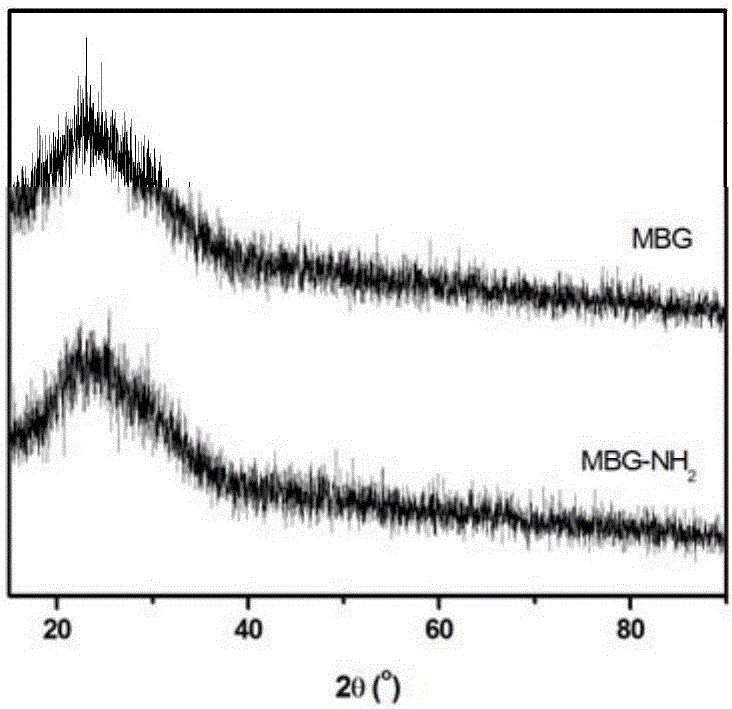
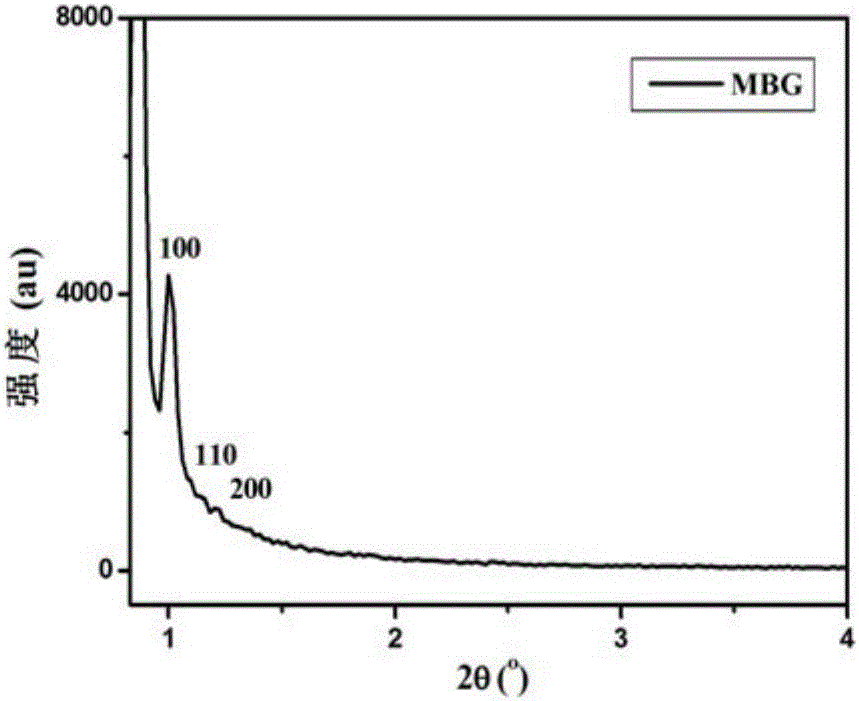
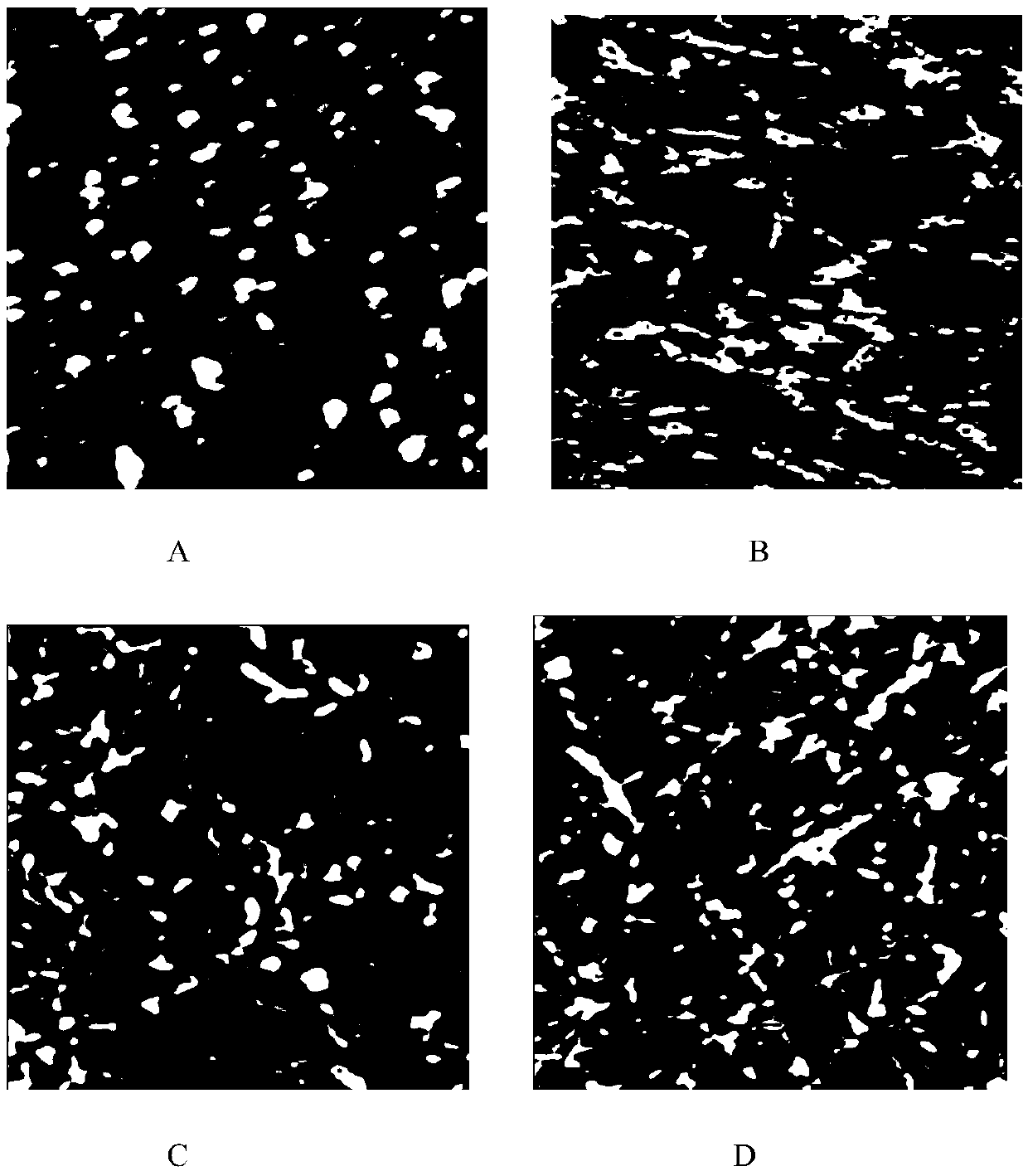
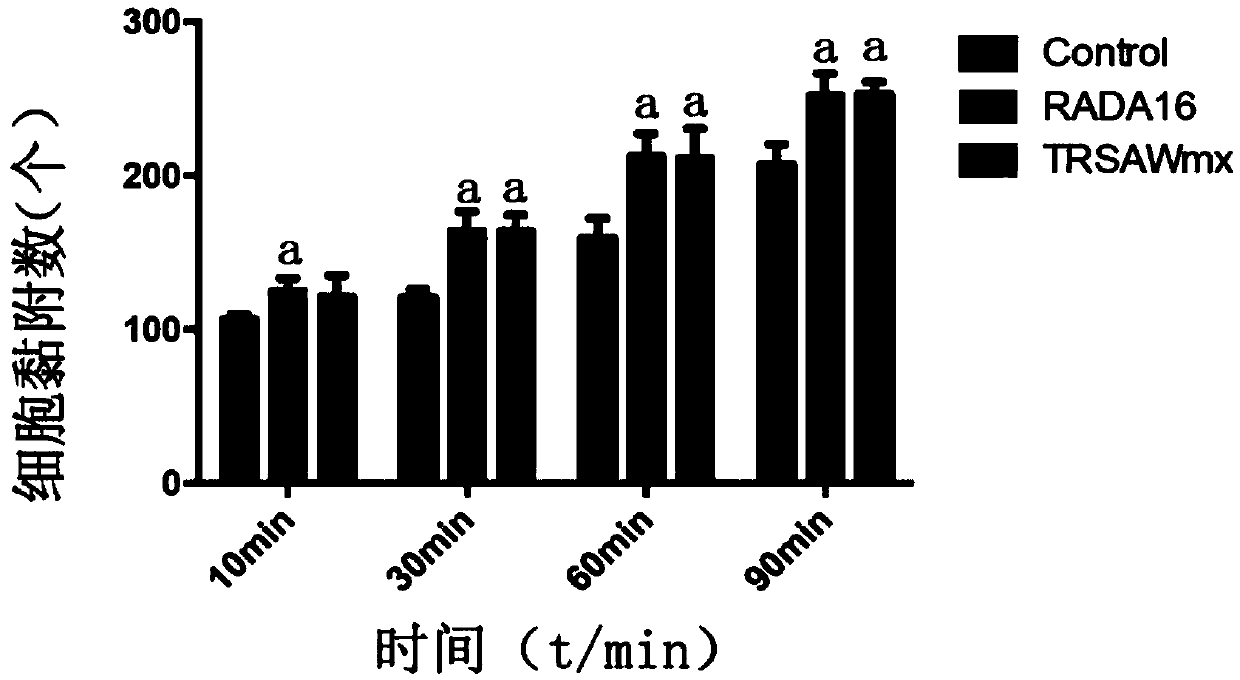
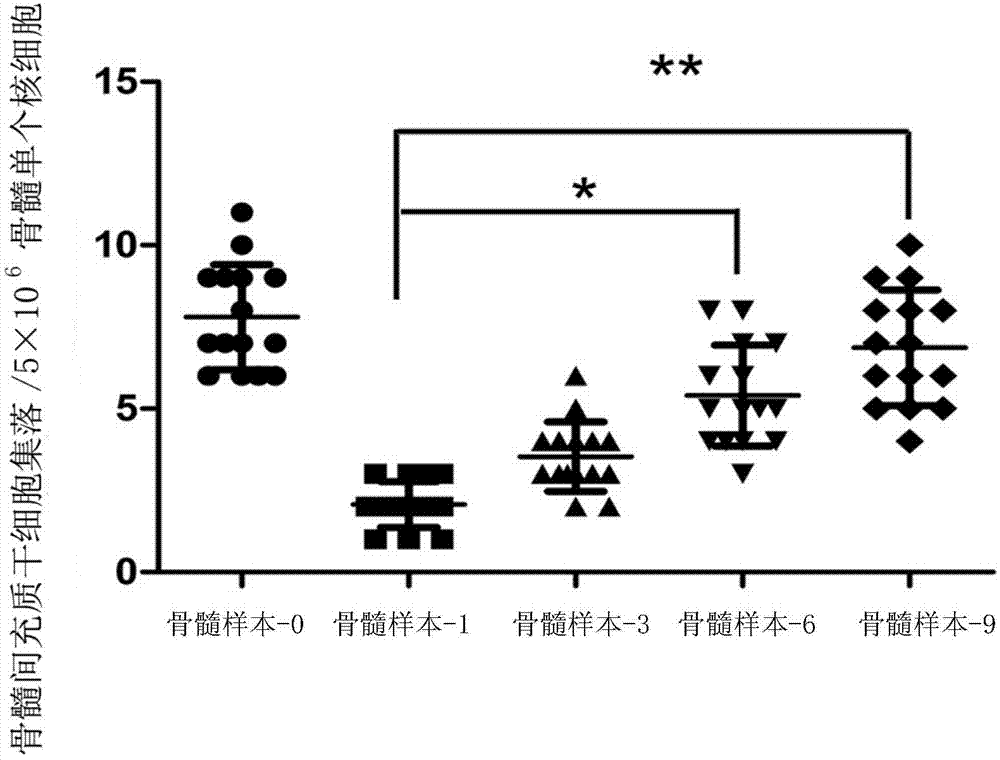
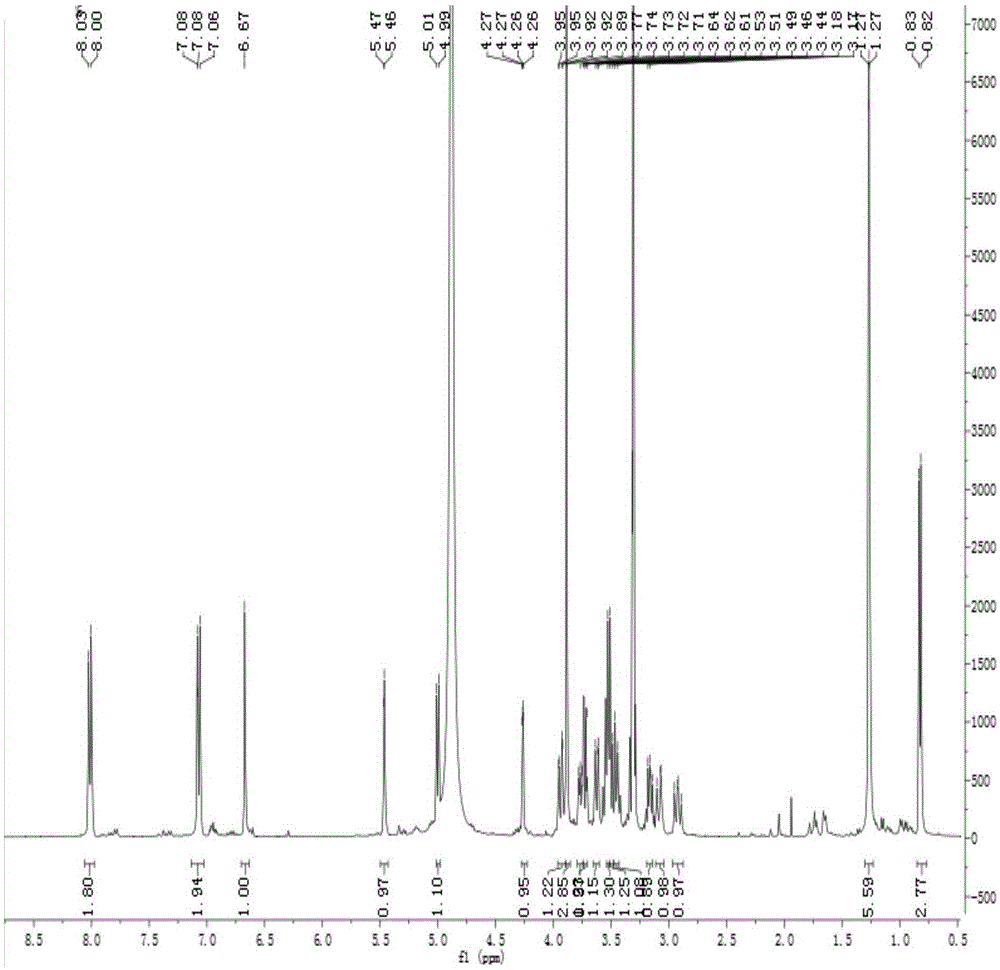
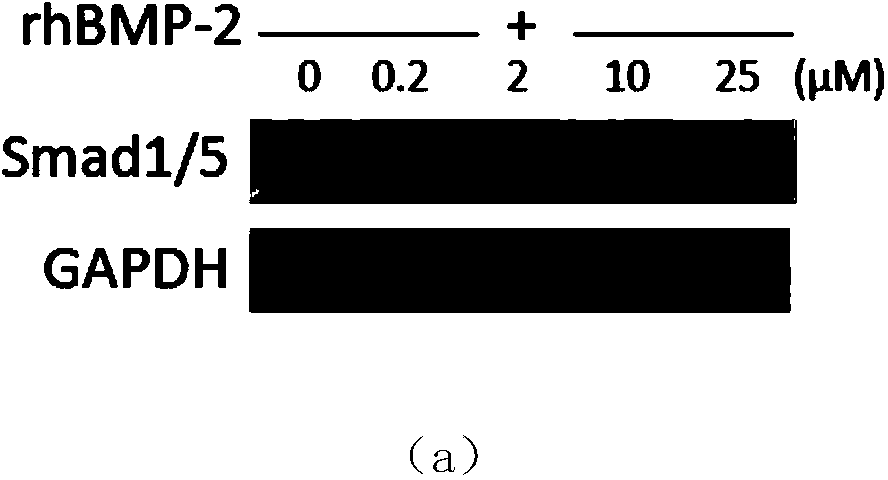Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Osseous Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
(os'tē-ō-sīt'), A cell of osseous tissue that occupies a lacuna and has cytoplasmic processes that extend into canaliculi and make contact by means of gap junctions with the processes of other osteocytes. Synonym(s): bone cell, bone corpuscle, osseous cell.
