terminal. A first resistor is connected between the gate and the p-well, while a second resistor is connected between the p-well and the grounded source. For a positive ESD pulse to VSS, the p-well is pulled up to approximately 0.7 V during the initial ESD event, such that the source junction is forward biased and that the trigger voltage of the NMOS device is lowered. At the same time the gate voltage is coupled within the range of approximately 1 to 2 V to promote the uniform turn on of the gate fingers of the NMOS devices during the initial ESD event.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Controlled silicon structure used for CMOS electrostatic discharge protection
ActiveCN101174629AMeet the needs of integrationMeet integration needsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSEngineering
The invention discloses a thyristor structure for CMOS static discharge protection, which is capable of both-way break-over and both-way flyback. The invention is characterized in that: a deep N well is longitudinally arranged on a P type substrate; a second N well, a second P well, a first N well, a first P well and another second N well are arranged transversely in parallel on the deep N well, and a P+ area and an N+ area are respectively transversely arranged in the second P well and the first P well in parallel; wherein, the P+ areas are close to the second N well, the N+ areas are near to the first N well, and the P+ areas and the N+ areas are divided by field oxide. The invention has the advantages of avoiding the defects in the traditional SCR structure such as single-way flyback feature, and meeting the demands for integration level.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Low trigger voltage silicon control rectifier and its circuit
InactiveCN101047178AIncrease the trigger voltageLower the trigger voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSilicon-controlled rectifierElectrical conductor
The present invention relates to a low voltage triggering silicon controlled rectifier (SCR). It is characterized by that it utilizes addition of second doped zone which is set between the described low voltage triggering silicon controlled rectifier anode and its parasitic PNP transistor emitter to raise the holding voltage when the described low voltage triggering silicon controlled rectifier is triggered. The described low voltage triggering silicon controlled rectifier includes a semiconductor substrate with first conducting type and a grid. The described semiconductor substrate contains a first doped zone with second conducting type, a second doped zone with first conducting type, a third doped zone with second conducting type, a fourth doped zone with second conducting type and a fifth doped zone with first conducting type. The described grid is characterized by utilizing lower trigger voltage to trigger the described low voltage triggering silicon controlled rectifier.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOG TECH INC
Electrostatic discharge circuit
InactiveUS20060189189A1Low triggering voltageFast reaction timeTransistorIncorrect coupling preventionElectrostatic dischargeStatic electricity
An electrostatic discharge circuit, connected between at least three terminals, the electrostatic discharge circuit including at least one electrostatic discharge circuit element further including at least one circuit element including a body in a floating state. The body in a floating state may provide a path to discharge an electrostatic current. The electrostatic discharge circuit may be a pull-up circuit, a plurality of pull-up circuits, a pull-down circuit, a plurality of pull-down circuits, a power clamp, a plurality of power clamps, or other similar circuit or circuits. The at least three terminals may include one or more power terminals, one or more ground terminals, and / or one or more I / O terminals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
BiCMOS electrostatic discharge power clamp
InactiveUS7068482B2Avoid problemsLower the trigger voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesBiCMOSDrain current
A BiCMOS electrostatic discharge (ESD) protecting circuit is triggered by a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) for achieving ESD protection. Due to the layout area of the BJT ESD protecting circuit being smaller than the layout area of an RC circuit, layout area can be reduced. Moreover, the BJT reduces leakage current problems and has a lower triggering voltage. Therefore, the BJT in the ESD protecting circuit can effectively reduce problems of a higher triggering ESD voltage and leakage current.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Electrostatic discharge prevention circuit based on complementary SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier)
InactiveCN101834433ALower the trigger voltageLow electrostatic discharge protectionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrostatic dischargePositive power
The invention discloses an electrostatic discharge prevention circuit based on a complementary SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) for preventing the electrostatic discharge among an input / output end of a core circuit, a positive power line and a negative power line. The electrostatic discharge prevention circuit comprises a power supply clamping unit of which both ends are respectively connected with a positive power line and a negative power line, a PNPNP type bidirection SCR of which both connection terminals are respectively connected with the positive power line and an input / output end of the core circuit, and an NPNPN type bidirection SCR of which both connection terminals are respectively connected with the negative power line and an input / output end of the core circuit. The prevention scheme of the complementary SCR utilizes the power supply clamping unit as an auxiliary trigger unit, can realize the electrostatic discharge prevention of low trigger voltage, and has reliable electrostatic discharge prevention on the internal core circuit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Electrostatic discharge protection apparatus
