Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
132 results about "Impact fracture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A: An impacted fracture is a bone fracture in which the parts of the broken bone are driven toward or into each other by force, according to WiseGeek. This type of fracture often occurs as a result of a fall or an impact.
Safety glass protection screen for LCD, LCD using the same
InactiveCN101295030AHigh light transmittanceIncrease productivityLayered productsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayTransmittance
The invention provides a safety glass protective screen with high light transmittance used for a liquid crystal display device, comprising a glass substrate, wherein, at least one surface of the glass substrate is compounded with a layer of plastic film by using a resin binder, the glass substrate and / or the plastic film surface are / is plated with a transmission-increasing and reflection-deducting film syngenic membrane which is composed of an Nb2O5 / SiO2 film or a TiO2 / SiO2 film. The protective screen of the invention can reduce the reflectivity and improve the light transmittance and the effect of an optical image, fully improve the impact fracture resistant capacity of a display screen and become the safe protective screen. The invention also provides the liquid crystal display device using the glass protective screen.
Owner:甘国工
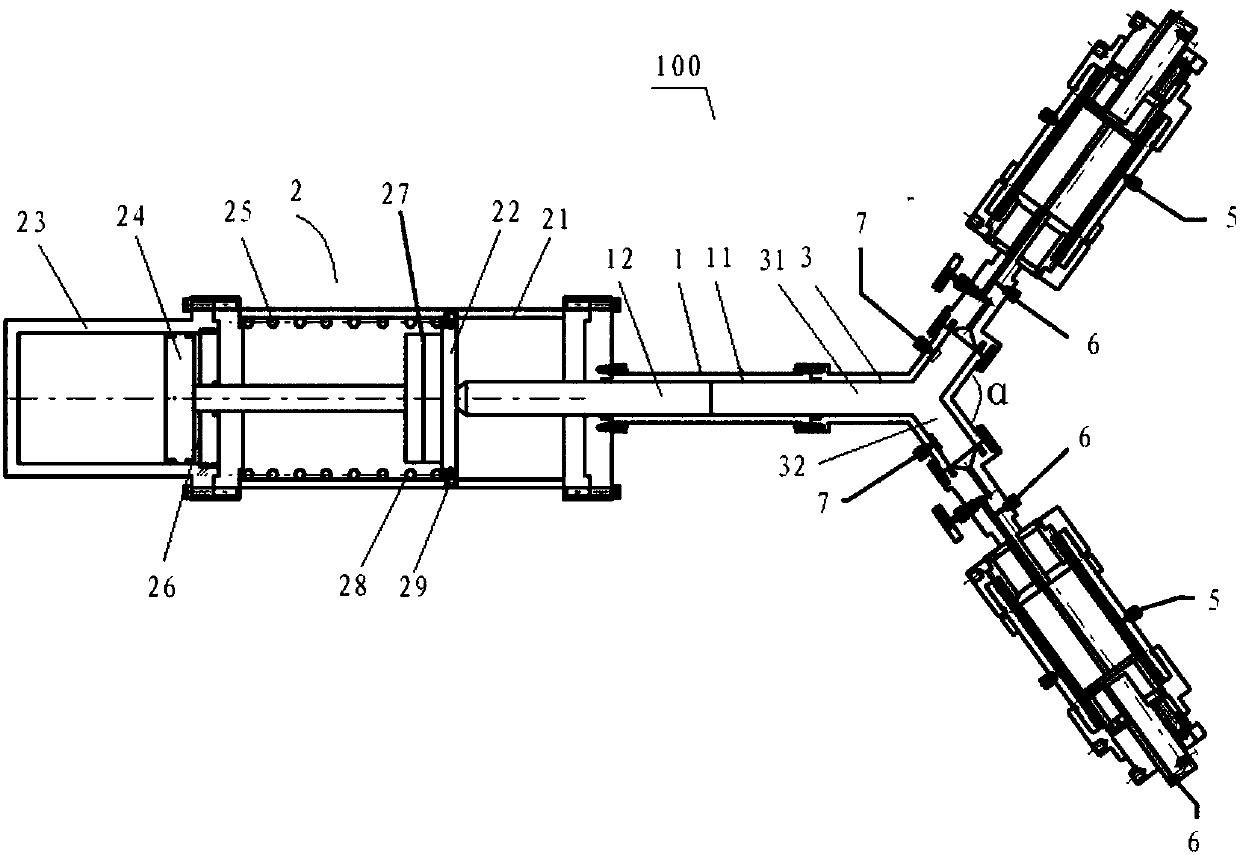
High Speed, Increased Hydrodynamic Efficiency, Light-Weight Molded Trawl Door and Methods for Use and Manufacture
A trawl door having enhanced and rather high efficiency, lightness of weight in water and ease of manufacture. The trawl door preferably includes at least one slat and preferably two slats (6, 7) disposed forward of the leading edge (31) of a single main deflector body (2), and the main deflector has a profile wherein: (I) the outer side surface (28) of said main deflector body exhibits greater camber than does the inner side surface (29) of said main deflector body; (II) the thickest part of the profile of said main deflector body is located front of center; and (III) the outer side surface (28) is convex and the inner side surface (29) is concave. In one aspect the trawl door of the invention including at least a synthetic portion, preferably a mixture of a polyamide and an elastomer, whereby the synthetic material forming the at least a synthetic portion of the trawl door receives impacts fracture free.
Owner:CANDIS EHF
Combined using method for optical cable and mine cable and mine cable as fiber-optical communication
ActiveCN101750685ASolve communication coverage problemsFix coverage issuesCommunication cablesFibre mechanical structuresFiberLow voltage
The invention provides a combined using method for an optical cable and a mine cable and the mine cable used as fiber optical communication, which is to arrange the optical fiber in the mine cable to ensure that the optical fiber and the cable are combined to a whole to form the mine cable used as fiber optical communication. In a connecting line cavity of explosion-proof type electrical equipment of high voltage feed switch, a low voltage feed switch, an electromagnetic initiator and the like, the end of the optical cable is manufactured into a pigtail and is connected with an optical interface of an optical transmitter and receiver through an optical fiber connector and a jumper; the optical transmitter and the receiver is connected with an intelligent integrated protective device in a main cavity through a communication interface; the jumper and the optical transmitter and receiver are connected through an optical cable explosion-proof cavity connection device, or are connected through wiring terminals on a separator of two cavities; and non-disconnected connection of non explosion proof equipment and the explosion proof high voltage equipment can adopt an optical fiber connector. The optical cable and the cable are combined into a whole without impacting fracture and insulation of the cable, so that the underground optical cable applying range is the same as that of cables to solve the problem of optical fiber communication between electric equipment; and the method saves cost because the optical cable is not required to be applied independently, so that the underground power supply and fiber-optical communication can be organically combined.
Owner:赵振海
Gas shielded welding wire with 900MPa tensile strength
InactiveCN102152025AReduce contentImprove welding strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaUltimate tensile strengthToughness
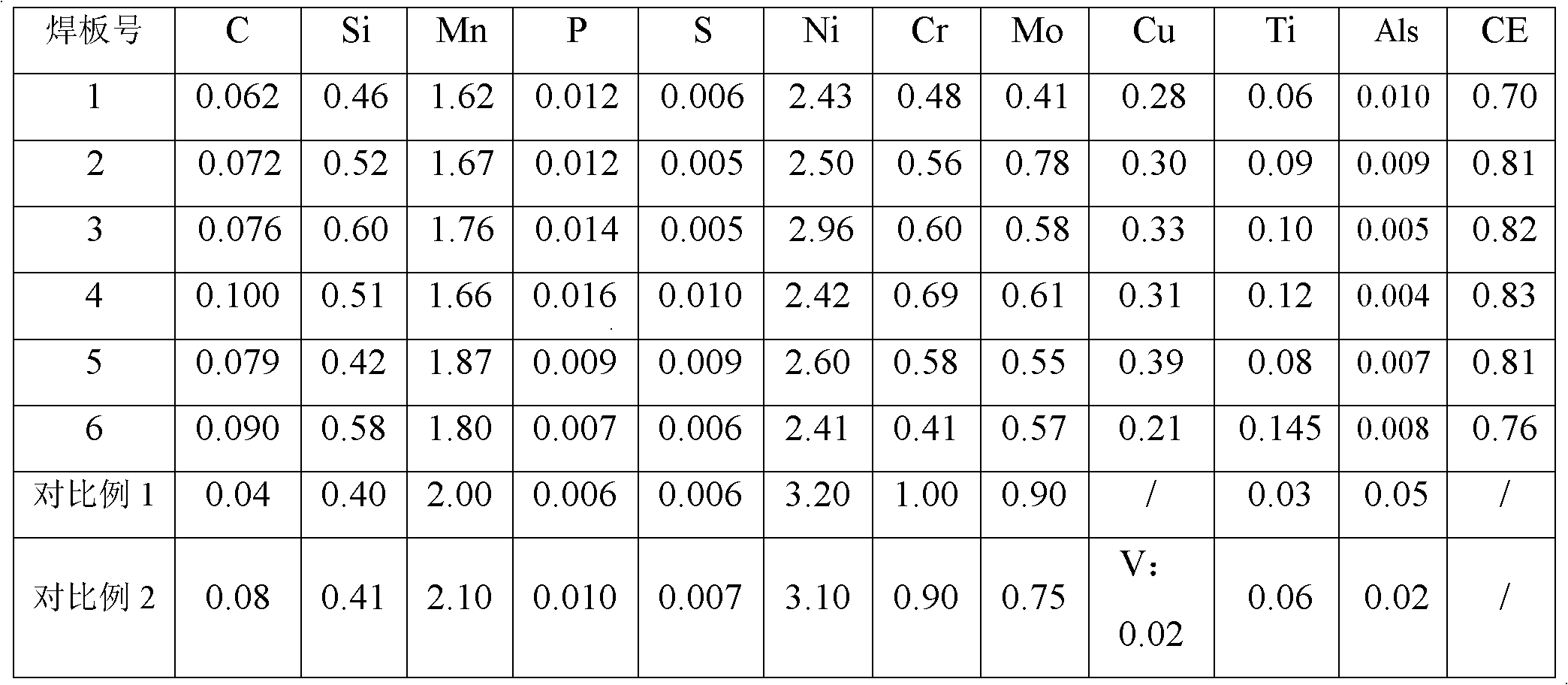
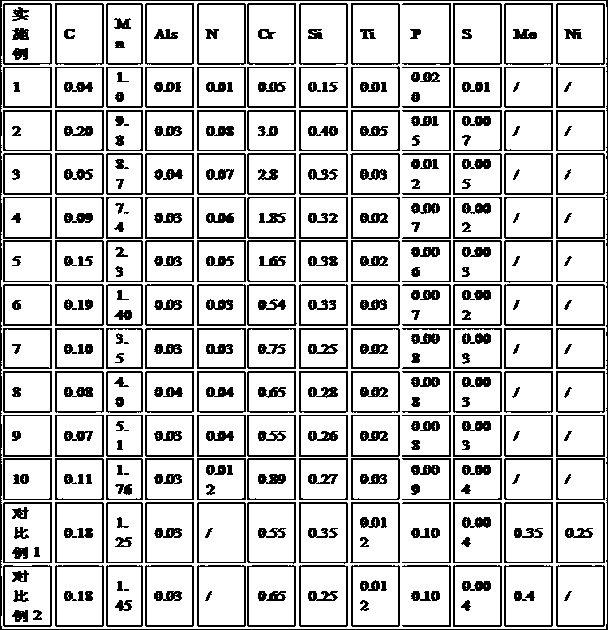
The invention relates to a gas shielded welding wire with 900MPa tensile strength, which comprises the following components in percents by weight: 0.06-0.10% of C, 0.40-0.60% of Si, 1.60-1.90% of Mn, not more than 0.020% of P, not more than 0.020% of S, 2.40-3.00% of Ni, 0.40-0.69% of Cr, 0.40-0.80% of Mo, 0.20-0.40% of Cu, 0.05-0.15% of Ti, not more than 0.005% of N, not more than 0.015% of Al and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The carbon equivalent CE of the welding wire is 0.70-0.85, and CE = C + Mn / 6 + (Ni+Cu) / 15 + (Cr+Mo+V) / 5. The invention provides a super-high strength gas shielded welding wire. The strength of welding joints is higher than 900MPa, and the toughness of the welding joints is higher than 227J at -20 DEG C KV. The textures of all parts of multiple layers of welding joints are uniform. The impact fractures are mainly dimple fractures. In the invention, the matched welding material for the application of super-high strength steel in China is provided.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
