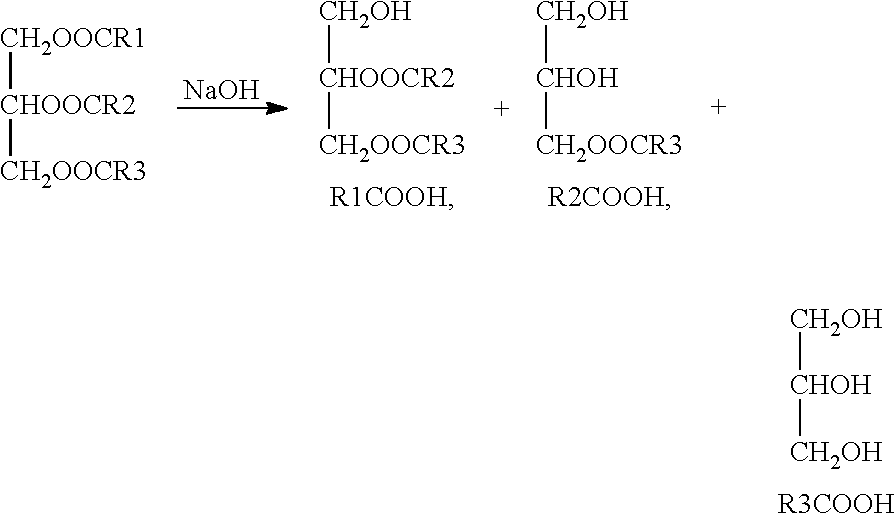Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Carbon Additive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
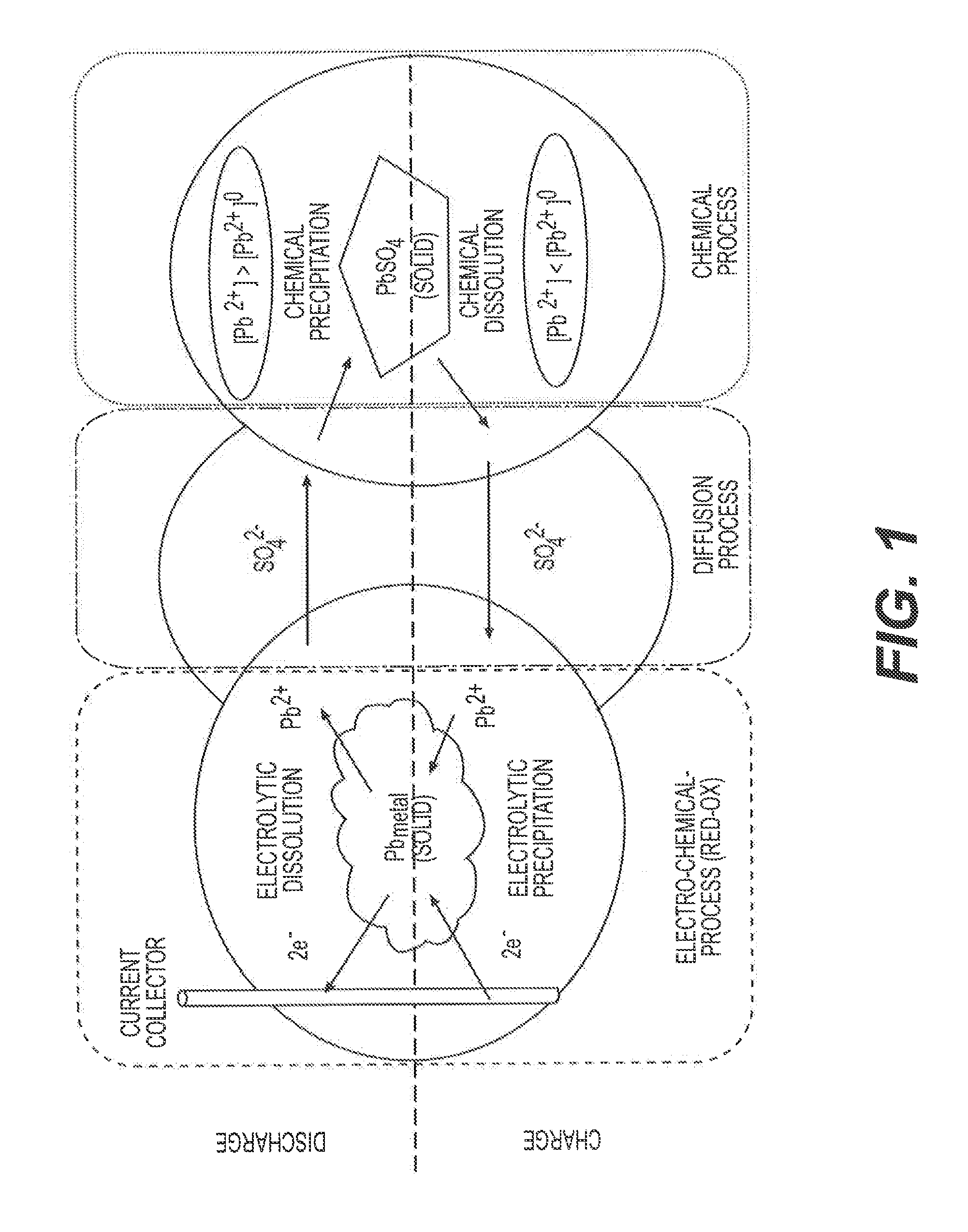
Carbon additive is a product that is added to molten steel. Carbon additive includes calcined petroleum coke, graphite petroleum coke, calcined anthracite coal, electrical calcined anthracite, and natural graphite. For the steel-making industry, the most suitable carbon additive is calcined petroleum coke with fixed carbon of 98.5%min. Sulfur in calcined petroleum coke is a crucial element, for sulfur impacts the quality of steel. The lower the sulfur, the better quality of calcined petroleum coke. The sulfur content of calcined petroleum coke is decided by the sulfur content in petroleum coke. Northeast China is the only source of low sulfur (≤ 0.5) petroleum coke in the world. G-high carbon has been the origin for many trading companies and metallurgical factories when they look for qualified carbon additives.
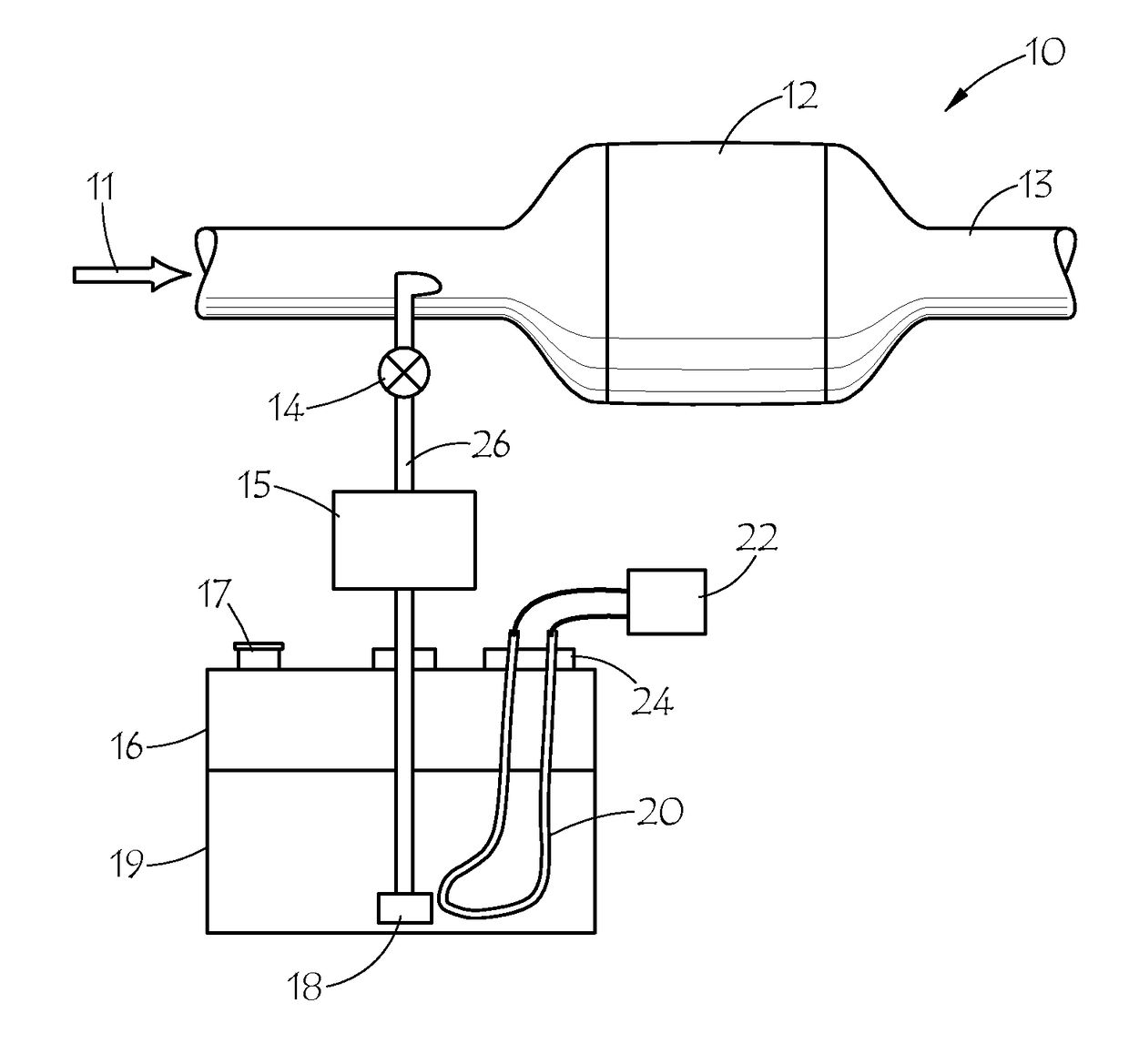
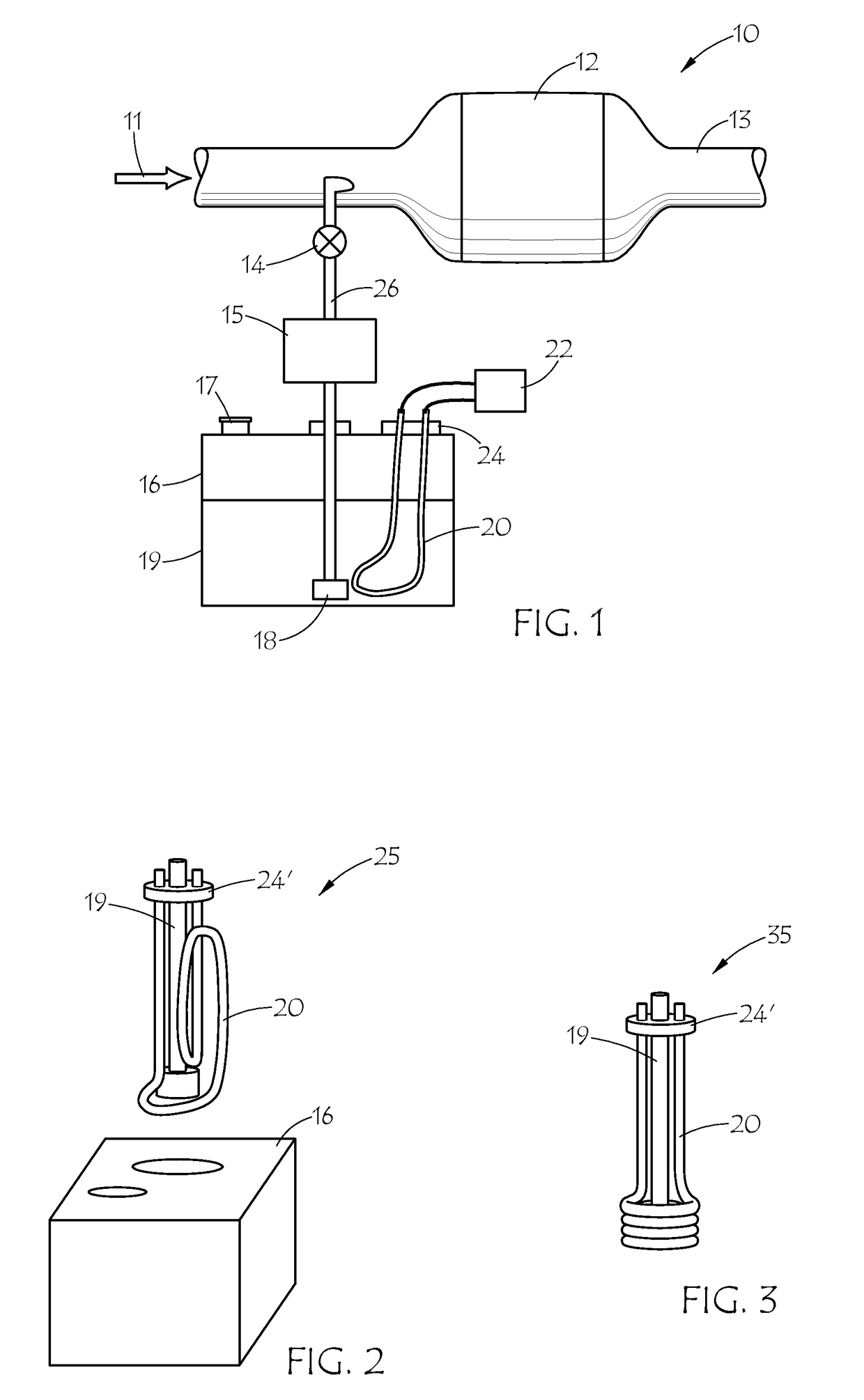
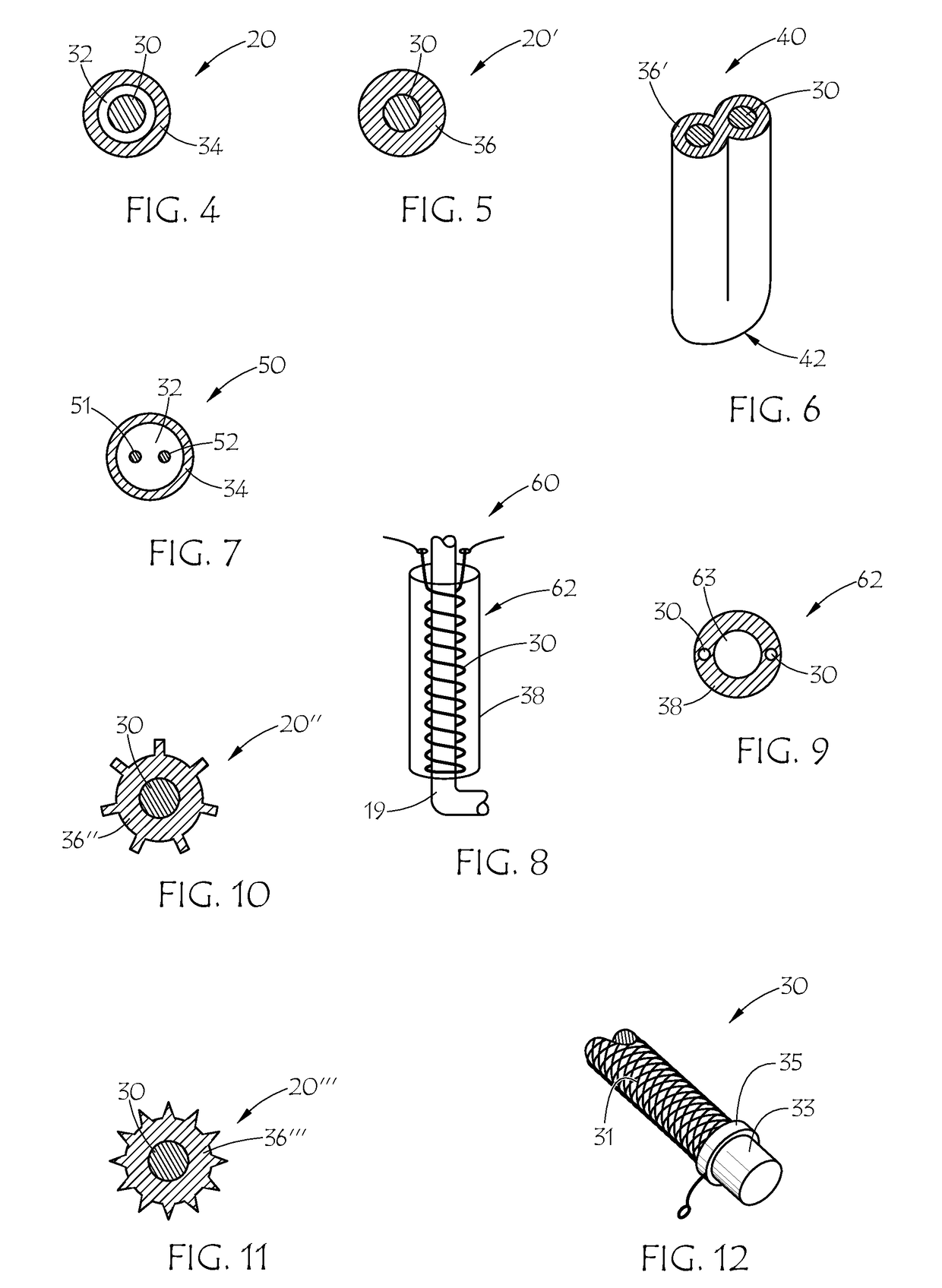
High pressure sintering with carbon additives
A method for forming a cutting element that includes sintering a mixture comprising carbide particles, a sp2-containing or sp2-convertible carbon additive, and a metallic binder at a first processing condition having a pressure of greater than about 100,000 psi to form a sintered object is disclosed. A method for forming a cutting element that includes sintering a mixture comprising diamond particles and a sp2-containing carbon additive at a first processing condition having a pressure of greater than about 100,000 psi to form a polycrystalline diamond layer is also disclosed, as well as cutting elements having diamond grains non-uniformly distributed therethrough.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Method for preparing carbon/carbon composite profiles
