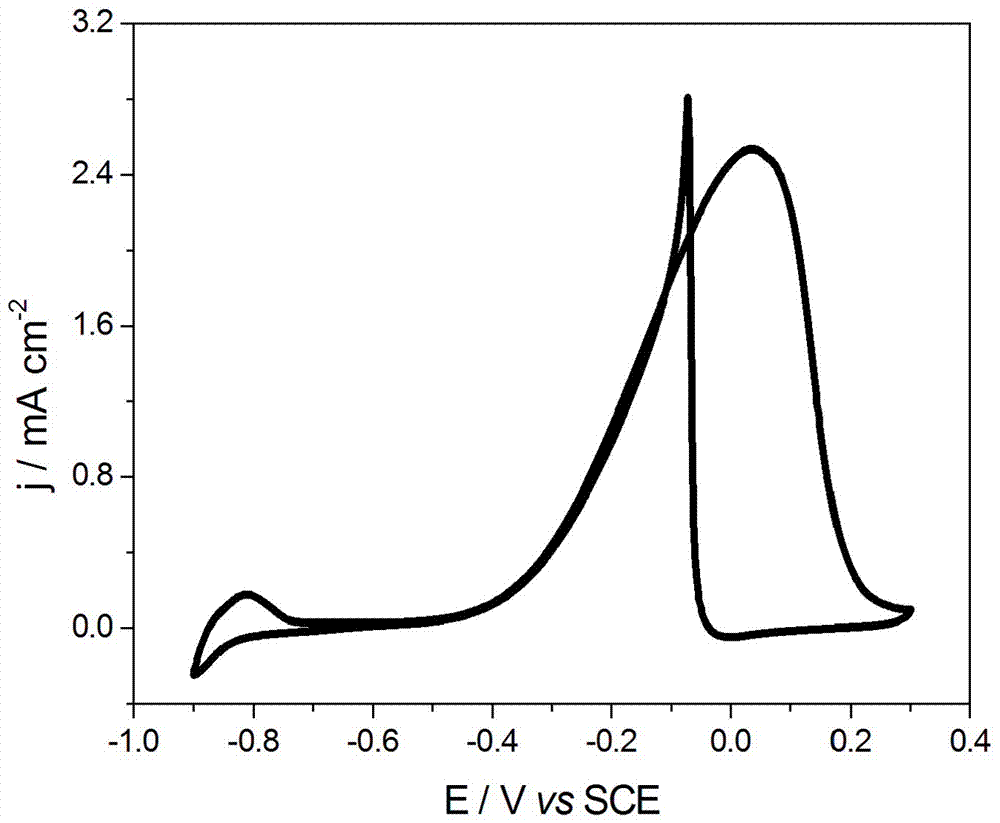
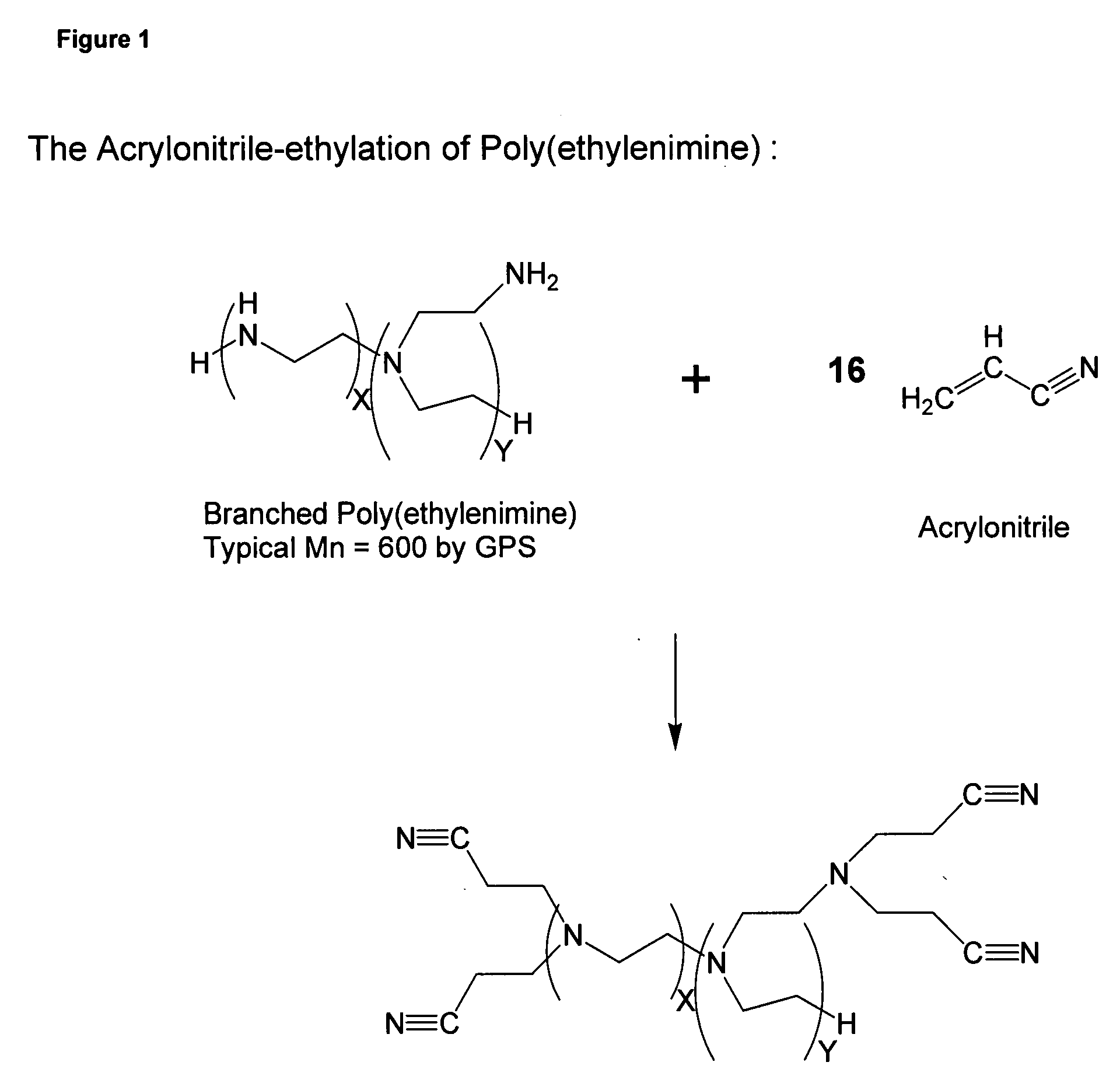
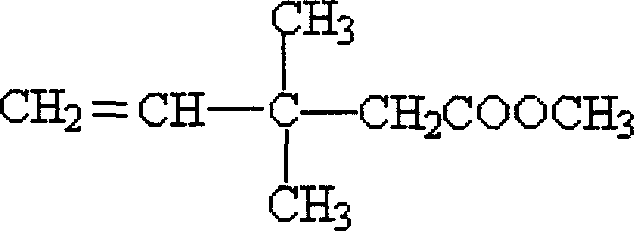
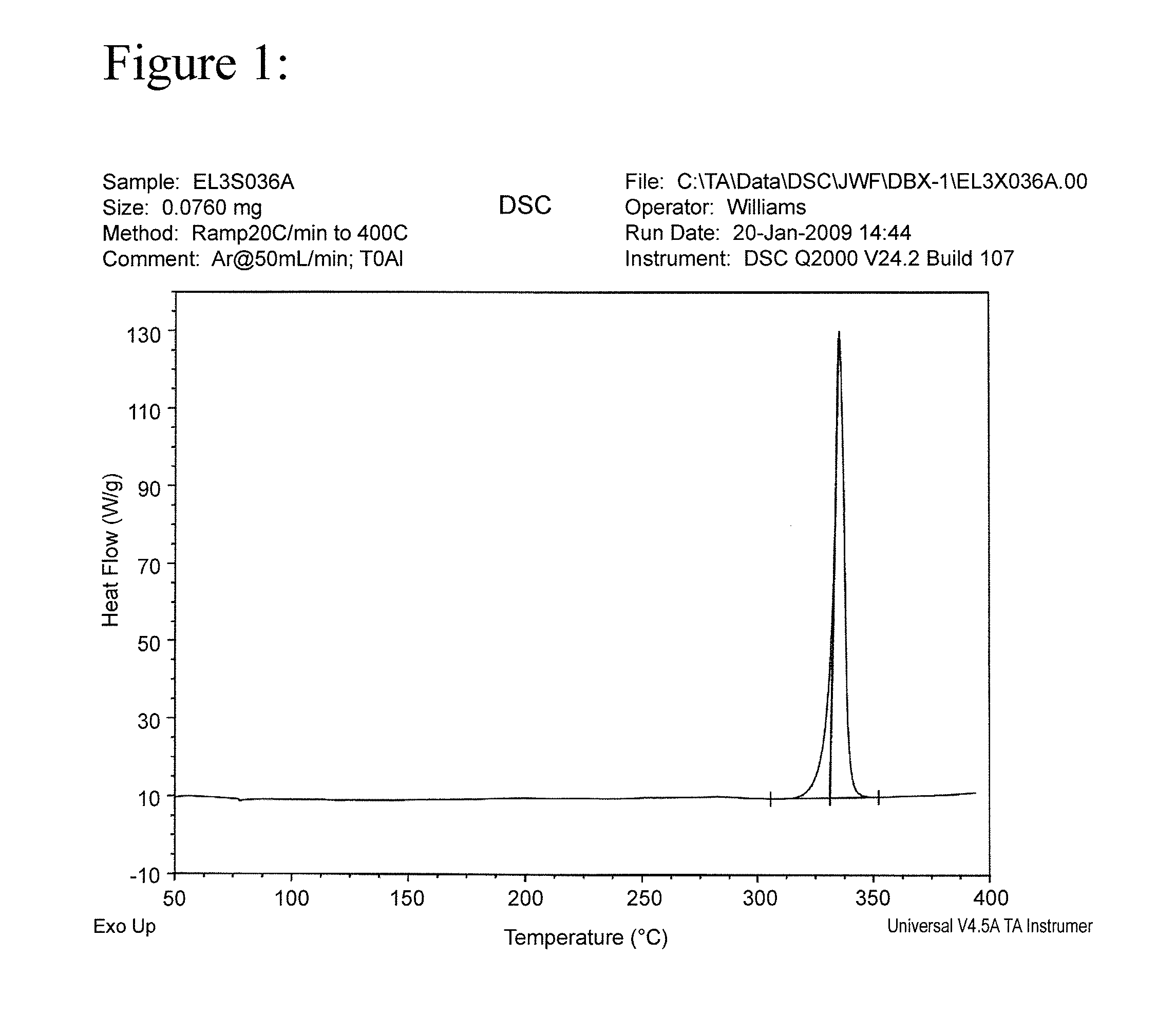
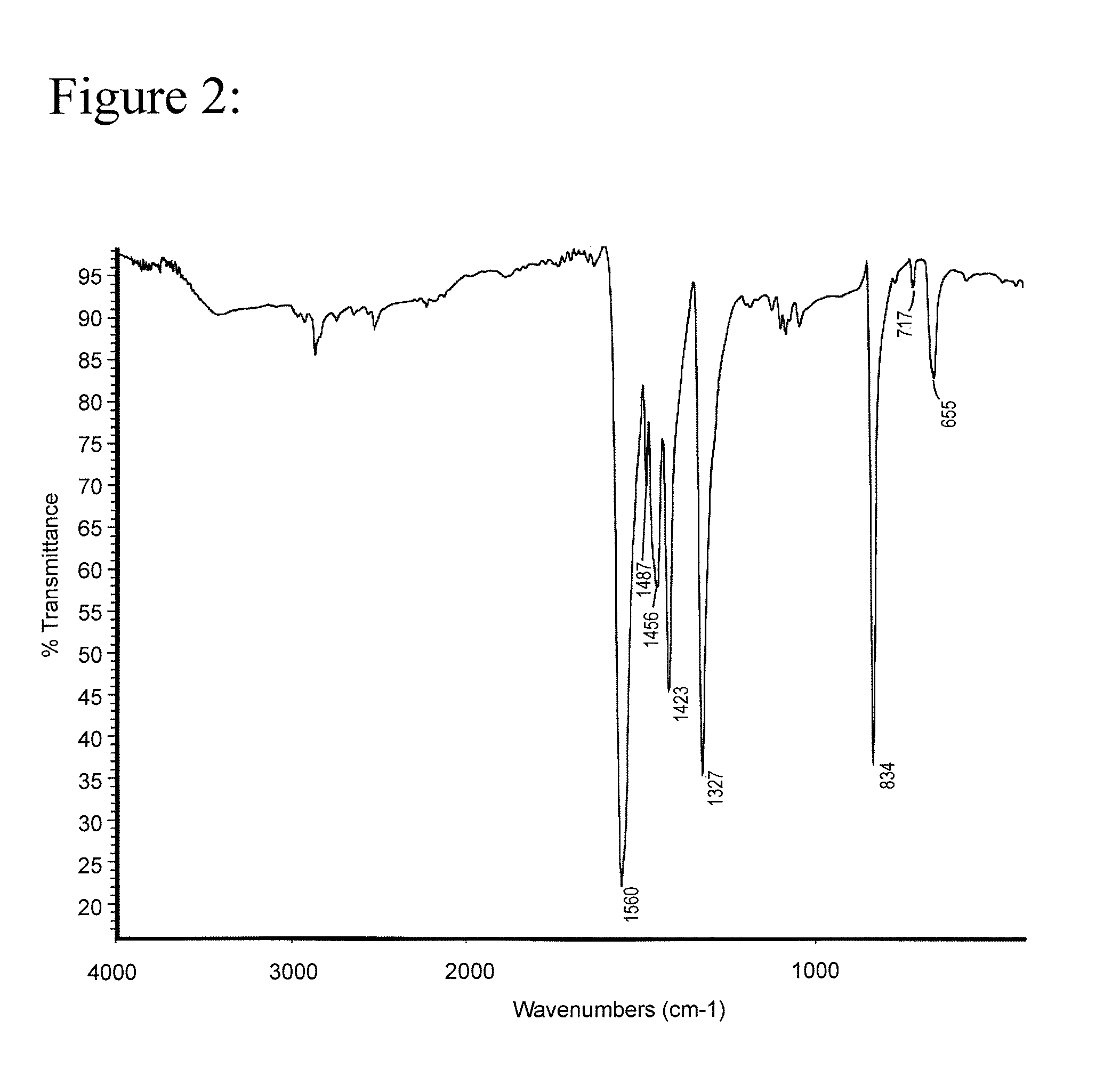
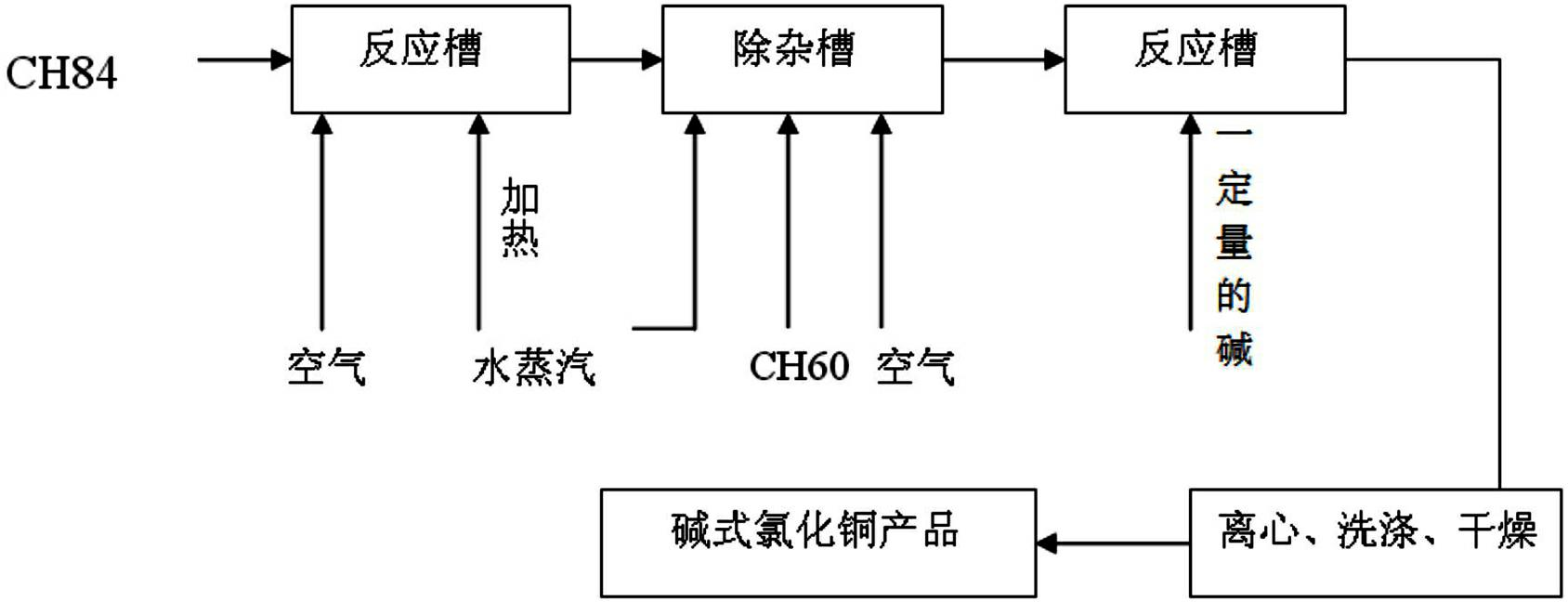
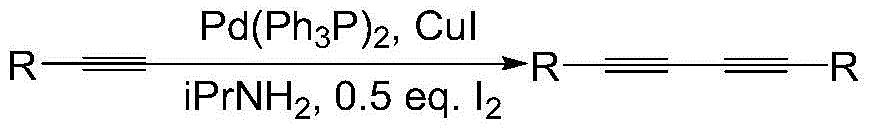Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
214 results about "Cupric chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Copper 0.4 mg/mL (Cupric Chloride Injection, USP) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution intended for use as an additive to intravenous solutions for total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Each mL of solution contains 1.07 mg cupric chloride, dihydrate and 9 mg sodium chloride.
