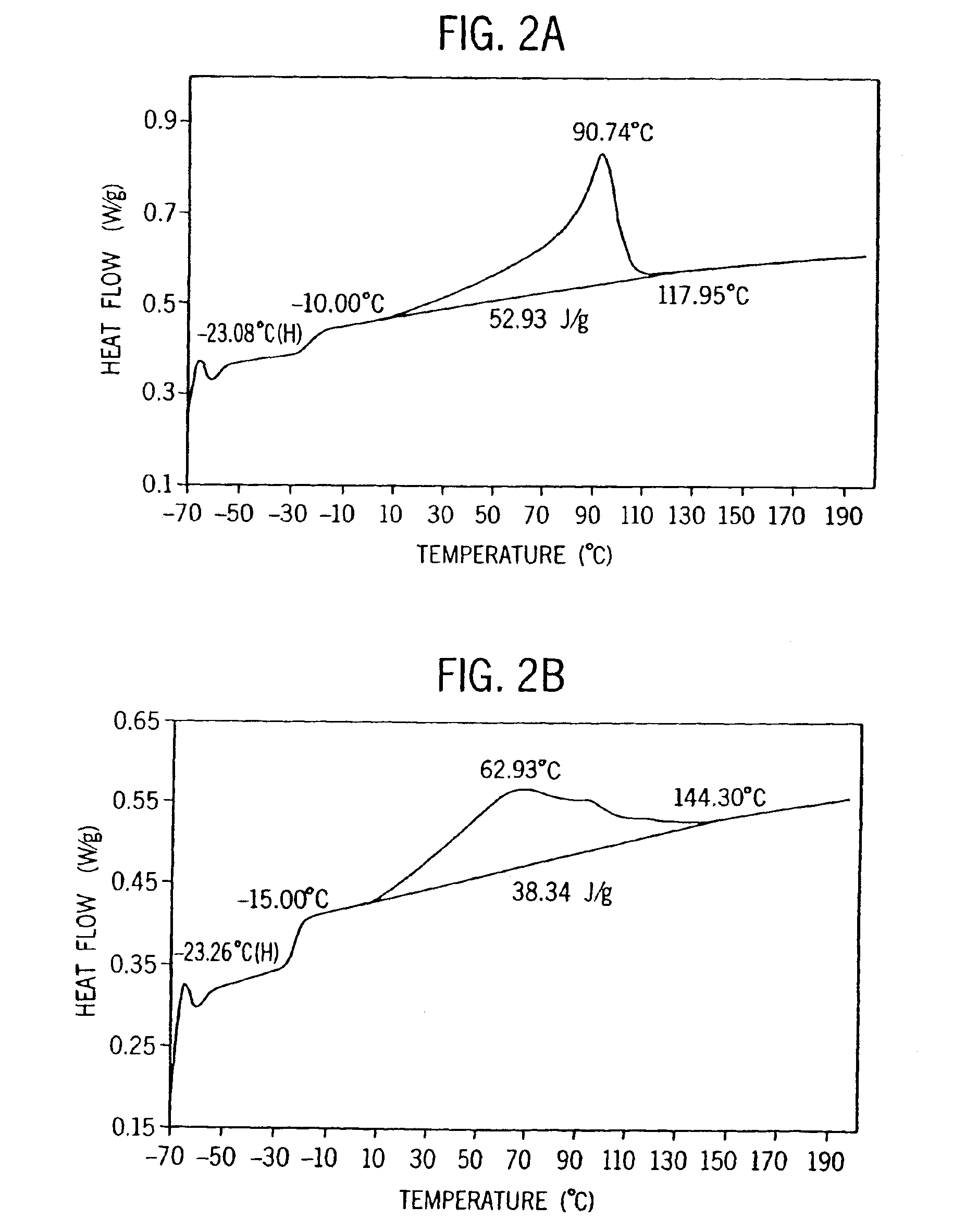
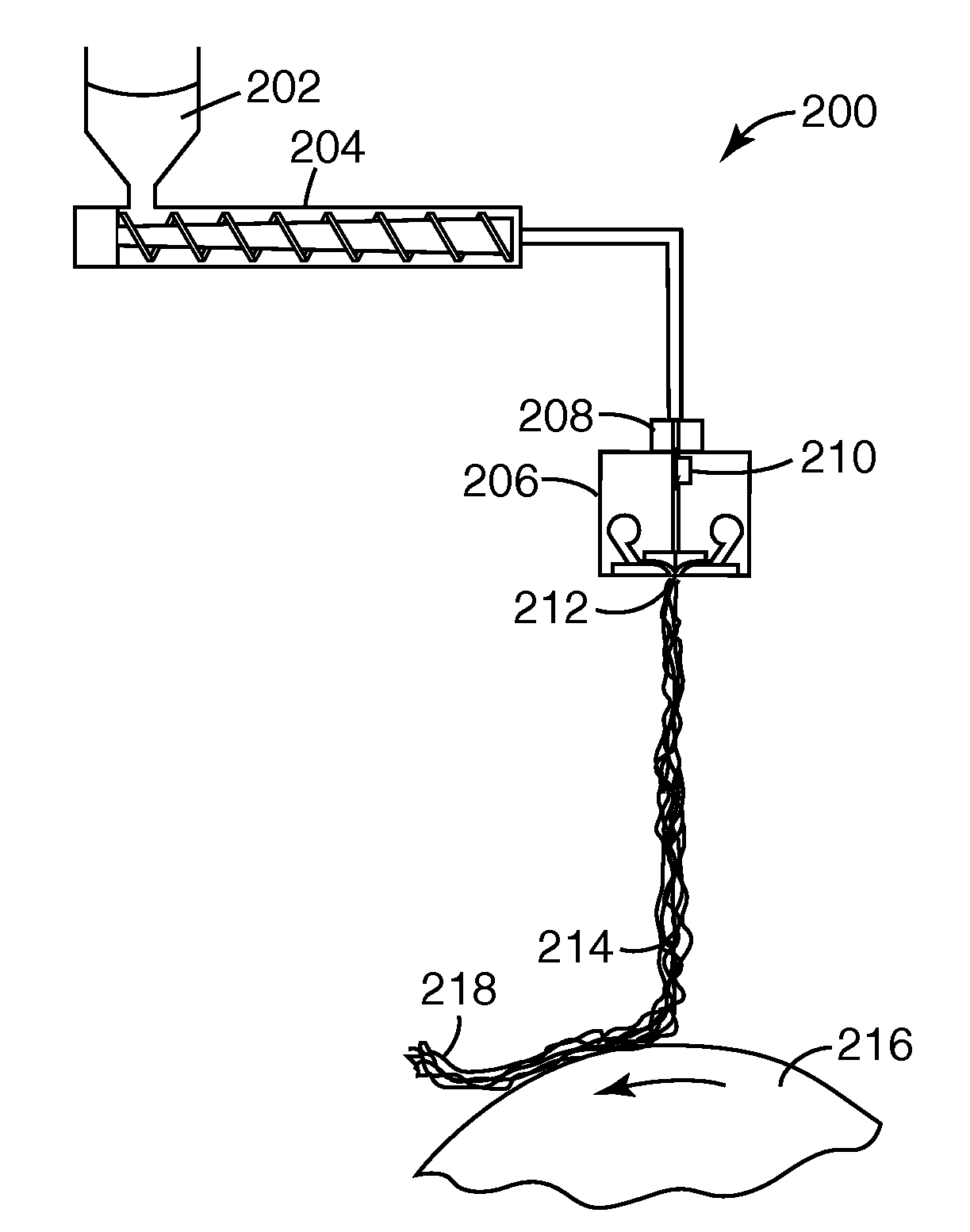
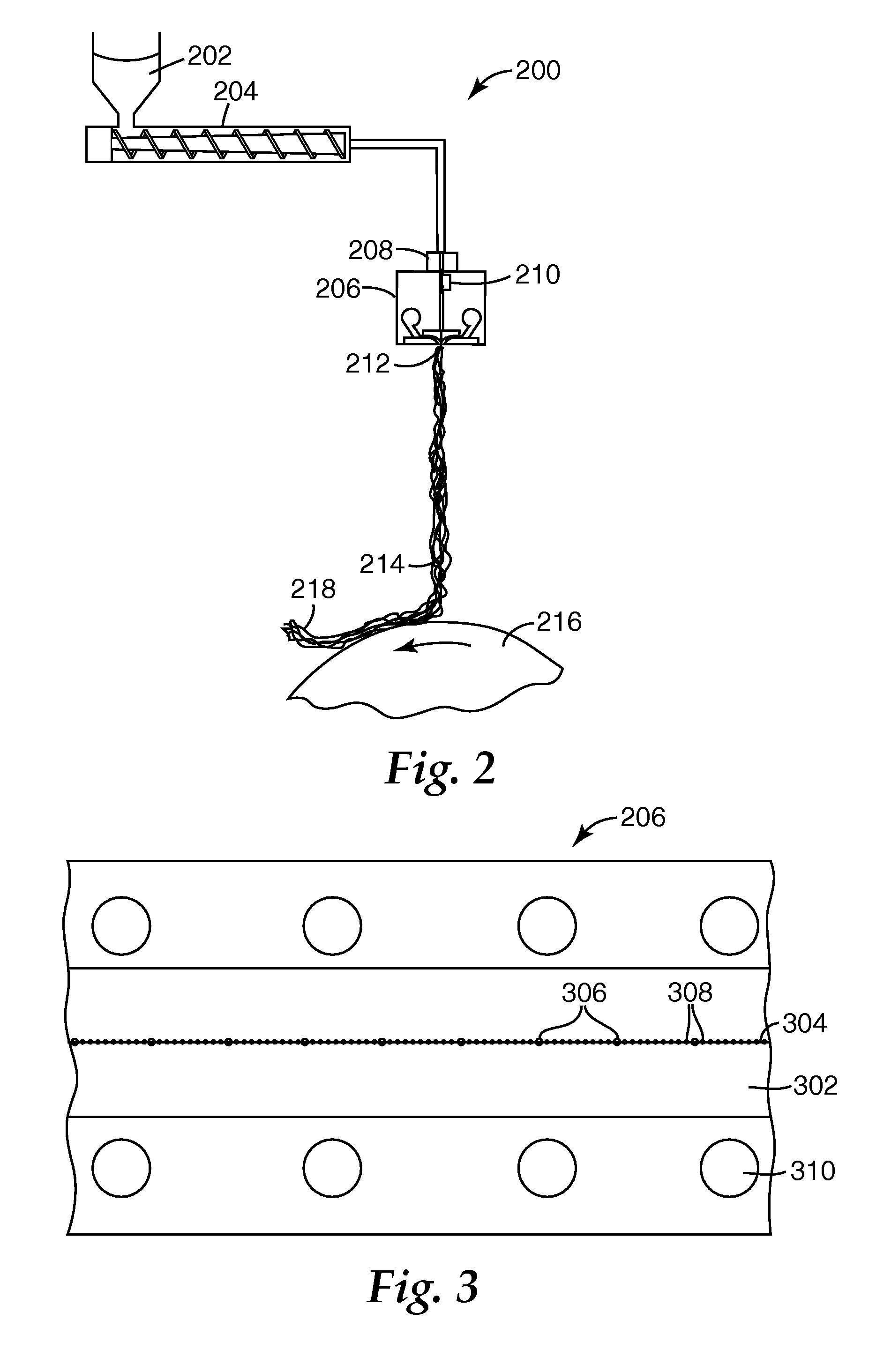
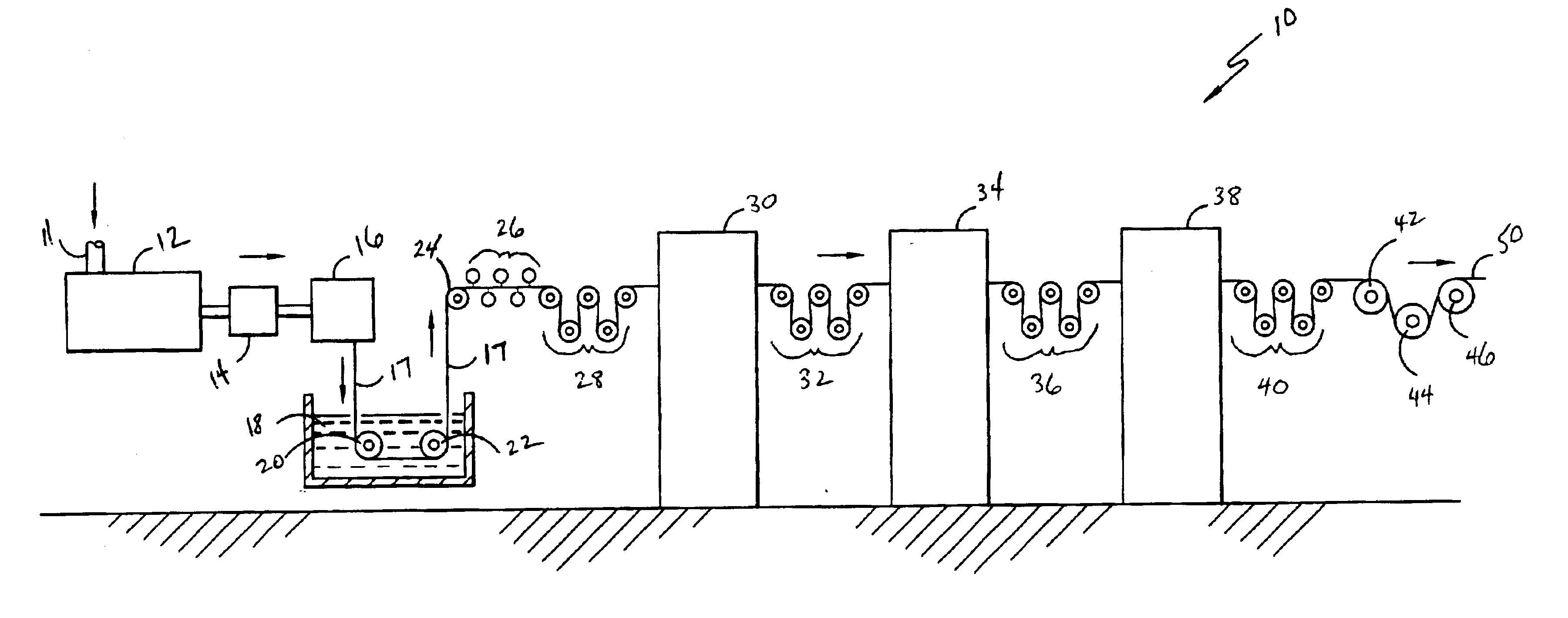
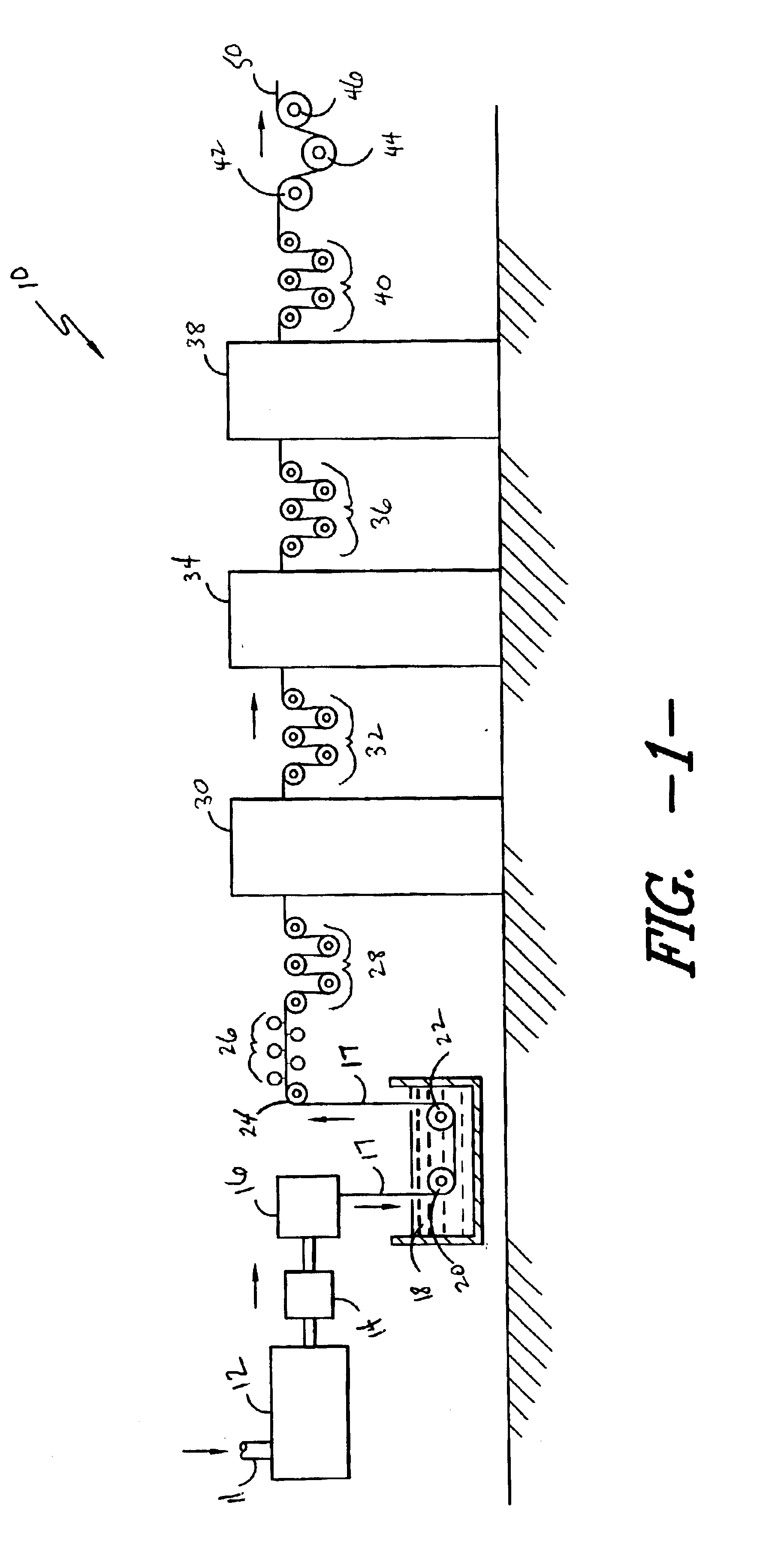
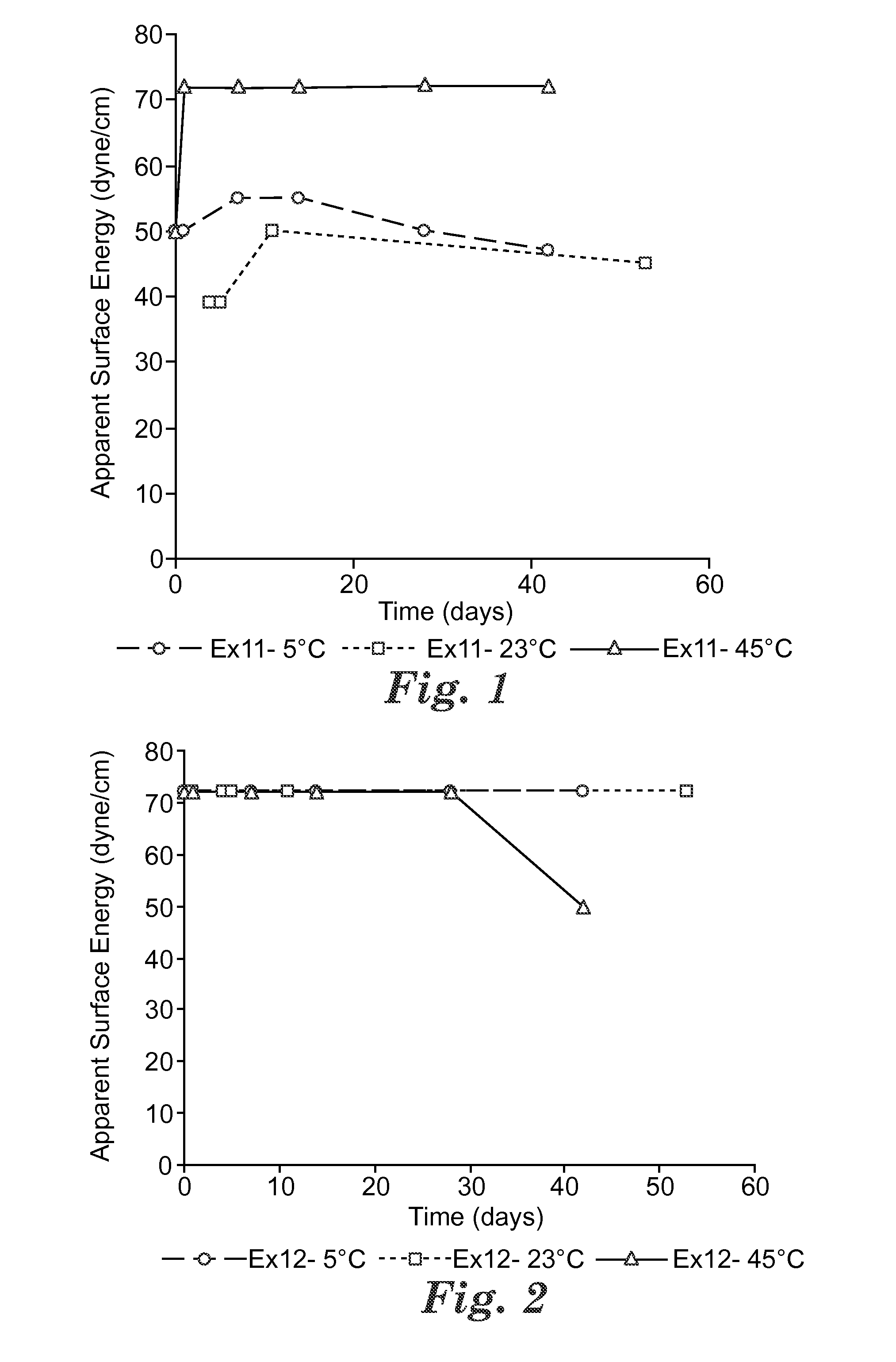
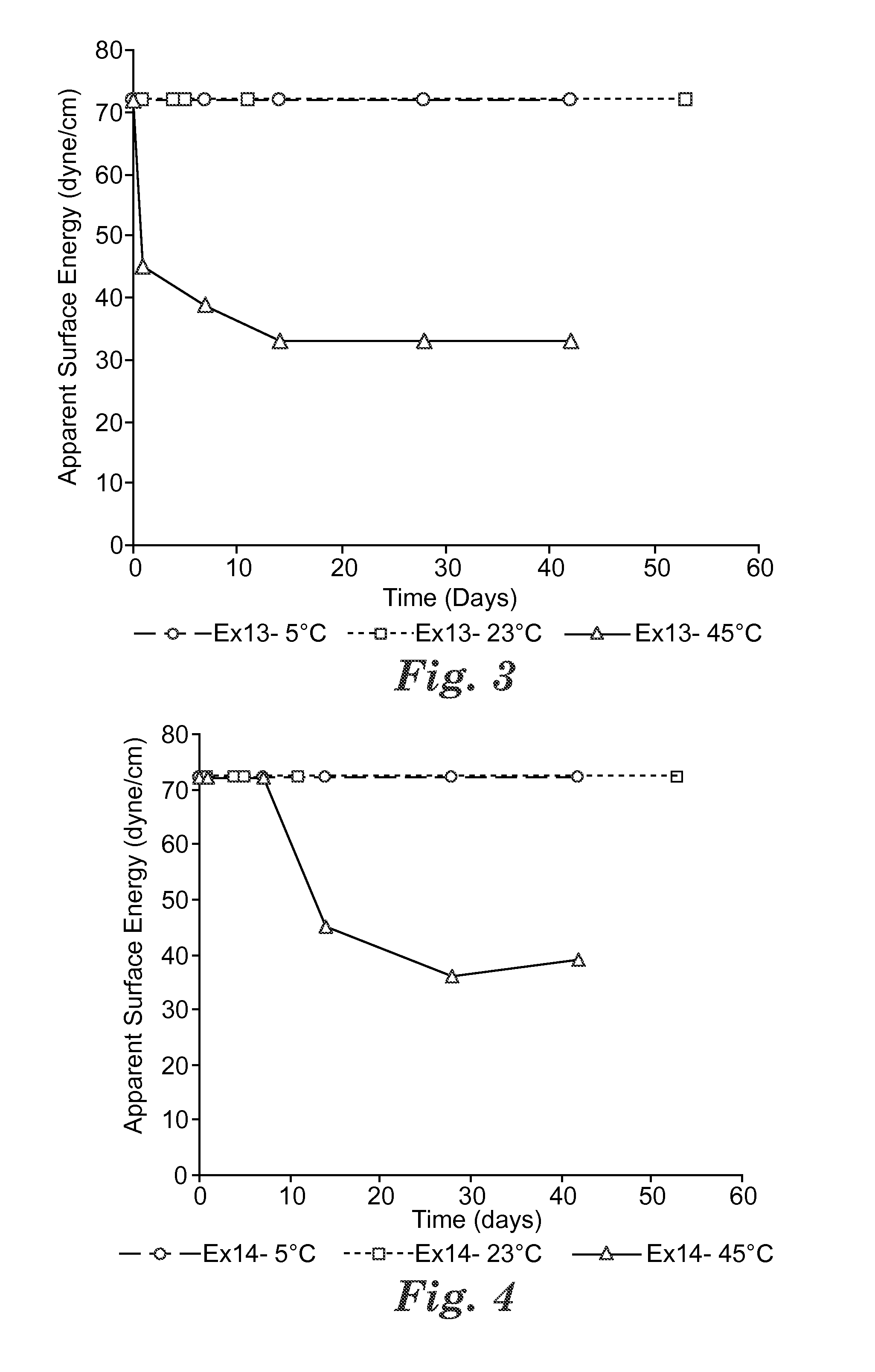
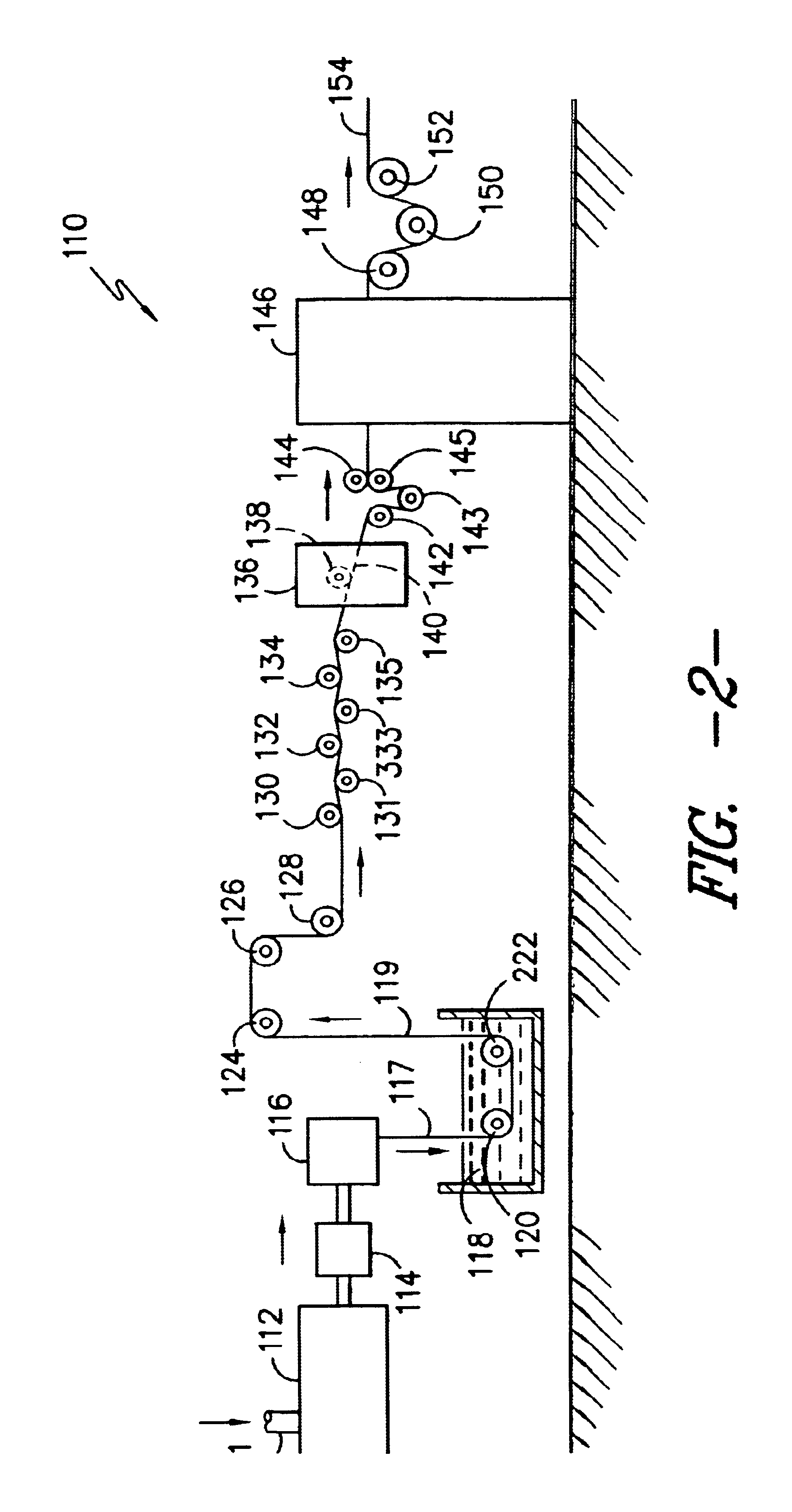
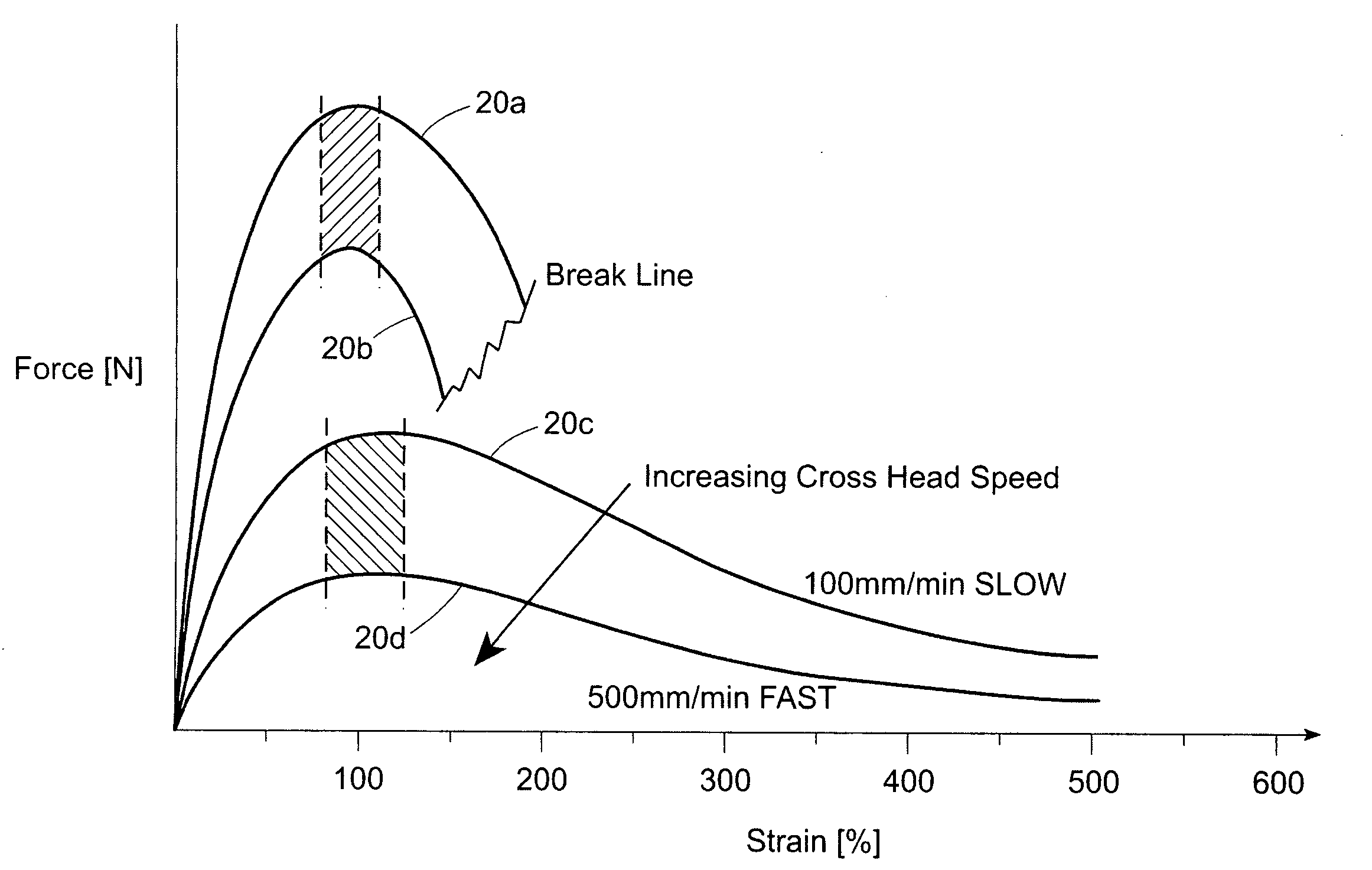
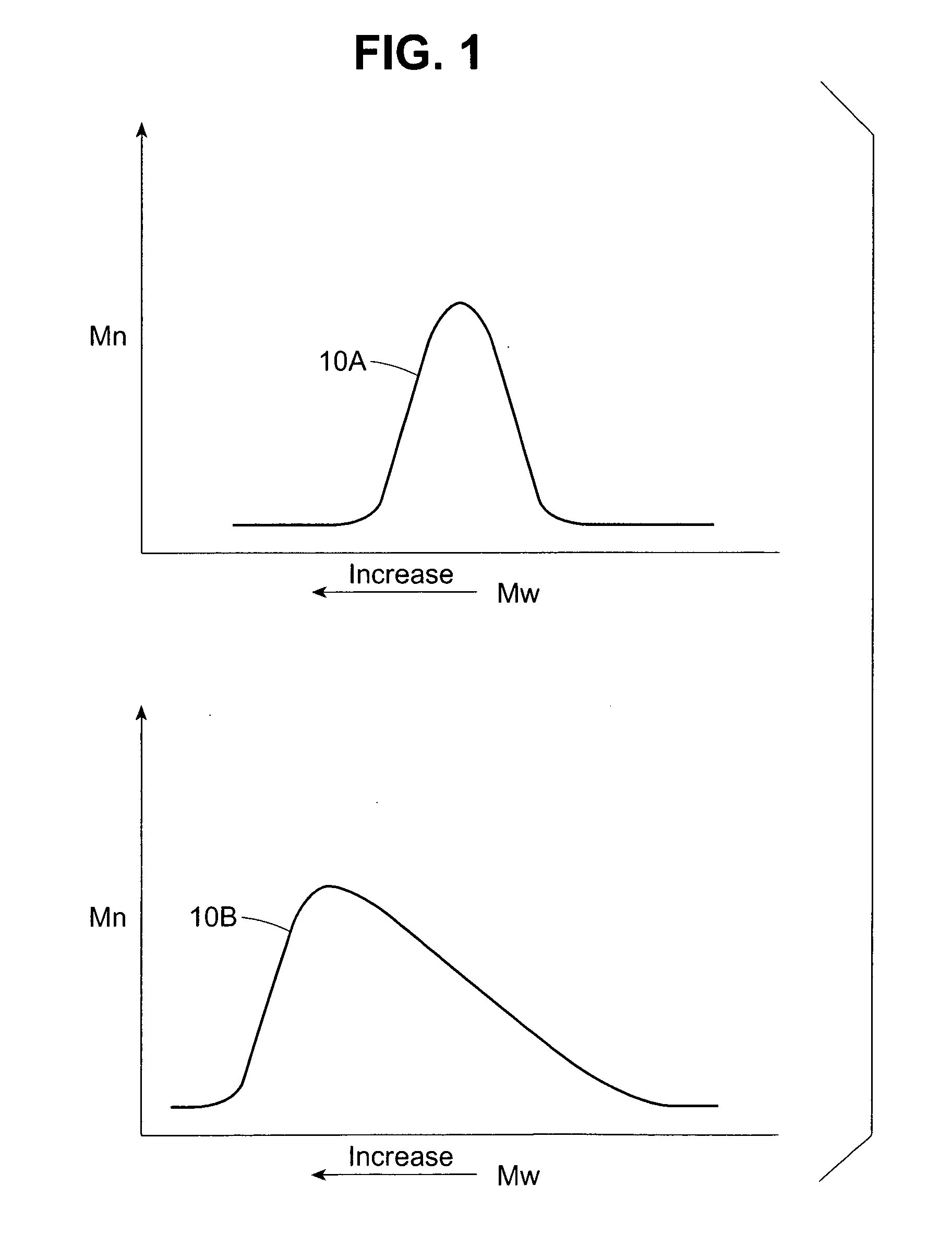
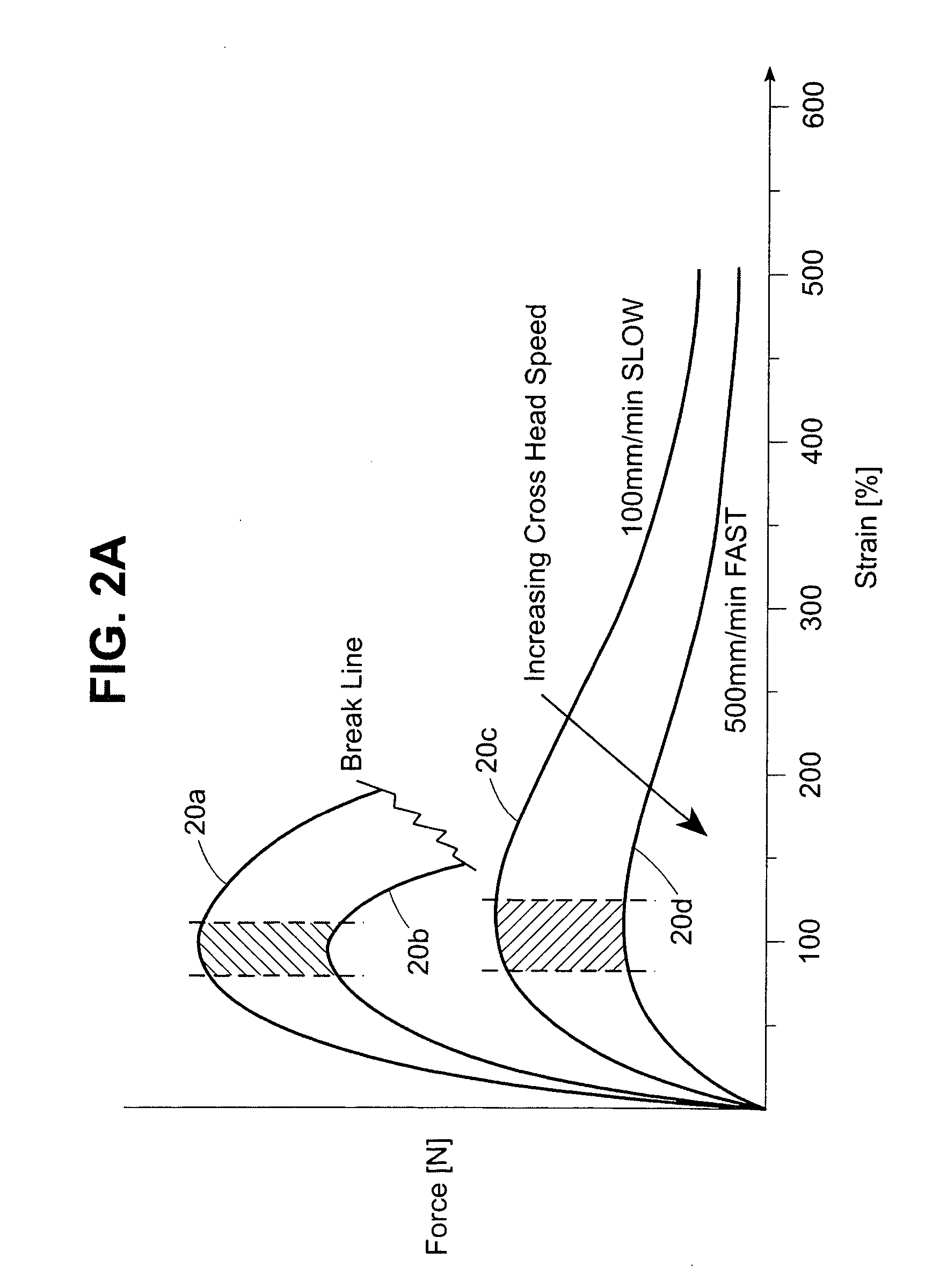
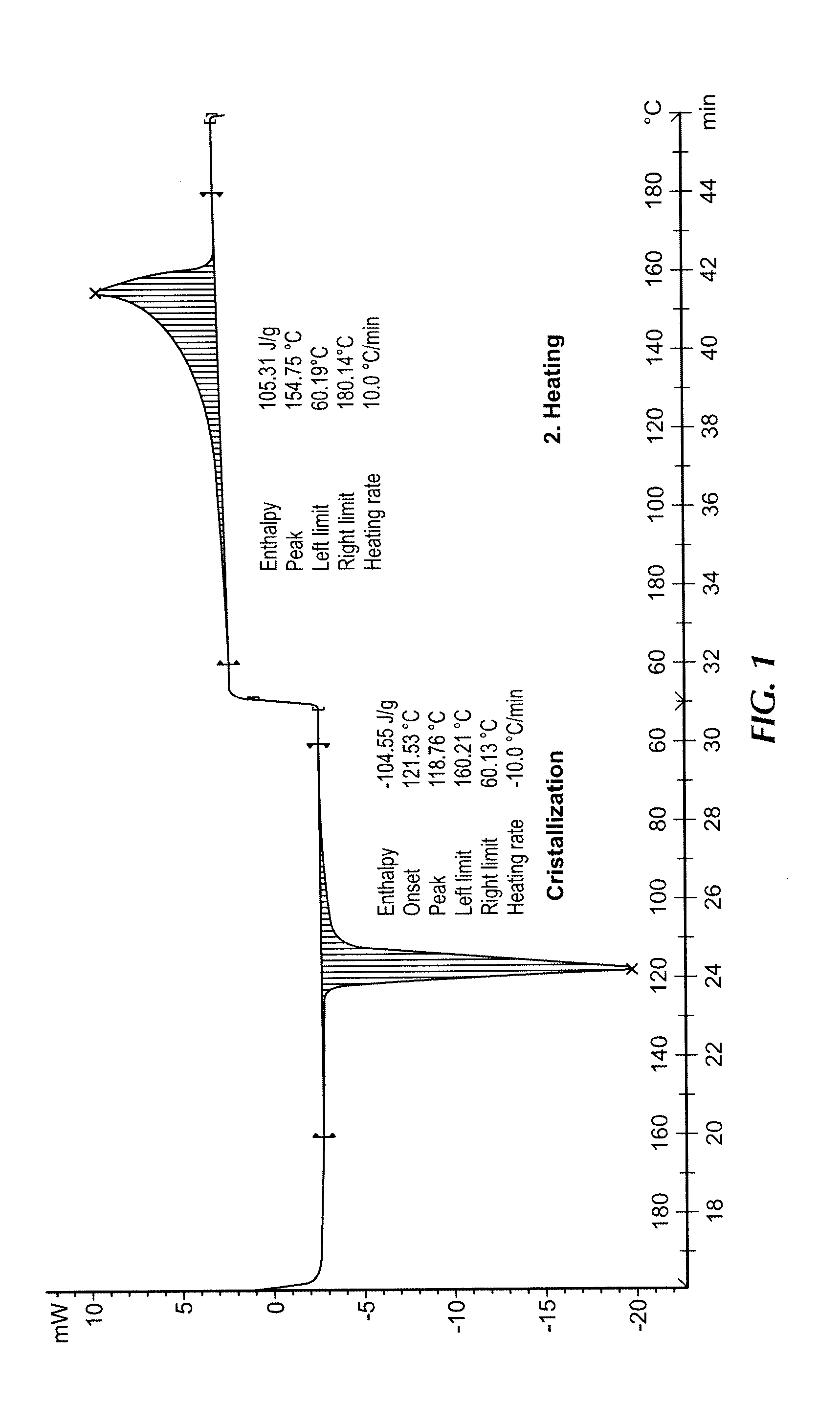
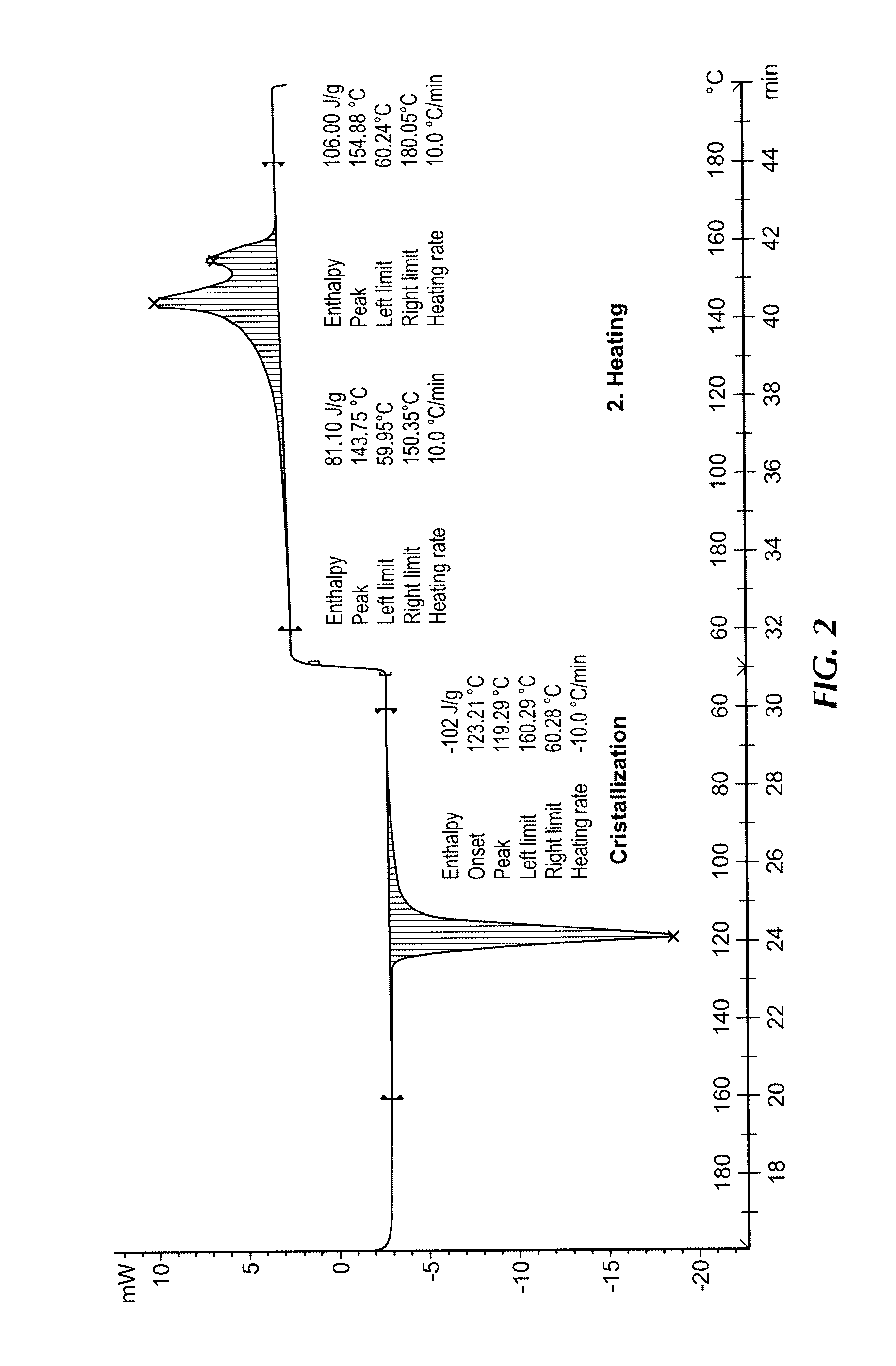
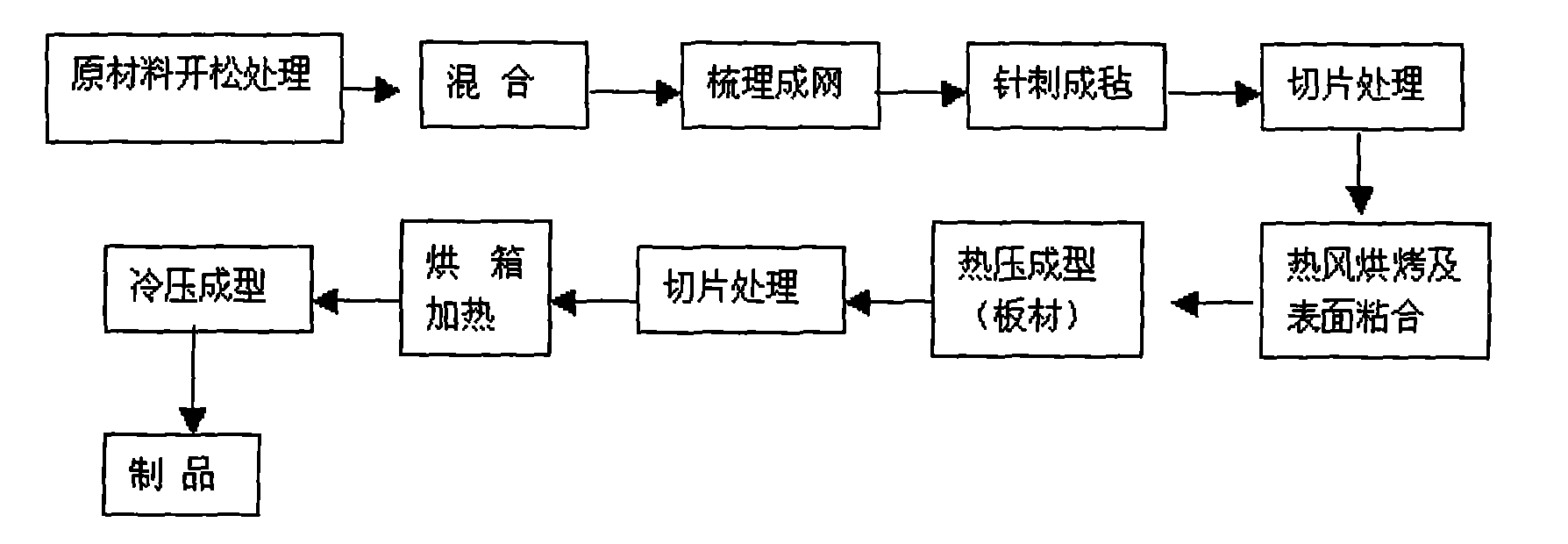
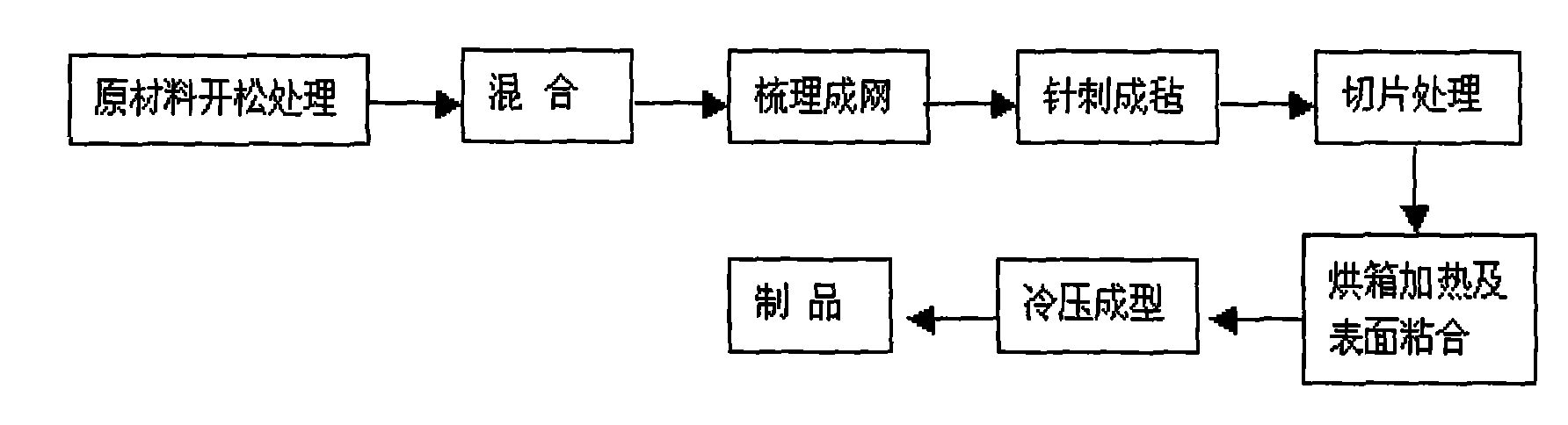
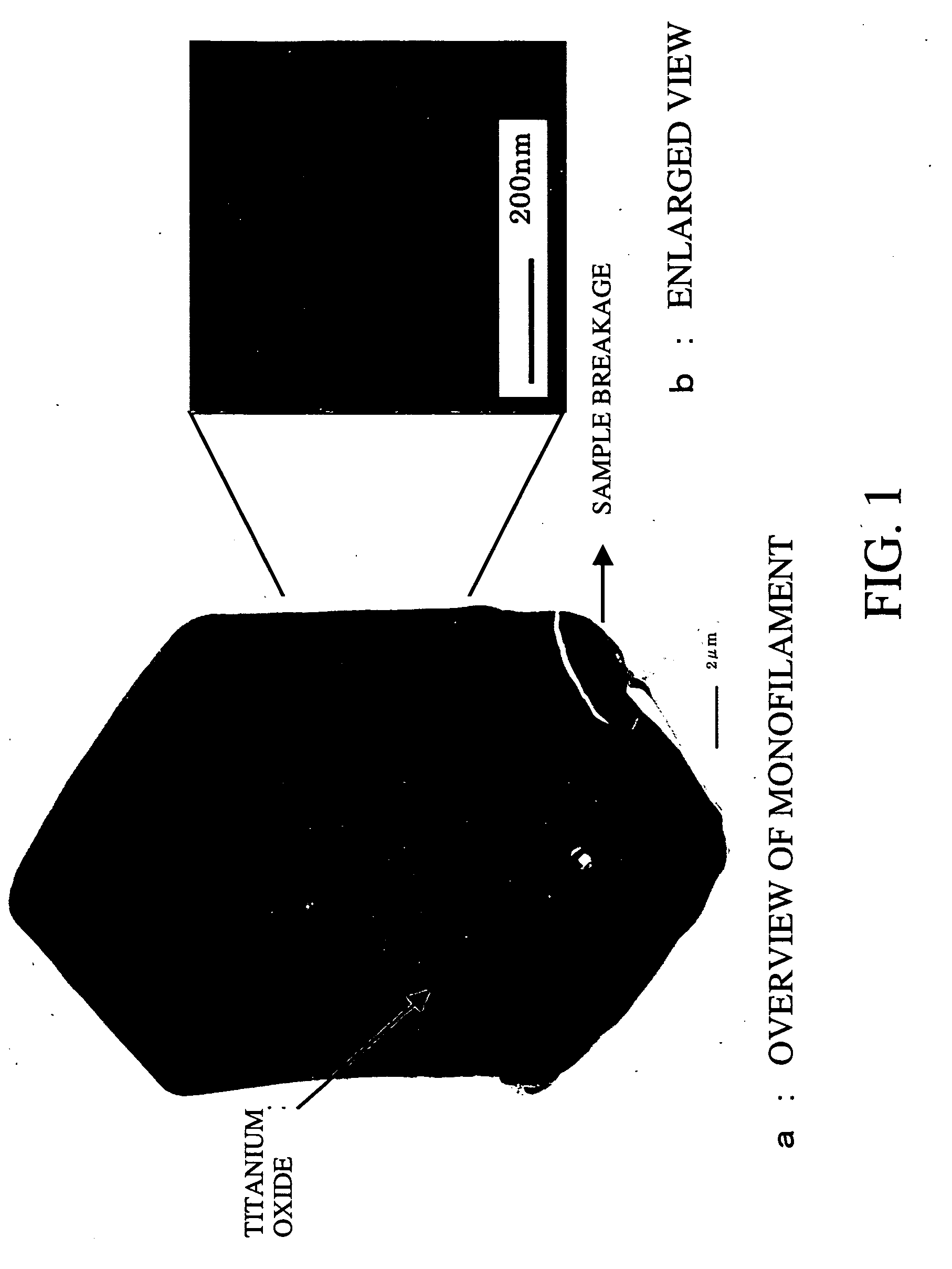
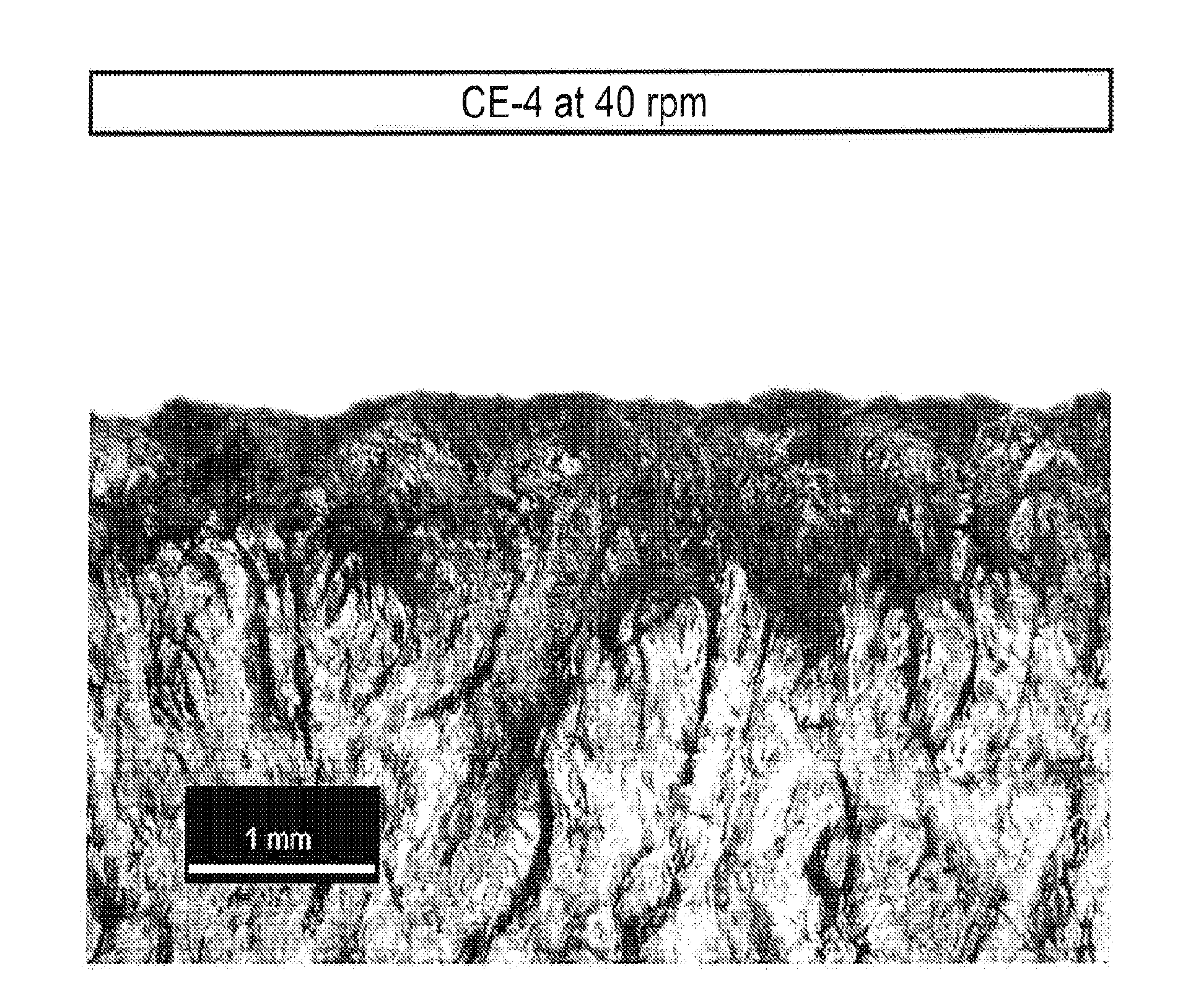
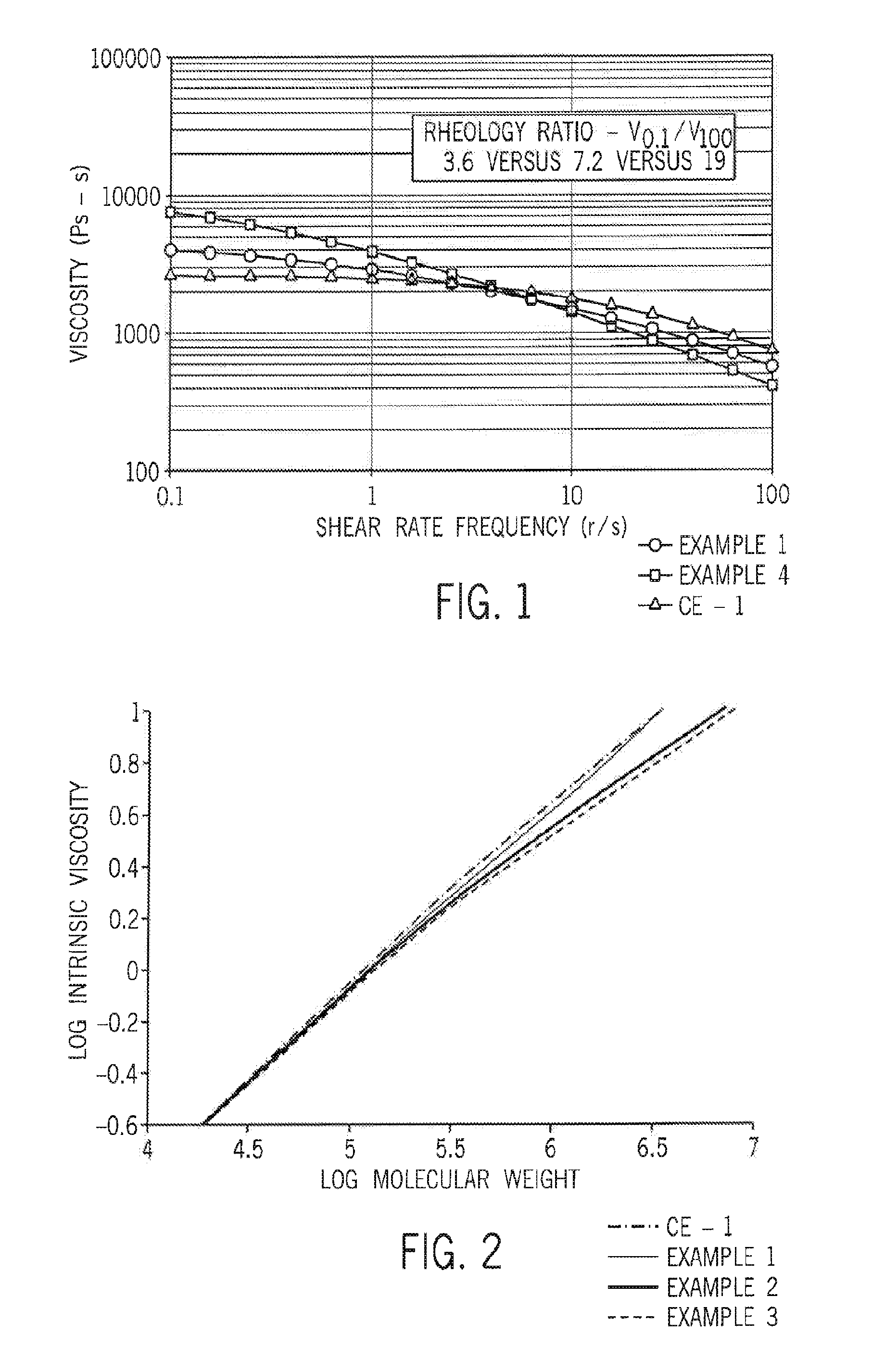
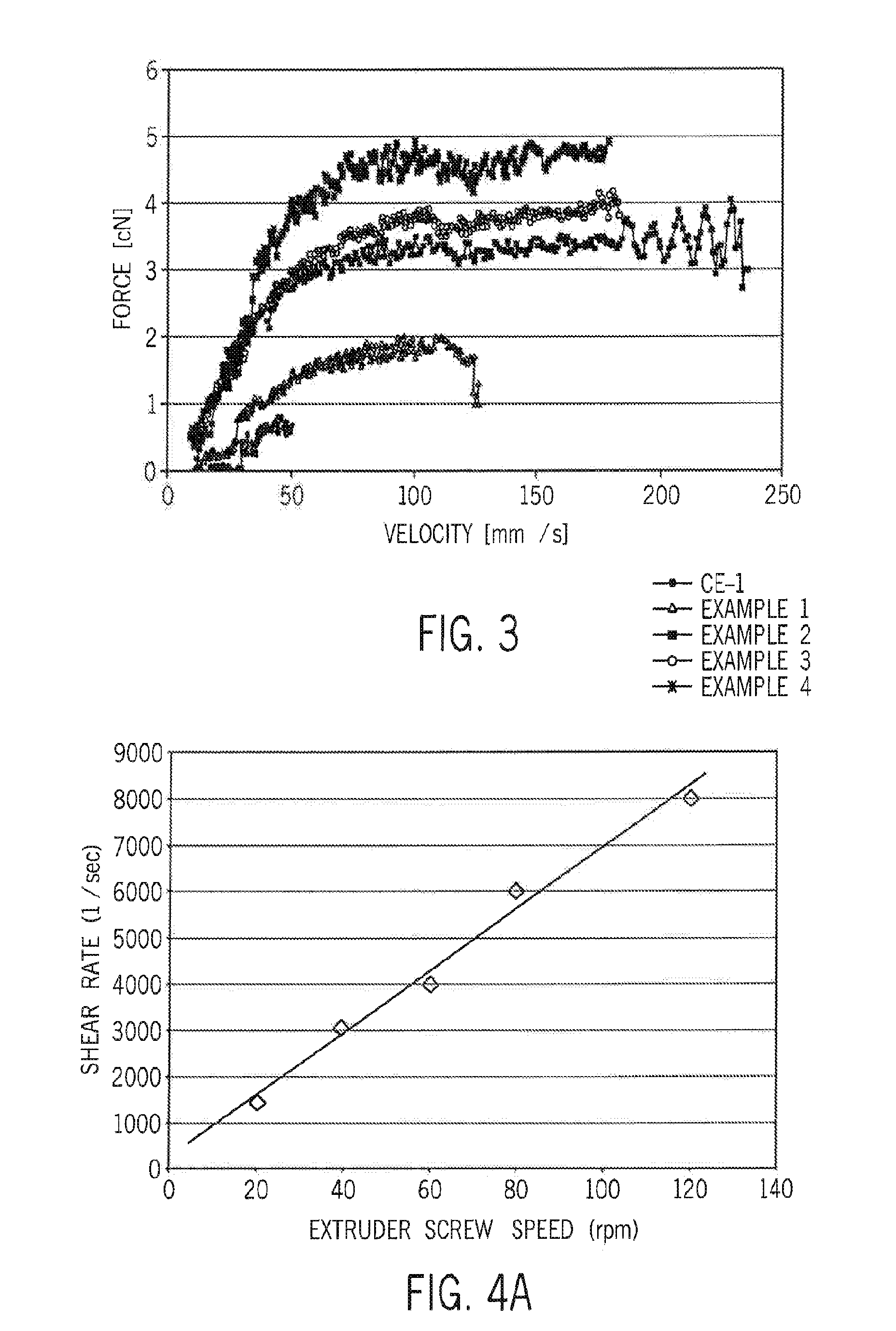
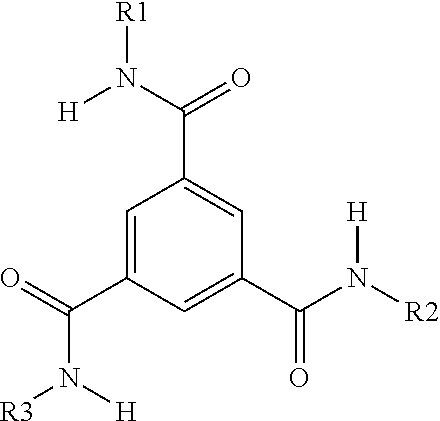
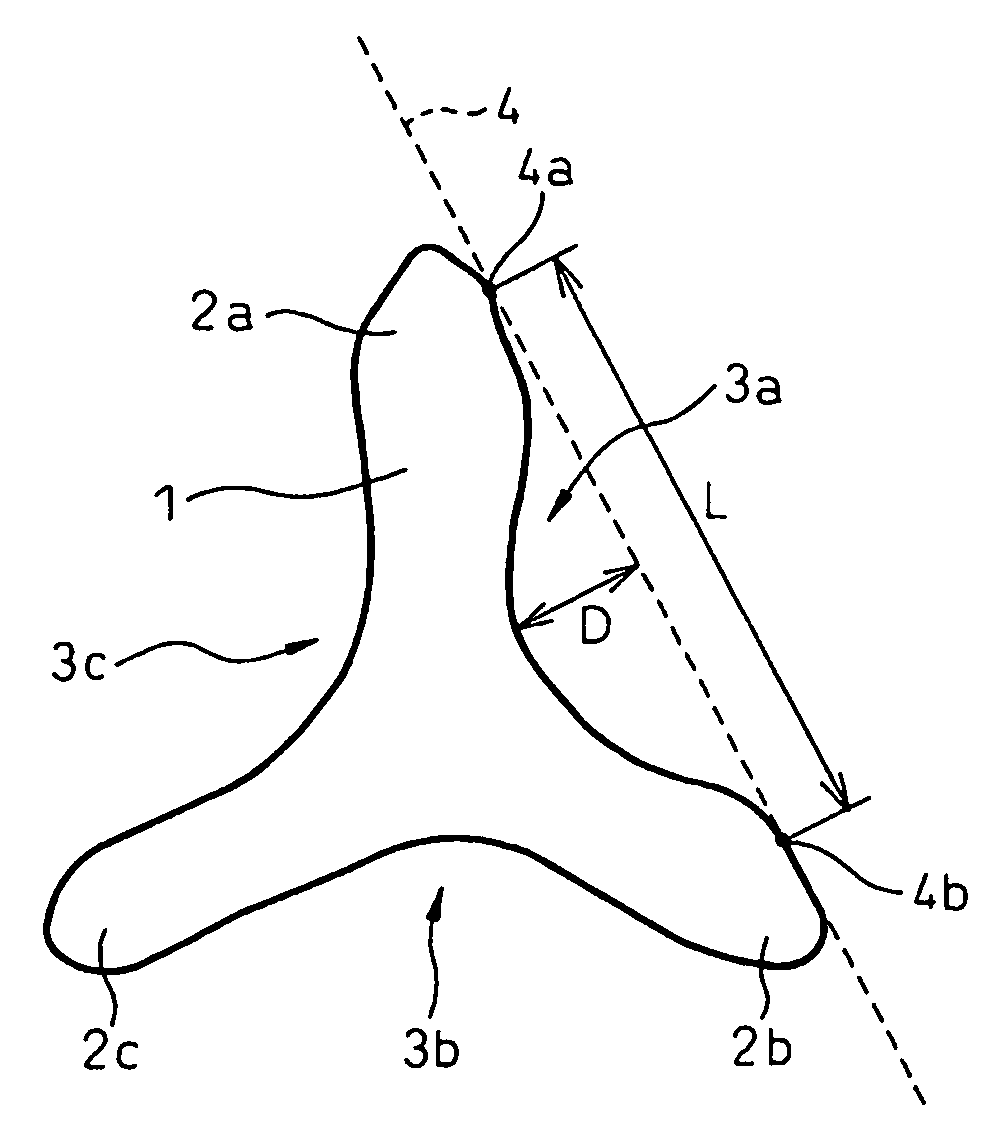
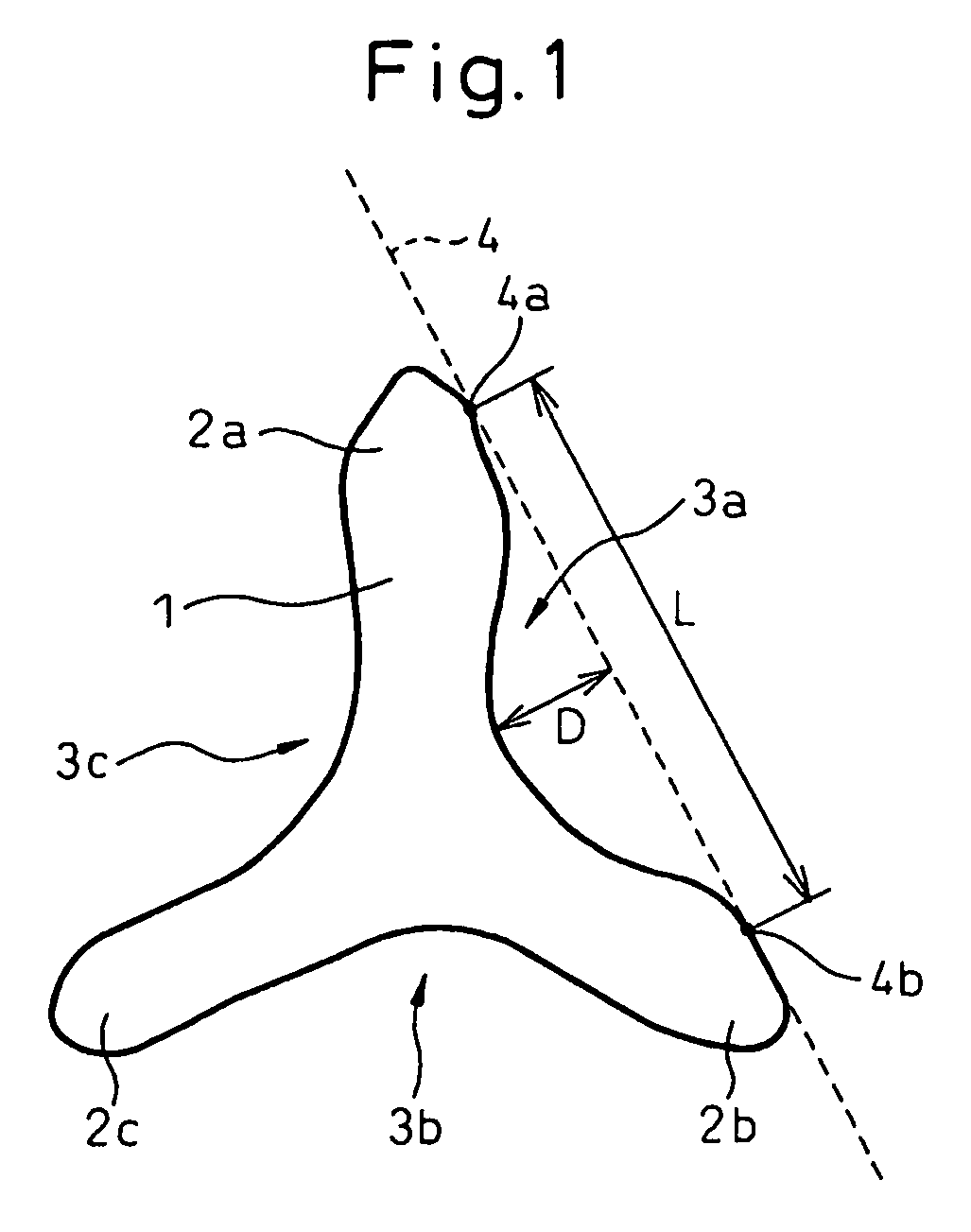
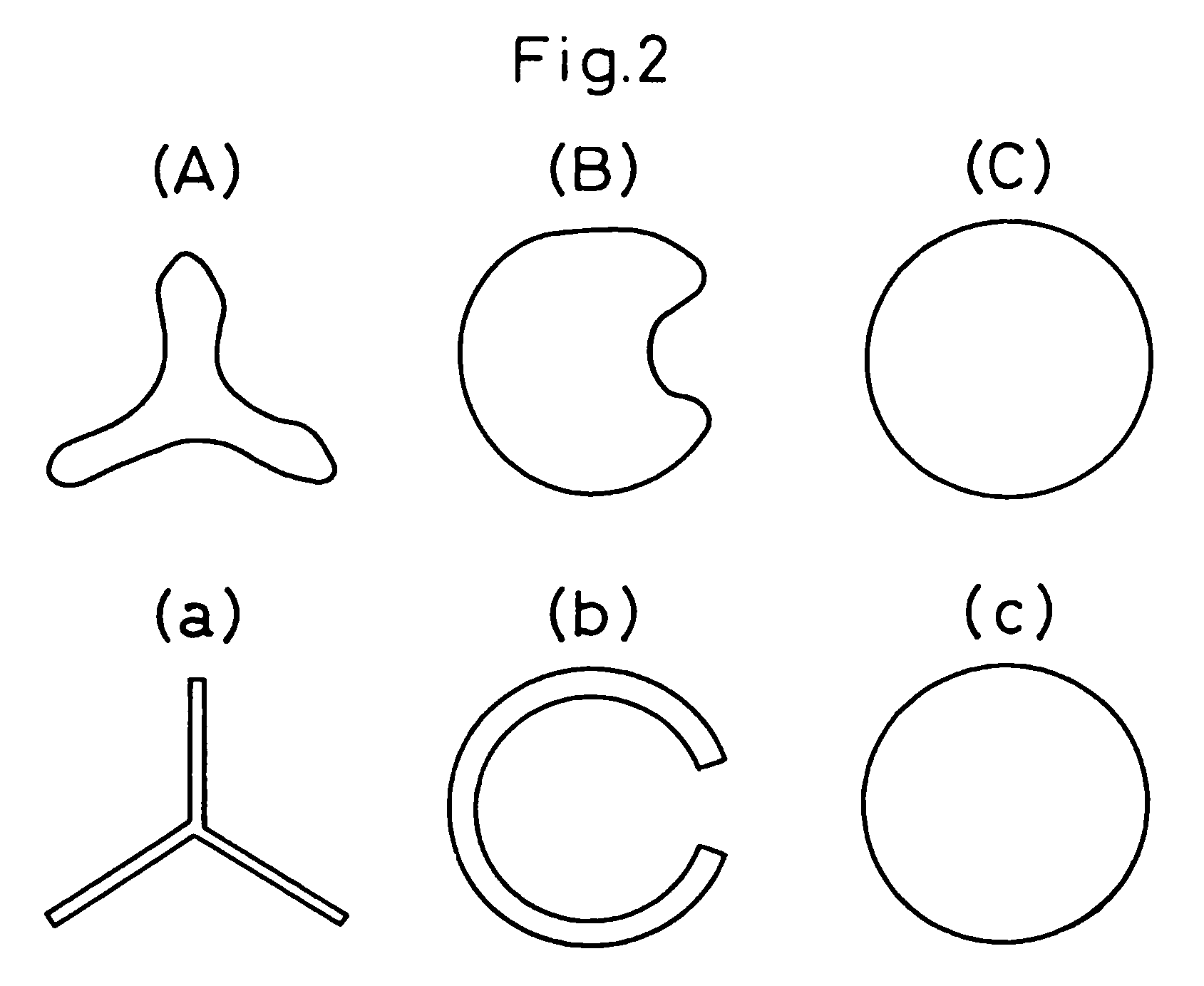
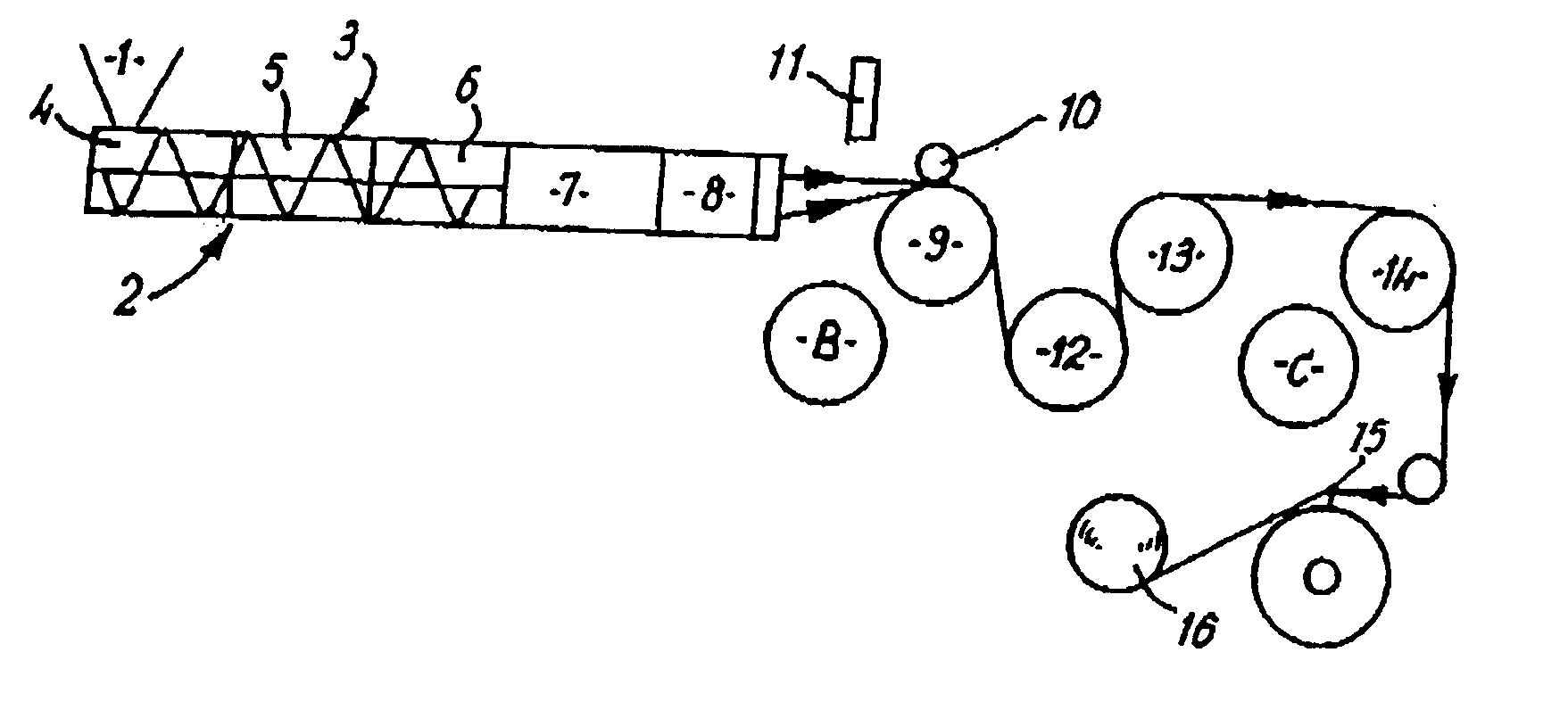
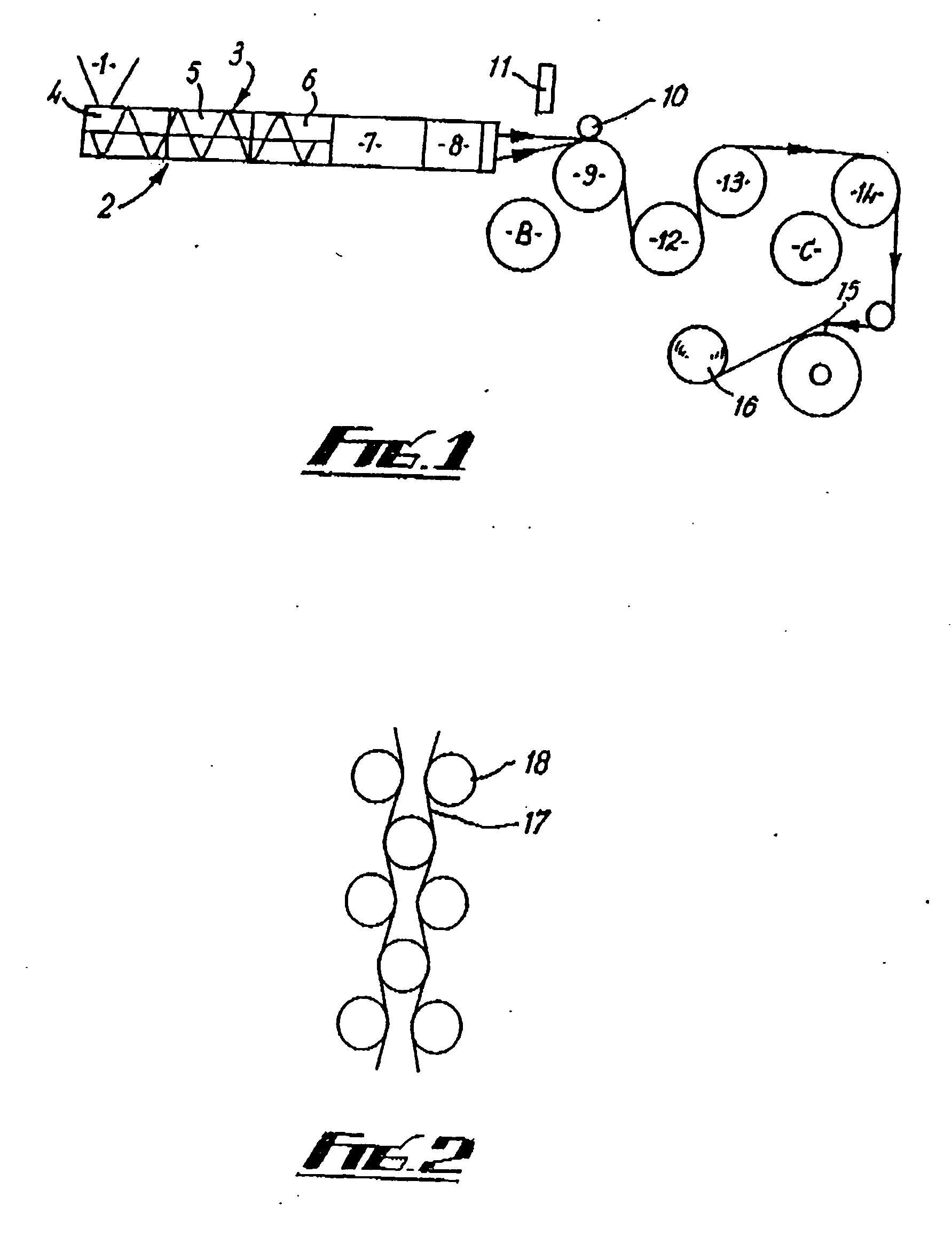
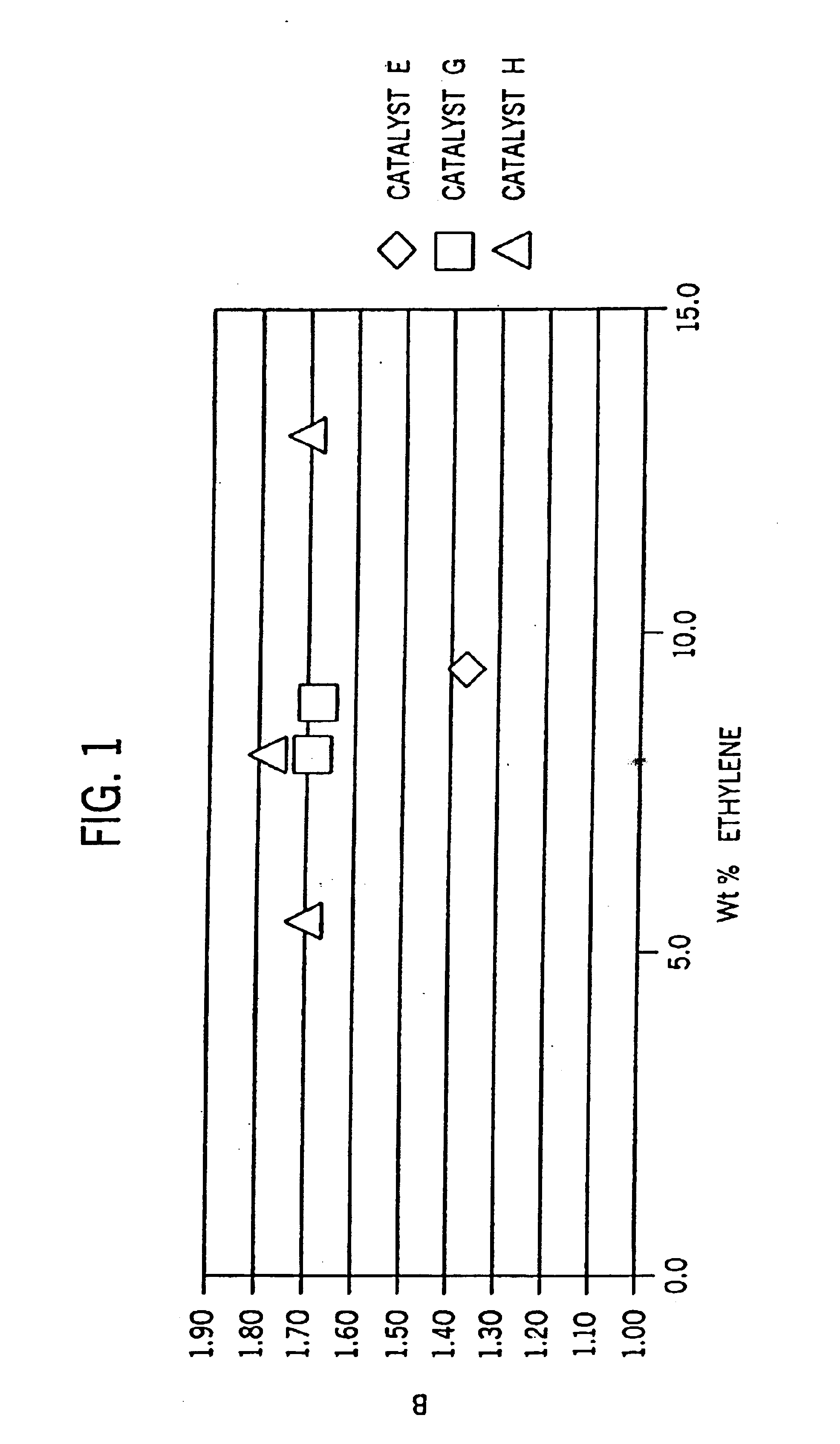
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
581results about "Monocomponent polypropylene artificial filament" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
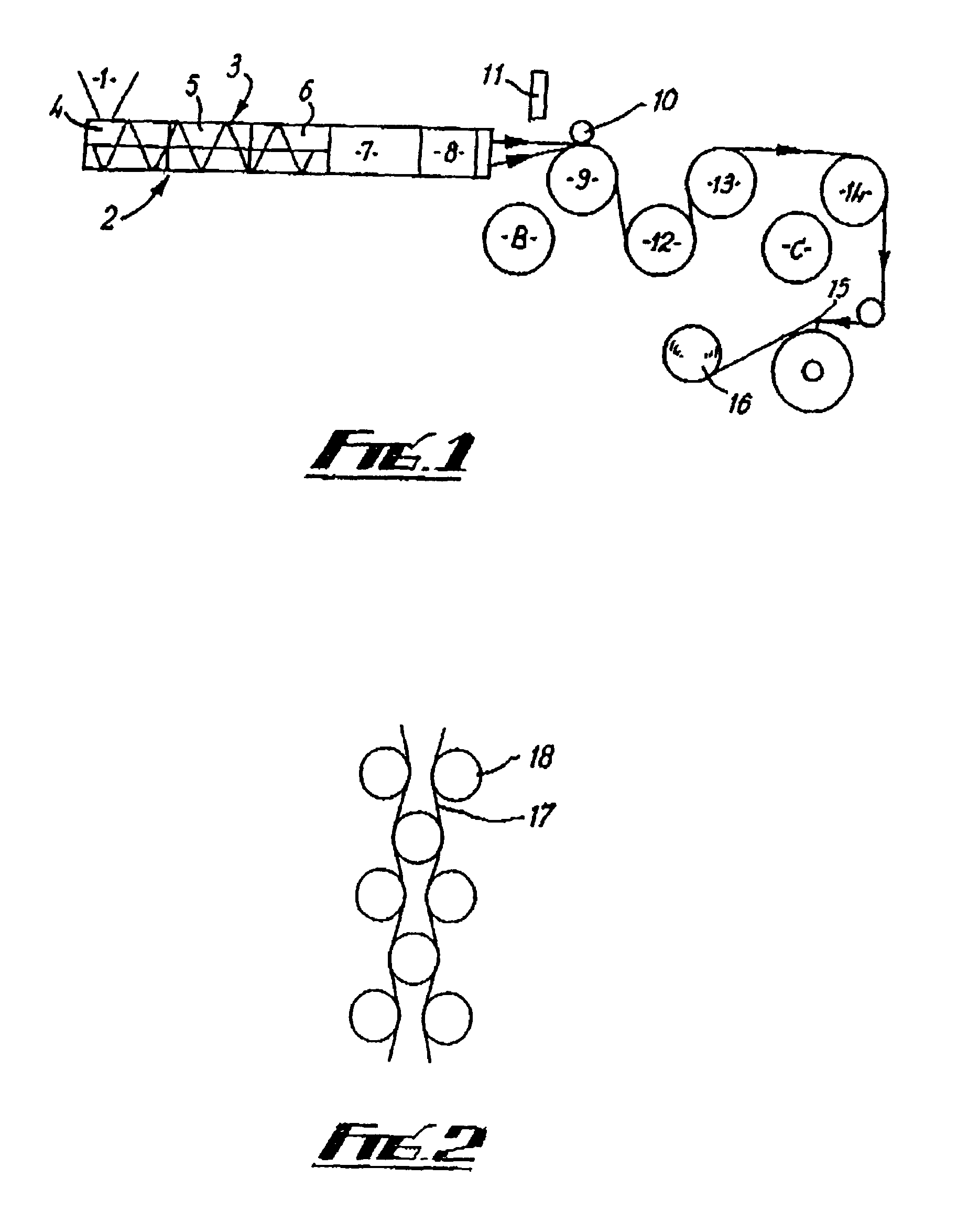
Isotactic propylene copolymers, their preparation and use
InactiveUS6960635B2Group 4/14 element organic compoundsOther chemical processesFiberZiegler–Natta catalyst
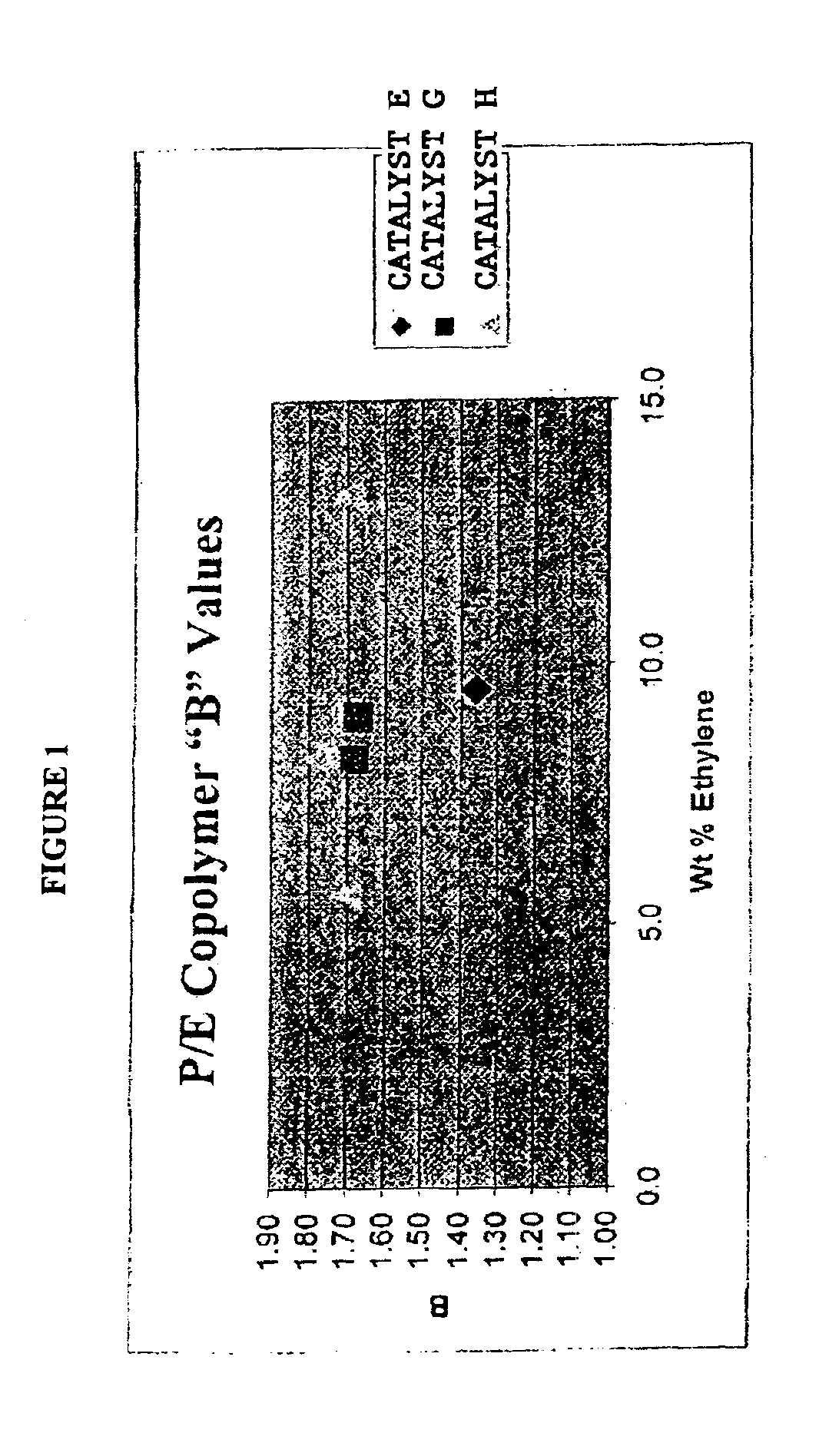
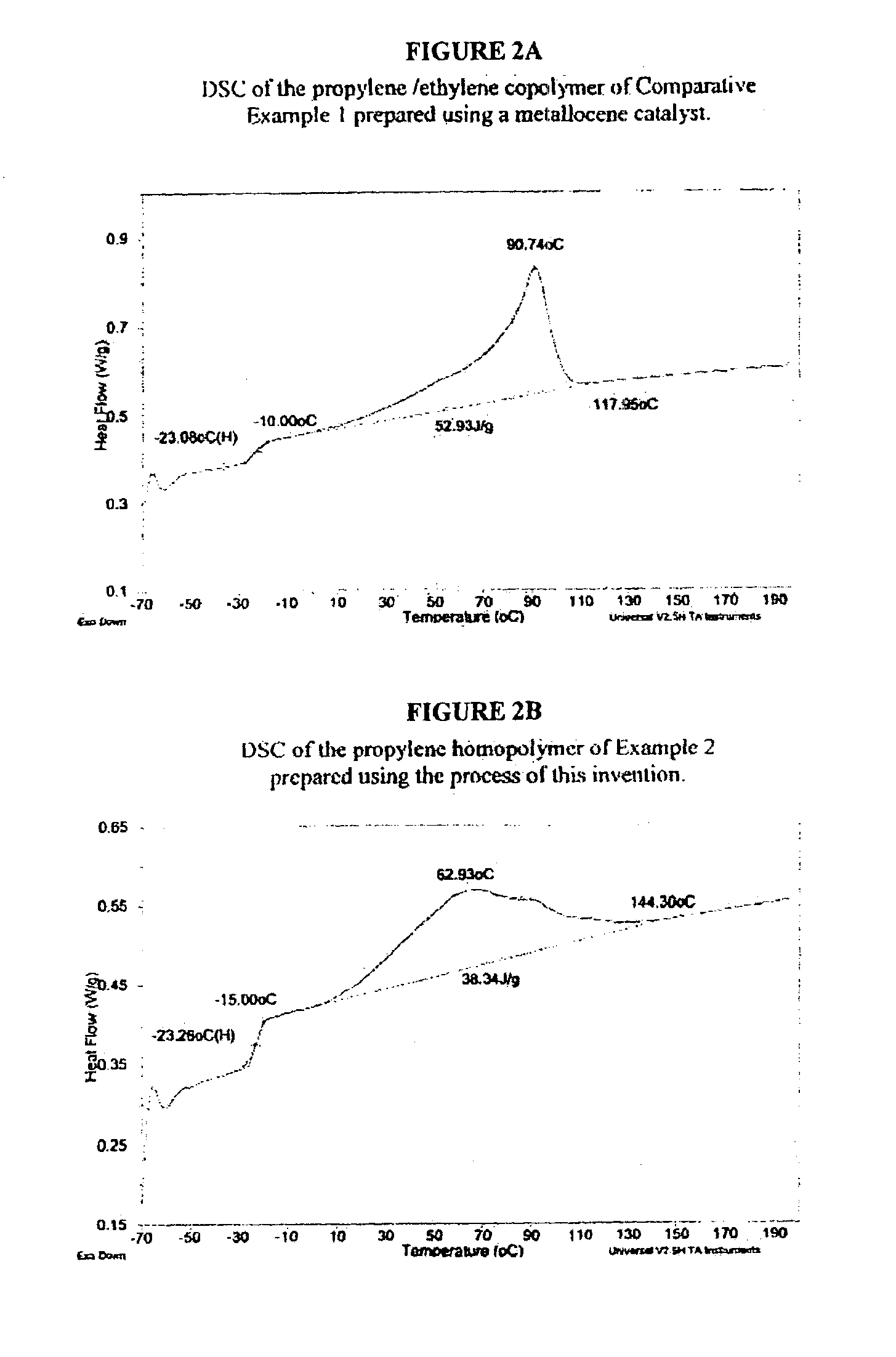
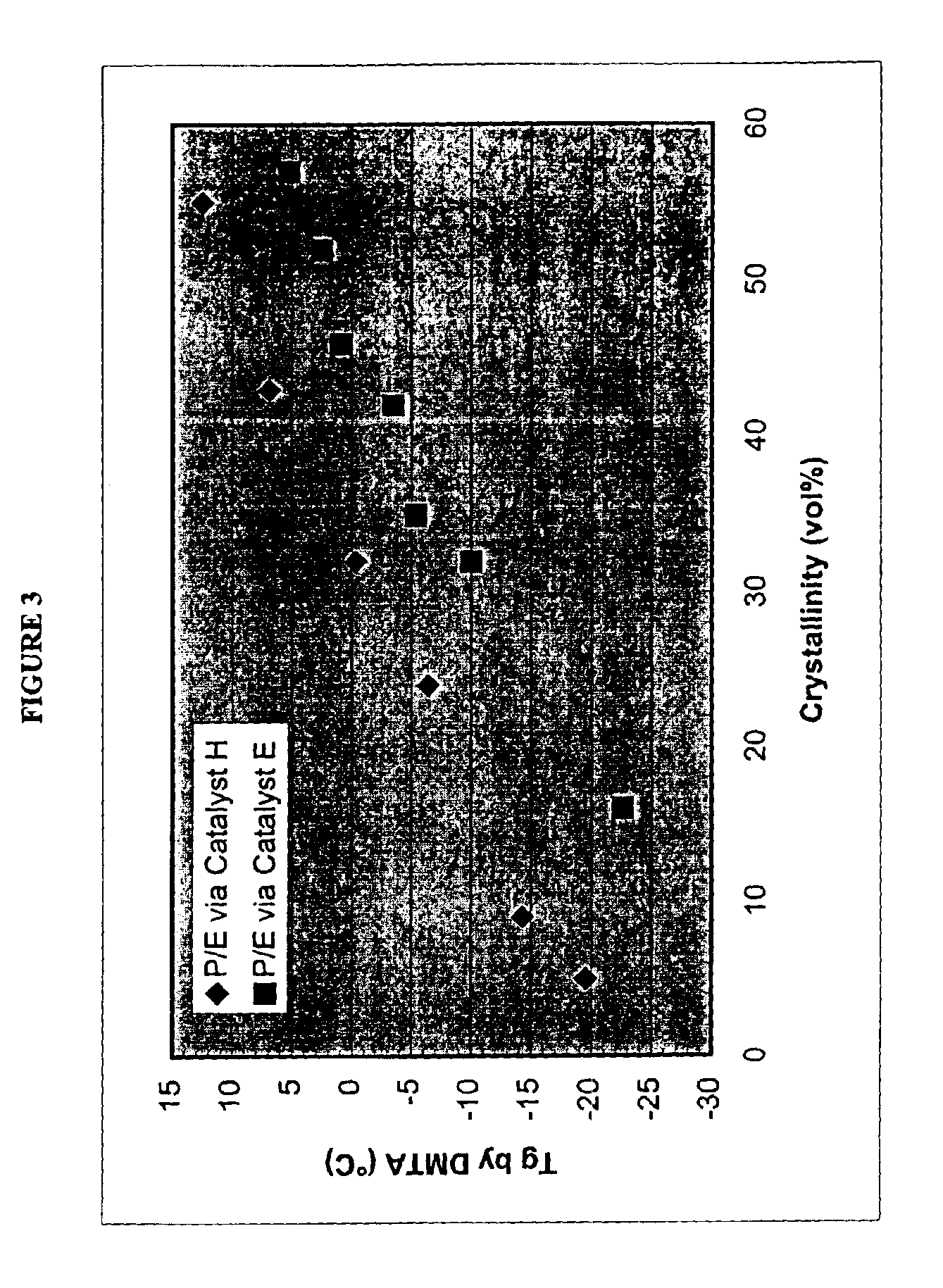
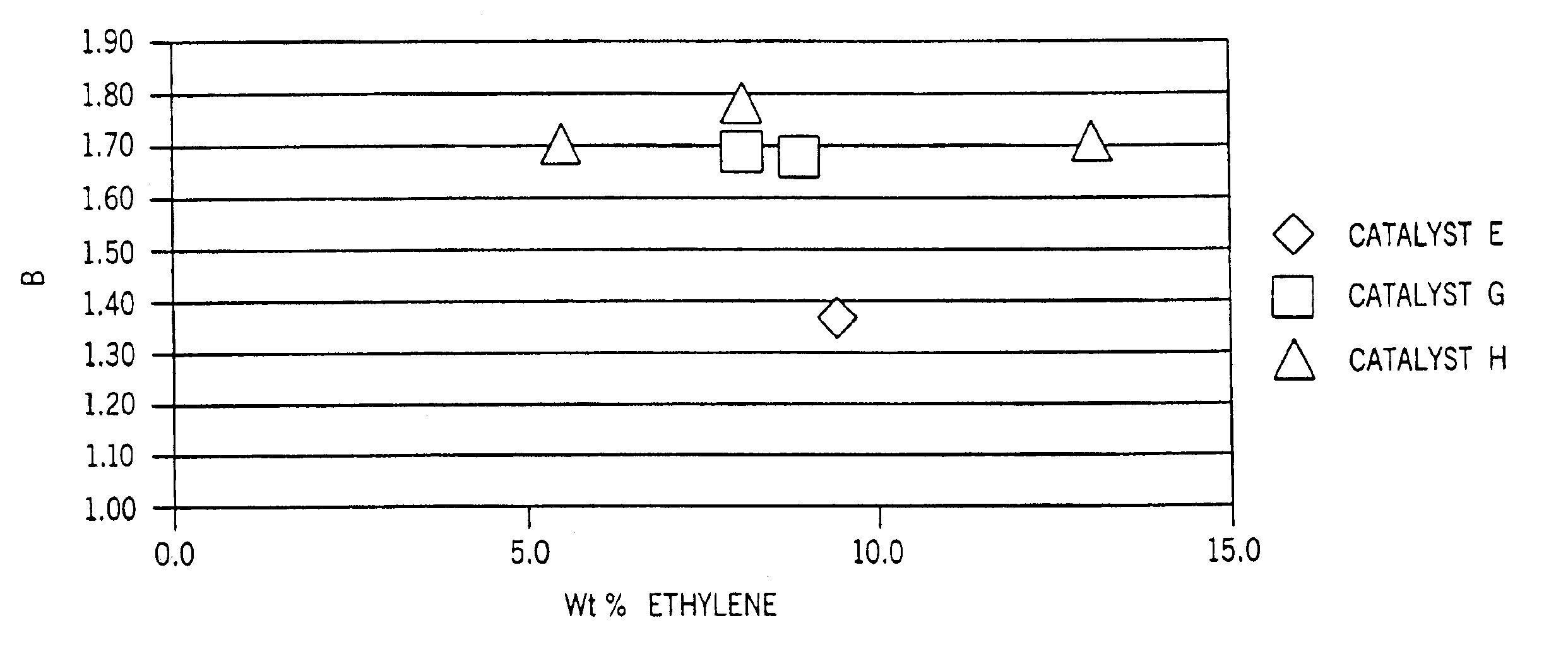
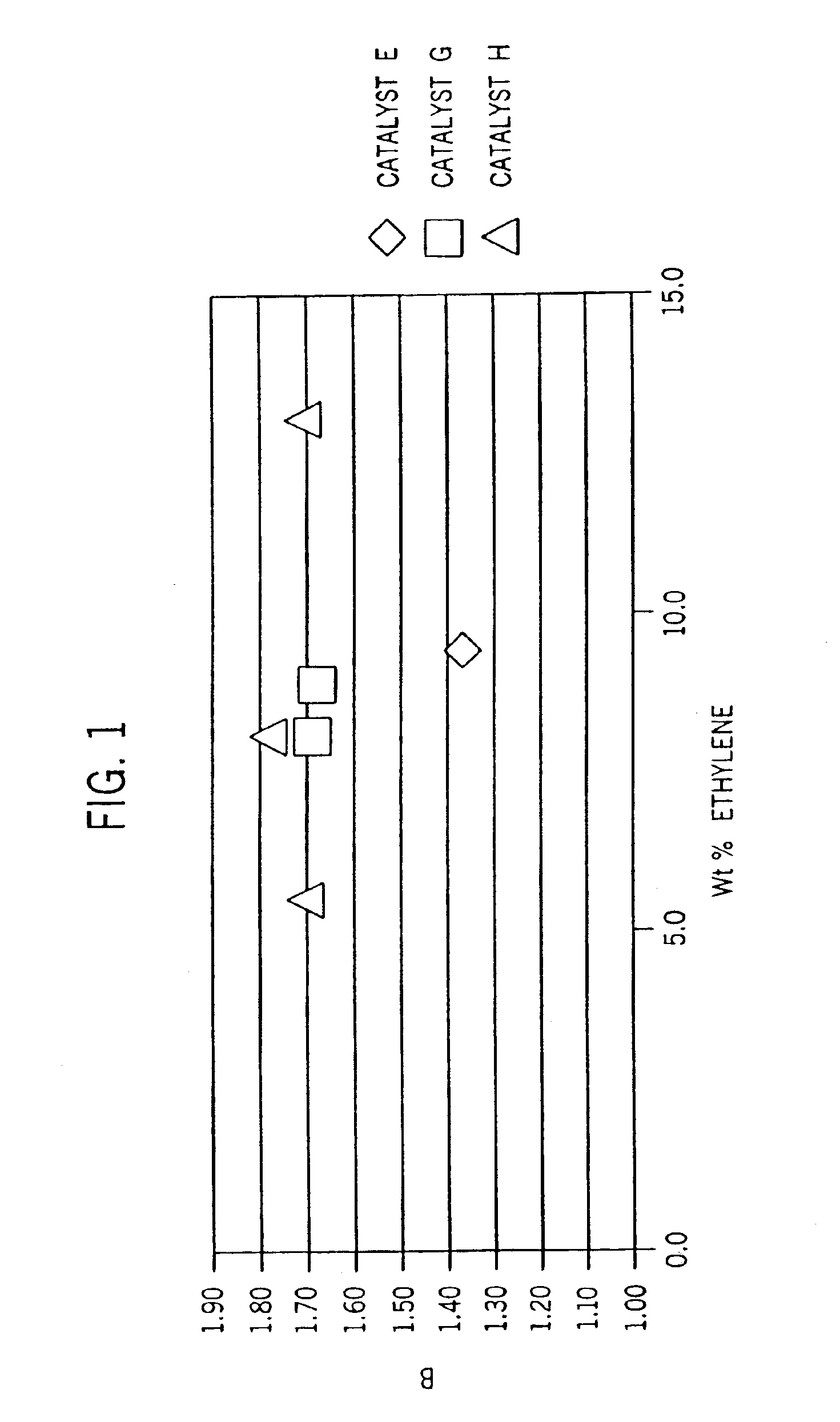
Unique copolymers comprising propylene, ethylene and / or one or more unsaturated comonomers are characterized as having: at least one, preferably more than one, of the following properties: (i) 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity, (ii) a B-value greater than about 1.4 when