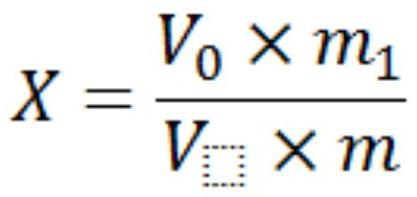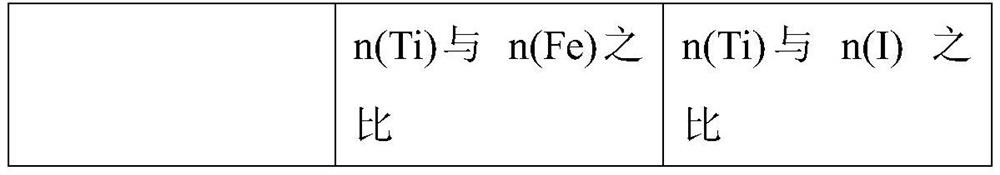Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "IODATE ION" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An iodate is a conjugate base of iodic. acid. In the iodate anion, iodine is bonded to three oxygen. atoms and the molecular formula is IO3−.
Color stabilized antimicrobial polymer composites
A polymer composite comprising a melt-processed polymer compounded with a color stabilizer comprising a bromate or iodate ion, and a silver-based antimicrobial agent. The specified color stabilizers are particularly superior in inhibiting undesirable darkening or discoloration of melt-processed polymers compounded with silver-based antimicrobial agents containing a grain-size controlling additive.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Color stabilized antimicrobial polymer composites
Owner:SANDFORD DAVID W +1
Encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105772093AStable crystal structureStable and efficient electrocatalytic activityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsModified carbonCarbon paste electrode
The invention provides an encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material, and a preparation method and an application thereof and relates to a multi-acidic group micropore crystalline state material, and a preparation method and the application thereof. The invention aims to solve the problems that the synthesis difficulty of the present multi-acidic group metal-organic frame crystalline state material is high and the effect of detecting iodate according to an electrochemical method is poor. The chemical formula of the encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material is [Co2(bimb)2VW12O40].[bimb].5H2O. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a reaction solution; 2) causing the reaction solution react for 3 days in a polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle, and then cooling to room temperature. An encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material modified carbon paste electrode is taken as an electrocatalyst for reducing potassium iodate and is used for efficiently detecting iodate ions. According to the method provided by the invention, the encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material can be acquired.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for recovering iodine
The invention discloses a method for recovering iodine, which is coupled with the electrochemical method to control the redox level, and recovers the inorganic iodine in liquid waste. A sodium hypochlorite solution is used for oxidizing and recovering organic iodine. The iodide ion content of the recovered liquid waste is about 0.3%. The iodine in the recovered liquid waste is gathered and recovered by using strong basicity anion exchange resin. The iodate ion is reduced to iodine by the method in one step. The complicated operations of reducing iodate ions into iodide ions firstly and then oxidizing into iodine are prevented. The usage amount of the oxidizing and reducing agents is reduced. Therefore, the cost is reduced, and the method for recovering iodine can bring high economic benefit to industrial production.
Owner:施一飞
Rapid quantitative detection method for determining iodine content in well and rock salt
