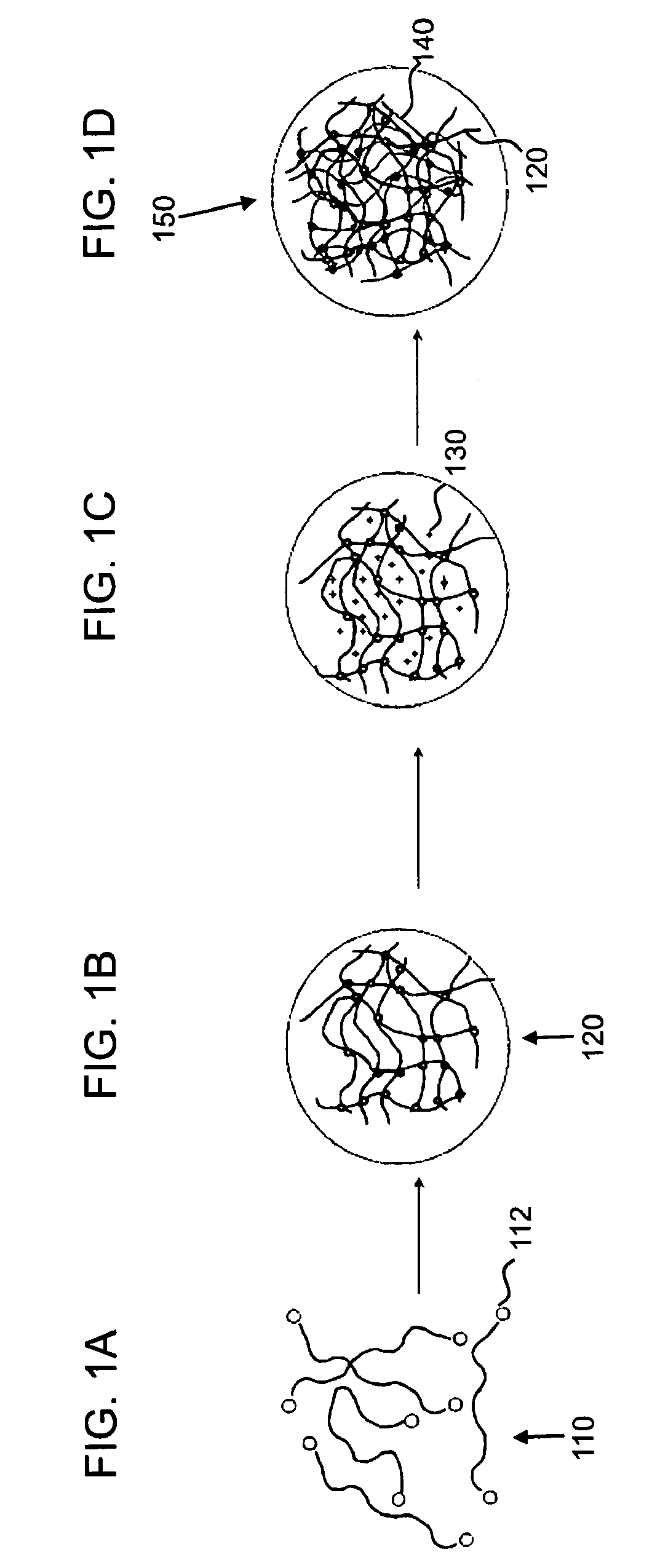
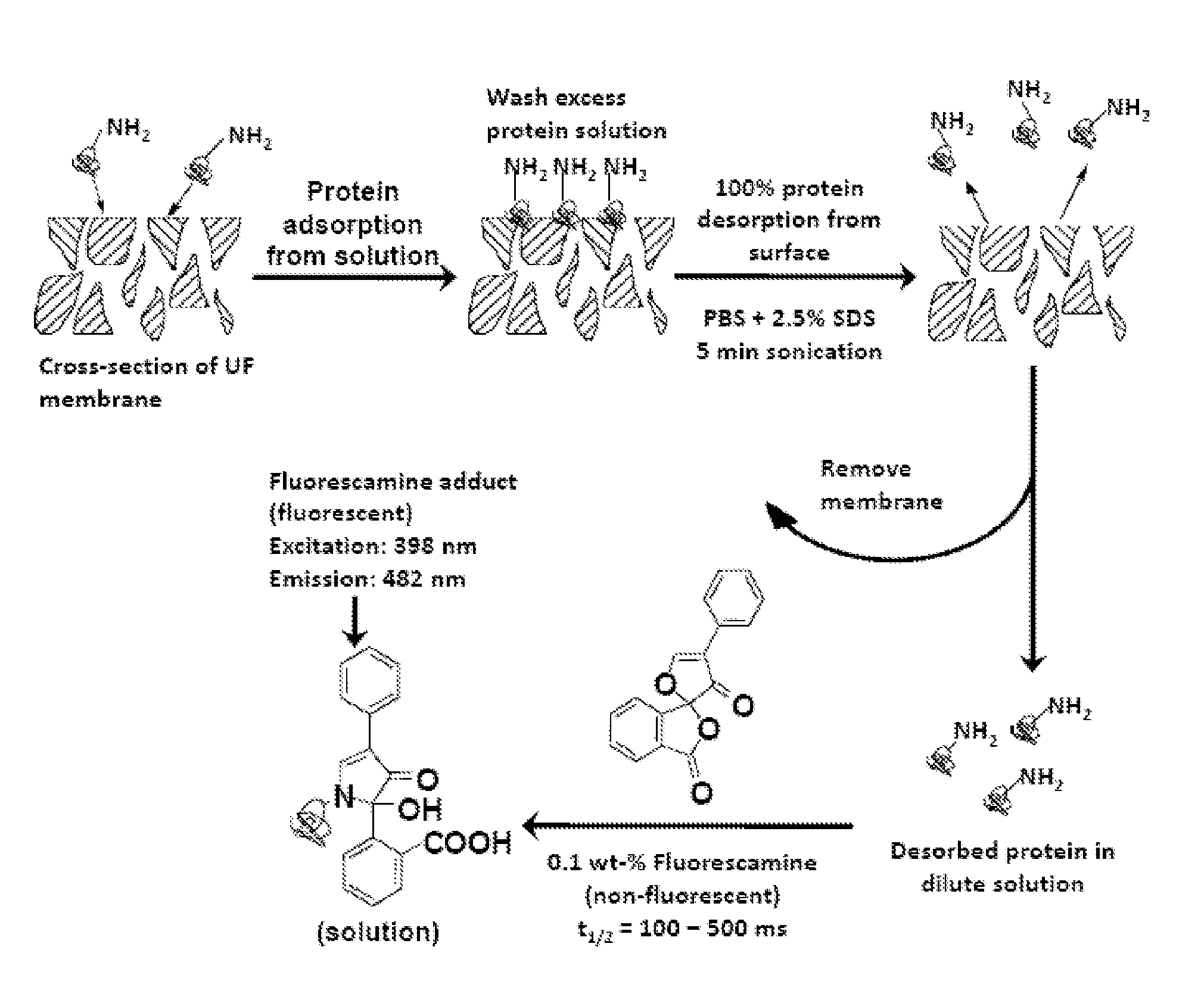
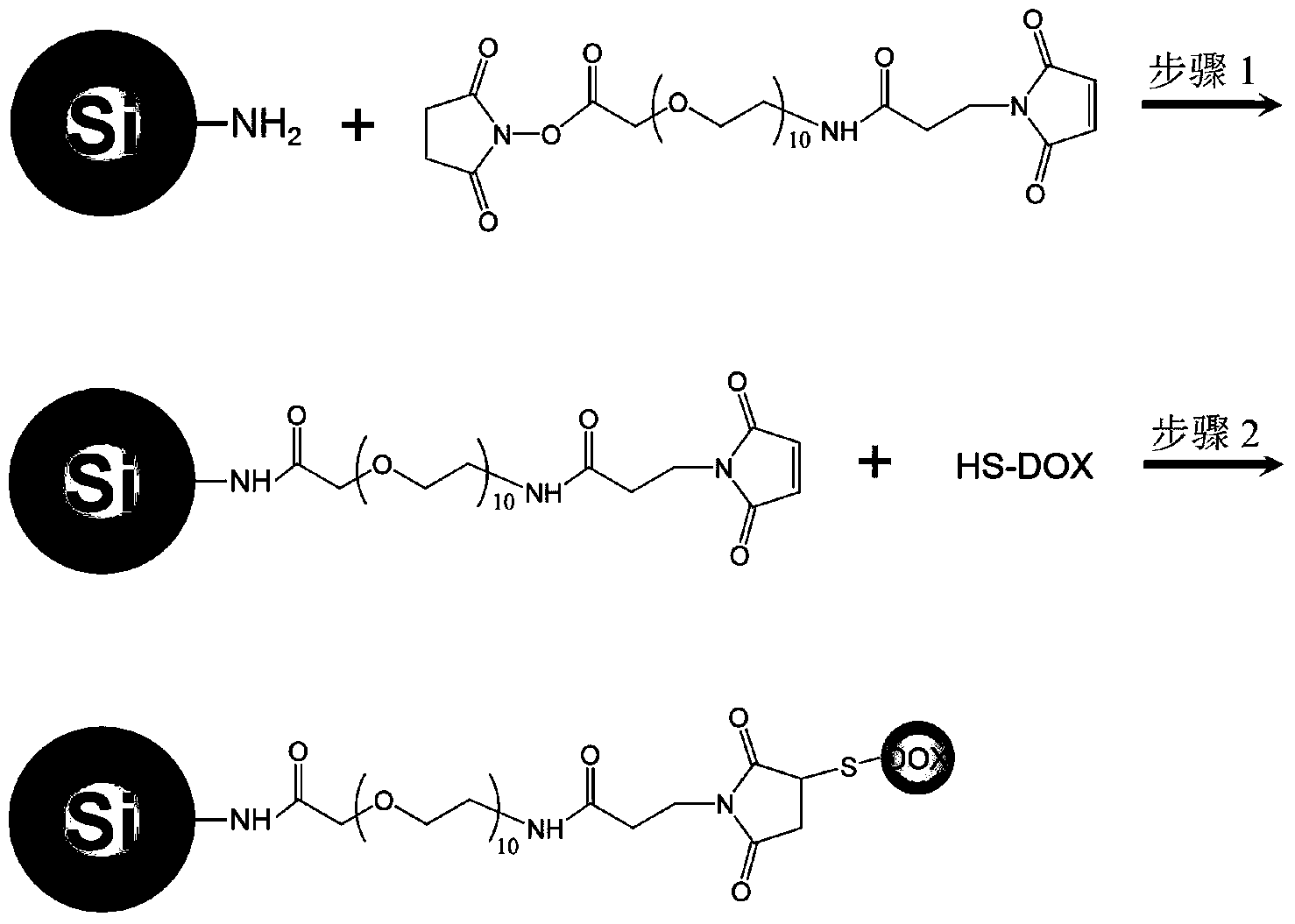
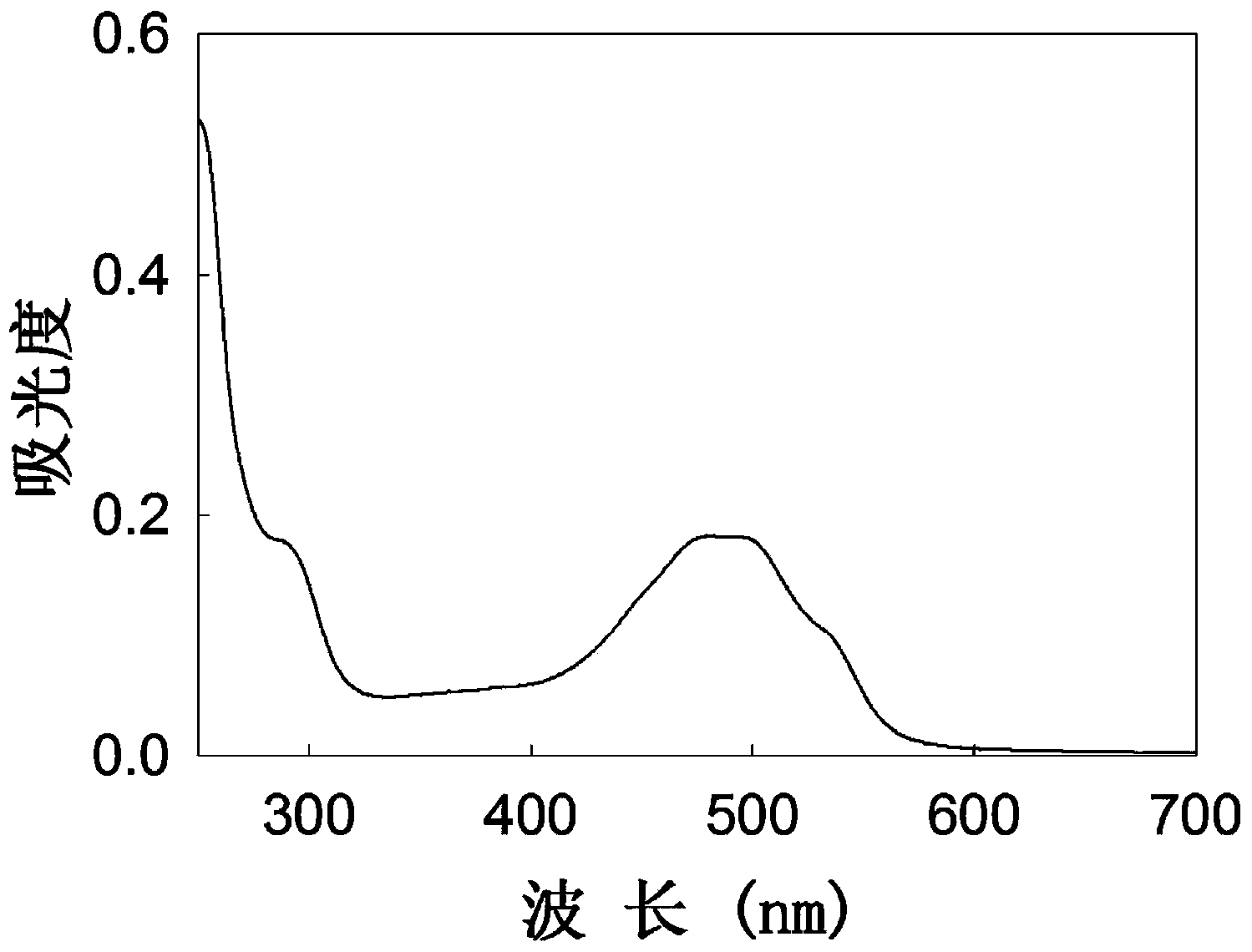
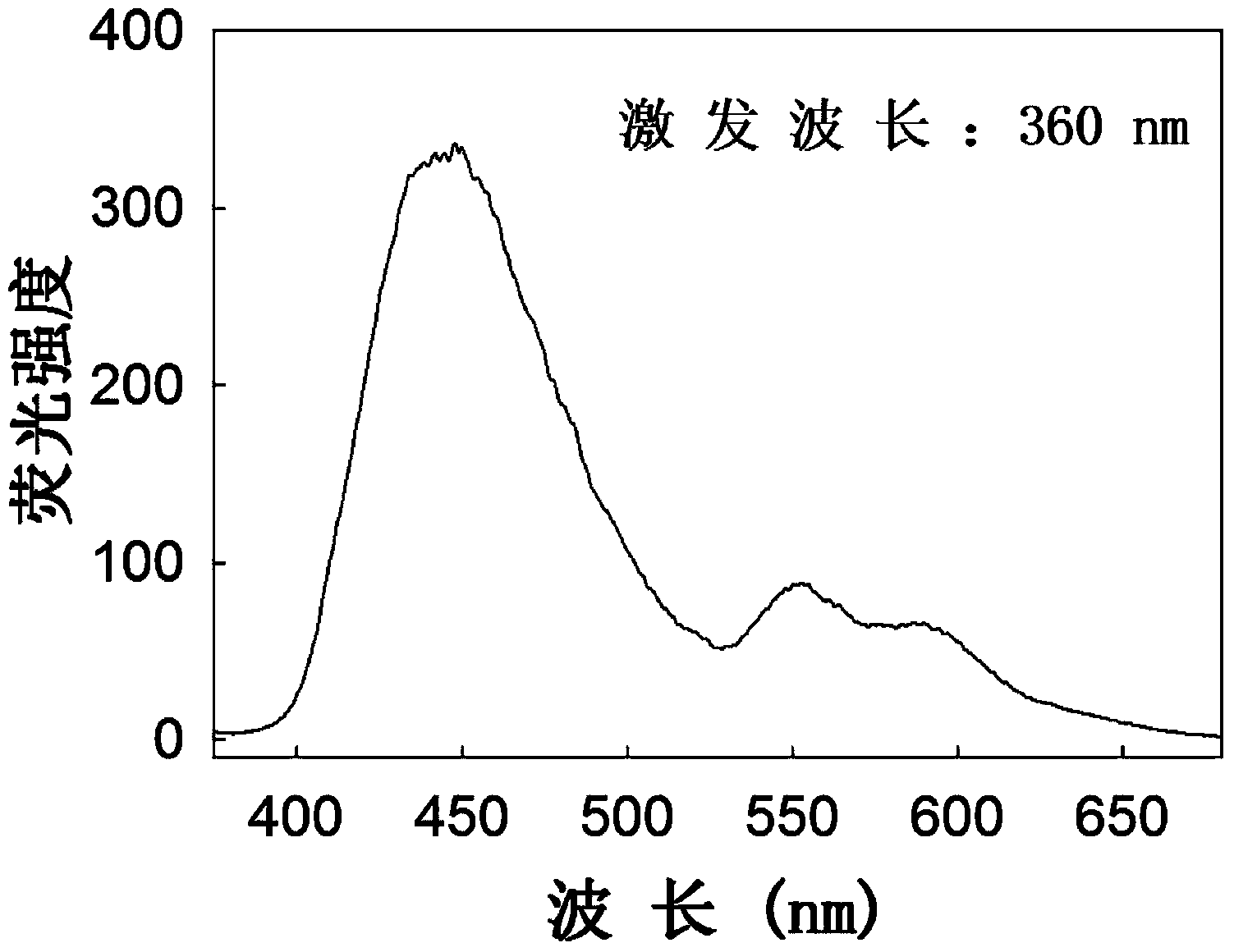
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
540 results about "Protein adsorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
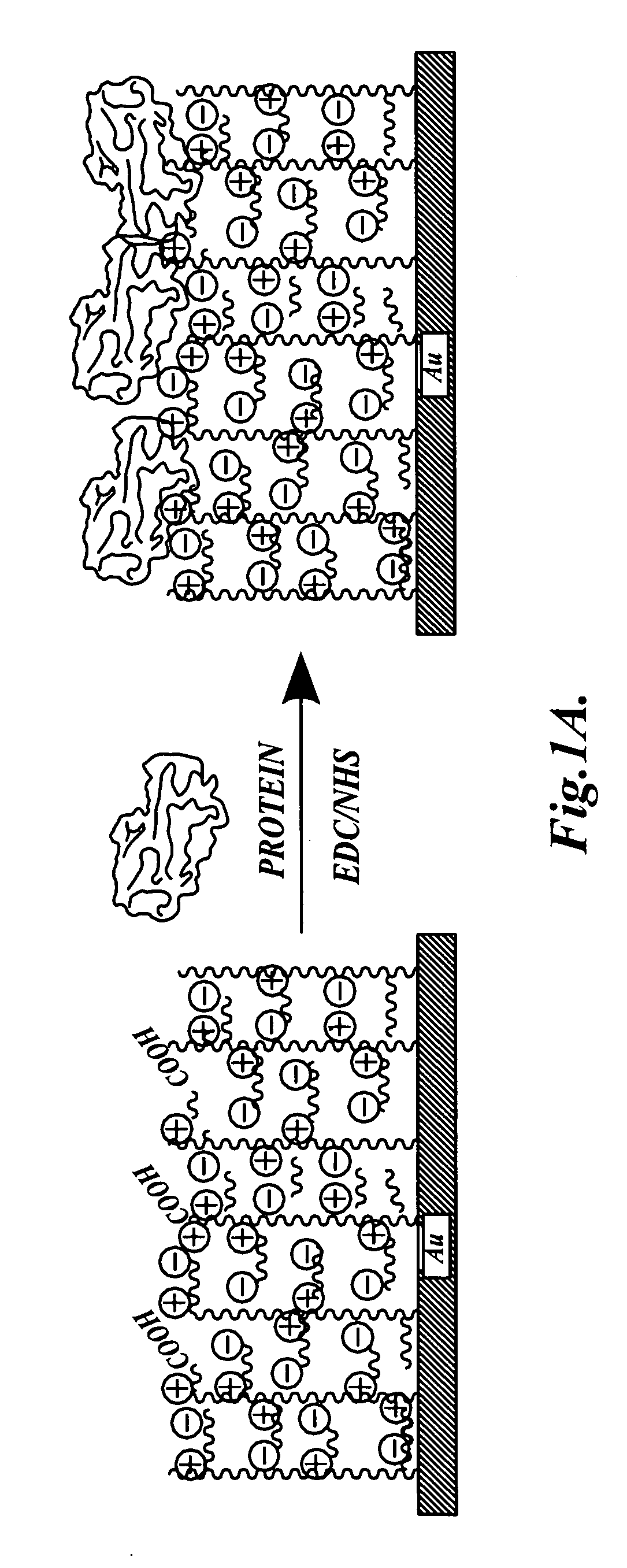
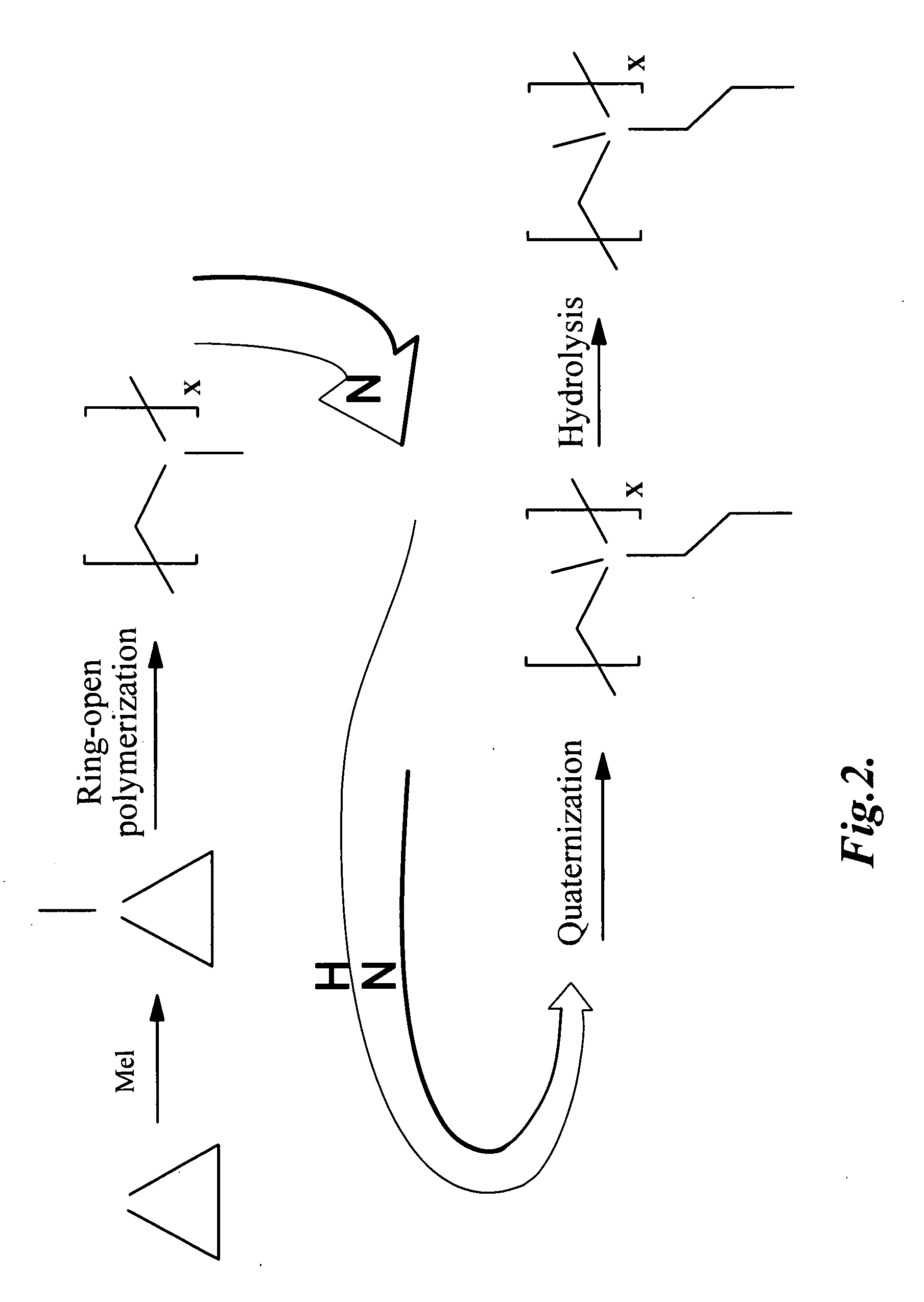
Adsorption (not to be mistaken for absorption) is the accumulation and adhesion of molecules, atoms, ions, or larger particles to a surface, but without surface penetration occurring. The adsorption of larger biomolecules such as proteins is of high physiological relevance, and as such they adsorb with different mechanisms than their molecular or atomic analogs. Some of the major driving forces behind protein adsorption include: surface energy, intermolecular forces, hydrophobicity, and ionic or electrostatic interaction. By knowing how these factors affect protein adsorption, they can then be manipulated by machining, alloying, and other engineering techniques to select for the most optimal performance in biomedical or physiological applications.
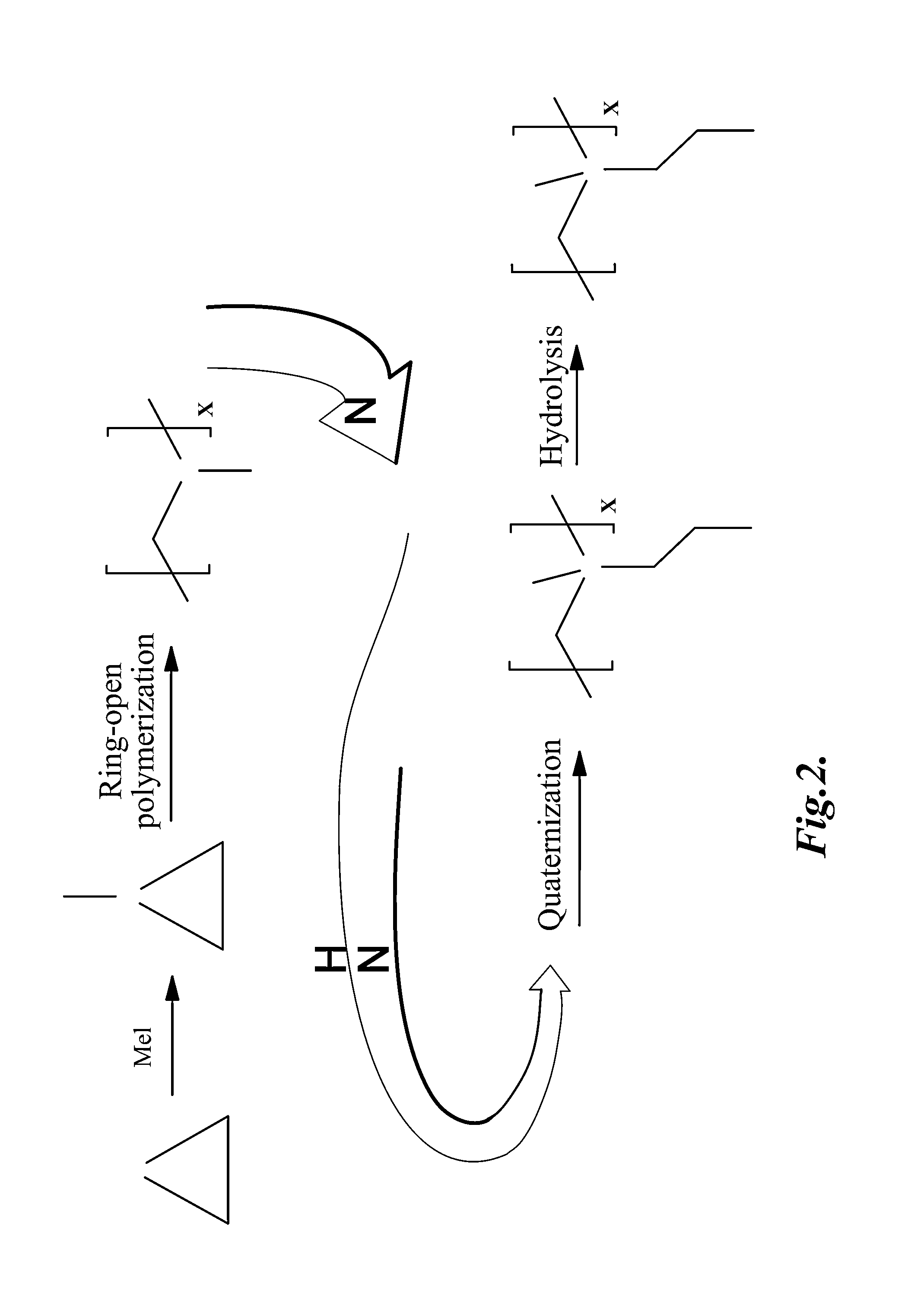
Non-leaching non-fouling antimicrobial coatings
InactiveUS20090155335A1Solve the lack of flexibilityPromote adequate mobilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDendrimerFiber
Compositions containing one or more types of membrane-targeting antimicrobial agents immobilized on a substrate with activity in relevant biological environments, and methods of making and using thereof, are described herein. The antimicrobial agents retain their activity in the presence of blood proteins and / or in vivo due to improved molecular structures which allow for cooperative action of immobilized agents and hydrophilic chemistries which resist non-specific protein adsorption. Suitable molecular structures include branched structures, such as dendrimers and randomly branched polymers. The molecule structures may also include hydrophilic tethers which provide both flexibility and resistance to non-specific protein adsorption. The membrane targeting antimicrobial agent coatings can be applied to a variety of different types of substrates including medical implants such as vascular grafts, orthopedic devices, dialysis access grafts, and catheters; surgical tools, surgical garments; and bandages. The substrates can be composed of metallic materials, ceramics, polymers, fibers, inert materials such as silicon, and combinations thereof. The compositions described herein are substantially non-leaching, resistant to non-specific protein adsorption, and non-hemolytic.