High-strength high-toughness anti-corrosion aluminum alloy for rail traffic and extrusion method of high-strength high-toughness anti-corrosion aluminum alloy
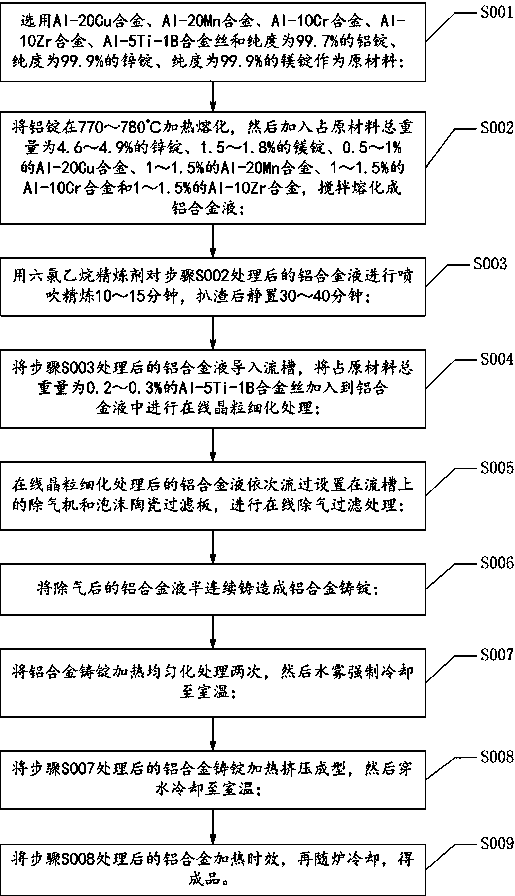
The invention discloses high-strength high-toughness anti-corrosion aluminum alloy for rail traffic and an extrusion method of the high-strength high-toughness anti-corrosion aluminum alloy. The high-strength high-toughness anti-corrosion aluminum alloy is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 4.6 to 4.9 percent of Zn, 1.5 to 1.8 percent of Mg, 0.1 to 0.2 percent of Cu, 0.2to 0.3 percent of Mn, 0.1 to 0.15 percent of Cr, 0.1 to 0.15 percent of Zr, 0.01 to 0.015 percent of Ti, 0.002 to 0.003 percent of B, less than or equal to 0.15 percent of Fe, less than or equal to 0.1 percent of Si and the balance of Al and other inevitable impurities. The extrusion method comprises the following steps: melting of aluminum alloy liquid, in-furnace spray blowing refining, onlinegrain refining, online degassing and filtering, semicontinuous casting, ingot homogenizing, heating and extruding, online quenching and artificial ageing treatment. The high-strength high-toughness anti-corrosion aluminum alloy disclosed by the invention is high in strength and good in plasticity, has excellent impact fracture toughness and excellent stress corrosion resistance, and is suitable for rail traffic vehicles.
Owner:佛山市三水凤铝铝业有限公司 +1
Method for rapidly acquiring impact fracture characteristics of brittle material
InactiveCN102129508AFast access to crack growthGet crack extensionMaterial strength using single impulsive forceSpecial data processing applicationsInternal memoryComputer science
The invention discloses a method for rapidly acquiring the impact fracture characteristics of a brittle material, which comprises the steps that: the serial numbers of fracture-pending finite elements are obtained through finite element positioning components; according to the serial numbers of the finite elements, discrete element generating components are used for generating 8 discrete elementsinside each finite element by means of an isoparametric inverse transformation method, and according to the scale of the discrete elements, memory spaces are allocated in an internal memory of a computer adopting the method; and kinematic and mechanic information of each finite element is transferred to the 8 discrete elements generated therein through element information transferring components so that the kinematic and mechanic information of the finite elements and the discrete elements before and after replacement are approximately equivalent; yjr information of the finite elements and the discrete elements in the internal memory are updated through element information updating components; and finally, fracture characteristics, such as crack extension, splashing of fragments and the like, of the brittle material under the action of impact load are rapidly acquired through fracture characteristic acquiring components.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
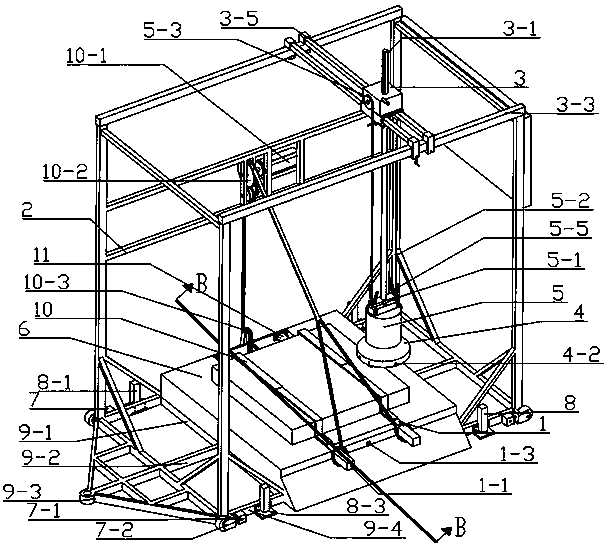
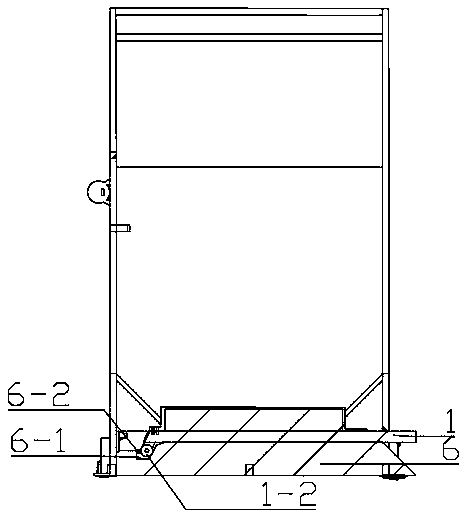
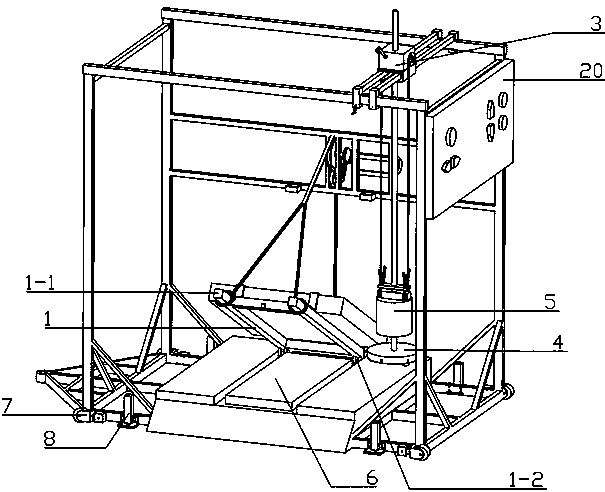
Novel multifunctional impact fracture test device and use method thereof
The invention discloses a novel multifunctional impact fracture test device and a use method thereof. The device comprises a movable test frame capable of ascending and descending, a combined supporting plate, a multi-form hammer, a multi-azimuth hammer movable assembly and an impact drop hammer, wherein the combined supporting plate is arranged at the bottom of the movable test frame capable of ascending and descending; a trolley is arranged on the combined supporting plate, the front part of the trolley is rotationally connected with the combined supporting plate, the rear part of the trolley is detachably connected with the front side of the movable testing frame capable of ascending and descending, and the lower part of the trolley is matched with the combined supporting plate; the multi-form hammer is movably connected with the movable test frame capable of ascending and descending through the multi-azimuth hammer movable assembly; the upper part of the multi-form hammer is matched with the lower part of the impact drop hammer, the impact drop hammer is arranged between the multi-form hammer and the multi-azimuth hammer movable assembly, the upper part of the impact drop hammer is movably connected with the multi-azimuth hammer movable assembly, and the multi-azimuth hammer movable assembly is movably connected with the upper part of the movable test frame capable of ascending and descending. The device has the advantages of being flexible, convenient to use and suitable for various working conditions.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Labeled resin container
ActiveUS20050276943A1Easy to peelReduced adhesion strengthEnvelopes/bags making machineryContainer decorationsPolymer scienceEngineering
Disclosed is an in-mold labeled thermoplastic resin container specifically so designed that the ratio of the product A of the Gurley stiffness (m·kgf) and the 3% elongation load (kgf) of the label-edge part of the labeled area thereof to the product B of the Gurley stiffness and the 3% elongation load of the label-surrounding part of the non-labeled area thereof, A / B, is at most 0.6. The container has good drop impact fracture resistance and has good producibility, and it is lightweight.