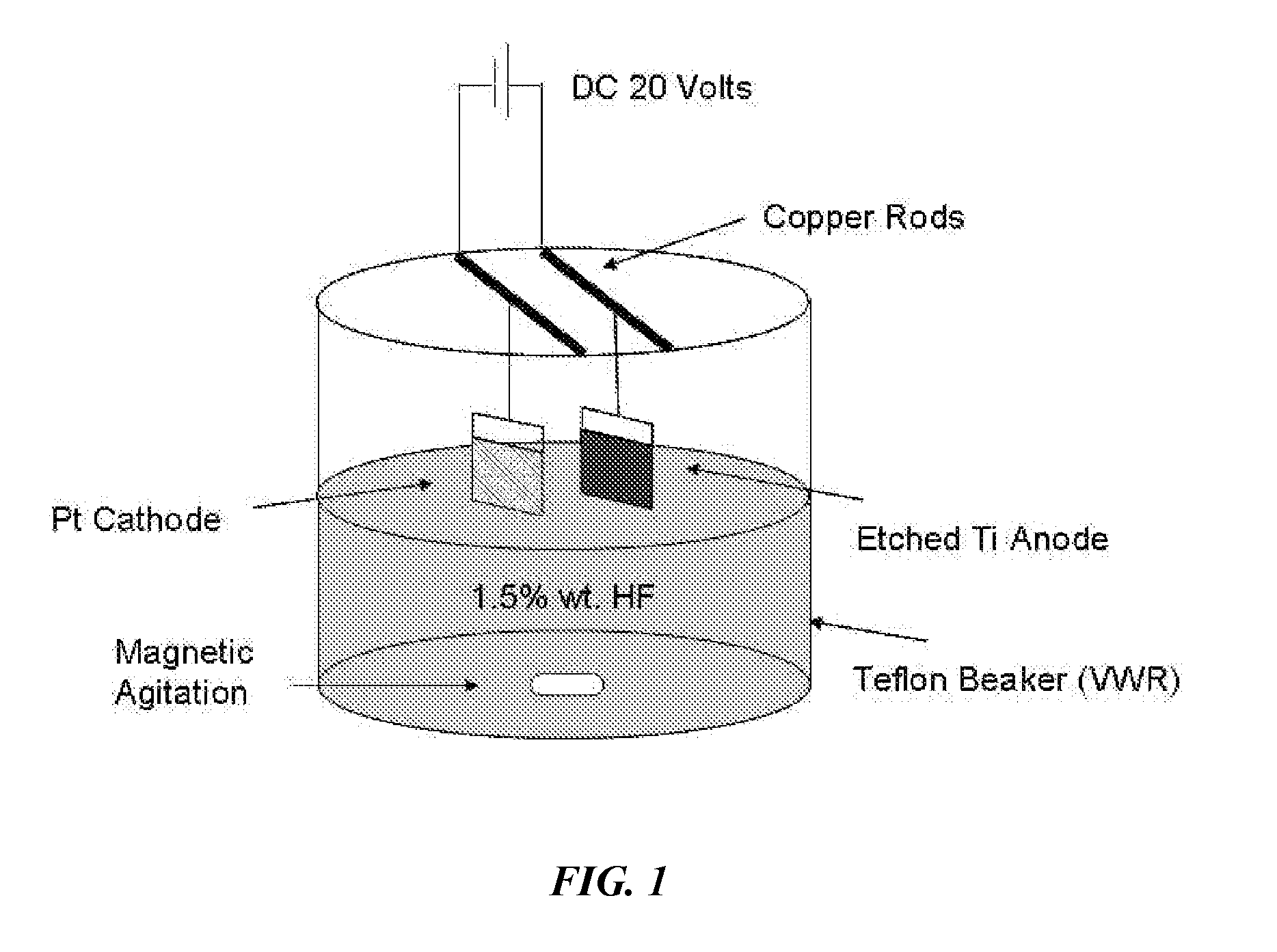
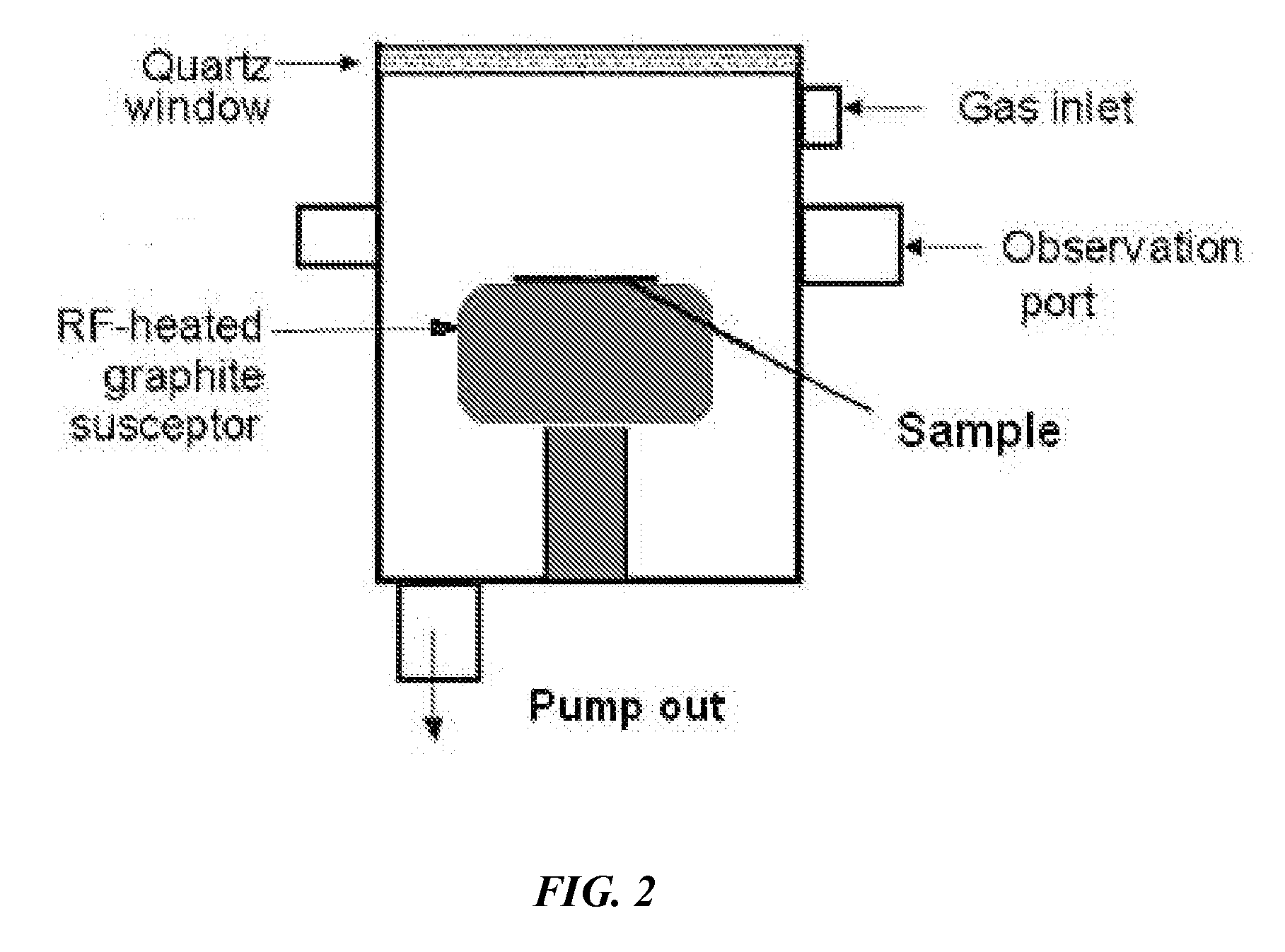
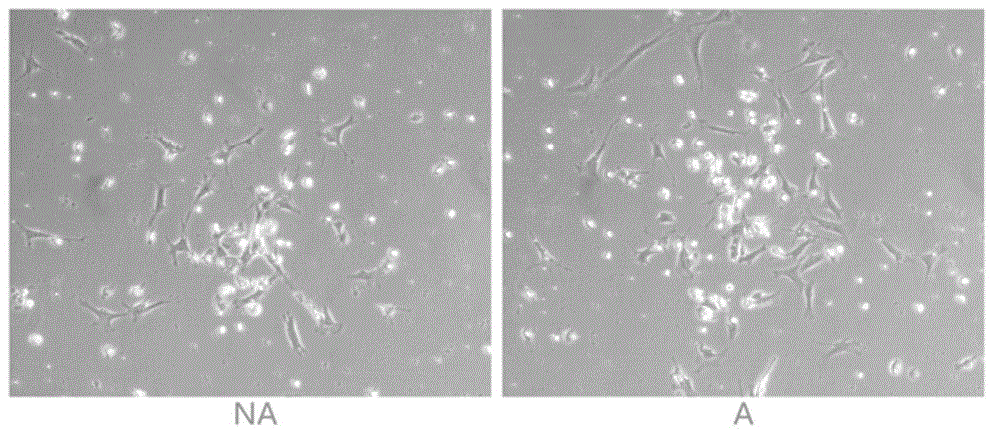
Method to enhance osteoblast functionality and measure electrochemical properties for a medical implant
InactiveUS20110301716A1Good cell compatibilityEnhancing and increasing functionalityAnodisationElectrotherapyOsseous CellElectrochemistry
A method to enhance osteoblast functionality of a medical implant. The method may include obtaining the medical implant and treating a surface of the medical implant to modify the surface characteristics causing increase functionality of adjacent positioned osteoblasts. A method of increasing cellular activity of a medical implant is also disclosed. A medical device having enhanced cytocompatibility capabilities includes a metallic substrate with an outer surface. Attached to the outer surface is a composition of nanosized structures. A biosensor for use with a medical device, includes an electrode that is attached to an outer surface of the medical device. The biosensor measures electrochemical changes adjacent to the medical implant. Further, a method of manufacturing a medical implant with a biosensor for use in vivo and a method of integrating a biosensor with a medical implant for use in monitoring conductivity and electrochemical changes adjacent to the medical implant are disclosed.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Bone cartilage repair material and preparation method of scaffold for tissue engineering
InactiveCN109364302AEasy to prepareRealize the loadAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationOsteoblastSolvent
The invention discloses a bone cartilage repair material and a preparation method of a scaffold for tissue engineering. The material comprises a subchondral bone layer, an interface layer and a cartilage layer arranged in sequence, wherein the interface layer is positioned between the subchondral bone layer and the cartilage layer; the material contains the following components in parts by weight:10-40 parts of oil-soluble high polymer materials, 10-50 parts of biological ceramic powder, 50-100 parts of oily solvents, 0.1-1 part of a water-soluble bio-active material, 2-30 parts of water, more than 0 and less than 1 part of an emulsifier, 10-30 parts of a hydrogel material, 0-10 parts of seed cells and 50-100 parts of a culture medium. The preparation method comprises the following steps:preparing printing ink according to the ratio of the materials, and transferring into 3D printing equipment for printing molding. The bone cartilage scaffold having a personalized appearance can be prepared, load and controlled release of different growth factors or peptides in different zones of the scaffold can be realized, and directional differentiation of bone marrow stem cells at differentparts to osteoblast and chondrocyte can be promoted.
