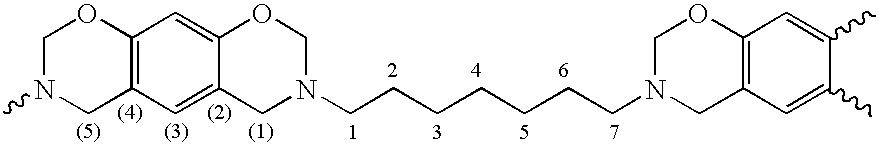
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
158 results about "EM - Electron microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM, also sometimes conventional transmission electron microscopy or CTEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid.
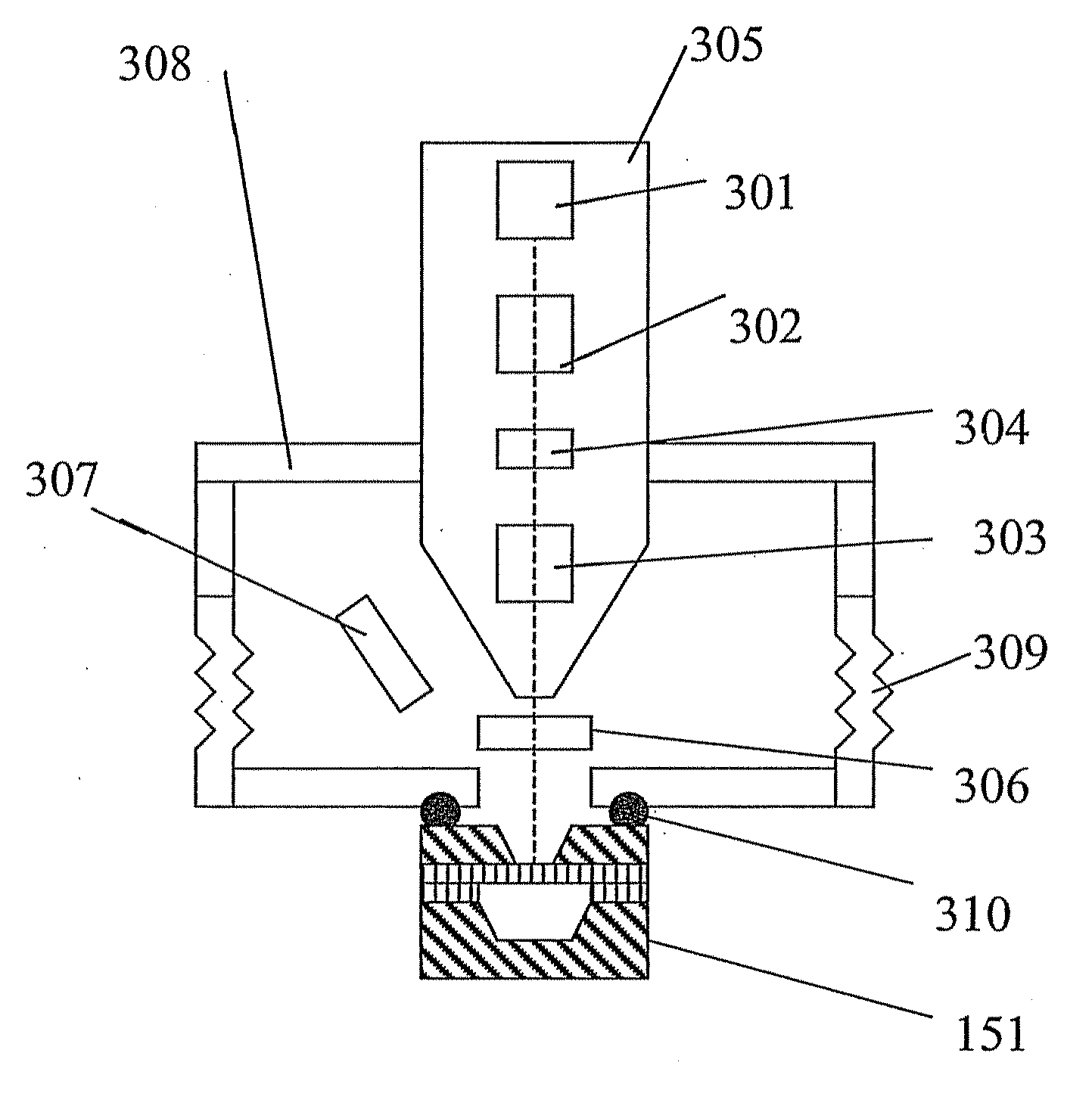
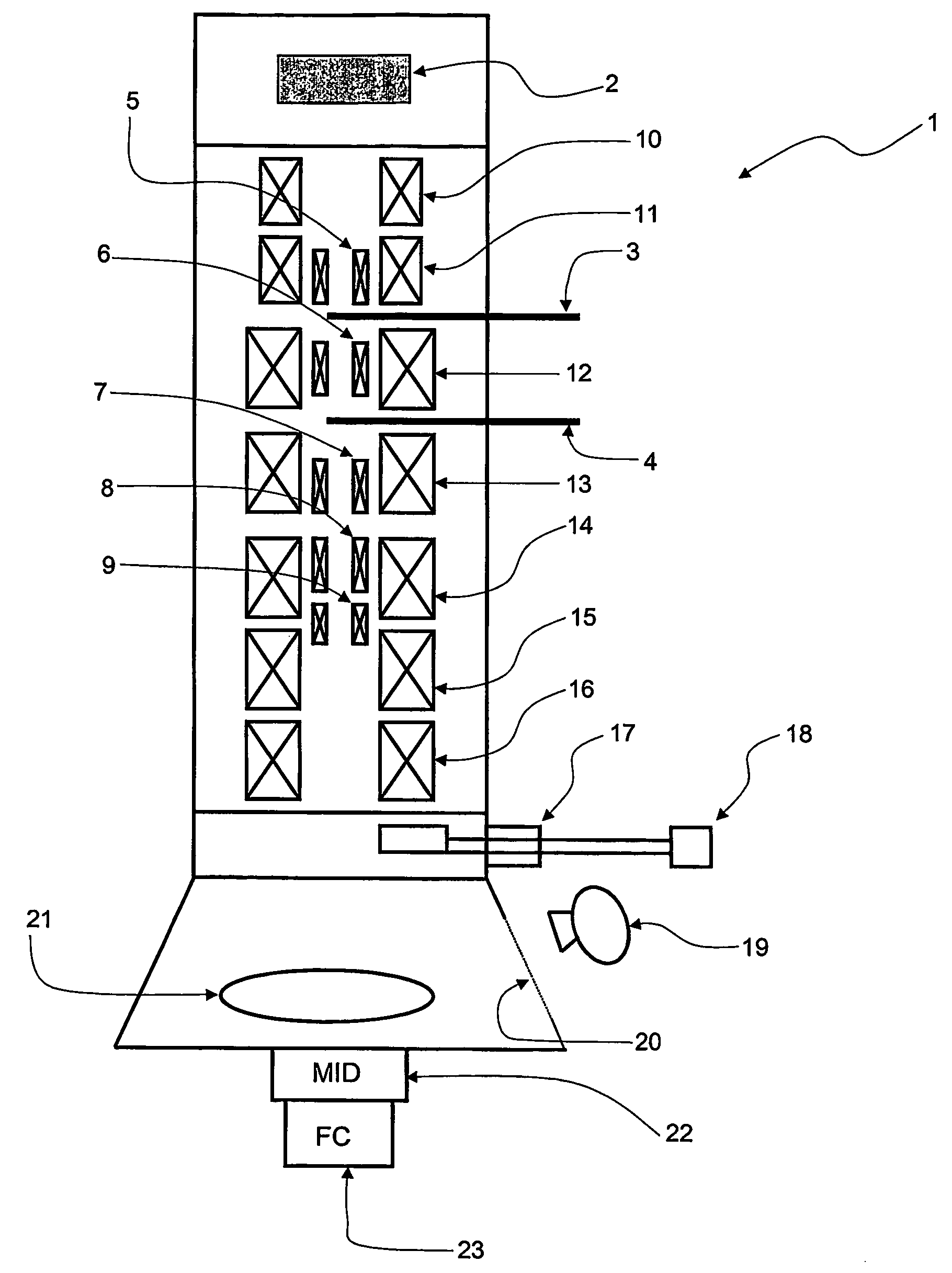
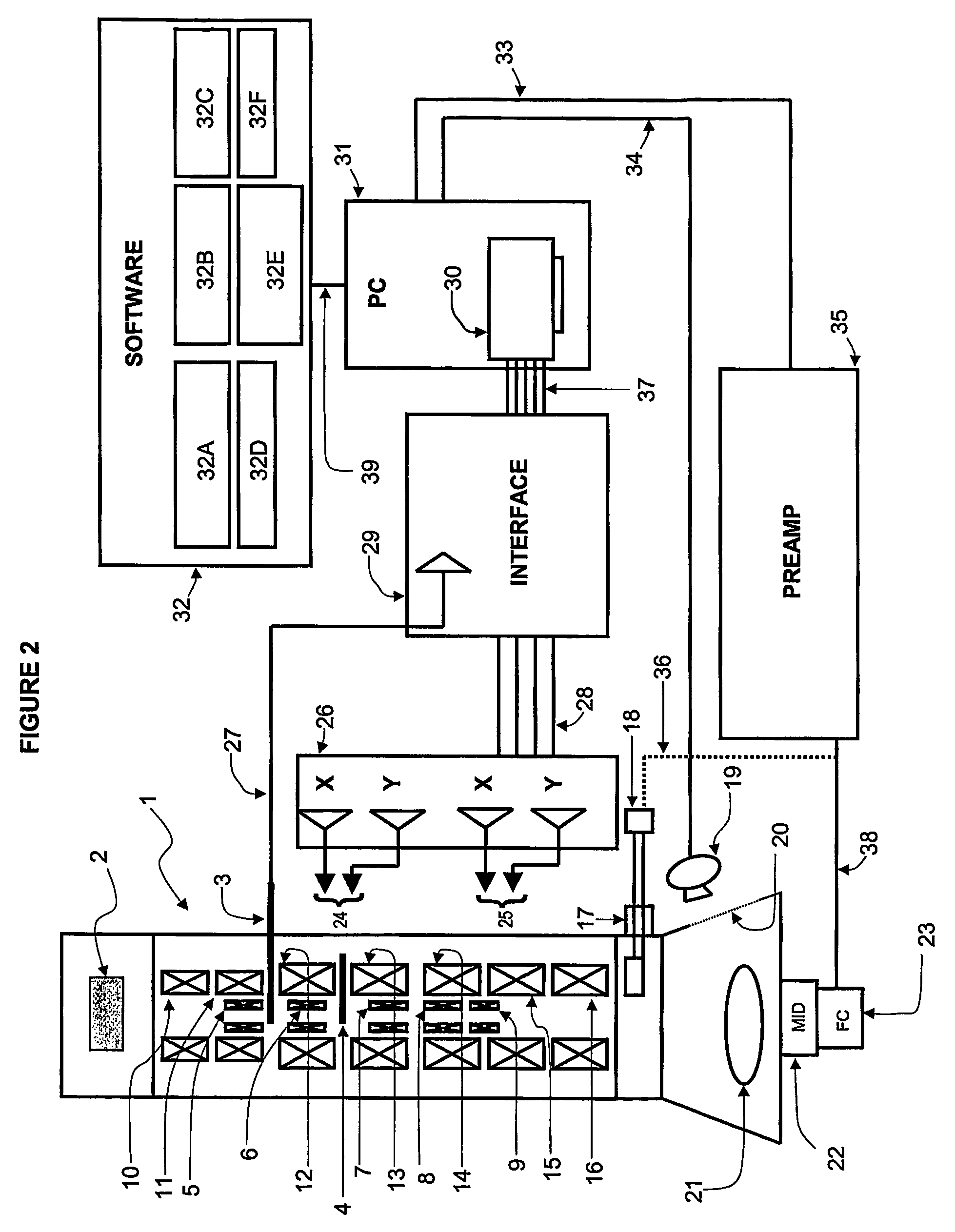
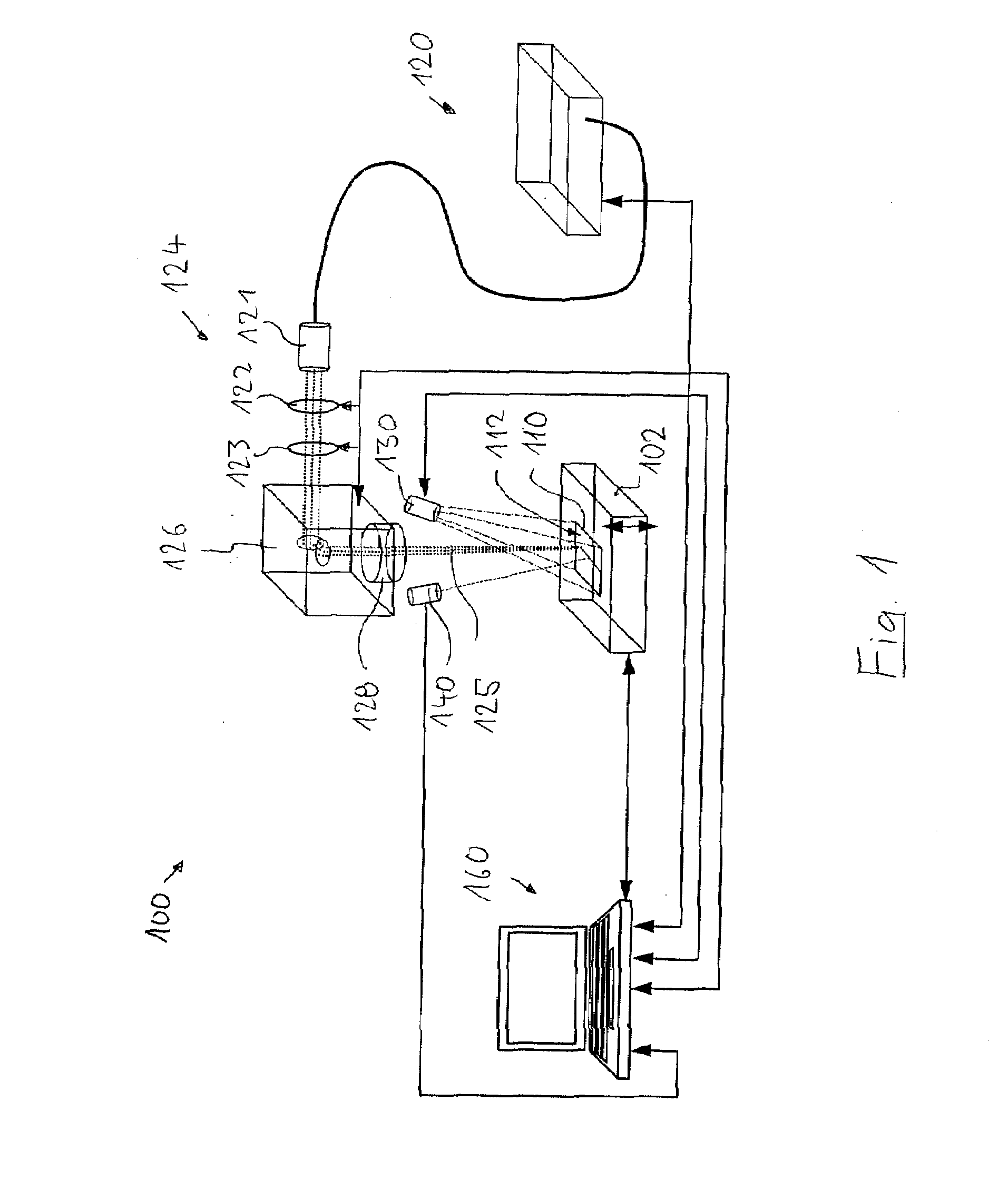
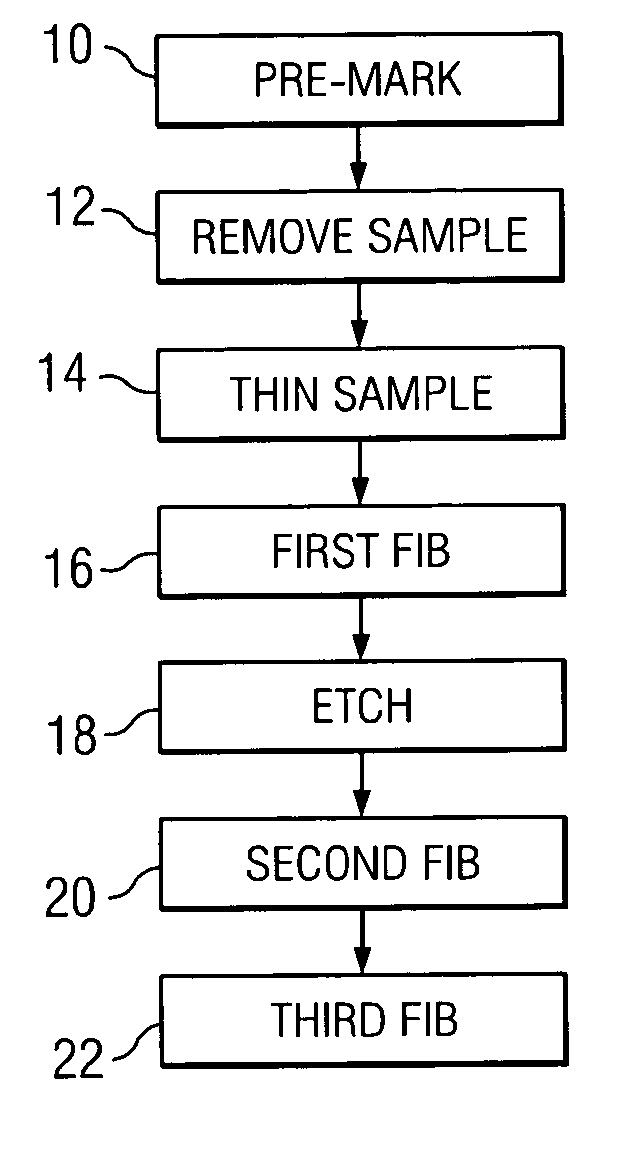
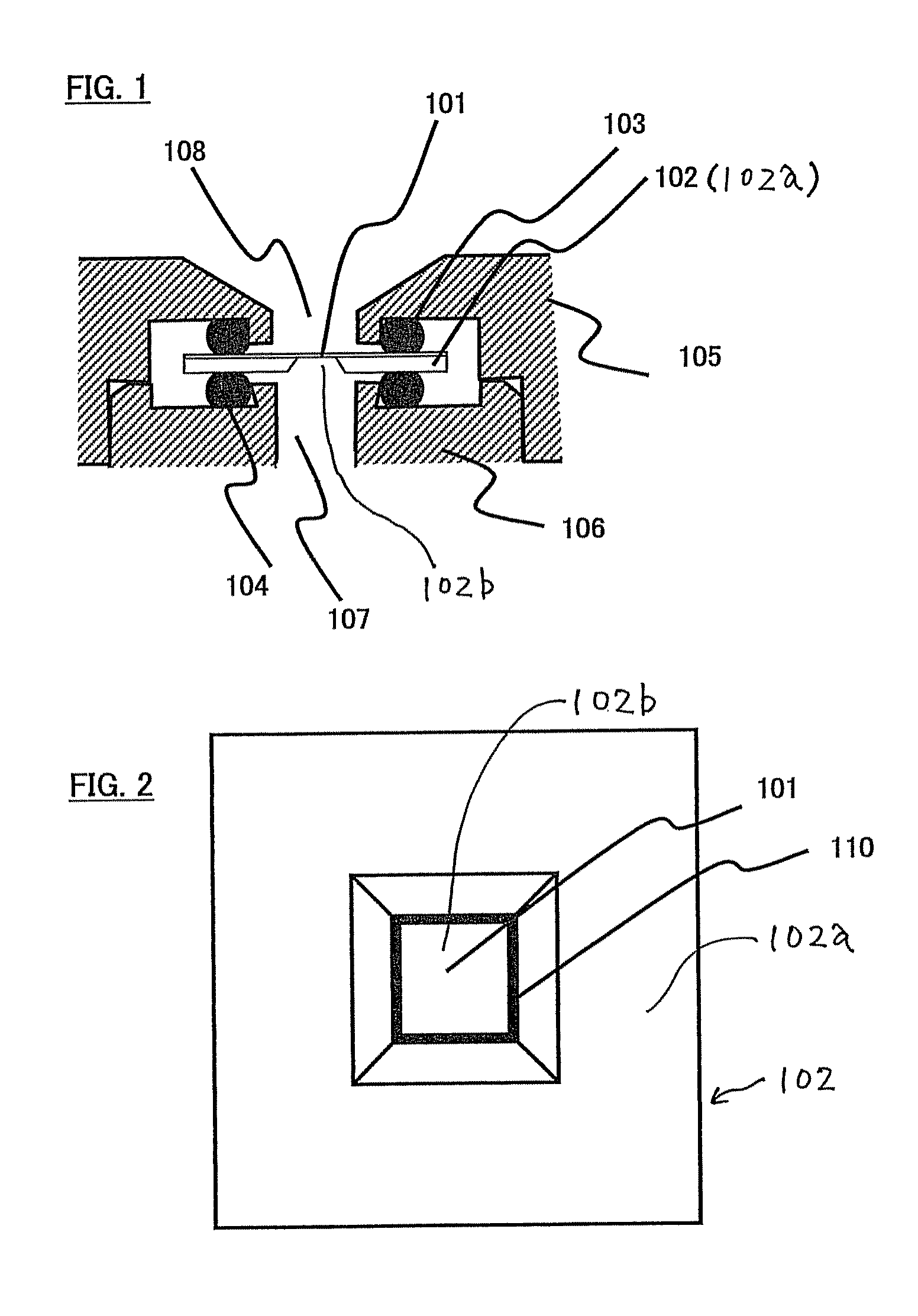
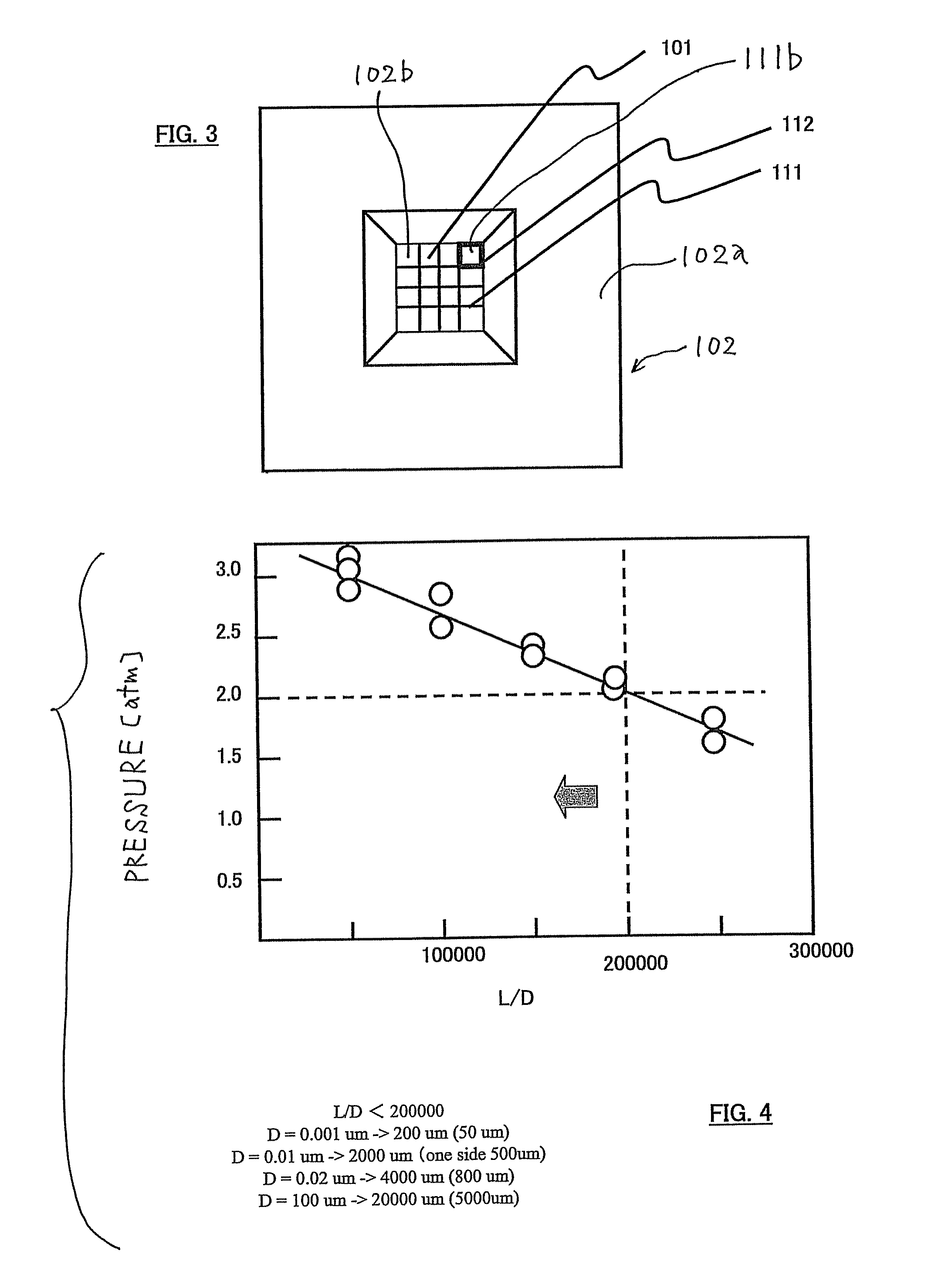
Sample Holder, Method for Observation and Inspection, and Apparatus for Observation and Inspection