Owner:YUPO CORP
Deflagration fracturing and hydraulic impact fracturing combination pipe column and combination method
The invention belongs to the technical field of oil and gas field reservoir reconstruction and discloses a deflagration fracturing and hydraulic power impact fracturing combination pipe column and combination method. The combination pipe column is connected in series with a hydraulic power impact fracturing device and a deflagration fracturing device through an oil pipe or a drill pipe and an adapter buckle. A central tube is built in the hydraulic power impact fracturing device and is used for transmitting liquid pressure applied by a ground pump through the combination pipe column so as to perform deflagration fracturing operation; according to the combination method, the combination pipe column is lowered to a predetermined working position, deflagration fracturing operation is first performed, and then the hydraulic power impact fracturing operation is performed; the value of liquid pressure applied in the deflagration fracturing operation needs to be smaller than the value of liquid pressure applied in the hydraulic power impact fracturing operation; after reverse circulation well killing operation, the combination pipe column is taken out. Via the deflagration fracturing andhydraulic impact fracturing combination pipe column and combination method, deflagration fracturing and hydraulic impact fracturing combination of the pipe column can be realized in one trip, work trip frequency can be reduced, crack expansion and extension can be facilitated after the deflagration fracturing operation, and pipe column and work safety can be realized.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Method for screening reasonable welding process parameters based on impact toughness
ActiveCN106513925AEase of detection of deteriorationAdjust welding process parametersWelding accessoriesHeat-affected zoneAbsorbed energy
The invention discloses a method for screening reasonable welding process parameters based on impact toughness and belongs to the fields of evaluation and representation of mechanical properties of materials. The method comprises the steps: 1) pretreating a steel plate; 2) carrying out single-path welding on the steel plate to obtain a welding plate comprising a complete welding heat affected zone; 3) intercepting an impact specimen on the welding plate, and forming a V / U-shaped gap; 4) detecting the impact toughness of the impact specimen to obtain the impact absorbing energy of the impact specimen, and determining the impact fracture behavior of the heat-affected zone; and 5) judging that the welding process parameters are reasonable when the impact absorbing energy of the welding plate is larger than or equal to that of 1 / 2 of the original steel plate and the impact fracture behavior of the heat-affected zone is ductile fracture, or else, judging that the welding process parameters are unreasonable. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the welding heat-affected zone is prepared by carrying out single-pass welding on a flat plate, so that the welding process parameters can be regulated within a wide range, the deterioration degree of the impact toughness of the heat-affected zone is evaluated for different welding processes, and reasonable process parameters are screened; and the method is few in welding process, convenient and rapid in operation, capable of reducing cost and high in efficiency.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
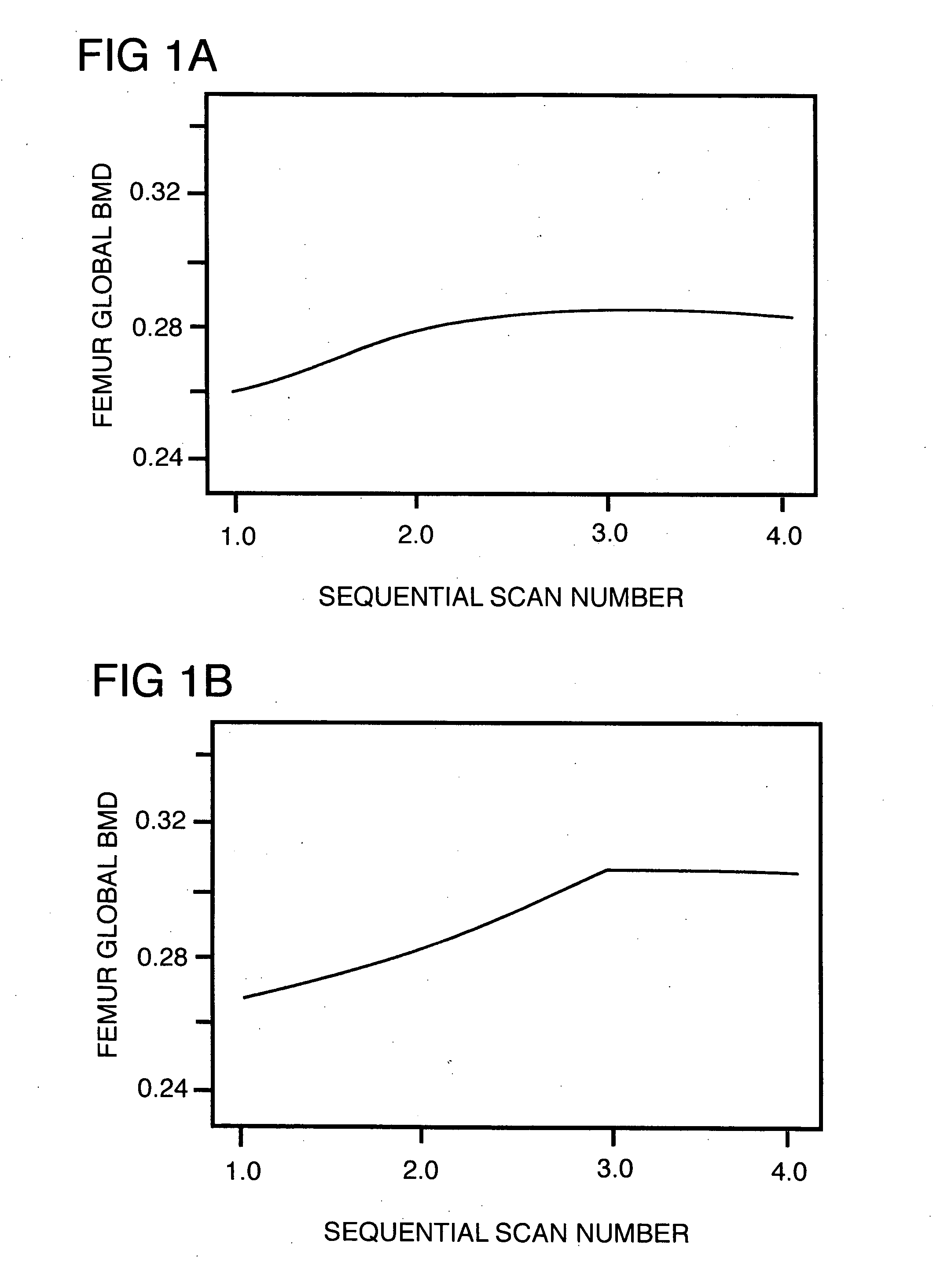
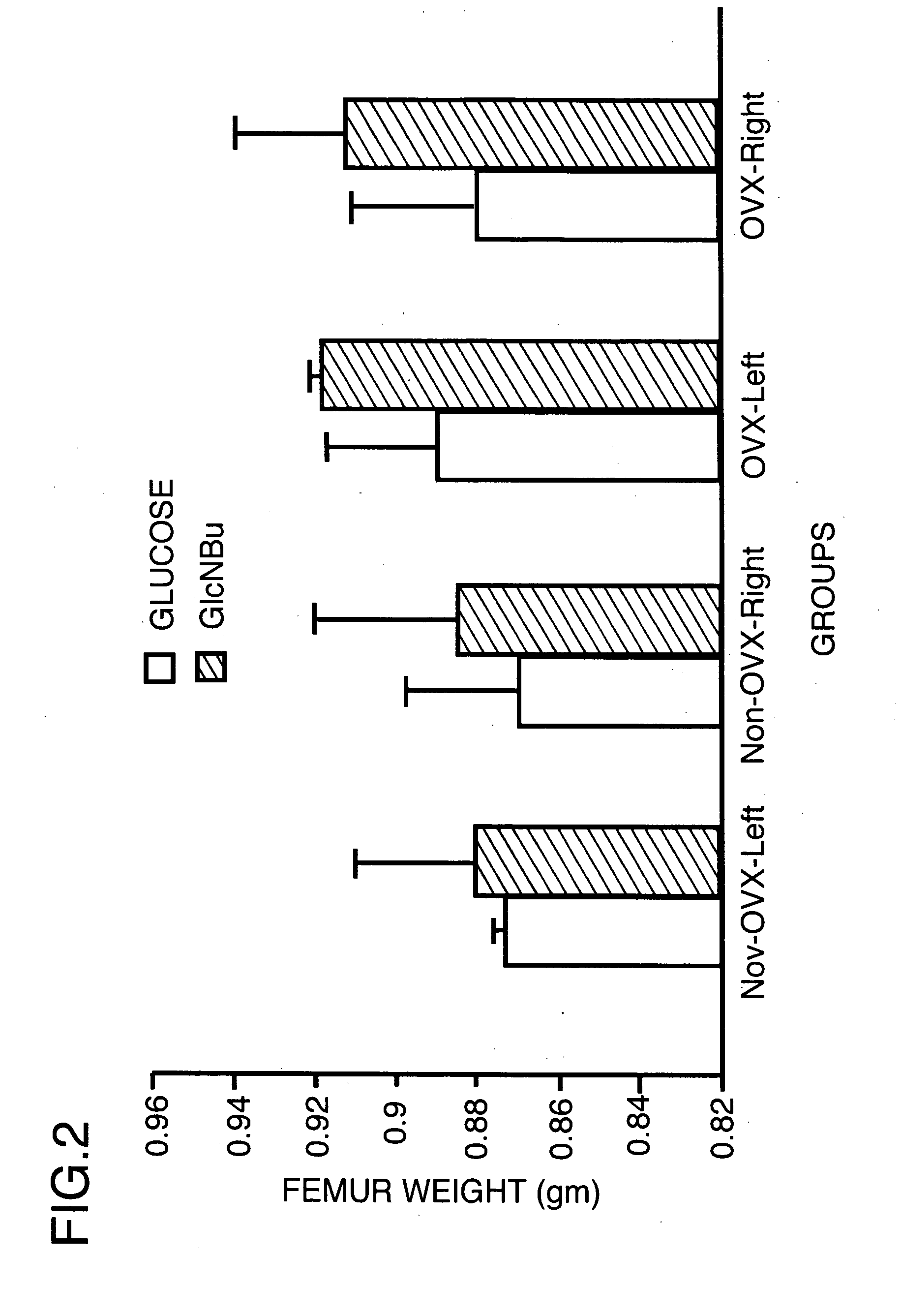
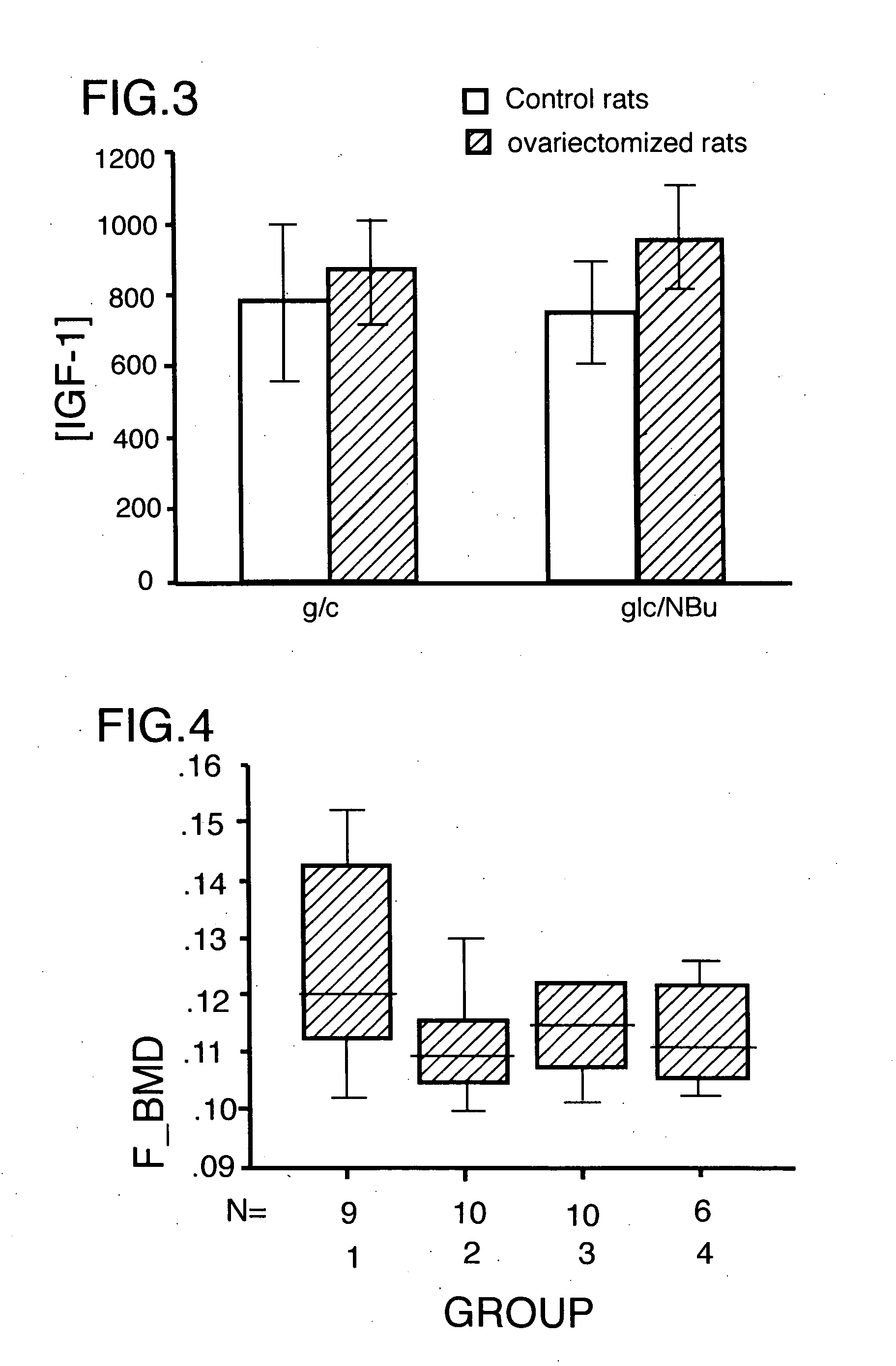
Method for increasing the bone mineral density and bone micro-architecture or connectivity of a mammal using N-acylated glucosamines
ActiveUS20060046976A1Prevent and diminish risk of fracturePromote healingBiocideSugar derivativesMammalVolumetric Mass Density
A method of treating a mammal for a purpose selected from the group consisting of (a) increasing bone mineral density (BMD), (b) treating low BMD, (c) preventing and treatment of low impact fractures, (d)treatment of high impact fractures; (e) treating osteoporosis; (f) modulating a growth factor that influences bone metabolism; and (g) improving bone micro-architecture or connectivity of bone; the method comprising administering to the mammal an effective amount of a N-acylated-2-glucosamine derivative of the general formula (I):- wherein R is an alkyl radical of the general formula CnH2n+1 and n is selected from 2-12; or pharmaceutically-acceptable salts, esters and glucosides thereof; or pharmaceutically-acceptable compositions thereof.