Owner:ARROW INT INC
Method for producing nanostructures on a surface of a medical implant
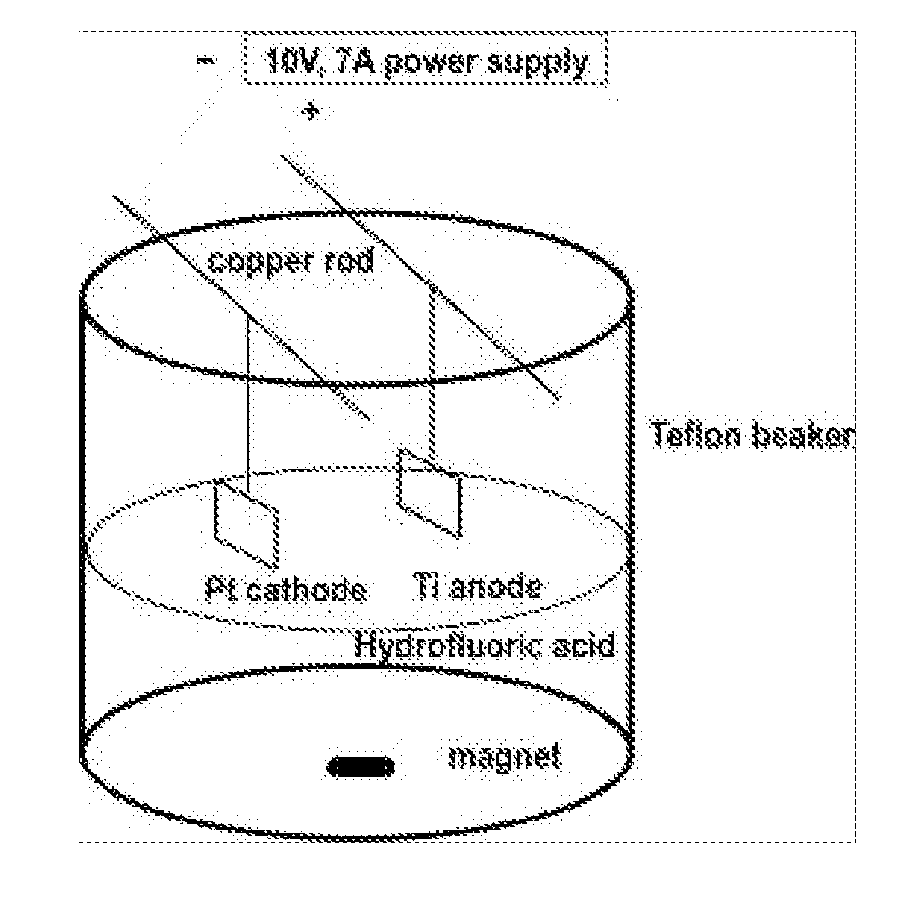
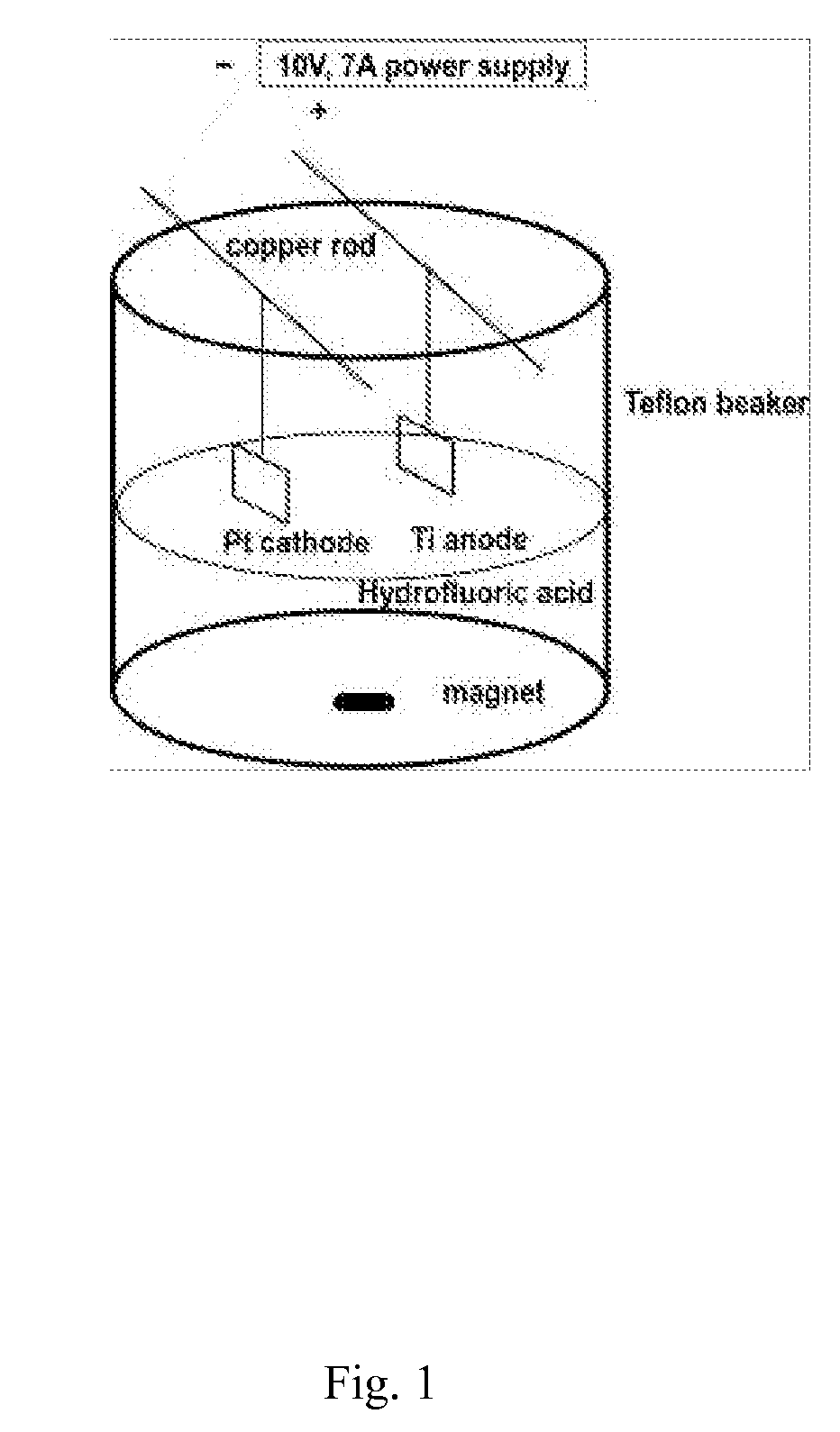
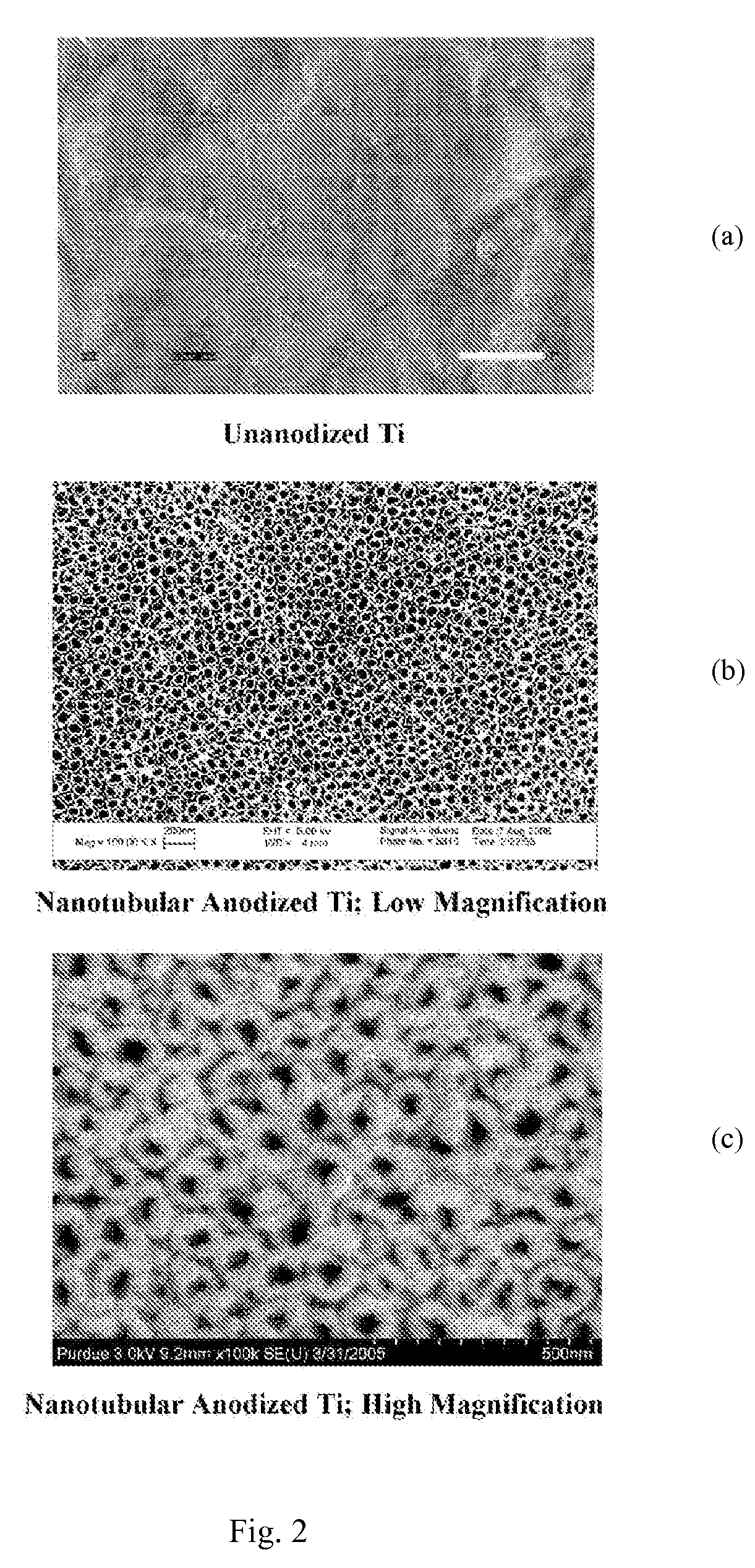
InactiveUS20110125263A1Enhanced and increased in vivo chondrocyte functionalityImprove adhesionSurface reaction electrolytic coatingPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPorosityIn vivo
A method for treating a surface of a medical implant to create nanostructures on the surface that results in increased in-vivo chondrocyte adhesion to the surface. Further, disclosed is a method to fabricate a drug delivery system. The drug delivery system includes a medical implant that has undergone a surface treatment process that results in the modification of the surface configuration and topography. The modified surface acts as a depot or reservoir for loaded biological material, biologic agents or pharmaceutical products. Additionally, a device for delivering pharmaceutical products or other biological materials is disclosed. The device includes integrally attached nanostructures that retain or adsorb the loaded pharmaceutical products and / or biological materials. Further disclosed is a medical implant that includes a surface configured to allow for and regulate protein adsorption. The surface of the medical implant has a layer of nanostructures rigidly attached with varying porosity and orientation that allow for surface protein adsorption to be controlled.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials
ActiveUS20100099160A1Vegetable proteins working-upOn/in organic carrierCell adhesionBiological materials
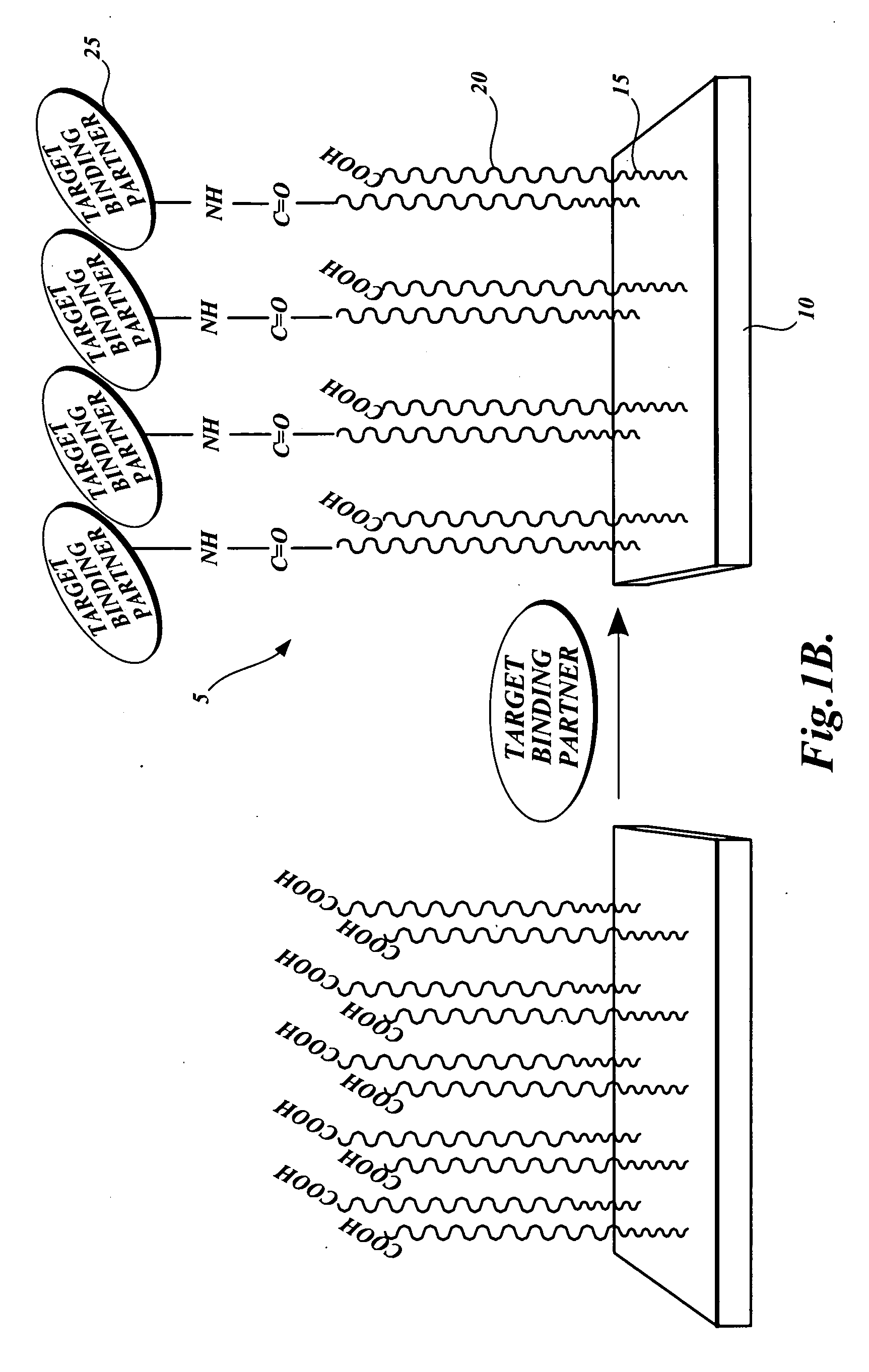
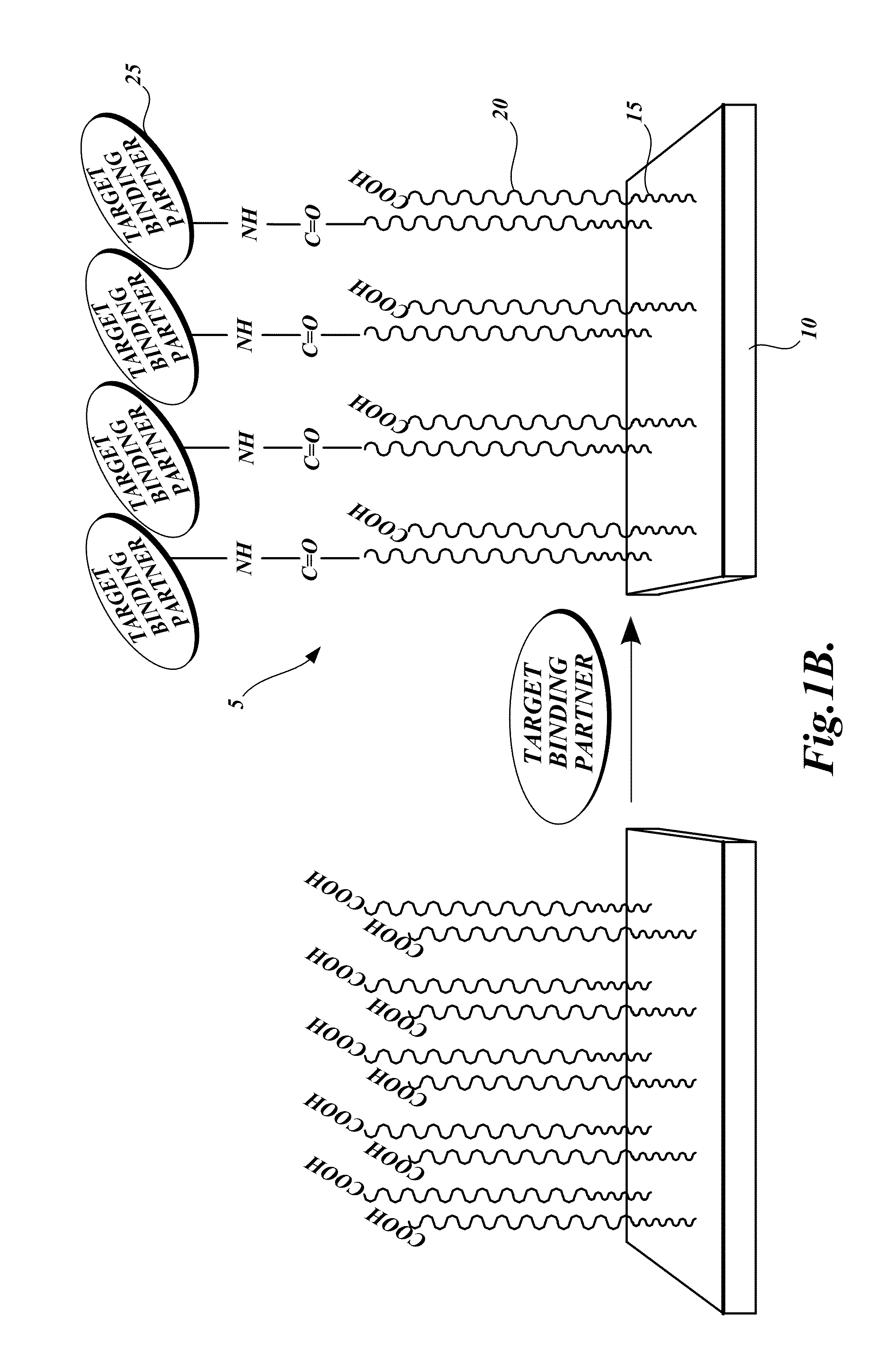
Dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials, methods for making dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials, and devices that include dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials. The dual-functional surfaces are nonfouling surfaces that resist non-specific protein adsorption and cell adhesion. The dual-functional surfaces and materials include covalently coupled biomolecules (e.g., target binding partners) that impart specific biological activity thereto. The surfaces and materials are useful in medical diagnostics, biomaterials and bioprocessing, tissue engineering, and drug delivery.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Waveguide immunosensor with coating chemistry and providing enhanced sensitivity
InactiveUS7022515B2High strengthOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCouplingWaveguide
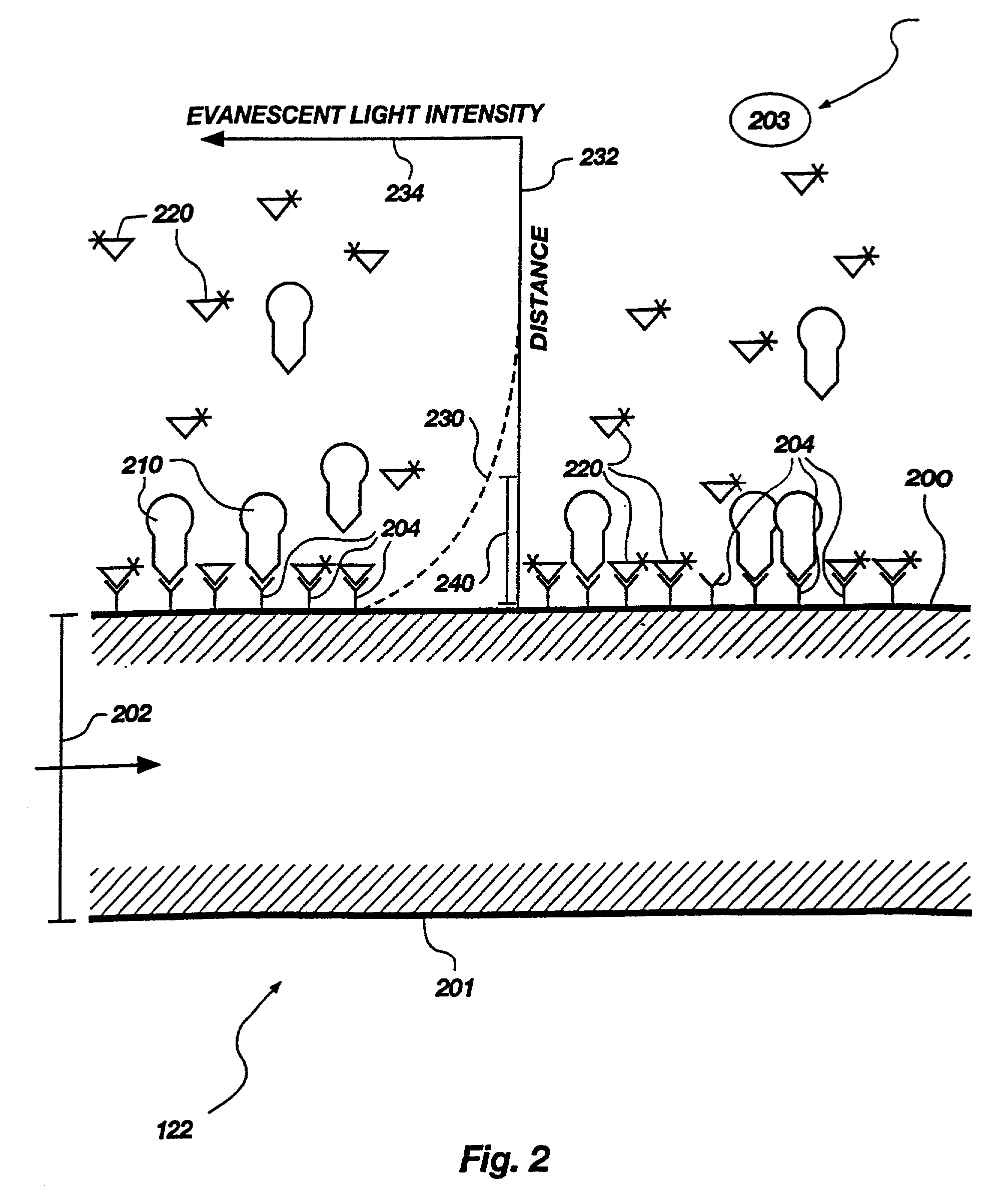
Methods and apparatus for evanescent light fluoroimmunoassays are disclosed. The apparatus employs a planar waveguide and optionally has multi-well features and improved evanescent field intensity. The preferred biosensor and assay method have the capture molecules immobilized to the waveguide surface by site-specific coupling chemistry. Additionally, the coatings used to immobilize the capture molecules provide reduced non-specific protein adsorption.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel corneal prosthesis
InactiveUS20070179605A1High tensile strengthHigh nutrient permeabilityNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsCross-linkHydrophilic monomer
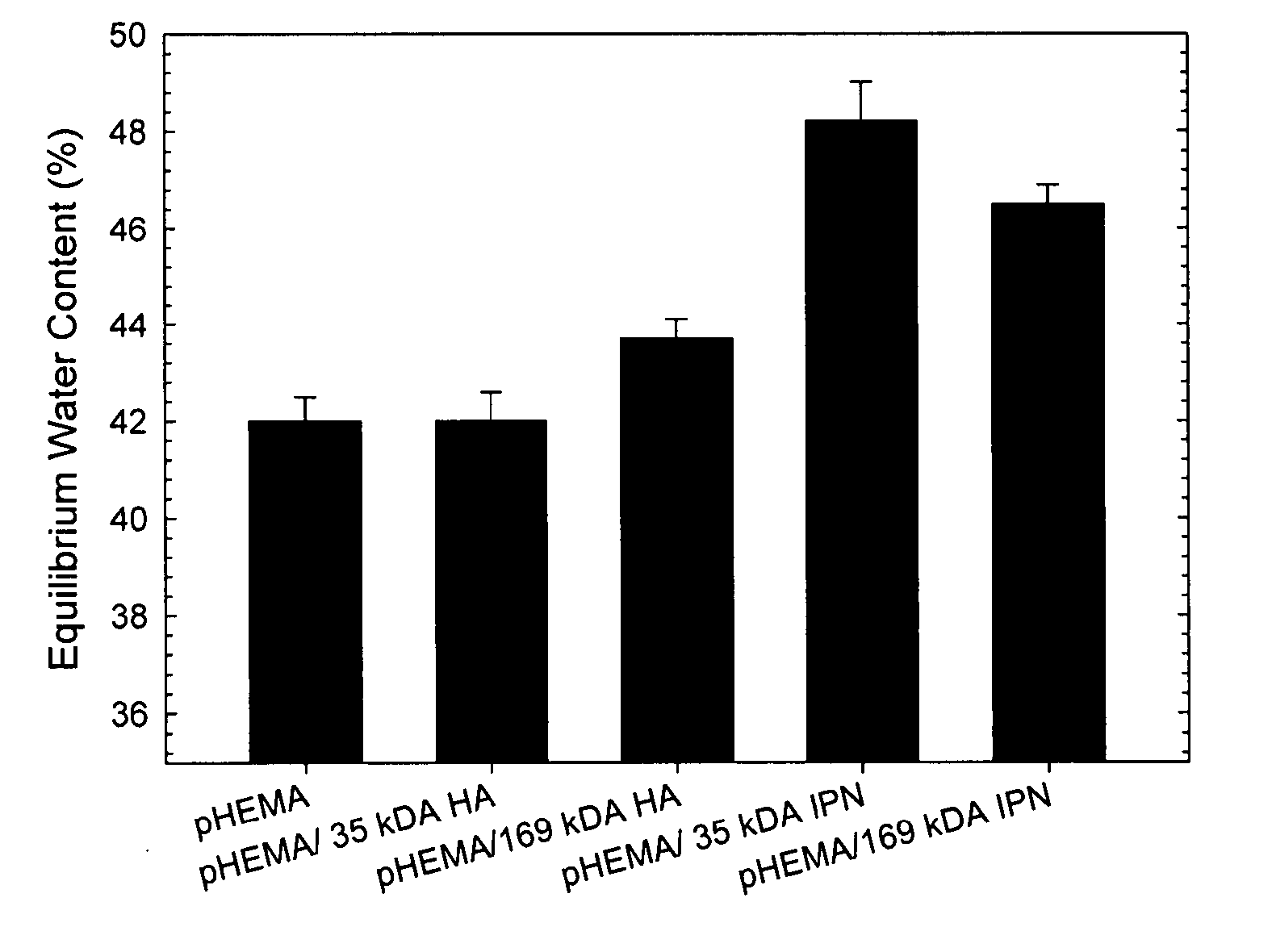
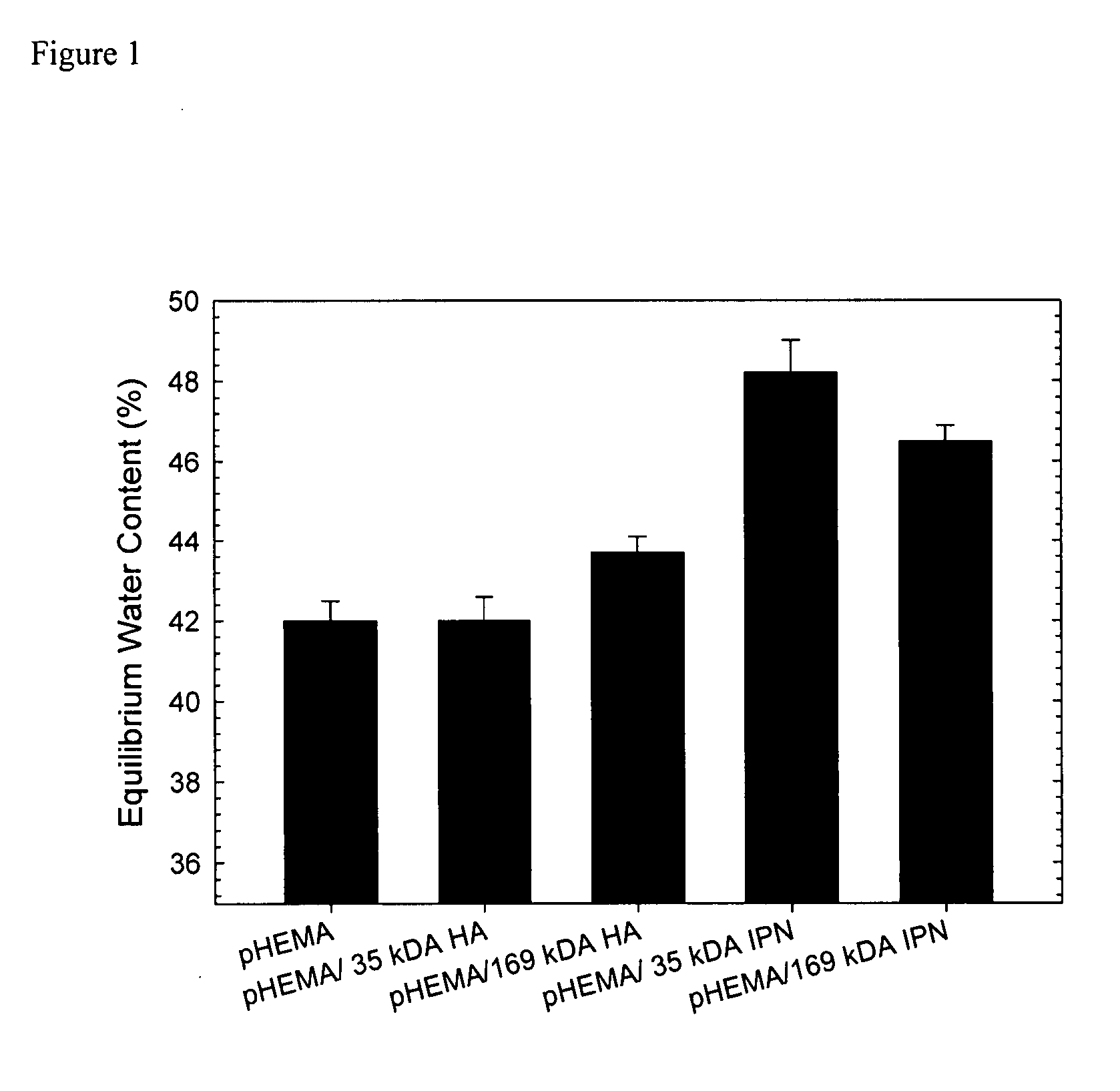
The present invention provides materials that have high glucose and oxygen permeability, strength, water content, and resistance to protein adsorption. The materials include an interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) hydrogel that is coated with biomolecules. The IPN hydrogels include two interpenetrating polymer networks. The first polymer network is based on a hydrophilic telechelic macromonomer. The second polymer network is based on a hydrophilic monomer. The hydrophilic monomer is polymerized and cross-linked to form the second polymer network in the presence of the first polymer network. In a preferred embodiment, the hydrophilic telechelic macromonomer is PEG-diacrylate or PEG-dimethacrylate and the hydrophilic monomer is an acrylic-based monomer. Any biomolecules may be linked to the IPN hydrogels, but are preferably biomolecules that support the growth of cornea-derived cells. The material is designed to serve as a corneal prosthesis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
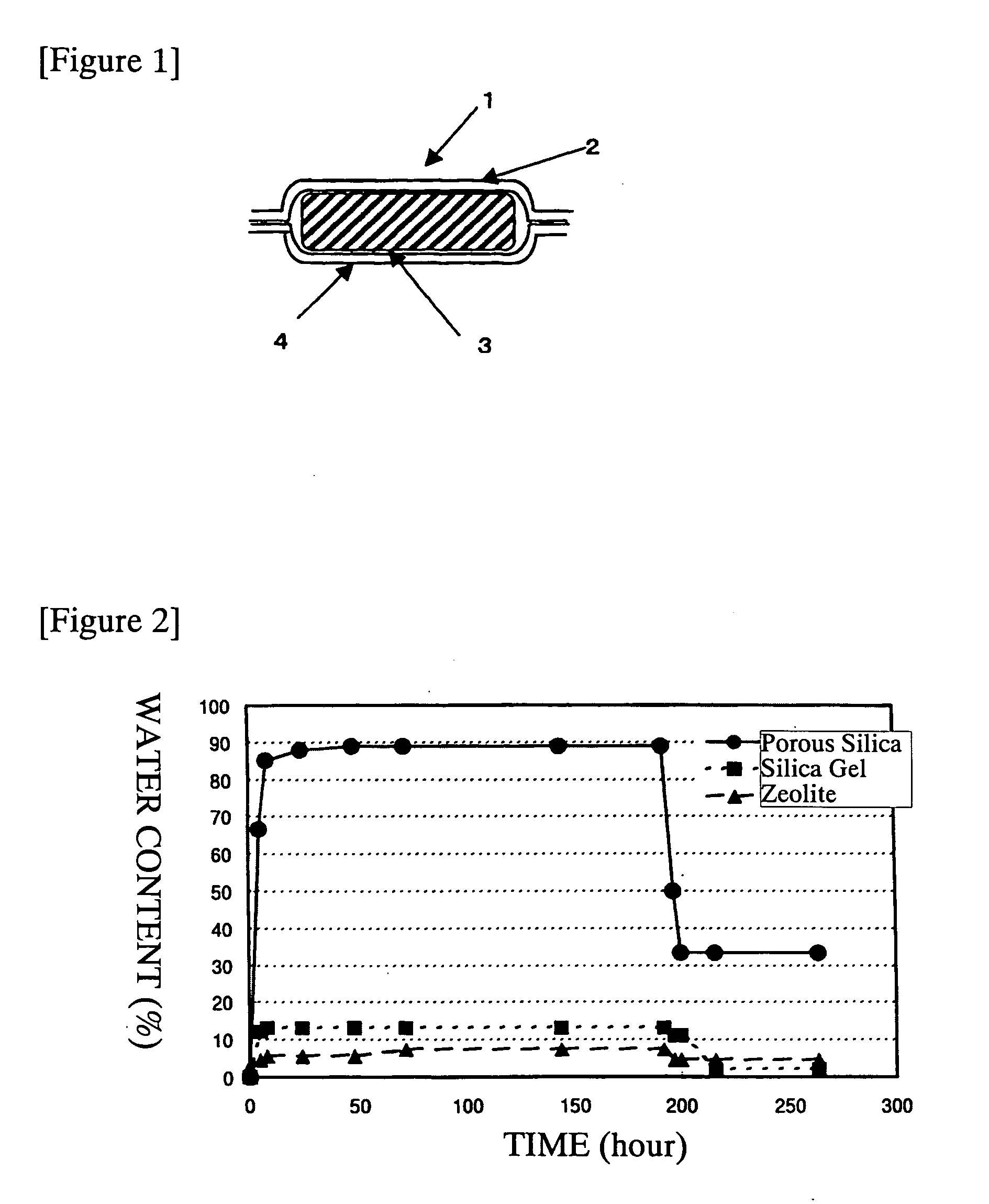
Adsorptivity imparting agent containing porous silica
InactiveUS20070166438A1Improve adsorption capacityNot lose tasteCosmetic preparationsDough treatmentFiltrationSilicon dioxide
