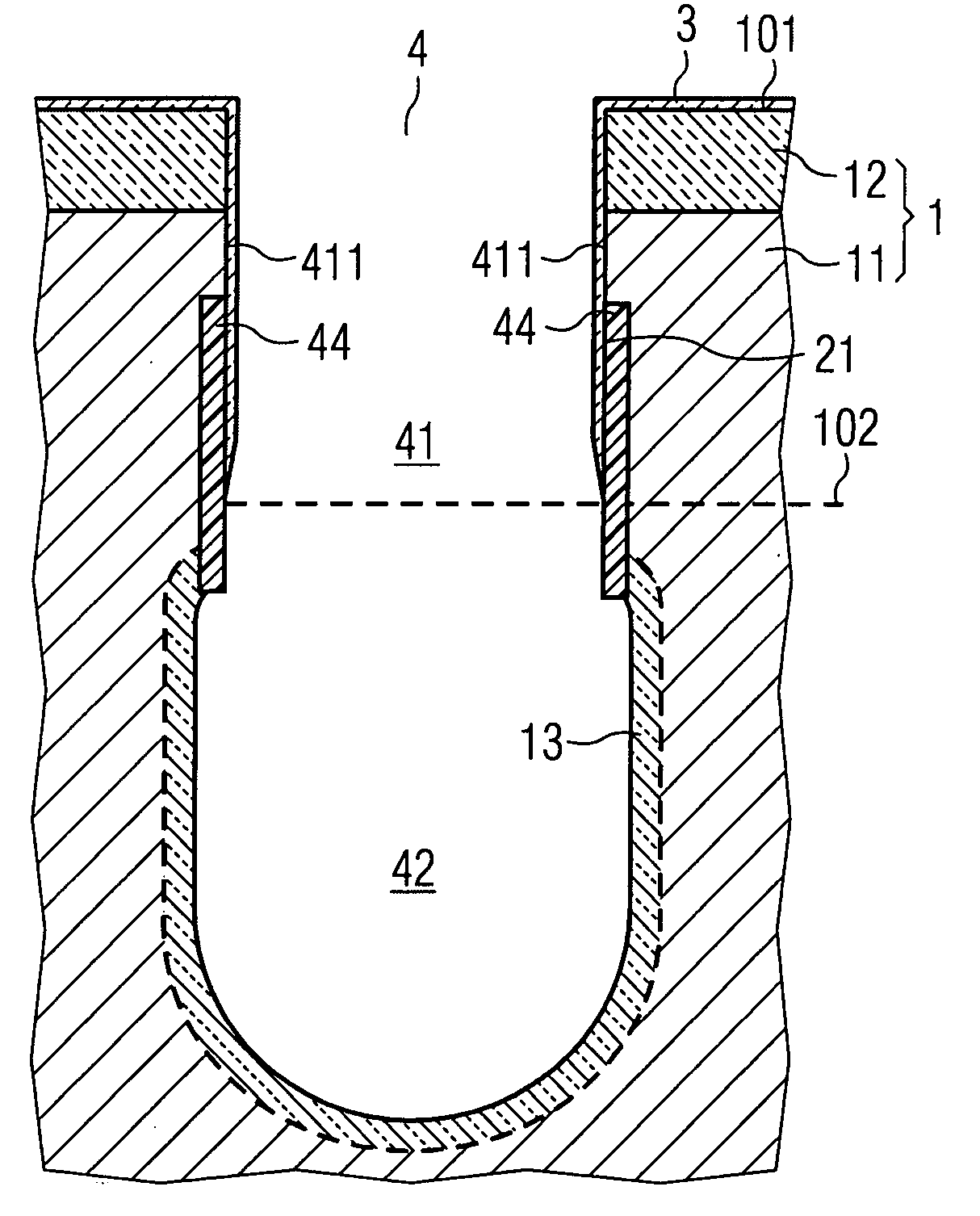
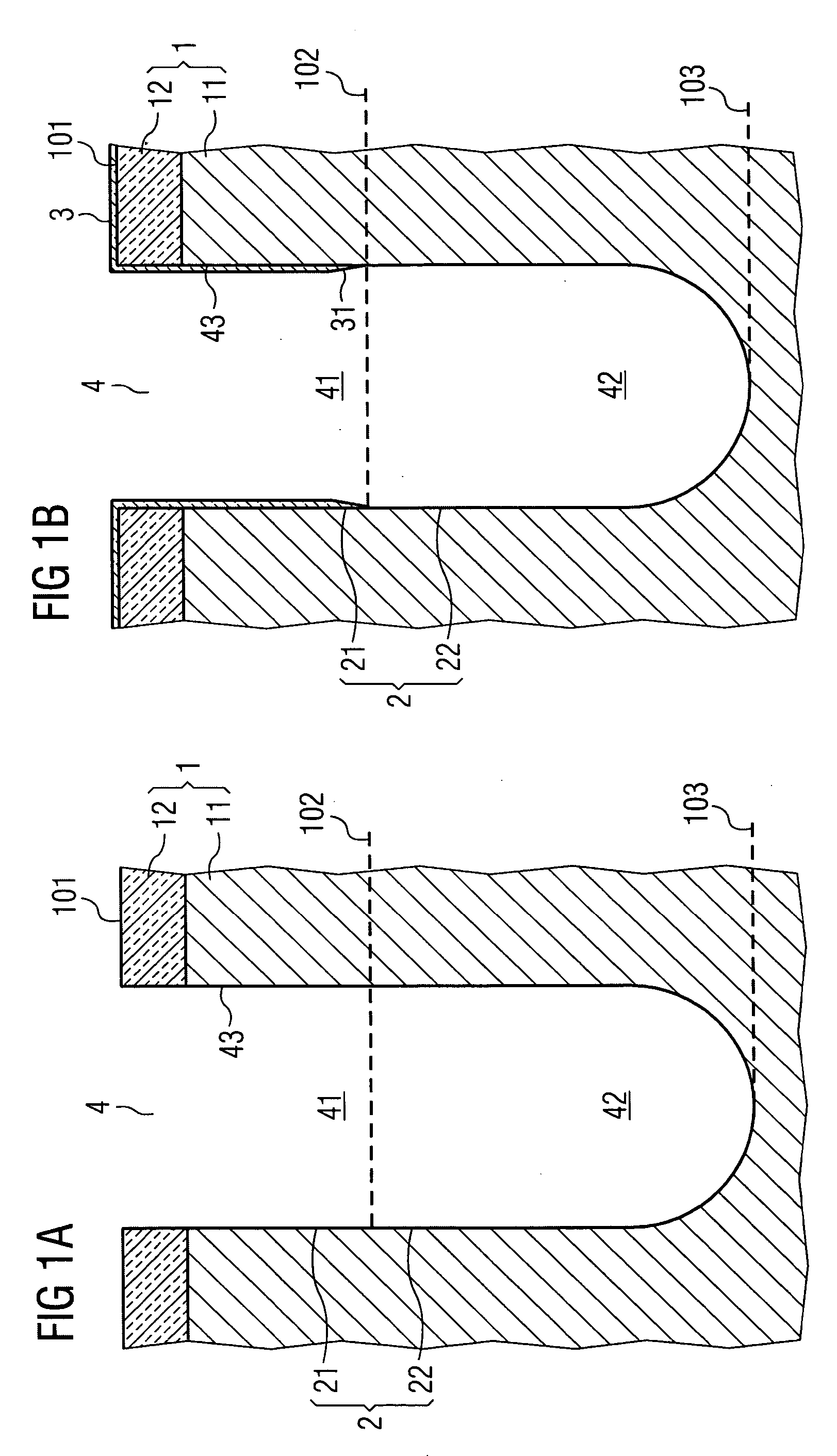
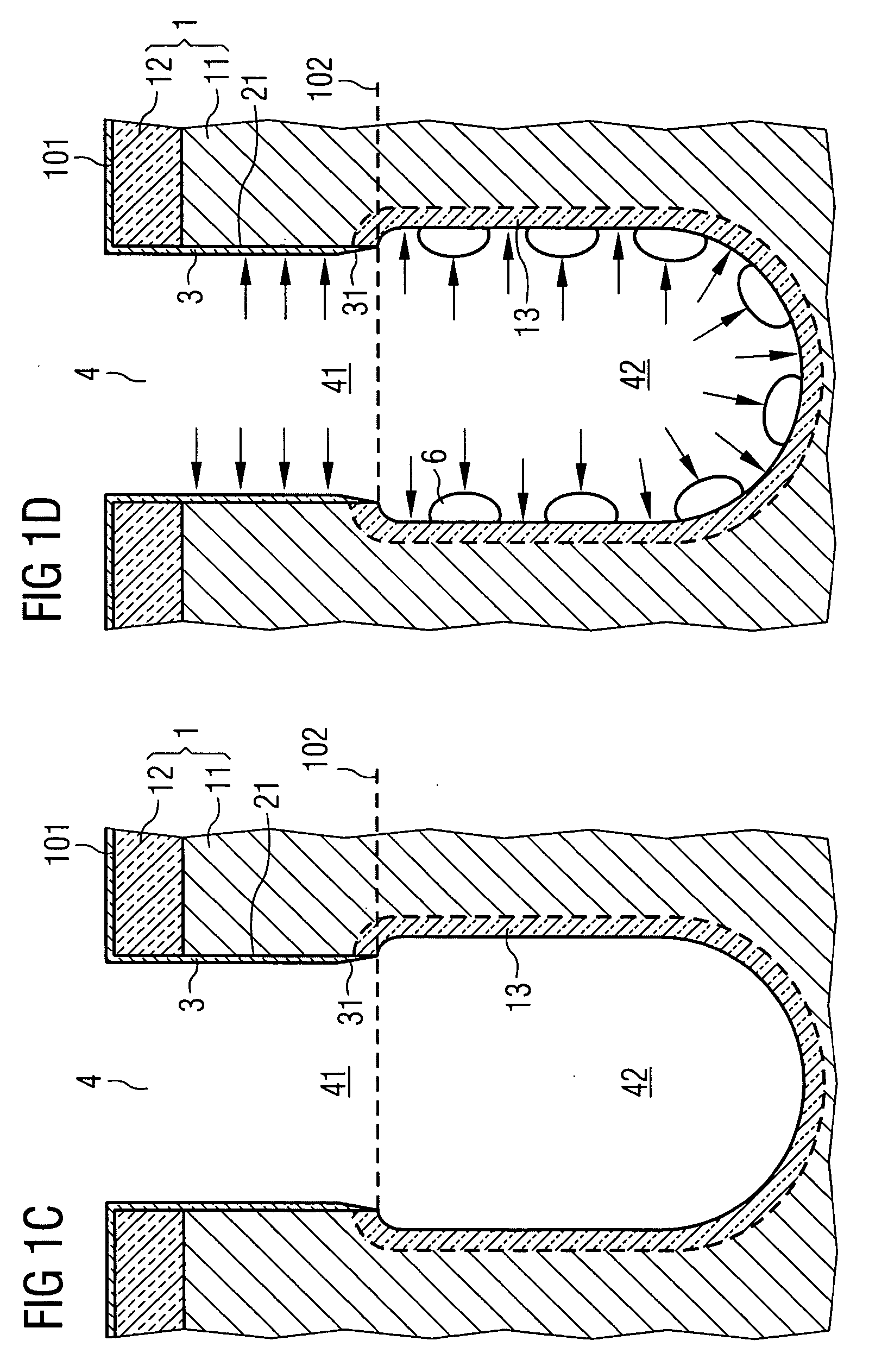
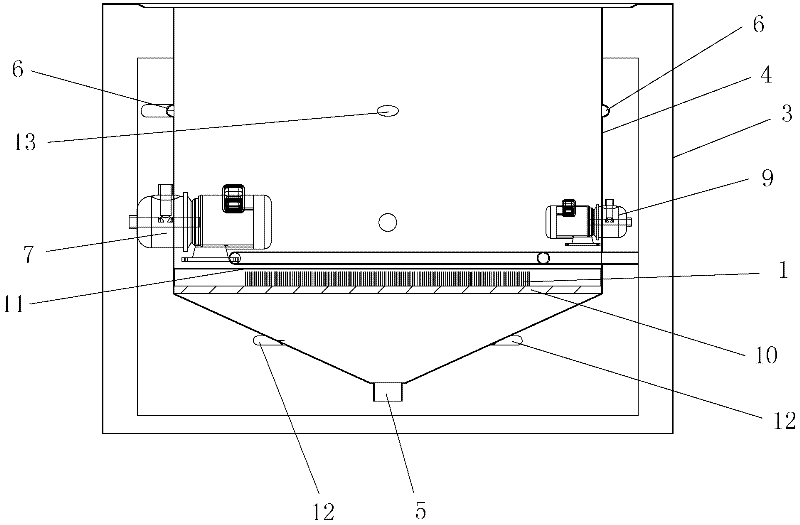
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79results about How to "Uniform layer thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
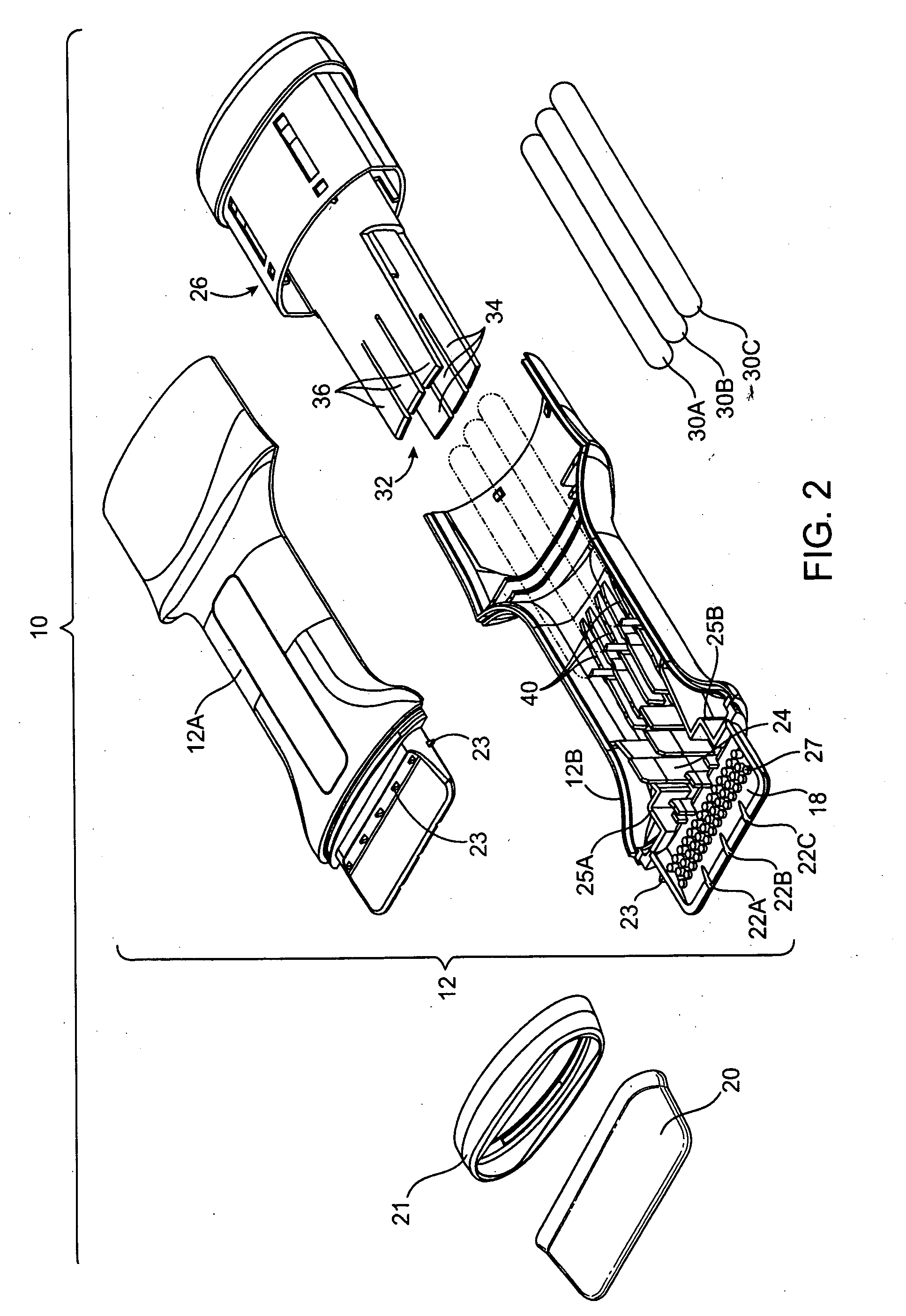
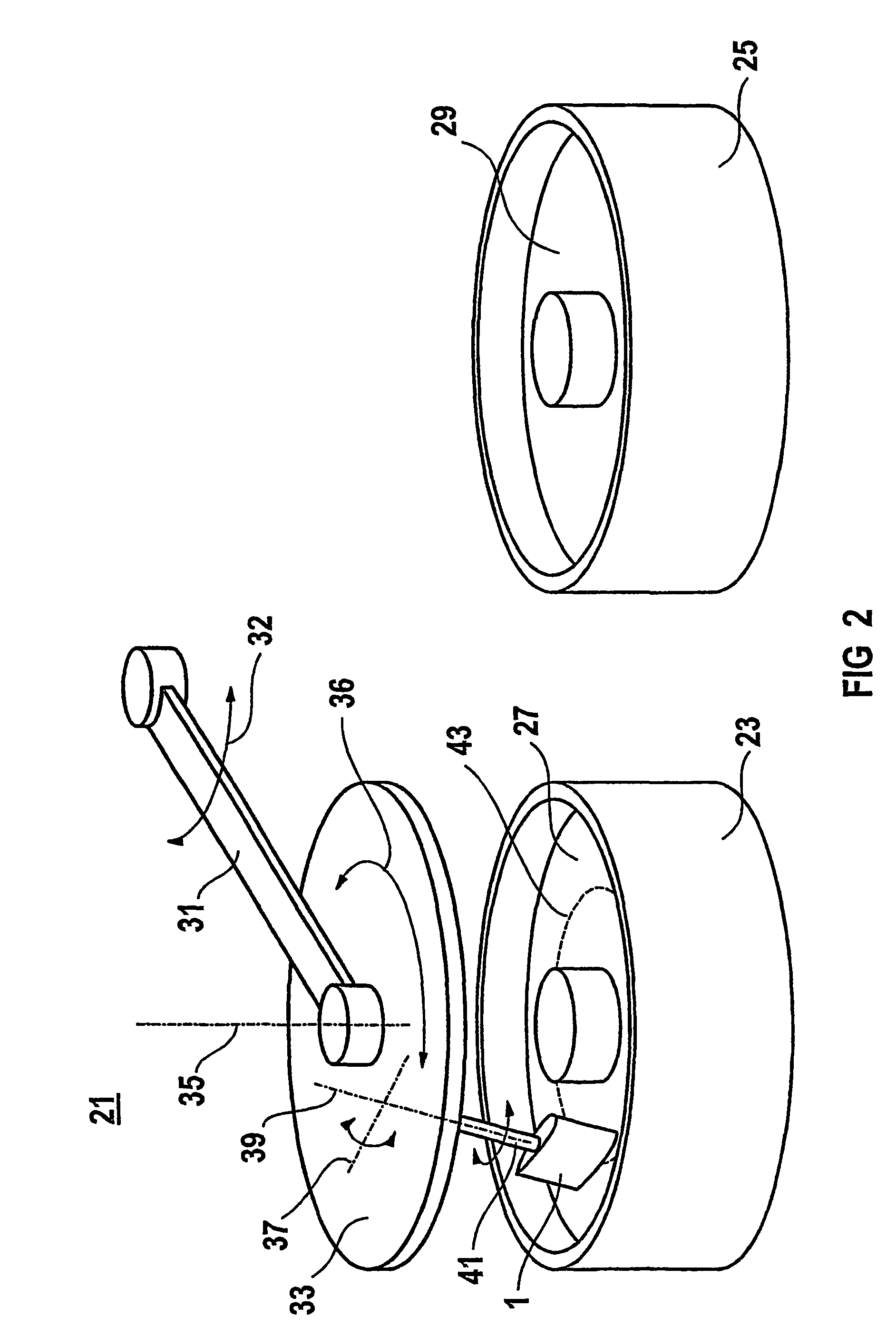
Liquid applicator and method of use
An applicator for dispensing uniform thickness layers of liquid to surfaces and especially surgical sealants to surgical sites to create, in situ, a surgical incise drape is disclosed. The applicator employs a supported thin layer of foam which achieves layer thickness which are substantially independent of the pressure applied to the applicator during use. Methods of using the applicator are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS PLYMOUTH
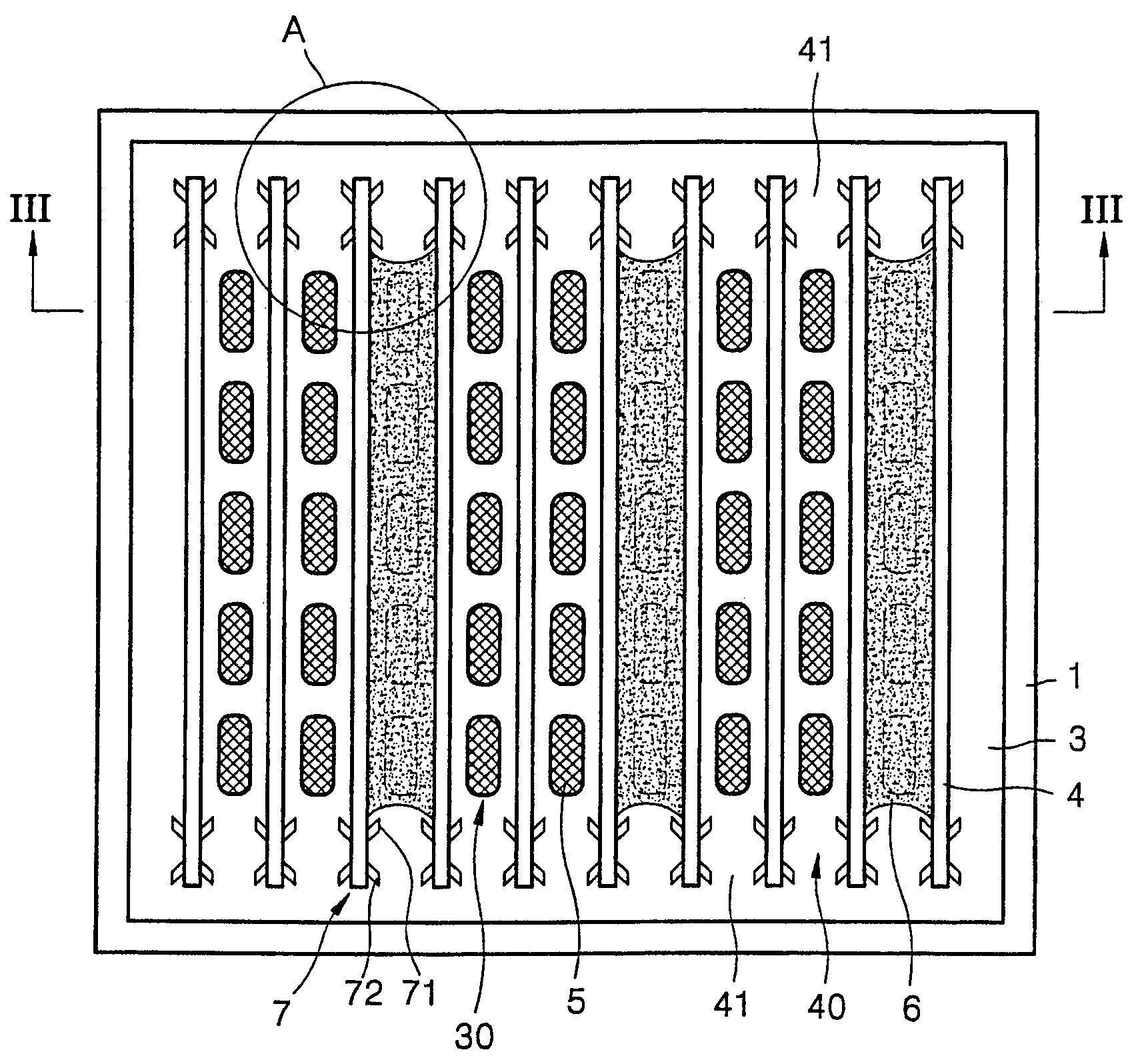
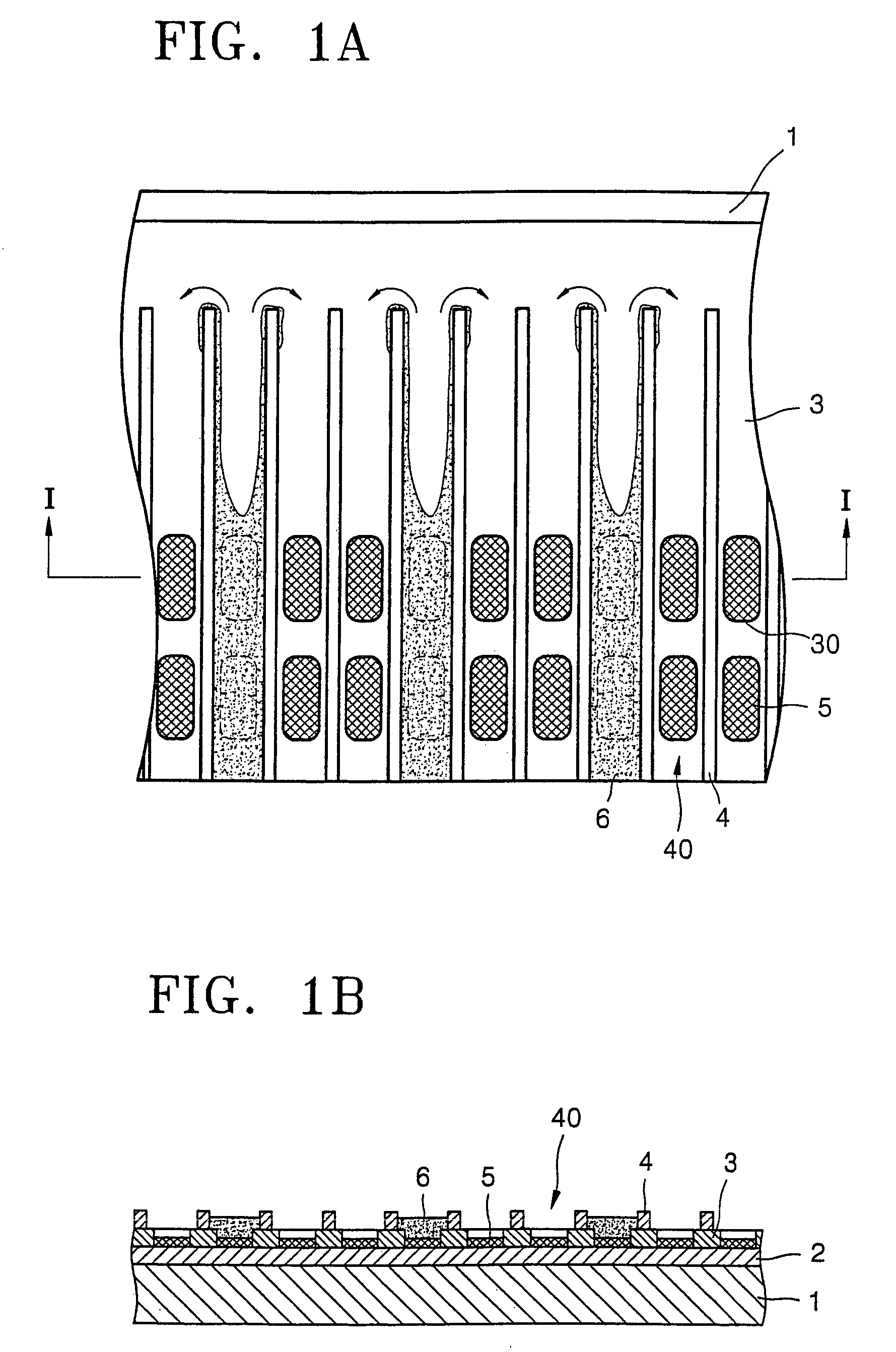
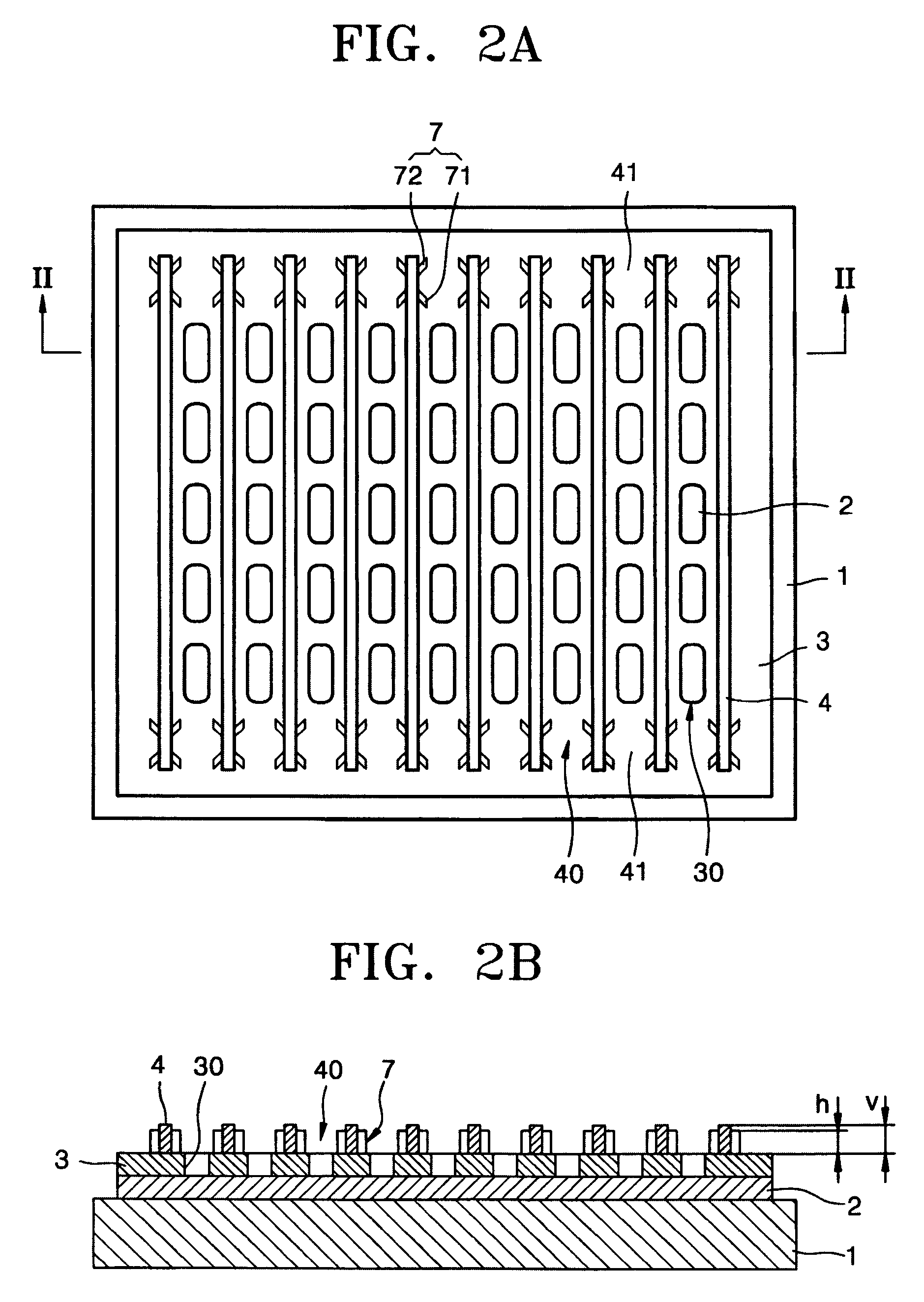
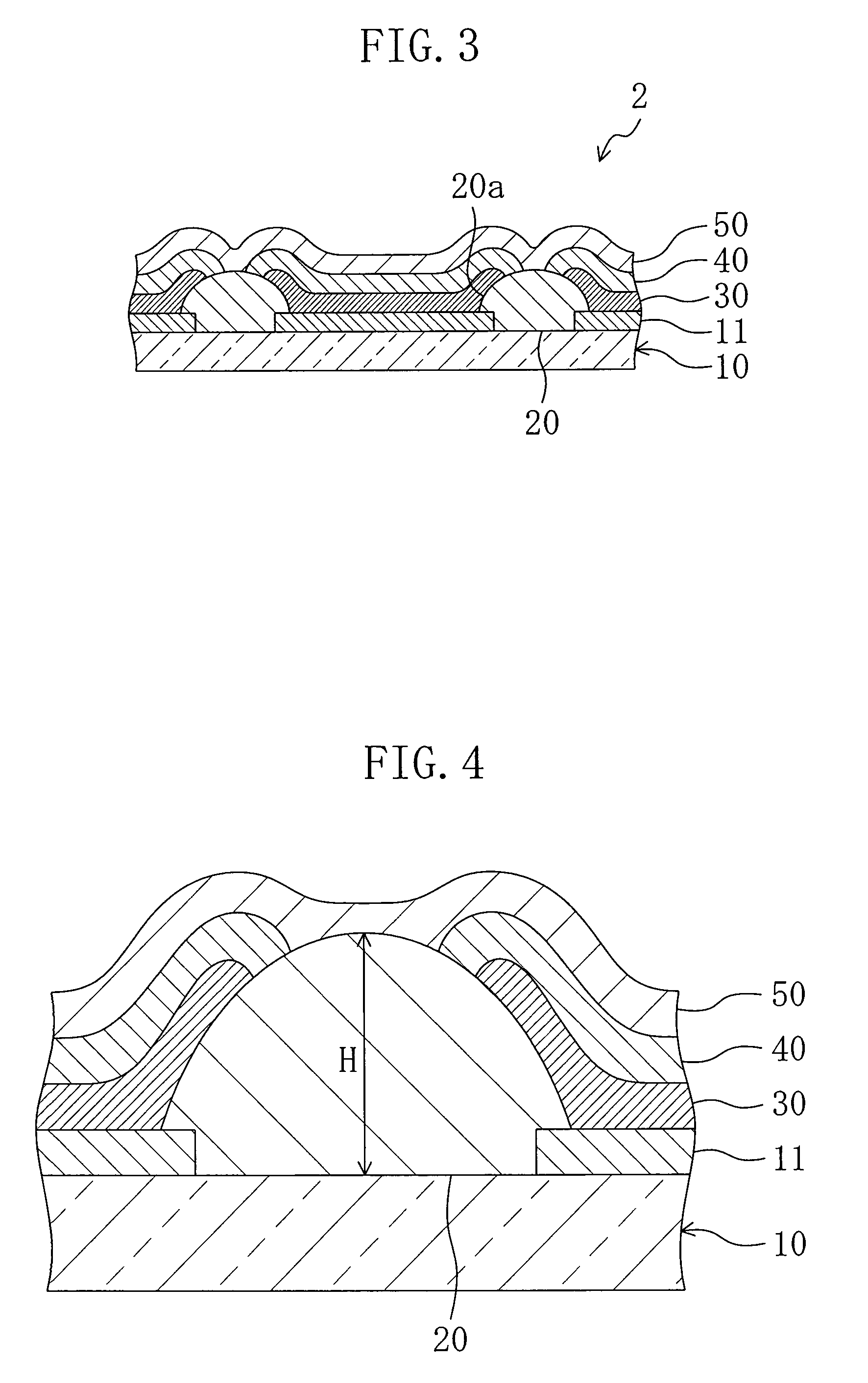
Polymer organic light emitting diode
ActiveUS7091660B2Uniform layer thicknessAvoid mixing colorsDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhysicsColor mixing
An organic light emitting diode (OLED) is used to realize a full-color display device. More particularly, a polymer OLED is used to increase uniformity in thickness of a layer formed of polymer ink, and to prevent mixing of colors. The OLED includes a substrate having a first electrode layer formed thereon in a predetermined pattern, an insulator layer formed on the substrate forming a channel in a predetermined pattern, an organic polymer layer formed based on the channel and having at least an emission layer, a barrier formed at either side of the insulator layer of at least one end of the channel for preventing ink for the organic polymer layer from running out of both ends of the channel, and a second electrode layer formed on the polymer organic layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Process for vertically patterning substrates in semiconductor process technology by means of inconformal deposition
