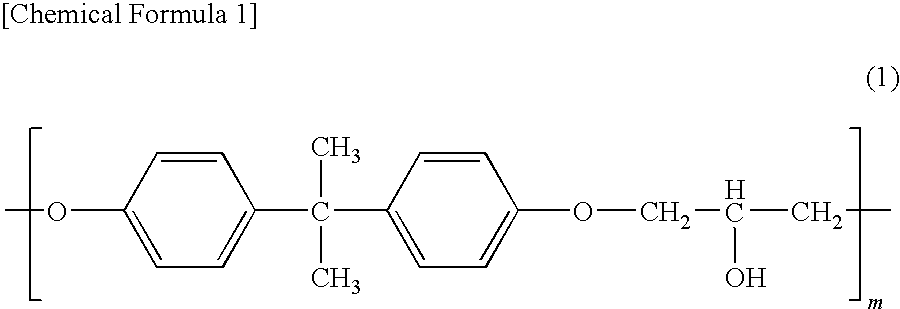
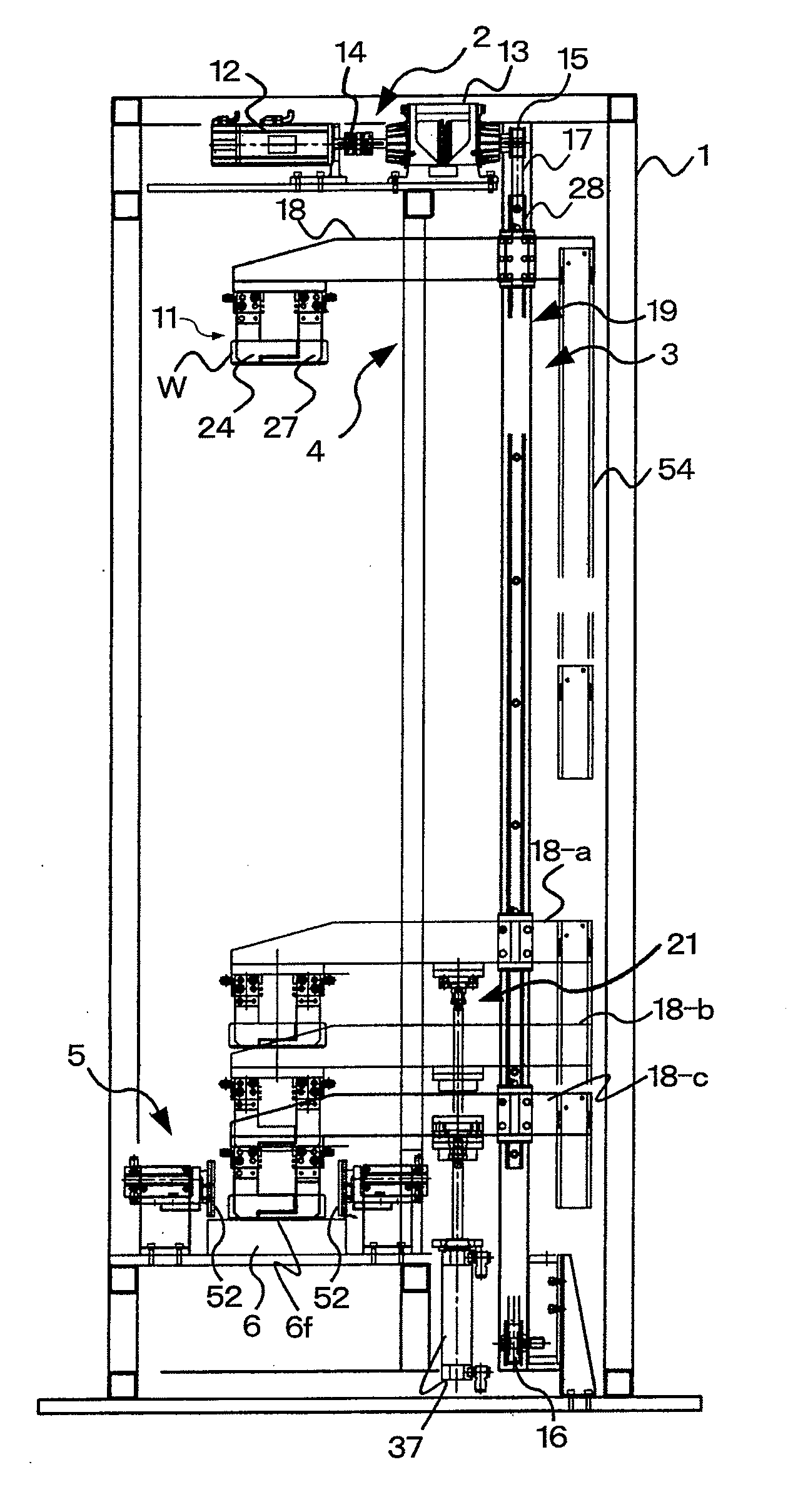
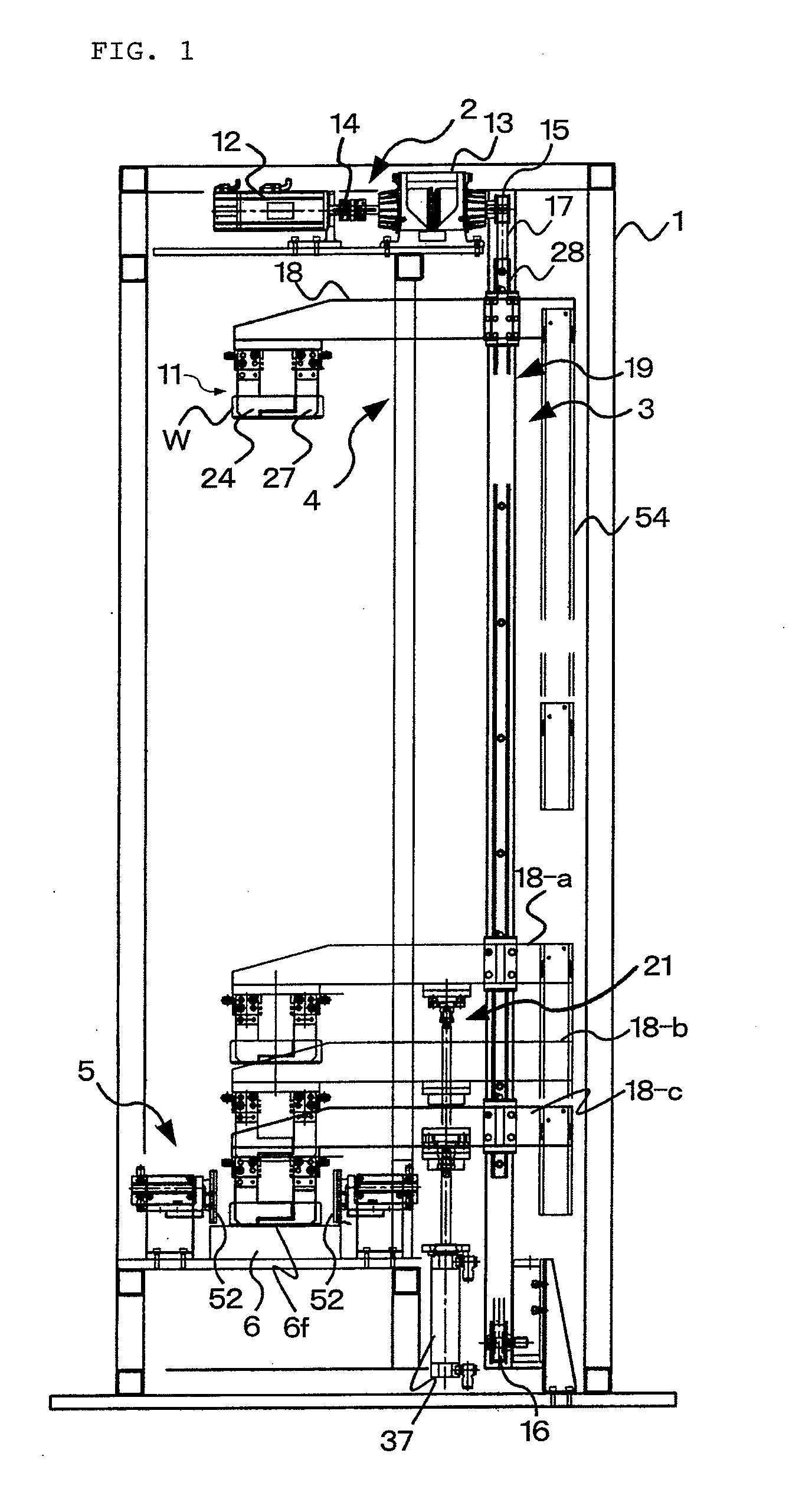
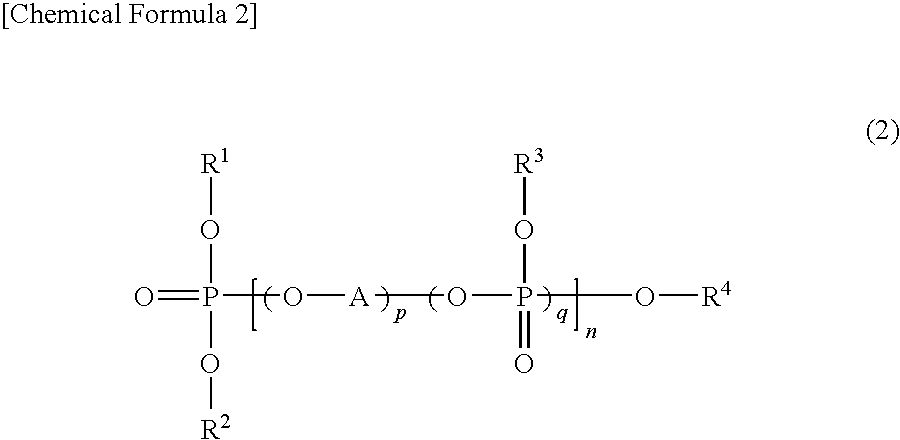Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
266 results about "Drop impact" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drop impact occurs when a liquid drop strikes a solid or liquid surface. The resulting outcome depends on the properties of the drop, the surface, and the surrounding fluid, which is most commonly a gas.
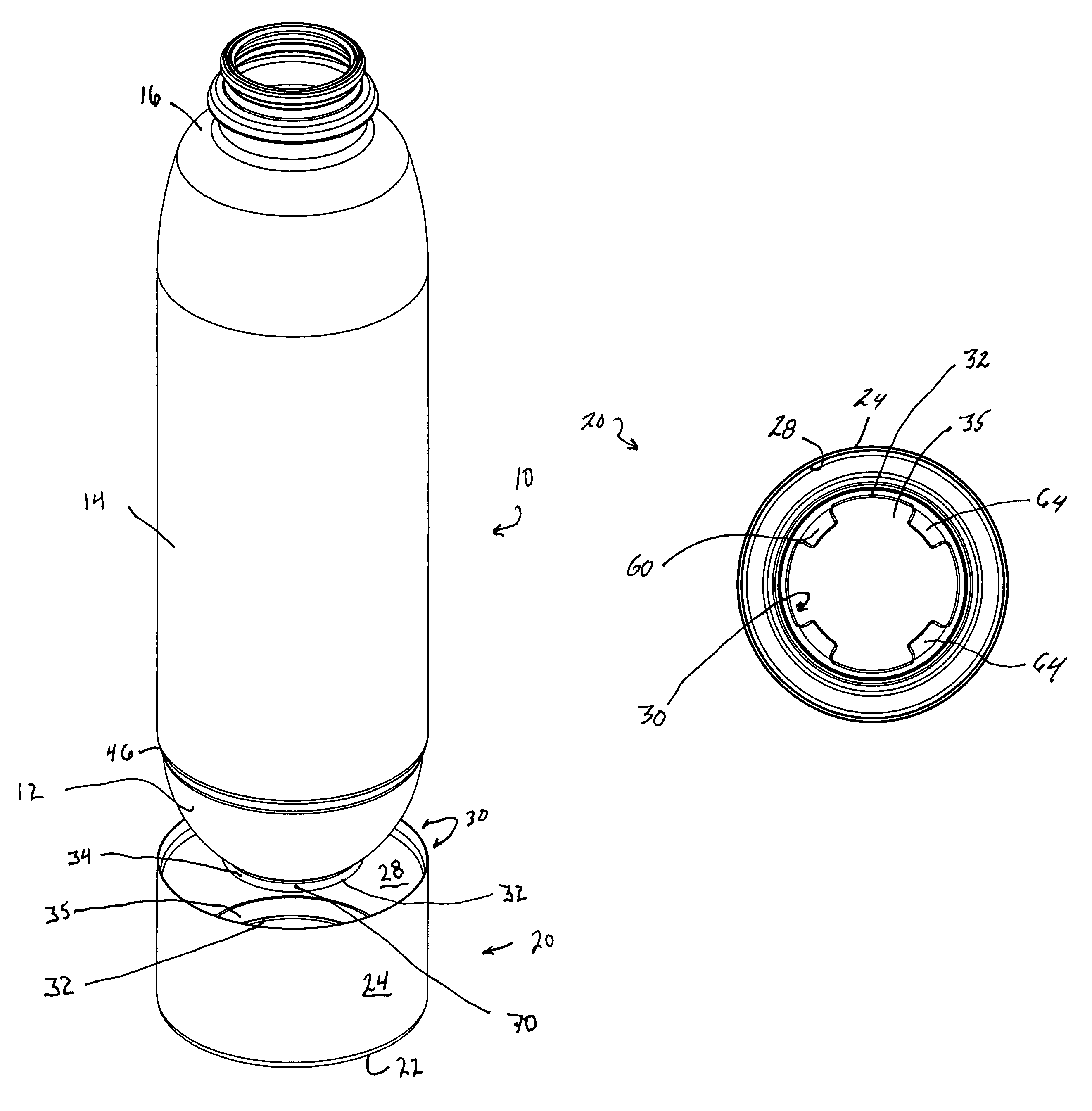
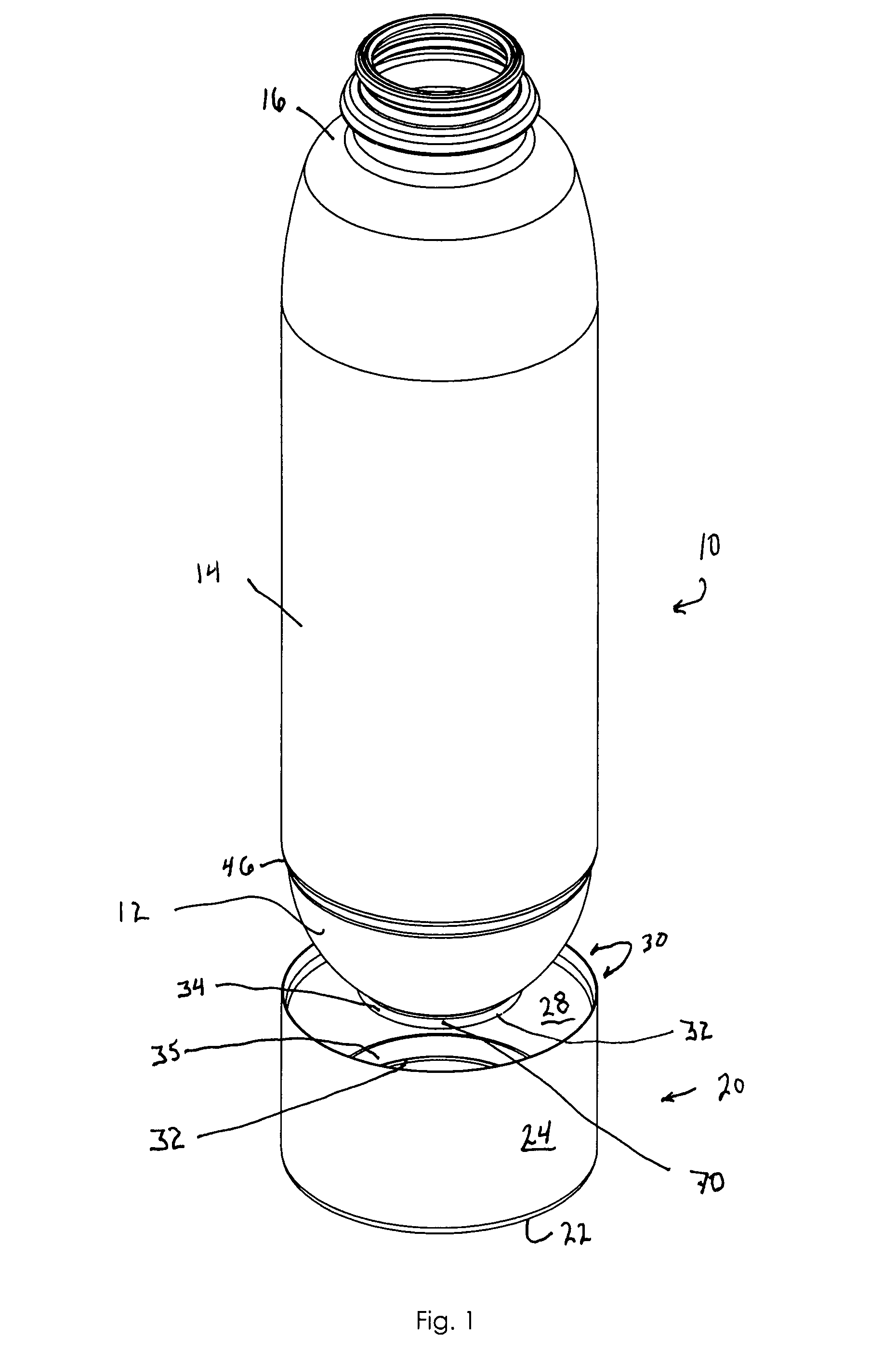
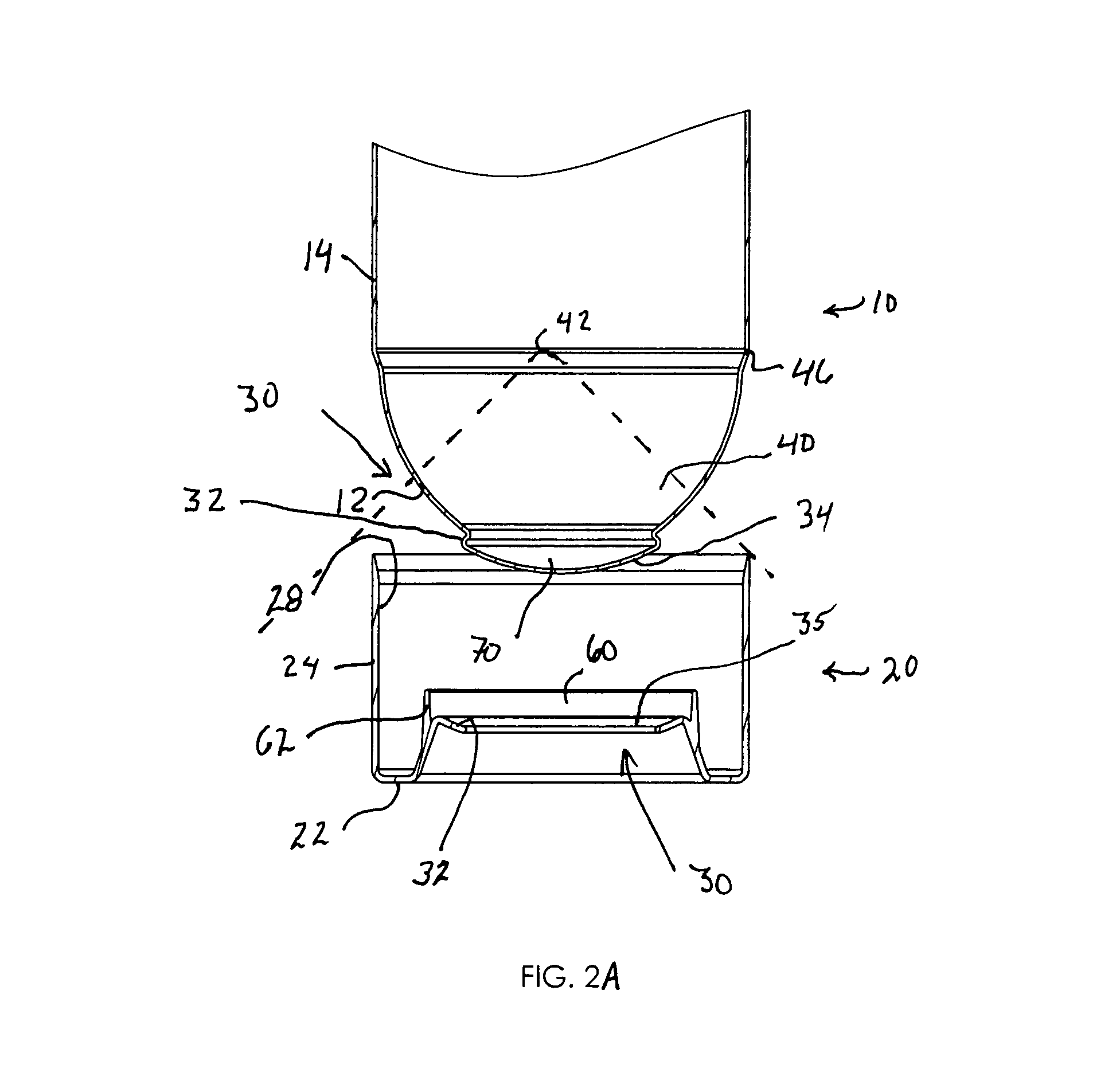
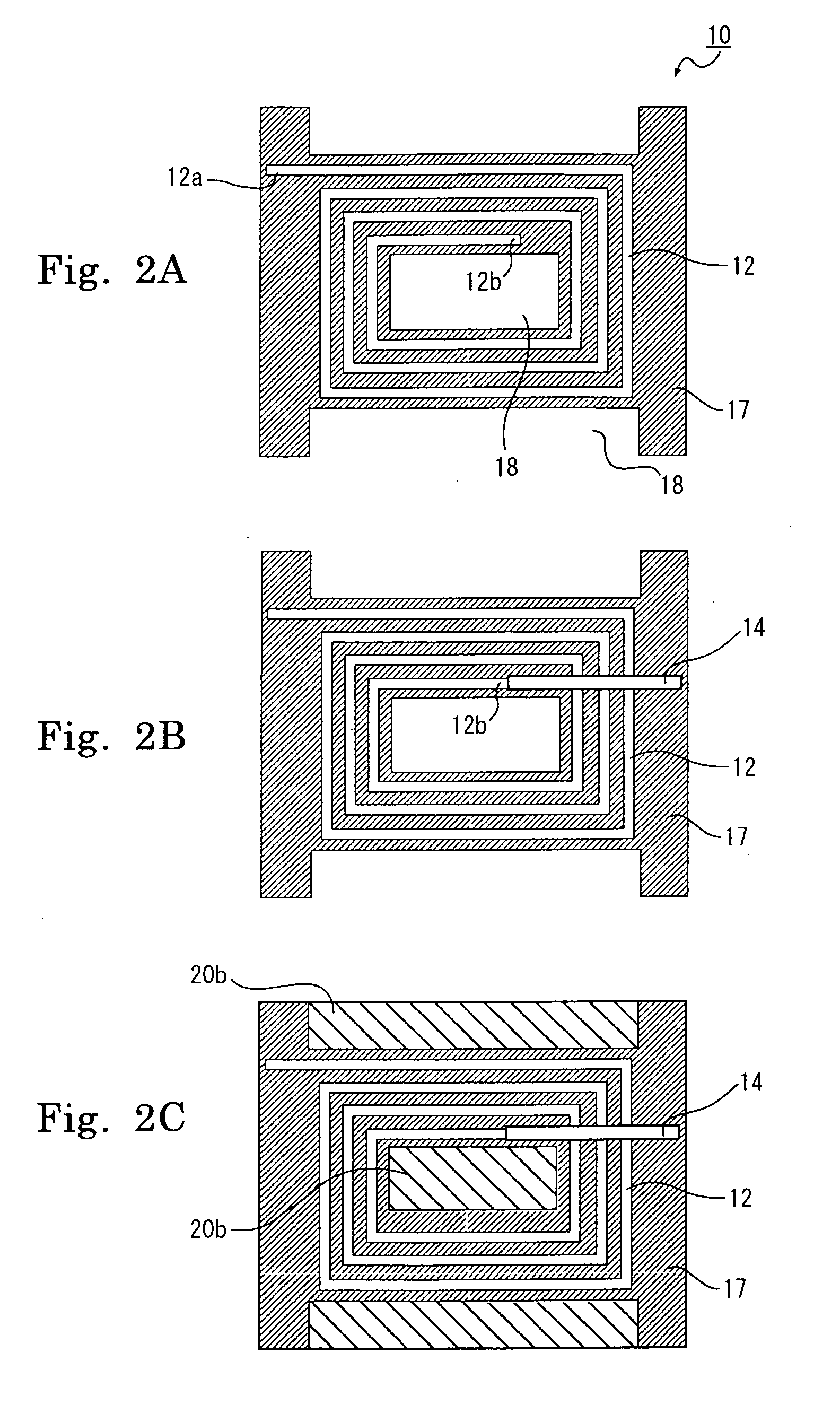
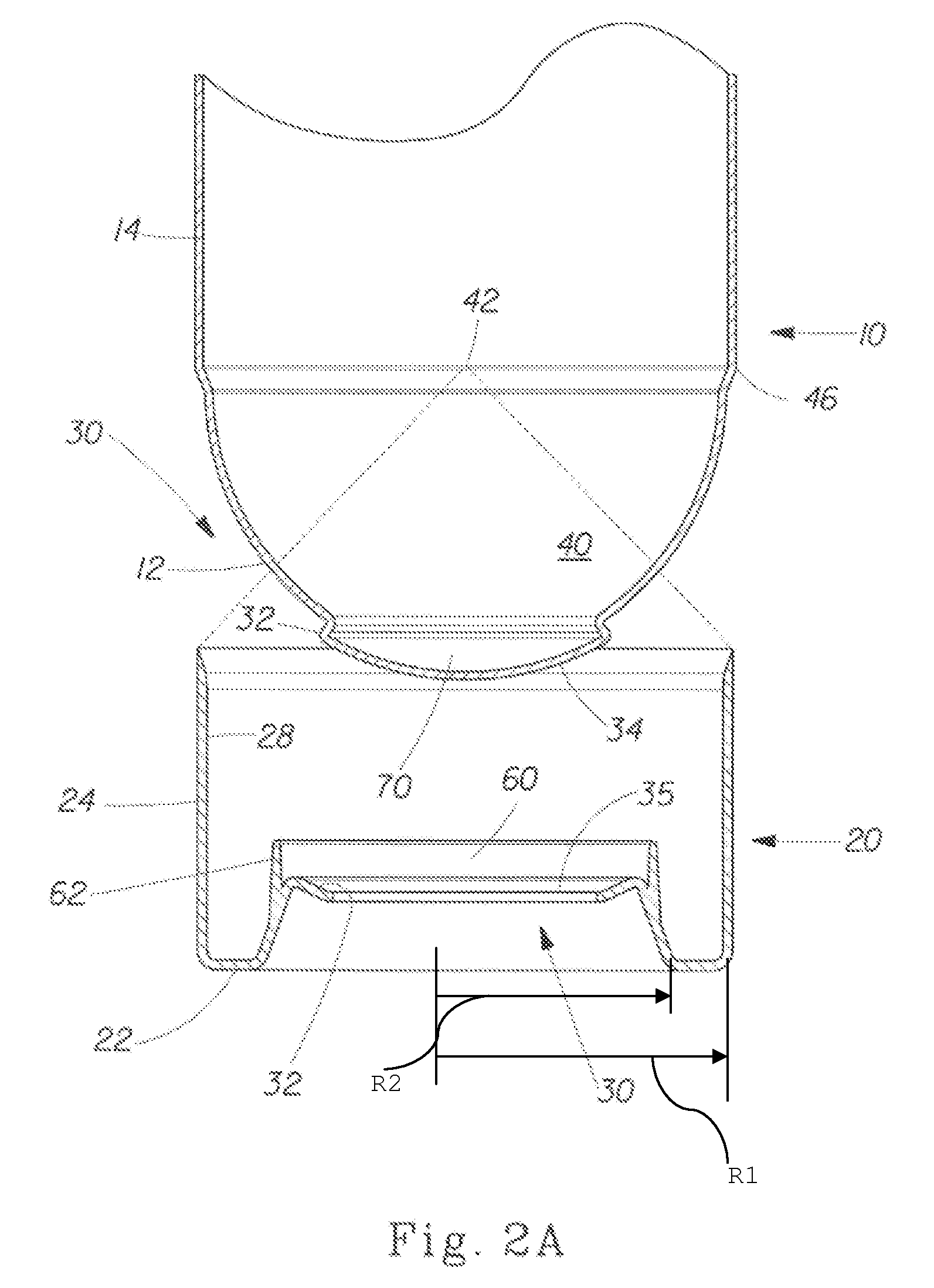
Supportable pressurizable container and base cup therefor with alignment tabs
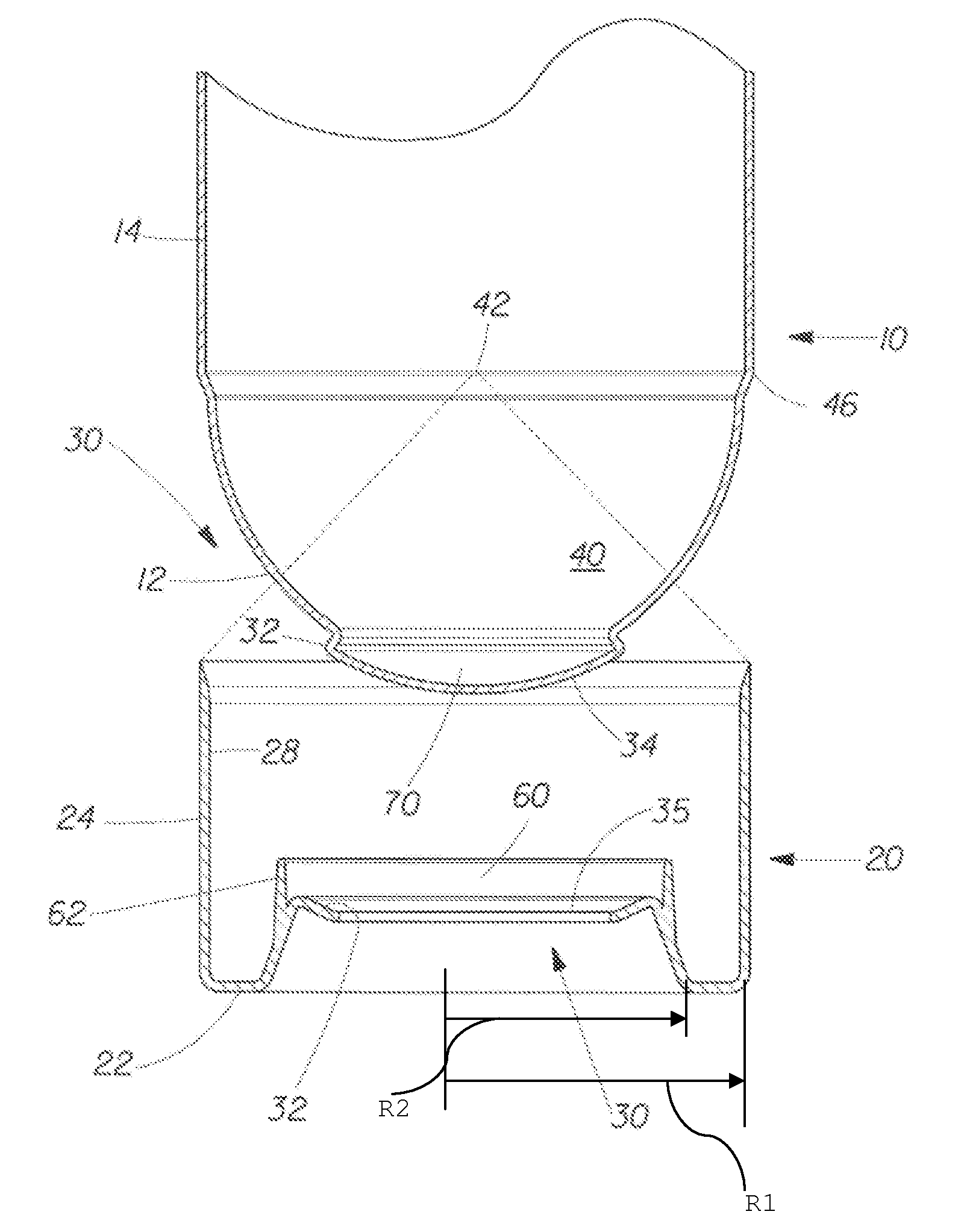
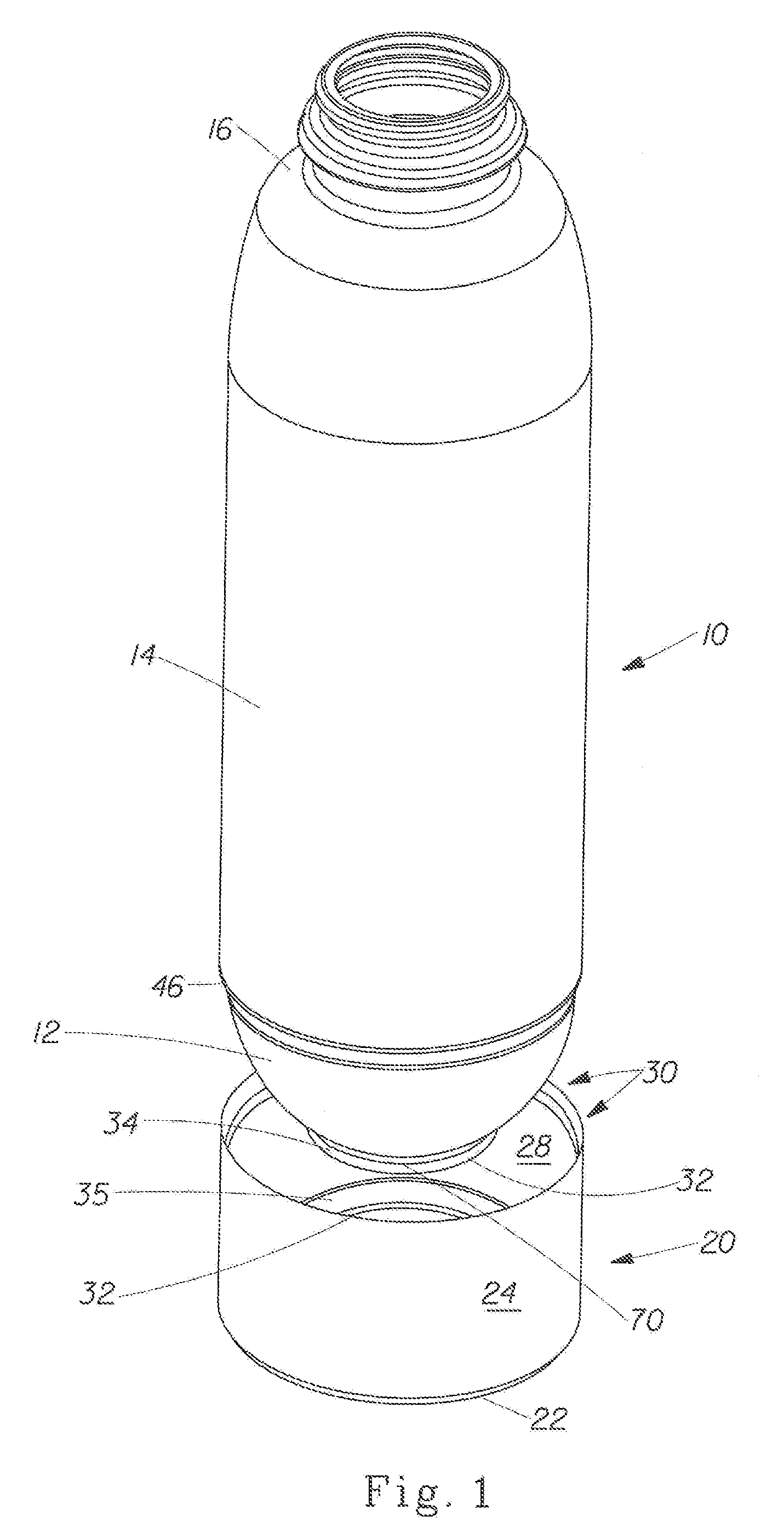
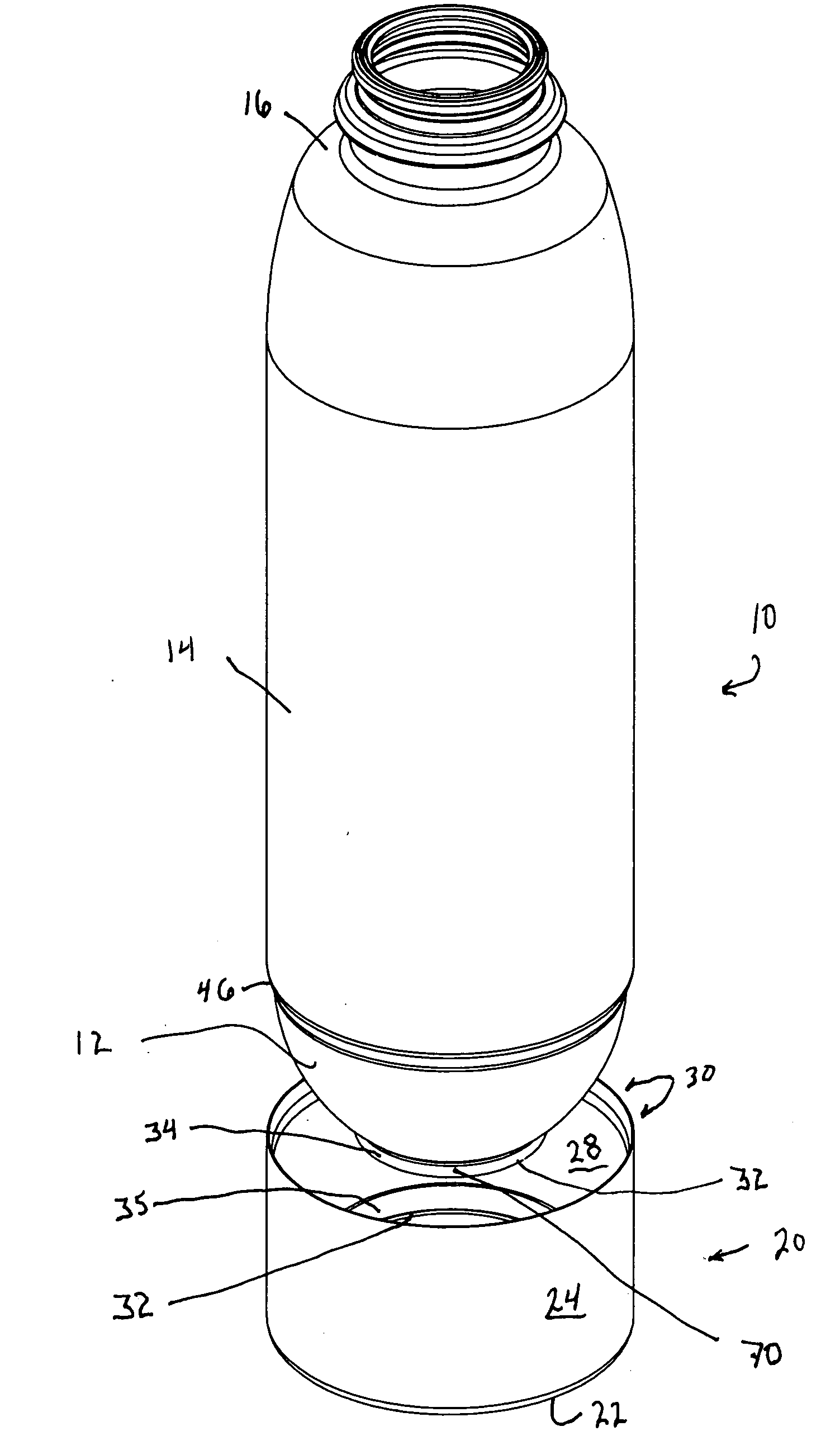
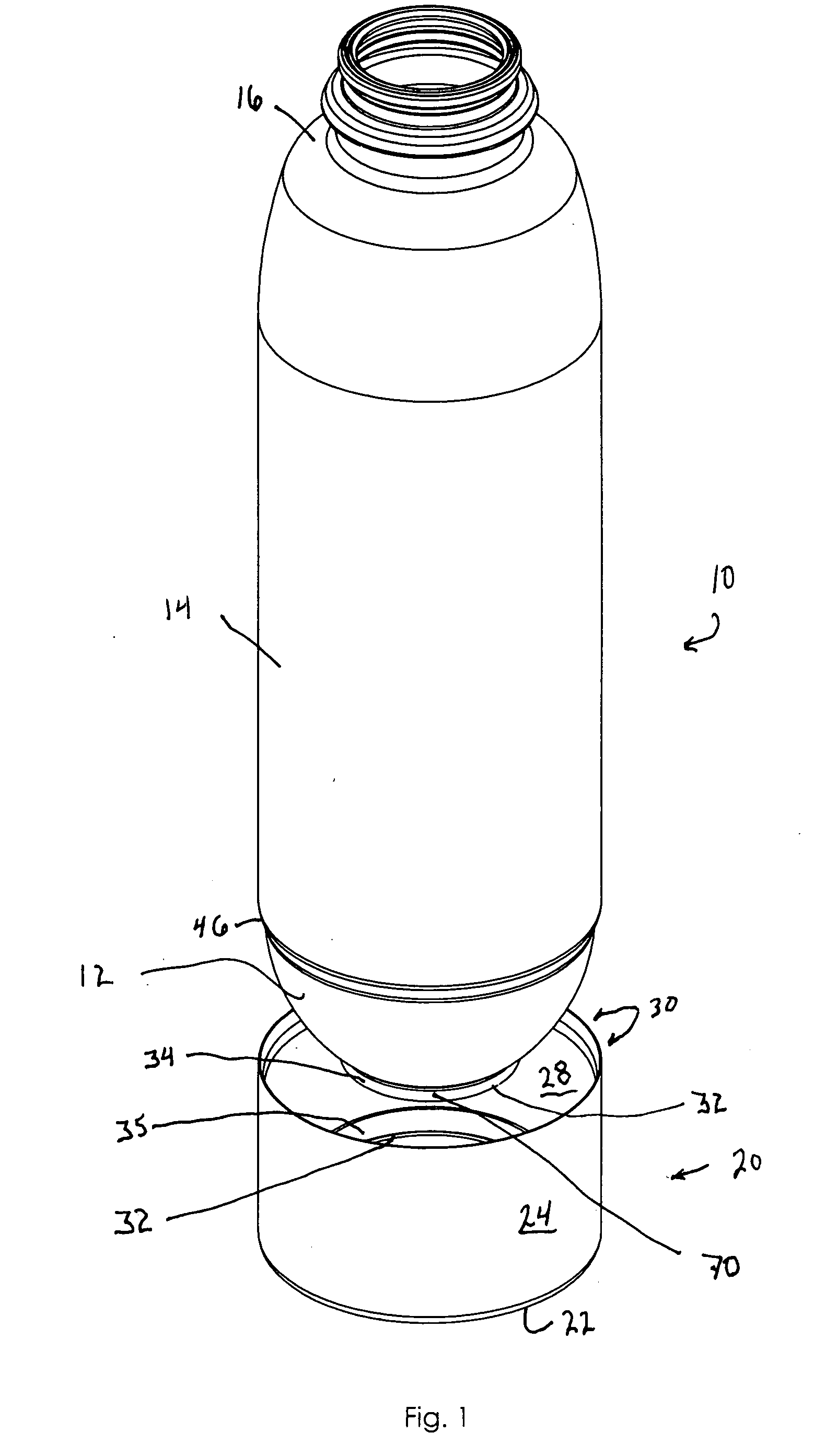
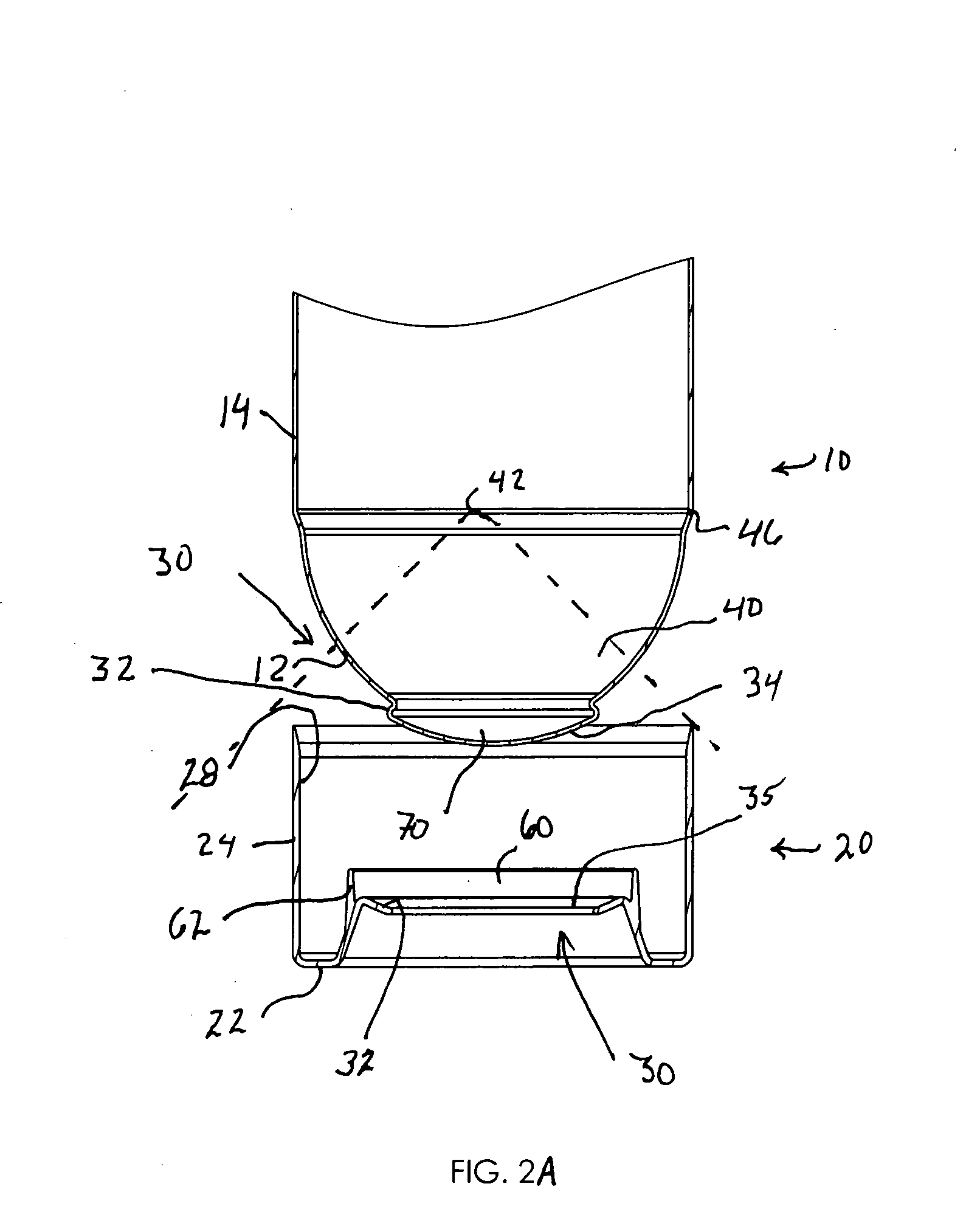
A container having a curved bottom and base cup which allows the container to stand upright. The container and base cup are fitted together by a mechanical engagement having portions on the container and base cup. The mechanical engagement of the container is disposed within the bottom cone of the container. The mechanical engagement of the base cup is cantilevered from the bottom of the base cup. Such disposition reduces stress at the interface between the side wall of the container and edge of the base, providing for a smoother transition and better appearance. Also, this disposition provides resistance to separation of the container and base cup during drop impact. The bottom of the container may be curved and have a well therein for receiving the contents of the container and a dip tube.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
