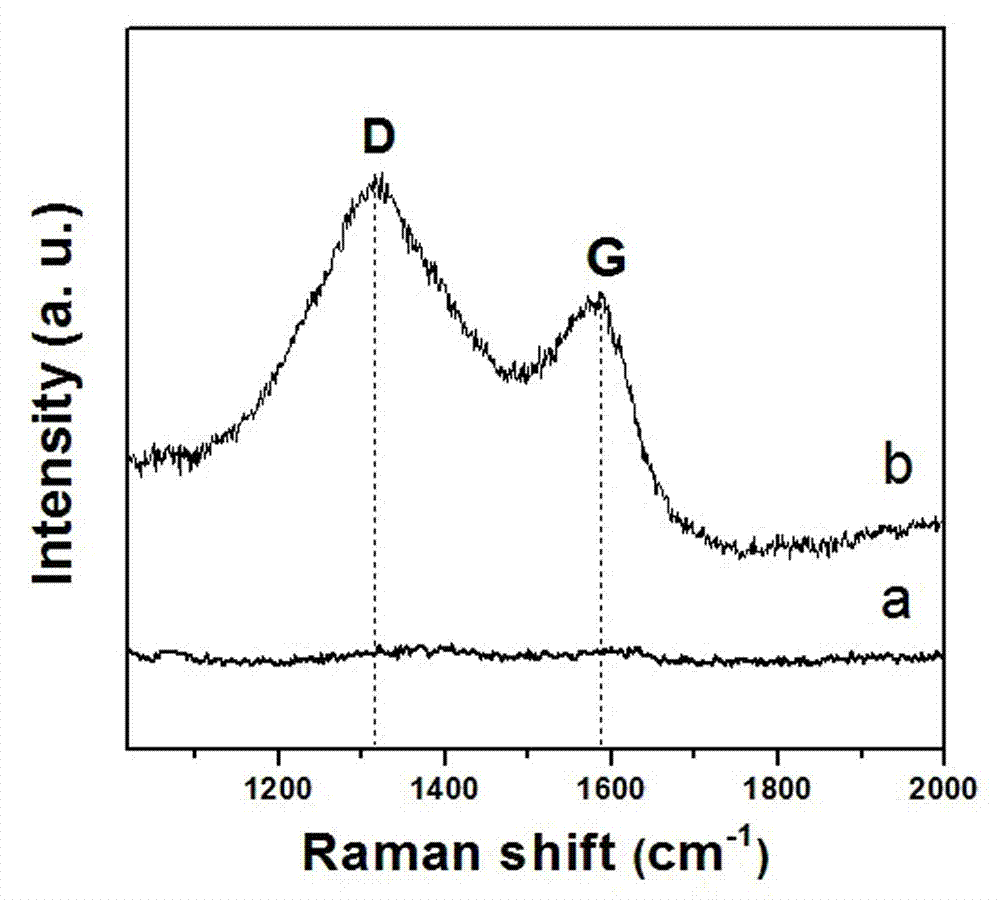
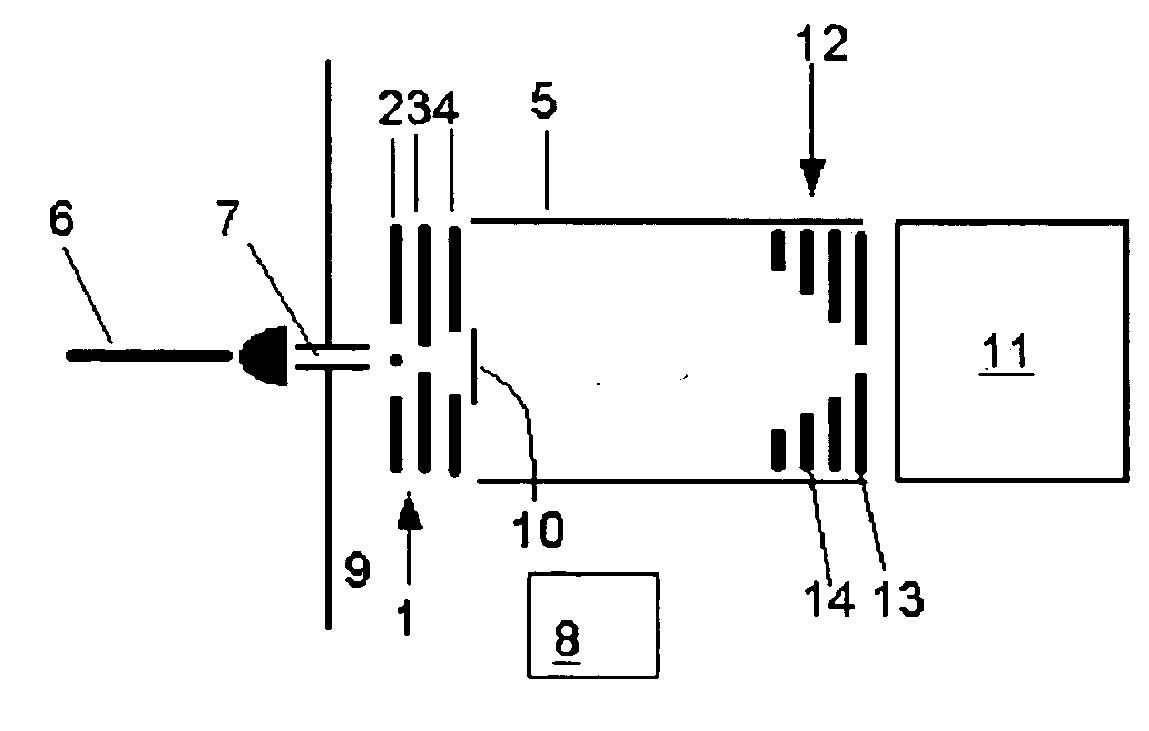
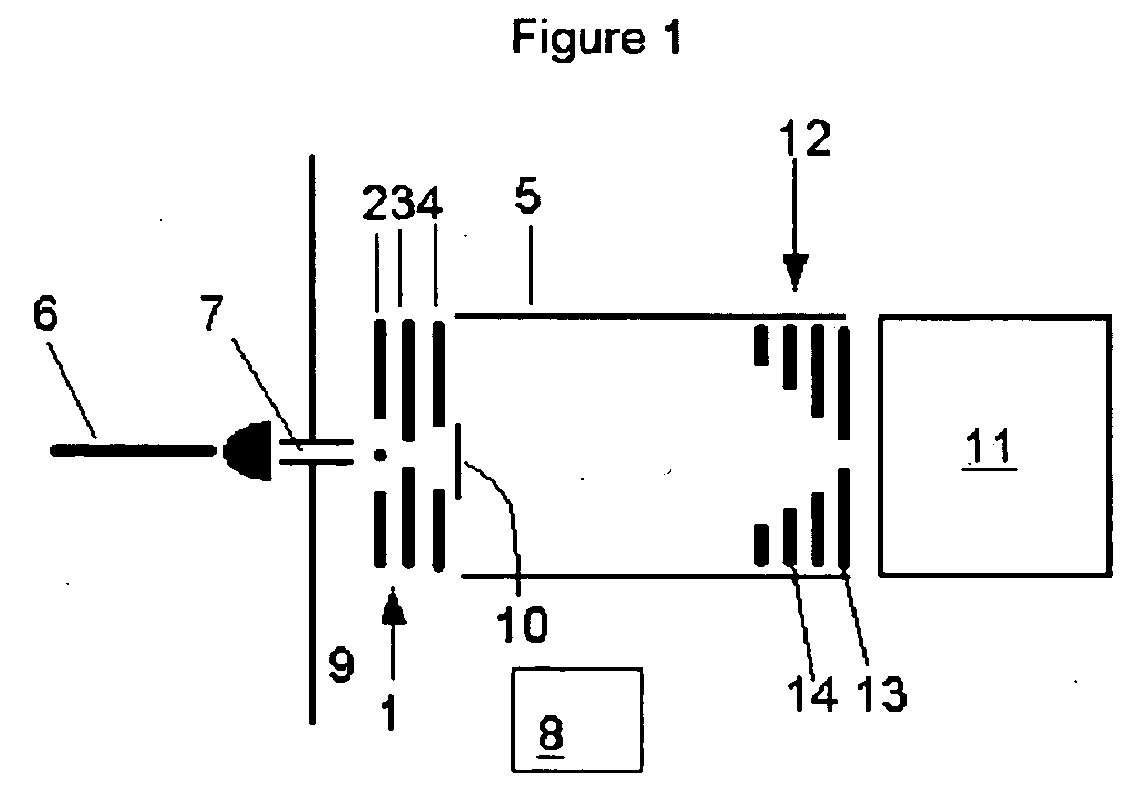
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1288 results about "Ion migration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
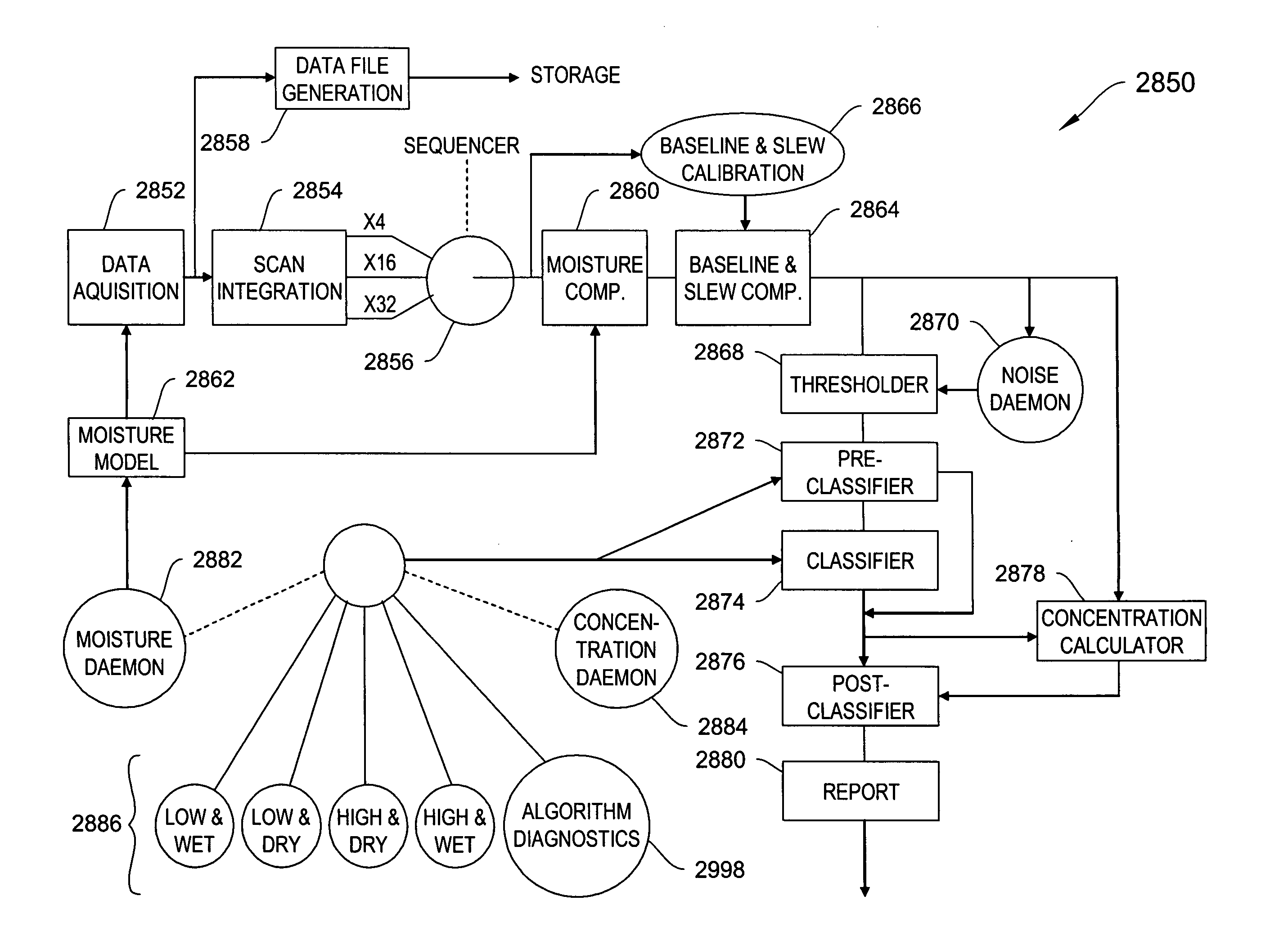
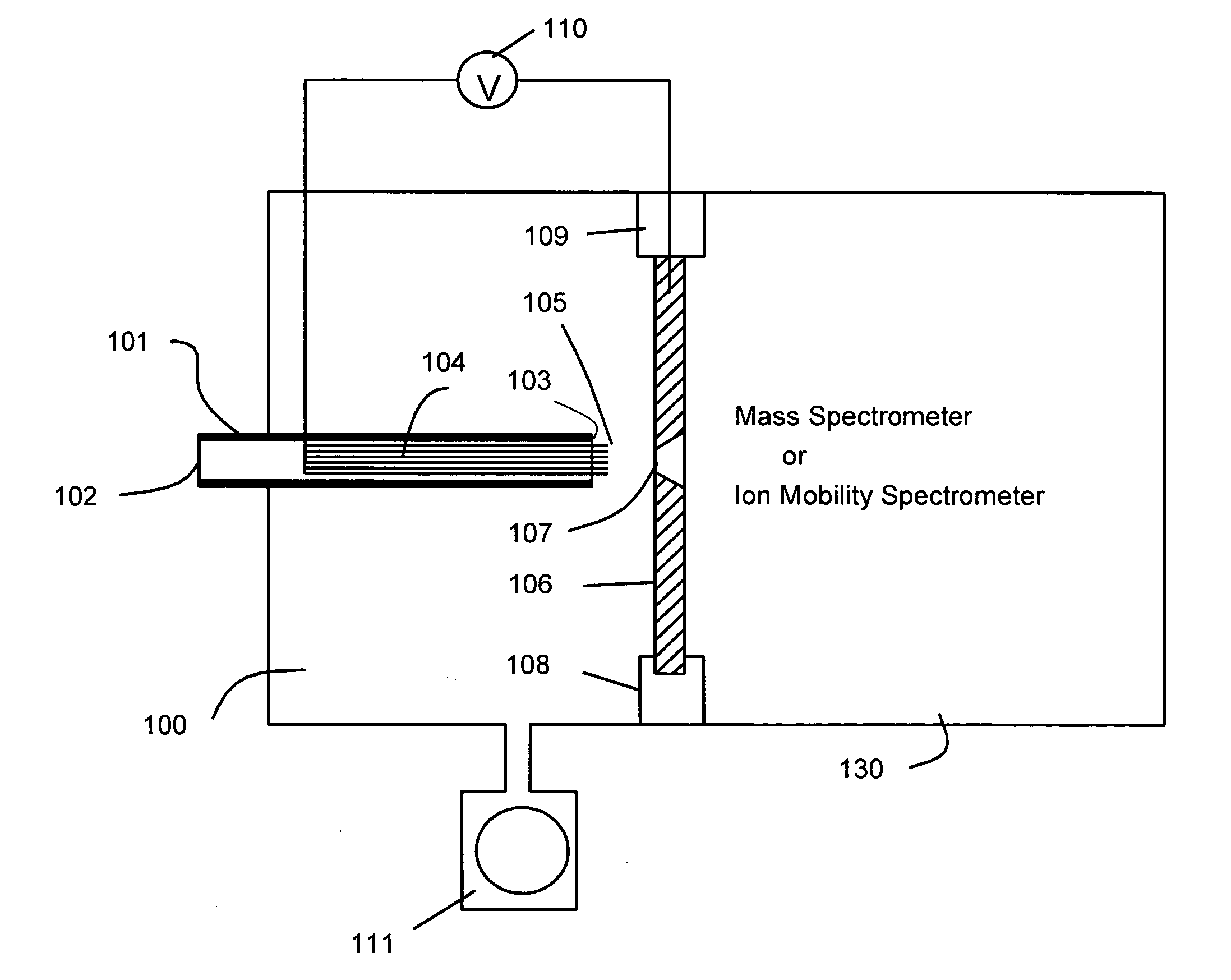
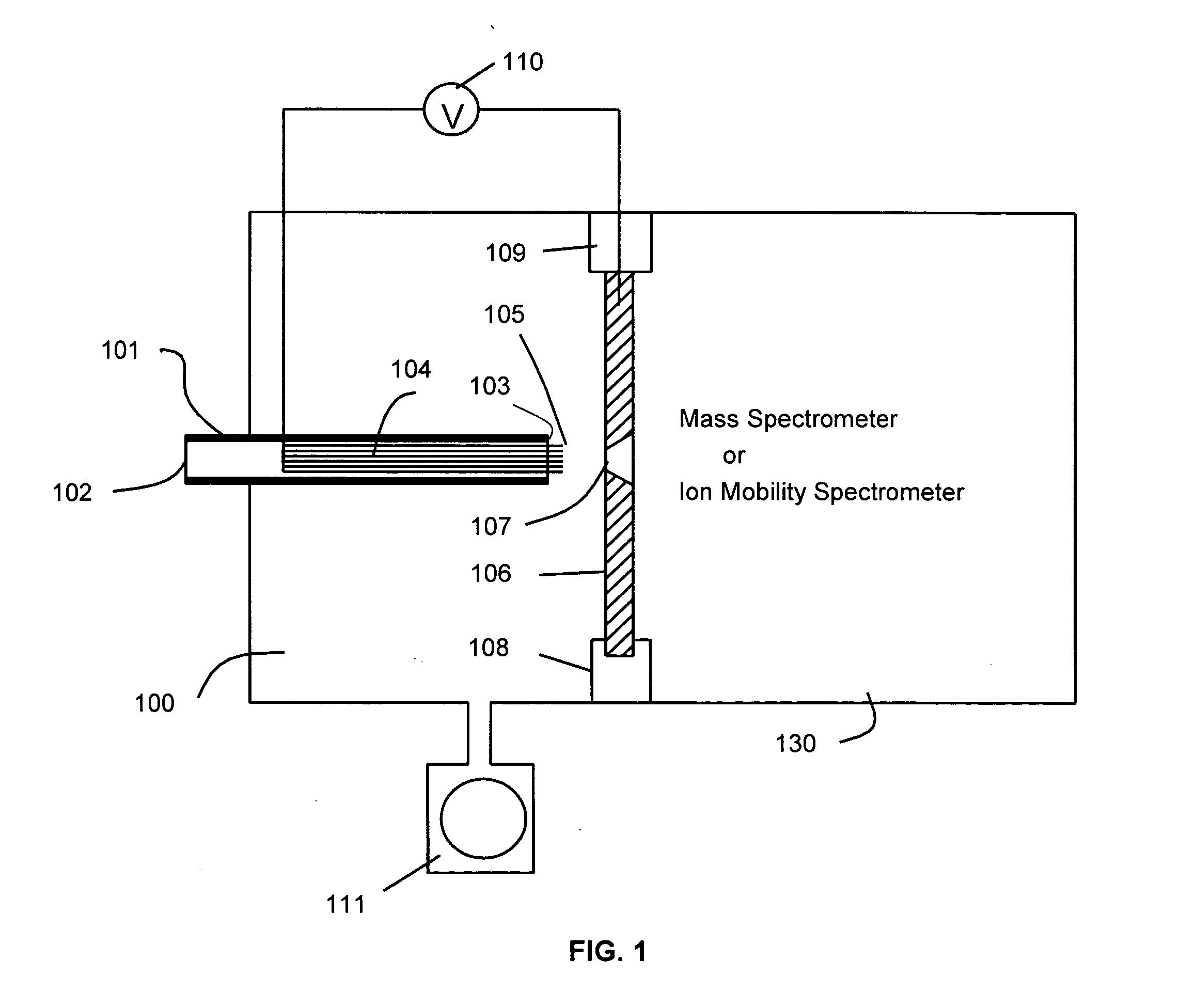
Systems and methods for ion species analysis with enhanced condition control and data interpretation
ActiveUS20050253061A1Reduces spectral peak overlapHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSystems approachesComputer science
The invention relates generally to ion mobility based systems, methods and devices for analyzing samples and, more particularly, to sample detection using enhanced condition control and data interpretation.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6906319B2High sensitivityIncrease delay timeStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer is disclosed wherein ions having a particular desired charge state are selected by operating an ion mobility spectrometer in combination with a quadrupole mass filter. Precursor ions are fragmented or reacted to form product ions in a collision cell ion trap and sent back upstream to an upstream ion trap. The fragment or product ions are then passed through the ion mobility spectrometer wherein they become temporally separated according to their ion mobility. Fragment or product ions are then re-trapped in the collision cell ion trap before being released therefrom in packets. A pusher electrode of a time of flight mass analyzer is energized a predetermined period of time after a packet of ions is released from the collision cell ion trap. Accordingly, it is possible to select multiply charged precursor ions from a background of singly charged ions, fragment them, and mass analyze the fragment ions with a near 100% duty cycle across the whole mass range.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
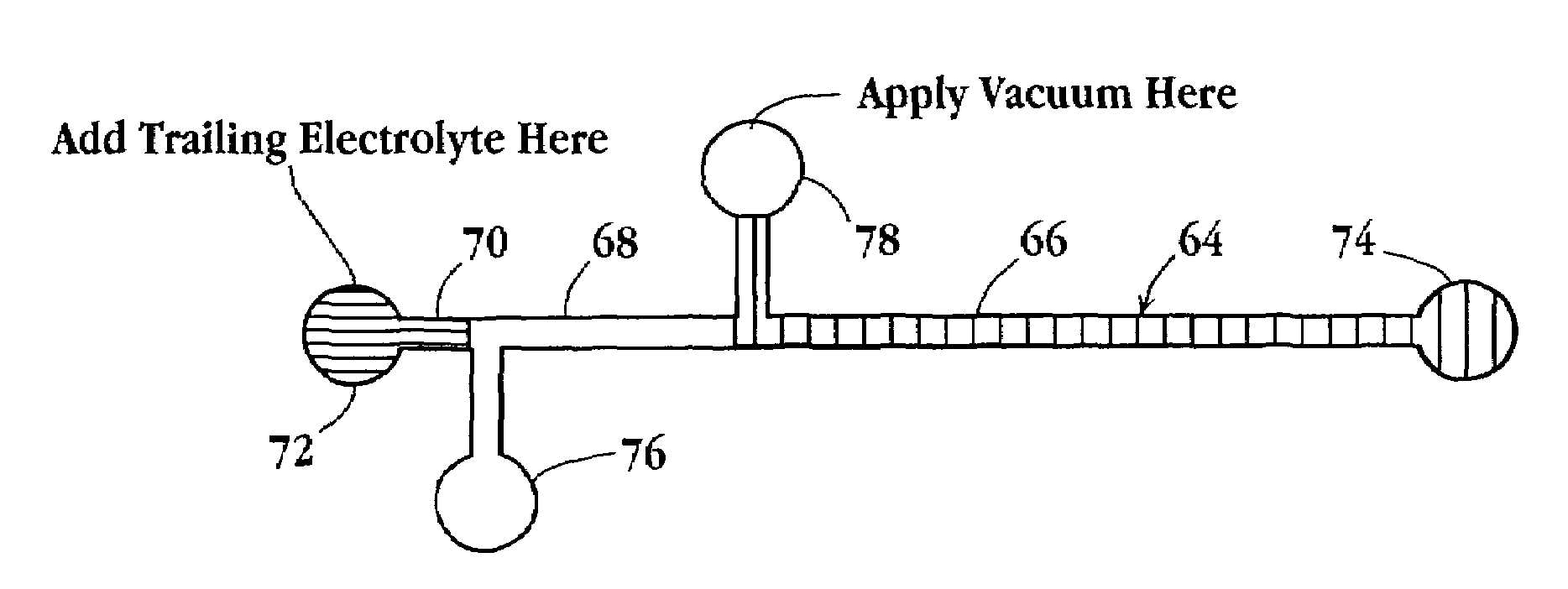
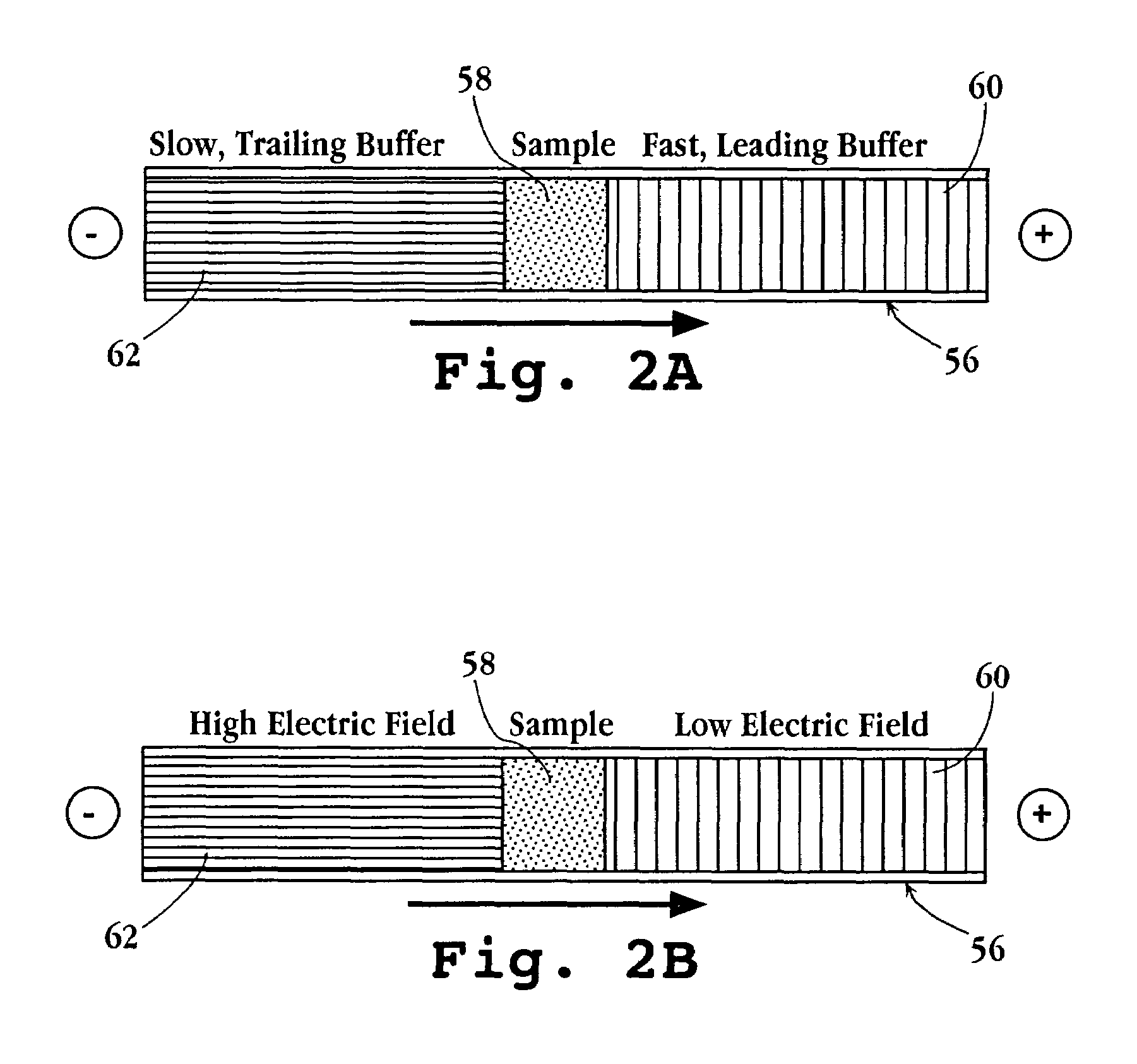
Tandem isotachophoresis/zone electrophoresis method and system
A method of separating components having a given negative or positive charge and contained in a sample is disclosed. The method involves, in one embodiment, loading a microchannel with a sample, placed between a trailing-edge electrolyte having a selected concentration of a titratable species, and a leading-edge electrolyte. With the application of a voltage potential across the microchannel, charged components in the sample stack by isotachophoresis, and electrolytic hydroxyl or hydrogen ions formed by electrolysis at the upstream-end electrode migrate into the trailing-edge ion buffer, titrating the titratable species therein, where the concentration of the titratable species in the trailing-edge electrolyte is selected , in relation to the lengths of the upstream channel region and sample-loading volume, to permit the sample to stack into a relatively small sample volume before electrolytic-ion migration from the upstream electrode into and through the sample-volume region is effective to overtake the charge sample components. With continued application of an electric potential across the channel ends, charged sample components in the stacked sample volume separated by zone electrophoresis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Laser desorption ion source
ActiveUS20050056776A1Efficient extractionImprove ionization efficiencyElectron/ion optical arrangementsIsotope separationPhysicsIonization
