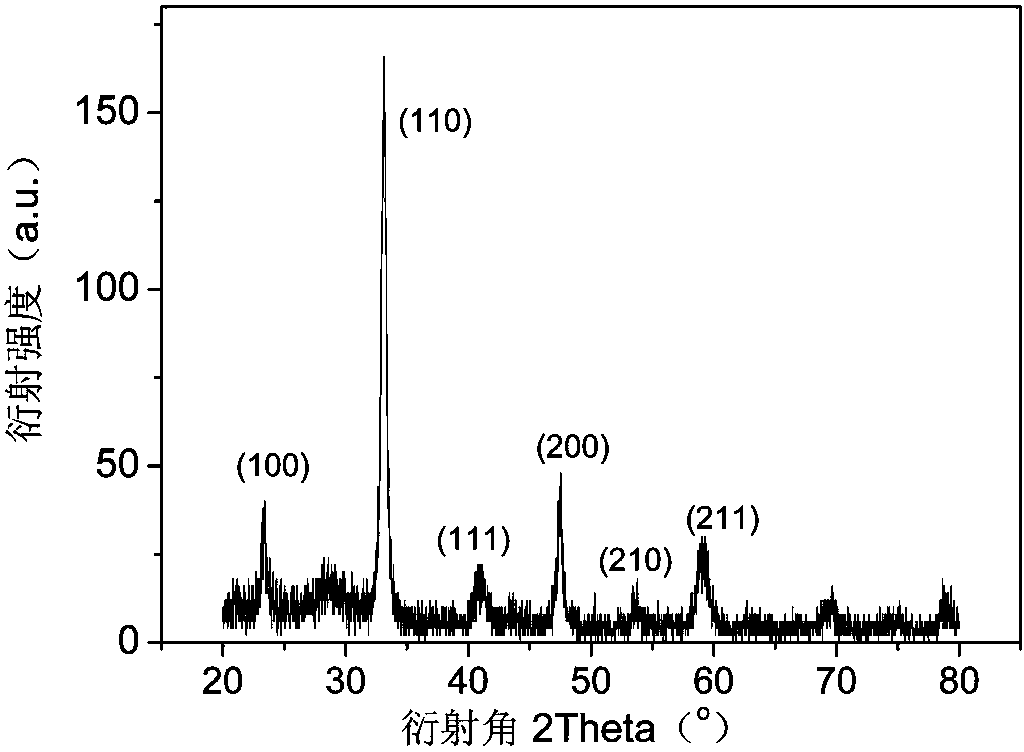
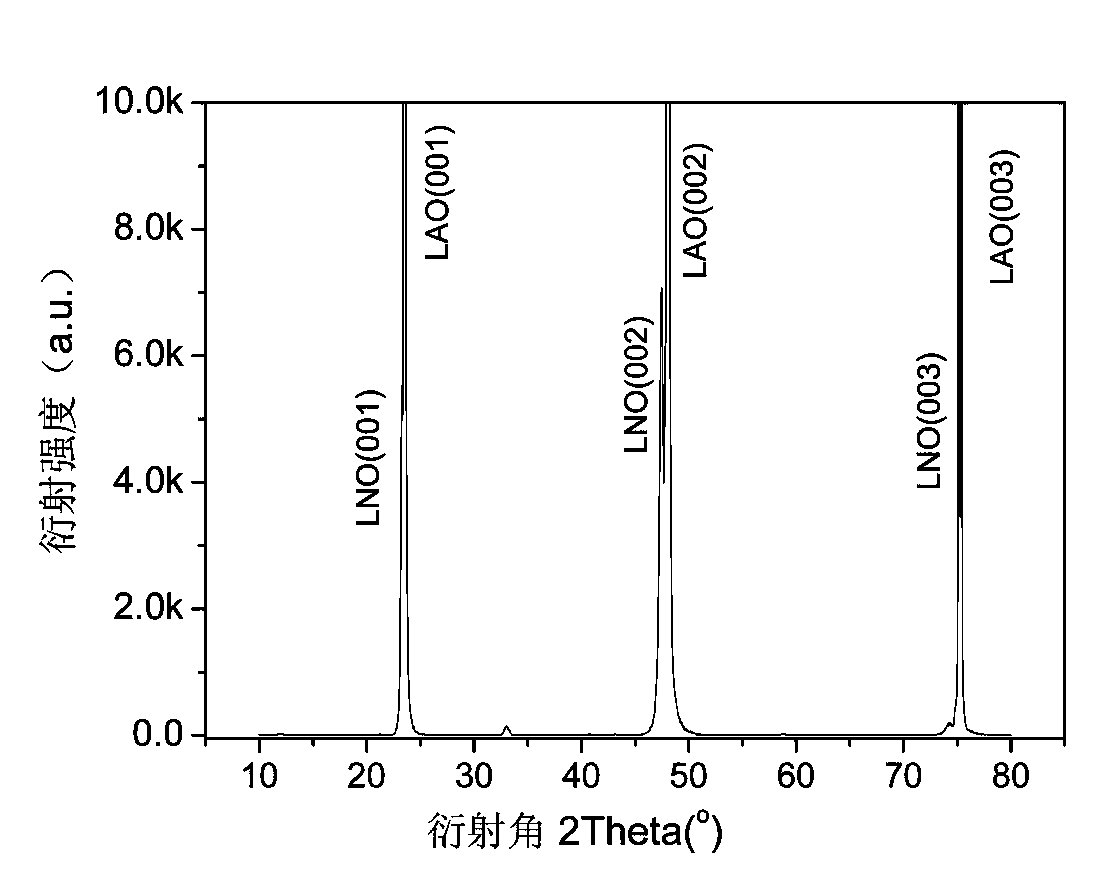
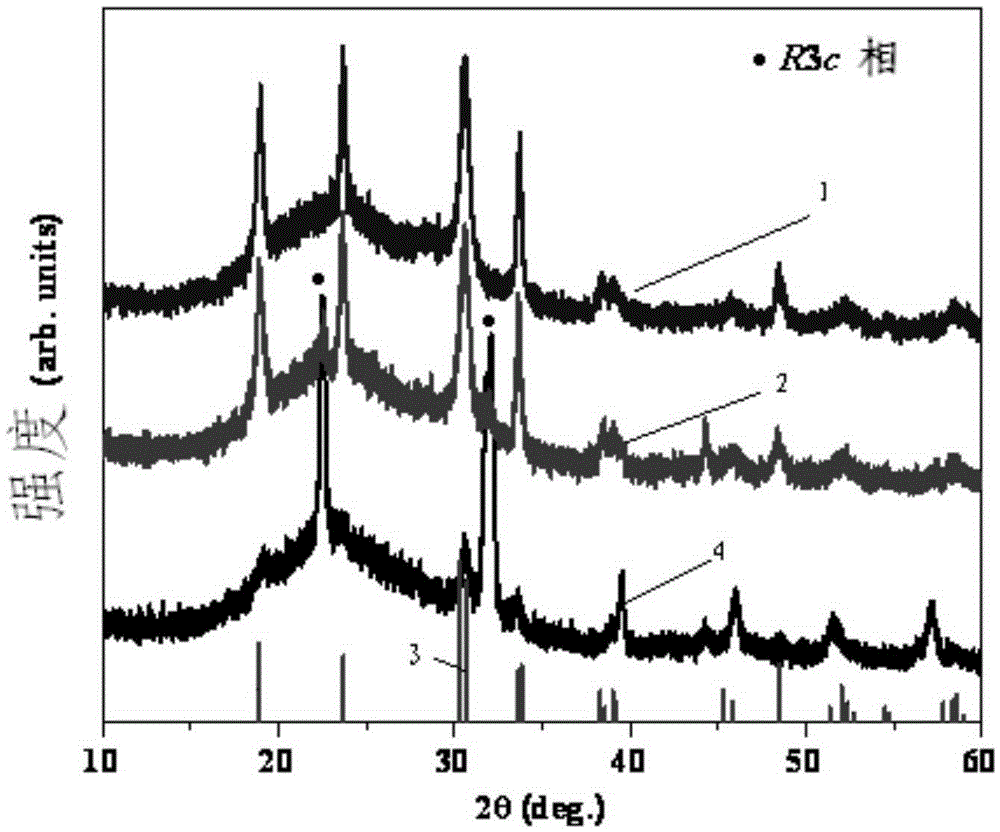
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Chemical solution deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low-cost preparing method for high-temperature superconductive coated conductor strip
ActiveCN103985479AReduce thicknessImprove manufacturing speedSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectrical conductorRadio frequency magnetron sputtering
The invention provides a low-cost preparing method for a high-temperature superconductive coated conductor strip and belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of high-temperature superconductive materials. The low-cost preparing method comprises the following steps that (1) the surface of a metal base band is cleaned; (2) by the adoption of the chemical solution deposition planarization (SDP) method, an isolating layer is prepared on the metal base band; (3) by the adoption of an ion beam auxiliary radio frequency magnetron sputtering method (IBAD-MgO), a biaxial texture magnesium oxide layer is prepared on the isolating layer; (4) a lanthanum manganate layer is prepared by the adoption of the radio frequency magnetron sputtering method; (5) a cerium oxide layer is prepared by the adoption of a direct-current magnetron reactive sputtering method; (6) a superconductive layer is prepared by the adoption of a metal organic deposition decomposition method (MOD); (7) a silver protective layer is prepared by the adoption of a direct-current magnetron sputtering method; (8) annealing is conducted in high-purity oxide; (9) a copper stable layer is arranged in an electroplating mode according to use requirements. According to the low-cost preparing method for the high-temperature superconductive coated conductor strip, through comprehensive application of physical preparation methods and chemical preparation methods, high-temperature superconductive strips can be produced in a large-scale mode at low cost.
Owner:赵遵成
Magnesium Fluoride and Magnesium Oxyfluoride based Anti-Reflection Coatings via Chemical Solution Deposition Processes
InactiveUS20140147594A1Control levelPretreated surfacesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPorous coatingPhysical chemistry
Chemical solution deposition process can be used to deposit porous coatings containing magnesium fluoride and / or magnesium oxyfluoride. The chemical solution deposition process can utilize a solution containing a magnesium precursor, a fluorine precursor, together with a surfactant porogen. The surfactant porogen can improve the wettability of the coated layers, together with increase the control of the porosity level and morphology of the coated layers.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC +1
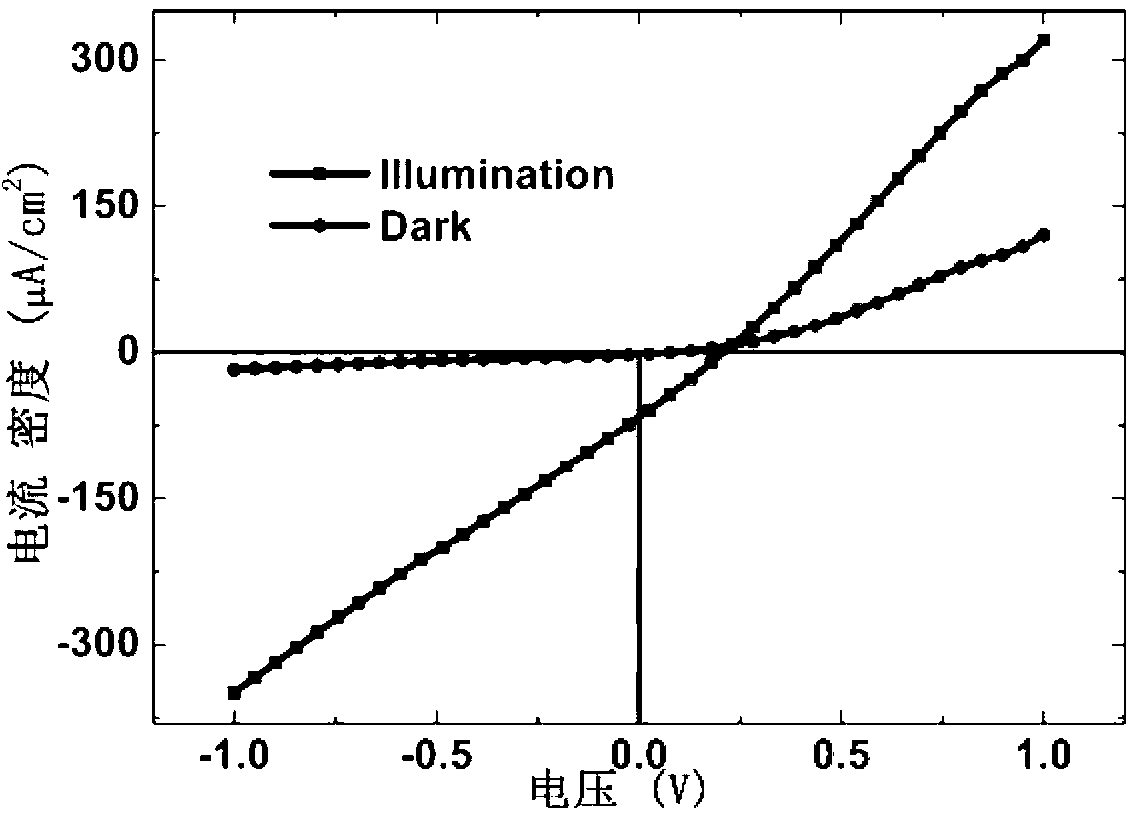
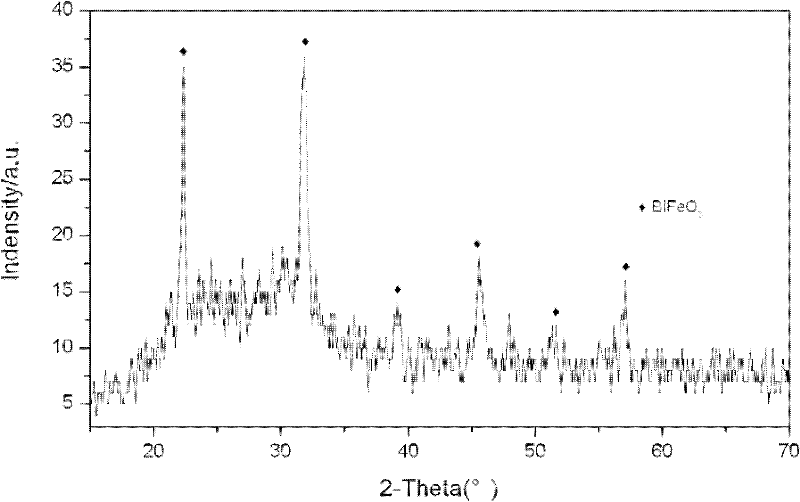
Method for preparing BiFeO3 ferroelectric thin film photovoltaic battery on glass substrate
InactiveCN102544216AUniform grainReduce manufacturing costFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingFerroelectric thin filmsMaterials science
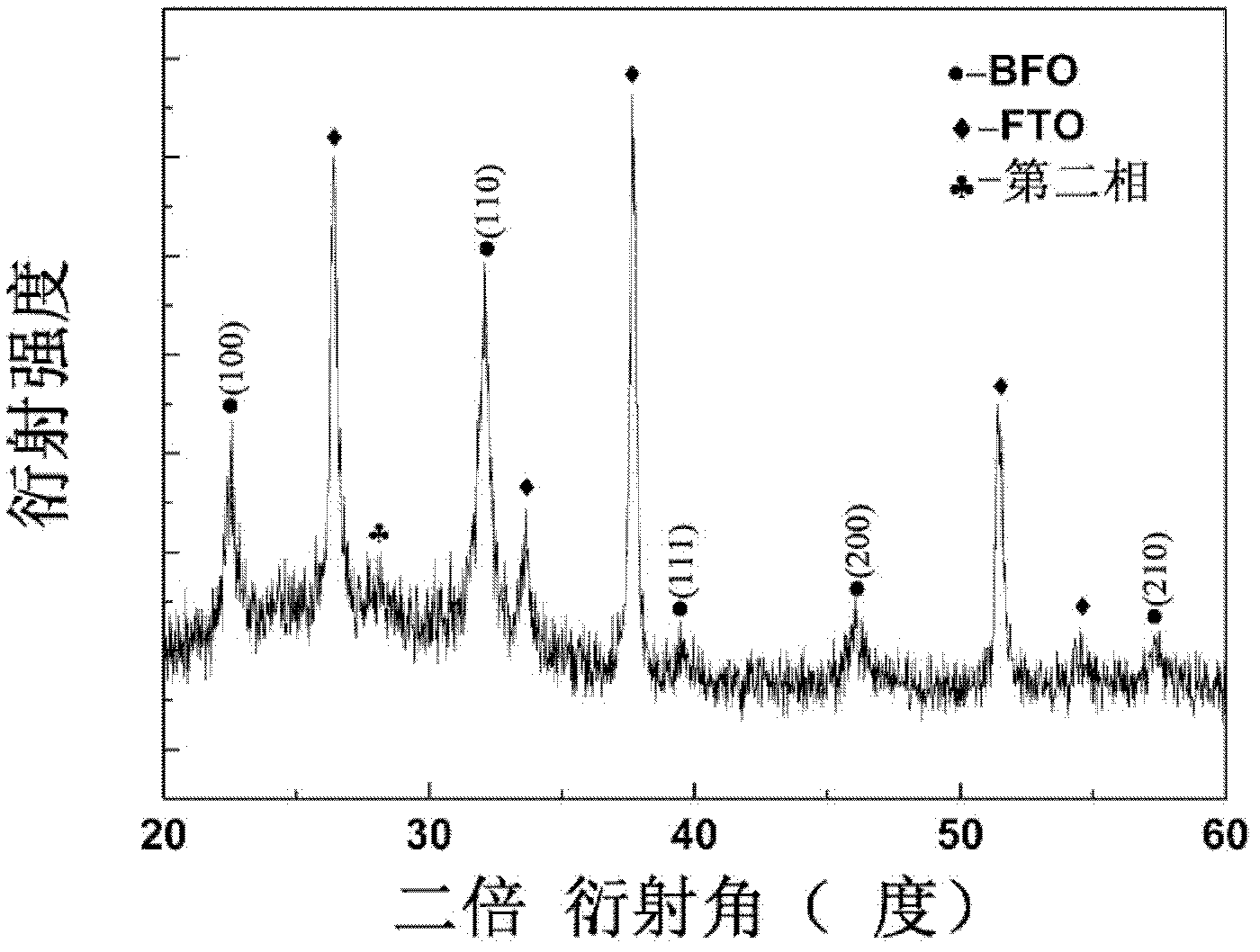
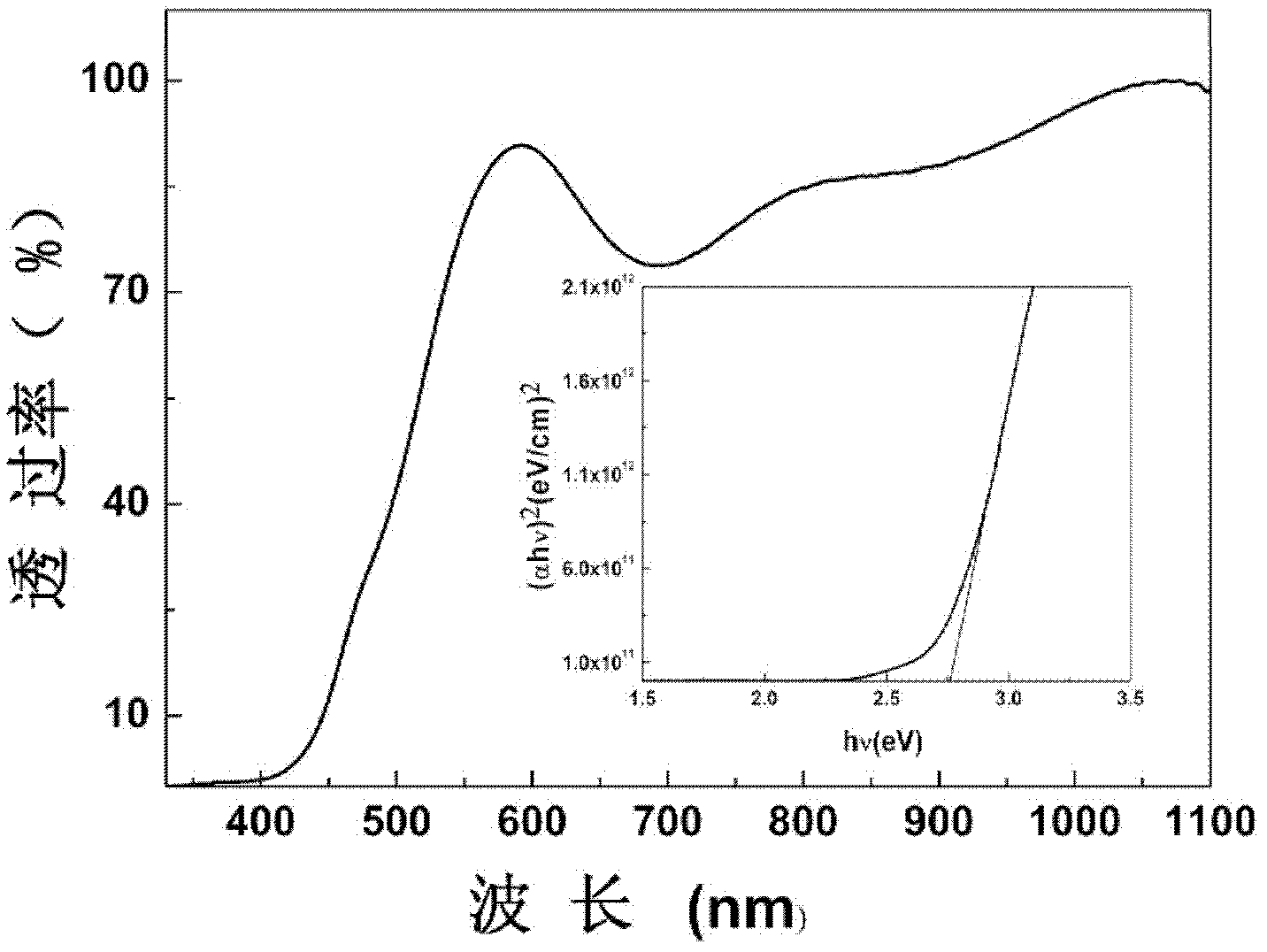
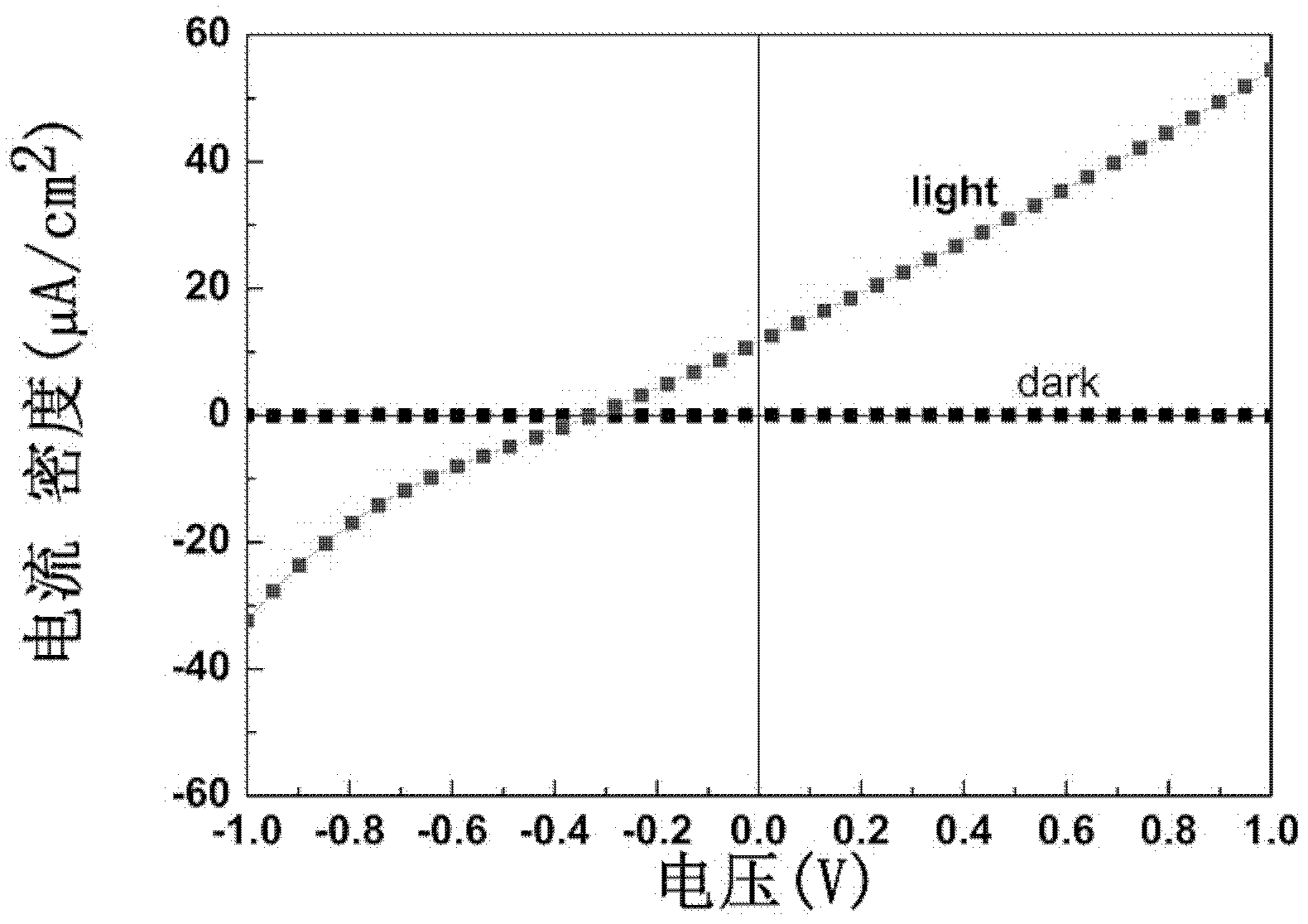