the comonomer content of the copolymer is at least about 3 wt %, (iii) a skewness index, Six, greater than about −1.20, (iv) a DSC curve with a Tme that remains essentially the same and a Tmax that decreases as the amount of comonomer in the copolymer is increased, and (v) an X-ray diffraction pattern that reports more gamma-form crystals than a comparable copolymer prepared with a Ziegler-Natta catalyst. These polypropylene polymers are made using a nonmetallocene, metal-centered, heteroaryl ligand catalyst. These polymers can be blended with other polymers, and are useful in the manufacture of films, sheets, foams, fibers and molded articles.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method of forming an implantable device
ActiveUS9352071B2Greater and beneficial tissue ingrowthLow melting pointWeft knittingMedical devicesImplanted devicePliability
Owner:ETHICON INC
Reinforced polymers
InactiveUS6331265B1Less tangleImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyWood working apparatusPolymer scienceNanotube
Provided is a method for the production of a reinforced polymer, which method comprises:(a) introducing carbon nanotubes into a polymer to provide a mixture of the polymer and the nanotubes;(b) stretching the mixture at or above the melting temperature (Tm) of the polymer to orient the carbon nanotubes; and(c) stretching the mixture in the solid state to further orient the carbon nanotubes.
Owner:FINA RES SA
Blends and sealant compositions comprising isotactic propylene copolymers
Films with excellent machine direction (MD) tear properties comprise at least one layer made from a polymer comprising:(A) at least 50 weight percent (wt %) propylene; and(B) at least 5 wt % ethylene and / or one or more unsaturated comonomers.Representative of component (B) unsatuarated comonomers are the C4-20 α-olefins, C4-20 dienes, styrenic compounds, and the like. Preferably, the film has at least one of a (i) haze value of less than about 10, (ii) 45 degree gloss of greater than about 65, and (iii) dart value of greater than about 100 g / mil. In one preferred embodiment, the layer comprises a compolymer characterized as having at least one of the following properties: (i) 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity, (ii) a B-value greater than about 1.4 when the comonomer content, i.e., the units derived from ethylene and / or the unsaturated comonomer(s), of the copolymer is at least about 3 wt %, (iii) a skewness index, Six, greater than about −1.20, (iv) a DSC curve with a Tme that remains essentially the same and a Tmax that decreases as the amount of comonomer, i.e., the units derived from ethylene and / or the unsaturated comonomer(s), in the copolymer is increased, and (v) an X-ray diffraction pattern that reports more gamma-form crystals than a comparable copolymer prepared with a Ziegler-Natta (Z-N) catalyst.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Monocomponent Monolayer Meltblown Web And Meltblowing Apparatus
ActiveUS20080026659A1Good molding effectIncrease fiber surface areaDispersed particle filtrationMagnetic materials for record carriersPolymer scienceRespirator
A porous monocomponent nonwoven web contains a bimodal mass fraction / fiber size mixture of intermingled continuous microfibers and larger size fibers of the same polymeric composition. There are at least five times as many microfibers as larger size fibers, and a histogram of the mass fraction of fibers vs. fiber size exhibits a larger size fiber mode greater than 10 μm. The web may be made by flowing fiber-forming material through a die cavity having larger size orifices and at least five times as many smaller size orifices to form filaments, attenuating the filaments into fibers and collecting the attenuated fibers to form the nonwoven web. The web is especially well suited to the manufacture of self-supporting three dimensional articles such as molded cup-shaped respirators and pleated air filters.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Thermoplastic monofilament fibers exhibiting low-shrink, high tenacity, and extremely high modulus levels