ActiveCN103048318ARapid determinationAccurate measurementMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorIodidePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a rapid quantitative detection method for determining iodine content in well salt. The method comprises the following steps: (1), an appropriate amount of iodized salt is weighted, placed in a bottle and dissolved in water; (2), an appropriate amount of phosphoric acid is added in the bottle first to provide an acidic condition, then an appropriate amount of sodium hypochlorite solution is added and mixed evenly to oxidize iodine ions into iodate ions, and then an appropriate amount of oxalic acid solution is added to remove the residual sodium hypochlorite after the reaction with iodide irons; (3), an appropriate amount of potassium iodide solution is added in the bottle to allow full reaction between potassium iodide and iodate ions; (4), the solution in the bottle is titrated with sodium thiosulfate solution until the color of the solution in the bottle turns to be faint yellow; (5), starch indicator solution is added in to the bottle and shook evenly and then the solution in the bottle is titrated with the sodium thiosulfate solution until the color of the solution in the bottle disappear; and (6), the iodine content of the iodized salt is worked out according to the consumption amount of the sodium thiosulfate solution. Therefore, the method provided by the invention can be used to quickly and accurately determine the total iodine content in the well and rock salt.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for removing iodo-X-ray contrast medium in water
InactiveCN109293103AControl concentrationHigh removal rateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsFiltrationUltraviolet
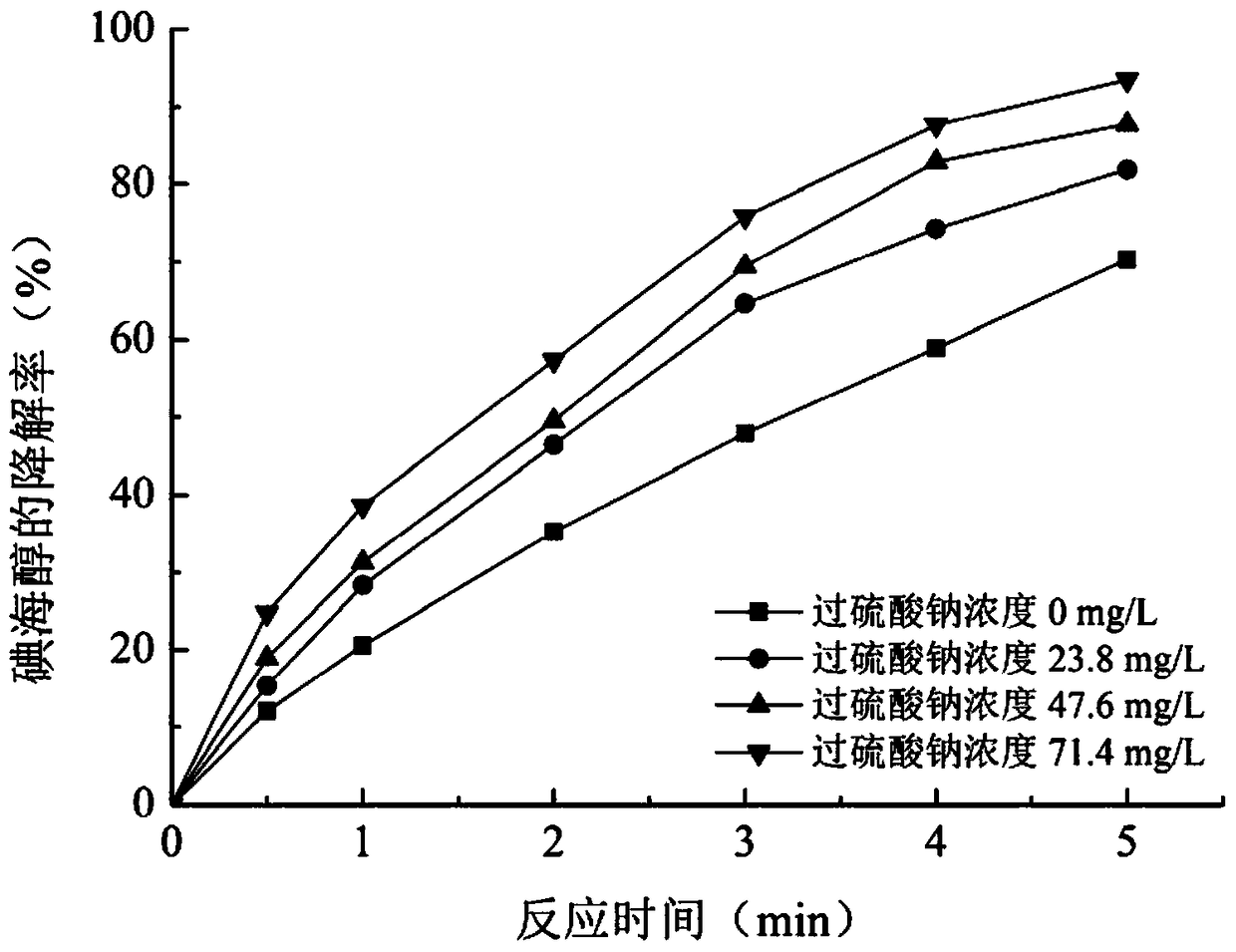
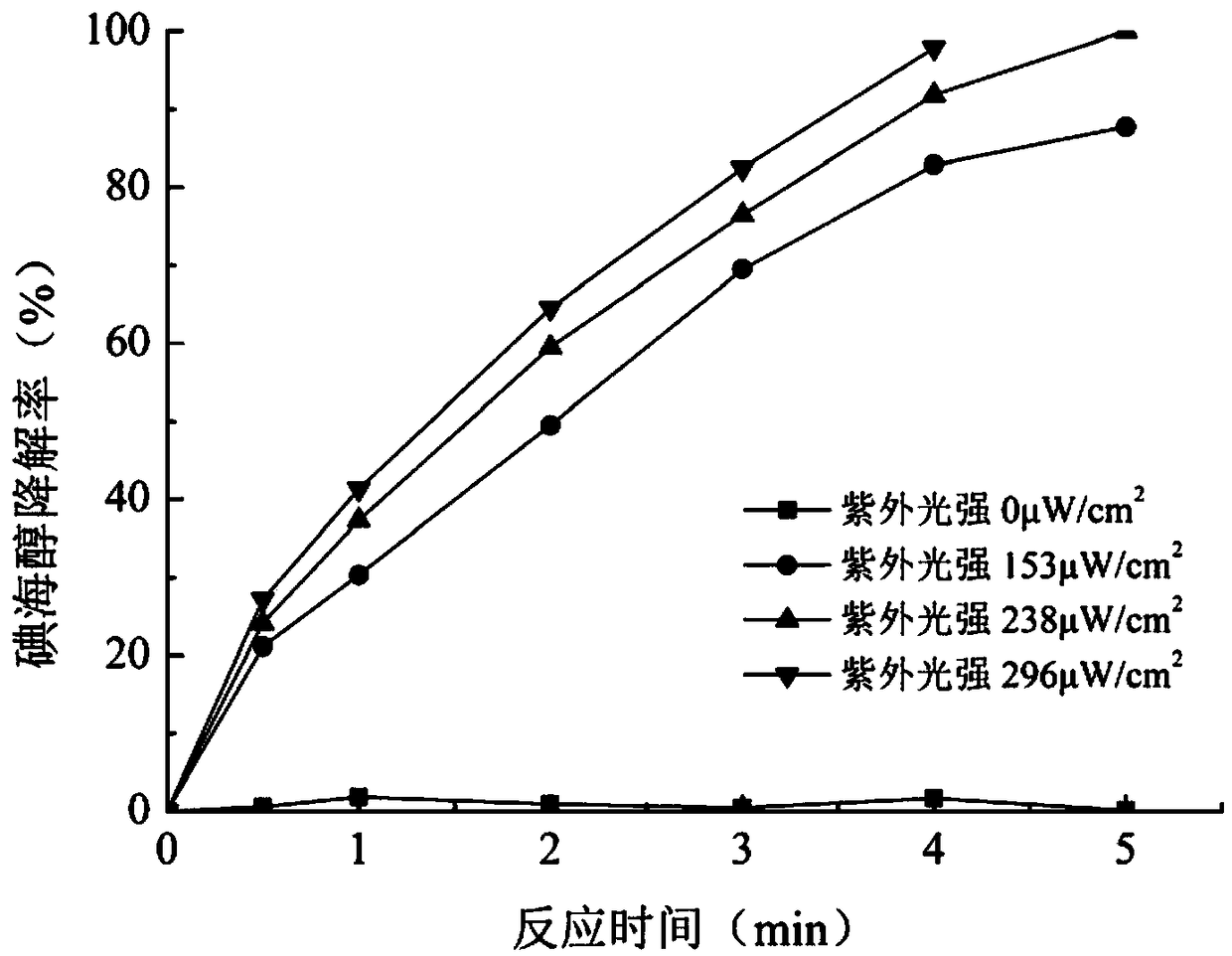
The invention relates to a method for removing an iodo-X-ray contrast medium in water. The method includes the steps: oxidant feeding, to be more specific, adding sodium persulfate into to-be-treatedwater until the concentration of sodium persulfate in the water reaches 23.8-71.4mg / L; ultraviolet irradiation, to be more specific, subjecting the to-be-treated water to ultraviolet irradiation for 5-10 minutes after oxidant feeding. Compared with the prior art, the method has advantages that high degradation efficiency is achieved, the concentration of the ICM (iodo-X-ray contrast medium) in thewater can be decreased by 87% or more, the method is slightly affected by pH (potential of hydrogen) changes, and reaction products are mainly sulfate ions and iodate ions and can be removed by simple coagulation, precipitation or membrane filtration, so that the method is a safe and stable drinking water treatment method.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Iodine replenisher with control released iodine and its preparing method and use
InactiveCN1857304AEasy to implementSuitable for industrial productionMetabolism disorderAccessory food factorsBiocompatibility TestingHigh surface
The present invention discloses iodine replenisher with control released iodine and its preparation process and use. The iodine replenisher is hydrotalcite containing interchangeable iodate radical or iodine ion with iodine content of 0.5-5%. The preparation process includes inserting iodate radical or iodine ion into layers of hydrotalcite; or calcining hydrotalcite at 450-550 deg.c to obtain bimetal oxide and carrying iodate radical or iodine ion to the layered structure of the bimetal oxide. Supporting iodine onto hydrotalcite, which possesses excellent biocompatibility, excellent gastrointestinal mucous membrane affinity, high interlayer interchangeability, high surface activity and great specific surface area, can obtain controlled releasing of iodine and raise utilization of iodine. The control released iodine preparation has low toxicity and high efficiency and may be used as iodine replenisher for human body and animal.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ion chromatography-valve switching analysis system for simultaneously detecting iodide ions and iodate ions