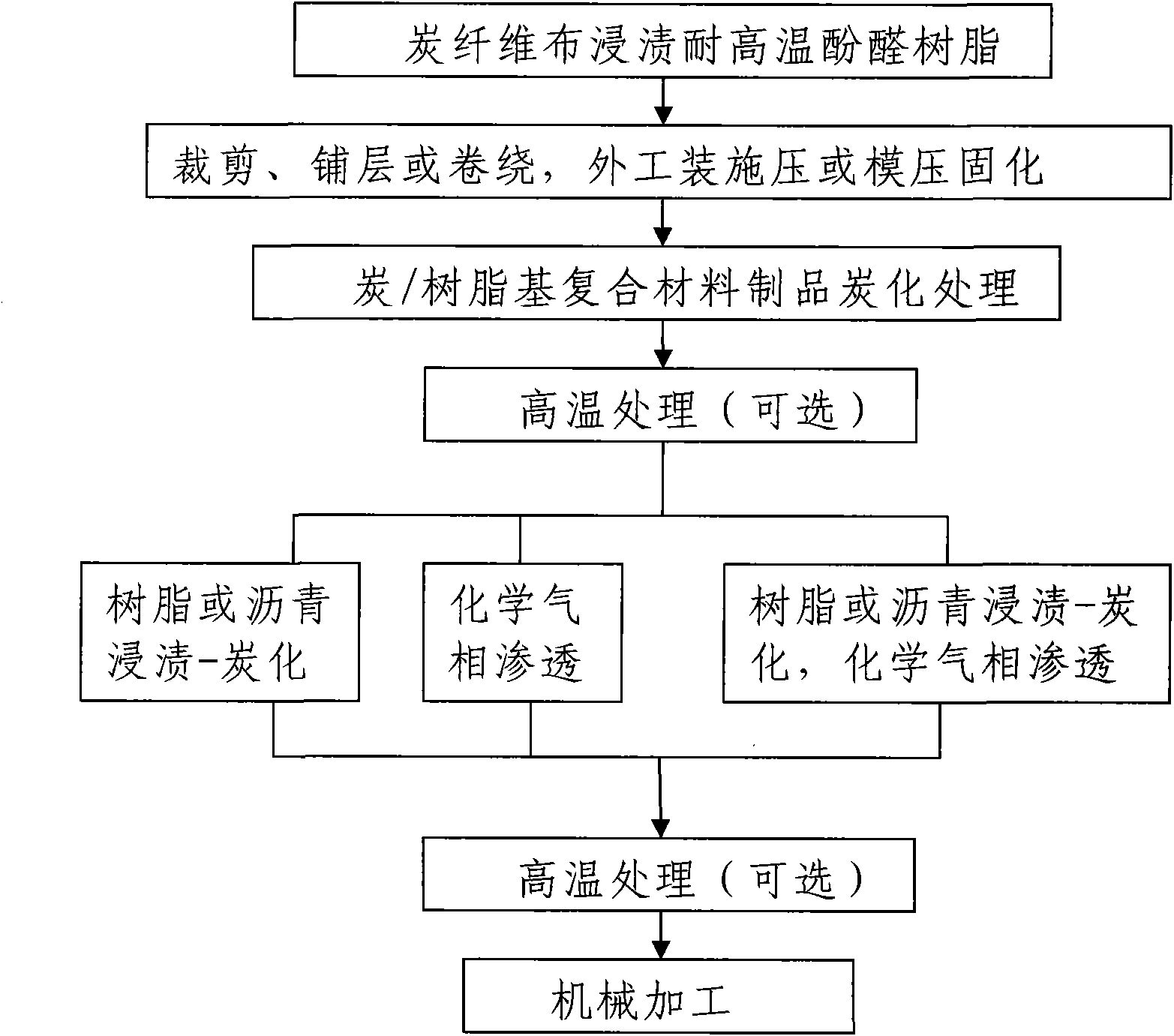
The invention discloses a method for preparing carbon / carbon composite profiles, comprising the following steps: after carbon fiber cloths are impregnated into resins, curing the carbon fiber cloths by way of external tooling pressing or mould pressing after cutting, layering or winding, and preparing carbon / resin based composite profile products after curing and demoulding; carrying out carbonization treatment under the protection of N2 to prepare carbon / carbon composite profile semi-finished products; carrying out supplementary densification treatment on the carbonized carbon / carbon composite profile semi-finished products by metallic or graphite moulds and tooling; carrying out mechanical processing on the carbon / carbon composite profile semi-finished products subjected to supplementarydensification to prepare the carbon / carbon composite profile products. The technology of the invention is simple, low in cost and strong in implementation. As carbon additive cloth cutting, layeringor winding and external tooling pressing or mould pressing curing and shaping modes are adopted, the prepared carbon / carbon composite profiles have a series of advantages as follows: the shaping modeis simple; the sizes of the products are hardly limited and mechanical processing is unnecessary in the thickness direction, thereby having superior performance-price ratio.
Owner:XIAN CHAOMA SCI TECH
Process for hydrocracking heavy oil and oil residue with a carbonaceouse additive
A process for the hydroprocessing of heavy oils and / or oil residues, the process comprising the steps of contacting a non-metallised carbonaceous material with an acid to form a non-metallised carbonaceous additive; and contacting the heavy oils and / or oil residues with the non-metallised carbonaceous additive in the presence of a hydrogen-containing gas at a temperature of from 250° C. to 600° C.