Atmospheric pressure, intermediate pressure and vacuum laser desorption ionization methods and ion sources are configured to increase ionization efficiency and the efficiency of transmitting ions to a mass to charge analyzer or ion mobility analyzer. An electric field is applied in the region of a sample target to accumulate ions generated from a local ion source on a solid or liquid phase sample prior to applying a laser desorption pulse. The electric field is changed just prior to or during the desorption laser pulse to promote the desorption of charged species and improve the ionization efficiency of desorbed sample species. After a delay, the electric field may be further changed to optimize focusing and transmission of ions into a mass spectrometer or ion mobility analyzer. Charged species may also be added to the region of the laser desorbed sample plume to promote ion-molecule reactions between the added ions and desorbed neutral sample species, increasing desorbed sample ionization efficiency and / or creating desired product ion species. The cycling of electric field changes is repeated in a timed sequence with one or more desorption laser pulse occurring per electric field change cycle. Embodiments of the invention comprise atmospheric pressure, intermediate pressure and vacuum pressure laser desorption ionization source methods and devices for increasing the analytical flexibility and improving the sensitivity of mass spectrometric analysis.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC +1
Remote reagent chemical ionization source
InactiveUS7095019B1Facilitate efficient sample ionizationEasy to collectTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationChromatographic separationGas phase
An improved ion source and portable analyzer for collecting and focusing dispersed gas-phase ions from a reagent source at atmospheric or intermediate pressure, having a remote source of reagent ions generated by direct or alternating currents, separated from a low-field sample ionization region by a stratified array of elements, each element populated with a plurality of openings, wherein DC potentials are applied to each element necessary for transferring reagent ions from the remote source into the low-field sample ionization region where the reagent ions react with neutral and / or ionic sample forming ionic species. The resulting ionic species are then introduced into the vacuum system of a mass spectrometer or ion mobility spectrometer. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when gas and liquid chromatographic separation techniques or probes containing samples are coupled to atmospheric and intermediate pressure photo-ionization, chemical ionization, and thermospray ionization sources.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOCS
Mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6914241B2Time-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass analyzerParticle physics
A mass spectrometer comprising an ion mobility separator for separating ions according to their ion mobility is disclosed. The ion mobility separator comprises a plurality of electrodes and one or more transient DC voltages or one or more transient DC voltage waveforms are progressively applied to the electrodes so that ions having a certain ion mobility are separated from other ions having different ion mobilities.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Mass spectrometer
ActiveUS6992283B2Increase speedLow ion mobilityTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass analyzerSpectrometer
A mass spectrometer is disclosed wherein ions are passed through an ion mobility separator and are then mass analysed by a Time of Flight mass analyzer. Multiple sets of mass spectral data are obtained which are then post-processed so that mass spectral data relating to ions having undesired charge state(s) is filtered out. The resultant mass spectrum comprises ions having a desired charge state.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
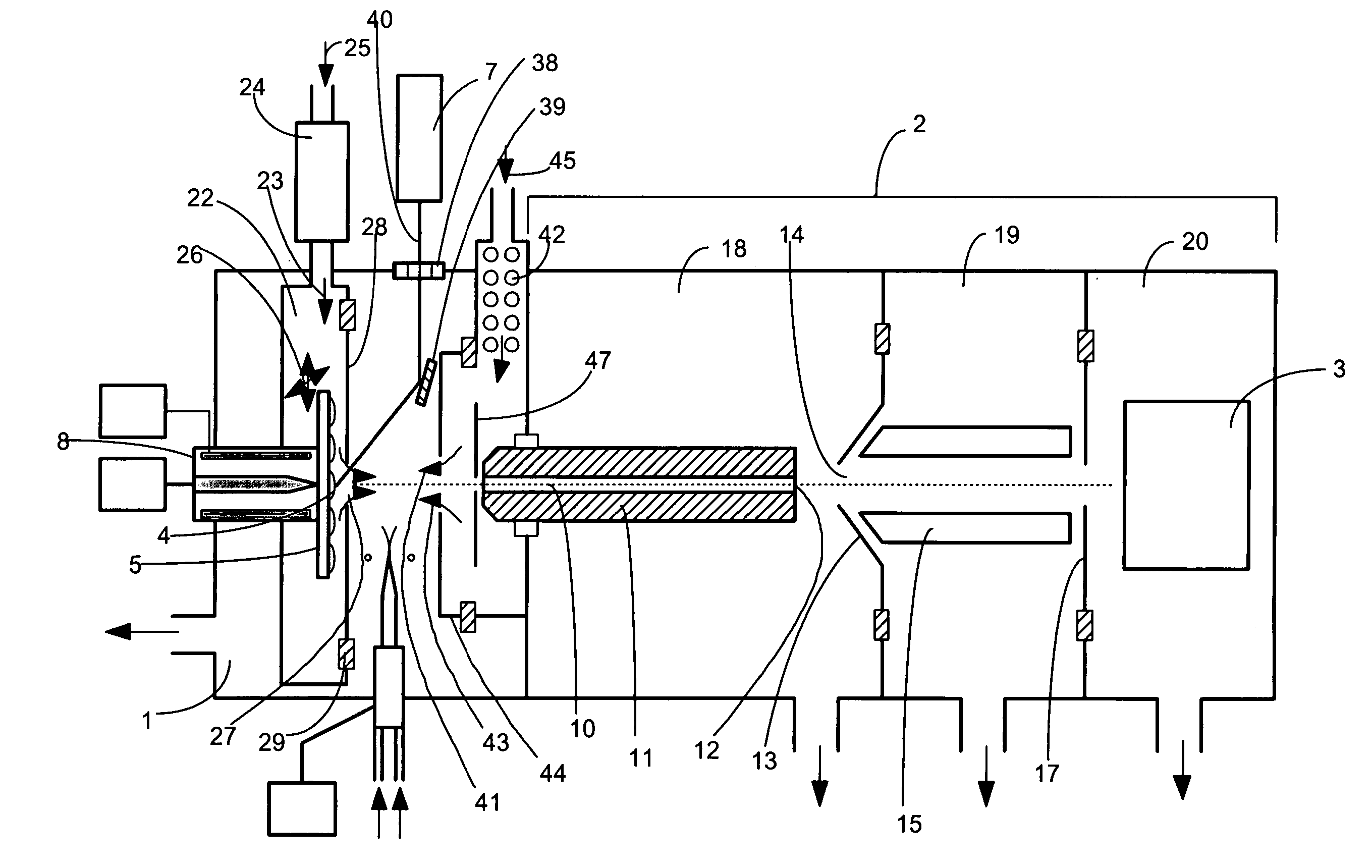
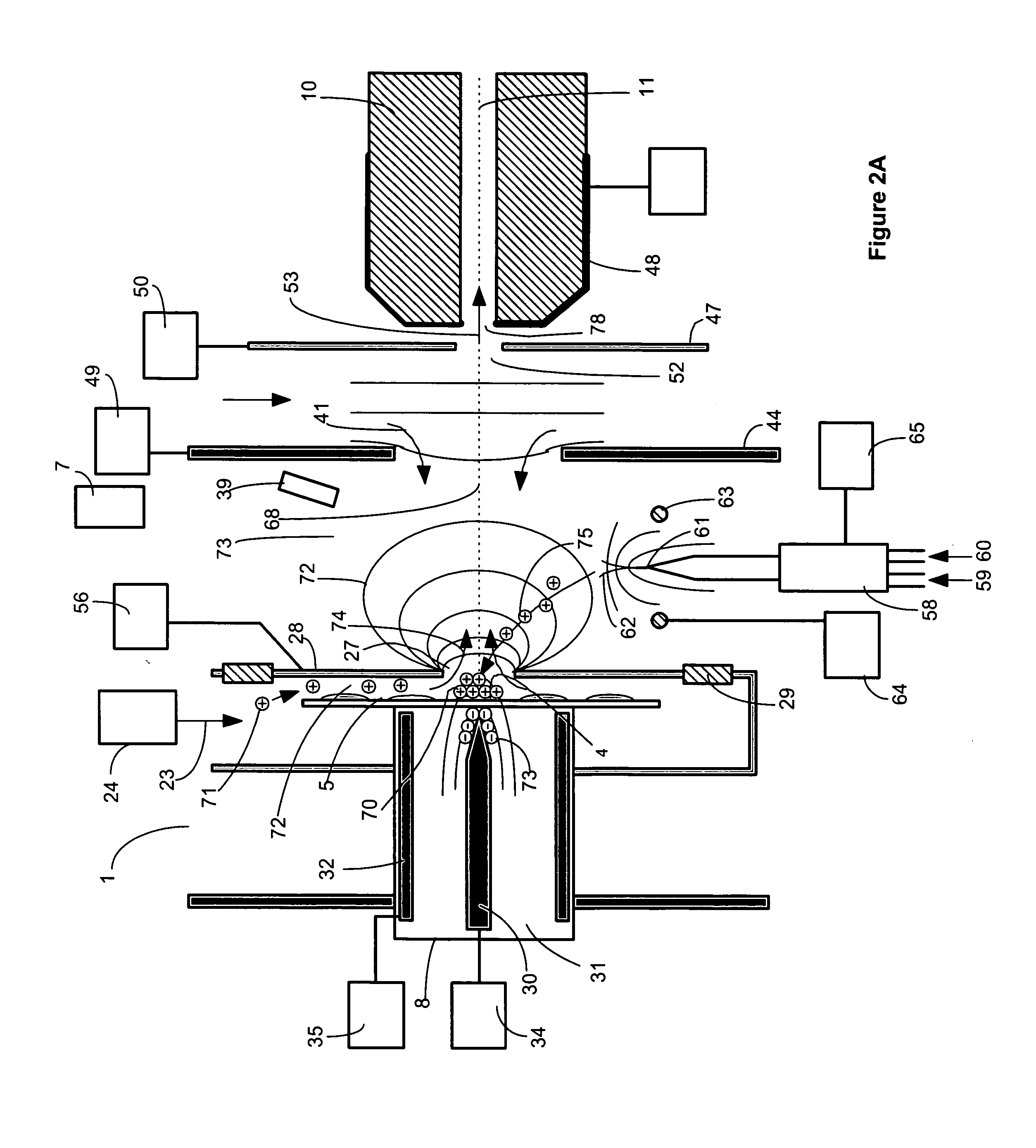
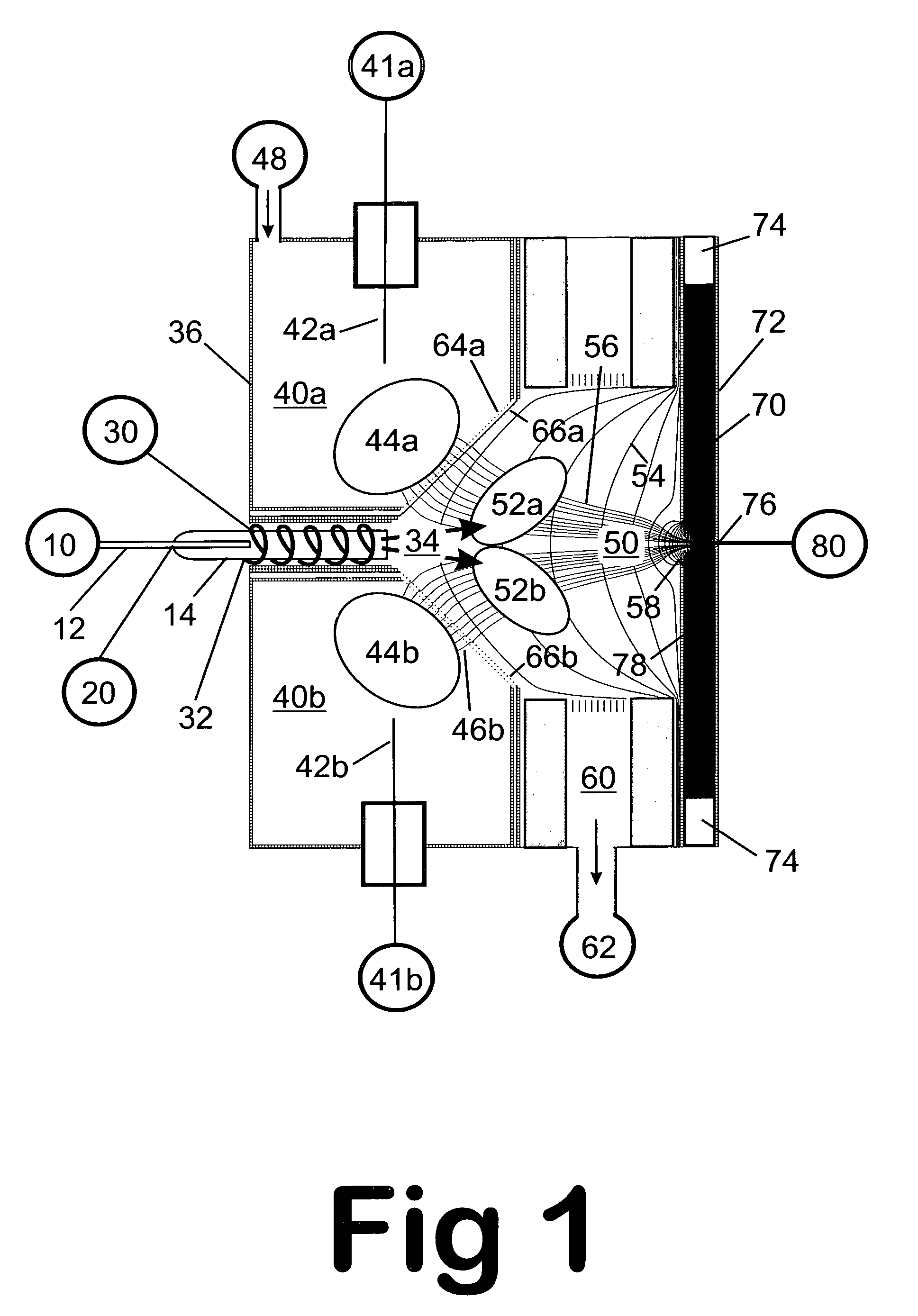
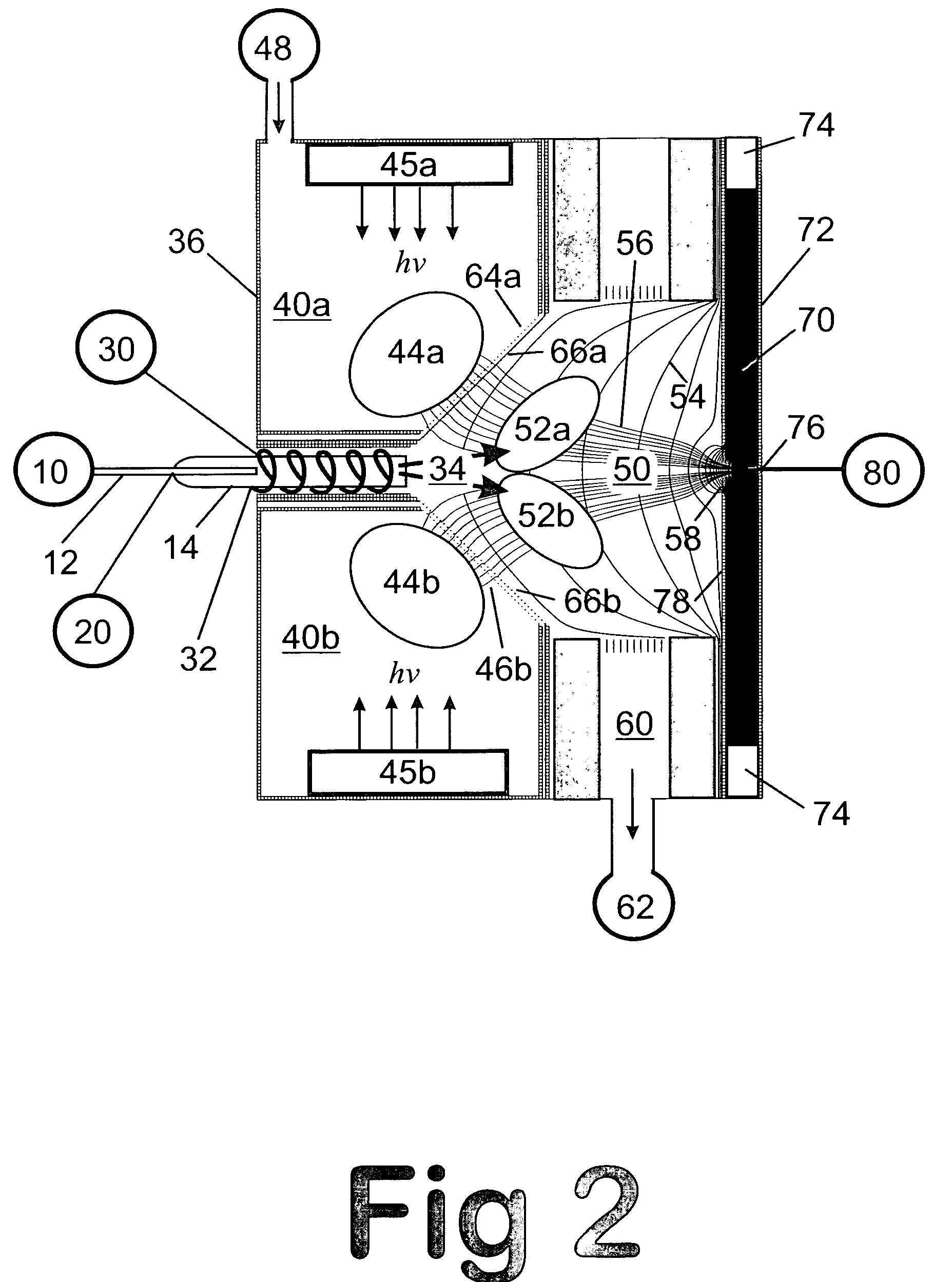
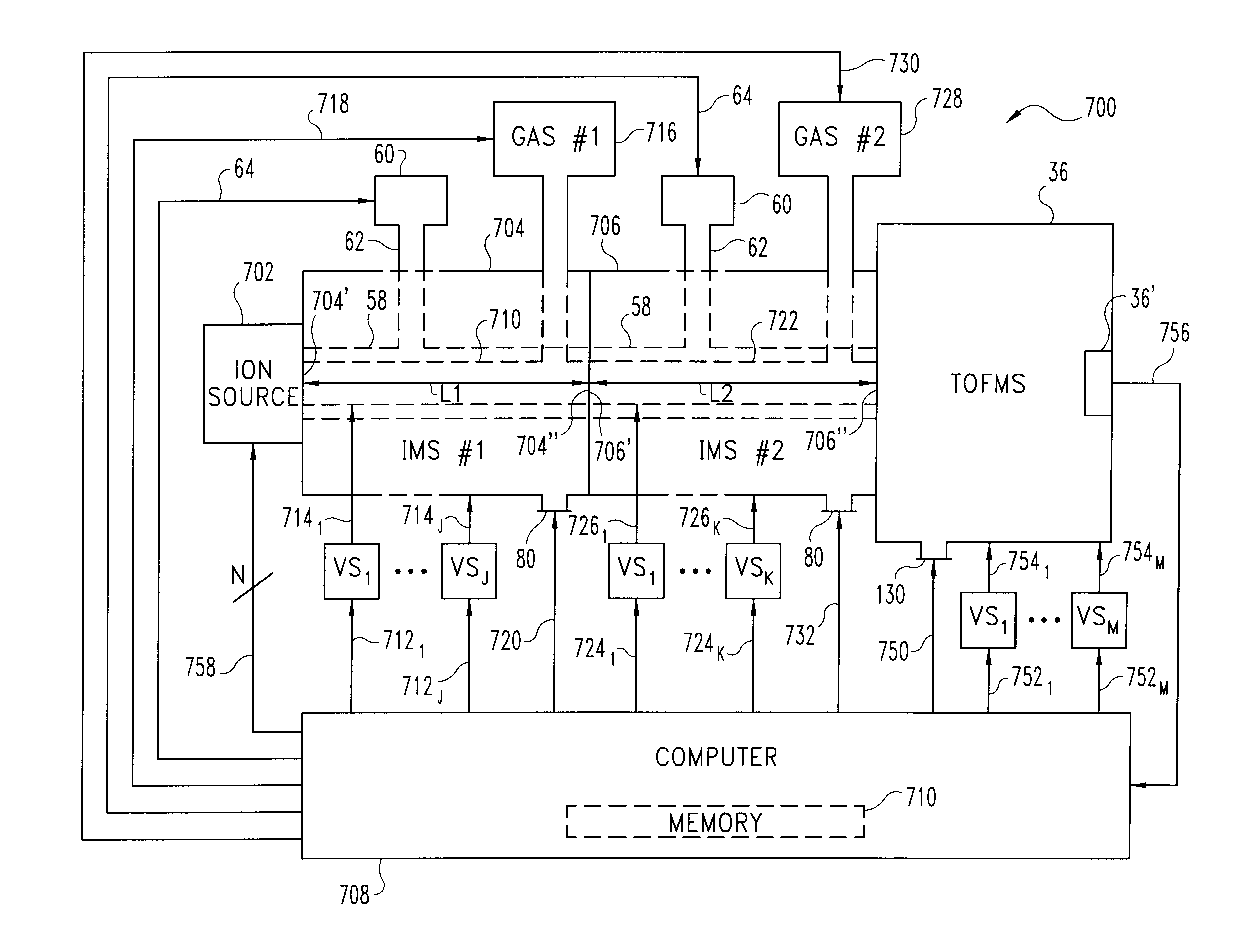
Method and apparatus for enhanced ion mobility based sample analysis using various analyzer configurations
InactiveUS20070176092A1Easy to analyzeEasy to identifyTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAtomic physicsIon flow