InactiveUS20090166536A1High resolutionDistanceElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionElectron
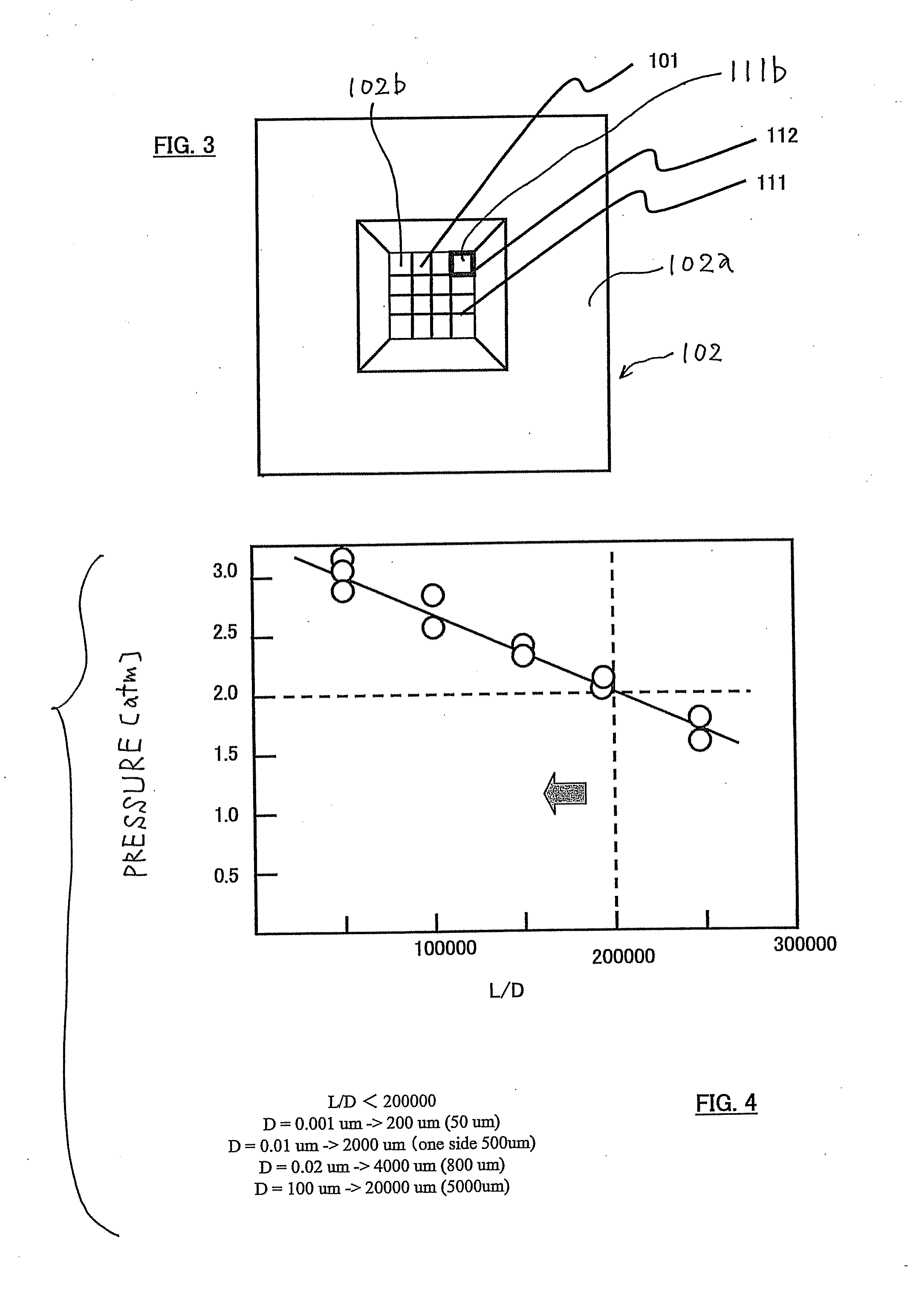
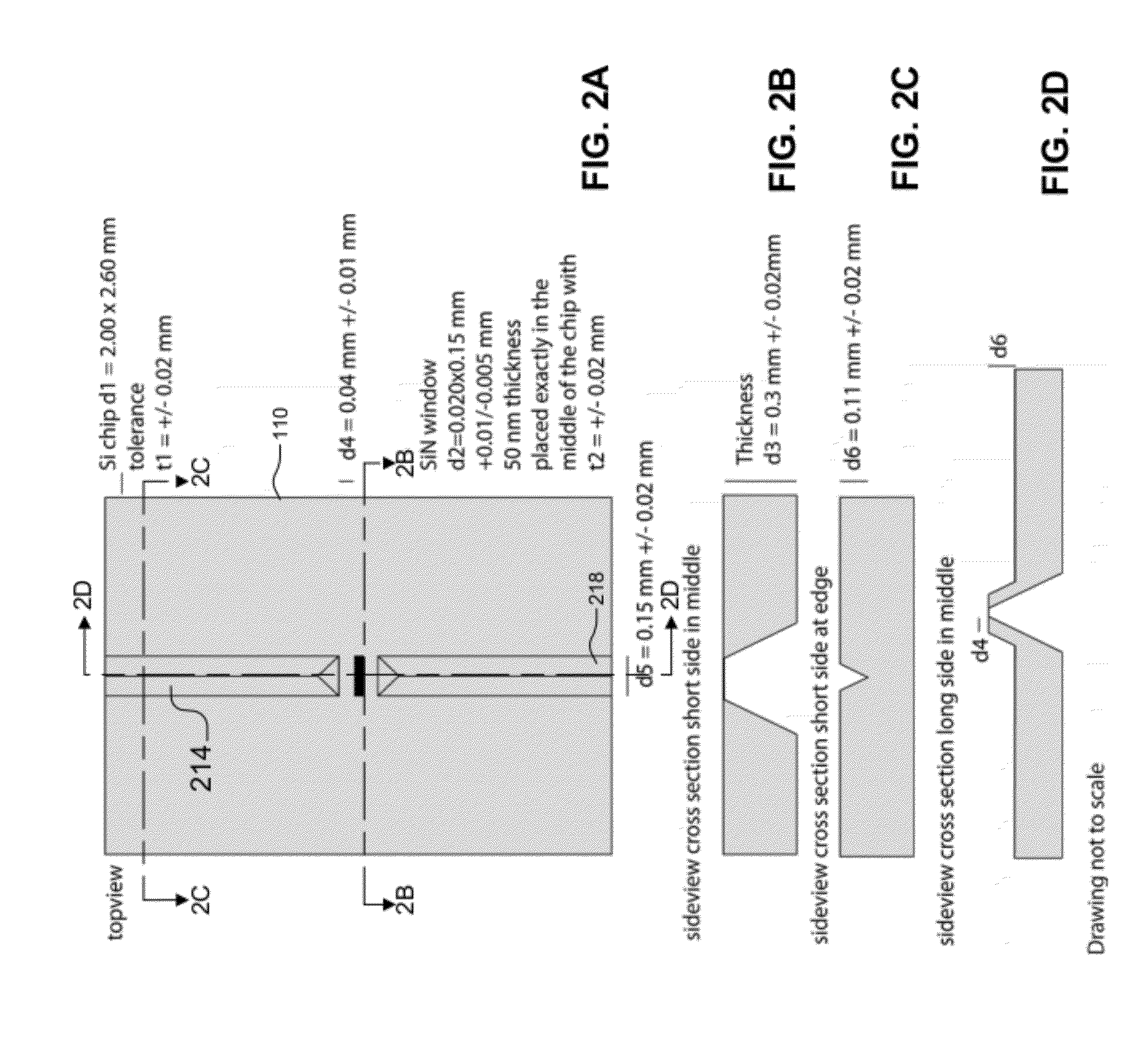
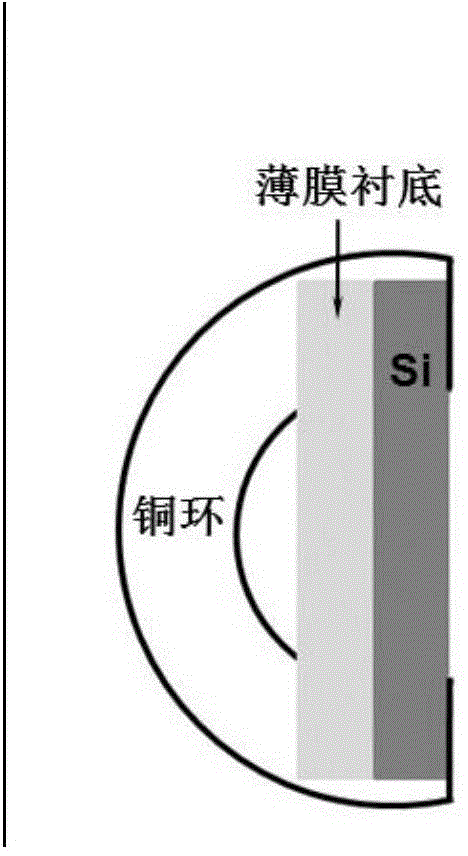
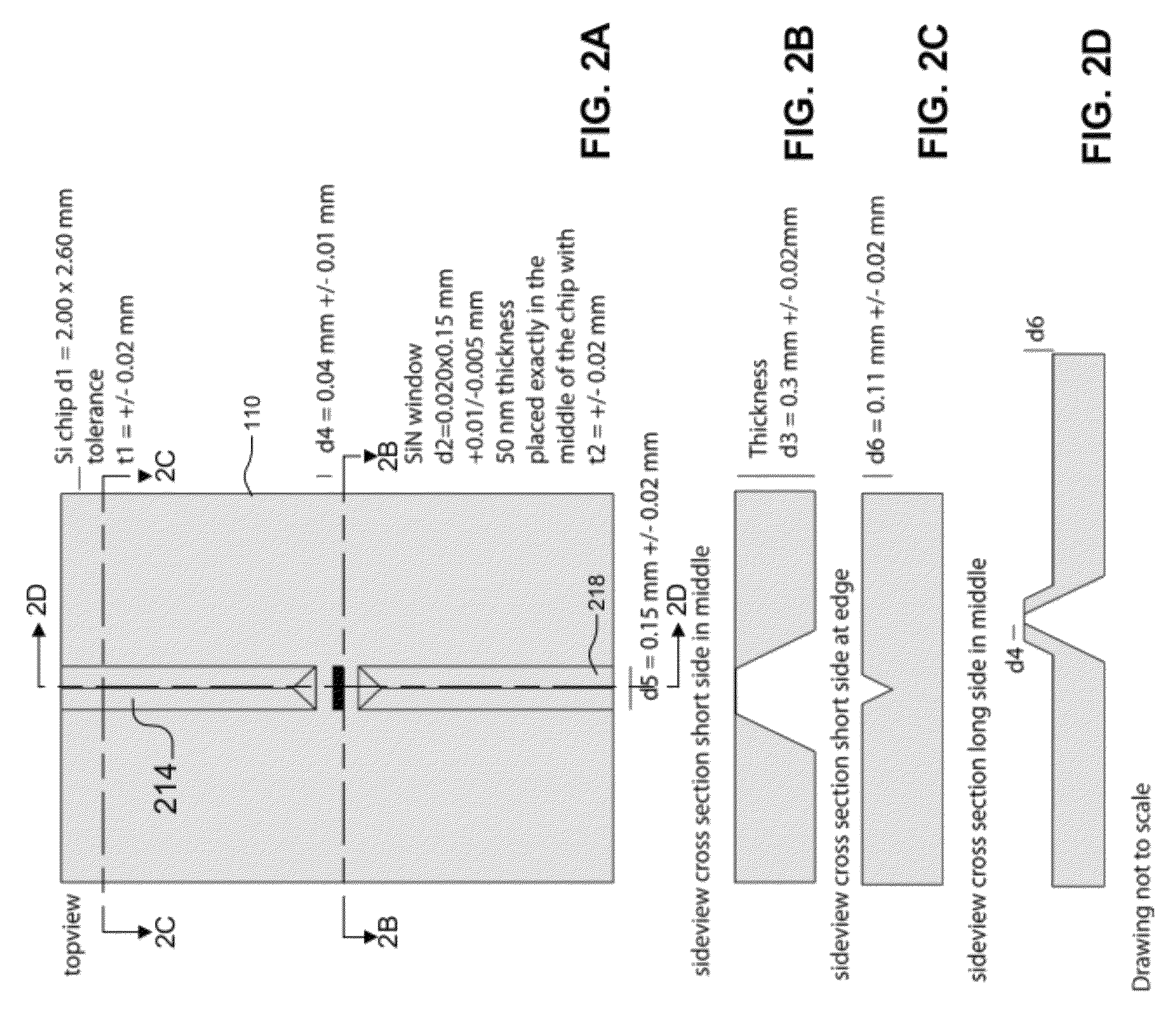
A sample holder used in SEM (scanning electron microscopy) or TEM (transmission electron microscopy) permitting observation and inspection at higher resolution. The holder has a frame-like member provided with an opening that is covered with a film. The film has a first surface on which a sample is held. The thickness D of the film and the length L of the portion of the film providing a cover over the opening in the frame-like member satisfy a relationship given by L / D <200,000.