Owner:BP EUROPE SE
Negative plate for lead acid battery
InactiveUS20110027653A1Reduce layeringReduce maintenanceLead-acid accumulatorsElectrode carriers/collectorsCarbon AdditiveMass ratio
Capacitor pastes for flooded deep discharge lead-acid batteries include lead oxide, a carbon additive, and an aqueous acid. The capacitor paste contains lead and carbon in a lead to carbon mass ratio of about 5:1 to 82:1. Hybrid negative plates for flooded deep discharge lead-acid batteries can be made using such pastes in combination with traditional pastes. The hybrid negative plates include a capacitor paste on a bottom portion of the plate, and a traditional paste on the remainder of the plate. Batteries using the capacitor paste and hybrid plates exhibit improved performance over batteries with conventional plates and pastes and require less overcharge to prevent electrolyte stratification.
Owner:TROJAN BATTERY
Footwear cover with scent-suppressing carbon additive
A stretchable protective cover for footwear, formed from a natural rubber or elastomeric material. Small particles of activated carbon are interspersed in the material making up the cover, in order to suppress the scent of a wearer. The footwear cover may have a textured bottom surface to resist slippage. The cover is configured to completely cover and surround at least a portion of the footwear below the ankle area thereof.
Owner:EASTMAN HLDG
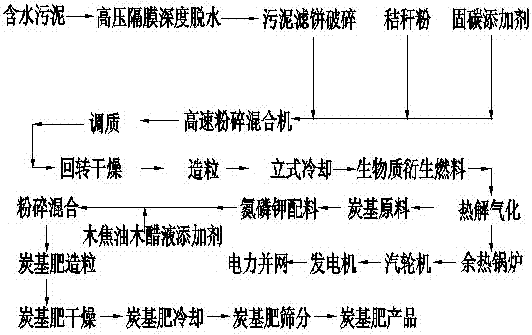
Carbon-based compound fertilizer and biomass gas co-production technology based on municipal sludge
InactiveCN107324941AImprove adsorption capacityLight weightAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersCropTar
The invention discloses a carbon-based compound fertilizer and biomass gas co-production technology based on municipal sludge. The technology comprises the following steps: 1) dehydration; 2) crushing; 3) mixing: 53%-92% by mass of sludge particles, 1%-40% by mass of straw powder and 3%-8% by mass of a carbon sequestration additive are mixed, wherein the carbon sequestration additive contains diatomite, calcium oxide and magnesium ore powder; 4) drying; 5) granulation; 6) pyrolysis and gasification: biomass derived fuel particles are fed into a gasifier and subjected to pyrolysis and gasification under the micro-oxygen condition of air equivalent ratio being 0.18-0.25 at 600-800 DEG C, biomass mixed fuel containing part of purities is obtained, and carbon residues in the gasifier are discharged; 7) gas separation: wood tar and wood vinegar are removed from the biomass mixed fuel through purification, and the purified biomass mixed fuel is taken as gas fuel; 8), carbon-based compound fertilizer preparation: 40%-60% of the carbon residues, 12%-20% of a wood tar and wood vinegar mixed liquid, 20%-35% of inorganic nitrogen phosphorus and potassium fertilizer and 2%-5% of diatomite are mixed. Biomass in the municipal sludge and residues obtained after energy conservation treatment can be used efficiently, by means of the obtained compound fertilizer, soil granulation can be increased, the rate of utilization of the fertilizer by crops is increased, heavy metal components are solidified, secondary pollution to the environment is avoided, few resources are consumed, and the comprehensive economic benefits are increased.
Owner:四川雷鸣环保装备有限公司
Method and apparatus for improving charge acceptance of lead-acid batteries
InactiveUS20140186712A1Increase charge inputLead-acid accumulatorsConductive materialCarbon AdditiveEngineering
An electrode and a lead-acid battery including the same are disclosed. The electrode comprises active material comprising lead and a carbon additive configured to increase a charge input of the lead-acid battery by at least 17%, relative to a negative electrode without the carbon additive.
Owner:ENERGY POWER SYST
Cold-emission film-type cathode and method for producing the same
The present invention may be used in the production of highly efficient films for electron field emitters. The cold-emission cathode of the present invention comprises a substrate having a carbon film with an irregular structure applied thereon. This structure comprises carbon micro- and nano-ridges and / or micro- and nano-threads which are perpendicular to the surface of the substrate, which have a typical size of between 0.005 and 1 micron as well as a distribution density of between 0.1 and 100 mum-2, and which are coated with a diamond nano-film whose thickness represents a fraction of a micron. The method for producing the cathode involves sequentially depositing two carbon films. A carbon film with nano-barbs is first deposited on a substrate arranged on an anode by igniting a direct-current discharge at a density of between 0.15 and 0.5 A. This deposition is carried out in a mixture containing hydrogen and a carbon-containing additive, under a global pressure of between 50 and 300 torrs, using vapors of ethylic alcohol at a 5 to 15% concentration or vapors of methane at a 6 to 30% concentration, and at a temperature on the substrate of between 600 and 1100° C. A diamond nano-film is then deposited on the graphite film thus grown.
Owner:BLYABLIN ALEXANDR ALEXANDROVICH +7
High heat conductivity carbon brick for blast furnace and its producing method
InactiveCN1683280AEliminate the calcination processConducive to the rational use of resourcesBlast furnace componentsBlast furnace detailsBrickCarbon Additive