InactiveUS6759124B2High tensile strengthLow shrinkageSynthetic resin layered productsFilament/thread formingThermoplasticYarn
Unique thermoplastic monofilament fibers and yarns that exhibit heretofore unattained physical properties are provided. Such fibers are basically manufactured through the extrusion of thermoplastic resins that include a certain class of nucleating agent therein, and are able to be drawn at high ratios with such nucleating agents present that the tenacity and modulus strength are much higher than any other previously produced thermoplastic fibers, particularly those that also simultaneously exhibit extremely low shrinkage rates. Thus, such fibers require the presence of certain compounds that quickly and effectively provide rigidity to the target thermoplastic (for example, polypropylene), particularly after heat-setting. Generally, these compounds include any structure that nucleates polymer crystals within the target thermoplastic after exposure to sufficient heat to melt the initial pelletized polymer and allowing such an oriented polymer to cool. The compounds must nucleate polymer crystals at a higher temperature than the target thermoplastic without the nucleating agent during cooling. In such a manner, the "rigidifying" nucleator compounds provide nucleation sites for thermoplastic crystal growth. The preferred "rigidifying" compounds include dibenzylidene sorbitol based compounds, as well as less preferred compounds, such as [2.2.1]heptane-bicyclodicarboxylic acid, otherwise known as HPN-68, sodium benzoate, certain sodium and lithium phosphate salts [such as sodium 2,2'-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphate, otherwise known as NA-11]. Specific methods of manufacture of such inventive thermoplastic fibers, as well as fabric articles made therefrom, are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Hydrophilic polyproylene melt additives