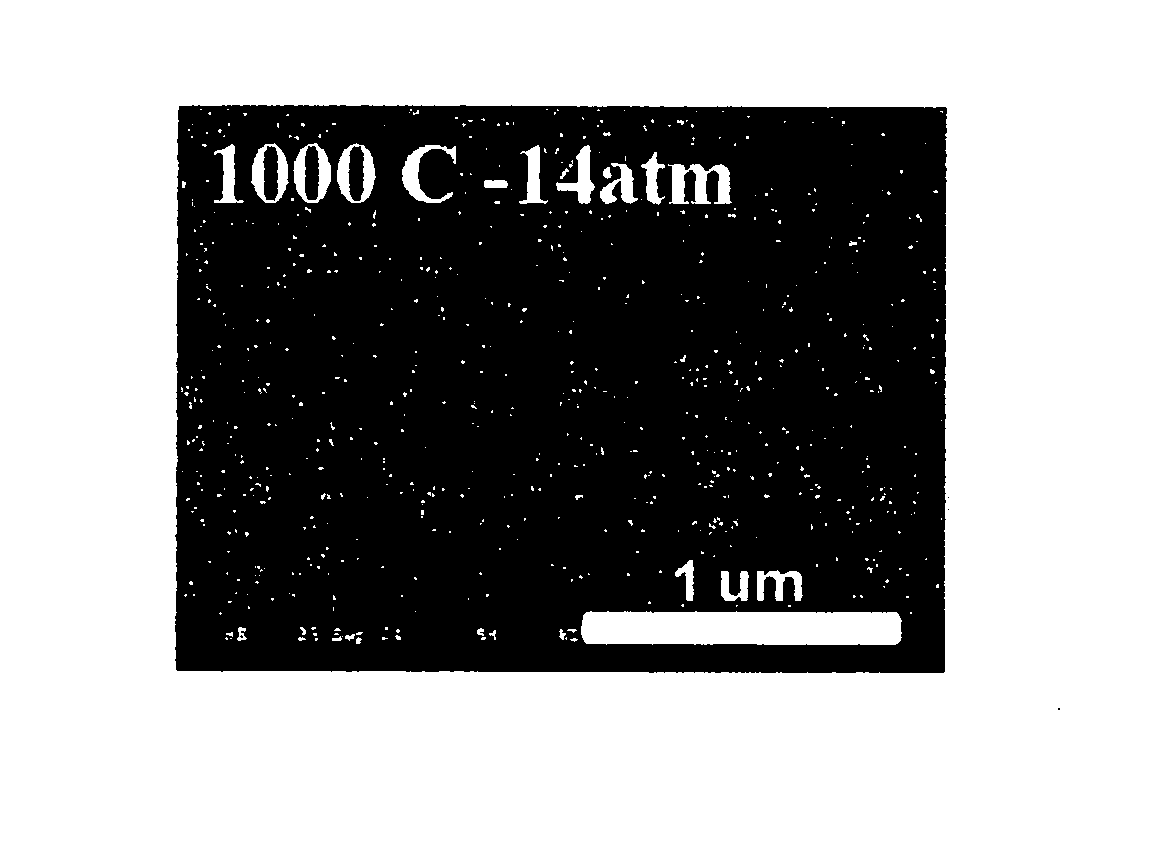
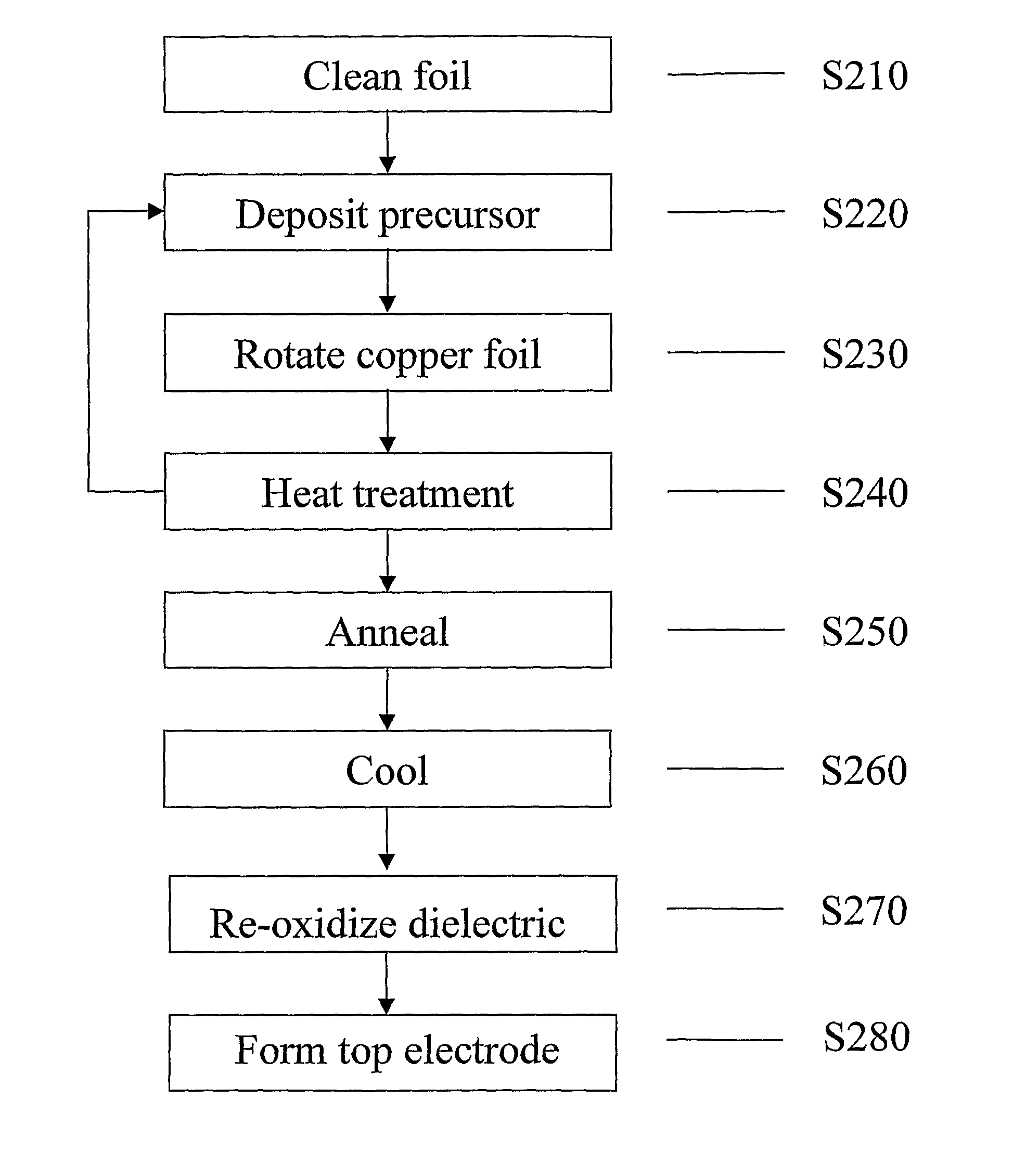
The invention relates to a method for preparing a BiFeO3 ferroelectric thin film photovoltaic battery on a glass substrate, comprising the following steps of: selecting glass as a substrate; preparing a BiFeO3 ferroelectric thin film with a perovskite structure through a chemical solution deposition method; and preparing a top electrode with a size of 0.5*0.5 mm on the thin film through a physical sputtering method. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the BiFeO3 ferroelectric and photovoltaic thin film with a perovskite structure, which has the advantages of high consistency and good repeatability on the glass substrate, by a low cost. The prepared thin film has the advantages of excellent photovoltaic property and single-directional conductive property of a diode. The BiFeO3 ferroelectric thin film can be applicable to the fields of a photovoltaic battery and an optical electronic device due to the excellent properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Microcontact printed thin film capacitors
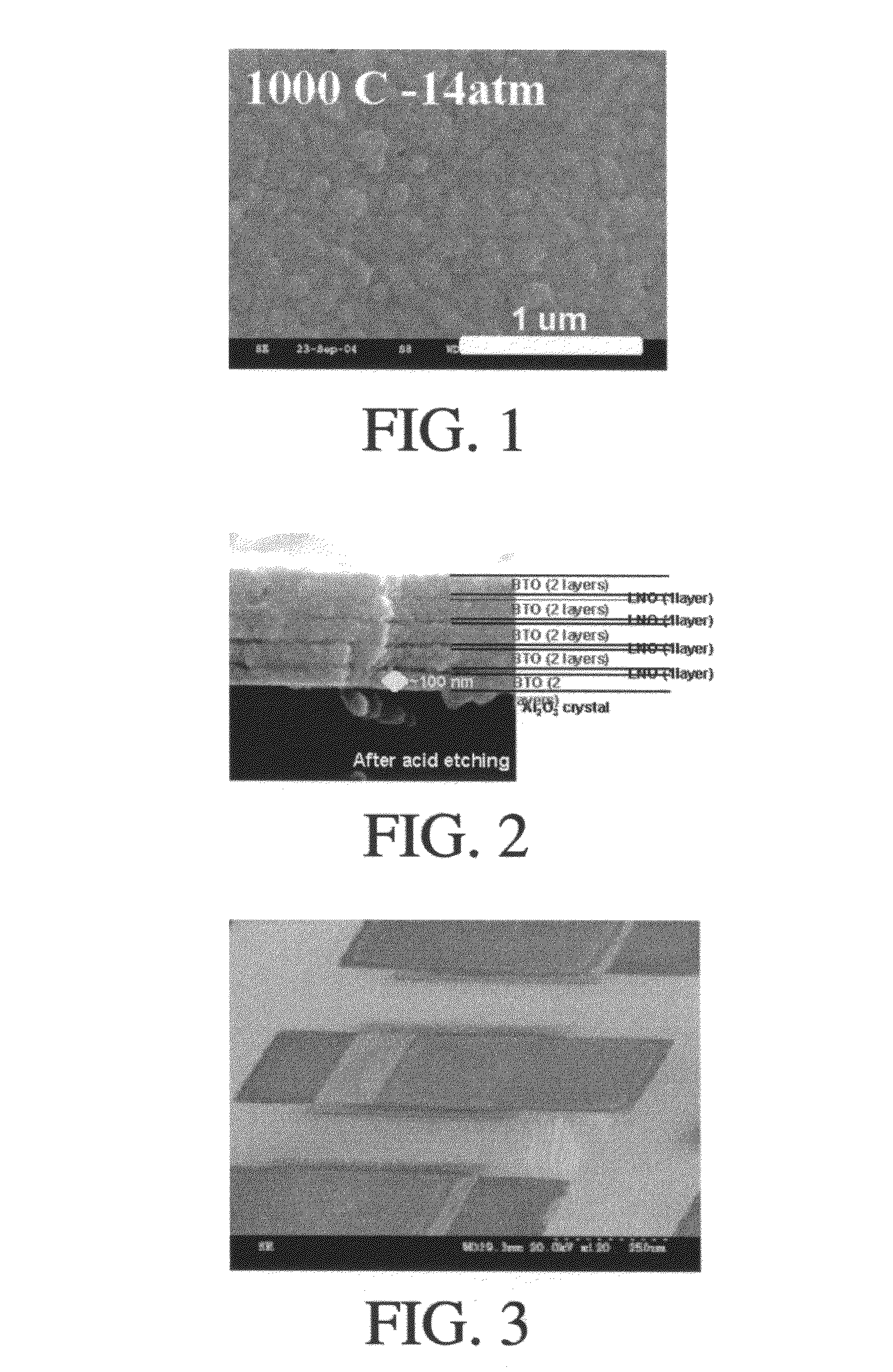
The invention relates to thin film single layers, electronic components such as multilayer capacitors which utilize thin film layers, and to their methods of manufacture. Chemical solution deposition and microcontact printing of dielectric and electrode layers are disclosed. High permittivity BaTiO3 multilayer thin film capacitors are prepared on Ni foil substrates by microcontact printing and by chemical solution deposition. Multilayer capacitors with BaTiO3 dielectric layers and LaNiO3 internal electrodes are prepared, enabling dielectric layer thicknesses of 1 μm or less. Microcontact printing of precursor solutions of the dielectric and electrode layers is used.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
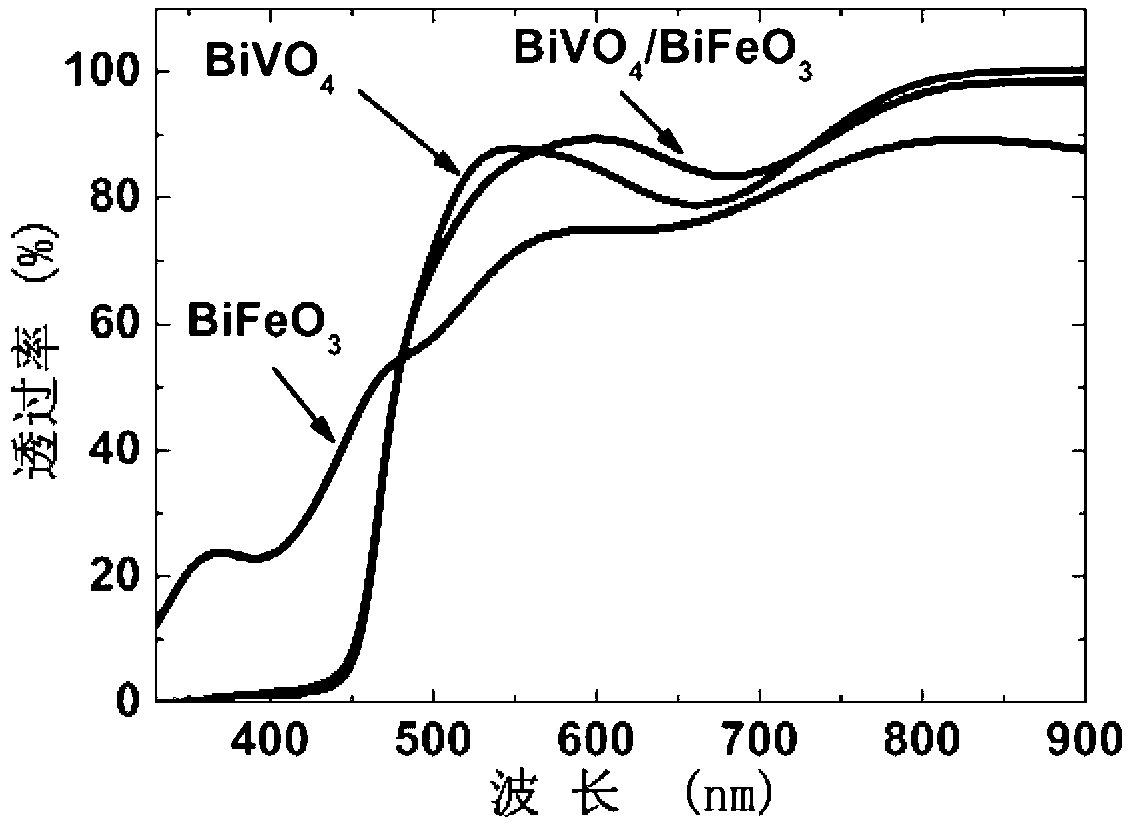
Method for preparing bismuth vanadate/bismuth ferrite heterojunction film solar cells
InactiveCN103078013ANo impurityReduce manufacturing costRenewable energy productsSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionBismuth vanadate
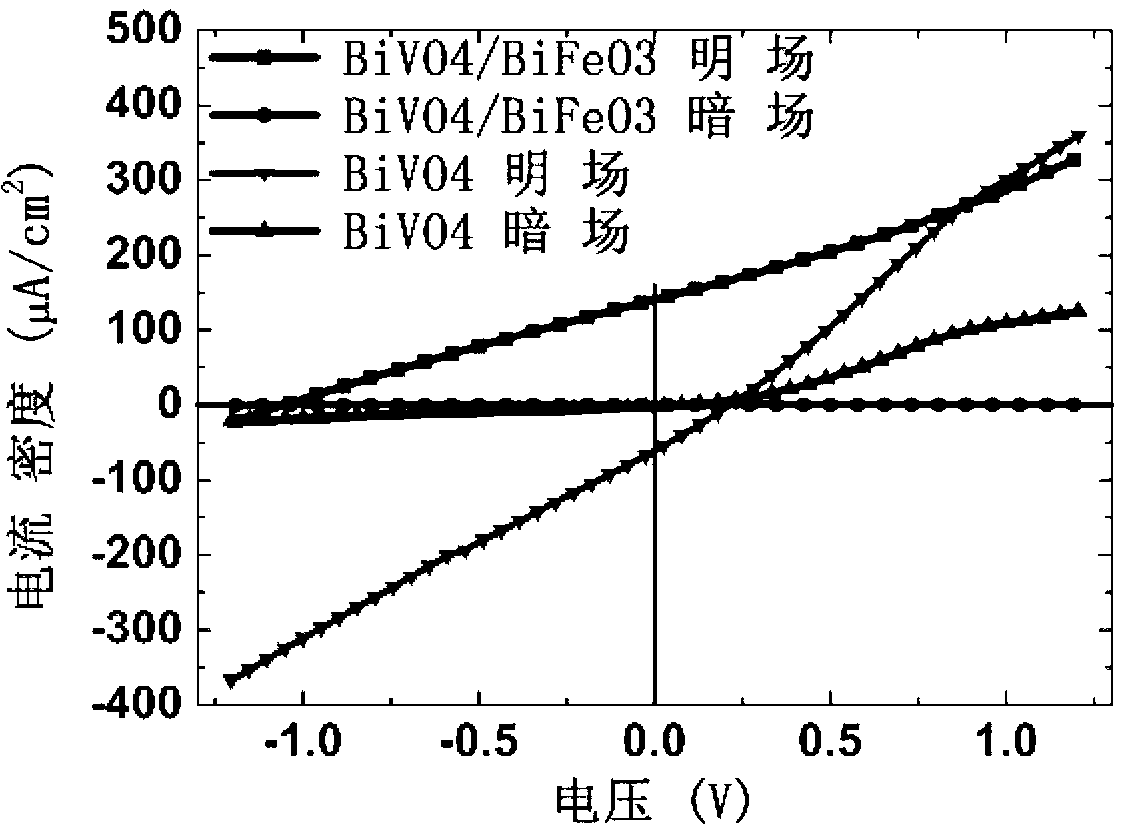
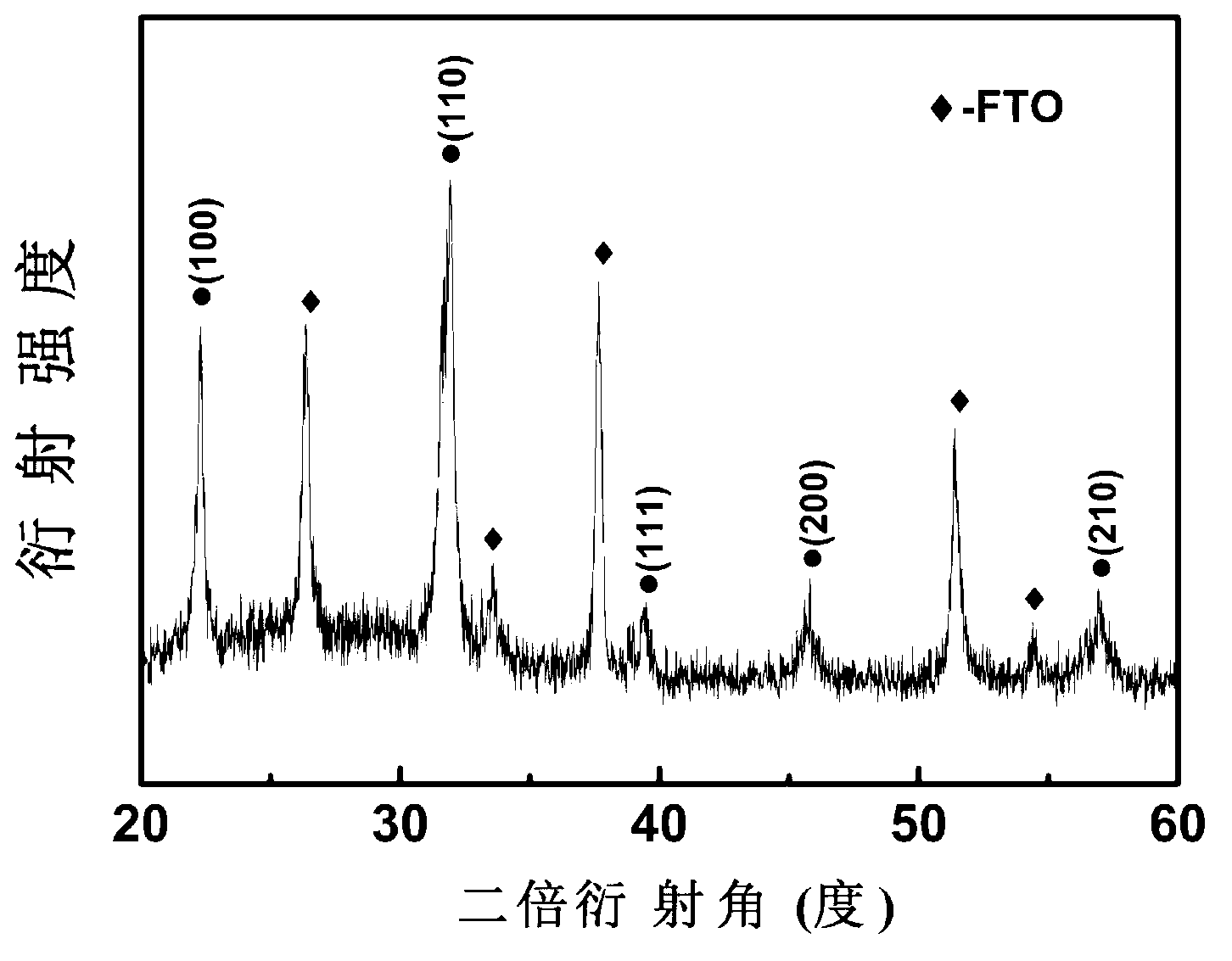
The invention relates to a method for preparing bismuth vanadate / bismuth ferrite heterojunction film solar cells on a glass substrate. The method comprises the following steps: selecting FTO (Fluorinedoped Tin Oxide) conductive glass as a base, preparing a perovskite-structure bismuth vanadate / bismuth ferrite heterojunction film with a chemical solution deposition method, and then preparing a top electrode on the film with a physical sputtering method to obtain the solar cells. The photovoltaic effect of the bismuth vanadate film can be increased and is reversed by utilizing an ultra-thin bismuth ferrite layer. The method can prepare the bismuth vanadate / bismuth ferrite heterojunction film with high consistency and good repeatability on the glass substrate with a low cost. The prepared heterojunction film has good photovoltaic properties, the diode direction of the heterojunction film is opposite to the diode direction of a pure bismuth vanadate film, and ultra-thin bismuth ferrite ferroelectric films and similar bismuth vanadate / bismuth ferrite heterojunction films have a wide application prospect in the fields of solar cells and photoelectric devices due to the good properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of solar battery with bismuth ferrite/sodium bismuth titanate-barium titanate heterostructure ferroelectric film