ActiveUS20130208379A1High carrier mobilityLower the trigger voltageTransistorDiodeSemiconductorElectrostatic discharge protection
A semiconductor ESD protection apparatus comprises a substrate; a first doped well disposed in the substrate and having a first conductivity; a first doped area having the first conductivity disposed in the first doped well; a second doped area having a second conductivity disposed in the first doped well; and an epitaxial layer disposed in the substrate, wherein the epitaxial layer has a third doped area with the first conductivity and a fourth doped area with the second conductivity separated from each other. Whereby a first bipolar junction transistor (BJT) equivalent circuit is formed between the first doped area, the first doped well and the third doped area; a second BJT equivalent circuit is formed between the second doped area, the first doped well and the fourth doped area; and the first BJT equivalent circuit and the second BJT equivalent circuit have different majority carriers.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
SCR electrostatic protection device and electrostatic protection circuit
InactiveCN108336082ALow spurious noiseLower the trigger voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice formEngineering
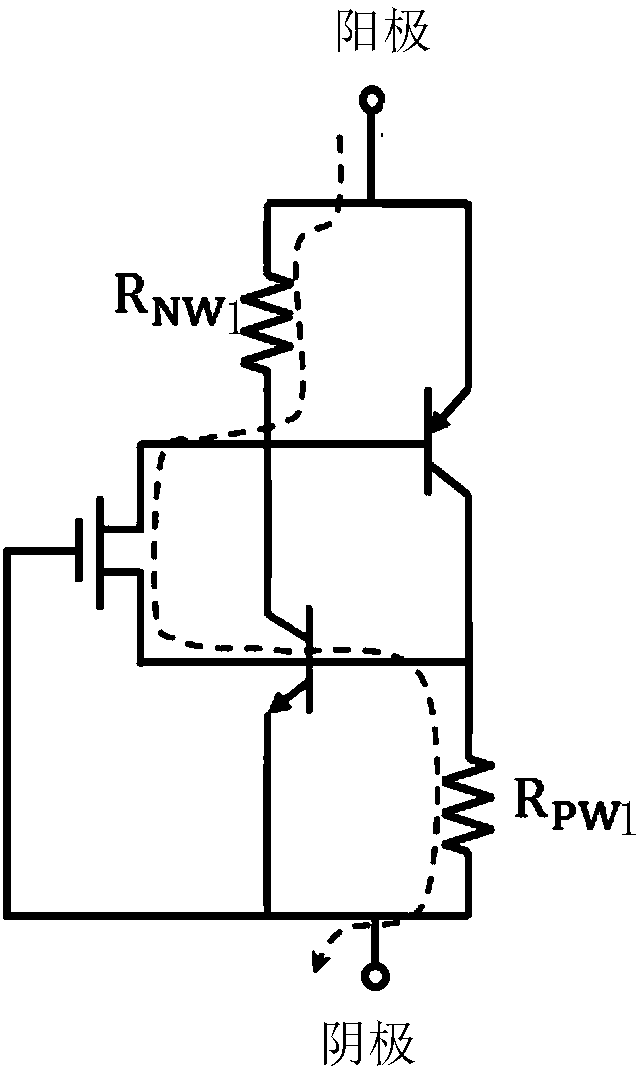
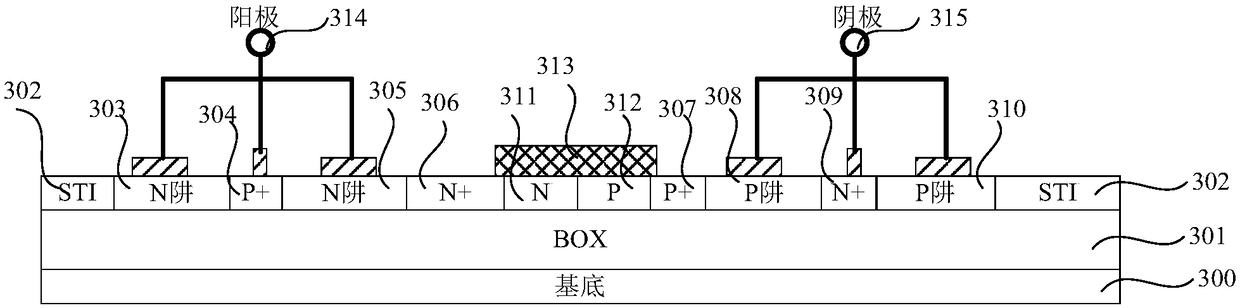
The invention provides an SCR electrostatic protection device and an electrostatic protection circuit. The SCR electrostatic protection device formed in a continuous active region of a top semiconductor layer on an insulating layer includes two N wells encircling a P doping region of an SCR and two P wells encircling an N doping region of the SCR to form a finger type diode structure, so that a parasitic PNP transistor and a parasitic NPN transistor of the SCR are formed; an additional N doping region adjacent to one N well and an additional P doping region adjacent to one P well are added between each two adjacent N well and P well and thus a parasitic gate controlled diode or PN junction diode is generated between the N well and the P well, so that the base electrode of the parasitic PNPtriode is connected to the base electrode of the parasitic NPN triode by the parasitic gate controlled diode or PN junction diode. According to the SCR electrostatic protection device and the electrostatic protection circuit, the low SCR trigger voltage and high maintaining voltage are provided and electrostatic protection is provided for the integrated circuit formed by processes like an SOI.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Longitudinal-BJT-triggered SCR device used for ESD protection
The invention belongs to the field of electronic technologies, and particularly provides a longitudinal-BJT-triggered SCR device used for ESD protection. The longitudinal-BJT-triggered SCR device (VBTSCR) introduces an extra triggering path on the basis of a traditional LSCR device. An ESD injection layer is introduced into a first conduction type well region, so as to form a longitudinal-structure base region floating NPN transistor. The ESD injection layer is a P-type doped region with a medium doping concentration, and the doping concentration thereof is between a drain / source heavily-dopedactive region concentration and a well region doping concentration. According to the SCR device, a common-emitter collector junction avalanche breakdown voltage BV<CEO> of the longitudinal-structurebase region floating NPN transistor is very low, when the base region floating NPN transistor serves as a triggering device of the SCR, significant reduction of the triggering voltage of the SCR device can be realized, thereby realizing the effect of providing effective ESD protection for circuits in an advanced nanometer technology.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Static suppressor with overcurrent protection functions, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103943291AExcellent over-current and over-voltage protectionImprove reliabilityCurrent responsive resistorsResistor manufactureSuppressorCopper
The invention discloses a static suppressor with overcurrent protection functions, and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises following steps: (1) a ceramic substrate is selected; (2) a front side electrode and a back side electrode are formed via printing on the upper surface and the lower surface of the ceramic substrate respectively, and are dried; (3) an upper surface electrode is formed via printing on the upper surface and the lower surface, or one selected from the upper surface and the lower surface of the ceramic substrate, and is dried; (4) the electrodes above are subjected to sintering; (5) insulating layers are formed via respective printing on the surface electrodes; (6) the insulating layers are subjected to sintering; (7) the surface electrodes and the insulating layers are subjected to cutting so as to form gaps; (8) printing of pressure sensitive material layers is performed so as to fill the gaps, and solidification is realized; (9) printing of a first protection layer is carried out, and solidification is realized; (10) melt layers are formed; (11) printing of a second protection is carried out, and solidification is realized; (12) first cutting is carried out; (13) side surface internal electrodes are formed; (14) second cutting is carried out; (15) copper internal electrodes are formed; and (16) nickel coatings and tin coatings are formed via electroplating so as to obtain the static suppressor with overcurrent protection functions.