Owner:王翀
Preparation method of multifunctional layered joint cartilage support
InactiveCN108355174ARealize regulationReduce rejectionAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationCartilage cellsOsteoblast
The invention provides a preparation method of a multifunctional layered joint cartilage support. The multifunctional layered joint cartilage support capable of simulating the biological property andthe mechanical property of natural cartilage is prepared by taking hydrogel as a support material, taking mesenchymal stem cells, cartilage cells and osteoblasts as inducing and developing objects andby adopting a 3D printing technology. The multifunctional layered joint cartilage support can accurately simulate the internal tissue form and the contour of each layer of the natural cartilage and can realize that different layers have different mechanical and biological characteristics. The prepared artificial cartilage support cells are derived from patients, the support serves as a degradablehydrogel material and the rejection reaction after implantation is greatly reduced. Various nutritional substances and growth factors are mixed in the hydrogel support, so that the sustained releaseeffect can be achieved and regulation and control of the growth and development of the artificial cartilage can be realized.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Expansion in vitro purification culture method of mesenchymal stem cells and culture medium
InactiveCN102978156AFacilitate early purificationDoes not affect vitalitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsPenicillinCell culture media
The invention provides an expansion in vitro purification culture method of mesenchymal stem cells and a cell culture medium used in a culture process. According to the method, mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to osteogenic stem cells. The cell culture medium comprises the following components: 8-12mu g / L of bFGF (Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor), 8-12mu g / L of EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor), 8-12mu g / L of PDGF-BB (Platelet Derived Growth Factor-BB), 10 percent of fetal calf serum, 100U / mL of penicillin and 100mg of L of streptomycin; a solvent is a basic culture medium; and the basic culture medium is a DMEM (Dulbecco Modified Eagle Medium) culture solution, an F12 culture solution or a mixture of the DMEM culture solution and the F12 culture solution. The mesenchymal stem cells obtained by adopting a method comprising the steps of early replacement of the cell culture medium, cell adherence passage and combined addition of cell factors (bFGF, EGF and PDGF-BB) in the culture solution are high in purity and strong in vitro proliferation capacity, and have good capability of differentiation to osteogenic stem cells.
Owner:HUZHOU CENT HOSPITAL
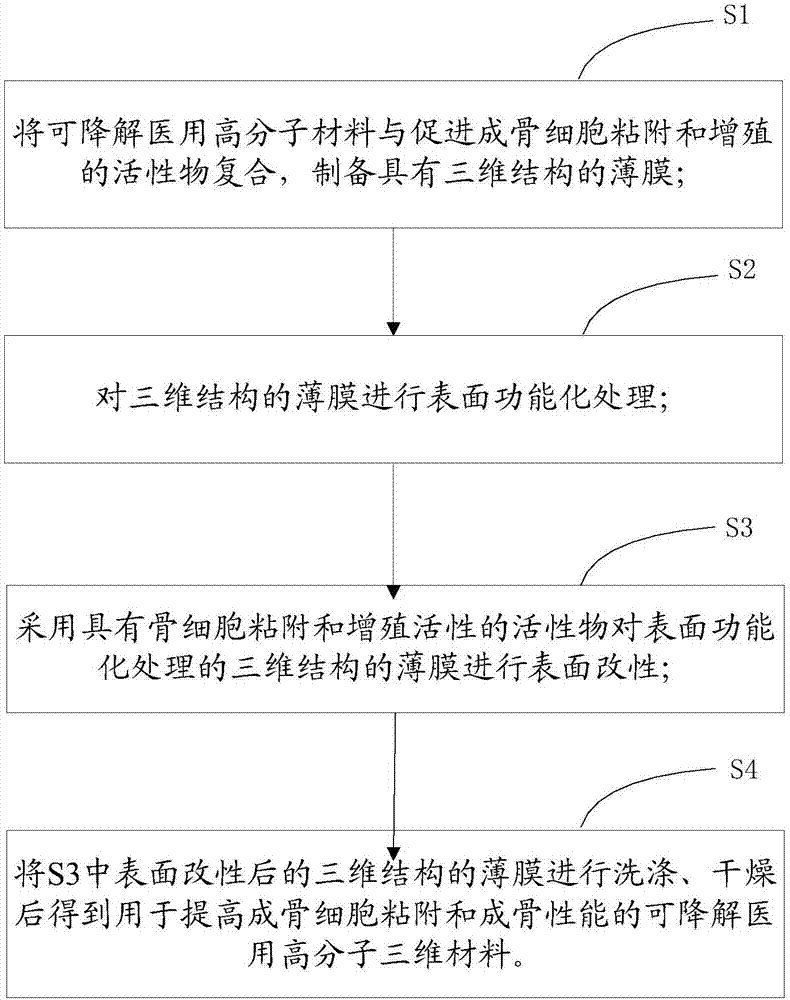
Preparation method of degradable medical macromolecular three-dimensional material for improving osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic property
ActiveCN107213529AGood osteogenic propertiesNo toxicitySurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHigh concentrationOsteoblast adhesion
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SUZHOU UNIV
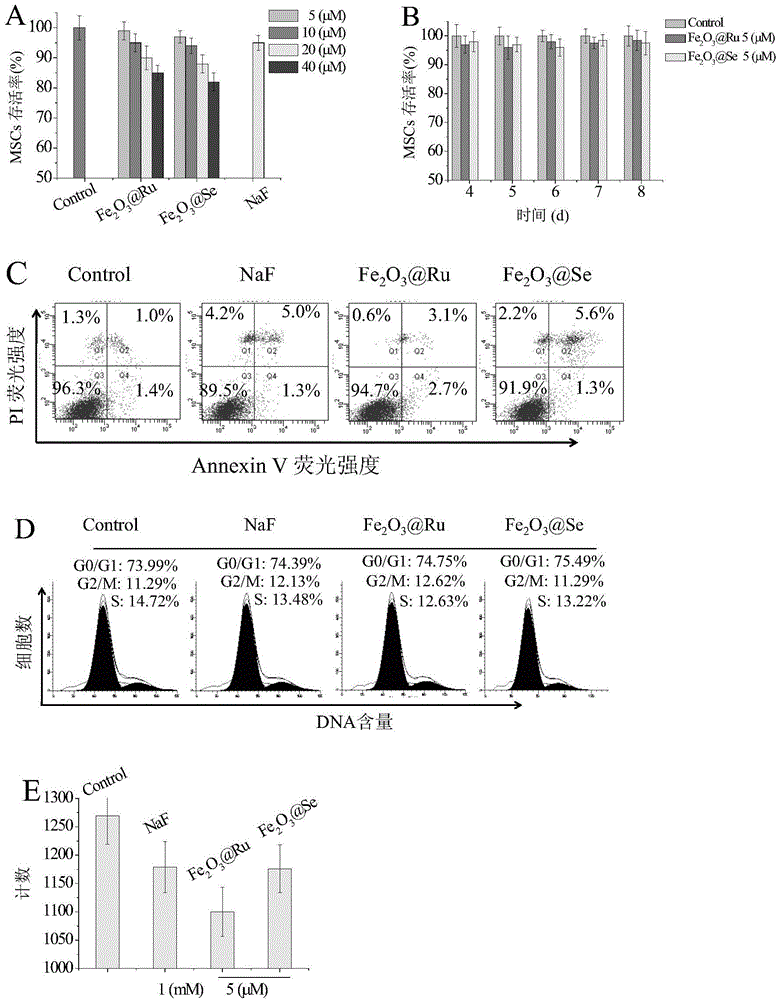
Application of magnetic nano materials in promotion of mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation
The invention belongs to the technical field of promotion of the mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation, and discloses application of magnetic nano materials in promotion of the mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation. The magnetic nano materials are active ingredients and have the function of promoting a mesenchymal stem cell to differentiate into an osteoblast. Toxicity tests prove that nano ruthenium magnetic nano materials nano-modified by ferric oxide, and the nano selenium magnetic nano materials nono-modified by the ferric oxide are almost nontoxic for the mesenchymal stem cell; alizarin red and oil red O dying proves that the magnetic nano materials prepared have the functions of promoting the mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation, and inhibiting adipogenic differentiation; the prepared magnetic nano materials such as the nano ruthenium or nano selenium nano-modified by the ferric oxide, are nano-coupled with the ferric oxide in excessive amount directly, and no other auxiliary reagent is needed for the preparation process, the product system is simple, and a product can be preserved and used directly.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
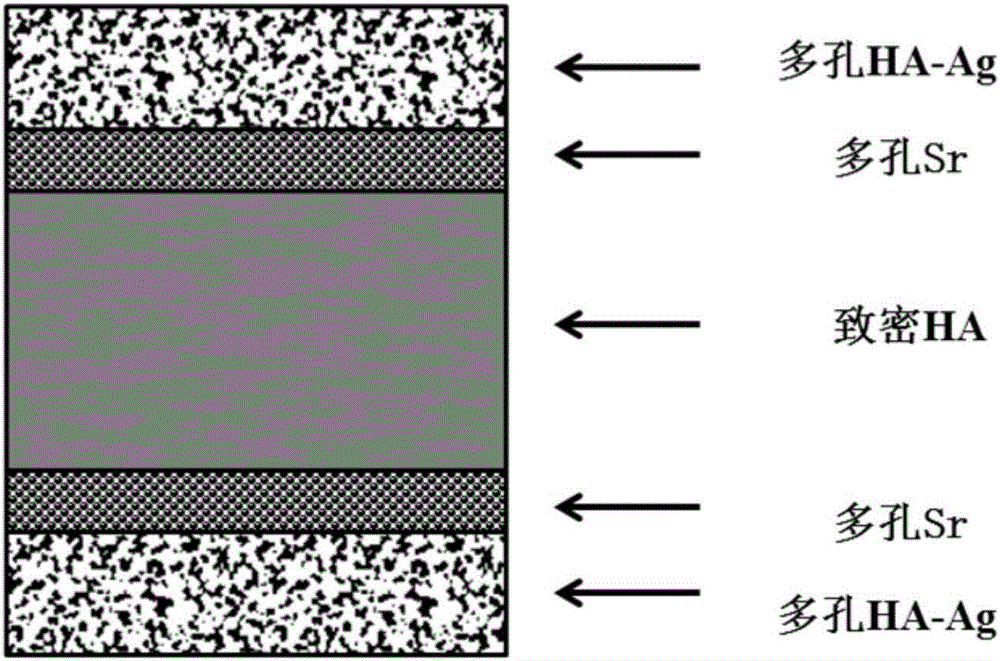
Preparation method of antibacterial functional gradient porous HA-Ag bone filling scaffold with active interlayer
ActiveCN106312050AWill not destroy the mechanical strengthEnsure mechanical stabilityTissue regenerationProsthesisMaterials preparationPorosity
The invention discloses an antibacterial functional gradient porous HA-Ag bone filling scaffold with an active interlayer and belongs to the technical field of biomedical material preparation. The functional gradient porous HA-Ag bone filling scaffold material with the active interlayer is prepared by weighing and ball-milling hydroxyapatite HA and Ag powder according to an ingredient proportion, weighing and mixing mixed powder and an ammonium bicarbonate pore former according to a porosity proportion, preparing three kinds of powder, then laying the powder in a gradient manner, mechanically pressing into a block pressed blank, putting the pressed blank into a discharge plasma sintering furnace, performing sintering after vacuuming a system to 2-6Pa, heating at a rate of 50-100min / DEG C, keeping at 800-1000 DEG C for 5-10min, and cooling to room temperature in the furnace. The material can induce adhesion and proliferation of bone cells on the surface of the material actively, has good osteogenesis activity and antibacterial property, high porosity and mechanical stability at the same time, and can serve as a good artificial bone filling material.