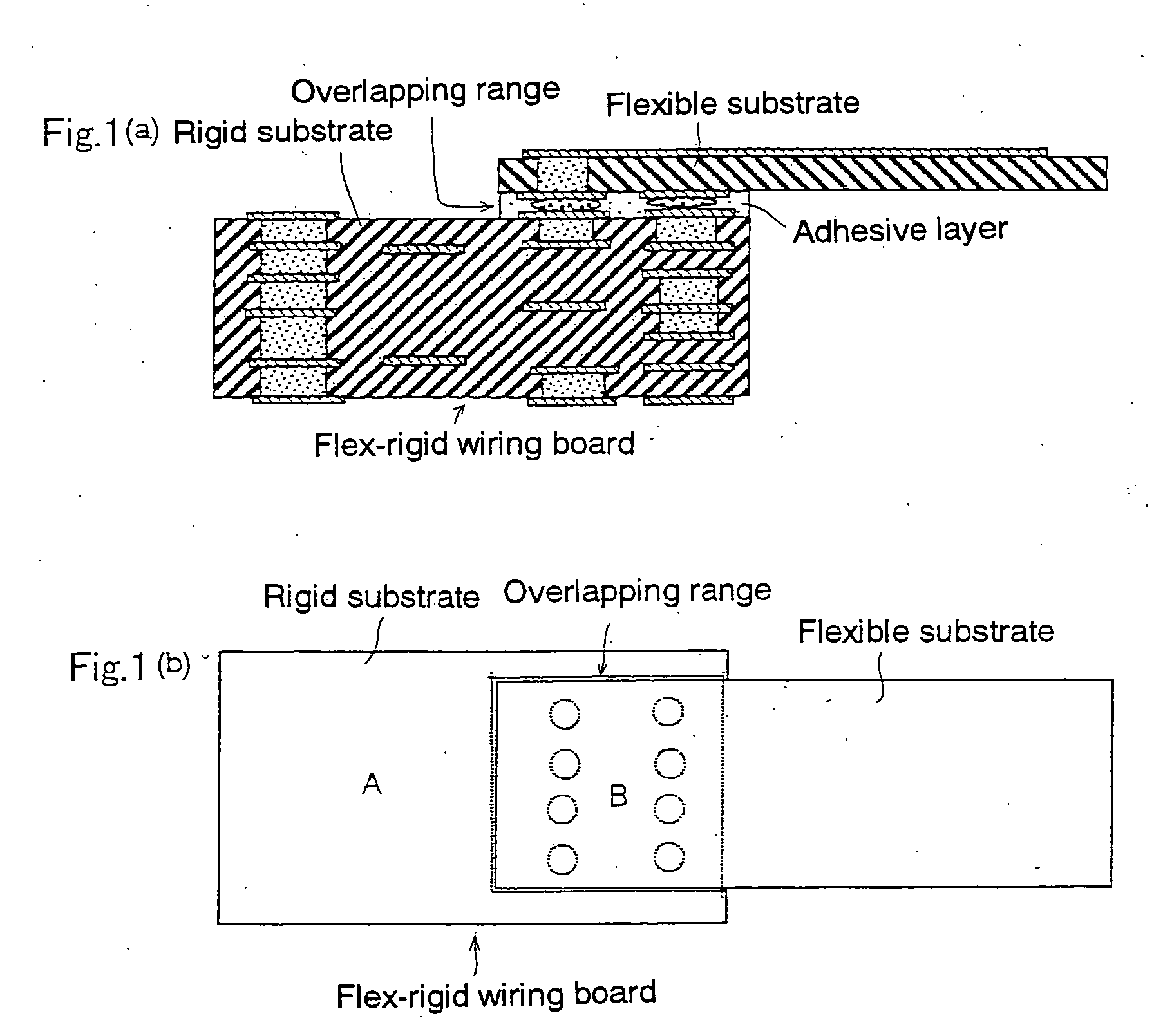
Rigid-flex wiring board
InactiveUS20060169485A1Reduce inductanceImprove reliabilityElectrical connection printed elementsCircuit susbtrate materialsNoise generationDrop impact
A flex-rigid wiring board has an insulative adhesive interposed between portions, lapping over each other, of the rigid and flexible substrates; and the interconnecting electrode pads on the rigid and flexible substrates are electrically connected to each other through a conductor lump penetrating the insulative adhesive, thereby providing lowered inductance in the high-frequency band, shortened signal-delay time, reduced noise generation due to signal reflected-wave, reduced drop impact, high connection reliability and high freedom of wire connection, and the wiring board can advantageously be manufactured with a reduced cost and a high yield.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
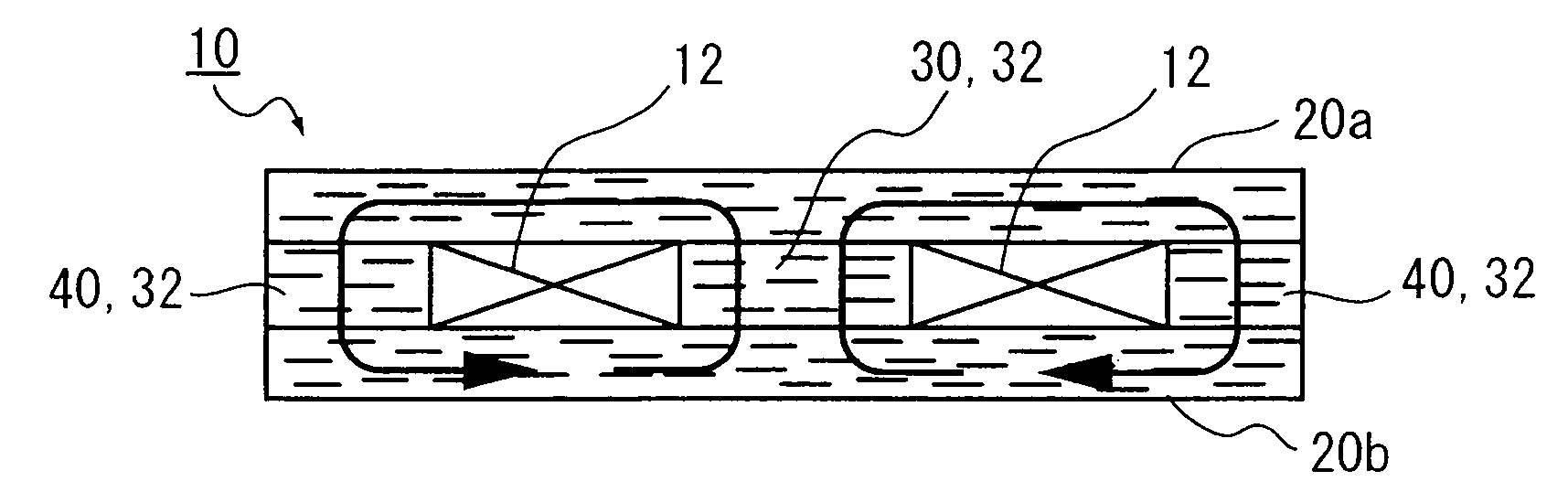
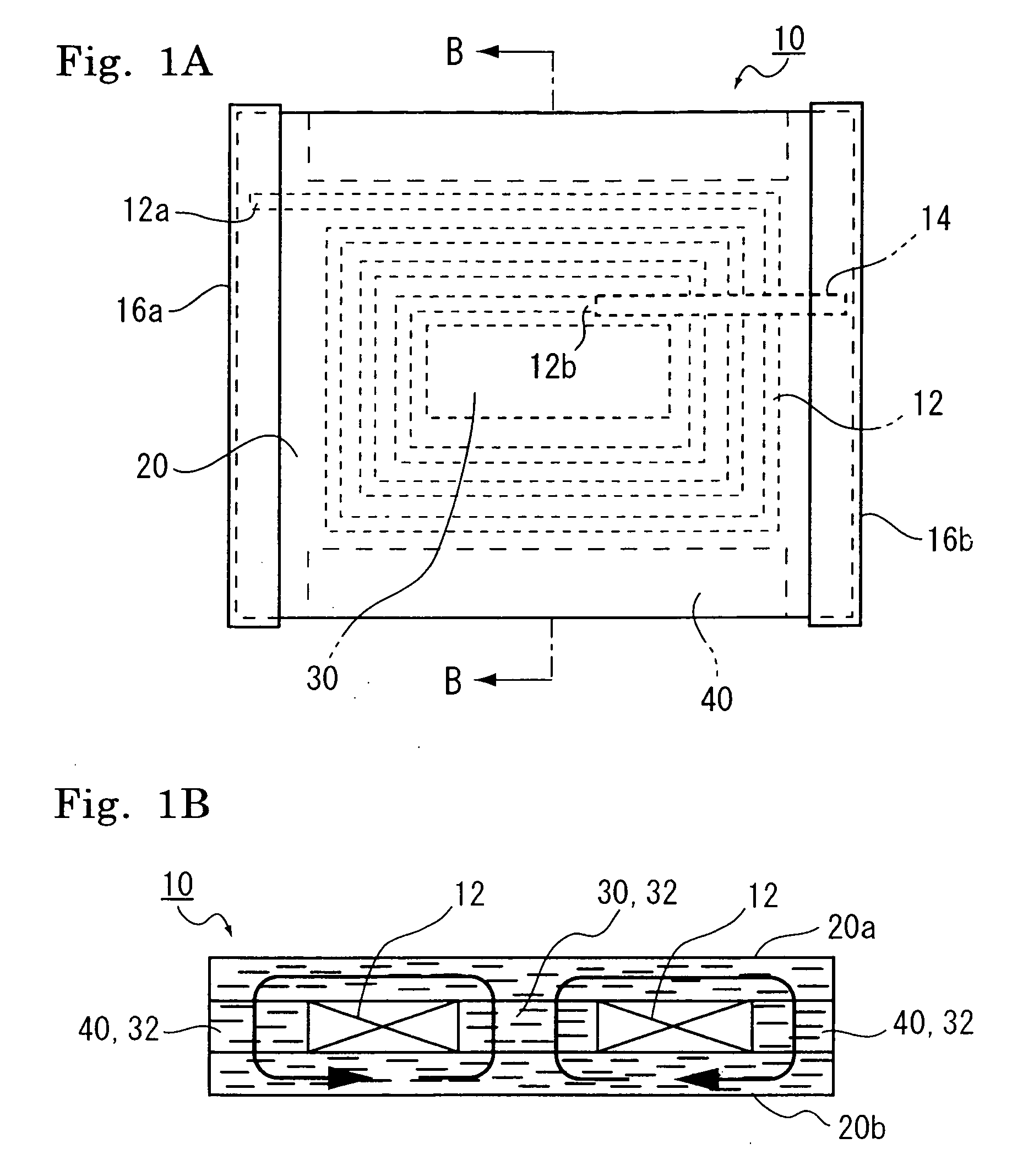
Coil component
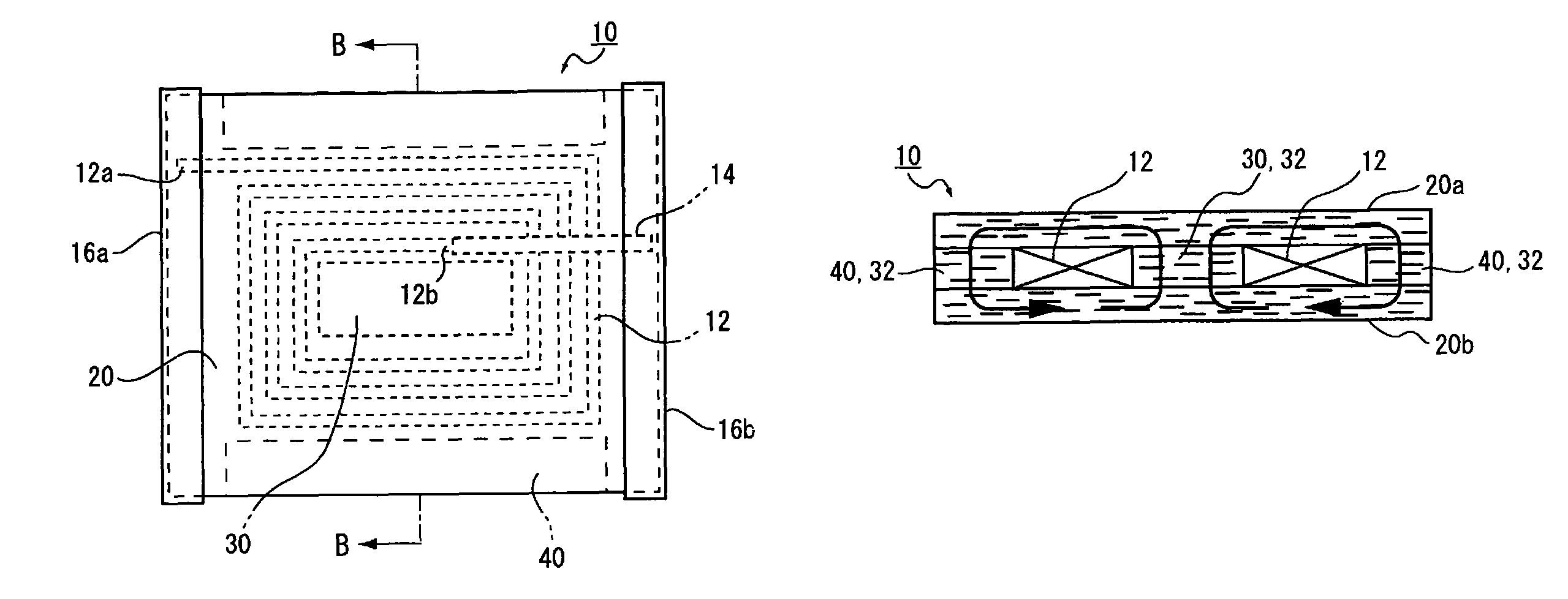
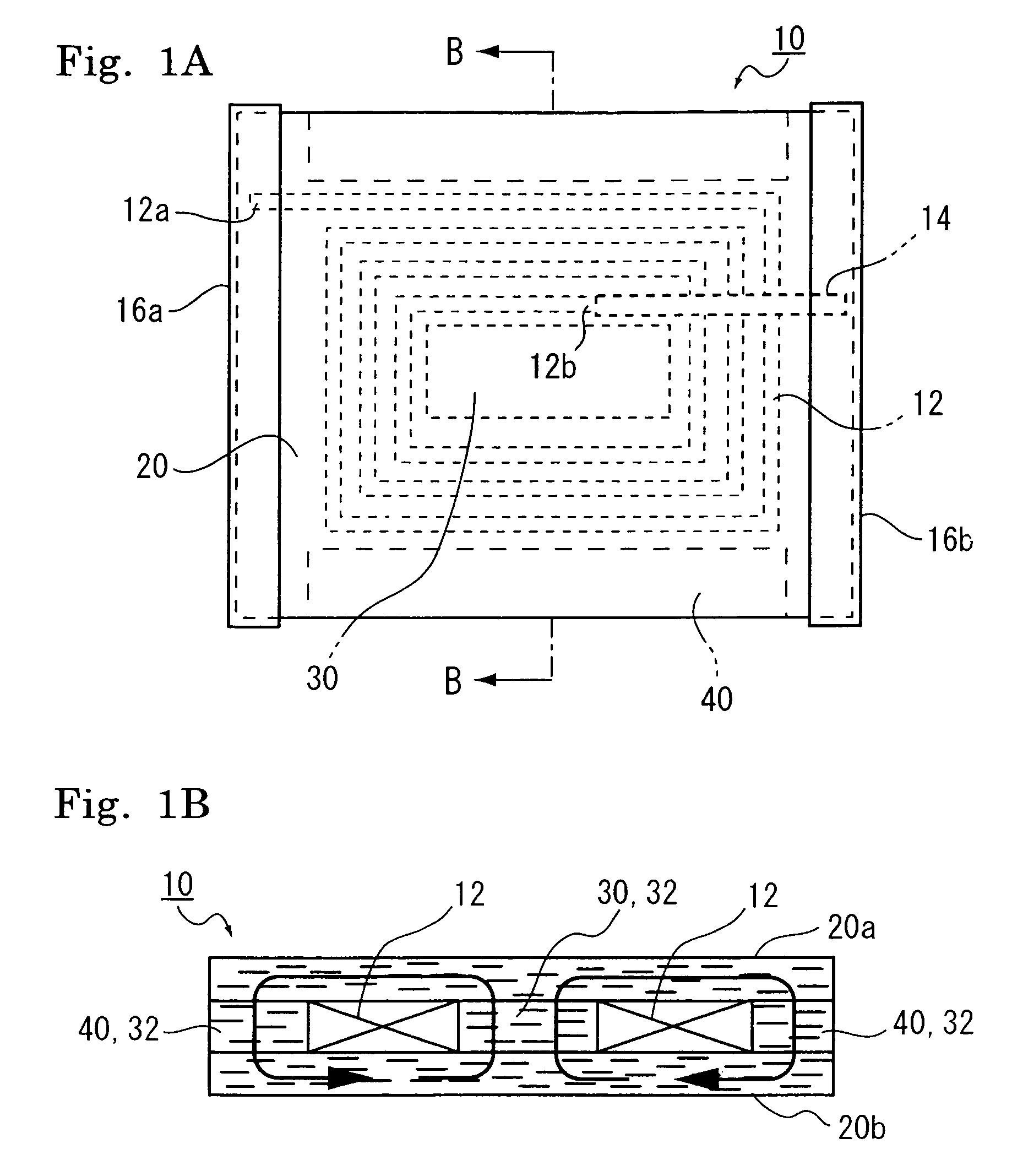
ActiveUS20090002117A1Avoid breakingMagnetic permeabilityTransformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresIn planeHigh resistance
A coil component is provided, and the coil component for an inductor is deformable dependent on flex of a flexible printed board due to elapse of time when mounted thereon, and has high resistance against dropping impact and has an inductance value. The coil component includes an anisotropic compound magnetic sheet which is layered on at least any one or both of the upper surface and the lower surface of an air core coil formed spirally in a plane and which is composed of flat or needle-shaped soft magnetic metal powder, which has a major axis and a minor axis and is dispersed in a resin material, the major axis of which corresponds to an in-plane direction of the air core coil.