Owner:JEOL LTD
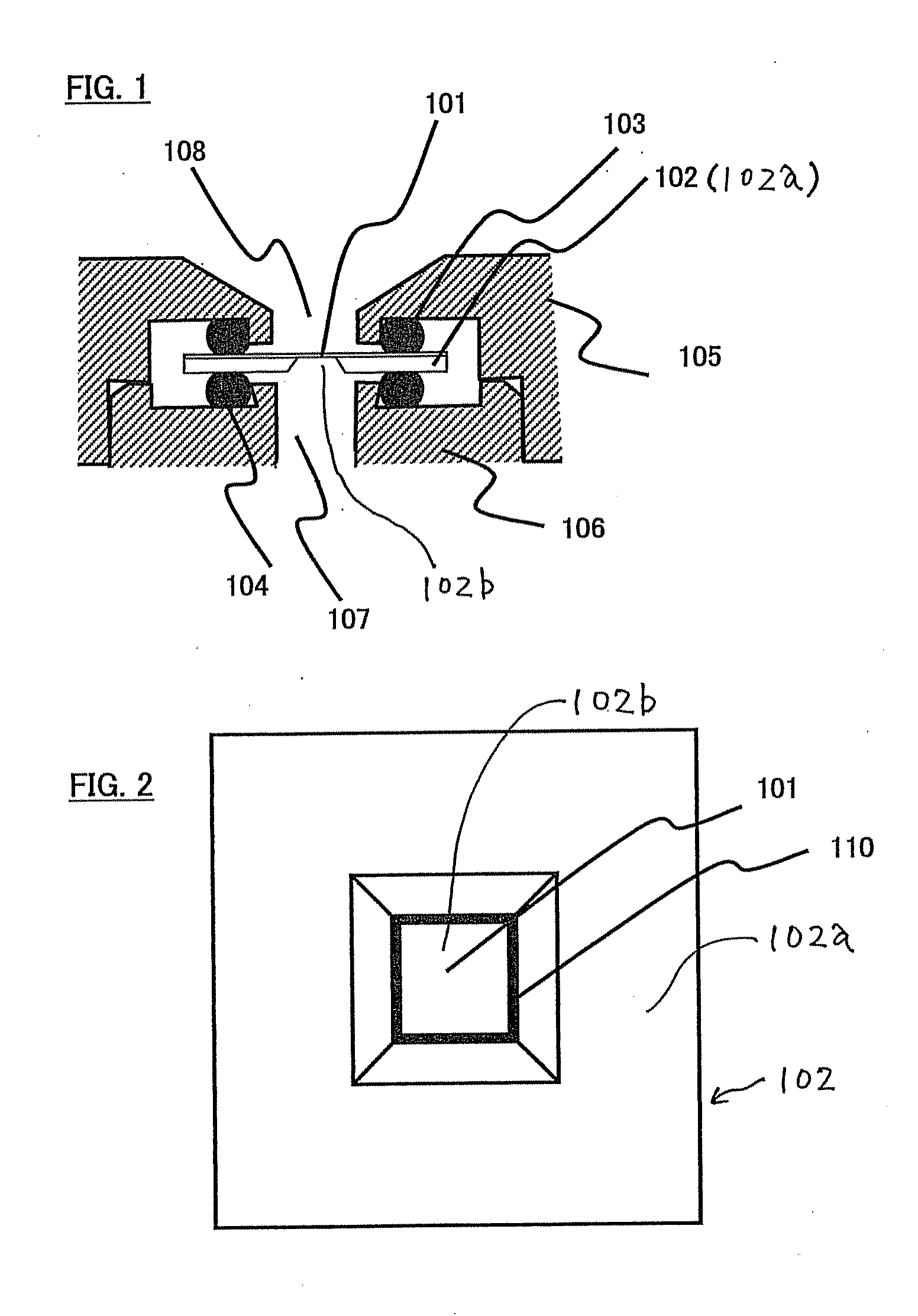
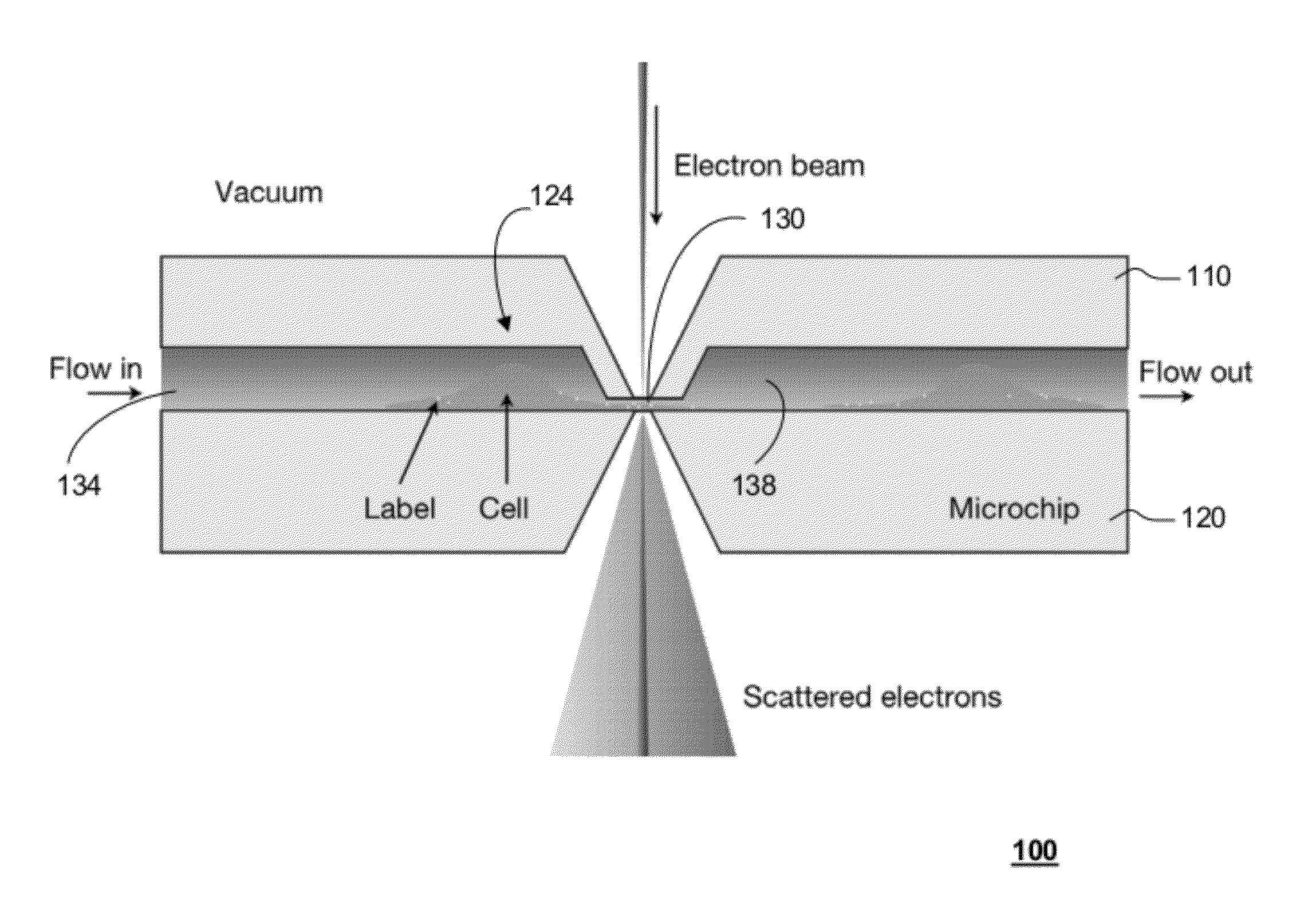
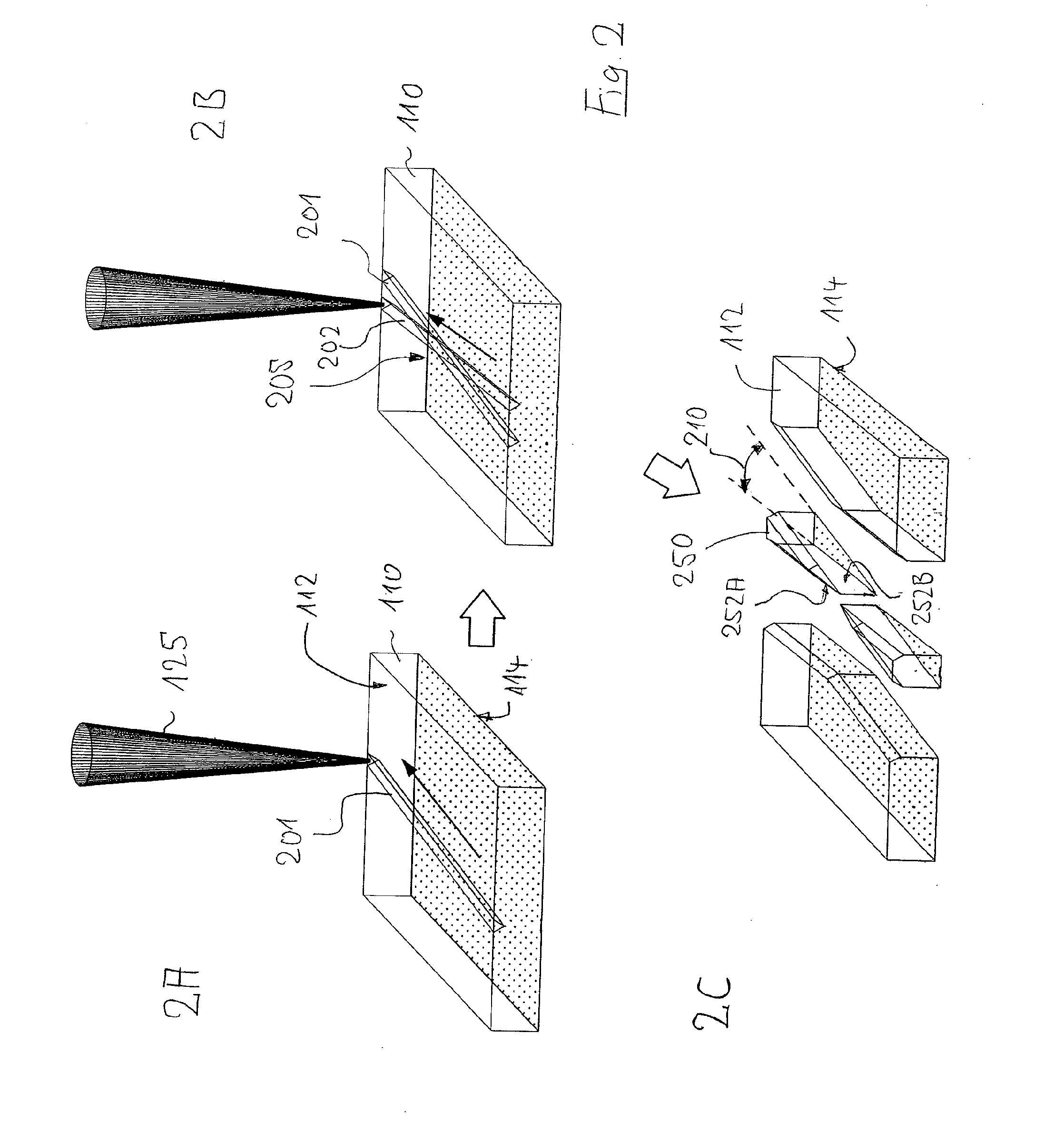
Transmission electron microscopy for imaging live cells
ActiveUS20120120226A1Not to damageReduce intensityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesMedicineLive cell imaging
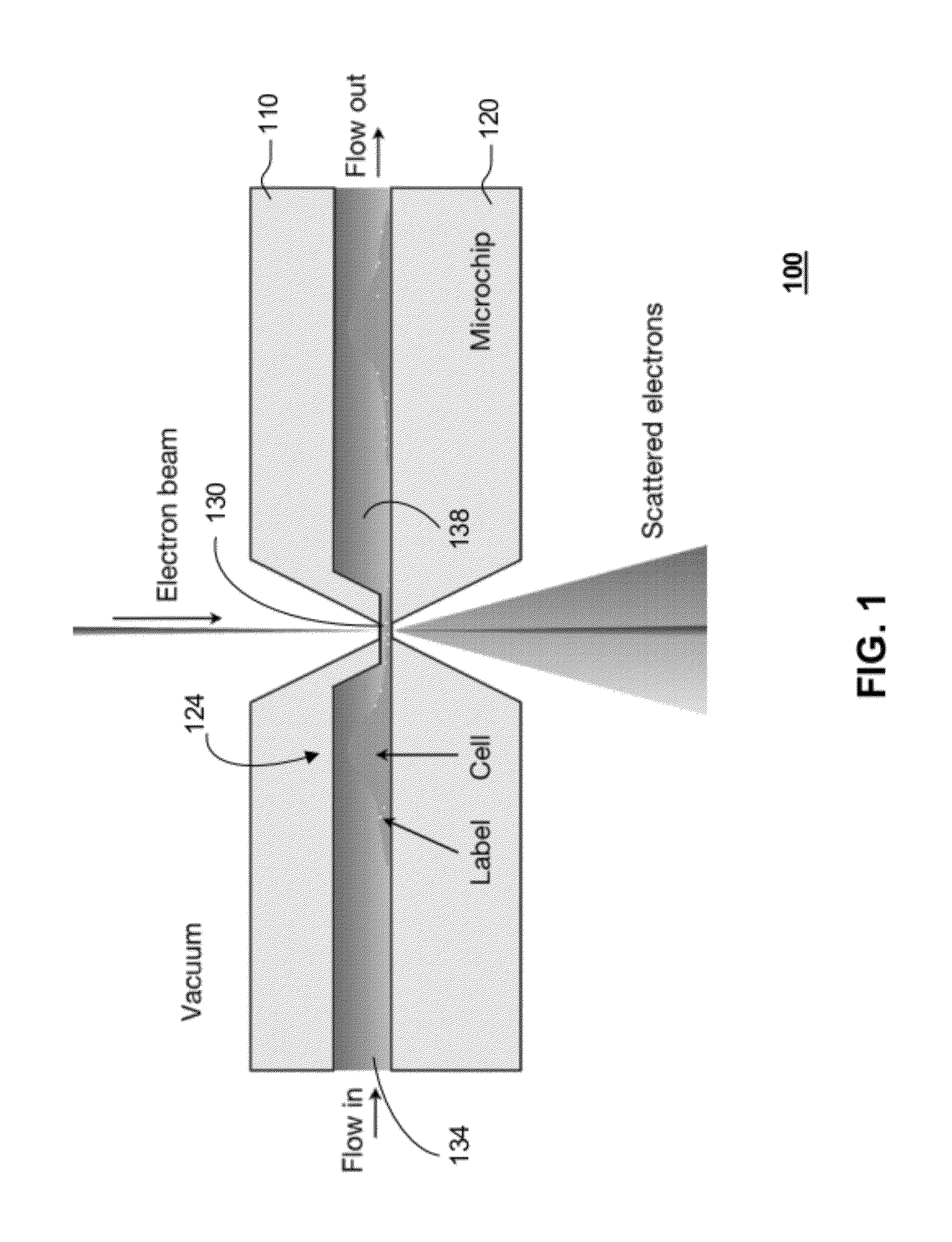
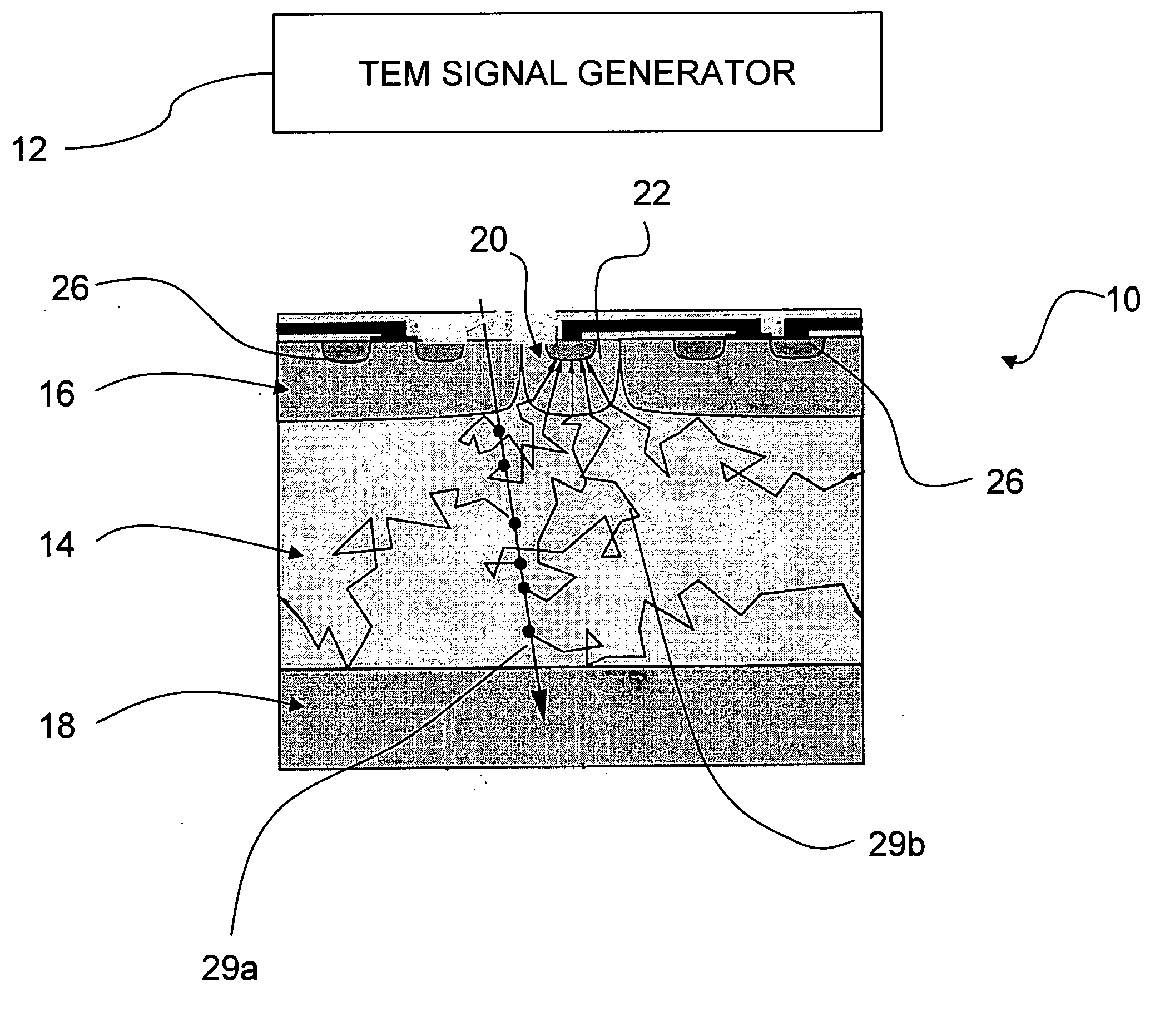
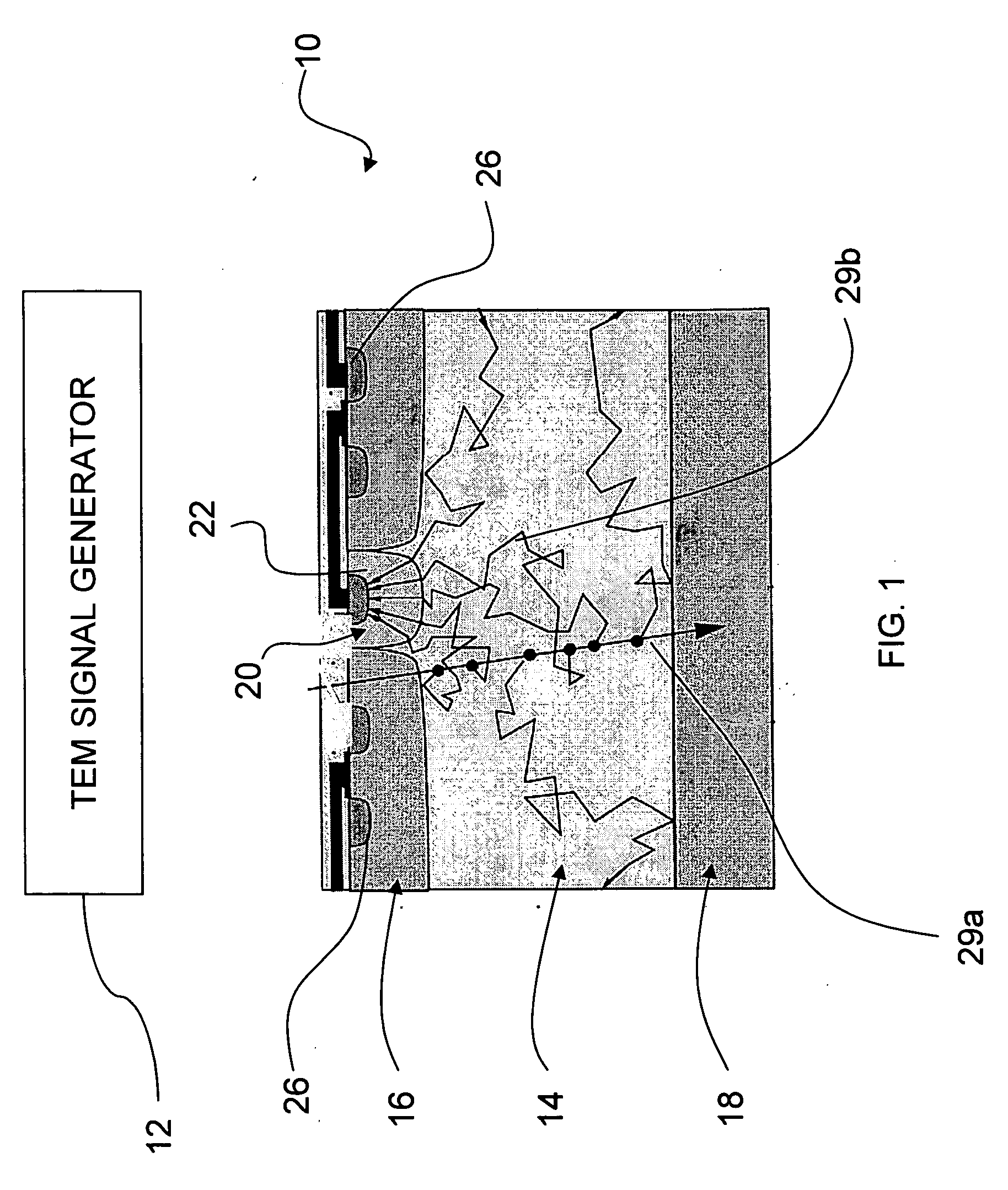
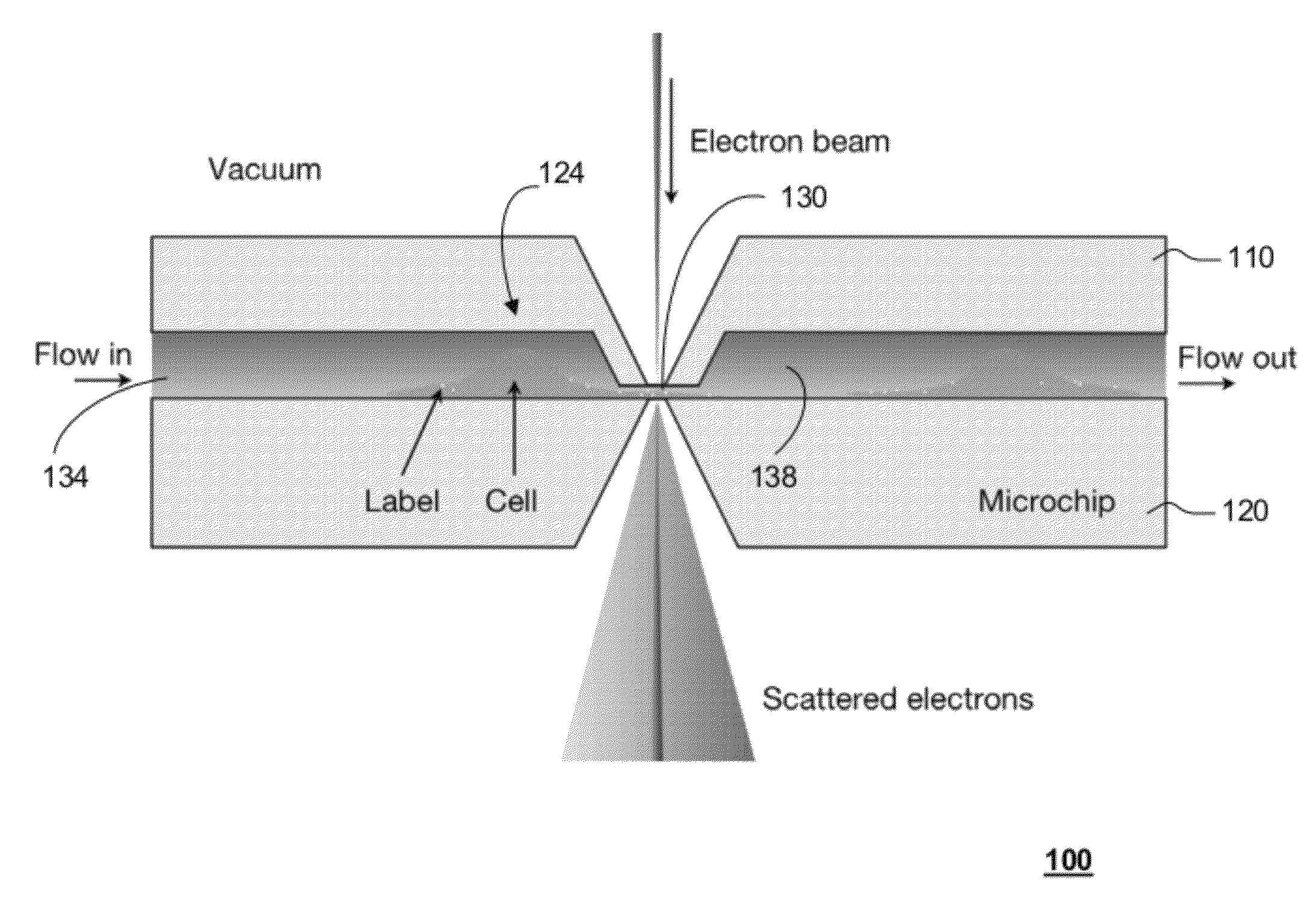
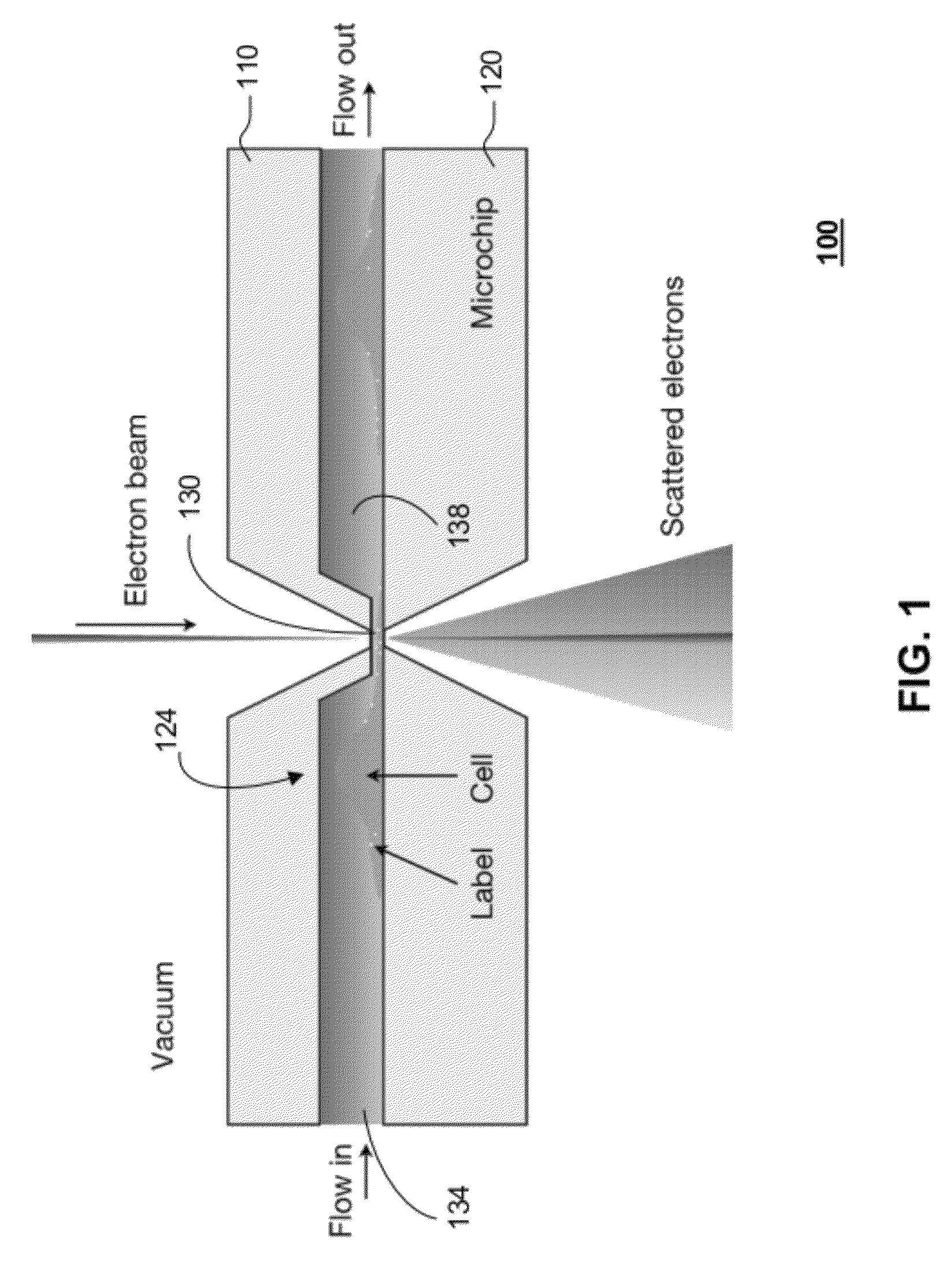
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a microfluidic chamber. In one embodiment, the microfluidic chamber has a first sub-chamber and at least one second sub-chamber. The first sub-chamber has a first window and a second window. Both the first window and the second window are transparent to electrons of certain energies. The second window is positioned substantially parallel and opposite to the first window defining a first volume therebetween. The first window and the second window are separated by a distance that is sufficiently small such that an electron beam that enters from the first window can propagate through the first sub-chamber and exit from the second window. The at least one second sub-chamber is in fluid communication with the first sub-chamber and has a second volume that is greater than the first volume of the first sub-chamber.