A system for analyzing one or more ion species of a sample including a first ion mobility filter associated with a first flow path for passing first ions of the sample, a second ion mobility filter associated with a second flow path for passing second ions of the sample, a first outlet from the first flow path for passing a portion of the first ions from the first flow path to the second flow path, and a first outlet from the second flow path for removing neutral particles from the second flow path where the first outlet from the second flow path is upstream of the second ion mobility filter in relation to the ion flow in the second flow path.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Ion mobility spectrometry method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050109930A1Time-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricitySolvent
The invention includes an ion mobility spectrometer having a liquid filled drift chamber. The chamber has an ionization region partitioned from and an ion separation region by a reversible ion-migration block. An electrical field within the chamber allows ions to migrate toward the electrode collector. Passage of ions from the ionization region is triggered by reversing the block allowing ions to migrate into the ion separation region. The invention includes a method of ion mobility analysis in liquid phase. Ions are mobilized to migrate through a drift liquid and are detected at an end of a drift chamber. The invention also includes a method of generating ions in a sample. A sample containing molecules in a first solvent is introduced into a second solvent through a charged capillary where the electrically charged sample is electro-disperses to ionize the molecules.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Instrument for separating ions in time as functions of preselected ion mobility and ion mass
InactiveUS6960761B2Fast analysisFast sequencingTime-of-flight spectrometersIon-exchanger regenerationMass analyzerIon-mobility spectrometry
An ion separation instrument includes an ion source coupled to at least a first ion mobility spectrometer having an ion outlet coupled to a mass spectrometer. Instrumentation is further included to provide for passage to the mass spectrometer only ions defining a preselected ion mobility range. In one embodiment, the ion mobility spectrometer is provided with electronically controllable inlet and outlet gates, wherein a control circuit is operable to control actuation of the inlet and outlet gates as a function of ion drift time to thereby allow passage therethrough only of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range. In another embodiment, an ion trap is disposed between the ion mobility spectrometer and mass spectrometer and is controlled in such a manner so as to collect a plurality of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range prior to injection of such ions into the mass spectrometer. In yet another embodiment, an ion inlet of the ion trap may be electronically controlled relative to operation of the ion mobility spectrometer as a function of ion drift time to thereby allow passage therein only of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range. The mass spectrometer is preferably a Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance mass spectrometer, and the resulting ion separation instrument may further include therein various combinations of ion fragmentation, ion mass filtering, ion trap, charge neutralization and / or mass reaction instrumentation.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
MALDI target plate utilizing micro-wells
ActiveUS7695978B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGlass fiberSpectroscopy
An arrangement for a MALDI sample plate for ion mass spectroscopy is disclosed. The sample is configured to shape the hypersonic explosion which creates the ions generated in a MALDI-type time-of-flight mass spectrometer. The MALDI sample plate includes a glass wafer formed from a plurality of clad glass fibers and has a first planar surface. The plate also has a plurality of micro-wells formed in the glass wafer. The micro-wells extend to a depth that is less than the thickness of the glass wafer and act to hold a spot sample in a manner that prevents spreading, maximizes the formation of ions, and shapes the resulting ion cloud to improve ion migration.