Owner:SUMIDA CORP
Piezoelectric device for generating acoustic signal
InactiveUS20070057601A1Optimize assembly structureEasy to assemblePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesBone conduction transducer hearing devicesDrop impactPiezoelectric actuators
There is provided a piezoelectric device for generating an acoustic signal in which an expansion mechanism expands a disposition of a laminated piezoelectric actuator by the principle of leverage. The mass of a base member placed in the expansion mechanism is larger than the mass of a vibration output member. An overall device size is small. The piezoelectric device has a pressurization structure for reducing a tractive force acting on the laminated piezoelectric actuator which is generated by the amplification. This enables provision of a piezoelectric device for generating an acoustic signal that is a small size, highly resistant to dropping impact, and has god acoustic performance with less sound leakage.
Owner:TOKIN CORP
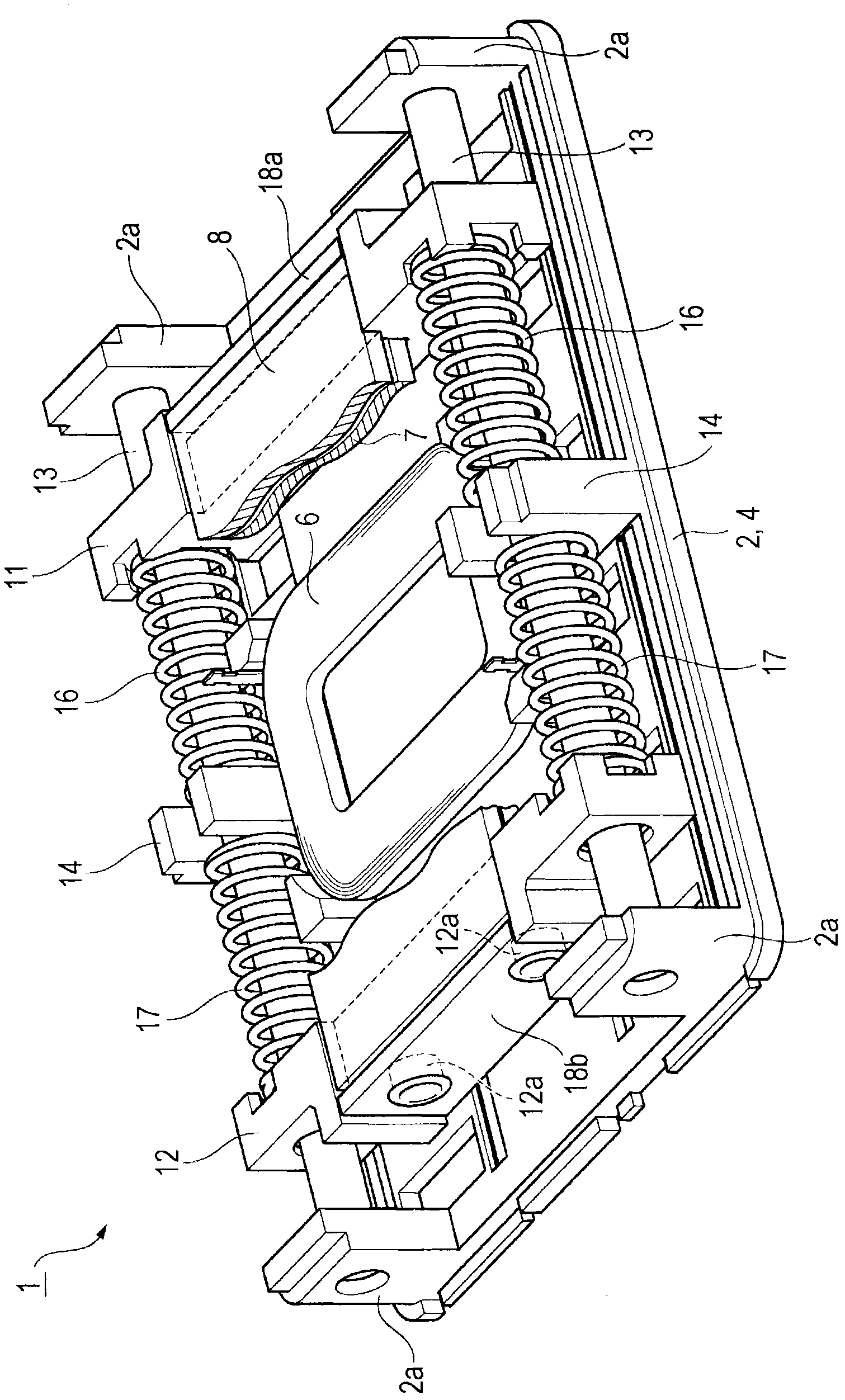
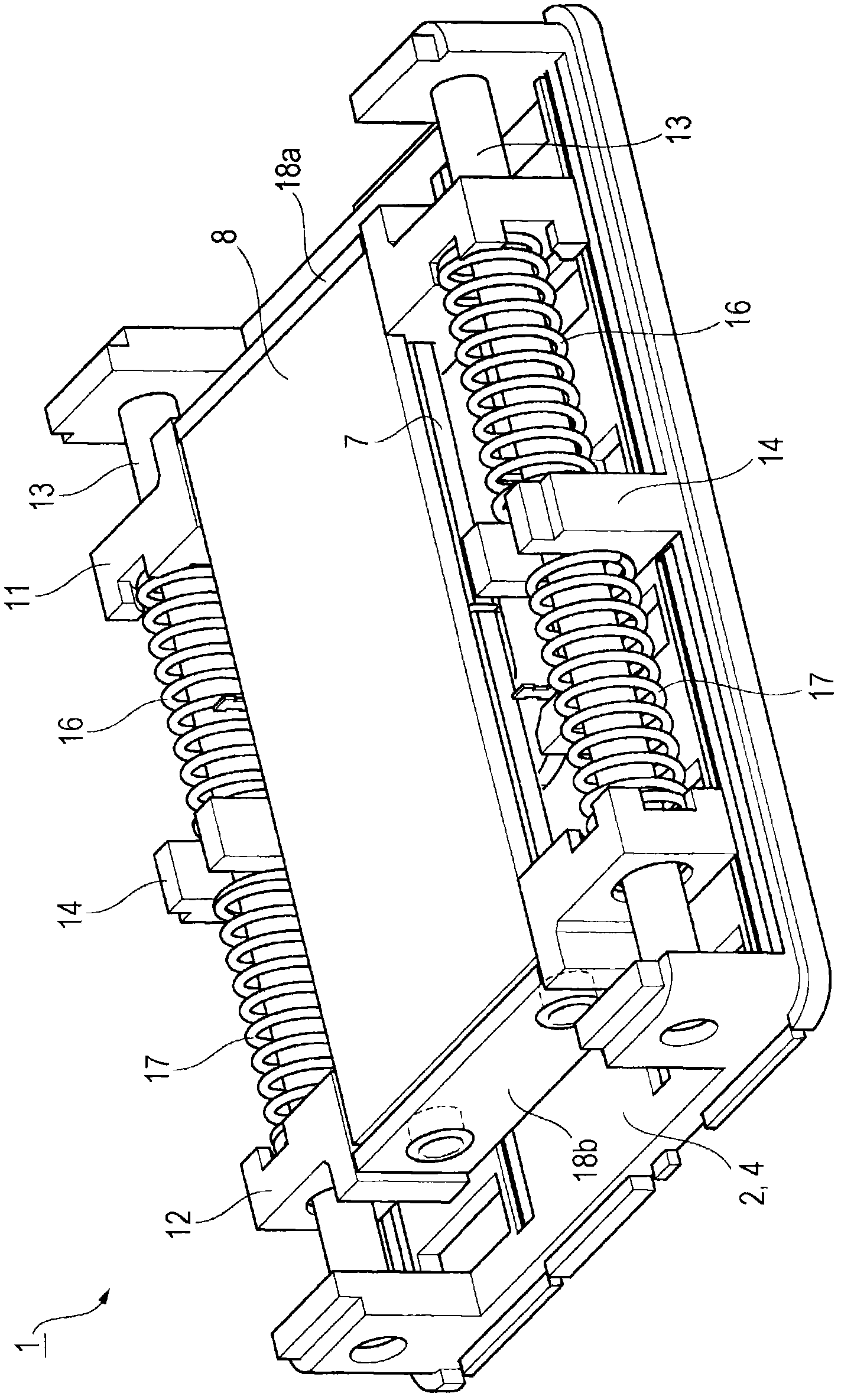
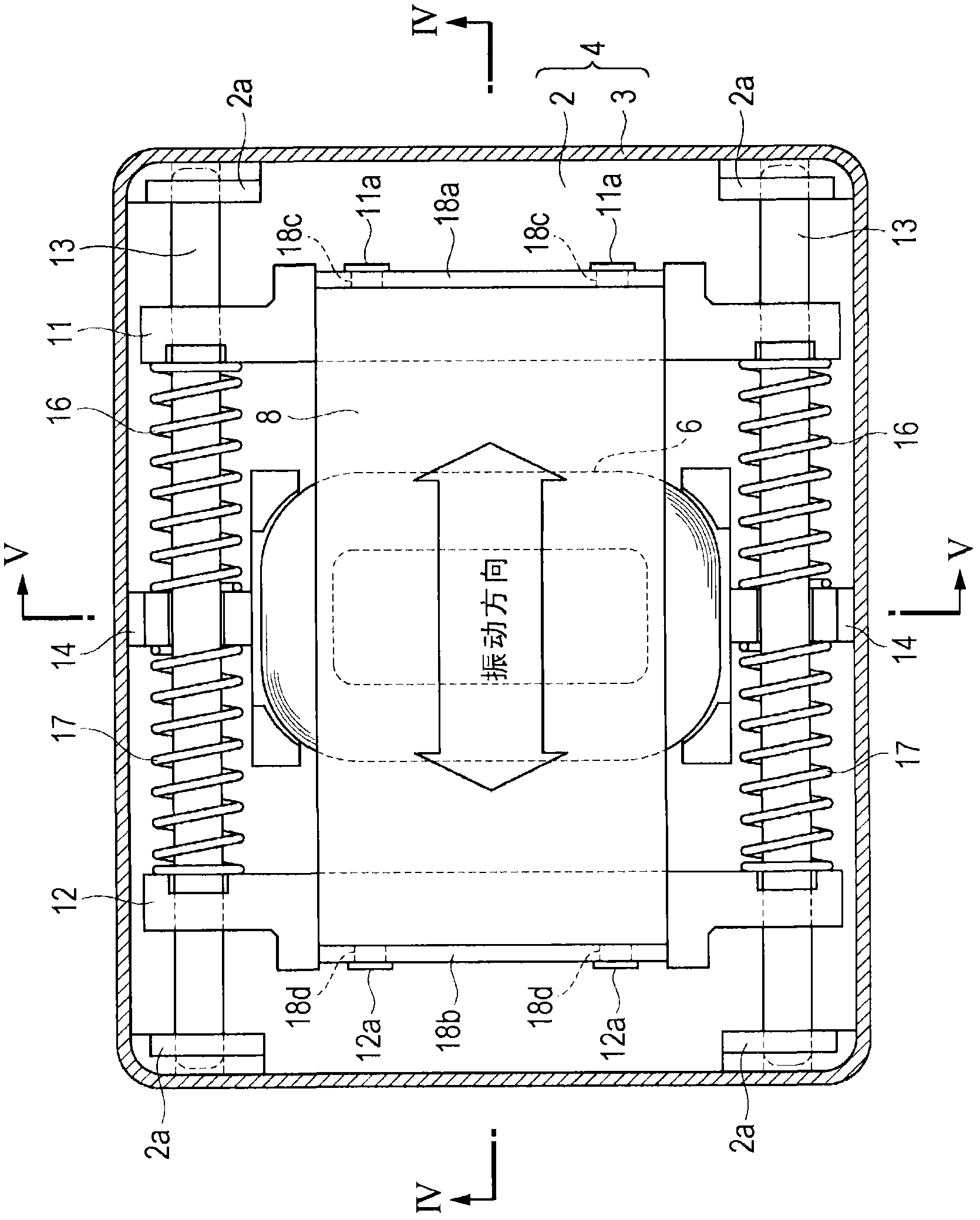
Vibration actuator
A vibration actuator includes a coil that extends in a vibration direction and has a flat shape and a magnet that extends in the vibration direction and has a flat shape, so that a case can be made flat or low profile. A weight portion is supported by a shaft, so that, when a drop impact is applied, the weight portion can move along the shaft and the weight portion is not freely moved in the case. A coil spring is disposed between a spring receiving portion and a weight portion. Therefore there is no unnecessary space in the case, so that space can be saved and the vibration actuator can be made compact.