InactiveUS20050164464A1Uniform layer thicknessTransistorSolid-state devicesDeposition processEngineering
On a substrate surface, which has been patterned in the form of a relief, of a substrate, typically of a semiconductor wafer, a deposition process is used to provide a covering layer on process surfaces which are vertical or inclined with respect to the substrate surface. The covering layer is patterned in a direction which is vertical with respect to the substrate surface by limiting a process quantity of at least one precursor material and / or by temporarily limiting the deposition process, and is formed as a functional layer or mask for subsequent process steps.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Water catalyst sterilizing and detoxifying device and producing and using method thereof
InactiveCN102370106ASimple structureReasonable designCleaning using gasesCleaning using liquidsTitanium electrodePesticide residue
The invention discloses a water catalyst sterilizing and detoxifying device and a producing and using method thereof. The device comprises a water catalyst generator and a DC (direct current) power supply, wherein the water catalyst generator comprises an anode electrode and a cathode electrode which are both titanium electrodes; and the anode electrode is coated with a composite material coating. The producing method comprises the following steps of: (I) making electrodes; and (II) making the composite material coating: preparing composite material coating liquid, and brushing, drying and sintering the coating liquid in multiple times. The using method comprises the following steps of: a, placing the cleaned article and the water catalyst generator in the cleaning water; b, connecting the water catalyst generator with the DC power supply; and c, purifying the cleaned article with the water catalyst generator and the cleaning water. According to the invention, the design is reasonable, the producing and using processes are simple, and the purifying effect is good; and moreover, the problems of poor using effect, possible new pollution, easy damage to the nutrient components of thecleaned food and the like of the existing sterilizing and pesticide residue removing methods can be solved.