Owner:DE JONGE VILIJA +2
Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite nanotubes
ActiveUS20050036939A1Reduce the amount requiredThe instrumentation is simpleDigital storageGermanium dioxideStrontium titanateBarium titanate
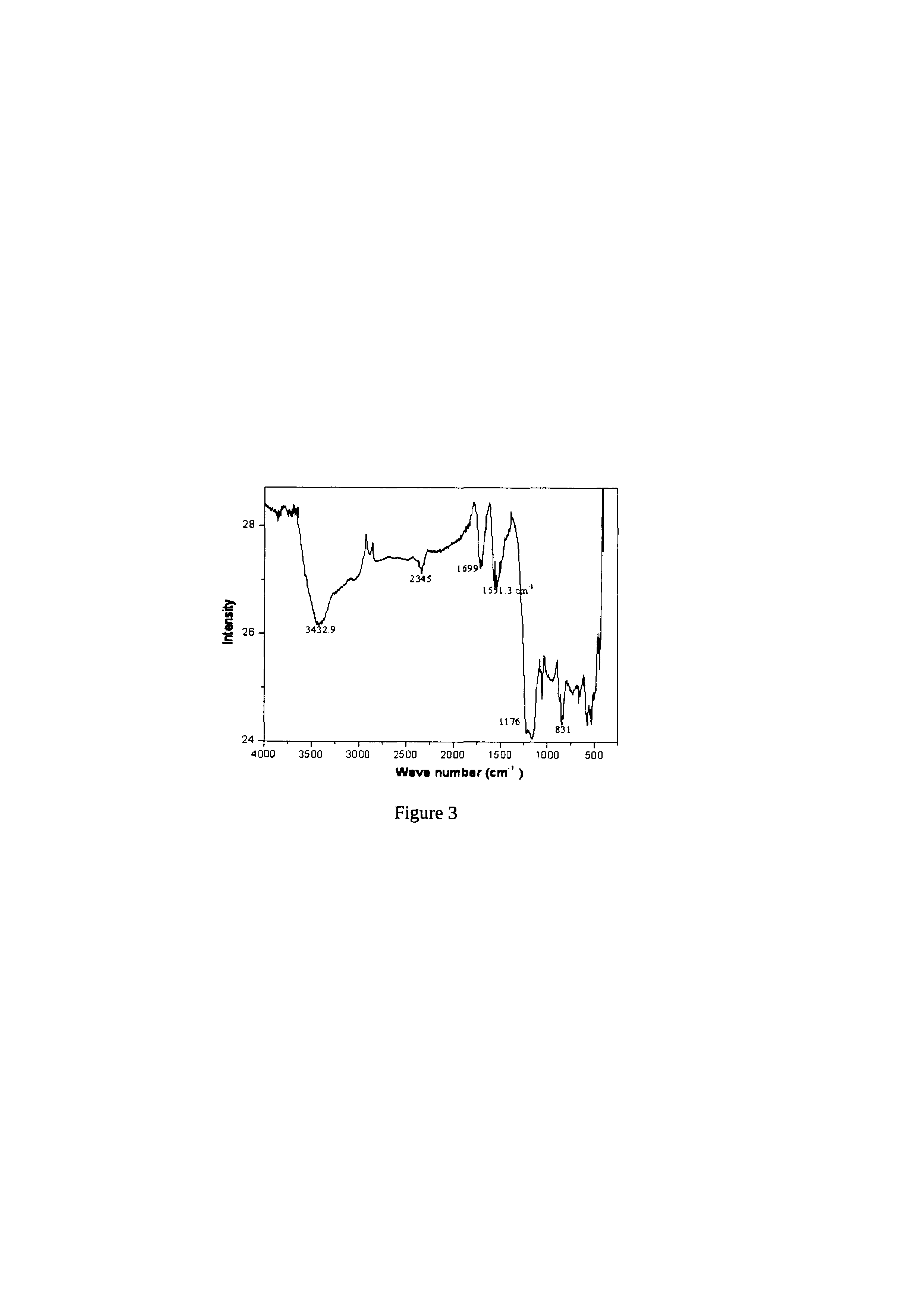
A low-temperature hydrothermal reaction is provided to generate crystalline perovskite nanotubes such as barium titanate (BaTiO3) and strontium titanate (SrTiO3) that have an outer diameter from about 1 nm to about 500 nm and a length from about 10 nm to about 10 micron. The low-temperature hydrothermal reaction includes the use of a metal oxide nanotube structural template, i.e., precursor. These titanate nanotubes have been characterized by means of X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy, coupled with energy dispersive X-ray analysis and selected area electron diffraction (SAED).
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Direct collection transmission electron microscopy
InactiveUS20060169901A1Fast readoutEasy data collectionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSingle electronPhotodiode
A preferred method for transmission electron microscopy includes a step of generating a microscopy signal. The microscopy signal is then detected with an active pixel detector that includes a plurality of pixels. Each of the pixels includes at least one photodiode. Each pixel integrates an incident signal over a collection time period. Using a massibel parallel on chip analog to digital conversion, very fast read out times can be achieved, e.g., many frames per second. In a preferred embodiment, the read out time permits there to be a single electron event recorded per pixel, indicating either a single electron or the lack thereof. This permits simple accumulation of the pixel counts for each pixel in read-out and storage electronics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing gold nano-rods
The invention discloses a method for preparing gold nano-rods. The method includes the steps: adding chloroauric acid solution and optional gold seed generating regulating agents into CTAB (cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide) solution, adding silver nitrate solution, weak reducing agents and strong reducing agents into the CTAB solution and reacting at the constant temperature of 25-40 DEG C for 5-30min to obtain reaction liquid A; and adding silver nitrate solution, optional gold nano-rod growth regulating agent solution and water into the reaction liquid A to obtain reaction liquid B, and continuing reaction to obtain the gold nano-rods. The method is simple in process and operation and fine in reproducibility, the diameter of coverage of the prepared gold nano-rods is as small as 5nm to tens of nanometers, LSPR (localized surface plasmon resonance) peak value coverage in the length direction ranges from 630nm to 1010nm, counts in a TEM (transmission electron microscopy) graph indicate that more than 90% of rod products among obtained gold nano-particle products are high in rod yield, and the ratio of an LSPR peak value to a TSPR (transverse surface plasmon resonance) peak value is not lower than 2 in a UV-Vis (ultraviolet visible) absorption spectrogram. Raw materials used in the method are widely and easily obtained, and production cost is low.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CLUSTERBIOPHOTON TECH CO LTD
Directionally controlled growth of nanowhiskers
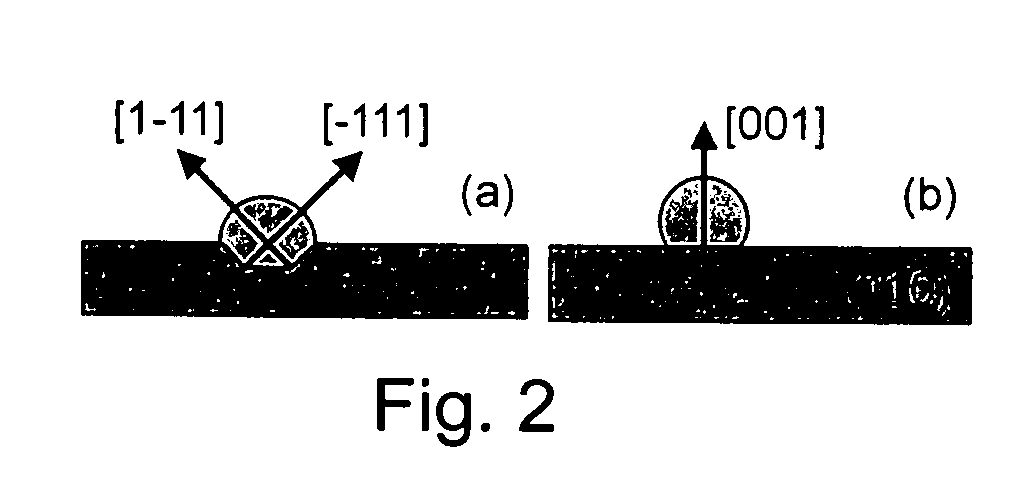
InactiveUS20060019470A1Well-defined surfaceReduce the temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanowireStacking fault
Nanowhiskers are grown in a non-preferential growth direction by regulation of nucleation conditions to inhibit growth in a preferential direction. In a preferred implementation, <001> III-V semiconductor nanowhiskers are grown on an (001) III-V semiconductor substrate surface by effectively inhibiting growth in the preferential <111>B direction. As one example, <001> InP nano-wires were grown by metal-organic vapor phase epitaxy directly on (001) InP substrates. Characterization by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy revealed wires with nearly square cross sections and a perfect zincblende crystalline structure that is free of stacking faults.
Owner:QUNANO
Apparatus and Method for Producing Specimens for Electron Microscopy
ActiveUS20140360286A1Easy to analyzeLower the volumeElectric discharge tubesWithdrawing sample devicesElectron microscopeExcess fluids
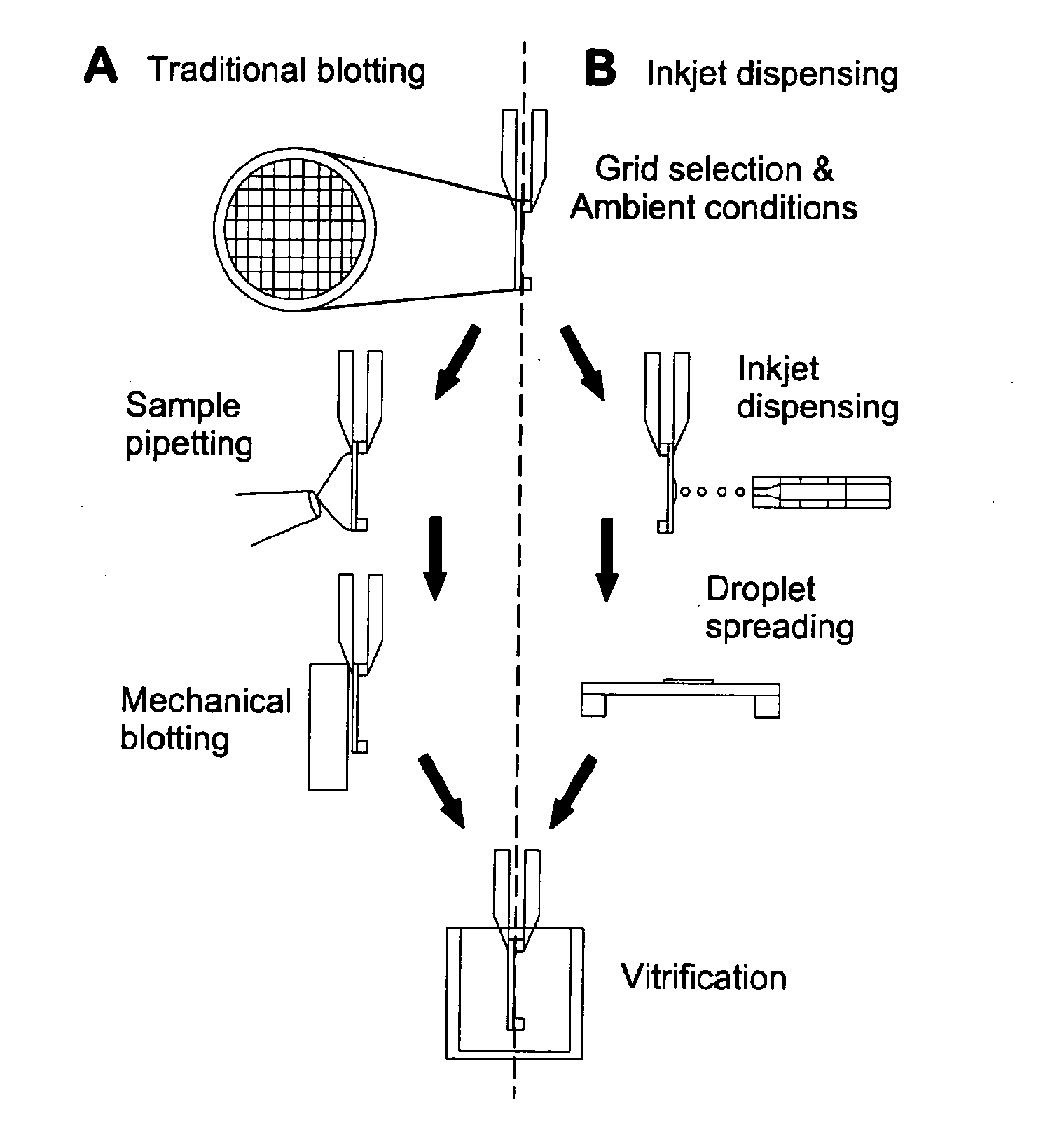
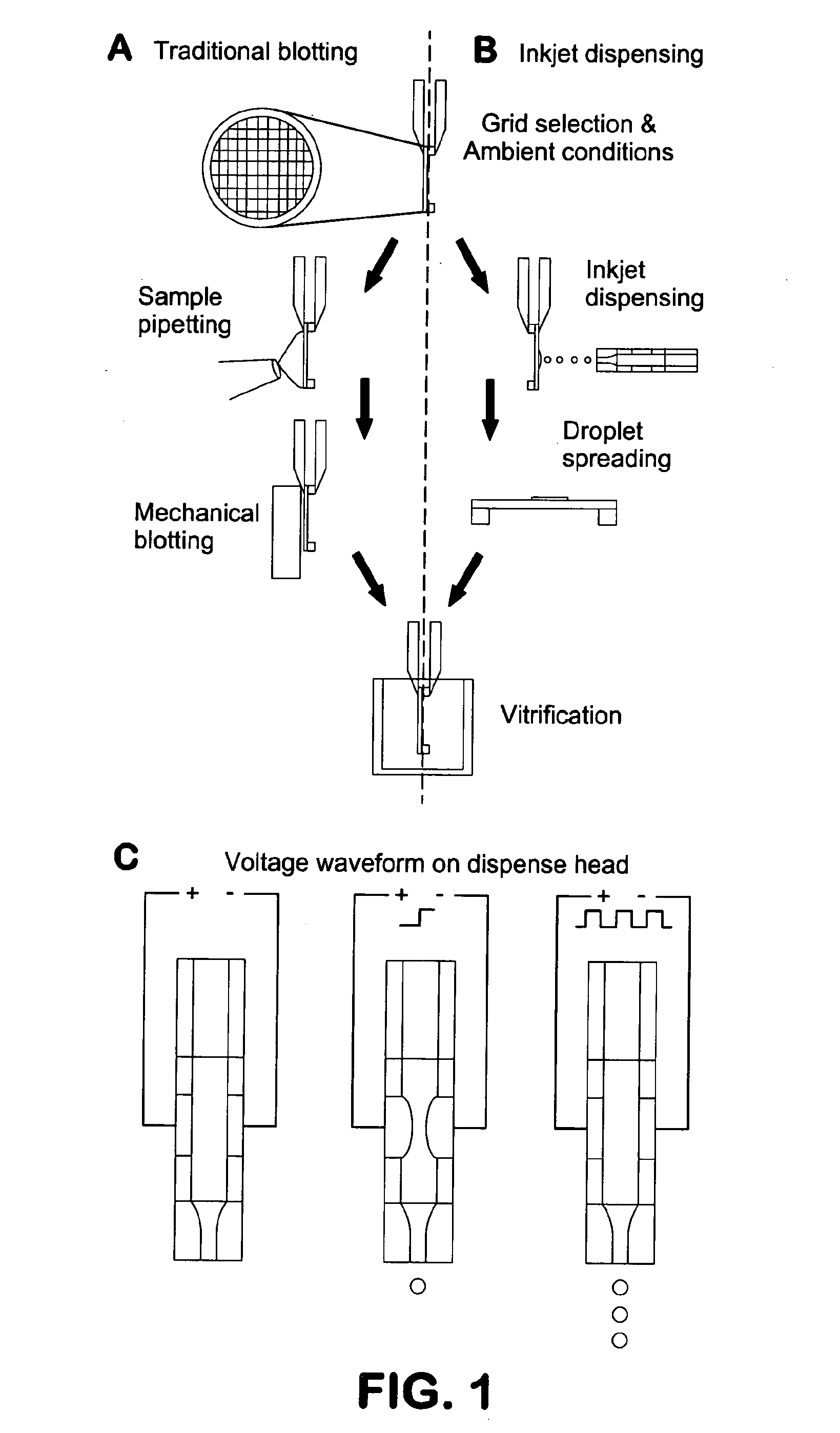
The invention provides methods and devices for preparing frozen vitrified samples for transmission electron microscopy. By reducing the volume of sample from microliter scale to picoliter scale, the requirement for blotting of excess fluid is minimized or eliminated.