Adsorption powder containing cupric chloride
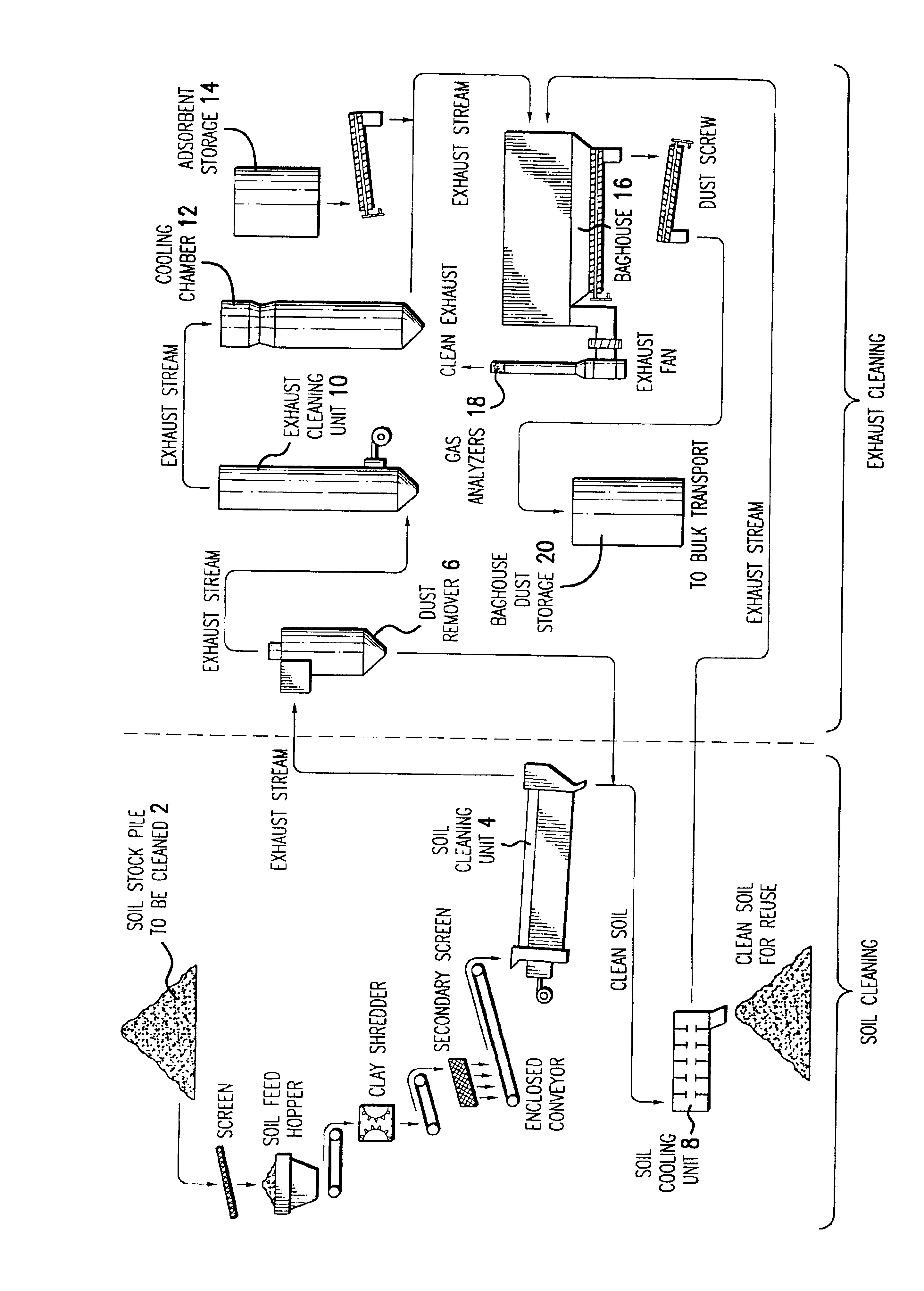
An adsorption powder useful for the removal of mercury and other metals, as well as furans, dioxins and other organic compounds from gaseous streams. The powder may be characterized as containing a carbon-based powder and an effective amount of cupric chloride suitable for removing metals and organic compounds from high temperature and moisture gaseous streams. The powder may contain calcium hydroxide, sulfur, potassium permanganate, potassium iodide, and combinations thereof.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Etching solution, method of etching and printed wiring board
ActiveUS20060199394A1Efficient processEfficient coatingInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementDecorative surface effectsTriazole antifungalsHigh concentration
There is provided an etching solution comprised of a cupric chloride solution and a high-concentration triazole type compound added to the cupric chloride solution and capable of forming an etching-inhibiting coating. In a process of forming a circuit pattern by etching with the etching solution, an etching-inhibiting coating is selected formed on parts of a copper foil laid under the edge of an etching resist to effectively inhibit horizontal side-etching of the copper foil from the edge of the etching resist. Also, nonuniform irregularities formed on the side wall of the circuit pattern by the etching improves the adhesion between the circuit pattern and an insulating resin layer covering the circuit pattern.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Electrolysis Cell for the Conversion of Cuprous Chloride in Hydrochloric Acid to Cupric Chloride and Hydrogen Gas
The present invention provides an electrochemical cell for producing hydrogen gas and cupric chloride, comprising an anode compartment including an anode disposed in an anolyte, wherein the anolyte is cuprous chloride in hydrochloric acid, a cathode compartment including a cathode, wherein the cathode comprises an electrocatalyst, and a cation exchange membrane disposed between the anode compartment and the cathode compartment.
Owner:ATOMIC ENERGY OF CANADA LIMITED
Etching solution, method of etching and printed wiring board
InactiveCN1899003AInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh concentrationResist
The invention discloses an etching solution, which is obtained by adding a high-concentration triazole compound capable of forming a film with an etching-inhibiting effect to a copper chloride solution. In the process of forming a circuit pattern by etching using this etchant, an etching inhibiting film is selectively formed on a part of the copper foil located below the etching resist from the edge of the etching resist, thereby effectively preventing The side etching of the copper foil occurs in the horizontal direction at the edge of the etching resist. In addition, non-uniform fine unevenness is formed on the side wall of the circuit pattern formed by the etching process, thereby improving the adhesion between the circuit pattern and the resin insulating layer covering the circuit pattern.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Austenitic stainless steel welding seam structure corrosive agent and application method thereof
InactiveCN107843592AEasy to prepareEasy to storePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansGranularityWeld seam
The invention discloses an austenitic stainless steel welding seam structure corrosive agent and an application method thereof. The corrosive agent is composed of concentrated hydrochloric acid, cupric chloride, and absolute ethyl alcohol. The application method comprises the following steps: 1) preparation of a metallographic sample: a stainless steel weld sample block is subjected to grinding bywaterproof abrasive paper with different granularity and mechanical polishing; 2) corrosion of the metallographic sample: the metallographic sample is immersed to corrosion liquid for corrosion; and3) observation of the corrosive metallographic sample: the corrosive sample is taken and the sample is flushed with a lot of water and alcohol, and air drying is performed and dendritic structure is observed under a microscope. The austenitic stainless steel welding seam structure corrosive agent has the advantages of simple preparation, easy storage, convenient operation, and obvious corrosion effect; the corrosive fusion line and weld dendrite are obvious, the structure is intelligible, and over corrosion or nonuniform corrosion phenomenon cannot be generated. The improved welding mode is improved, and according to bonding of austenitic stainless steel weld, each performance of stainless steel weld assembly is greatly improved.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Polymide-to-substrate adhesion promotion in HDI
Methods for adhering polyimide dielectric materials to copper-, titanium-, aluminum-, or copper-and-titanium-containing portions of a substrate are described. The methods include the steps of applying adhesion promoter to a clean surface of the substrate, and curing the adhesion promoter. SPIE varnish is applied over the cured adhesion promoter, and is itself cured. A further layer of adhesion promoter is applied over the cured SPIE varnish, and is cured. The polyimide dielectric material is then laminated to the adhesion promoter. Cleaning of the copper-containing substrate portions is performed by etching with etchant including cupric chloride, cleaning of the titanium-containing substrate portions is performed with etchant including HF, and cleaning of copper- and titanium-containing portions is performed by HF etching followed by cupric chloride etching. Aluminum-containing portions of the substrate are not etched.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
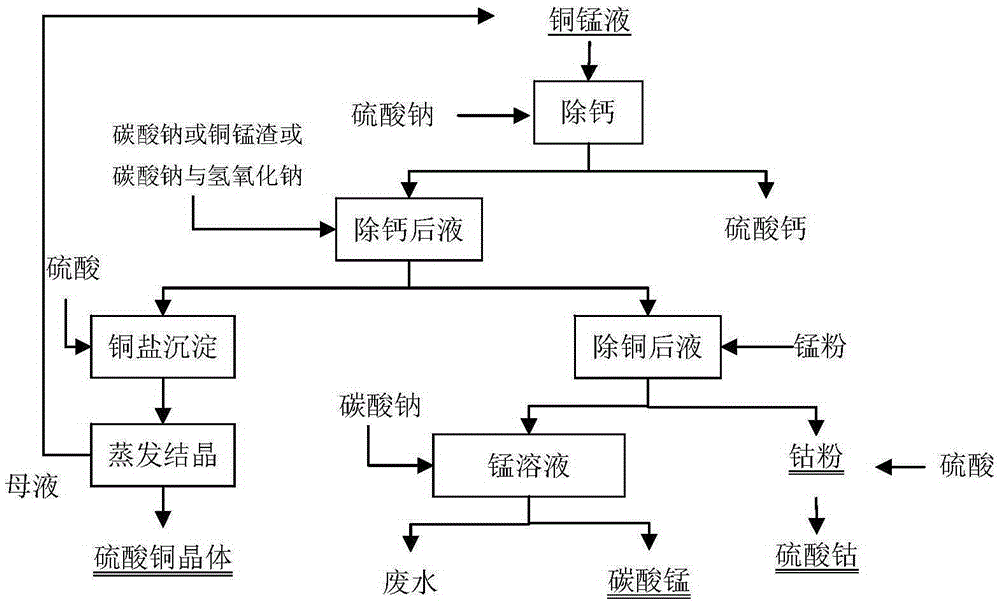
Method for separating copper, cobalt and manganese from cupric chloride manganese-cobalt-calcium-zinc impurity removal solution
ActiveCN105296754AShort processLow costRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesManganese(II) carbonateSulfate
The invention relates to a method for separating copper, cobalt and manganese from a cupric chloride manganese-cobalt-calcium-zinc impurity removal solution. The method comprises the steps that sodium sulfate is added to the cupric chloride manganese-cobalt-calcium-zinc solution, and calcium sulfate is removed by filtration; then sodium carbonate is added to a solution obtained in step one, a pH value is adjusted to 4.0-6.0 to allow copper ions in the solution to be precipitated, and copper precipitates are obtained by filtration separation; the copper precipitates are dissolved with sulfuric acid and are subjected to evaporation crystallization to form copper sulfate crystals; manganese powder is added to a solution after copper removal to allow cobalt ions to be reduced to cobalt powder to be precipitated, and cobalt powder is obtained after the filtration separation and is dissolved with acid to form a cobalt solution; and a solution after cobalt removal contains manganese and a little zinc and calcium, manganese is precipitated through the evaporation crystallization or by adding sodium carbonate, and manganese salts such as rough manganese carbonate are obtained. With the adoption of the method, three main valuable metals, namely copper, cobalt and manganese, can be separated and extracted economically and conveniently.