Owner:姚广兴
Ultra-fast boriding of metal surfaces for improved properties
InactiveUS20100018611A1Fast boridingDesirable mechanical propertySolid state diffusion coatingMetallurgyUltra fast
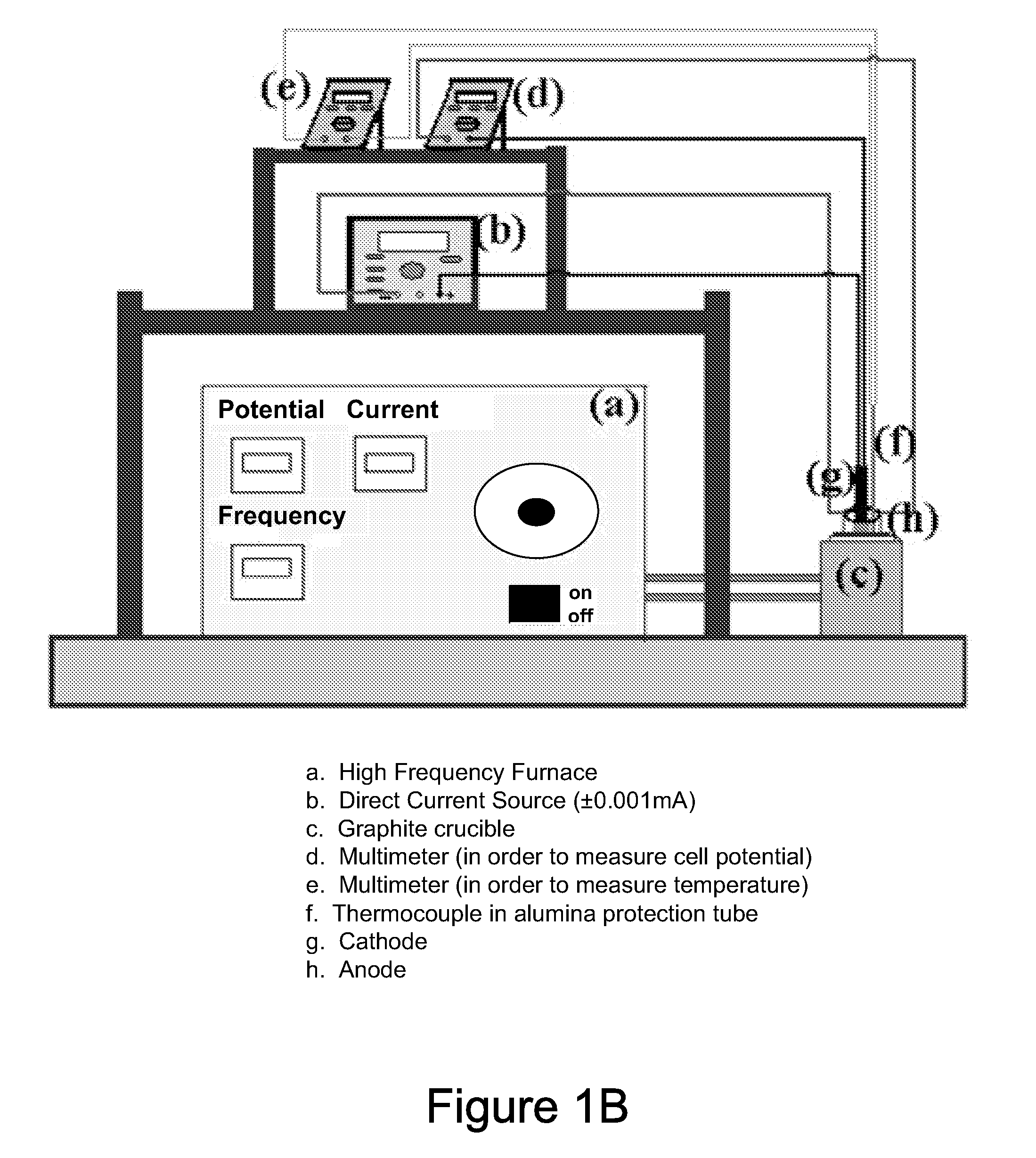
A method of ultra-fast boriding of a metal surface. The method includes the step of providing a metal component, providing a molten electrolyte having boron components therein, providing an electrochemical boriding system including an induction furnace, operating the induction furnace to establish a high temperature for the molten electrolyte, and boriding the metal surface to achieve a boride layer on the metal surface.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Organic light emitting diode and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6924504B2Uniform layer thicknessElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLight-emitting diodeOLED
An organic light emitting diode (OLED) includes a substrate having a first electrode layer formed thereon in a predetermined pattern, an insulator layer defining the upper portion of the substrate having the first electrode layer in a predetermined pattern, an organic polymer layer formed based on the pattern defined by the insulator layer, a barrier for blocking flow of the organic polymer layer at both ends of the pattern defined by the insulator layer, and a second electrode layer formed on the organic polymer layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
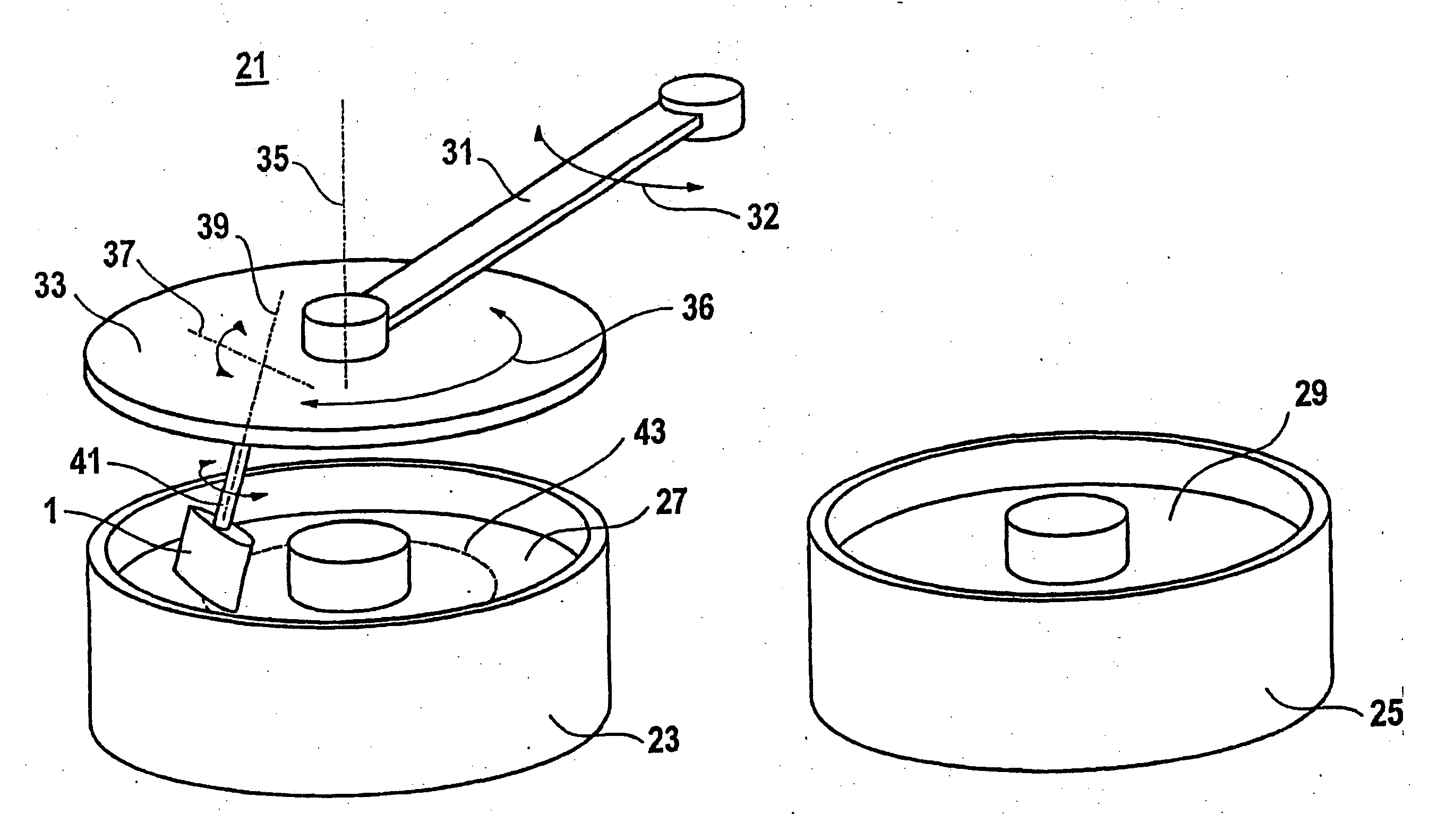
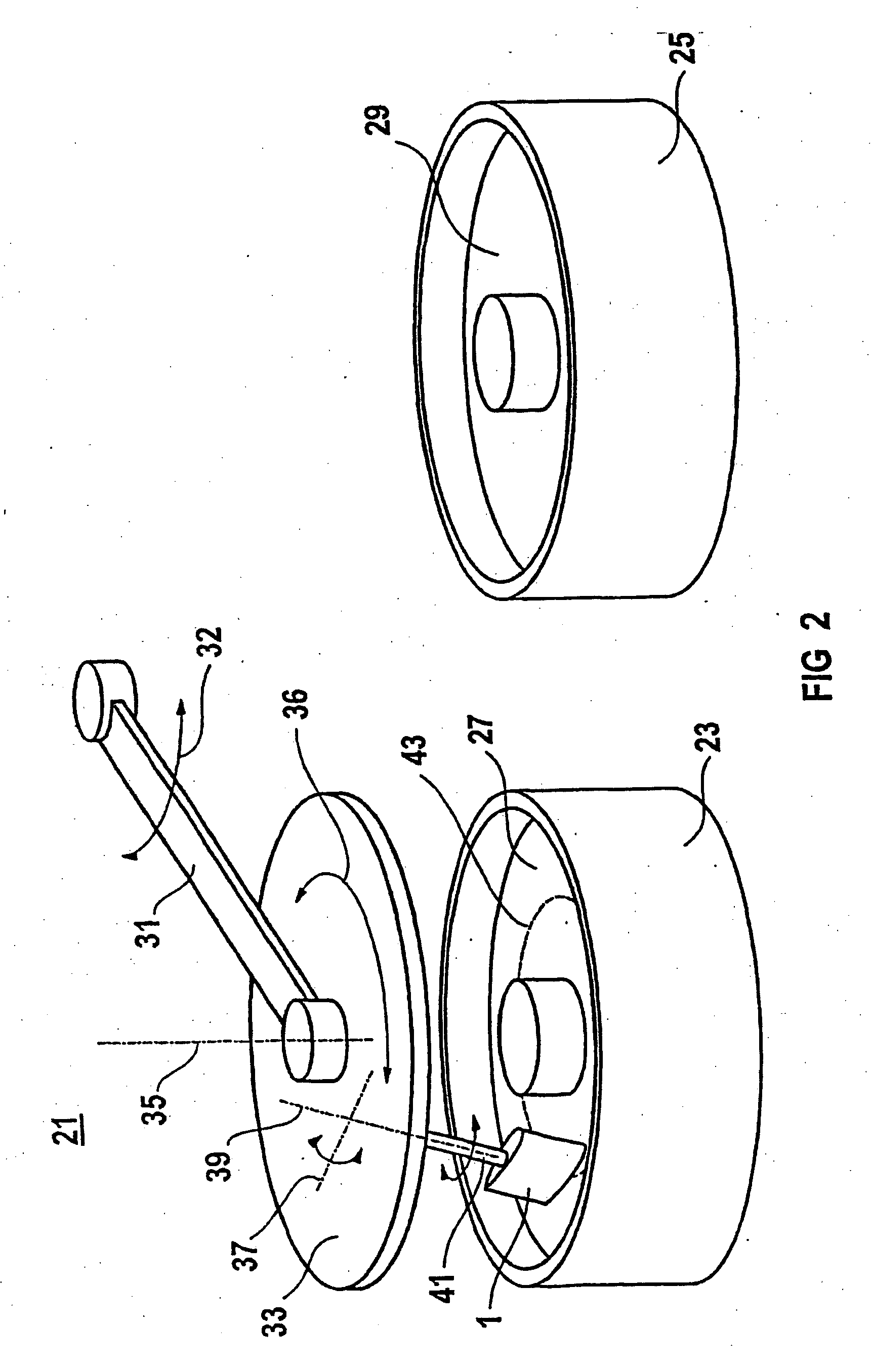
Method for smoothing the surface of a gas turbine blade
InactiveUS20060246825A1Efficient and cost-effectiveFlat surfaceEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesEngineeringGas turbines
A surface of the gas turbine blade is smoothed by way of a drag finish process. A first ring-shaped container is filled with a liquid abrasive medium. A second container which is arranged next to the first container is filled with a second liquid abrasive medium. A pivoting arm is arranged between and above the containers and can be pivoted along a pivoting direction. A drag device is arranged on the pivoting arm. The drag device leads a gas turbine blade on a carrier arm through the abrasive medium.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
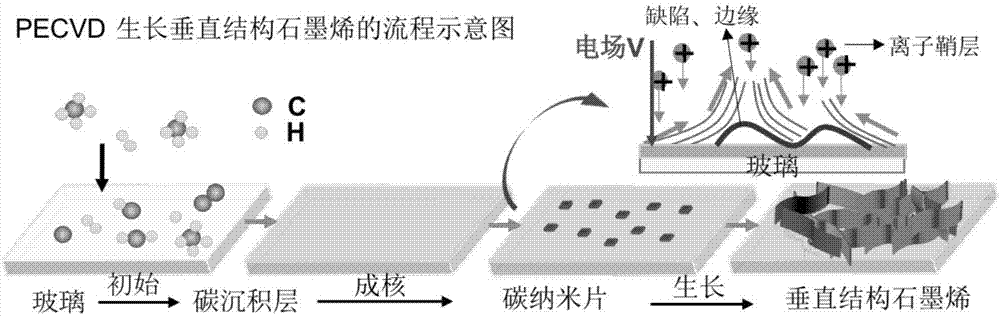
Method of preparing three-dimensional graphene glass composite
The invention discloses a method of preparing a three-dimensional graphene glass composite, which comprises the steps of providing a glass substrate, and directly growing graphene on the surface of the glass substrate by a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition method. Compared with graphene glass prepared by the traditional transfer and oxidation reduction method, the preparation method is simple; cohesion with the glass substrate is high; vertical height control of a graphene nanosheet is precise; and the repeatability is high. In addition, the preparation method adopts the most common soda lime glass in daily life of people, so that compared with quartz glass and sapphire glass used in other experiments, the cost is greatly lowered. The method can realize uniform, controllable and quick preparation of graphene glass below the glass softening point temperature (600 DEG C), requires no catalyst, greatly simplifies a preparation growth technology of the graphene glass, and provides a premise for a subsequent industrial application.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for smoothing the surface of a gas turbine blade