InactiveCN103078014AUniform grainReduce manufacturing costRenewable energy productsSemiconductor devicesBarium titanateSolar battery
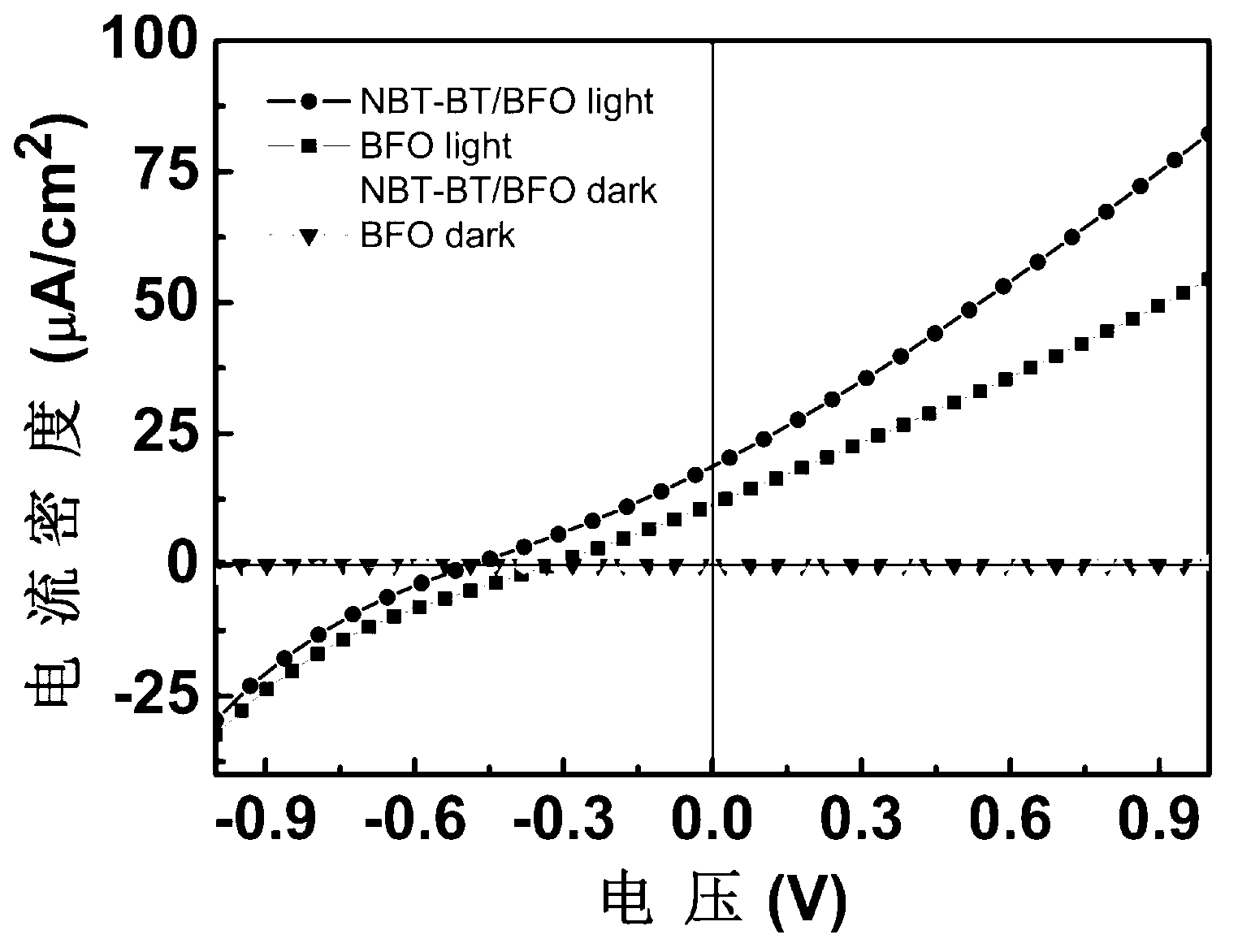
The invention relates to a preparation method of a solar battery with a bismuth ferrite / sodium bismuth titanate-barium titanate heterostructure ferroelectric film. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: selecting SnO2 transparent conducting glass doped with fluorine (FTO for short) as a substrate, preparing the (Na0.5Bi0.5)0.94Ba0.06TiO3 and BiFeO3 ferroelectric film by a chemical solution deposition method, then preparing an electrode on the surface of the film by a physical sputtering method. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages that the ferroelectric photoelectric film with high consistency and good repeatability is prepared on the FTO substrate by low cost. The prepared heterostructure film has more excellent photovoltaic performance than that of the pure BiFeO3, and can be applied in the fields of photoelectric batteries and photoelectronic devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
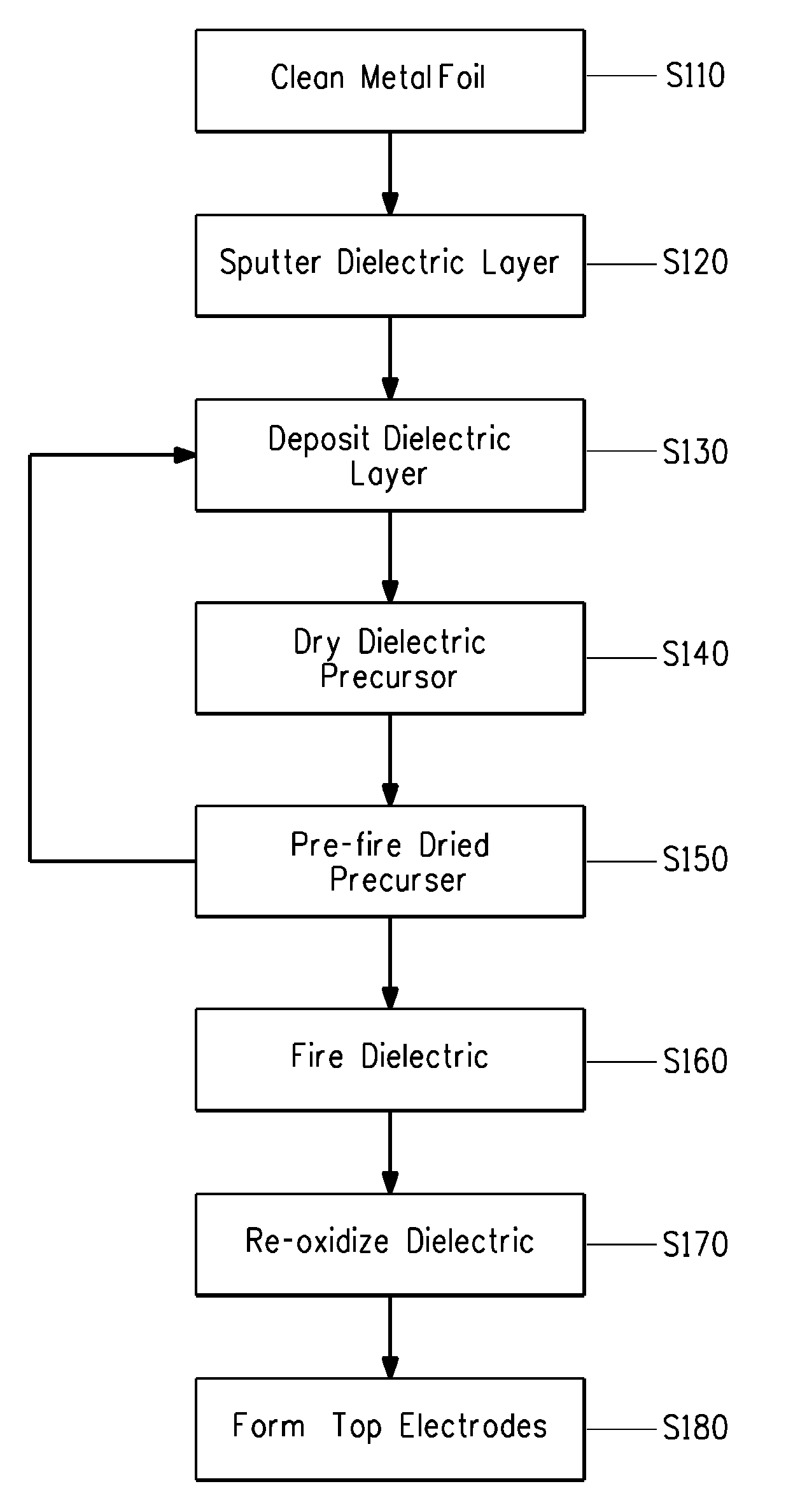
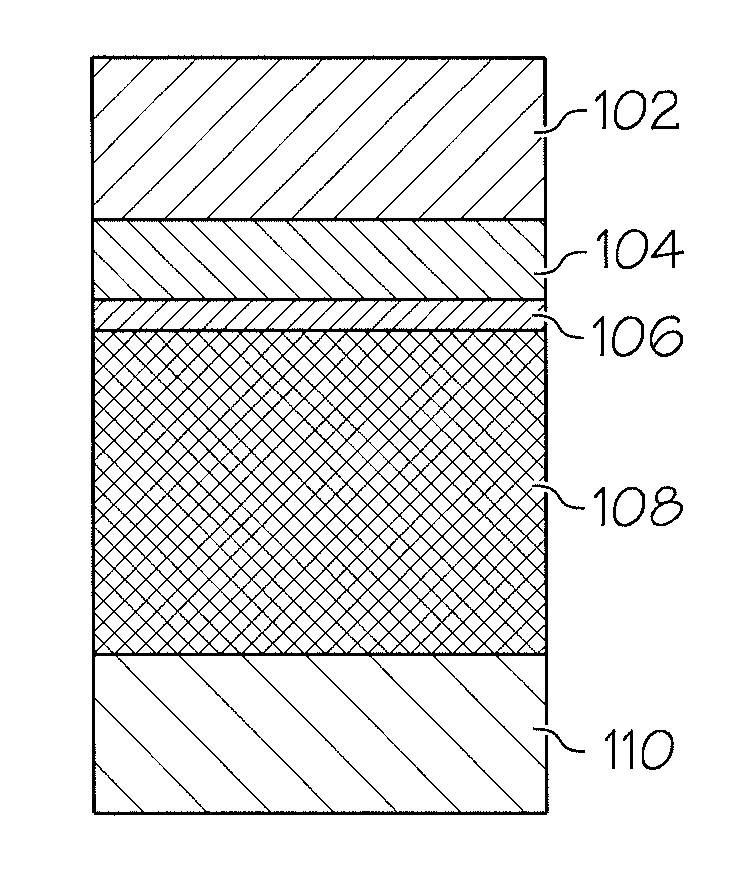
Thin film capacitors on metal foils and methods of manufacturing same
Disclosed are methods of making a dielectric on a metal foil, and a method of making a large area capacitor that includes a dielectric on a metal foil. A first dielectric layer is formed over the metal foil by physical vapor deposition, and a dielectric precursor layer is formed over the first dielectric layer by chemical solution deposition. The metal foil, first dielectric layer and dielectric precursor layer are prefired at a prefiring temperature in the range of 350 to 650° C. The prefired dielectric precursor layer, the first dielectric layer and the base metal foil are subsequently fired at a firing temperature in the range of 700 to 1200° C.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Cd-Free, Oxide Buffer Layers For Thin Film CIGS Solar Cells By Chemical Solution Deposition Methods
A process described herein provides an economical means for producing the oxide-based buffer layers using a wet chemical CSD process wherein the desired buffer layer material results from the evaporation of a chemical already containing the material in solution. Thus, no residual liquid chemical elements remain after deposition, and as there is no reaction to create the buffer material, as is the case with CdS CBD, the liquid elements in CSD have sufficiently long shelf life after mixing to as to improve manufacturability and further reduce waste. Furthermore, as there is no in-chamber reaction to create the buffer material solution, there are many options for delivering said solution to the CIGS absorber layer. Finally, as the oxide films for the CdS replacement have inherently better transmission in the blue spectrum, aggressive thinning of films to improve current generation is unnecessary.