Owner:PHOTONIS SCI INC
Programmable resistor, switch or vertical memory cell
InactiveUS20080173975A1Decrease resistivity and hence resistanceSimple processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMetal electrodes
Disclosed are embodiments of a device and method of forming the device that utilize metal ion migration under controllable conditions. The device embodiments comprise two metal electrodes separated by one or more different dielectric materials. One electrode is sealed from the dielectric material, the other is not. The device is adapted to allow controlled migration of embedded metal ions from the unsealed electrode into dielectric material to form a conductive path under field between the electrodes and, thereby, to decrease the resistance of the dielectric material. Reversing the field causes the metal ions to reverse their migration, to break the conductive metallic path between the electrodes and, thereby, to increase the resistance of the dielectric material. Thus, the device can comprise a simple switch or programmable resistor. Additionally, by monitoring the resistance change, a two-state, two-terminal, silicon technology-compatible, flash memory device with a very simple tuning process can be created.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
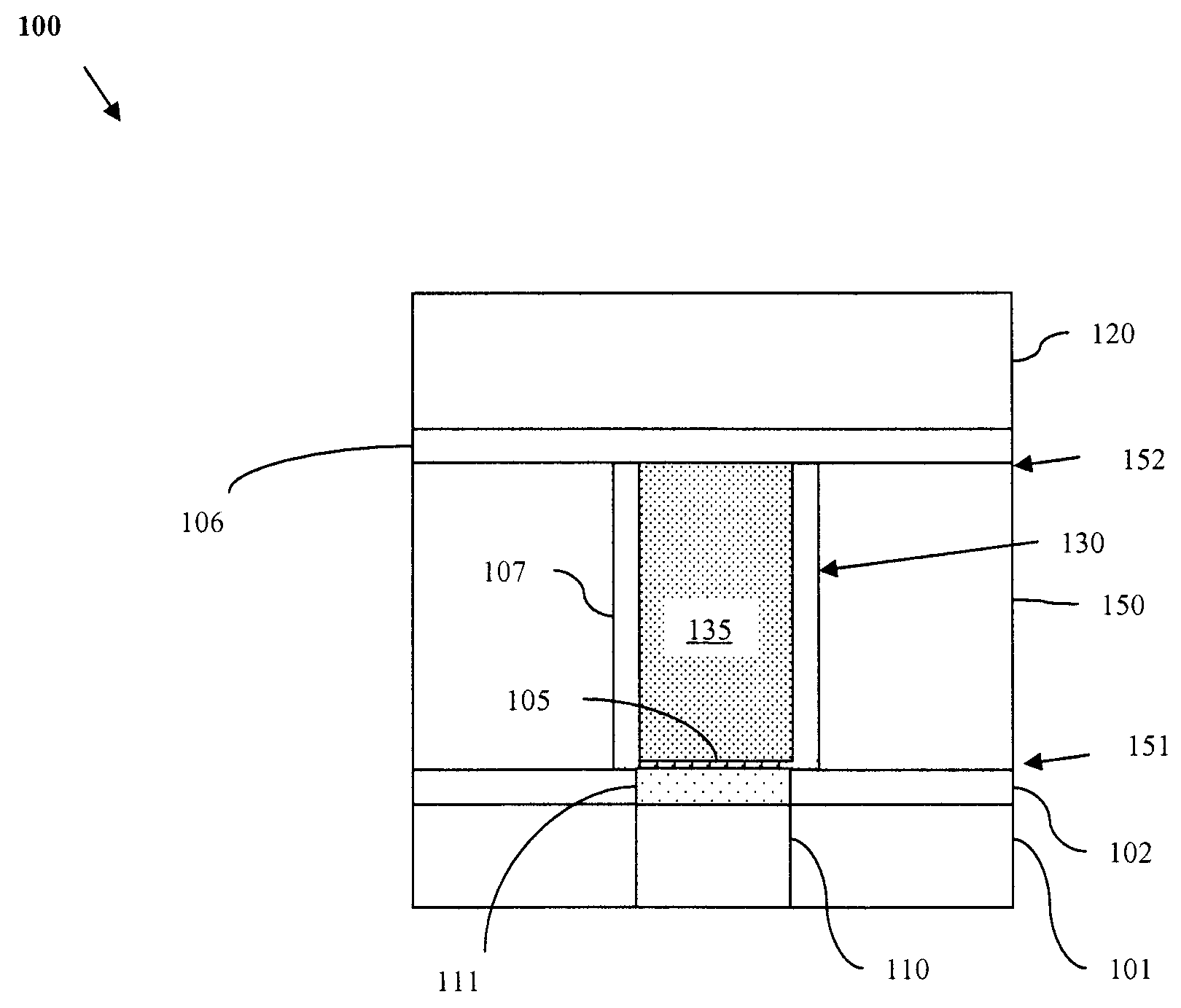
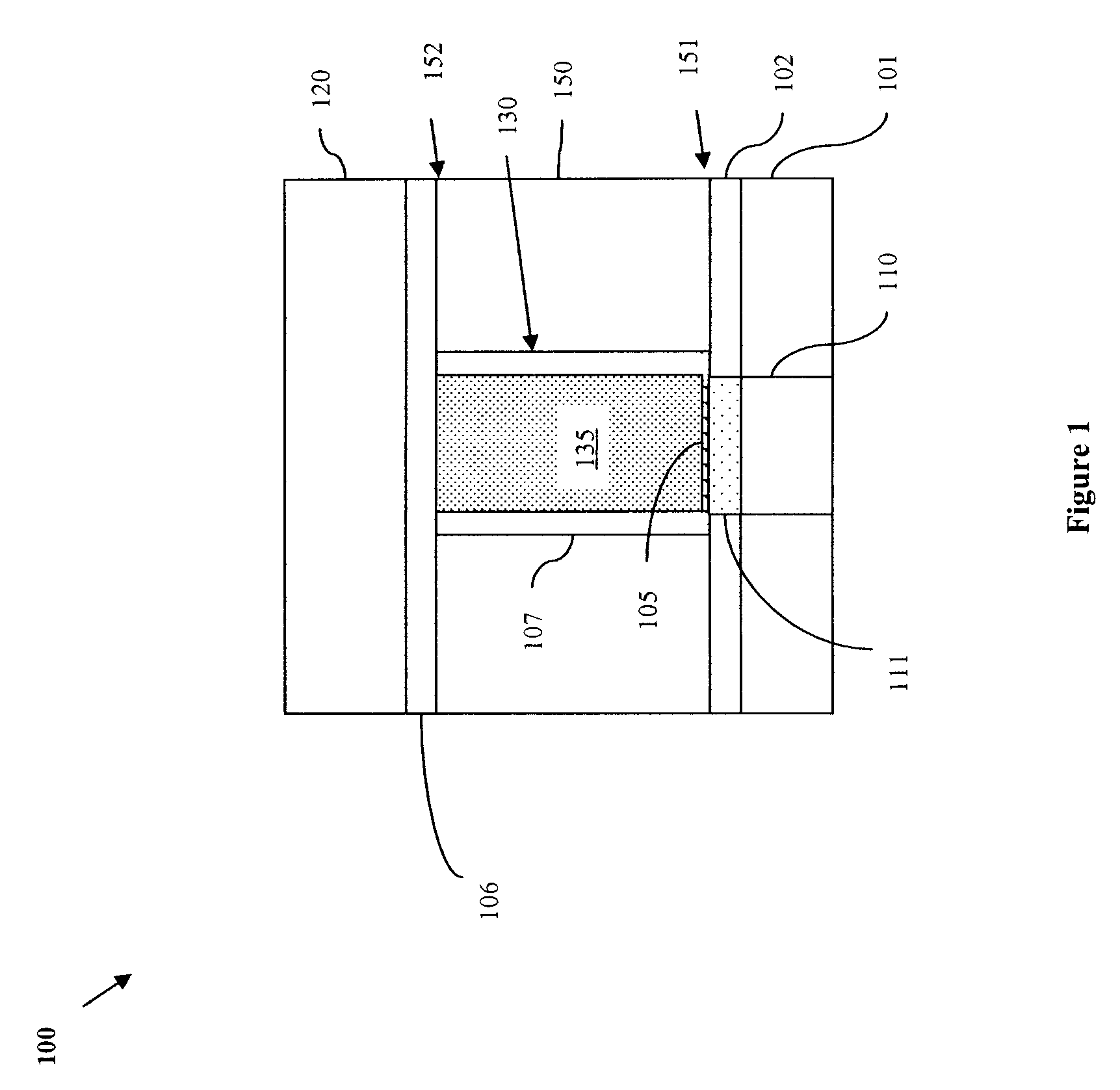
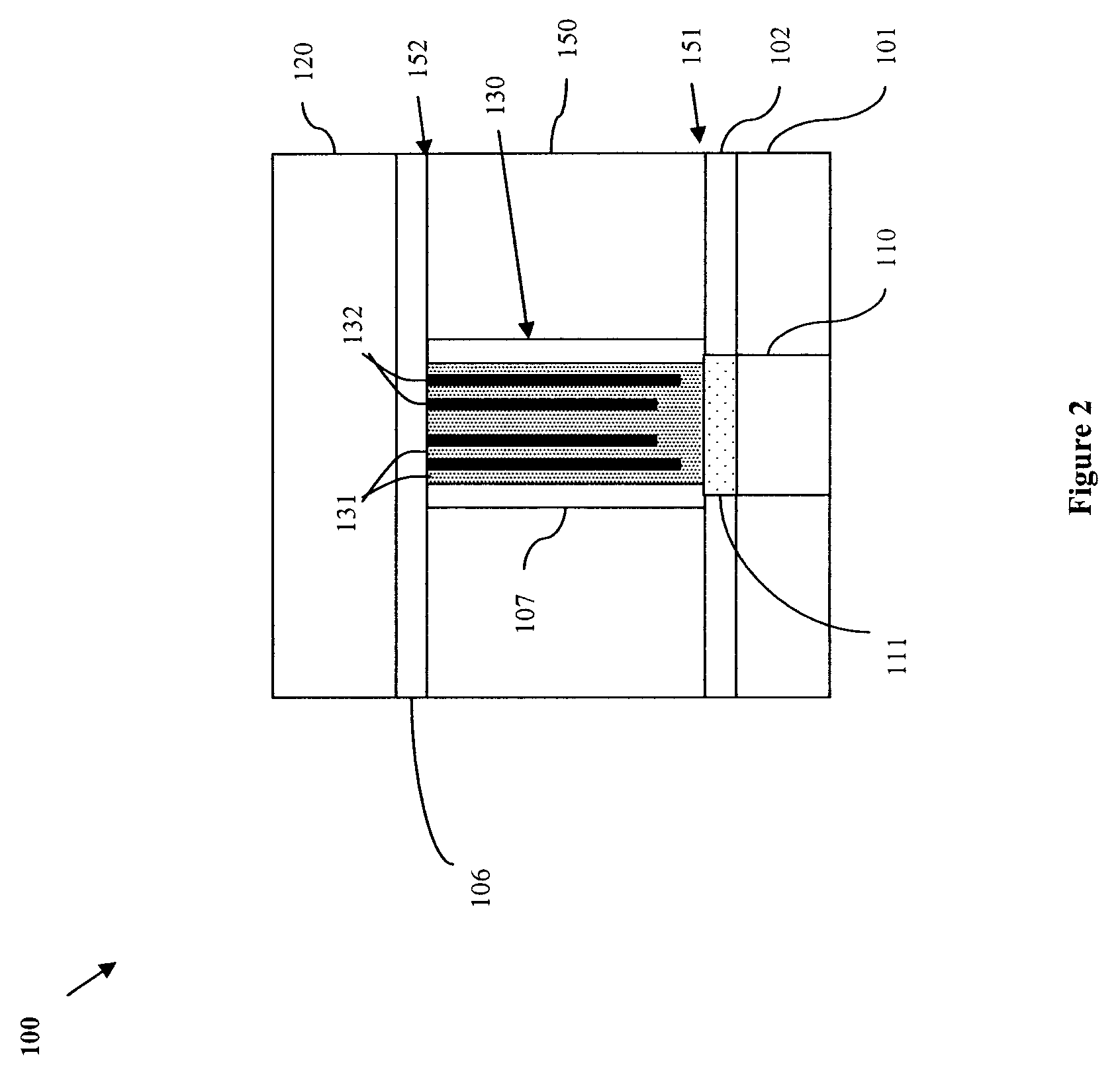
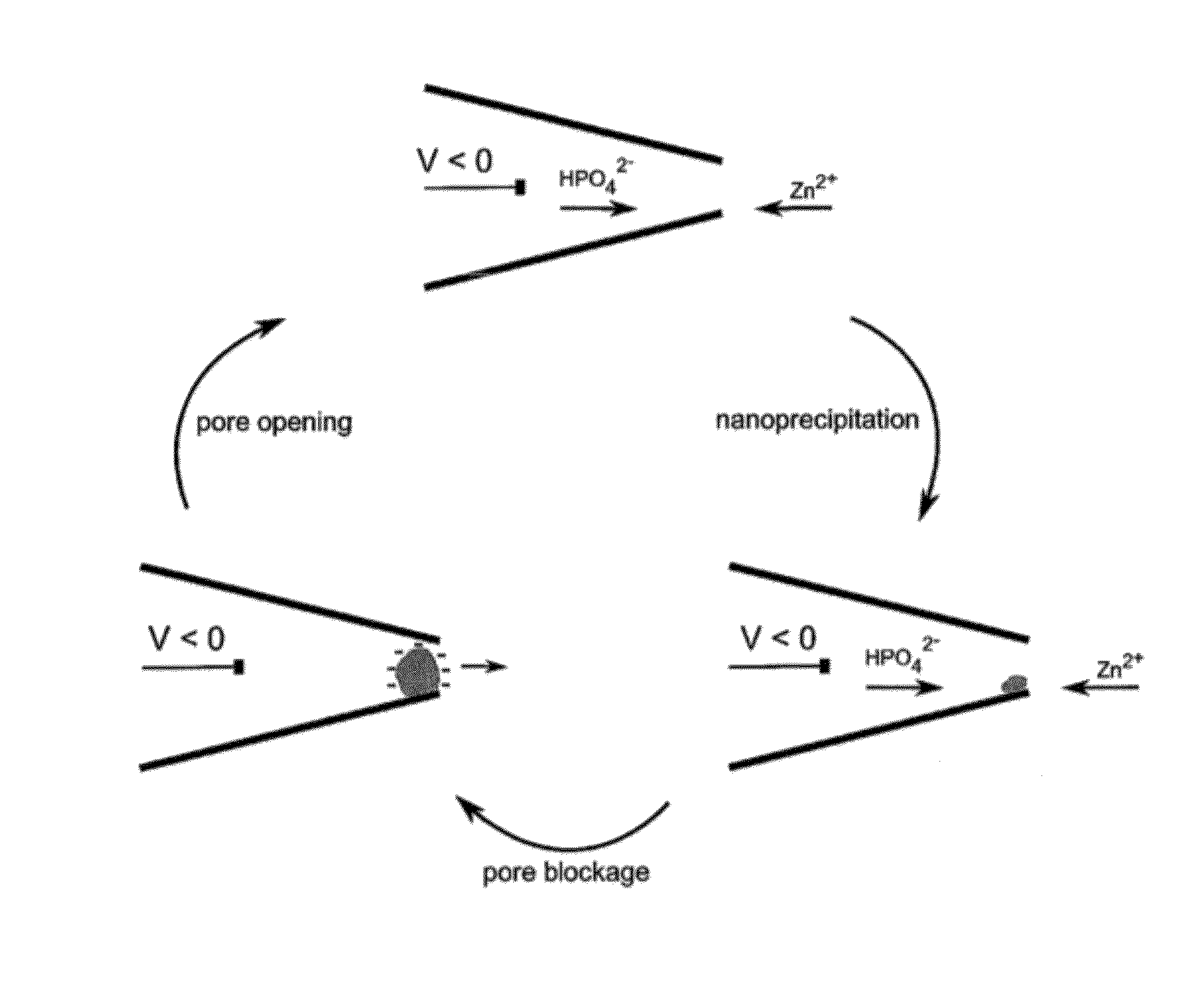
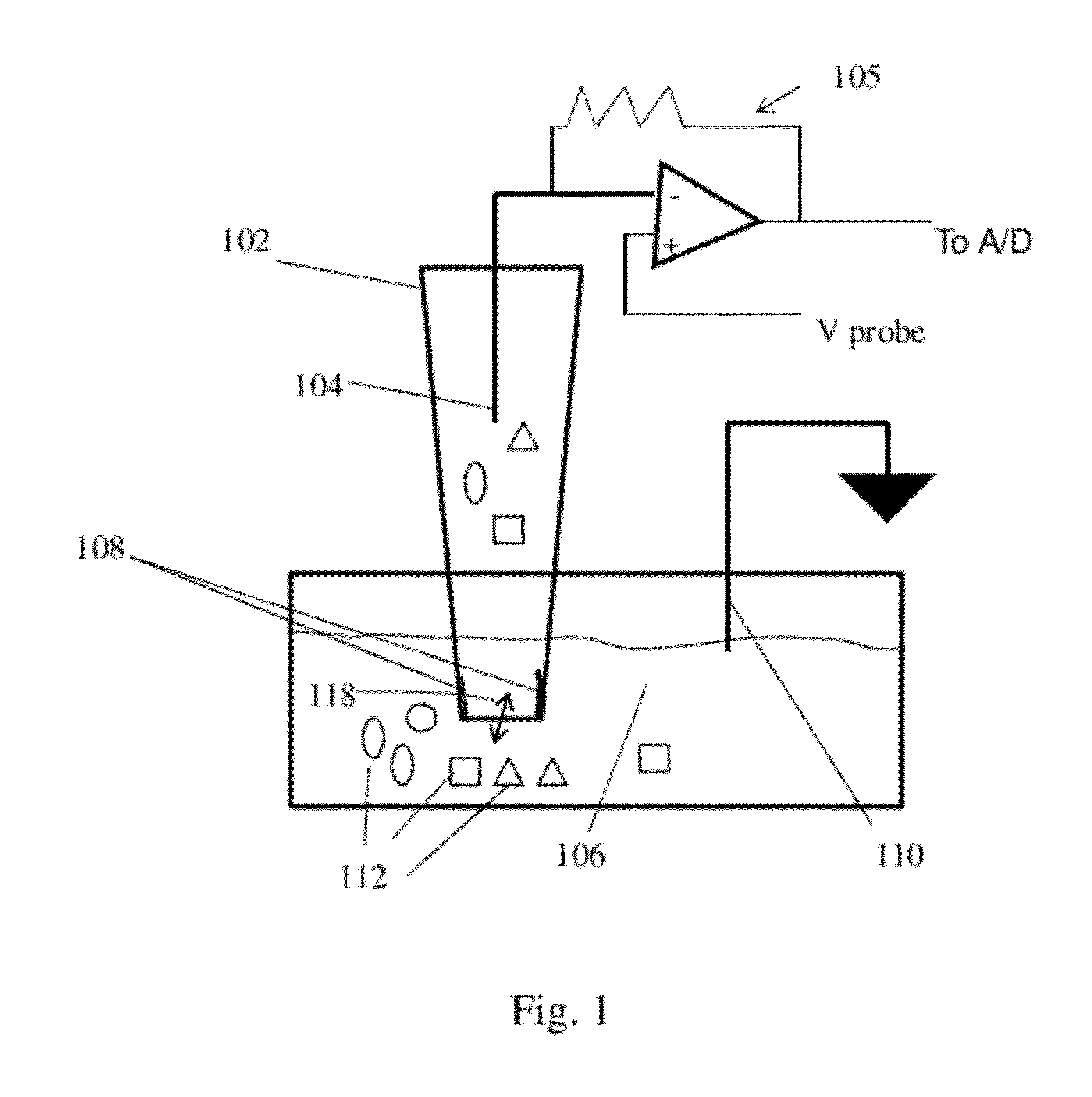
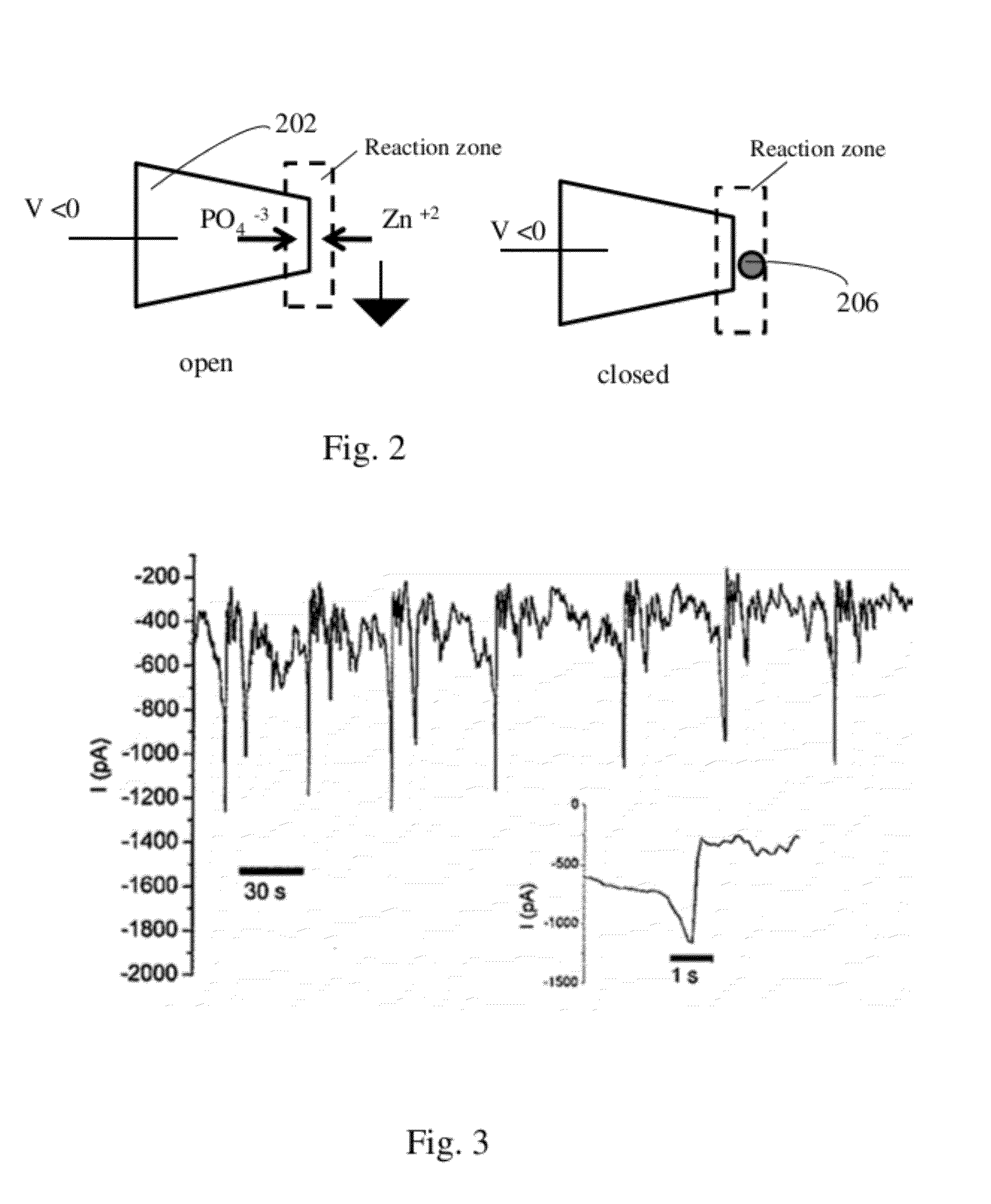
Nanopore Device for Reversible Ion and Molecule Sensing or Migration
Disclosed are methods and devices for detection of ion migration and binding, utilizing a nanopipette adapted for use in an electrochemical sensing circuit. The nanopipette may be functionalized on its interior bore with metal chelators for binding and sensing metal ions or other specific binding molecules such as boronic acid for binding and sensing glucose. Such a functionalized nanopipette is comprised in an electrical sensor that detects when the nanopipette selectively and reversibly binds ions or small molecules. Also disclosed is a nanoreactor, comprising a nanopipette, for controlling precipitation in aqueous solutions by voltage-directed ion migration, wherein ions may be directed out of the interior bore by a repulsing charge in the bore.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Mass spectrometer
ActiveUS7071467B2Eliminate the effects ofHigh duty cycleStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryTrapping region
A mass spectrometer is disclosed comprising an ion trap wherein ions which have been temporally separated according to their mass to charge ratio or ion mobility enter the ion trap. Once at least some of the ions have entered the ion trap, a plurality of ion trapping regions are created along the length of the ion trap in order to fractionate the ions. Alternatively, the ions may be received within one or more axial trapping regions which are translated along the ion trap with a velocity which is progressively reduced to zero.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
System for DMS peak resolution
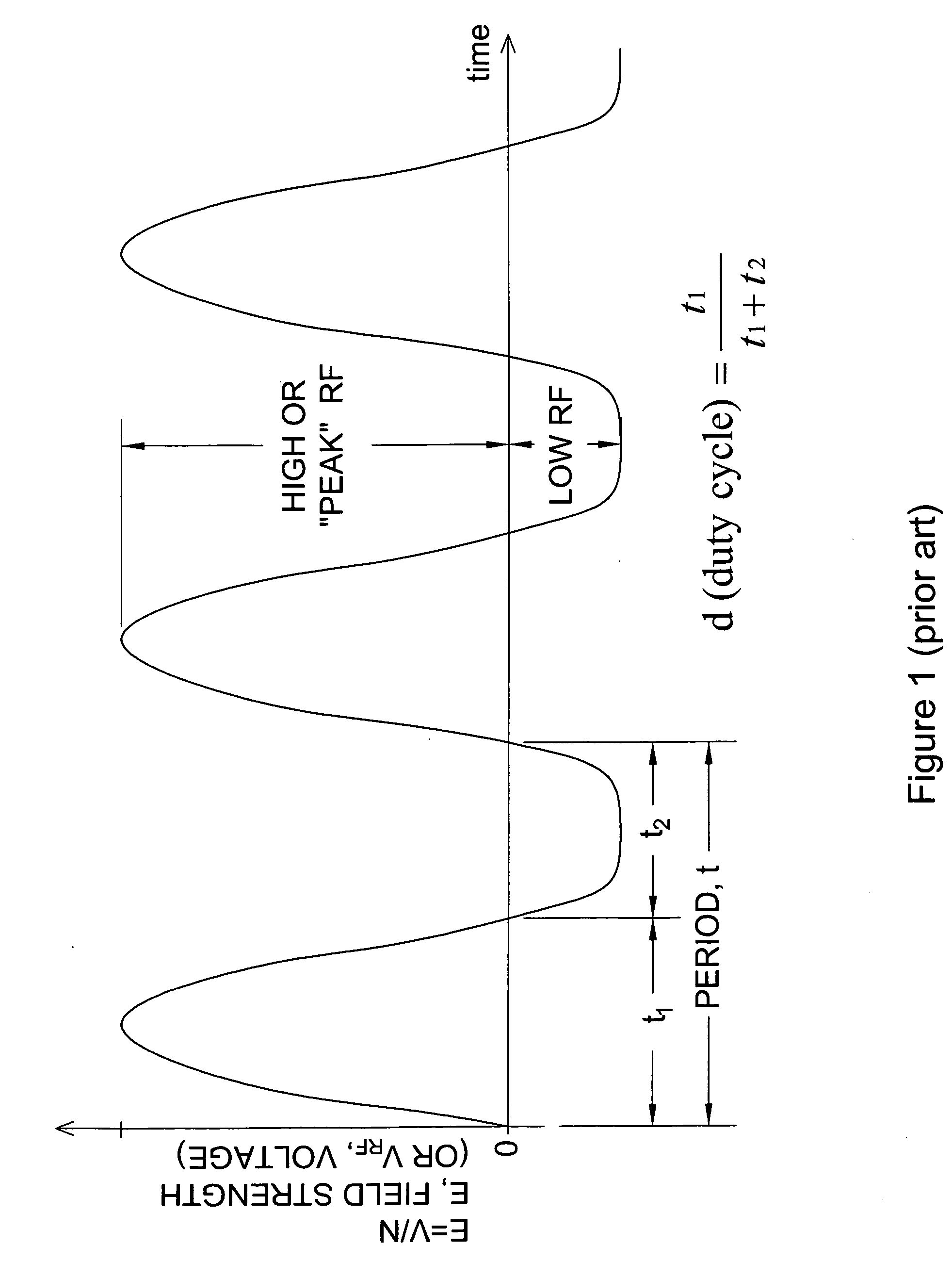
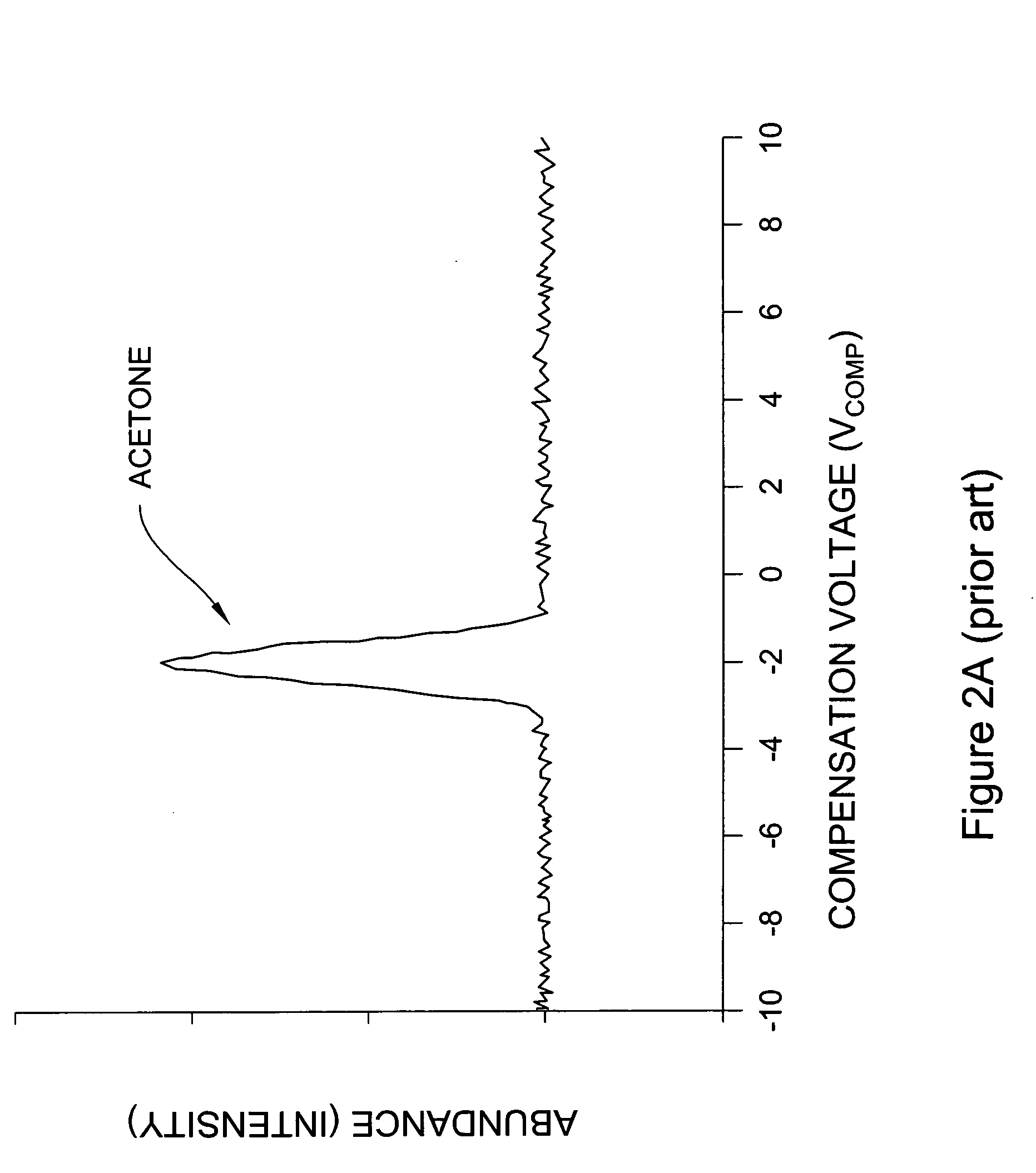
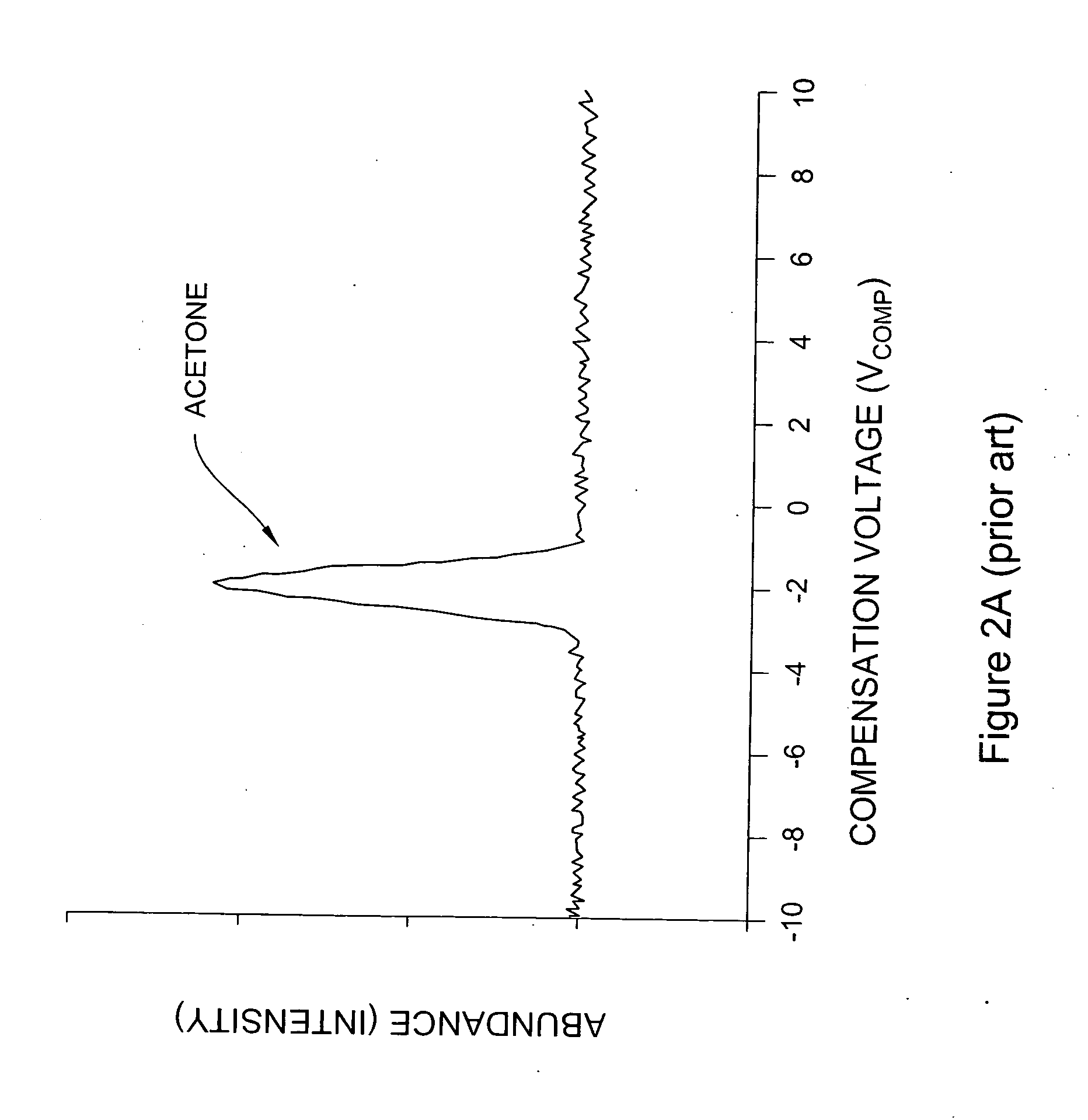
InactiveUS20050040330A1Positively identifying the speciesImprove reliabilityTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhysicsIon
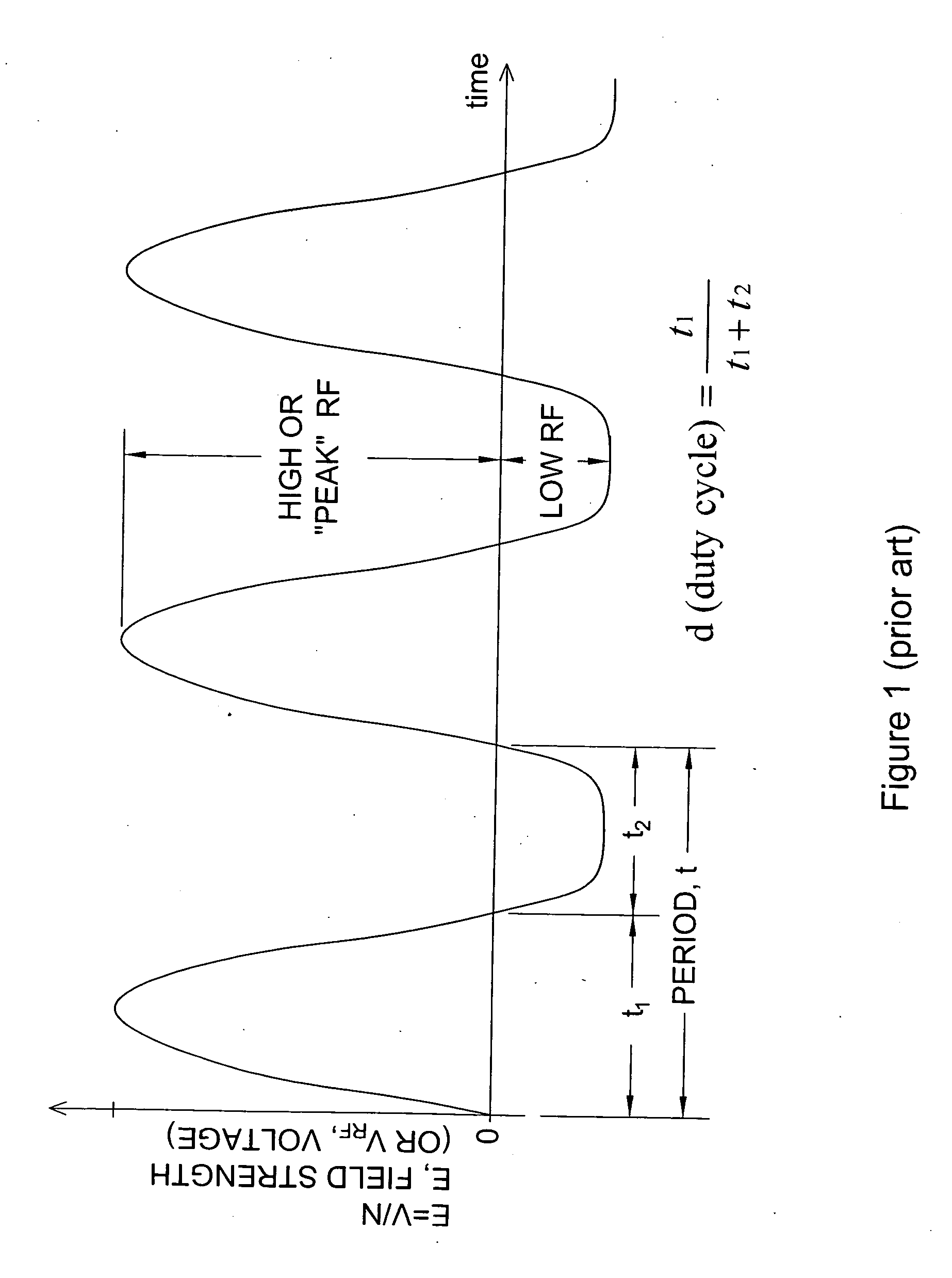
An apparatus for identification of chemical species by measurement of mobility as a function of high electric field and for generating unique compound-dependent signatures based on ion mobility at a plurality of peak RF voltages for a given compensation. The resulting detection data is compared against a library of data in order to identify a detected chemical species.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Ion extraction devices, mass spectrometer devices, and methods of selectively extracting ions and performing mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7405401B2Prevent extractionHigh sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsIon trap mass spectrometryEffective potential