Owner:ANACOTI
In-situ structure analytical method for nodular cast iron metal material before and after impact fracture
InactiveCN104406847AStrength propertiesMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionMicro structureMetallography
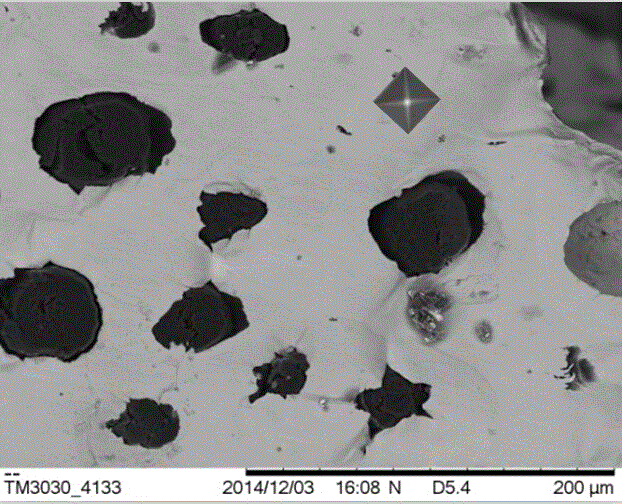
The invention belongs to the metallographic field and particularly relates to an observing and analyzing method of researching a micro structure metallograph of nodular cast iron before and after impact fracture at different temperatures. The method comprises the following steps: coarsely grinding, finely grinding, polishing and corroding two side faces of a V-shaped notch of a nodular cast iron impact test sample; observing under a microscope; selecting a classical region near the V-shaped notch; pressing a microhardness indentation at the center of the region as a mark, and photographing and storing; then, carrying out a Charpy notch impact test at different temperatures ranging from 20 DEG C to minus 80 DEG C; finally, combining the microhardness indentation and surrounding graphite nodule morphology features to obtain micro structure photos of a same region before and after impact so as to achieve comparative analysis of detail change of the nodular cast iron structure behind and after impact. The method is an in-situ structure analytical method which is wide in application range, simple to operate and high in reliability.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Large-span well segmented hydraulic impact fracturing pipe column and implementing method thereof
ActiveCN108952662AImprove work efficiencyReduce operating costsFluid removalHydraulic pumpSteel ball
The invention belongs to the technical field of oil-gas field reservoir transformation and discloses a large-span well segmented hydraulic impact fracturing pipe column and an implementing method thereof. The pipe column comprises two or more hydraulic impact fracturing devices connected in series. Except for the hydraulic impact fracturing device on the lowermost portion, the remaining hydraulicimpact fracturing devices are internally provided with guiding pipes, ball seats and central pipes and used for transmitting the liquid pressure and conducting hydraulic impact fracturing on the nextoperation section. During implementing, firstly, the pressure is increased to the pressure resistance value of an impact piece in the hydraulic impact fracturing device on the lowermost portion through a ground pump, and hydraulic impact of an operation section on the lowermost portion is completed; then, steel balls suitable for the ball seats in the hydraulic impact fracturing devices at the sections are sequentially released segment by segment from bottom to top, and pressurizing is conducted again through the ground pump, so that the central pipes are sealed by the steel balls falling intothe ball seats, pressure relief holes are opened through a pressurizing hole-opening valve, then continuous pressurizing is conducted, and when the pressurizing value reaches the pressure resistancevalue of an impact piece in the hydraulic impact fracturing device at the corresponding section, hydraulic impact of the operation section is completed; and the steps are repeated till hydraulic impact of all the operation sections is completed.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Wear-resistant alloy, silicon alloy grinding ball, silicon alloy grinding section and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102965565AReduced chromium contentBreakage resistantGrain treatmentsSilicon alloyManganese
The invention relates to a wear-resistant alloy, a silicon alloy grinding ball, a silicon alloy grinding section and a preparation method thereof. The wear-resistant alloy comprises the following substances in percentage by weight: 3.30-4.5% of carbon, 1.0-3.20% of silicon, 0.30-1.50% of manganese, 0.10%-1.30% of chromium, 0.006%-0.07% of rare earth, 0.007%-0.08% of magnesium and the balance of iron and inevitable impurities. The wear-resistant alloy provided by the invention has low content of the chromium and has the advantages of excellent resistance to impact fracture, wear resistance, crushing resistance and corrosion resistance.