The invention relates to a use system for instrumental analysis, in particular to an ion chromatography-valve switching analysis system for simultaneously detecting iodide ions and iodate ions. The ion chromatography-valve switching analysis system is provided with an anion exchange chromatographic column comprising a chromatographic column with low exchange capacity and a chromatographic column with high exchange capacity, wherein the chromatographic column with the low exchange capacity retains the iodide ions to a certain degree while hardly retaining some weak retention ions including the iodate ions, and the chromatographic column with the high exchange capacity is capable of effectively separating various weak retention ions. The iodide ions can be rapidly eluted only through the chromatographic column with the low exchange capacity, by means of simple valve switching, the weak retention ions including the iodate ions and the like can be effectively separated, analysis time is shortened, and analysis efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for effectively removing iodinated X-ray contrast agent in water
InactiveCN109607857AEasy to operateImprove securitySpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsDisinfection by-productX-ray
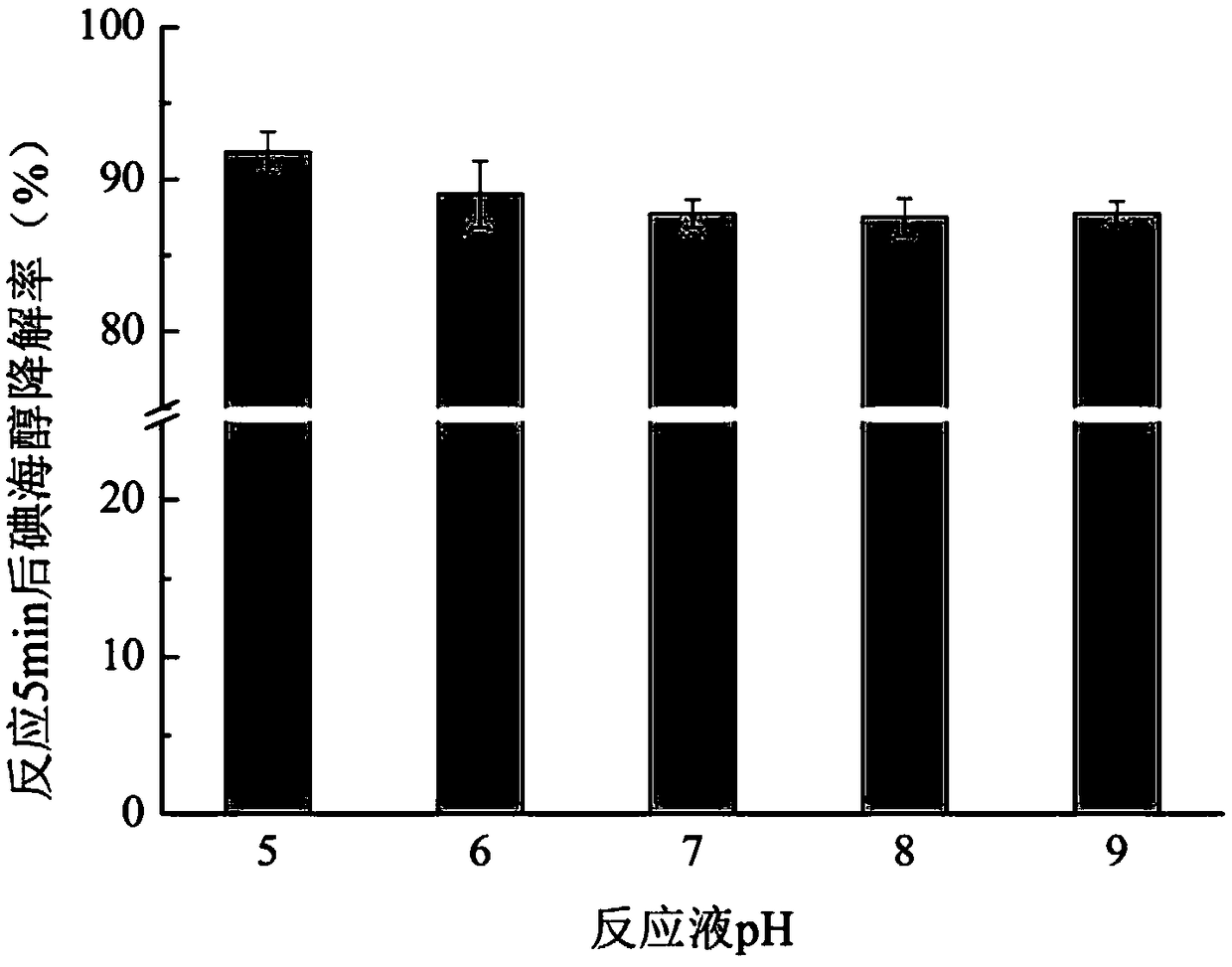
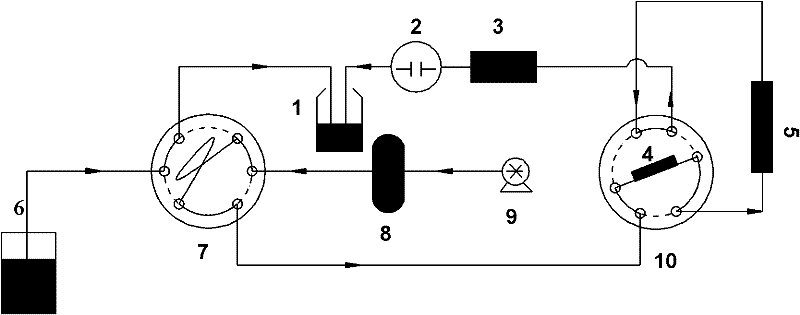
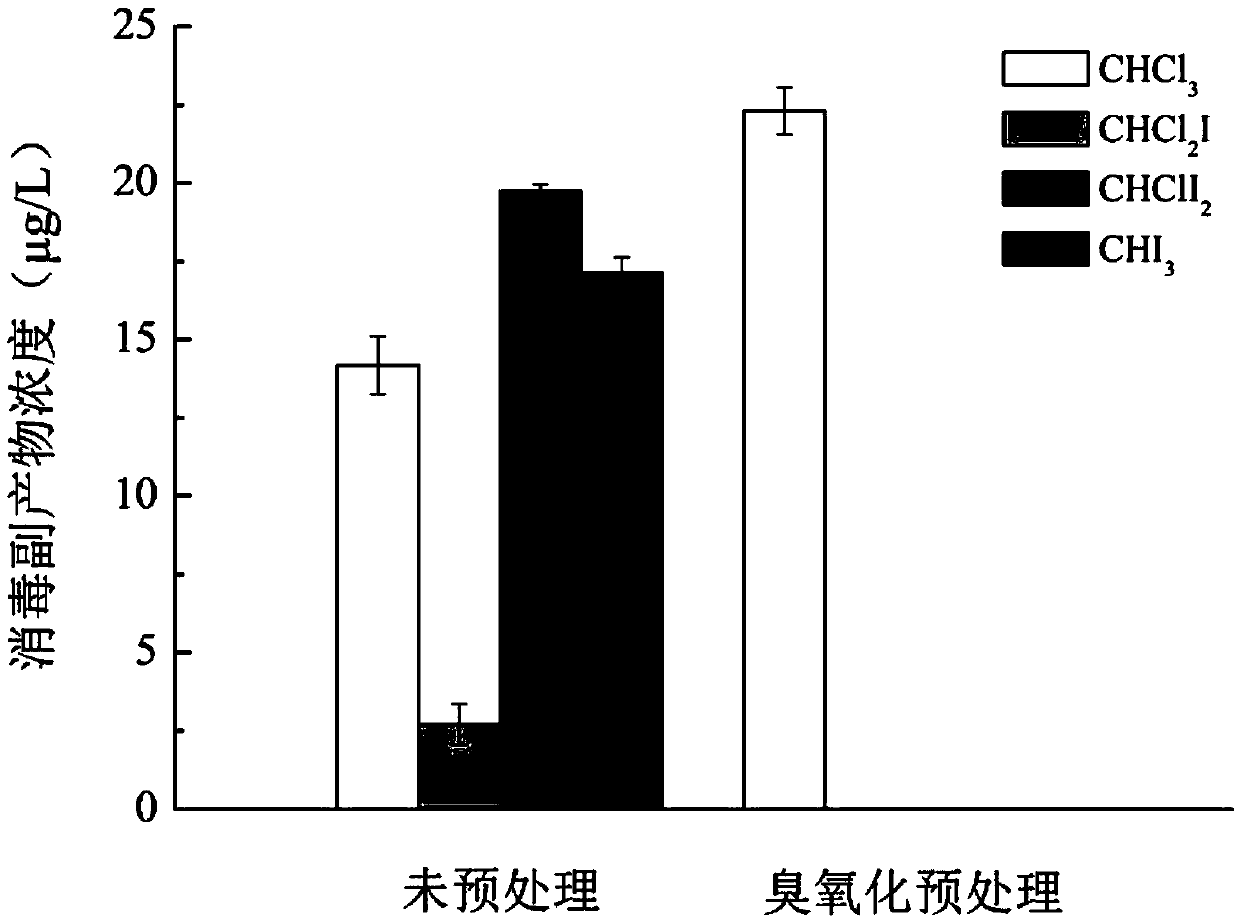
The invention relates to a method for effectively removing iodinated X-ray contrast agent in water, which can control the generation of trace strongly carcinogenic disinfection by-product iodinated trihalomethane. The method takes ozone as oxidant, controls the pH of the reaction solution to be equal to or less than 9 and equal to or more than 5, the solution is subjected to stirring and mixing evenly, so as to reduce the concentration of ICM in water, and control the concentration of I-THMs in water. The method of the invention eliminates the ICM existing in the water body, does not need complicated operation process, has certain difference for the degradation efficiency of the ICM under different pH conditions, but can avoid the generation of I-THMs. The main products of the reaction areiodate ions and so on. The invention is a safe and stable drinking water treatment method.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
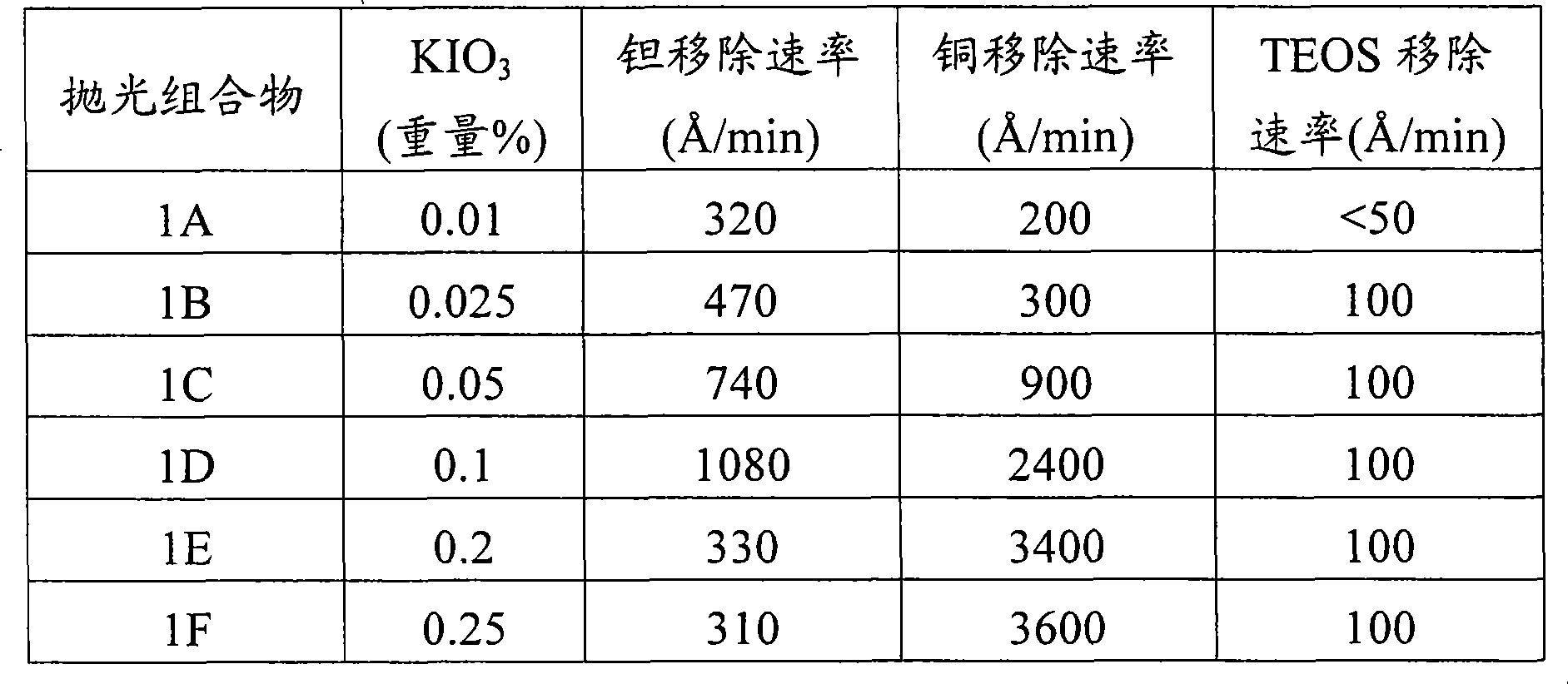
Iodate-containing chemical-mechanical polishing compositions and methods
InactiveCN101389723AOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenCompound (substance)
The invention provides compositions and methods for planarizing or polishing a substrate. The composition comprises an abrasive, iodate ion, a nitrogen-containing compound selected from the group consisting of a nitrogen-containing C4-20 heterocycle and a C1-20 alkylamine, and a liquid carrier comprising water.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
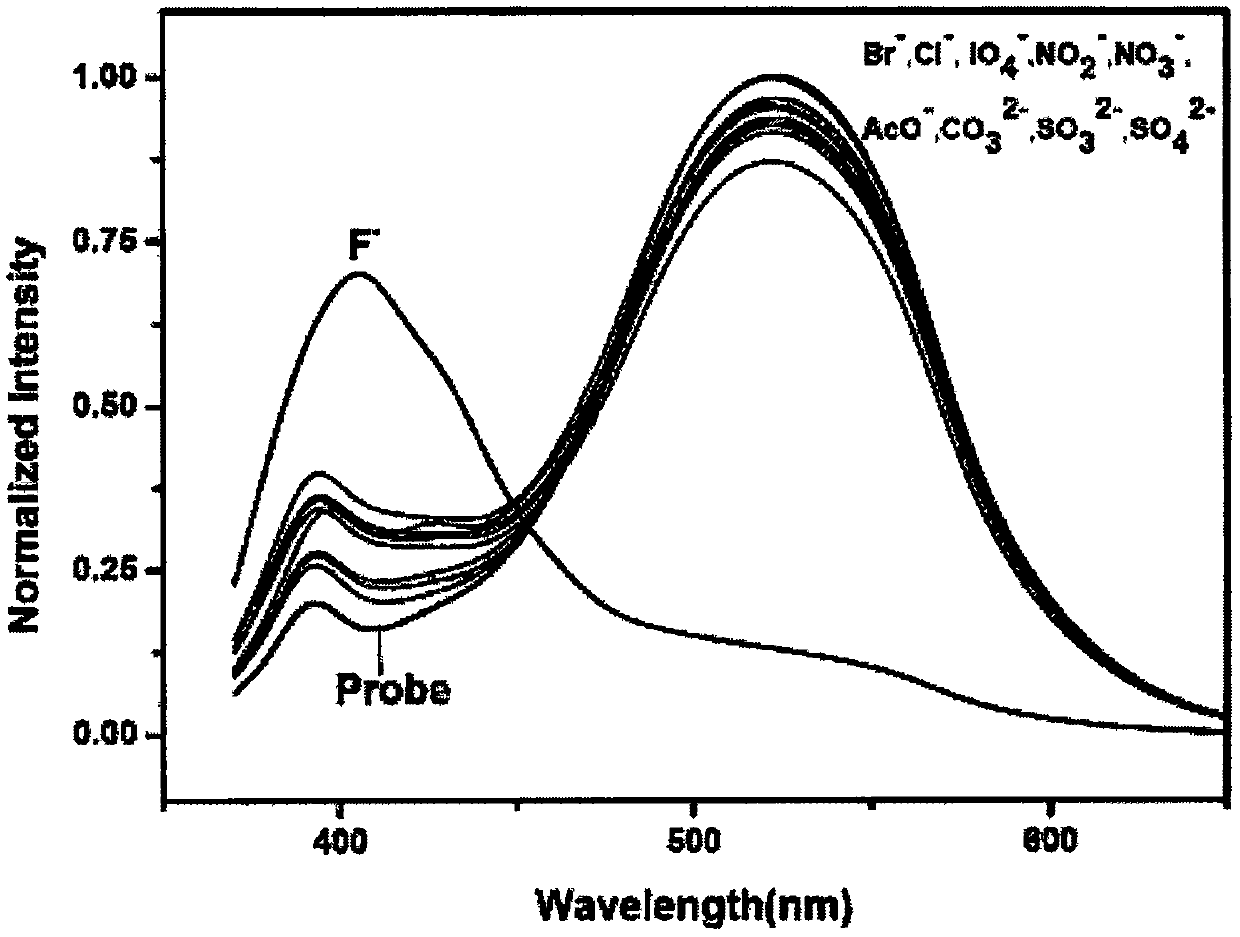
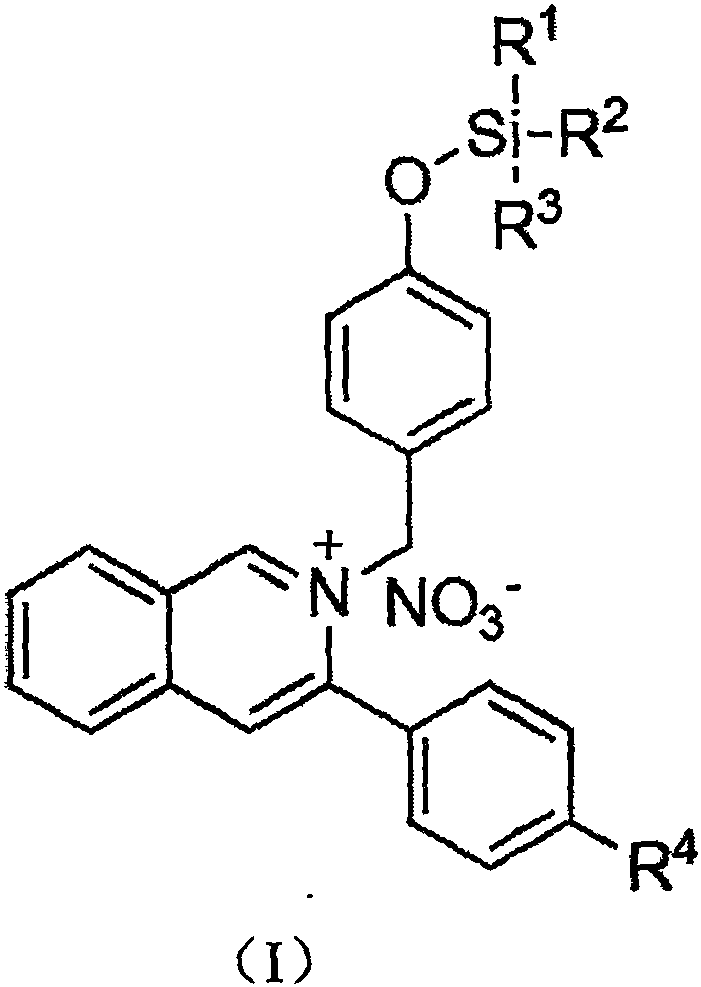
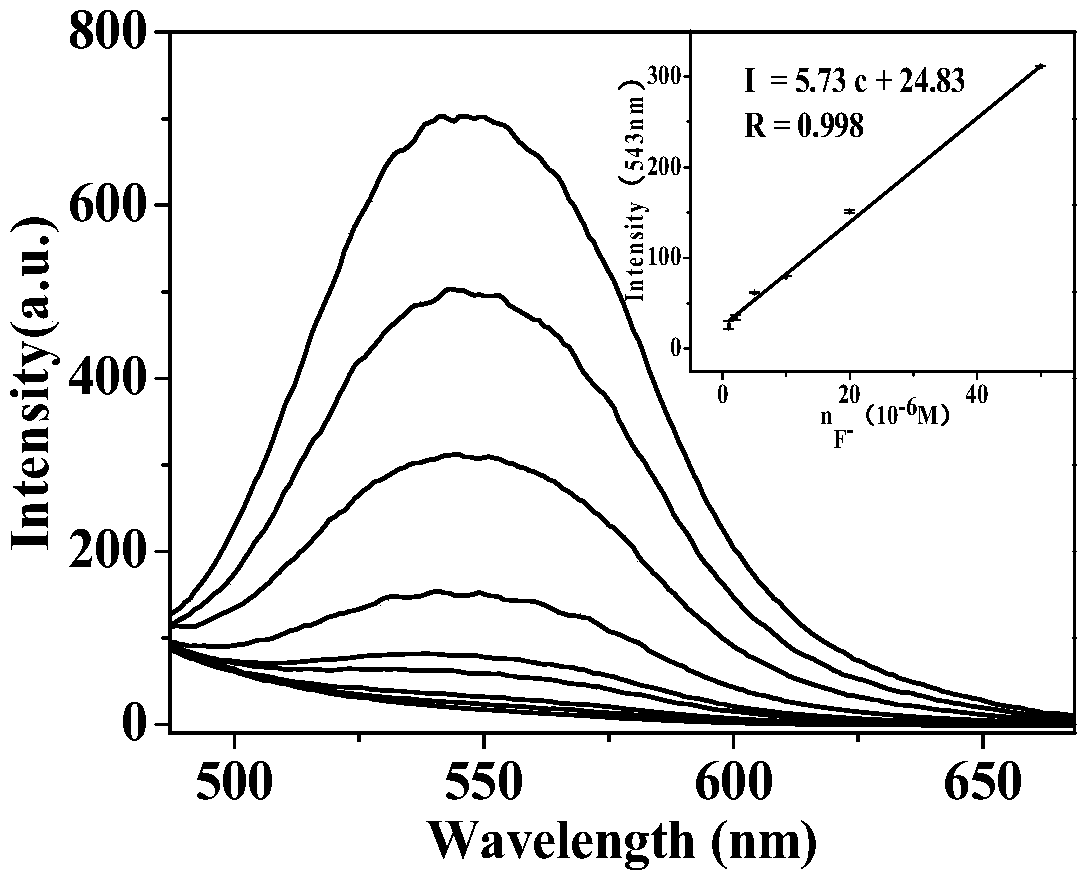
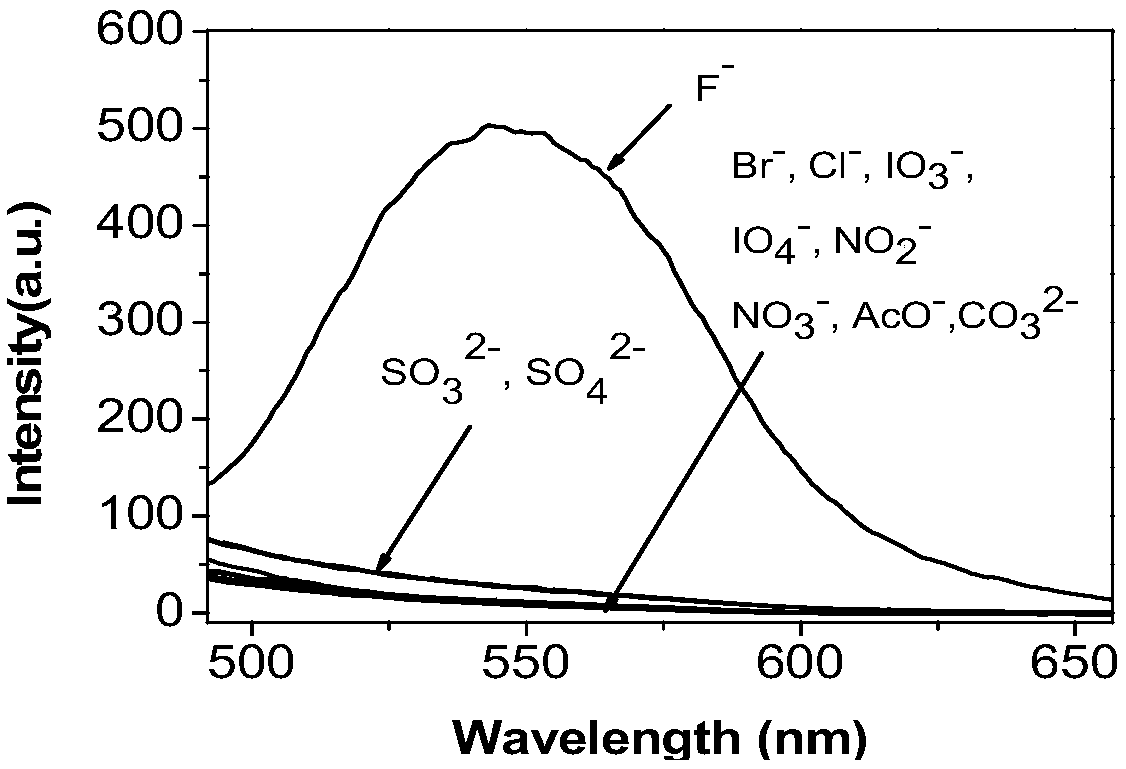
Isoquinoline-based ratio-dependent detecting probe for fluoride ions and preparation method and application of isoquinoline-based ratio-dependent detecting probe
PendingCN110396405ASensitive recognitionStrong specificityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceNitrite ionBase Ratio
