Rechargeable battery and electrode compound for same
A recharging and composite technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, lead-acid batteries, etc., can solve the problems of poor conductivity, low safety of liquid electrolyte, large interface resistance, etc., to reduce resistance and enhance deep discharge Circulation, the effect of reducing interface resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
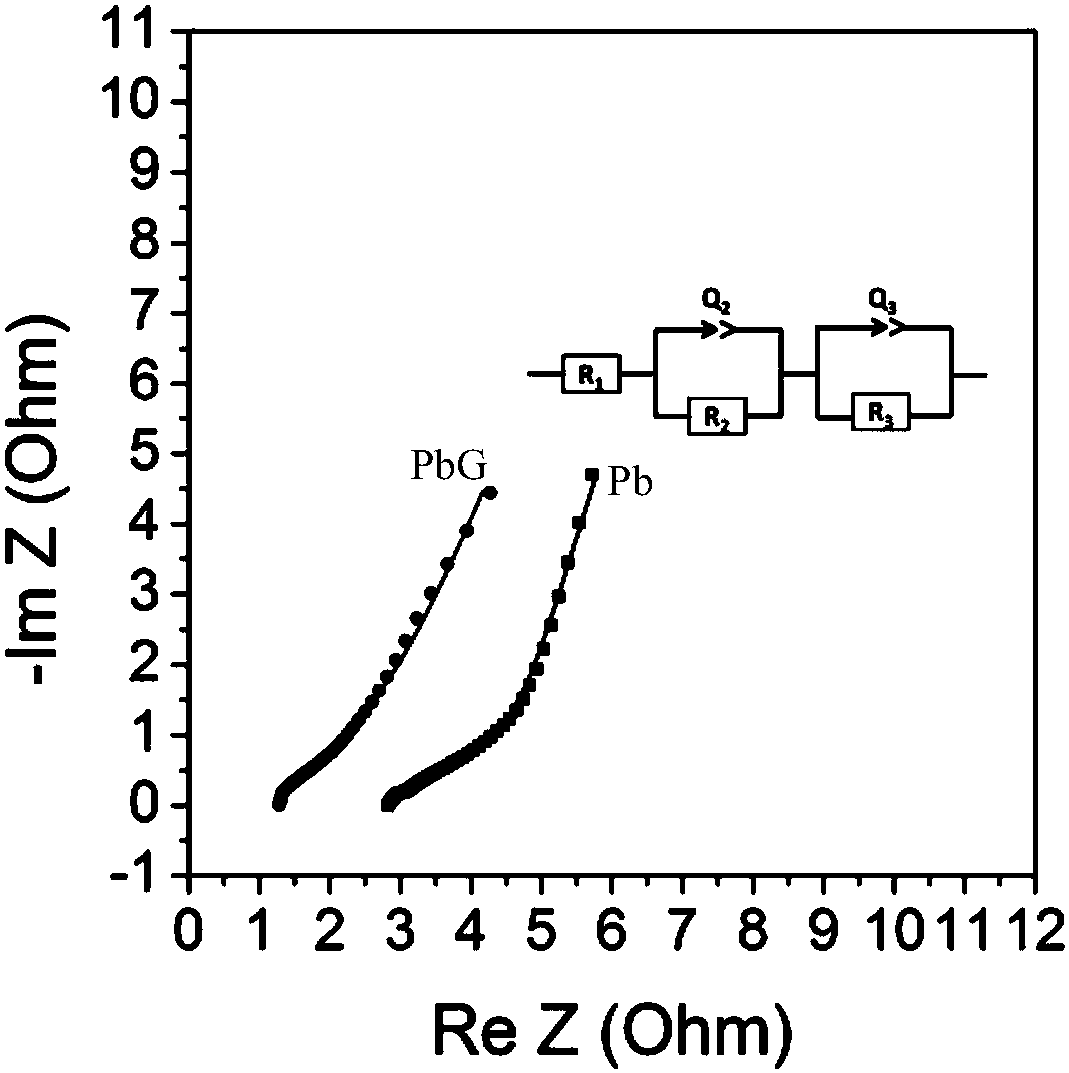
[0045] In a lead-acid battery system, the electrode compound is prepared by mixing 94.8 parts by mass of active material Pb, 5 parts by mass of polyaniline (PANI) gel and 0.2 part by mass of Gr. Using a planetary mixer, according to the above mass ratio, the active material Pb and Gr are mixed, and PANI and sulfuric acid are added, wherein the mass ratio of the added amount of sulfuric acid to PANI is 1. The resulting paste was printed on the existing current collector and then placed in an oven to cure the active material Pb and polyaniline (PANI) gel. The fabricated electrode structure is as figure 1 As shown, Gr and polyaniline (PANI) gel are uniformly distributed inside the electrode.
[0046] The second semi-solid electrolyte between the two electrodes is prepared from polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) gel and sulfuric acid, and the mass ratio of sulfuric acid to PVA is 1.
[0047] The lead-acid battery system assembled in Example 1 was tested by electrochemical full resistance s...
Embodiment 2
[0049]In a lead-acid battery system, the electrode compound is prepared by mixing 99.8 parts by mass of active material Pb, 0.1 part by mass of polyaniline (PANI) gel and 0.1 part by mass of carbon nanotubes. Using a planetary mixer, according to the above mass ratio, the active material Pb and Gr were mixed, and PANI and sulfuric acid were added, wherein the mass ratio of sulfuric acid to PANI was 0.25. The resulting paste was printed on the existing current collector and then placed in an oven to cure the active material Pb and polyaniline (PANI) gel. Gr and polyaniline (PANI) gel are evenly distributed inside the electrode.
[0050] The second semi-solid electrolyte between the two electrodes is prepared from PVA gel and sulfuric acid, and the mass ratio of sulfuric acid added to PVA is 0.25.
[0051] The lead-acid battery system assembled in this embodiment has been tested by electrochemical full resistance spectroscopy (EIS), and the test frequency is 10-10000 Hz. Imped...
Embodiment 3
[0053] In a lead-acid battery system, the electrode compound is prepared by mixing 70 parts by mass of active material Pb, 10 parts by mass of polyaniline (PANI) gel and 20 parts by mass of Gr oxide. Using a planetary mixer, according to the above mass ratio, the active material Pb and Gr oxide were mixed, and PANI and sulfuric acid were added, wherein the mass ratio of sulfuric acid to PANI was 20. The resulting paste was printed on the existing current collector and then placed in an oven to cure the active material Pb and polyaniline (PANI) gel. Gr oxide and polyaniline (PANI) gel are evenly distributed inside the electrode.
[0054] The second semi-solid electrolyte between the two electrodes is prepared from PVA gel and sulfuric acid, and the mass ratio of sulfuric acid to PVA is 20.
[0055] The lead-acid battery system assembled in this embodiment has been tested by electrochemical full resistance spectroscopy (EIS), and the test frequency is 10-10000 Hz. Impedance da...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com