Owner:NANJING SART SCI & TECH DEV
Latch-up-free ESD protection circuit using SCR
InactiveUS7102864B2Improve discharge efficiencyQuick switchTransistorPulse automatic controlOvervoltageTransient mode
A latch-up-free ESD protection circuit using SCR is disclosed, in which an SCR is connected between the input pad and the negative power supply; a turn-on switch and a turn-off switch are connected between the positive power supply VDD (or the input pad) and the SCR; and a transistor gating circuit is connected to the turn-on switch and the turn-off switch to direct the operation of the SCR. When overvoltage stress develops over the input pad in the fast-transient mode, the turn-on switch enables the NPN transistor to switch on the SCR to form a discharging path for electrostatic discharge; and when overvoltage stress is released, the turn-off switch enables the PNP transistor to switch off the SCR, thus making it immune to any latch-up after the overvoltage stress is released, and having the advantages of fast triggering, low trigger voltage, no latch-up, and full ESD protection in the active and passive modes.
Owner:KING BILLION ELECTRONICS
Method for manufacturing body-contact structure of partially depleted SOI MOSFET
ActiveCN101621009AReduce possession effectInhibition of possession effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETBody contact
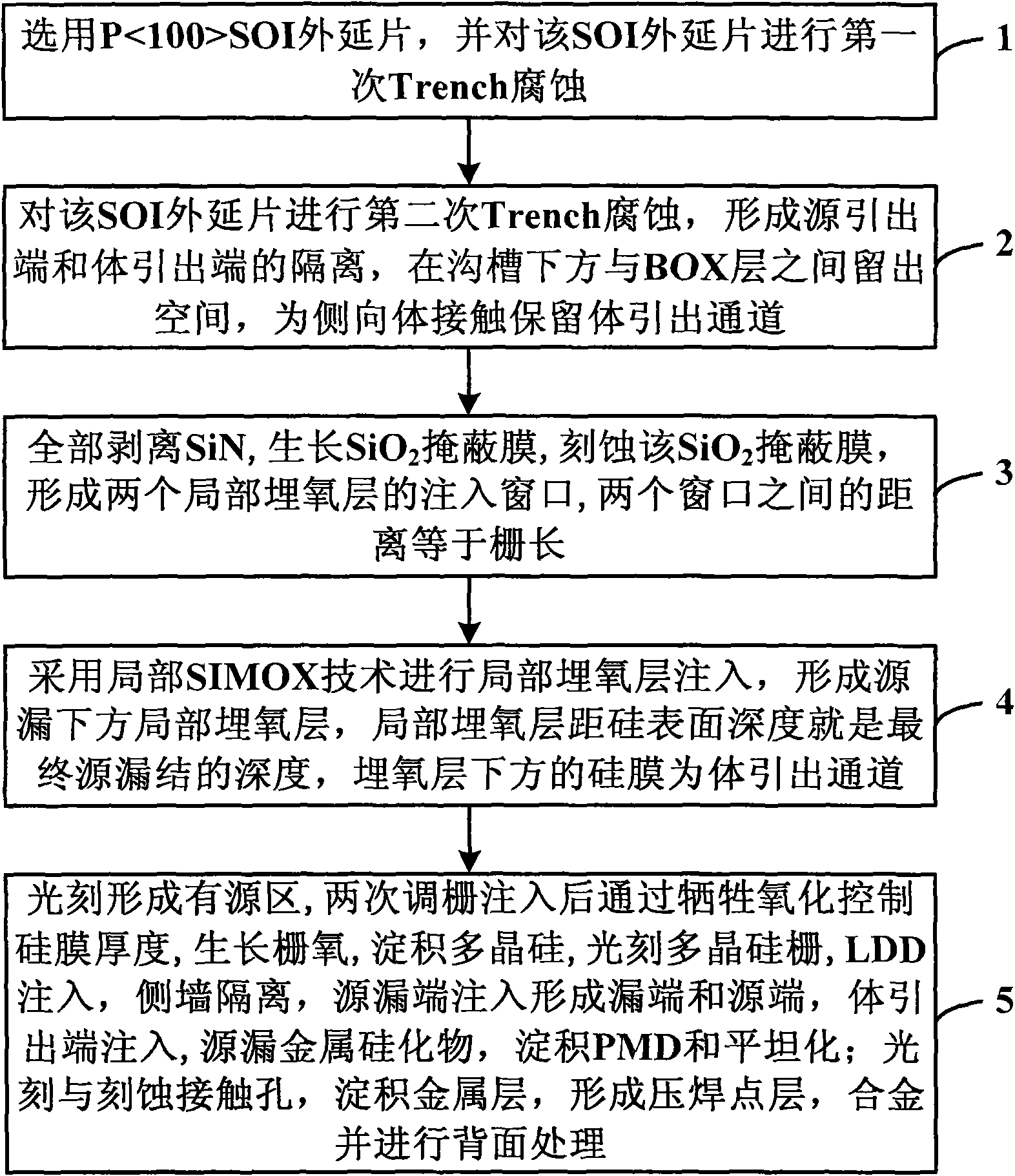
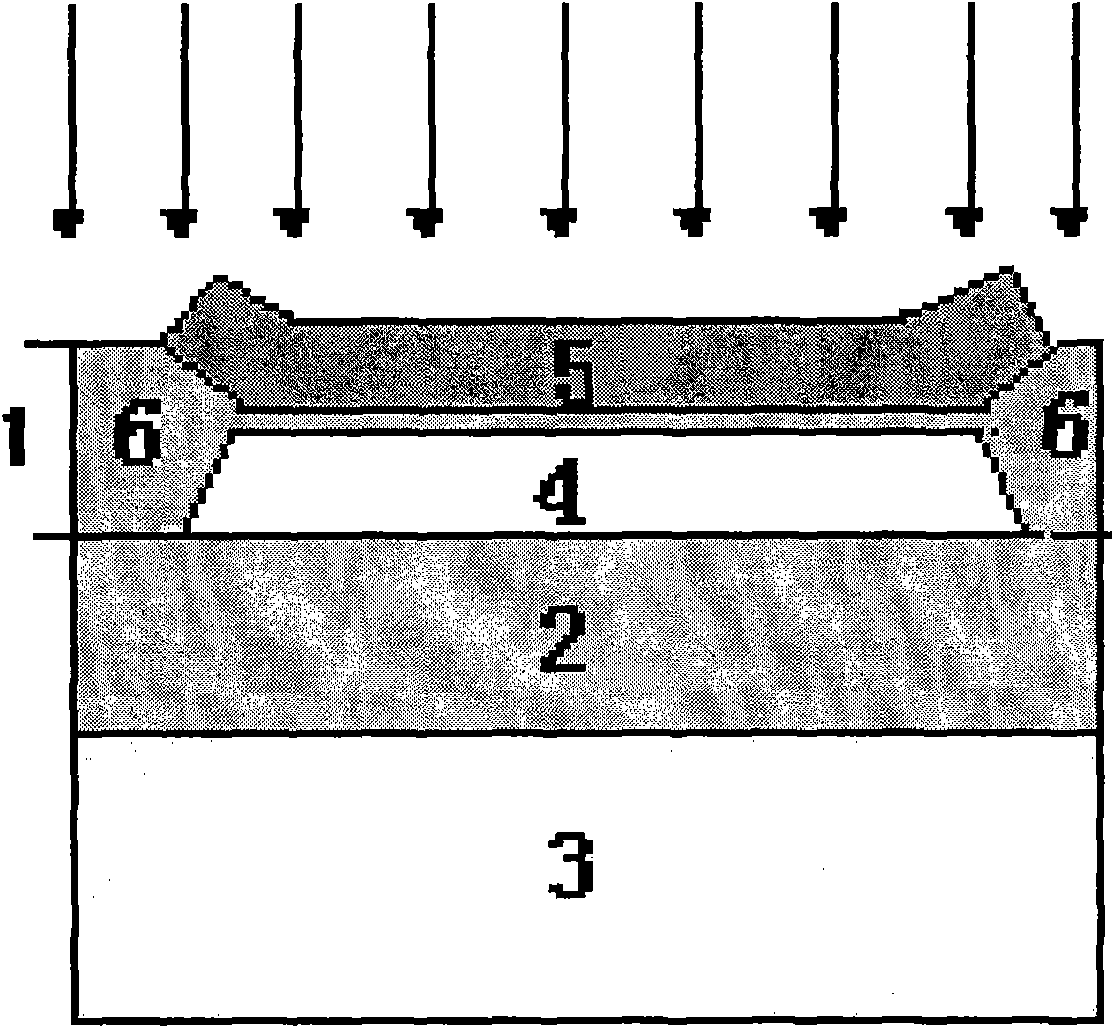
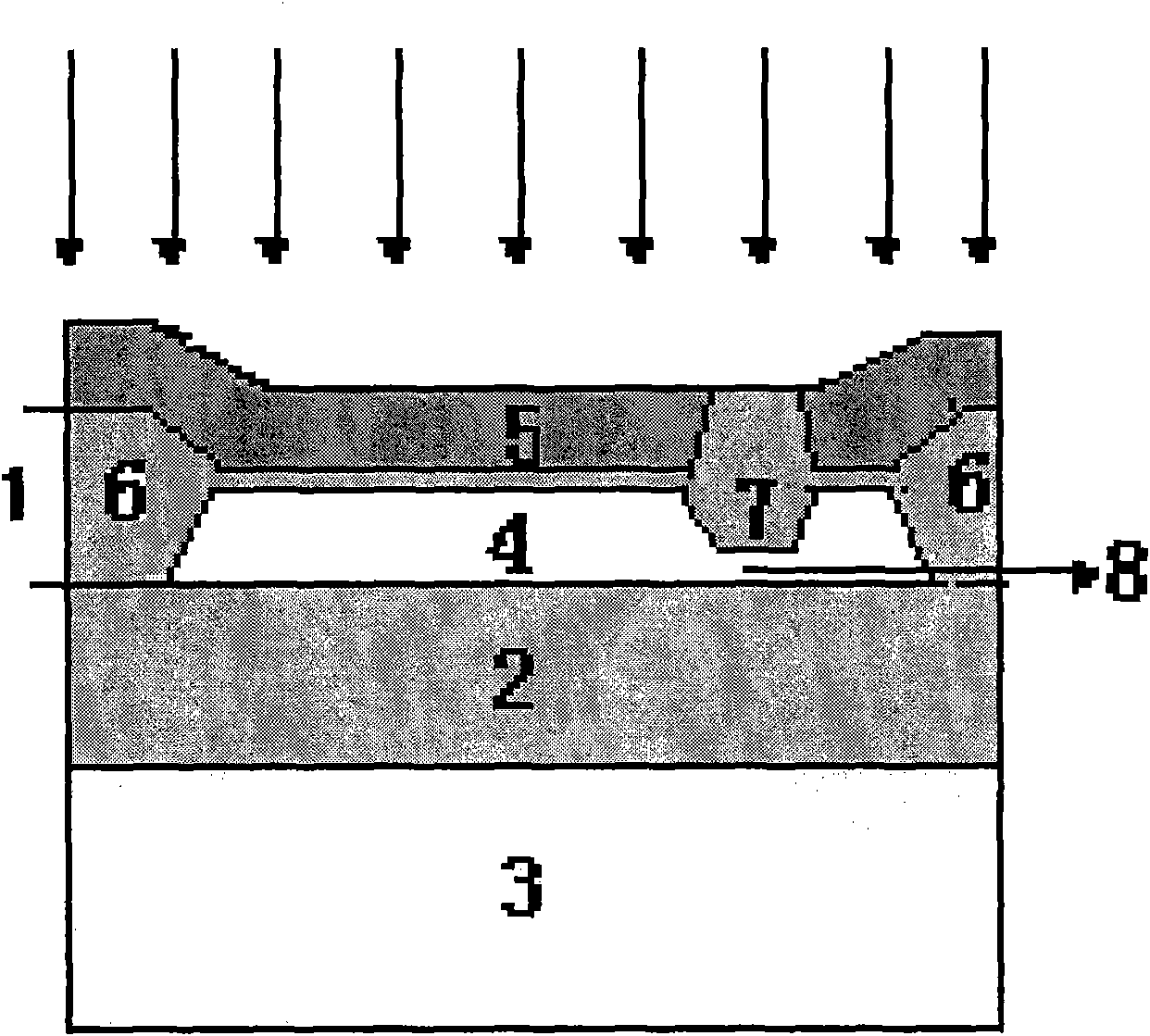
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a body-contact structure of a partially depleted SOI MOSFET, which comprises the following steps: selecting a P<100>SOI epitaxial wafer and subjecting the SOI epitaxial wafer to primary Trench corrosion; performing secondary Trench corrosion to form an isolation layer between a source leading-out end and a body leading-out end and preserving a space between the bottom