Owner:长沙百汇新材料科技有限公司
Dendritic crystal corroding agent for high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106596235ADisplay clearAccurate displayPreparing sample for investigationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationAusteniteMaterials science
The invention provides a dendritic crystal corroding agent for high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of inspection and analysis of steel billet at low magnification. The dendritic crystal corroding agent is prepared from 0.6-2.1 g of cupric chloride, 0.1-0.3 g of magnesium chloride, 1-3 g of ferric chloride, 100 mL of water, 9-12 mL of hydrochloric acid, 1-4 mL of nitric acid and 125-130 mL of absolute ethyl alcohol. The preparation method comprises the steps of step 1, based on the proportioning, adding in sequence water, cupric chloride, magnesium chloride, ferric chloride, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and absolute ethyl alcohol, stirring uniformly, keeping the solution static for 5-15 minutes, and step 2, polishing the surface of the test surface of the austenitic stainless steel, corroding the surface with corroding agent for 2-5 minutes, waiting until the generation of clearly visible dendritic crystal solidified structure, then rinsing and blow-drying the test surface, then testing and observing the corrosion effect. The corroding agent can easily, quickly and effectively show the corrosion condition of the dendritic crystal of the high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel, can explicitly manifest the solid dendritic crystal structure, and can accurately manifest the solidification defects. The corroding agent is good in repeatability.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Synthesis process of nanometer silver sulfide/copper sulfide in controlled shape
InactiveCN1887719ALower decomposition temperatureHigh yieldCopper sulfidesSilve compoundsReaction temperatureAmmonium bromide
The synthesis process of nanometer silver sulfide / copper sulfide in controlled shape relates to shape controlling synthesis technology of silver sulfide / copper sulfide in nanometer structure. The present invention aims at lowering the synthesis temperature of silver sulfide / copper sulfide, and raising the yield and structure controllability. The technological scheme is that under magnetic stirring, silver nitrate or copper chloride solution of 6-15 mmol / L concentration is drop-by-drop added into sodium thiosulfate solution of 9-52.5 mmol / L concentration, cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide in 2.0-3.5 mmol is then added into the solution, the solution is stirred strongly at 30-60 deg.c for 30 min, acid is added to regulate pH to 1-5, and through further heating at the same temperature for 1-8 hr and natural cooling, the product is obtained.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Erosion agent capable of displaying solidified dendritic structure of Fe-36 Ni invar alloy and erosion method of erosion agent
ActiveCN105386057AModerate erosion timeSimplify operating proceduresPreparing sample for investigationInvar alloyAlcohol
Disclosed are an erosion agent capable of displaying the solidified dendritic structure of a Fe-36 Ni invar alloy and an erosion method of the erosion agent. The erosion agent includes 1 g-2 g of picric acid, 0.5 g-1 g of anhydrous cupric chloride, 50 ml-60 ml of absolute ethyl alcohol, 0.5 ml-1 ml of hydrochloric acid and 1 g-2 g of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate. The erosion method of the erosion agent includes the steps that the prepared erosion agent is heated to the temperature of 50 DEG C-60 DEG C, a processed sample with the downward polishing face is suspended in the heated erosion agent to be eroded for 20 s-30 s, the eroded surface is wiped with ethyl alcohol firstly after erosion is completed, and then the sample is slightly polished at the one fourth radius position of a polishing machine for 4 s-6 s so that a copper film generated on the eroded surface can be removed. According to the method, the operating procedure is simple, the erosion effect is good, and the solidified dendritic structure of an invar alloy can be observed quickly and clearly, so that the solidification condition corresponding to continuous casting is obtained, and technical bases are provided for optimizing the continuous casting process technologies.
Owner:山西高义钢铁有限公司
Aqueous polyaniline and preparation method thereof
The invention provides aqueous polyaniline and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: adding aniline into a doped acid solution so as to prepare an aniline salt solution with a concentration of 1 mol / L to 3 mol / L, wherein, doped acid is phosphate ester containing ethoxy groups or sulfonate containing ethoxy groups; dissolving an oxidizing agent in water so as to prepare an oxidizing agent solution with a concentration of 1 mol / L to 3 mol / L, wherein, the oxidizing agent is ferric nitrate, ferric trichloride, ferric sulfate or cupric chloride; at a temperature of -30 to 10 DEG C, dropwise mixing the aniline salt solution with the oxidizing agent solution according to a mol ratio of aniline to the oxidizing agent of 1: 1.2-15 at a constant speed, and standinga mixed solution obtained after uniform mixing at a temperature of -30 to 10 DEG C so as to obtain aqueous polyaniline. Aqueous polyaniline prepared by using the method has a large specific surface area and excellent water-solubility thanks to a regular line style structure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
PtCu electric catalyst for fuel battery, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106058274AUnique regular cube shapeExcellent performance in electrocatalytic oxidation of methanolCell electrodesSynthesis methodsPotassium iodine
The invention relates to a PtCu electric catalyst for a fuel battery and a preparation method thereof. The method adopts the one-step hydro-thermal synthesis technology, the synthesis method comprises the following steps: dissolving triblock copolymer P123 in the secondary distilled water; adding chloroplatinic acid hexahydrate, cupric chloride and potassium iodide in a P123 solution, stirring, ultrasonically dissolving; transferring the mixed solution to a liner of a polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle in 50mL, tightly sealing the reaction kettle, and placing the reaction kettle in a blast drying oven, reacting for 6-12 hours at 120-200 DEG C; naturally cooling to room temperature, centrifuging, washing for three to five times to obtain the PtCu electric catalyst for the fuel battery. The triblock copolymer P123 is simultaneously used as the protection agent and the reducing agent, the potassium iodide is used as the morphology control agent, the obtained PtCu electric catalyst is good in dispersibility, has a regular cubic appearance, and excellent performance of electrically catalyzing and oxidizing methanol, and is a fuel battery catalyst which has excellent development prospects.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Preparation method and application of Cu2ZnSnS4/graphene composite semiconductor film
Belonging to the technical field of semiconductor film preparation, the invention relates to a preparation method and application of a Cu2ZnSnS4 / graphene composite semiconductor film. The preparation method includes: taking ethanol as the solvent, using a cupric chloride hydrate as the copper source, zinc chloride as the zinc source, stannous chloride as the tin source, and thiourea as the sulfur source, and adopting cetyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as the surfactant to prepare a reaction precursor solution; putting a cleaned FTO glass conductive surface up, adding an ethylene glycol solution of graphene dropwise, putting the FTO glass into a drying box to conduct drying, then putting the FTO glass conductive surface up into a high pressure reaction kettle lining, pouring the prepared reaction precursor solution into the high pressure reaction kettle lining, performing sealing, then putting the high pressure reaction kettle into a blasting drying box, and carrying out constant temperature reaction so as to obtain a Cu2ZnSnS4 / graphene composite semiconductor film on the FTO conductive glass substrate. The method provided by the invention has a simple process and is low in cost. The prepared Cu2ZnSnS4 / graphene composite semiconductor film has good application effect, can be directly used a counter electrode of a dye-sensitized solar cell, and also can be used as an absorption layer of a copper-based film solar cell.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of PtPdCu electrocatalyst for fuel cells
ActiveCN107342424AExcellent performance in electrocatalytic oxidation of methanolCell electrodesFuel cellsPotassiumDissolution
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a PtPdCu electrocatalyst for fuel cells. The method adopts a one-step hydro-thermal synthesis technology, and the synthetic method comprises the following steps: taking triblock copolymer P123 to be dissolved in redistilled water; adding chloroplatinic acid hexahydrate, potassium chloropalladite, anhydrous cupric chloride and potassium iodide into a P123 solution, and carrying out stirring and ultrasonic dissolution; transferring the mixed solution into the liner of a 50 mL polytetrafluoroethylene reaction still, sealing the reaction still, putting in an air blowing drying box, and reacting at the temperature of 120 to 200 DEG C for 6 to 12 hours; naturally cooling to room temperature, centrifuging and washing three to five times to obtain the PtPdCu electrocatalyst for the fuel cells. The triblock copolymer P123 serves as a protective agent and a reducing agent simultaneously, the potassium iodide serves as a morphological control agent and a surface modification agent, and the obtained PtPdCu electrocatalyst is of a hollow nanometer chain structure, so that the PtPdCu electrocatalyst has excellent electrocatalytic oxidation methyl alcohol performance and is a fuel-cell catalyst with excellent development prospects.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Metal surface treatment composition
ActiveUS20080264900A1Improve adhesionControl of characteristicDecorative surface effectsAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentPropionitrileThermal stability
A process is described for treating metal surfaces with roughening compositions that use poly(ethyleneamino propionitrile)polymer as an additive in the composition to improve adhesion of polymeric materials to the metal surfaces and to improve peel strength for thermal stability. The polymer of the invention may be added to compositions containing for example, cupric chloride and hydrochloric acid and is also usable in compositions containing an oxidizer / acid / azole mixture. Other additives, such as adiponitrile may also be beneficially added to compositions of the invention.