There is disclosed a method of selectively extracting ions comprising the steps of:providing a supply of ions in a body of gas;generating a ponderomotive ion trapping potential generally along an axis;generating further potentials to provide an effective potential which prevents ions from being extracted from an extraction region;trapping ions in said effective potential; andselectively extracting ions of a predetermined m / z ratio or ion mobility from the extraction region;in which the characteristics of the effective potential which prevent ions from being extracted from the extraction region are caused, at least in part, by the generation of the ponderomotive ion trapping potential.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Method and device for generating and analyzing ions
ActiveCN102221576AEffective after ionizationEffective combinationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon sources/gunsSpectrographMass analyzer
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB SHANGHAI
Periodic field focusing ion mobility spectrometer
InactiveUS6639213B2Improve transmission efficiencyTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsImage resolutionIon-mobility spectrometry
This invention is generally in the field of improved ion mobility spectrometry. The improvement lies in the use of periodic focusing electric fields that minimize the spatial spread of the migrating ions by keeping them in a tight radius about the axis of travel. The resulting enhancement in sensitivity is accomplished without a concomitant loss in resolution as would normally be expected when non-linear fields are used.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Corona discharge ionization sources for mass spectrometric and ion mobility spectrometric analysis of gas-phase chemical species
InactiveUS20070007448A1Improve ionization efficiencyImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansIon sources/gunsChemical speciesGas phase
A corona discharge mass spectrometer or an ion mobility spectrometer is provided with a robust corona discharge ionization source. The corona discharge ionization source, which can be operated at atmospheric pressures or at low vacuum, includes a multi-thread electrode and plane electrode. The multiple thread electrode has multiple discharge tips which provide redundancy, and improve ionization stability and the reliability and efficiency of the ionization source.
Owner:WANG YANG
Method of making a photovoltaic device or front substrate with barrier layer for use in same and resulting product
InactiveUS20080295884A1Increase power and efficiencyPrevent ion migrationSpecial surfacesCoatingsSilanesSolvent
A method of making a photovoltaic device including an antireflective coating, including: forming a coating solution by mixing a mono-metal oxide, a bi-metal oxide, a silane, or a siloxane with a solvent, such that the coating solution may be used as a barrier between the antireflective coating and a glass substrate that inhibits sodium ion migration in the glass substrate after exposure to environmental factors including humidity and temperature. A photovoltaic device including a photovoltaic film, a glass substrate, and a barrier layer provided on the glass substrate; an anti-reflection coating provided on the glass substrate and on the barrier layer; wherein the barrier layer comprises one or more of the following: a mono-metal oxide, a bi-metal oxide, a silane, or a siloxane.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Mass analysis of mobility selected ion populations
ActiveUS20070158543A1Time-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon trap mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Particular aspects provide novel methods for analysis of ion populations, the methods comprising filtering and selecting an ion population using a low-field dual-gate ion mobility spectrometer comprising a drift tube, the spectrometer operating at a pressure of at least 100 Torr, to provide mobility-selected ions. Certain aspects comprise: (i) subsequently accumulating the low-field selected ions in an ion trap (e.g., an MS ion trap) and mass spectrometry analysis; (ii) introducing the low-field selected ions into a high-field ion mobility spectrometer for separating thereby (optionally followed by mass spectrometry); and (iii) introducing the low-field selected ions into an ion trap mass spectrometer, and subsequently into a second low-field ion mobility spectrometer (e.g., a non-dual gate spectrometer operating at less than about 100 Torr). Additional aspects provide novel apparatus and combination thereof for performing the disclosed methods.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Storing type photo-ionisation ion migration mass spectrum