of a trench and a BOX layer to preserve a body leading-out channel for lateral body contact; stripping SiN completely, growing a SiO2 mask film and etching the SiO2 mask film to form injection windows of two local buried oxide layers; injecting the local buried oxide layers to form local buried oxide layers under source and drain regions; forming an active region by photoetching, performing tuned grid injection twice, controlling the thickness of a silicon film by sacrificial oxidation, growing gate oxide, depositing polysilicon, etching a polysilicon gate, performing LDD injection and side wall isolation, performing source and drain end injection to form a drain end and a source end, performing body leading-out end injection, growing source and drain silicide and performing PMD and planarization; and photoetching and etching contact holes, depositing a metal layer to form a pad layer and alloy, and performing back treatment.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGKE XINWEITE SCI & TECH DEV
Bidirectional ESD protection anti-latch-up device of holosymmetric dual-grid-control-diode triggering SCR structure
ActiveCN107658295ALower the trigger voltageOpen fastSolid-state devicesDiodeCapacitanceHemt circuits
The invention discloses a bidirectional ESD protection anti-latch-up device of a holosymmetric dual-grid-control-diode triggering SCR structure, and the device can be used for improving the capabilityof an IC chip in resisting ESD. The device mainly consists of a P substrate, a P epitaxial part, a first N well, a P well, a second N well, a first N+ injection region, a first P+ injection region, asecond N+ injection region, a second P+ injection region, a third N+ injection region, a third P+ injection region, a fourth N+ injection region, a first polysilicon gate, a first thin gate oxide layer covering the first polysilicon gate, a second polysilicon gate, and a second thin