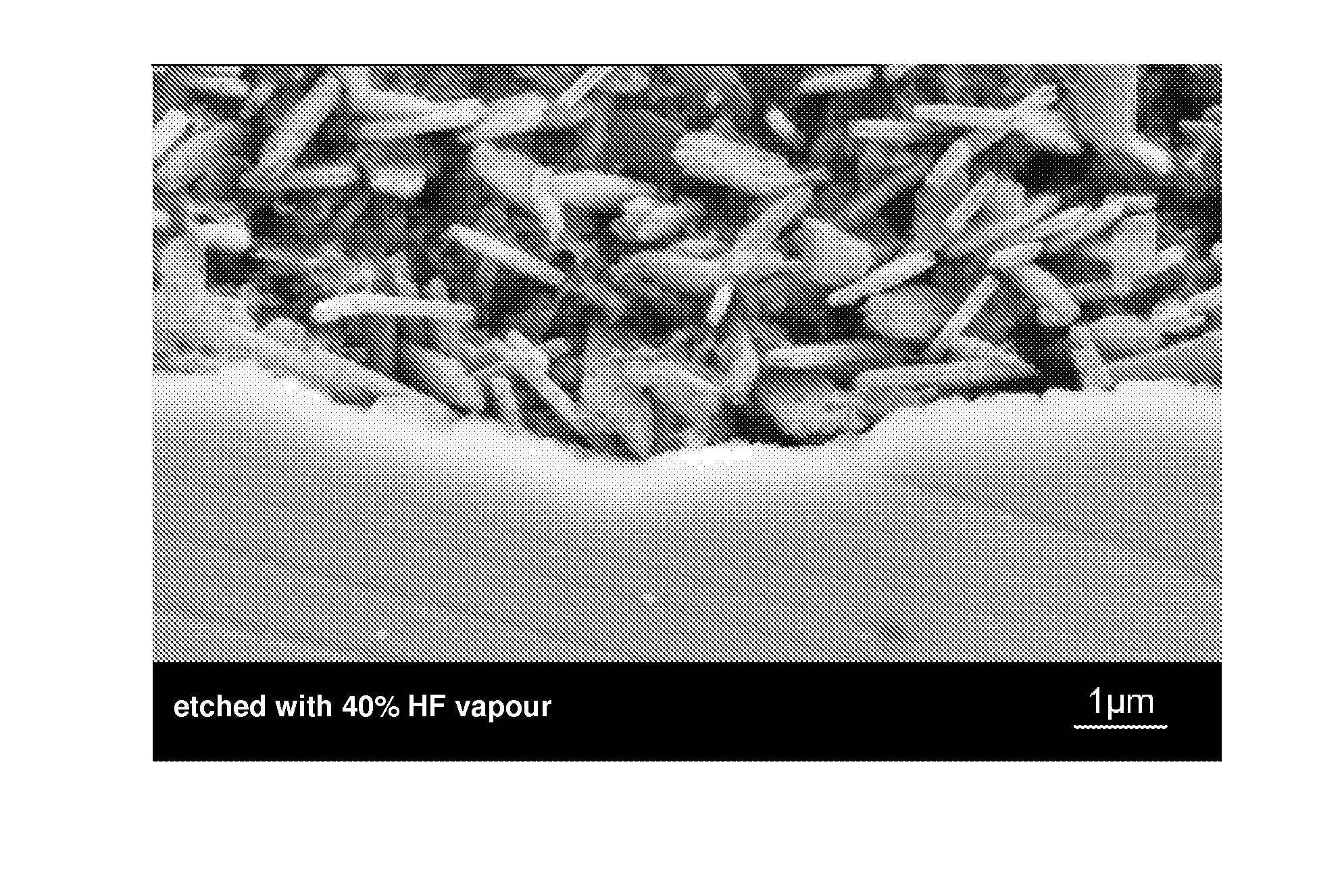
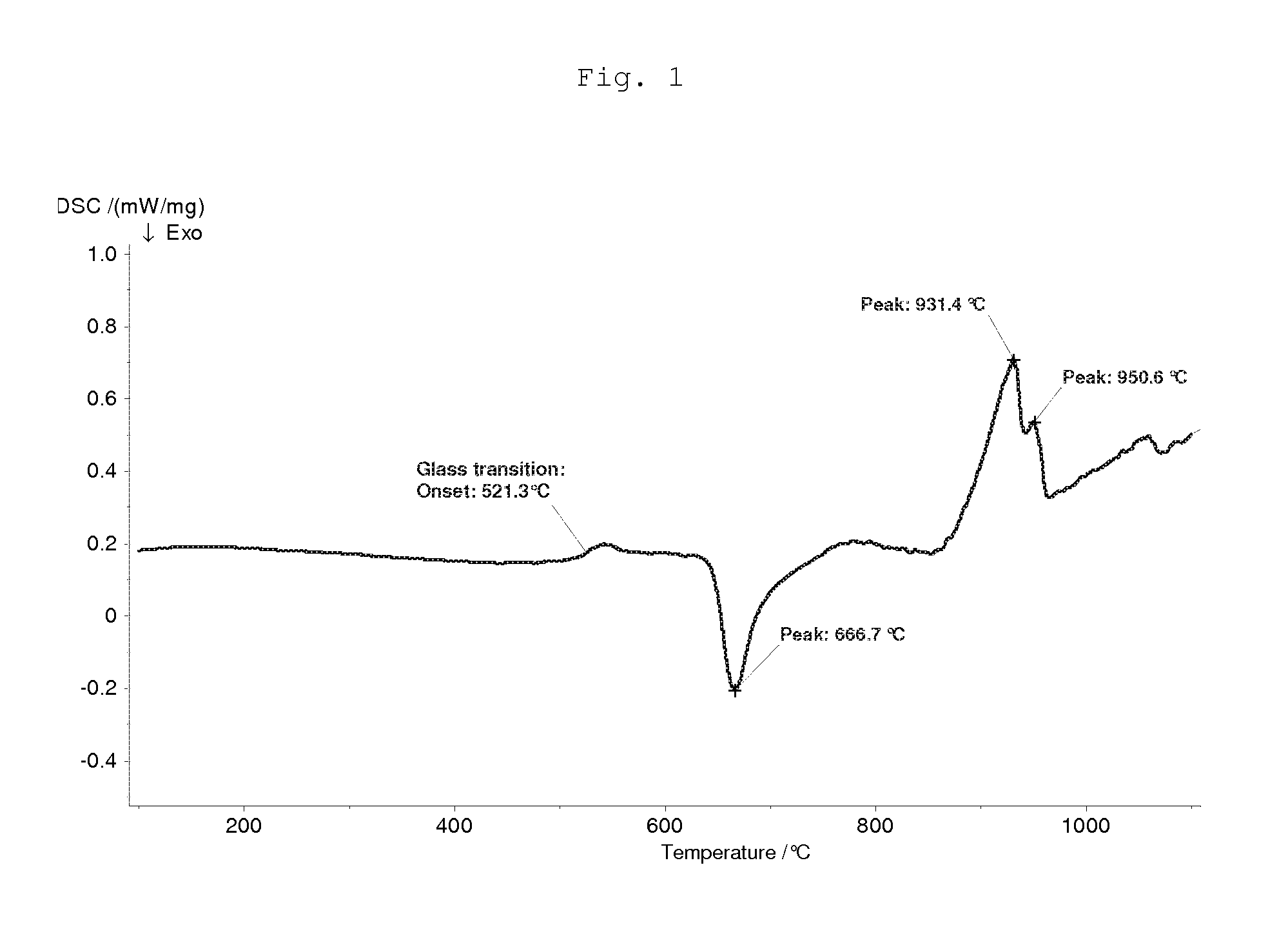
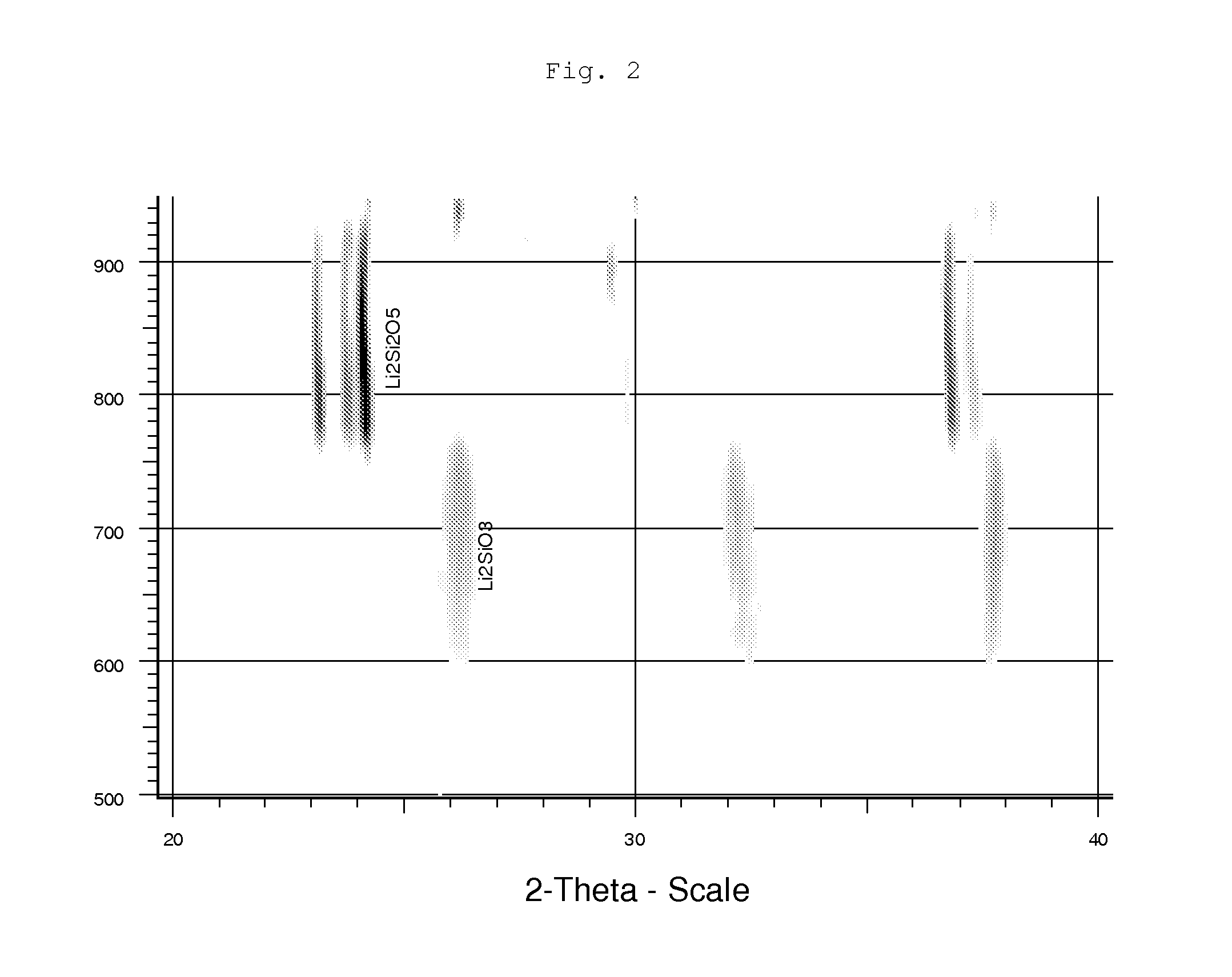
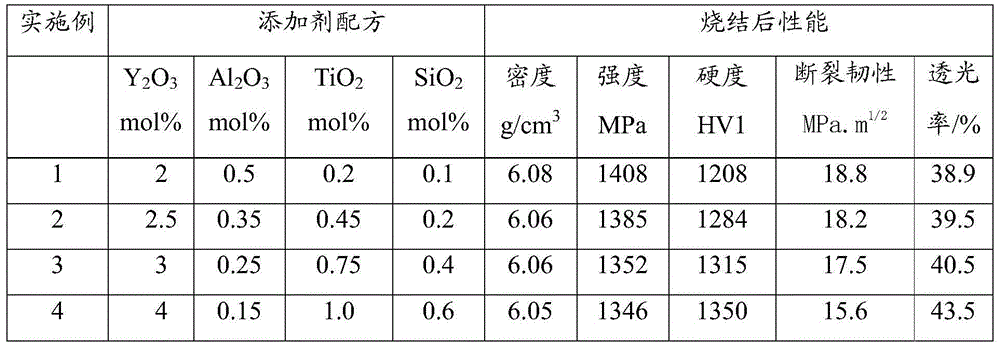
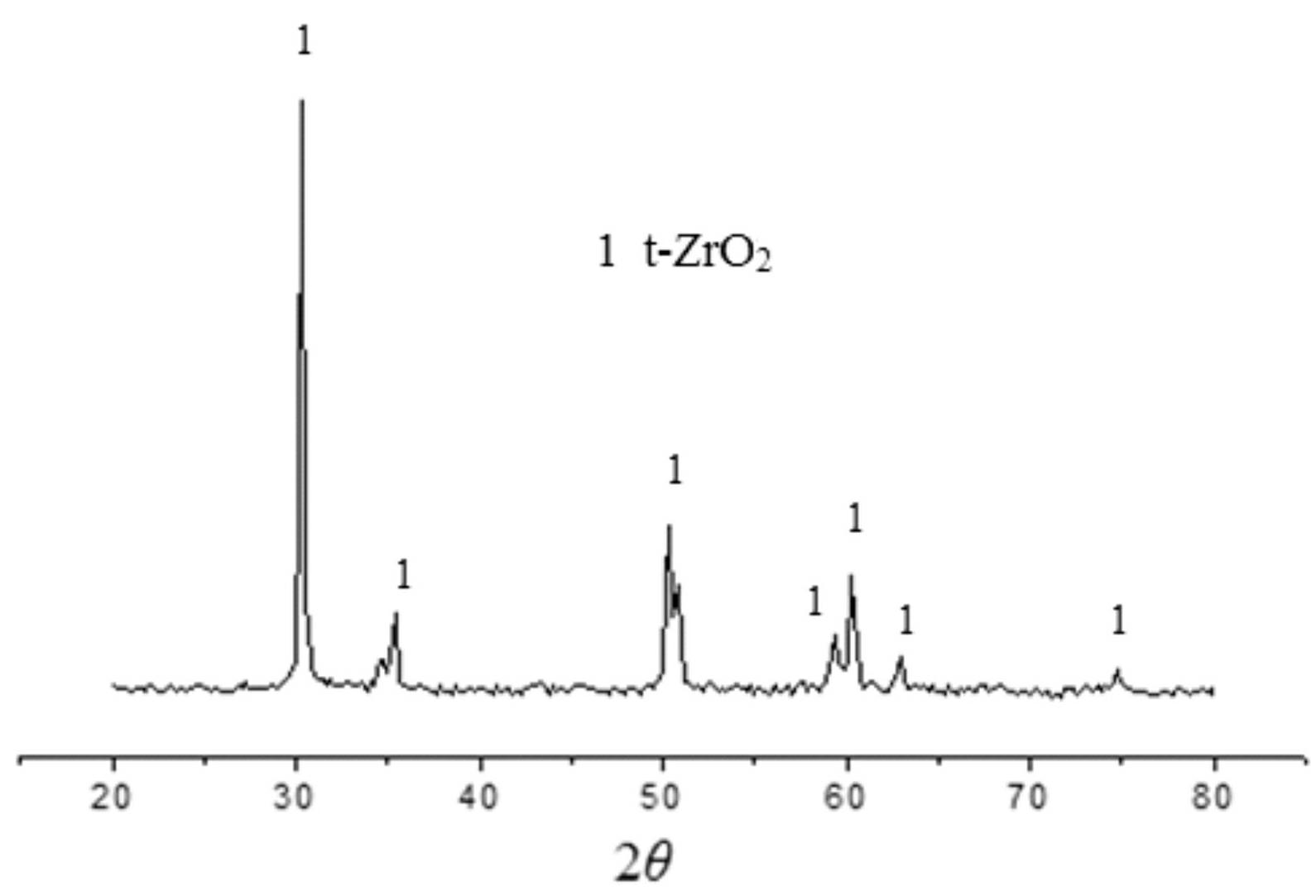
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1369 results about "Zirconia ceramic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zirconia ceramics are ceramic materials made from zirconium oxide (ZrO2) with high chemical inertness and very high thermal expansion as well as a very high resistance to wear and to crack propagation. It has the highest toughness and strength at room temperature of all the advanced ceramic materials.