A moisture- or protein-adsorbability imparting agent, comprising a porous silica having a hexagonal pore structure, an average pore size of from 0.8 to 20 nm, an average particle size of 50 nm to 100 μm, a specific surface area of from 400 to 2000 m2 / g, and a pore volume of from 0.1 to 3.0 cm3 / g; a material having an adsorbability of moisture or a protein, comprising the moisture- or protein-adsorbability imparting agent; and use of the moisture- or protein-adsorbability imparting agent for imparting absorbability of moisture or a protein to a material selected from the group consisting of food wrapping materials; filtration aid agents; sanitary articles; compositions containing a synthetic resin; moisture-controlled material; covering materials for wounds; insulation substrates; coating materials for semiconductor devices; cosmetics; inkjet recording media; and compositions containing synthetic fibers.
Owner:TAIYO KAGAKU CO LTD +1
Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel contact lenses
InactiveUS7857447B2High tensile strengthHigh oxygen permeabilityIntraocular lensOptical partsCross-linkHydrophilic monomer
The present invention provides interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels that have high oxygen permeability, strength, water content, and resistance to protein adsorption. The hydrogels include two interpenetrating polymer networks. The first polymer network is based on a hydrophilic telechelic macromonomer. The second polymer network is based on a hydrophilic monomer. The hydrophilic monomer is polymerized and cross-linked to form the second polymer network in the presence of the first polymer network. The telechelic macromonomer preferably has a molecular weight of between about 575 Da and about 20,000 Da. Mixtures of molecular weights may also be used. In a preferred embodiment, the hydrophilic telechelic macromonomer is PEG-diacrylate or PEG-dimethacrylate and the hydrophilic monomer is an acrylic-based monomer. The material is designed to serve as a contact lens.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for modifying hydroophilicity of highly active separation membrane made from polymer
InactiveCN1539550AImprove hydrophilicityGood biocompatibilitySemi-permeable membranesChemical LinkagePolymer science
A process for hydrophilic modification of efficient separating polymer membrane includes coating the grafting monomer containing glycosyl compound on the surface of polymer membrane, evaporating solvent, and radiating said monomer for triggering graft reaction to modify said polymer membrane. Its advantages are high hydrophilic effect, and easy washing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dental implant and surface treatment method thereof
InactiveCN103654979AStrong oxidation abilityImprove hydrophilicityDental implantsSurface reaction electrolytic coatingAcid etchingDentistry
The invention discloses a dental implant and a surface treatment method thereof. The surface treatment method for the dental implant comprises the following steps of dental implant cleaning, sandblasting, surface acid etching, surface nanocrystallization processing, soaking, calcinating, and cleaning and the like, so that the dental implant adopting a micron and nanometer mixed structure and having the visible-light catalytic activity through nitrogen doping is obtained. The dental implant achieves preferable hydrophilia, protein adsorption capacity and good biological activity.
Owner:广东省口腔医院
Antimicrobial substrates and uses thereof
A new substrate makes it possible to modify surface properties relating to antimicrobial properties. Said substrate has an electron donating surface, characterized in having metal particles on said surface, said metal particles comprising palladium and at least one metal chosen from gold, ruthenium, rhodium, osmium, iridium, and platinum, wherein the amount of said metal particles is from about 0.001 to about 8 μg / cm2. The substrate is suggested for different uses, such as for modifying the hydrophobicity, protein adsorption, adhesion of bacteria, as well as preventing bacterial transmission and in particular preventing nosocomial infections.
Owner:BACTIGUARD AB
Preparation method of anticoagulation polylactic acid hemodialysis membrane