The invention discloses an isoquinoline-based ratio-dependent detecting probe for fluoride ions and a preparation method and application of the isoquinoline-based ratio-dependent detecting probe. Thefluorescent probe has a structure as shown in a formula I, o-alkynyl aldehyde is adopted as a raw material of the probe, and a reaction is performed between the raw material and a benzylamine derivative so as to obtain the probe. The probe has stable optical performance, high detection sensitivity to fluoride ions, a lower limit of detection, a detection limit of 3.79 nM and a response range of 0.2-10 [mu]M; good selectivity is achieved, no responses to chloride ions, bromide ions, iodate ions, periodate ions, nitrate ions, nitrite ions, acetate ions, carbonate ions, sulfate ions, sulfite ionsand other negative ions are generated; and synthesis is simple, the conditions are mild, and the yield is high. The fluorescent molecular probe has practical application values in biochemistry and environmental chemistry and other fields, especially detection of fluoride ions in water.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Holmium metal iodate fluorescent material and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103011236AHigh particle purityGood dispersionRare earth metal compoundsLuminescent compositionsLuminous intensityHolmium
The invention discloses a holmium metal iodate fluorescent material and a preparation method and applications thereof. The molecular formula of the compound is Ho(IO3)3, the space group is P21n, the parameters of unit cells comprise that a is equal to 8.7376 angstrom, b is equal to 5.9706 angstrom, c is equal to 15.0677 angstrom, alpha is equal to 90.000, beta is equal to 97.240, g is equal to 90.000, and Z is equal to 2; and the volume V of the unit cells is equal to 779.8(10) angstrom<3>. The material adopts hydrothermal reaction to obtain crystals; Ho<3+> fluorescence radiation intensity of the material can be enhanced through iodate ions; and the material is used for producing fluorescence radiation devices.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
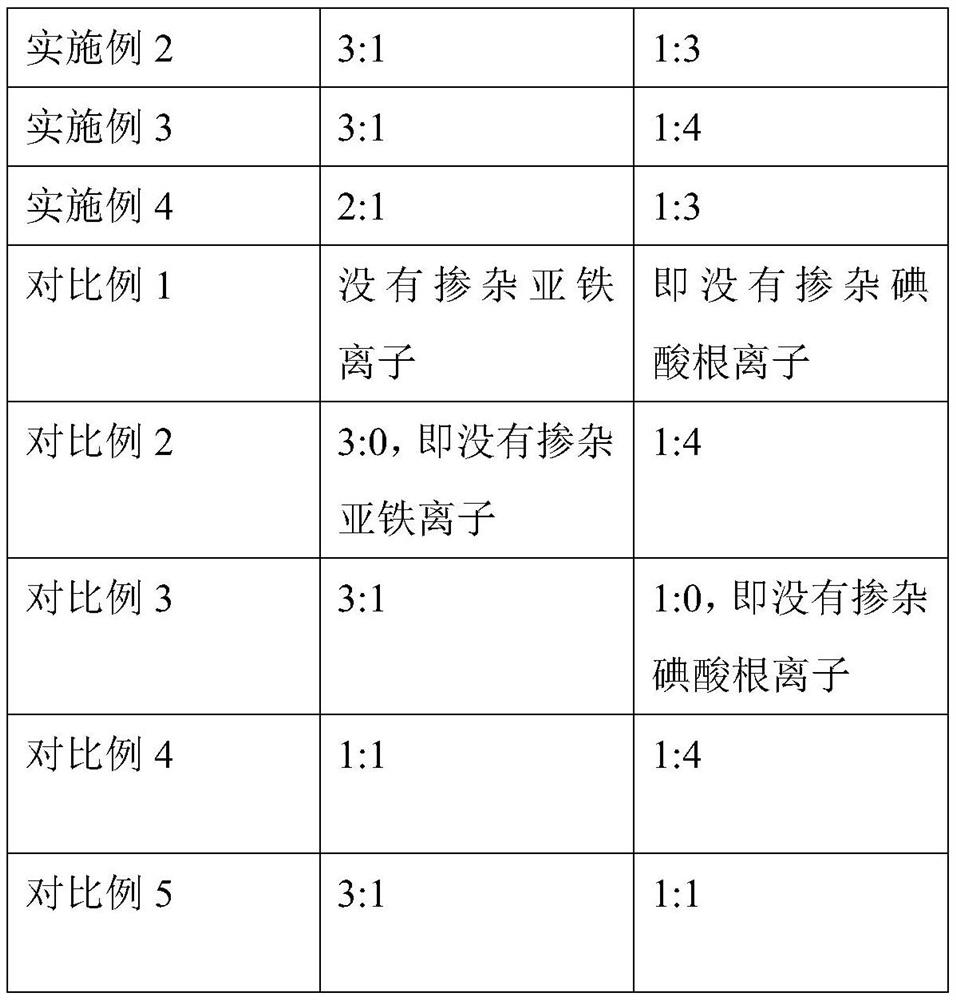
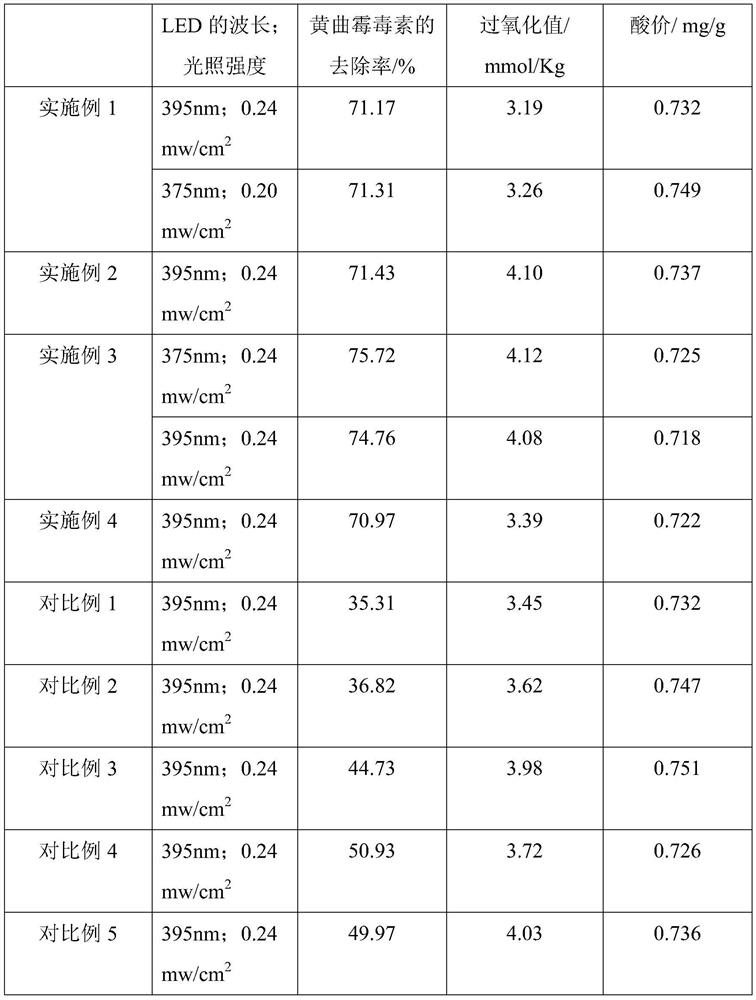
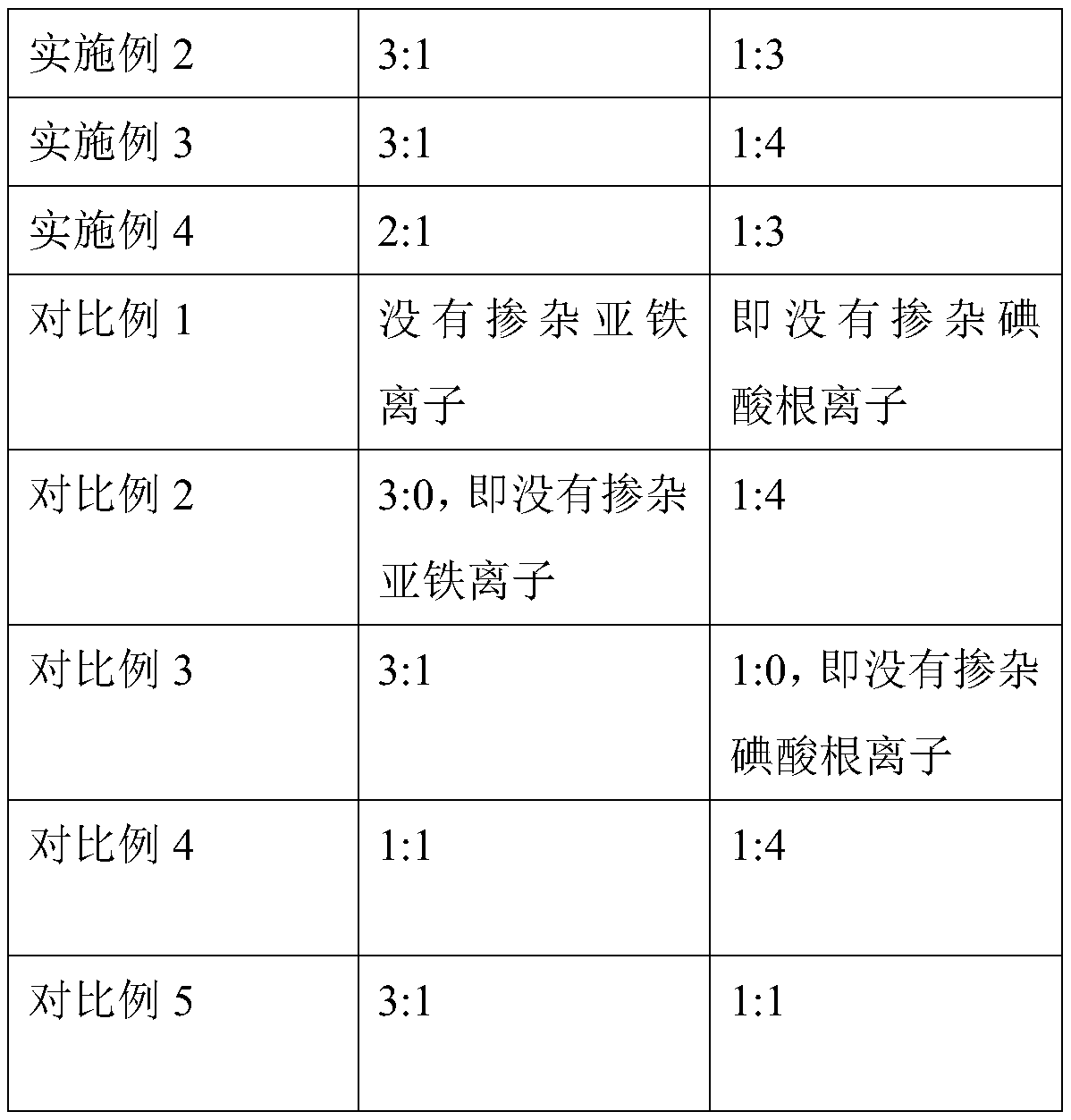
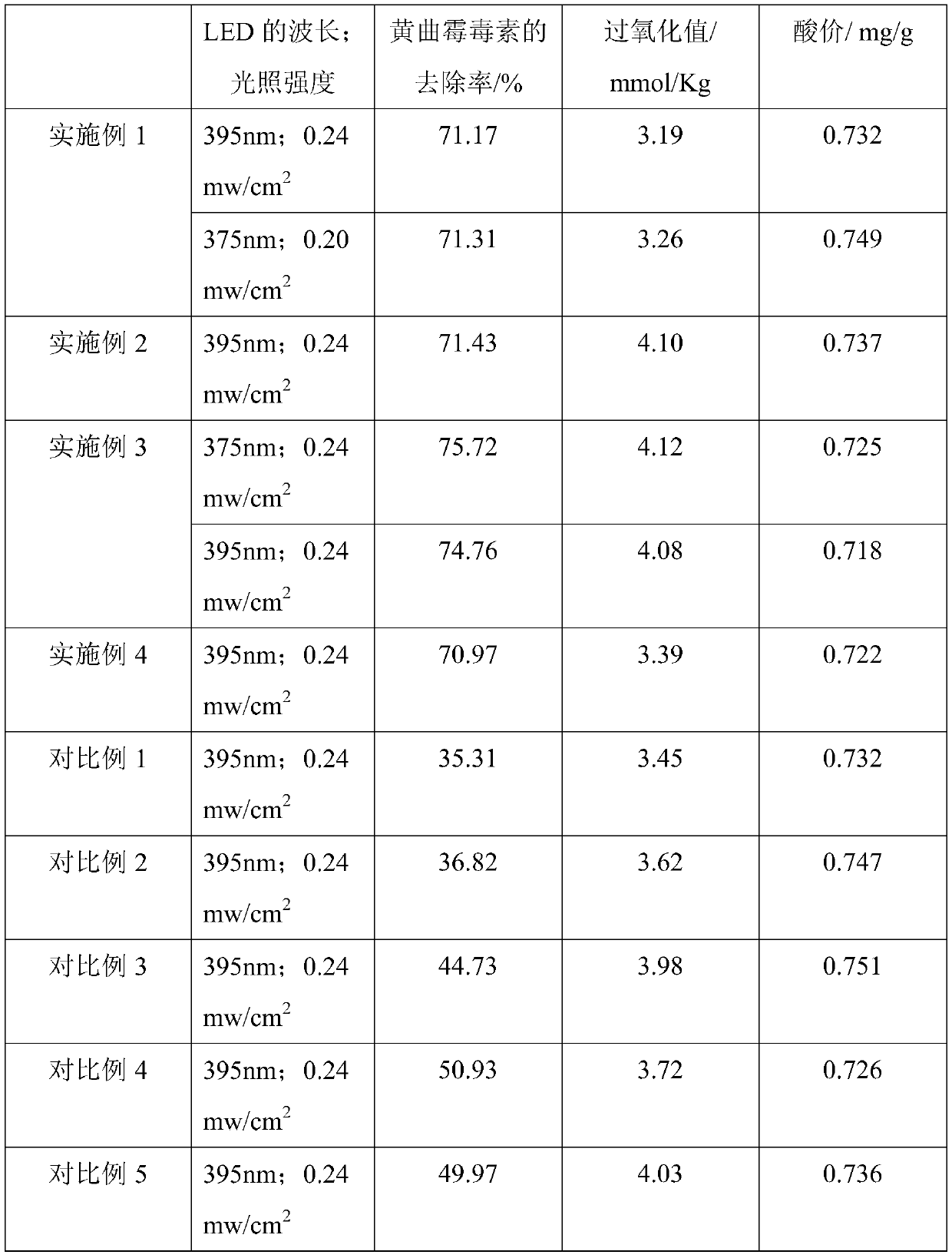
Doping-modified TiO2 photocatalytic thin film, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110935476AWide photoresponse rangeImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsFatty-oils/fats refiningPhoto catalyticPhotocatalytic degradation
The invention provides a doping-modified TiO2 photocatalytic thin film, and a preparation method and an application thereof, wherein the preparation method includes: performing composite doping modification on TiO2 thin film by using ferrous ion and iodate ion, thus effectively improving the photocatalytic absorption wavelength of the TiO2 photocatalytic thin film to 375-395 nm. The thin film is wide in photo-responding range and can employ a light-emitting diode as a photo-catalytic light source. The photocatalytic activity of the doping-modified TiO2 photocatalytic thin film is high, so thatthe thin film can be widely applied to edible oil processing field and can effectively photo-catalytically degrade aflatoxin in edible oil, and has very great application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Process for the preparation of stable iodate-exchanged synthetic hydrotalcite with zero effluent discharge