Owner:COPAL CO LTD
Base cup for a supportable pressurizable container
A container having a curved bottom and base cup which allows the container to stand upright. The container and base cup are fitted together by a mechanical engagement having portions on the container and base cup. The mechanical engagement of the container is disposed within the bottom cone of the container. The mechanical engagement of the base cup is cantilevered from the bottom of the base cup. Such disposition reduces stress at the interface between the side wall of the container and edge of the base, providing for a smoother transition and better appearance. Also, this disposition provides resistance to separation of the container and base cup during drop impact. The bottom of the container may be curved and have a well therein for receiving the contents of the container and a dip tube.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Glass reinforced nylon blend with improved knitline strength
The present invention provides a polymer alloy including from about 40% to about 75% by weight of at least one polyamide, from about 10% to about 50% by weight polypropylene, from about 0.01% to about 1.0% by weight of at least one block copolymer including a vinyl aromatic monomer and a conjugated diene, and also includes an unsaturated dicarboxylic reagent, from about 0.1% to about 5.0% by weight of at least one block copolymer or terpolymer, wherein the terpolymer may have an unsaturated dicarboxylic reagent grafted thereto, from about 0.01% to about 7.5% of a compatibilizing agent, and from about 5% to about 50% by weight of a filler. The alloy of the present invention exhibits improved knitline strength and improved drop impact results compared with prior art fiberglass-reinforced nylon blends.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ADVANCED POLYMERS INC
Sealed cell using film outer casing body
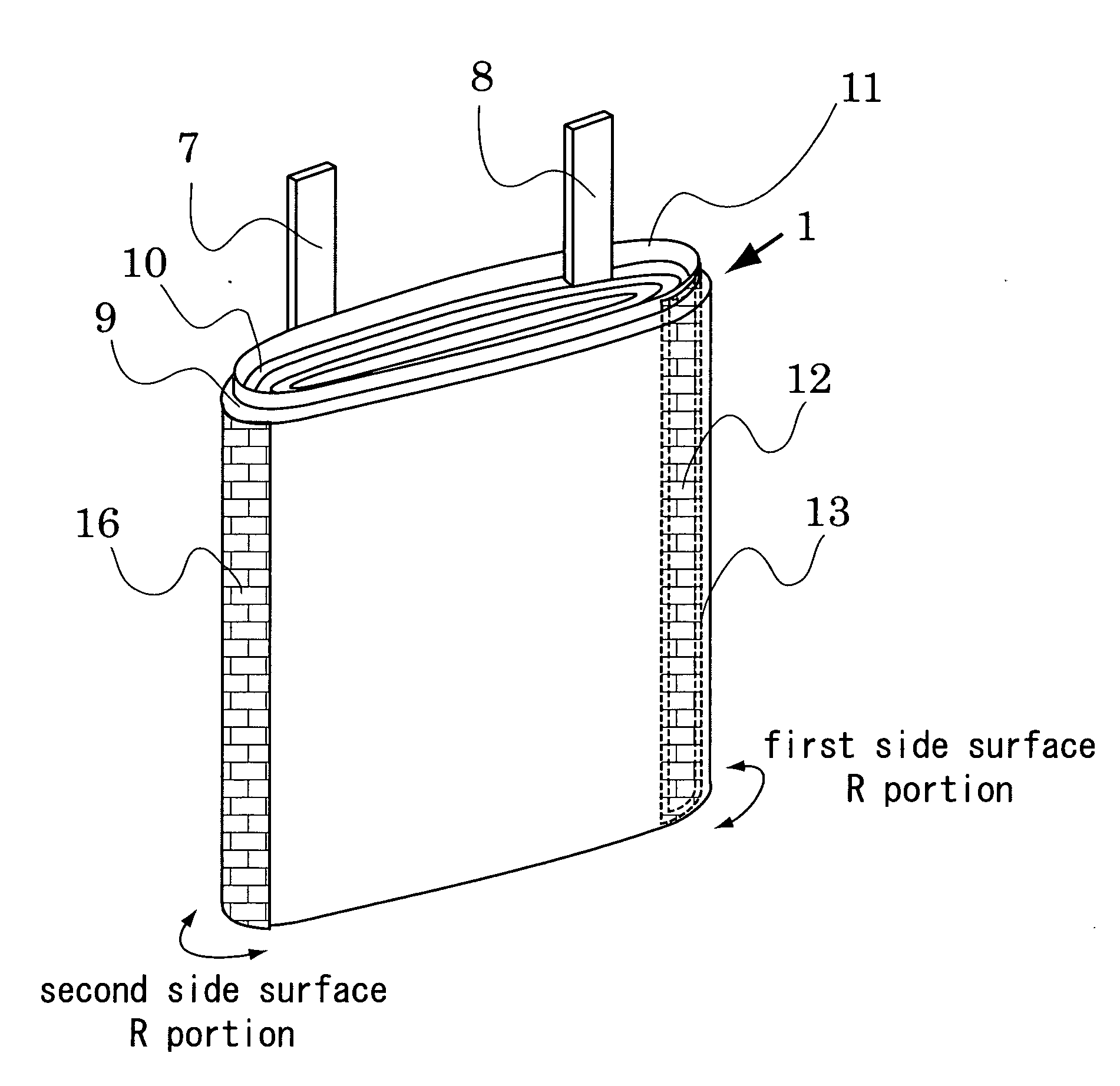
InactiveUS20050069764A1Increase credibilityEasy to transformNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsFinal product manufactureDrop impactBiomedical engineering
The present invention prevents a cell with a film outer casing body from suffering internal short-circuiting caused by dropping impacts. This is accomplished by a sealed cell with a film outer casing body having a flat electrode body. The flat electrode body has first and second electrodes and a separator therebetween, which are wound into a flat shape having first and second flat side surface R portions. The first electrode is the outermost surface of the electrode body. An insulation member is provided on the electrode body to completely cover the lower edge and / or upper edge of the first flat side surface R portion. Specifically, the insulation film is provided between the outermost portion of the first electrode and a portion of the second electrode immediately inside the outermost portion, and between the portion of the second electrode and another portion of the first electrode immediately inside the portion of the second electrode.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Vibration actuator
InactiveCN102055299AAchieve thinningDoes not complicate the structureDynamo-electric machinesDrop impactCoil spring
Owner:COPAL CO LTD
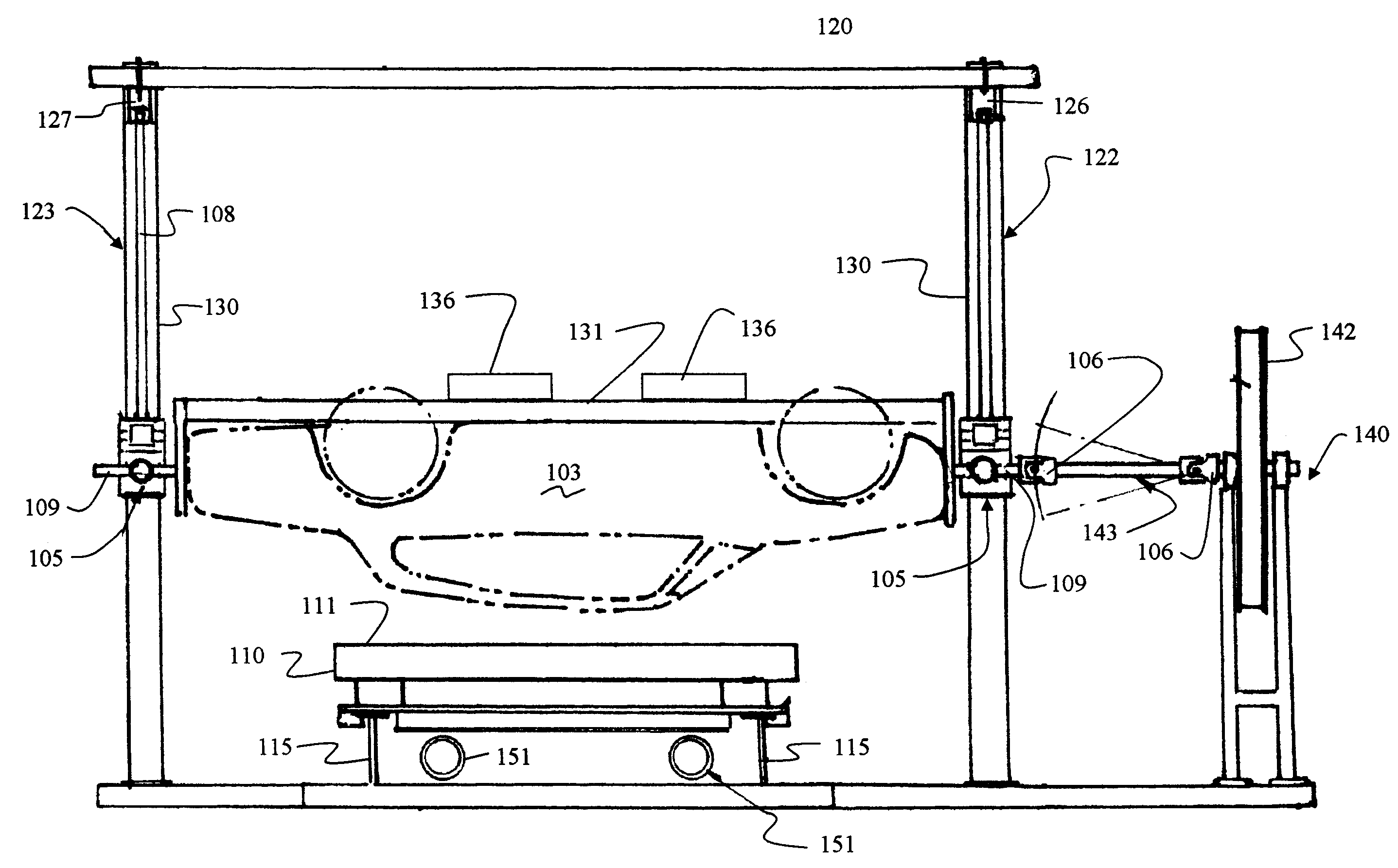
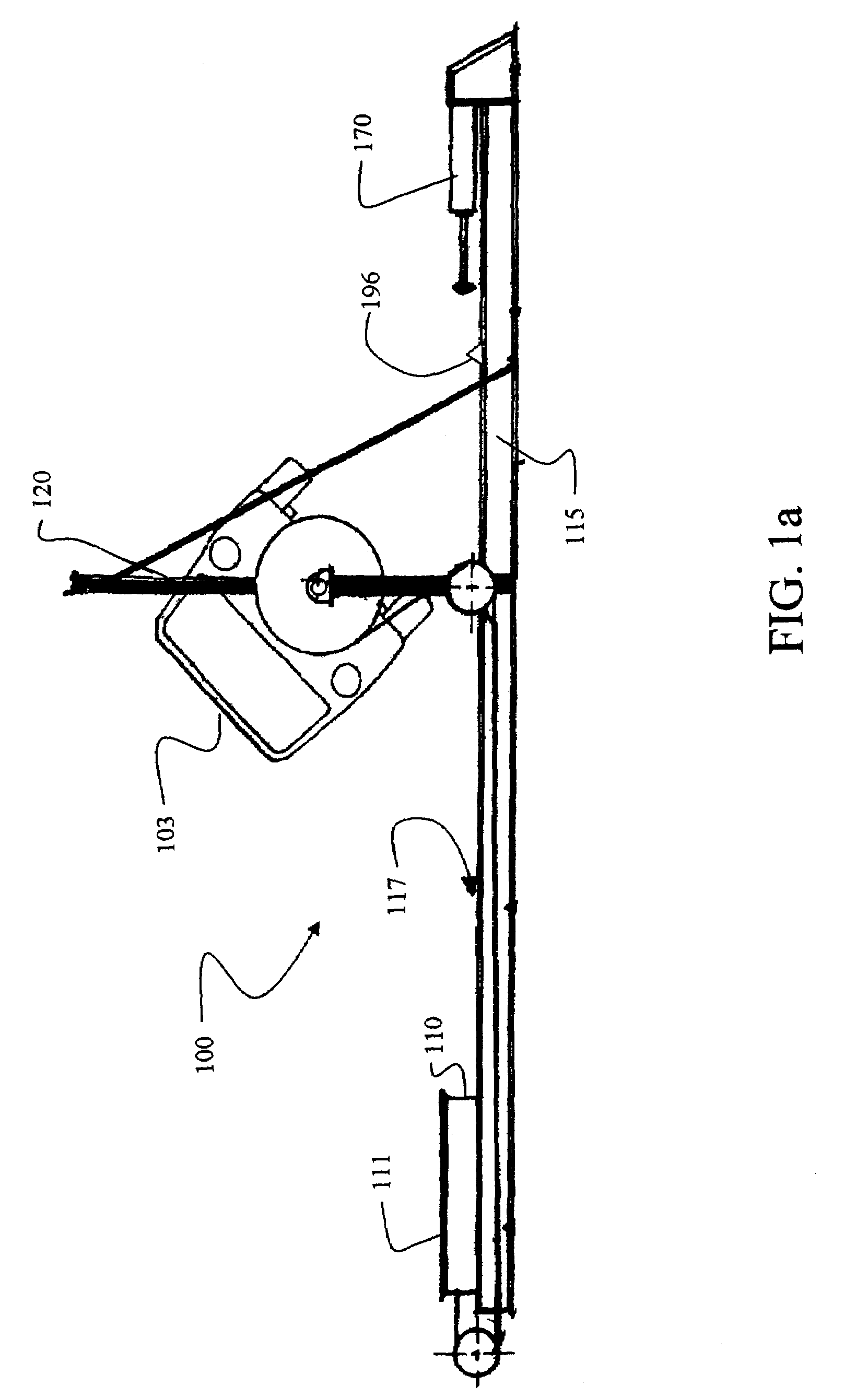
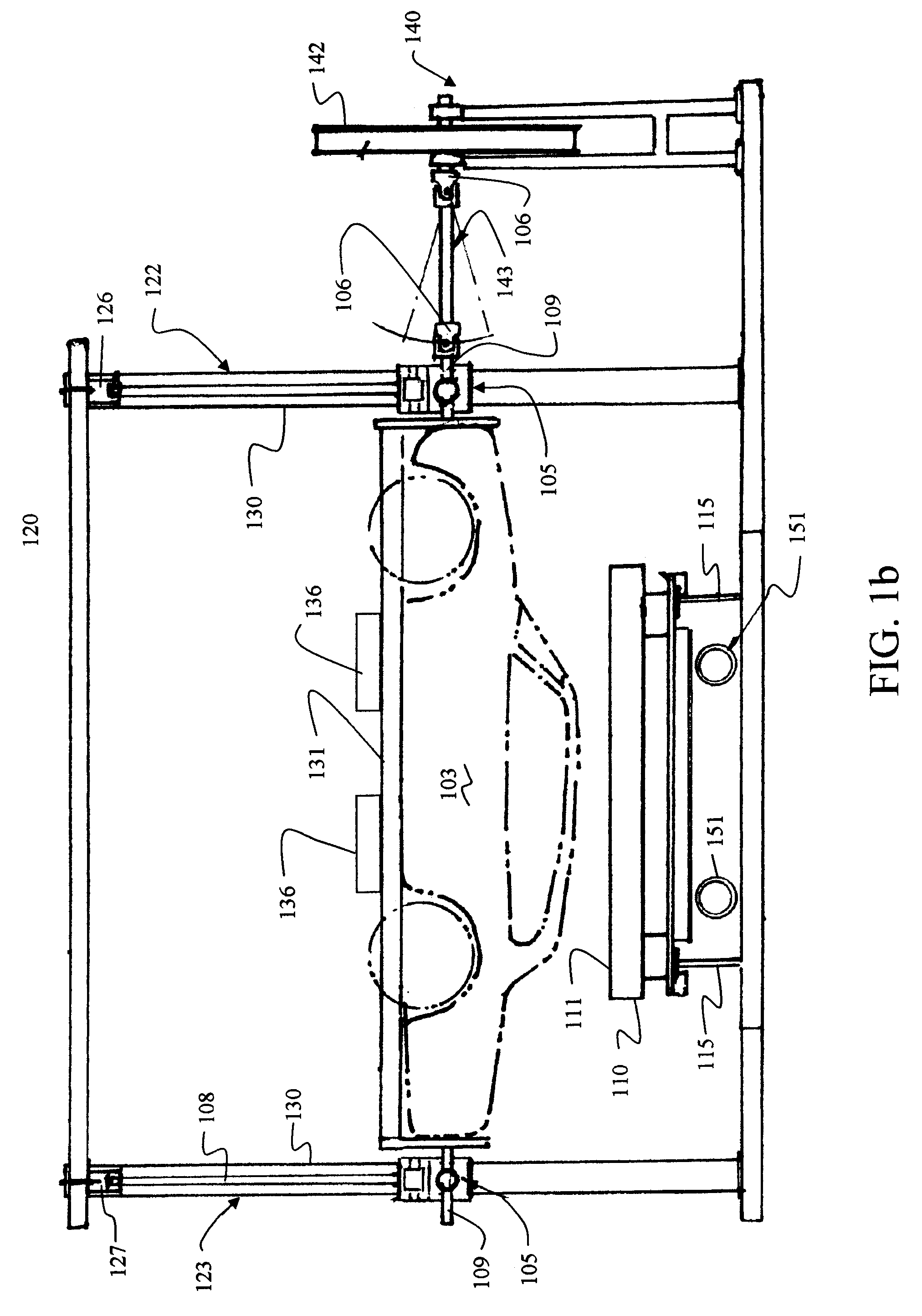
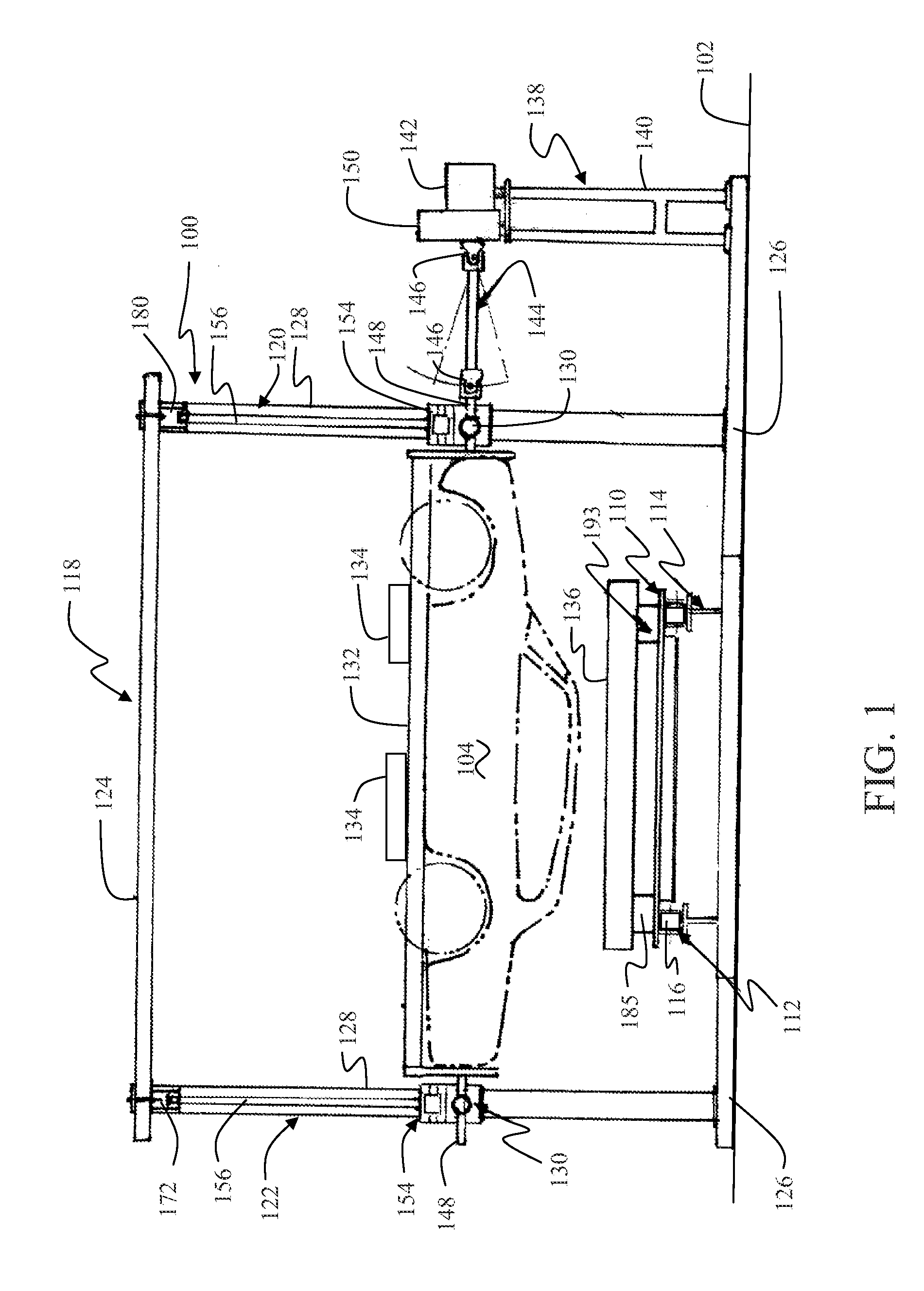
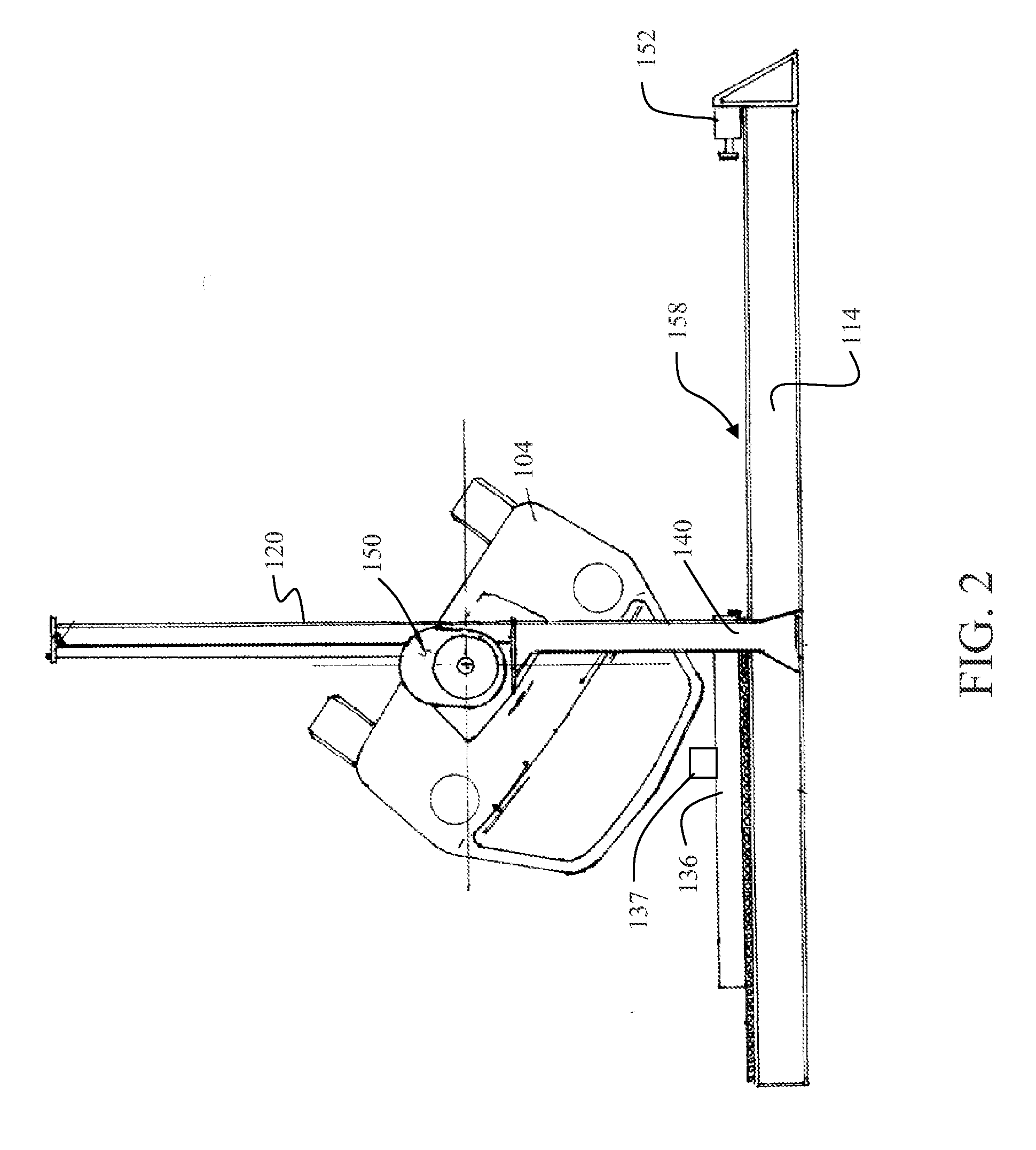
Vertical dropping impact test system
ActiveCN104236840AEasy to convertThe test result is accurateVibration testingShock testingDrop impactEngineering
The invention provides a vertical dropping impact test system which comprises a weight-adjustable load, a suspension assembly, a monitoring subsystem, a support frame and a failure protective device. The weight-adjustable load is used for impacting a tested device, the suspension assembly is used for controlling the dropping height of the weight-adjustable load, and the monitoring subsystem is used for monitoring impact procedures; the weight-adjustable load is arranged on the support frame and can move up and down along the support frame, the tested device is arranged right below the weight-adjustable load, the suspension assembly is arranged on the support frame and can adjust the dropping height of the weight-adjustable load, the failure protective device is arranged on the support frame, can move up and down along the support frame and can be locked with the support frame so that the weight-adjustable load can stop dropping, and the suspension assembly and the failure protective device can act under the control of the monitoring subsystem. The vertical dropping impact test system has the advantages that integral procedures of impact or vibration tests and test parameters can be completely recorded, test results are accurate, and the vertical dropping impact test system is high in reliability.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Impact detecting apparatus and package device
InactiveUS8240270B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMeasurement apparatus componentsDrop impactIndustrial engineering
Owner:RICOH KK
Coil component
ActiveUS7859377B2Highly resistant against drop shockIncrease the inductance valueTransformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresHigh resistanceIn plane
A coil component is provided, and the coil component for an inductor is deformable dependent on flex of a flexible printed board due to elapse of time when mounted thereon, and has high resistance against dropping impact and has an inductance value. The coil component includes an anisotropic compound magnetic sheet which is layered on at least any one or both of the upper surface and the lower surface of an air core coil formed spirally in a plane and which is composed of flat or needle-shaped soft magnetic metal powder, which has a major axis and a minor axis and is dispersed in a resin material, the major axis of which corresponds to an in-plane direction of the air core coil.