InactiveUS7144302B2Efficient and cost-effectiveFlat surfaceEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesEngineeringGas turbines
A surface of the gas turbine blade is smoothed by way of a drag finish process. A first ring-shaped container is filled with a liquid abrasive medium. A second container which is arranged next to the first container is filled with a second liquid abrasive medium. A pivoting arm is arranged between and above the containers and can be pivoted along a pivoting direction. A drag device is arranged on the pivoting arm. The drag device leads a gas turbine blade on a carrier arm through the abrasive medium.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and apparatus for manufacturing quartz glass crucible
ActiveCN101605732AEasy to flow outReduction of internal circulation flowBy pulling from meltGlass shaping apparatusCrucibleTemperature difference
Provided is a method for manufacturing a quartz glass crucible by employing a rotating molding method. The method is characterized in performing arc-melting by arranging an electrode at a position deviated from a molding center line. The eccentric arc controls glass temperature differences among the temperatures of glass being melted at a straight trunk portion, a curved portion and a bottom portion to be 300 DEG C or below. The eccentric arc also controls the thicknesses of a transparent layer at the straight trunk portion and at the bottom portion to be within 70-120% of the thickness of the transparent layer at the curved portion.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
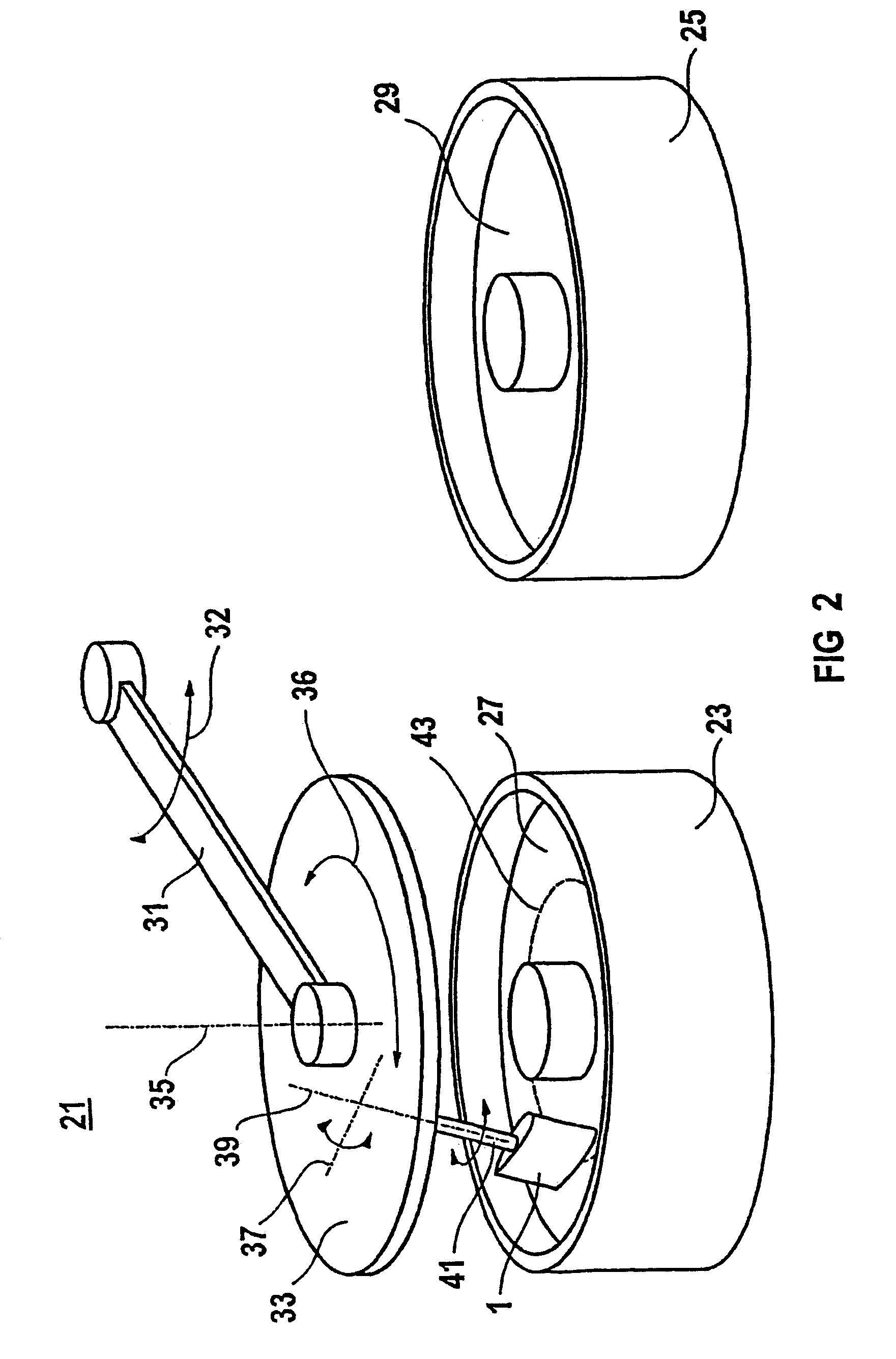
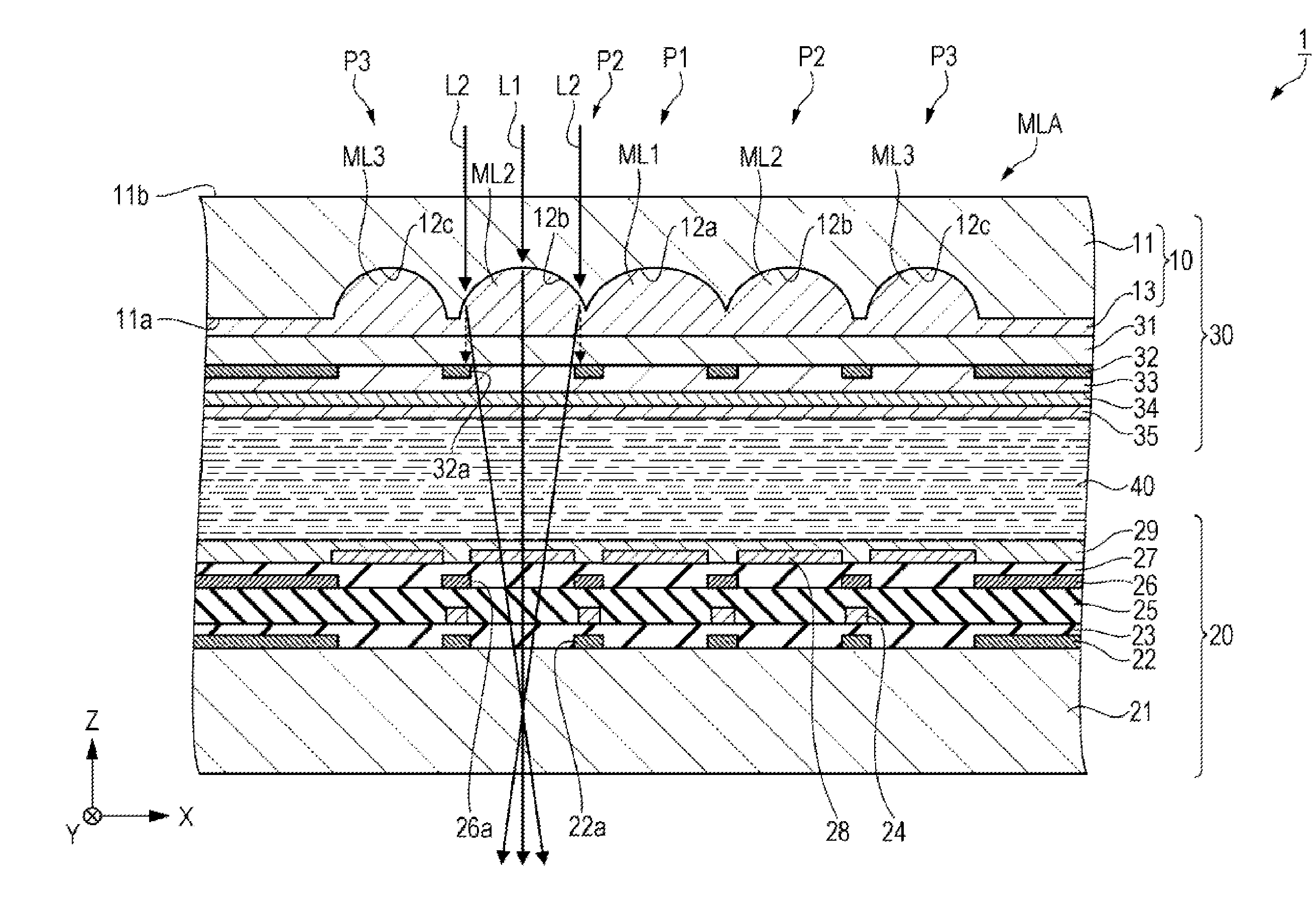
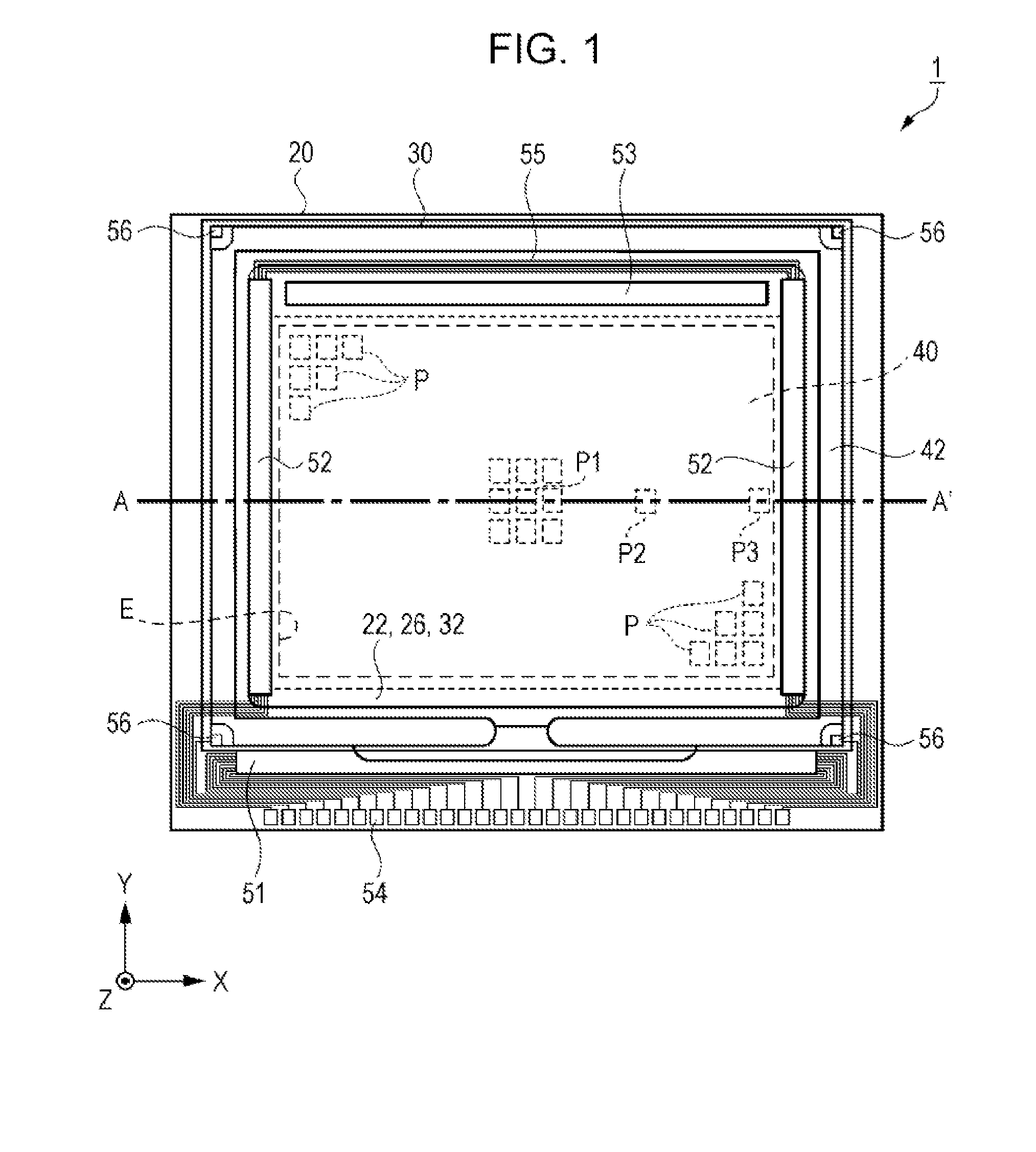
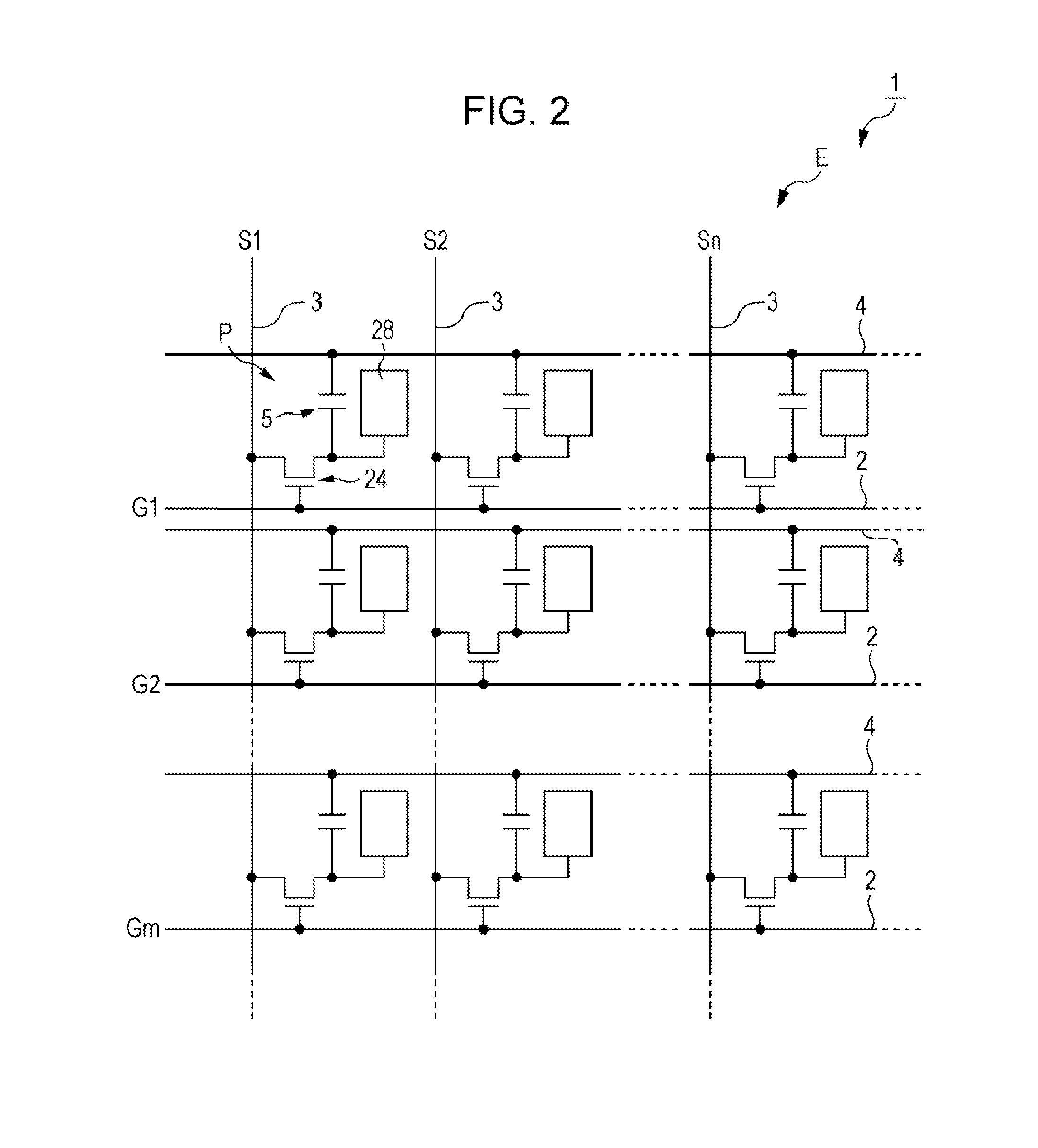
InactiveUS20140152908A1Uniform illuminationImprove flatnessProjectorsColor television detailsMicro lens arrayElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electroplating device and method
InactiveCN101426962AReduce intervalMulti-accumulationTanksContacting devicesElectrolyteSurface cover
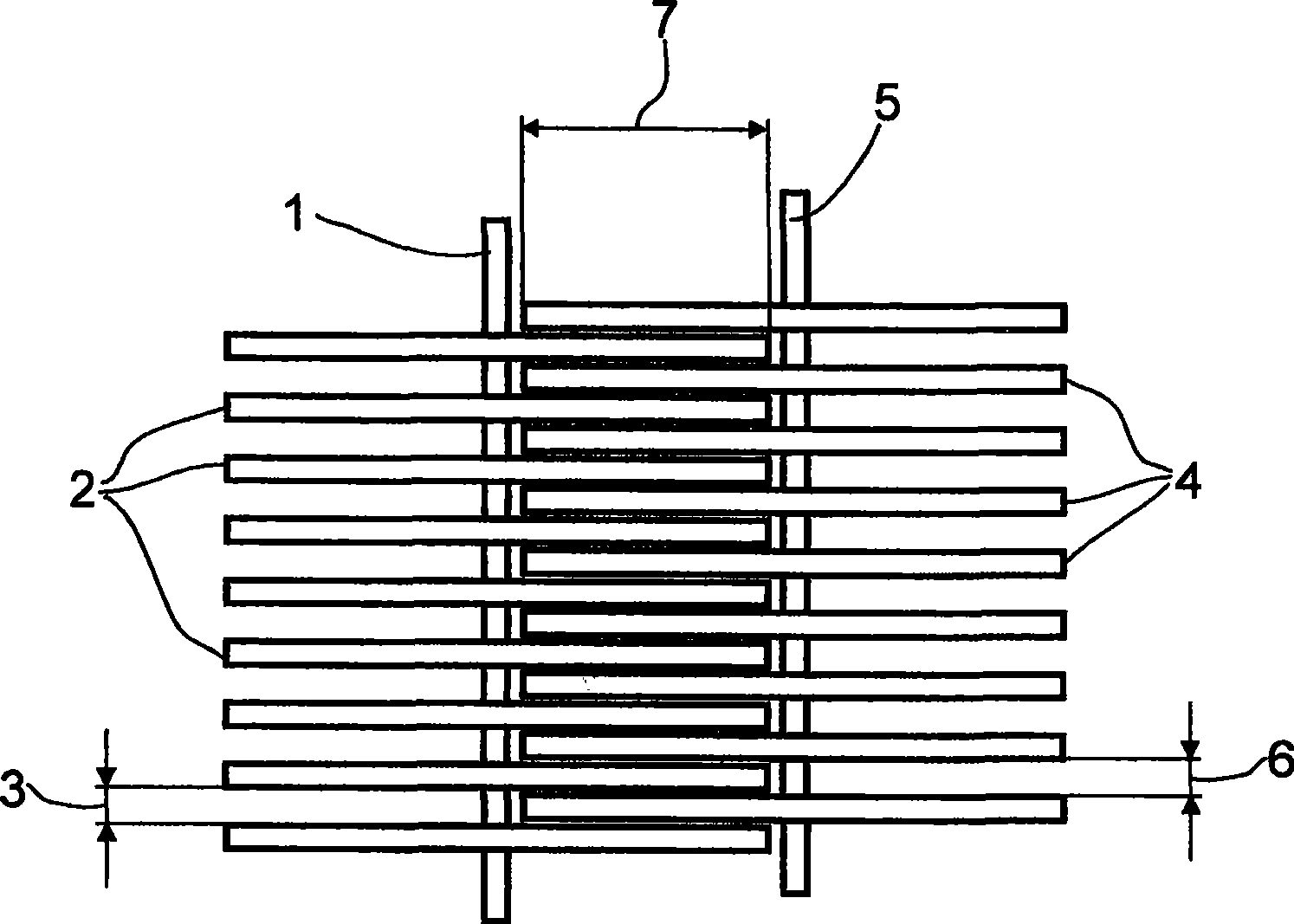
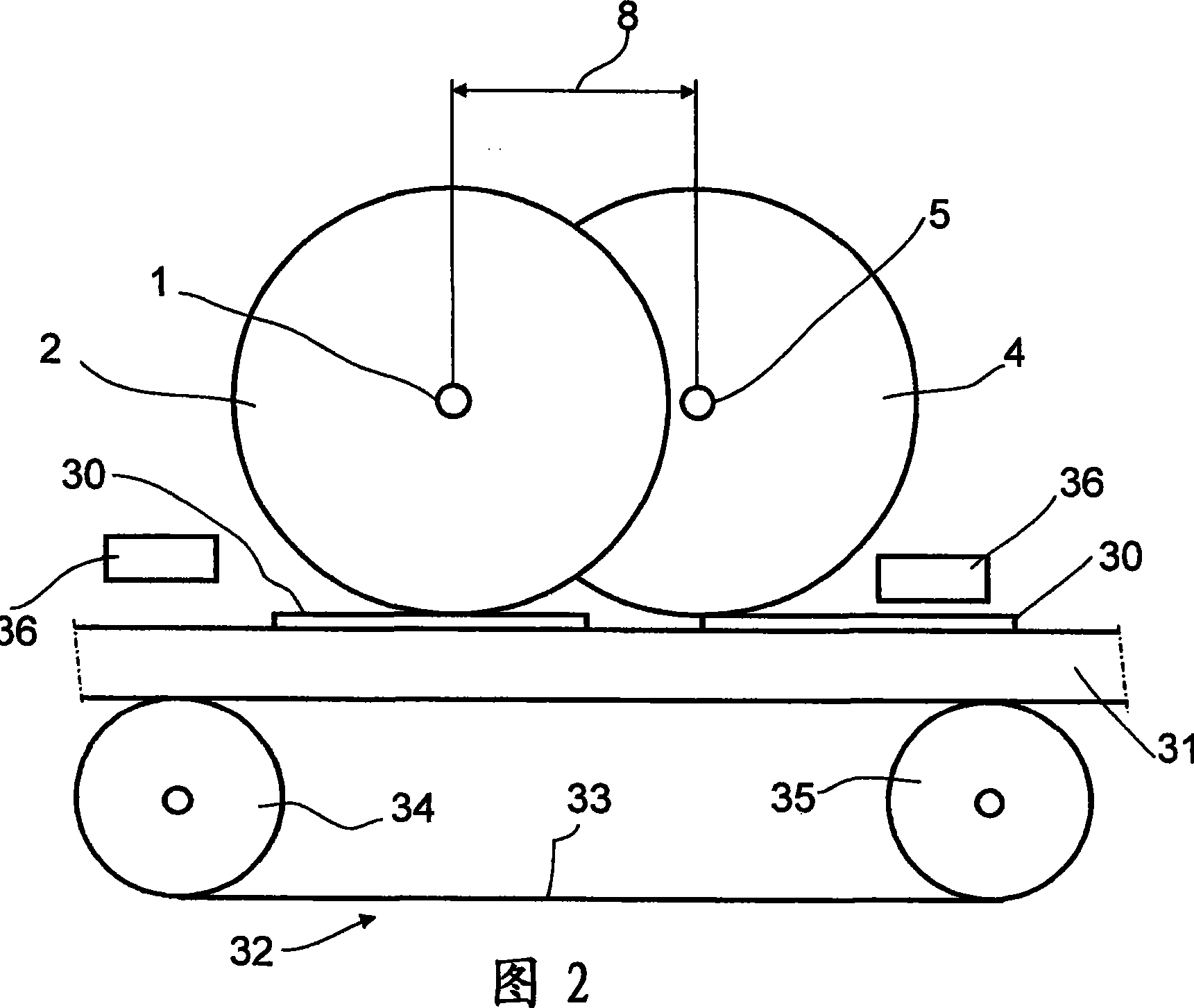
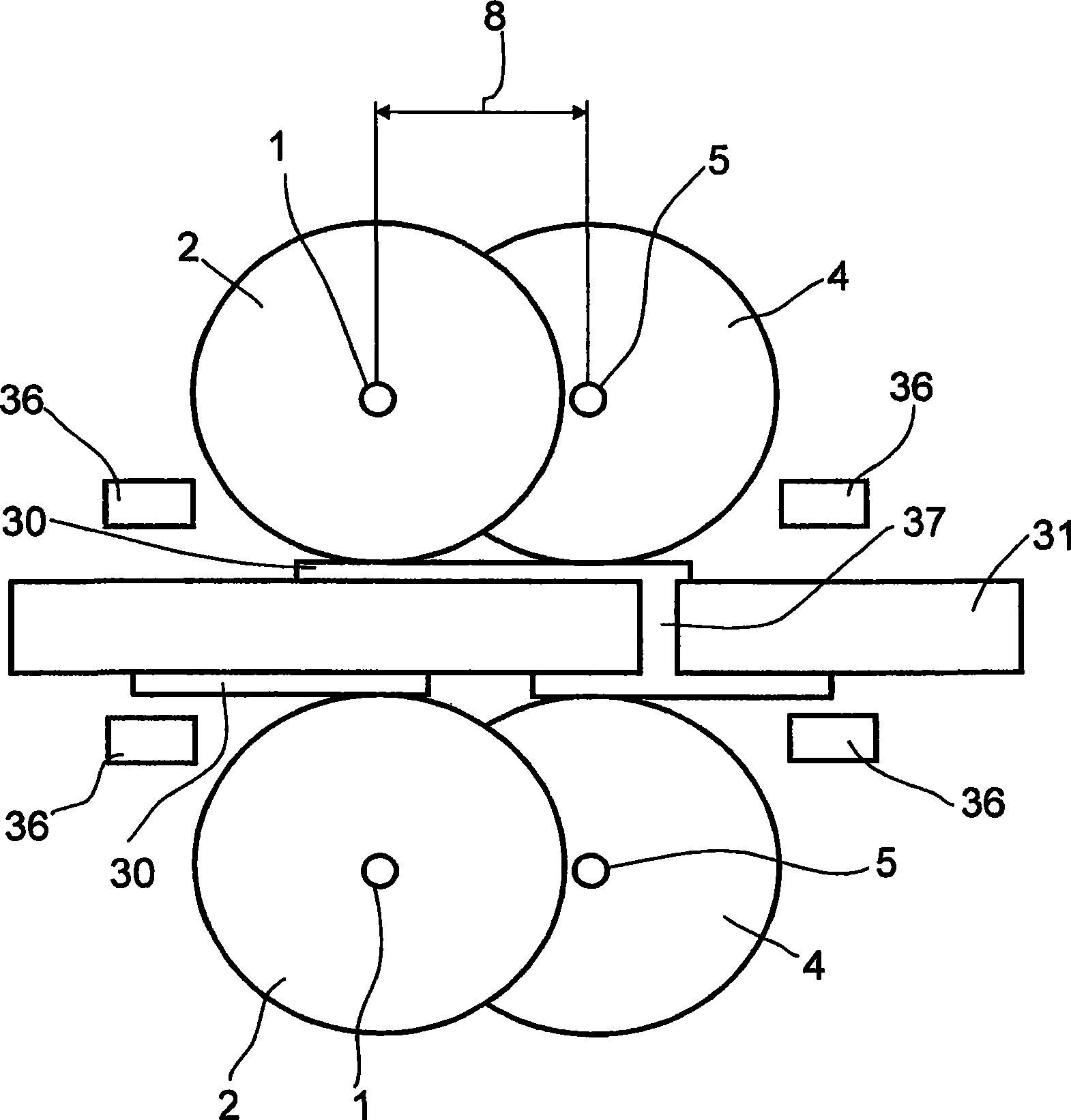
The invention relates to a device for electroplating at least one electrically conductive substrate or a structured or electrically conductive surface covering the whole area of a non-conductive substrate. Said device comprises at least one bath, an anode and a cathode. The bath contains an electrolyte solution, which comprises at least one metal salt and from which metal ions are deposited on electrically conductive surfaces of the substrate to form a metal layer, as the cathode is brought into contact with the surface of the substrate to be coated and said substrate is conveyed through the bath. The cathode comprises at least two discs (2, 4, 10) that are rotatably mounted on a respective shaft (1, 5, 14), said discs (2, 4, 10) intermeshing. The invention also relates to a method for electroplating at least one substrate, said method being carried out in a device according to the invention. The invention further relates to the use of said device for electroplating electrically conductive structures situated on an electrically non-conductive support.