Owner:清原满族自治县三方耐磨材料有限公司 +2
Time discontinuous state-based near-field dynamics method for structure impact elastic-plastic fracture analysis
ActiveCN114186456AEasy to handleOvercome the difficulty of accurately capturing the crack growth pathDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsNeighborhood searchDynamic models
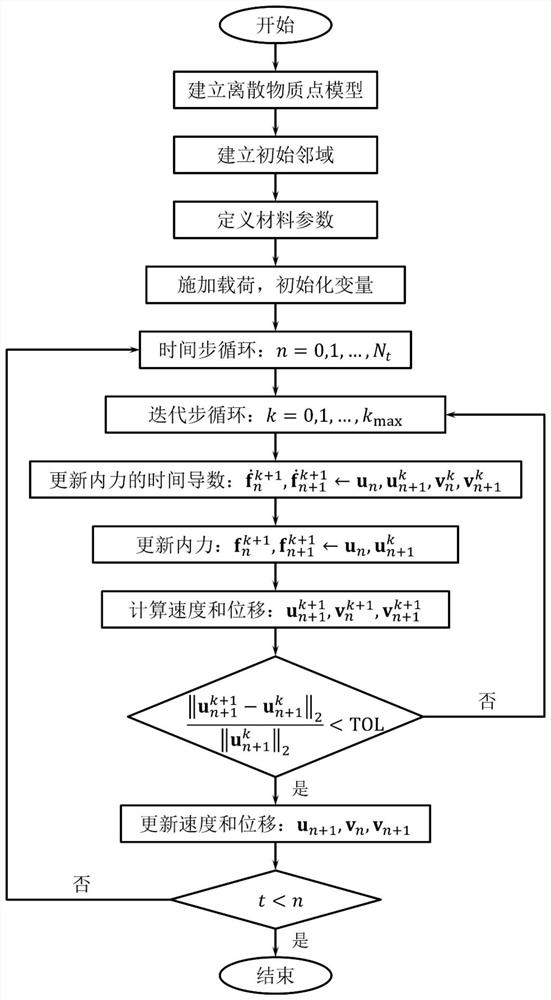
The invention belongs to the field of computational mechanics, and provides a time-discontinuous state-based near-field dynamics method for structural impact elastic-plastic fracture analysis, which introduces a time-discontinuous idea into a state-based near-field dynamics theory, and effectively improves the precision of near-field dynamics explicit dynamic analysis and the capability of accurately predicting structural fracture damage. According to the method, false numerical oscillation caused by a traditional time-history integral method can be effectively controlled by adopting a time-discontinuous explicit time-history integral format, and complex mechanical behaviors of the material under the impact load are simply, conveniently and comprehensively described by adopting an unconventional state-based near-field dynamic model; and the impact fracture failure mode of the structure is effectively represented through a plurality of damage fracture criteria. In addition, a material point neighborhood is constructed and a contact neighborhood is updated by adopting a fast neighborhood search algorithm, so that the calculation efficiency is improved. As a new numerical solution format, the method provided by the invention can be realized by simply modifying an original calculation program, and the numerical implementation complexity is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
PA6/AES composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a PA6 / AES composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material contains the following components in parts by weight: 40-70 parts of PA6, 15-30 parts of AES high rubber powder, 5-30 parts of an acrylonitrile-styrene copolymer, 3-8 parts of a compatilizer, 0.2-0.6 part of a small molecule absorbent, 0.1-0.5 part of an antioxidant and 0.2-0.5 part of a lubricant. By adding a proper amount of the compatilizer, the wear resistance of the PA6 / AES composite material is improved; the particle size of rubber in the AES high rubber powder is relatively large, and the brakeage energy can be effectively absorbed during impact fracture, so that the impact property of the composite material is improved; and by adding a proper amount of the small molecule absorbent, small molecule substances produced in the processing material can be absorbed, so that the thermal stability of the composite material is improved.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Specially-made bolt of gland of injection molding machine and heat treatment process of specially-made bolt
InactiveCN104295582AHigh tensile strengthImprove fatigue resistanceWashersNutsEngineeringInjection molding machine
The invention discloses a specially-made bolt of a gland of an injection molding machine and a heat treatment process of the specially-made bolt. The heat treatment process comprises a body treatment procedure and a heat treatment procedure. The body comprises a bolt body and a nut, the upper end of the bolt body is of an external thread-shaped structure, a spring is arranged in the middle of the bolt body, the nut is screwed into the external thread-shaped structure and presses the spring, a cylindrical baffle is arranged below the spring, the bottom of the baffle is arranged to be of a conical structure, and a circular through hole is formed in the middle of the baffle. The heat treatment process is characterized in that after the bolt is heated to be austenitized, the bolt is immersed in appropriate quenching media to be cooled at a high speed. The tensile strength of the bolt is high enough, so the bolt is resistant to lengthening, breaking, thread slipping and abrasion; the bolt also has high fatigue resistance and impact toughness, so the bolt can resist fatigue and impact fracture and be well applied to the injection molding machine.
Owner:金方明
Glass fiber web reinforced bamboo fiber mould pressing sliding plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109795182AHigh bonding strengthGood resistance to impact fractureGlass/slag layered productsEpoxyFiberglass mesh
The invention provides a glass fiber web reinforced bamboo fiber mould pressing sliding plate, which is made of bamboo veneers and prepreg arranged between the two layers of bamboo veneers, and the invention also provides a preparation method, which comprises the following steps of: sorting bamboo fibers, sequentially and crossly paving a glass fiber net and the bamboo fibers from bottom to top toobtain a preformed body, impregnating an adhesive, covering the surface of the preformed body with an epoxy resin adhesive film to obtain the prepreg, assembling the bamboo veneers and the prepreg and carrying out hot pressing molding to obtain the sliding plate. According to the invention, the assembly is simple and convenient; in the hot pressing molding process, after the epoxy resin adhesivefilm on the surface layer of the prepreg is heated, the epoxy resin adhesive can be adhered to the bamboo veneers, so that the bonding strength of the sliding plate is increased; after the hot pressing molding, the epoxy resin adhesive film has elasticity, and the sliding plate is good in shock resistance and fracture resistance; the prepreg is formed by overlapping glass fiber nets and bamboo fibers layer by layer, so that the longitudinal performance and transverse performance of the sliding plate are good; and the prepared sliding plate is light.
Owner:INT CENT FOR BAMBOO & RATTAN
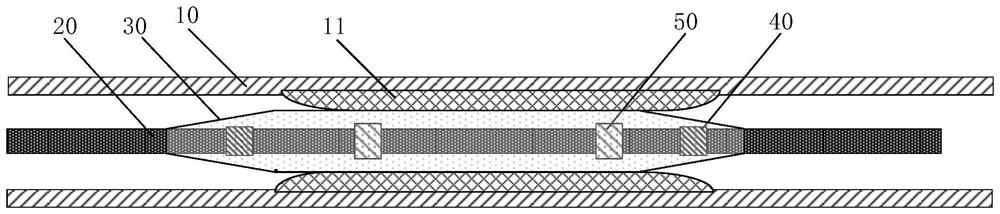
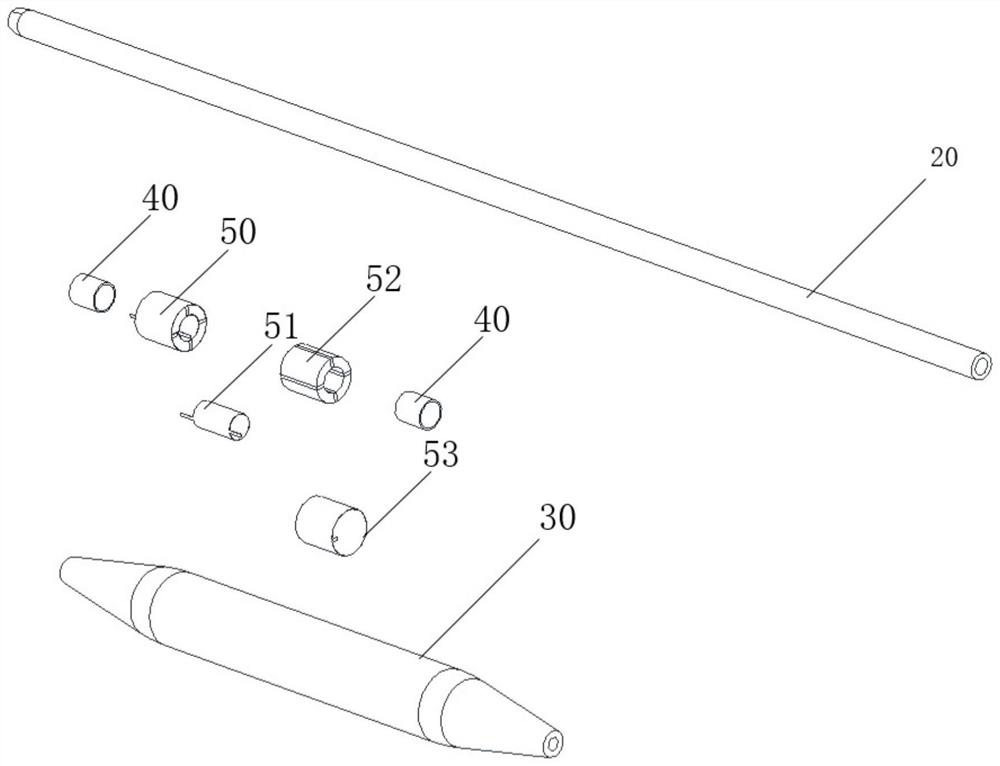
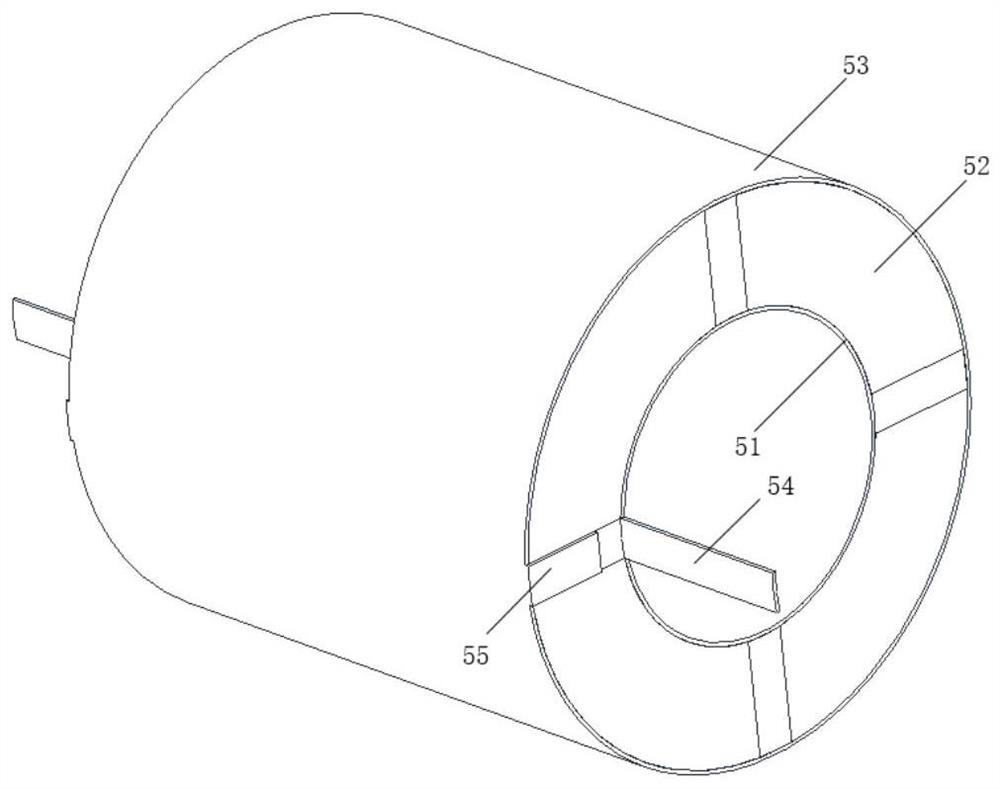
Intravascular calcified plaque impact fracture device
PendingCN114027926AImprove electromechanical conversion efficiencyReduce lossBalloon catheterSurgeryStent implantationBalloon catheter
The invention provides an intravascular calcified plaque impact fracture device, which comprises a balloon catheter, an ultrasonic transducer and a balloon arranged on the balloon catheter, wherein the ultrasonic transducer comprises a first conductive lead, a second conductive lead and an annular body arranged in the balloon and arranged on the balloon catheter in a sleeving mode, the annular body comprises a first annular electrode layer, a piezoelectric effect layer and a second annular electrode layer, the first annular electrode layer is located on the inner side in the radial direction, the second annular electrode layer is located on the outer side in the radial direction, the piezoelectric effect layer is located between the first annular electrode layer and the second annular electrode layer, and comprises a plurality of piezoelectric ceramic parts and a plurality of polymer parts without piezoelectricity, and the polymer parts and the piezoelectric ceramic parts are distributed in the circumferential direction of the annular body at intervals. According to the intravascular calcified plaque impact fracture device, the intravascular calcified plaque impact fracture effect can be well achieved, a stress ring on the calcified plaque is broken, and balloon plasty and stent implantation can be conveniently carried out.