InactiveCN1544931AWith ion storage functionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRadioactive decayIon migration
The invention relates to a storage photoionization ion migration mass spectrum, mainly solving the problems of the complex line spectrum measured and weaker signals obtained by adopting radioactive component as ionization source. It includes acceleration grid electrode, ionization light source, sampling mouth, ionization region, drift region and ion collecting plate, and its character: the ionization light source is vacuum ultraviolet lamp, it sets an ion storage region structure between the ionization and drift regions to replace the ion gate. It has ion storing function, largely enhances monitoring sensitivity, clear migration mass spectrum chart of the matter to be measured, reduces influence of noise and enhances collecting efficiency.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
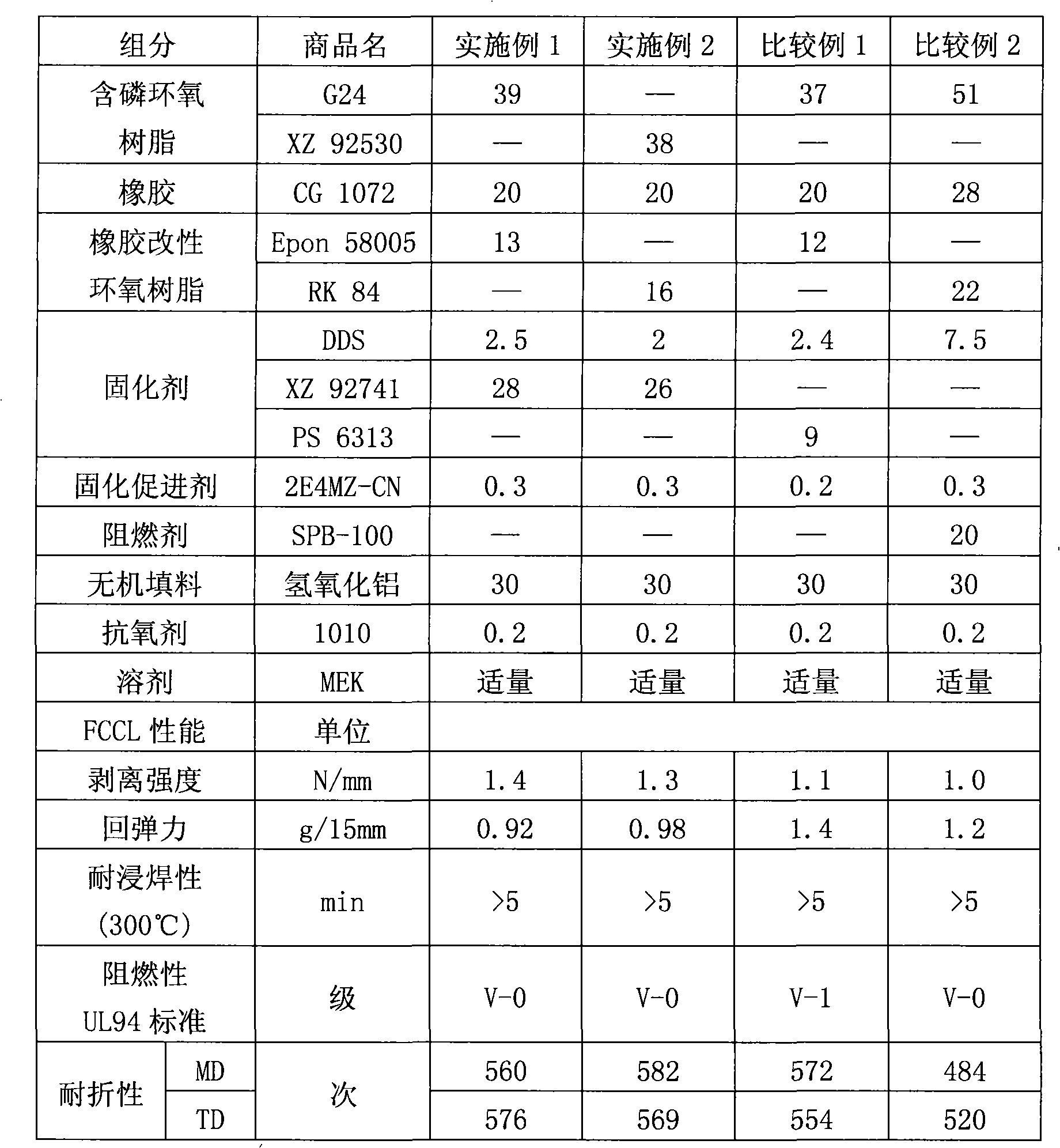
Halogen-free flame-retardant epoxy resin composition, flexible copper clad laminate made therefrom and preparation of the flexible copper clad laminate
InactiveCN101280093AGood compatibilityImprove mechanical propertiesCircuit susbtrate materialsSolid componentEpoxy
The invention relates to a halogen-free flame-retardant epoxy resin composite, the flexible copper clad laminate made from the epoxy resin composite and the production method. The halogen-free flame-retardant epoxy resin composite is composed of solid components and organic solvents, wherein, the solid components include: phosphorus epoxy resin, synthetic rubber, rubber-modified epoxy resin and composite curing agent. The flexible copper clad laminate made from the halogen-free flame-retardant epoxy resin composite is a three-layer flexible copper clad laminate, including a polyimide insulation film, a coating of halogen-free flame-retardant epoxy resin composite coated on the polyimide insulation film, and a copper foil pressed on the coating of halogen-free flame-retardant epoxy resin composite. The resin composite of the invention is halogen-free and dispenses with other organic phosphorus flame retardants; the flexible copper clad laminate made from the composite has the flame retardancy up to UL94 V-0-level and has the advantages of high peeling strength, excellent dimensional stability, softness, good ion migration resistance and processing performance.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGYI SCI TECH
Method for performing carbon coating modification on nano-powder by adopting water-soluble polymer
InactiveCN103035899AInhibition of agglomerationHigh performance advantageCell electrodesCarbon coatingActive agent
The invention discloses a method for performing carbon coating modification on nano-powder by adopting a water-soluble polymer. The method comprises the following steps: weighing the water-soluble polymer (such as one or more of industrial modified starch, glucose and the like), surface active agent and the nano-powder according to the weight ratio of (0.1-10) : (0-5) : (80-100) as solid raw materials, preparing slurry with a dissolution and dispersion agent according to the solid-liquid ratio of (1-1000) g / 50mL, uniformly stirring and dispersing, then performing suction filtration (or centrifugation) and drying to get a precursor, and then annealing at the temperature of 300 DEG C-700 DEG C under a protective atmosphere to get the nano-powder with good carbon-coating property. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the surface uniform carbon coating can be effectively performed on nano-material, electron and ion migration ratio in the material can be accelerated, the agglomeration of the nano-material can be inhibited, the void ratio and the like of the material can be improved, and the performance advantages of the nano-material can be further enhanced.