The invention discloses a preparation method of an anticoagulation polylactic acid hemodialysis membrane. Cellulose acetate membranes and polysulfone membranes are widely used in current clinical application. Poly lactic acid has a good membrane-forming property, but is inclined to hydrophobicity, and blood contacting materials are often required to have good hydrophilicity, can reduce the protein adsorption on material surfaces and reduce platelet aggregation. In the preparation method, firstly a polylactic acid hollow fiber membrane with epoxy groups is prepared by a one-step method, then diamine activation of the polylactic acid hollow fiber membrane is carried out, finally heparin is introduced into the activated polylactic acid hollow fiber membrane to obtain the anticoagulation polylactic acid hemodialysis membrane. In the preparation method, the polylactic acid is used as a dialysis membrane material, and the novel dialysis membrane is prepared through use of the wet / dry solution spinning method; and through in-situ polymerization of monomers having double bonds and the epoxy groups, groups of high reaction activity are introduced into a polylactic acid matrix, and reaction conditions of subsequent diamine grafting process and heparin fixing process are mild, so the method is a simple and convenient modification method.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
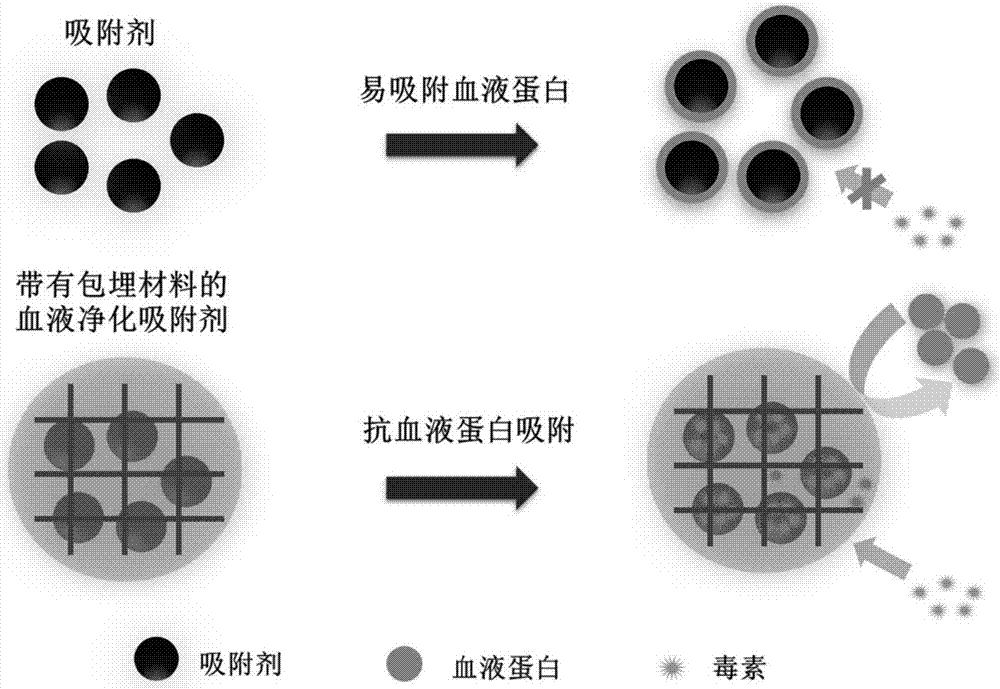
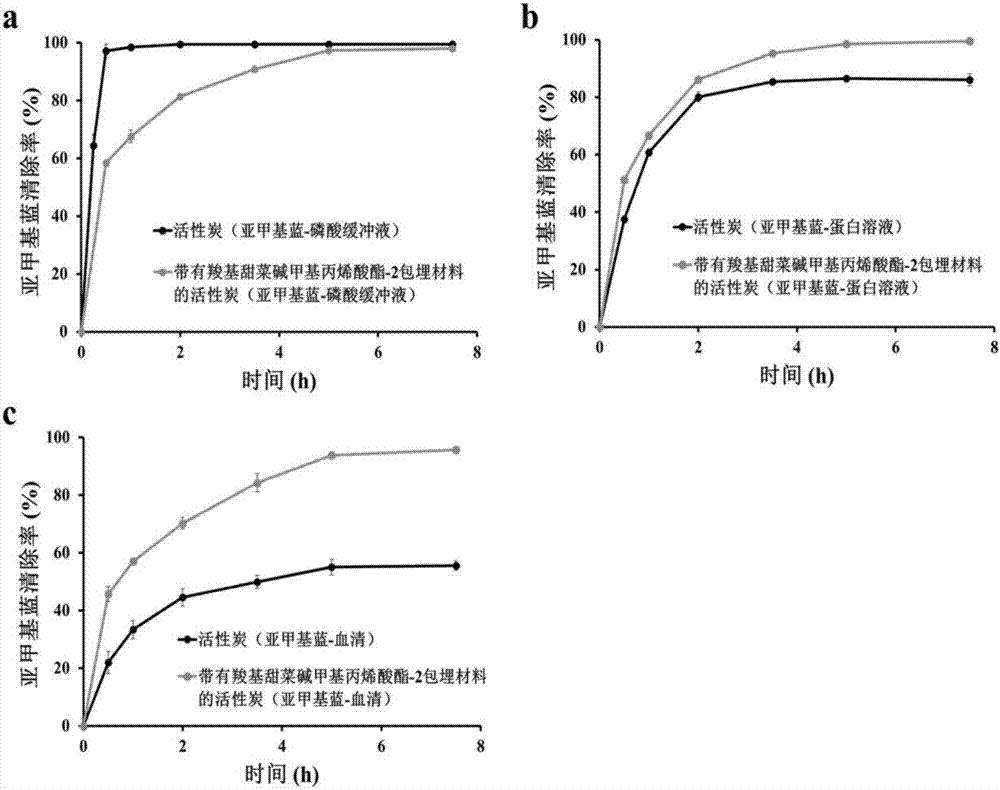
Blood purification adsorbent with embedding material and preparation method of blood purification adsorbent
ActiveCN107126936ARetention of adsorptionExcellent anti-protein adsorption performanceOther blood circulation devicesOther chemical processesCross-linkBetaine
The invention relates to a blood purification adsorbent with an embedding material and a preparation method of the blood purification adsorbent. The embedding material comprises zwitterionic monomer, a cross-linking agent, an initiator and a solvent, and the zwitterionic monomer comprises one or two types of zwitterionic molecules of carboxyl betaine, sulfobetaine and phosphorylcholine. The method includes: mixing the zwitterionic monomer, the cross-linking agent, the initiator and the solvent; adding activated carbon or resin to form mixed solution, wherein the mass of added activated carbon or resin is 6%-50% of that of the zwitterionic monomer; subjecting the mixed solution with activated carbon or resin to ultraviolet radiation or heating or normal-temperature standing to enable curing of the monomer on the surface of the adsorbent through cross-linking polymerization to form the adsorbent with the zwitterionic embedding material. The embedding material is excellent in protein adsorption resistance and biocompatibility and is extremely high in toxin diffusion efficiency in application to blood adsorption. The blood purification adsorbent is easy to store, and the preparation method is simple and feasible.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
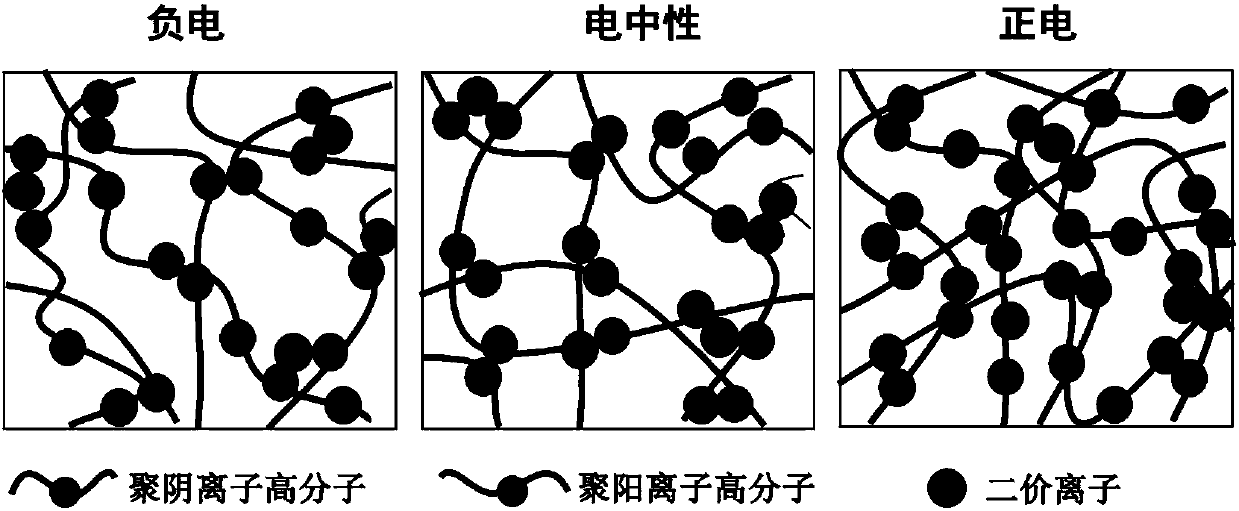
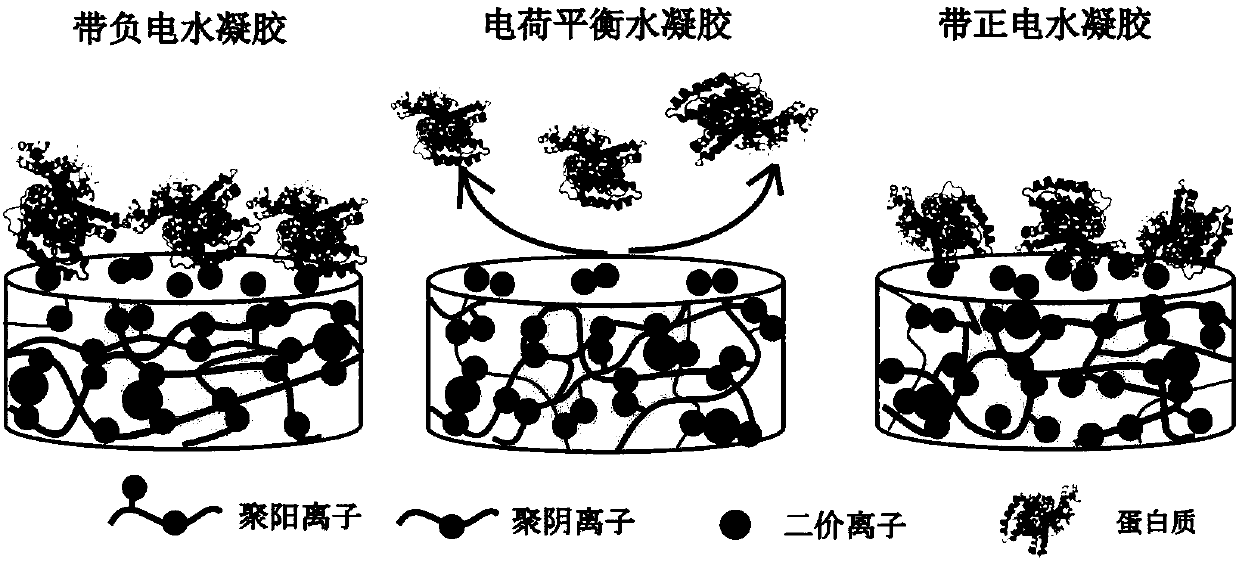
Anti-bioadhesion polyelectrolyte gel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107753421AAvoid immune rejectionTo achieve the effect of sustained releaseMetabolism disorderAerosol deliveryDiabetes mellitusWound dressing
The invention relates to anti-bioadhesion polyelectrolyte gel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of uniformly mixing one or several polyelectrolyte polymer solutions with opposite charges in a charge ratio of 1 to 1, and generating gel by virtue of a physical crosslinking method, or a chemical crosslinking method or the combination of two methods, wherein positive charges and negative charges are balanced, and the form gel is electroneutral. The preparation method of the polyelectrolyte gel is simple and easy to operate, and theprepared gel has good protein adsorption resistance, is high in water content, does not cause inflammatory reaction and is beneficial to the mass transfer between a transplant and an organism. Therefore, the polyelectrolyte gel can be widely applied to the biomedical fields, particularly can be used for treating diabetes mellitus through packaging of islet cells and can be used as a drug release carrier, a wound dressing, a tissue repair scaffold material and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel contact lenses
InactiveUS20070126982A1High tensile strengthHigh oxygen permeabilityIntraocular lensOptical partsHydrophilic monomerCross-link
