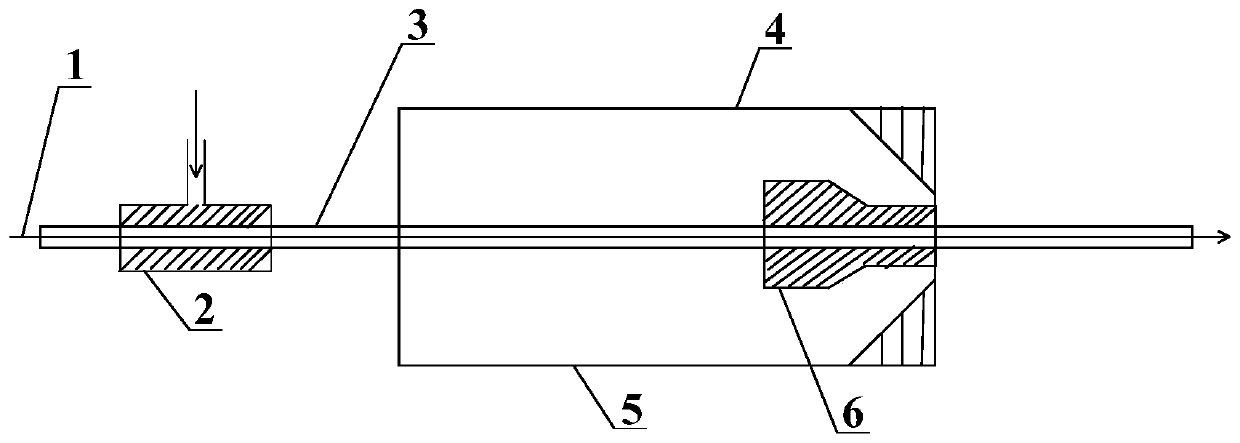
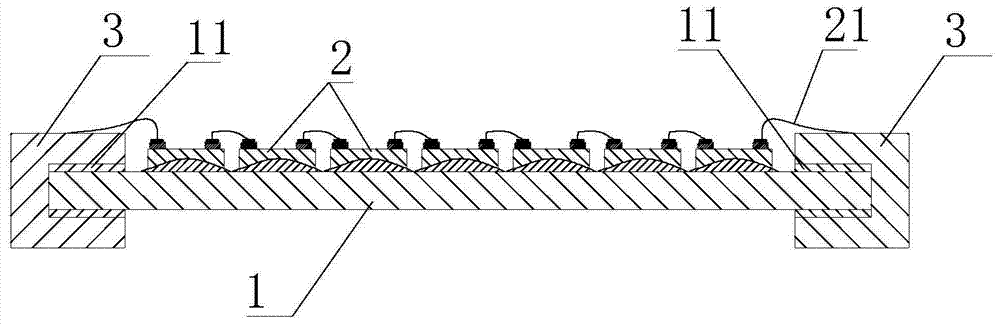
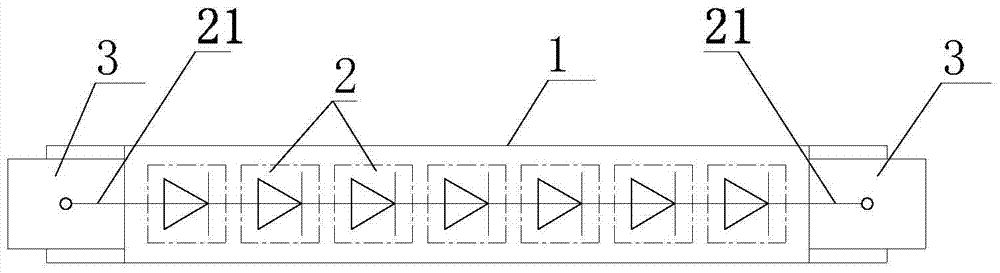
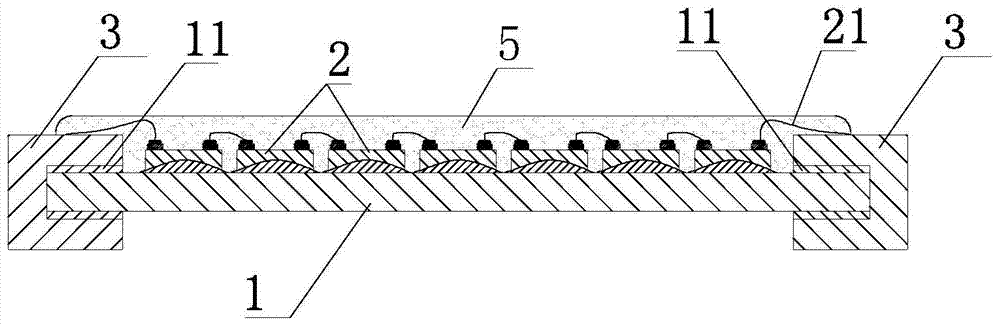
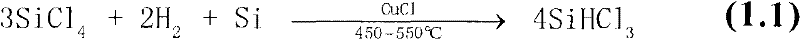Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53results about How to "Reduce the difficulty of production operations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
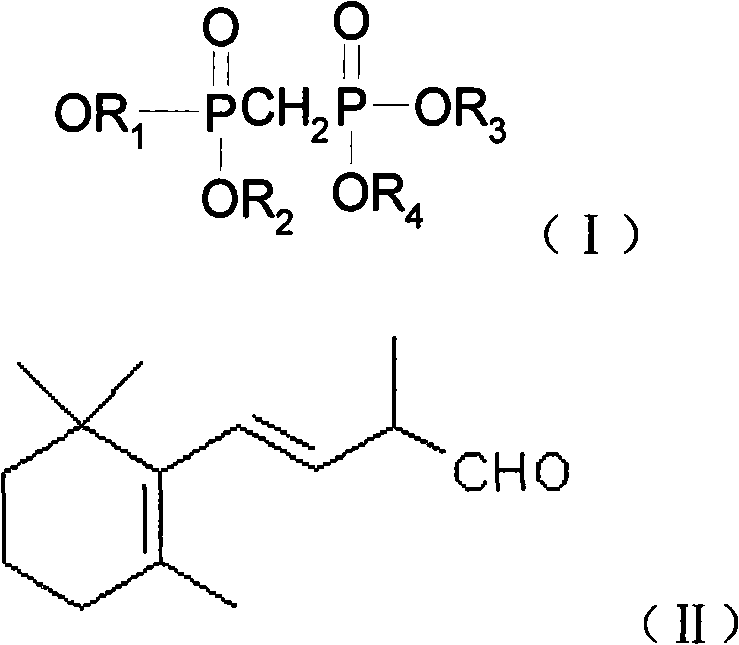
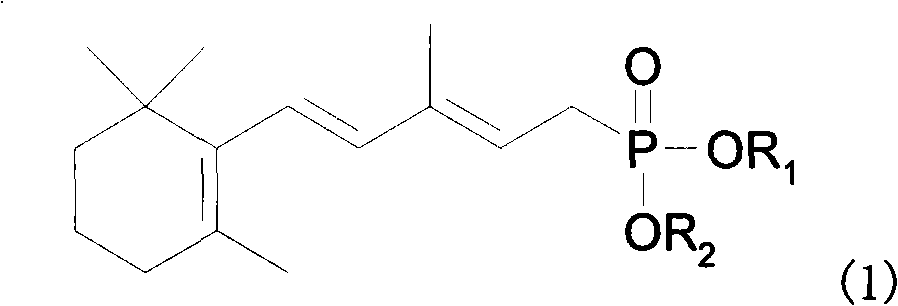
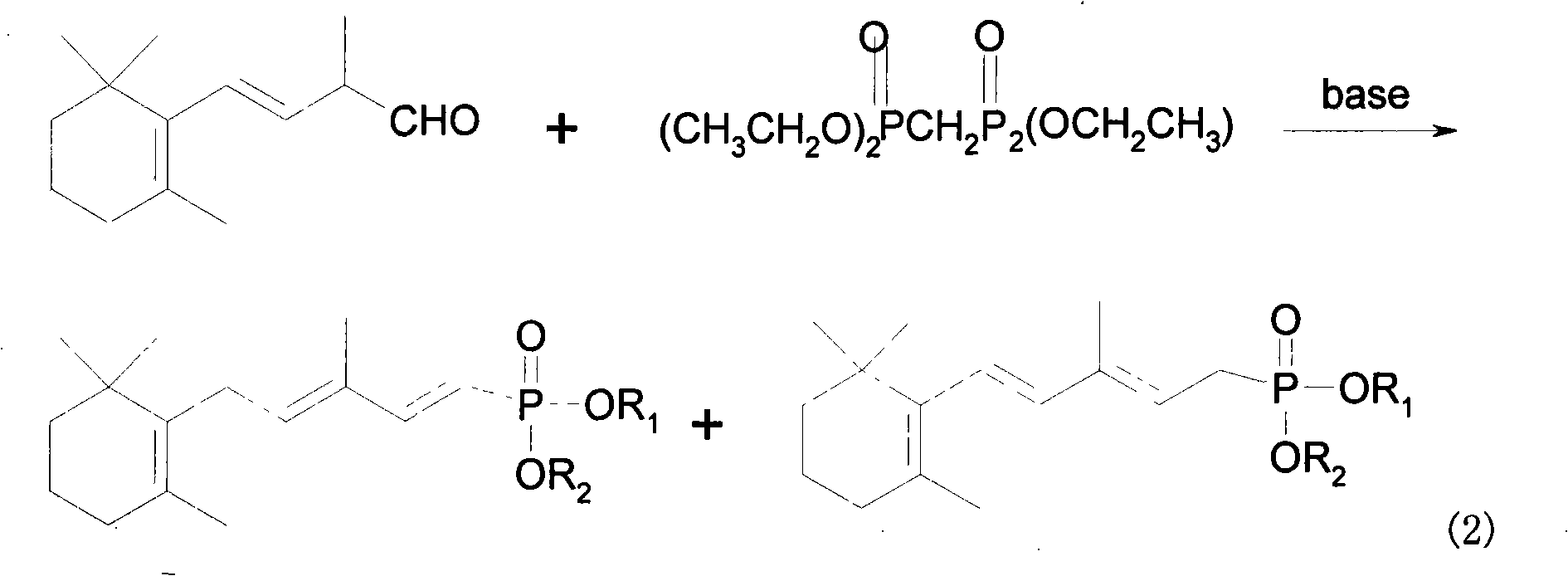
Method for preparing 3-methyl-5-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexene-1-base)-2, 4-pentadiene-dialkyl phosphoric ester
InactiveCN101318975AReduce energy consumption and difficulty of production operationsConducive to industrial productionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsTolueneCyclohexenes
The invention provides a method for preparing 1, 3-methyl-5-(2, 6, 6-trimethyl-1- cyclohexene-1-yl)-2, 4-pentadiene methyl phosphonate. In the method, a benzophenone compound preventing transposition is added in the process of generating the 1, 3-methyl-5-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexene-1-yl)-2,4-pentadiene methyl phosphonate by the reaction of methylene diphosphate four alkyl and C14 aldehyde in a mixed solvent of methylbenzene and tetrahydrofuran, thereby inhibiting the generation of a target product isomer in order that the content of the target product in a final product reaches up to 97 percent.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WISDOM BIO TECH
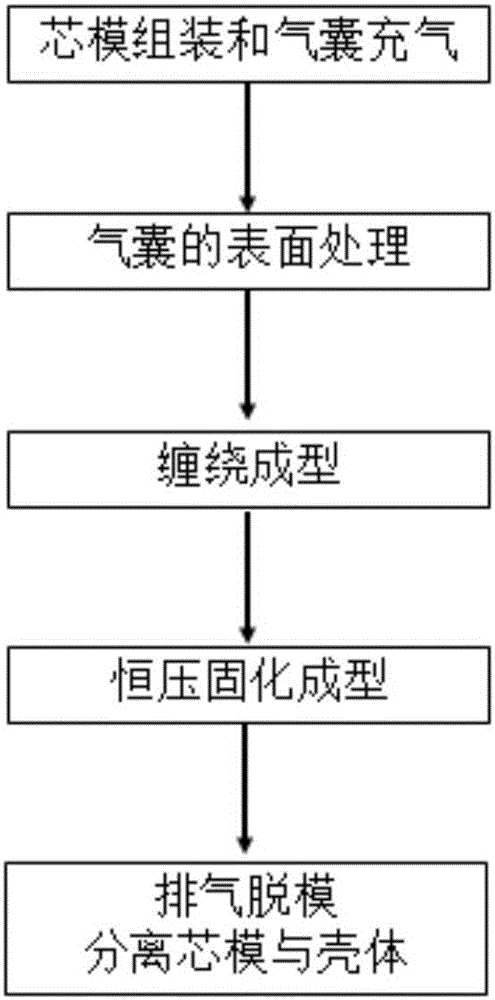
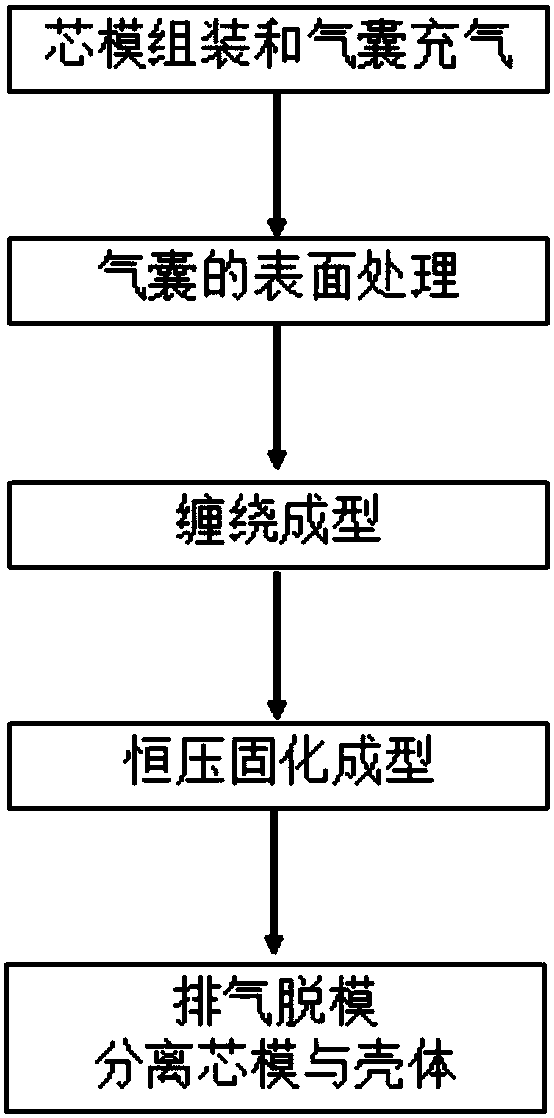
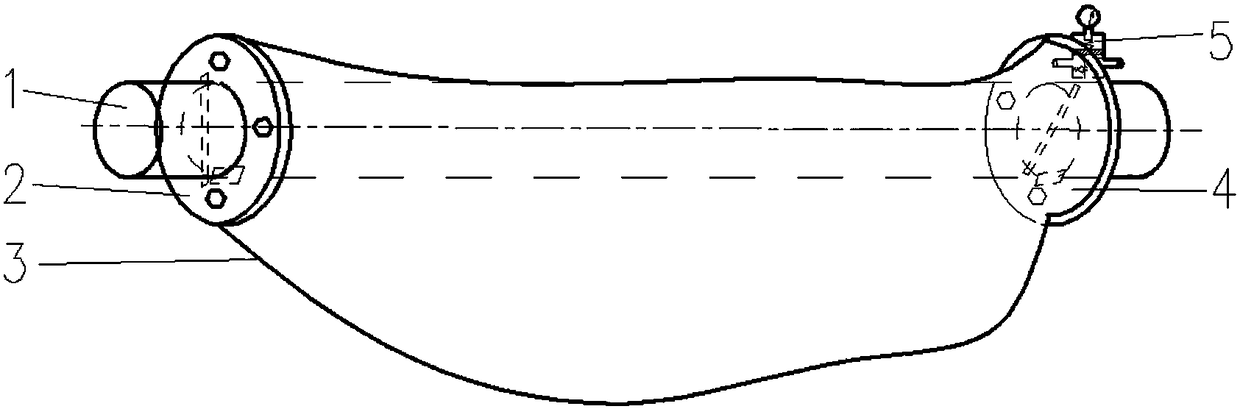
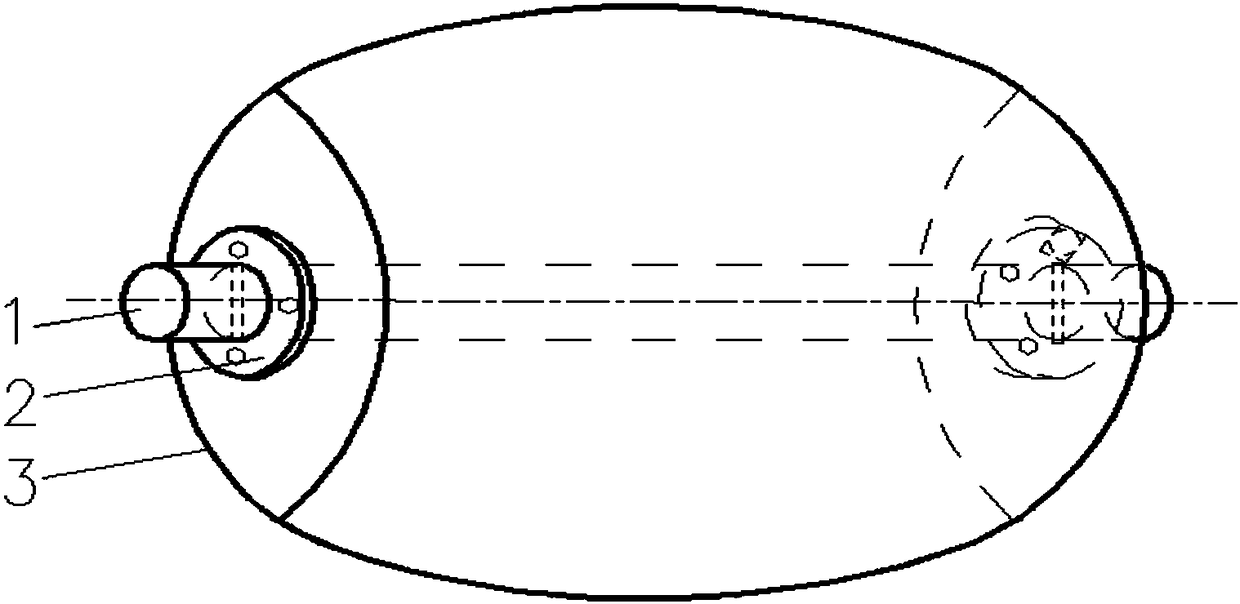
Winding molding method of all-composite material shells
The invention discloses a winding molding method of all-composite material shells, belongs to the technical field of molding process, and relates to the winding molding method of the all-composite material shells. The winding molding method comprises the steps: firstly, assembling a core mold, and filling a gas bag with light gas; next, carrying out surface treatment of the gas bag; then adopting the winding molding control program to control a winding machine to wind the outer surface of the gas bag with fiber bundles or cloth belts according to the program, and curing and molding according to temperature and time requirements required for molding; and finally, obtaining the composite material shells through a demolding process. The winding molding method has wide applicability, and can be used for manufacturing the composite material shells with different shapes and sizes and meeting a requirement of asymmetric front and back sealing surfaces. The