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of stable iodate-exchanged hydrotalcite with zero effluent discharge. The iodate-exchanged hydrotalcite produced is useful as iodizing agent. The invention further relates to utilization of alkaline effluent generated in the process of ion exchange of iodate into SHT so as to fully recycle the residual iodate anion and also utilize the alkali generated in the process for production of additional quantities of iodate through reaction with iodine crystals followed by electrochemical oxidation to obtain pure aqueous solution of iodate salt which can be reused for preparation of the stable iodizing agent. The process gives zero effluent discharge hence economical.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method and device for producing potassium iodate through oxygen cathode non-diaphragm electrolysis
InactiveCN102021600BPrevent restoreReduce energy consumptionElectrolysis componentsPotassium hydroxidePotassium iodine
The invention relates to a method and device for producing potassium iodate through oxygen cathode non-diaphragm electrolysis. In the device in the invention, the mixed solution of potassium iodide and potassium hydroxide is used as electrolyte, wherein iodine ions are oxidized at the anode to generate iodate ions, oxygen is reduced at the cathode to generate hydroxyl ions; the liquid generated by electrolysis is cooled to precipitate potassium iodate crystals; and after potassium iodide and water are added in mother liquor, the mixture is send back to the electrolytic cell for electrolysis. The cathode of the electrolytic cell is an oxygen-consuming cathode and the anode is a corrosion resistant non-sacrificial anode, thus the cationic film or diaphragm is not required and the reduction of iodate ions at the cathode can be avoided. The method is obviously characterized in that the cell voltage is only about 0.6-1.0V, thus the energy consumption can be greatly reduced; the whole flow is performed circularly; and the electrolytic cell has simple structure, no ion film and low operating cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Modified electrode for detecting iodate and preparation method
InactiveCN101995423AEasy to prepareImprove stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesSodium acetateCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a modified electrode for detecting iodate and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps of using a piece of metallographic sand paper to polish a glassy carbon electrode, cleaning respectively with acetone, ethanol, a NaOH solution, an HNO3 solution and secondary distilled water, and drying; scanning the glassy carbon electrode in 0.5mol / L H2SO4 between the voltage of 0.2V below 0.2V and 1.2V to stably drying with a scanning speed of 50mV.S<-1>; and heating a multi-wall carbon nano-tube to 120 DEG C with concentrated nitric acid, refluxing for 14h, pumping, filtering, washing to be in a neutral state, arranging the glassy carbon electrode in a suspension to obtain a repeated voltammetric signal, and washing with the secondary distilled water to make a load phospho-molybdic acid modified electrode of the multi-wall carbon nano-tube. The load phospho-molybdic acid modified electrode is arranged into iodate ion solutions with different concentrations, an acetate-sodium acetate buffer solution is added, and the concentration of iodate ions is calculated. The invention has the advantages of simpleness, rapidness and good stability of the electrode. Analysis and detection of the iodate by using the modified electrode have the advantages of rapid analysis speed, wide detection range and good repeatability.