InactiveUS20120077886A1Stable and durable hydrophilicityLow costBiocideCosmetic preparationsPolymer scienceThermosetting polymer
Melt additive ionic and non-ionic surfactants to impart stable durable hydrophilicity to thermoplastic polymers or blends thereof.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Porous fiber
InactiveUS7097904B2Good color propertiesMaintain good propertiesFilament/thread formingNanotechnologyMetallurgyNanopore
The present invention provides a nanoporous fiber being substantially free from coarse pores and having homogeneously dispersed nanopores, unlike conventional porous fibers. A porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, and the pores are unconnected pores, or a porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, the pores are connected pores, and the fiber has a strength of 1.0 cN / dtex or more.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Monocomponent monolayer meltblown web and meltblowing apparatus
ActiveUS7902096B2Narrow distributionReduced service lifeDispersed particle filtrationFilament/thread formingPolymer scienceAir filter
A porous monocomponent nonwoven web contains a bimodal mass fraction / fiber size mixture of intermingled continuous microfibers and larger size fibers of the same polymeric composition. There are at least five times as many microfibers as larger size fibers, and a histogram of the mass fraction of fibers vs. fiber size exhibits a larger size fiber mode greater than 10 μm. The web may be made by flowing fiber-forming material through a die cavity having larger size orifices and at least five times as many smaller size orifices to form filaments, attenuating the filaments into fibers and collecting the attenuated fibers to form the nonwoven web. The web is especially well suited to the manufacture of self-supporting three dimensional articles such as molded cup-shaped respirators and pleated air filters.