The present invention relates to refractory carbon material for iron smelting blast furnace, and is especially high heat conductivity carbon brick for blast furnace lining and its production process. The high heat conductivity carbon brick for furnace lining has material comprising adhesive 20-24 wt%, crushed graphite 40-50 wt%, roasted segment 25-37 wt% and non-carbon additive 1-3 wt%. The main materials are side products from carbon plant, needs no calcining, and results in low cost. Using great amount of crushed graphite makes the carbon brick possess heat conducting coefficient up to 30 W / m.K, and is favorable to strengthening the furnace bottom cooling effect and prolonging blast furnace life.
Owner:CHENGDU CARBON
Air Cathode Battery Using Zinc Slurry Anode with Carbon Additive
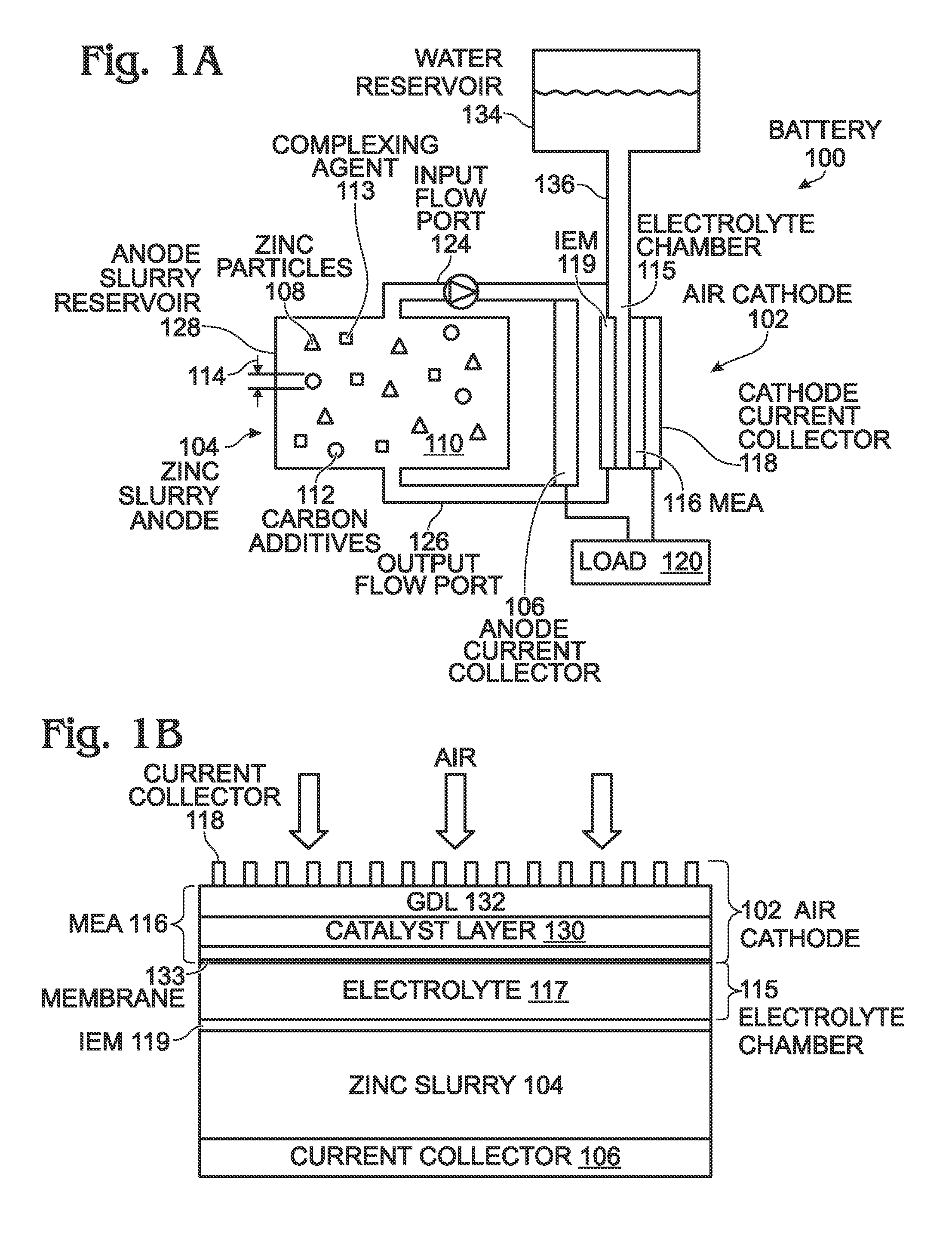
ActiveUS20140370401A1Scalable capacityLow costFuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsFiberCarbon Additive
An air cathode battery is provided that uses a zinc slurry anode with carbon additives. The battery is made from an air cathode and a zinc slurry anode. The zinc slurry anode includes zinc particles, an alkaline electrolyte, with a complexing agent and carbon additives in the alkaline electrolyte. A water permeable ion-exchange membrane and electrolyte chamber separate the zinc slurry from the air cathode. The carbon additives may, for example, be graphite, carbon fiber, carbon black, or carbon nanoparticles. The proportion of carbon additives to zinc is in the range of 2.5 to 10% by weight. The proportion of alkaline electrolyte in the zinc slurry is in the range of 50 to 80% by volume.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method For Manufacturing An Electrode For A Lithium-Sulfur Battery Using Li2S As An Active Material
InactiveUS20190123342A1Improve particle size distributionSimplify dispersionElectrode thermal treatmentElectrode carriers/collectorsActivated carbonCarbon Additive
The invention relates to a method for preparing a positive electrode for a lithium-sulfur battery, comprising the following steps:a) a step of preparing a first mixture by placing a carbon additive which is carbon black and / or activated carbon; a carbon organic binder, and a solvent in contact;b) a step of carbonising said first mixture, by means of which the result is a powder comprising agglomerates of carbon black and / or activated carbon;c) a step of placing the powder obtained in b) in contact with a powder of Li2S thus forming a second mixture;d) a step of melting the powder of Li2S of the second mixture, by means of which the result is a composite powder comprising agglomerates of carbon black and / or activated carbon and particles of Li2S;e) a step of dispersing the powder obtained in d) in an organic binder;f) a step of depositing the dispersion obtained in e) on a substrate, which is a material comprising carbon fibres or a metal strip; andg) a step of drying said dispersion thus deposited.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +3
Nanocarbon-reinforced polymer composite and method of making
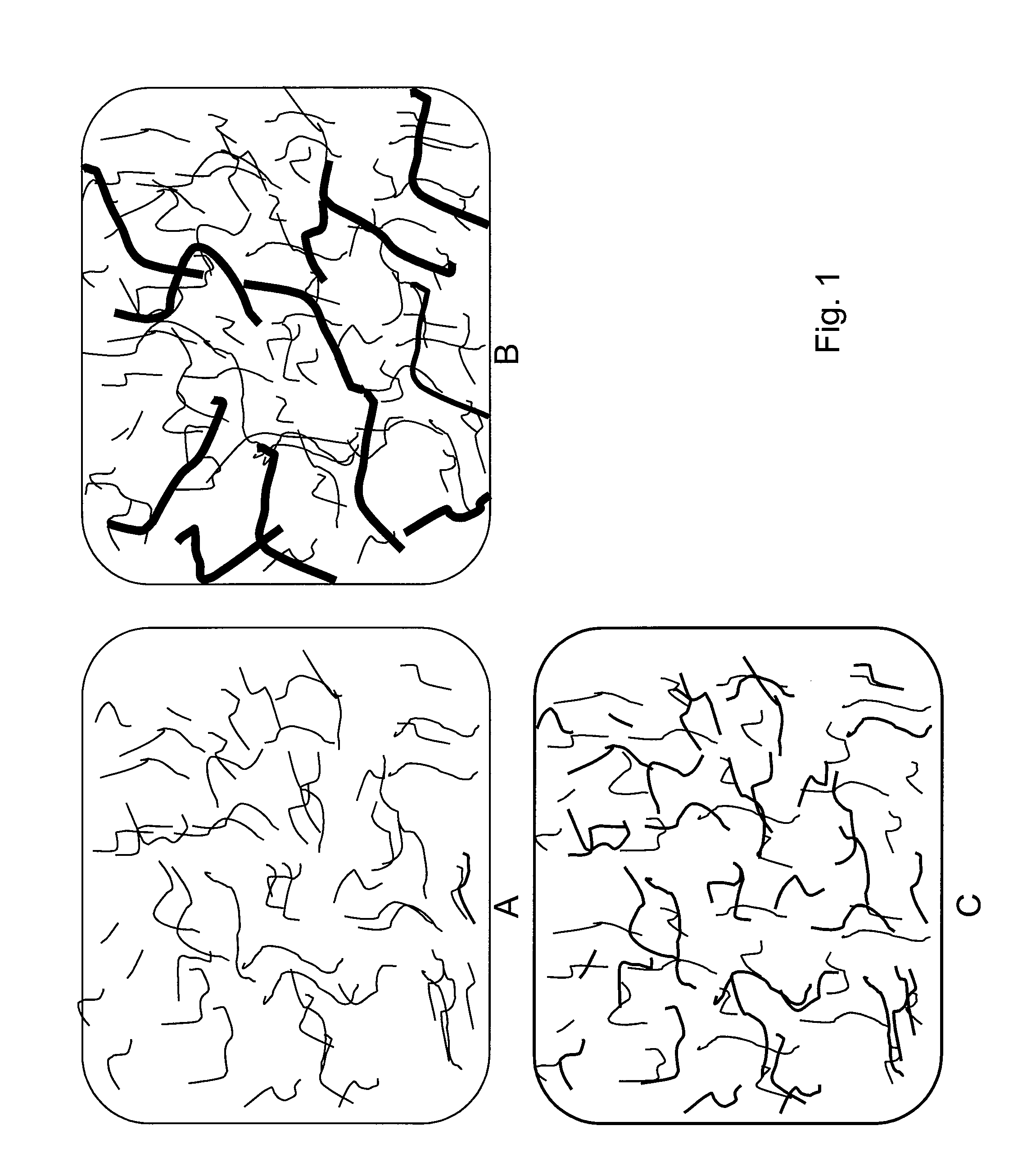
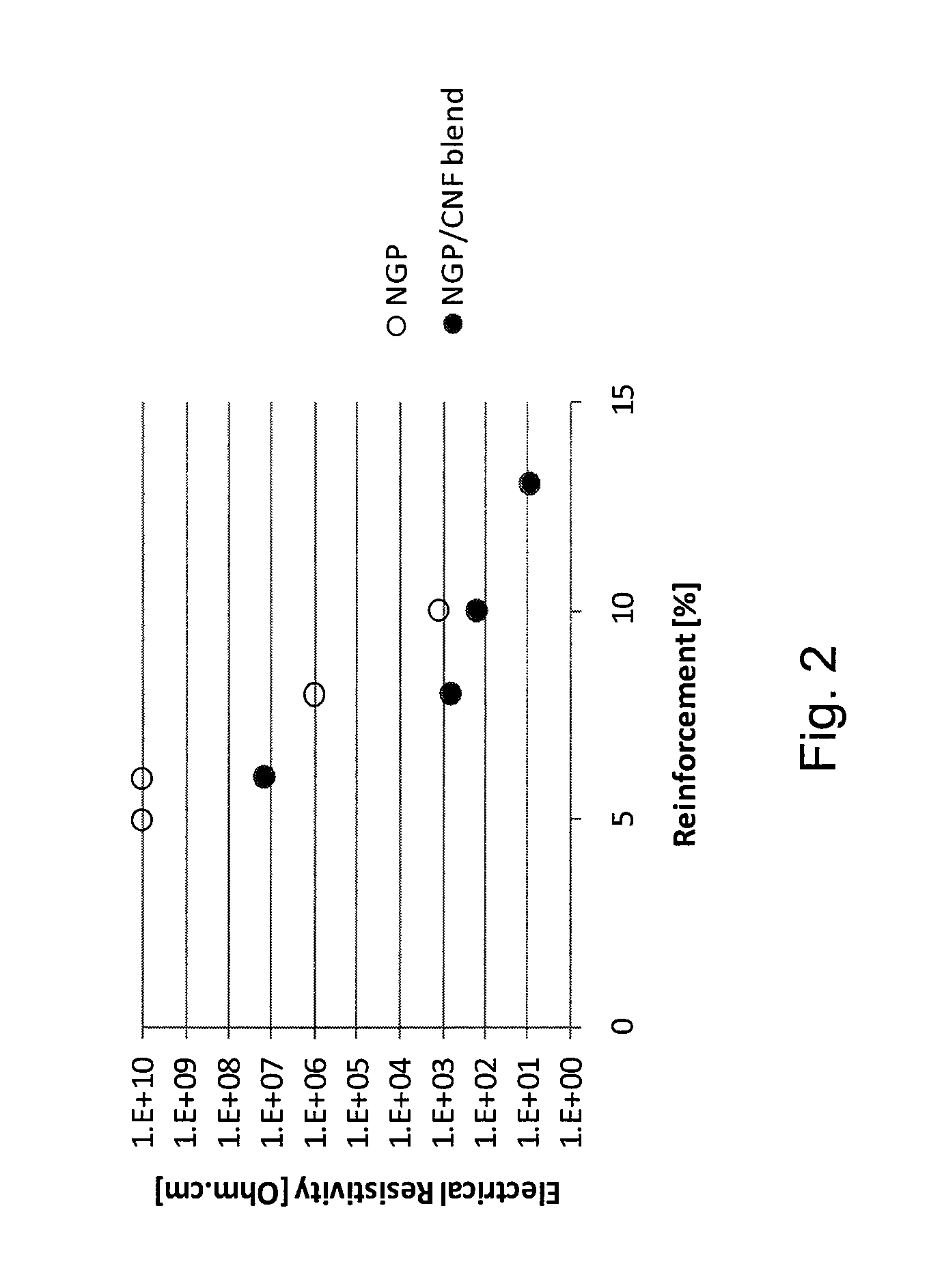
InactiveUS8048341B2Low resistivityLarge specific surface areaNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyFiberCarbon Additive
A method of making a polymer composite from a mixture of a polymeric material, carbon nanofibers, and nano-scale particles is provided. The carbon nanofibers are less than about 1 micrometer in diameter, and the nano-scale particles are shorter in length than the carbon nanofibers. The nano-scale particles are selected from nano-scale carbon additives, non-conductive nano-clays, nano-scale conductive metallic additives, or combinations thereof. The components are mixed to form a polymer composite. A polymer composite having a resistivity of less than about 107 ohm-cm is also described.
Owner:APPLIED SCI
Dry distillation carbonizing treatment system for urban and rural lightweight wastes
PendingCN106833694AImprove insulation effectSave fuelGas treatmentDispersed particle separationThermal energyWaste treatment
The invention relates to a dry distillation carbonizing treatment system for urban and rural lightweight wastes, and belongs to the technical field of garbage treatment. The dry distillation carbonizing treatment system comprises three parts including a dry distillation carbonizing kiln device, a dust-removal purification device and a wastewater circulation treatment device, wherein the dry distillation carbonizing kiln device is communicated with the dust-removal purification device by a flue positioned on a kiln body of the dry distillation carbonizing kiln; after the wastes are subjected to treatment of dust removal, washing and purification by heat energy and flue gas which are produced by dry distillation carbonizing, the flue gas is exhausted from the top of a chimney; wastewater flows into the wastewater circulation treatment device through a wastewater drainage pipe, is precipitated and filtered, and then is pumped into the dust-removal purification device for sprinkling the flue gas to realize circulation treatment and utilization of wastewater. When the system is used by combination with the steel-making field, high-temperature gas produced by dry distillation carbonizing can be used for drying steel-making auxiliary materials or generating electro-thermal energy, carbide can be used as raw materials for steel-making carbon additives and ladle covering agents, and ash contents can be used as raw materials in cement plants or used for preparing organic fertilizers, so that minimization, detoxification and resource of urban and rural lightweight waste treatment can be realized to a maximized extent.