process has good stability, equipment is simple and convenient, low in weight and strong in controllability, and the method is simple, practical, and easy to operate and popularize. Workers are prevented from entering the interior of the core mold for operation, the complex assembly and disassembly processes in a traditional winding process are greatly reduced, the difficulty of production operation is reduced, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
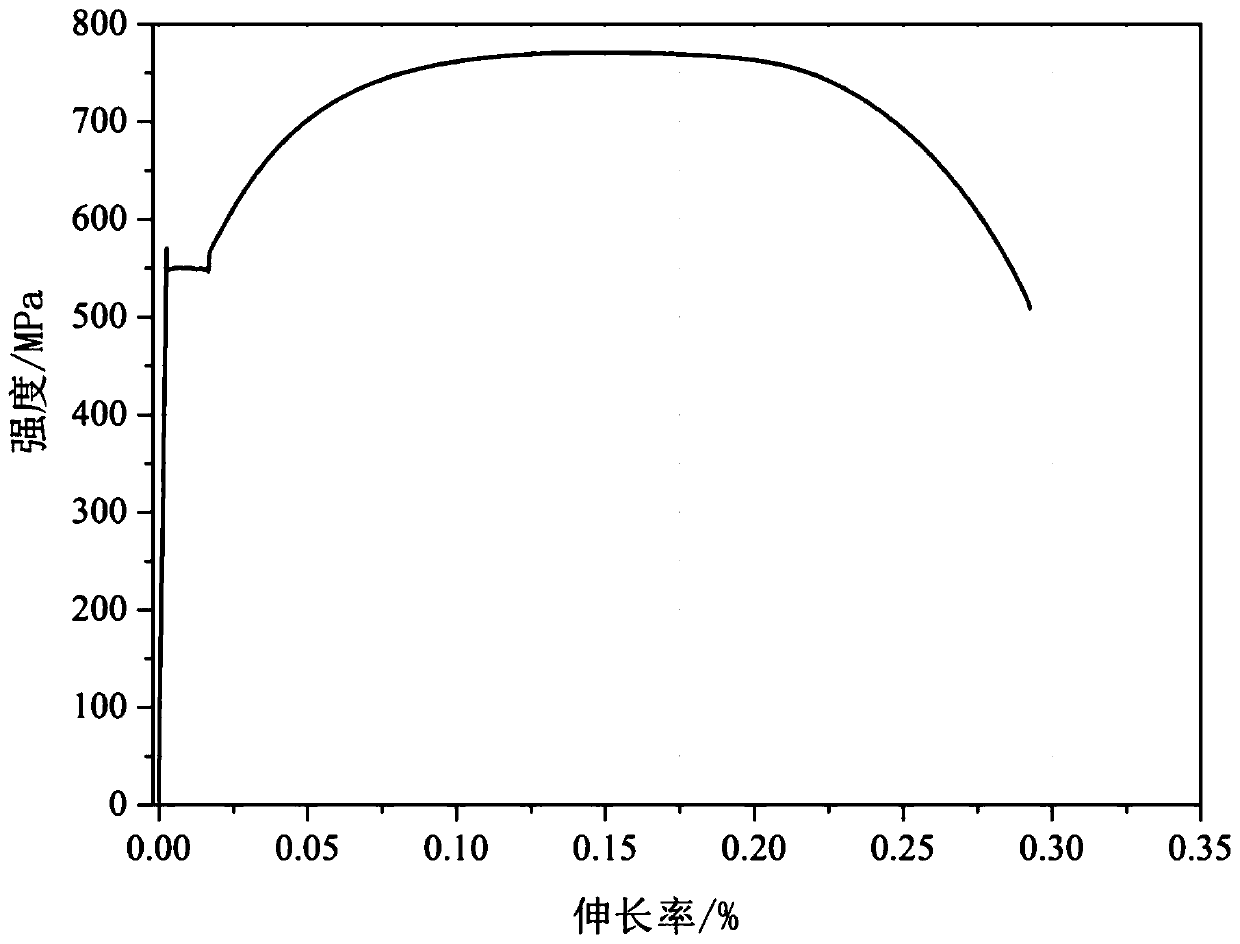
400-MPa-grade fine-grain hot rolled steel bar and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveCN110042303AImprove performanceHigh strengthProcess efficiency improvementManganese sulfideRebar
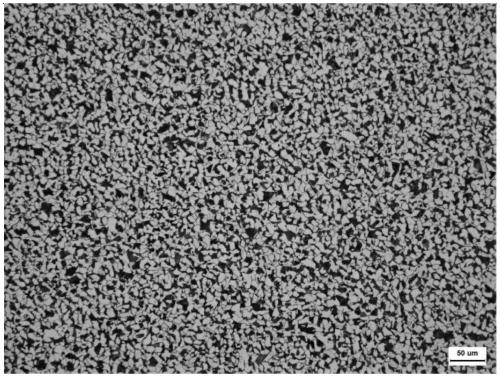
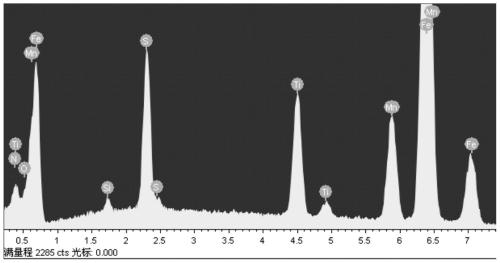
The invention discloses a 400-MPa-grade fine-grain hot rolled steel bar and a manufacturing process thereof, and belongs to the field of hot-rolled steel bar production. The steel bar comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.20-0.25% of C, 0.3-0.8% of Si, 1.2-1.6% of Mn, 0.01-0.04% of P, 0.01-0.04% of S, 0.005-0.03% of Ti, 0.001-0.08 % of Cr, 0.0001-0.008% of V, 0.0001-0.008% ofNb, 0.0001-0.008% of Al, 0.01-0.02% of O, 0.003-0.01% of N, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities; and the steel bar further comprises manganese silicate inclusions, titanium oxide manganese sulfide multiphase inclusions, manganese sulfide inclusions, and other inevitable inclusions. The manufacturing process comprises the following steps of smelting molten steel, heating a continuous casting billet, and rolling a steel bar. According to the process, by combining optimization of the components and the inclusions with smelting continuous casting and rolling improvement as well as the inclusion induced fine grain strengthening mechanism, the strength of the steel bar is improved, the addition of precious alloy elements is reduced, and low-cost and high-quality production of the hot-rolled steel bar is achieved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
400 MPa level fine grain threaded reinforcing bar and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109930056AImprove performanceHigh strengthTemperature control deviceBuilding reinforcementsRebarAlloy element
The invention discloses a 400 MPa level fine grain threaded reinforcing bar and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the field of threaded reinforcing bar production. The reinforcing bar comprises, by mass percentage, 0.20-0.25% of C, 0.3-0.8% of Si, 1.2-1.6% of Mn, 0.01-0.04% of P, 0.01-0.04% of S, 0.004-0.02% of Ti, 0.001-0.08% of Cr, 0.0001-0.008% of V, 0.0001-0.008% of Nb, 0.0001-0.008% of Al, 0.003-0.01% of