Owner:BASF AG
Arc-coating process with rotating cathodes
InactiveUS6926811B2Modification can be limitedUniform layer thicknessElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingDeposition processVacuum chamber
A method is provided for coating objects in a vacuum chamber in which a physical vapor deposition (PVD) can be carried out. The chamber has at least one anode means, at least one cathode and at least one magnetic field source. An arc can be ignited between the at least one anode means and the at least one cathode, and the cathode separates material. The at least one magnetic field can be turned relative to the at least one cathode and the objects to be coated are arranged in the chamber. The magnetic field is turned before the beginning of the coating process so that the separated material does not coat the objects to be coated in the coating process. The arc for the physical deposition process is produced by means of at least two cathodes, said cathodes are constructed as substantially cylindrical tubular cathodes and the at least one magnetic field source is constructed as a permanent or coil magnet arranged in the tubular cathodes and the tubular-cathodes turn about their cylinder axis during the coating process.
Owner:PLATIT
Ultra-fast boriding of metal surfaces for improved properties
ActiveUS20130056363A1Fast boridingDesirable mechanical propertySolid state diffusion coatingBoridingUltra fast
A method of ultra-fast boriding of a metal surface. The method includes the step of providing a metal component, providing a molten electrolyte having boron components therein, providing an electrochemical boriding system including an induction furnace, operating the induction furnace to establish a high temperature for the molten electrolyte, and boriding the metal surface to achieve a boride layer on the metal surface.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Electrostatic screen for an hvdct component
ActiveCN102007552AEasy to transformEasy to fixShielding materialsFixed inductances without magnetic coreAir coreEngineering
An electrostatic screen (17) for an HVDCT component (1), the connections (11, 12) of which are at a higher potential than earth (15) during operation, in particular for an HVDCT air-cored induction coil, is distinguished by a casing (18) which is provided at at least one end with a collector electrode (19, 20) which runs essentially over its circumference, for connection to one of the connections (11, 12) of the HVDCT component (1), wherein the casing (18) is manufactured from a sheet (22) of electrostatically dissipative material having a surface resistance in the range from 109 to 1014 ohm / units square.
Owner:西门子能源全球两合公司
Electroplating device and method
InactiveCN101473072AIncrease contact areaLong contact time per unit areaContacting devicesConductive pattern reinforcementElectrolysisMetal salts
The invention relates to a device for electroplating at least one electrically conductive substrate (8), or an electrically conductive structure situated on a non-conductive substrate (8). Said device comprises at least one bath, an anode and a cathode (2). The bath contains an electrolyte solution, which comprises at least one metal salt and from which metal ions are deposited on electrically conductive surfaces of the substrate, as the cathode is brought into contact with the surface of the substrate to be coated and said substrate is conveyed through the bath. The cathode comprises at least one strip (2) with at least one electrically conductive segment (12) and is guided around at least two rotating shafts (3). The invention also relates to a method for electroplating at least one substrate that is carried out in a device according to the invention. According to said method, to produce the coating, the strip lies on the substrate and circulates at a speed corresponding to the speed at which the substrate is conveyed through the bath. The invention further relates to the use of said device for electroplating electrically conductive structures situated on an electrically non-conductive support.
Owner:BASF AG
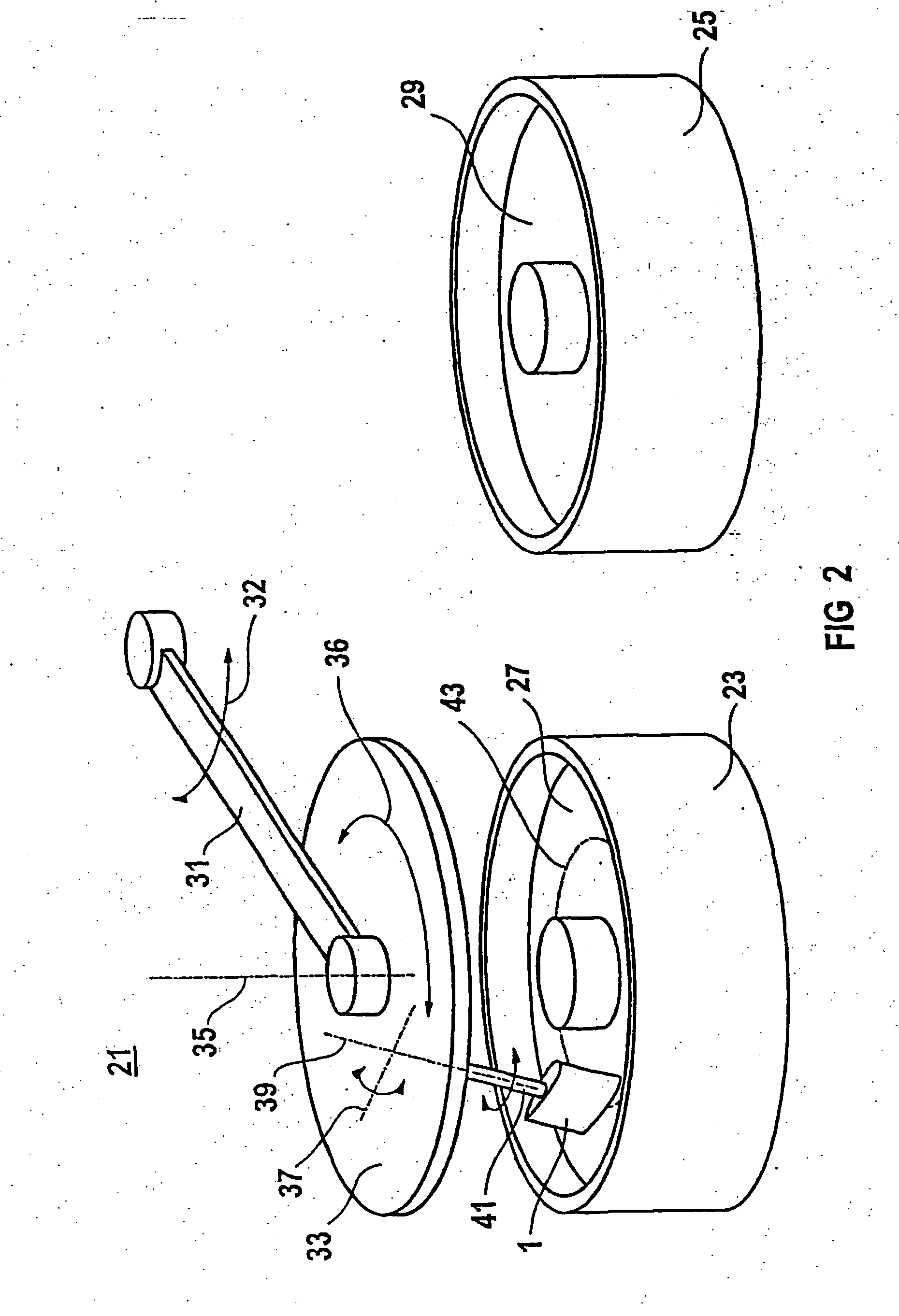
Methods of and apparatus for pre-planarizing a substrate
ActiveUS7090562B1Uniform layer thicknessEdge grinding machinesSupport wheelsRotation velocityEngineering
Methods and apparatus are provided to provide a substantially uniform layer thickness above a wafer contour as the wafer rotates and is traversed past a pre-planarization tool. The tool has a shank defining an axis of rotation, and a planarization member coupled to the shank has a hook-shaped section supporting a pre-planarization surface spaced by an at-rest-distance from the axis of during an at-rest condition of the shank. The hook-shaped section has a modulus of elasticity selected so that upon rotation, the hook-shaped section flexes and moves the pre-planarization surface to rotation-distances spaced from the axis in response to a velocity of rotation of the hook-shaped section around the axis in a range of velocities. As the tool rotates, metrology intermittently directly senses the layer thickness and controls the velocity of rotation so the rotation-distances have values in excess of a value of the at-rest-distance.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
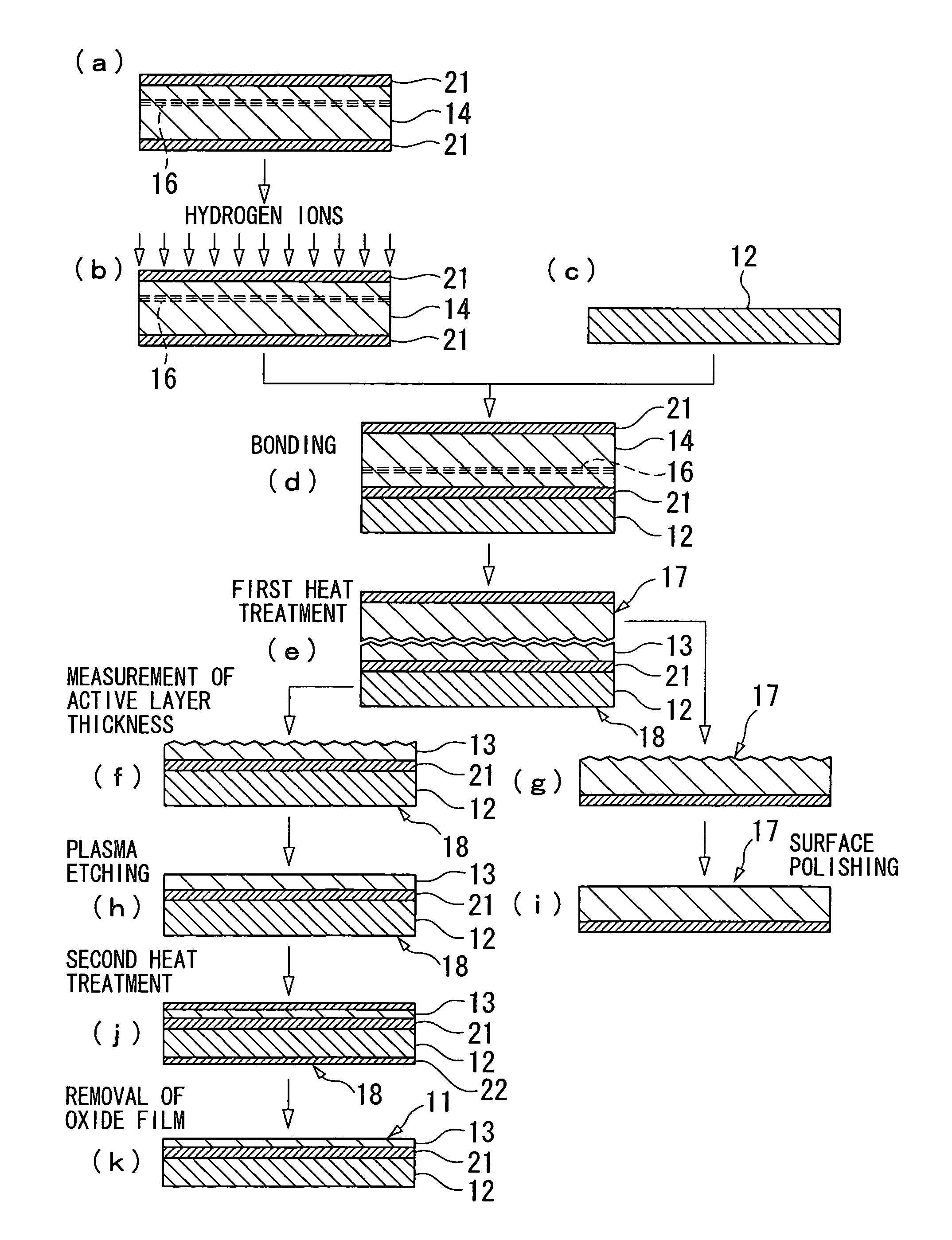
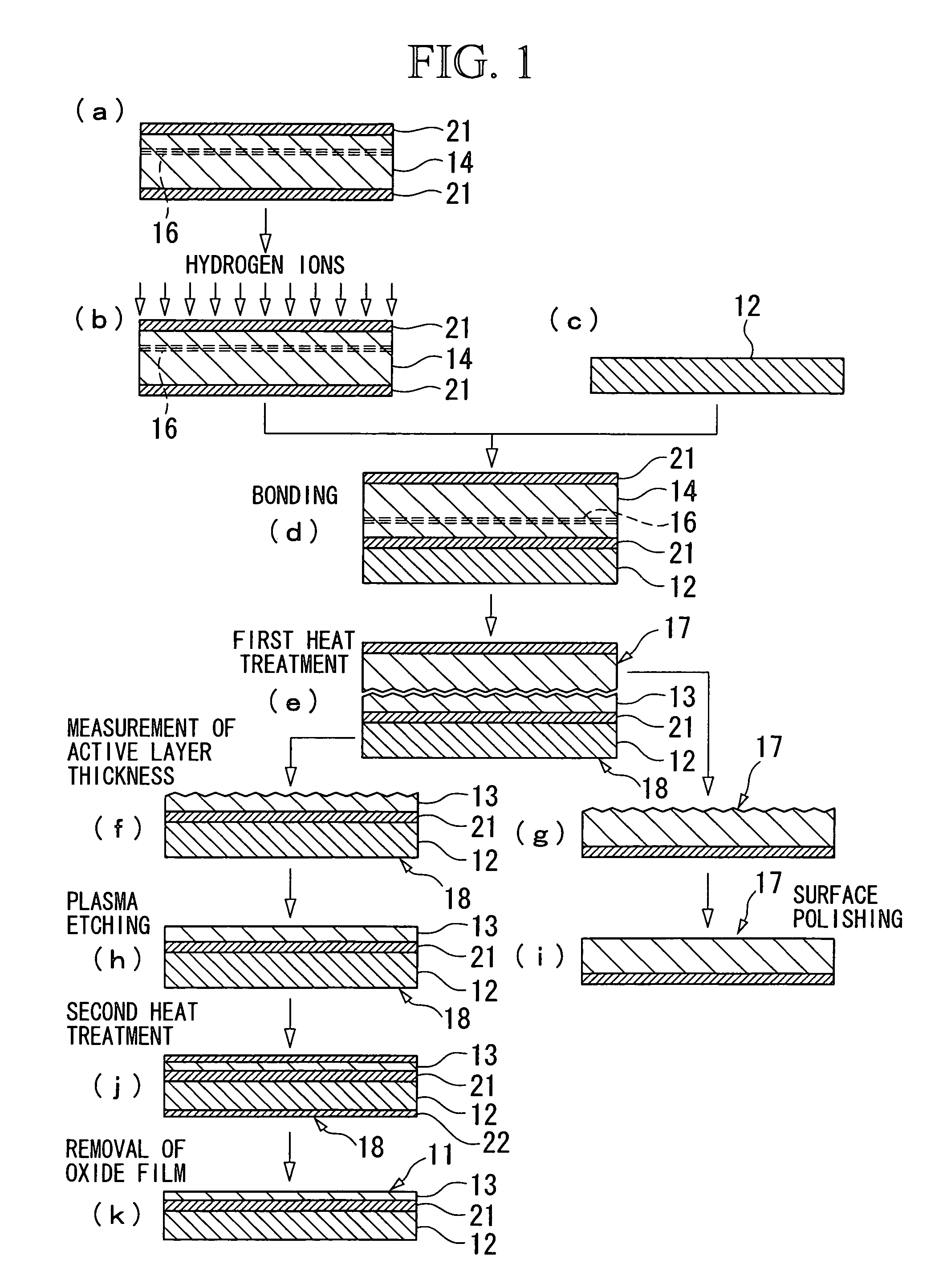
Silicon-on insulator substrate and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7736998B2Reduce variationUniform layer thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLayered productsSoi substrateSingle crystal
This SOI substrate includes a base substrate which includes a single-crystal semiconductor and an active layer which includes a single-crystal semiconductor and is bonded to the base substrate with an oxide film therebetween. The oxide film is formed only in the active layer. The active layer is formed with a thickness of 10 to 200 nm and a thickness variation throughout the active layer of 1.5 nm or less by etching a surface of the active layer while selectively using only the reactive radicals generated by a plasma etching process.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Method for producing a steel component provided with a metallic coating providing protection against corrosion
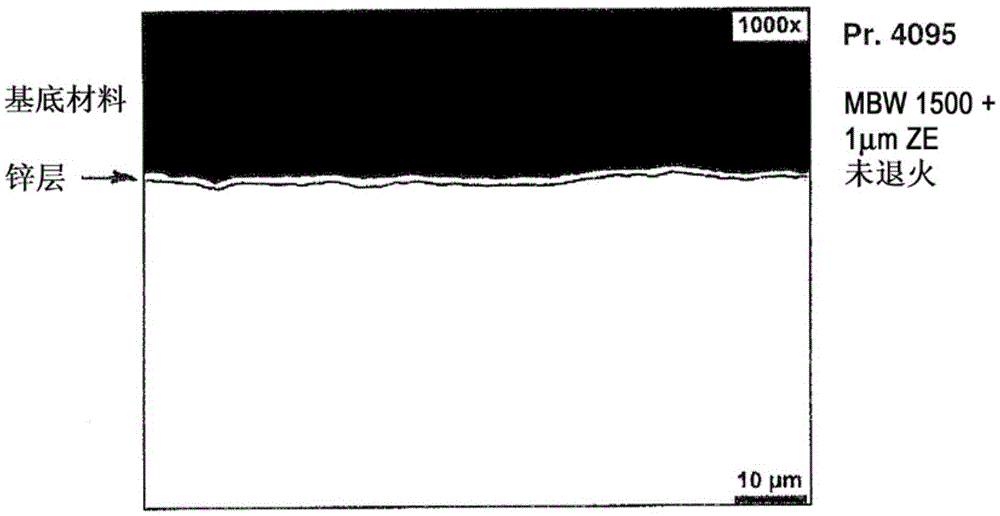
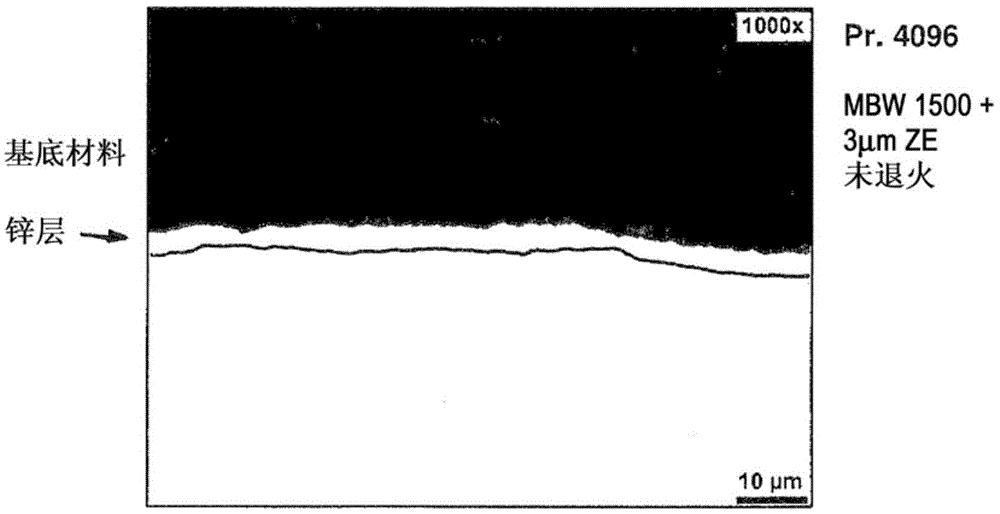
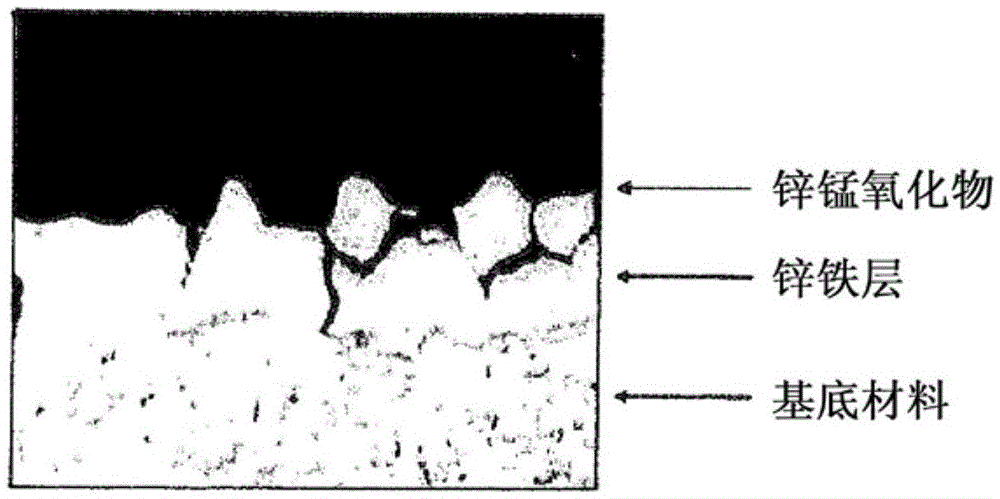
InactiveCN105531404AReduce absorptionDifferent intensityFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencyElectrolysisLayer thickness