Owner:FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF YUNNAN PROVINCE
Culture method for inducing mesenchymal stem cell to differentiate for forming osteocyte under condition without CO2
InactiveCN102586181ADoes not affect activityNormal growthSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSodium bicarbonateVitamin C
The invention provides a culture method for inducing mesenchymal stem cell to differentiate for forming osteocyte under the condition without CO2. The culture method comprises the following steps of: culturing the third-generation human mesenchymal stem cell under the conditions of 5 percent of CO2 and 37 DEG C and standing overnight; after the cell is completely attached to the wall and grows until 80 percents of cell is fused, replacing an inductive culture medium and culturing under the conditions of 37 DEG C without CO2 for 14-21 days to obtain osteoblast, wherein the inductive culture medium is formed by adding fetal calf serum, penicillin, streptomycin, hexadecadrol, beta-sodium glycerophosphate and vitamin C in a basal medium and is prepared from the following components calculatedby final concentration: 0.41g / L of sodium bicarbonate, 1.5g / L of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate, 0.07g / L of monopotassium phosphate and 8.17g / L of sodium chloride; and solvent of the inductive culture medium is an L-DMEM cell culture medium free of sodium bicarbonate. According to the novel culture medium formula provided by the invention, the mesenchymal stem cell osteoblast can be normally induced to differentiate; the differentiation effect is favorable, so that the consumption of equipment is reduced; and the novel culture medium formula is suitable for cell culture and research on induced differentiation under the condition without CO2.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bone repairing material, and preparation method and application of bone repairing material
ActiveCN106806939APromote growthPromote differentiationTissue regenerationProsthesisHigh cellBone formation
The invention provides a bone repairing material, and a preparation method and application of the bone repairing material. The preparation method of the material comprises the steps: dissolving a structure directing agent and a pore-enlarging agent, adding a calcium source, a silicon source and a phosphorus source, adjusting a pH (potential of hydrogen) value to 9-11, placing for 56-80 h at 90-110 DEG C, baking for 6-10 h at 550-600 DEG C to form bioactivity glass, mixing the bioactivity glass and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane for 14-20 h, baking for 20-30 h at 80-150 DEG C, washing with chloroform, drying to form amino modified bioactivity glass, and incubating the amino modified bioactivity glass and a cell factor in a carbon dioxide incubator at 37 DEG C for 4-6 h to promote adsorption to form the bone repairing material. The material can promote osteoblast proliferation, osteogenesis direction differentiation and mineralization processes, has high cell compatibility and a good effect of promoting bone formation and has wide application prospects as the repairing material in a bone defect repairing process.
Owner:杭州维叶莫生物科技有限公司
Surface-modified porous-tantalum biological material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107998445AAperture size controllableOptimize layoutSurface reaction electrolytic coatingPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMicro nanoOsteoblast
The invention relates to a surface-modified porous-tantalum biological material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological medical materials. The surface-modified porous-tantalum biological material and the preparation method have the beneficial effects that an electrochemical anodic oxidation technology is adopted for modifying the surface of a tantalum sheet to prepare a porous tantalum-pentoxide layer with a micro-nano-scale three-dimensional through porous structure, the pore-diameter size can be controlled, the distribution and the communication ofpores are good, and a hydroxyapatite layer is further constructed on the surface of an oxidation layer, so that protein absorption and cell diffusion and proliferation are obviously enhanced, the biocompatibility and the osteoconduction are improved, the microenvironment beneficial to cell growth is generated, the adhesion, the proliferation, the differentiation and the mineralization of primary osteoblasts of human are promoted, the growth of bone tissues into the porous tantalum is promoted to form a unique bone-implant interface, the stability and the function of the implant in the bone tissues are obviously enhanced, the osseointegration of the bone-implant interface is accelerated, and the stability of the implant into the bone tissues is obviously enhanced. The surface-modified porous-tantalum biological material has the advantages of high corrosion resistance and bright application prospect.
Owner:吕莉
Method of in-vitro amplification and purification culture of mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN104480068AReduce harmLow costSkeletal/connective tissue cellsFluid replacementCell culture media
The invention relates to a method of in-vitro amplification and purification culture of mesenchymal stem cells in differentiation from mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts. A used cell culture medium comprises the following components: 5-20% of PL platelet lysate, 2-5U / ml of heparin, 5-10microgram / ml of doxycycline, and a basic culture medium DMEM or a basic culture medium AMEM. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the method comprising steps of separation and extraction of mesenchymal stem cells, cell inoculation, cell culture, cell culture fluid replacement and cell propagation are adopted, and the obtained mesenchymal stem cells are high in purity, high in in-vitro amplification capacity, and good in the capacity of differentiation to osteoblasts.