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Flash spun web containing sub-micron filaments and process for forming same
A nonwoven fibrous structure and process for forming it, which is an interconnecting web of polyolefin filaments having filament widths greater than about 1 micrometer which are further interconnected with webs of smaller polyolefin filaments having filament widths less than about 1 micrometer, wherein the smaller polyolefin filaments comprise a majority of all filaments.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Thermoplastic fibers exhibiting durable high color strength characteristics
InactiveUS6849330B1Reduce extractionQuick and efficient changeoverFireproof paintsSynthetic resin layered productsYarnPolymer science
Improvements in permitting brighter colorations within polypropylene fibers and / or yarns while simultaneously providing more efficient production methods of manufacturing of such colored fibers as well are provided. Generally, such fibers and / or yarns have been colored with pigments, which exhibit dulled results, or dyes, which exhibit high degrees of extraction and low levels of lightfastness. Such dull appearances, high extraction levels, and less than stellar lightfastness properties negatively impact the provision of such desirable colored polypropylene fibers and / or yarns which, in turn, prevents the widespread utilization of such fibers and yarns in various end-use applications. Thus, it has surprisingly been determined that brighter colorations, excellent extraction, and more-than-acceptable lightfastness characteristics can be provided, preferably, through manufacture with certain polymeric colorants that include poly(oxyalkylene) groups thereon. Fabric articles comprising such novel fibers and / or yarns are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Plastically deformable nonwoven web