Owner:ASCENT SOLAR TECH
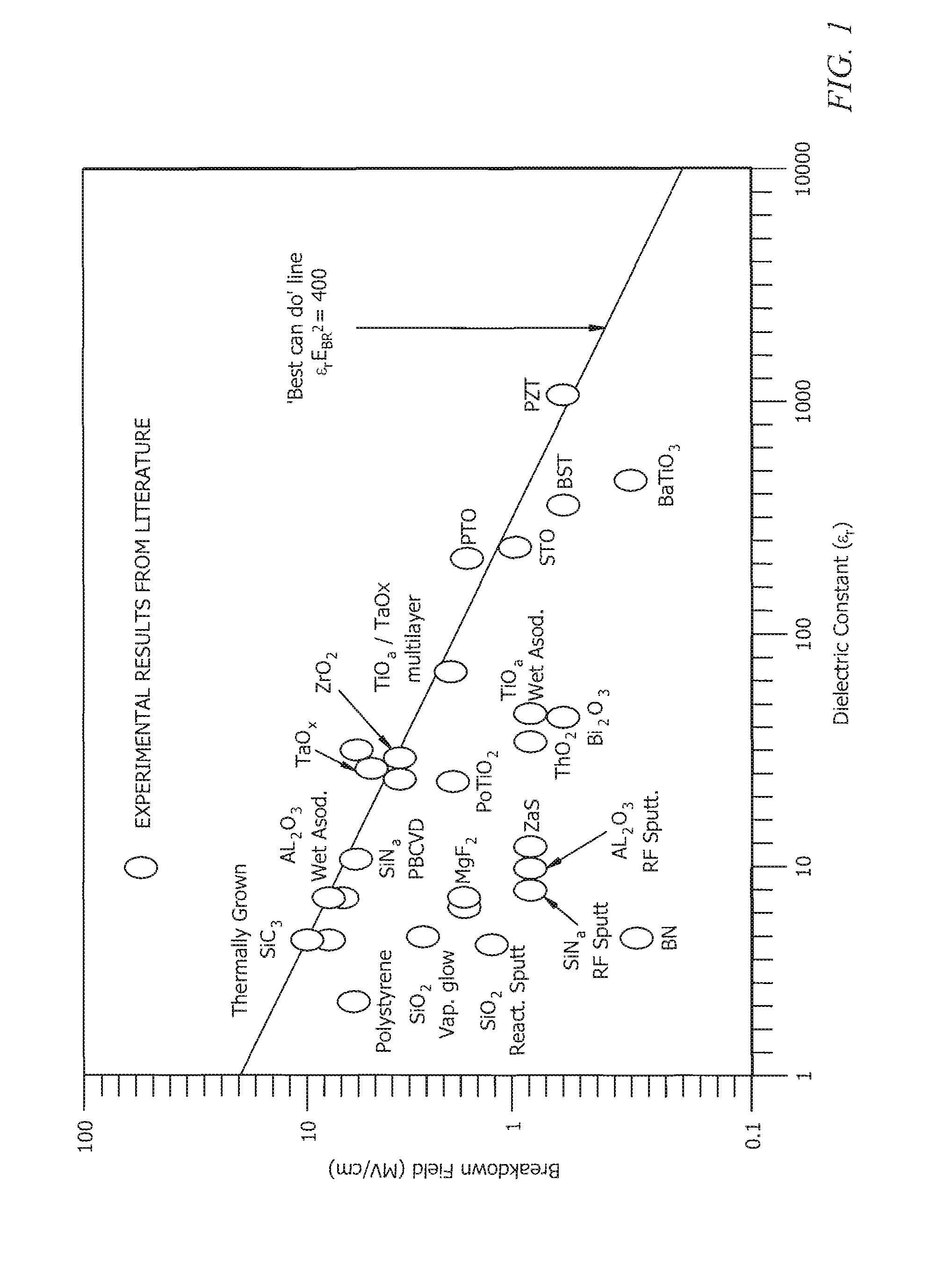
High-dielectric constant thin film metal oxides on silicon wafers for capacitor applications and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20080220153A1Low costHigh bulk densityRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingDielectricCapacitor
A method of fabrication of high-k paraelectric metal oxide films at low temperatures utilizing ordered mesoporous metal oxide thin films synthesized by organic templating methodology. The process consisting of (a) chemical solution deposition of periodic ordered mesoporous structures containing high-k metal oxide films, (b) removal of organic template additives, (c) infiltration of the pores with an appropriate second phase, and (d) low temperature thermal and / or annealing of infiltrated films.
Owner:SBA MATERIALS
Method for preparing bismuth vanadate solar cell on glass substrate
InactiveCN103107242ALow costGood photovoltaic effectRenewable energy productsSemiconductor devicesState of artSemiconductor materials
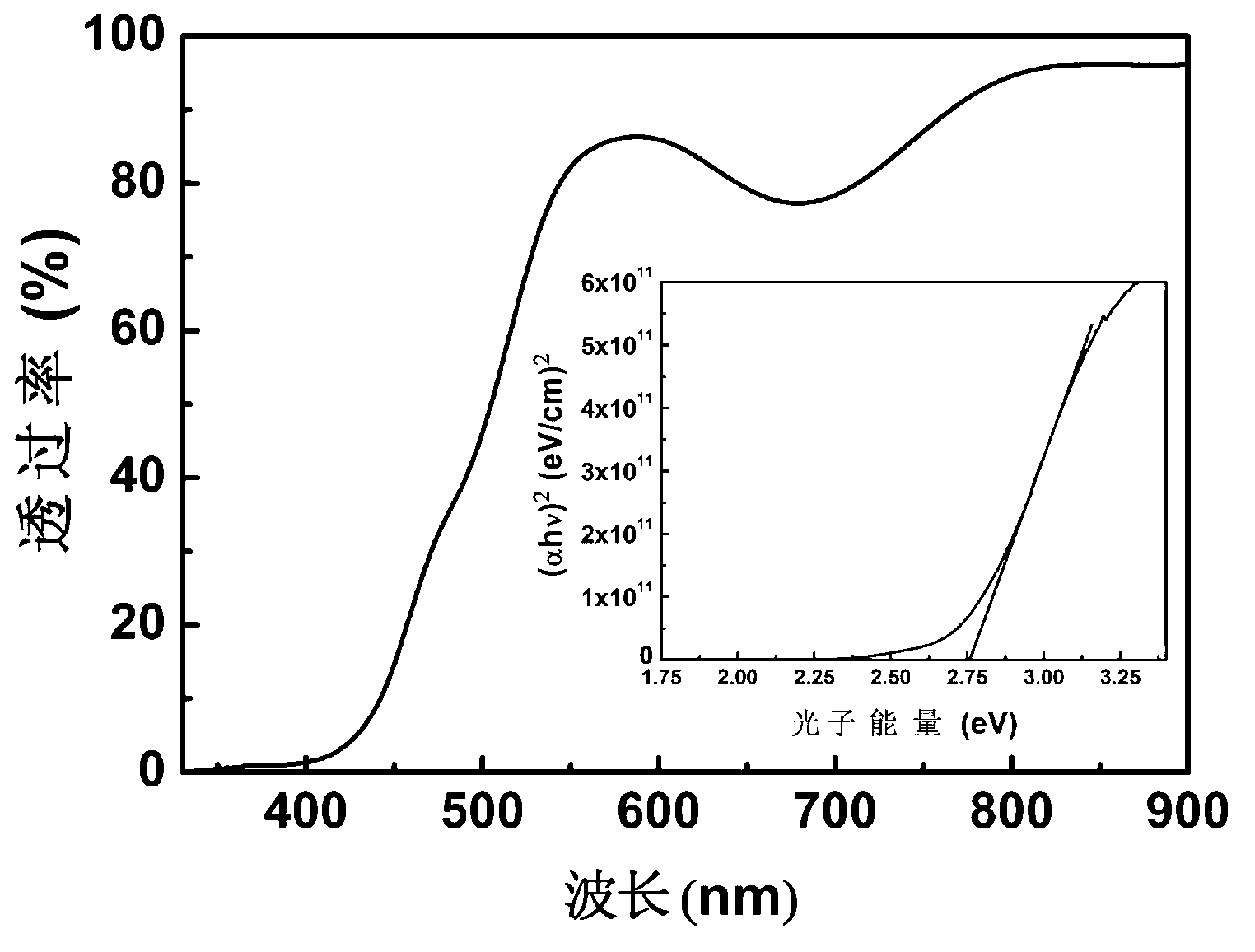
The invention relates to a method for preparing a bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) solar cell on a fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass substrate. The method includes preparing precursor solution and preparing a monoclinic polycrystalline bismuth vanadate thin film. The glass substrate is utilized as a substrate, the BiVO4 oxide thin film in a perovskite structure is prepared through a chemical solution deposition method, then electrodes are prepared on the thin film through a physical sputtering method, and therefore the BiVO4 solar cell is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method for preparing the BiVO4 solar cell on the FTO glass substrate can be used for preparing the perovskite-structure BiVO4 thin film which is high in consistency and good in repeatability at low cost. The thin film has good photovoltaic properties and the unidirectional conductive property of a diode, can meet the requirements of microelectronic devices and photoelectric devices on semiconductor materials, and has a significant promoting role in the preparation technology of bismuth vanadate thin films.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
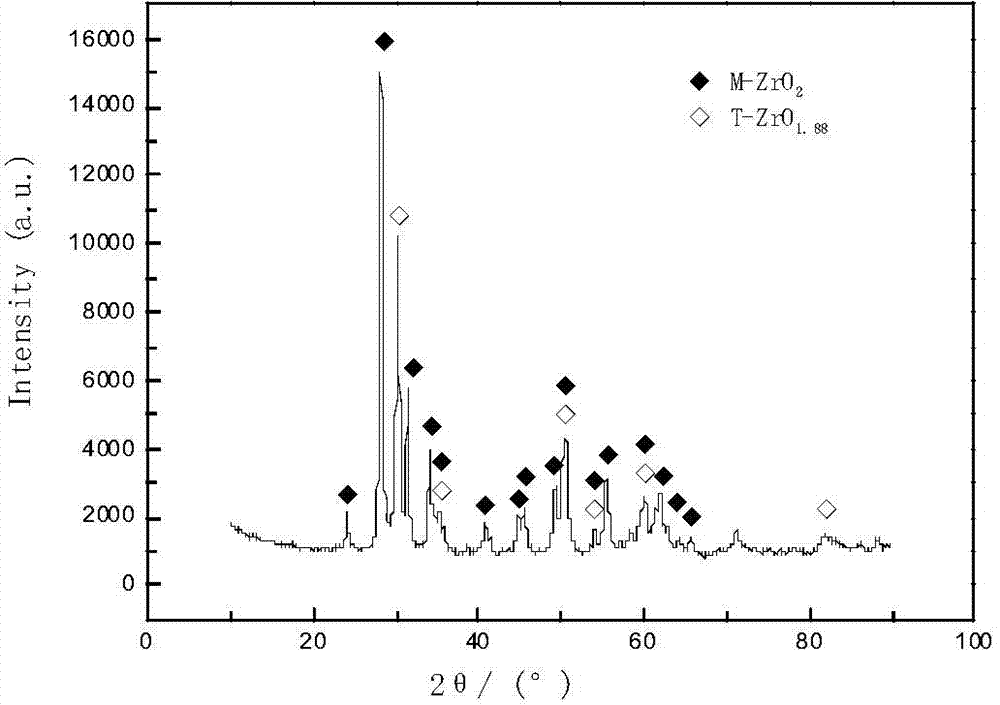
Preparation method for hydrogen-resistant coating on surface of zirconium hydride
ActiveCN103484917AContinuous surfaceSurface integrityNuclear energy generationSurface reaction electrolytic coatingZirconium hydrideElectrolytic agent
The invention relates to a preparation method for a hydrogen-resistant coating on the surface of zirconium hydride. The method is characterized in that a micro-arc oxidation and chemical solution precipitation and hole sealing combined technology is adopted for the preparation of a continuous and compact hydrogen-resistant coating on the surface of the zirconium hydride. According to the invention, a phosphate electrolyte system is adopted, and a zirconia ceramic layer is prepared on the surface of the zirconium hydride through micro-arc oxidation firstly, then a chemical solution method is adopted for hole sealing, and finally, a perfectly repaired zirconia hydrogen-resistant coating is prepared on the surface of the zirconium hydride. By utilizing the preparing method, the zirconia ceramic layer with the continuous and integral surface and the thickness bigger than 50 mum is prepared on the surface of the zirconium hydride; the zirconia ceramic layer is remarkable in hydrogen-resistant effect and better in high-temperature oxidation resistance.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing porous bismuth ferrate thin film by CSD (Chemical Solution Deposition) method
The invention provides a method for preparing a porous bismuth ferrate thin film by a CSD (Chemical Solution Deposition) method. The method comprises the steps of: (1) cleaning an ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) / glass substrate, blow-drying with nitrogen gas, and irradiating with an ultraviolet illumination instrument for 20min; (2) respectively dissolving Fe(NO3)3.9H2O and Bi(NO3)3.5H2O in ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and glacial acetic acid, mixing to form a precursor solution, and magnetically stirring to obtain a stable BiFeO3 precursor; and (3) carrying out coating treatment on the substrate surface with the precursor, drying after coating is finished, repeating coating treatment multiple times to obtain set thin film thickness, finally rapidly heating to 350 DEG C, pre-annealing for 5min, and then annealing at 500 DEG C for 30-120min. The bismuth ferrate thin film prepared by the method is few in internal defects and high in catalysis performance.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of lanthanum nickelate conductive film by chemical solution deposition
ActiveCN103833416AIncrease contentReduce proportional imbalancesConductive layers on insulating-supportsCzochralski methodHeating furnace
The invention relates to a preparation method of a lanthanum nickelate conductive film by chemical solution deposition, belonging to the technical field of microelectronic manufacture. The step mainly includes the preparation of LaNiO3 sol, comprising: preparing a LaNiO3 gel film on a substrate by using a dipping Czochralski method or a spin-coating method, then drying the gel film to form a LaNiO3 gel dry film; transferring the substrate coated with the LaNiO3 gel dry film to a quartz tube heating furnace, performing thermolysis in a mixed atmosphere of H2O and O2; finally putting the thermolyzed gel dry film and the substrate into a quartz tube sintering furnace, performing high temperature calcining in the mixed atmosphere of H2O and O2, so as to form the conductive film on the substrate. The conductive film formed by the method has lower resistivity.