Owner:黄相杰
Two-layer mimetic periosteum material with HAp loaded inner layer and VEGF loaded outer layer,
The present invention relates to a two-layer mimetic periosteum material with a HAp loaded inner layer and a VEGF loaded outer layer, a preparation method and applications. According to the present invention, silk fibroin (SF) and poly(racemic lactic acid-co-caprolactone) (P(DLLA-co-CL)) are used as base materials, the fibrous porous two-layer mimetic periosteum material is constructed through anelectrospinning technology, the inner layer can promote the bone regeneration by doping HAp, and the outer layer can promote the vascularization by doping VEGF; the two-layer mimetic periosteum material has the fibrous porous structure similar to the autologous bone growth microenvironment, such that the adhesion and the growth of osteoblasts can be easily achieved; and by respectively loading HApand VEGF on the inner layer and the outer layer, the two-layer mimetic periosteum material induced osteoblast growth and vascularization synergy can be effectively promoted, such that the important theoretical research significance and practical value can be provided for the rapid repair of bone tissues.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Fusion peptide capable of promoting osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic differentiation as well as preparation method and application of fusion peptide
ActiveCN105504069AInfluence of self-assembly abilityStabilizes the β-sheet structurePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOsteoblast adhesionOsseous Cell
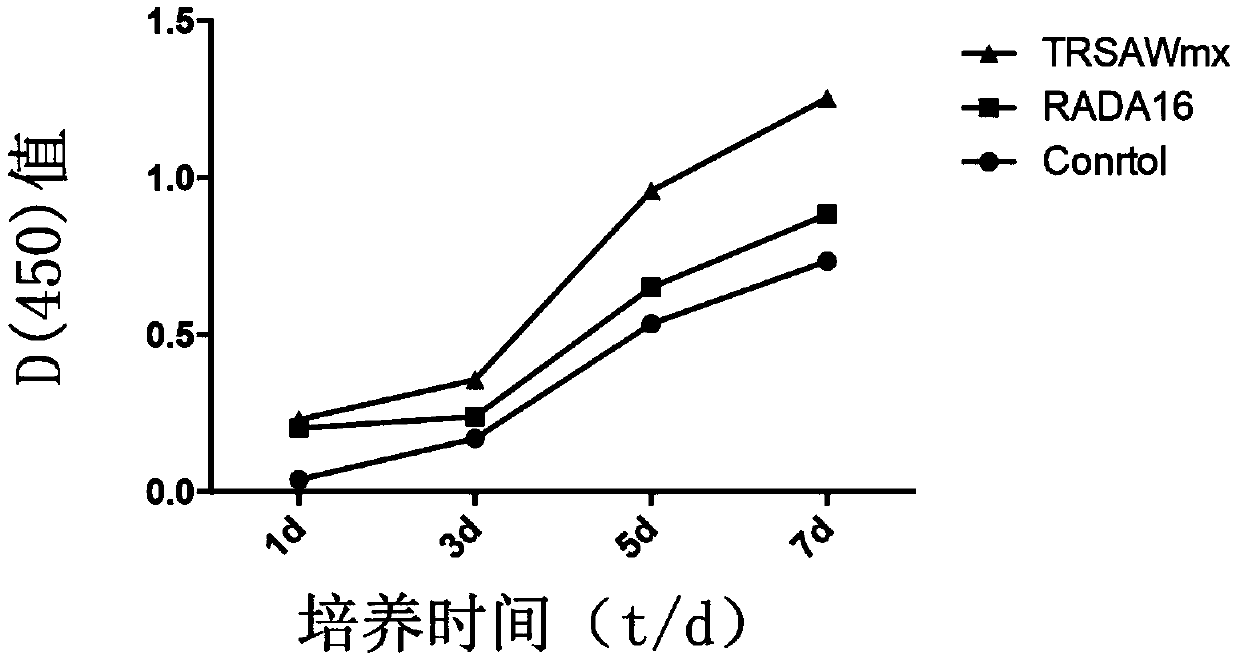
The invention provides a fusion peptide capable of promoting osteoblast adhesion and osteogenic differentiation as well as a preparation method and application of the fusion peptide. The fusion peptide comprises an RADA16-I peptide and an osteostatin (TRSAW) peptide coupled at the C end of the RADA16-I peptide sequence, wherein the amino acid sequence of the RADA16-I peptide is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in the specification. The invention further provides a medicine composition comprising the fusion peptide. The fusion peptide provided by the invention not only can promote MC3T3-E1 osteocyte adhesion and proliferation, but also can promote osteogenic differentiation, and further has a good application prospect.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Active peptide for promoting osteoblast proliferation and application thereof
ActiveCN110627897AHigh activityConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyOsseous Cell
The invention discloses active peptides for promoting osteoblast proliferation and application thereof. The active peptides have amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 to SEQ ID NO: 5. The active peptides can promote osteoblast proliferation so as to prevent or treat osteoporosis. These active peptides can further be developed as pharmaceuticals, food or health products.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Vascular Calcification Prevention and Treatment
ActiveUS20180042962A1Efficient reductionEffectively preventing unwanted systemic calcificationDispersion deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsCirculating Stem CellBeta-catenin
The invention encompasses compositions and methods for effectively interfering, reducing and preventing conversion of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and circulating stem cells to osteoblastic bone-like cells, thereby reducing and / or preventing vascular calcification (VC) or calcium mineral (hydroxyapatite) deposition in the vasculature. The severity and extent of calcification in the major arteries reflect atherosclerotic plaque burden and strongly predict cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. The present inventive compositions used for administration to human and other mammalian subjects comprise select actives that inhibit, interfere or regulate the biochemical processes leading to such calcification and include (1) at least one agent that modulates expression and / or activity of peroxisome activated protein receptor gamma (PPAR-γ); (2) at least one agent that inhibits expression and / or suppresses activity of one or more of the osteogenic transcription factors (Cbfα1 / Runx2, Osterix, Msx2) and β-catenin signaling; (3) at least one agent that inhibits expression and / or suppresses activity of one or more of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs: BMP 2 and 4), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and osteocalcin; (4) at least one agent that inhibits the activity of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS); and (5) at least one agent that suppresses one or more of inflammatory mediators including interleukins IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, NF-κB, TNF-α, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The compositions may further comprise at least one agent that promotes expression and / or carboxylation of matrix Gla protein (MGP). Advantageously, these select actives include materials such as phytonutrients, vitamins and minerals that have been broadly used in food and drink products and are safe for human and pet / animal consumption. Compositions with such combinations have the ability to prevent, treat and reverse VC not only in coronary arteries but also in other tissues capable of undergoing undesirable calcification. In addition the present compositions are effective against associated conditions or contributory factors / inducers to VC, including diabetes, obesity, hypertension, inflammation, oxidative stress, osteoporosis and arthritis.
Owner:SUMMIT INNOVATION LABS LLC
Small-molecule inhibitor for bone formation negative regulatory factor Smurf1
ActiveCN103655567AFast signal responseHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderOsteoblastBone formation
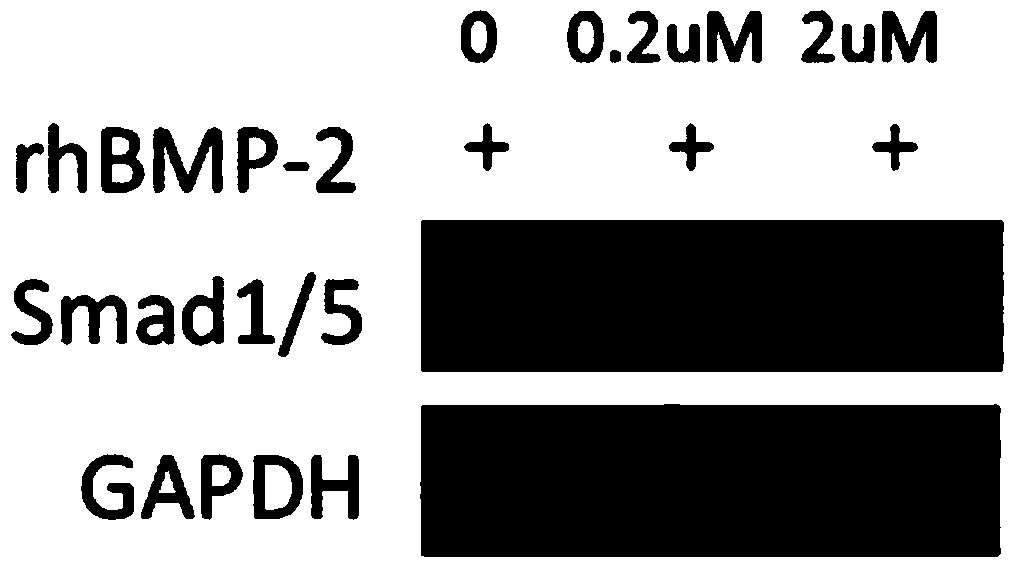
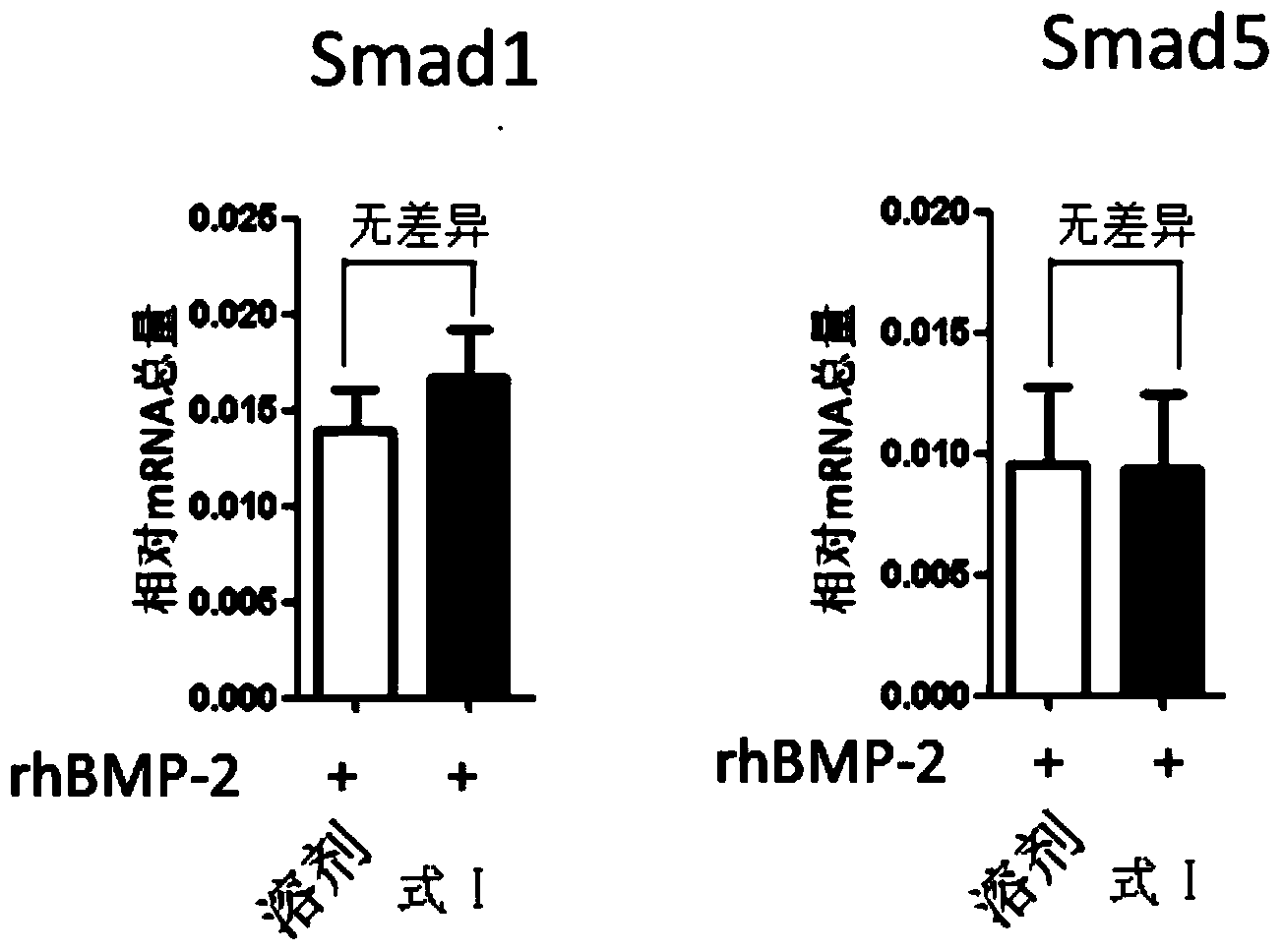