InactiveUS20050244619A1Structural extensibility of the web substantiallyButtonsDecorative surface effectsFiberEthylene Homopolymers
A nonwoven web formed of substantially continuous spunmelt fibers is formed from a homopolymer of polypropylene having a skewed molecular weight distribution and a polydispersity of less than 3.5. The web, when subjected to high speed incremental deformation, is plastically deformed and characterized by, e.g., a tensile strength at 400% elongation which is at least 10% of the peak tensile strength, a tensile strength at 250% elongation which is at least 40% of the peak tensile strength, and a ratio of the viscoelastic deformation energy after the peak tensile strength to the viscoelastic deformation energy before the peak tensile strength which is greater than one.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY NONWOVENS
Polyolefin fibers and method for the production thereof
InactiveUS6811716B1Poor propertyPoor processabilityOther chemical processesFibre typesFiberPolyolefin
A method for producing hydrophobic polyolefin-containing fibers or filaments, in particular cardable staple fibers, using spin finishes applied after spinning and stretching, that comprise at least one water-insoluble ester of a mono-, di-, tri- or tetrahydric alcohol with a molecular weight not exceeding 500 and a branched or straight chain fatty acid with between 12 and 30 carbon atoms, e.g. a water-insoluble ester of ethylene or propylene glycol, glycerol, neopentyl glycol, trimethylolethane or trimethylolpropane and at least one saturated or unsaturated fatty acid residue having 12-24 carbons atoms, an anionic or nonionic antistatic agent preferably being applied after crimping; fibers produced by the method; and nonwovens produced from such fibers.