Owner:SUMIDA CORP
Coil component
InactiveCN101615490AFlexibleNo brittle failureTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsPrinted inductancesIn planeHigh resistance
A coil component is provided, and the coil component for an inductor is deformable dependent on flex of a flexible printed board due to elapse of time when mounted thereon, and has high resistance against dropping impact and has an inductance value. The coil component includes an anisotropic compound magnetic sheet which is layered on at least any one or both of the upper surface and the lower surface of an air core coil formed spirally in a plane and which is composed of flat or needle-shaped soft magnetic metal powder, which has a major axis and a minor axis and is dispersed in a resin material, the major axis of which corresponds to an in-plane direction of the air core coil.
Owner:SUMIDA CORP
Liquid crystal display apparatus
ActiveUS20070279728A1Improve deformationIncrease display areaOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsDrop impactLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display apparatus includes an optical sheet for uniformly diffusing light toward a light-emitting face, and a resin frame onto which the optical sheet is attached. The optical sheet has the first fixing portion or the second fixing portion. The optical sheet is attached to the resin frame by fitting the first fixing portion or the second fixing portion to a concavity created at the resin frame at a part corresponding to the first fixing portion or the second fixing portion. At least one notch is created at a boundary area between a display area of the optical sheet and the first fixing portion or the second portion so that deformation in the optical sheet caused by a significant mechanical stress, such as drop impact, does not extend to the display area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Elevator safety airbag device
The invention discloses an elevator safety airbag device. The elevator safety airbag device consists of a hydraulic cylinder, a buffer plate, a buffer spring, a crash sensor, a controller, a gas emitter and an airbag. Hydraulic oil is filled in the hydraulic cylinder, dropping impact force of an elevator is absorbed by utilizing the hydraulic oil, and the impact force is converted into pressure energy of the hydraulic oil; partial drop impact force of the elevator is reduced by utilizing the buffer spring; and moreover, the airbag is exploded to inflate and cushion the elevator, the dropping impact force of the elevator is reduced, and casualties or financial losses are prevented or reduced.
Owner:林智勇
Glass substrate for information recording medium and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100215993A1Improve balanceHighly smooth surface propertyMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersDrop impactYoung's modulus
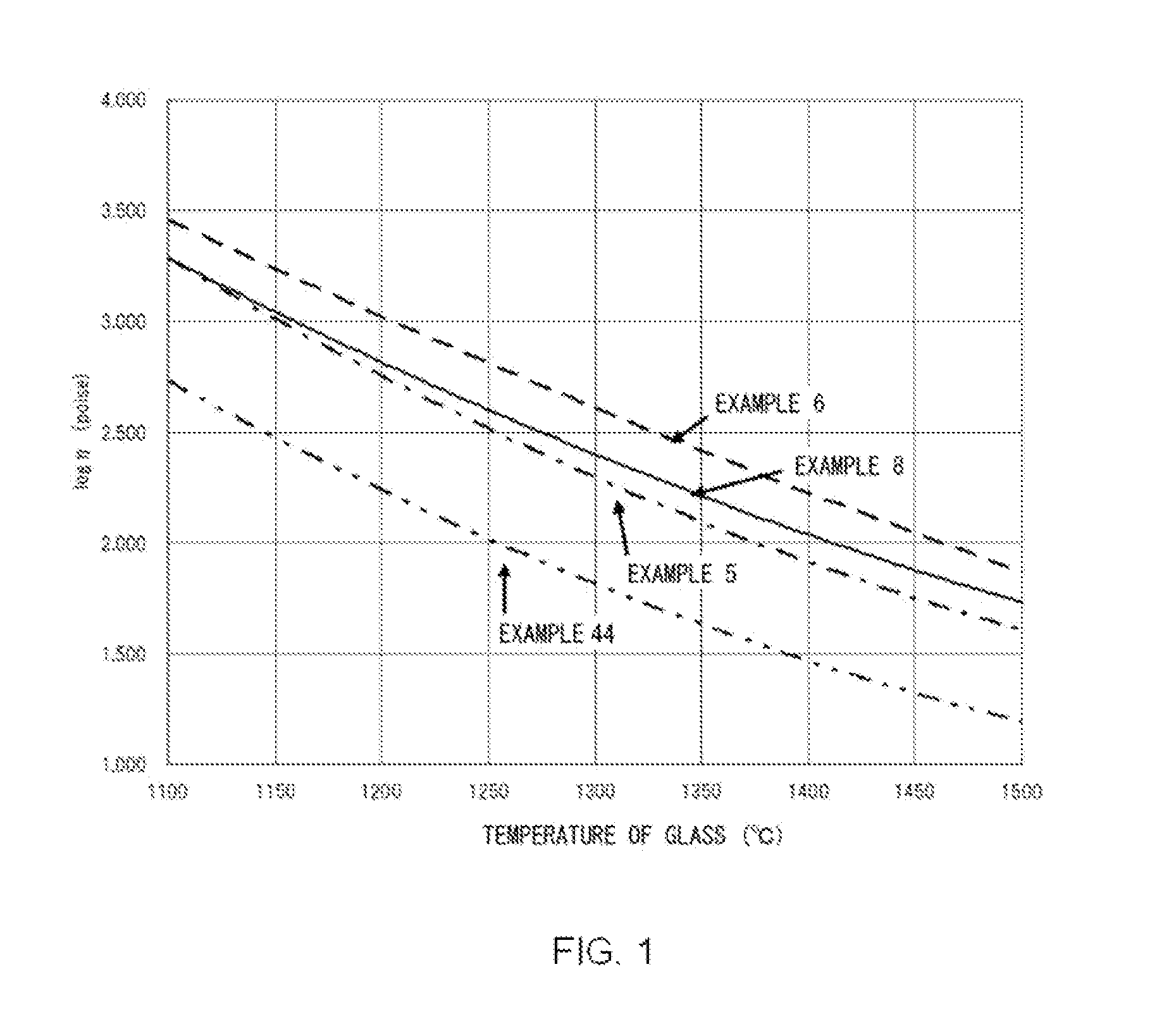
There is provided a glass substrate which has the properties required in the use as a substrate for an information recording medium of the next generation such as a perpendicular magnetic recording system, and can be applied as a substrate for an information recording medium of the next generation particularly on the premise of using the glass substrate in a dynamic environment. More particularly, there is provided a glass substrate for an information recording medium which has sufficiently high surface hardness, has a good balance between specific gravity and mechanical strength, and has high strength to withstand high speed rotation or drop impact, and which can be produced with a high productivity adequate for a direct press method, without the occurrence of bubbles in the glass blank or reboil upon pressing even if arsenic components or antimony components are not substantially used. A glass substrate for an information recording medium, includes, as expressed in terms of percent by mass on the oxide basis: 52 to 67% of SiO2, 3 to 15% of Al2O3, and 0.2 to 8% of P2O5, the glass substrate having a Young's modulus of 85 GPa or greater, a specific gravity of 2.60 or less, and a ratio of Young's modulus to specific gravity (Young's modulus / specific gravity) of 33.0 or greater.
Owner:OHARA
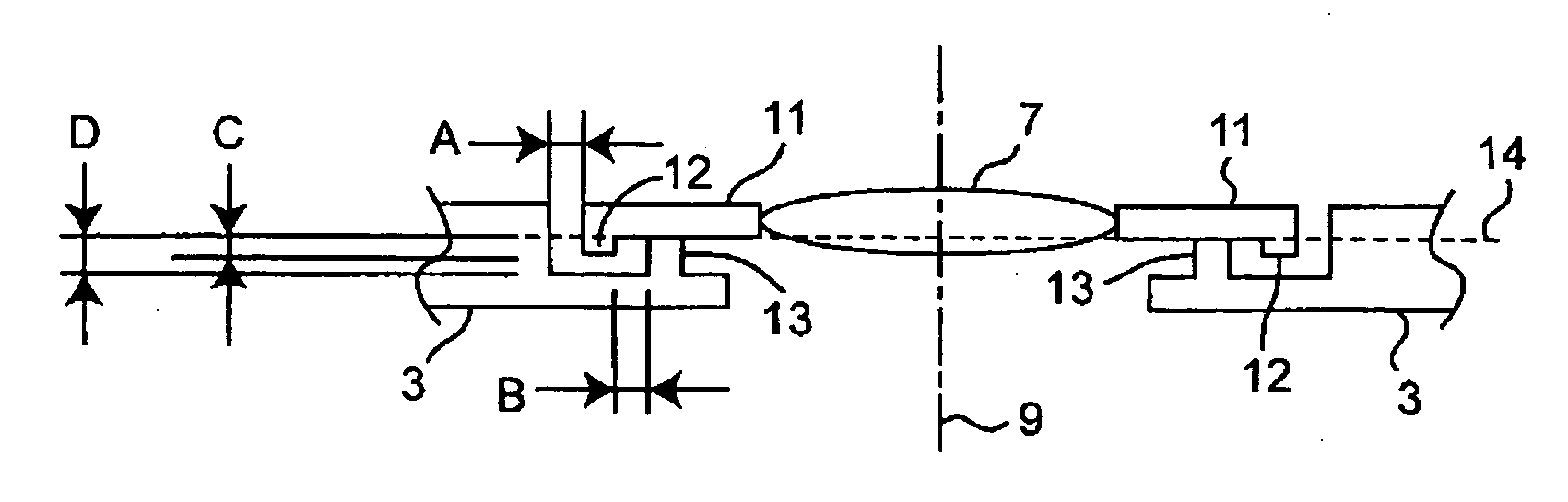
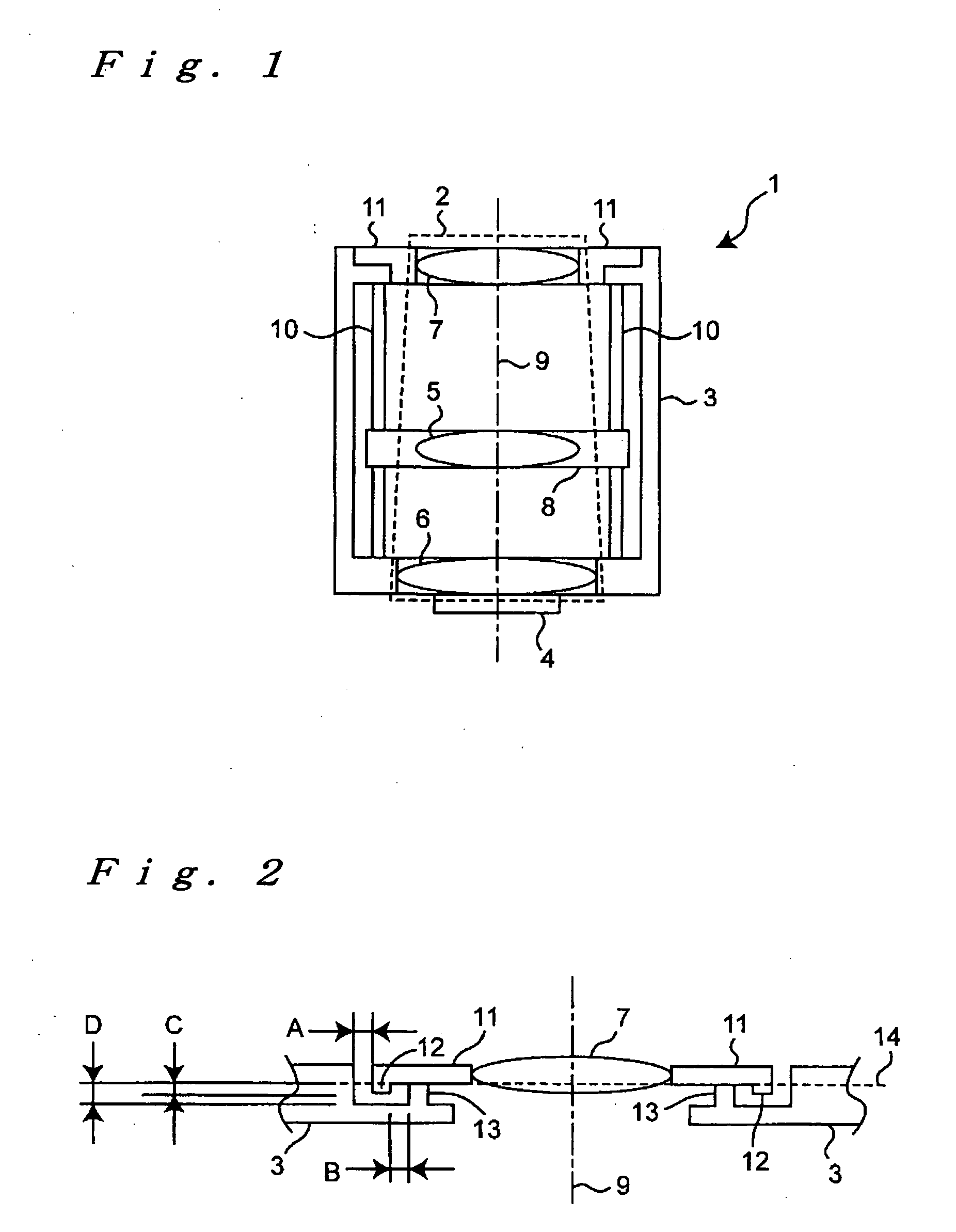
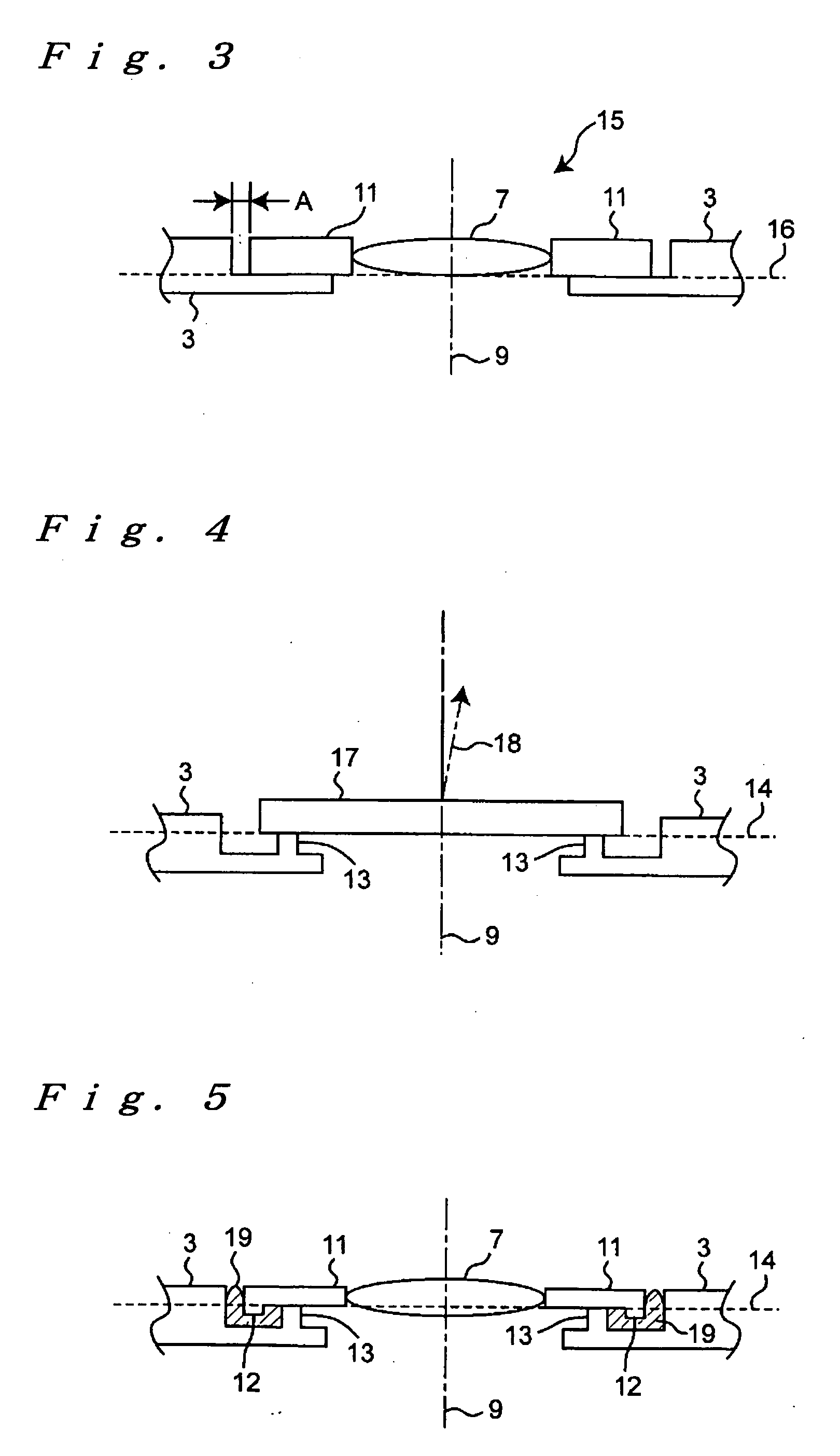
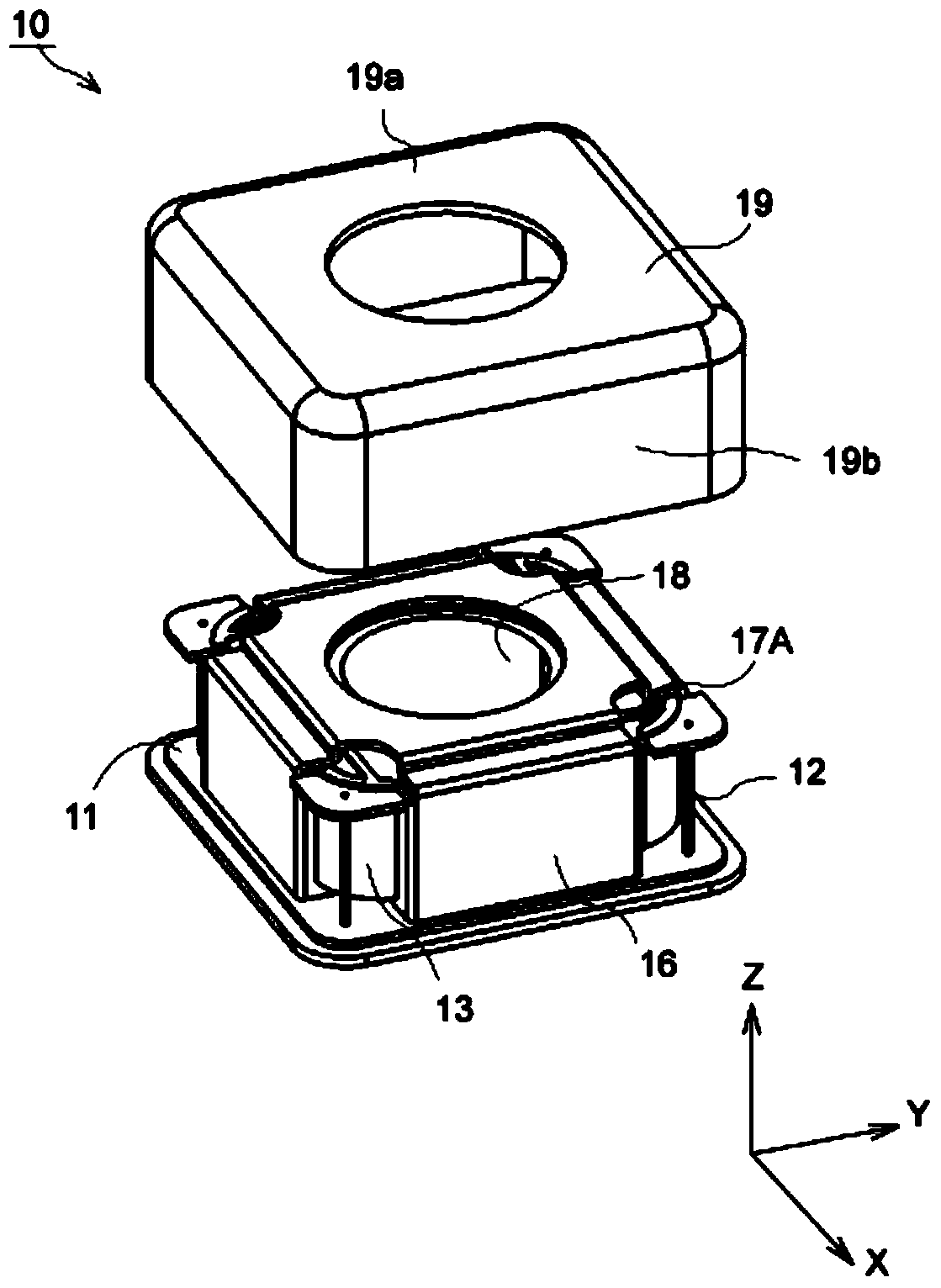
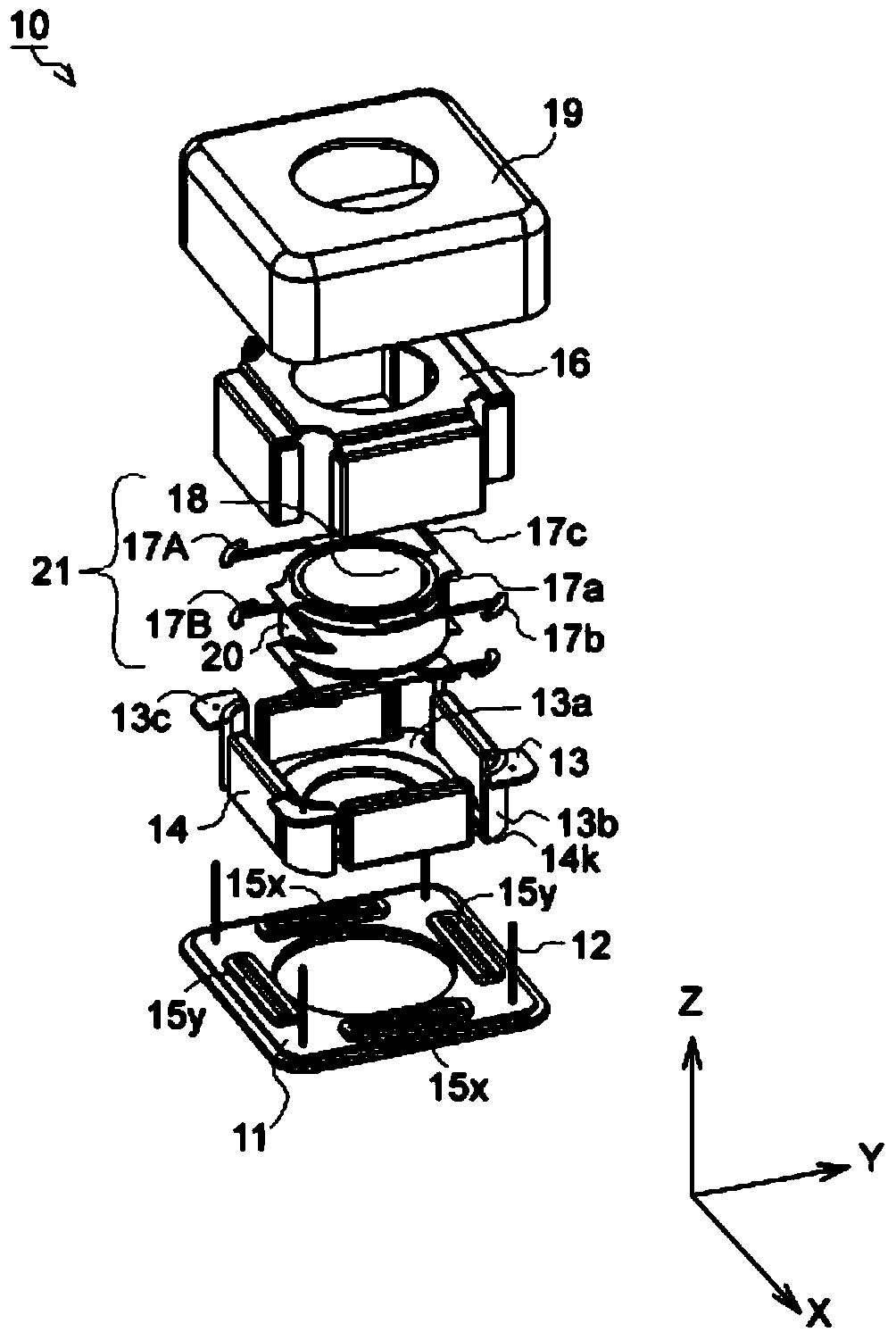
Camera Module