Owner:ENG ARTS +1
Cellulose composites comprising hydrophobic particles and their use in paper products
InactiveUS20080041542A1Non-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSolventAlkaline hydrolysis
Polymer composite films were prepared by solvent casting suspensions of quantum dots (QDs) in cellulose triacetate (CTA) solution. The films were robust and possessed the optical properties characteristic of QDs. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of the films revealed that the QDs were well dispersed within the CTA film matrix. The selective alkaline hydrolysis of QD / CTA films in 0.1N NaOH over 24 hours resulted in the surface conversion of CTA to regenerated cellulose. Optical properties of the films were probed both before and after the hydrolysis reaction using fluorescence spectroscopy, and were found generally unaltered. The cellulose surfaces of the alkaline treated films allow for facile incorporation of the films into paper sheets.
Owner:ABITBOL TIFFANY +1
Ultra-hard low friction coating based on AlMgB14 for reduced wear of MEMS and other tribological components and system
InactiveUS20050100748A1Superior protective coatHigh hardnessVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesMicroelectromechanical systemsAlloy
Performance and reliability of microelectromechanical system (MEMS) components enhanced dramatically through the incorporation of protective thin film coatings. Current-generation MEMS devices prepared by the LIGA technique employ transition metals such as Ni, Cu, Fe, or alloys thereof, and hence lack stability in oxidizing, corrosive, and / or high temperature environments. Fabrication of a superhard, self-lubricating coating based on a ternary boride compound AlMgB14 is described in this letter as a potential breakthrough in protective coating technology for LIGA microdevices. Nanoindentation tests show that hardness of AlMgB14 films prepared by pulsed laser deposition ranges from 45 GPa to 51 GPa, when deposited at room temperature and 573 K, respectively. Extremely low friction coefficients of 0.04-0.05, which are thought to result from a self-lubricating effect, have also been confirmed by nanoscratch tests on the AlMgB14 films. Transmission electron microscopy studies show that the as-deposited films are amorphous, regardless of substrate temperature; however, analysis of FTIR spectra suggests that the higher substrate temperature facilitates formation of the B12 icosahedral framework, therefore leading to the higher hardness.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
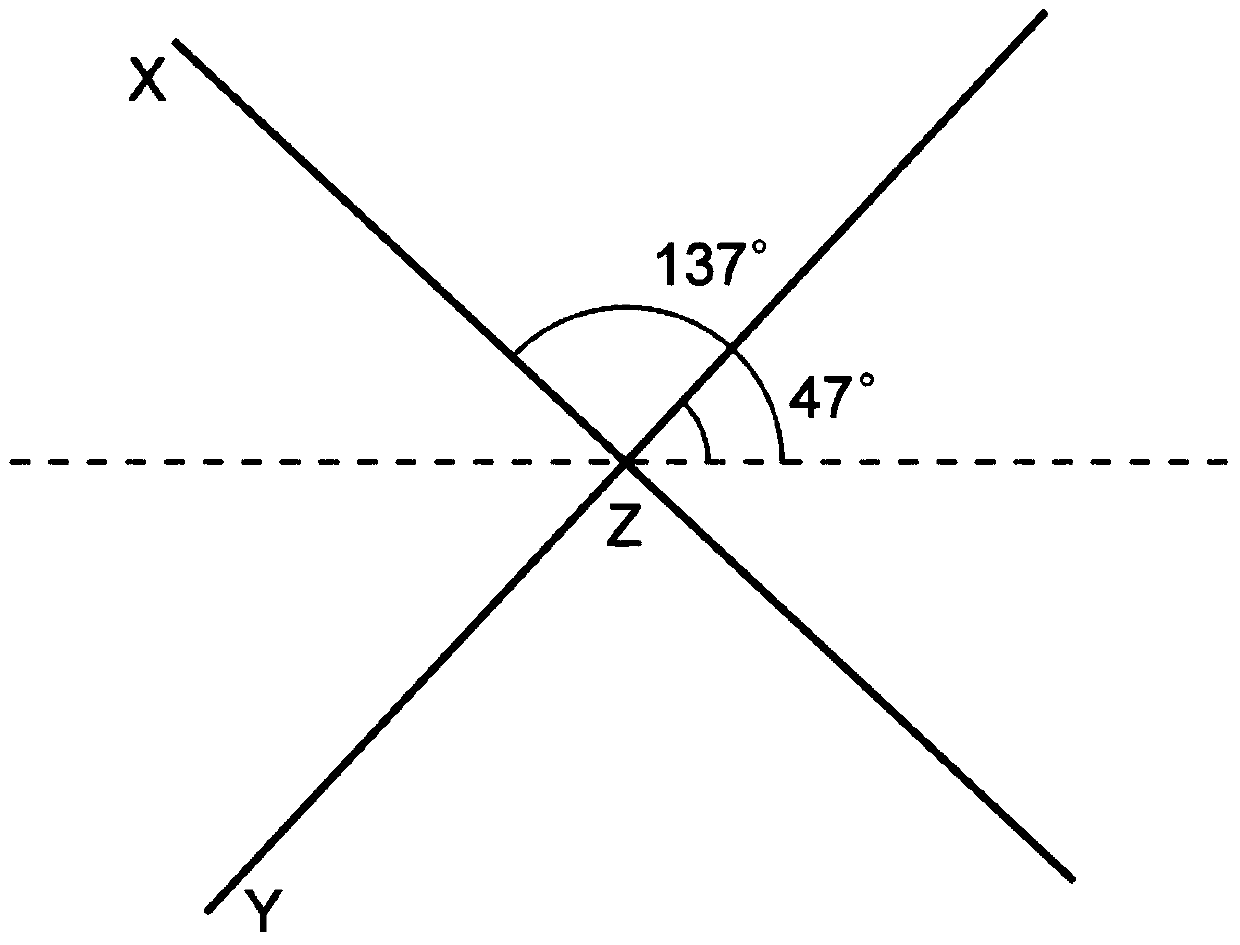
Method for measuring diffraction patterns from a transmission electron microscopy to determine crystal structures and a device therefor
InactiveUS20070023659A1Minimize damageMinimizing damageElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionPrecessionCrystal structure
A device and method which enable a transmission electron microscope to measure electron diffraction patterns of a sample very precisely are disclosed. The patterns are suitable for structure determination. The electron beam is precessed by means of deflector coils (6) in the transmission electron microscope before the sample (4), in combination with a similar precession of the electron diffraction pattern by means of deflector coils (9) situated after the sample. The electron diffraction pattern is scanned by means of deflector coils (9) situated after the sample.
Owner:SERGEEVICH AVILOV ANATOLY +1
Method for automatically adjusting the crystal orientation through double-inclination sample stage of transmission electron microscopy
InactiveCN103995014ARealize automatic positioningReduce hands-on timeMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionTest efficiencyHigh energy
The invention provides a method for automatically adjusting the crystal orientation through a double-inclination sample stage of a transmission electron microscopy. The method comprises the following steps: calibrating the double-inclination sample stage; recording a single-crystal electronic diffraction pattern of a positive zone axis, and a camera constant, and recording five readings X1, Y1, Z1, A1 and B1 of the double-inclination sample stage; calibrating the diffraction pattern by utilizing the known lattice type and parameters of a to-be-detected sample; determining a reference coordinate system through the projection positions of two rotating shafts of the double-inclination sample stage to obtain double-inclination stage readings X2, Y2, Z2, A2 and B2 needed by assigned orientation; and inputting the calculated X2, Y2, Z2, A2 and B2 values by a user through a control panel of the transmission electron microscopy, thus being capable of realizing the automatic tilting and translation process. The calculation process is easily programmed and realized, the dependence degree of an operator is reduced, the testing efficiency can be greatly improved, and the sample damage caused by long-time high-energy electronic beam radiation can also be avoided.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
High energy crystal generators and their applications
InactiveUS7741615B2Improve efficiencyFiner and pixilatedNanoinformaticsMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energyX-ray
Ferroelectric, pyroelectric and piezoelectric crystals are used to generate spatially localized high energy (up to and exceeding 100 keV) electron and ion beams, which may be used in a wide variety of applications including pulsed neutron generation, therapeutic X-ray / electron devices, elemental analysis, local scanning chemical analysis, high energy scanning microscopy, point source compact transmission electron microscopy, compact ion beam sources, positron sources, micro-thrusters for ion engines, and improved fusion efficiency especially of the Farnsworth type. The high-energy emission can be created by simply heating the material or by application of external coercive electromagnetic and acoustic fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and Apparatus for Producing Samples for Transmission Electron Microscopy
InactiveUS20100090108A1Rapid productionEfficient reproductionLaser detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAcute angleIrradiation
In the case of a method for producing samples for transmission electron microscopy, a sample is prepared from a substrate of a sample material. To this end, the sample material is irradiated by means of a laser beam along an irradiation trajectory in order to produce a weak path in the sample material. The irradiation is controlled such that the weak path crosses a further weak path, which is likewise preferably produced by laser irradiation, running in the sample material, at an acute angle in a crossing region. The substrate is broken along the weak paths. A sample is thereby produced which has a wedge-shaped sample section bounded by fracture surfaces and has in the region of a wedge tip at least one electron-transparent region.
Owner:3D MICROMAC AG
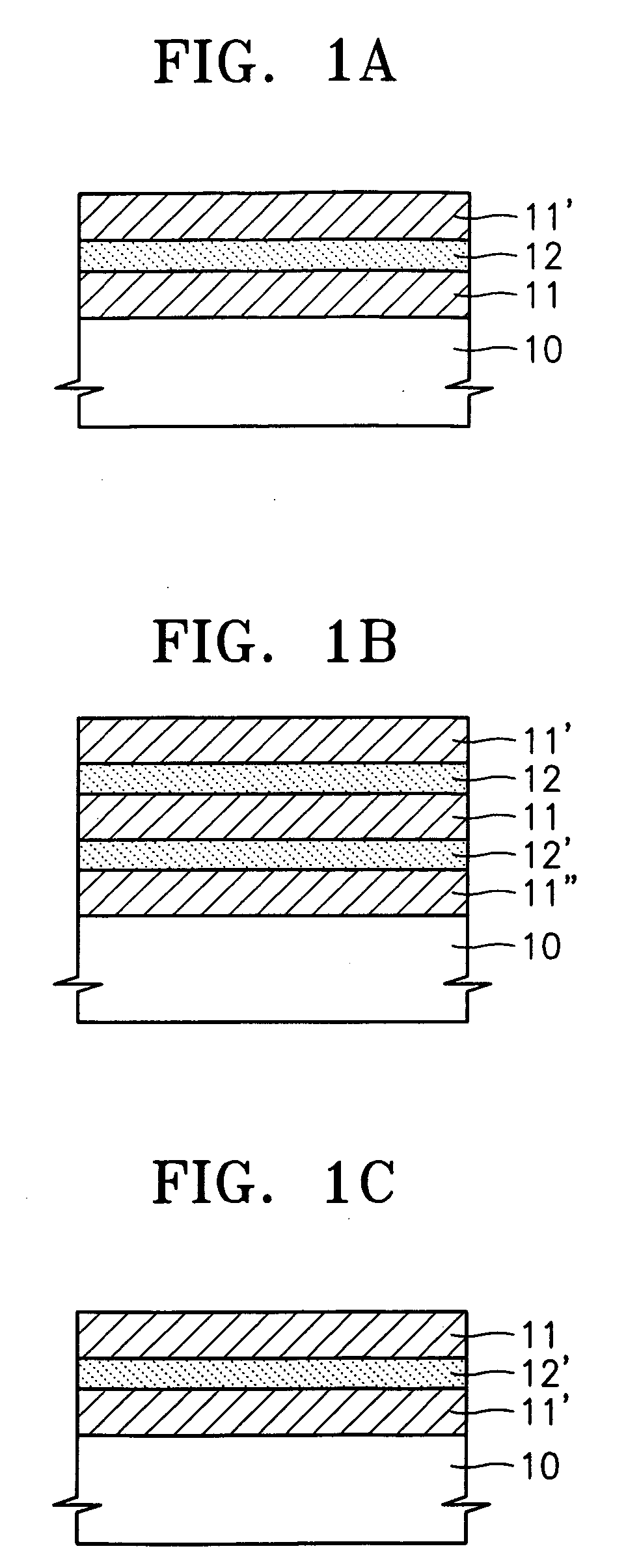
Standard sample for transmission electron microscope (TEM) elemental mapping and TEM elemetal mapping method using the same
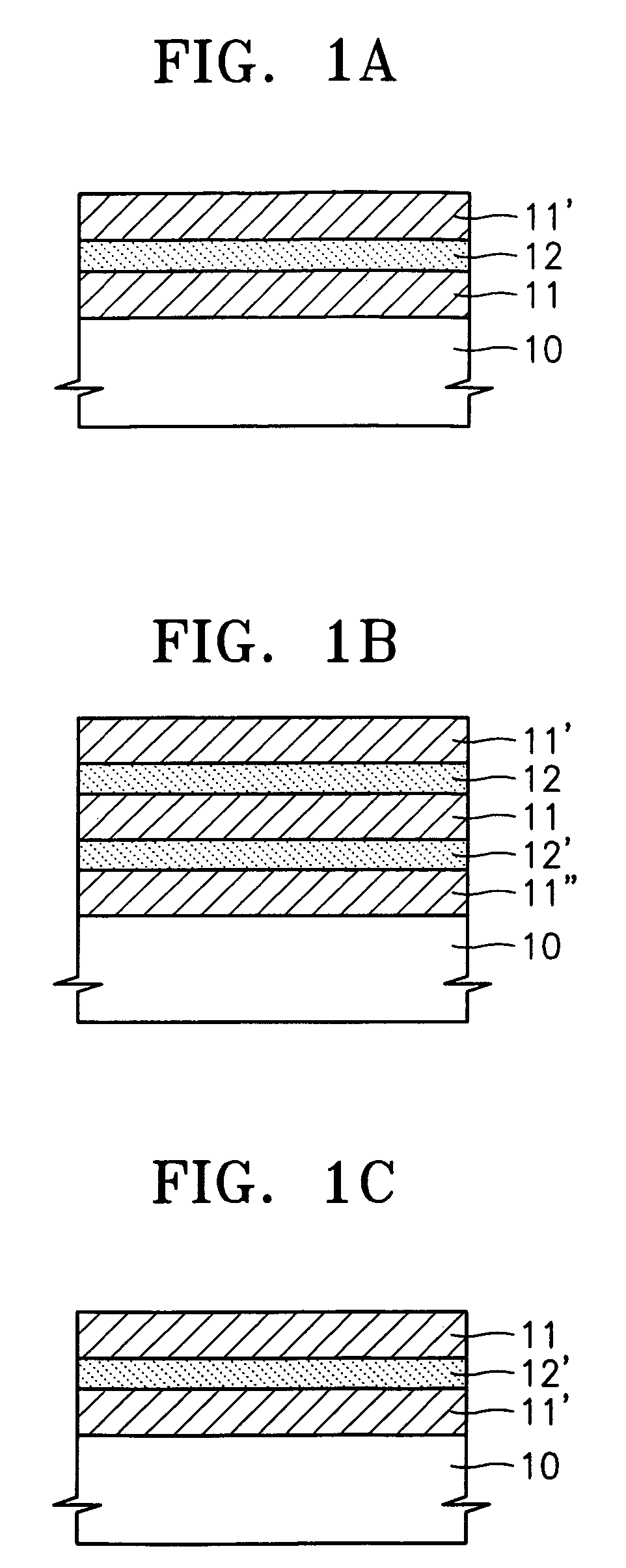
A standard sample for transmission electron microscopy (TEM) elemental mapping and a TEM elemental mapping method using the same are provided. The standard sample includes a substrate; a first crystalline thin film containing heavy atoms formed on the substrate; a first amorphous thin film having oxides or nitrides containing light atoms and having a thickness of 1-5 nm or 6-10 nm formed on the first crystalline thin film; a second crystalline thin film containing heavy atoms formed on the first amorphous thin film. The standard sample can be used to correct TEM, EDS and EELS mapping results of a multi-layered nanometer-sized thin film and to optimize mapping conditions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +2