Owner:高俊萍
Method for preparing alumina passivation film on surface of crystalline silicon solar energy battery
InactiveCN103928564AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationAluminium chlorideChemical solution
The invention discloses a method for preparing an alumina passivation film on the surface of a crystalline silicon solar energy battery. The method involves plating an alumina film on the surface of the crystalline silicon solar energy battery. The method comprises the following steps: (1), selecting materials, i.e., reacting waterless ethanol to aluminum chloride so as to obtain aluminum; (2), preparing alumina sol, i.e., dissolving the aluminum chloride material in the waterless ethanol with a certain concentration, performing full stirring and concussion until a solution becomes clear, and adjusting the pH value of the solution to be within 1-2; and (3), preparing the alumina passivation film, i.e., dropping the prepared alumina sol on surface of the crystalline silicon solar energy battery and performing spin coating, then drying a spin-coated sample, under a certain condition, performing annealing, and performing uniform cooling to a normal temperature after the annealing is finished, such that the alumina passivation film is prepared on the surface of the crystalline silicon solar energy battery, and the film has a quite good passivation effect for the crystalline silicon solar energy battery. According to the invention, a chemical solution sedimentation method is employed, the method is simple and easy to implement, and the cost is low. The crystalline silicon solar energy battery is selected as a substrate, and the alumina film has the excellent passivation effect for the crystalline silicon solar energy battery.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Bismuth ferrite-based thin film containing doping elements, and preparation method thereof
Owner:BAIC MOTOR CORP LTD
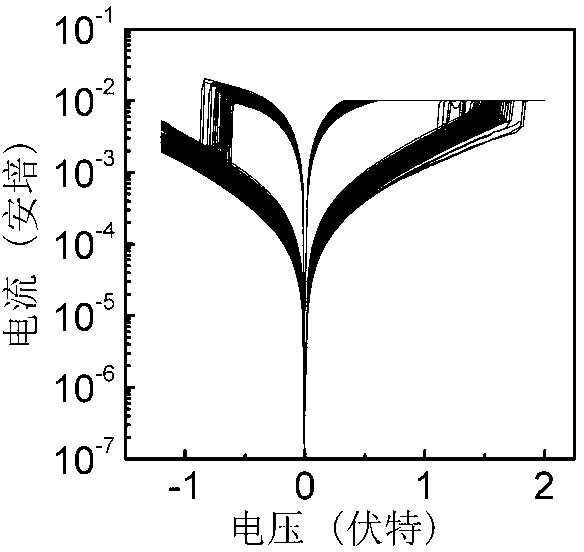
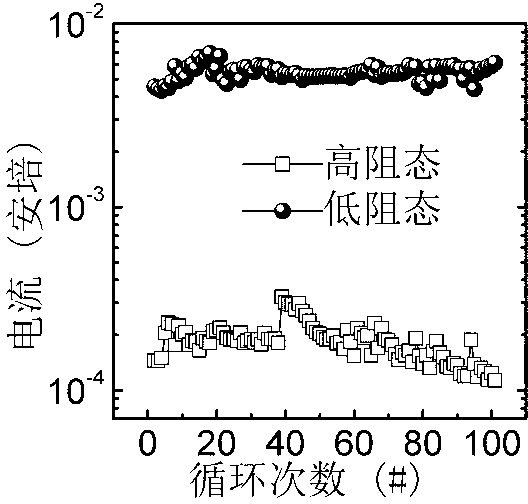
Ferroelectric resistive random access memory and adjustment and control method of switching ratio of ferroelectric resistive random access memory
InactiveCN107623070AGuaranteed ferroelectricityIncreased resistive effectElectrical apparatusStrontium titanateLead zirconate titanate
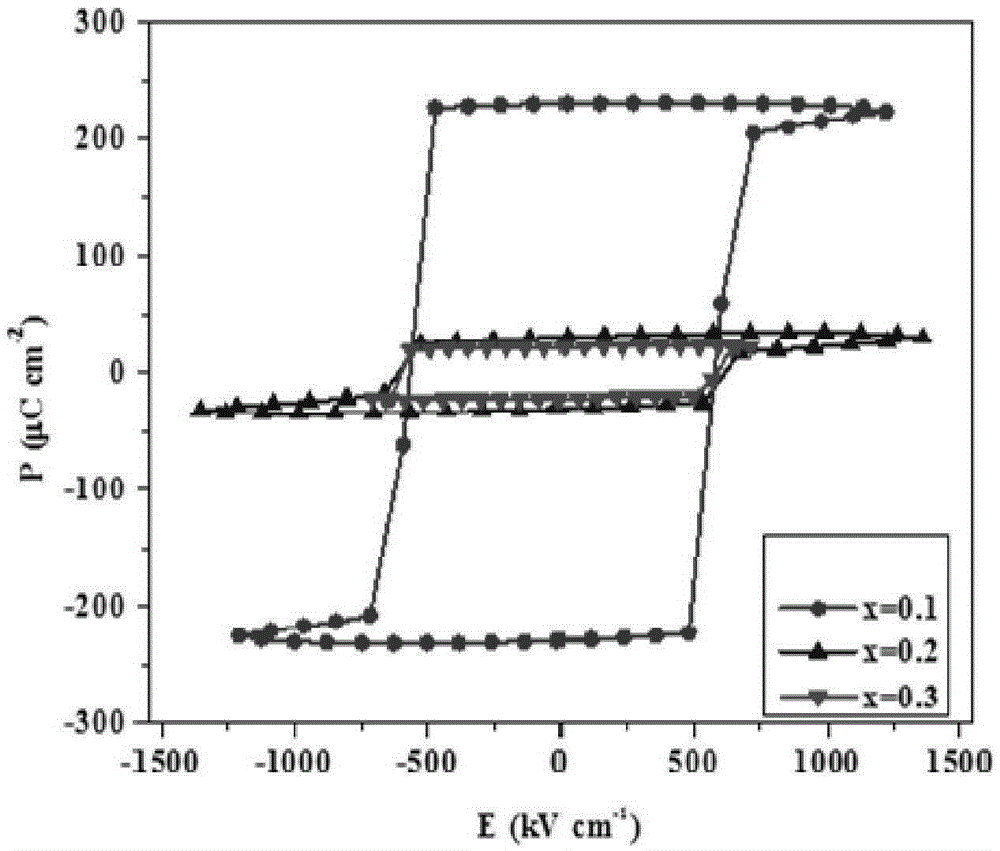
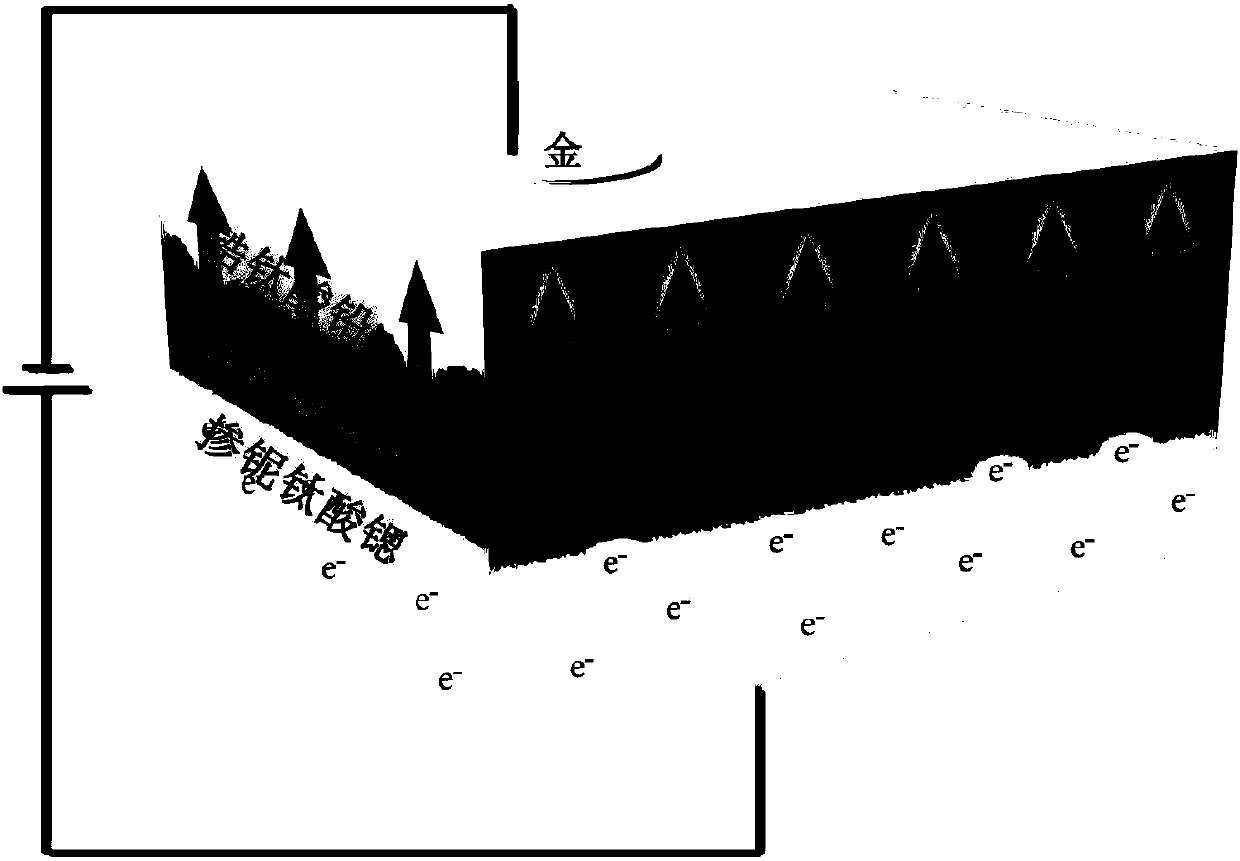
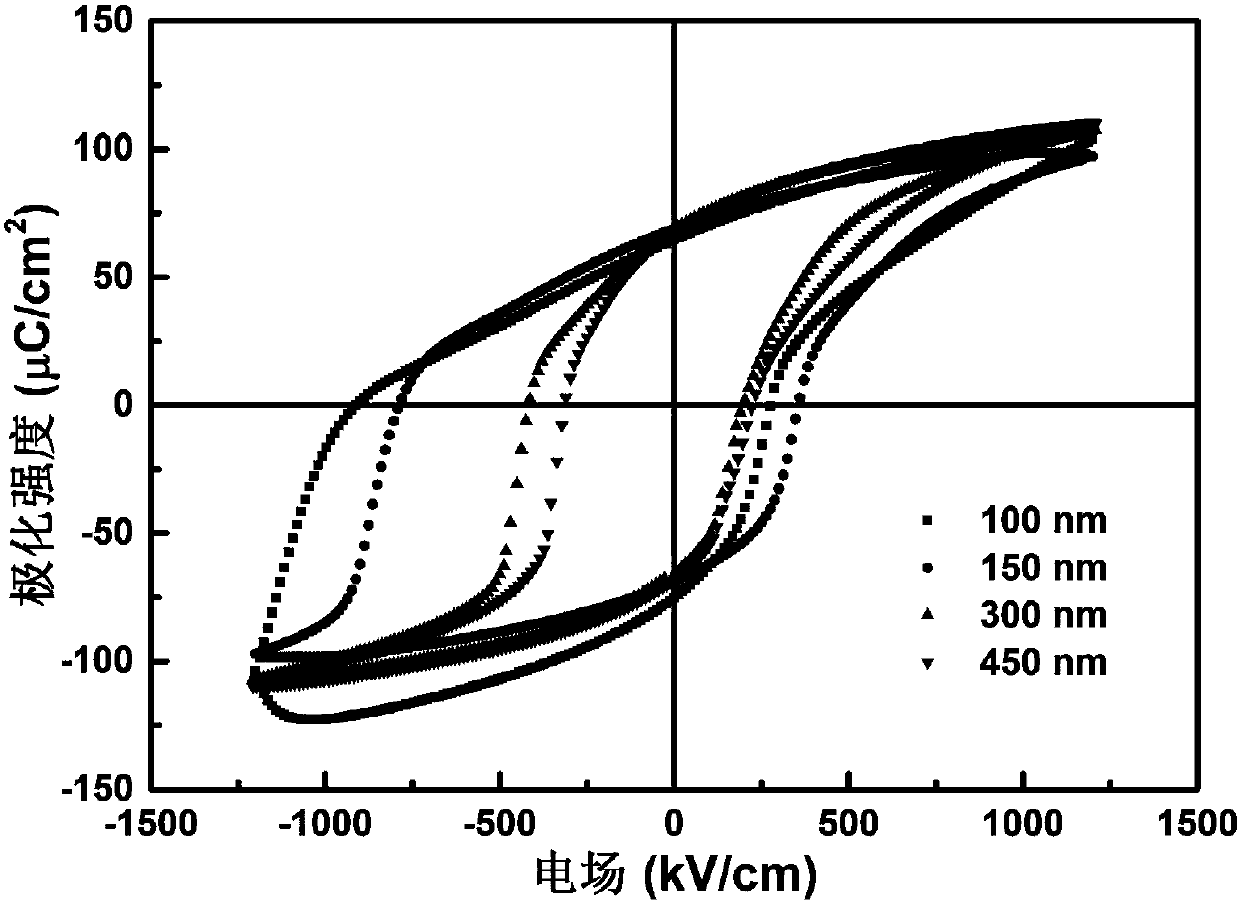
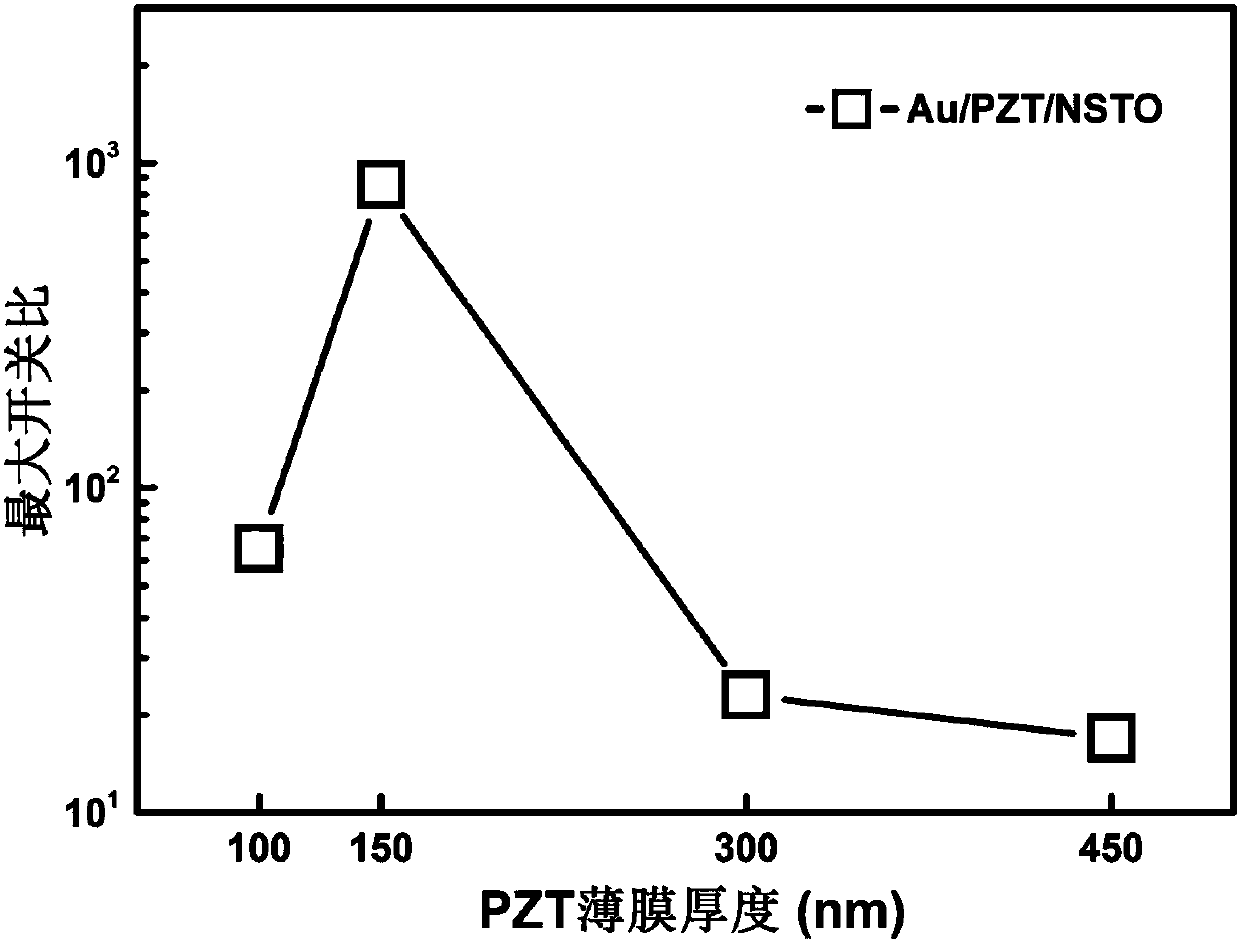
The invention provides a gold / lead zirconate titanate / niobium-doped strontium titanate ferroelectric resistive random access memory and an adjustment and control method of the switching ratio of the ferroelectric resistive random access memory. The ferroelectric resistive random access memory is composed of an upper electrode gold material, a bottom electrode and substrate niobium-doped strontiumtitanate material and a lead zirconate titanate ferroelectric material. According to the preparation method of the memory, a lead zirconate titanate thin film is deposited on a niobium-doped strontiumtitanate substrate through using a chemical solution deposition method; gold is deposited on the lead zirconate titanate thin film by using a sputtering method, so that an upper electrode can be formed. The thickness of the lead zirconate titanate ferroelectric material ranges from 100 to 450 nm; the switching ratio of the gold / lead zirconate titanate / niobium-doped strontium titanate ferroelectric resistive random access memory can vary from 17 to 846 through adjusting and controlling the thickness of the lead zirconate titanate ferroelectric material, and is improved by 50 times. With the method adopted, the switching ratio of the ferroelectric resistive random access memory can be effectively adjusted and controlled. The method has the advantages of simplicity, high feasibility and convenience in practical application.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metallic oxide resistor storage unit and low-temperature photochemical preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103346257AIncreased durabilityImprove stabilityElectrical apparatusPhysical chemistryMaterials science
The invention discloses a metallic oxide resistor storage unit and a low-temperature photochemical preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of novel non-volatile memory devices. The resistor storage unit is formed by a conducting bottom electrode, an InxGayZnzO membrane and a conducting top electrode. The preparation method of the storage unit comprises the step that the conducting bottom electrode and the conducting top electrode are prepared on a substrate and the InxGayZnzO membrane respectively by means of the vacuum coating technique. A chemical solution deposition method is adopted in preparation of the InxGayZnzO membrane, then a precursor membrane of the InxGayZnzO membrane is placed under an ultraviolet lamp, and photochemical processing of indoor temperature illumination is carried out on the precursor membrane. According to the metallic oxide resistor storage unit and the low-temperature photochemical preparation method, the InxGayZnzO resistor storage unit shows excellent resistance transformation characteristics under a voltage scanning mode, the metallic oxide resistor storage unit has good durability in resistance transformation characteristics and stability in voltage transformation, the excellent characteristics shown that the metallic oxide resistor storage unit and the low-temperature photochemical preparation method have potential application value in the technical field of non-volatile memory devices.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
High-dielectric constant thin film metal oxides on silicon wafers for capacitor applications and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS8481106B2High bulk densityImprove performanceRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingDielectricCapacitor
Owner:SBA MATERIALS
Coating conductor superconducting film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103367626AImprove performanceHigh puritySuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentPermanent superconductor devicesElectrical conductorRare earth ions
The invention discloses a coating conductor superconducting film, which consists of a YHfxBa2+xCu3Oz superconducting layer and a Y0.9Gd0.1Ba2Cu3Oy film layer which is coated on the surface of the YHfxBa2+xCu3Oz superconducting layer, wherein x is from 0.02 to 0.04. Moreover, the invention also discloses a preparation method for the superconducting film. The superconducting film disclosed by the invention has defect structures of various types; barium hafnate is introduced into a first layer; ion defects are introduced into a second layer by changing rare earth ion stoichiometric ratio; a second layer film can be induced by nano dot columnar defects of the surface of the first layer to form interface induced pinning centers, and the performance of the superconducting film is improved by the pinning centers formed by the defect structures. According to the superconducting film, a good interface is provided on the basis of the YHfxBa2+xCu3Oz superconducting layer, and thus, the homoepitaxial growth of the second layer film prepared from chemical solution deposition can be promoted to obtain the superconducting film with a biaxial structure. The thickness of the superconducting film is increased.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
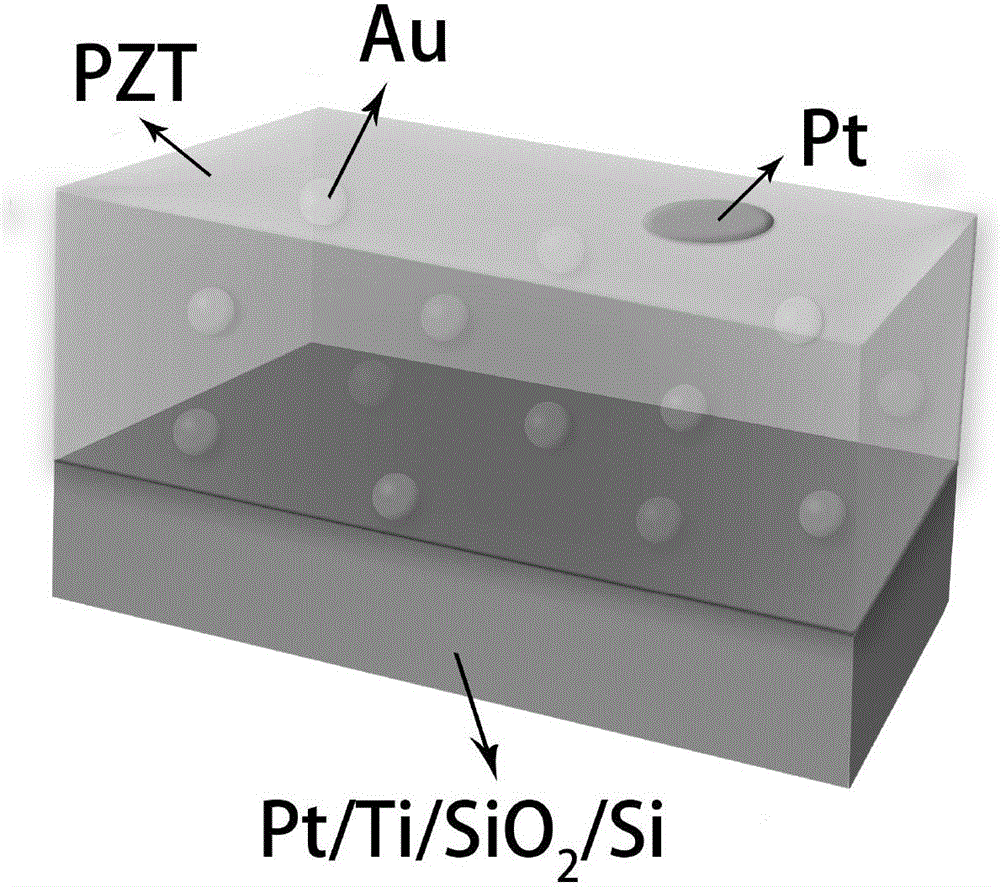
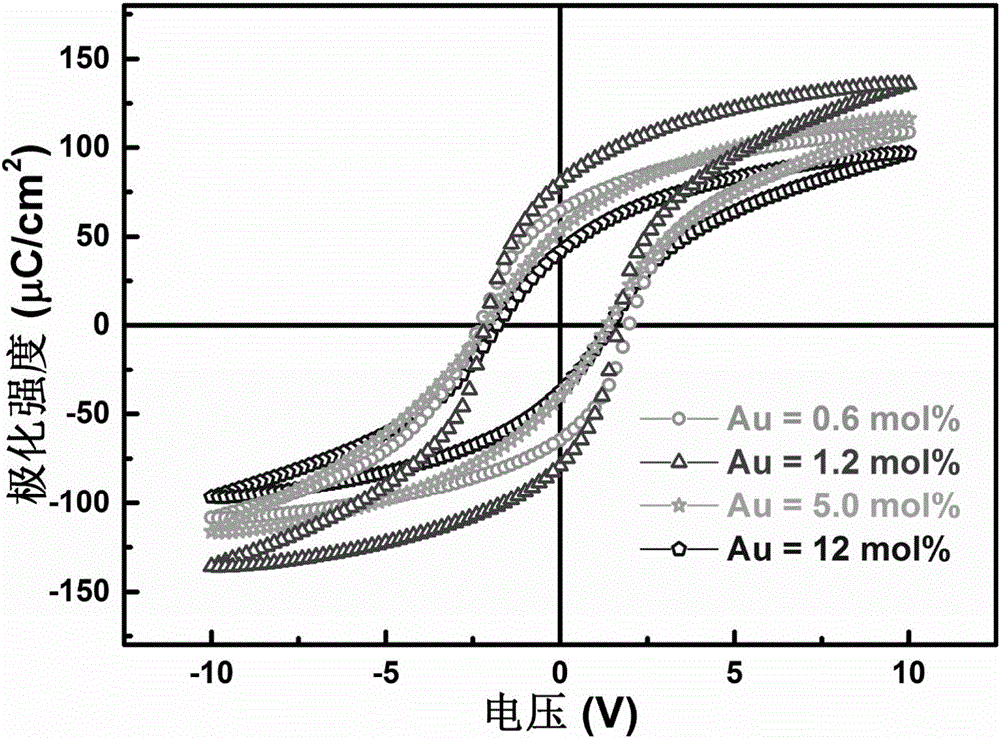
Gold-lead zirconate titanate nanocomposite ferroelectric thin film material and preparation method thereof
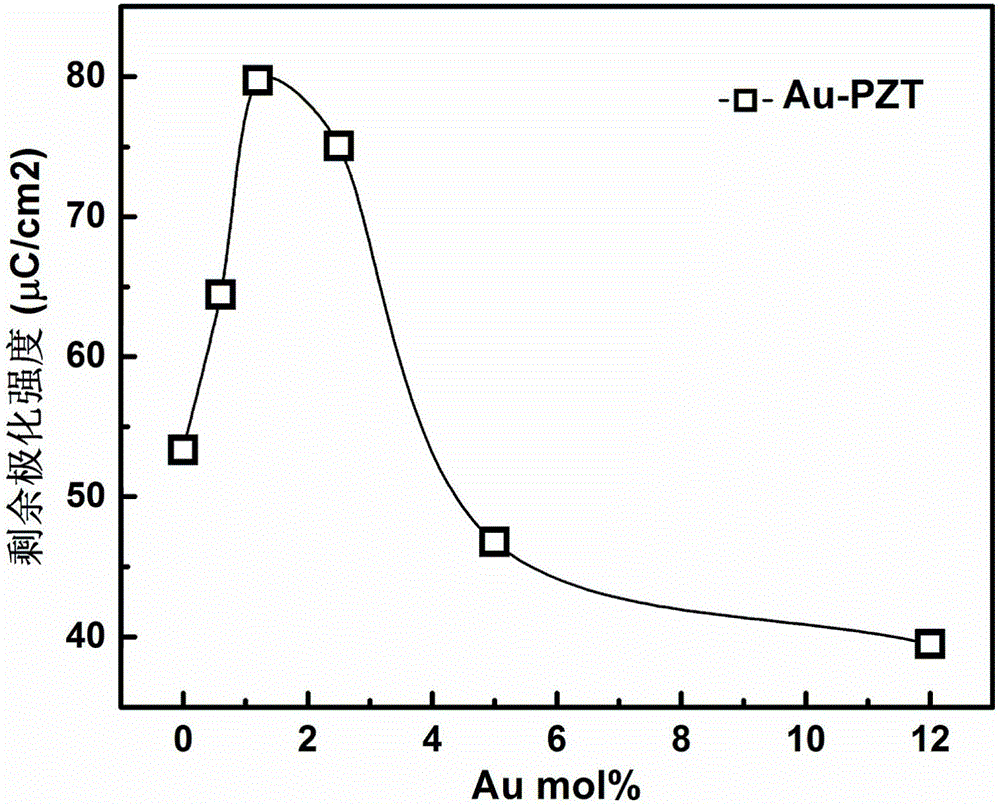
InactiveCN106783810AHigh polarizationSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead zirconate titanateFerroelectric thin films
The invention provides a gold-lead zirconate titanate nanocomposite ferroelectric thin film material and a preparation method thereof. The thin film material has a molar composition of 0.6 to 12 mol% of Au and 88 to 99.4 mol% of Pb(Zr, Ti)O3, and the ferroelectric remanent polarization of the thin film material is 30 to 80 muC / cm<2>. The material preparation method comprises steps: according to the material molar ratio requirements, lead acetate, zirconium n-propoxide, titanium propoxide and chloroauric acid are weighed; with water, isopropanol and acetic acid as a solvent, a light yellow transparent solution is obtained after thoroughly stirring; then, the obtained solution is placed on a Pt / Ti / SiO2 / Si bottom electrode material, and a chemical solution deposition method is adopted for spin coating and film forming; then, the raw material film is dried at a temperature of 120 DEG C for 10 minutes, thermal decomposition of an organic matter at a temperature of 350 DEG C for 10 minutes is carried out, the temperature rises to 600 DEG C, annealing is carried out, and after 30 minutes, air cooling is carried out; and the above process is repeated for multiple times to obtain the gold-lead zirconate titanate nanocomposite ferroelectric thin film material with a needed thickness. The thin film material has a wide application prospect in fields such as memories, super capacitors and solar photovoltaic cells.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microcontact printed thin film capacitors
The invention relates to thin film single layers, electronic components such as multilayer capacitors which utilize thin film layers, and to their methods of manufacture. Chemical solution deposition and microcontact printing of dielectric and electrode layers are disclosed. High permittivity BaTiO3 multilayer thin film capacitors are prepared on Ni foil substrates by microcontact printing and by chemical solution deposition. Multilayer capacitors with BaTiO3 dielectric layers and LaNiO3 internal electrodes are prepared, enabling dielectric layer thicknesses of 1 μm or less. Microcontact printing of precursor solutions of the dielectric and electrode layers is used.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
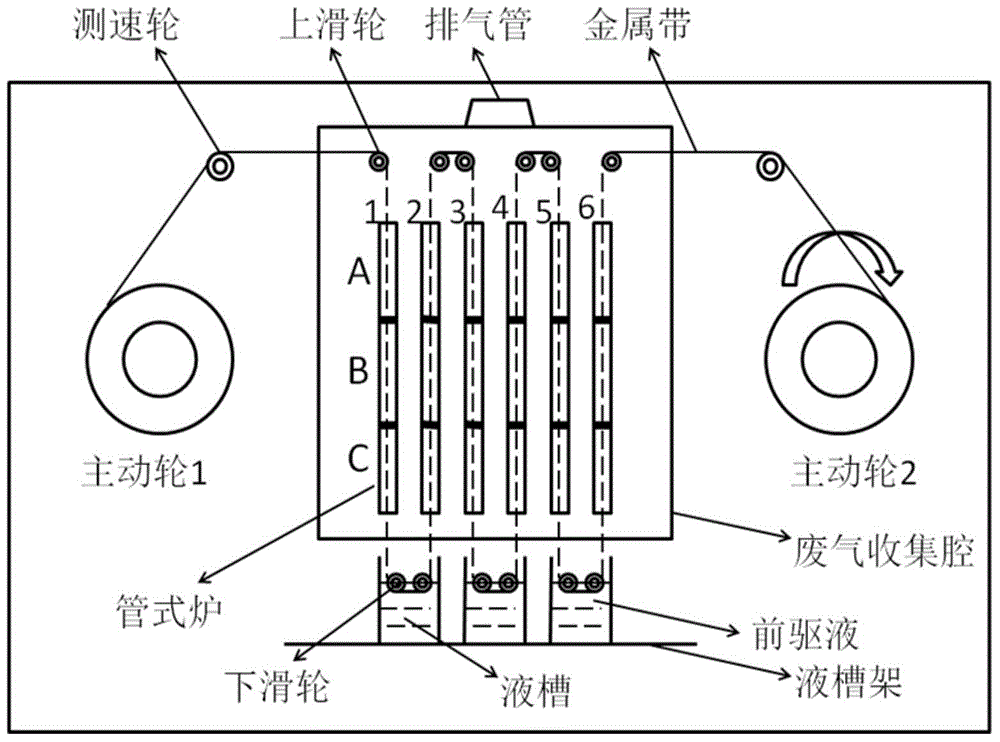
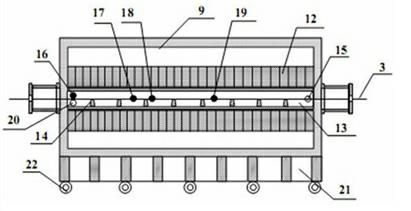
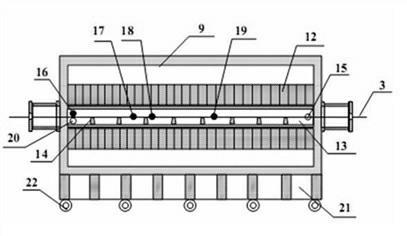
Heat treatment furnace for dynamically and continuously preparing high-temperature superconductive strip with fluorine-free chemical solution deposition method
InactiveCN102135377ARealize dynamic continuous preparationGuaranteed stabilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsFurnace typesCarbide siliconThermocouple device
The invention discloses a heat treatment furnace for dynamically and continuously preparing a high-temperature superconductive strip with a fluorine-free chemical solution deposition method. The continuous heat treatment furnace (9) has the structure that a hearth (12) comprises a silicon carbide pipe with a thermocouple; a high-temperature-resistant stainless steel furnace pipe (13) is installed in the hearth, and air inlets (16), (17), (18) and (19) and exhaust openings (15) and (20) are arranged on the high-temperature-resistant stainless steel furnace pipe; brackets (14) with equal distance are installed in the furnace pipe (13); a bracket (21) is installed under the furnace body; and a pulley (22) is installed under the bracket (21). The invention can simultaneously realize different heat treatment processes controlled by various atmosphere subareas and has high productivity. The equipment disclosed by the invention is used for preparing the strip on the basis of the fluorine-free chemical solution deposition method under a non-vacuum condition, has the advantages of no need of matched facilities for fluorine exhaust, low cost and simple process and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Glass flux assisted sintering of chemical solution deposited thin dielectric films