On an outer peripheral portion of an adjusting lens holder (11), a ring-shaped first protrusion (12) is arranged to protrude to a housing (3). On an inner peripheral portion of the housing (3), a ring-shaped second protrusion (13) is arranged to protrude to the adjustment lens holder (11). The first protrusion (12) is arranged outside the second protrusion (13), an interval (B) between the both protrusions (12, 13) is smaller than a clearance (A) between the adjustment lens holder (11) and the housing (3), and the height of the first protrusion (12) is lower than that of the second protrusion (13). The minimum value of the clearance (A) is “A−B” and a space is provided between the first protrusion (12) adjacent to the clearance (A) and the housing (3). Thus, an adhesive is prevented from leaking out at the time of applying the adhesive in the clearance (A), and the space is filled with the adhesive. An optical system is prevented from breaking due to dropping impact by strongly fixing the adjusting lens holder (11) to the housing (3).
Owner:SHARP KK
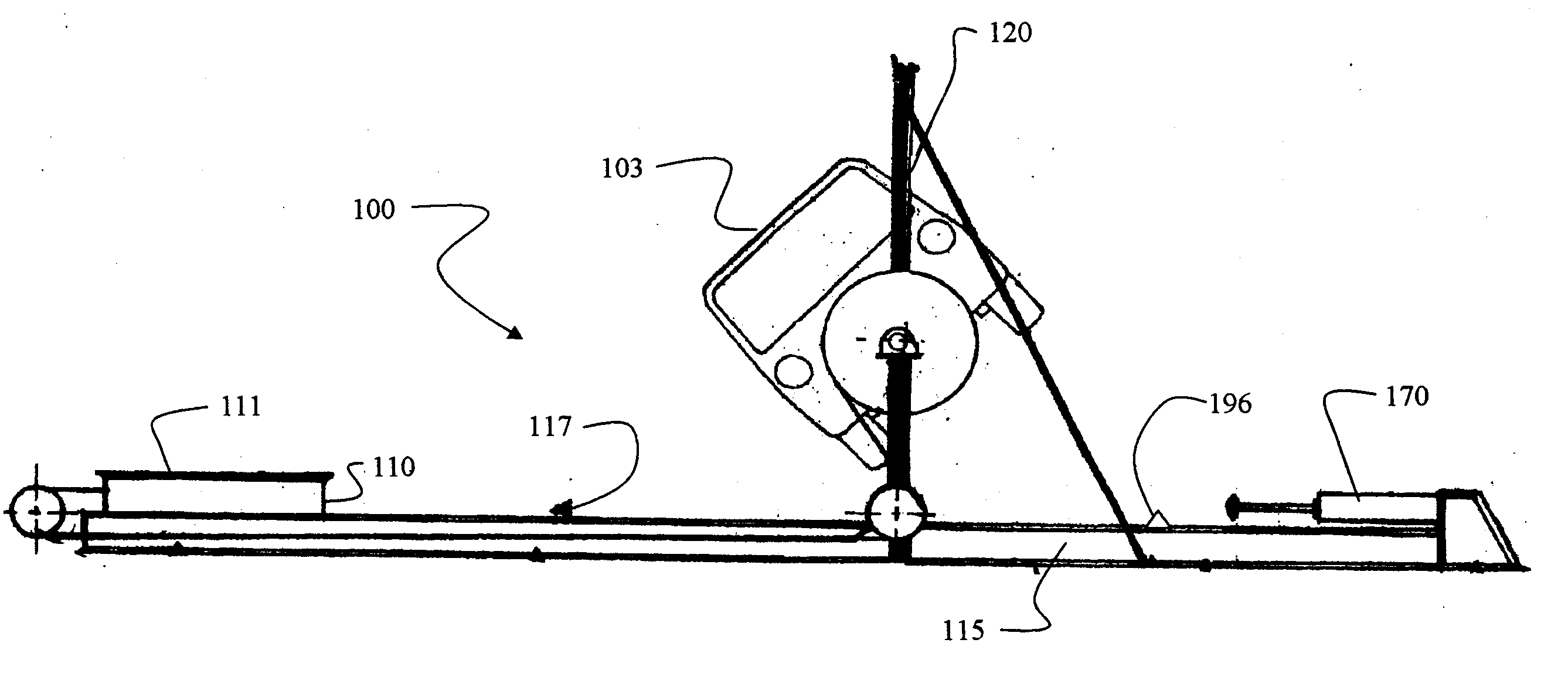
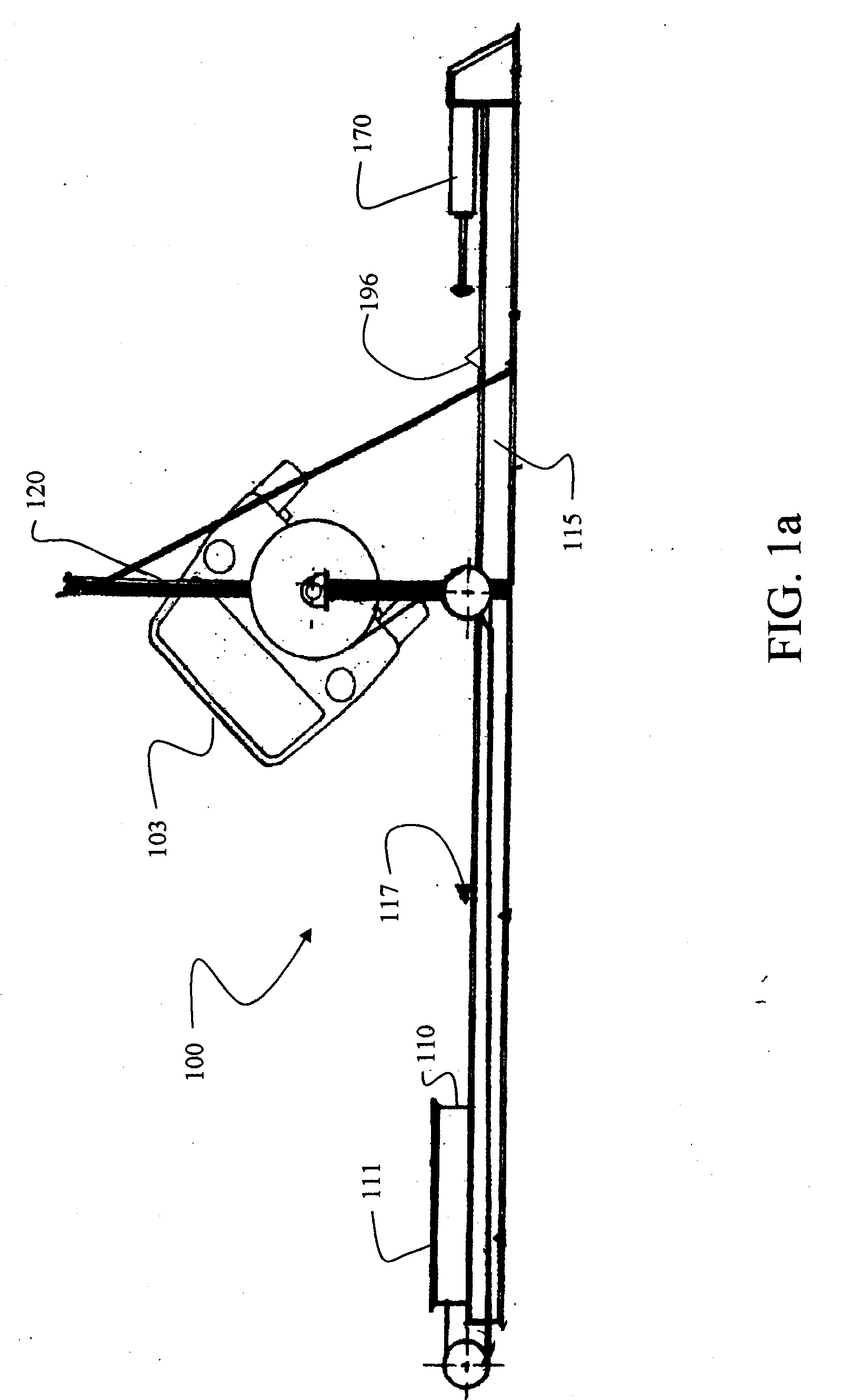
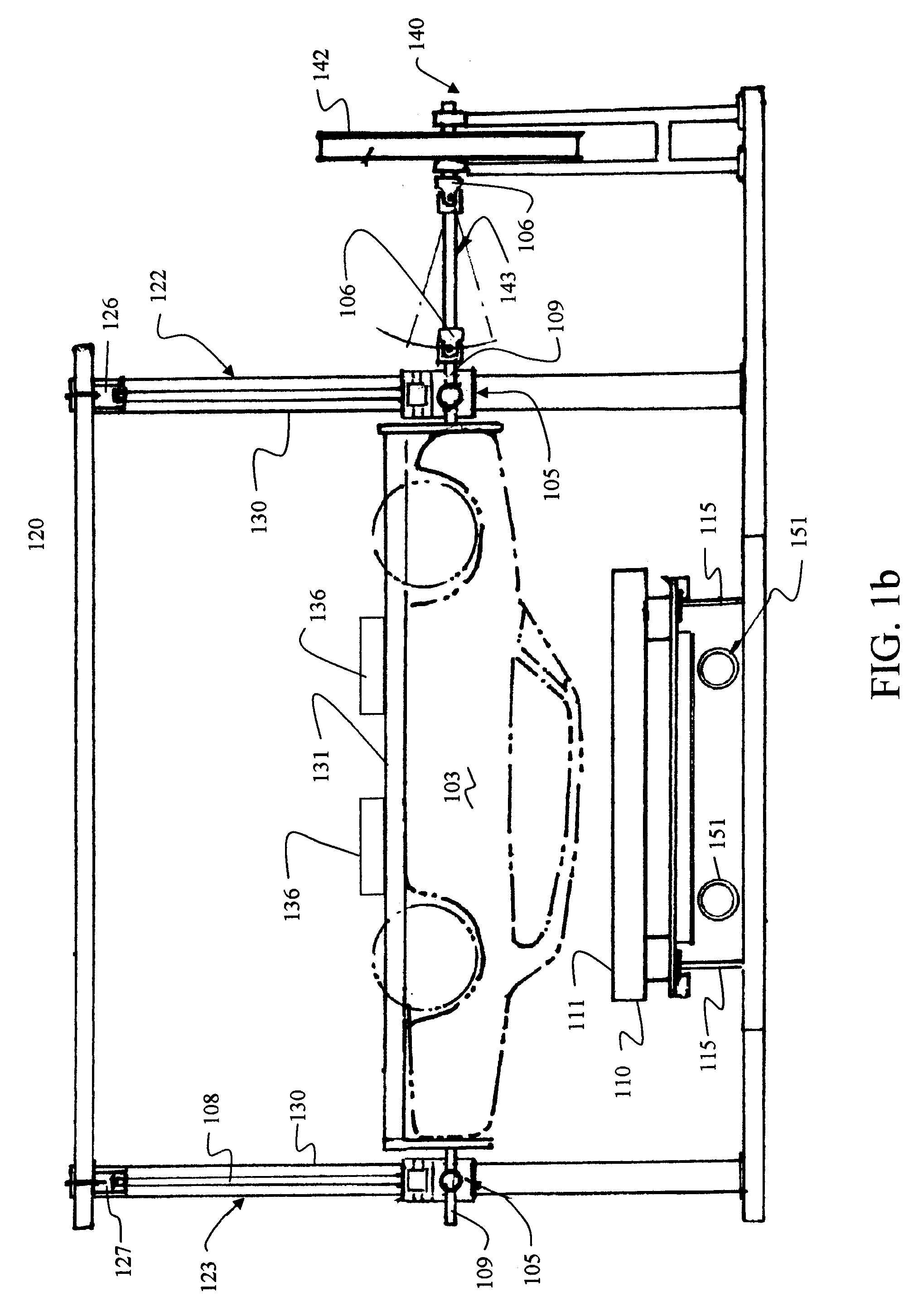
Vehicle Rollover Test Fixture
InactiveUS20060278026A1Avoid damageLimiting further damageWeather/light/corrosion resistanceAcceleration measurementRolloverDrop impact
A test fixture for rollover crash testing of a test vehicle onto a moving surface employs a cradle to support and rotate the test vehicle. A vertical support structure to positions and releasably holds the cradle. A moving sled having a contact surface is carried by a guide extending beneath the structure and the cradle fixture. The cradle is rotated and released from the structure responsive to a sensor for contact within a drop impact zone on the contact surface of the moving sled. Vertical motion of the cradle is then arrested to prevent further damage to the test vehicle or the test structure.
Owner:SAFETY TESTING INT
Reinforced Thermoplastic Resin Composition And Molded Article
The present invention relates to a reinforced thermoplastic resin composition having excellent moldability, processability, and mechanical strengths, as well as being capable of improving the drop impact resistance (surface impact strength determined by a falling ball test). The reinforced thermoplastic resin composition of the present invention includes 10 to 60% by mass of a graft copolymer (A) having a graft chain (A2) grafted to a rubber polymer (A1); 40 to 90% by mass of a matrix polymer (B) which includes one or more types of polymers selected from the group consisting of a vinyl-based copolymer (B-1), a polycarbonate resin (B-2), and a polyester resin (B-3); 0.1 to 50 parts by mass of an inorganic filler (D) and 0.5 to 20 parts by mass of a glycidyl ether unit-containing polymer (E) having a mass average molecular weight of 3,000 to 200,000.
Owner:TECHNO UMG CO LTD
Drop test apparatus
InactiveUS20090031783A1Avoid influenceEasy to holdUsing mechanical meansStrength propertiesFree fallingDrop impact
Drop test apparatus, for performing a drop impact test by dropping an article to be tested on a landing surface in a free fall state and by colliding the article with the landing surface, is equipped with a holder for holding the article and an acceleration means for accelerating the holder. The holder with the article is accelerated in the dropping direction of the article by the acceleration means, and the article is released from the holder at the point when the holder is accelerated to a predetermined speed and is dropped to the landing surface. The reproducibility of the test can be enhanced due to an elimination of an unstable factor such as frictional resistance when the holder is dropped, and a higher test in a dropping height without scaling-up the apparatus can be achieved.
Owner:HITACHI TECH & SERVICES
Lead-free solder alloy
ActiveCN101208174AAvoid yellowingInhibited porosityPrinted circuit assemblingWelding/cutting media/materialsDrop impactImpurity
Disclosed is a lead-free solder alloy exhibiting improved drop impact resistance even after thermal aging while being good in soldering properties, void formation and discoloration. Specifically disclosed is a solder alloy consisting essentially of, in mass %, (1) 0.8-2.0% of Ag, (2) 0.05-0.3% of Cu, (3) one or more elements selected from not less than 0.01% and less than 0.1% of In, 0.01-0.04% of Ni, 0.01-0.05% of Co and 0.01-0.1% of Pt, and if necessary (4) one or more elements selected from Sb, Bi, Fe, Al, Zn and P in an amount of not more than 0.1% in total, and the balance of Sn and unavoidable impurities.