Owner:MACDERMID ACUMEN INC
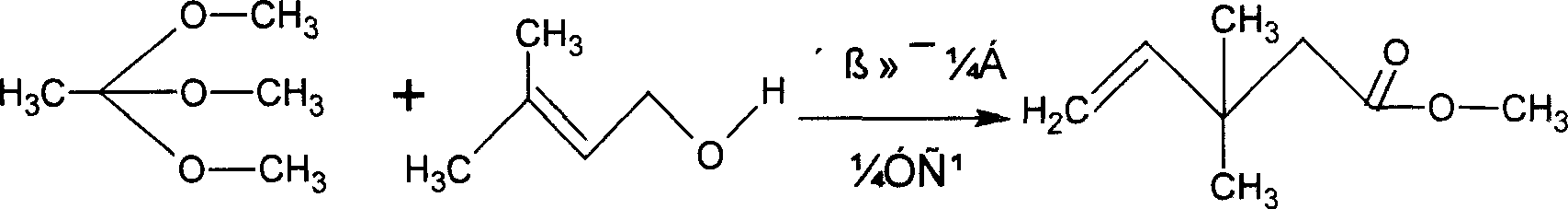
Method of preparing 3,3-dimethyl-4-pentenoic acid methyl ester with industrial scale
InactiveCN1907947AEasy to separateHigh reaction yieldPreparation by ester-hydroxy reaction4-pentenoic acidAcetic acid
The invention belongs to the industrial scale production methods for methyl pentenoate, involving a synthesis method for methyl pantenate through a reaction of isopentenol with methyl orthoacetate through catalytic synthesis under pressure. The molar ratio of isopentenol : methyl orthoacetate : catalyst is 1:1.0~2.0 : 0.01~0.1. The reaction conditions include stirring pressure of 1~3.2MPa and temperature of 150~250DEG C, and the reaction time of 6~10h. The catalysts are removed after cooling and the final product is obtained by distilling the filtrate. The catalyst is solid anhydrous zinc chloride, nickel sulfate, nickel acetate, copper acetate, anhydrous cupric chloride, or anhydrous ferric chloride. The invention has the advantages of simple catalyst separation as using solid catalyst, short reaction time as reacting at high temperature and pressure, high yield of 88%, low production cost, high product content above 99%, simple process, and less wastes.
Owner:YINGKOU YINGXIN CHEM TECH CO LTD
High tin solder etching solution
InactiveUS20090120999A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSulfateAlloy
A method is provided for the removal of tin or tin alloys from substrates such as the removal of residual tin solder from the molds used in the making of interconnect solder bumps on a wafer or other electronic device. The method is particularly useful for the well-known C4NP interconnect technology and uses an etchant composition comprising cupric ions and HCl. Cupric chloride and cupric sulfate are preferred. A preferred method regenerates cupric ions by bubbling air or oxygen through the etchant solution during the cleaning process.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Comprehensive utilization method of waste liquor in production of basic cupric carbonate
ActiveCN103449501AAchieve reuseRealize recycling of resourcesCopper chloridesCopper nitratesSulfate radicalsIndustrial waste water
The invention discloses a comprehensive utilization method of waste liquor in the production of basic cupric carbonate and relates to the field of treatment methods of industrial wastewater. The invention aims at providing a comprehensive utilization method of waste liquor in the production of basic cupric carbonate, and in particular relates to a method for reusing sodium bicarbonate in the waste