The invention discloses a small-molecule inhibitor for a bone formation negative regulatory factor Smurf1. The compound shown as a formula I can be used in preparation of medicines for promoting bone formation and preparation of a BMP sensitizing agent. The invention also provides one of the applications of the compound shown as the formula I: (1) preparation of products for improving osteogenic potential of cells, wherein the cells are specifically myogenic precursor cells or osteogenic precursor cells; (2) preparation of products for improving alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin and / or type I collagen mRNA levels in cells, wherein the cells are specifically myogenic precursor cells or osteogenic precursor cells; (3) preparation of products for improving activity of alkaline phosphatase in myogenic precursor cells or osteogenic precursor cells or osteoblasts; (4) preparation of products for inhibiting degradation of an Smad1 / 5 protein under the condition of BMP pathway activation; and (5) preparation of products for reducing ubiquitination level of the Smad1 / 5 protein under the condition of BMP pathway activation.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Method and culture media for inducing osteogenic differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cell of mouse
InactiveCN103710310AShort cycleHigh differentiation rateSkeletal/connective tissue cellsForeign genetic material cellsOsteoblastOsseous Cell
The invention discloses a method and culture media for inducing osteogenic differentiation of an induced pluripotent stem cell of a mouse. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps of inoculating the pluripotent stem cell of the mouse into a differentiation culture medium I to form an embryoid body with enriched mesenchymal cells, then separating the embryoid body and culturing in a differentiation culture medium II to obtain an osteoblast, wherein the differentiation culture medium I disclosed by the invention is formed by adding all-transretinoic acid and basic fibroblast growth factor on the basis of a fibroblast culture medium, and the differentiation culture medium II is formed by reducing the D-glucose content and adding BMP4 or BMP7 on the basis of an osteoblast culture medium. The method and the culture media provided by the invention can significantly promote the osteogenic differentiation of the pluripotent stem cell of the mouse, have the characteristics of short cycle, high differentiation rate, stable effect and the like, and have broad application prospect and practical value.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
circRNA (circular Ribonucleic Acid) related to adipose derived stem cell osteogenic differentiation, and application of circRNA
InactiveCN110564865AHelp clinical treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOsseous CellRNA
The invention relates to a circRNA (circular Ribonucleic Acid) related to adipose derived stem cell osteogenic differentiation, and an application of the circRNA. The circbase ID of the circRNA is hsa_circ_0006618. A correlation between the expression level of the RNA has-circ-0006618 and the osteogenic differentiation is analyzed, and a result indicates that the circRNA has-circ-0006618 is up-regulated in an oosteogenic differentiation sample. The circRNA is subjected to target gene prediction to indicate that the circRNA participates in an osteogenic differentiation pathway, so that a detection preparation which aims at the circRNA is used for predicting the differentiation of a human adipose derived stem cell to osteoblast, meanwhile, the differentiation of the human adipose derived stem cell to the osteoblast through induction by the circRNA has-circ-0006618 can be used for repairing bone wounds and is favorable for clinic treatment.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF CHINA MEDICIAL UNIV
Application of APS (astragalus polysaccharide) to prevention of BMSCs (bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells) injury caused by radiation A549 cell bystander effect
PendingCN107603946AEnhanced radiationIncrease the number ofNervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInjury causeAstragalus polysaccharide
The invention relates to application of APS (astragalus polysaccharide) to prevention of BMSCs (bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells) injury caused by the radiation A549 cell bystander effect. After theAPS interference is performed in advance, the influence on the BMSCs by radiation and radiation bystander injury can be obviously reduced, so that the quantity of cells differentiated into nerve cells is increased; the length of synapses differentiated into the nerve cells is increased; the expression of Nissl substances and neuro-specific marker proteins NSE and Nestin is increased; meanwhile, the osteoblast cell differentiation calcium nodule area and the osteoblast cell differentiation mature labelled proteins OPN and OCN are increased, so that the protection effect is achieved on the influence of the BMSCs differentiation potential caused by radiation and radiation bystander injury can be realized by the APS.
Owner:GANSU UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for analyzing periodontal ligament stem cell osteoblastic differentiation by application of gene chip
The invention provides a method for analyzing periodontal ligament stem cell osteoblastic differentiation by the application of a gene chip. A periodontal ligament stem cell is prepared to obtain a single-cell suspension, a periodontal ligament cell in logarithmic phase is sorted from the single-cell suspension; and by a STRO-1-PE marker, STRO-1 positive cells are sorted and collected through a FACS flow cytometer so as to obtain the required periodontal ligament stem cell. Then, the collected periodontal ligament stem cell undergoes clone culture, and when the periodontal ligament stem cell grows to 80% collection degree, pancreatin therein is also digested to obtain a seed solution. The seed solution is inoculated in a 6-well plate or a 24-well plate. After 24 hours, an induced liquid is used for culture. Periodontic treatment analysis by a gene chip is of profound significance for detecting changes of miRNA expression profile during the PDLSC osteoblastic differentiation process.
Owner:福建医科大学附属口腔医院
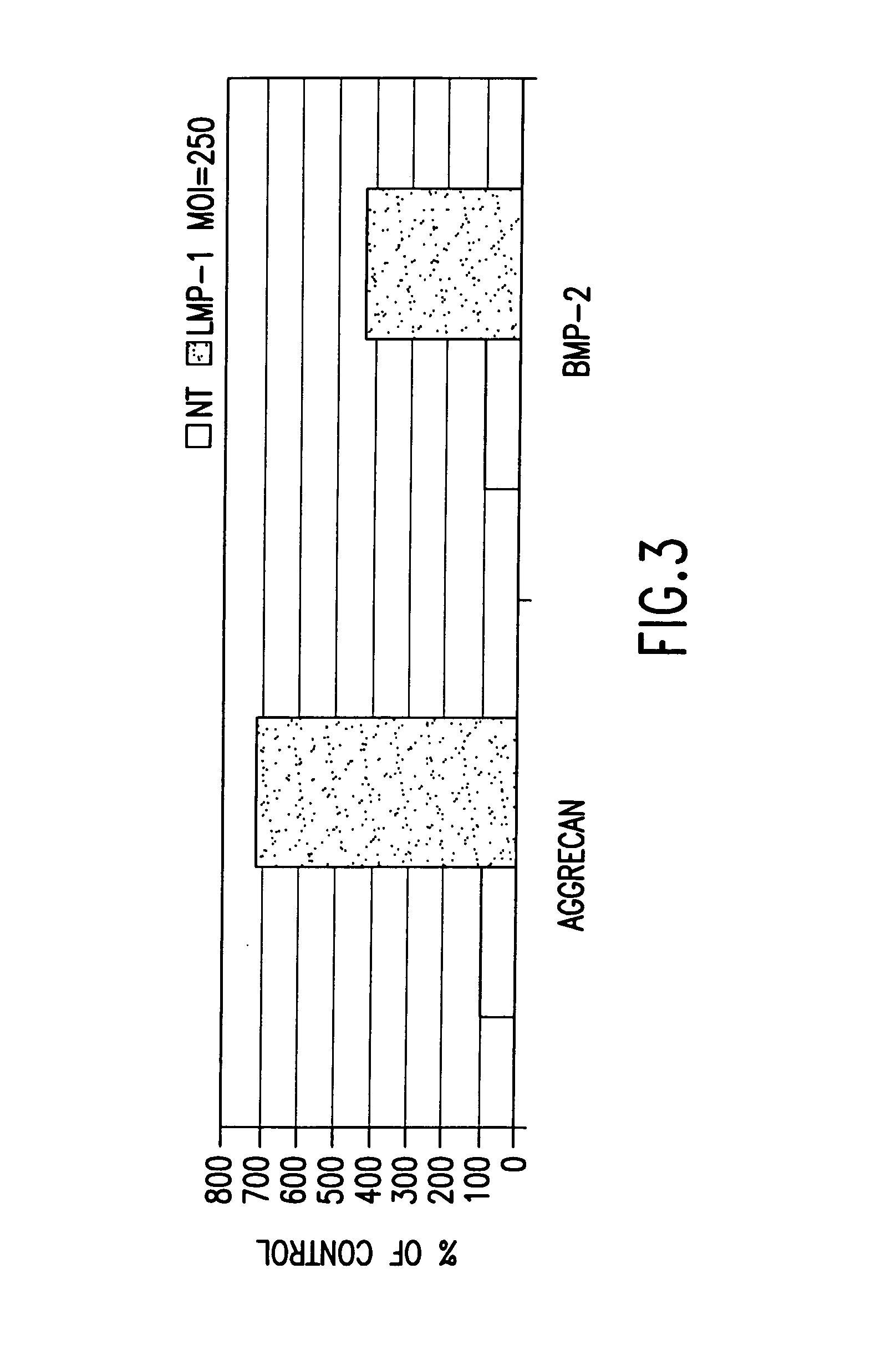
Methods of inducing or increasing the expression of proteoglycans such as aggrecan in cells
Methods of inducing the expression of a proteoglycan such as aggrecan in a cell are described. A method is described which includes transfecting a cell with an isolated nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a LIM mineralization protein operably linked to a promoter. The LIM mineralization protein can be rLMP, hLMP-1, hLMP-1s, or hLMP-3. Transfection maybe accomplished ex vivo or in vivo by direct injection of virus or naked DNA, or by a nonviral vector such as a plasmid. The method can be used to induce proteoglycan synthesis in osseous cells or to stimulate proteoglycan and / or collagen production in cells capable of producing proteoglycan and / or collagen (e.g., intervertebral disc cells including cells of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus).