Owner:SENJU METAL IND CO LTD
Base cup for a supportable pressurizable container
A container having a curved bottom and base cup which allows the container to stand upright. The container and base cup are fitted together by a mechanical engagement having portions on the container and base cup. The mechanical engagement of the container is disposed within the bottom cone of the container. The mechanical engagement of the base cup is cantilevered from the bottom of the base cup. Such disposition reduces stress at the interface between the side wall of the container and edge of the base, providing for a smoother transition and better appearance. Also, this disposition provides resistance to separation of the container and base cup during drop impact. The bottom of the container may be curved and have a well therein for receiving the contents of the container and a dip tube.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Cell safety valve and cell having same
InactiveUS7140380B2Quickly release generatedAvoid breakingEqualizing valvesSafety valvesDrop impactEngineering
A cell according to the present invention comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, an electrolyte solution, and an outer casing, wherein the outer casing comprises a valve plate 30 having a thickness, an annular-shaped break groove 4 formed on the valve plate, and one or more of break aiding grooves 1 in the inner area of the break groove, and wherein the break aiding groove comprises such configurations that remaining thickness of the valve plate at the break aiding groove is thicker than remaining thickness of the valve plate at the break groove, and at least one end of the break aiding groove is connected with the break groove. In a cell provided with a valve plate which is a safety valve 9 comprising the break groove and the break aiding groove, the safety valve operates smoothly and releases a gas inside the cell quickly, and resistance to dropping impact is improved.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
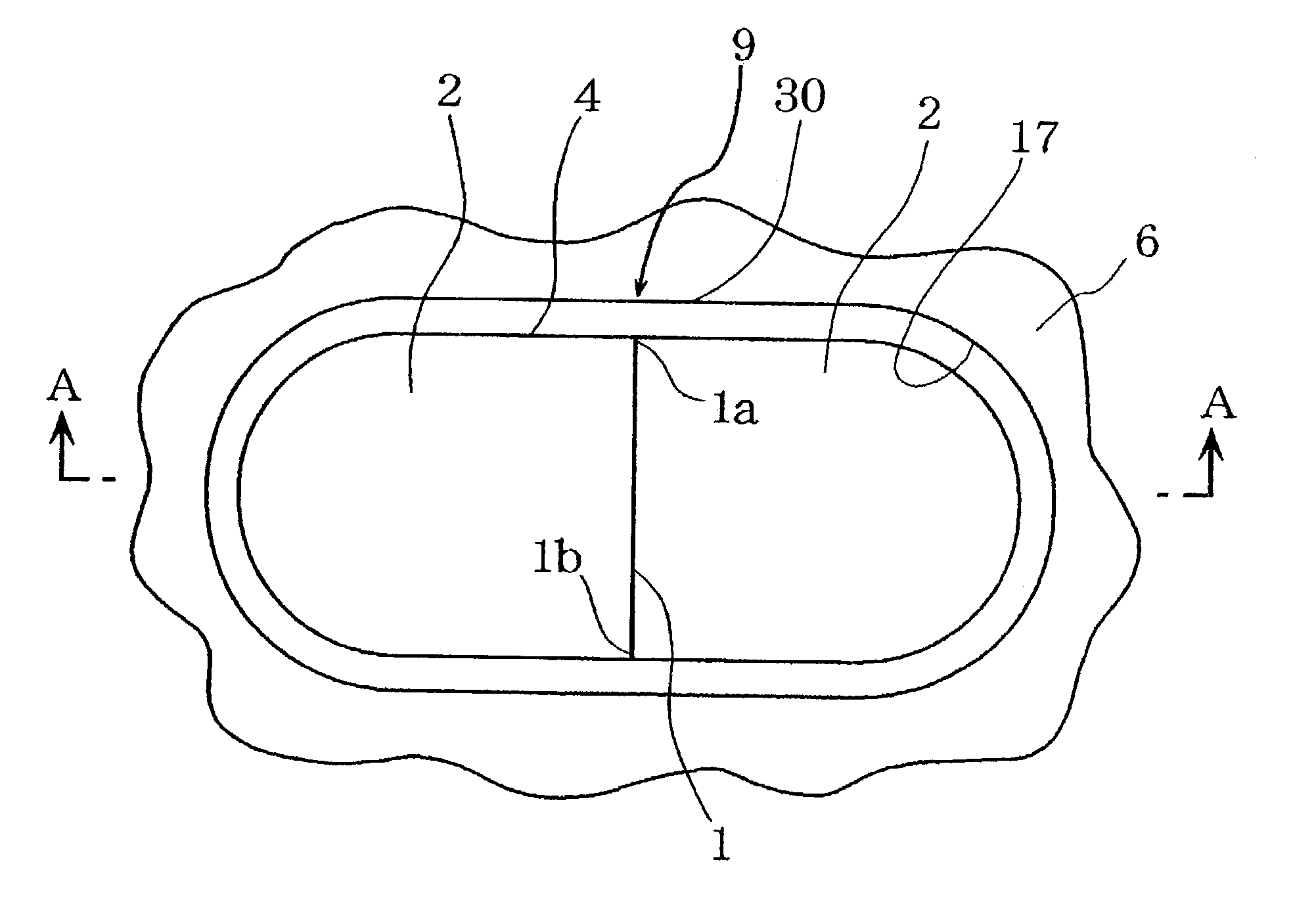
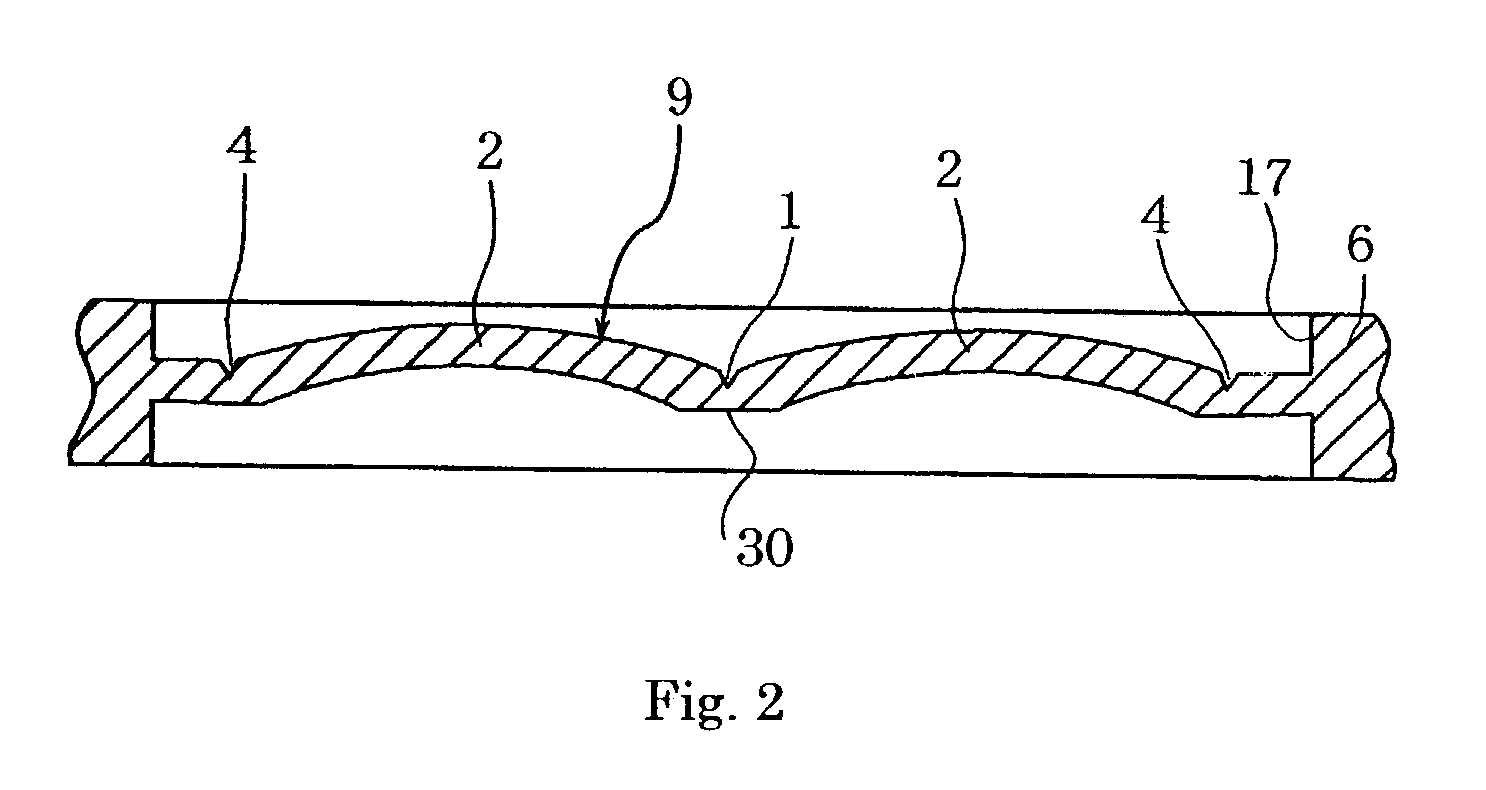
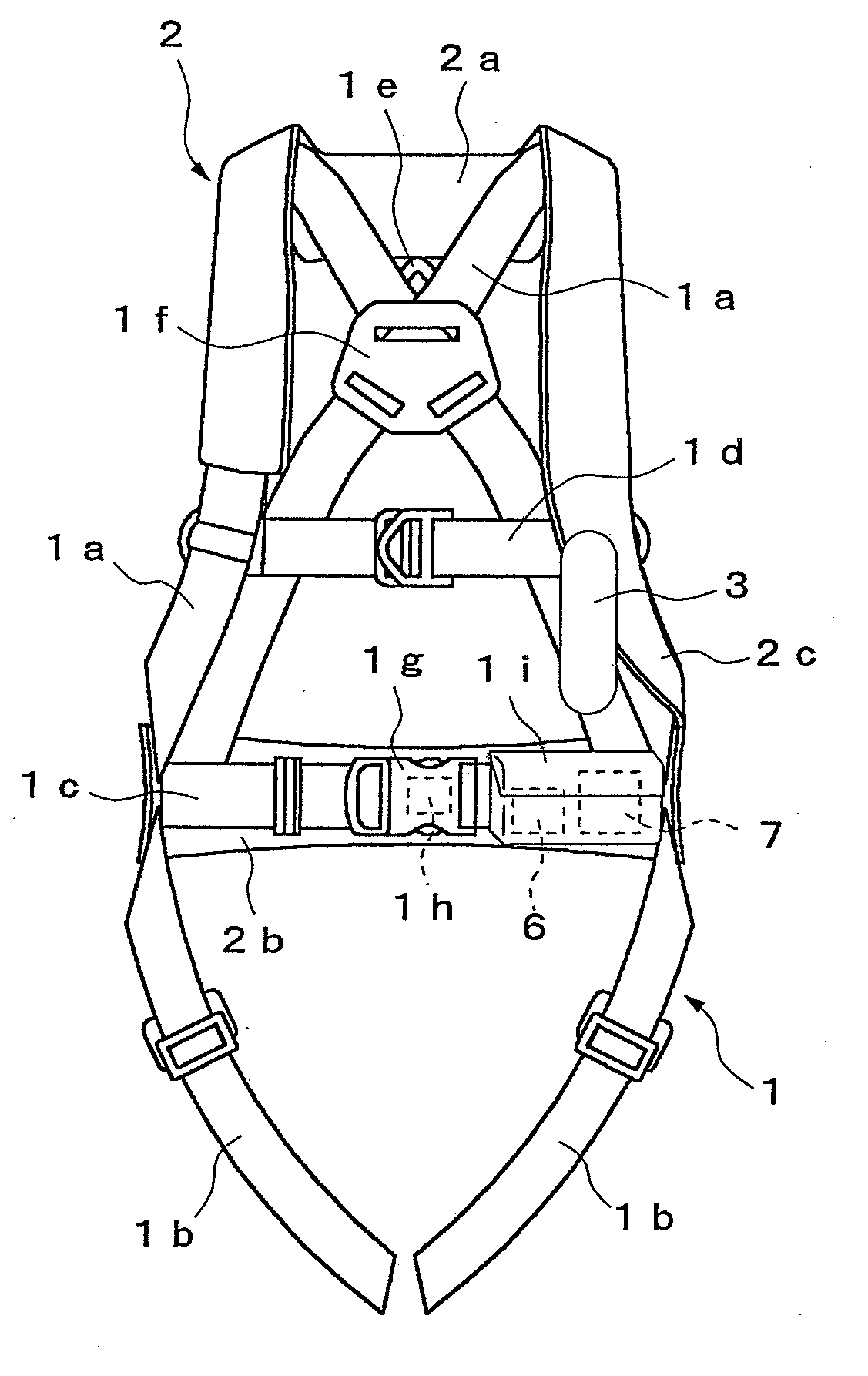
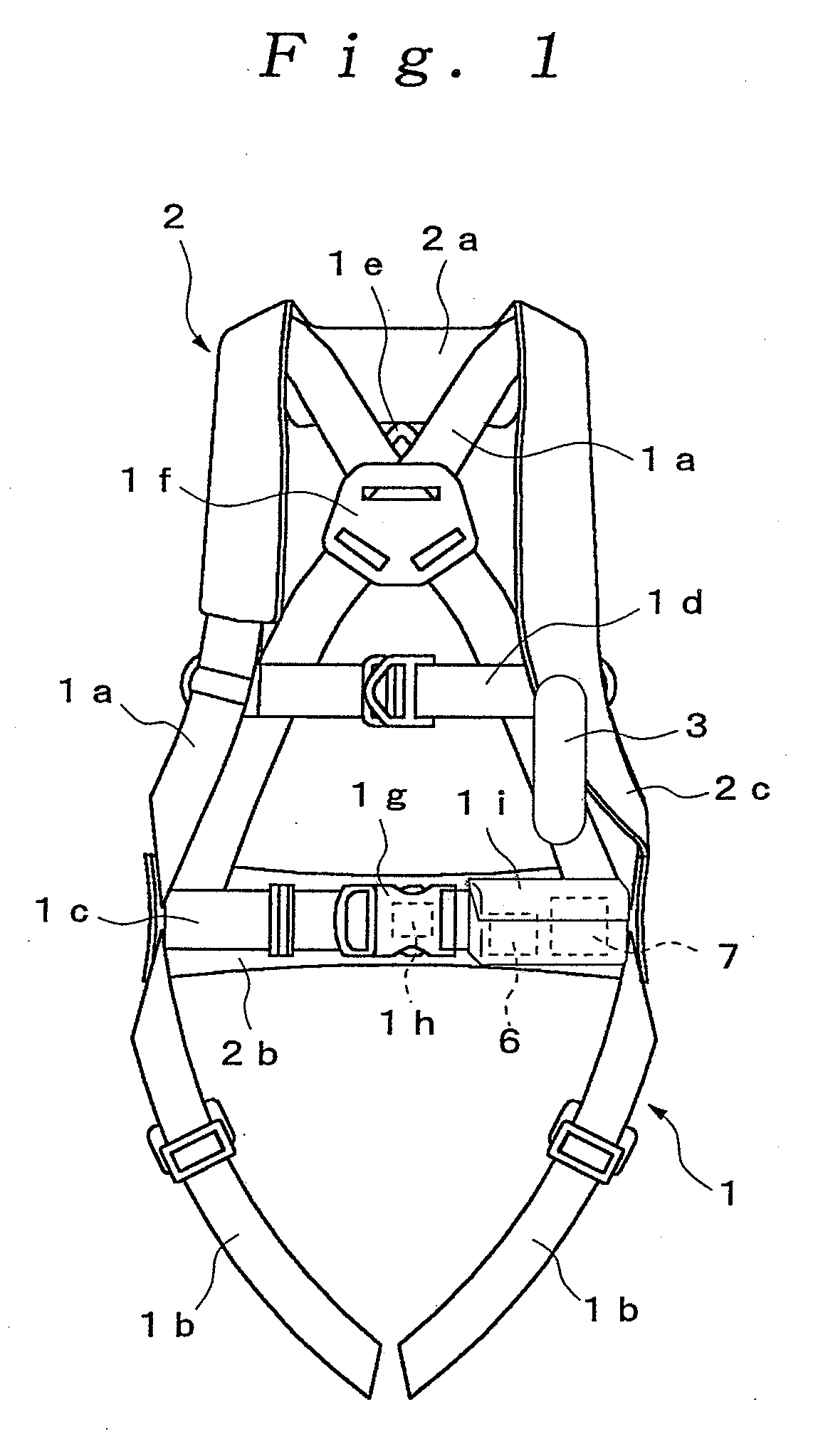
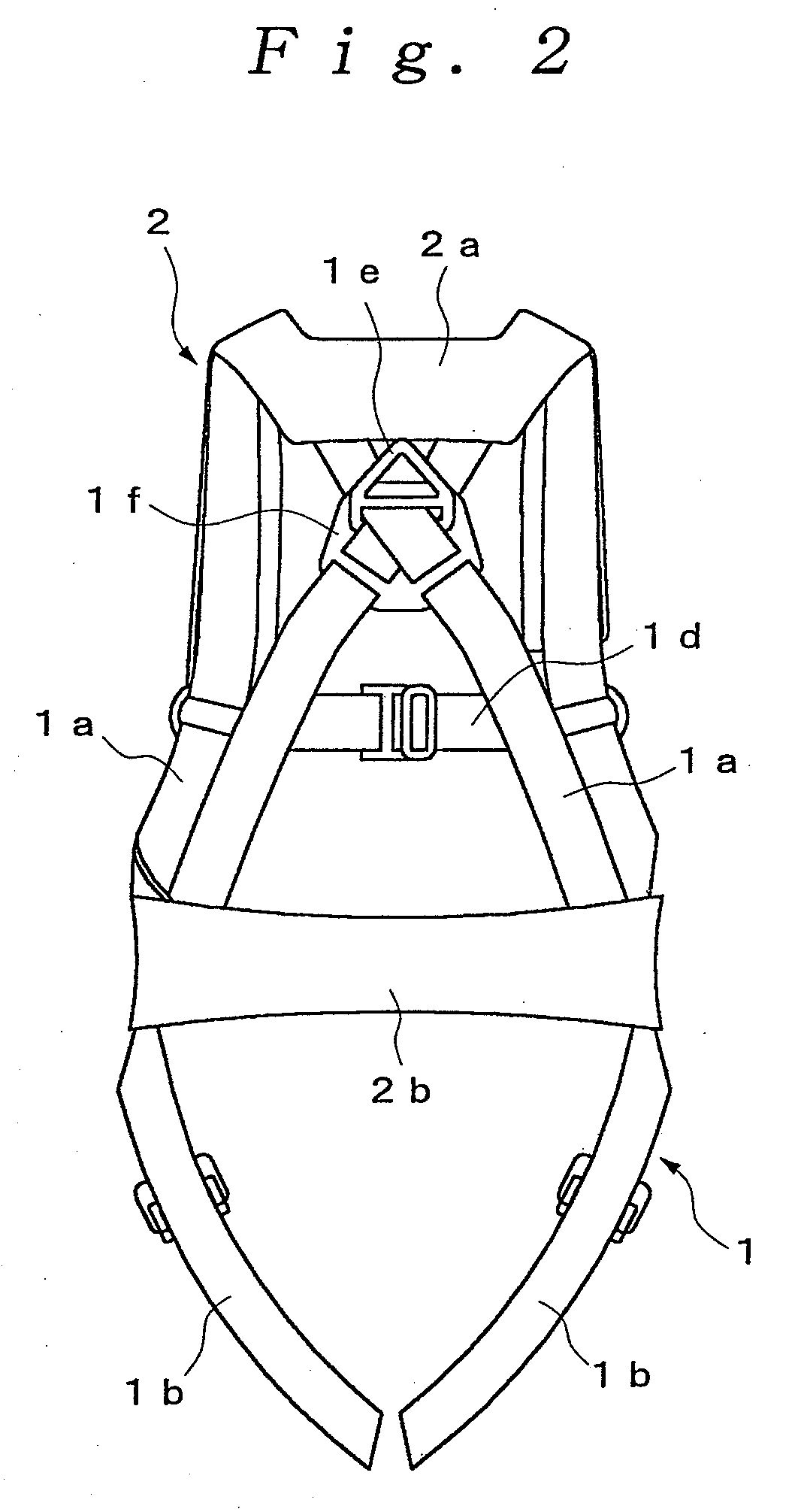
Harness type safety belt
InactiveUS20090019623A1Firm supportReduce the impactChemical protectionHeat protectionDrop impactThigh part
The present invention provides a harness type safety belt capable of absorbing a dropping shock to a user even if the user accidentally falls from an elevated position. According to the present invention, in such a case that a user A fails to apply a hook of a rope to a life line and the user A falls from an elevated position, an air bag 2 provided in a mounting body 1 is inflated. Therefore, the air bag 2 can absorb a dropping shock and the dropping impact applied to the user A can be reduced. In addition, in the case where the user A falls with the hook of the rope being connected to the life line, the user A is suspended by the rope. The body of the user A is supported by not only a waist part belt 1b but also shoulder part belts 1a and thigh part belts 1c. Therefore a tension applied from the rope to the body of the user can be dispersed to each of the belts 1a, 1b and 1c and the body of the user can be stably supported.
Owner:PROP
Vehicle rollover test fixture
InactiveUS7373801B2Avoid damageLimiting further damageWeather/light/corrosion resistanceAcceleration measurementRolloverDrop impact
A test fixture for rollover crash testing of a test vehicle onto a moving surface employs a cradle to support and rotate the test vehicle. A vertical support structure to positions and releasably holds the cradle. A moving sled having a contact surface is carried by a guide extending beneath the structure and the cradle fixture. The cradle is rotated and released from the structure responsive to a sensor for contact within a drop impact zone on the contact surface of the moving sled. Vertical motion of the cradle is then arrested to prevent further damage to the test vehicle or the test structure.
Owner:SAFETY TESTING INT
Vehicle rollover test fixture
A test fixture for rollover crash testing of a test vehicle onto a movable sled surface employs a cradle to support and rotate the test vehicle. A suspension assembly is attached to each end of the cradle for vertically supporting and dropping the cradle. A gantry has a cross beam supported by a first telescoping column for support of a first of the suspension assemblies and translationally supported by a second telescoping column for support of a second of the suspension assemblies to position and releasably hold the suspension assembly. Roll control arms rotate the cradle and a trigger assembly releases the cradle and test vehicle from the cross beam for contact within a drop impact zone on the contact surface of the sled. A brake assembly then arrests vertical motion of the cradle.