liquor. The waste liquor in the production of the basic cupric carbonate is the waste liquor generated after the basic cupric carbonate is produced by a reaction between an acidic copper chloride solution or an acidic copper sulfate solution and a sodium carbonate solution. The comprehensive utilization method of the waste liquor in the production of the basic cupric carbonate mainly comprises the following steps: adding a little distilled water into a reaction kettle as a base solution; when the reaction temperature rises to 35-90 DEG C, starting a stirring device, and adding the waste liquor containing sulfate radicals or chlorine and the acidic copper solution into the reaction kettle for reaction, wherein the pH value during the addition of the solutions is controlled to be 3-6; and filtering, washing, drying and sieving reaction products to obtain the basic copper salt. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, easy to control reaction conditions, and widely applicable to the recycling and reusing of the waste liquor in the production of basic cupric carbonate.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHENTOU ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
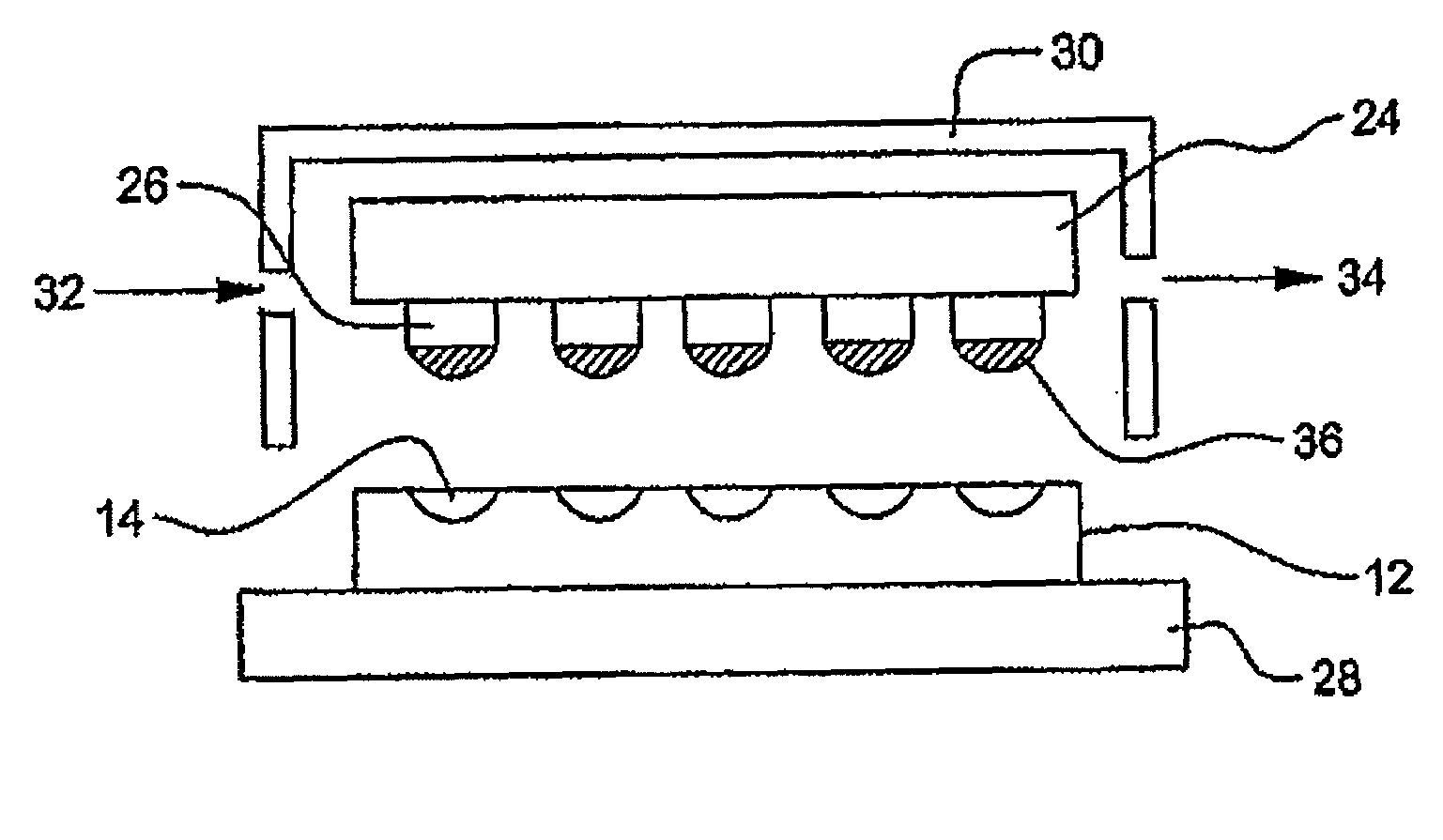
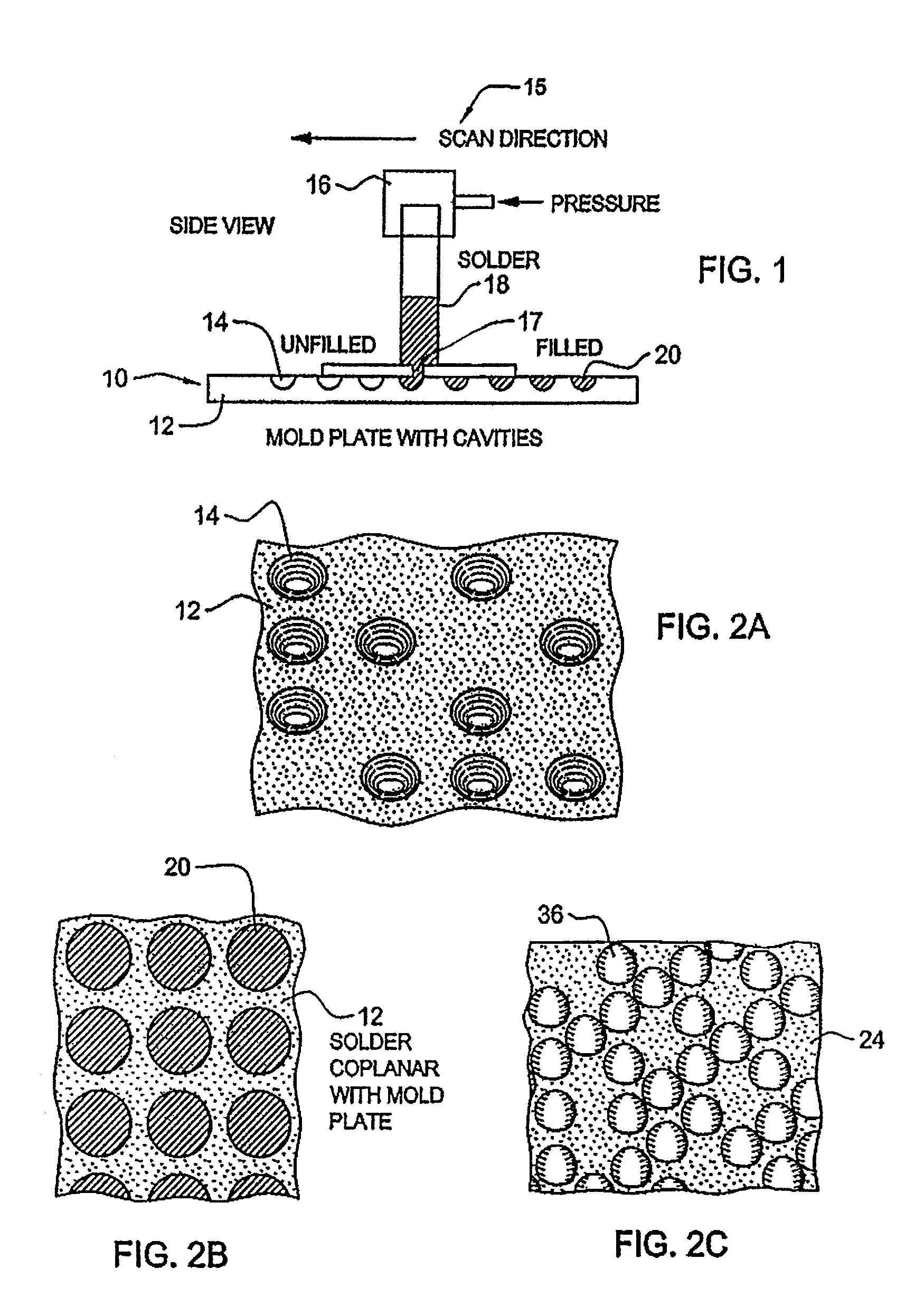
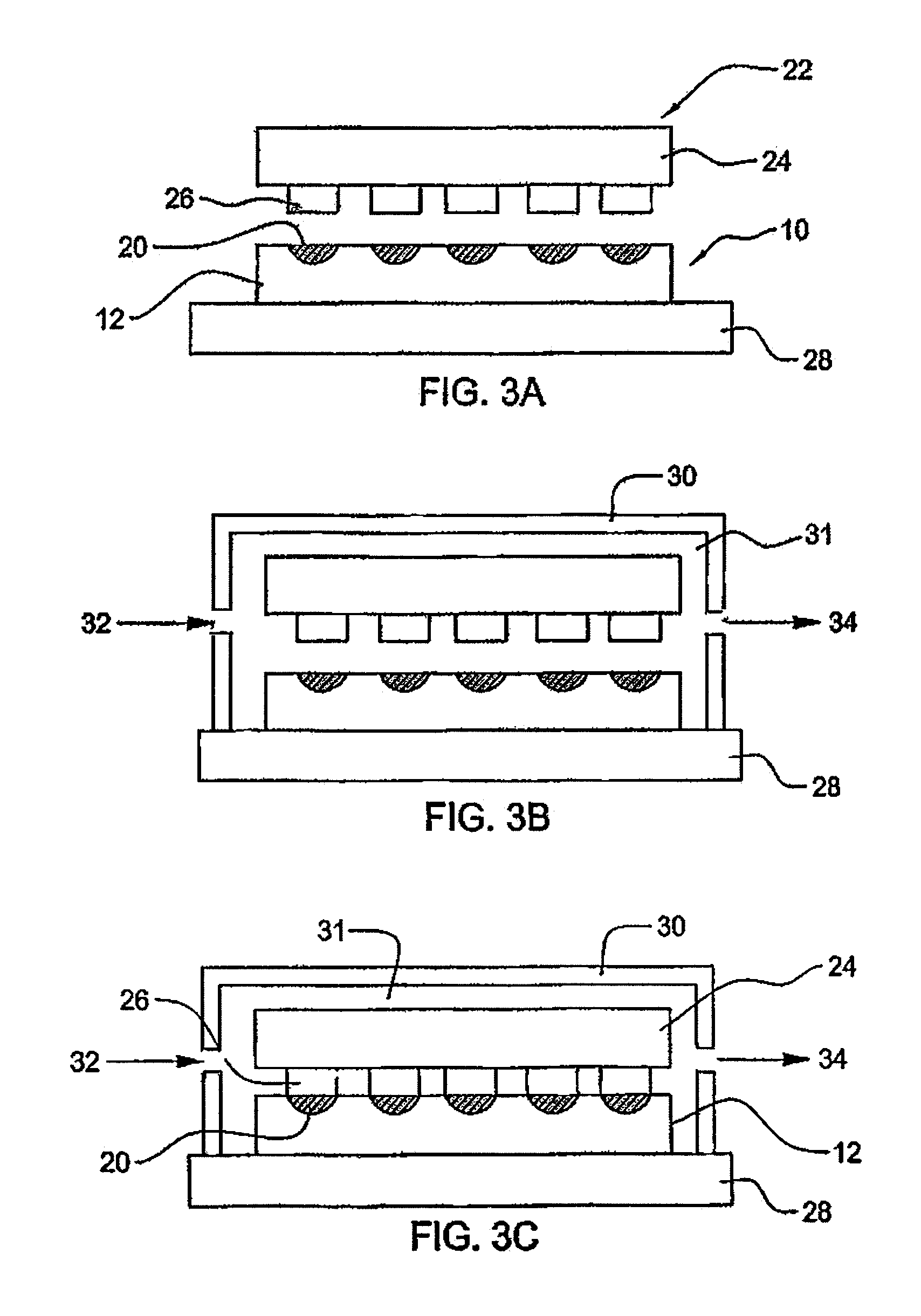
Method for electrolytic recycling and regenerating acidic cupric chloride etchants
ActiveUS20170058408A1Improving manufacture safetyReduce environmental impactElectrolysis componentsInsulating layers/substrates workingProduction lineElectrolysis
A method for electrolytic recycling and regenerating acidic cupric chloride etchants, comprising: (1) employing an acidic cupric chloride etchant that contains iron ions in PCB etching, controlling the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) of said acidic cupric chloride etchant within the range of 360-700 mV; (2) transferring an etchant waste of step (1) to an electrolysis tank and electrolysing said etchant waste; (3) the chlorine gas generated by electrolysis oxidizes the electrolyte in the electrolysis tank and thereby dissolved into the electrolyte, in the effect of the ORP of the electrolyte; (4) regenerating an etchant by oxidizing Fe(II) ions and Cu(I) ions in the electrolyte to Fe(III) ions and Cu(II) ions using the chlorine gas of step (3) that is dissolved into the electrolyte, and when the chlorine gas is fully dissolved into the electrolyte, the oxidizing step of the electrolyte is finished and an etchant is regenerated; (5) transferring the etchant regenerated in step (4) to an etching production line.