Owner:JIAXING JIACHUANGZHI MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
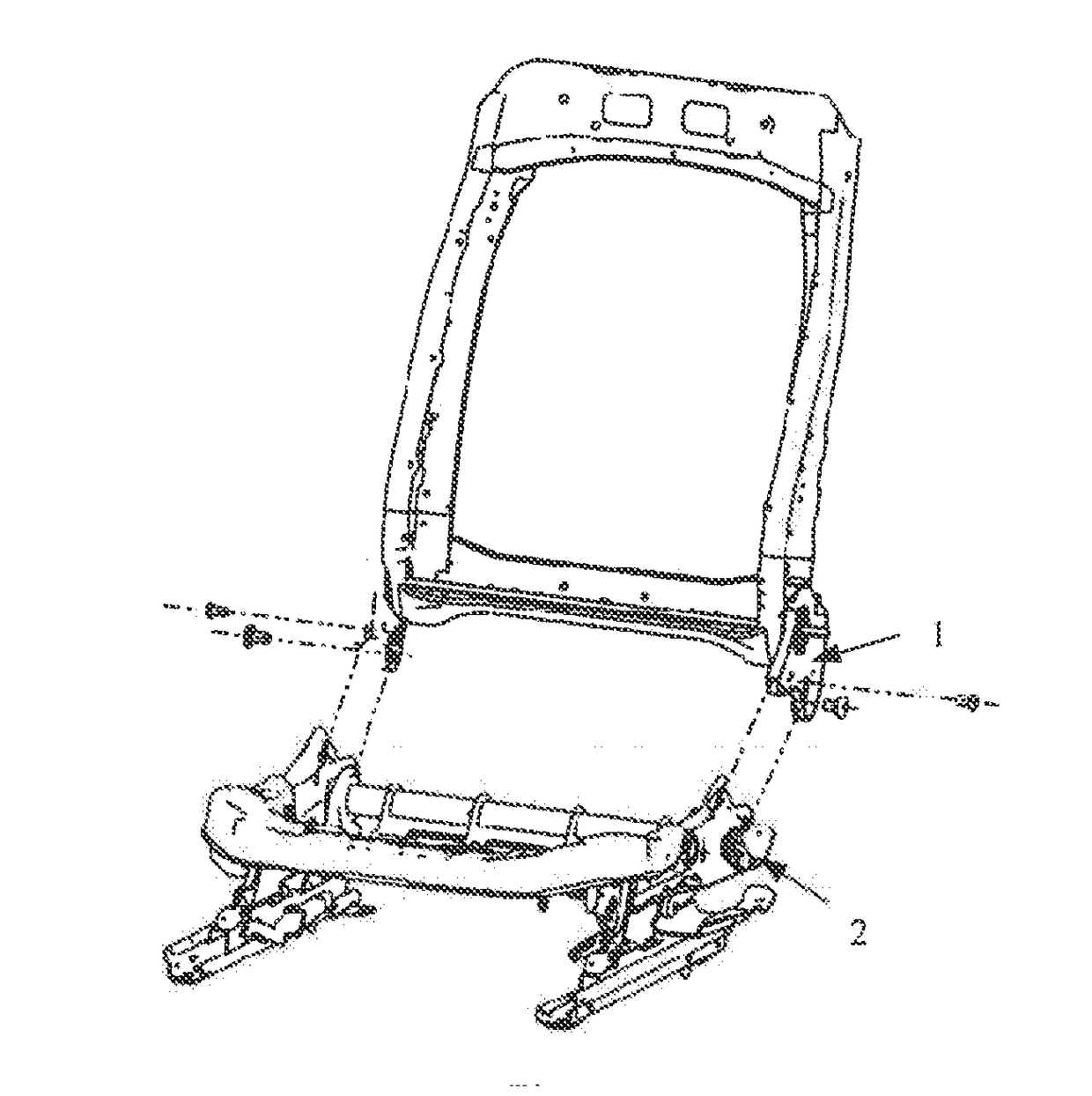
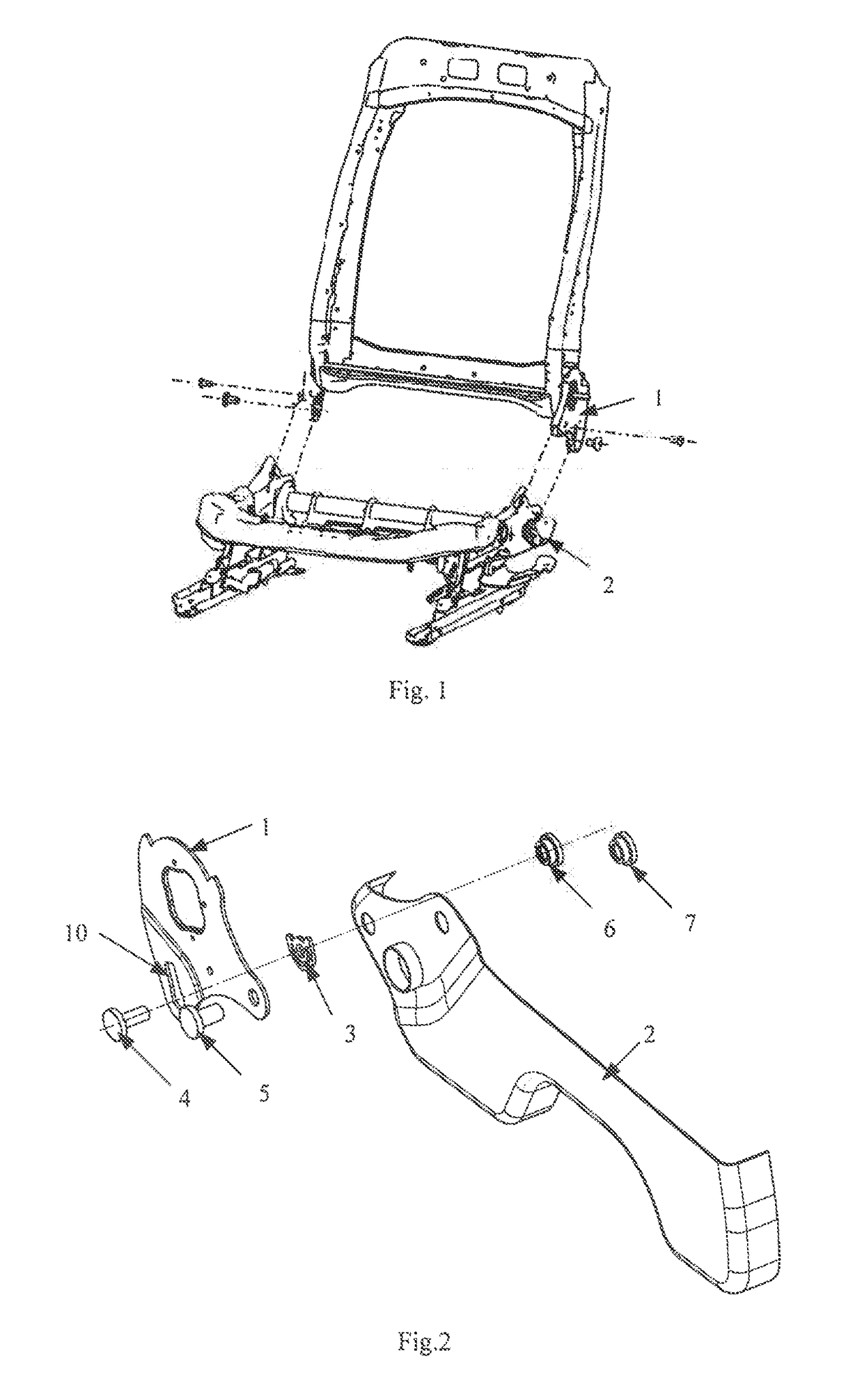
Vehicle seat with energy absorption structure
ActiveUS20180009342A1Simple structureConveniently installedSeat framesMovable seatsEnergy absorptionAbsorbed energy
A vehicle seat with an energy absorption structure, includes a cushion side plate and an angle adjuster lower connection plate, wherein an impact groove is provided on the angle adjuster lower connection plate, and the impact groove includes a straight groove part and a circular groove part communicating each other from top to bottom. The vehicle seat further includes an energy absorption disc including an annular part, a position part and impact fracture parts connected between the annular part and the position part. A first nut is securely coupled to the cushion side plate. A step bolt is provided including a head part, a step part and a stud which are coaxially connected in sequence. The stud bolt passes through the circular groove part, the annular part and threads to the first nut to make the step part passing through the circular groove part and press-fitting with the energy absorption disc. The vehicle seat has a simple structure, convenient installation, and can absorb energy during collision so as to reduce the head rebound speed during the vehicle collision and protect passengers, thereby improving vehicle safety level.