O, 0.003-0.01% of N and the balanced of Fe and unavoidable impurities; manganese silicate inclusion, titanium oxide manganese sulfide complex inclusion, manganese sulfide complex inclusion and other unavoidable inclusions are included. The method comprises the steps of molten steel smelting, inclusion controlling, continuous casting, continuous casting blank heating and rolling cooling. The method has the advantages that optimizing designing is conducted on components and the inclusions, smelting and rolling are combined, a reinforcing mechanism of using the inclusions to induce fine crystalline to improve the strength of the reinforcing bar, the addition of precious alloy elements is reduced, and therefore the low-cost high-quality production of the threaded reinforcing bars is achieved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Dissolving-out process for large-sized pipeline remaining tank of diasporite bauxite ore
InactiveCN101767806ALarge pulp capacityImprove heat utilizationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesBoehmiteMother liquor
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV ENG & RES INST CO LTD
Method for preparing perchlorate by electrolysis of chlorate
InactiveCN1508291AIncrease productionImprove current efficiencyElectrolysis componentsChlorate ionElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method to prepare perchlorate by electrolyzation. Make the electrobaths is greater than or equal to 3 in series become a group and arrange according to graded position difference, make the electrolyte flow from the high-position electrobath to the highest-position one, after electrolyzed, overflow into next one for electrolyzation, then overflow into next one, and electrolyzed in the final one to obtain the finished electrolyte, and control the conversion within 65-85%, to use the finished electrolyte to produce perchlorate product. It improves the current efficiency by above 15%, each ton of perchlorate can reduce electric consumption by 800kw.h, and the output of the perchlorate can be raised by 15% above.
Owner:吴建国 +2
Method for preparing canthaxanthin by electrocatalytic oxygen-oxidized beta-carotene
ActiveCN110372555ARich sourcesEasy to useOrganic chemistryElectrolytic organic productionOrganic solventBeta-Carotene
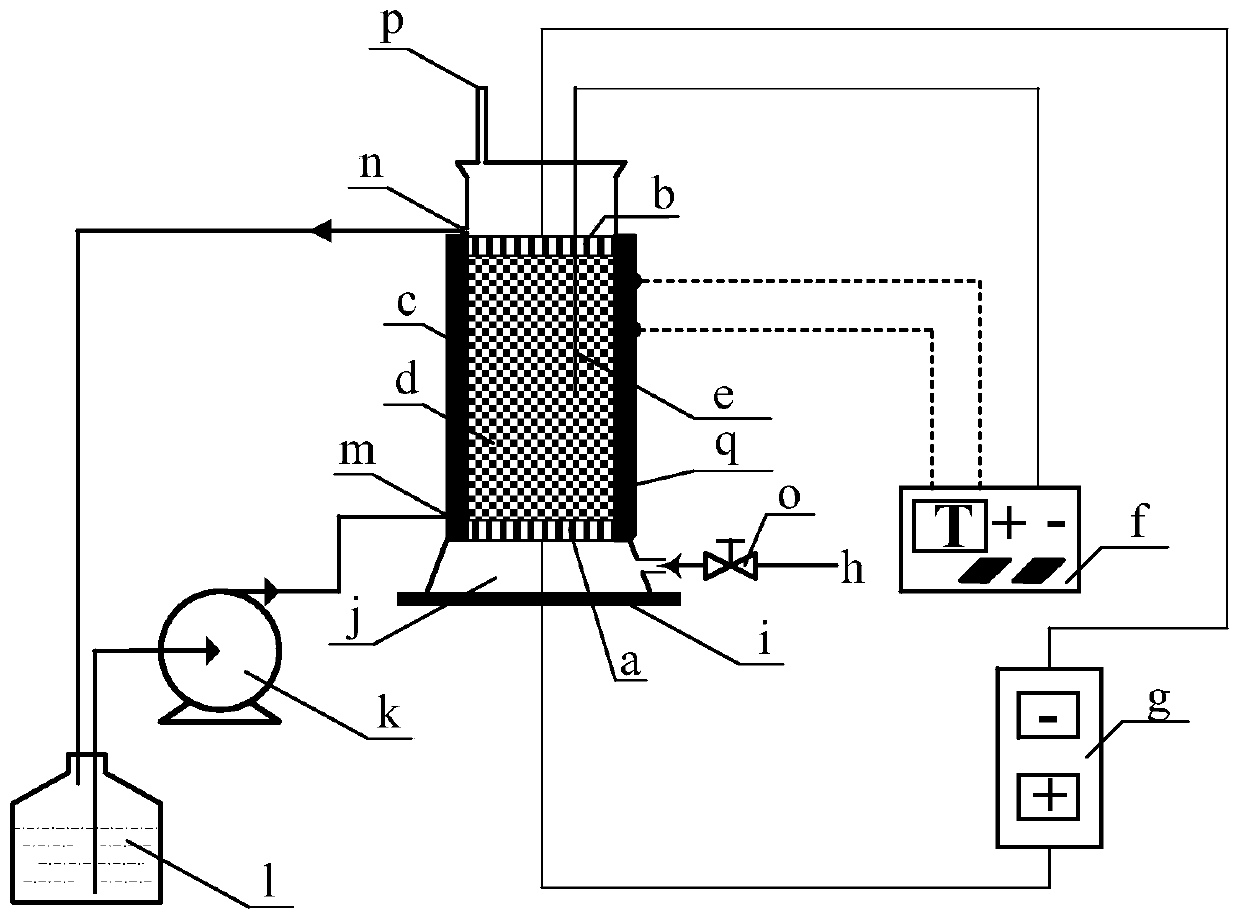
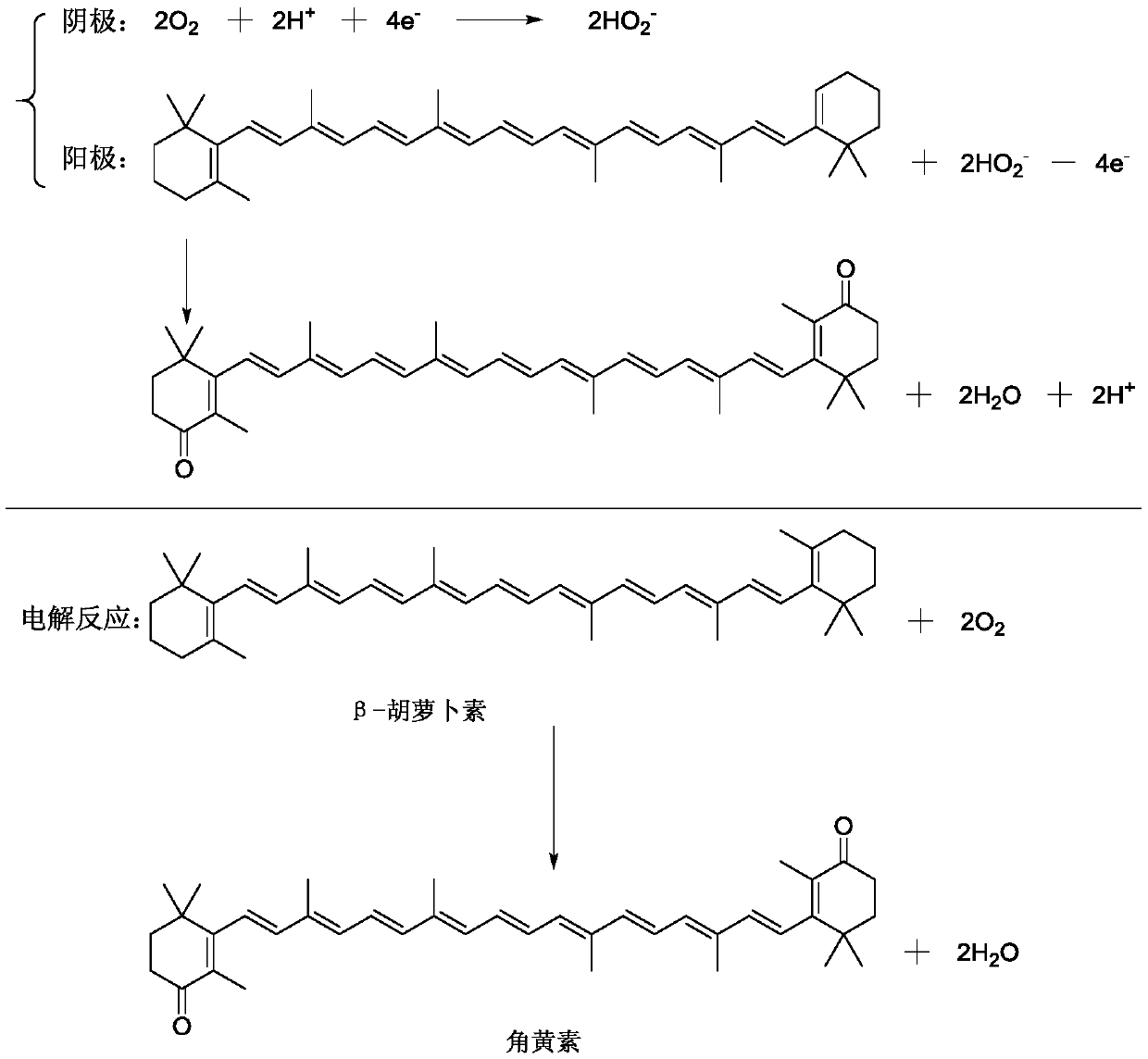