Owner:YE YITING
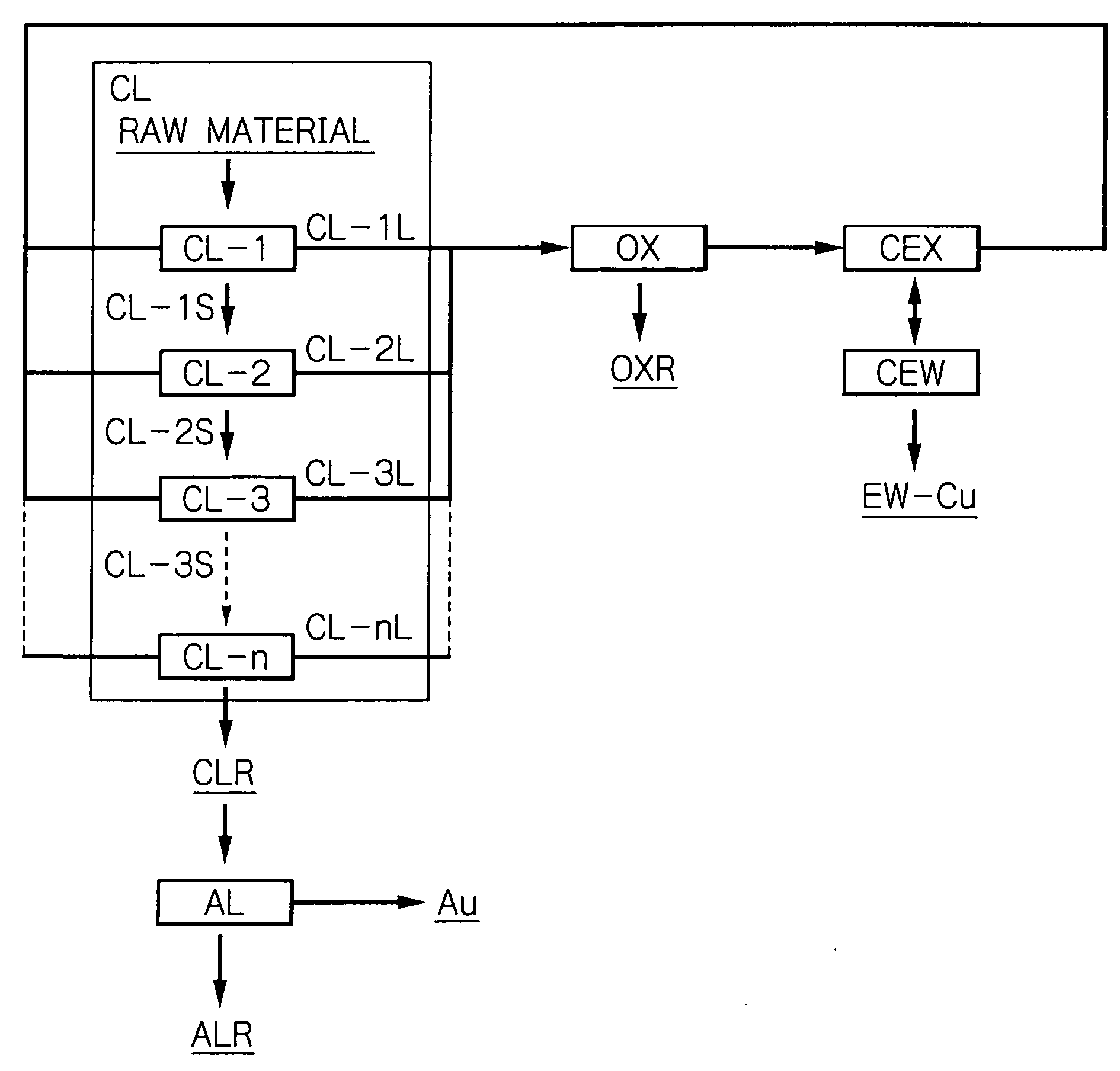
Method for recovering metal from ore
ActiveUS20090241736A1Drawback can be obviatedProcess efficiency improvementImpurityMaterials science
The copper sulfide ore is leached in the halide bath without using a special oxidant but with the use of only air. The copper and gold in the copper sulfide ore can be leached at high leaching ratio.The treating steps are as follows.(1) Copper leaching process (CL). The raw material is charged into the first acidic aqueous solution, which contains cupric chloride, ferric chloride, 7 g / L of hydrochloric acid, and sodium chloride. The post-leach liquor contains copper in cuprous state ions and copper in cupric state ions.(2) Solid-Liquid separation step. The resultant solid and liquid of CL step are separated.(3) Air oxidation step (OX). Air is blown into the post solid-liquid separation liquor. The copper in cuprous state ions are oxidized to the copper in cupric state ions. The iron leached in the step (1) is oxidized. Simultaneously, the impurities leached in the step (2) are precipitated.(4) Copper extracting step (CEX). The copper is recovered from the post-liquor of the step (3)(5) Gold recovering step (AL). The residue separated in the step (2) is added to the leach liquor similar to that of the step (1). The steps (1) and (5) are carried out under the atmospheric pressure and at the temperature of boiling point or lower, while blowing air into the leach liquor.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
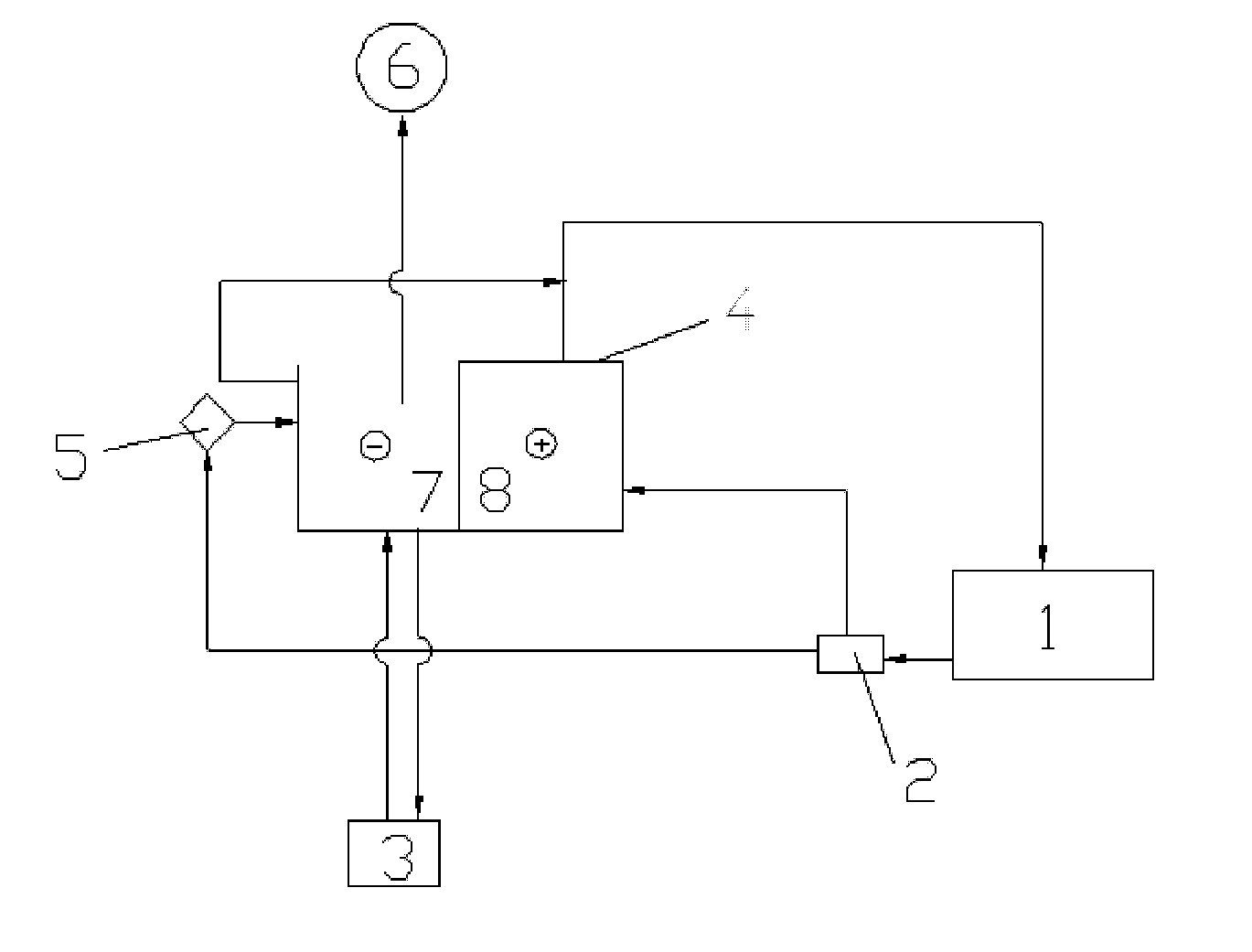
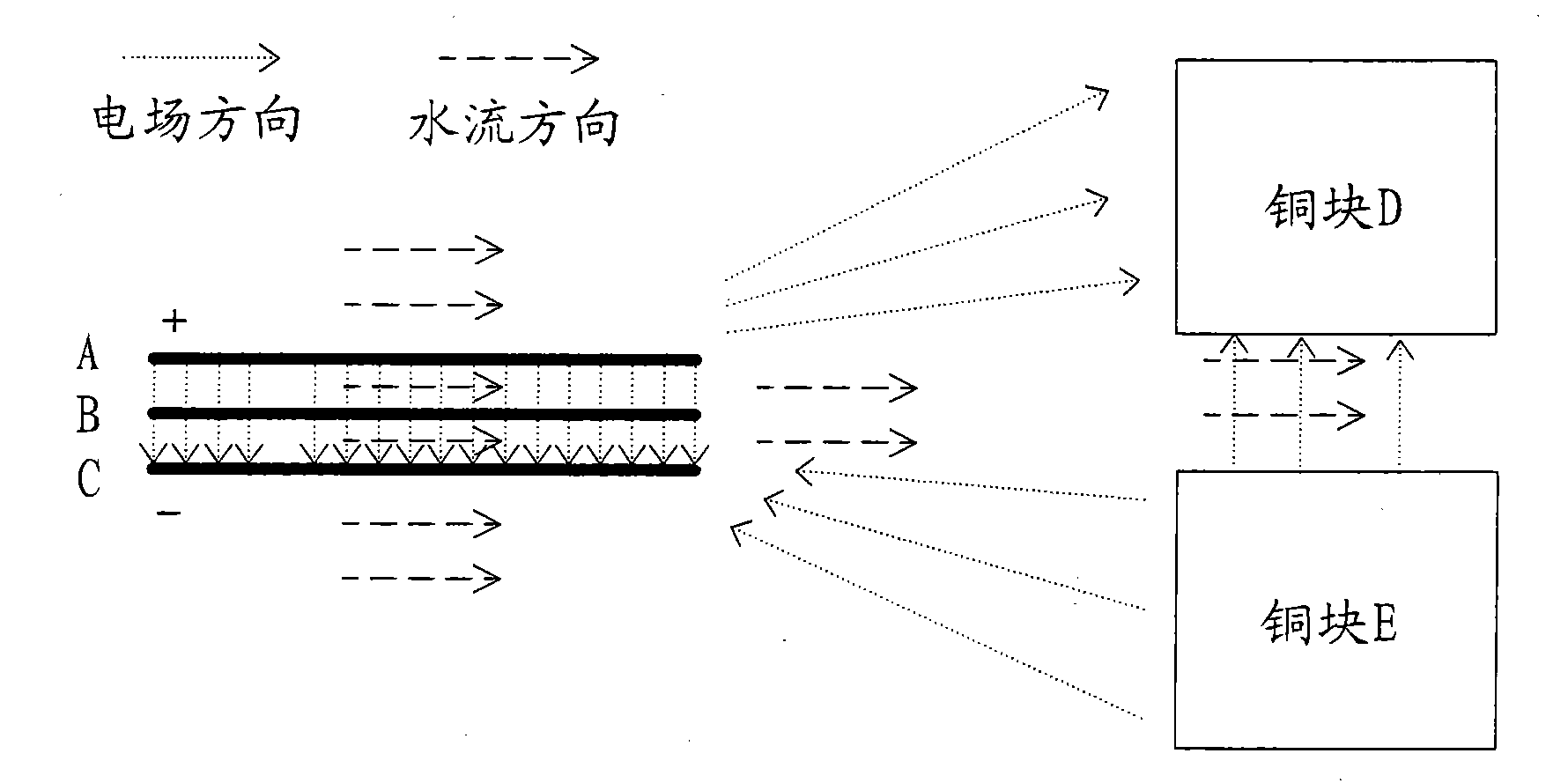
Two-in-one cupric chloride/cupric bromide disinfecting apparatus for swimming pool and control method thereof
ActiveCN101993135AInhibition releaseThe amount of release is controllableWaste water treatment from bathing facilitiesGymnasiumCupric bromideGraphite electrode
The invention discloses a control method of a two-in-one cupric chloride / cupric bromide disinfecting apparatus for a swimming pool, comprising the following steps of: when copper is released, periodically inverting an anode and a cathode of a copper block and allowing an anode and a cathode of titanium plate / graphite electrode plate to be in a suspending state simultaneously; and when chloride / bromide is released, periodically inverting the anode and the cathode of the titanium plate / graphite electrode plate and short connecting the anode and the cathode of the copper plate simultaneously and then connecting the copper block with the cathode of the titanium plate / graphite electrode plate or applying the voltage lower than the voltage of the titanium plate / graphite electrode plate. In the method, by short connecting the copper block when not in work with the cathode of the titanium plate / graphite electrode plate or applying the voltage lower than the voltage of the cathode, the release amount of copper ions can be controlled, the volume of the disinfecting apparatus can be reduced and the corrosion between the anode and the cathode of the copper block is balanced. The invention also discloses the two-in-one cupric chloride / cupric bromide disinfecting apparatus for the swimming pool.
Owner:INTEX IND (XIAMEN) CO LTD
Preparation of a lead-free primary explosive
ActiveUS20100280254A1BiocideGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesSodium ascorbateSubject matter