Owner:ZUNYI NORMAL COLLEGE
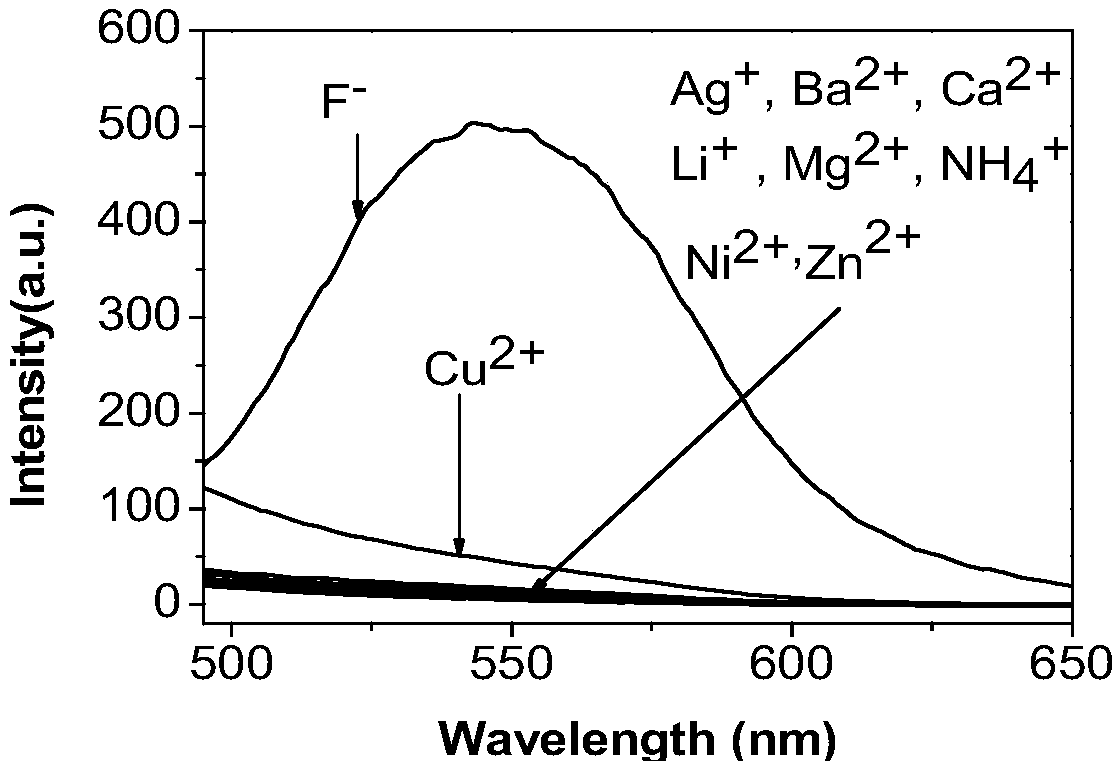
A fluoride ion detection probe based on aggregation-induced luminescence and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106632450BSensitive recognitionStrong specificityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescenceRaw material
The invention discloses a fluorine ion detection probe based on aggregation-induced emission as well as a preparation method and application of the fluorine ion detection probe. The structure of a fluorescent probe is shown as a formula (I); the fluorescent probe is formed by taking salicylic aldehyde as a raw material, forming salicylic aldehyde azine through the raw material and hydrazine hydrate and carrying out silicon protection. The probe disclosed by the invention has stable optical performances, high fluorine ion detection sensitivity and low detection lower limit; the detection limit is 1mu.M and a response range is 1mu.M to 50mu.M. The fluorine ion detection probe has good selectivity and no response on negative and positive ions including chlorine ions, bromine ions, iodate ions, periodate ions, nitrate ions, nitrite ions, acetate ions, carbonate ions, sulfate ions, sulfite ions, silver ions, barium ions, calcium ions, lithium ions, magnesium ions, ammonium ions, nickel ions, zinc ions and the like. The fluorine ion detection probe has the advantages of simple synthesis, moderate conditions and high yield. The fluorescent molecular probe has an actual application value in the fields of biochemistry and environmental chemistry, especially detection of fluorine ions in water and the like. (The formula (I) is shown as the description.).
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Iodate-containing chemical-mechanical polishing compositions and methods
The invention provides compositions and methods for planarizing or polishing a substrate. The composition comprises an abrasive, iodate ion, a nitrogen-containing compound selected from the group consisting of a nitrogen-containing C4-20 heterocycle and a C1-20 alkylamine, and a liquid carrier comprising water.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Method for attaching two surfaces to each other using a bioadhesive polyphenolic protein and periodate ions
The present invention pertains to a method for attaching two surfaces to each other or coating a surface by providing a bioadhesive composition consisting of an aqueous solution of a bioadhesive polyphenolic protein derived from a byssus-forming mussel, and mixing said bioadhesive composition with a preparation comprising non-enzymatic oxidising periodate ions so that the concentration of periodate ions is at least 1.80 mmol / g in the final composition before applying the mixture to at least one of two surfaces to be attached to each other or coated or applying said composition and said periodate ions without any specific order, to at least one of two surfaces to be attached to each other or the surface to be coated, thereby mixing the bioadhesive composition and the periodate ions. The surfaces are then joined (if necessary) and left for sufficiently long time for curing to occur. The invention can be provided as a kit of parts comprising the MAP-solution, a preparation comprising the periodate ions and optionally a device to apply the compositions of the invention to surfaces that are to be attached to each other or coated.
Owner:BIOPOLYMER PRODS OF SWEDEN
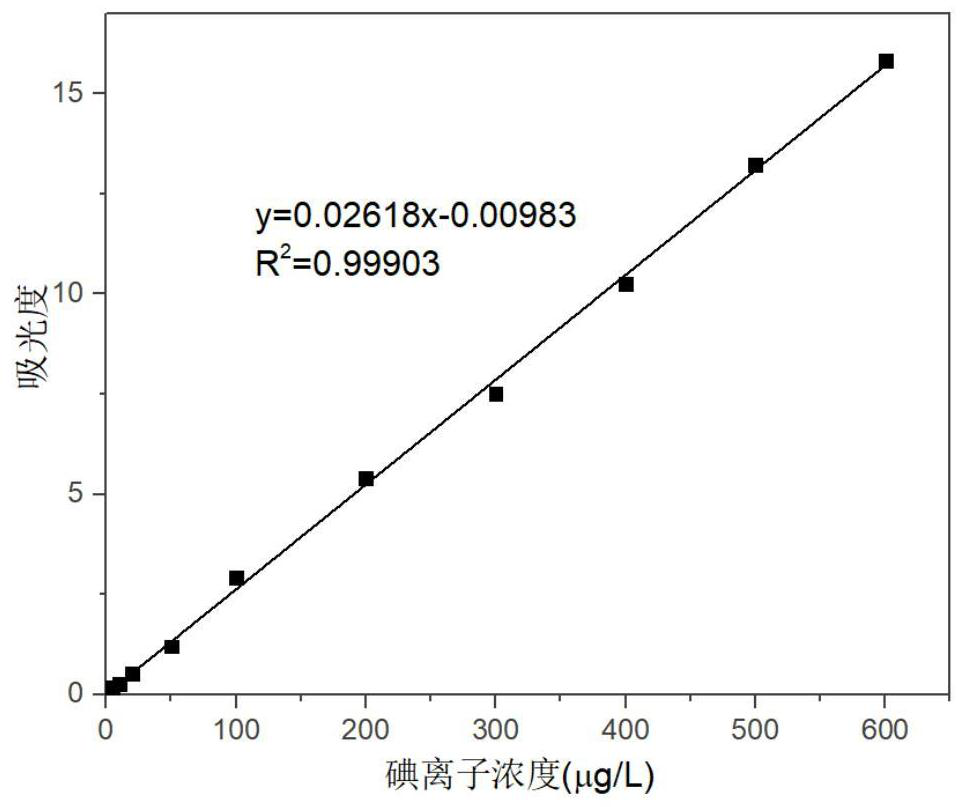
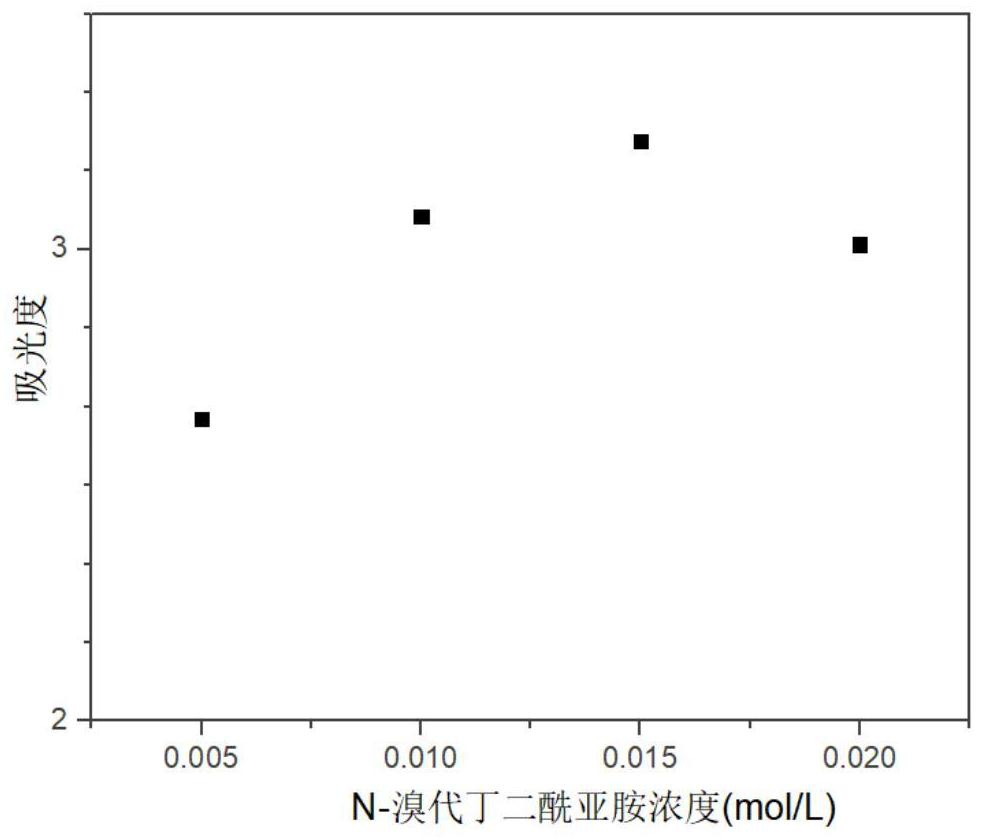
A high-precision urine iodine test method
ActiveCN111175241BHigh-precision urine iodine test safetyHigh-precision urine iodine test is convenientColor/spectral properties measurementsTriiodideUrine iodine
The invention discloses a high-precision urine iodine detection method which comprises the following steps: by taking N-bromosuccinimide as an oxidizing agent, oxidizing iodide ions in urine into iodate ions, introducing tetrabutylammonium iodide to react with the iodate ions, and forming an ion association compound by utilizing the electrostatic attraction effect between tetrabutylammonium cations and triiodide anions; and the ionic association compound is subjected to extraction and absorbance detection to establish a linear relationship between the iodine ion concentration and absorbance, thereby implementing high-precision detection on urine iodine. By means of the mode, the urine iodine can be safely and conveniently subjected to high-precision detection, the detection method is simple, convenient and easy to implement, high in detection speed and low in detection cost, the detection process has high sensitivity, precision and accuracy, high-precision detection of the urine iodinecan be achieved, the requirements of practical application can be met, and high application value is achieved.