The invention discloses a method for preparing canthaxanthin by electrocatalytic oxygen-oxidized beta-carotene. The raw material beta-carotene is dissolved in an organic solvent, a gas oxygen source is used as an oxidizing agent, and electrolytic reaction is carried out in an electrocatalytic oxidation device filled with catalysts for one-step synthesis to obtain the canthaxanthin. The method forpreparing the canthaxanthin by the electrocatalytic oxygen-oxidized beta-carotene has the advantages that the reaction condition is mild, the reaction process is easy to control, green and environmental protection are achieved, the method for preparing the canthaxanthin by the electrocatalytic oxygen-oxidized beta-carotene is suitable for industrial production, and the yield of the canthaxanthin is higher than 95%.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Hot-rolled seamless steel tube and deformation and phase transformation integrated type structure regulation and control method thereof
ActiveCN113025904AImprove performanceInhibition of abnormal phase transition tissueTemperature control deviceFurnace typesChemical compositionToughness
The invention discloses a hot-rolled seamless steel tube and a deformation and phase transformation integrated type structure regulation and control method thereof, and belongs to the field of hot-rolled seamless steel tube production. The hot-rolled seamless steel tube comprises the following elements: 0.04% to 0.4% of C, 0.1% to 0.8 % of Si, 0.3% to 2.5% of Mn, 0.001% to 0.03% of P, 0.001% to 0.03% of S, 0.001% to 0.05% of Al, 0.003% to 0.03% of Ti, 0.001% to 0.01% of Mg+Ca +Zr +B, 0.001% to 0.008% of O, 0.003% to 0.012% of N and the balance Fe and inevitable impurity elements. According to the regulation and control method, chemical components and inclusion distribution of the steel tube are optimally designed, smelting, rolling and cooling processes are reasonably controlled, special inclusion particles are utilized to play a role in structure refinement, so that coarse unfavorable structures such as grain boundary ferrite, a widmannstatten structure and side bar ferrite are eliminated, a fine grain structure is obtained, and the strength and toughness of the tube are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
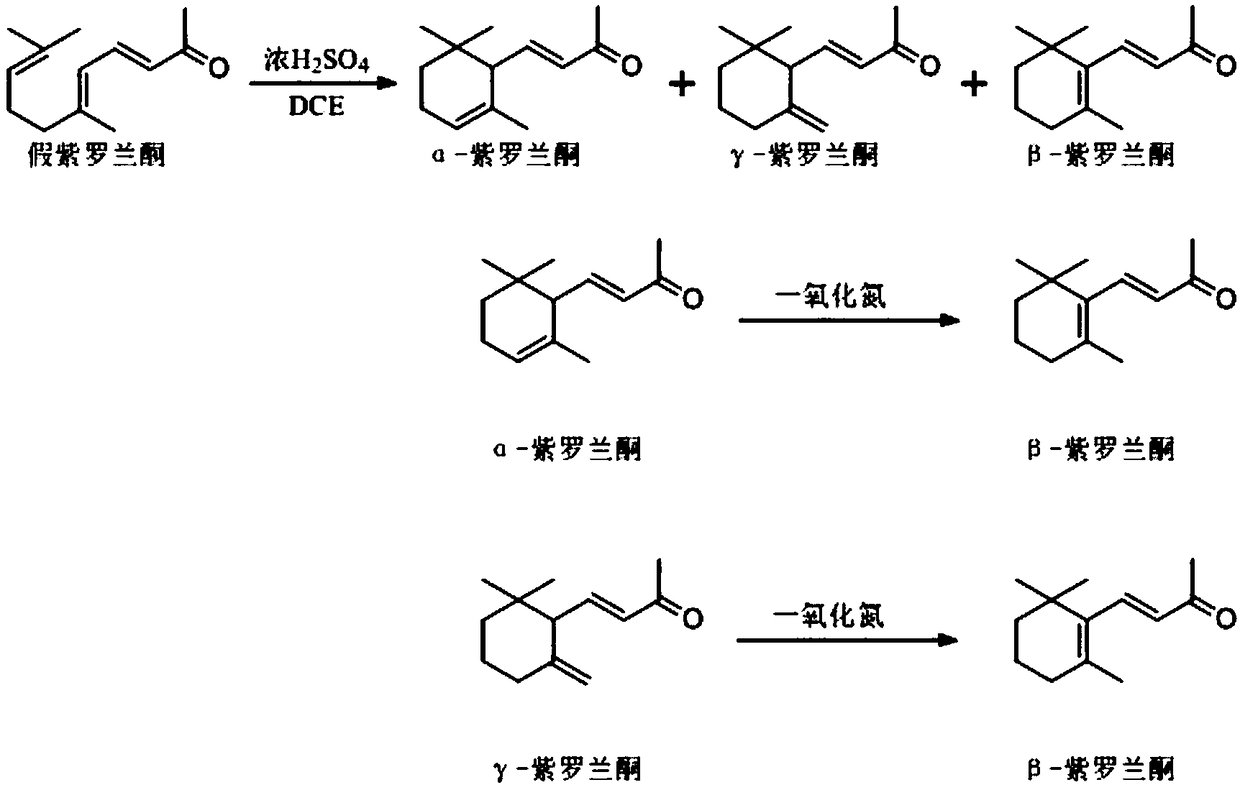
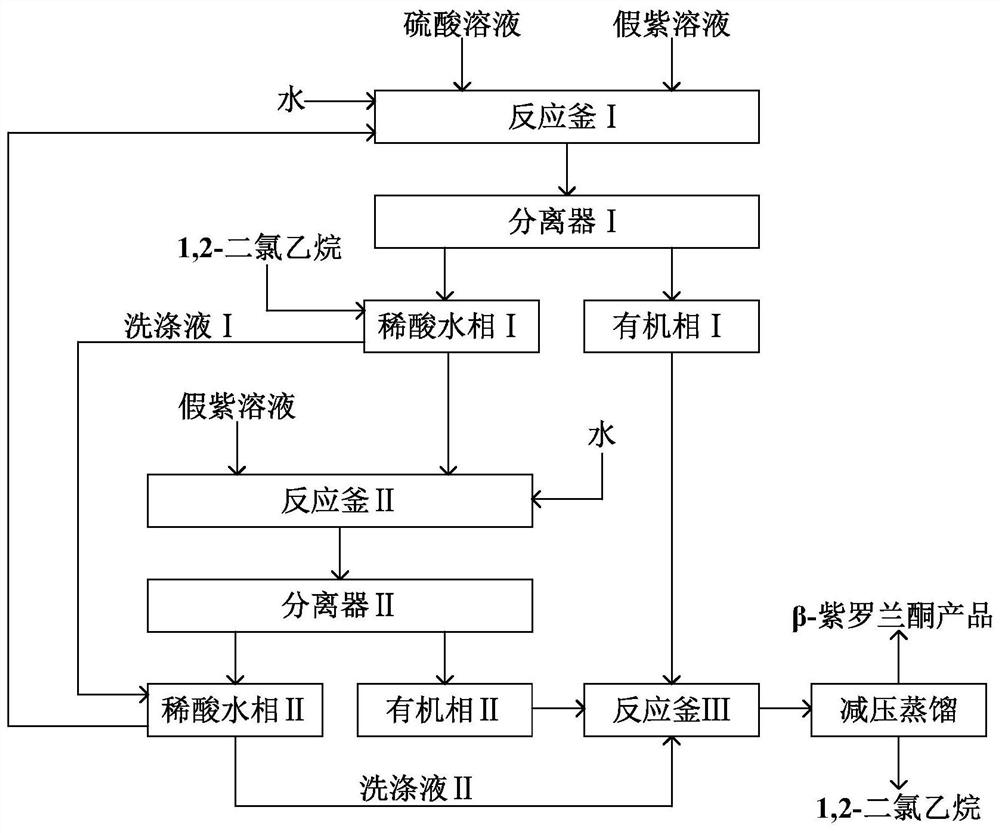
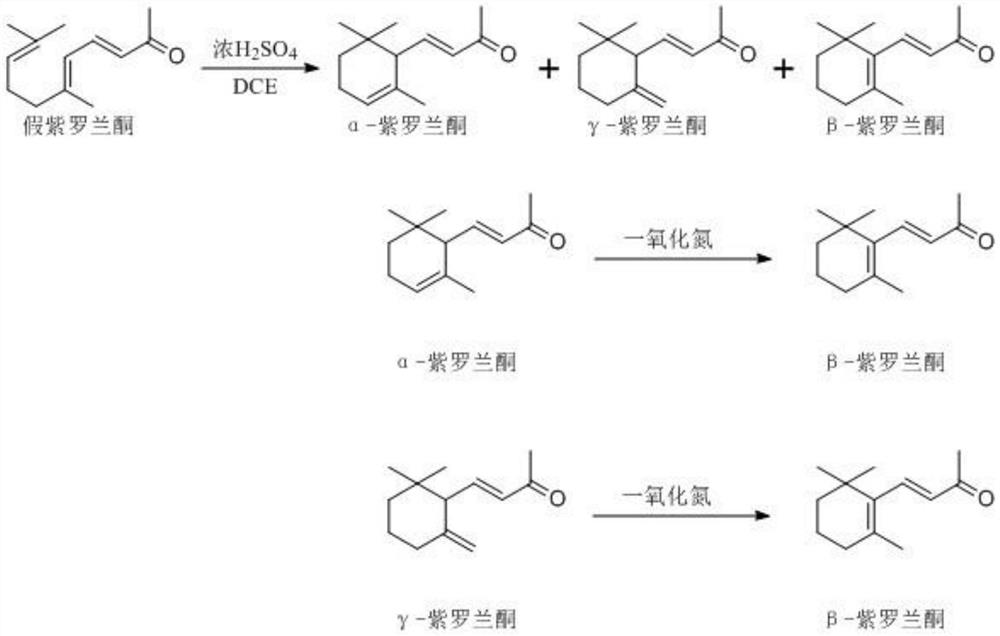
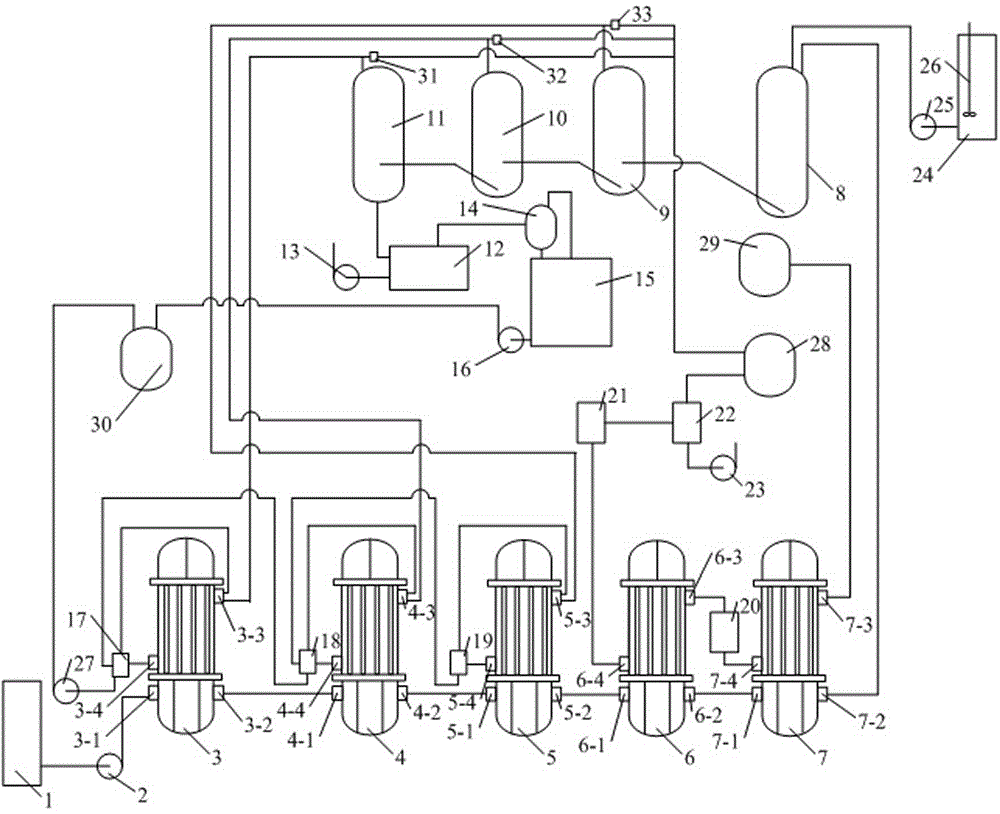
Method for preparing beta-ionone by using pseudoionone as raw materials
ActiveCN108329200AHigh purityIncrease profitOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIsomerizationNitric oxide gas
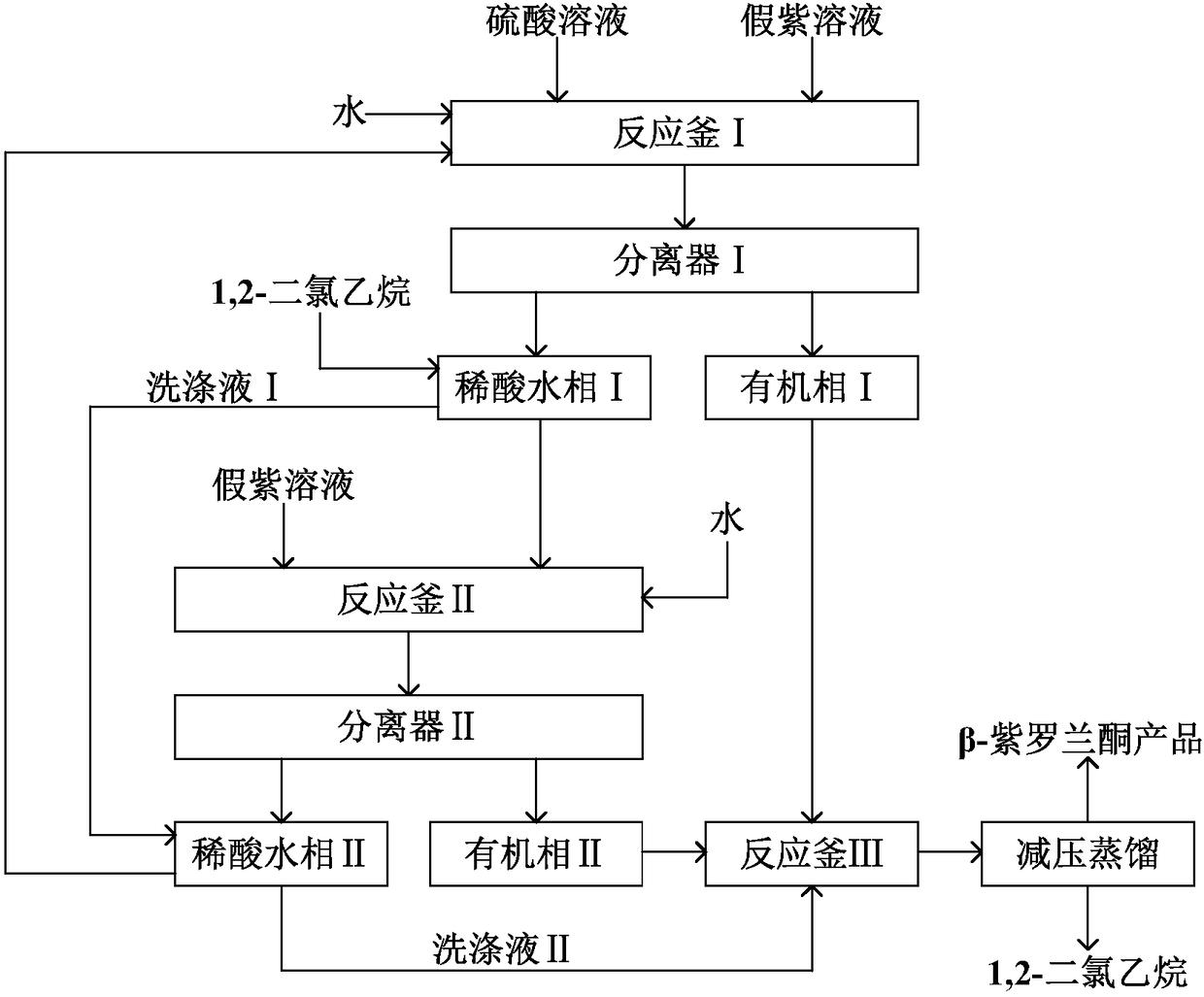