Owner:山东天润丰新能源科技有限公司
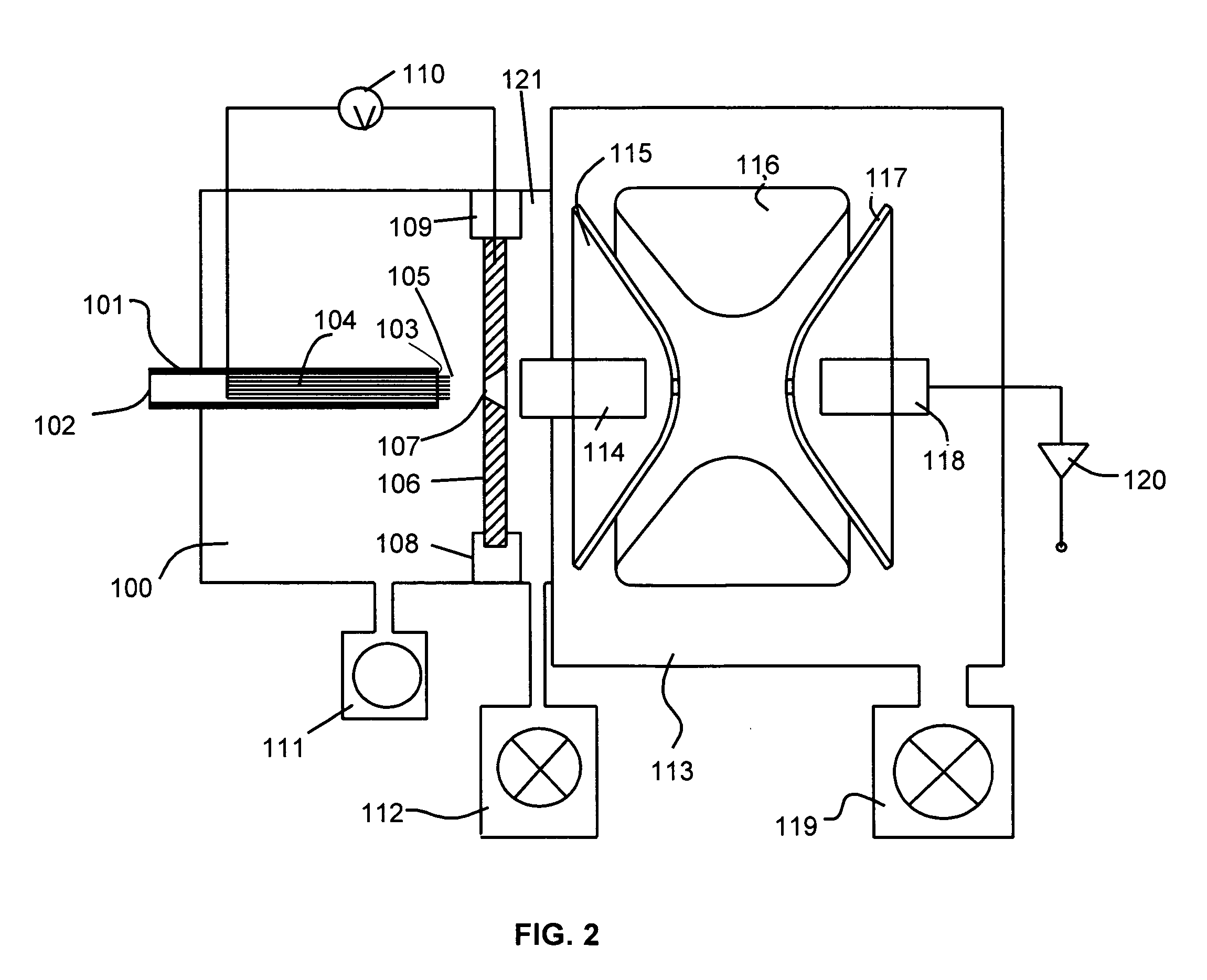
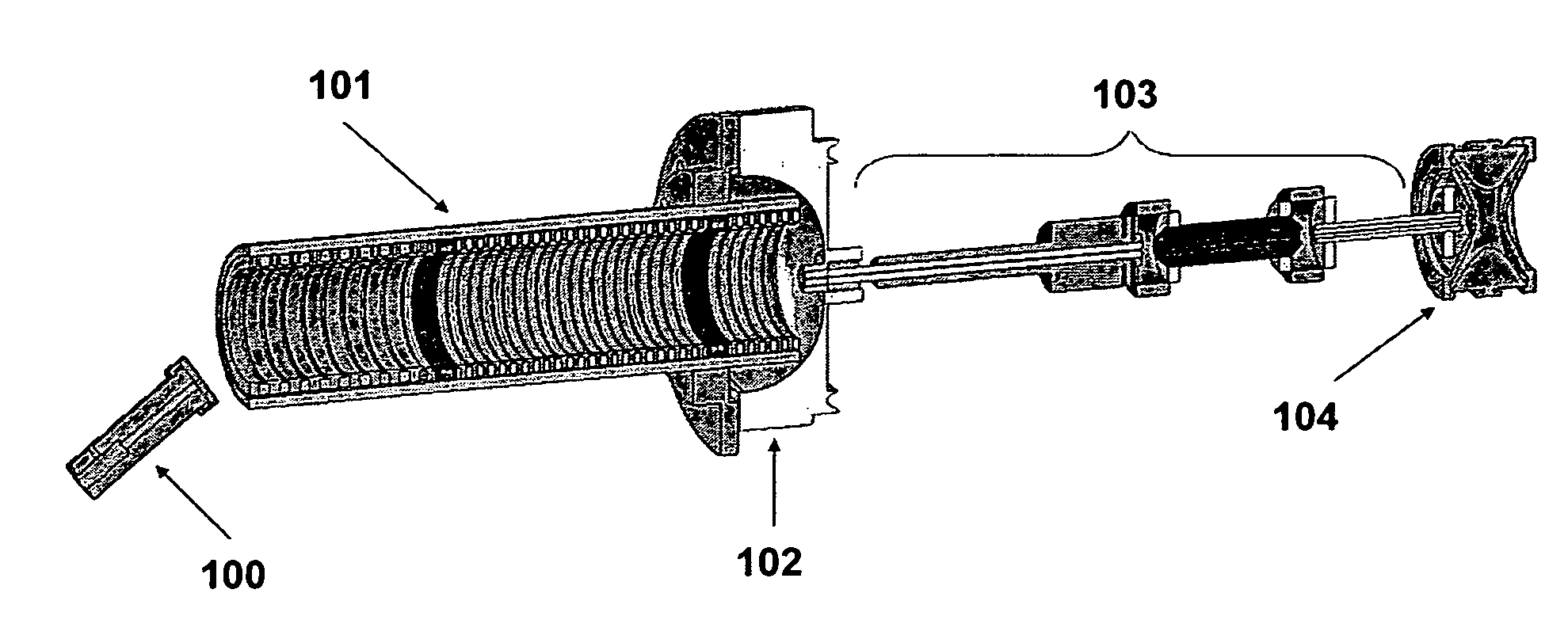
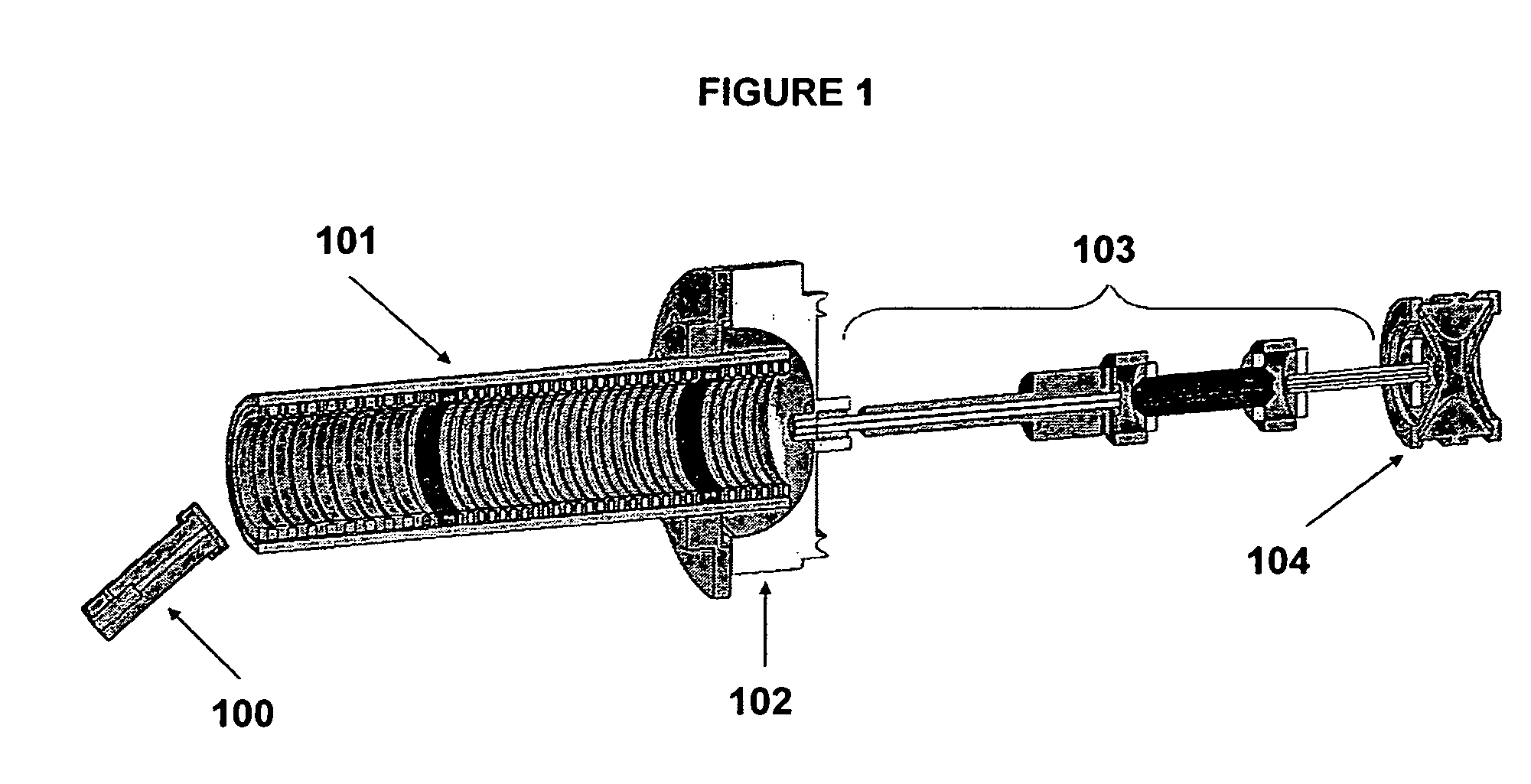
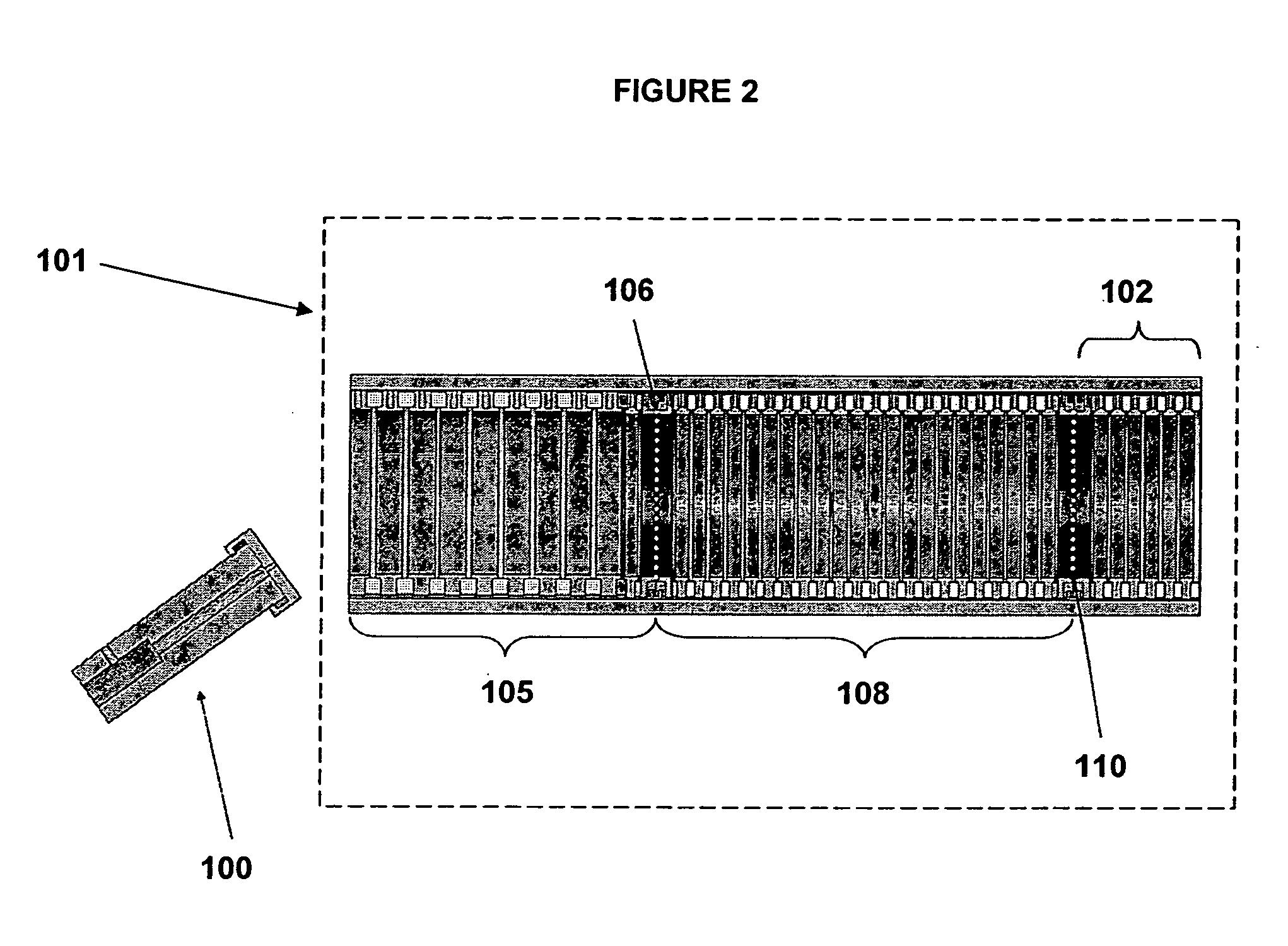
High performance ion mobility spectrometry using hourglass electrodynamic funnel and internal ion funnel
ActiveUS20050092918A1High sensitivityReduce lossesStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryDrift tube
A method and apparatus enabling increased sensitivity in ion mobility spectrometry / mass spectrometry instruments which substantially reduces or eliminates the loss of ions in ion mobility spectrometer drift tubes utilizing a device for transmitting ions from an ion source which allows the transmission of ions without significant delay to an hourglass electrodynamic ion funnel at the entrance to the drift tube and / or an internal ion funnel at the exit of the drift tube. An hourglass electrodynamic funnel is formed of at least an entry element, a center element, and an exit element, wherein the aperture of the center element is smaller than the aperture of the entry element and the aperture of the exit elements. Ions generated in a relatively high pressure region by an ion source at the exterior of the hourglass electrodynamic funnel are transmitted to a relatively low pressure region at the entrance of the hourglass funnel through a conductance limiting orifice. Alternating and direct electrical potentials are applied to the elements of the hourglass electrodynamic funnel thereby drawing ions into and through the hourglass electrodynamic funnel thereby introducing relatively large quantities of ions into the drift tube while maintaining the gas pressure and composition at the interior of the drift tube as distinct from those at the entrance of the electrodynamic funnel and allowing a positive gas pressure to be maintained within the drift tube, if desired. An internal ion funnel is provided within the drift tube and is positioned at the exit of said drift tube. The advantage of the internal ion funnel is that ions that are dispersed away from the exit aperture within the drift tube, such as those that are typically lost in conventional drift tubes to any subsequent analysis or measurement, are instead directed through the exit of the drift tube, vastly increasing the amount of ions exiting the drift tube.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
System and Methods for Ionizing Compounds using Matrix-assistance for Mass Spectometry and Ion Mobility Spectometry
ActiveUS20130306856A1Facilitated ionizationLow costSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansVacuum assistedGas phase
An ionization method for use with mass spectrometry or ion mobility spectrometry is a small molecule compound(s) as a matrix into which is incorporated analyte. The matrix has attributes of sublimation or evaporation when placed in vacuum at or near room temperature and produces both positive and negative charges. Placing the sample into a region of sub-atmospheric pressure, the region being in fluid communication with the vacuum of the mass spectrometer or ion mobility spectrometer, produces gas-phase ions of the analyte for mass-to-charge or drift-time analysis without use of a laser, high voltage, particle bombardment, or a heated ion transfer region. This matrix and vacuum assisted ionization process can operate from atmosphere or vacuum and produces ions from large (e.g. proteins) and small molecules (e.g. drugs) with charge states similar to those observed in electrospray ionization.
Owner:MSTM LLC
Carbon nanotube-MXene composite three-dimensional porous carbon material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109671576AExpand migration spaceHigh yieldMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesFreeze-dryingPorous carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method of a carbon nanotube-MXene composite three-dimensional porous carbon material. According to the preparation method of the material, based on the hydrophilic property of the MXene material, the MXene material is dispersed in a carbon nanotube stabilizing solution, and then is added into a PVA water solution to form a uniformly dispersed stable system. The three-dimensional porous composite carbon material is obtained through freeze drying and carbonization. According to the preparation method, a carbon nanotube can be inserted into a two-dimensionallayer structure of MXene, so that sheet agglomeration is prevented. The specific surface area is increased, and the ion migration space is enlarged. The improvement of the unit capacity and the cycling stability is facilitated. The problem that an MXene material and a graphene material are not easy to disperse uniformly is solved. The mesoporous and macroporous composite three-dimensional porous carbon material is prepared. The preparation method is simple, green, environment-friendly, low in cost, high in yield and easy for industrial production.