gate oxide layer covering the second polysilicon gate. The device has a resistance-capacitance coupling auxiliary triggering path under the action of ESD stress, does not need an additional layout area, also can make the most of the advantages of low triggering voltage of a resistance-capacitance coupling circuitand the short start time, and shortens the voltage hysteresis amplitude of the device. In addition, the device also employs the conduction characteristics of the gate control diodes, improves the potential of a parasitic well resistor of the N well, and speeds up the starting of a current releasing path of the SCR structure. Moreover, the device has two ESD current releasing paths and a holosymmetric structure, facilitates the improvement of the ESD robustness of the device, and can achieve the bidirectional protection of ESD.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Electrostatic Discharge Protection Device Comprising a Silicon Controlled Rectifier
ActiveUS20170012036A1Lower the trigger voltageHigh resistivityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon-controlled rectifierHigh resistivity
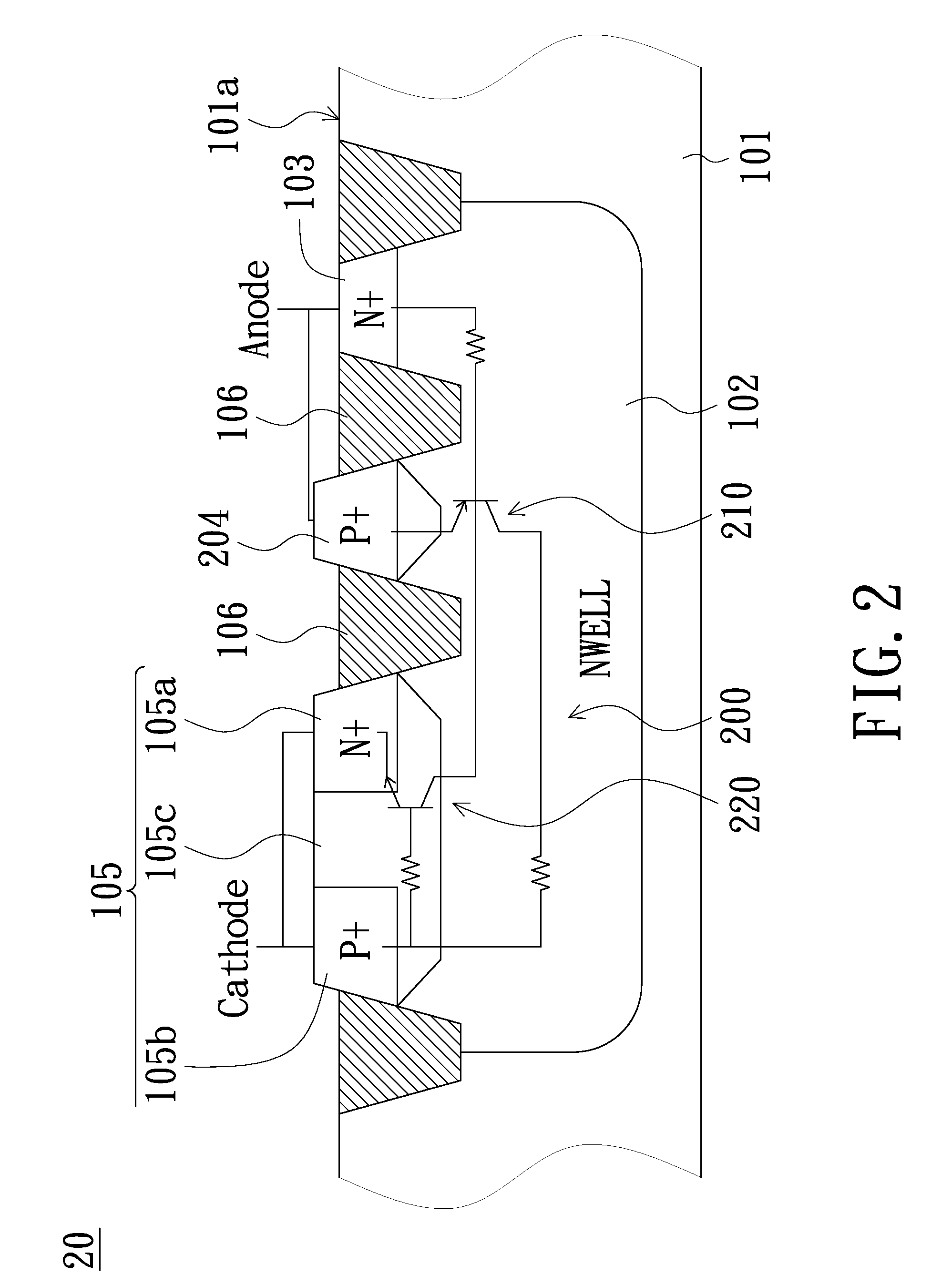
An electrostatic discharge protection device including a silicon controlled rectifier. In one example, the silicon controlled rectifier includes a first n-type region located in a semiconductor substrate. The silicon controlled rectifier also includes a first p-type region located adjacent the first n-type region in the semiconductor substrate. The silicon controlled rectifier further includes an n-type contact region and a p-type contact region located in the first n-type region. The silicon controlled rectifier also includes an n-type contact region and a p-type contact region located in the first p-type region. The silicon controlled rectifier further includes a blocking region having a higher resistivity than the first p-type region. The blocking region is located between the n-type contact region and the p-type contact region in the first p-type region for reducing a trigger voltage of the silicon controlled rectifier.