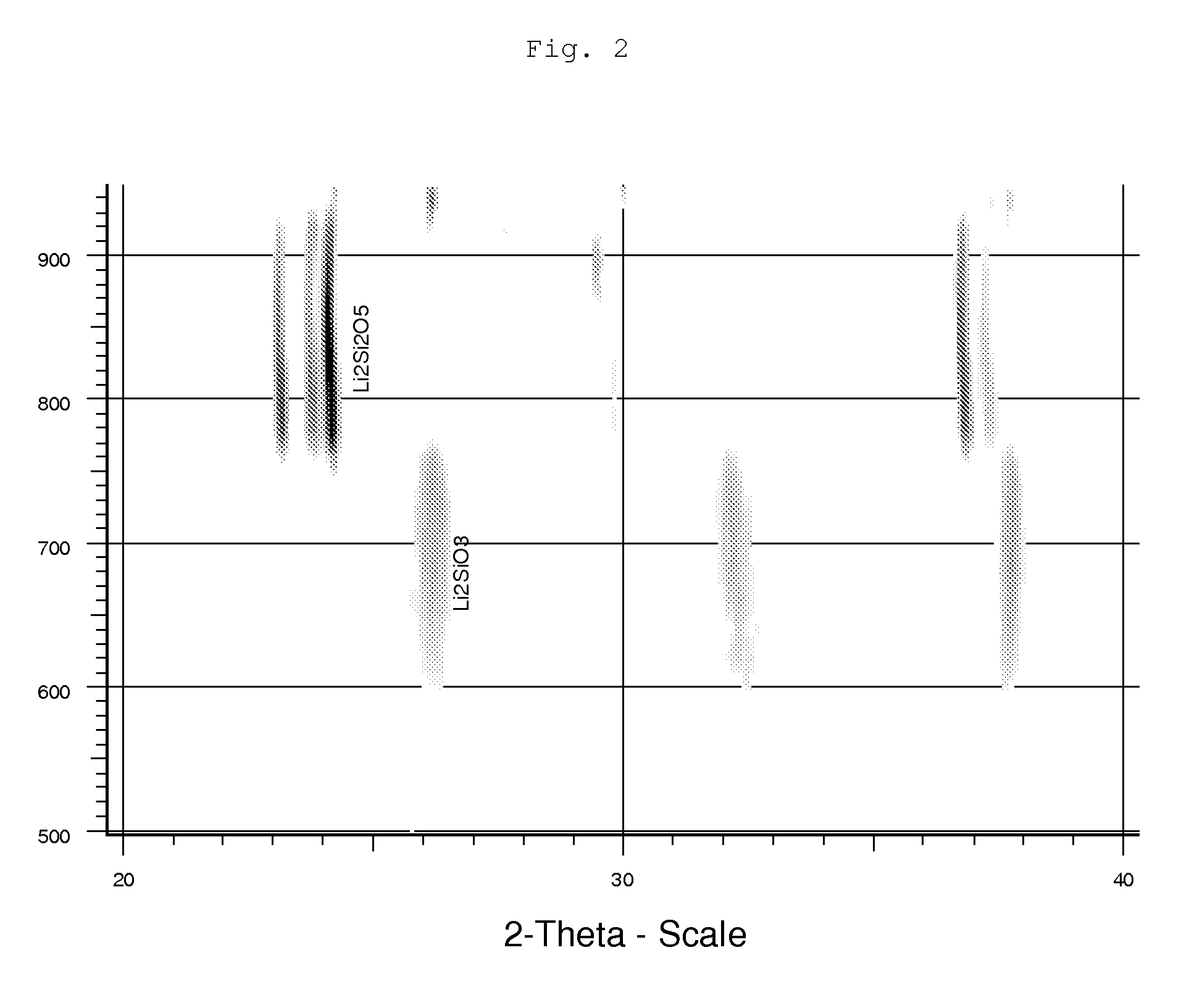
Lithium Silicate Glass Ceramic and Glass With ZrO2 Content
ActiveUS20110256409A1Substantial deterioration in translucencyInhibition formationPretreated surfacesTooth crownsLithiumSolid Bond
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Preparation method for zirconia ceramic rear cover of mobile phone
The invention provides a preparation method for a zirconia ceramic rear cover of a mobile phone. The zirconia ceramic rear cover of the mobile phone prepared in the invention has the characteristics of high strength, high toughness, high size precision, etc. The rear cover with a maximum size is applicable to a mobile phone with a size of 6 inches, and the thickness of the rear cover may be 0.15 to 0.8 mm. Moreover, the zirconia ceramic rear cover may be in a flat shape, a 2D shape, a 3D shape or other complex shapes in virtue of different shaping dies, so requirements of mobile phones of different specifications can be met. The preparation method for the zirconia ceramic rear cover of the mobile phone has high production efficiency and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:NANCHONG THREE CIRCLE ELECTRONICS +1
Dental complex color machinable zirconia ceramics and preparation method
InactiveCN102285795AHigh simulationFull aestheticsImpression capsDentistry preparationsAll ceramicAbutment
A dental multi-color machinable zirconia ceramic and its preparation method. The zirconia ceramic has the characteristics of translucence and color gradient, and contains more than five porcelain layers with the same hue and different saturation. The lightness gradually decreases from the top of the ceramic to the bottom layer, and the saturation The density gradually increases, and the color transitions naturally with a sense of hierarchy; the pre-sintered porous ceramic body of the zirconia ceramic is easy to cut and shape, and can be used to make personalized and beautiful dental zirconia all-ceramic restorations through the CAD / CAM system, which is conducive to preserving the abutment teeth. Improve the repair success rate. The preparation method of the dental complex color machinable zirconia ceramic is simple, effective and easy to popularize.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY +1
Lithium silicate glass ceramic and glass with ZrO2 content
ActiveUS20120248642A1Substantial deterioration in translucencyInhibition formationDental implantsWristbandsLithiumSolid Bond
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Alumina/zirconia ceramics and method of producing the same
InactiveUS7148167B2Excellent abrasionHigh hardnessCeramic shaping apparatusClaywaresHigh fractureHardness
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Thermal barrier coatings with improved impact and erosion resistance
InactiveUS6869703B1Increase impactIncrease resistanceMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingPorosityBond coat
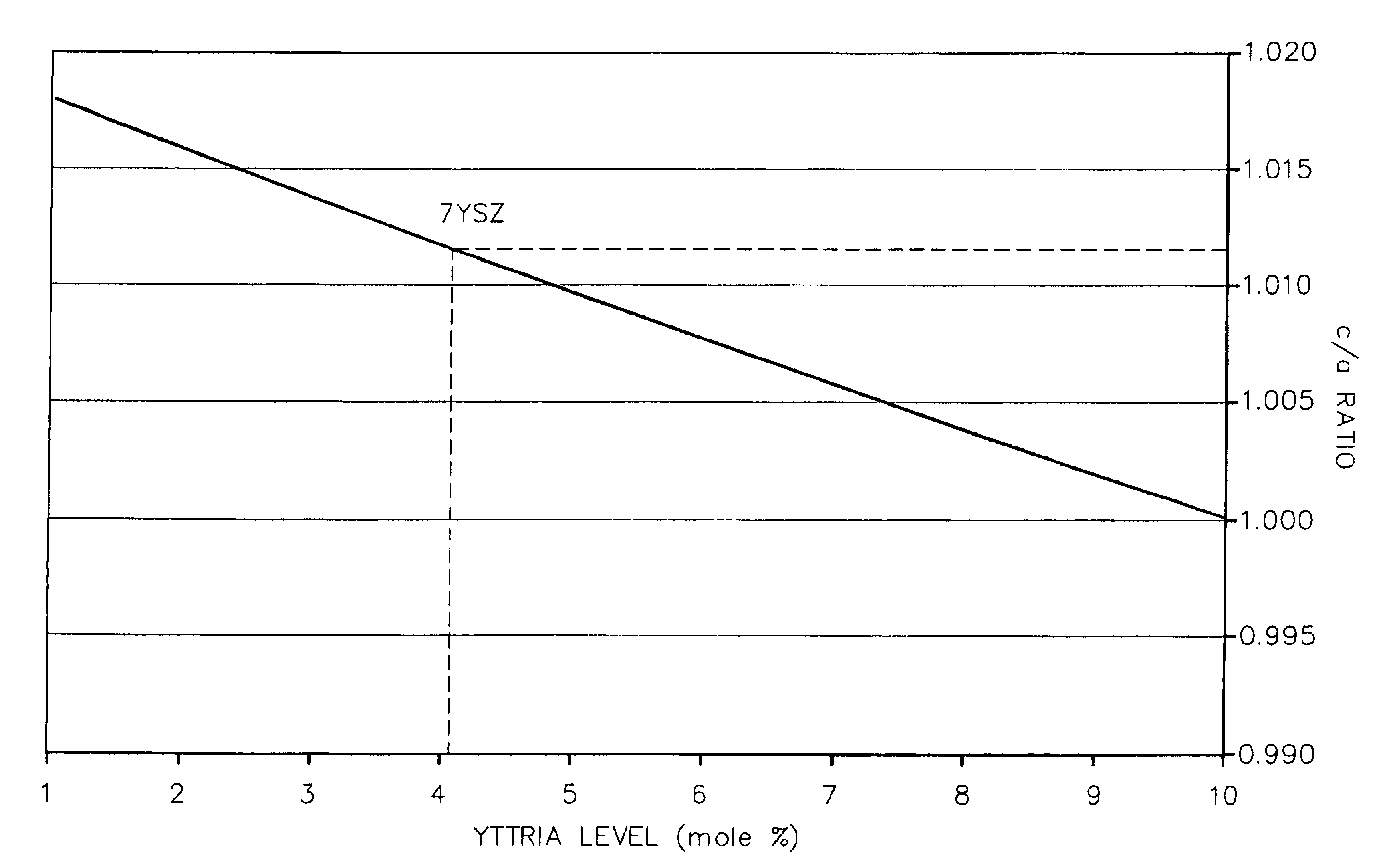
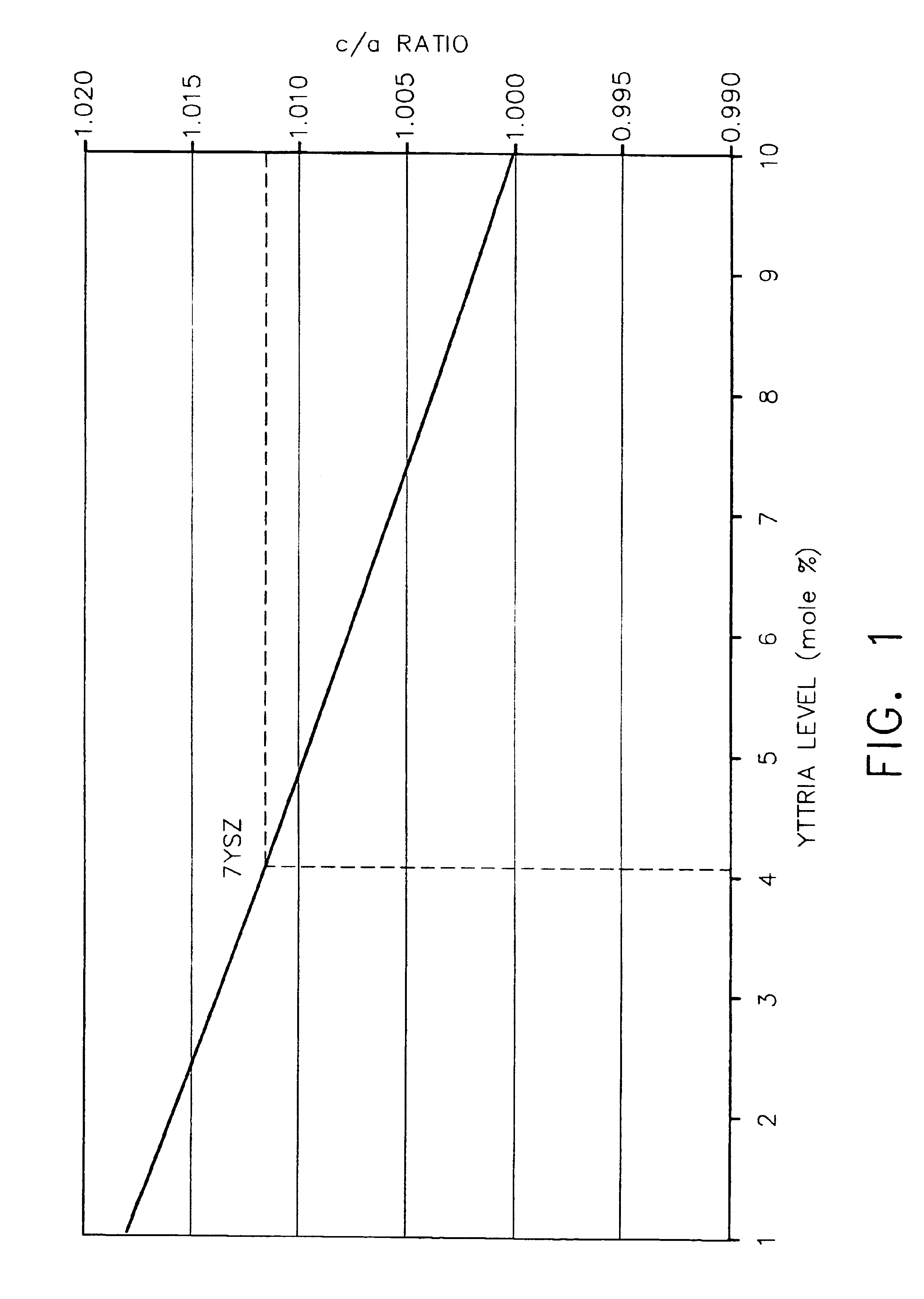
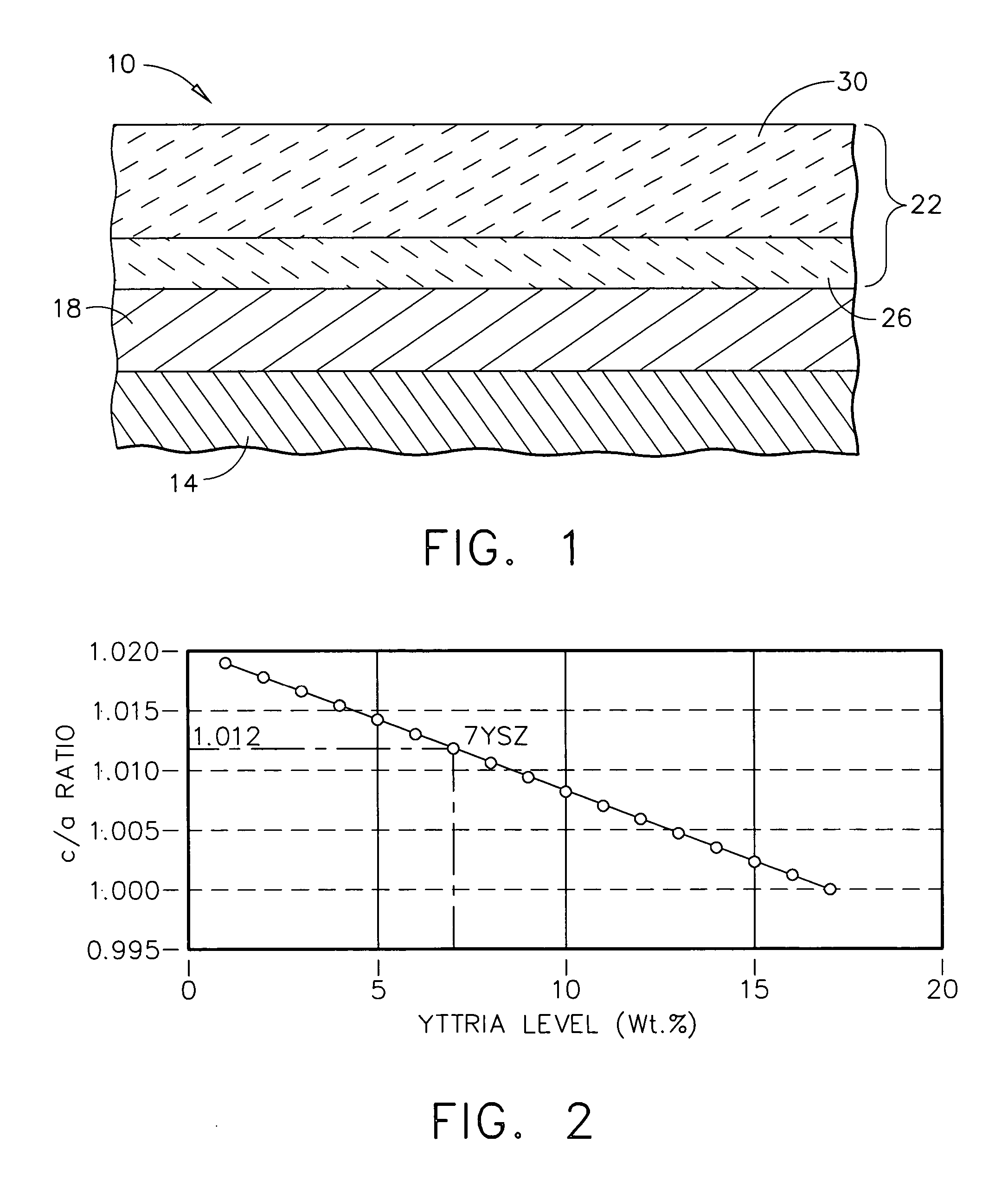