The invention discloses a method for preparing beta-ionone by using pseudoionone as raw materials. The pseudoionone performs cyclization reaction under the catalysis effect of sulfuric acid; quenchingis performed; nitric oxide gas is introduced into reaction liquid after the quenching; then, isomerization reaction is performed to obtain the beta-ionone. The method has the advantages that the process is simple; no harsh reaction conditions are needed; sulfuric acid and solvents can be cyclically used for many times; in addition, the purity of the beta-ionone in the obtained product is high, and is higher than 97.5 percent.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Lithium ion battery pack capable of outputting multiple voltages
PendingCN104064720ALess varietyUnified structureFinal product manufactureCell component detailsElectrical batteryPrinted circuit board
Owner:SHENZHEN GREPOW BATTERY CO LTD
Tube array and remaining tank dissolving-out system and method for gibbsite bauxite
InactiveCN102249271ANo scarring effectSmall footprintAluminium oxides/hydroxidesProcess engineeringHeat conservation
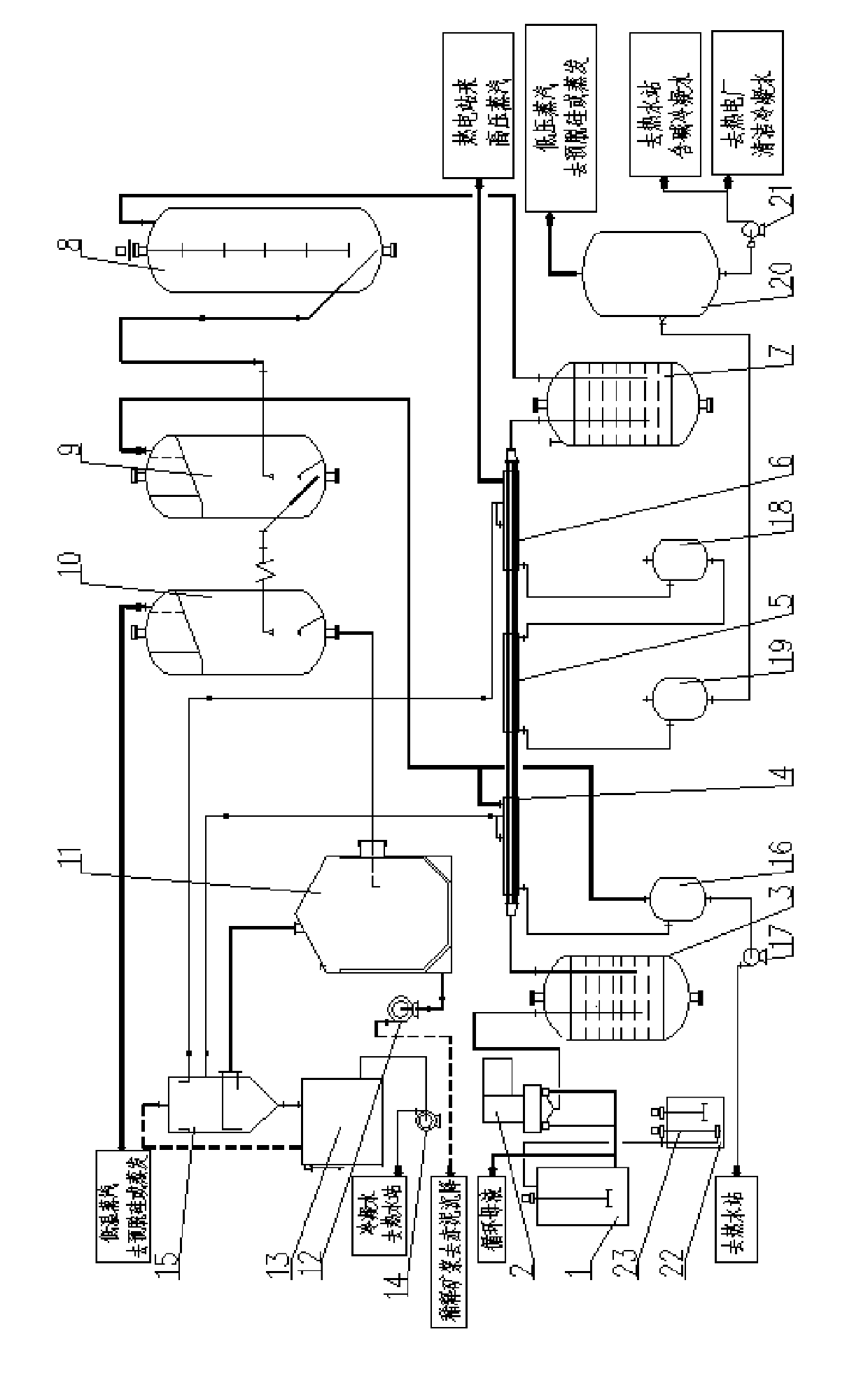
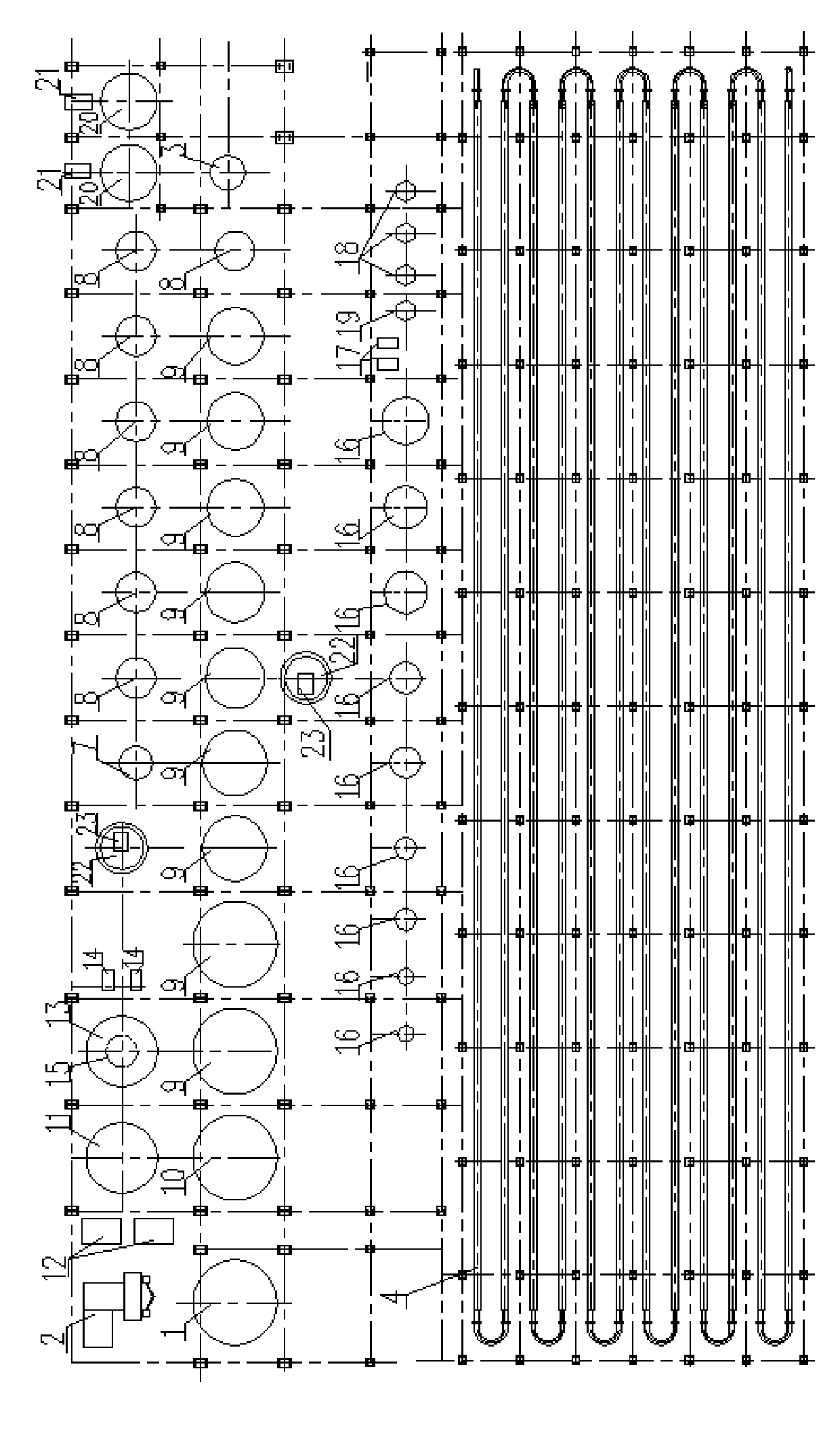
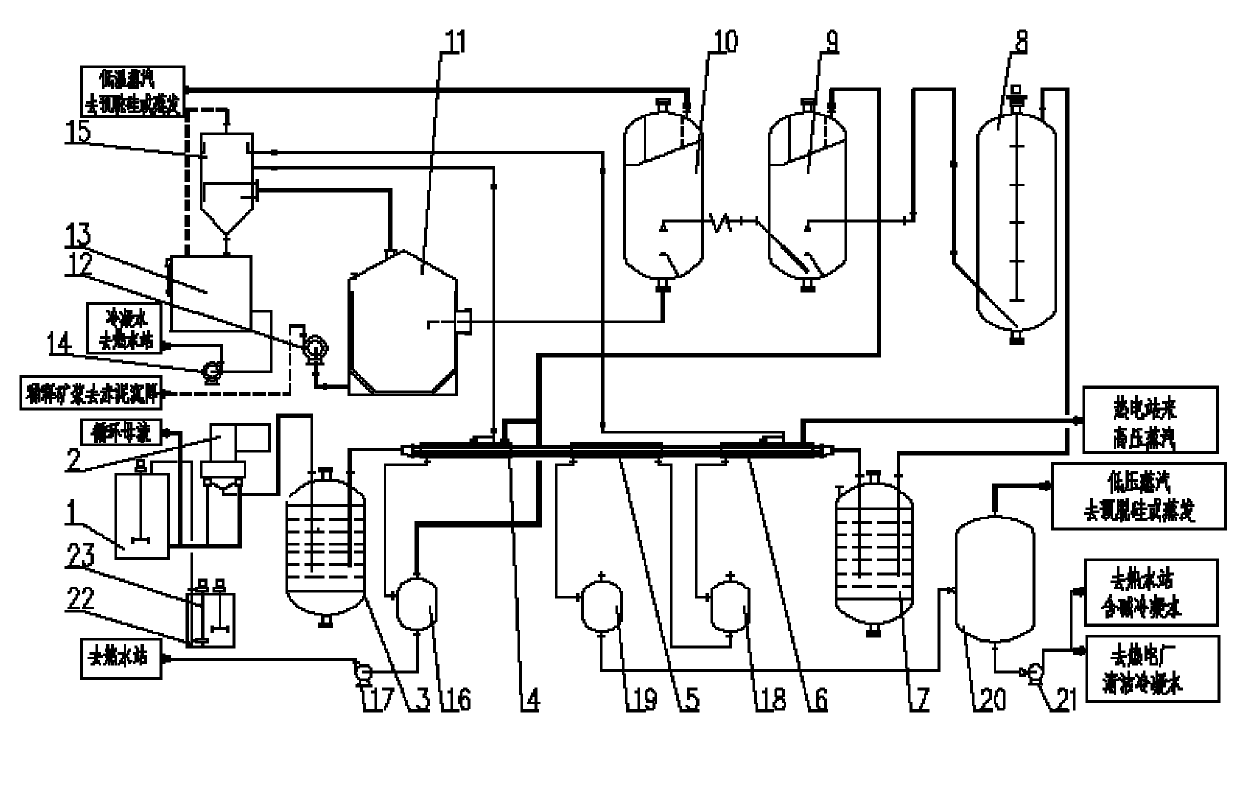
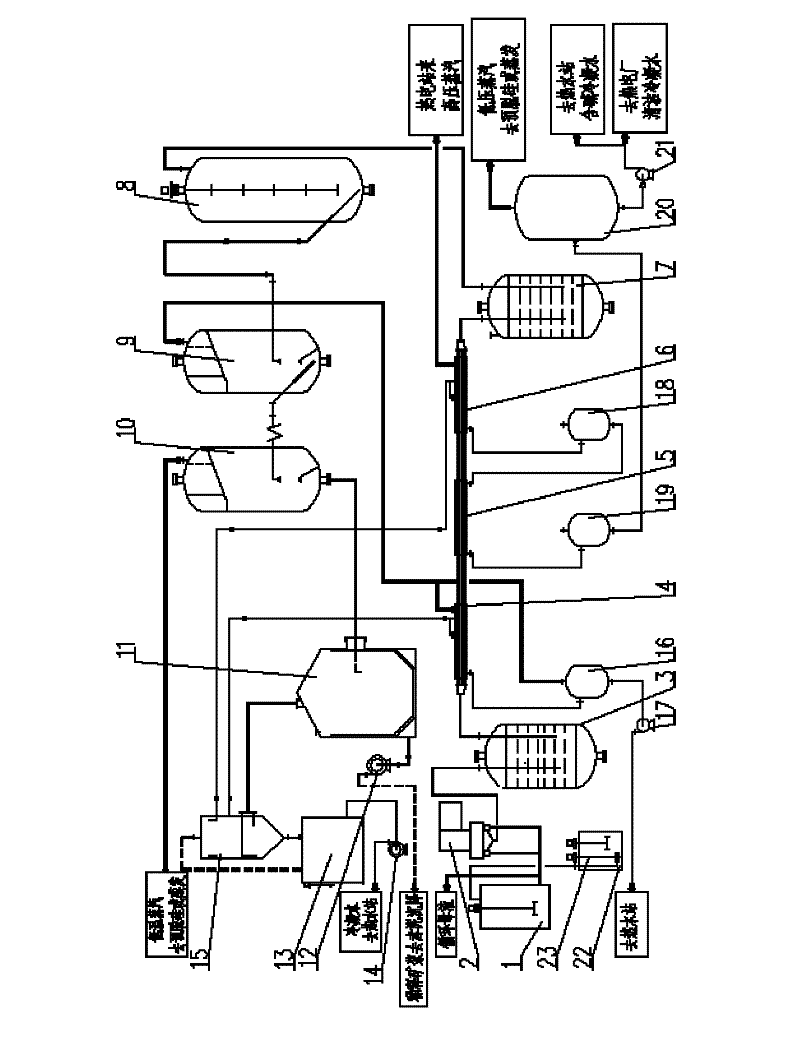
The invention discloses a tube array and remaining tank dissolving-out system and a tube array and remaining tank dissolving-out method for gibbsite bauxite and belongs to the technical field of alumina production. The dissolving-out system comprises a circulating mother liquor groove, a heat preservation remaining tank, a flash evaporation device and a dilution device; the circulating mother liquor groove is communicated with a tube array heating device through a mother liquor feed pump; the tube array heating device is formed by connecting a first-level tube array preheater, a second-level tube array preheater and a third-level tube array preheater, a condensed water tube array preheater, and a live steam tube array preheater in series; the method comprises the following steps of: conveying the circulating mother liquor in the circulating mother liquor groove into the tube array heating device by using the mother liquor feed pump, heating to 180 to 190 DEG C, and feeding the circulating mother liquor into the heat preservation remaining tank; and conveying desilicication ore pulp in a desilicication groove into the heat preservation remaining tank, mixing the desilicication ore pulp and the circulating mother liquor, and dissolving out, feeding the pulp obtained after dissolving into the flash evaporation device and performing flash evaporation and then feeding into the dilution device. The system and the method can improve the treatment capacity of pulp, save energy sources, and reduce the production cost and equipment corrosion.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV ENG & RES INST CO LTD