Owner:YANFENG ADIENT SEATING CO LTD
Preparation method of rubber powder composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rubber powder composite material, relating to the technical field of rubber preparation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: rubber powder preparation, rheologic treatment and compression molding. The rubber powder is treated by plasma to introduce the polar groups to the surface so as to enhance the surface hydrophilicity of the rubber powder. The observation on the impact fracture shape of the prepared product proves that after the plasma treatment, the interfacial bonding is enhanced, the material is integrally destroyed, and the mechanical properties of the composite material are enhanced. The waste tires are used as the raw material of the rubber powder, thereby saving the material cost; and the composite material has the advantages of environment friendliness and energy saving.
Owner:ANHUI TONGFENG RUBBER & PLASTIC IND
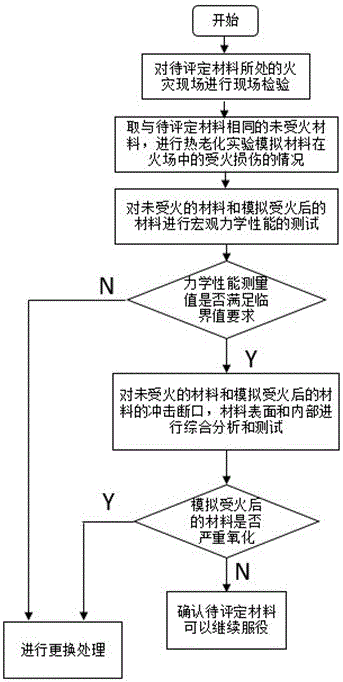
Method for safety assessment of high density polyethylene material after fire
InactiveCN106093363AAccurately judge serviceShorten the timeMaterial testing goodsStrength of materialsMicroscopic exam
The invention belongs to the field of assessment of the performances of polymer materials, and concretely relates to a method for detecting and evaluating the performances of a high density polyethylene material after a fire. The method comprises the following steps: simulating the fire damage condition of the material to obtain the mechanical performance indexes of the material at a certain temperature at a certain time; and carrying out impact fracture analysis and microscopic examination (comprising infrared analysis and thermal analysis) on the fire damaged material, and judging that whether the mechanical performances of the material are obviously decreased or not, whether the material obviously oxidized or not and whether the material can be continuously used or not according to the examination result. The method comprehensively evaluates the performance change condition of the material after fire by combining the macroscopic mechanical performance change of the material with the microstructure change of the material and utilizing various modern analyzers. The method can accurately judges that whether the material is continuously used or not, can effectively reduce the replacement time and the replacement cost of high density polyethylene pipelines after fire hazard, and has practical reference values in the evaluation of the performances of other polymer materials after fire damages.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for repairing concrete pavement by using virgin fiber cement-based repairing material
PendingCN110240454AChange brittlenessOvercome the broken plateIn situ pavingsSurface layerRepair material
The invention relates to a method for repairing a concrete pavement by using a virgin fiber cement-based repairing material. The method comprises: before construction, carrying out a mixing ratio experiment on a cement-based composite material, and carrying out experimental verification to obtain the optimal mixing ratio of the cement-based composite material; carrying out rubblization on an old cement concrete pavement, wherein the whole cement concrete pavement plate is broken into broken blocks at one time by impact equipment, such that the pavement plate is converted from the whole working state to the granule-based combination body working state; after breaking the pavement, compacting to ensure the stability and the flatness of the breaking layer, such that the conversion of the old concrete plate from the old surface layer plate to the new pavement base layer is achieved; preparing a virgin fiber cement-based composite material according to the optimal mixing ratio of the cement-based composite material, pouring, and carrying out vibrating flattening; and after 1 h, covering with a geotextile, and carrying out watering curing. According to the present invention, with the method, the damaged pavement is repaired by using the material, such that the plate breaking and impact fracture phenomenon of the concrete pavement due to the brittleness can be improved so as to avoid the occurrence of wide cracks and improve the durability of the road surface.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
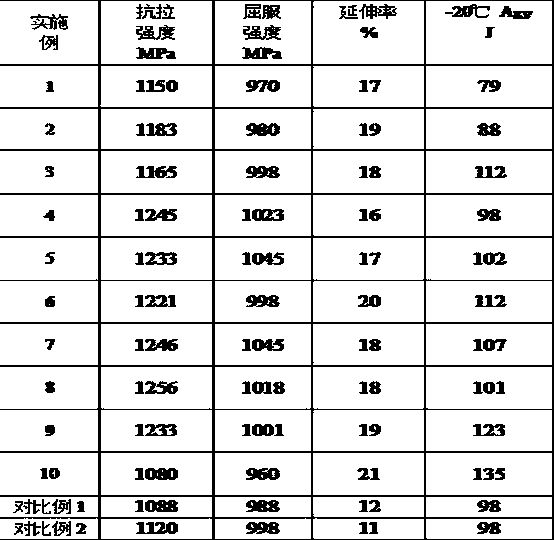
A kind of steel for construction machinery with yield strength ≥ 960mpa and its production method
Provided is engineering machinery steel with the yield strength being larger than or equal to the 960 MPa grade. The engineering machinery steel comprises the components of, by weight, 0.04%-0.20% of C, 0.15%-0.40% of Si, 1.0%-10% of Mn, 0.01%-0.08% of N, 0.010%-0.050% of Ti, 0.01%-0.06% of Als, 0-0.020% of P, 0-0.010% of S and 0.05%-3% of Cr. Production steps comprise smelting and vacuum treatment, steel tapping, casting for blank forming, heating, a hot rolling process, and cold rolling. The engineering machinery steel provided by the invention is larger than or equal to 960 MPa in yield strength, larger than or equal to 15.0% in elongation, not lower than 60 J in -20 DEG C AKV and very excellent in matching of strength and toughness, and has an impact fracture with a dimple characteristic. Adaptive N is added to the chemical components so as to ensure the strength of the steel, and adding of Mo, V, Nb and other expensive microalloy elements is cancelled. Rolling technology of the engineering machinery steel is simple and easy to operate, cold control is not needed in the rolling process, and heat treatment is not needed as well.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
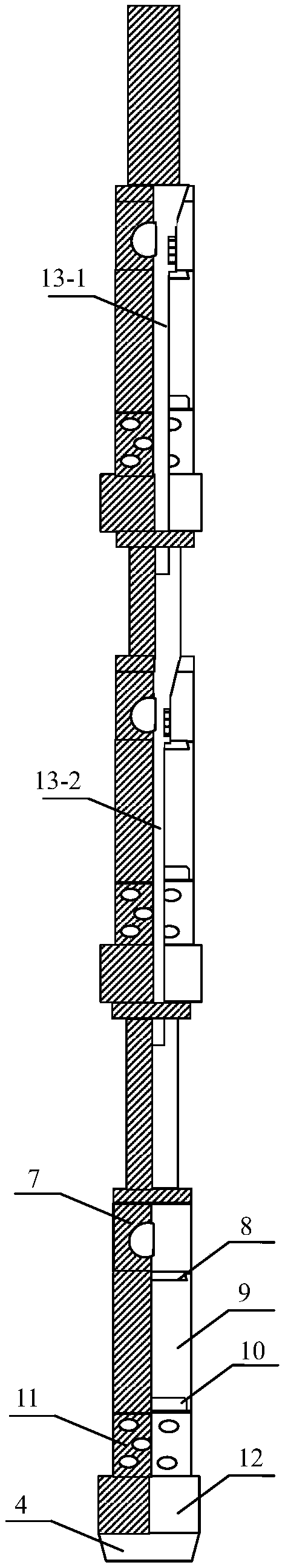
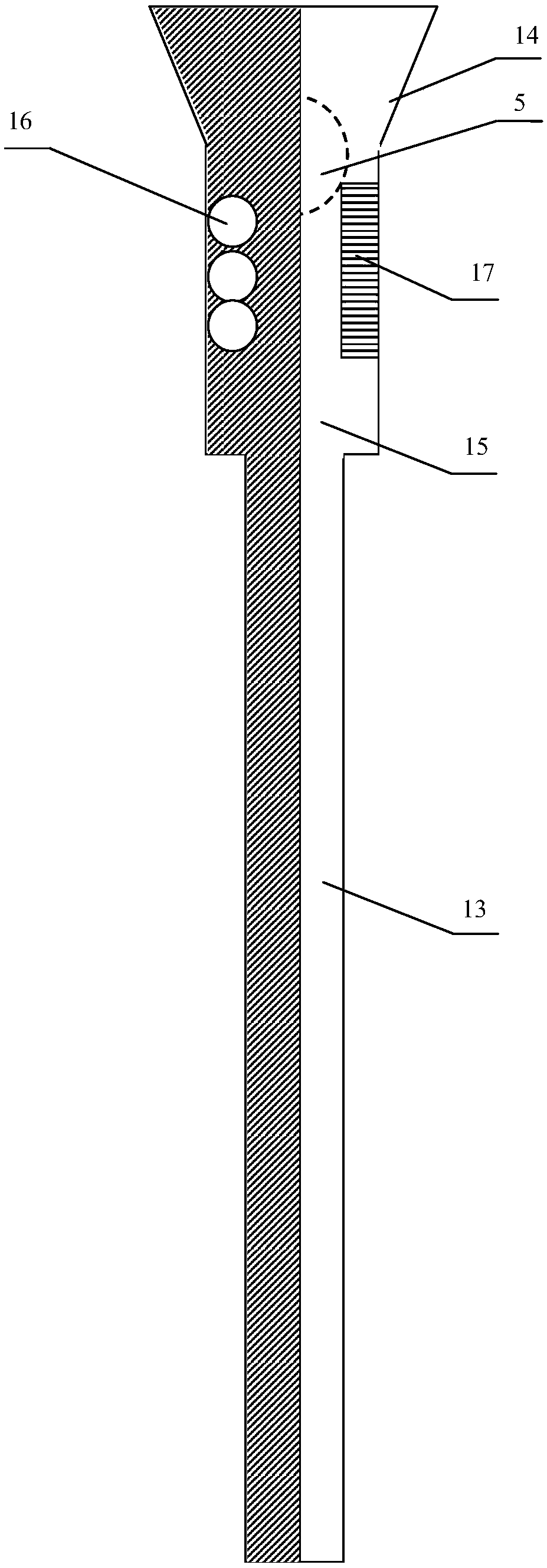
Simulating device for dynamic impact fracture of horizontal well
The invention provides a simulating device for dynamic impact fracture of a horizontal well. The simulating device comprises a force transmitter, a driver, a connector and a core clamping device. Theforce transmitter comprises a cylindrical shell and a force transmitting column arranged in the shell; a driver is arranged at the first end of the force transmitter and used for pushing the force transmitting column to move relative to the shell; the connector is arranged at the second end of the force transmitter, and an inner cavity of the connector communicates with an inner cavity of the shell; and the core clamping device is arranged at the second end of the connector. According to the simulating device, pulse pressure can be formed so as to simulate the real state in a shaft, and accordingly the crack forms of rock fracturing at the long well section and the multilayer section of the horizontal well are simulated.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Oil pipe joint of numerical control lathe and thermal treatment process thereof
InactiveCN104266016AHigh tensile strengthImprove fatigue resistanceSleeve/socket jointsFurnace typesNumerical controlThermal treatment
The invention discloses an oil pipe joint of a numerical control lathe and a thermal treatment process thereof. The oil pipe joint of the numerical control lathe and the thermal treatment process thereof comprise a body and a thermal treatment process, wherein the upper end of the body is provided with a cylindrical structure, the middle part of the body is provided with an outside hexagonal structure, and the lower part of the body is provided with a toothed cylinder structure; the upper part in the body is provided with a cylindrical through hole structure which is arranged to be a first through hole structure, and the lower part of the body is similarly provided with a cylindrical through hole structure which is arranged to be a second through hole structure; the external diameter of the first through hole structure is greater than that of the second through hole structure; the thermal treatment process of the oil pipe joint is characterized in that the oil pipe joint is immersed into a proper quenching medium to cool at a higher speed after being heated to be austenitized. The oil pipe joint has high enough tensile strength to resist stretch, snap, slipping and wear, has higher fatigue resistance and impact toughness, can resist fatigue and impact fracture and can be excellently applied to the numerical control lathe.