The present invention provides interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels that have high oxygen permeability, strength, water content, and resistance to protein adsorption. The hydrogels include two interpenetrating polymer networks. The first polymer network is based on a hydrophilic telechelic macromonomer. The second polymer network is based on a hydrophilic monomer. The hydrophilic monomer is polymerized and cross-linked to form the second polymer network in the presence of the first polymer network. The telechelic macromonomer preferably has a molecular weight of between about 575 Da and about 20,000 Da. Mixtures of molecular weights may also be used. In a preferred embodiment, the hydrophilic telechelic macromonomer is PEG-diacrylate or PEG-dimethacrylate and the hydrophilic monomer is an acrylic-based monomer. The material is designed to serve as a contact lens.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Amphipathic three block copolymer and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101265312AEvade captureAvoid the effect of adsorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyesterPolymer science
The invention relates to a polyethylene glycol / aliphatic polyester / cationic polymer amphiphilic triblock copolymer. The copolymer contains a hydrophilic non-ionic polymer block, a hydrophobic block and a pH-sensitive cationic polymer block. Potassium hydride is taken as an initiator, the polyethylene glycol and the aliphatic polyester monomers and the cationic monomer are sequentially added in a polymerization reactor for respective reaction, methanol is added for terminating the reaction; n-hexane is used for the precipitation and the purification of the triblock copolymer in tetrahydrofuran, the precipitation is repeated for 3 times, and a product undergoes the vacuum drying. The copolymer can form a micelle or a nanoparticle by self-assembly in a water medium, wherein, a core of a loading hydrophobic drug is formed by clustering the hydrophobic cationic polyester block, the polyethylene glycol block is assembled into a hydrophilic shell, thus having the functions of stabilizing the micelle and effectively avoiding the capture and protein absorption of a reticuloendothelial system of an organism; the cationic polymer block can be further acted with DNA, protein, peptide and other biological macromolecules, thus forming the biodegradable and pH-sensitive drug-loading polymer micelle or the nanoparticle which can be further dispersed,.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Polymer electrostatic spinning film, preparation and use in biological detection
ActiveCN101413183AEasy to operateEnhanced interactionFilament/thread formingMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentElectrospinningOperability
The invention relates to a macromolecular electrostatic spinning film, a preparation method thereof and an application of the macromolecular electrostatic spinning film to bioinstrumentation. The macromolecular electrostatic spinning film is a membranoid substance which is formed by disorderly interlacing macromolecular electrostatic spinning which are not water-soluble; and the diameter of the macromolecular electrostatic spinning is between 50 and 1,000 nanometers, and the thickness of the film is between 5 mu m and 1 millimeter. The preparation method comprises the following steps: electrostatic spinning is performed in an electrostatic spinning device, and the spinning obtained is subjected to pressing, waterlogging and secondary pressing to obtain the dense and smooth macromolecular electrostatic spinning film with strong operability. The film can be applied to bioinstrumentation and taken as a protein absorbing vector, and has a larger absorption quantity compared with the prior protein absorbing vector film. The preparation method for the film is simple, has low cost, can solve the problems that the electrostatic spinning is puffy, unsmooth and easy to fall off, converts electrostatic spinning non-woven fabrics into the electrostatic spinning film used for bioinstrumentation, and can also be applied in the fields of tissue engineering, bioinstrumentation, catalyst load, filter materials and so on.
Owner:BEIJING NANO ACE TECH CO LTD
Biocompatible substrates and uses thereof
A new substrate makes it possible to modify surface properties relating to biocompatibility. Said substrate has an electron donating surface, characterized in having metal particles on said surface, said metal particles comprising palladium and at least one metal chosen from gold, ruthenium, rhodium, osmium, iridium, and platinum, wherein the amount of said metal particles is from about 0.001 to about 8 μg / cm2. The substrate is suggested for different uses, such as for modifying the hydrophobicity, protein adsorption; tissue ingrowth, complement activation, inflammatory response, thrombogenicity, friction coefficient, and surface hardness.