The invention provides a method by which a steel component provided with a metallic coating which has good adhesion and provides protection from corrosion can be produced. The problem addressed by the invention is especially that of specifying a corresponding hot forming process which enables a wide range of processing variants. The emphasis here is not on long-lasting corrosion protection but more on high flexibility of the processing properties. For this purpose, a thin zinc layer having a mean layer thickness of less than 5 mum, preferably in the range of 1-4 mum, more preferably in the range of 2-4 mum, is applied by electrolytic means to a flat steel product consisting of a steel material which can be annealed by quenching in a hot forming process and has a yield point of 150-1100 MPa and a tensile strength of 300-1200 MPa. A billet is then obtained from the flat steel product and is heated directly to at least 800 DEG C and then formed to give the steel component, or is first formed to give the steel component which is then heated to at least 800 DEG C. The steel component obtained in each case is subsequently annealed by cooling it with sufficient speed from a sufficiently high temperature.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Method for smoothing the surface of a gas turbine blade
InactiveUS7014533B2Efficient and cost-effectiveFlat surfaceEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesGas turbinesFuel gas
A surface of the gas turbine blade is smoothed by way of a drag finish process. A first ring-shaped container is filled with a liquid abrasive medium. A second container which is arranged next to the first container is filled with a second liquid abrasive medium. A pivoting arm is arranged between and above the containers and can be pivoted along a pivoting direction. A drag device is arranged on the pivoting arm. The drag device leads a gas turbine blade on a carrier arm through the abrasive medium.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
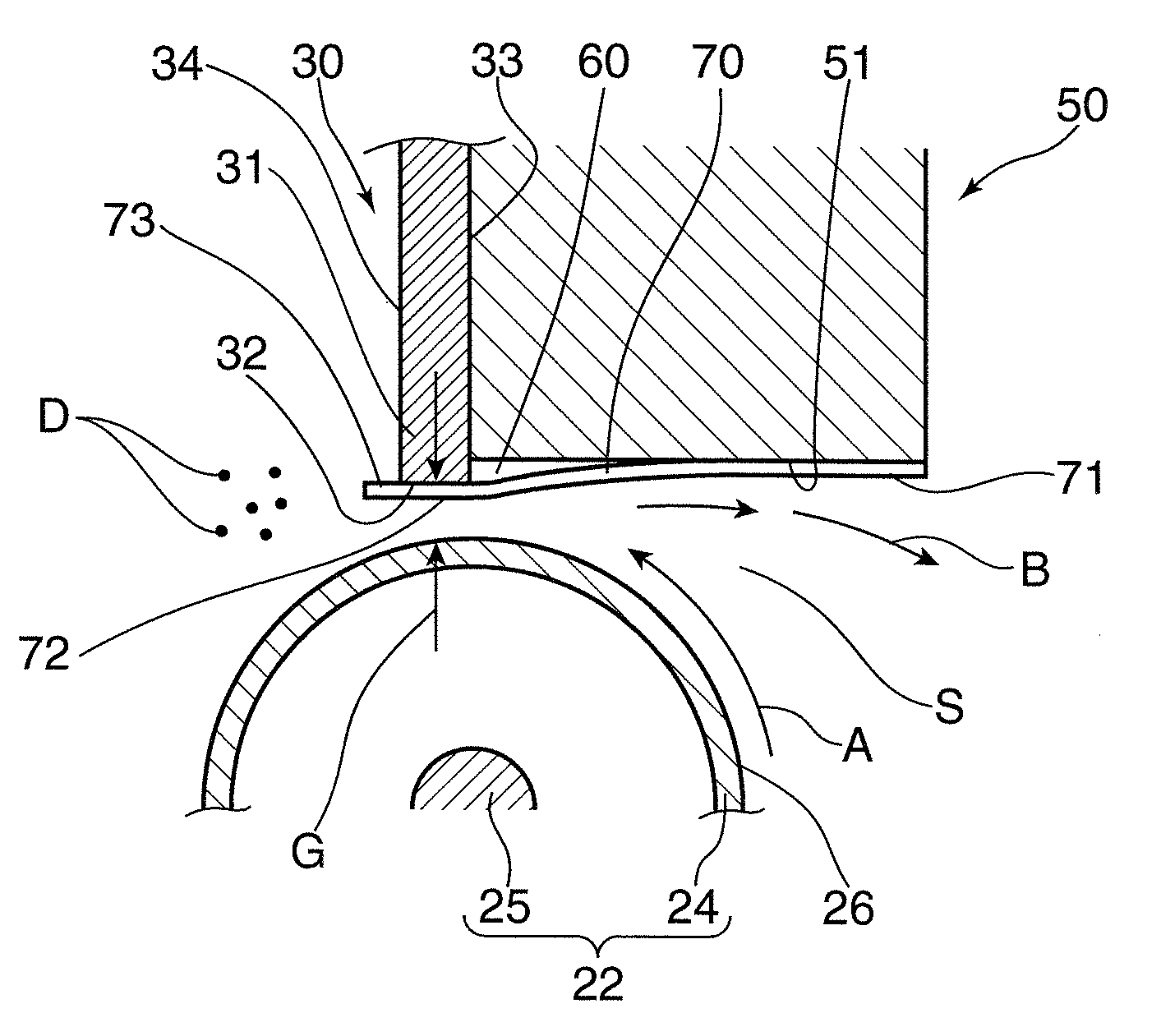
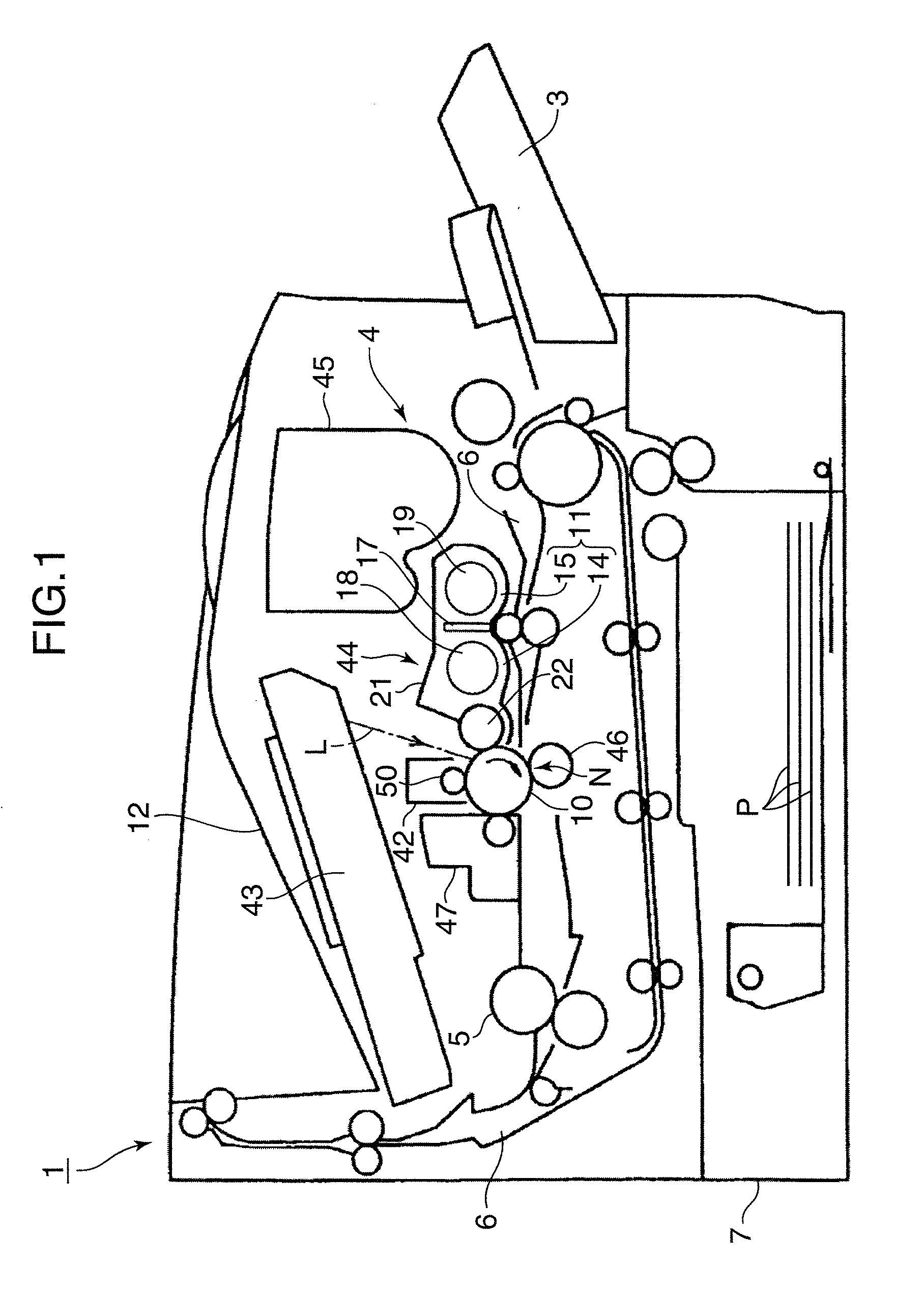
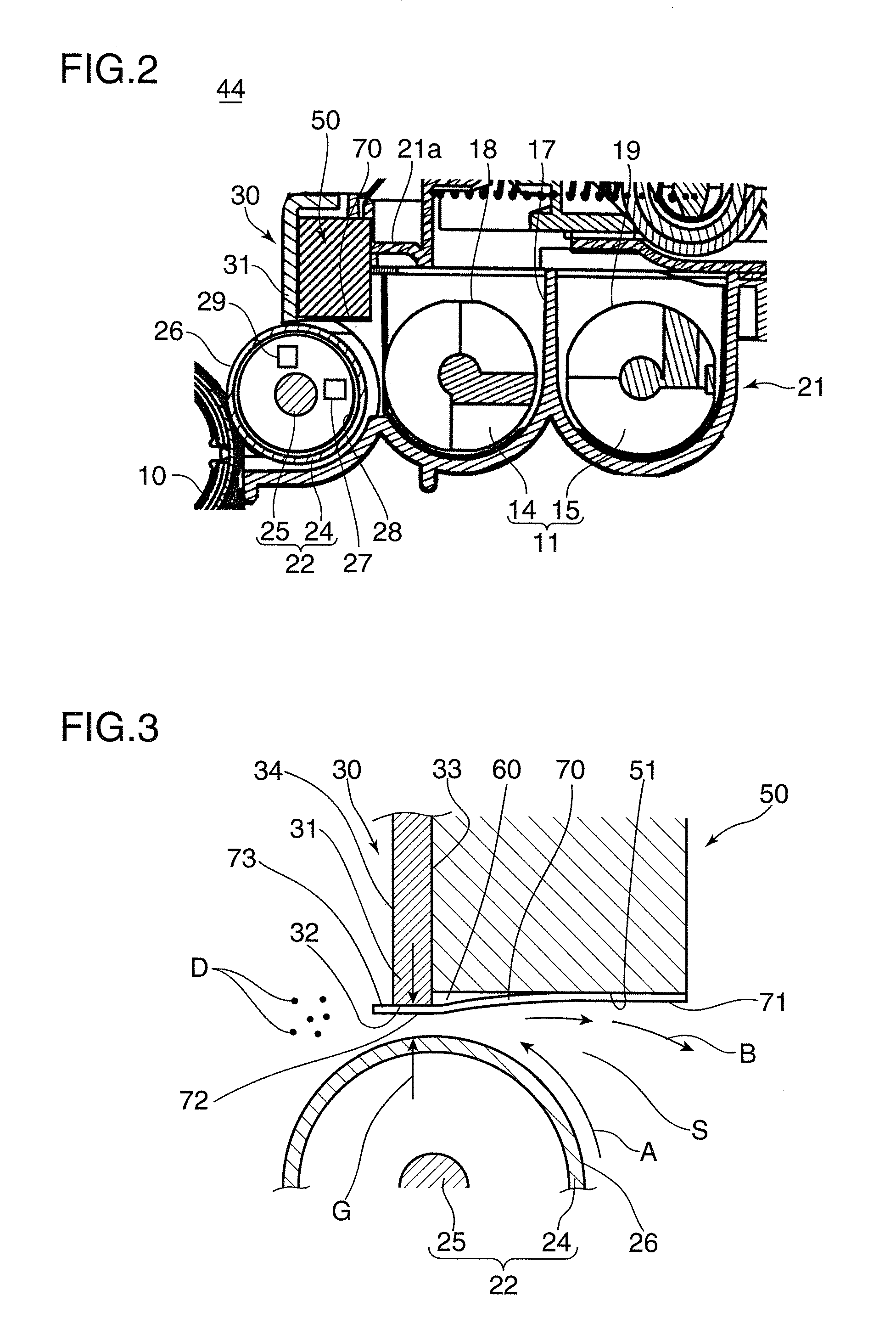
Developing device and image forming apparatus provided with same
InactiveUS20110064484A1Favorable toner imageUniform layer thicknessElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
A developing device includes a developer storing portion, a developer carrying body, a first regulating member having a first regulating surface regulating a layer thickness of the developer on the developer carrying body, a second regulating member having a second regulating surface that is set so as to gradually become apart from the developer carrying body toward the upstream side with respect to the rotation direction of the developer carrying body to regulate an amount of the developer conveyed to the first regulating surface, the second regulating surface being arranged with a step formed between the second regulating surface and the first regulating surface, and a sheet member so attached to the second regulating surface as to cover at least a portion of the step between the first regulating surface and the second regulating surface.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
Modified planar cell (MPC) and electrochemical device battery (stack) based on MPC, manufacturing method for planar cell and battery, and planar cell embodiments
InactiveUS20150004522A1Even air distributionEnhances reagent feed 's uniformityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureForming gasEngineering
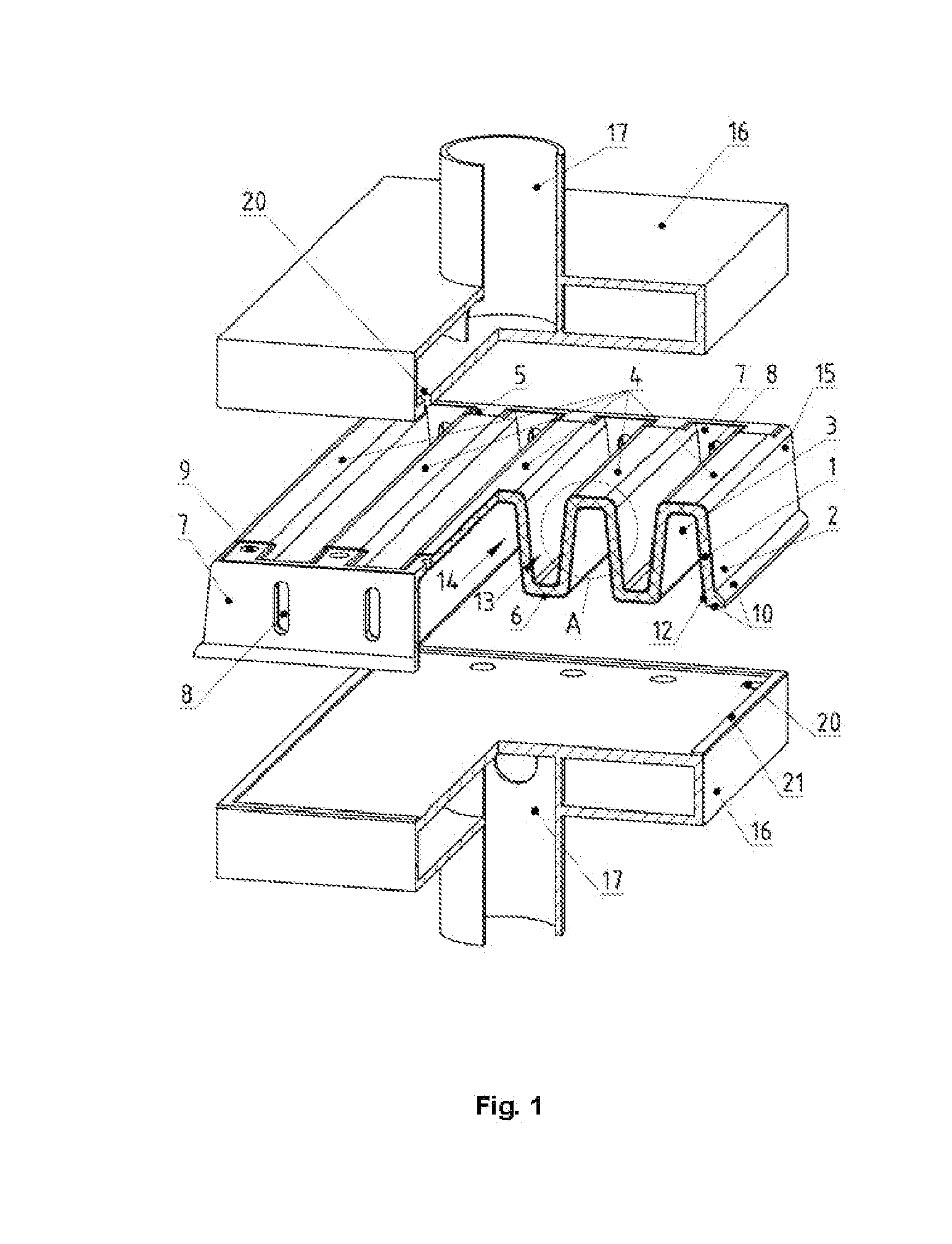
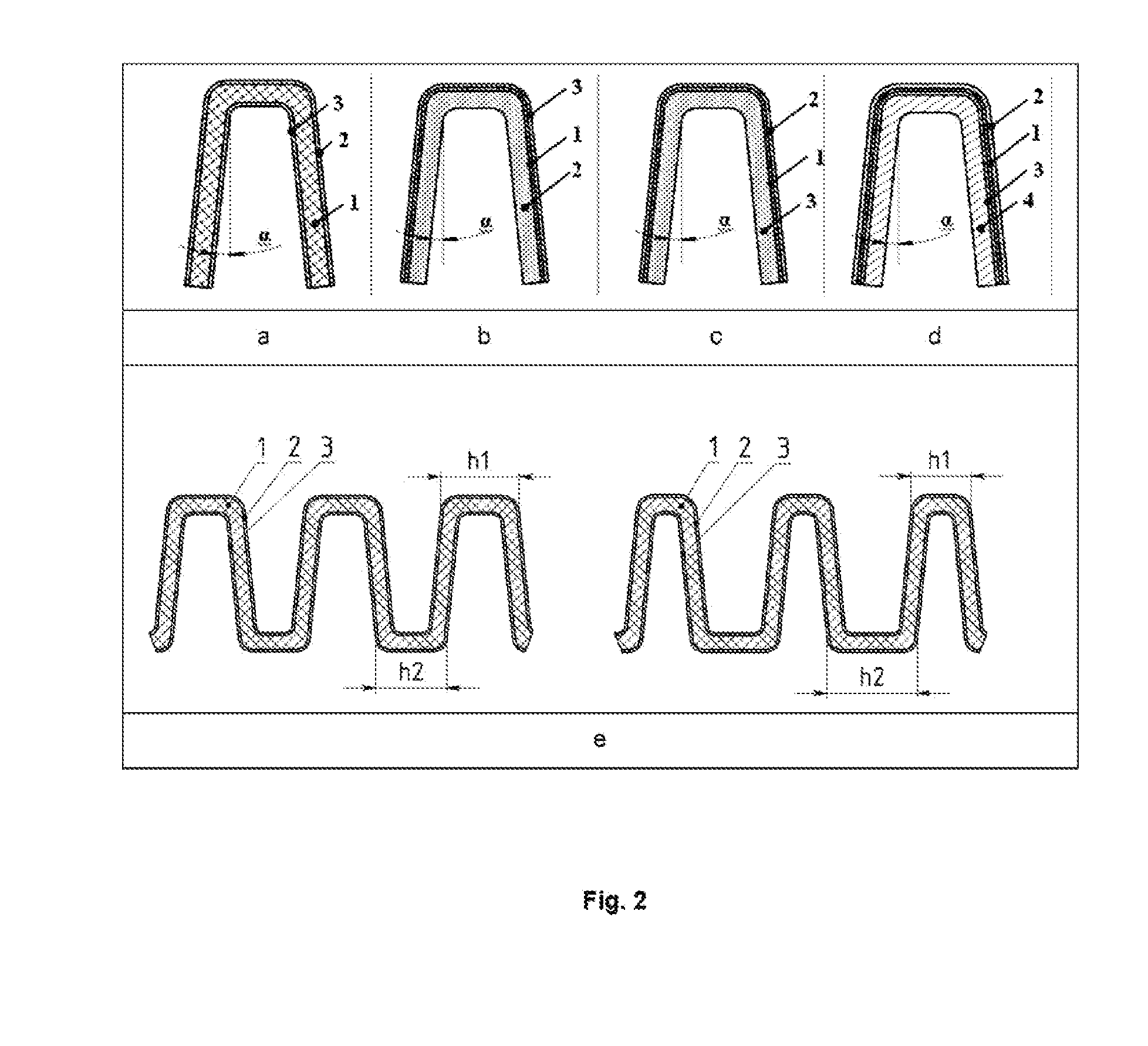
The invention relates to a modified planar cell with a solid-oxide solid electrolyte, a gas-diffuse anode, a cathode, a metal or oxide current path and a current-gas supply. The supporting solid electrolyte of the cell is in the form of a corrugated plate consisting of corrugations. In cross-section, the corrugations of the plate constitute an isosceles, identical-height trapezium, without a larger lower base with holes. The holes are formed on one side in the upper part of each corrugation, for supplying one of the reagents, e.g. fuel in case of a fuel cell. The corrugations are connected to one another at their base in order to form gas space channels of the cell. The gas space channels are in the form of inverted isosceles trapezia without a larger upper base and the angle α at their smaller base is 0.1 to 89.9°. The corrugated plate is connected to two opposing walls, a front wall and a rear wall. The latter is arranged perpendicular to the corrugations of the plate and thus of equal height, and is furnished with holes. The holes in one wall are used for introducing a second reagent, e.g. air in the case of a fuel cell, into each channel of the electrode environment in the form of inverted isosceles trapezia without the larger upper base and the holes of the other opposing wall for discharging the hypoxic mixture. On one side of the gas space channels constituting, in cross-section, an isosceles trapezium without larger lower base, the corrugated plate of the supporting solid electrode is coated with an electrode, e.g. a nickel-cermet anode in the case of a fuel cell. On the side of the gas space channels of the electrode environment, which are shaped in the form of inverted isosceles trapezia without the larger upper base, the plate is coated with a second, counter-electrode, e.g. a cathode based on strontium-lanthanum-manganite. The metallic box-like gas supply duct ensures the supply of reagents and the discharge of reaction products with a series of holes. The width and the length of the gas supply duct coincide with those of the cell. These holes correspond to the holes in the upper parts of the corrugations of the cell that constitute, in cross-section, an isosceles trapezium without a larger lower base and are connected in a gas-tight manner to the periphery of the holes. A gas-tight space is formed in the planar cell for the reagent introduced via a tube, for the uniform distribution thereof via the gas space channels and for the exit of the exhaust gases through a similar discharge gas manifold. The discharge gas manifold is rotated by 180° relative to the vertical axis and is connected in a gas-tight manner to the ceramic part at the periphery. The flat surfaces of the gas manifolds furnished with holes are connected to the electrodes. They are simultaneously used as current collectors and the tubes are used as current terminals of the planar cell.