A reduced thermal conductivity thermal barrier coating having improved impact and erosion resistance for an underlying metal substrate of articles that operate at, or are exposed to, high temperatures. This coating comprises a zirconia-containing ceramic composition having a c / a ratio in the range of from about 1.0117 to about 1.0148 and stabilized in the tetragonal phase by a stabilizing amount of a stabilizer metal oxide. The coating has a fraction of porosity of from about 0.10 to about 0.25, and an impact and erosion resistance property defined by at least one of the following formulas: (a) I=exp.[5.85−(144×s)−(3.68×p)]; and / or; (b) E=[187−(261×p)−(9989×s)], wherein s=1.0117−c / a ratio; p is the fraction of porosity; I is least about 140 g / mil; and E is least about 130 g / mil. This coating can be used to provide a thermally protected article having a metal substrate and optionally a bond coat layer adjacent to and overlaying the metal substrate. The thermal barrier coating can be prepared by depositing the zirconia-containing ceramic composition on the bond coat layer, or the metal substrate in the absence of the bond coat layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ceramic compositions for low conductivity thermal barrier coatings
InactiveUS6858334B1Reduced and thermal conductivityGood producibilityMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingThermal barrier coatingZirconia ceramic
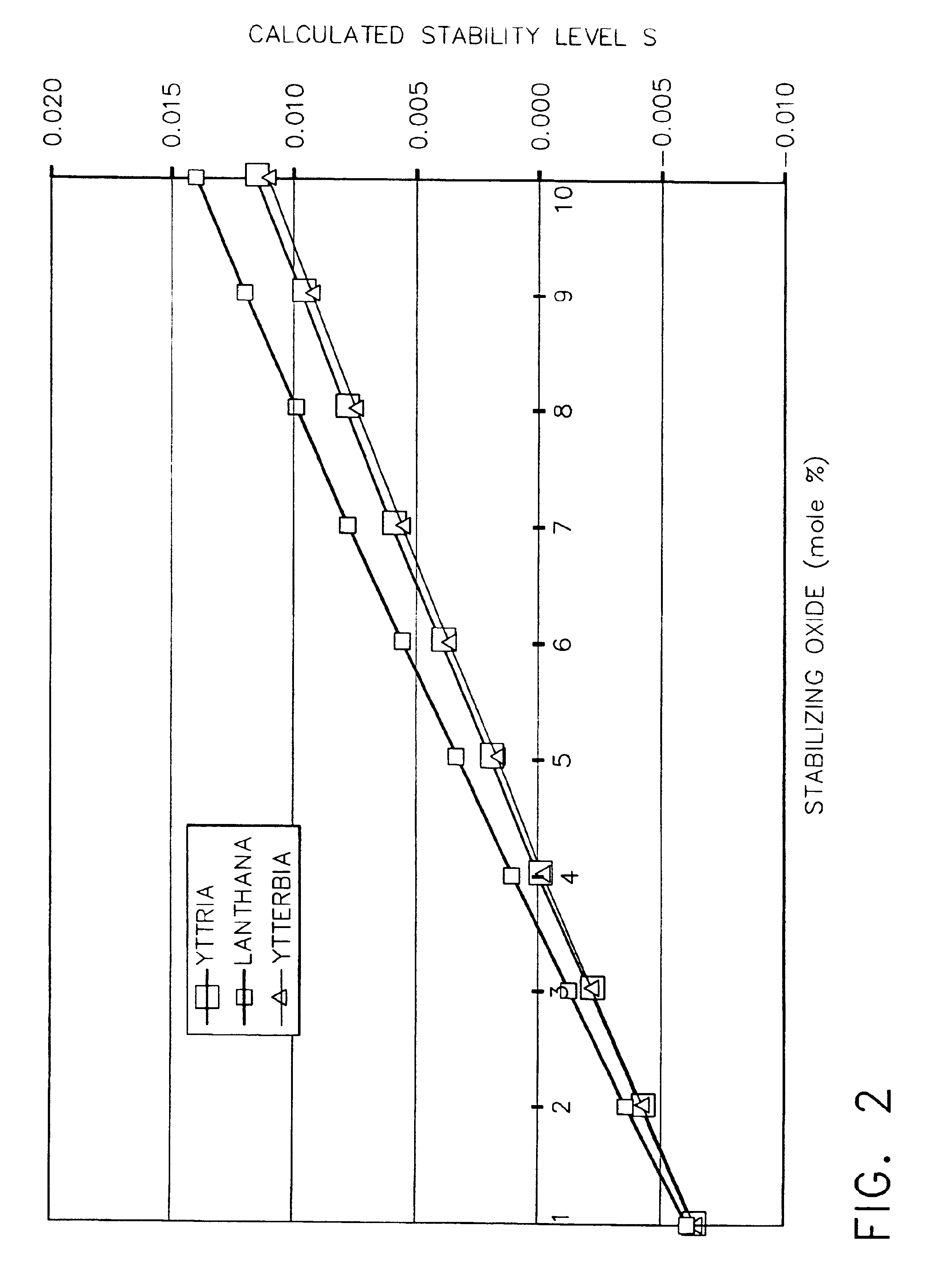
Zirconia-containing ceramic compositions having a c / a ratio of the zirconia lattice in the range of from about 1.005 to about 1.016. These compositions comprise a stabilizing amount up to about 10 mole % of the composition of a stabilizer component which comprises: (1) a first metal oxide selected from the group consisting of yttria, calcia, ceria, scandia, magnesia, india and mixtures thereof in an amount of from about 1.5 to about 6 mole % of the composition of; (2) a second metal oxide selected from the group consisting of lanthana, neodymia and mixtures thereof in an amount of from about 0.5 to about 4 mole % of the composition; and (3) optionally ytterbia in an amount of from about 0.5 to about 4 mole % of the composition. These compositions further comprise hafnia in an amount of from about 0.5 to about 15 mole % of the composition; and optionally tantala in an amount of from about 0.5 to about 1.5 mole % of the composition. These compositions are useful in preparing thermal barrier coatings having a balance of reduced thermal conductivity with good producibility, spallation resistance and erosion / impact resistance for an underlying substrate of articles that operate at, or are exposed to, high temperatures.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Modified zirconium oxide ceramic material and application thereof
InactiveCN104446457ARich Appearance StyleHigh dielectric constantBarium titanateUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a modified zirconium oxide ceramic material. The modified zirconium oxide ceramic material comprises the following components in percentage by molar concentration: 0-6mol% of yttrium oxide, 0-15mol% of cerium oxide, 0.02-1mol% of titanium oxide, 0-20mol% of aluminum oxide, 0-5mol% of barium titanate and the balance of zirconium oxide. The invention also discloses zirconium oxide ceramic and a dielectric cover plate prepared from the modified zirconium oxide ceramic material. The dielectric cover plate prepared from the modified zirconium oxide ceramic material has the advantages of high hardness, good toughness, high strength and high dielectric constant.