Owner:FIBERVISIONS LP
Anti-bacterial bamboo charcoal nano-fiber and production method thereof
ActiveCN101440533AImprove adsorption capacityGood moisture absorptionMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentMelt spinning methodsRenewable resourceProcess conditions
The invention relates to a nanometer bamboo charcoal antibacterial fiber and a method for producing the same, in particular to a melt-spinning method for producing the nanometer bamboo charcoal antibacterial fiber. The nanometer bamboo charcoal antibacterial fiber consists of nanometer bamboo charcoal, nanometer silver and a carrier slice, wherein the carrier slice is one of terylene, polypropylene fiber or chinlon. An antimicrobial master batch is prepared first and is mixed with the carrier slice according to certain proportion, and then the mixture is used for preparing the required nanometer bamboo charcoal antibacterial fiber through the melt-spinning method. The nanometer bamboo charcoal antibacterial fiber has the advantages that the bamboo charcoal is a renewable resource which is rich, can be produced through adjusting part of the process conditions by using the prior equipment, and passes test and detection with the antibacterial rate of more than 98 percent; and the nanometer bamboo charcoal antibacterial fiber is not only applied in the aspect of dress, but also widely applied to transportation, environmental protection, medical treatment and other industries.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGDA TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO LTD +1
Fibers and Nonwovens with Improved Mechanical Properties
InactiveUS20110081817A1Reduce the overall diameterReduce decreaseWood working apparatusMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentPolymer scienceNonwoven fabric
The present invention relates to fibers, particularly to as-spun fibers, having improved properties, in particular improved mechanical properties. In particular, the present invention relates to fibers comprising a metallocene polypropylene having a broader molecular weight distribution. The present invention further relates to nonwovens comprising such fibers and to a process for producing such fibers and nonwovens. The fibers and the nonwoven of the present invention are characterized by improved properties, in particular improved mechanical properties, when compared to the prior art fibers and nonwovens.
Owner:TOTAL RES & TECH FELUY
Short cut microfibers
InactiveUS20120302119A1Reduce blockingReduce fusionFilament/thread formingMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentPolymer scienceProduced water
A short-cut, water non-dispersible polymer microfiber is provided comprising at least one water non-dispersible polymer wherein the water non-dispersible polymer microfiber has an average fineness of less than 1 denier per filament; and wherein said water non-dispersible short-cut polymer microfiber has an aspect ratio of about 300 to about 1000. A process for producing water non-dispersible polymer microfibers and a process for producing nonwoven articles are also provided.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Nonwoven and yarn polypropylene with additivation
InactiveUS20120108714A1Improve abilitiesFilament/thread formingWood working apparatusYarnEngineering
A process to produce improved polypropylene nonwovens or yarns by extruding a mixture of polypropylene(s) and beta nucleating agent(s), or in the alternative, certain clarifiers, to form the improved polypropylene filaments.
Owner:LUMMUS NOVOLEN TECH
Fibrilia automobile inner decoration member and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101549671ANo pollution in the processReduce lossMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentSuperstructure subunitsRaw materialPolypropylene fiber
The present invention relates to a fibrilia automobile inner decoration member and a method of manufacturing the same, the steps is that implementing a opening treatment to packaged raw material, mixing jute fiber and polypropylene fiber according to proportionality in a cotton opener, and fiber netting simultaneously; then needling to form a felt by a needle machine, and implementing a sliced sheet treatment to the product after felting; baking and heating the felt directly in a baking oven to bond the surface, the baking temperature is from 180 to 200 DEG C; then cold press molding by a product mold, finally manufacturing a finished product; or preparing the belt into a sheet material to store, then baking and heating the sheet material, and a corresponding product molding according to requirements.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Methods of making low-shrink polypropylene fibers
InactiveUS6656404B2Monocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentWoven fabricsPhosphateLITHIUM PHOSPHATE
Improved polypropylene fibers exhibiting greatly reduced heat- and moisture-shrink problems and including certain compounds that quickly and effectively provide rigidity to the target polypropylene fiber after heat-setting are disclosed herein. In such a manner, the "rigidifying" compounds provide nucleation sites for polypropylene crystal growth. After drawing the nucleated composition into fiber form, the fiber is then exposed to sufficient heat to grow the crystalline network, thus holding the fiber in a desired position. The preferred "rigidifying" compounds include dibenzylidene sorbitol based compounds, as well as less preferred compounds, such as sodium beuzoate, certain sodium and lithium phosphate salts (such as sodium 2,2'-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphate, otherwise known as NA-11).
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Porous fiber
ActiveUS20050260911A1Good color propertiesExcellent moisture adsorptionWarp knittingCeramic shaping apparatusMetallurgyNanopore
The present invention provides a nanoporous fiber being substantially free from coarse pores and having homogeneously dispersed nanopores, unlike conventional porous fibers. A porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, and the pores are unconnected pores, or a porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, the pores are connected pores, and the fiber has a strength of 1.0 cN / dtex or more.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Long Chain Branched Propylene-Alpha-Olefin Copolymers
ActiveUS20100285253A1Higher shear thinning behaviorSpeed up the processSynthetic resin layered productsMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentAlpha-olefinAlkene
Substantially isotaclic propylene interpolyraets comprise (A) at least 60 weight percent (wt %) units derived from propylene, and (B) between greater than zero and 40 wt % units derived from ethylene, the propylene interpolyrner further characterized by at least one of the following properties: (1) a ratio of less than 1 measured at interpolyraer number average molecular weight (Mn), (2) a relative compositional drift of less than 50%, arid (3) propylene chain segments having a chain isotacticity triad index of at least 70 mole percent.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fibers and Nonwovens with Improved Bonding Properties
InactiveUS20110059668A1Wood working apparatusMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
The present invention relates to fibers, in particular to as-spun fibers, having an improved bonding performance. In particular, the present invention relates to as-spun fibers comprising a metallocene random copolymer of propylene and one or more comonomers. The present invention further relates to nonwovens comprising such fibers and to a process for producing such fibers and nonwovens. The fibers and nonwovens of the present invention are characterized by a wider bonding window as the prior art fibers and nonwovens.
Owner:TOTAL RES & TECH FELUY
Synthetic staple fibers for an air-laid nonwoven fabric
InactiveUS7560159B2Few defectQuality improvementSynthetic fibresFilament/thread formingMetallurgyNonwoven fabric
Synthetic staple fibers having good air opening property and useful for producing an air-laid nonwoven fabric having excellent quality, have a fiber length of 0.1 to 45 mm and a cross-sectional profile having 1 to 30 concavities, in which cross-sectional profile the ratio D / L, of a largest depth D of each concavity to a largest width L of the opening of the concavity, is in the range of from 0.1 to 0.5.
Owner:TEJIN FIBERS LTD
Antibiotic multifunctional fibre material and method for making same
InactiveCN101063235AMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentArtifical filament manufactureFiberFar infrared
The invention relates to an antibiosis multifunctional fiber material and a relative preparation, wherein the material is composed of polypropylene and antibiosis multifunctional mother particles which mass ratio is 80-85:15-20, the mother particle comprises 4-5% negative ion micro powder, 5-8% optical catalysis micro powder, 2-3% far infrared micro powder, 4-5% inorganic antibiosis powder, and 60-78% PP (polypropylene) as mass percentage. The material is extruded into the mother particles to be mixed with the polypropylene, spinned, drawn, twisted and oiled. The antibiosis rate of the invention can reach 99%, which can remove 80% formaldehyde in 2h, while the negative ion release rate is 1000r / cm3.
Owner:德邦新材料有限公司
Auxetic filamentary materials
InactiveUS20050159066A1Improve energy absorptionFibre pulloutWood working apparatusCork mechanical workingPolymer sciencePolymer
An auxetic material, which has a negative Poisson ratio so that it has the property of expanding or contracting transversely to a direction in which it is extended or compressed, is made in filamentary or fibrous form. A suitable process involves cohering and extruding heated polymer powder so that the cohesion and extrusion is effected with spinning to produce auxetic filaments. Typically the powder is heated to a temperature sufficient to allow some degree of surface melting yet not high enough to enable bulk melting.
Owner:AUXETIC TECH
Impact resistant polymer blends of crystalline polypropylene and partially crystalline, low molecular weight impact modifiers
InactiveUS6943215B2Group 4/14 element organic compoundsOther chemical processesPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
Polymer blends that exhibit good impact resistance comprise a crystalline polypropylene matrix and a partly crystalline copolymer impact modifier with a molecular weight lower than that of the matrix polymer. The matrix polymer can comprise any crystalline propylene homo- or copolymer. The impact modifying copolymers are characterized as comprising at least about 60 weight percent (wt %) of units derived from propylene and, in certain embodiments, as having at least one, preferably two or more, of the following properties: (i) 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity, (ii) a B-value greater than about 1.4 when the comonomer content of the copolymer is at least about 3 wt %, (iii) a skewness index, Six, greater than about −1.20, (iv) a DSC curve with a Tme that remains essentially the same and a Tmax that decreases as the amount of comonomer in the copolymer is increased, and (v) an X-ray diffraction pattern that reports more gamma-form crystals than a comparable copolymer prepared with a Ziegler-Natta (Z-N) catalyst.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Electret polypropylene melt-blown nonwovens and method for preparation
InactiveCN1544724AMature technologyWell mixedElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureFibre treatmentHigh humidityPolymer science
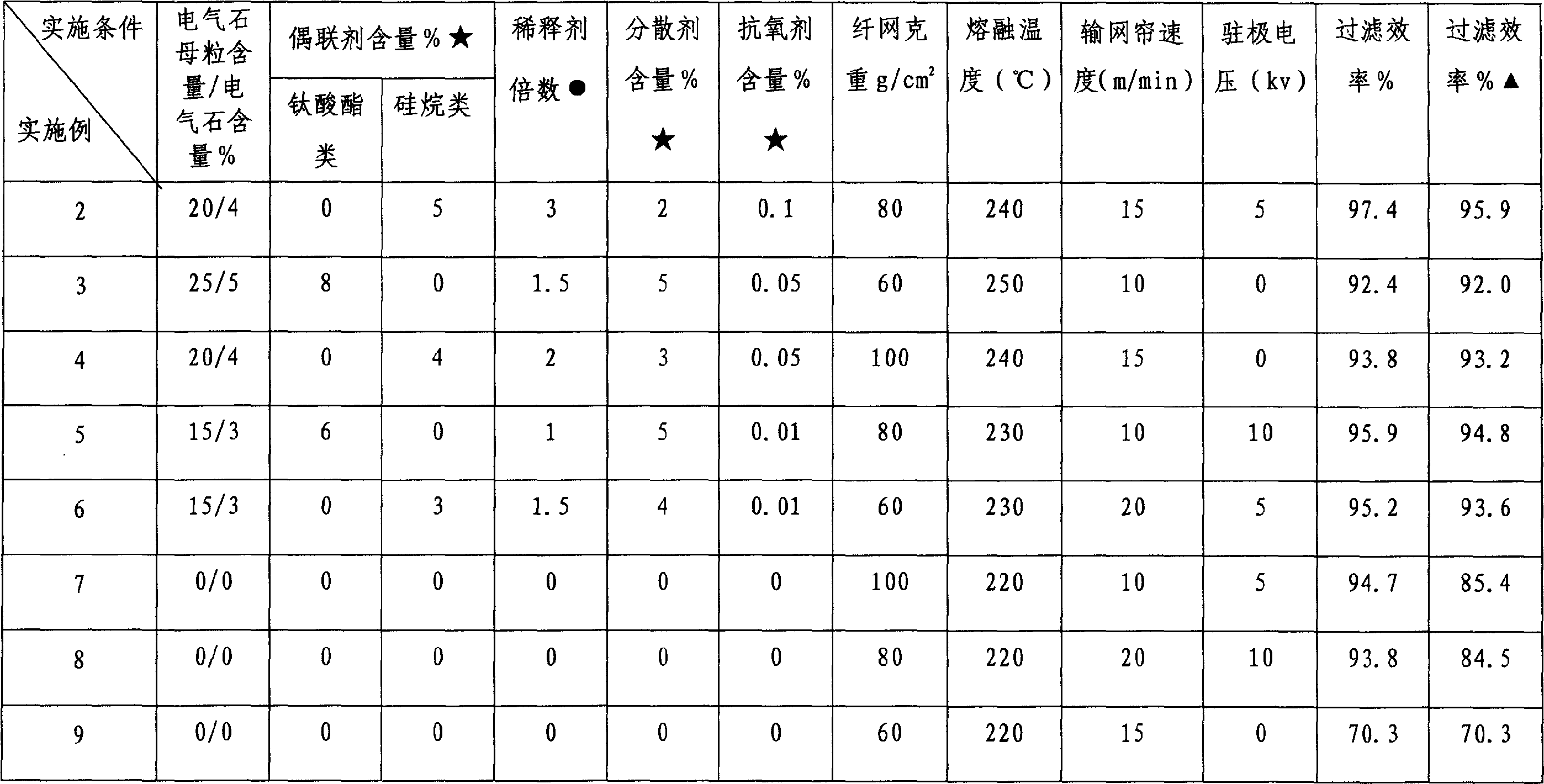
The invention relates to an electret polypropylene melt-spray nonwoven cloth and its making method, the components in weight percent: polypropylene 95-97%, and tourmaline 3-5% with average particle size not greater than 0.5mum; its making method: (1) uniformly mixing and fusing the tourmaline particles and the polypropylene slices to make particles; the assistants of making the tourmaline particles in weight percent: coupling agent 3-10%; dispersant 2-5% and chemical inhibitor 0.01-0.1%; (2) uniformly mixing, fusing and extruding the particles with the polypropylene slices, stretching under the high-speed hot air flow to make the product. The product has better adaptability to high temperature and high humidity environment, can be used in filtering liquid; the making method has the characters of simple technique, no special devices, easy industrialized implementation, etc.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Auxetic filamentary materials
InactiveUS7247265B2Improve propertiesIncrease resistanceWood working apparatusCork mechanical workingPolymer sciencePolymer
An auxetic material, which has a negative Poisson ratio so that it has the property of expanding or contracting transversely to a direction in which it is extended or compressed, is made in filamentary or fibrous form. A suitable process involves cohering and extruding heated polymer powder so that the cohesion and extrusion is effected with spinning to produce auxetic filaments. Typically the powder is heated to a temperature sufficient to allow some degree of surface melting yet not high enough to enable bulk melting.
Owner:AUXETIC TECH
Thermoplastic constructs with improved softness
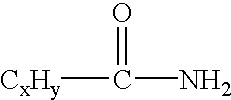
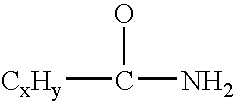
InactiveUS7238313B2Monocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentWoven fabricsCombined usePolymer chemistry
The present invention is directed to the combined use of first and second fatty acid amides to improve the softness of a thermoplastic polymer construct. A combination of fatty acid amides is provided in the blend ratio of about 10 to 90 percent by weight of a first fatty acid amide and 90 to 10 percent by weight of a second fatty acid amide. The first and second fatty acid amides are compounded into a thermoplastic polymer carrier resin and, preferentially, produced as concentrate pellets containing 0.5 to 75 percent by weight total fatty acid amide loading. The concentrate pellets are introduced into a thermoplastic polymer base, to form a thermoplastic resin, at a letdown level in the range of about 1 to 15 percent, with the range of 2 to 10 percent being preferred, and the range of 3 to 6 percent being most preferred.
Owner:AVINTIV SPECIALTY MATERIALS INC
Spun-bonded nonwoven fabric and fiber product
InactiveUS20120208422A1Small fiber diameterFeel goodPersonal careLayered productsFiber diameterNonwoven fabric
The present invention provides a spunbond nonwoven fabric made of a specific crystalline resin composition having a melt flow rate of 25 to 80 g / 10 min and a melting endotherm ΔH of 65 to 100 J / g. More particularly, the invention provides a polypropylene spunbond nonwoven fabric having a very small fiber diameter and providing an excellent feel to the touch, and a polypropylene spunbond nonwoven fabric exhibiting high softness.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com