Owner:北京中西医结合医院
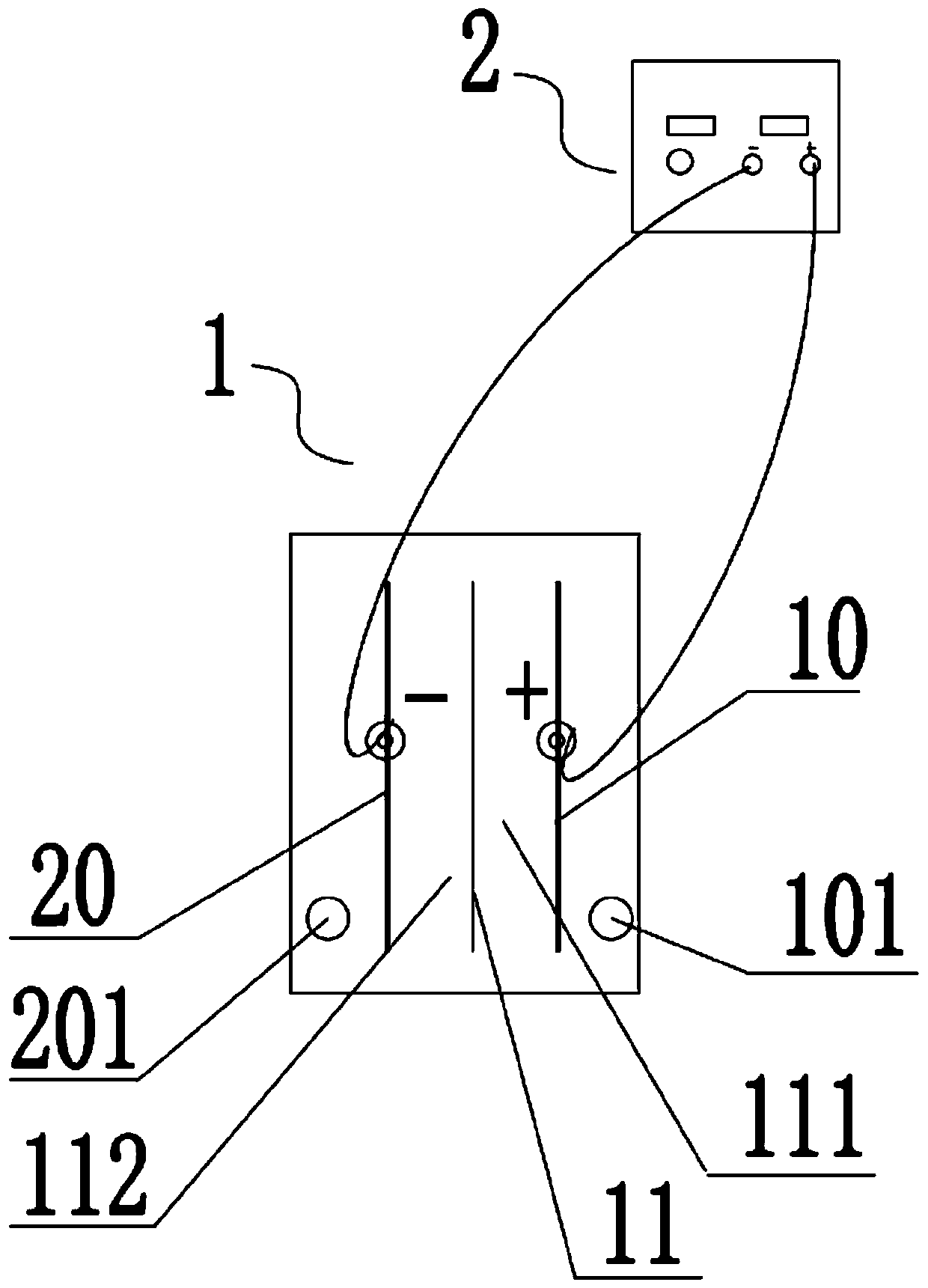
Vehicle-mounted power battery
InactiveCN110504442ASolve the problem of longevitySolve charging problemsCell electrodesFinal product manufacturePower batteryNew energy
The invention relates to a vehicle-mounted power battery, which relates to the technical field of new energy, and is used for solving the technical problems of low efficiency, non safety and non environmental protection in the prior art and solving the problem of inconvenient charging of a new energy power vehicle. According to the vehicle-mounted power battery, hydroiodic acid and iodic acid areadopted as raw materials of the vehicle-mounted power battery; when the vehicle is started, a reduction reaction is generated in a positive electrode chamber, iodate ions obtain electrons to form elemental iodine, an oxidation reaction occurs in a negative electrode chamber, and iodine ions lose electrons to generate elemental iodine; when the electric quantity of the power battery is reduced to acertain value, the hydroiodic acid and the iodic acid are replaced; liquids discharged from different discharge holes are subjected to redox treatment so as to meet the re-replacement requirements; and the liquids are infinitely recycled, so that the problems that a traditional vehicle-mounted battery is difficult to charge and slow in charging are solved, and the problem on the battery life is also solved.
Owner:SHANDONG RUIKE ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Metal-organic nanotube microporous crystalline material encapsulating [vw12]4-clusters and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN105772093BStable crystal structureStable and efficient electrocatalytic activityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsModified carbonCarbon paste electrode
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring iodine content in multi-mineral calcium iodate
PendingCN114018839AConsistent transformation processConsistent ratePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsIron sulfatePotassium thiocyanate
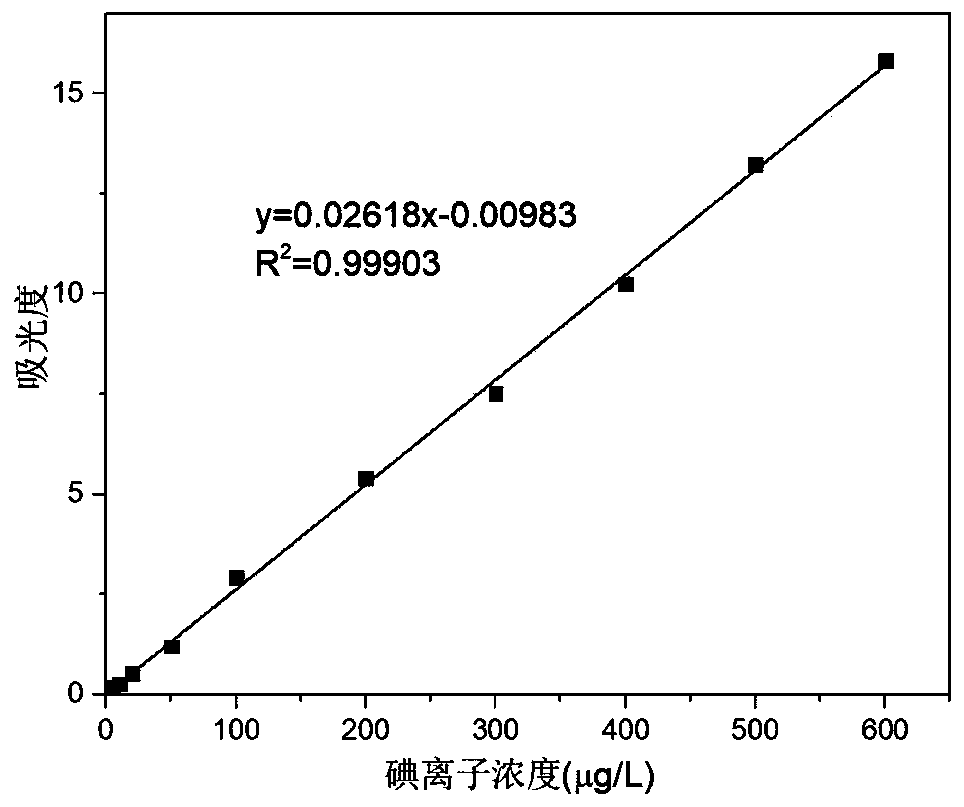
The invention belongs to the field of feed additive detection, and particularly relates to a method for measuring iodine content in multi-mineral calcium iodate, which comprises the following steps: 1) pretreatment of a sample: dissolving the sample with an acid solution, adding a sulfide reducing agent to reduce iodate ions into iodide ions, and fixing the volume to obtain a sample solution; and 2) measuring the absorbance value of the sample solution, comparing the absorbance value with a standard curve of iodate ions, and calculating and obtaining the iodine content of the sample. A drawing method of the standard curve of the iodate ions comprises the following steps: dissolving a calcium iodate standard sample with acid, adding a sulfide reducing agent to reduce the iodate ions into iodide ions, and fixing the volume; and adding a potassium carbonate solution, distilled water and a potassium thiocyanate-sodium nitrite solution, uniformly performing mixing, adding an ammonium ferric sulfate-nitric acid solution, uniformly performing mixing, keeping the constant temperature, adding a color fixing agent, performing mixing, and measuring absorbance values to obtain a standard curve of iodate ions. The measurement method is higher in accuracy.