Owner:攀枝花市银江金勇工贸有限责任公司
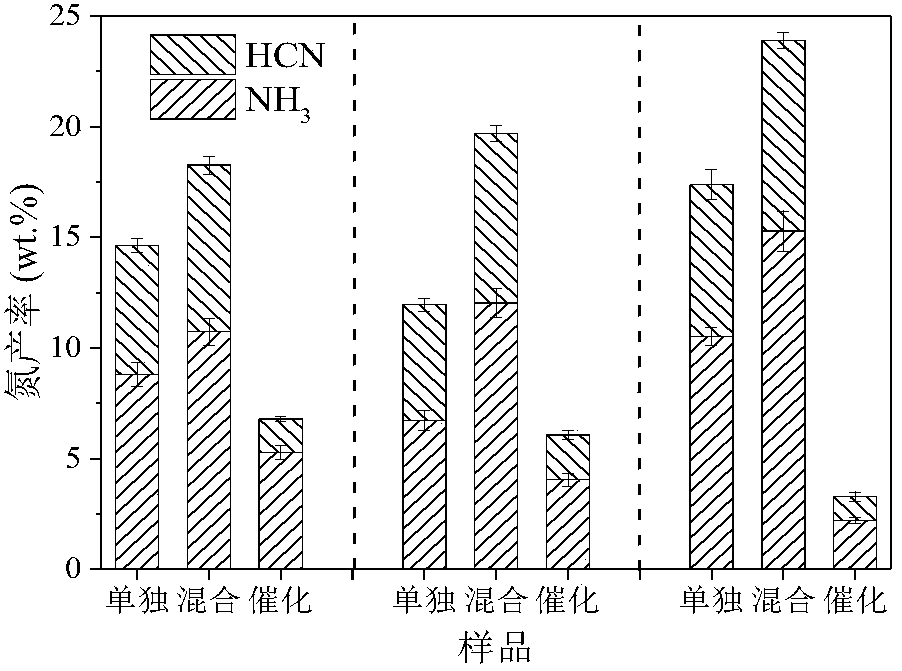
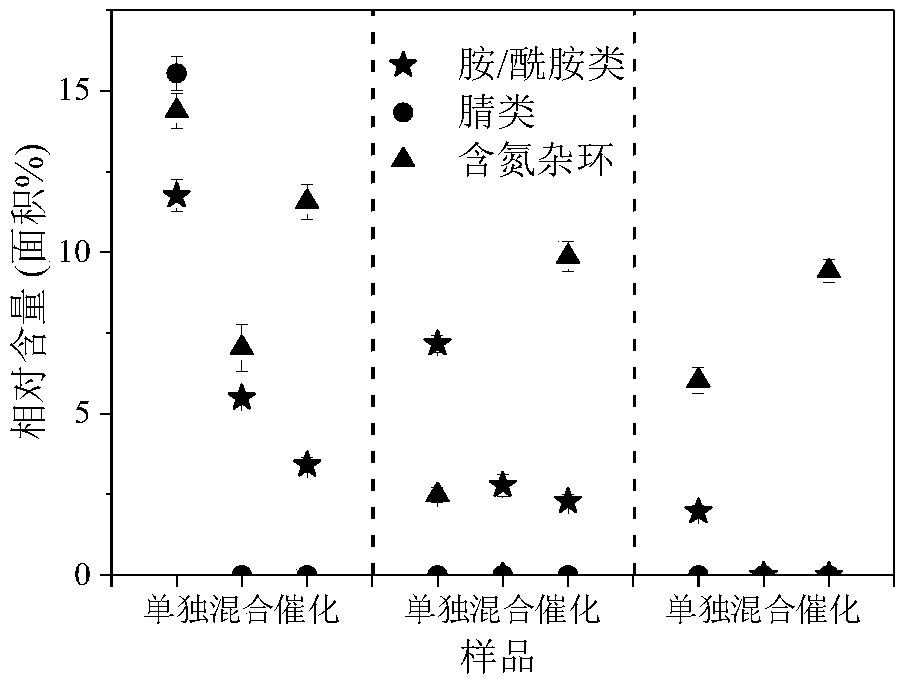
Method for controlling nitrogen emission in process of preparing liquid oil from algae
InactiveCN108048122AWide variety of sourcesReduce manufacturing costGas treatmentDispersed particle separationBiomass carbonCarbon Additive
The invention belongs to the field of biomass utilization and discloses a method for controlling nitrogen emission in a process of preparing liquid oil from algae. The method comprises the following steps: S1: grinding and drying algae biomass and lignocellulose biomass; S2: putting the lignocellulose biomass in the step S1 into a fixed bed reactor and carrying out a pyrolytic reaction to obtain abiomass carbon additive; S3: mixing the algae biomass and the lignocellulose biomass in the step S1, and pyrolyzing the mixture to obtain a pyrolytic carbon solid and pyrolytic volatile components; S3: enabling a part of the nitrogen-containing substances in the pyrolytic volatile components to fully react with the biomass carbon additive obtained in the step S2, so as to fix a part of the nitrogen in the biomass carbon additive and achieve an aim of reducing nitrogen emission. According to the method provided by the invention, the nitrogen emission is effectively reduced, and the nitrogen can be converted into a nitrogen-doped carbon material with a high added value, thereby facilitating green utilization of the algae biomass.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
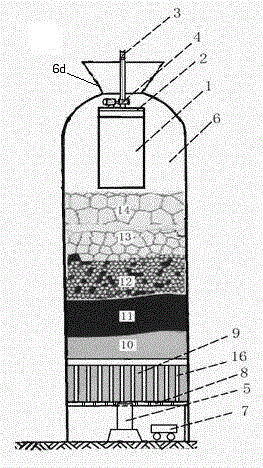
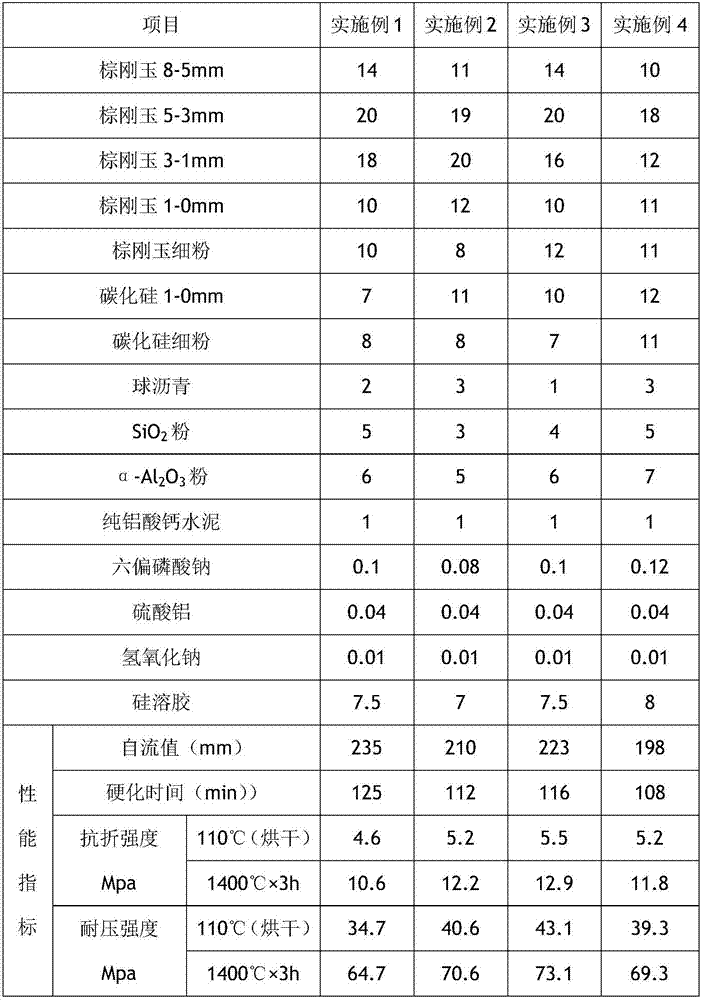
Rapidly-hardened blast furnace hearth repair material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a rapidly-hardened blast furnace hearth repair material, which comprises a solid material, an admixture and a binding agent, wherein the solid material contains corundum particles and / or fine powder, silicon carbide particles and / or fine powder, a carbon additive and composite superfine powder, and the admixture includes a dispersant and a coagulation accelerator. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the rapidly-hardened blast furnace hearth repair material. The repair material belongs to a downgrade flow type and rapidly-hardened type, can be pumped and poured by clinging to a hearth carbon brick formwork, a pouring body and carbon bricks are closely attached, the construction is rapid and simple and convenient, the repair material is rapidly hardened, the construction period can be effectively shortened by 25%, the structure integrity of the repaired hearth is good, no brick joint exists, and the compactness is high.
Owner:CHINA JINGYE ENG +2
Specific engine oil for natural gas and gasoline dual-fuel engine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104745279AMeet environmental protection requirementsHigh viscosity indexLubricant compositionHeat stabilityEvaporation
The invention relates to specific engine oil for natural gas and gasoline dual-fuel engine and a preparation method thereof. The specific engine oil comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 46.18% of 220N base oil, 15% of 400N base oil, 20% of polyalpha-olefin base oil PAO-10, 0.02% of an antioxidant, 7.0% of a viscosity index improver, 0.02% of a pour point depressant, 1.6% of a complexing agent, 1.7% of a clearing dispersing agent, 4.0% of trinitrogen molybdenum phosphorus oxide, 0.3% of a clearing agent, 1% of zinc borate, 0.3% of an antidetonant, 0.02% of nanocopper, 0.14% of an oiliness agent, 0.42% of an anti-wear agent and 2.3% of an ash-free low-carbon additive. The specific engine oil for natural gas has the beneficial effects that (1) the specific engine oil can meet requirements of two fuels and can be normally used at relatively high and low temperatures; (2) the specific engine oil is prominent high in viscosity index, relatively high in saturability and relatively low in evaporation loss ratio; (3) the specific engine is relatively high in explosion resistance and can meet environment-friendly requirements; (4) the specific engine oil has ultrastrong piston cylinder body repair capacity and excellent heat stability; (5) the specific engine oil is relatively strong in lubricating capacity and relatively low in operation resistance, and the service life is prolonged; and (6) the specific engine oil is relatively strong in oxidization and wear resistance.
Owner:山东浩泰天然气股份有限公司
Flame-retardant adhesive and sealant with improved mechanical properties
ActiveUS20190169476A1Improve flame retardant performanceImprove mechanical propertiesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolymer scienceCarbon Additive
A moisture-curable composition having flame retardant properties and to the use thereof as an adhesive, sealant or coating. The composition according to the invention contains at least one moisture-reactive polymer in a proportion of 10% to 50% by weight, at least one precipitated, surface-coated aluminum trihydrate in a proportion of 30% to 60% by weight and in preferred embodiments up to 25% by weight of at least one phosphorus-containing compound and up to 20% by weight of at least one carbon additive. The inventive moisture-curable composition has excellent flame retardant properties and after curing remains resistant for a long time at high heat levels.
Owner:SIKA TECH AG
Dissolution method of monohydrate bauxite ore
ActiveCN102976377AReduce lossesReduce the burden onAluminium oxides/hydroxidesCarbon AdditiveRed mud
The invention discloses a dissolution method of monohydrate bauxite ore. An organic additive or a carbon additive is added to a bauxite dissolution system, and therefore, inhibition of a titanium mineral on the dissolving process of aluminum oxide is solved. Compared with the existing dissolution method of adding lime in the aluminum oxide industry, with the adoption of the dissolution method disclosed by the invention, the loss of the aluminum oxide can be reduced; the amount of discharged red mud is reduced by about 30%; and the burden of a dissolved ore slurry separating and washing system is reduced, and meanwhile, enrichment of iron mineral is facilitated and the iron mineral is transformed into easy-to-separate magnetic iron component.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Negative electrode carbon additive for improving charging acceptance of lead-carbon battery and application thereof
InactiveCN110571433AIncrease kinetic activityImprove charge acceptanceNegative electrodesCarbon preparation/purificationElectrochemical responsePorous carbon
The invention discloses a negative electrode carbon additive for improving charging acceptance of a lead-carbon battery, which belongs to the technical field of lead-acid battery manufacturing. In numerous biomass materials, the content of nanoscale silicon dioxide in the rice husks is as high as 20%. The rice husk is subjected to alkali treatment to remove most of nanoscale silicon dioxide on thesurface, and carbonization is performed to obtain the rice husk-based porous carbon mainly comprising macropores / mesopores. Macroporous and mesoporous structures of the rice husk-based porous carboncan provide a good ion conductor for an energy storage device, so that the kinetic activity of electrochemical reaction is improved. The rice husk-based porous carbon is uniformly mixed with one or more of activated carbon, carbon black, graphite, expanded graphite, graphene, single-walled carbon nanotubes, multi-walled carbon nanotubes and the like, so that the conductivity of the negative electrode carbon additive is further enhanced. The carbon additive for the negative electrode of the lead-carbon battery can effectively improve the charging acceptance of the lead-carbon battery, inhibit the sulfation phenomenon of the negative electrode of the lead-acid battery in a partial state of charge (PSoC) and prolong the cycle life of the battery in the PSoC.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for preparing hematite oxidized pellets
The invention discloses a method for preparing hematite oxidized pellets. The method comprises the following steps: mixing hematite powder, carbonaceous additives, bentonite and water according to the mass ratio of 79.5-86:1-1.5:1-2:10~ 18 ratio to obtain a material mixture; said material mixture is pressed into balls to obtain green balls, wherein said green balls have at least one opening therethrough; and said green balls are sequentially dried, preheated And oxidation roasting treatment, in order to obtain the hematite oxide pellets. The method can effectively prepare and obtain high-reactivity hematite oxidized pellets, and the obtained hematite oxidized pellets have low roasting fuel consumption, high strength and good metallurgical performance, and are especially suitable for use in gas-based shaft furnaces.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
High heat conductivity carbon brick for blast furnace and its producing method
InactiveCN1304329CEliminate the calcination processConducive to the rational use of resourcesBlast furnace componentsBlast furnace detailsBrickCarbon Additive
The present invention relates to refractory carbon material for iron smelting blast furnace, and is especially high heat conductivity carbon brick for blast furnace lining and its production process. The high heat conductivity carbon brick for furnace lining has material comprising adhesive 20-24 wt%, crushed graphite 40-50 wt%, roasted segment 25-37 wt% and non-carbon additive 1-3 wt%. The main materials are side products from carbon plant, needs no calcining, and results in low cost. Using great amount of crushed graphite makes the carbon brick possess heat conducting coefficient up to 30 W / m.K, and is favorable to strengthening the furnace bottom cooling effect and prolonging blast furnace life.