Preparation method of transmission electron microscopy film sample for in-situ application of electric field and stress
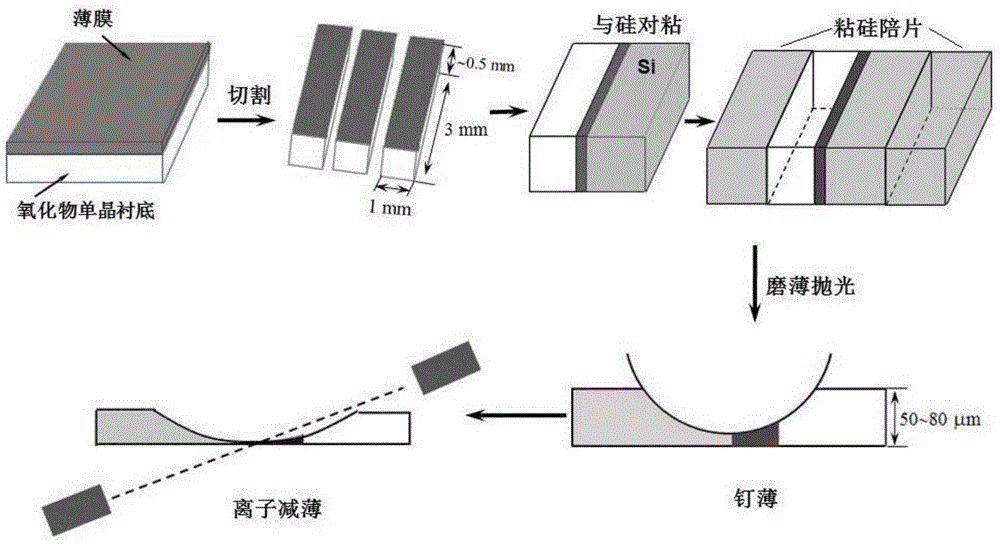
ActiveCN104819876AThin area is largeIncrease stressPreparing sample for investigationSingle crystalThinning
The present invention provides a preparation method of a transmission electron microscopy film sample for in-situ application of the electric field and the stress. The preparation method comprises: (1) cutting a film to be detected and a single crystal Si substrate into a strip shape with a size of 3 mm*1 mm*0.5 mm, and adhering the film surface of the film strip and the polishing surface of the Si strip; (2) carrying out mechanical grinding and polishing on both surfaces having the film strip thickness; (3) using a nail thinning instrument to carry out nail thinning; (4) adhering a half copper ring; and (5) selecting an ion thinning instrument to carry out ion thinning, setting the ion gun voltage to 4 kV, setting the angle to 6 DEG, thinning for 20-40 min, changing the angle into 4 DEG, thinning for 15-30 min, and finally polishing for 3 min by adopting the angle of 3 DEG and the voltage of 3 kV so as to obtain the large area perforation on the adhering seam, wherein the large area adhered Si sheet is bombarded, the film is exposed, the electric field and the stress can be applied by using the probe, and the large area thin region suitable for observation by the transmission electron microscopy exists on the edge.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Unsupported, electron transparent films and related methods
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Ultra-hard low friction coating based on A1MgB14 for reduced wear of MEMS and other tribological components and system
InactiveUS7238429B2Convenient coatingHigh hardnessSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingMicroelectromechanical systemsAlloy
Performance and reliability of microelectromechanical system (MEMS) components enhanced dramatically through the incorporation of protective thin film coatings. Current-generation MEMS devices prepared by the LIGA technique employ transition metals such as Ni, Cu, Fe, or alloys thereof, and hence lack stability in oxidizing, corrosive, and / or high temperature environments. Fabrication of a superhard, self-lubricating coating based on a ternary boride compound AlMgB14 is described in this letter as a potential breakthrough in protective coating technology for LIGA microdevices. Nanoindentation tests show that hardness of AlMgB14 films prepared by pulsed laser deposition ranges from 45 GPa to 51 GPa, when deposited at room temperature and 573 K, respectively. Extremely low friction coefficients of 0.04-0.05, which are thought to result from a self-lubricating effect, have also been confirmed by nanoscratch tests on the AlMgB14 films. Transmission electron microscopy studies show that the as-deposited films are amorphous, regardless of substrate temperature; however, analysis of FTIR spectra suggests that the higher substrate temperature facilitates formation of the B12 icosahedral framework, therefore leading to the higher hardness.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Electrochemical process for synthesis of graphene
InactiveUS20130175182A1Few defectUniform layer thicknessMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsGraphene nanoribbonsCarbon nanotube
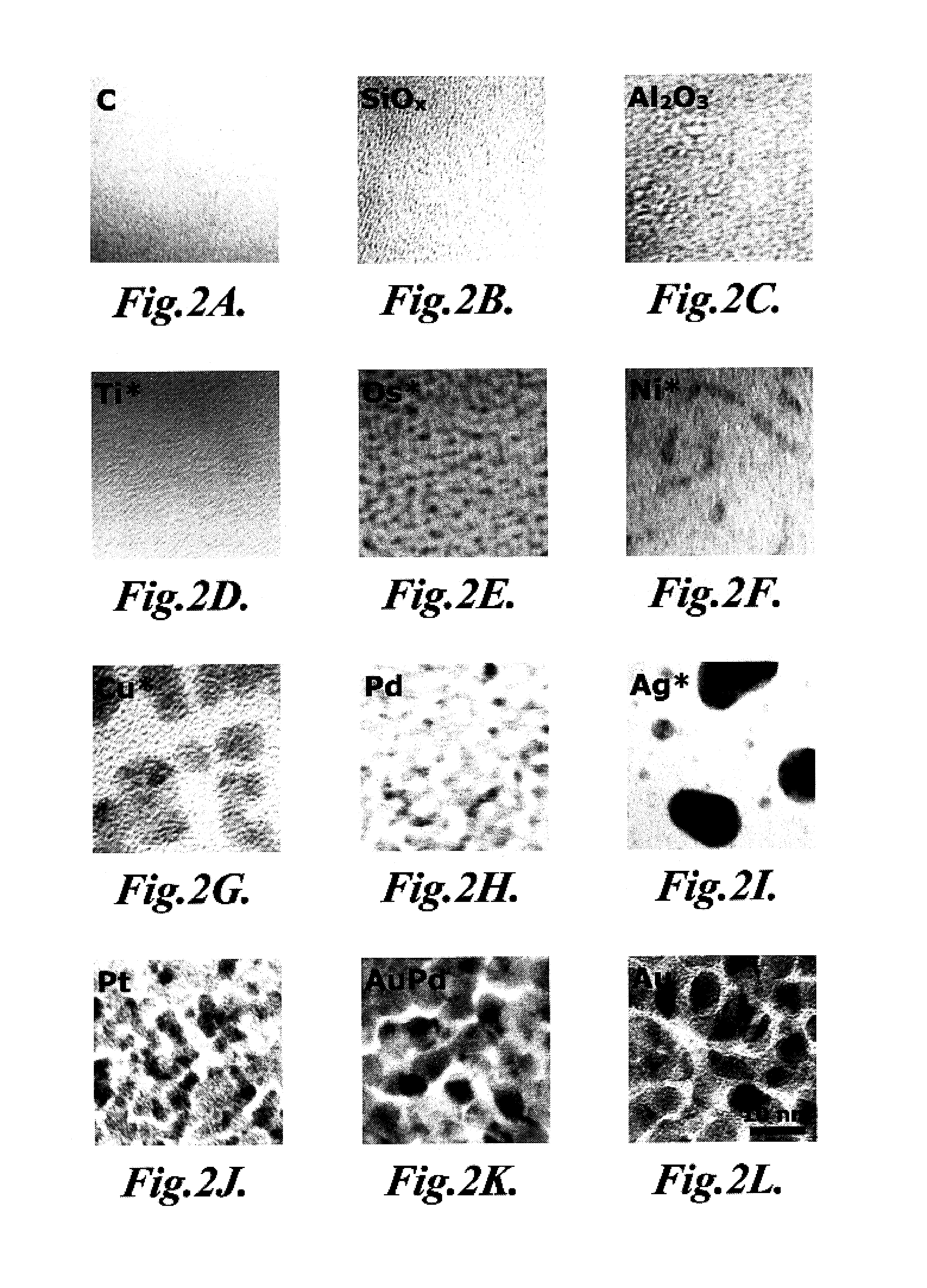
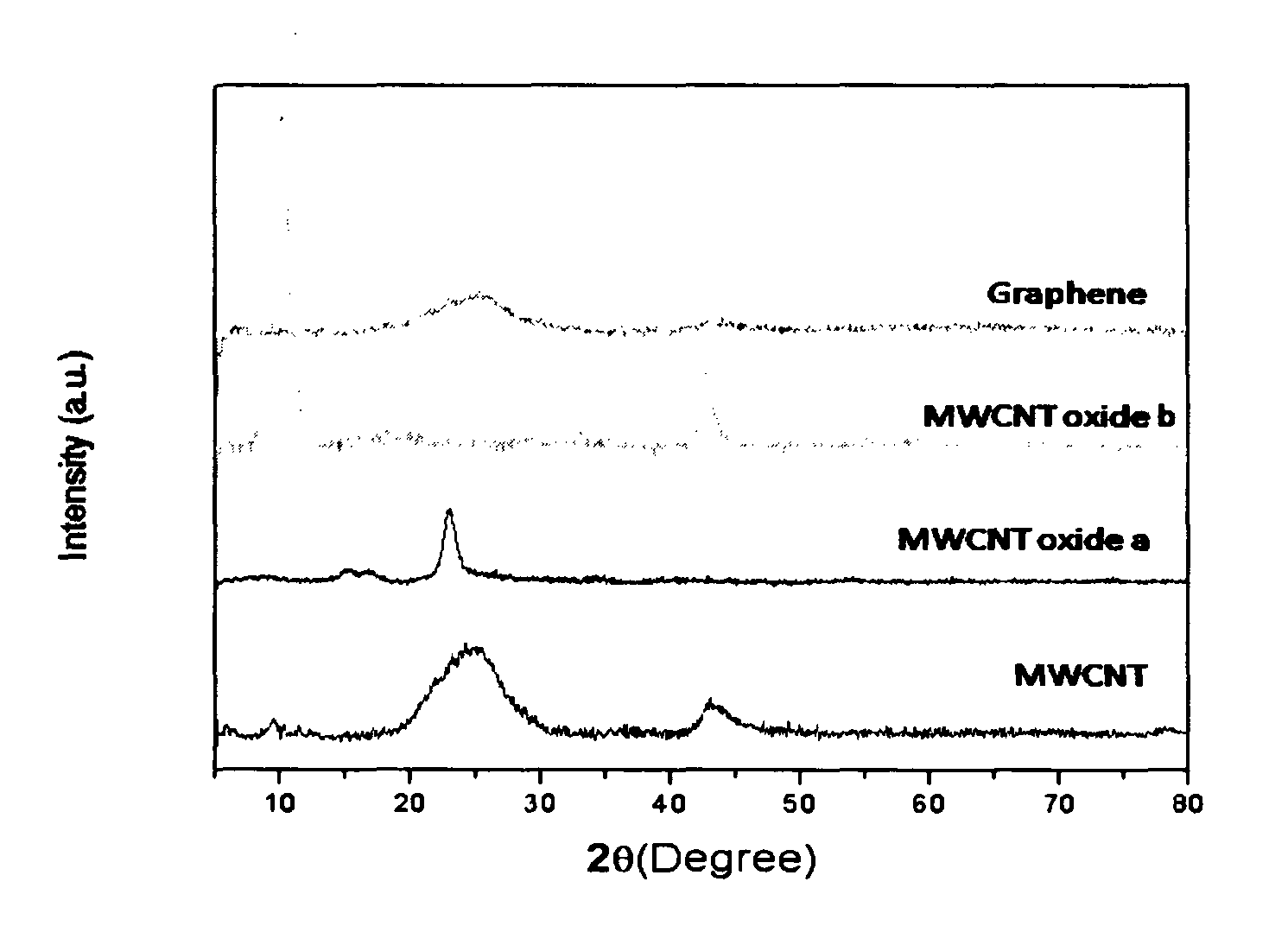
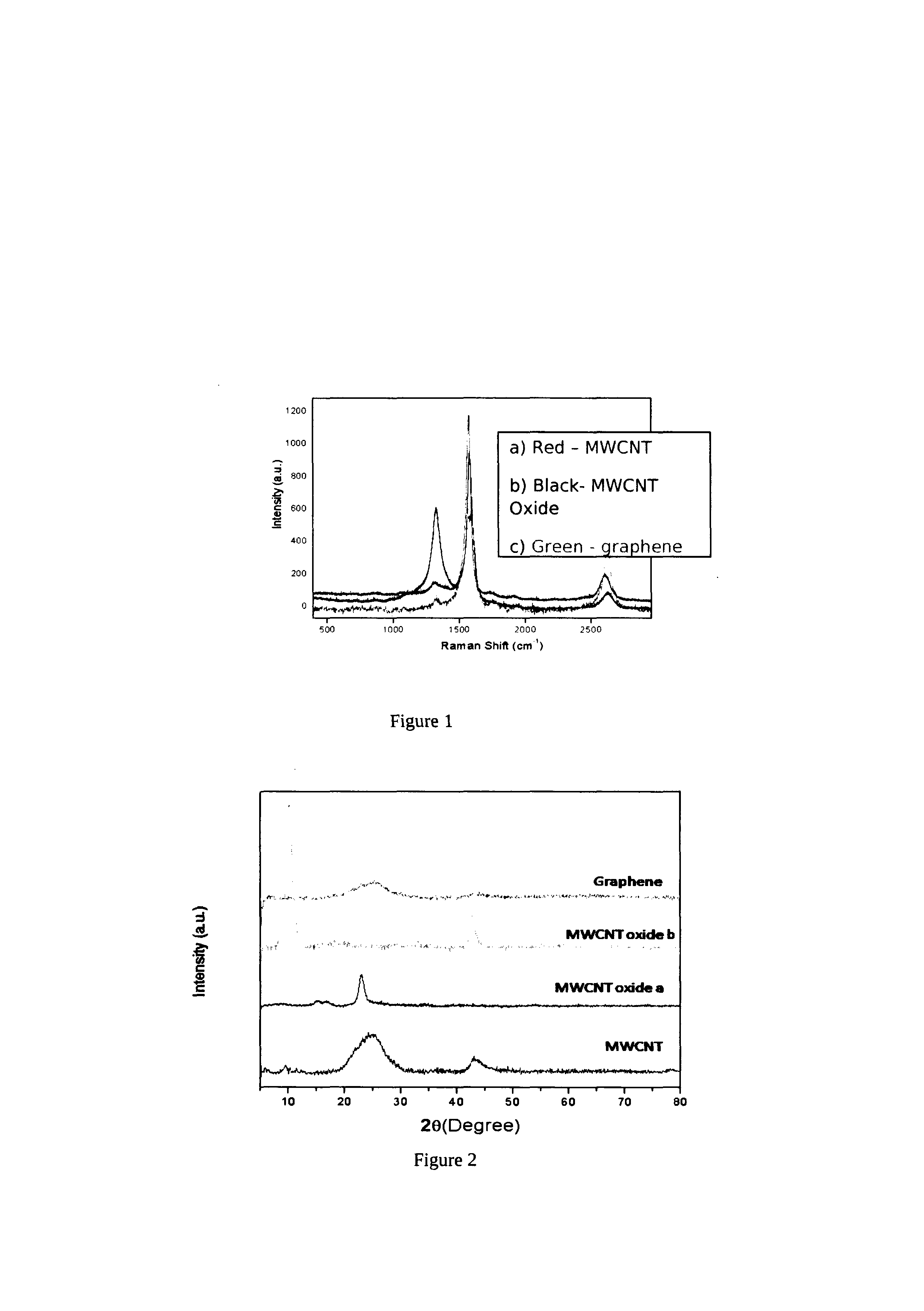
A process for the transformation of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to nanoribbons composed of a few layers of graphene by a two-step electrochemical approach is disclosed in this invention. This consists of the oxidation of CNTs at controlled potential, followed by reduction to form graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) having smooth edges and fewer defects, as evidenced by multiple characterization techniques, including Raman spectroscopy, atomic force micro-scopy, and transmission electron microscopy. This type of ‘unzipping” of CNTs (single-walled, multi-walled) in the presence of an interfacial electric field provides unique advantages with respect to the orientation of CNTs, which might make possible the production of GNRs with controlled widths and fewer defects. The extent of oxidation was confirmed by various characterization techniques like XRD, XPS and Raman spectroscopy. In the second step of experiments, the CNT oxide were reduced for different periods such as 4, 8, 12 hours at fixed negative potentials of −0.5 V, so as to get layers of graphene ribbons as tabulated herein.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Preparation and application of Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7-zincosilicate molecular sieve composite porous nanometer catalytic material
ActiveCN104646003AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMolecular sieve catalystsElemental compositionX-ray
According to the invention, a powder catalytic material Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) is prepared by adopting a supercritical hydrosynthesis method and a chemical vapor condensation and deposition method; a composite porous nanometer catalytic material Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) -zincosilicate molecular sieve is prepared by adopting an impregnating and baking method; and a novel photoelectrode Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) is prepared. The three novel materials are represented: tissue morphology analysis is performed by a transmission electron microscopy, and results show that catalyst particles are irregular in shape, with the average particle size of 150 nm; phase analysis is performed by an X-ray diffractometer, and results show that Nd2CoNbO7 has a single phase, and relatively high crystallinity; the chemical speciation of the surface of the catalyst and the elementary composition of a microcell as well as the structural characteristics of an electronic shell are discussed by an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; and a characteristic absorption edge of the Nd2CoNbO7 is determined by a UV-Vis diffuse reflection spectroscopy to obtain the band gap width of the Nd2CoNbO7 which is 2.412 eV. Finally, the catalyst is used for decomposing water to produce hydrogen, and carrying out catalytic degradation on organic pollutants such as microcystic toxins, methylene blue and sulfamethoxazole in a water body under visible light. Experimental results show that the catalyst prepared according to the invention is good in catalytic effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Transmission electron microscopy for imaging live cells
ActiveUS9207196B2Not to damageReduce intensityElectric discharge tubesLaboratory glasswaresEnergy filtered transmission electron microscopyLiving cell
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a microfluidic chamber. In one embodiment, the microfluidic chamber has a first sub-chamber and at least one second sub-chamber. The first sub-chamber has a first window and a second window. Both the first window and the second window are transparent to electrons of certain energies. The second window is positioned substantially parallel and opposite to the first window defining a first volume therebetween. The first window and the second window are separated by a distance that is sufficiently small such that an electron beam that enters from the first window can propagate through the first sub-chamber and exit from the second window. The at least one second sub-chamber is in fluid communication with the first sub-chamber and has a second volume that is greater than the first volume of the first sub-chamber.