Owner:LIPILIN ALEKSANDR S +1
Organic electroluminescent element manufacturing method
ActiveUS20090253223A1Easy to manufactureLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic electroluminescenceEngineering
An ink containing an electroluminescent light emitting material is discharged onto a buffer layer. The discharge amount of the ink is larger than a maximum volume where the ink is retained by the surface tension thereof on the top surface of the buffer layer.
Owner:SHARP KK
Apparatus for smoothing the surface of a gas turbine blade
InactiveUS20060194526A1Efficient and cost-effectiveFlat surfaceEdge grinding machinesMolten spray coatingEngineeringGas turbines
An abrasive device may include first ring-shaped container filled with a liquid abrasive medium. A second container may be arranged next to the first container and filled with a second liquid abrasive medium. A pivoting arm may be arranged between and above the containers and can be pivoted along a pivoting direction. A drag device may be arranged on the pivoting arm. The drag device may lead a gas turbine blade on a carrier arm through the abrasive medium.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Device and method used for spraying liquid
InactiveCN102114441AHigh coating efficiencyEfficient sprayingLiquid spraying apparatusEngineeringWhirlwind
The invention relates to a method used for pneumatically spraying liquid especially such as colourant, enamel paint, paint, and the like and generating spray that is applied to an object, wherein the method is characterized in that a spraying device (1) is utilized. In the method, liquid basically departs from the spraying device (1) under zero pressure. Spraying air in the spraying device is formed through rotation at a first angle (14) relative to a longitudinal axis (6) of the spraying device and at a second angle (21) relative to an axes (22) perpendicular to the longitudinal axis (6) of the spraying device, so that spraying air can depart from the spraying device in a whirlwind manner. The first angle (14) ranges from 25 to 40 degrees, and the second angle (21) ranges from 35 to 55 degrees. Liquid is sprayed by spraying air after departing from the spraying device.
Owner:EIC GRP GMBH (DE)
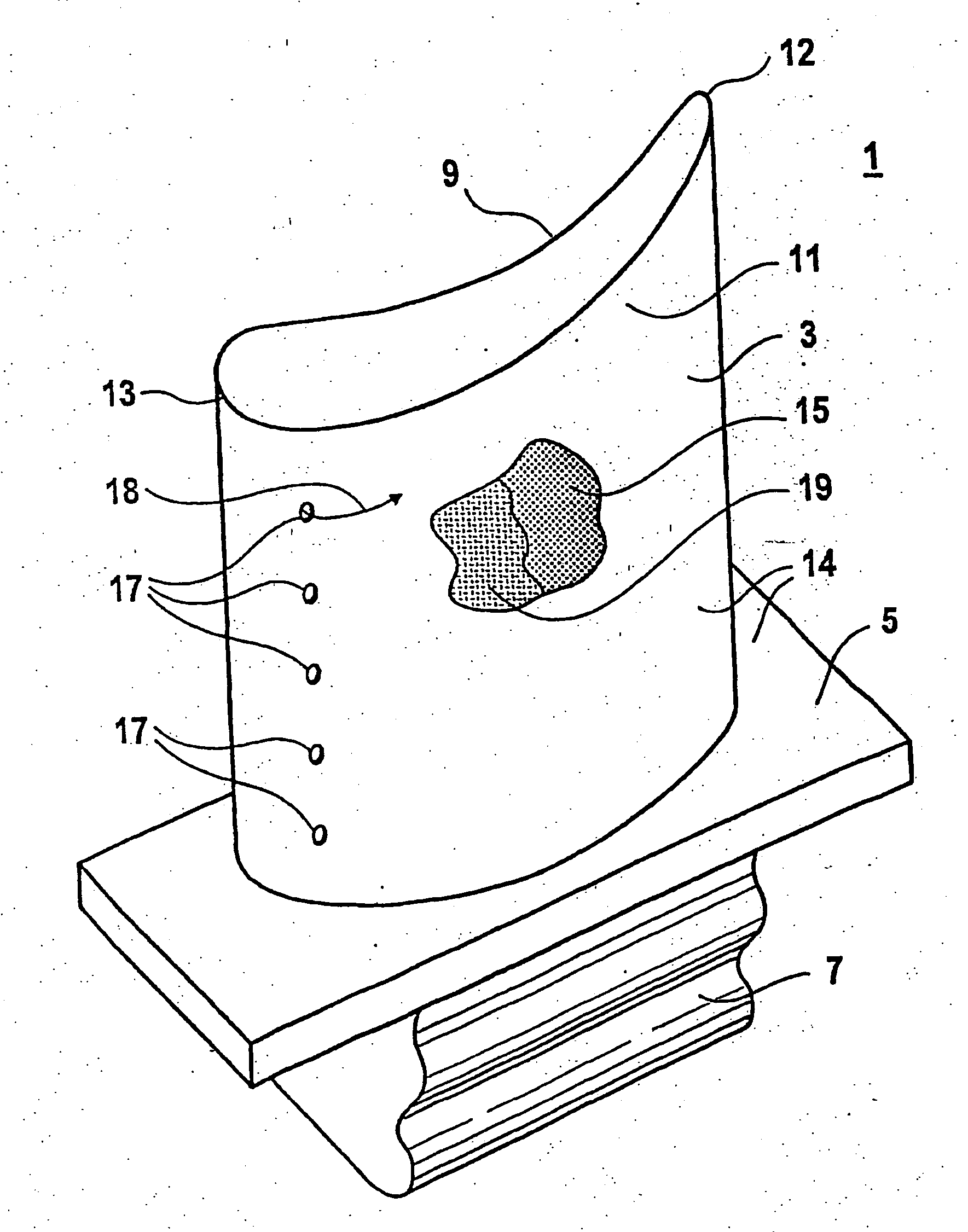
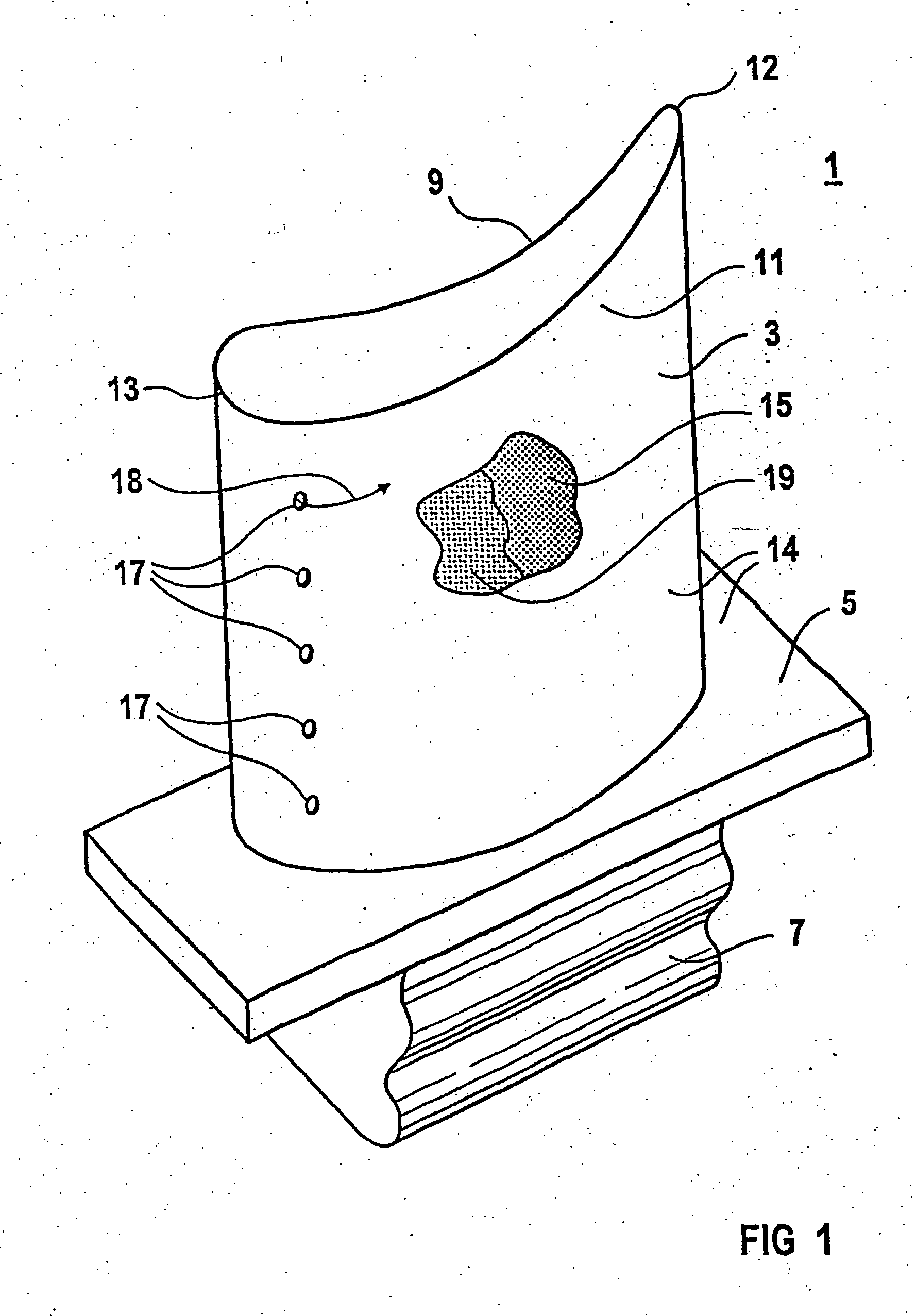
LCD-cell including one spacer exhibiting a dimension and a material property different from another spacers dimension and material property
InactiveUS6876423B2Improve structural strengthSmall thermal expansionNon-linear opticsColor effectLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display (LCD) cell is provided having transparent plates that are substantially parallel to each other and contain a liquid crystal display material. A plurality of spacers are interposed between the transparent plates to define a distance between the plates. At least one of the spacers exhibits dimensions and properties different than another of the spacers. The different dimensions and properties operate to control the distance at various temperatures to prevent non-uniform color effects and vacuum void formations.
Owner:AEG FUR MODERNE
Inversion type restricted ultraviolet light 3D (three-dimensional) printer
InactiveCN106626385AGuaranteed to be verticalGuaranteed parallelAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresControl systemUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses an inversion type restricted ultraviolet light 3D (three-dimensional) printer, which comprises a machine frame, wherein the machine frame comprises an upper base and a lower base; a plurality of support posts are arranged between the upper base and the lower base; an upright post is arranged at one side of the upper base; the upright post is vertical to the upper base; a curing work table is fixed at the side surface of the upright post through an ascending and descending mechanism; the ascending and descending mechanism is connected with a control system; a resin groove is formed in the upper base arranged under the curing work table; the curing work table is parallel to the resin groove; a laser system is arranged on the lower base arranged under the resin groove. The structure is reasonable; the stability and the accuracy of equipment are greatly improved; the printing performance is good; the printing formed layer thickness is uniform; the fault rate is low.
Owner:RES INST OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV & SUZHOU
Liquid applicator and method of use
An applicator for dispensing uniform thickness layers of liquid to surfaces and especially surgical sealants to surgical sites to create, in situ, a surgical incise drape is disclosed. The applicator employs a supported thin layer of foam which achieves layer thickness which are substantially independent of the pressure applied to the applicator during use. Methods of using the applicator are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS PLYMOUTH
Device and method for preparing an electrochemical sensor
InactiveUS7862698B2Easy to operateReliable preparationElectrolysis componentsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceEngineeringElectrolyte
A device and method for preparing an electrochemical sensor may enable the sensor head thereof to be provided with an electrolyte and a membrane. The device may include a retaining means for the sensor in addition to means for depositing the electrolyte and means for depositing the membrane.