Owner:NXP BV
Manufacturing method for ESD gate grounding NMOS transistor
InactiveCN101452851ANo need to increase the areaReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
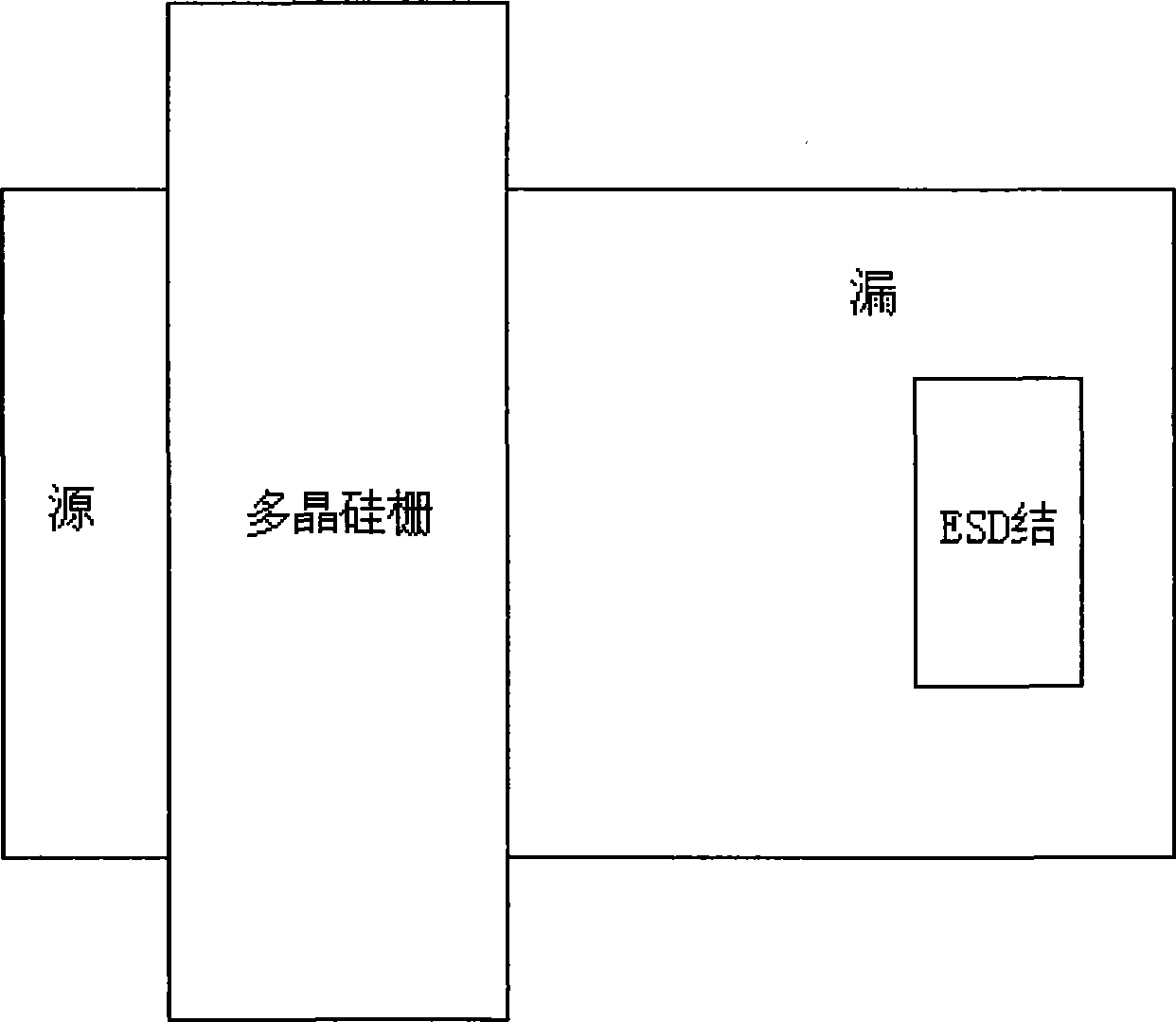
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing an ESD gate grounded NMOS transistor. Through photoetching, the drain end and the edge of the grid electrode of the ESD transistor are in certain distance; a region (a drift region) between the drain end and the grid electrode is only provided with a lightly-doped source drain (LDD) region and no high-dosage drain adulteration; as square resistance of the LDD region is much larger relative to the high doped drain end, the method can ensure that larger series resistance is obtained under the condition of shorter length of the drift region without increasing area occupied by the transistor, thereby saving the area of the transistor; moreover, as the breakdown voltage of an LDD junction is lower than the drain end, the transistor decides the trigger voltage through the LDD junction, well achieves the aim of reducing the trigger voltage, does not need any extra ESD photoetching and ESD ion injection, thereby simplifying a process and saving cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUA HONG NEC ELECTRONICS
Complementary-type SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) structure triggered by diode string in an auxiliary way
InactiveCN101771040ALower the trigger voltageWafer Area ReductionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitPositive power