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Capsule for increasing bone density and preparation method of capsules
InactiveCN106420905AHigh activityPromote productionSkeletal disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsOysterOsteoblast
The invention relates to a capsule for increasing bone density and a preparation method of the capsules. The capsule comprises a capsule body and filler filling the capsule body, wherein the filler is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 25 parts of extracts of fortune's drynaria rhizome, 25 parts of eucommia bark extracts, 80 parts of milkvetch root extracts, 70 parts of Kudzuvine root extracts, 180 parts of oyster extracts, 18 parts of starch and 2 parts of magnesium stearate. The capsule strengthens the activity of osteoblasts, promotes production and secretion of bone matrixes and bone mineralization and improves the body immune function; the components are applied compatibly, realize a synergistic effect, improve calcium absorption of human bodies together and increase the bone density; the preparation method is reasonable in process and high in operability and easily realizes large-scale production.
Owner:高振达
Polylactic acid/hydroxyapatite/acellular amniotic membrane composite stent and construction method thereof
ActiveCN107684637AImprove mass transfer effectRich attachment sitesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationPorosityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a polylactic acid / hydroxyapatite / acellular amniotic membrane composite stent and a construction method thereof. The polylactic acid / hydroxyapatite / acellular amniotic membrane composite stent is characterized in that polylactic acid, hydroxyapatite / acellular and amniotic membrane are dissolved into dichloroethane and n-hexane by steps, and a non-solvent induced phase separation method is adopted to construct the composite stent which is of a composite pore structure using large pores to coat small pores. The polylactic acid / hydroxyapatite / acellular amniotic membrane composite stent has the advantages that by using the polylactic acid as a substrate, the mechanical strength and biodegradability of the stent are guaranteed; by compounding with the hydroxyapatite, whilethe bone inducing property and bone conduction property of the stent are improved, the acidifying of the metabolism environment is relieved; by compounding with the acellular amniotic membrane, the water-absorbing property, biocompatibility and identification property of the stent are improved, and the sticking and propagation of cells on the stent are promoted; the porosity is high, the pore communication property is good, the mechanical property is strong, the biocompatibility is good, the osteogenesis inducing activity is high, and the like; the good biology function on important seed cells and osteogenesis cells in bone tissue engineering is realized, and the polylactic acid / hydroxyapatite / acellular amniotic membrane composite stent can be used as an excellent biomedical material to be applied to the field of bone tissue engineering.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Kit used for identifying hematopoietic stem cell transplantation effect
The invention discloses a kit used for identifying hematopoietic stem cell transplantation effect. The kit comprises assemblies A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H. The assembly A is a substance used for preparing bone marrow mononuclear cells; the assembly B is a substance used for culturing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to form colonies; the assembly C is a substance used for counting the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell colonies; the assembly D is a substance used for identifying whether bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are capable of being differentiated into osteoblasts; the assembly E is a substance used for identifying whether bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are capable of being differentiated into adipocytes; the assembly F is a substance used for identifying whether bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells have capacity of inhibiting T lymphocyte proliferation; and the assembly G is a substance used for identifying whether bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are capable of being feeder cells of hematopoietic stem cells. The kit provided by the invention is convenient and practical, and is simple to operate. The kit can be used for detecting bone marrow hematopoietic microenvironment recovery condition after a hematopoietic stem cell transplantation operation. With the kit, a basis is provided for the researched on mesenchymal stem cells.
Owner:CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY AIR FORCE GENERAL HOSPITAL
Regulation and control research method of cell cilium transportprotein 80 in rapid maxillary expansion mechanical biological signal transduction
InactiveCN108753701APromote calcificationReduce absorptionMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOsteoblastStudy methods
The invention discloses a regulation and control research method of cell cilium transportprotein 80 in rapid maxillary expansion mechanical biological signal transduction. The method comprises the following steps: a, establishing a rapid maxillary expansion mouse animal model; b, establishing IFT80 gene silence osteoblast; c, establishing an in-vitro stretching culture osteoblast model; d, establishing a co-culture model of osteoblast and osteoclast; e, carrying out in-vivo transfection experiment; f, confirming a relationship of IFT80 spatio-temporal expression and rapid maxillary expansion midline palatine suture bone remolding; g, confirming regulation and control mechanisms of IFT80 upon proliferation and differentiation of in-vitro stretching cultured osteoblast, primary cilium formation and mechanical biological signal transduction; h, confirming influence of IFT80 gene silence upon in-vitro stretching cultured osteoblast in regulating functions of osteoclast. The method has great instruction significances for treating such malocclusion.
Owner:AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105384786APromote value-addedTreat osteoporosisSugar derivativesSkeletal disorderOsteoblastOsseous Cell
The invention provides a compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has a structure shown as formula (I), and the compound can treat osteoporosis; moreover, by virtue of cell experiments, the compound is discovered to have an effect on promoting the proliferation of osteoblasts; and when the sample concentration is 10mu M, the proliferation rate can reach 11.24 percent.
Owner:JIANGSU KANION PHARMA CO LTD +1
A method of titanium metal modification with antibacterial properties and promoting osteoblast growth
ActiveCN104258468BImprove stabilityImprove antibacterial propertiesProsthesisHuman bodyTitanium metal
The invention discloses a modification method of titanium metal having antibacterial property and capable of promoting the growth of osteoblast. The modification method comprises the following steps: pretreating titanium metal, preparing a mixed liquid which can be adhered on the surface of the titanium metal and contains a certain crosslinking space structure, wherein the mixed liquid contains silver nitrate with an antibacterial function; then adding osteoblast and the pretreated titanium metal, and performing vacuum drying to obtain titanium metal the coating of which is coated by osteoblast; and finally immersing into a pancreatin solution for 15-45 seconds, performing ultrasonic elution and vacuum drying to obtain modified medical titanium metal capable of promoting the growth of osteoblast. The method is simple, and mild in preparation conditions, no harmful substances are generated during preparation, the modified titanium metal can effective recognize osteoblast, promote the fast growth of the osteoblast on the surface of the titanium metal, and effectively inhibit the growth of bacteria; and after being implanted into a human body as an implant, the modified titanium metal is beneficial to fixed growth of osteoblast on the surface of the titanium metal.
Owner:陕西德健众普生物科技有限公司
Energy-Providing Bone-Repair Degradable Porous Scaffold, Preparation Method Thereof, and Application Thereof
ActiveUS20170246343A1Good biocompatibilityFacilitating cell growth cellTissue regenerationProsthesisSurgical operationAlcohol
The invention discloses an energy-providing bone-repair degradable porous scaffold, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof. The invention obtains an energy-based biomaterial solution by compositing gelatin, a polyatomic acid and derivatives thereof, a dibasic alcohol and derivatives thereof, and a tribasic alcohol and derivatives thereof in a chemical cross-linking manner by using diisocyanate, and further obtains a porous scaffold through a drying method. The porous scaffold can avoid the problem of an acidic microenvironment caused by in vivo implantation of the existing biomaterial and keep the activity of an osteoblast cell, thereby improving the rate of repairing the damaged bone tissue with the energy-based biomaterial. The porous scaffold of the invention can be used as a filling material for bone repair in a surgical operation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods of inducing or increasing the expression of proteoglycans such as aggrecan in cells
InactiveUS20070134218A1Prevent mineralizationDecrease osteocalcin productionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideEukaryotic plasmids
Methods of inducing the expression of a proteoglycan such as aggrecan in a cell are described. A method is described which includes transfecting a cell with an isolated nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a LIM mineralization protein operably linked to a promoter. The LIM mineralization protein can be rLMP, hLMP-1, hLMP-1s, or hLMP-3. Transfection maybe accomplished ex vivo or in vivo by direct injection of virus or naked DNA, or by a nonviral vector such as a plasmid. The method can be used to induce proteoglycan synthesis in osseous cells or to stimulate proteoglycan and / or collagen production in cells capable of producing proteoglycan and / or collagen (e.g., intervertebral disc cells including cells of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus).
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Preparation method of three-dimensional bone-like tissue used for study of microgravity effect stimulation
A preparation method of a three-dimensional bone-like tissue used for the study of microgravity effect stimulation relates to a preparation method of a three-dimensional bone-like tissue. The invention is to solve the problem that two-dimensional osteoblast models used for the study of microgravity effect stimulation at present can not truly represent the process of bone loss during spaceflight, and can not truly represent intercellular biological characteristics of in-vivo tissues. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, the mixing of a PBS buffer or normal saline, sodium alginate, gelatin and hydroxyapatite; 2, the induction of osteoblasts; 3, the induction of osteoclasts; 4, the preparation of microspheres for enwrapping the mixed cells; 5, the formation of the three-dimensional bone-like tissue. The invention forms a three-dimensional stent by sodium alginate, and embeds osteoblasts and osteoclasts together in a sodium alginate microsphere; the three-dimensional culture can simulate the growth condition of cells in a physiological state better, which solves the deficiency of existing two-dimensional osteoblast models. The invention is applicable to research fields of space biology, aerospace medicine and tissue engineering.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com