Owner:CHENGDU CARBON
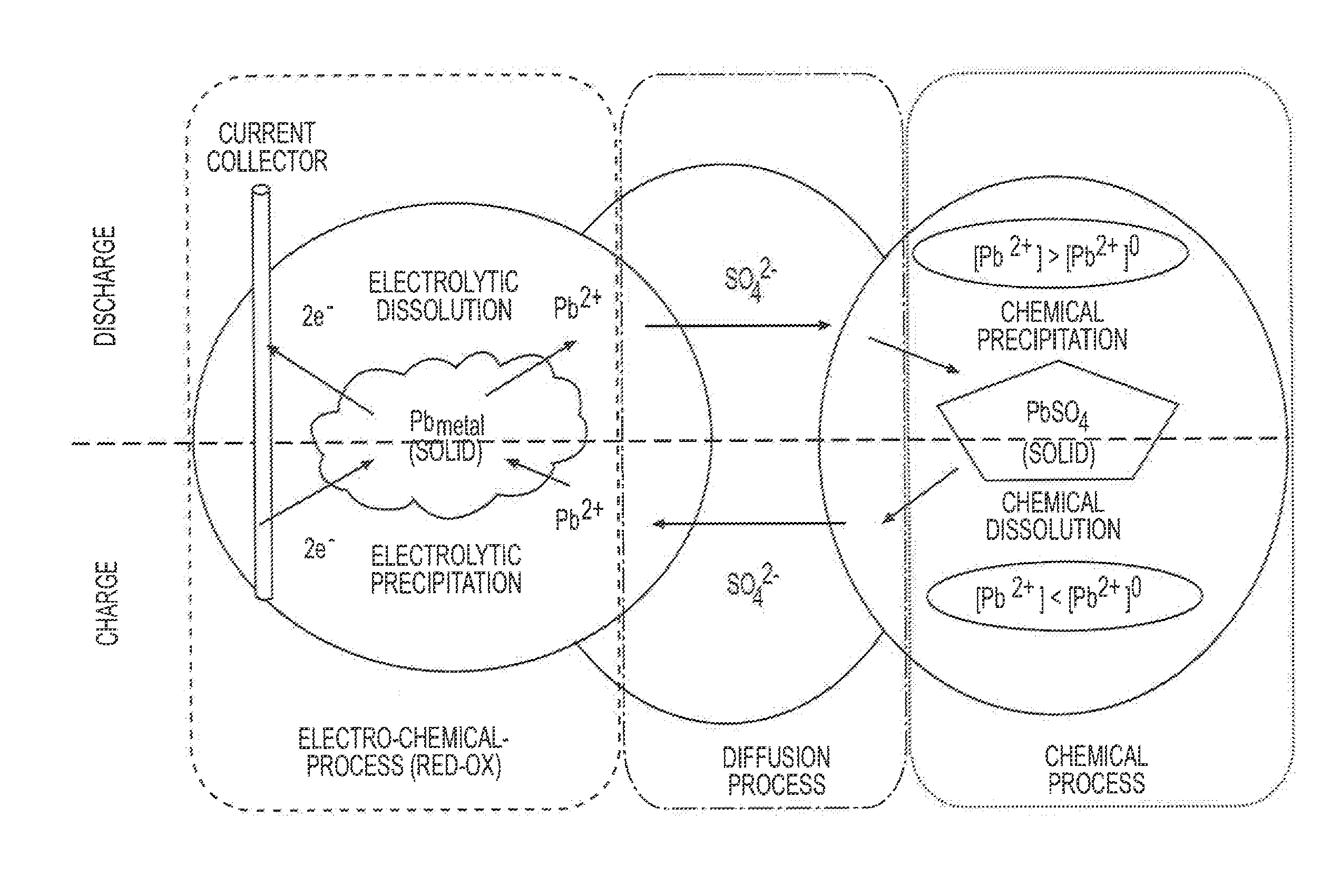
Preparation method of pure lead lead-carbon battery and pure lead lead-carbon battery
InactiveCN107863500AImprove charge acceptanceImprove cycle performanceLead-acid accumulatorsCell electrodesHigh rateCarbon Additive
The invention provides a preparation method of a pure lead lead-carbon battery and a pure lead lead-carbon battery. Specifically, the preparation method of a negative lead plaster in preparation of the pure lead lead-carbon battery includes: subjecting lead powder and auxiliary materials to dry blending a obtain a mixed ingredient; dispersing a carbon additive in a mixed solution, and performing stirring to obtain a carbon pre-dispersion solution; mixing the mixed ingredient with the carbon pre-dispersion solution, adding sulfuric acid and performing stirring to obtain the lead-carbon batterynegative lead plaster. The battery made by the method provided by the invention not only accords with the nominal capacity and high-rate discharge performance, but also has charging acceptance abilityimproved by 30% or more compared with ordinary lead-acid storage batteries, and has PSoC cycle performance improved by 50% or more.
Owner:JIANGSU LEOCH BATTERY
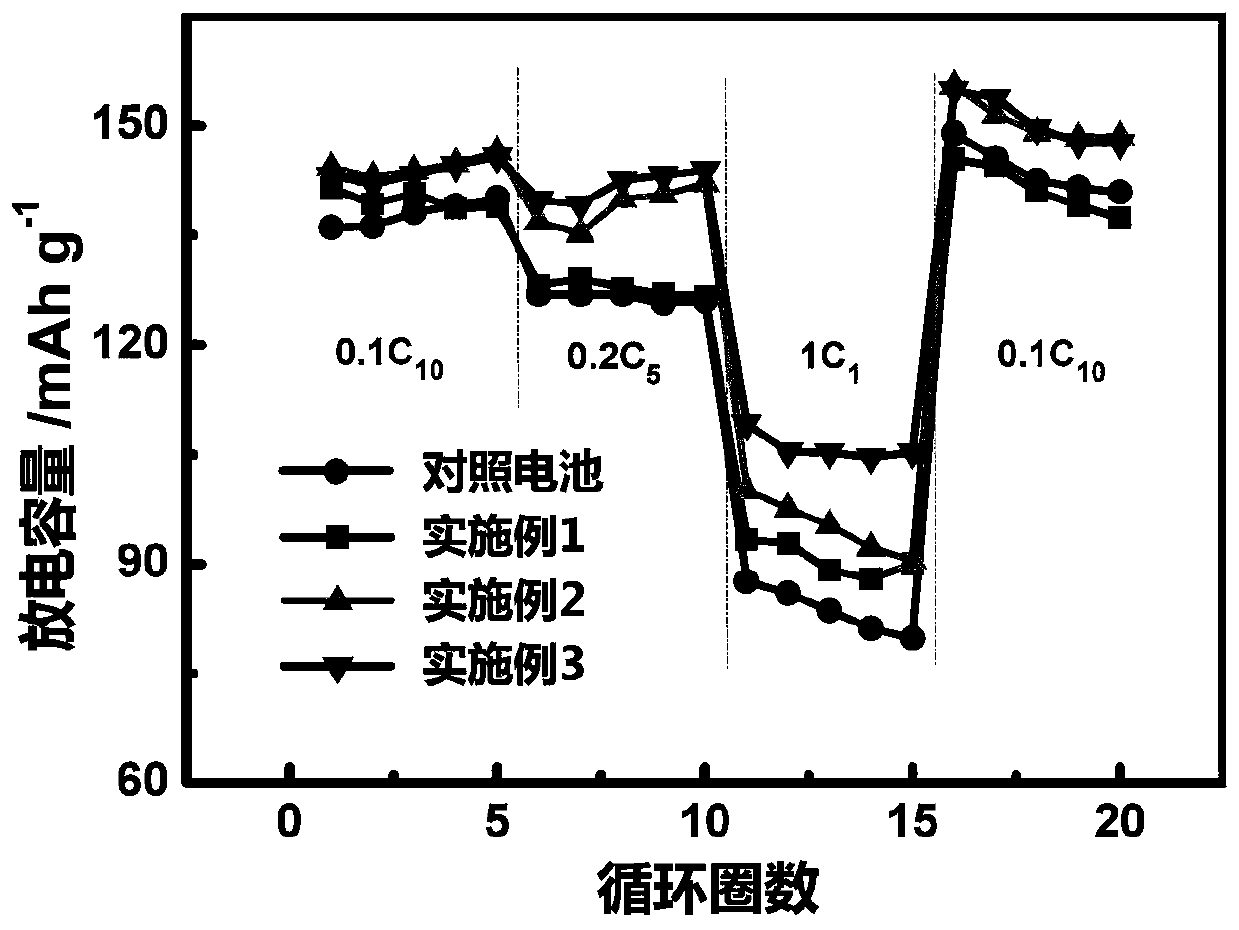
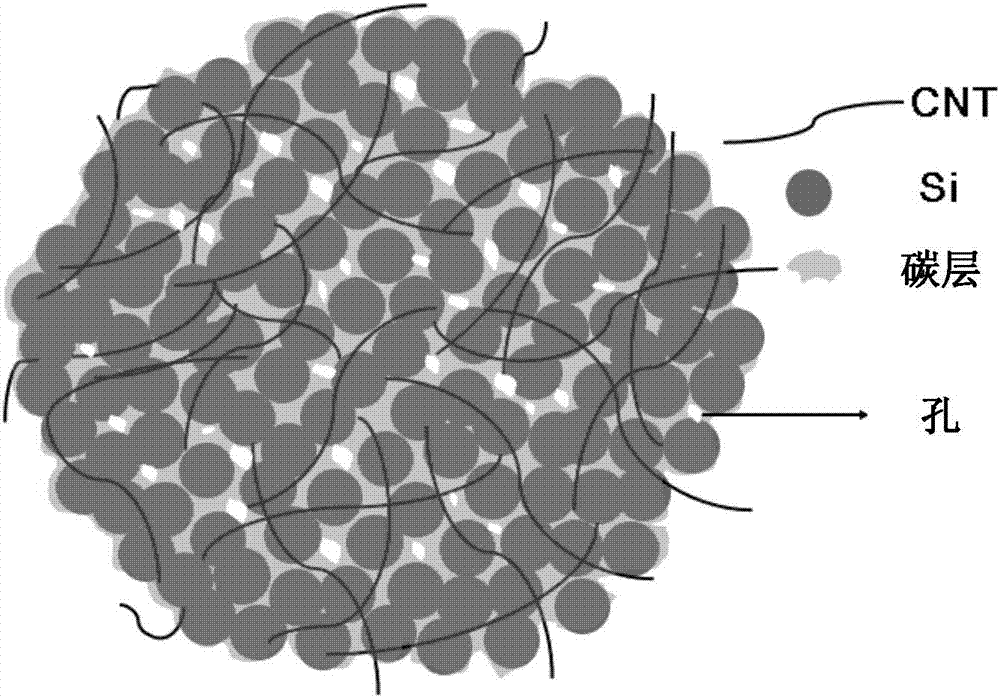
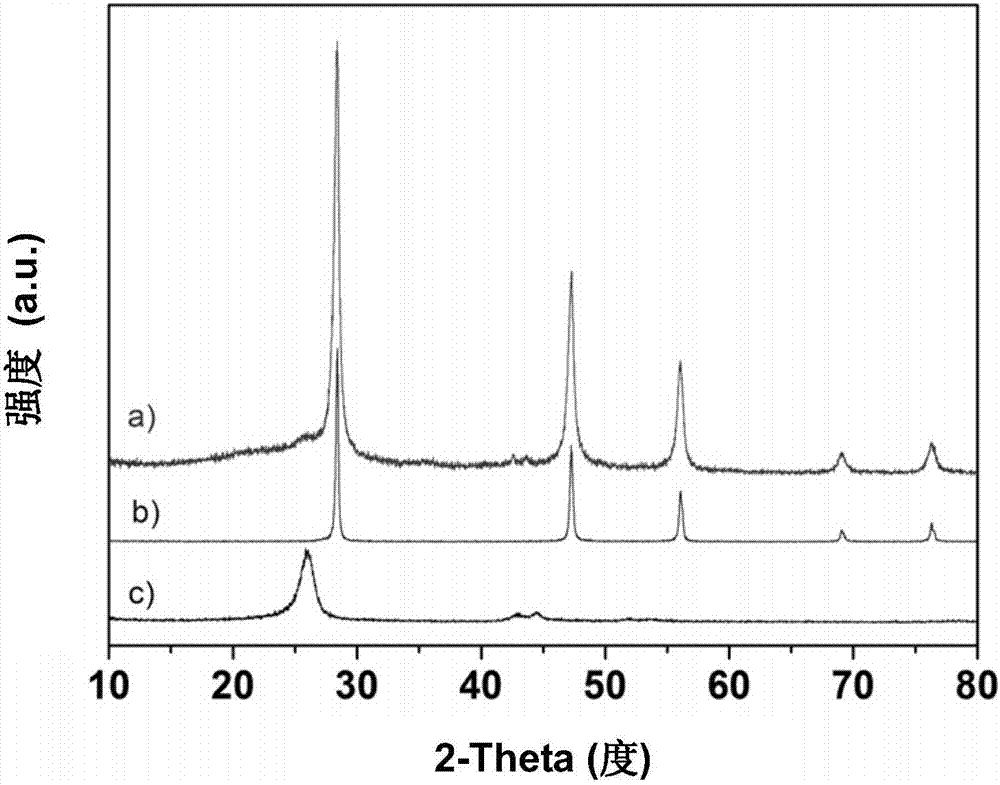
Silicon-carbon composite, a method for preparing said composite, and an electrode material and a battery comprising said composite
The present invention relates to a silicon-carbon composite, which is present in a form of porous secondary particle and contains silicon nanoparticles, one or more conductive carbon additives, and a conductive carbon coating layer. The present invention further relates to a method for preparing said composite, and an electrode material and a battery comprising said composite.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electric immersion heater for diesel exhaust fluid reservoir
ActiveUS20180171849A1Faster and efficient heatingFaster and efficient and thawingInternal combustion piston enginesSilencing apparatusFiberYarn
An immersion heater including an encapsulated, semi-conductive, heating element. The heating element may be a non-metallic, carbon-based material in the form of a monofilament, a yarn or bundle of semi-conductive fibers which may be twisted, braided fibers or yarns, or the like. The encapsulation may be in the form of a tube of one or more layers of encapsulation material(s) with the heating element inserted therein. Alternately, the heating element may be thermoplastic with semi-conductive carbon additive, and the heating element may be coated with one or more external layers of insulating encapsulation material(s). The encapsulation material may be a rubber or thermoplastic material with sufficient chemical resistance to be immersed in a reservoir of fluid subject to freezing or thickening at low temperatures, such as DEF. The heater may be thermoformed into a predetermined fixed shape.