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
Ceramic manufactures
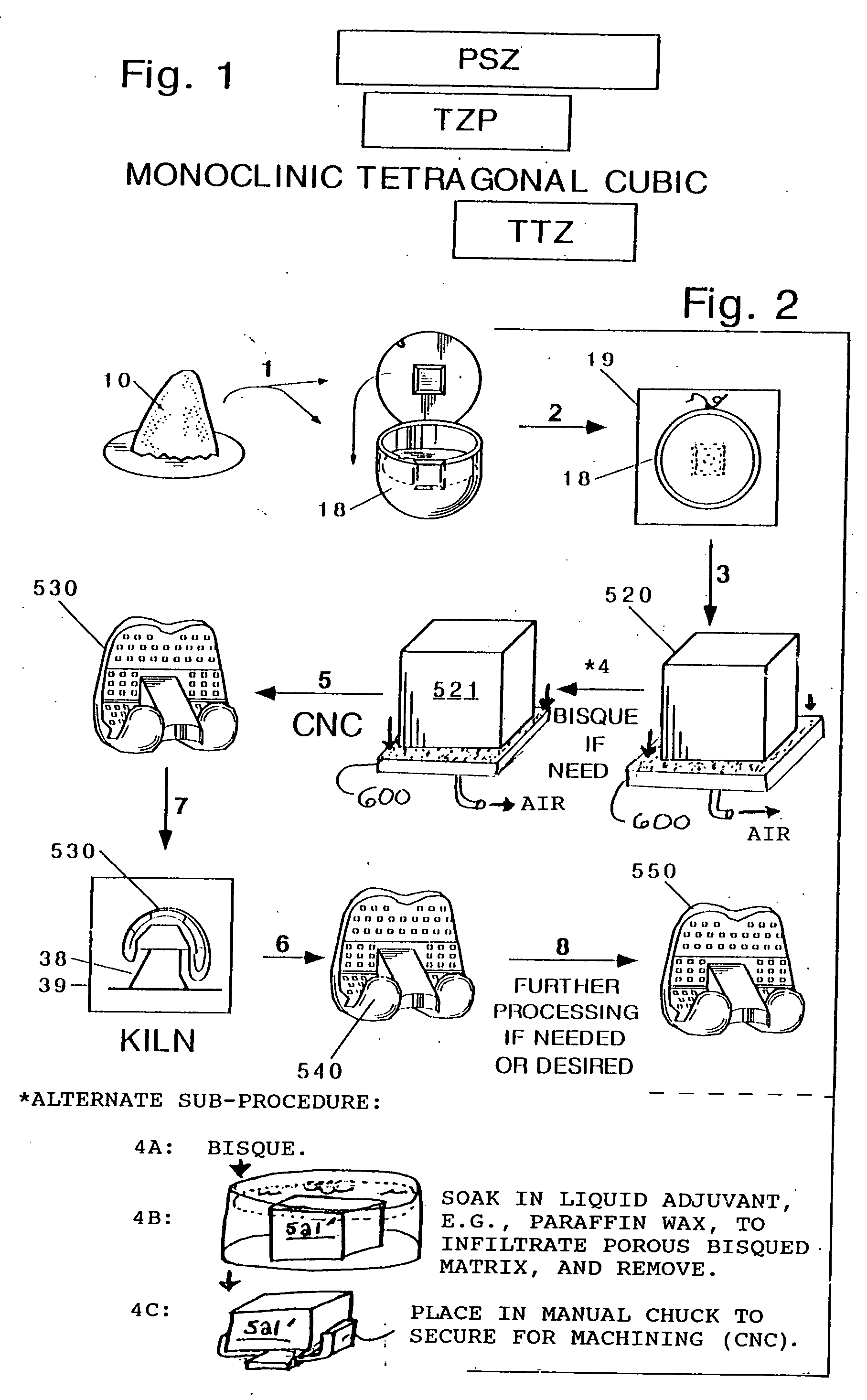
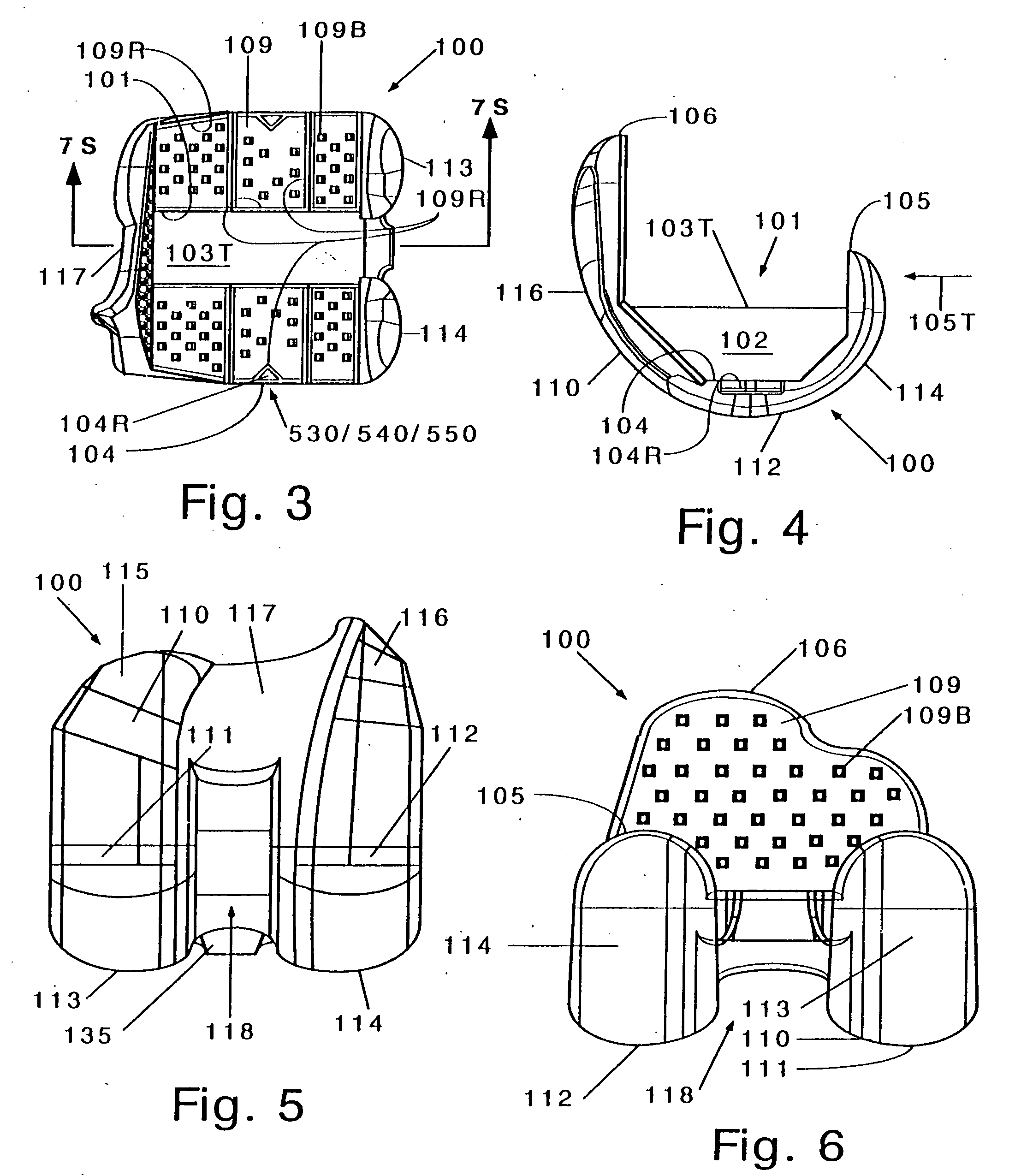
Ceramic bodies can be made by providing an initial green body of ceramic; and machining the initial green body to provide a machined green ceramic body. Embedding the initial green body in an embedding mass can be avoided. The initial green body can be bisqued, infiltrated an adjuvant such as machining wax, removing the infiltrated body, and machining it. Highly detailed ceramic products can be generated. The machined green ceramic body may be fired and / or further processed to provide a more finished ceramic body. Examples include a femoral component for a posterior stabilized knee implant, a component body for an artificial rotation device containing knee implant prosthesis a dental implant or bridge, an ice skating blade, and so forth. Zirconia ceramics are advantageously employed, for an example, Mg-TTZ.
Owner:LOUIS A SERAFIN JR TRUST +1
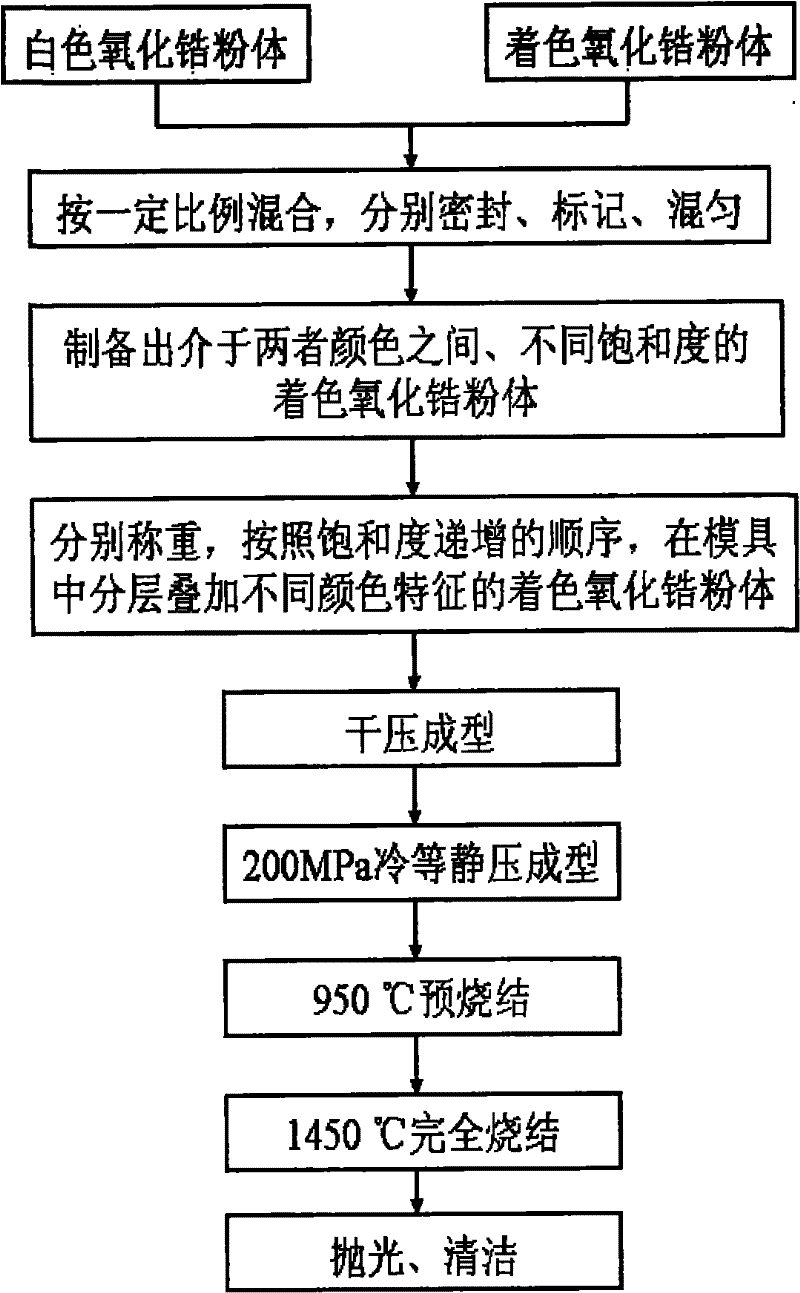
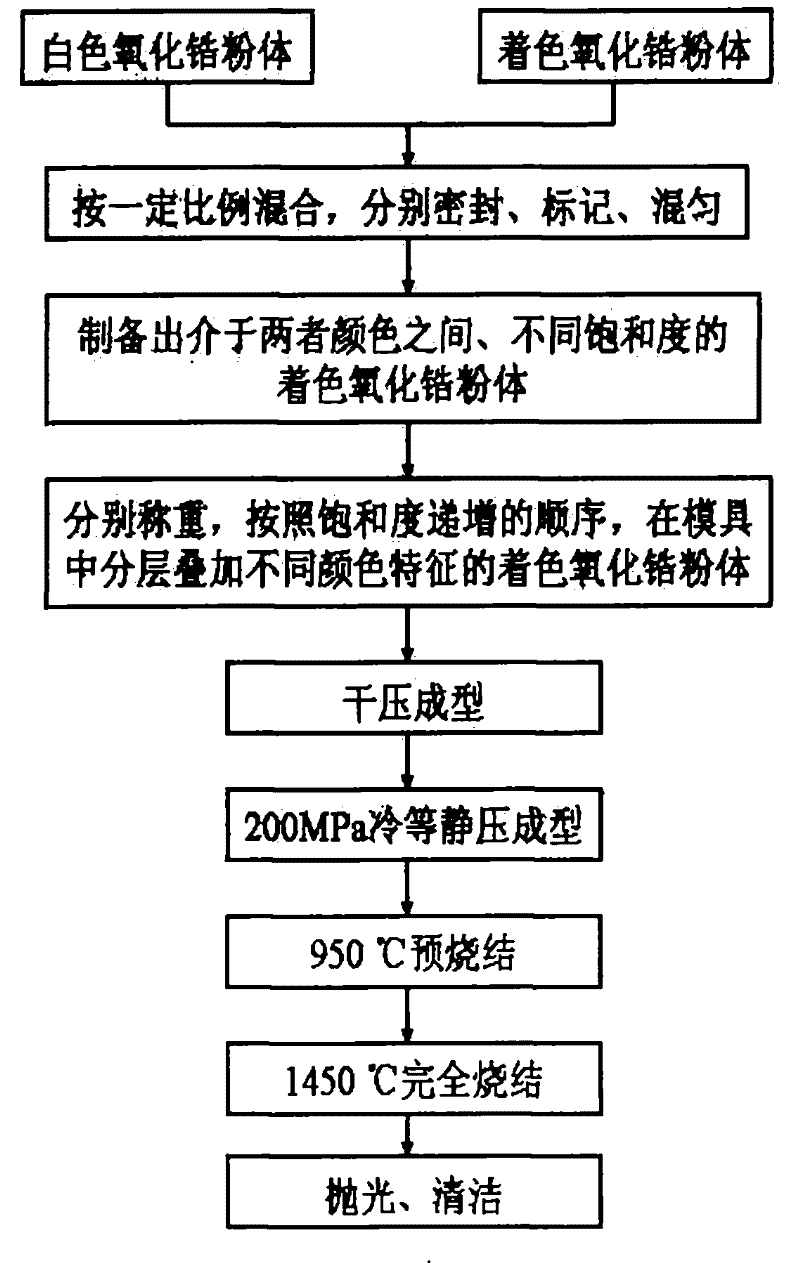
Preparation method of colored zirconia ceramics
The invention discloses a preparation method of colored zirconia ceramics, which belongs to the field of doped ceramic material preparation. The method comprises the following steps that: stabilizer and colorant are added into the suspension of zirconia powder by the mixture ratio of 850 to 980 parts of zirconia powder, 10 to 50 parts of stabilizer and 10 to 120 parts of colorant; by controlling the pH value of the solution or using various precipitant, the stabilizer and the colorant are precipitated on the surface of the zirconia powder; the solution is filtered and dried; the obtained powder is ground, screened, formed, degreased and sintered to obtain the colored zirconia ceramics. In nano-scale, the preparation method realizes the homogeneous compounding of the stabilizer, the colorant and the nano zirconia powder, can greatly reduce the volatilization of the colorant in the high-temperature sintering phase of the zirconia ceramics, has uniform sample color and good repeatability, and the colored zirconia ceramics prepared by the method can be widely applied to arts and crafts decoration, clocks and watches, mobile phone cases, jewelry and other fields.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ultra-wear-resistant alumina ceramic ball and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an ultra-wear-resistant alumina ceramic ball. The ultra-wear-resistant alumina ceramic ball comprises the following chemical components: 90-95% by weight of Al2O3, 5-8% by weight of SiO2, 0.3-0.5% by weight of CaO, 0.5-0.9% by weight of MgO, 1-2% by weight of ZrO and 0.1-0.5% by weight of La2O3 / Y2O3, wherein the equivalent wear loss is less than 72 per mil. A provided preparation method comprises the following process steps of: adopting alumina powder and other mineral raw materials for burdening, refining mud, drying, calcining, synthesizing, ball-milling, granulating, forming and firing to obtain a product. According to the invention, the wear resistance of the product can achieve the standard of the alumina ceramic ball; and furthermore, the ultra-wear-resistant alumina ceramic ball has the advantages of lower cost of the raw materials, better grinding performance and high performance-price ratio of the product, is more suitable for being applied in production, and can reduce the production cost of an enterprise and improve the production efficiency of the enterprise.