Owner:BACTIGUARD AB
Method for forming simulated cell outer layer membrane structure on surface of cross-linked chitosan
The invention discloses a method for forming a simulated cell outer layer membrane structure on the surface of cross-linked chitosan. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, the chitosan is cross-linked by glutaraldehyde; and secondly, the surface of the cross-linked chitosan is grafted with phosphinylideyne choline groups to construct the simulated cell membrane structure, the reaction of the grafted phosphinylideyne choline groups is carried out in an anhydrous non-protonic solvent, the reaction temperature is between 40 and 80 DEG C, and the concentration of phosphorylcholine dichloride is between 0.1 and 20mg / ml. The test results show that for the surface modified by the simulated cell outer layer membrane structure, the capabilities of adsorbing protein and blood platelet are obviously reduced, and the blood compatibility is obviously improved. The modified material with the simulated cell outer layer membrane structure has wide application prospect in fields such as blood purification, body implantation materials, tissue engineering, slow release of medicines, biological sensors, and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Method for preparing amorphous calcium carbonate nanospheres
ActiveCN103663532ASimple processEasy to operateCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesMaterial nanotechnologyTissue repairAmorphous calcium carbonate
The invention discloses a method for preparing amorphous calcium carbonate nanospheres. The method comprises the following steps: water soluble calcium salt is dissolved in de-ionized water; then a stabilizing agent is added; the pH value of a solution is adjusted to 7-11 to obtain a solution A; water soluble carbonate is dissolved in the de-ionized water to obtain a solution B; the solution B is dropwise added in the solution A; the pH value of the solution system is controlled to be 7-11; after the dripping is finished, the stirring is conducted at the room temperature for a certain time; then the centrifugal separation, the washing and the drying are conducted to obtain the amorphous calcium carbonate nanospheres. The method has the advantages that the process is simple; the operation is convenient; complex and expensive equipment is not required; industrialization is easy to achieve; raw materials are cheap in cost and easily obtained. The amorphous calcium carbonate nanospheres prepared through the method, as biomedical materials, can be applied to the fields of medicine delivery, protein adsorption, gene transfection, tissue repair and the like, and has good application prospect.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
Dual-functional nonfouling surfaces comprising target binding partner covalently coupled to polymer attached to substrate
Dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials, methods for making dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials, and devices that include dual-functional nonfouling surfaces and materials. The dual-functional surfaces are nonfouling surfaces that resist non-specific protein adsorption and cell adhesion. The dual-functional surfaces and materials include covalently coupled biomolecules (e.g., target binding partners) that impart specific biological activity thereto. The surfaces and materials are useful in medical diagnostics, biomaterials and bioprocessing, tissue engineering, and drug delivery.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Antifouling and antibacterial coating paint and applications thereof
InactiveCN104327663ADurable antifouling and antibacterial abilityStrong antibacterial activityAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesMethacrylateBetaine
The invention discloses an antifouling and antibacterial coating paint, which is prepared by taking methanol as a solvent through carrying out quaterisation reaction on copolymers methoxy polyethylene glycol-b-poly(ethyl methacrylate) dimethyl sulfo-propane betaine-b-poly dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate and 3-triethoxysilane. The invention also discloses applications of the paint in preparing coatings on the surfaces of ships, marine engineering machineries and sewage treatment equipment so as to implement antifouling and antibacterial treatment. Experiments show that a polymer coating prepared by using the paint disclosed by the invention has excellent protein adsorption and microbial contamination resistance, and has lasting antifouling and antibacterial abilities, and therefore, the paint has a board market prospect, and has significant social and economic values.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
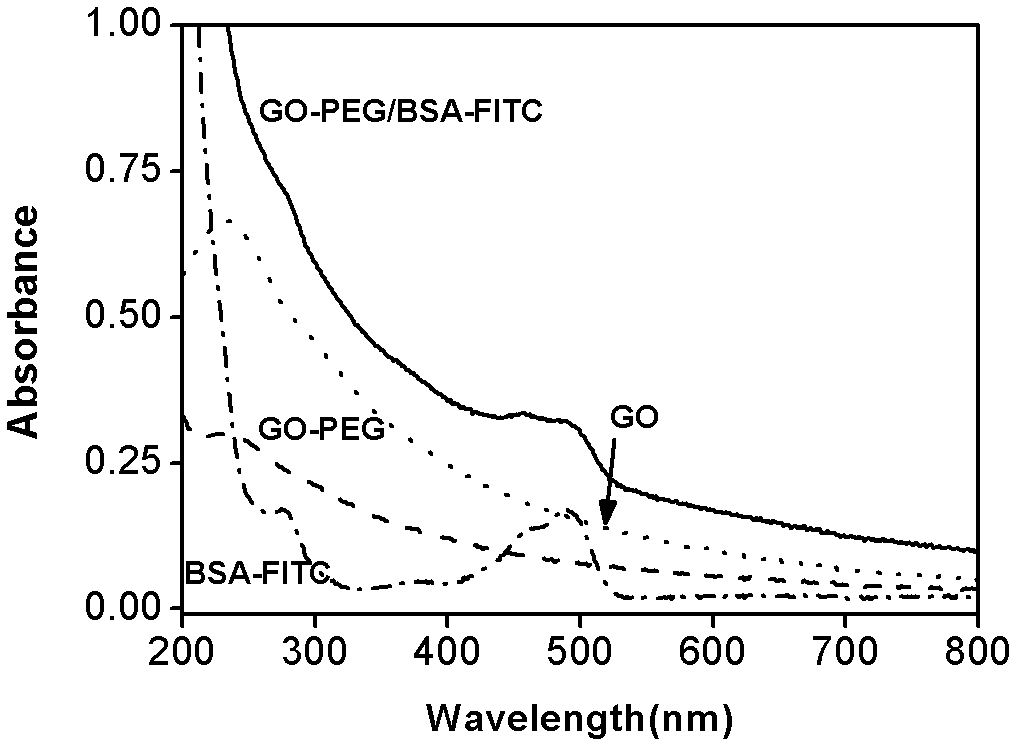
Nano graphene oxide protein complex, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102603896AAvoid enzymatic hydrolysisImprove the effect of regulating control of physiological activitiesCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesTumor/cancer cellsEnzyme digestionFluorescence
The invention discloses a nano graphene oxide protein complex, a preparation method of the nano graphene oxide protein complex and applications of the nano graphene oxide protein complex. The complex is of a complex structure that protein is absorbed on the surface of the nano graphene oxide. The nano graphene oxide protein complex is prepared as follows: conducting fluorescence labeling on protein drugs, modifying the nano graphene oxide protein by polyethylene glycol (PEG), and combining and gathering the protein drugs on the nano graphene oxide through a physical adsorption mode. The nano graphene oxide protein complex designed by the invention has extremely high loading efficiency and stability; in an in-vitro physiological environment, the protein physically absorbed on the surface of the graphene oxide can be released gradually, the enzyme digestion and the hydrolysis to the protein, caused by the protease can be avoided effectively, and simultaneously, in the cells, the protein can be effectively delivered into the cells from the surface of the graphene oxide. According to the invention, the effects of regulating and controlling the physiological activities of the cells can be improved, the powerful guaranteeing can be provided for the medical application under the physiological conditions; and according to the preparation method provided by the invention, the method is simple and convenient, the cost is low and the volume production is facilitated.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Fabrication of surfaces with reduced protein adsorption and/or cell adhesion
InactiveUS20050118595A1Simple and inexpensiveImprove adhesionPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell adhesionAdhesion process
Fabrication of surfaces with reduced protein adsorption and / or cell adhesion comprising a vapor deposition coating process such that the coating includes polymer interfaces containing chemical groups reducing the protein adsorption and / or cell adhesion. The invention allows precise anchoring and presentation of biomolecules in their biological context. The resulting systems comprise superior surfaces for design of protein- or cellbased bioassays, because of high-signal-to-noise ratios. Background adsorption is suppressed while specific interaction with capturing molecules is not affected.
Owner:LAHANN JOERG
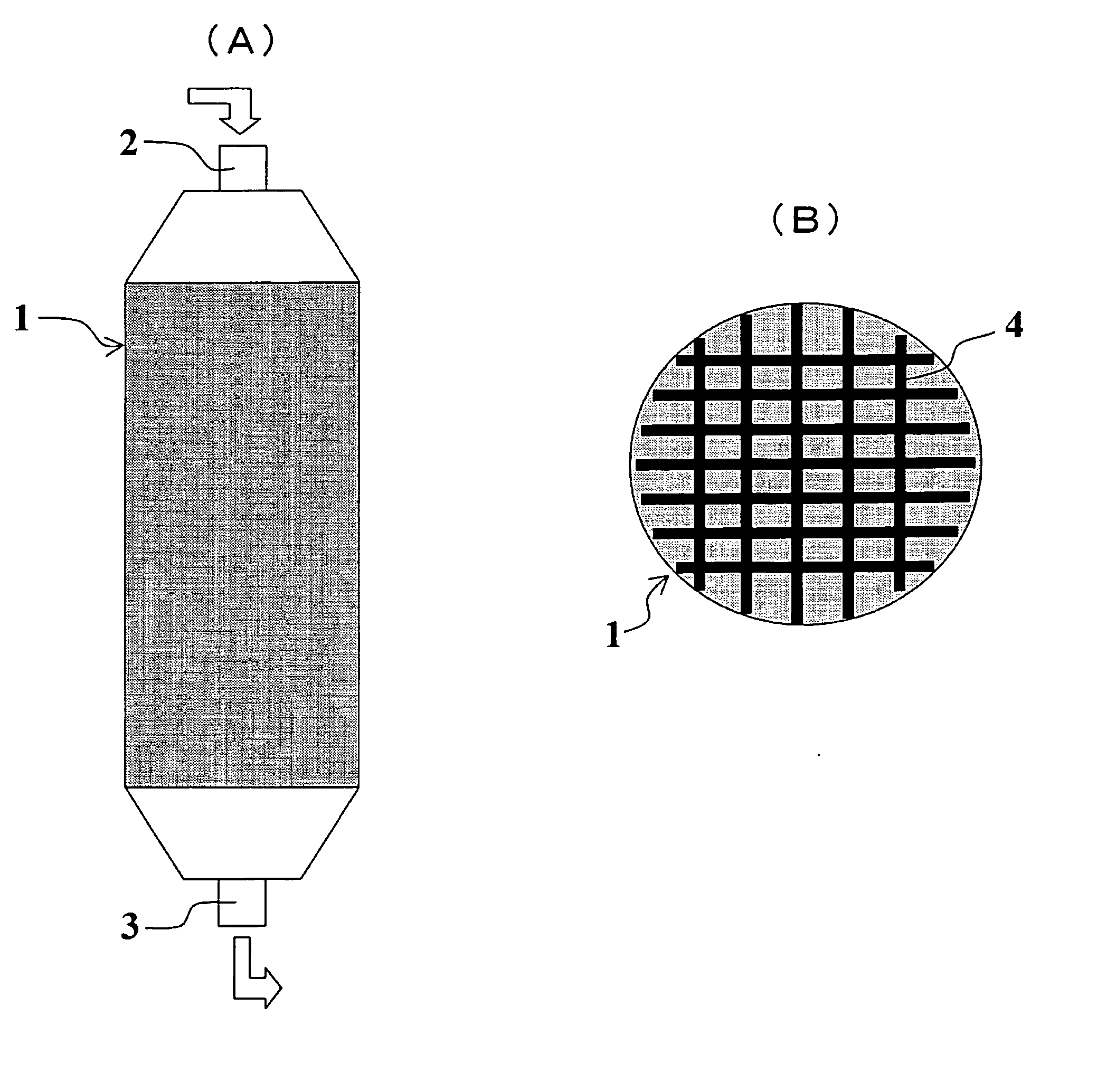
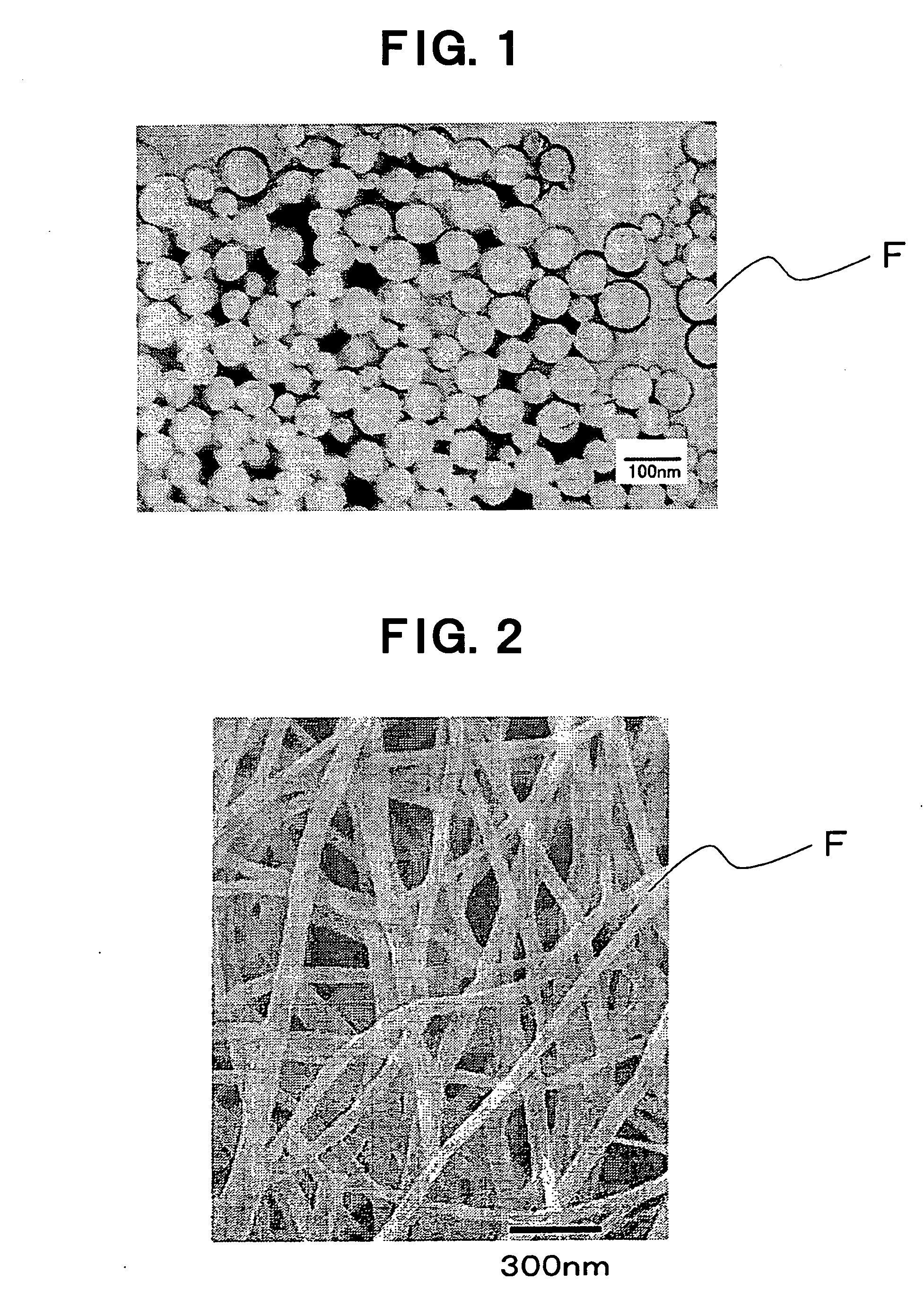
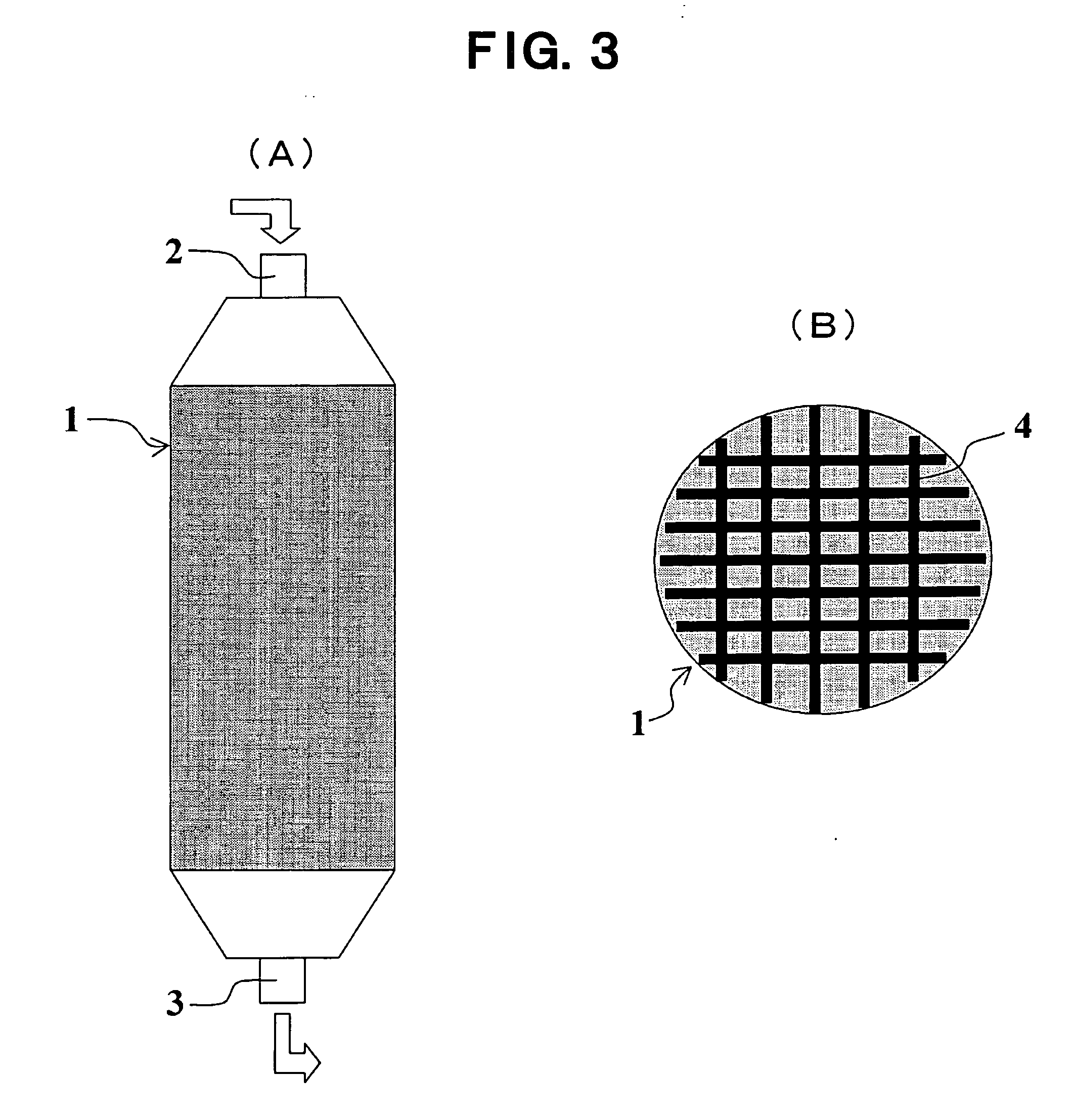
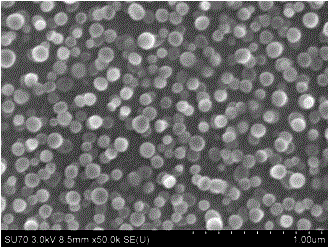