500MPa-grade niobium-containing screw-thread reinforcing steel bar and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to a 500MPa-grade niobium-containing screw-thread reinforcing steel bar and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the field of screw-thread reinforcing steel bar production. The reinforcing steel bar comprises 0.20 to 0.25 percent of C, 0.5 to 0.8 percent of Si, 1.2 to 1.6 percent of Mn, 0.01 to 0.04 percent of P, 0.01 to 0.04 percent of S, 0.005 to 0.02 percent of Ti, 0.001 to 0.01 percent of RE, 0.015 to 0.035 percent of Nb, 0.003 to 0.01 percent of O, 0.003 to 0.01 percent of N, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. In the reinforcing steel bar, the quantity of Nb-compound-containing precipitates with the equivalent diameter being 0.003 to 0.03mum is 50 to 500pcs / mum<2>; and the total quantity of RE-compound-containing and / or Tti-compound-containing occluded foreign substances with the equivalent diameter being 0.03 to 3mum is 2000 to 4000pcs / mm<2>. The preparation method of the 500MPa-grade niobium-containing screw-thread reinforcing steel barcomprises the steps of smelting, controlling the occluded foreign substances, continuously casting, heating a continuous casting blank, and rolling the reinforcing steel bar. The method can realize the low-cost high-quality production of the 500MPa-grade screw-thread reinforcing steel bars.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Preparation of high-purity Momordica grosvenori mogroside V
Owner:桂林市振达生物制药有限公司
High-thermal-conductivity corrosion-resistant electrical steel self-bonding coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113004770AImprove adhesionImprove corrosion resistanceAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxy resin coatingsFiberAdhesive
The invention discloses a high-thermal-conductivity corrosion-resistant electrical steel self-bonding coating and a preparation method thereof. The self-adhesive coating comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 25%-35% of bisphenol A type epoxy resin, 4%-8% of novolac epoxy resin, 0.2%-0.5% of isooctyl phosphate, 5%-10% of propylene glycol monomethyl ether, 5%-8% of an emulsifier, 1%-3% of dimethylaminoethoxy trioxaborooctacycle, 0.5%-2% of ammonium blocked Lewis acid salt, 3%-12% of boron nitride fiber, 0.4%-1.0% of alumina fiber, 0.2%-0.3% of a grinding aid and the balance of pure water. An activated self-adhesive coating formed after the self-adhesive coating is subjected to primary curing remarkably improves the corrosion resistance to an electrical steel substrate, the self-adhesive coating has high heat conductivity, and the operation difficulty of primary curing and secondary hot-pressing curing process conditions is remarkably reduced. The preparation method of the self-adhesive coating is easy to operate and high in implementation feasibility.