Owner:HUNAN DEBANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Process for the preparation of stable iodate-exchanged synthetic hydrotalcite with zero effluent discharge
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of stable iodate-exchanged hydrotalcite with zero effluent discharge. The iodate-exchanged hydrotalcite produced is useful as iodizing agent. The invention further relates to utilization of alkaline effluent generated in the process of ion exchange of iodate into SHT so as to fully recycle the residual iodate anion and also utilize the alkali generated in the process for production of additional quantities of iodate through reaction with iodine crystals followed by electrochemical oxidation to obtain pure aqueous solution of iodate salt which can be reused for preparation of the stable iodizing agent. The process gives zero effluent discharge hence economical.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
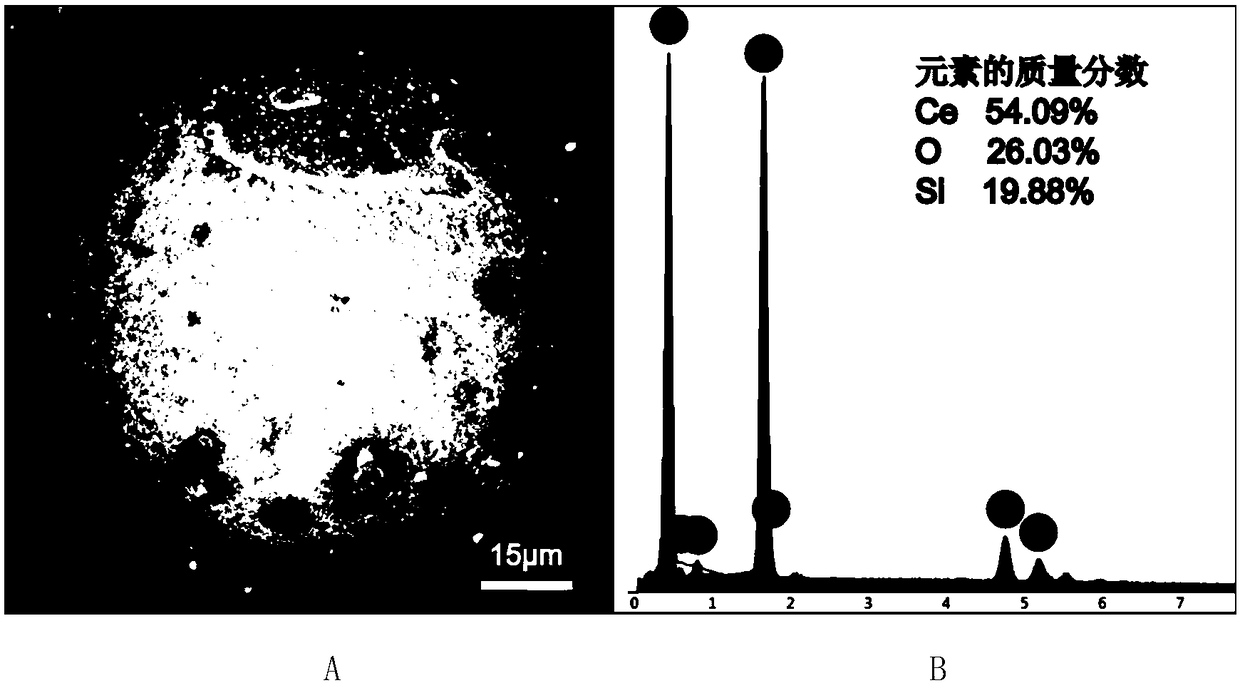
Preparation and application of cerium oxide modified porous silicon-based microsphere adsorbent
ActiveCN108499518AReduce consumptionReduce usageOther chemical processesWater contaminantsEvaporationCerium
The invention discloses a preparation method of cerium oxide modified porous silicon-based microspheres. A cerium salt aqueous solution is supported on porous silicon-based microspheres by using a vacuum rotary evaporation technology. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, a vacuum rotary evaporation technology is adopted, the reaction condition in a whole experimental process is mild, high-temperature calcination is not needed, the energy consumption is reduced, the experimental cost is saved, the preparation process is simple, the operation is easy, and the use of binders and other additives is avoided. Experiments show that the efficiency of preparing CeO2.nH2O@SiO2 porous microspheres by the method provided by the invention is high, the sphericity of the productis high, the particle size distribution is uniform, the specific surface area is up to 70m<2> / g, and the microspheres can be directly packed into a column for a column separation experiment. A resultshows that CeO2.nH2O@SiO2 porous microspheres provided by the invention have a high CeO2 loading capacity, have a good adsorption effect on fluoride ions and iodate ions in water, and have a wide application prospect in the treatment of water pollution.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Urine iodine determination kit and determination method thereof
InactiveCN111693517AReduce labor costsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsSulfate radicalsPhenanthroline
The invention discloses a urine iodine determination kit. The urine iodine determination kit comprises the following raw materials: a reagent R1 and a reagent R2. According to the invention, the urineiodine determination kit and the determination method thereof are strictly controlled; the proportion of each component of the urine iodine determination kit and preparation process parameters are strictly controlled; the urine is digested through ammonium persulfate; the urine does not need to be pretreated before detection; ferric ions react with iodide ions to generate ferrous ions and iodine,iodine reacts with sulfite ions and iodate ions to generate sulfate ions and iodide ions, the concentration of iodide ions in urine is determined by utilizing the indicator effect of phenanthroline on different iron ions, large-batch detection can be carried out, and a large amount of labor cost is reduced.
Owner:程明
A doped modified tio 2 Photocatalytic film and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110935476BWide photoresponse rangeImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsFatty-oils/fats refiningPhotocatalytic degradationEdible oil
The invention provides a doped modified TiO 2 Photocatalytic thin film and its preparation method and application. The preparation method adopts successively ferrous ion and iodate ion to TiO 2 The compound doping modification of the thin film effectively improves the TiO 2 The photocatalytic absorption wavelength of the photocatalytic thin film is 375-395nm, the photoresponse range is wide, and the light-emitting diode can be used as the photocatalytic light source. The doped modified TiO of the present invention 2 The photocatalytic film has high photocatalytic activity, can be widely used in the field of edible oil processing, can effectively photocatalyze the degradation of aflatoxin in edible oil, and has a very broad application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
High-precision urine iodine detection method
ActiveCN111175241AHigh-precision urine iodine test safetyHigh-precision urine iodine test is convenientColor/spectral properties measurementsTriiodideUrine iodine
The invention discloses a high-precision urine iodine detection method which comprises the following steps: by taking N-bromosuccinimide as an oxidizing agent, oxidizing iodide ions in urine into iodate ions, introducing tetrabutylammonium iodide to react with the iodate ions, and forming an ion association compound by utilizing the electrostatic attraction effect between tetrabutylammonium cations and triiodide anions; and the ionic association compound is subjected to extraction and absorbance detection to establish a linear relationship between the iodine ion concentration and absorbance, thereby implementing high-precision detection on urine iodine. By means of the mode, the urine iodine can be safely and conveniently subjected to high-precision detection, the detection method is simple, convenient and easy to implement, high in detection speed and low in detection cost, the detection process has high sensitivity, precision and accuracy, high-precision detection of the urine iodinecan be achieved, the requirements of practical application can be met, and high application value is achieved.
Owner:北京中西医结合医院
Method suitable for continuously removing iodine in spent fuel dissolving liquid
ActiveCN112037954ASolve pollutionReduce generationNuclear energy generationRecycling and recovery technologiesFuel reprocessingChemical reaction
The invention belongs to the technical field of spent fuel post-treatment processes, and discloses a method for efficiently and continuously removing iodine in spent fuel post-treatment dissolving liquid. According to the method, oxynitride is used as expelling gas, iodine ions and iodate ions in the spent fuel dissolving solution are subjected to a chemical reaction through the expelling gas to generate molecular iodine, and then air is blown in to carry iodine molecules out, so that radioactive iodine in the spent fuel dissolving liquid can be continuously expelled. According to the method,the pollution of iodine to a post-treatment process can be avoided, the generation of organic iodine is reduced, the service life of the diluent is prolonged, iodine in the spent fuel element dissolving liquid is continuously expelled, and the expelling rate is as high as 95% or above.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Electroless nickel-phosphorus-cobalt plating bath, and electroless nickel-phosphorus-cobalt plating film
PendingCN111295466AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPrinted circuit manufactureElectroless nickelNickel salt
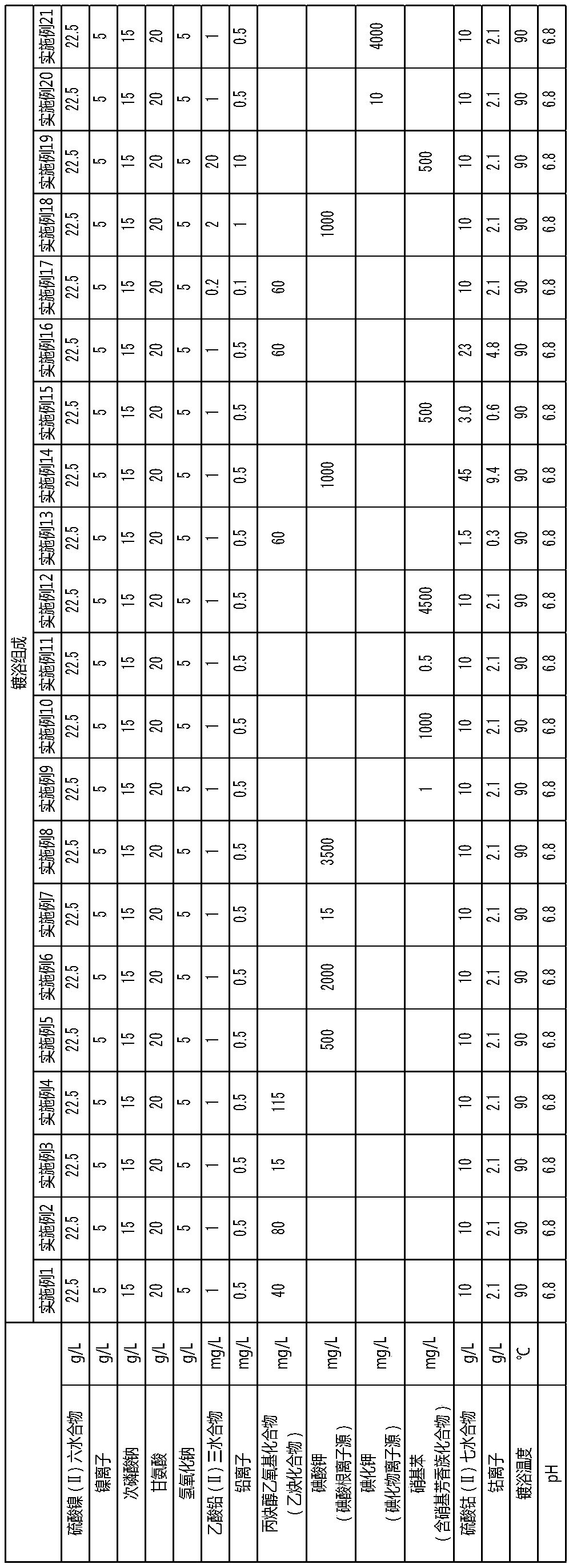
An electroless nickel-phosphorus-cobalt plating bath contains a water-soluble nickel salt, a hypophosphorous acid salt, a cobalt-containing compound and a heavy metal compound, and additionally contains at least one component selected from the group consisting of an acetylene compound, an iodide ion source or an iodic acid ion source, and a nitro-group-containing aromatic compound that contains atleast one nitro group. The concentration of the acetylene compound is 10 to 120 mg / L, the concentration of the iodide ion source or the iodic acid ion source is 10 to 4000 mg / L, and the concentrationof the nitro-group-containing aromatic compound is 0.1 to 5000 mg / L.
Owner:C UYEMURA & CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material, and preparation method and application thereof Encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material, and preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/140c304a-f5fc-48fd-be15-cff6d90c6dcd/HDA0000958057450000011.PNG)
![Encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material, and preparation method and application thereof Encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material, and preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/140c304a-f5fc-48fd-be15-cff6d90c6dcd/HDA0000958057450000012.PNG)
![Encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material, and preparation method and application thereof Encapsulated [VW12]4-cluster metal organic nanotube micropore crystalline state material, and preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/140c304a-f5fc-48fd-be15-cff6d90c6dcd/HDA0000958057450000021.PNG)











![Metal-organic nanotube microporous crystalline material encapsulating [vw12]4-clusters and its preparation method and application Metal-organic nanotube microporous crystalline material encapsulating [vw12]4-clusters and its preparation method and application](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/76647598-5140-43fa-808a-69d20e985baf/HDA0000958057450000011.png)
![Metal-organic nanotube microporous crystalline material encapsulating [vw12]4-clusters and its preparation method and application Metal-organic nanotube microporous crystalline material encapsulating [vw12]4-clusters and its preparation method and application](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/76647598-5140-43fa-808a-69d20e985baf/HDA0000958057450000012.png)
![Metal-organic nanotube microporous crystalline material encapsulating [vw12]4-clusters and its preparation method and application Metal-organic nanotube microporous crystalline material encapsulating [vw12]4-clusters and its preparation method and application](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/76647598-5140-43fa-808a-69d20e985baf/HDA0000958057450000021.png)