Owner:四川翔丰华新能源材料有限公司 +1
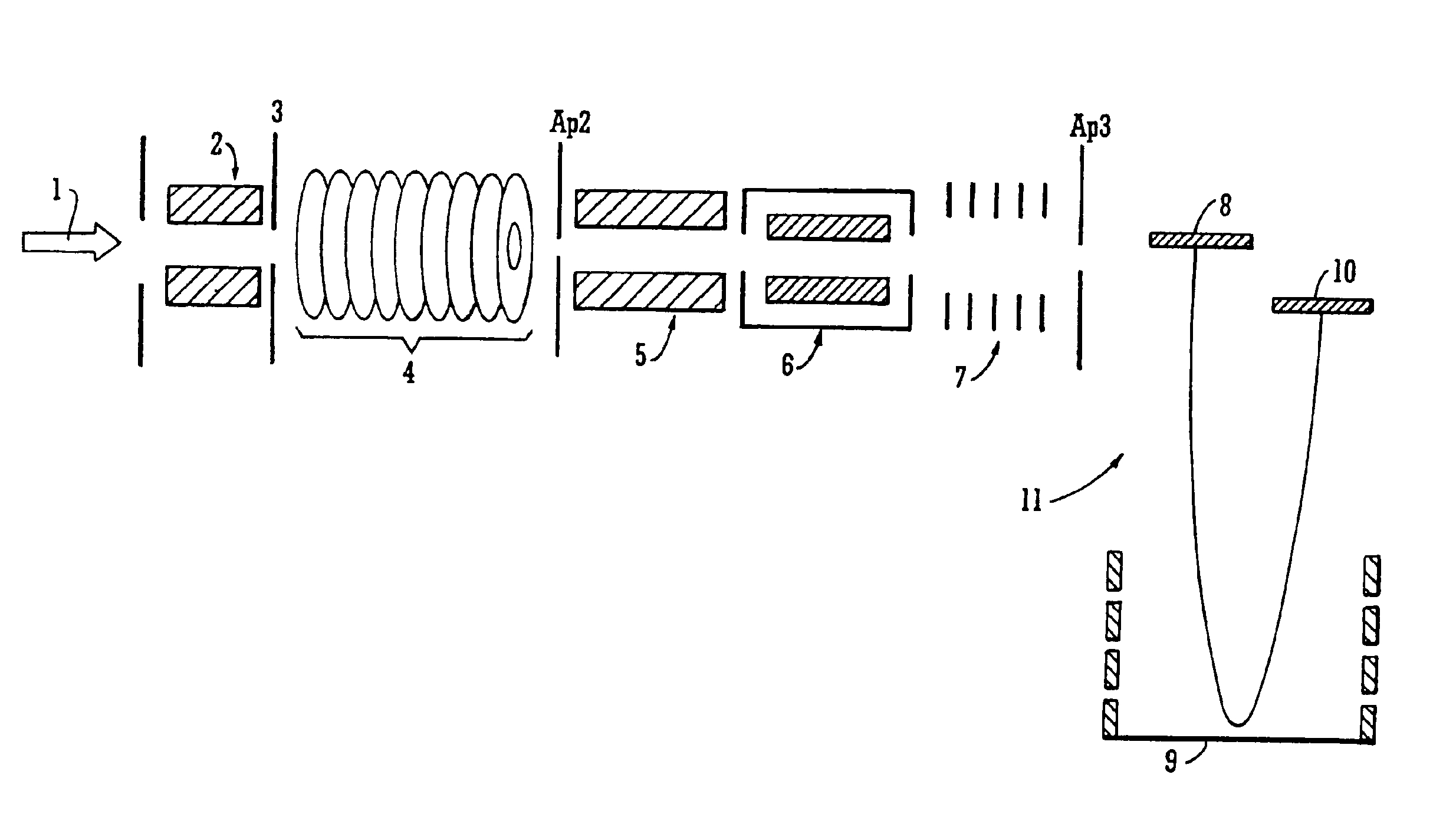
Method and apparatus for electrospray augmented high field asymmetric ion mobility spectrometry
InactiveUS6972407B2Improve performanceEasy to separateStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersChemical physicsControl signal
A field asymmetric ion mobility spectrometer apparatus and system including a sample preparation and introduction section, a head for delivery of ions from a sample, an ion filtering section, an output part, and an electronics part wherein the filter section includes surfaces defining a flow path, further including ion filter electrodes facing each other over the flow path that enables the flow of ions derived from the sample between the electrodes and wherein the electronics part applies controlling signals to the electrodes for generating a filter field for filtering the flow of ions in the flow path while being compensated to pass desired ion species out of the filter.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Perovskite solar cell with interface modification layers and preparation method of perovskite solar cell
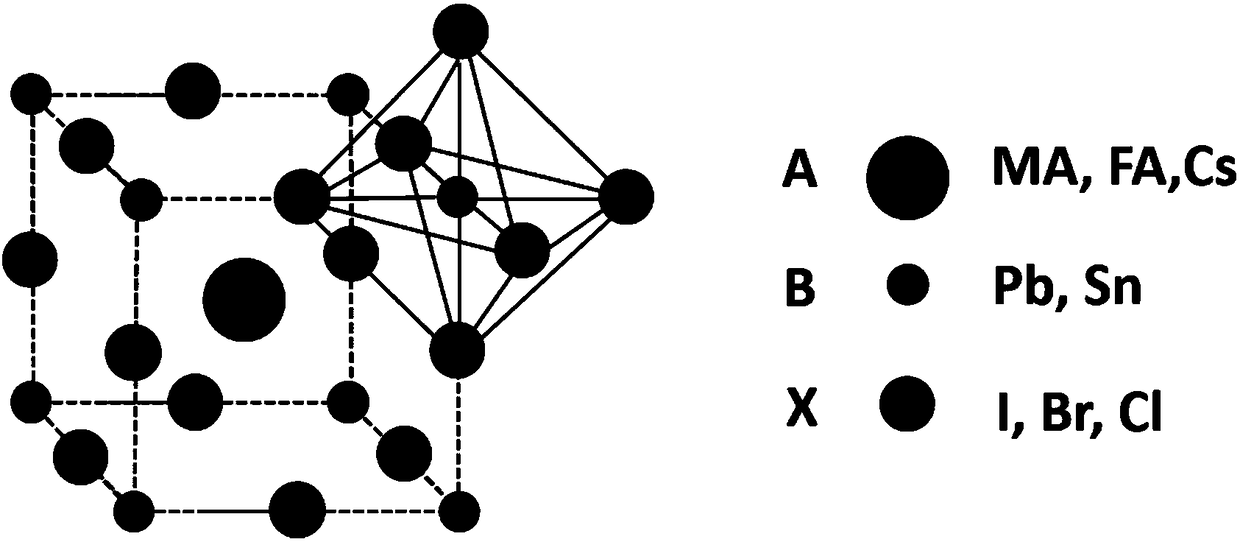
ActiveCN108258128AImprove crystal structureImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesPerovskite solar cellCrystal structure
The invention relates to a perovskite solar cell with interface modification layers. The cross-sectional structure of the perovskite solar cell includes a transparent conductive substrate, a first transmission layer, a perovskite active layer, a second transmission layer and a back electrode; at least one first interface modification layer is disposed between the perovskite active layer and the first transmission layer; and no or at least one second interface modification layer is disposed between the perovskite active layer and the second transmission layer. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the perovskite solar cell. According to the method, the interface modification layers are additionally arranged between the perovskite active layer and transmission layers of a perovskite solar cell, so that the perovskite solar cell with the interface modification layers can be prepared; the surfaces of the transmission layers are passivated; the crystal structure of the perovskite is optimized; ion migration in the perovskite active layer is suppressed to a certain extent; and therefore, the photoelectric conversion efficiency and long-term stability of the perovskite cellare improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU MICROQUANTA SEMICON CO LTD
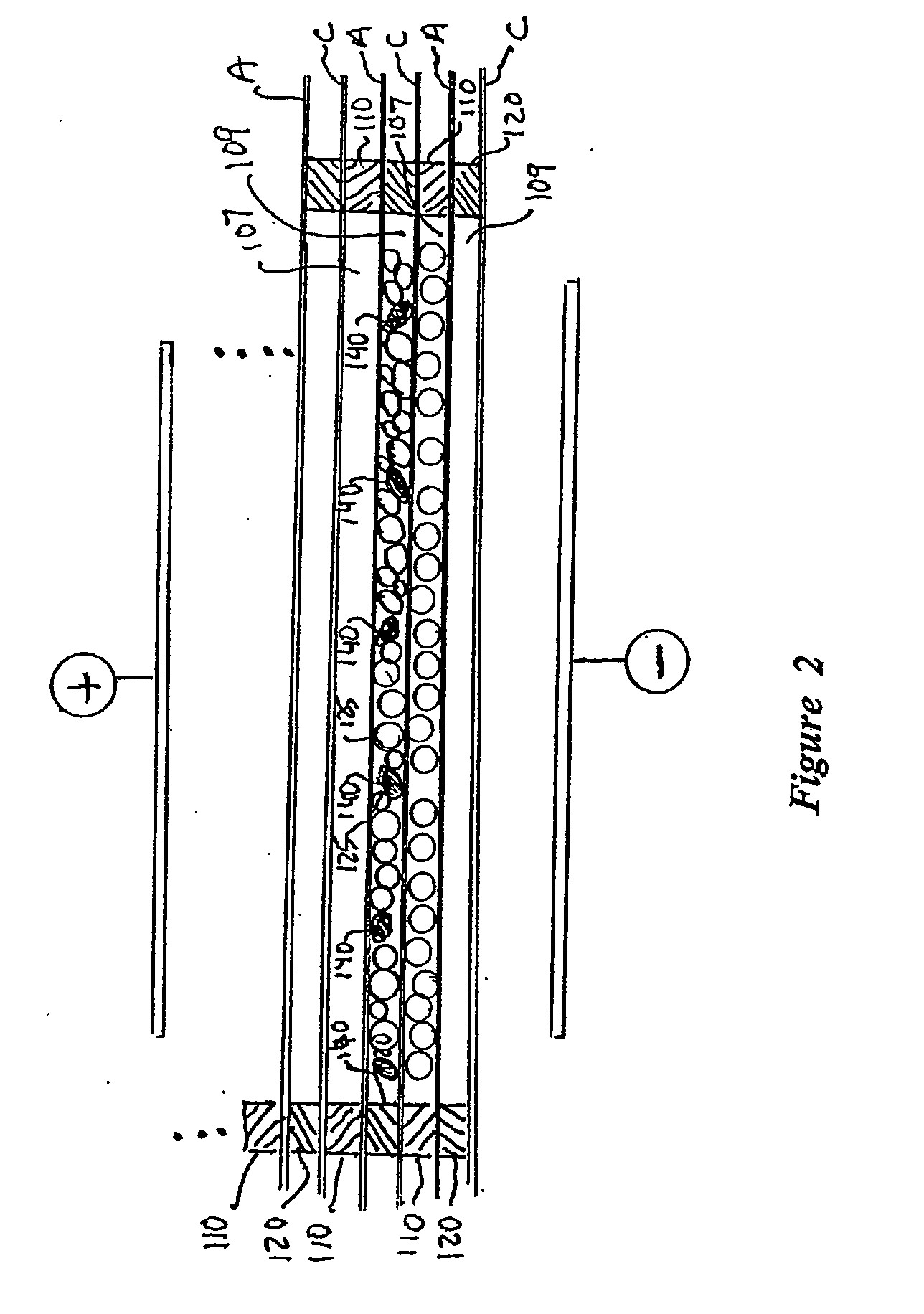
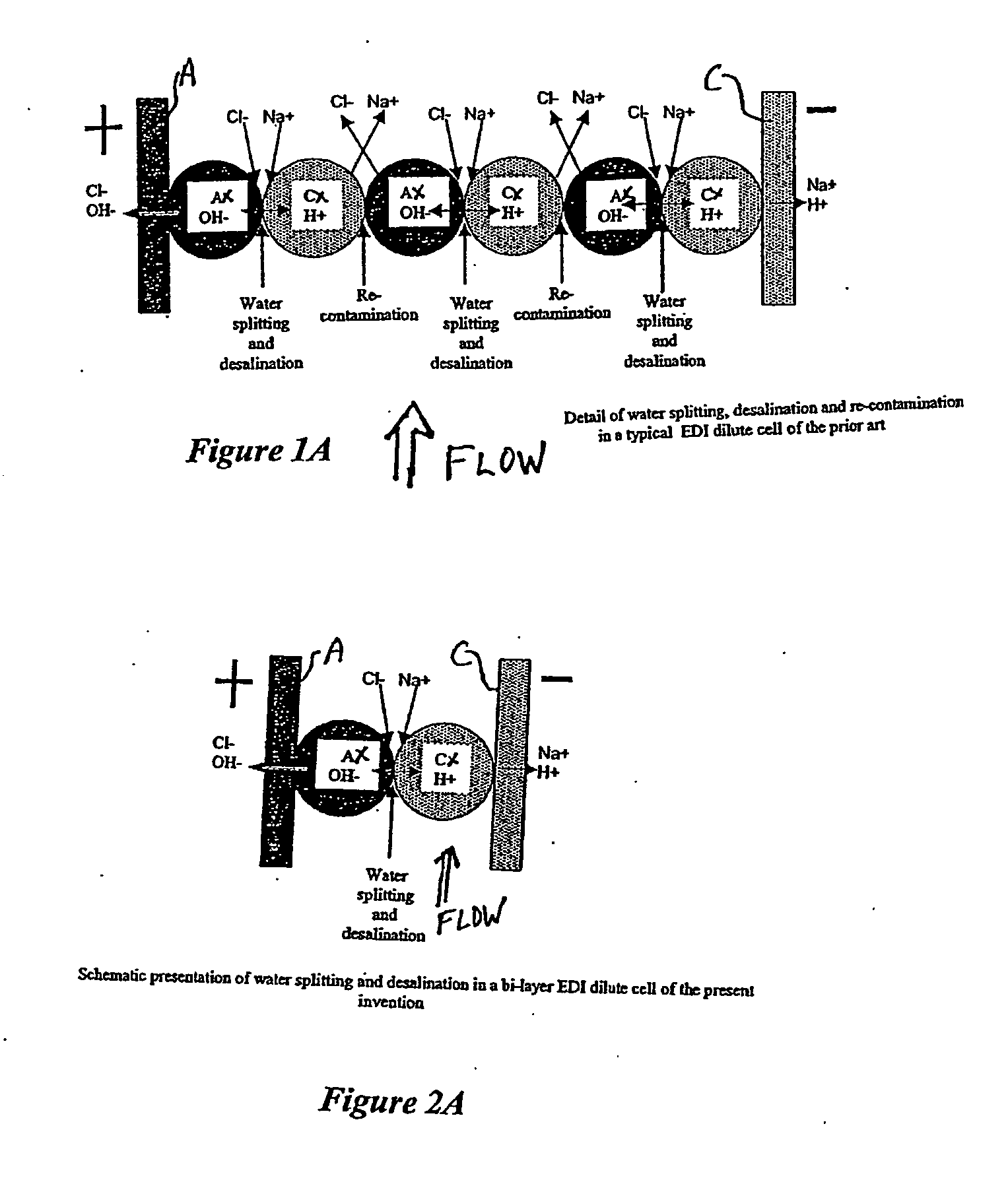
Sparse media edi apparatus and method
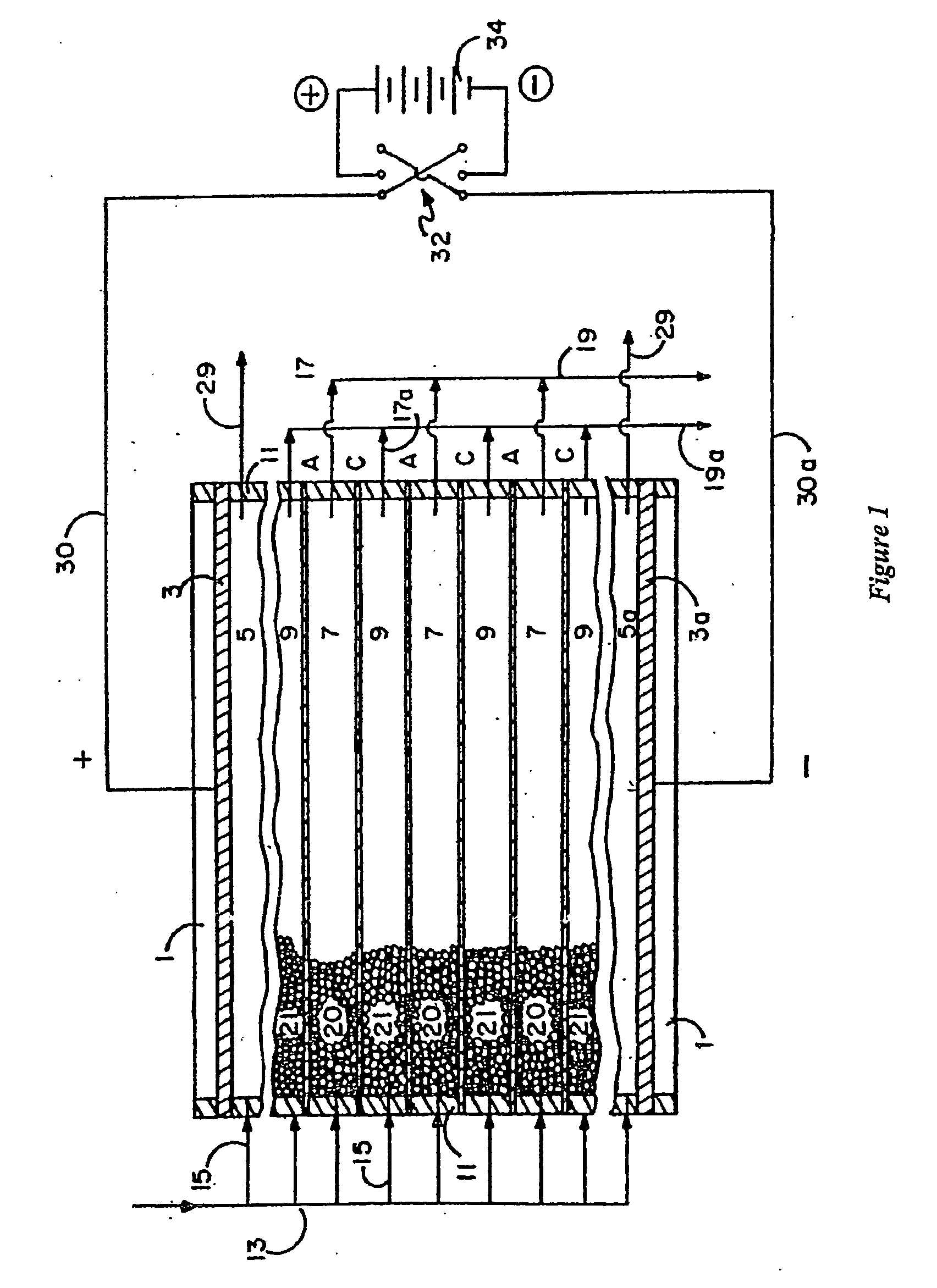
An electrodeionization, (EDI) apparatus has flow cells with a sparse distribution of ion exchange (IX) material or beads. The beads extend between membranes defining opposed walls of the cell to separate and support the membranes, and form a layer substantially free of bead-to-bead dead-end reverse junctions. The beads enhance capture of ions from surrounding fluid in dilute cells, and do not throw salt when operating current is increased. In concentrating cells, the sparse bead filling provides a stable low impedance bridge to enhanced power utilization in the stack. A monotype sparse filling may be used in concentrate cells, while mixed, layered, striped, graded or other beads may be employed in dilute cells. Ion conduction paths are no more than a few grains long and the lower packing density permits effective fluid flow. A flow cell thickness may be below one millimeter, and the beads may be discretely spaced, form a mixed or patterned monolayer, or form an ordered bilayer, and a mesh having a lattice spacing comparable to or of the same order of magnitude as resin grain size, may provide a distributed open support that assures a stable distribution of the sparse filling, and over time maintains the initial balance of uniform conductivity and good through-flow. The cells or low thickness and this resin layers relax stack size and power supply constraints, while providing treatment efficiencies and process stability. Reduced ion migration distances enhance the ion removal rate without reducing the product flow rate. The sparse resin bed may be layered, graded along the length of the path, striped or otherwise patterned. Inter-grain ion hopping is reduced or eliminated, thus avoiding the occurrence of salt-throwing which occurs at reverse bead junctions of prior art constructions. Conductivity of concentrate cells is increased, permitting more compact device construction, allowing increases in stack cell number, and providing more efficient electrical operation without ion additions. Finally, ion storage within beads is greatly reduces, eliminating the potential for contamination during reversal operation. Various methods of forming sparse beds and assembling the stacks are disclosed.
Owner:IONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com