Owner:JINGDEZHEN BETTERWEAR NEW MATERIALS
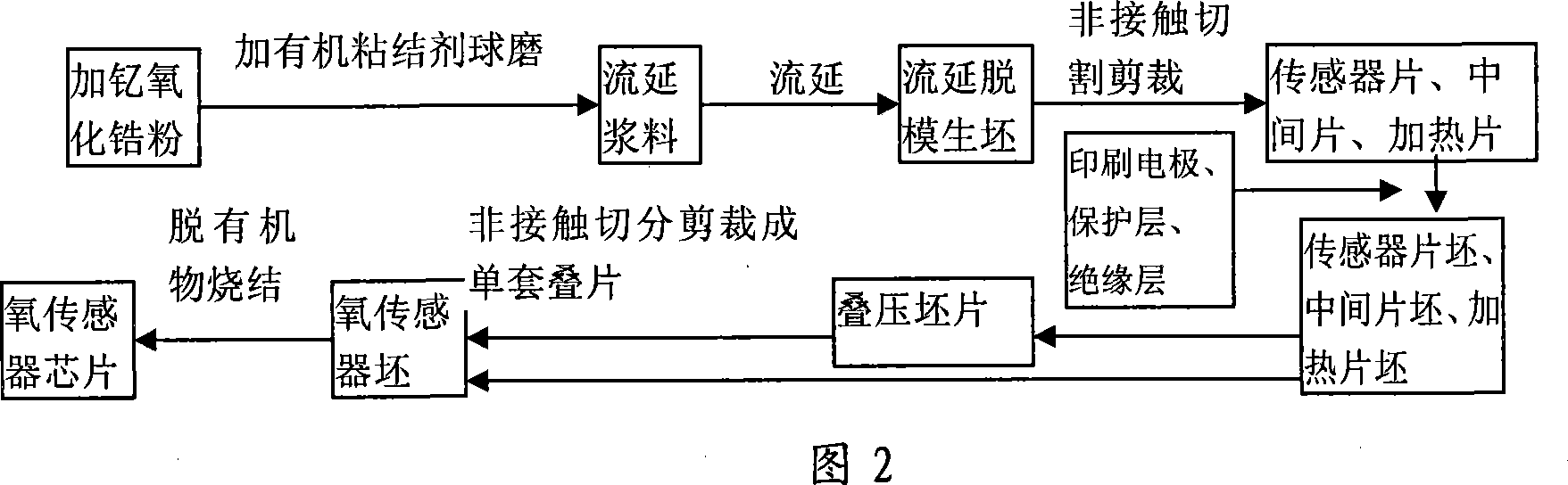
Manufacturing method of plate type oxygen sensor chip
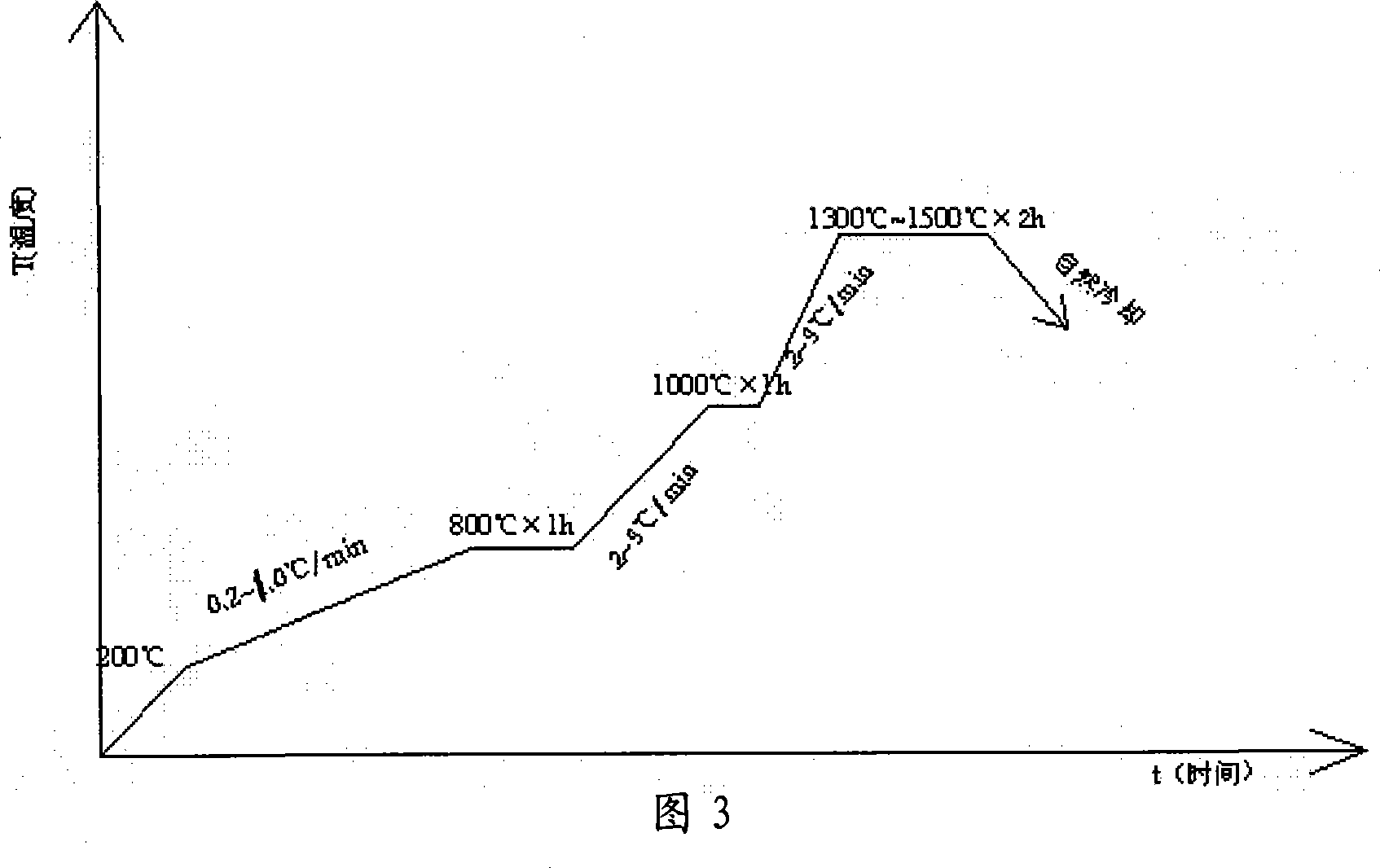
This invention relates to one process method to control cargo motor hollow burst plane oxygen sensor chip, which comprises the following steps: processing flow paste on zircite ceramics powder mixed with yttrium and processing bright and complete film through flow and then cutting into relative sensor slices, heating slice and middle slices by non-contact cut machine; printing electrode inside sensor slice and heating resistance on heating slices; then using overlap heating type to integrate three slices into plane sensor load to remove organism under temperature of 1300 to 1500 degrees.
Owner:ZHENJIANG NERNST AUTOMOTIVE TECH
Method for preparing colored zirconium oxide ceramic component
InactiveCN101857433ASuitable for industrial productionStain depth regulationMaterials preparationZirconia ceramic
The invention discloses a method for preparing a colored zirconium oxide ceramic component and belongs to the technical field of ceramic material preparation and ceramic injection molding. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing the following injection molding ingredients in percentage by mass: 85 to 90 percent of zirconium oxide powder, 8 to 12 percent of low-melting-point binder and2 to 4 percent of non-soluble skeleton binder; performing injection molding and blank degreasing; soaking a degreased blank in coloring ion-containing solution; and removing the binder from the blankand sintering the blank to obtain colored zirconium oxide ceramic, wherein dying degree can be controlled by controlling soaking time. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process, low cost, capability of saving coloring agent, environmental friendliness, combination of ceramic material preparation and molding technology and suitability for industrial production of colored zirconium oxide ceramic.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of preparing zirconium oxide ceramic by curtain coating method and product obtained from said method
A process for preparing the zirconium oxide ceramics by doctor blading method includes calcining the square-crystal zirconium oxide powder at 600-800 deg.C for 1-3 hr, proportionally mixing it with disperser, solvent and homogenizing agent, ball grinding for 10 hr, adding plasticizer and defoaming agent, ball grinding for 10 hr, vacuum stirring for defoaming, doctor blading, drying at 60-100 deg.C for 2-3 hr, degumming by heating to 600 deg.C and holding the temp for 4 hr, and sintering at temp lower than 1540 deg.C for 2-4 hr.