Owner:THE GATES CORP
Rechargeable battery and electrode compound for same
InactiveCN108269968AReduce resistanceImprove electronic conductivityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureSolid state electrolyteCarbon Additive
The invention relates to a rechargeable battery and an electrode compound for the same. The electrode compound comprises active substance, carbon additive and first semisolid electrolyte. The carbon additive and the first semisolid electrolyte are added into the electrode compound, so that electron conductivity can be enhanced, and interface resistance can be lowered; the first semisolid electrolyte is filled in gaps among active substance particles in an electrode, so that better contact and ion migration between active substance particles / first semisolid electrolyte interfaces are realized;the carbon additive can be uniformly distributed in the electrode or glued / coated on the surface of the electrode to serve as an electron conductive network for electron conduction and enhancing electron conductivity of the electrode. The electrode compound presents improved battery performance, and deep discharge cycling is enhanced.
Owner:HKUST SHENZHEN RES INST +1
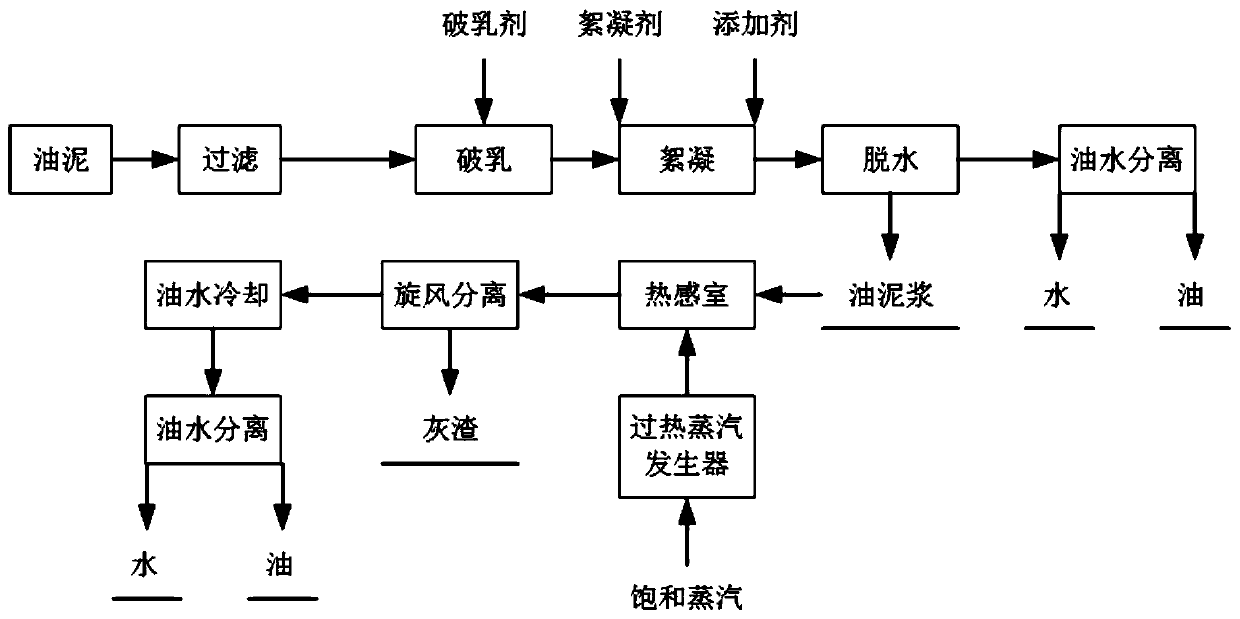
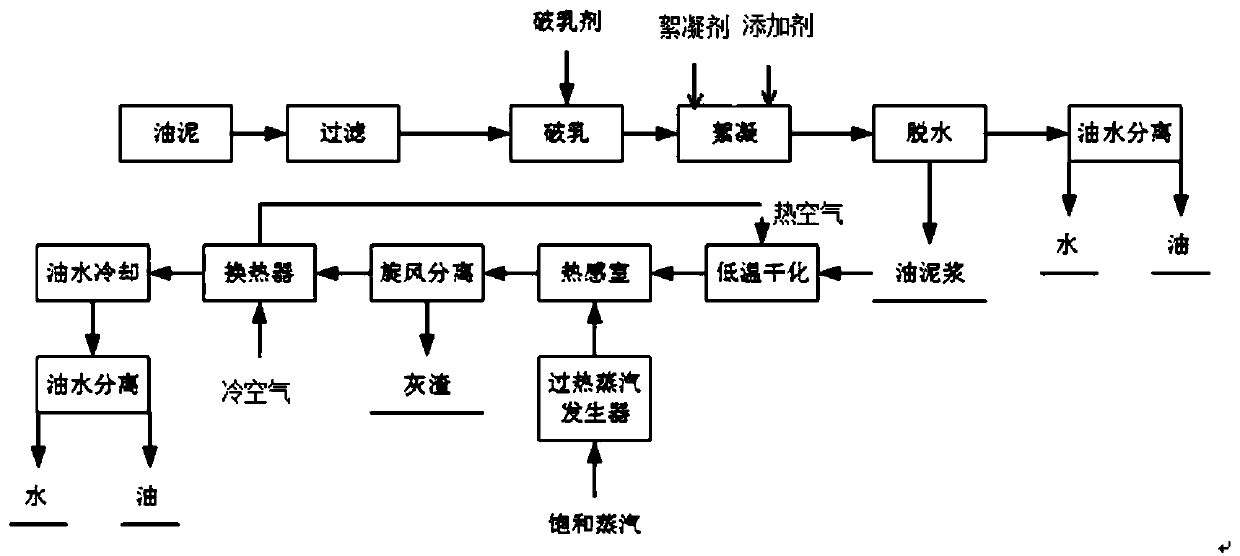
Oil sludge treatment method and system
PendingCN110330198AGood flocculation effectAccelerate evaporationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningCarbon AdditiveReduction treatment
The invention belongs to the technical fields of oil fields, petrochemical industry and hazardous waste environmental protection, and particularly relates to an oil sludge treatment method and system.The oil sludge treatment method comprises the following steps: 1) spraying superheated steam to oil sludge with carbon additives to obtain a mixture of oil-water steam and residues; 2) performing gas-solid separation on the mixture of the oil-water steam and the residues obtained in the step 1) to obtain the oil-water steam and the residues, and performing liquid-liquid separation on the oil-water steam to obtain oil and water. According to the oil sludge treatment method, reduction treatment of the oil sludge is effectively achieved, the residues can be harmless, and secondary pollution canbe prevented.