Owner:江苏晨光涂料有限公司 +1
Three-dimensional LED (light emitting diode) luminous body and processing method thereof
InactiveCN103872032AEasy to separateConvenient production operation and fixedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesAdhesiveEngineering
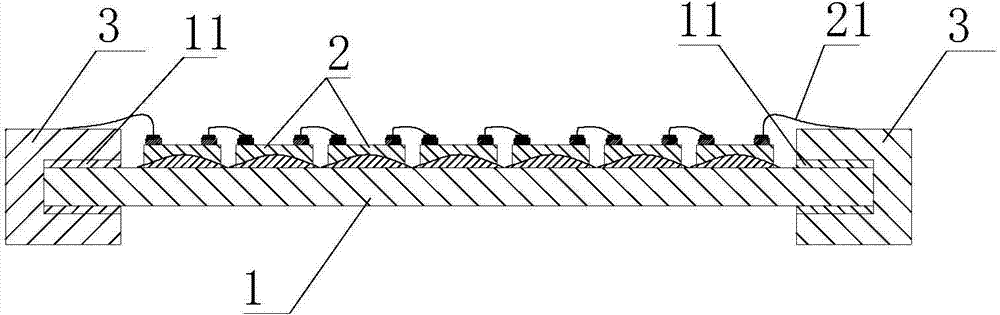
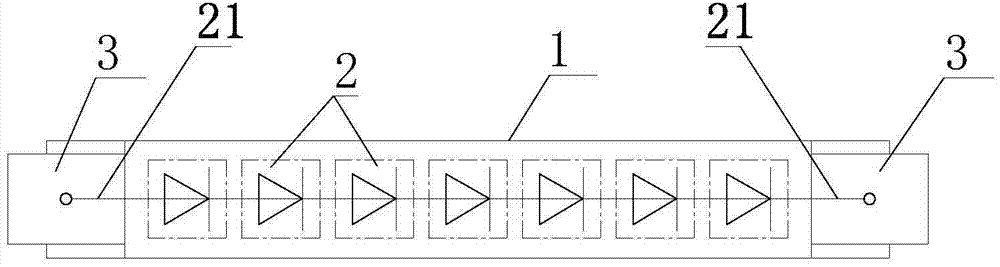
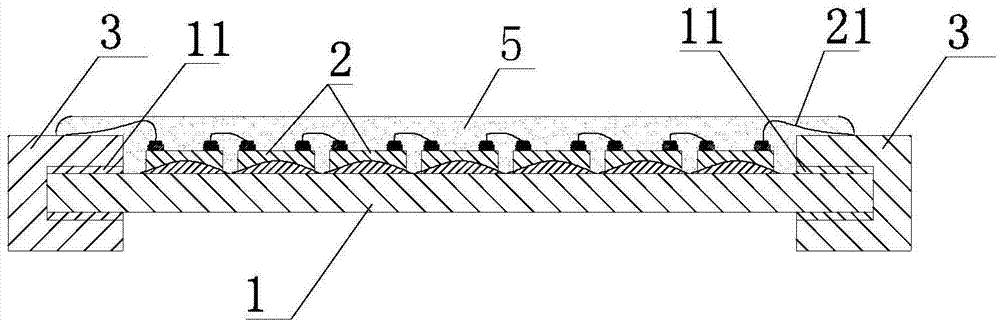
The invention relates to a three-dimensional LED (light emitting diode) luminous body and a processing method of the three-dimensional LED luminous body. The three-dimensional LED luminous body comprises a strip-shaped transparent base plate and a plurality of LED wafers in tandem connection, wherein the LED wafers are positioned on the transparent base plate through transparent silica gel, and two ends of the LED wafers are provided with leads, wherein two ends of the transparent base plate are respectively provided with metal connecting elements, the metal connecting elements are provided with U-shaped clamp openings and are clamped and buckled at two ends of the transparent base plate, adhesives are adopted between the metal connecting elements and the transparent base plate for fixation, and the leads are electrically connected with the metal connecting elements. The invention aims at providing the three-dimensional LED luminous body with simple structure and stable connection, and the processing method of the three-dimensional LED luminous body.
Owner:东莞市昱鸿光电有限公司
A 400mpa grade fine-grained hot-rolled steel bar and its production process
ActiveCN110042303BImprove performanceHigh strengthProcess efficiency improvementVulcanizationManganese sulfide
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Method for preparing high-purity dimethyl ether free from extraneous odour
ActiveCN101712595BSimple preparation processReduce manufacturing costEther separation/purificationEther preparation by compound dehydrationGas phaseCoal
Owner:YUNNAN REASCEND TOBACCO TECH GRP +1
Mogroside extraction method from grosvenor momordica
Owner:桂林市振达生物制药有限公司
Swinging material retreating device
InactiveCN107470494AEasy to take outReduce the difficulty of production operationsEjection devicesMachine partsEngineering
The invention discloses a oscillating unloading device, comprising: a driving structure, a transmission rod, a rotating shaft, a rocker arm, a base, an upper mold and a lower mold, and the driving structure drives the second end of the transmission rod to move relative to the first end of the transmission rod, That is, the first end of the transmission rod can be rotated, so that the rotating shaft and the rocker arm can be driven to rotate together, so that the second end of the rocker arm supports the workpiece from the bottom of the workpiece. Since the rocker arm rotates with the rotating shaft, the movement track of the rocker arm is arc shape, the workpiece can be pushed out at a certain angle close to the operator, and the operator can simply and conveniently complete the material removal; and because the driving structure is placed outside the lower mold, it is not limited by the inner space of the lower mold; therefore, the present invention It can reduce the difficulty of production operation and greatly improve production efficiency.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
A kind of winding molding method of all-composite material shell
The invention discloses a winding molding method of all-composite material shells, belongs to the technical field of molding process, and relates to the winding molding method of the all-composite material shells. The winding molding method comprises the steps: firstly, assembling a core mold, and filling a gas bag with light gas; next, carrying out surface treatment of the gas bag; then adopting the winding molding control program to control a winding machine to wind the outer surface of the gas bag with fiber bundles or cloth belts according to the program, and curing and molding according to temperature and time requirements required for molding; and finally, obtaining the composite material shells through a demolding process. The winding molding method has wide applicability, and can be used for manufacturing the composite material shells with different shapes and sizes and meeting a requirement of asymmetric front and back sealing surfaces. The process has good stability, equipment is simple and convenient, low in weight and strong in controllability, and the method is simple, practical, and easy to operate and popularize. Workers are prevented from entering the interior of the core mold for operation, the complex assembly and disassembly processes in a traditional winding process are greatly reduced, the difficulty of production operation is reduced, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Dissolving-out process for large-sized pipeline remaining tank of diasporite bauxite ore
InactiveCN101767806BRealize large-scaleIncrease throughputAluminium oxides/hydroxidesMining engineeringMineralogy
The invention provides a dissolving-out process for a large-sized pipeline remaining tank of diasporite bauxite ore. Processed raw materials include gibbsite and boehmite mixed bauxite ore or the diasporite bauxite ore. The dissolving-out process includes the following steps: pre-desiliconized ore pulp is mixed with circulating mother liquor at an outlet of a desiliconizing discharging groove, ispreheated by a sleeve preheater, is heated to the dissolving-out temperature by a sleeve heater, and then enters a heat-preservation remaining tank for remaining; finally, flash evaporation and separation are carried out on the ore pulp by a flash evaporator. The method in the invention realizes maximization of equipment, has strong capability of processing the ore pulp, and breaks through the capability limit of a pressing and stewing dissolving-out process to process the ore pulp; moreover, energy is saved, and the heat utilizing rate is high. The multi-inner-pipe sleeve preheater and the heater are adopted to preheat and heat the bauxite ore pulp; within the operating temperature range of the process, the heat transfer coefficient can be up to 900 to 1,200 Kcal / m2.h. DEG C. Compared with the traditional dissolving-out process, the dissolving-out process in the invention can save more than 30% of the energy in a comprehensive manner.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV ENG & RES INST CO LTD
A kind of high thermal conductivity corrosion-resistant electrical steel self-adhesive coating and preparation method
ActiveCN113004770BImprove adhesionImprove corrosion resistanceAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxy resin coatingsFiberAdhesive
The invention discloses a high thermal conductivity corrosion-resistant electrical steel self-adhesive coating and a preparation method. The self-adhesive coating of the invention comprises the following components in mass percentage: 25% to 35% of bisphenol A epoxy resin, phenolic aldehyde Epoxy resin 4% to 8%, isooctyl phosphate 0.2% to 0.5%, propylene glycol methyl ether 5% to 10%, emulsifier 5% to 8%, dimethylaminoethoxy trioxaborate ring 1 % to 3%, ammonium blocked Lewis acid salt 0.5% to 2%, boron nitride fiber 3% to 12%, alumina fiber 0.4% to 1.0%, grinding aid 0.2% to 0.3%, and the balance is pure water. The activated self-adhesive coating formed after the first curing of the self-adhesive coating significantly improves the corrosion resistance of the electrical steel substrate. The self-adhesive coating has good thermal conductivity, and the first curing and the second hot pressing The difficulty of operating process conditions is significantly reduced. The preparation method of the self-adhesive coating of the invention is simple to operate and has high implementation feasibility.
Owner:江苏晨光涂料有限公司 +1
Glass insulator hermetically sealed packaging structure and welding method for microwave devices
ActiveCN107134606BStop the spreadReduce difficultyWaveguide type devicesHermetic packagingProcess control
The invention discloses a hermetic packaging structure of a glass insulator of a microwave device, which comprises a gold-plated cavity wall and a glass insulator, the glass insulator is welded between the gold-plated cavity walls and is located in the center, and the upper part of the gold-plated cavity wall is arranged near the top. The solder tank is provided with a solder resist structure on the top of the solder tank. Compared with the prior art, the invention prevents the tin-based solder from spreading to the cavity wall, greatly reduces the difficulty of process control and production operation, and improves the sealing performance of the glass insulator hermetic packaging structure of the microwave device after welding.