Owner:珠海粤科京华电子陶瓷有限公司
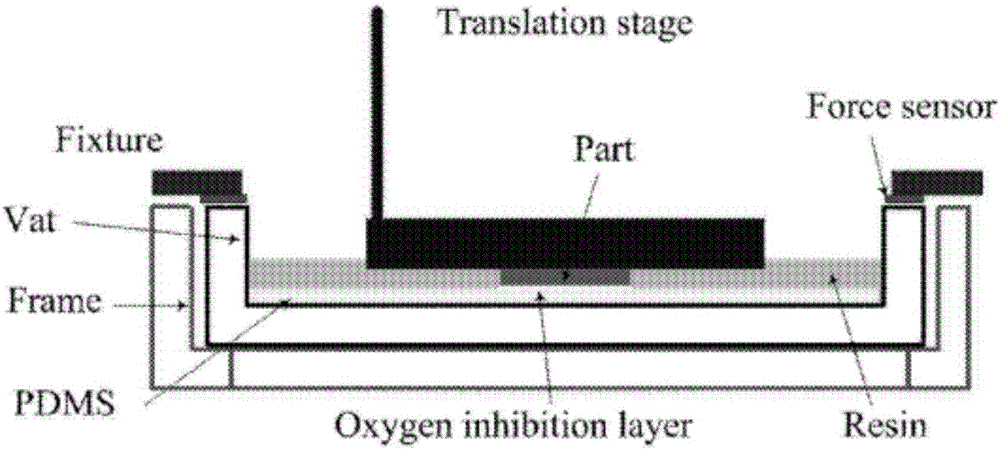
Method for preparing zirconium oxide ceramic by 3D (Three Dimensional) printing based on photo-curing molding
InactiveCN106673646AHigh surface finishHigh precisionAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurface finishPolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of 3D (Three Dimensional) printing and particularly relates to a method for preparing zirconium oxide ceramic by 3D printing based on photo-curing molding. The invention provides a composition which is prepared from the following raw materials: ceramic powder, a pre-mixed solution, a photoinitiator and a dispersant. The invention further provides a preparation method for preparing the zirconium oxide ceramic by utilizing the composition; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing slurry, molding, curing, drying, degreasing and sintering. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the molding efficiency is high, and ceramic particles are uniformly dispersed; a prepared blank body is not cracked or deformed, is dense and uniform and has good surface gloss finish, high precision and excellent blank body performances; and meanwhile, the method also has the advantage of high preparation efficiency. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the technical defects of a zirconium oxide ceramic molding method in the prior art that the dependence on a mold is too great and a complicated and precise structure cannot be prepared are overcome.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Graphene and oxide ceramic composite material and preparation method
The invention relates to a graphene and oxide ceramic composite material and a preparation method. Graphite oxide is used as a graphene precursor, the graphite oxide is mixed with zirconium oxide ceramic powder according to a certain proportion, and the mixture is molded and sintered so as to form the graphene and oxide ceramic composite material. The graphene and oxide ceramic composite material has a nanometer composite structure with network connections, nanometer layered graphene is uniformly distributed on a ceramic matrix to form the nanometer composite structure, the nanometer composite structure is conductive to strengthening of strength of the ceramic and endows the ceramic with the functional characteristics of semiconductor, electric conduction, heat conduction, electrochemistry, and the like, and the composite material can be used for developing sensors, electromagnetic shielding, electric heating devices, heat conduction materials, energy-storage electrodes, and the like and is used for the fields of aerospace, electronics, chemical engineering and energy sources. The graphene and oxide ceramic composite material is formed by one step in the sintering process, does not need the processes of functionalizing, mixing and the like, is simple in preparation process and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing black zirconia ceramics at low temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing black zirconia ceramics at the low temperature and belongs to the technical field of the preparation of high-temperature structural material. The method respectively uses a homogeneous precipitation method for synthesizing a nanometer coloring agent, and a coprecipitation method for synthesizing nanometer zirconia powder, and adopts Fe-Co-Ni-Mn as a coloring agent. The zirconia powder is not added with any sintering additive, only added with small amount of coloring agent and sintered at the temperature of 1150-1350 DEG C, thus obtaining the black zirconia ceramics with excellent performance and bright color. As the homogeneous precipitation method is adopted for synthesizing coloring agent powder, the monodisperse nanometer particles with uniform powder granules, narrow size distribution and high purity are obtained so that the coloring agent easily colors the particles. As the coprecipitation method is used for synthesizing zirconia powder, nanometer particles with small granularity, big superficial area and high activity are obtained, and can reduce the temperature of the solid-phase reaction, greatly reduce the sintering temperature and solve the problem that the black coloring agent oxide decomposes and volatiles at the high temperature. Simultaneously the method adopts the Fe-Co-Ni-Mn as the coloring agent, thus avoiding the poisonous function of Cr on the human body.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Black zirconia ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses black zirconia ceramic material composition which comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0-5% of ferric oxide, 0-5% of cobaltous oxide, 0-5% of chromic oxide, 0-5% of aluminum oxide, 0-5% of nickel oxide, 0-5% of manganese oxide, 0-5% of zinc oxide, 2-6% of yttrium oxide, 0-5% of titanium oxide, 0-5% of silicon dioxide, 0-5% of cerium oxide and the balance of zirconium oxide containing hafnium oxide. The black zirconia ceramic material composition disclosed by the invention is small in powder granularity and uniform in distribution, and black zirconia ceramic containing the black zirconia ceramic material composition is relatively good in covering power, high in blackness and relatively low in transmittance of light. Meanwhile the invention further discloses black zirconia ceramic prepared from the black zirconia ceramic material composition and a preparation method of the black zirconia ceramic.
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
Preparation of zirconia ceramic beaverboard
InactiveCN101462876AEvenly distributed and orderlyImprove long-term high-temperature service lifeFiberFiltration
The invention belongs to the inorganic refractory material field, and relates to a preparation method of a refractory and heat-insulating fiber board based on zirconia fiber. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps: stable cubic phase zirconia fiber is taken as a base phase, fine zirconia powder is taken as a filler, an organic binding agent is added to prepare slurry, and the slurry is formed by vacuum filtration, dried and sintered at a high temperature to prepare the ceramic zirconia fiber board. The preparation process is simple; the prepared fiber board has the advantages of even and single component and high-temperature resistance, and the fiber board can be used in an environment of 1700 DEG C-2160 DEG C for a long time.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Thermal barrier coatings with high fracture toughness underlayer for improved impact resistance
InactiveUS20060019119A1Improve fracture toughnessIncrease impactVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh fractureBond coat
A reduced thermal conductivity thermal barrier coating having improved impact resistance for an underlying substrate of articles that operate at, or are exposed to, high temperatures. This coating comprises an inner high fracture toughness layer nearest to the underlying substrate and having a thickness up to about 5 mils (127 microns) sufficient to impart impact resistance to the thermal barrier coating, and comprises a zirconia-containing ceramic composition having a c / a ratio of the zirconia lattice in the range of from about 1.011 to about 1.016 and stabilized in the tetragonal phase by a stabilizing amount of a stabilizing metal oxide selected from the group consisting of yttria, calcia, ceria, scandia, magnesia, india, lanthana, gadolinia, neodymia, samaria, dysprosia, erbia, ytterbia, europia, praseodymia, and mixtures thereof. The thermal barrier coating further includes an outer thermal insulating layer adjacent to and overlaying the inner layer and comprising a ceramic thermal barrier coating material. The thermal barrier can be used to provide a thermally protected article having a substrate (e.g., metal substrate) and optionally a bond coat layer adjacent to and overlaying the substrate. The thermal barrier coating can be prepared by forming the inner high fracture toughness layer, followed by forming on the inner layer the outer thermal insulating layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
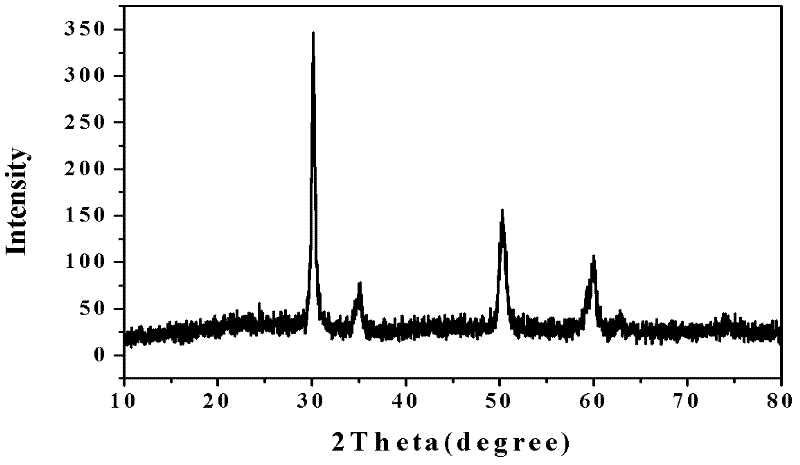
A kind of zirconia ceramic and its preparation method
The invention, belonging to the technical field of zirconia ceramic, discloses a zirconia ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The ceramic comprises matrix, sintering aid, neodymium oxide and additive, wherein, the matrix is yttria stabilized zirconia, the additive is selected from one or more of zinc oxide, barium carbonate and calcium fluoride, and the diffraction peak of the XRD appears when the 2 theta is 34.8-36.2 degrees. The zirconia ceramic has stable and beautiful purple. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding neodymium oxide particles in a diethanolamine solution for soaking, then carrying out solid-liquid separation; carrying out ball mill mixing of the matrix, processed neodymium oxide particles, sintering aid and additive, then carrying out die forming and high temperature sintering. The preparation method provided by the present invention is simple and easy, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Zirconia ceramic insert core and preparation method thereof
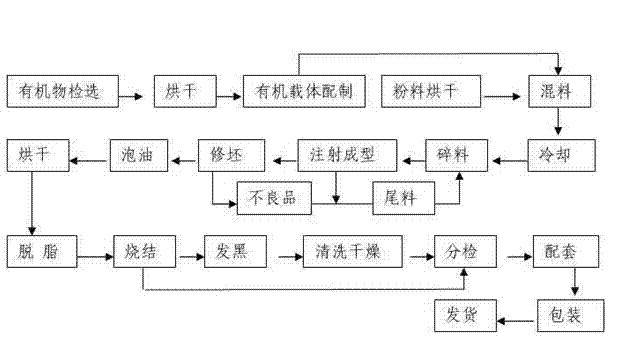
The invention discloses a production method of a zirconia ceramic insert core, which is characterized in that a zirconia ceramic insert core is produced by an injection molding method, zirconia powder containing a stabilizer is used as a main body, and the production method comprises the following steps of: mixing zirconia powder and an organic carrier at a weight ratio of 100:(10-30); performing banburying to obtain an injection molding material; making a green body by an injection molding technology; performing secondary degreasing treatment of oil soaking and hot degreasing; and making a high-performance zirconia ceramic insert core by a sintering technology. According to the invention, by adopting a ceramic injection molding technology for production and reasonably selecting materials and proportion thereof, the prepared ceramic insert core can ensure that the zirconia ceramic has the performance of high hardness, high toughness, high precision and easy processing, and the problem of relatively great tolerance caused by the production technologies such as isostatic pressing, slip casting, hot compression molding and the like is solved.
Owner:绵阳鑫通实业有限公司
Electrode sealing method in hydrogen furnace device for polysilicon production and device thereof
ActiveCN101565184AImprove flexural strengthHigh compressive strengthPolycrystalline material growthEngine sealsMulti materialHydrogen
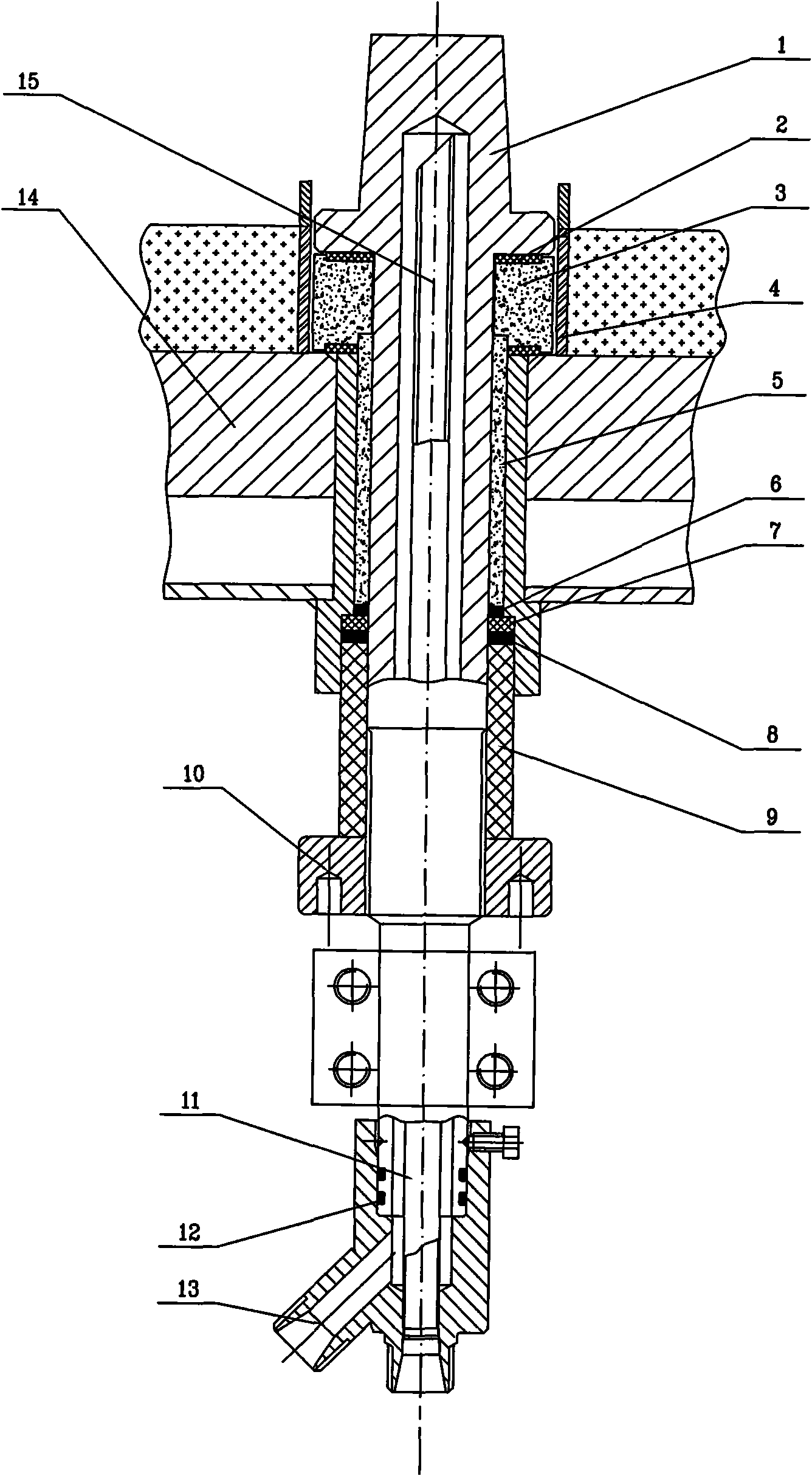
The invention discloses an electrode sealing method in a hydrogen furnace device for polysilicon production and relates to an electrode device in the hydrogen furnace for polysilicon production. By connecting cooling circulating water in the electrode and adopting special zirconia ceramics, flexible graphite, fluorubber O-shaped sealing rings and various materials, the problems of high-temperature resistance, insulation and sealing between the electrode and a chassis are solved, thereby improving the reliability of the hydrogen furnace device, ensuring the safe operation of the hydrogen furnace device and improving the productive efficiency of the hydrogen furnace device.