Owner:北京和荣工程技术有限公司
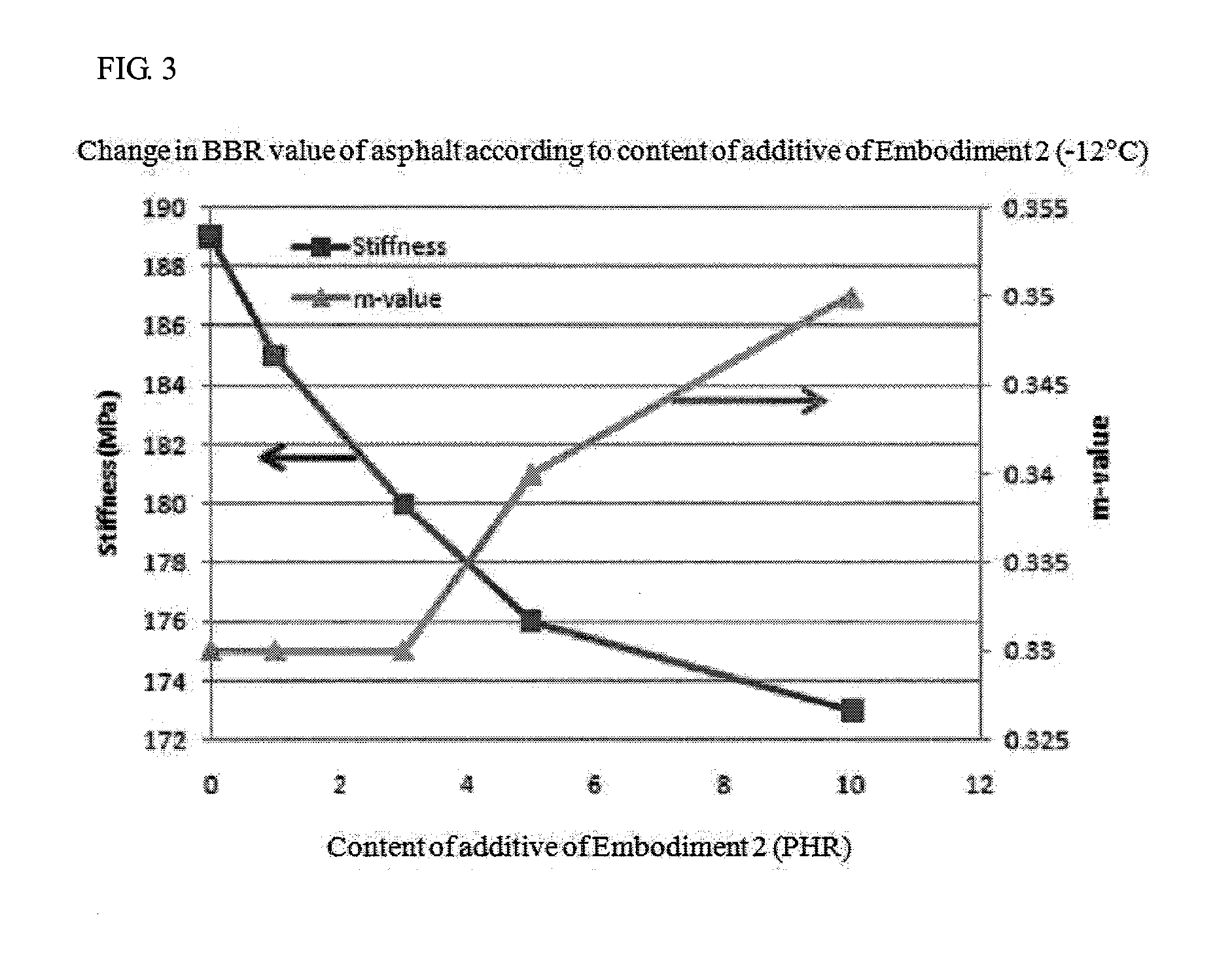
Low carbon-dioxide additive compositions and warm-mix asphalt binder and mixture production method using the additive
ActiveUS20110203484A1Weaken energyCarbon reductionClimate change adaptationCoatingsCarbon AdditiveStearic acid
Provided are a low carbon additive for a warm-mix asphalt (WMA) mixture, in which vegetable wax based on modified palm wax is mixed into polyethylene wax so as to be able to promote high-temperature physical properties of the WMA mixture as well as solve problems on low-temperature physical properties of the WMA mixture, warm-mix asphalt produced using the same, and a method of producing the WMA mixture using the using the warm-mix asphalt. The low carbon additive contains polyethylene wax and vegetable wax at a weight ratio of 20:1 to 1:2. The modified palm wax employs palm wax that melt-reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and stearic acid (CH3(CH2)16COOH). This low carbon additive enables the WMA mixture to be efficiently produced, and thus makes it possible to reduce heating energy required when the WMA mixture is produced. Thereby, it is possible to remarkably reduce the emission of carbon dioxide that is a principal factor of global warming.
Owner:KOREA INST OF CIVIL ENG & BUILDING TECH
Negative plate for lead acid battery
InactiveCN102576863AReduce maintenanceAvoid smallLead-acid accumulatorsElectrode carriers/collectorsCarbon AdditiveMass ratio
Capacitor pastes for flooded deep discharge lead-acid batteries include lead oxide, a carbon additive, and an aqueous acid. The capacitor paste contains lead and carbon in a lead to carbon mass ratio of about 5:1 to 82:1. Hybrid negative plates for flooded deep discharge lead-acid batteries can be made using such pastes in combination with traditional pastes. The hybrid negative plates include a capacitor paste on a bottom portion of the plate, and a traditional paste on the remainder of the plate. Batteries using the capacitor paste and hybrid plates exhibit improved performance over batteries with conventional plates and pastes and require less overcharge to prevent electrolyte stratification.
Owner:TROJAN BATTERY
Cold cathode and methods for producing the same
The present invention relates to the production of highly efficient films for field-effect electron emitters, wherein said films may be used in the production of flat displays, in electronic microscopes, in microwave electronics, in light sources as well as in various other applications. This invention more precisely relates to a cold cathode that comprises a substrate having a carbon film applied thereto. The carbon film has an irregular structure consisting of carbon micro-ridges and / or micro-threads which are perpendicular to the surface of the substrate, have a size ranging typically from 0.01 to 1 microns and a distribution density of between 0.1 and 10 mum2. This invention also relates to method for producing a cold electrode, wherein said method comprises generating a DC current discharge in a mixture comprising hydrogen and a carbon-containing additive, and further depositing the carbon phase on the substrate located at the anode. This method is characterized in that the discharge is generated at a current density of between 0.15 and 0.5 A / cm2. The deposition process is carried out in a mixture containing hydrogen and vapors of ethylic alcohol or methane, under an overall pressure of between 50 and 300 Torrs and at a substrate temperature of between 600 and 900° C. The concentration of ethylic alcohol vapors ranges from 5 to 10% while that of methane vapors ranges from 15 to 30%. This invention also relates to another method for producing a cold cathode, wherein said method comprises generating a microwave discharge at an absorbed power of between 100 and 1000 W. This discharge is generated in a mixture containing gaseous carbon oxide as well as methane in an 0.8-1.2 concentration and under a pressure of between 10 and 200 Torrs, the carbon phase being further deposited on the substrate. This method is characterized in that the deposition process is carried out at a temperature on the substrate surface that ranges from 500 to 700° C.
Owner:OBSCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOY OTVETSTVENNOSTYU VYSOKIE TEKHNOLOGII VOROBIOVY GORY
Novel negative electrode material for lithium-ion/potassium-ion battery and preparation method thereof
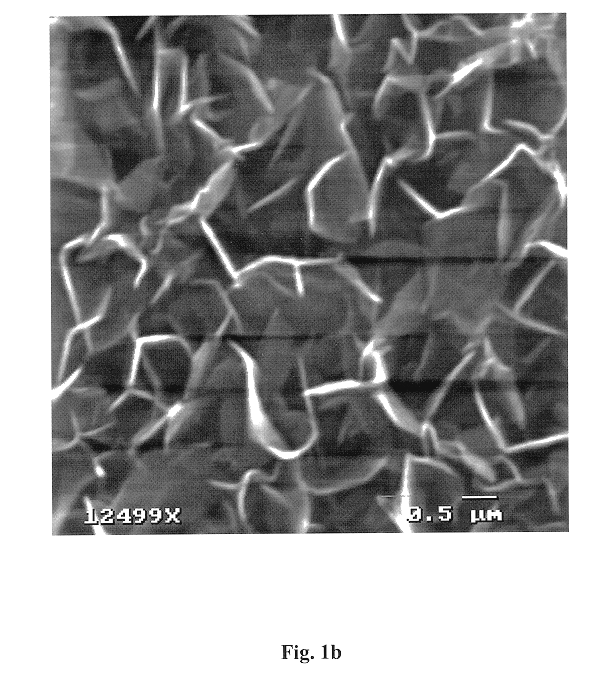
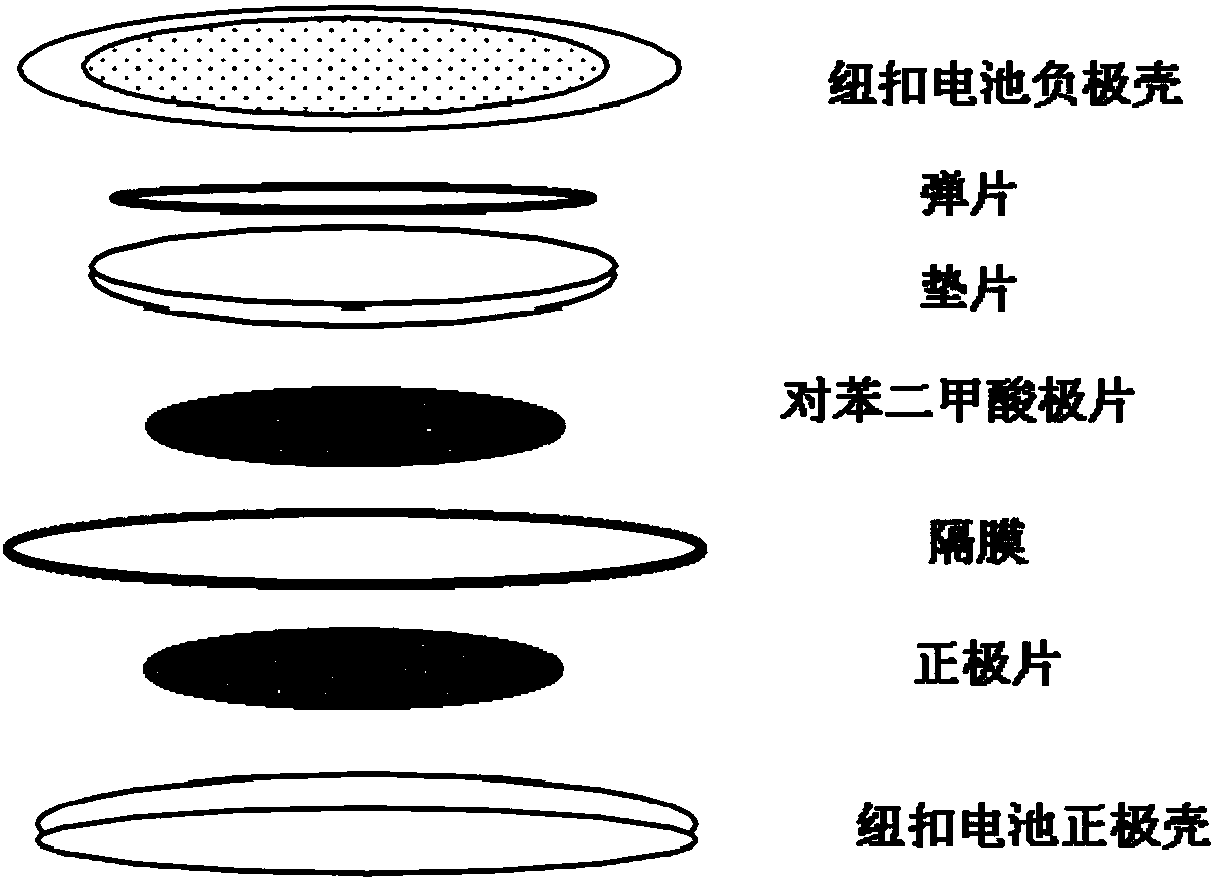
ActiveCN108258244AElectrochemically activeEasy to produceNegative electrodesSecondary cellsSlurryTerephthalic acid
The invention provides a novel negative electrode material for a lithium-ion / potassium-ion battery and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing terephthalic acid with conductive carbon additive, then adding distilled water, next, carrying out ball milling, and afterwards, drying; mixing a dried matter with a binder, and grinding, so as to obtainslurry; coating the obtained slurry on a matrix, and drying, so as to obtain the novel negative electrode material. The preparation method uses the terephthalic acid for preparing a negative electrodematerial for a battery; the obtained negative electrode material can be simultaneously used for the lithium-ion battery and the potassium-ion battery, so as to realize that one electrode material canbe simultaneously applied to two or more than two battery systems; the preparation method adopts the terephthalic acid as an important component of the negative electrode material; the terephthalic acid is jointly compounded with conductive carbon black and the binder, and the obtained negative electrode material, in the constant-electric-current charge and discharge processes of the lithium-ionbattery and the potassium-ion battery, can be used for improving the specific capacities of the lithium-ion battery and the potassium-ion battery, and meanwhile, has excellent cyclical stability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com