The invention discloses a complementary-type SCR structure triggered by a diode string in an auxiliary way. In the structure, two bipolar transistors form a first controlled silicon for ESD (Electro-Static discharge) protection between a positive power line and a chip pin to be protected; another two bipolar transistors form a second controlled silicon for ESD protection between the chip pin to be protected and a negative power line; and a bipolar transistor in the first controlled silicon and the second controlled silicon to form a third controlled silicon for ESD protection between the positive power line and the negative power line. The invention adopts the diode string to reduce the triggering voltage of each controlled silicon and is particular suitable for ESD protection in an integrated circuit by a deep submicron process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Silicon controlled device with double-conduction path
InactiveCN102148242AStrongIncrease the electric field strengthSolid-state devicesDiodeSilicon-controlled rectifierPower circuits
The invention discloses a silicon controlled device with a double-conduction path. The silicon controlled device comprises a P well and an N well, wherein an N+ injection region and a Pbody region are spanned between the P well and the N well. The N+ injection region spanned between the P well and the N well is used for realizing reduction of the silicon controlled trigger voltage; and the Pbody region at a junction between the N well and the P well is used for realizing separation between a silicon controlled surface current path and a silicon controlled internal current path. Compared with the common SCR (silicon controlled rectifier) structure which has the defects that more currents are concentrated on the surface of the device, and the conduction uniformity is bad, the silicon controlled device with the double-conduction path has simple structure, good conduction uniformity, high ESD (electro-static discharge) efficiency and good robustness and is suitable for electrostatic discharge protection of high voltage circuits and power circuits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