Owner:YICHANG CSG POLYSILICON CO LTD
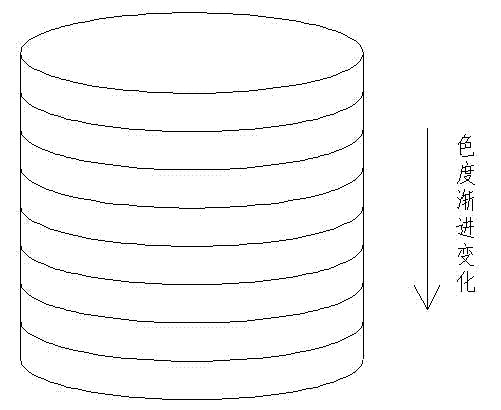
Gradient transparent zirconium oxide dental ceramic and preparation method thereof
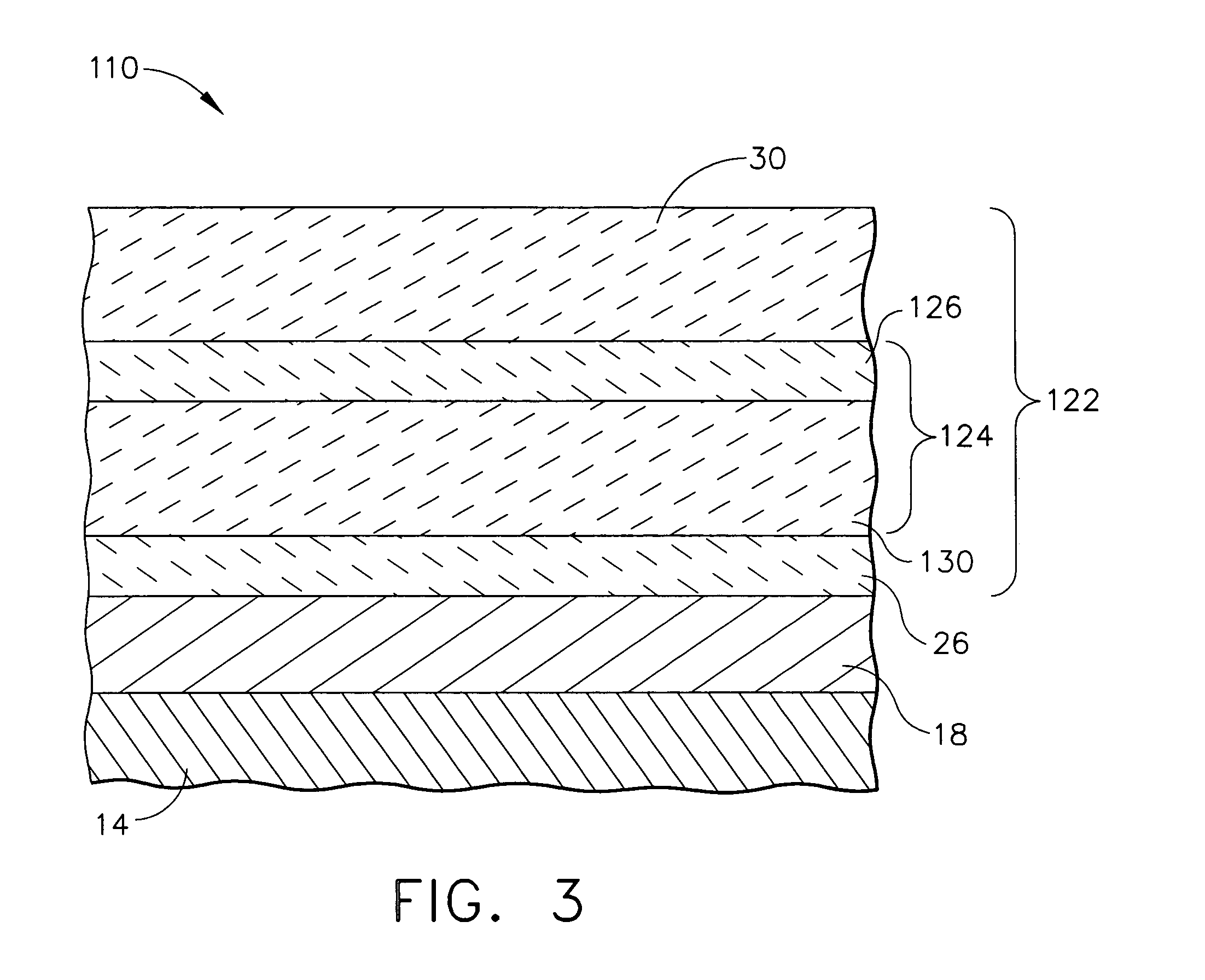
The invention discloses a gradient transparent zirconium oxide dental ceramic and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to the technical field of preparation of dental ceramics. The raw material is formed by mixing 2 to 5 kinds of zirconium oxide ceramic powder with different sintering transparences. The transparence of the sintered zirconium oxide ceramic from the bottom to the top is gradually increased, and the ceramic comprises 5 to 11 types of ceramic layers with different transparences. The preparation method comprises five steps, namely preparation of mixed powder, dry pressing, cold isostatic pressing, pre-sintering and blank restoration. The preparation method is simple and feasible, the transparence distribution characteristic of the prepared dental zirconium oxide full-ceramic material is similar to that of natural teeth, and the attractiveness of the zirconium oxide full-ceramic restoration is improved.
Owner:AIDITE (QINHUANGDAO) TECH CO LTD
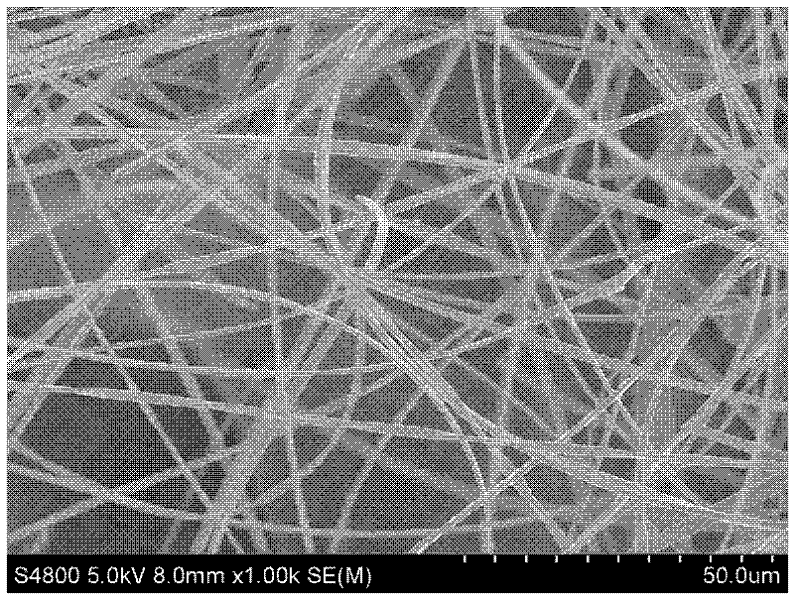
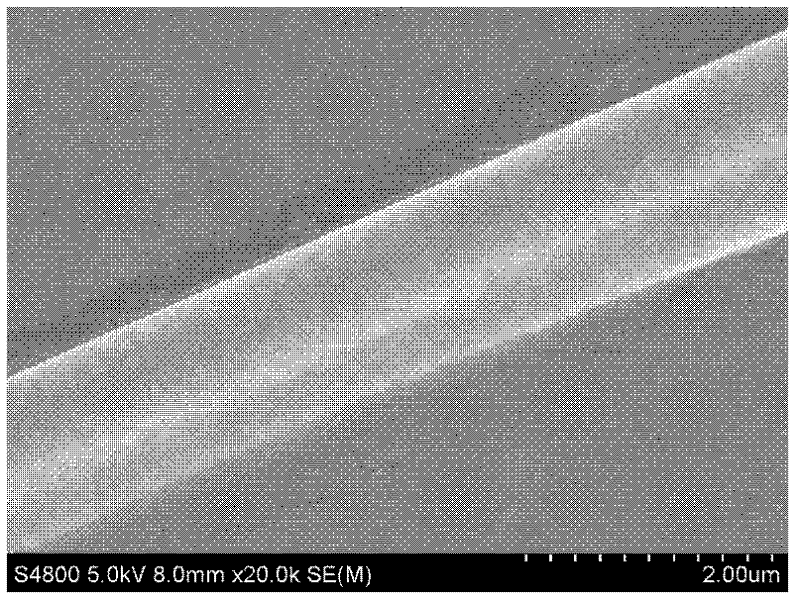
Flexible yttrium stable zirconium oxide ceramic fiber and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a flexible yttrium stable zirconium oxide ceramic fiber and a preparation method thereof. The particle diameters of zirconium oxide particles constructing the ceramic fiber are 10-400 nanometers, the diameter of the ceramic fiber is 0.5-3 mum, and the fiber is uniform and continuous, is prevented from being broken easily and has high flexibility. A zirconium oxide gel fiber is prepared by combining a sol-gel method with an electrostatic spinning technology, and the yttrium stable zirconium oxide ceramic fiber is obtained by calcining the gel fiber. The obtained yttrium stable zirconium oxide ceramic fiber has high thermal stability and excellent mechanical property, can be taken as a high-temperature catalyst carrier, a high-temperature heat insulating material aswell as a battery membrane, and can be applied to high-temperature filtering and the like. A process disclosed by the invention has high operability, and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Zirconium oxide ceramic cylinder jacket material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101514104AImprove liquidityHigh strengthPumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesPrice ratioYttrium
The invention provides a zirconium oxide ceramic cylinder jacket material, which comprises 65-75wt% of zirconium oxide, 3-6wt% of cerium oxide, 1-3wt% of yttrium oxide, 20-30wt% of aluminum oxide, and 0.5-2wt% of titanium dioxide. The invention also provides a preparation method for the zirconium oxide ceramic cylinder jacket material. The zirconium oxide ceramic cylinder jacket material provided by the present invention has higher strength, toughness and thermal shock resistance, and is able to resist wear, corrosion and high temperature. inner liner of slurry pumping cylinder sleeve prepared from the zirconium oxide ceramic cylinder jacket material has the following advantages that (1) service life is long, performance-price ratio is high, thereby reducing equipment cost consumption, greatly reducing frequency of shutdown to maintain cylinder jacket, reducing economical loss due to stop production and maintenance, and lightening labor intensity of workers; and (2) wearing for piston in the cylinder jacket is reduced, service life of the piston is prolonged, and piston cost is saved.