Medical Filter Material, and Extracorporeal Circulation Column and Blood Filter Utilizing the Filter Material
InactiveUS20080023394A1High strengthExcellent in hemadsorption performanceOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationExtracorporeal circulationProduction rate
A medical filter material characterized by comprising a dispersion of nanofibers of thermoplastic polymer having a number average diameter of 1 to 500 nm wherein the ratio of single fibers with a diameter of more than 500 nm and 1 μm or less is 3% or less in terms of weight ratio. Further, there are provided, utilizing the medical filter material, an extracorporeal circulation column and a blood filter. Through the employment of nanofibers small in fiber diameter dispersion, high in strength and high in productivity, there can be provided a medical filter material excellent in hemadsorption performance and protein adsorption performance. Through packing with this medical filter material, there can be provided high-performance extracorporeal circulation column and blood filter.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Europium-doped titanium dioxide/graphene oxide composite film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104596994AImprove luminous performanceGood biocompatibilityAnalysis by material excitationOxide compositeBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a europium-doped titanium dioxide / graphene oxide composite film and a preparation method thereof. According to the film, a substrate is provided with a europium-doped titanium dioxide nanodot and graphene oxide mixed layer, wherein titanium dioxide nanodots in the mixed layer are 30-150nm in size and 1.0*10<10>-1.0*10<11> / cm<2> in density, the molar concentration of Eu<3+> is 0.005-0.015mol / L, and the concentration of graphene oxide is 5-15mg / L. The preparation method is based on a sol-gel method and comprises the steps of preparing europium-doped titanium dioxide / graphene oxide precursor sol and then performing thermal treatment of the precursor sol on the substrate by a spin-coating method. The film provided by the invention has favorable biocompatibility, protein adsorption property and luminescence property, and can be used for in-situ semi-quantitative characterization of the protein adsorption capacity of a film surface. The film can be applied in the biomedical engineering fields of cell culture in vitro, tissue engineering and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
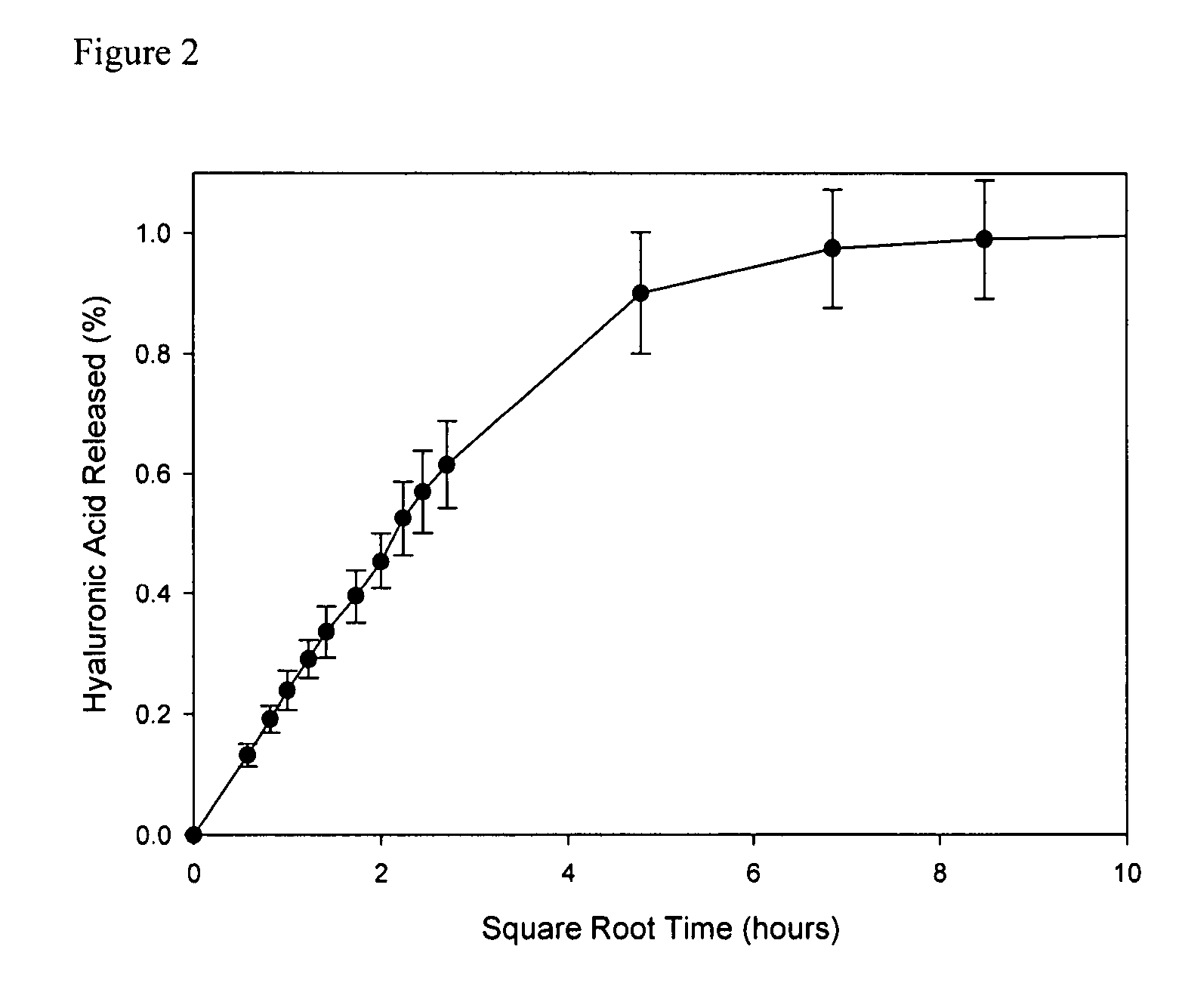
Hyaluronic acid-retaining polymers
InactiveUS20070293648A1Improve propertiesReduce surface frictionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBiopolymerHyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid-retaining biopolymer is provided which exhibits low levels of protein adsorption and surface friction. The biopolymer is useful for incorporation in products, such as contact lenses, used in biological environments.
Owner:SHEARDOWN HEATHER +2
Polymer coatings that resist adsorption of proteins
InactiveUS20100096327A1Easy to synthesizeOxidation stabilityMembranesUltrafiltrationPhosphoniumFiltration
The invention provides membranes useful for filtration of water and other liquids. The membrane may be a composite membrane having a polymer layer incorporating quaternary phosphonium or ammonium groups. The polymer layer may be resistant to protein adsorption in an aqueous environment. The membrane may also be a surface-modified membrane in which a polymer having quaternary phosphonium or ammonium groups is covalently attached to the membrane surface. Methods for making and using the membranes of the invention are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Application of water-soluble silicon quantum dots as drug carriers
InactiveCN104306984AGood water solubilityImprove purityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityPolyethylene glycol
The invention provides application of water-soluble silicon quantum dots as drug carriers. A preparation method of a silicon quantum dot-drug molecule composition comprises the following concrete steps: preparing aminated silicon quantum dots, performing maleimide treatment on the surfaces of the aminated silicon quantum dots, and preparing the silicon quantum dot-drug molecule composition. According to the method, the silicon quantum dots are connected with drug molecules through short-chain polyethylene glycol molecules, and the prepared silicon quantum dot-drug molecule composition has the advantages of high purity, good water solubility, protein adsorption resistance, no additional fluorescent mark, capability of achieving passive targeting in the body, capability of entering urine through the blood-brain barrier and the glomerular vascular wall to be discharged from the body, a certain drug slow-release effect and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Antifouling seal-cleaning aqueous polyurethane leather finishing agent and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an antifouling seal-cleaning aqueous polyurethane leather finishing agent and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly utilizing a macromolecule initiating technology to synthesize a novel copolymer which takes polyurethane as a main chain and takes polyethylene glycol as a side chain; and then introducing nano TiO2 into a polyurethane copolymer matrix grafted by the polyethylene glycol through a sol-gel method to prepare the novel polyethylene glycol grafted polyurethane nano composite leather finishing material. The good protein adsorption resistance of the polyethylene glycol, the photocatalytic activity of the TiO2 and the special nano effect of nano grains are combined, so that the transparency and the film-forming performance of a coating material are not influenced, and the photocatalytic seal-cleaning performance, the protein adsorption resistance and the microorganism adsorption property and the sterilization and the mildew resistance of the coating can be obviously improved; and the mechanical strength, the heat-resisting stability, the wear resistance, the ultraviolet aging resistance and the hygiene property of the coating are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method of high-flexibility amphoteric ionic hydrogel
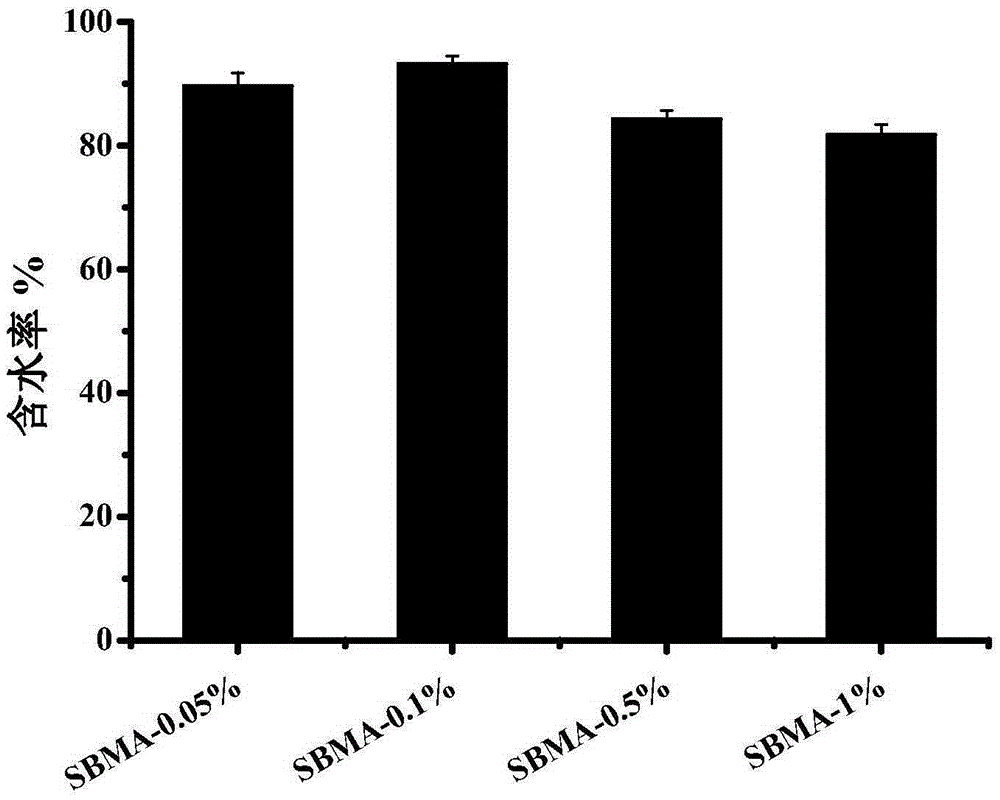
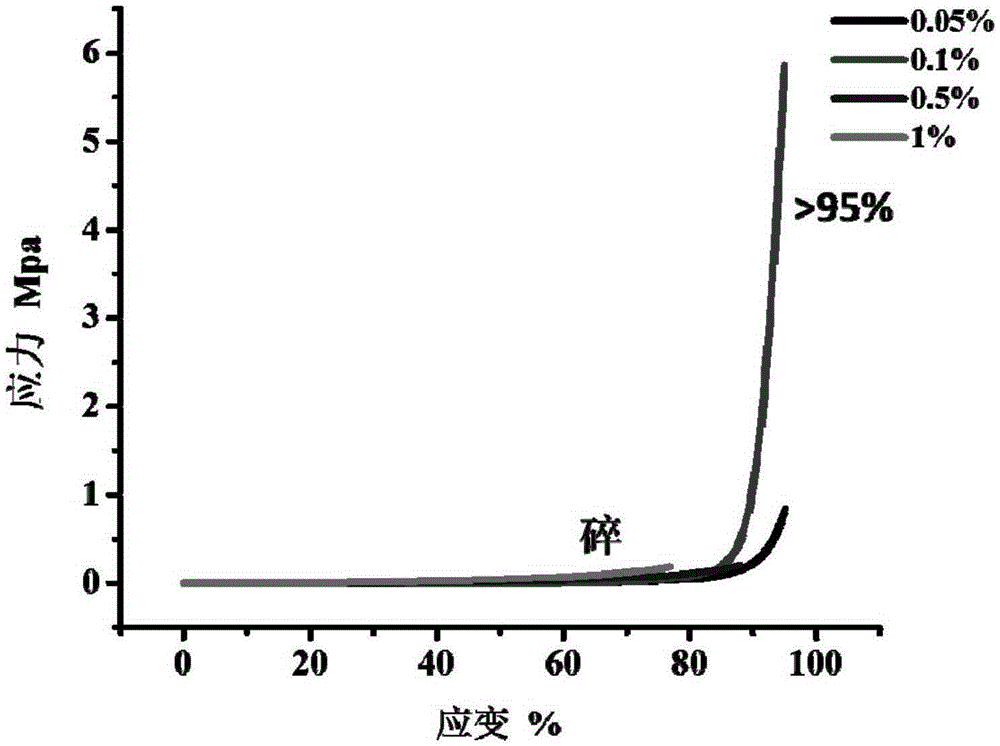
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-flexibility amphoteric ionic hydrogel. By changing the concentration of [2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] dimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl) ammonium hydroxide monomers, cross-linking agents and initiators, the high-flexibility amphoteric ionic SBMA hydrogel is obtained. The SBMA hydrogel prepared through the method has good mechanical property, protein adsorption resistance and cell adsorption performance through interaction of a large number of positive and negative charges of SB units, and meanwhile thermosensitivity and saline ion responding performance and self-restoration performance are achieved. Application of hydrogel based on amphoteric ions in the field of biomedical tissue engineering can be further expanded, and particularly in the fields, where certain mechanical strength is needed, such as artificial joints, blood vessels and the like. At the same time, the preparation method avoids the situation that traditionally, an amphoteric ionic SBMA main chain is modified through grafting, operation is easier, and industrialization of the whole process is easy.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com