A method of making dense dielectrics layers via chemical solution deposition by adding inorganic glass fluxed material to high dielectric constant compositions, depositing the resultant mixture onto a substrate and annealing the substrate at temperatures between the softening point of the inorganic glass flux and the melting point of the substrate. A method of making a capacitor comprising a dense dielectric layer.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
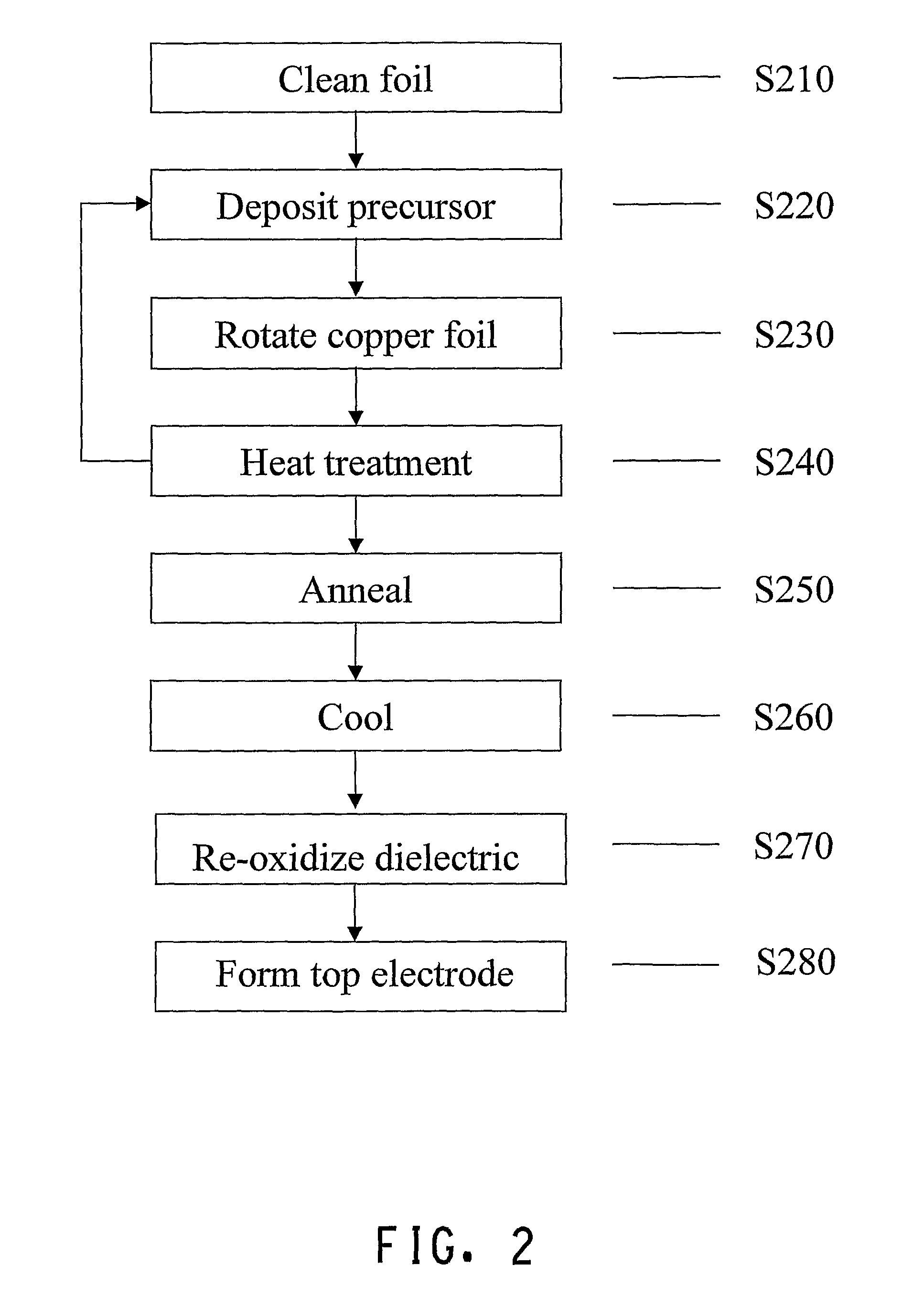
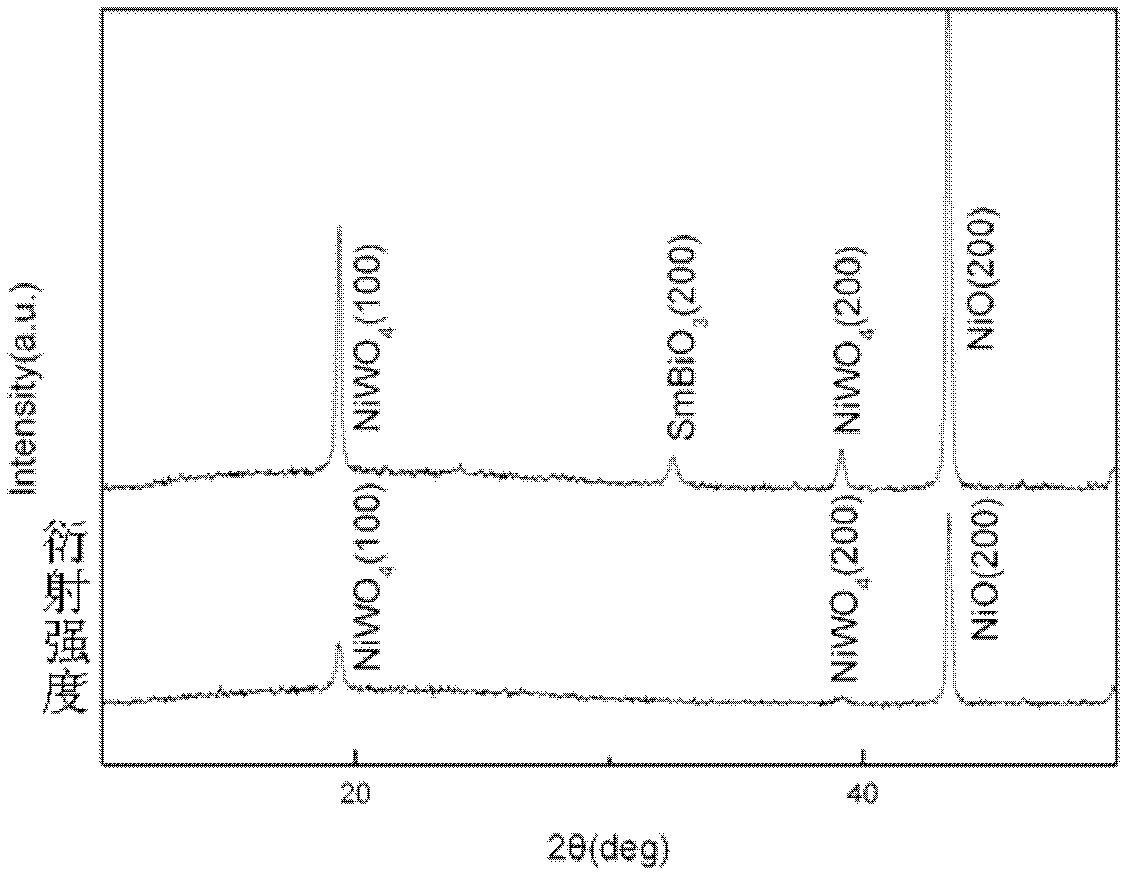
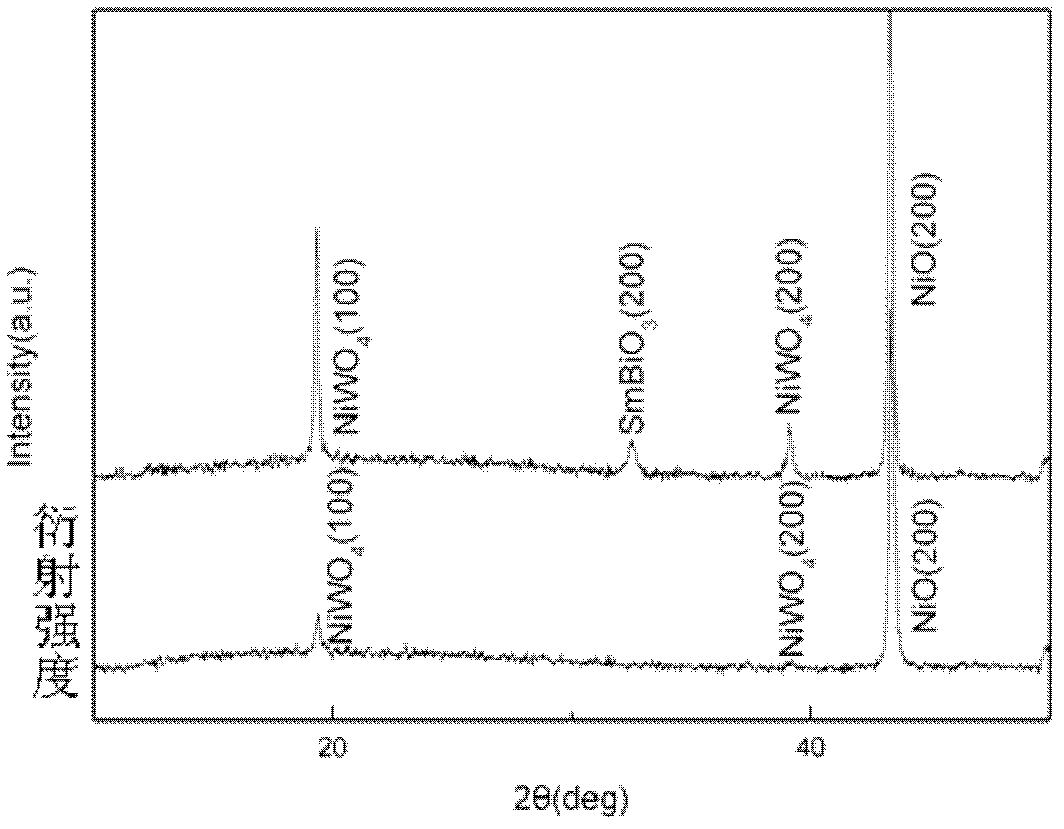
Method for preparing NiO/SmBiO3 composite buffer layer thin film of high-temperature super-conduction coating conductor on biaxially-textured NiW alloy substrate
InactiveCN102683572AActive promotionReduce the temperatureSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductorNitrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing a NiO / SmBiO3 composite buffer layer thin film of a high-temperature super-conduction coating conductor on a biaxially-textured NiW alloy substrate. A preparation method of a composite buffer layer comprises the following steps of: a, surface corrosion modification of a NiW alloy (200) substrate; b, oxidation heat treatment of a NiO buffer layer; c, preparation of a SmBiO3 buffer layer colloid; d, coating of a SmBiO3 buffer layer; and e, sintering and phase forming of the SmBiO3 buffer layer. According to the method, the NiO buffer layer is prepared by using an auto-oxidation extension preparation method which is low in manufacturing cost and easy in process, a high-quality NiO (200) buffer layer thin film is easy to manufacture, thickness is easy to control, and an effect of a coating conductor buffer layer can be effectively achieved. The SmBiO3 buffer layer which grows on the NiO buffer layer is prepared in air by using a chemical solution deposition method in which nitrate serves as a precursor, and the method is low in cost and applicable to large-scale deposition. A preparation process of the composite buffer layer, particularly the SmBiO3 buffer layer, breaks shackles of other foreign coating conductor composite buffer layer preparation processes and plays a positive promotion role in research and application process of the second-generation high-temperature super-conduction coating conductor of China.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
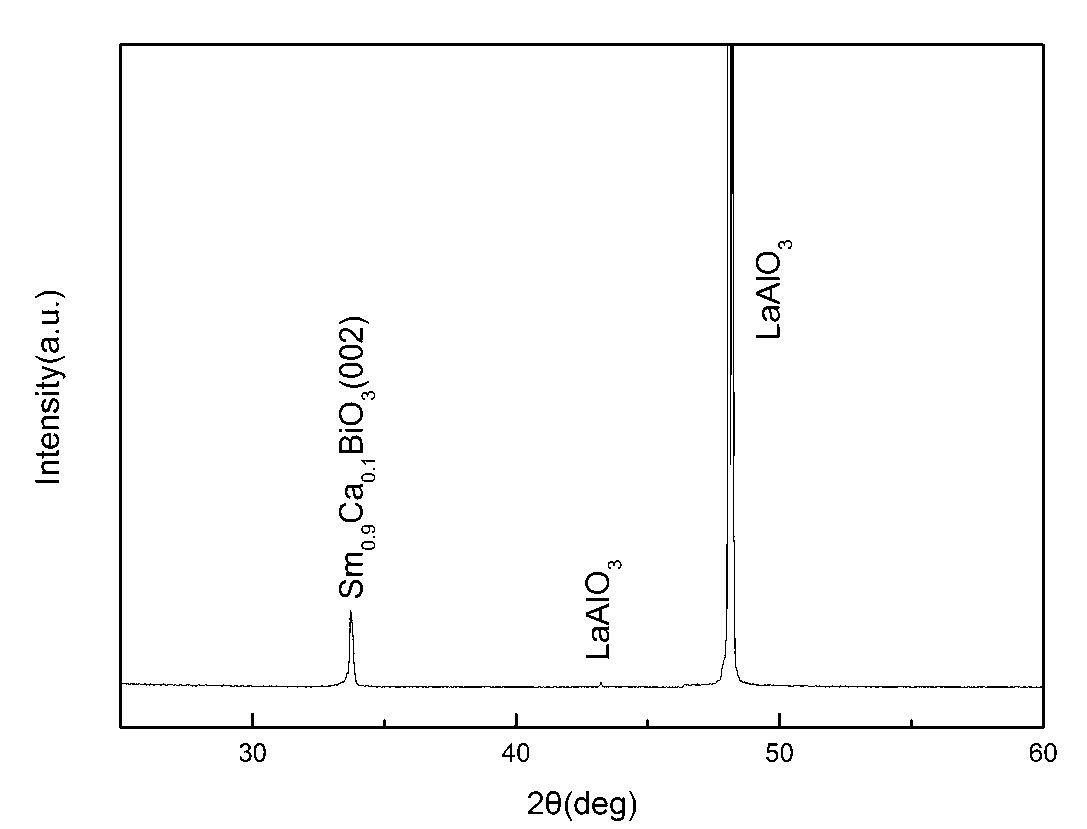
Sm1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of high-temperature superconductivity coated conductor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102701729ALow costSimple preparation processElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
The invention discloses a Sm1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of a high-temperature superconductivity coated conductor and a preparation method thereof. After Ca replaces Sm of a SmBiO3 buffering layer of the high-temperature superconductivity coated conductor, the element environment and lattice parameters of the SmBiO3 buffering layer are finely adjusted, accordingly the situation that lattices of the SmBiO3 buffering layer and an REBCO superconductivity layer are mismatched with each other is improved, and a series of novel Sm1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of the high-temperature superconductivity coated conductor is obtained, wherein the x is greater than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 0.4. In addition, the buffering layer can extend and grow in the air with the temperature of 800 DEG C and is compact in structure and flat in surface, and the structural stability is kept in the follow-up preparation process of the superconductivity layer of the high-temperature superconductivity coated conductor. The method adopts a chemical solution sedimentation process using nitrate as a predecessor to perform preparation in the air and has the advantages of being low in cost, suitable for large-scale sedimentation and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
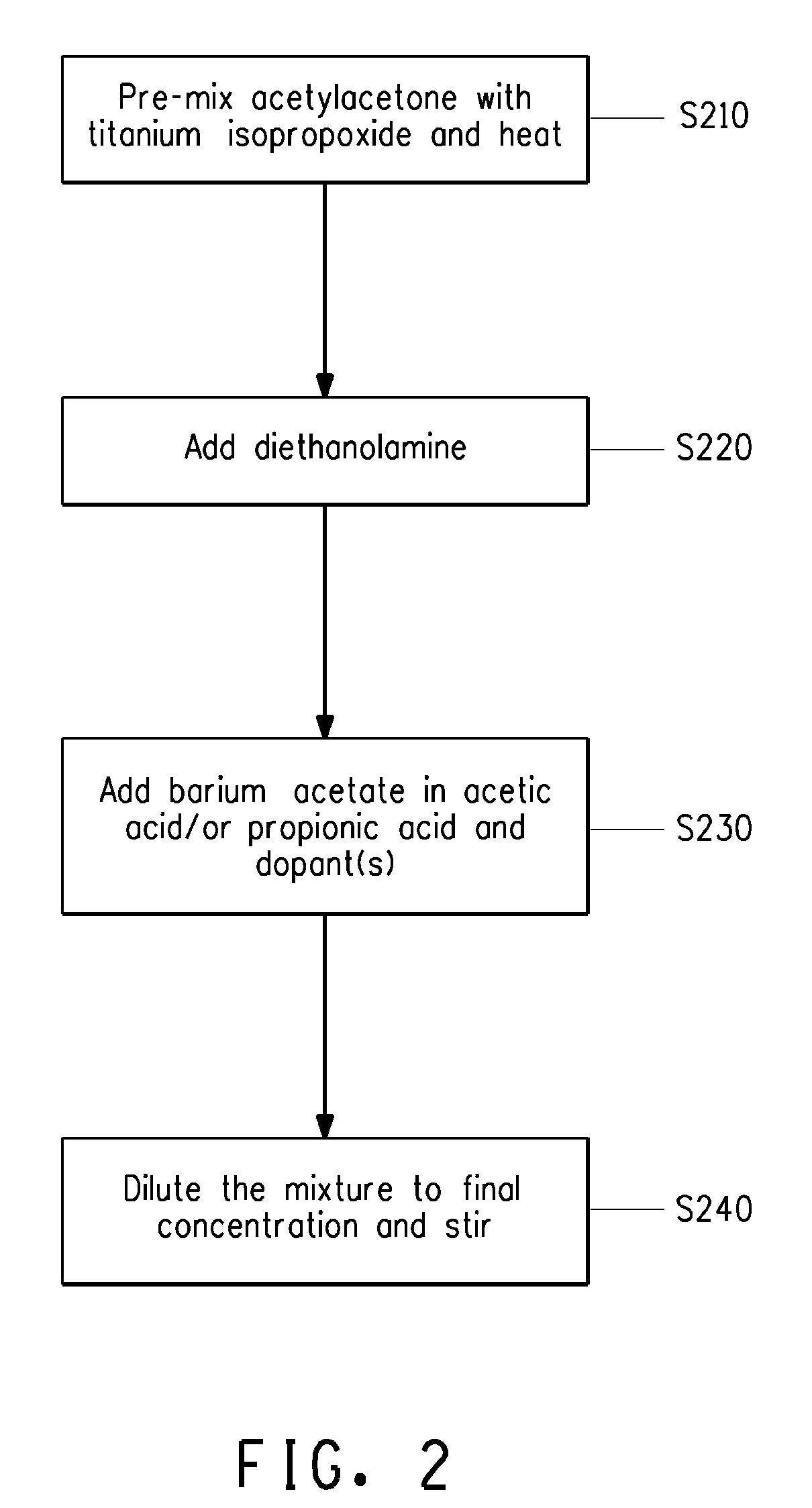
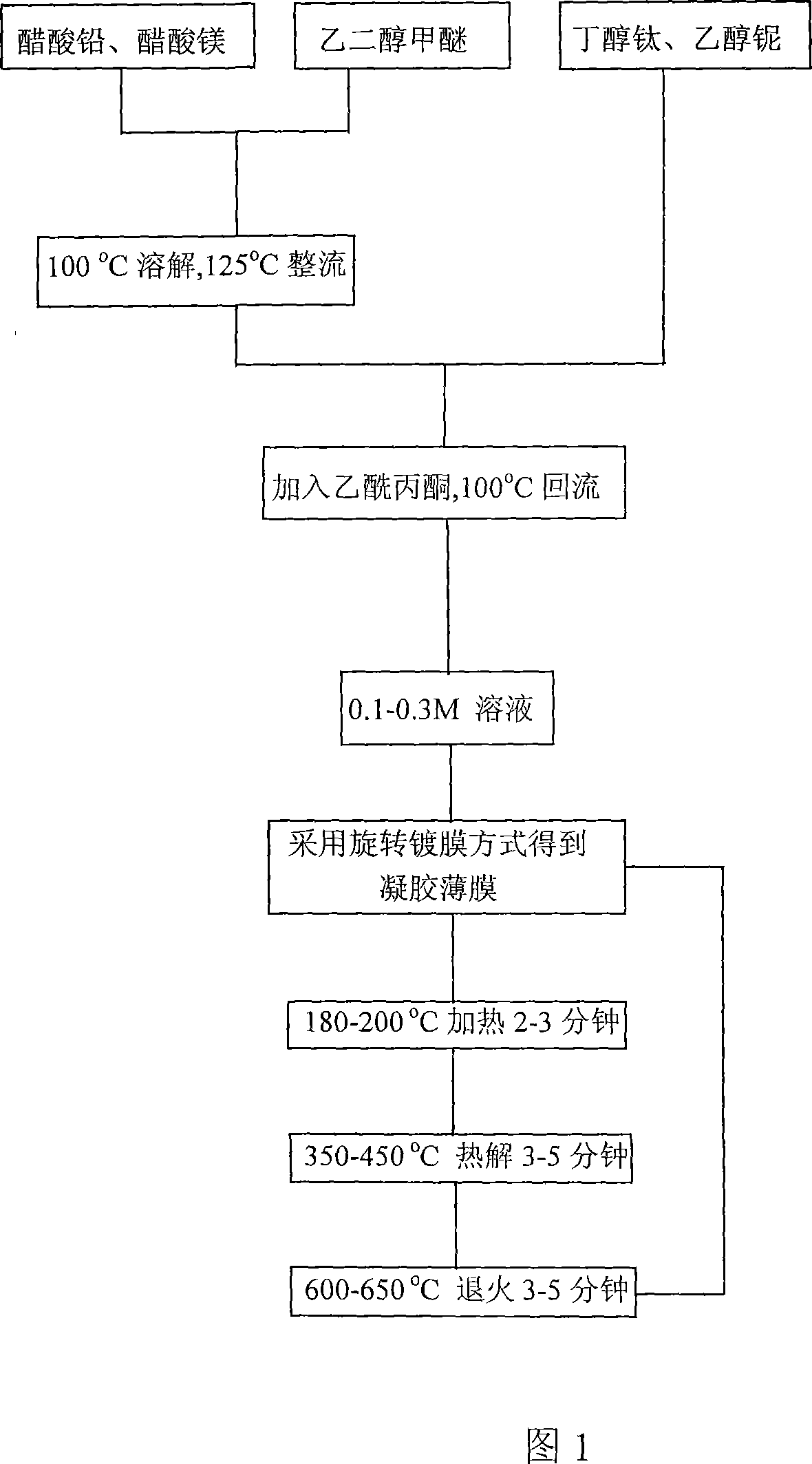
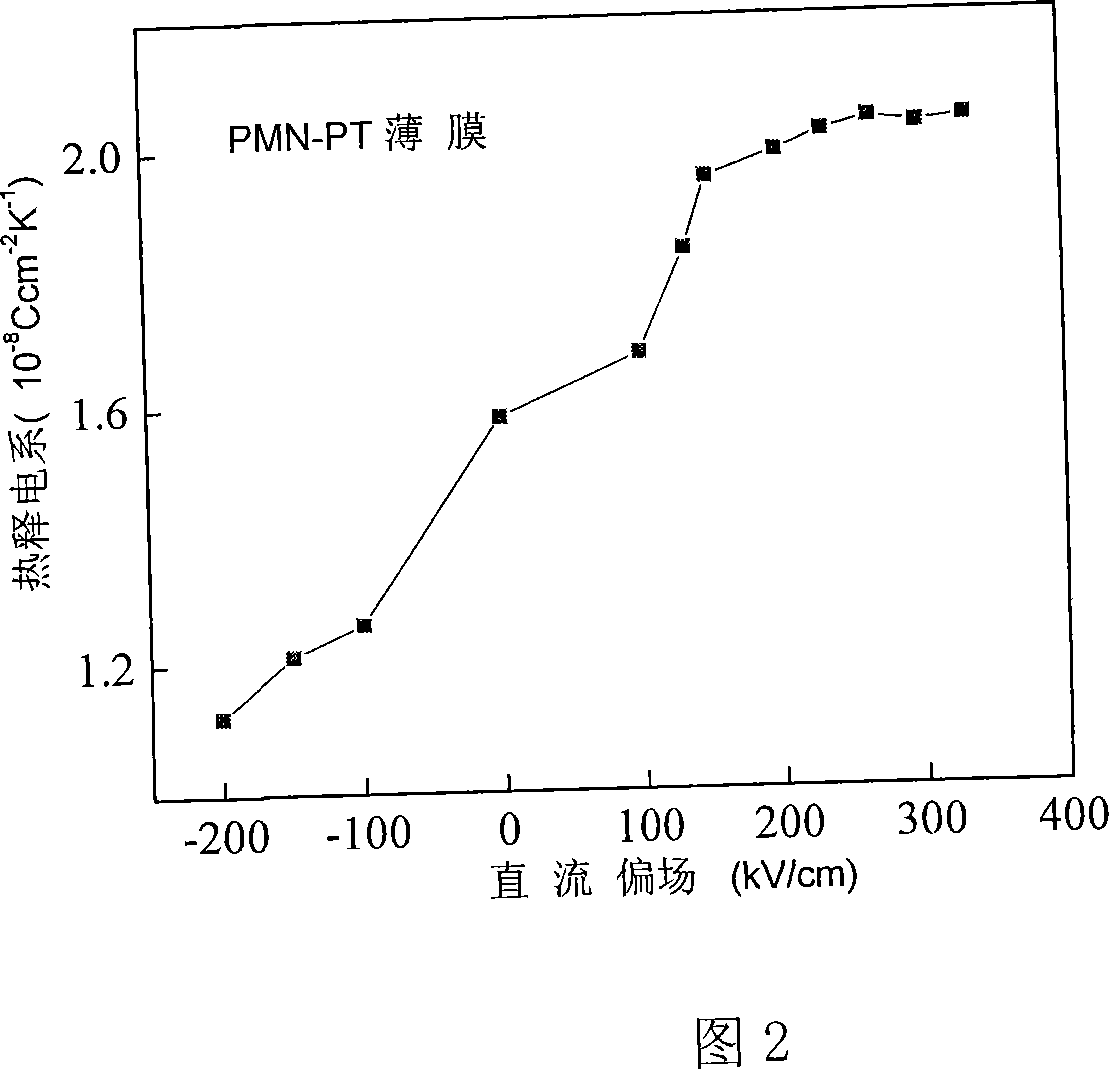
Making method for niobium-magnesium acid lead-Ti acid lead iron electric thin film with self-polarization effect
ActiveCN101170158ASelf-polarization effectSelf-heating and discharging characteristicsThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changePyrometry using electric radation detectorsNiobiumLead titanate
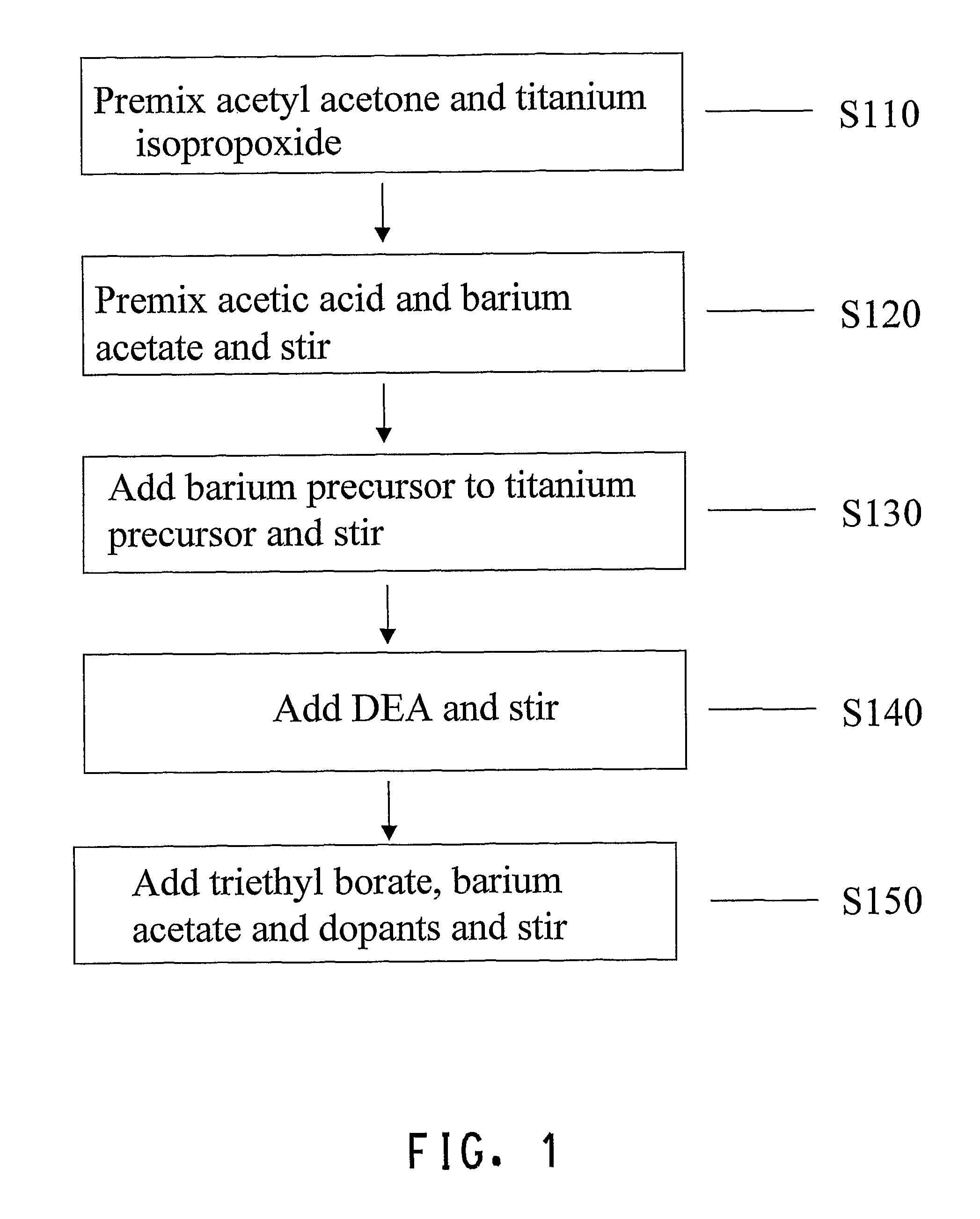
The invention discloses a method of preparing a lead magnesio-niobate (PMN)-lead titanate (PZT) ferroelectric film with self-polarizing effect. The method adopts the chemical solution deposition method and comprises the steps of: preparing solution consisting of lead acetate, magnesium acetate, niobium alcoholate, normal butanol titanium, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and acetylacetone to 0.1-0.3M precursor solution; adopting the rotary filming mode to obtain a gel film and performing heat treatment in subsection in short annealing and forming film material; repeating the course until obtaining the film material with ideal thickness. The invention has the advantages of simple and convenient process operation, lower cost, and large area even film preparation. The pyroelectricity coefficient of the film obtained by the invention on LaNiO3 / Pt / Ti / SiO2 / Si chip can reach 1.6 multiplies by 10 <-8> Ccm <-2>K<-1> with no deflecting field applied by test.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
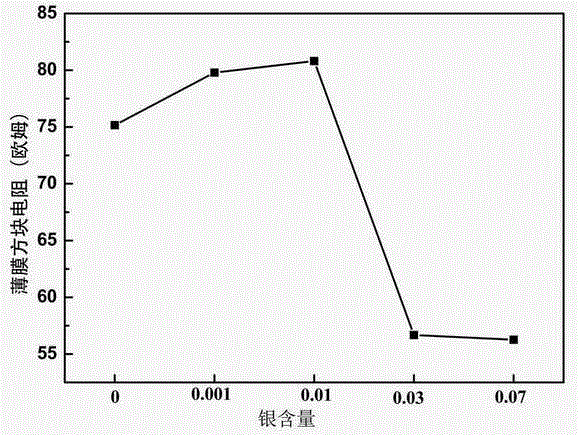