Owner:GUANGDONG ORIENT ZIRCONIC IND SCI & TECH CO LTD
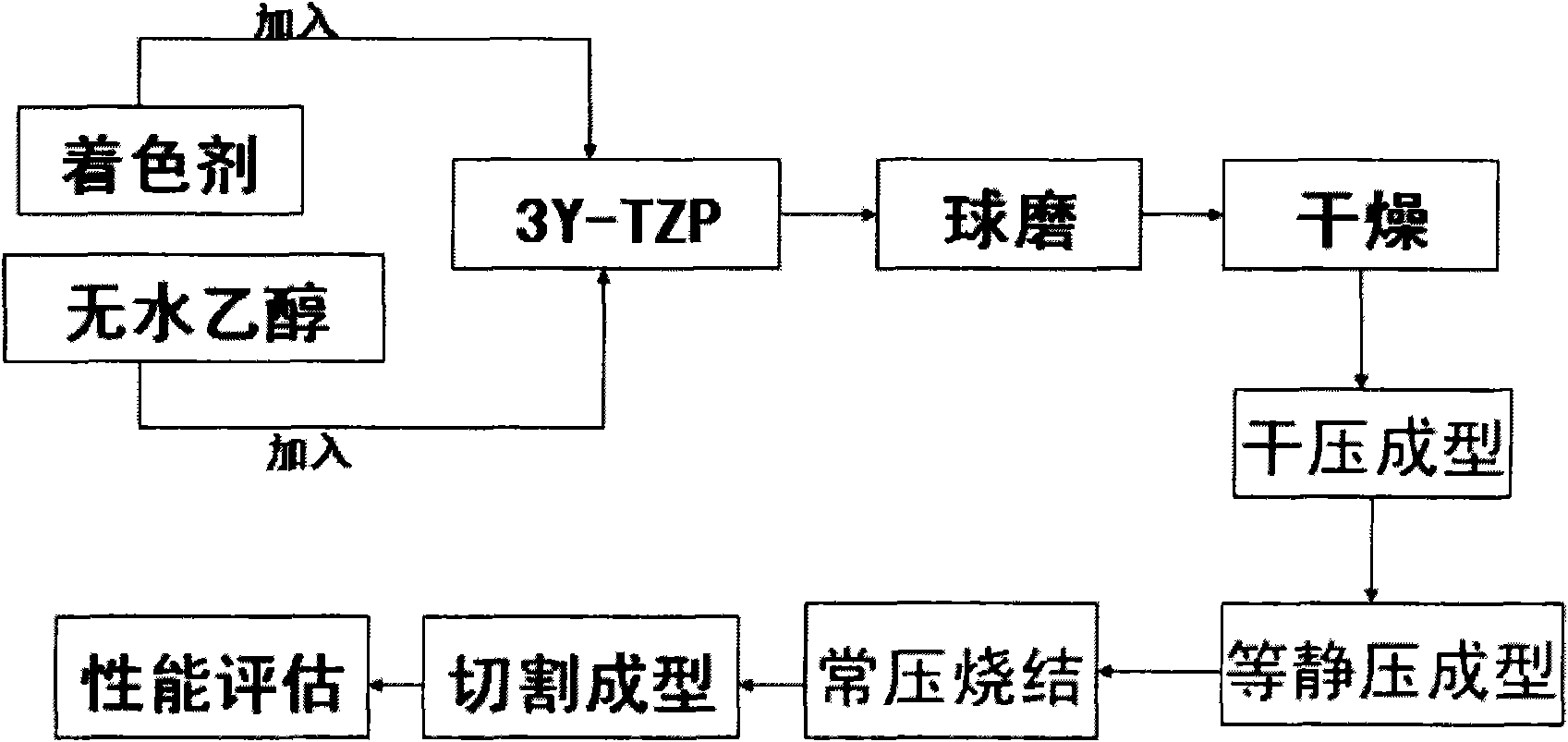
Preparation method of tooth color imitating dental tetragonal polycrystalline zirconia ceramics
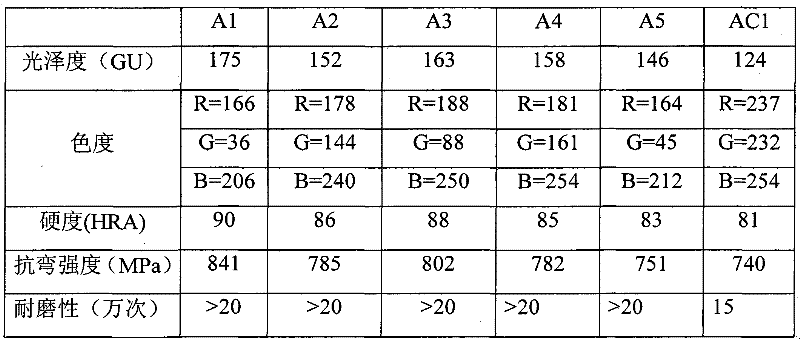
InactiveCN101870582AExpand the scope of indicationsImproved color stabilityImpression capsDentistry preparationsNatural toothMass ratio
The invention relates to a preparation method of tooth color imitating dental tetragonal polycrystalline zirconia ceramics, which specifically comprises the following steps: taking a 3Y-TZP ceramic ingot as the raw material, taking rare earth oxide and transition element oxide as the colorant, adding the colorant and absolute ethyl alcohol into 3Y-TZP, ball milling, adding the 3Y-TZP, the absolute ethyl alcohol and agate ball milling beads into an agate ball milling pot by the mass ratio of 1:1:1, then drying, dry pressing and forming, isopressing and forming; and sintering at normal pressure, cutting and forming to obtain the tooth color imitating dental tetragonal polycrystalline zirconia ceramics. The preparation method of tooth color imitating dental tetragonal polycrystalline zirconia ceramics has the advantages that the chromatic values of 6 types of zirconia ceramics are within the range of natural tooth color, the color stability is good, the mechanical properties are excellent, and a constructed two-stage sintering process is beneficial to industrialized popularization, expands the adaptation disease scope thereof in dental clinical medicine and provides bases for the localization thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
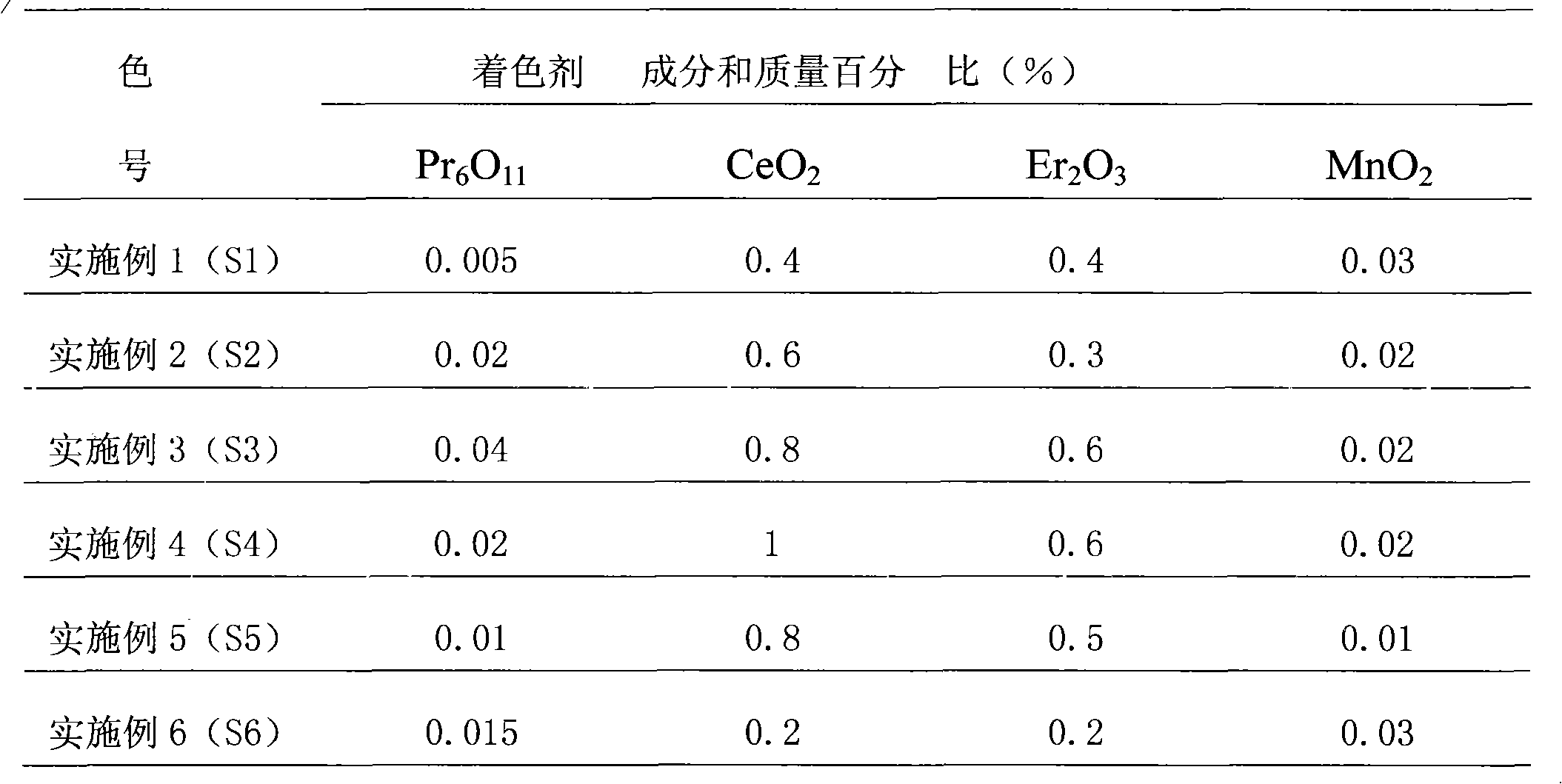
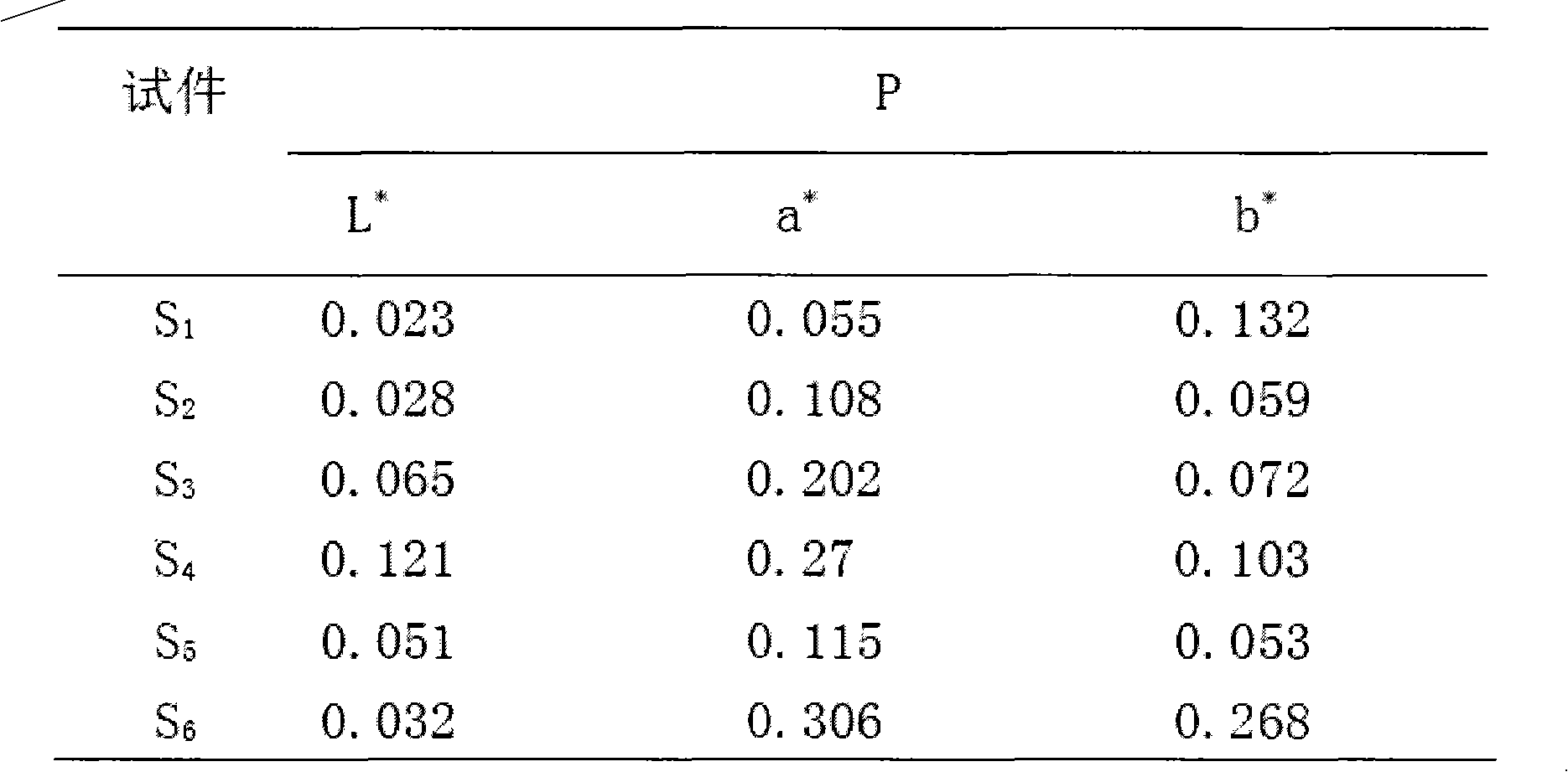
Multiple-oxide-doped gradient-color zirconia dental prosthesis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104844200AMeet the color distribution characteristicsGuaranteed uniformityNatural toothZirconia ceramic
The invention discloses a multiple-oxide-doped gradient-color zirconia dental prosthesis and a preparation method thereof. The multiple-oxide-doped gradient-color zirconia dental prosthesis is formed by mixing and overlaying more than one of dental zirconia porcelain mixed powder A, B and C with powder D on each porcelain layer according to different mass fractions. The three mixed powder is obtained by respectively doping ErO2, CeO2 and Fe2O3 with zirconia porcelain raw materials. The powder D refers to undoped zirconia porcelain raw materials. The preparation method includes mixed powder preparation, pre-dry-pressing, dry pressing, cold isostatic pressure forming, pre-sintering, blank engraving and final sintering. The preparation method is simple and easy to operate, the obtained prosthesis is wide in color regulation range and uniform in transition and has similar distribution characteristics to a natural tooth, and attractiveness of the zirconia all-porcelain prosthesis is improved. In addition, through the dry pressing process added during forming, uniformity of a powder overlaying and mixing stage is guaranteed and sintering body volume density and strength are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Zirconia ceramic cylinder liner material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102320830AWell mixedOvercome the disadvantage of uneven mixingComposite ceramicZirconia ceramic
The invention discloses a zirconia ceramic cylinder liner material and a preparation method thereof, and the material comprises the following components: 60-80 wt% of ZrO2, 20-30 wt% of Al2O3, 3.2-4.3 wt% of Y2O3, 3-4.2 wt% of TiO2, and 1.5-2.1 wt% of La2O3. The method prepares the ZrO2 ceramic cylinder liner material by using Al(NO3)3, ZrOCl2.8H2O, Y(NO3)3, TiCl4, LaCl3 as raw materials, using C6H12N4 as a precipitant, and by a coprecipitation method. Uniform mixing of each component at molecular level is effectively realized. The disadvantage of poor uniformity of the mixing of each component in the material due to routine ball milling mixing technology is overcome; the prepared zirconia ceramic powder has the characteristics of uniform dispersion, homogeneous particle size, and good fluidity; low-temperature sintering is realized; the ZrO2 composite ceramic material green body prepared by the method has bending strength of 980-1200 MPa, fracture toughness of 8.3-10 MPa.m1 / 2, vickers hardness of 2 GPa-14 GPa after calcination at 1330-1380 DEG C; the process is simple, and is applicable to large-scale production.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV +1
Manufacturing method of black zirconia ceramics
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of black zirconia ceramics which comprises, processing zirconium oxide ceramic powder into work piece blank, subjecting the obtained zirconium oxide to de-waxing, degreasing or low-temperature biscuit firing treatment with no protective atmosphere, then subjecting the pretreated zirconium oxide plain blank work piece to high-sintering under vacuum condition, or filling argon, hydrogen into the evacuated furnace, and conducting high-sintering in protective atmosphere.
Owner:钟伟 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com