Owner:SAFETY TESTING INT
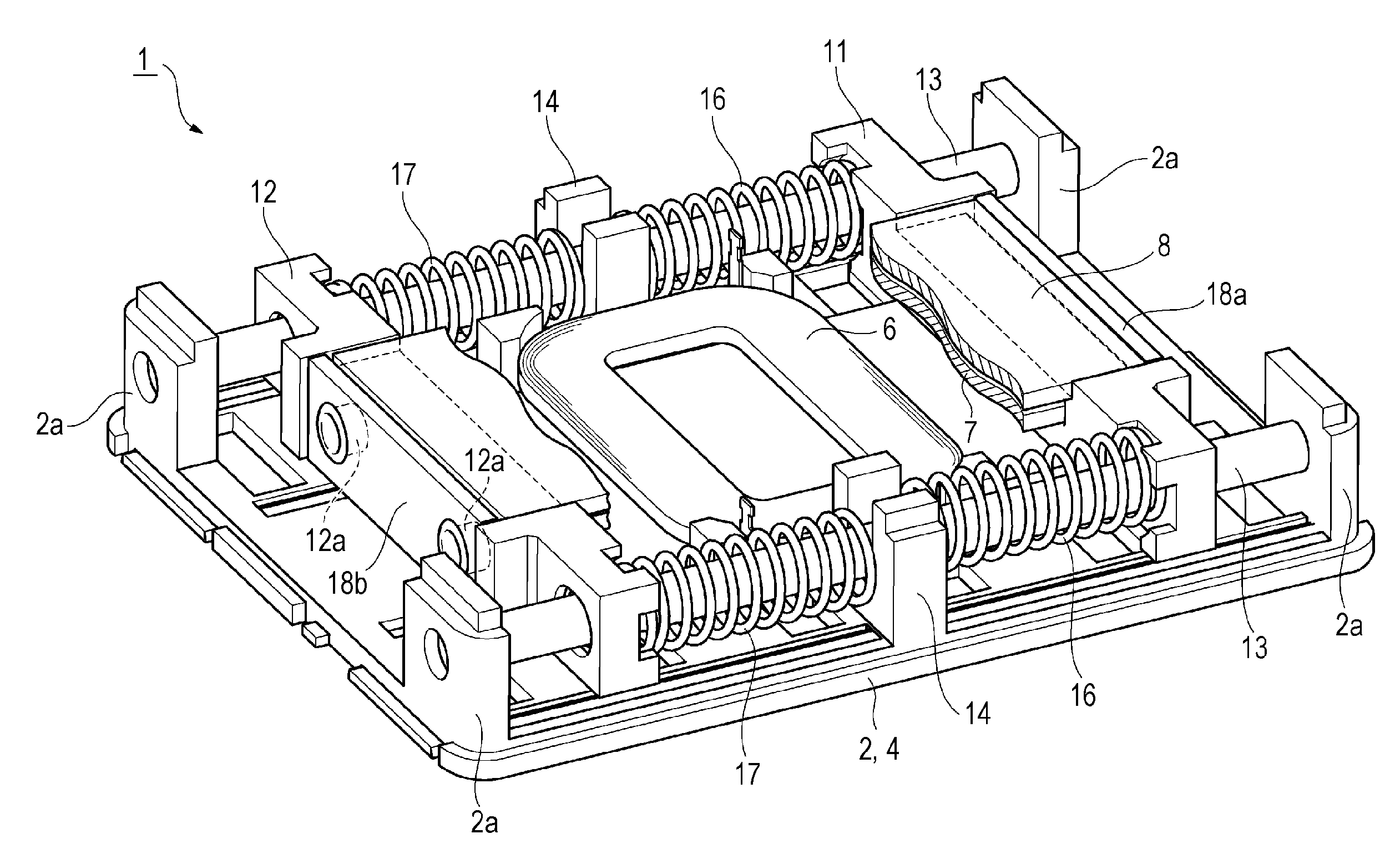
Hand shaking correction device
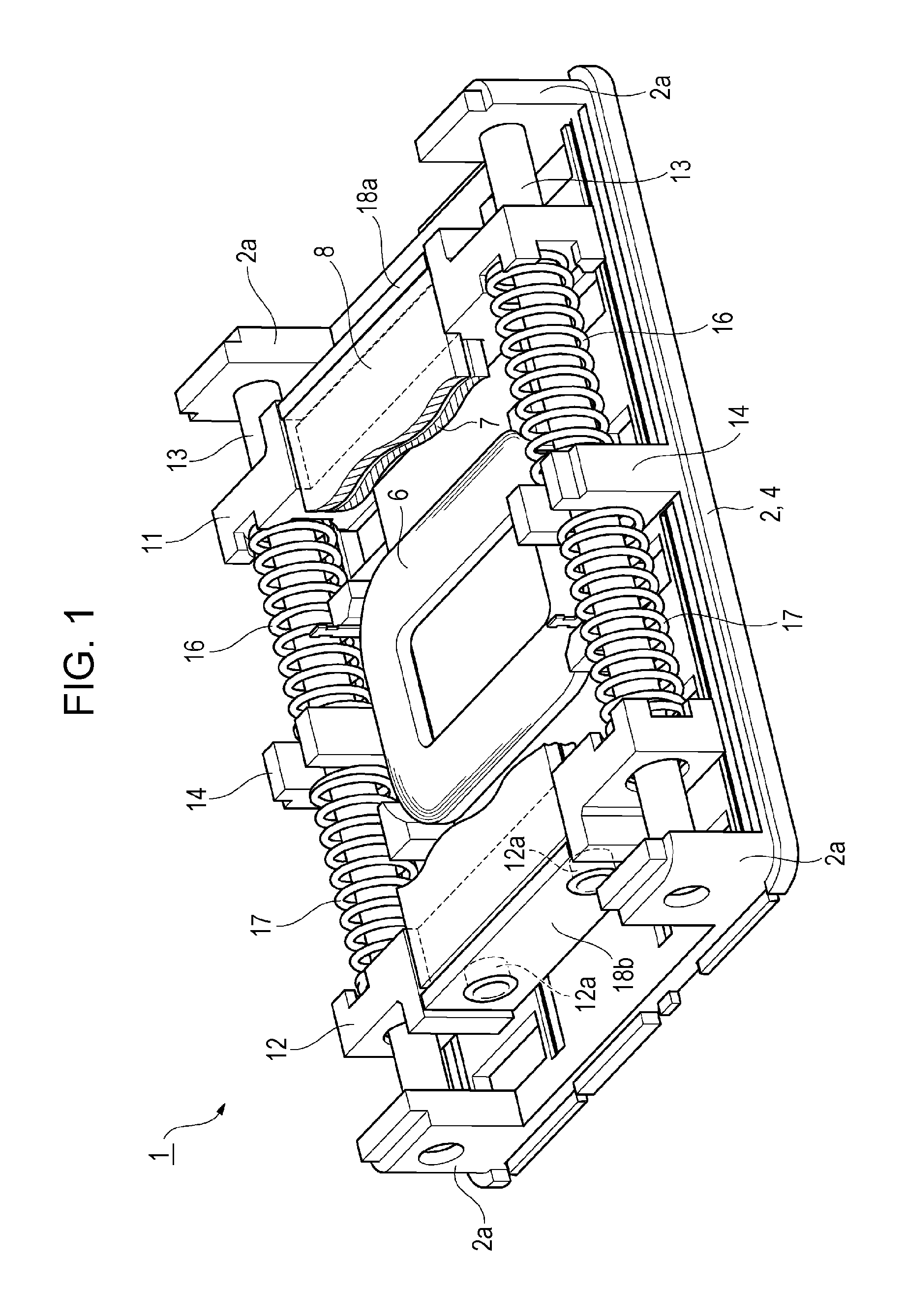
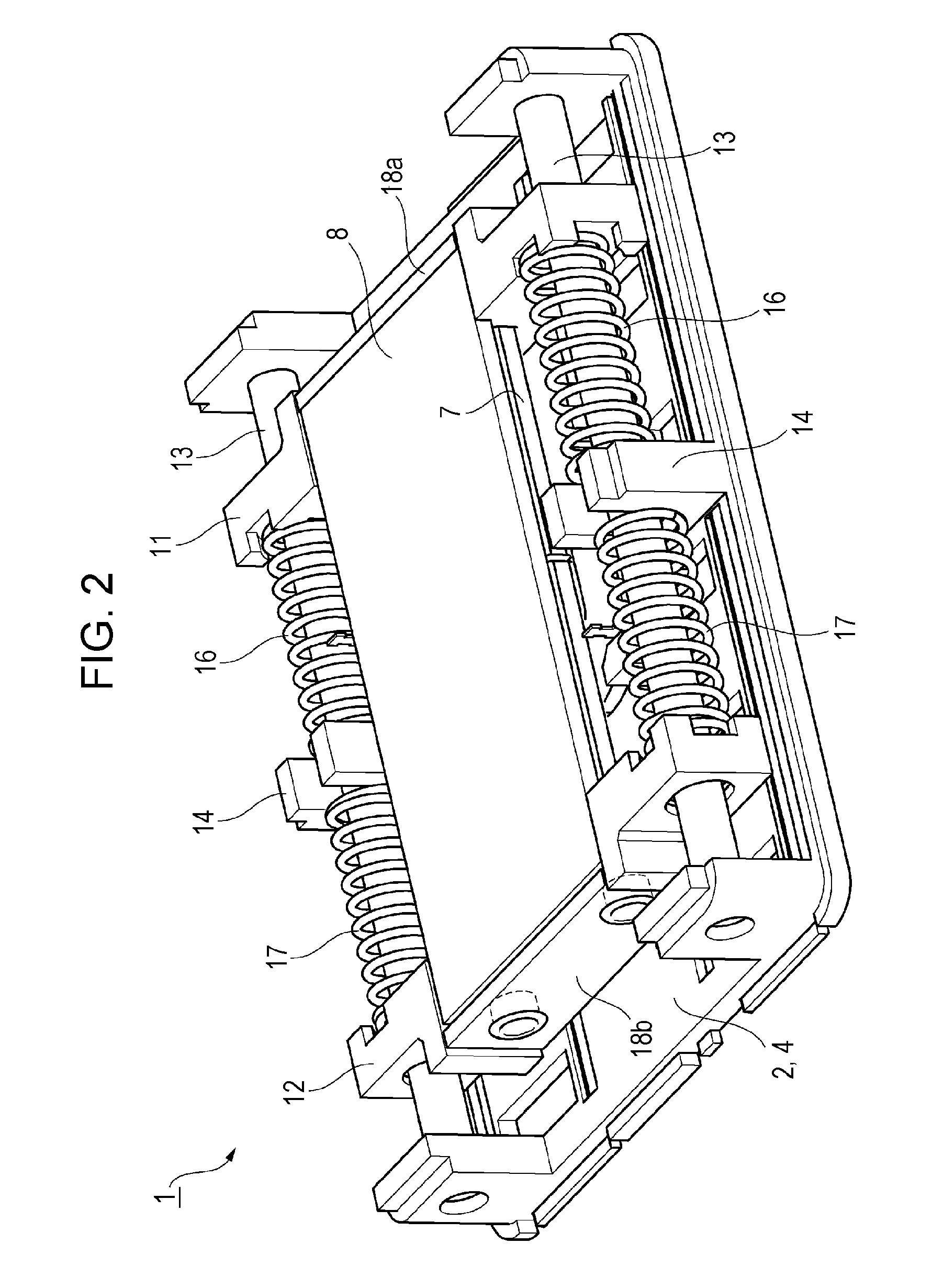
ActiveCN103901702ANo hysteresisSuppress resonanceTelevision system detailsPrintersHand shakesDrop impact
The present invention provides a shake correction device which can not generate the hysteresis phenomenon and can suppress unnecessary resonance and improve endurance with respect to drop impact. In this shake correction device, the eddy current induction plate 16a of +Z side is opposite to and has a gap with the surface (14a) of the +Z side of the permanent magnet (14) which is arranged to wind around the optical axis at an interval of 90 degree in the Z direction, the eddy current induction plate 16b of radial direction is opposite to and has a space with the surface (14b) of the outside in the radial direction, and the eddy current induction plate 16c of the periphery direction is opposite to and has a gap with the surface (14c) in the periphery direction.
Owner:JIANGXI SENYANG TECH
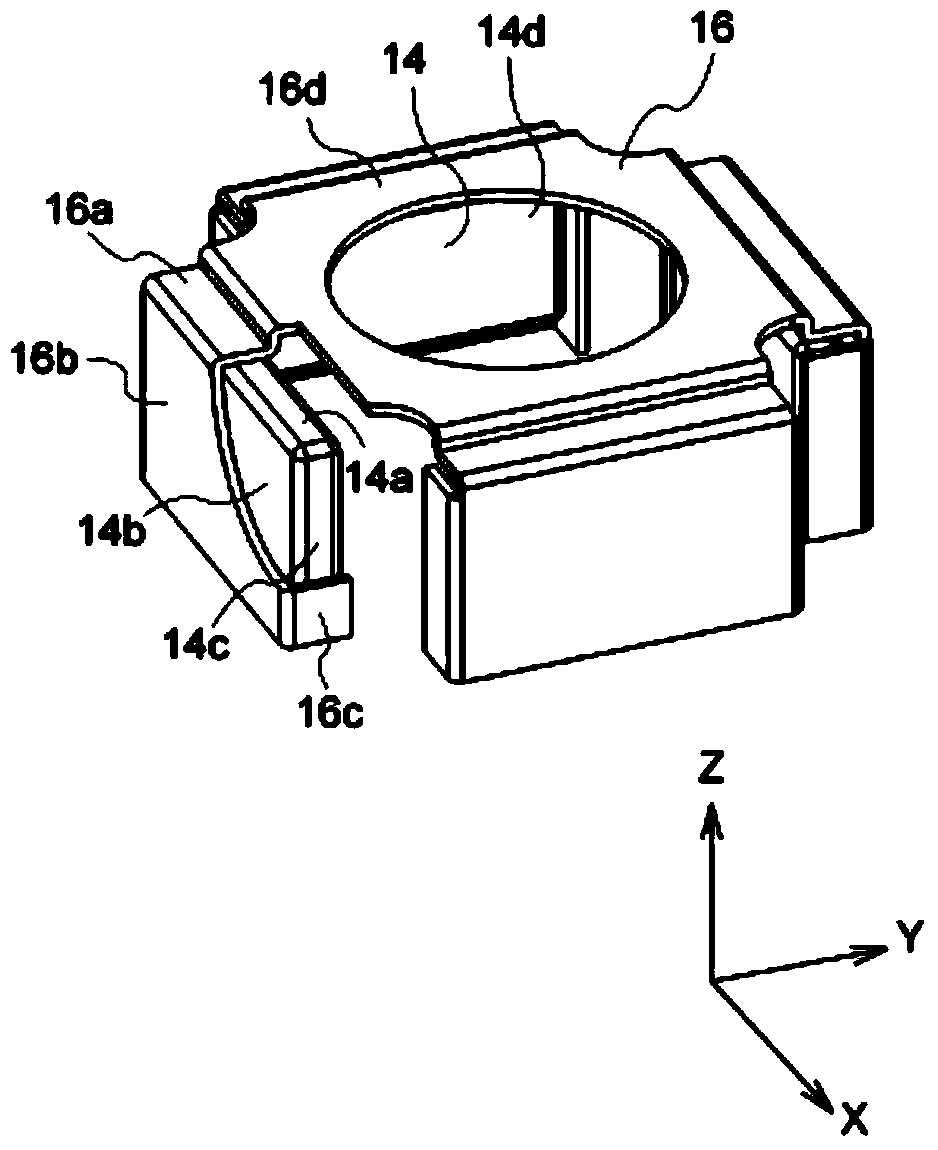
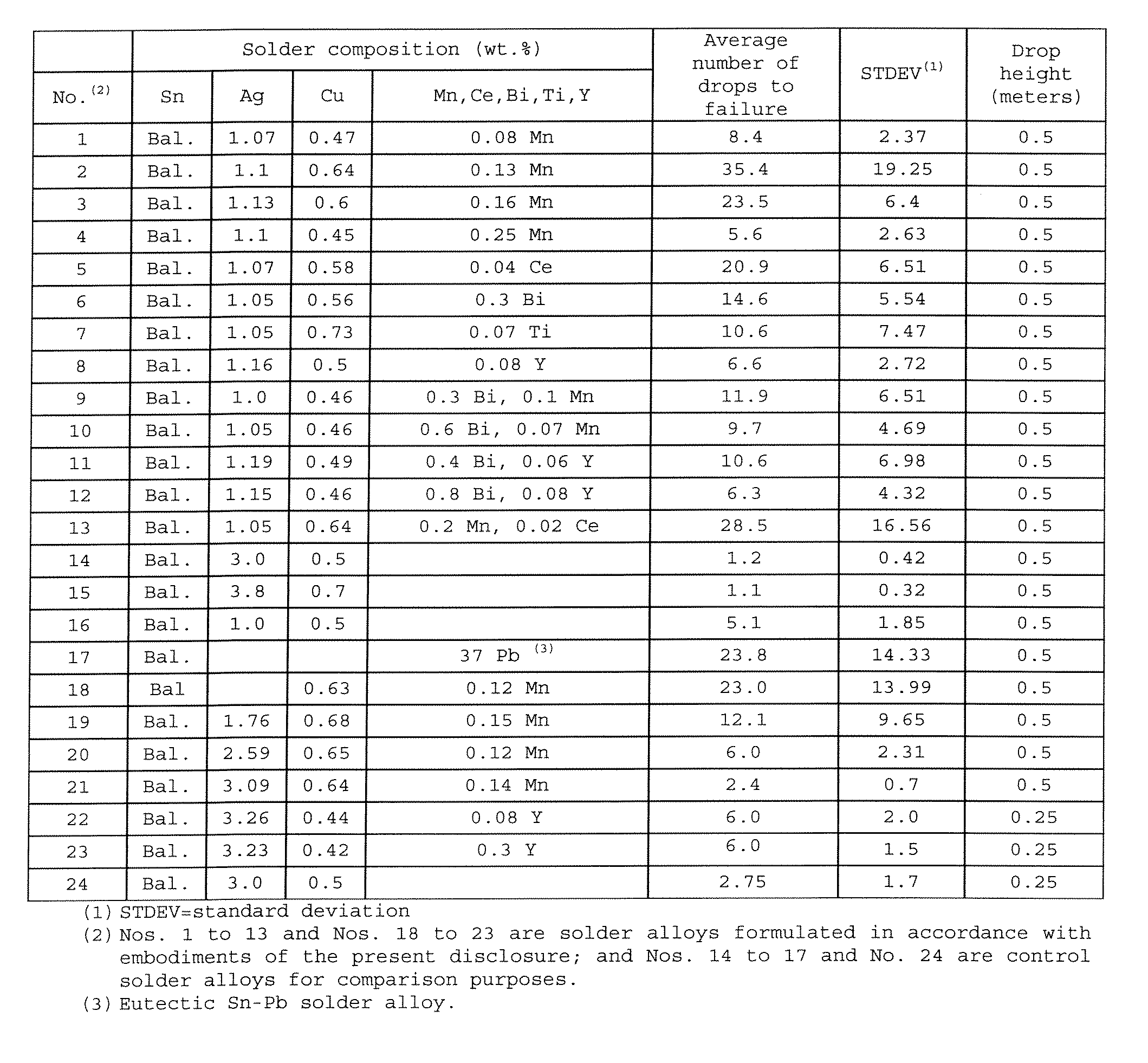
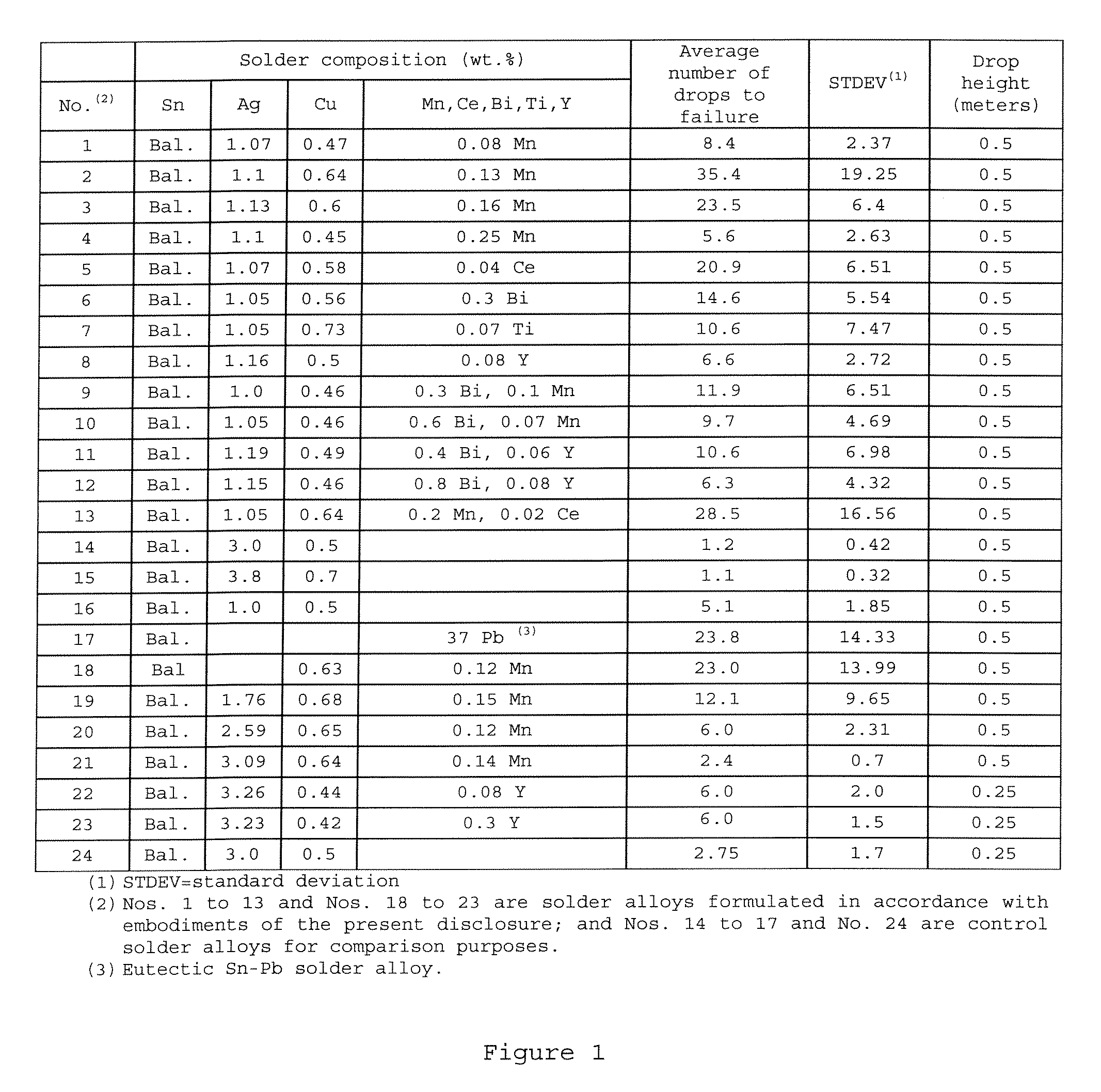
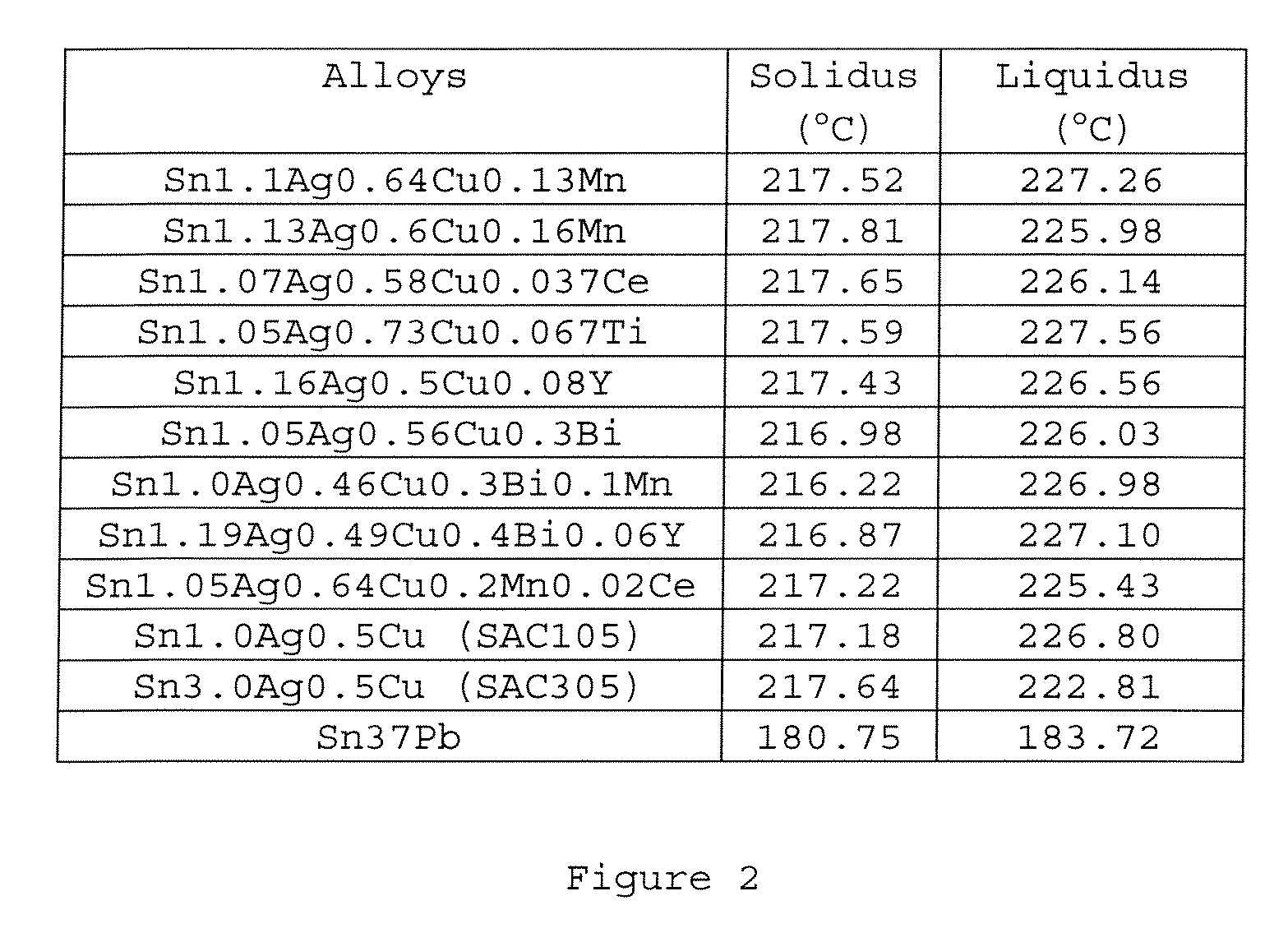
Lead-Free Solder Alloys And Solder Joints Thereof With Improved Drop Impact Resistance
Lead-free solder alloys and solder joints thereof with improved drop impact resistance are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the lead-free solder alloys preferably comprise 0.0-4.0 wt. % of Ag, 0.01-1.5 wt. % of Cu, at least one of the following additives: Mn in an amount of 0.001-1.0 wt. %, Ce in an amount of 0.001-0.8 wt. %, Y in an amount of 0.001-1.0 wt. %, Ti in an amount of 0.001-0.8 wt. %, and Bi in an amount of 0.01-1.0 wt. %, and the remainder of Sn.
Owner:INDIUM CORPORATION
Anti-dropping mobile phone housing
InactiveCN106453758AAvoid breakingProtection from being brokenDevices with sensorTelephone set constructionsDrop impactMobile phone
The invention belongs to the technical field of mobile phone accessories, and particularly relates to an anti-dropping mobile phone housing. The anti-dropping mobile phone housing comprises a mobile phone housing main body and elastic protection corners; the mobile phone housing main body is of a double-layer hollow structure; a first air bag, a second air bag and an air bag opening device are arranged in a cavity at each side edge of the mobile phone housing main body; air bag controllers and a power supply are arranged in the cavity at the bottom of the mobile phone housing main body; the elastic protection corners are arranged at four corners of the mobile phone housing main body; a pressure sensor and a spring component are arranged inside each of the elastic protection corners; the air bag controllers are connected with the pressure sensors; and each of the air bag opening devices includes a gas generator and an air bag ejection mechanism. When a dropping height of a mobile phone is too low, the time is too fast and the air bags are not opened timely, the elastic protection corners can effectively buffer the dropping impact force; and meanwhile, after the pressure sensors in the elastic protection corners receive signals and the signals are processed and are set by the air bag controllers, the air bag opening devices make responses and the air bags are ejected; and thus, a mobile phone screen is prevented from being broken or cracked.
Owner:大连圣多教育咨询有限公司
Electroconductive fine particles, anisotropic electroconductive material, and electroconductive connection structure
It is an object of the present invention to provide: a conductive fine particle, which is used for conductive connection between fine electrodes and tends not to give rise to a crack in the solder layer or disconnection caused by breakage in the connection interface between an electrode and the conductive fine particle even with a drop impact and the like, and tends not to have fatigue even after repetitive heating and cooling; an anisotropic conductive material obtained by using the conductive fine particle; and a conductive connection structure.The present invention relates to a conductive fine particle, which comprises a solder layer containing tin and being formed on a surface of a resin fine particle, with nickel adhered to a surface of the solder layer, and contains 0.0001 to 5.0% by weight of the nickel with respect to a total of a metal contained in the solder layer and the nickel adhered to the surface of the solder layer.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com