Owner:DE JONGE VILIJA +2
Curable benzoxazine-based compositions, their preparation and cured products thereof
The invention relates to a curable composition comprising: at least one benzoxazine and at least one toughening additive which can be bound to the at least one benzoxazine in the curing process, characterized in that the toughening additive is distributed in the cured composition in form of discrete domains, and that at least 50% of the discrete domains related to the total amount of discrete domains have a maximum length in any direction of space in the range of 10 nm to 500 nm as determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Transmission electron microscope sample fabrication
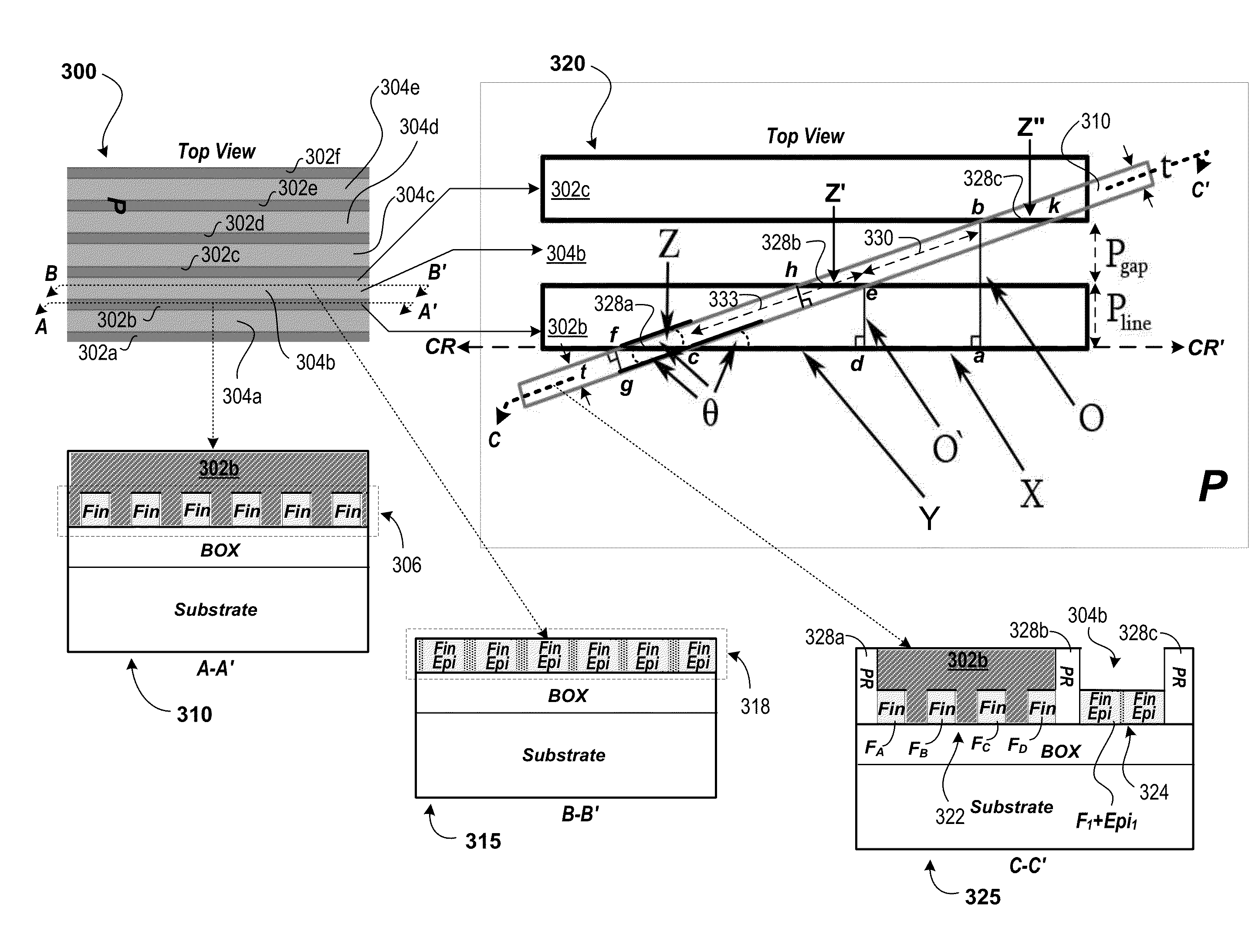
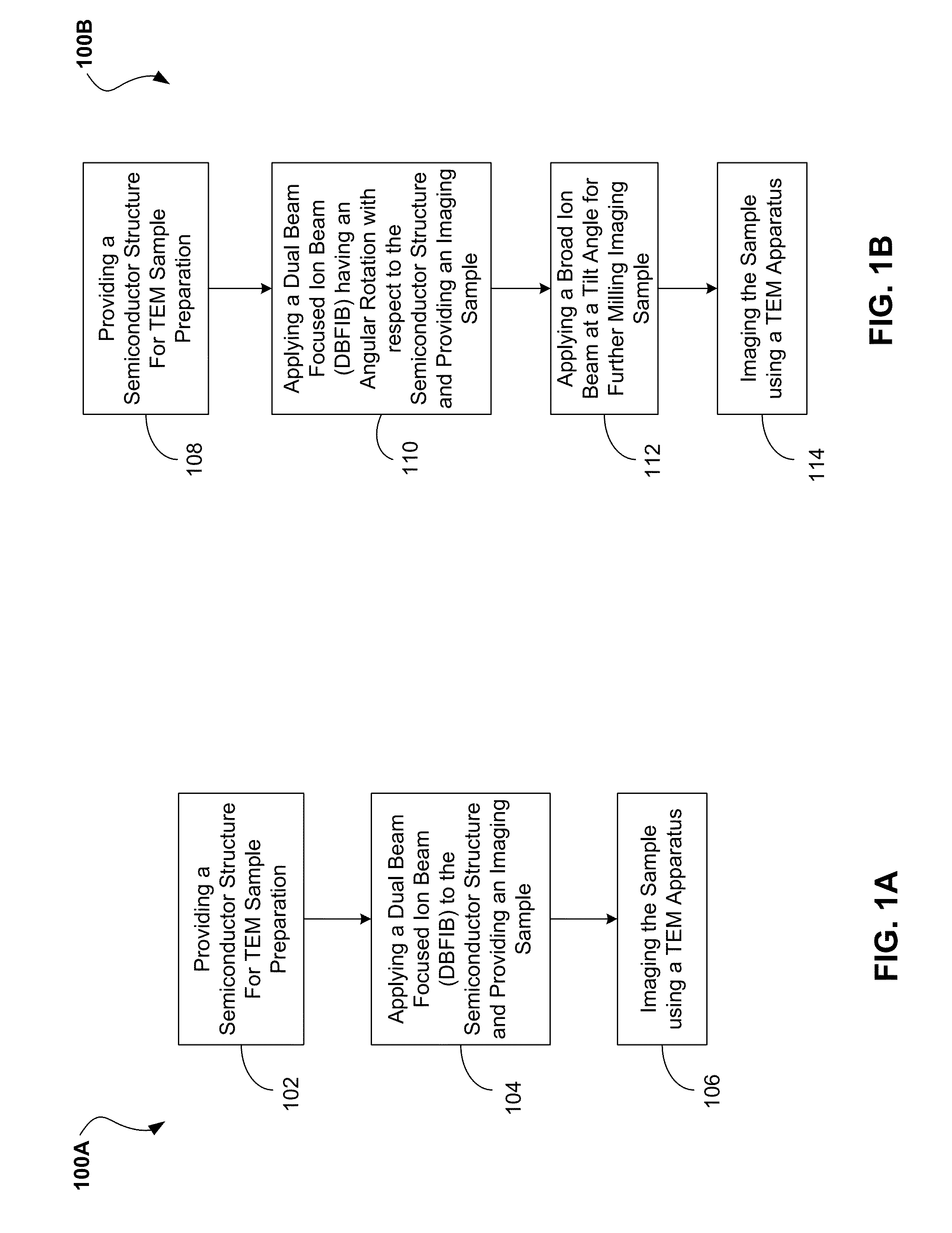
InactiveUS20140353497A1Enhanced TEM sample preparation processMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeSemiconductor structure
A method of preparing a transmission electron microscopy (TEM) sample from a semiconductor structure may include milling a region of the semiconductor structure with a focused ion beam and generating the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) sample. The focused ion beam providing the milling may include a rotation angle relative to the crystallographic axis of the semiconductor structure. A transmission electron microscopy image of a cross-sectional plane of the generated transmission electron microscopy (TEM) sample may be generated using a transmission electron microscope, whereby the transmission electron microscopy image of the cross-sectional plane includes an image projection-free region based on the rotation angle.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
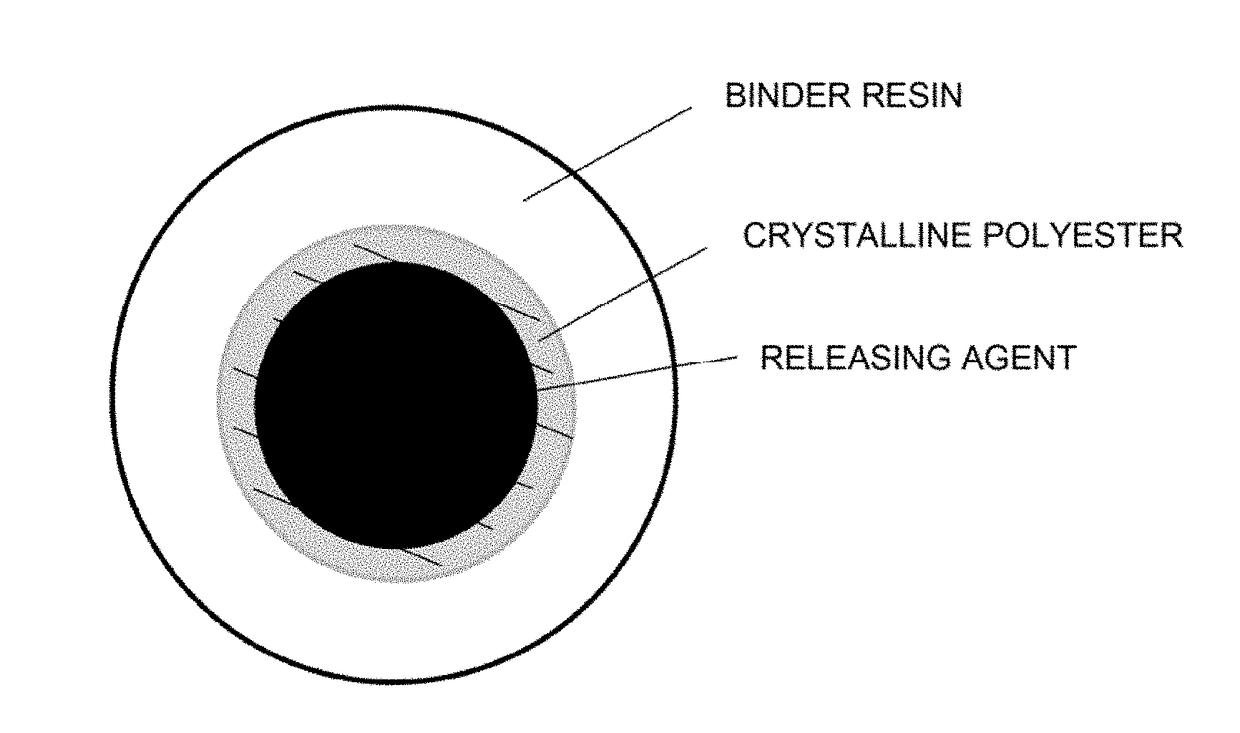
Toner
Provided is a toner including toner particles, each of which contains a binder resin, a colorant, a releasing agent and a crystalline polyester, wherein in an observation of a cross-section each of the toner particles by transmission electron microscopy, specific toner particles each of which has domains of the crystalline polyester and domains of the releasing agent, are present at a ratio of at least 70% by number of the toner particles in the toner, an arithmetic mean of maximum diameters of the domains of the releasing agent is within prescribed range, and the specific toner particles satisfy prescribed conditions.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for rapid preparation of multiple specimens for transmission electron microscopy
ActiveUS8258473B2Fast preparationImprove productivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSamplingProduction rateSputtering
A method and apparatus for in-situ lift-out rapid preparation of TEM samples. The invention uses adhesives and / or spring-loaded locking-clips in order to place multiple TEM-ready sample membranes on a single TEM support grid and eliminates the use of standard FIB-assisted metal deposition as a bonding scheme. Therefore, the invention circumvents the problem of sputtering from metal deposition steps and also increases overall productivity by allowing for multiple samples to be produced without opening the FIB / SEM vacuum chamber.
Owner:NANOTEM +1
Site-specific method for large area uniform thickness plan view transmission electron microscopy sample preparation
InactiveUS20050037625A1Great structural and mechanical supportImprove clarityElectric discharge tubesPreparing sample for investigationIon beamPhysics
A method for preparing a sample includes separating a portion of substrate from a sample, performing focused ion beam milling, and removing additional sample material using an etchant.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Sample holder, method for observation and inspection, and apparatus for observation and inspection
InactiveUS7928380B2High resolutionDistanceElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionElectron
A sample holder used in SEM (scanning electron microscopy) or TEM (transmission electron microscopy) permitting observation and inspection at higher resolution. The holder has a frame-like member provided with an opening that is covered with a film. The film has a first surface on which a sample is held. The thickness D of the film and the length L of the portion of the film providing a cover over the opening in the frame-like member satisfy a relationship given by L / D <200,000.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Preparation method of nano pesticide carboxymethyl-beta-cyclodextrin-Fe3O4-magnetic nano-diuron
ActiveCN103704232AReduce decompositionReduce churnBiocideAnimal repellantsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of nano pesticide carboxymethyl-beta-cyclodextrin-Fe3O4-magnetic nano-diuron, the nano pesticide is a clathrate compound prepared from carboxymethyl-beta-cyclodextrin-Fe3O4-magnetic nanoparticles as a subject and object diuron by Van der Waals force, electrostatic attraction and the like. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) show that carboxymethyl-beta-cyclodextrin is successfully grafted onto the surface of the Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Transmission electron microscopy analysis shows that the average particle size of the nano pesticide is 25 nm. The adsorption of the carboxymethyl-beta-cyclodextrin-Fe3O4-magnetic nanoparticles on the diuron is in line with the Langmuir isothermal adsorption curve. The new pesticide is good in water solubility and good in biocompatibility, has a slow release function, improves the pesticide utilization rate, extends pesticide efficacy preserving period, reduces the application amount and frequency, can be recycled, and reduces the harm of the pesticide on the environment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Preparation method for anisic aldehyde-modified sodium alginate and gel microspheres thereof
InactiveCN102977223AHigh load rateGood sustained release effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAerosol deliveryFluorescenceMicrosphere
Hydrophobically modified sodium alginate is obtained via acetalation reaction of sodium alginate with p-anisaldehyde (also called anisic aldehyde) in acid-catalyzed condition, and is prepared to be gel. Analysis of the product is performed by using fluorescence, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, UV, and thermal analysis, and analysis results shows that the anisic aldehyde successfully reacts with the sodium alginate. The gel can be used as a drug carrier for embedding and releasing bovine serum albumin, and results shows that drug loading ratio and releasing performance of the modified product are improved by some extent compared with the unmodified sodium alginate. The product of the present invention can be used as a drug carrier material to apply in the medical field.
Owner:孙寂呐
Metal-containing nanoparticles, their synthesis and use
A powder batch is described comprising single crystal metal-containing particles having a crystal size of less than 50nm as measured by X-ray diffraction and having a weight average particle size of from about 10 nanometers to less than 100 nanometers as measured by transmission electron microscopy and including a continuous or non-continuous coating of a ceramic material. The powder batch is preferably produced by flame spraying.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Standard sample for transmission electron microscope (TEM) elemental mapping and TEM elemetal mapping method using the same
A standard sample for transmission electron microscopy (TEM) elemental mapping and a TEM elemental mapping method using the same are provided. The standard sample includes a substrate; a first crystalline thin film containing heavy atoms formed on the substrate; a first amorphous thin film having oxides or nitrides containing light atoms and having a thickness of 1–5 nm or 6–10 nm formed on the first crystalline thin film; a second crystalline thin film containing heavy atoms formed on the first amorphous thin film. The standard sample can be used to correct TEM, EDS and EELS mapping results of a multi-layered nanometer-sized thin film and to optimize mapping conditions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com