Owner:成都玖信科技有限公司
A fracturing pump plug displacement detection device and its detection method
Owner:SICHUAN HONGHUA ELECTRIC
A kind of method using pseudoionone as raw material to prepare β-ionone
ActiveCN108329200BHigh purityIncrease profitOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIsomerizationNitrogen monooxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing β-ionone from pseudo-ionone. Pseudo-ionone undergoes a cyclization reaction under the catalysis of sulfuric acid and is quenched. After the quenched reaction solution is passed through nitric oxide gas, it undergoes isomerization reaction to obtain β-ionone. The invention has the advantages of simple process, no harsh reaction conditions, repeated recycling of sulfuric acid and solvent, and high purity of β-ionone in the prepared product, which is higher than 97.5%.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Tube array and remaining tank dissolving-out system and method for gibbsite bauxite
InactiveCN102249271BNo scarring effectSmall footprintAluminium oxides/hydroxidesSlurryHeat conservation
Disclosed is a gibbsite-type bauxite column tube plus retention tank dissolution system and method, which belong to the technical field of alumina production. The dissolution system includes a circulating mother liquor tank, a heat preservation retention tank, a flash device and a dilution device; The mother liquid feeding pump is connected with the tube heating device, which consists of the first tube preheater, the second tube preheater, the third tube preheater, the condensate tube heater and the fresh steam column Tube heaters are connected in series; the method is as follows: the circulating mother liquor in the circulating mother liquor tank is transported to the tube heating device through the mother liquor feeding pump, heated to 180-190°C and then enters the heat preservation tank; the desiliconization tank in the desiliconization tank The ore slurry is transported to the heat preservation retention tank and mixed with the circulating mother liquor for dissolution. After the dissolution is completed, the obtained dissolution slurry enters the flash evaporation device, and then enters the dilution device after flash evaporation. The invention can improve the pulp processing capacity, save energy, reduce production cost and reduce equipment corrosion.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV ENG & RES INST CO LTD
A kind of 500mpa level niobium-containing threaded steel bar and its manufacturing method
A 500MPa grade niobium-containing threaded steel bar and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the field of threaded steel bar production. The steel bar includes: C0.20~0.25%, Si0.5~0.8%, Mn1.2~1.6%, P0.01~0.04%, S0.01~0.04%, Ti0.005~0.02%, RE0.001~ 0.01%, Nb0.015~0.035%, O0.003~0.01%, N0.003~0.01%, the balance is Fe and inevitable impurities; in this steel bar, the equivalent diameter of the Nb-containing compound is 0.003~0.03μm The number of precipitates is 50 to 500 / μm 2 ;The total number of inclusions containing RE compounds and / or Ti compounds with equivalent diameters of 0.03 to 3 μm is 2000 to 4000 / mm 2 . The preparation methods are: smelting, inclusion control, continuous casting, heating of continuous cast billets, and rolling of steel bars. This method enables low-cost and high-quality production of 500MPa-level threaded steel bars.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Method for preparing trichlorosilane
ActiveCN101759189BReduce manufacturing costSolve bottlenecksHalogenated silanesHydrogenPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a method for preparing trichlorosilane. The method comprises the step that silicon tetrachloride and hydrogen react with optional hydrogen chloride and silicon powder by adopting at least one main catalyst selected from copper halide and nickel halide and at least one auxiliary catalyst selected from alkali metal compounds. Compared with the prior art, the method for preparing the trichlorosilane has the advantages of low preparing cost, simple and easy technique and high per-pass conversion rate of the silicon tetrachloride.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGNENG POLYSILICON TECH DEV
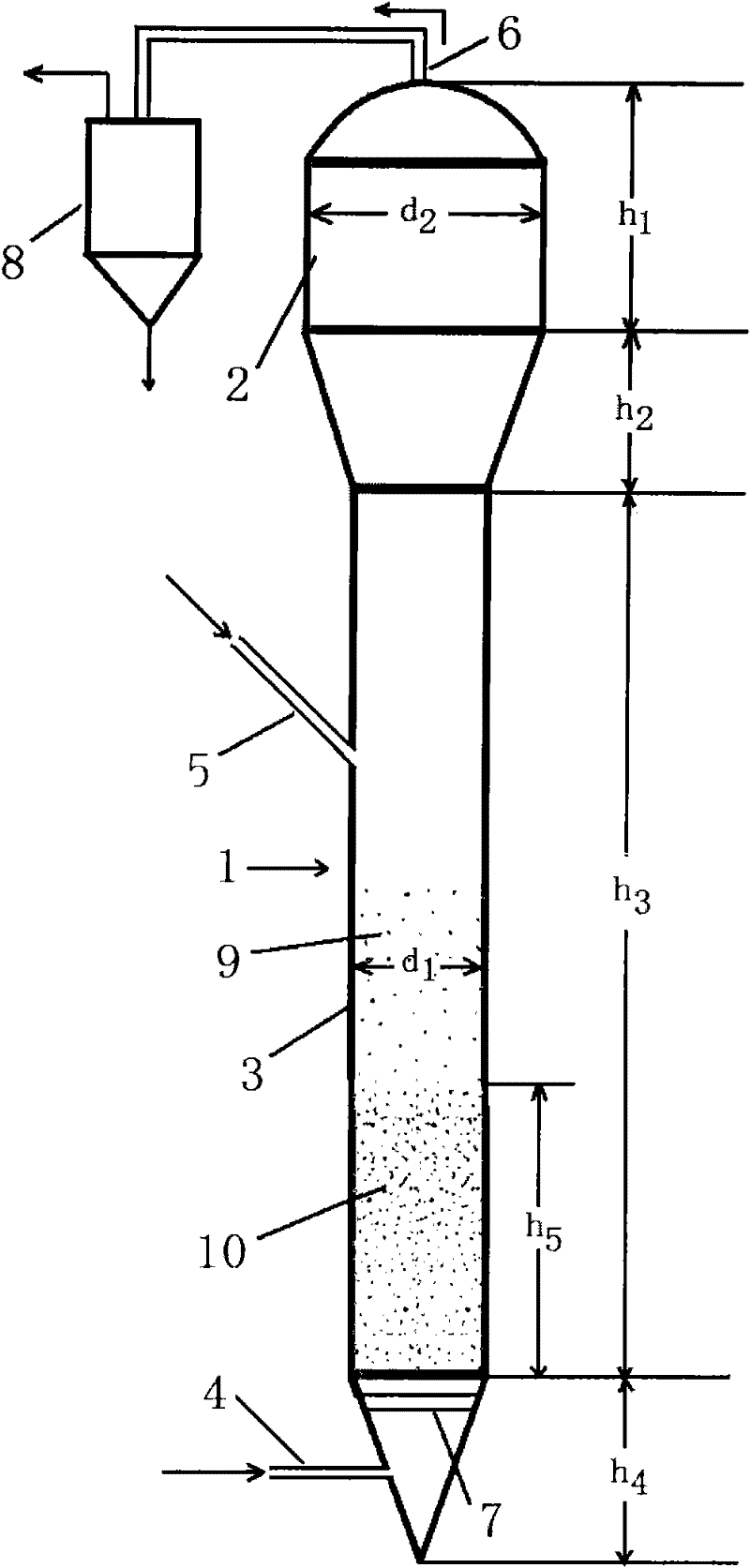
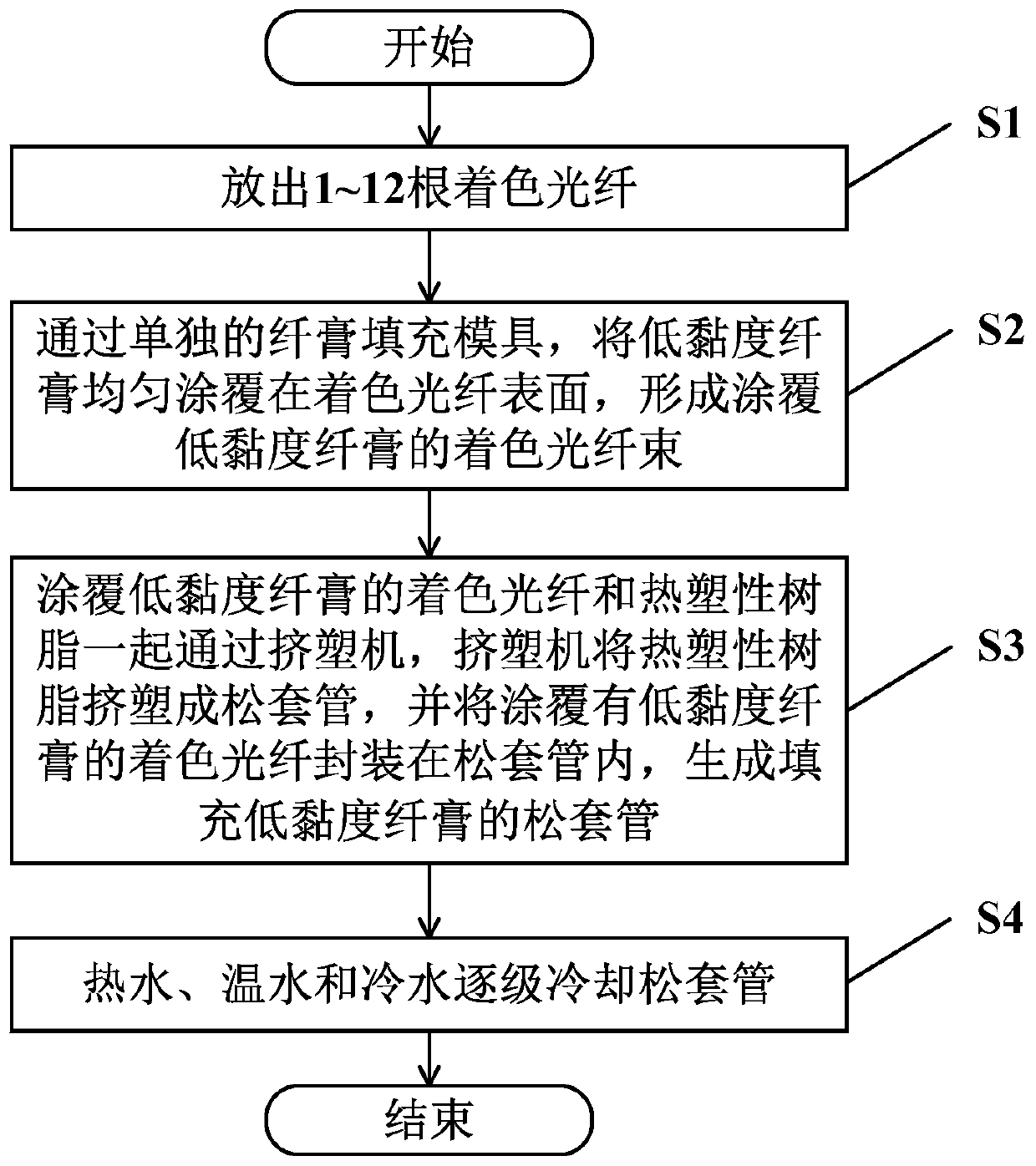
Loose Tube Low Viscosity Fiber Paste Filling Technology
ActiveCN106707436BReduce air bubble contentImprove the bulgeFibre mechanical structuresFiberWarm water
The invention discloses a loose tube low-viscosity fiber paste filling process and relates to the field of optical communication optical cable manufacture. The process comprises the following steps: 1-12 color fibers are taken out; an extruding machine comprises an independent fiber paste filling die, and the low-viscosity fiber paste can be coated on the surfaces of the color fibers uniformly through the independent fiber paste filling die to form a color fiber beam coated with the low-viscosity fiber paste; the color fiber beam coated with the low-viscosity fiber paste and thermoplastic resin pass through the extruding machine together, the extruding machine carries out extrusion molding on the thermoplastic resin to form a loose tube, and the color fiber beam coated with the low-viscosity fiber paste is packaged in the loose tube to form a loose tube filled with the low-viscosity fiber paste; and the generated loose tube is placed into a water tank, and then, is subjected to step-by-step cooling through hot water, warm water and cold water. The process can realize one-time centring of an oil gun rack, reduces bubble content of the loose tube, improves swell condition of the loose tube, reduces production operation difficulty, improves production efficiency, ensures uniform external diameter of the generated loose tube and realizes small fluctuation.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Stereo led illuminant and its processing method
InactiveCN103872032BEasy to separateConvenient production operation and fixedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesAdhesiveEngineering
A three-dimensional LED illuminant and its processing method according to the present invention, the three-dimensional LED luminous body comprises a strip-shaped transparent substrate and several LED chips connected in series, the LED chip is positioned on the transparent substrate through transparent silica gel, and leads are provided at both ends, Wherein: the two ends of the transparent substrate are respectively provided with metal connectors, and the metal connectors are provided with U-shaped bayonets, which are buckled on both ends of the transparent substrate, and the metal connectors and the transparent substrate are fixed with glue, The leads are electrically connected to the metal connectors. The invention aims to provide a three-dimensional LED illuminant with simple structure and stable connection, and a processing method of the three-dimensional LED illuminant.
Owner:东莞市昱鸿光电有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com