Owner:PINGHU CITY DANGHU STREET FEITIANREN MACHINERY GRAPHIC DESIGN SERVICE DEPT
Method for preventing corrosion of low-temperature fracture
PendingCN113670963ASimple methodEasy accessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial strength using single impulsive forceAlcoholTest sample
The invention discloses a method for preventing corrosion of a low-temperature fracture, which adopts common reagents absolute ethyl alcohol and a plastic beaker in a laboratory, is simple, convenient to obtain raw materials and reusable, does not need a laboratory power supply, an electric hair dryer and the like, does not need additional investment, and can be applied to protection of low-temperature impact fractures of various metal materials. The method is suitable for fracture protection of various low-temperature test samples, and a novel fracture protection method is provided for personnel engaged in experiments and research and development in the aspects of low-temperature experiments and tests.
Owner:BAOTOU IRON & STEEL GRP
20CrMnMo open gear, detection method thereof and heat treatment method for reducing cracks of blank forging of 20CrMnMo open gear
PendingCN112662846AReduce crack defectsImprove pass rateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCrazingScanning electron microscope
The invention relates to a 20CrMnMo open gear, a detection method thereof and a heat treatment method for reducing cracks of a blank forging of the 20CrMnMo open gear, and belongs to the technical field of hot forging treatment processes. The heat treatment method comprises the steps that a square billet enters a furnace to be heated, the initial forging temperature is 1200 DEG C, the final forging temperature is 800 DEG C, the forging ratio is 7.5, carburization and heat preservation are conducted for 60 hours at the temperature of 930 DEG C, and the square billet is discharged out of the furnace; the square billet is quenched, wherein austenitizing is conducted, heat preservation is conducted for 4.5 hours at the temperature of 850 DEG C, and the square billet is discharged out of the furnace (oil cooling); and the square billet is tempered, wherein the square billet is heated to 210 DEG C, heat preservation is conducted for 12 hours, and the square billet is discharged out of the furnace (air cooling). The open gear is manufactured through the heat treatment method. The detection method comprises the following steps: ultrasonic flaw detection, dissection sampling, macroscopic examination, metallographic examination, hardness test, impact and tensile test, and impact fracture scanning electron microscope analysis. By means of the detection method, the crack state can be observed, the crack occurrence time can be judged, and the detection method has extremely important production guidance significance.
Owner:NANJING DEV ADVANCED MFG
A Vacuum Cladding Surface Strengthening Method for Fracturing Pump Valve Body and Valve Seat
A vacuum cladding surface strengthening method for a fracturing pump valve body and a valve seat. Using the method of vacuum cladding, using nickel-based self-fluxing alloy powder as raw material, adding WC hard strengthening phase powder, a coating with high wear resistance, corrosion resistance and impact resistance is prepared on the surface of the valve body and valve seat of the fracturing pump. The process steps are: workpiece surface pretreatment—ball milling and mixing—making slurry—coating on workpiece surface—drying—vacuum sintering. The ingredients are composed of 5-30% of WC powder and 70-95% of Ni-Cr-Mo-Fe-B-Si-C alloy powder by weight percentage. The cladding coating prepared by the present invention has high density and small internal stress; a good metallurgical bond is formed between the coating and the substrate, which greatly improves the wear resistance, corrosion resistance and corrosion resistance of the cladding coating surface of the valve body and valve seat. Impact resistance, etc., thereby effectively improving the service life of the valve body and the valve seat; and the process of the invention is simple in operation, high in raw material utilization, low in cost, stable in process performance, and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Shale gas production promoting method based on combination of blasting fracturing and hydraulic fracturing
ActiveCN113338889APrevent unmineableGuaranteed gas productionSurveyFluid removalMining engineeringHorizontal wells
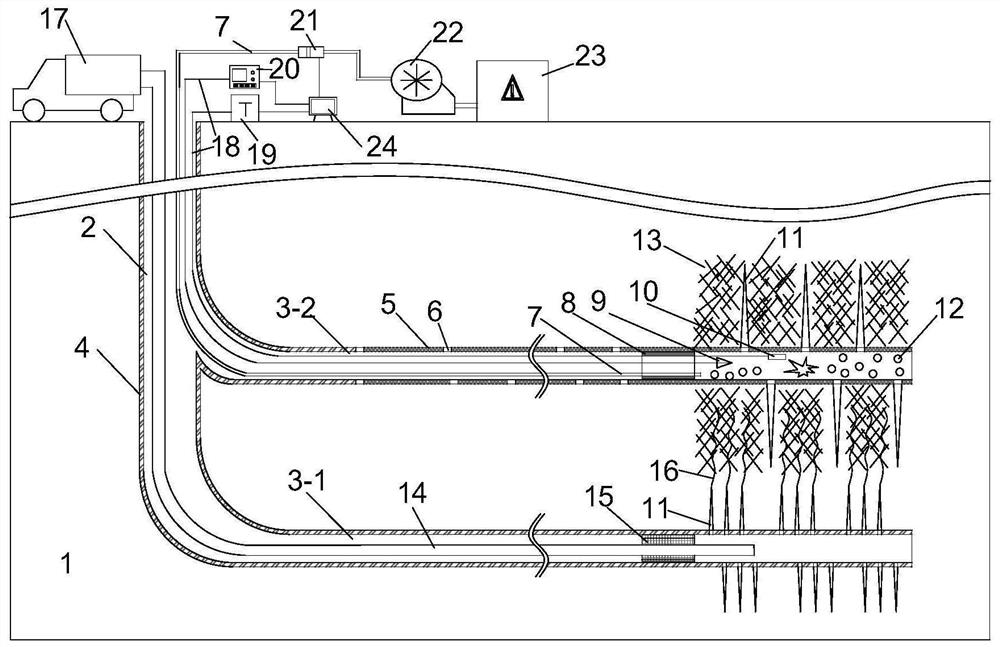
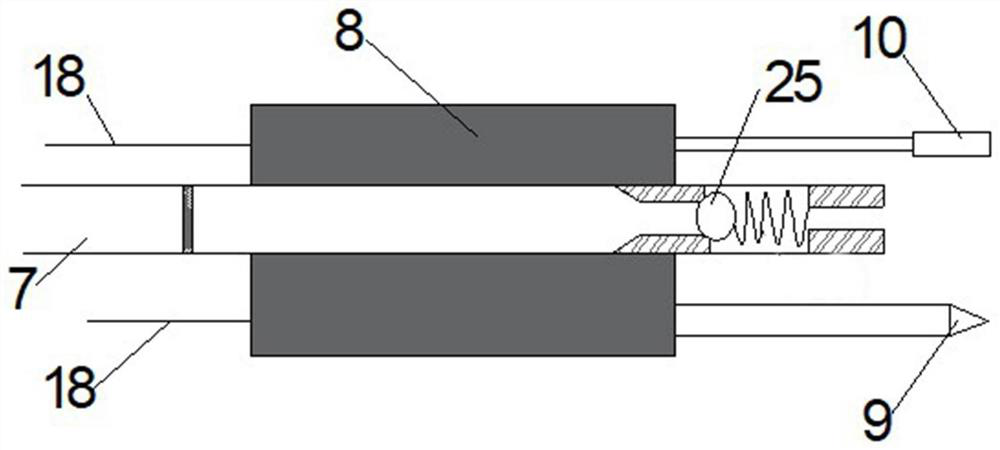
The invention discloses a shale gas production promoting method based on combination of blasting fracturing and hydraulic fracturing. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a blasting fracturing horizontal well is punched, then a perforation fracture is formed in the blasting fracturing horizontal well, a first blasting hole packer is installed, a hole sealing section is formed, and if the value required by explosion is reached in the hole sealing section within a set time, blasting gas is triggered to conduct primary impact fracturing on the perforation fracture; if the value required by explosion is not reached, blasting gas is supplemented into the hole sealing section, then one-time blasting fracturing is completed, next, the above process is repeated, a blasting fracturing fracture network is formed around the blasting fracturing horizontal well through retreating blasting fracturing, and hole sealing is conducted; and finally, a hydraulic fracturing horizontal well is punched below the blasting fracturing horizontal well, a hydraulic fracturing fracture area is formed around the hydraulic fracturing horizontal well by adopting a retreating hydraulic fracturing method, wherein the fracture area can be in communication with the blasting fracturing fracture network, and at the moment, shale gas extraction work is conducted on a shale reservoir through the hydraulic fracturing horizontal well.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com