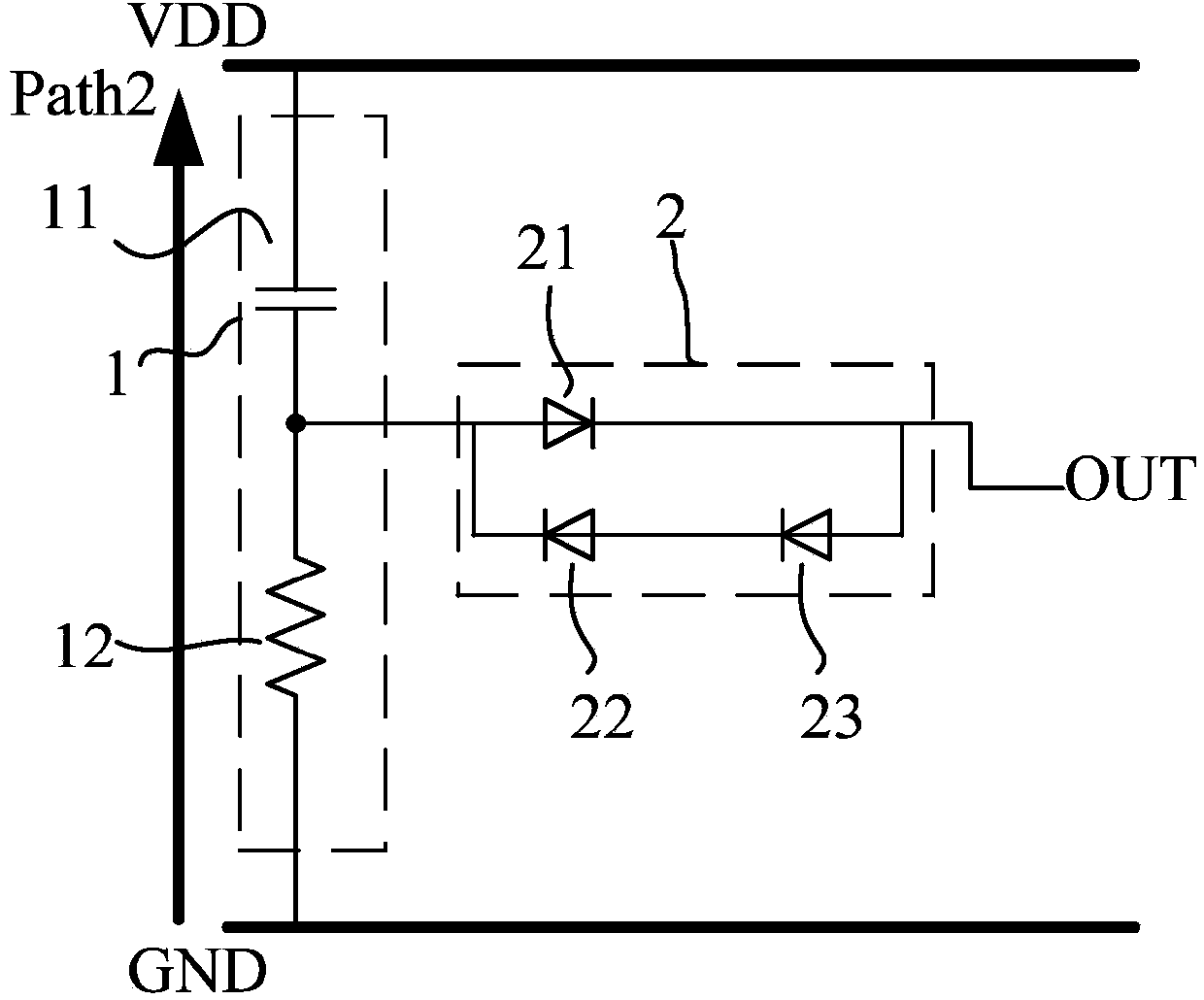
Anti-latch-up trigger circuit for ESD (Electronic Static Discharge)
InactiveCN104037748AMaximum current capabilityLower the trigger voltageEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentSilicon-controlled rectifierCapacitance
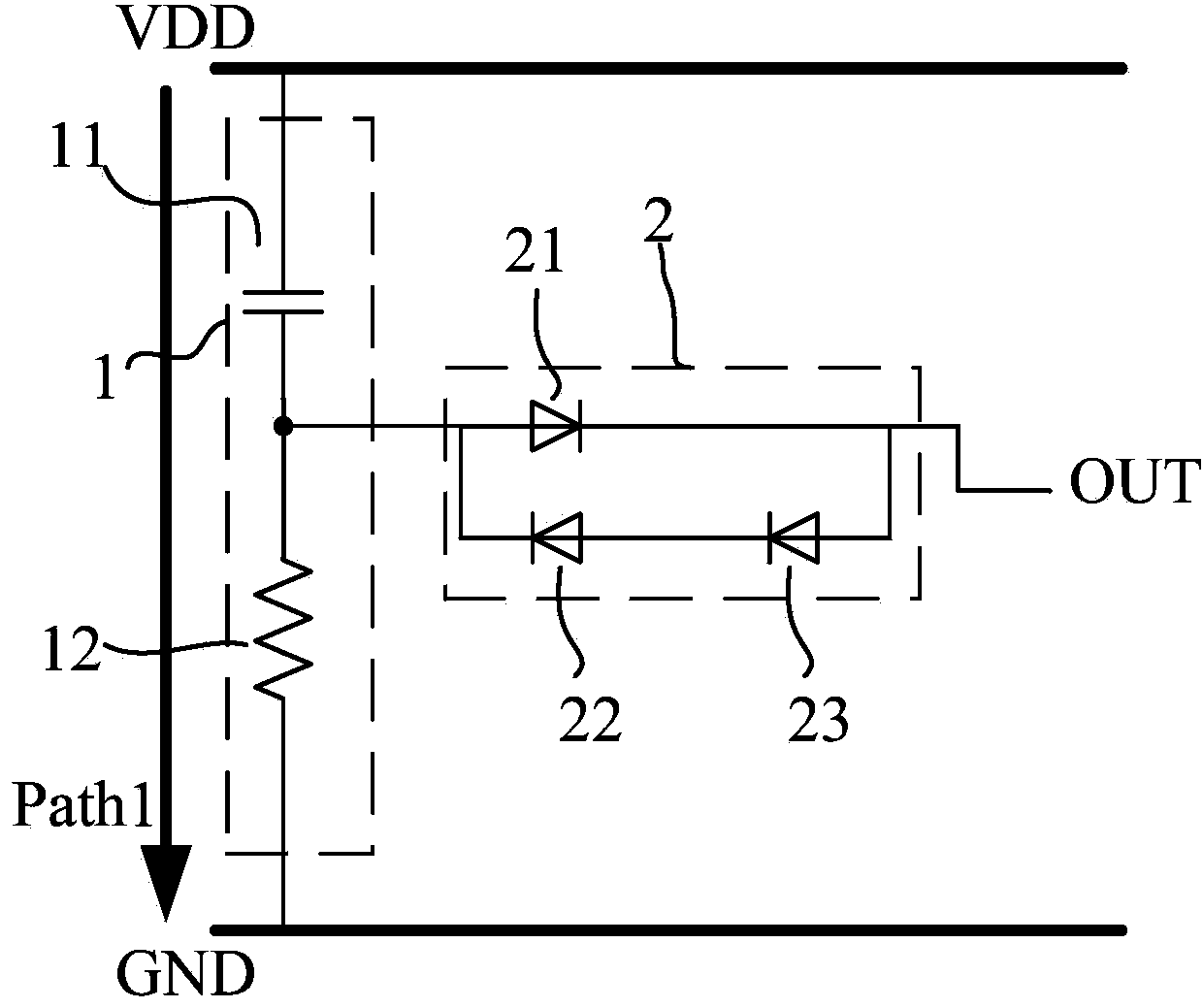
The invention relates to the electronic circuit technology, in particular to an anti-latch-up trigger circuit for ESD. The circuit comprises a detection circuit 1, an output stage circuit 2 and an SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) which are connected in sequence; the detection circuit is composed of a capacitor C11 and a resistor R12, and a power supply VVD is connected with the ground GND after sequentially passing through the capacitor C11 and the resistor R12; the output stage circuit is composed of a diode D21, a diode D22, a diode D23, the positive electrode of the diode D21 is connected with the power supply VDD after passing through the C11, the negative electrode of the diode D21 is connected with the positive electrode of the diode D23, the negative electrode of the diode D23 is connected with the positive electrode of the diode D22, and the negative electrode of the diode D22 is connected with the positive electrode of the diode D21; the gate pole of the SCR is connected with the negative electrode of the diode D21. The anti-latch-up trigger circuit for ESD has the advantages of having significant effects on maximizing the current capability of the SCR and reducing the trigger voltage of the SCR and being capable of capturing the falling edge of the ESD pulse and outputting negative voltage to turn off the SCR structure. The anti-latch-up trigger circuit is particularly suitable for ESD.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com