Owner:SENTEC AG
Device for depositing a layer on a semiconductor wafer by means of vapour deposition
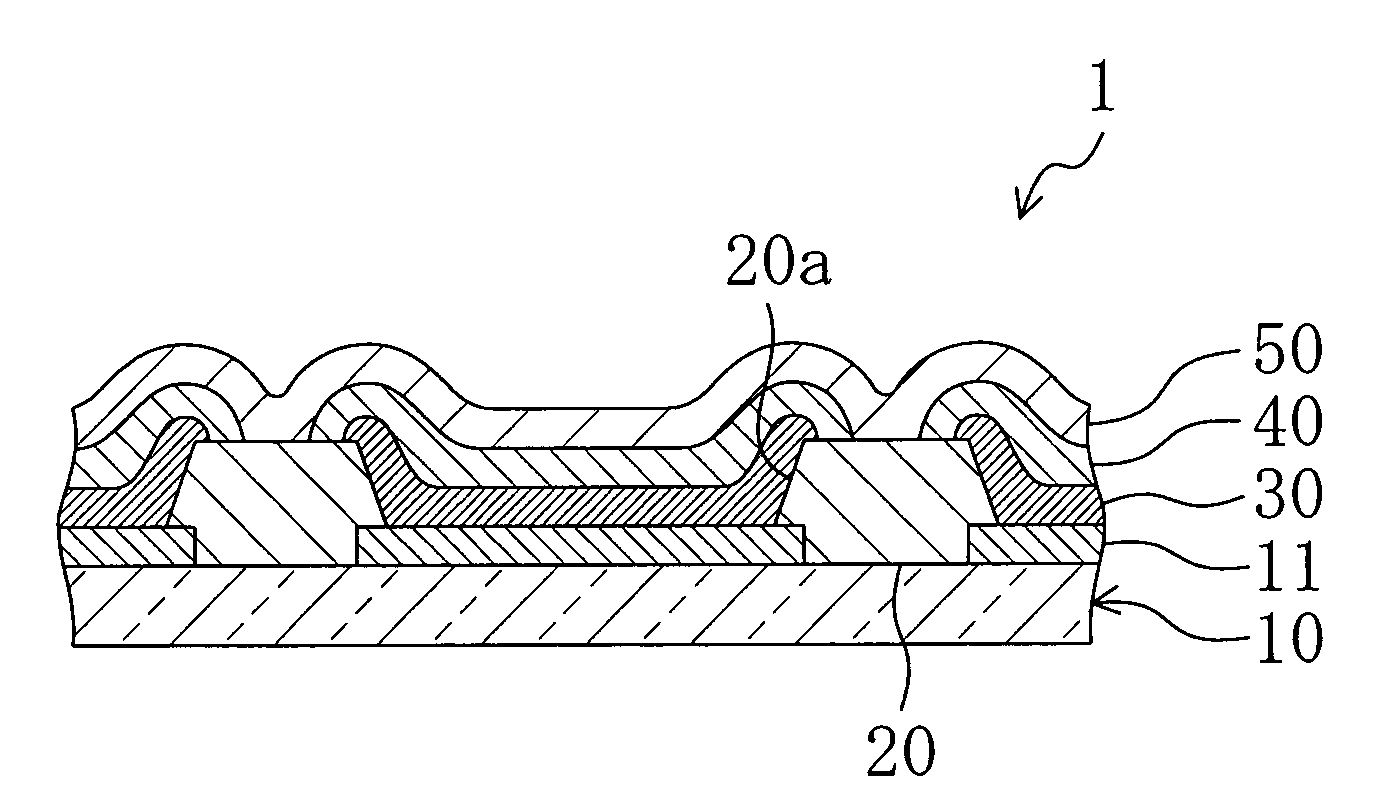
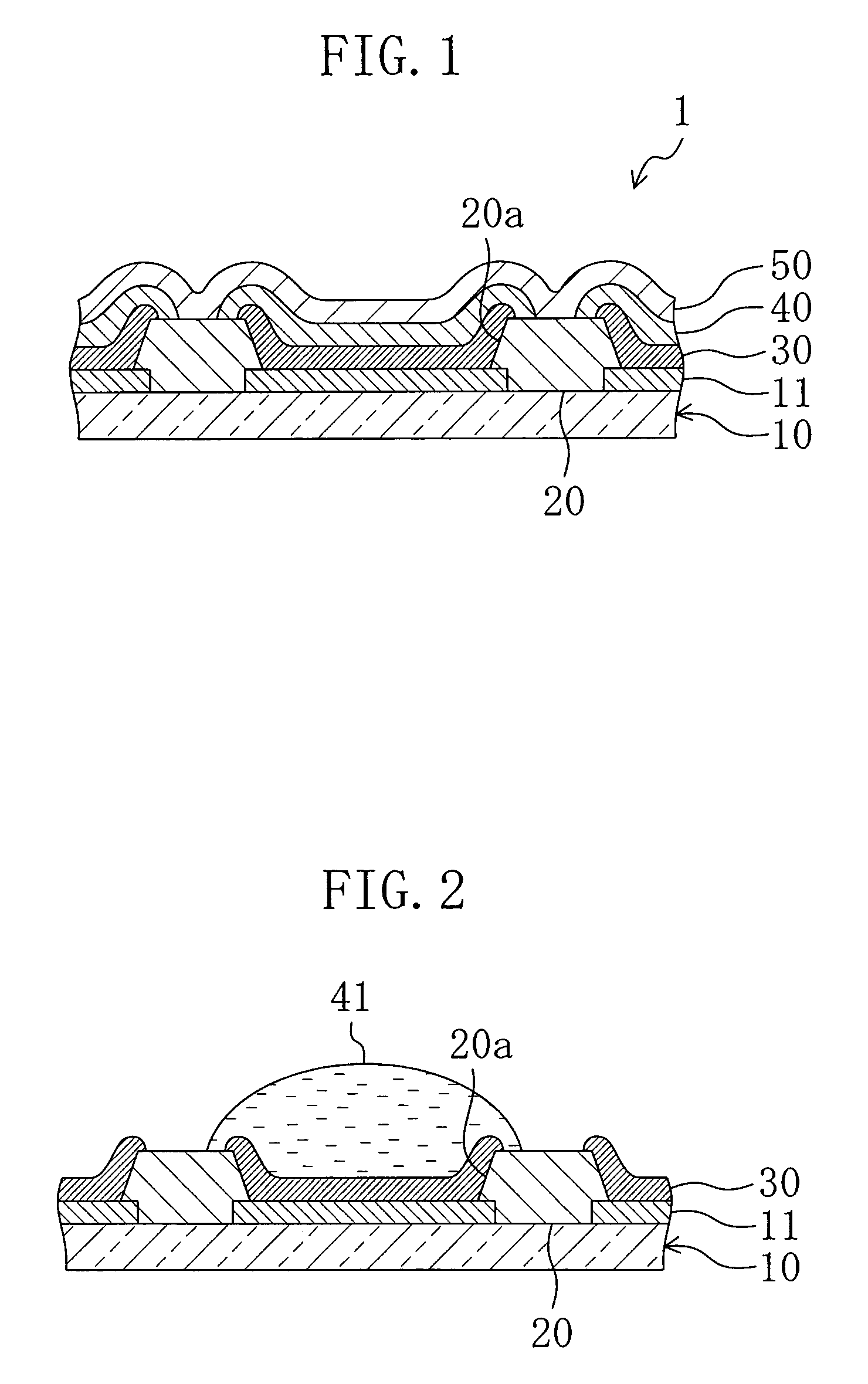
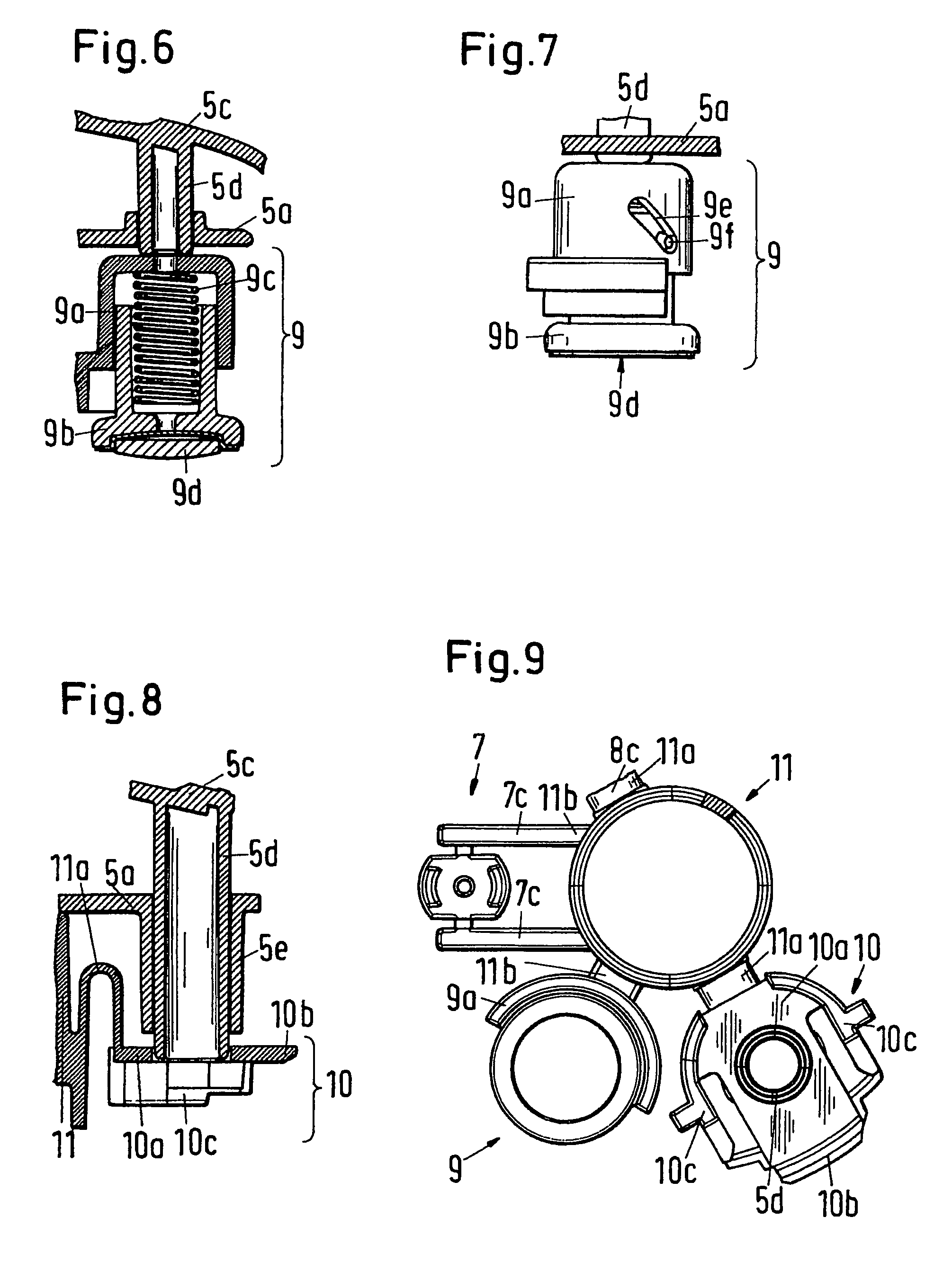
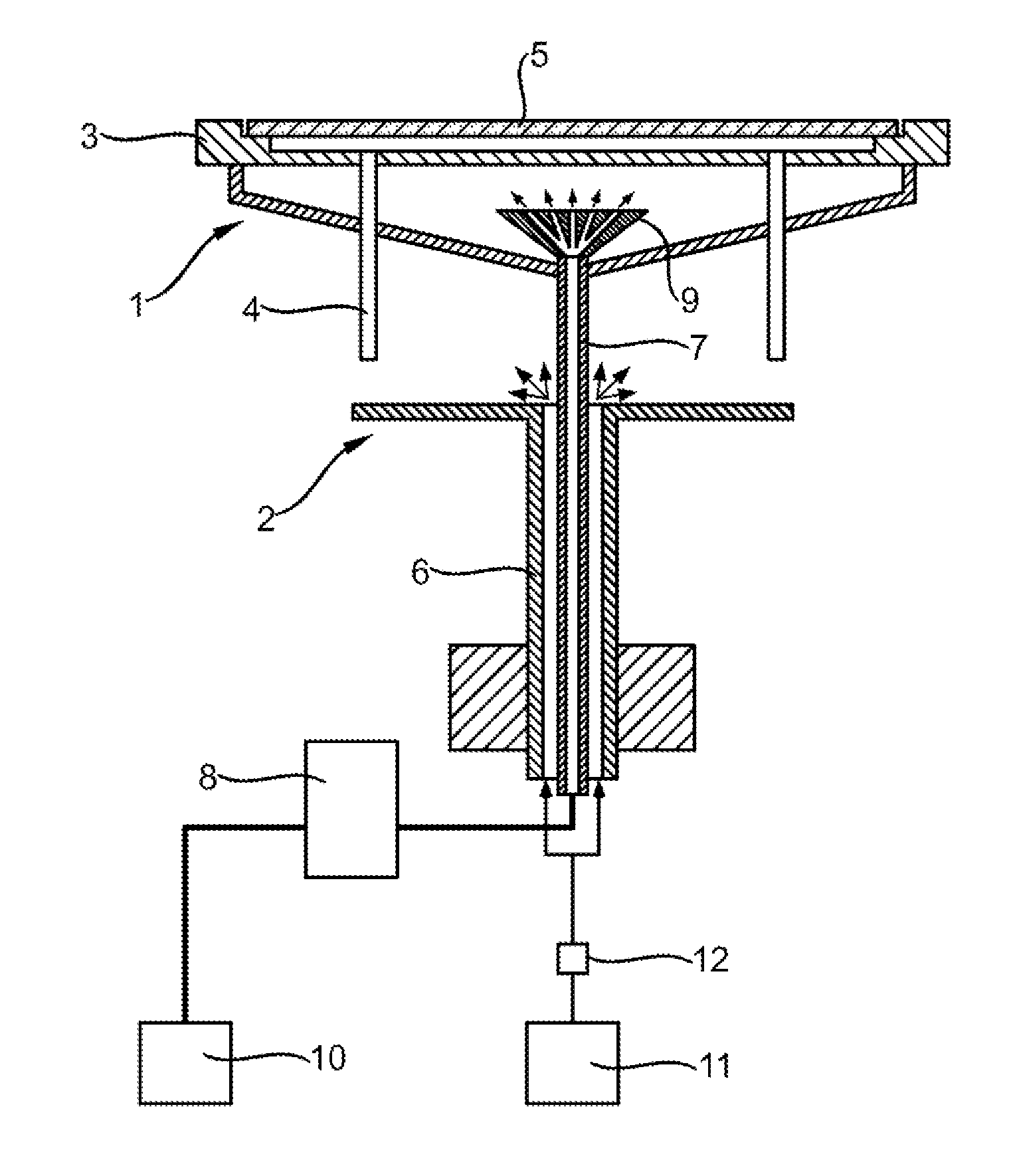
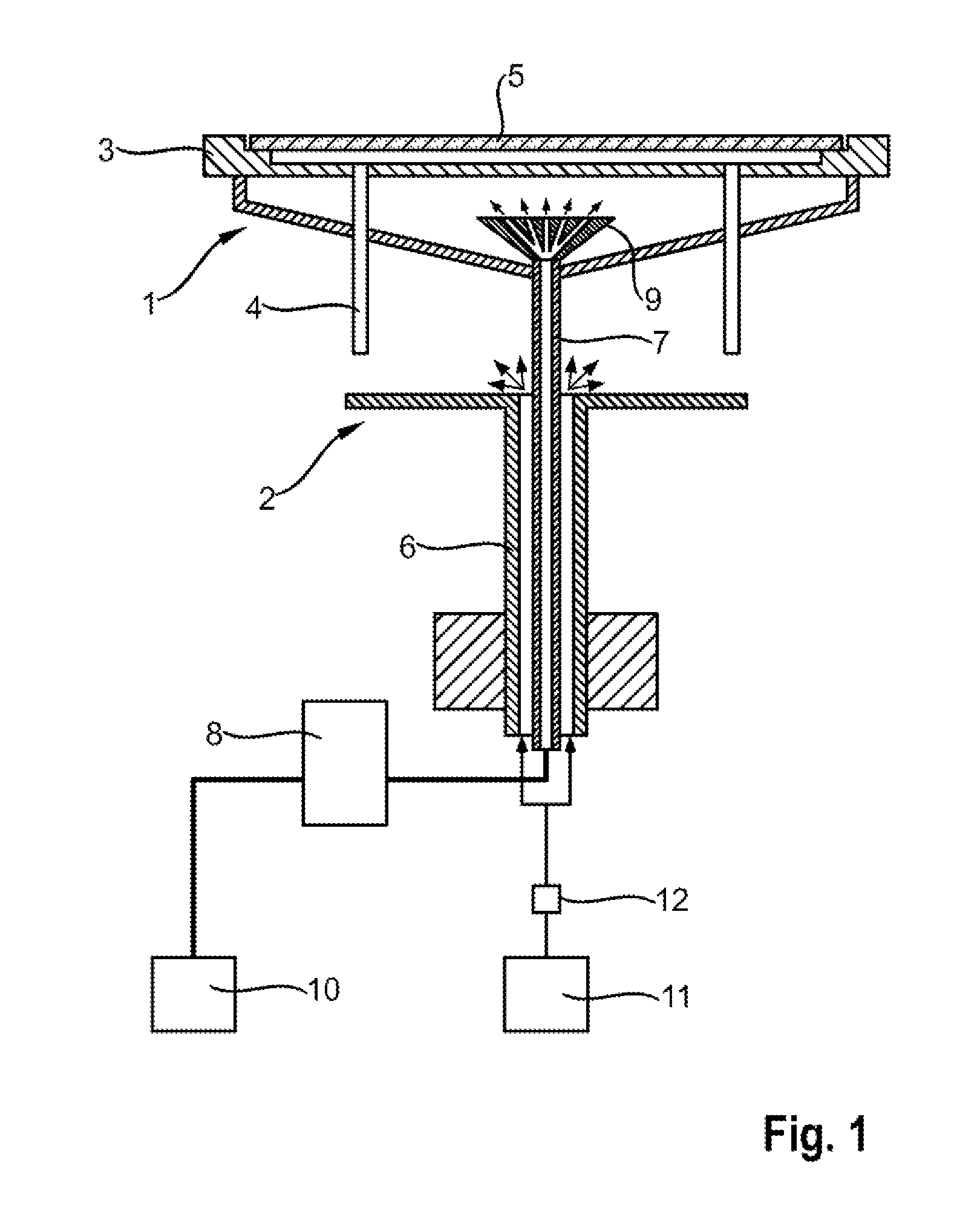
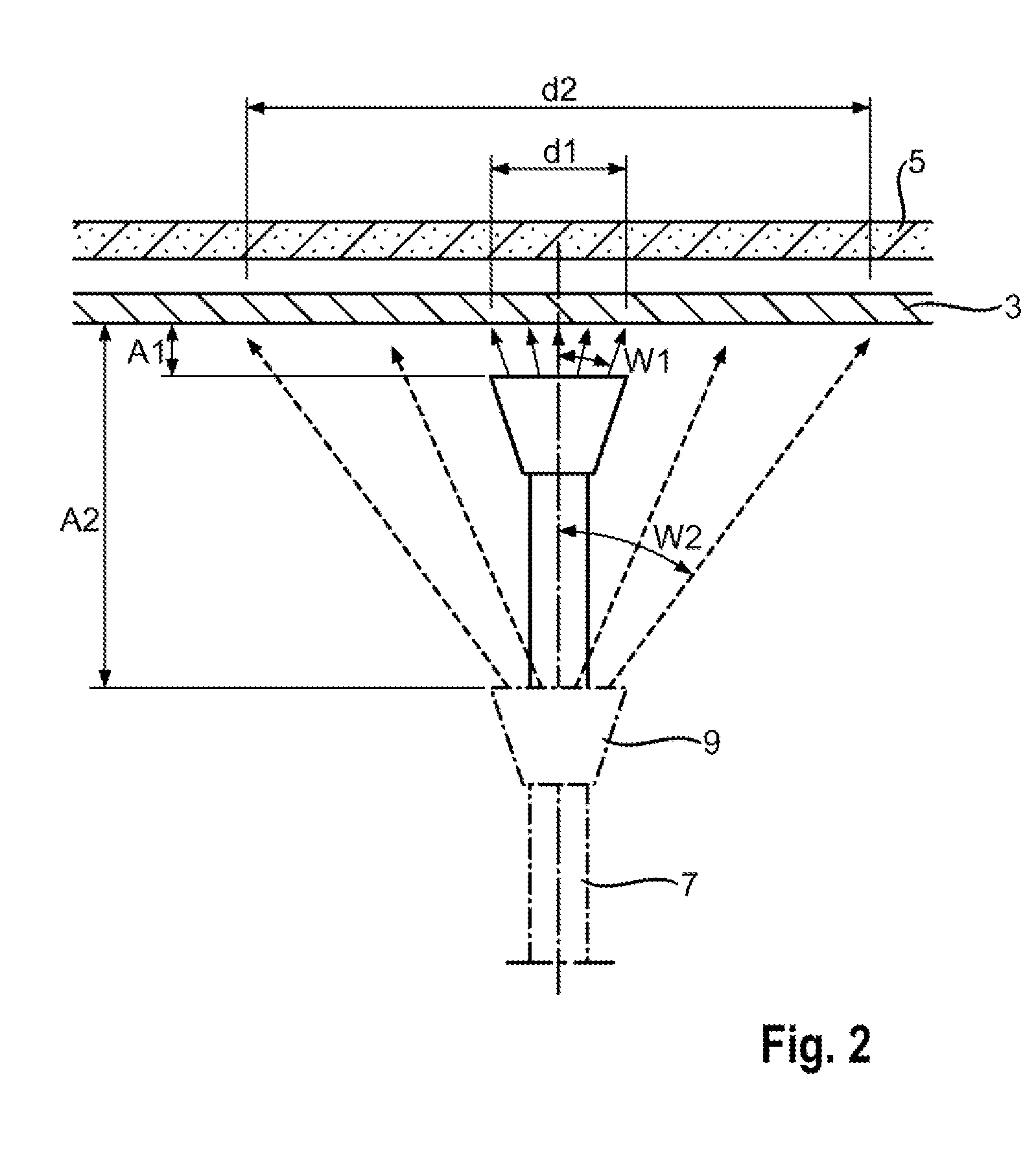
ActiveUS20150056787A1Increase layer thicknessUniform layer thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingWaferingSusceptor
Uniformity of vapor deposited coatings on semiconductor wafers is improved by employing an apparatus having a gas distributor head below a susceptor onto which the wafer is placed, the gas distributor head directing a fan of cooling gas at the rear side of the susceptor. The ratio of the diameter of the cooled section of the susceptor to the diameter D of the wafer is preferably from 0.1 to 0.4.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com