Preparation method of composite conductive silver-lanthanum nickelate thin-film material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite conductive silver-lanthanum nickelate thin-film material. The preparation method includes the following steps that 1, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether is used as a solvent, and lanthanum nitrate, nickel acetate and silver nitrate are used as a solute to prepare a green transparent solution; 2, the green transparent solution prepared in the step 1 is dropwise added to a substrate for spin coating, spin coating is firstly performed at the speed of 1000 r / min for 9 seconds, and then spin coating is performed at the speed of 4000 r / min for 50 seconds to obtain a precursor wet membrane; 3, the precursor wet membrane obtained in the step 2 is put in a muffle furnace, and annealing treatment is performed at the temperature of 750 DEG for 5 minutes; 4, the steps 2 and 3 are repeated for multiple times to obtain the composite conductive silver-lanthanum nickelate thin-film material with required thickness, wherein the annealing time of the last time is 30 minutes. The preparation method adopts a chemical solution deposition method to effectively improve the electrical conductivity of the composite conductive silver-lanthanum nickelate thin-film material and has the advantages of being simple in process, low in cost, uniform in composition, capable of forming a large-area film and the like.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for preparing lanthanum titanate thin film through sol coating method
InactiveCN106868477AExtended annealing timeLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPre treatmentSilicon
The invention discloses a method for preparing lanthanum titanate film by sol coating method. The invention can well improve its affinity for conductive sol by pretreating the surface of the silicon substrate, so that the conductive sol is more uniform during the spraying process. are distributed on the surface of the silicon substrate, and the lanthanum titanate conductive thin film material prepared by the chemical solution deposition method in the present invention effectively improves the conductivity of the lanthanum titanate conductive thin film material, and has the advantages of simple process.
Owner:SUZHOU NANER MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
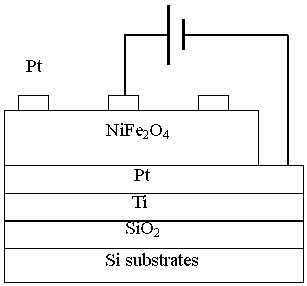
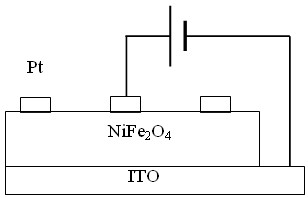
Resistance-type random storage component and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102185107AExcellent transformation characteristicsImprove featuresSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesContinuous scanningElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a resistance-type storage component and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of a novel nonvolatile memory. The resistance-type random storage component is composed of a conducting substrate, a NiFe2O4 film and a conducting top electrode. According to the preparation method, a vacuum coating technology is used to plate a conducting top electrode on the surface of a Nife2O4 film to prepare the resistance-type storage component. In the preparation method of the NiFe2O4 film, chemical solution deposition process or pulse laser deposition process and the like is used. The Nife2O4 resistance-type random storage component disclosed by the invention shows excellent high-low resistance state variation characteristic in a voltage continuous scanning mode, has stable variable voltage of high-low resistance state and excellent maintaining characteristic and continuous cycle reading and writing capacity. The excellent characteristics show that theresistance-type storage component has potential application value in the technical field of nonvolatile memory.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
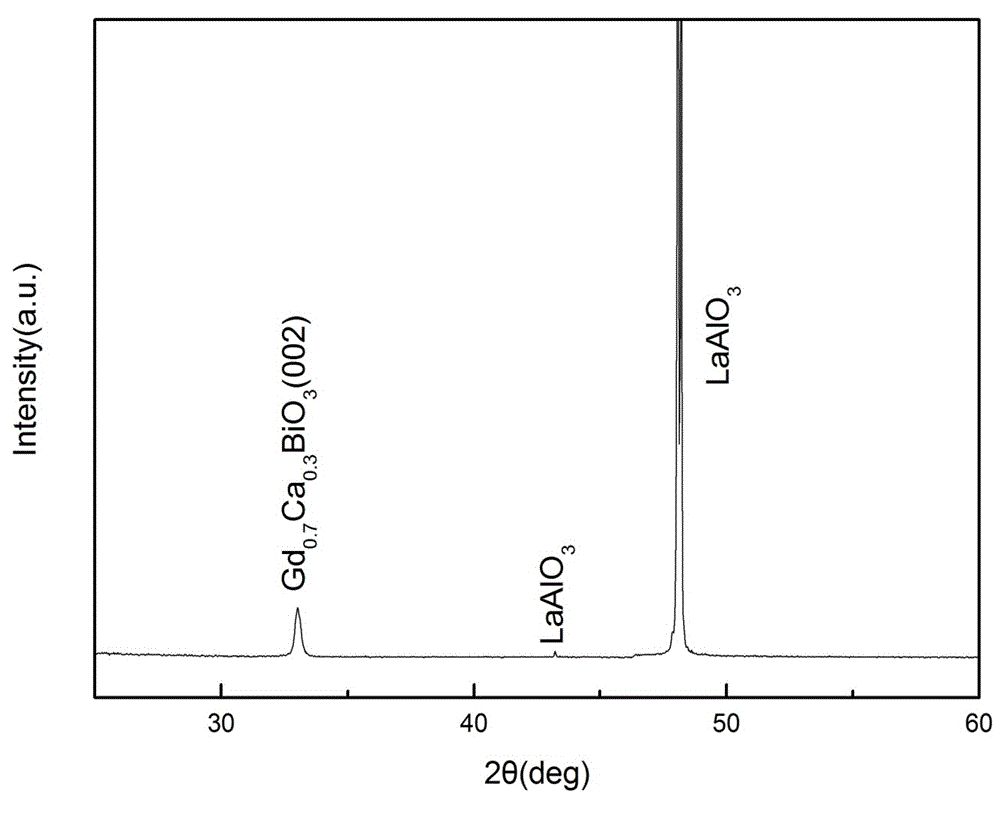
Gd1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of high temperature superconducting coated conductor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102723141ACompact structureFlat surfaceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectrical conductorNitrate
The invention discloses a Gd1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of a high temperature superconducting coated conductor. The buffering layer is characterized in that the Gd1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of the high temperature superconducting coated conductor epitaxially grows to generate an oxide Gd1-xCaxBiO3 solid solution through heat treatment after Gd in the Gd1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of the high temperature superconducting coated conductor is replaced with Ca, wherein x is not less than 0.1 and not more than 0.4. By using the Gd1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of the high temperature superconducting coated conductor disclosed by the invention, after Gd in the Gd1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer of the high temperature superconducting coated conductor is replaced with Ca, an element environment and crystal lattice parameters of the GdBiO3 buffering layer are finely adjusted and then the lattice mismatch situation of the GdBiO3 buffering layer and a REBCO superconducting layer is adjusted; the buffering layer can epitaxially grow in the air at about 810 DEG C and has compact structure and smooth surface; and the structure of the buffering layer is kept stable in the follow-up preparing process of a superconducting layer of a high temperature superconducting coated conductor. The invention provides a preparation method of the Gd1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer; in the method, the Gd1-xCaxBiO3 buffering layer is prepared in the air by using a chemical solution deposition method with nitrates as a precursor; therefore, the preparation method has the advantages of low cost, easiness in operation control, suitability for large-scale deposition and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com