Embodiments of the present subject matter provide a compound and material that may be used as a lead-free primary explosive. An embodiment of the present subject matter provides the compound copper(I) nitrotetrazolate. Certain embodiments of the present subject matter provide methods for preparing lead-free primary explosives. The method includes: providing a cupric salt; providing water; providing a 5-nitrotetrazolate salt; combining the cupric salt, water and 5-nitrotetrazolate salt to form a mixture, heating the mixture, adding a reducing agent and stirring with continued heating. The method may also include providing cupric chloride, sodium 5-nitrotetrazolate and sodium ascorbate. Certain embodiments of the present subject matter also provide methods for preparing copper(I) nitrotetrazolate. The method includes: providing cupric salt; providing water; providing 5-nitrotetrazolate salt; combining the cupric salt, water and 5-nitrotetrazolate salt to form a mixture, heating the mixture, adding a reducing agent and stirring with continued heating. The method may also include providing cupric chloride, sodium 5-nitrotetrazolate and sodium ascorbate.
Owner:PACIFIC SCI ENERGETIC MATERIALS
Process for the Manufacture of Bio-release Fertilizers of Zinc-iron-manganese, Iron-manganese-copper and Zinc-iron-manganese-copper
InactiveUS20100206032A1Improve nutrient availabilityImprove usabilityFertilisers by pryogenic processesPhosphatic fertiliser granulation/pelletisationPyrolusiteCompounds of zinc
A process for the preparation of water insoluble bio-release micronutrient fertilizers, containing iron and manganese with either zinc and / or copper, comprising (a) heating orthophosphoric acid at a temperature of 130° C.-150° C. with a mixture of (i) source of iron oxide, (ii) manganese dioxide or pyrolusite, and (iii) either or both compounds of zinc or copper selected from zinc ash or zinc oxide and cupric oxide, or cupric sulphate or cupric chloride and (iii) a basic compound such as oxide or carbonate of magnesium or calcium, to produce a multi-metallic polyphosphate; (b) neutralisation of the polyphosphate with a basic compound followed by drying and pulverisation to obtain a solid powdery material.
Owner:NAT RES DEV CORP
Preparation method of 1,3-diacetylene catalytic system
InactiveCN103980086AOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsReaction temperatureDiacetylene
The invention relates to a catalytic system for preparing 1,3-diacetylene. According to the catalytic system, cupric chloride, air and 8-hydroxyquinoline are respectively used as a catalyst, an oxidizing agent and an auxiliary ligand, the reaction temperature is only 100 DEG C, and only a catalytic amount of inorganic base is adopted.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV +1
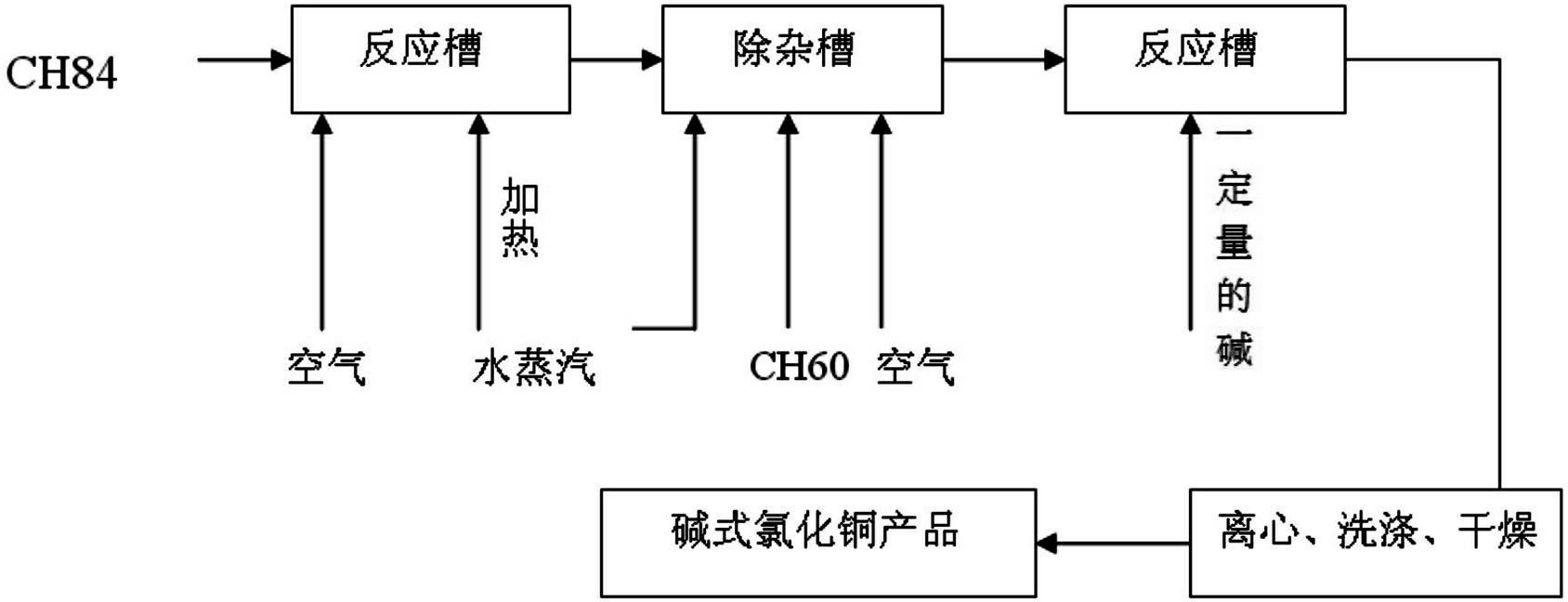
Method for producing cupric chloride basic by using scrap copper
InactiveCN102432058AEfficient recyclingReduce wasteCopper chloridesCupric chlorideProcess engineering
The invention discloses a method for producing cupric chloride basic by using scrap copper, which comprises the steps of: at first, adding the scrap copper into a reaction liquid containing hydrochloric acid, then heating the reaction liquid in a reaction kettle, performing a copper-dissolving reaction at a certain temperature and removing impurities after reaction to obtain a cupric chloride solution; performing a secondary reaction by using the cupric chloride solution prepared and alkali, wherein the molar ratio of cupric chloride and alkali is 1: (0.1-3); preparing a cupric chloride basic solution after reaction; and washing, centrifuging and drying to obtain the end product of cupric chloride basic. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple technological steps, low cost, ecological and environmental friendliness, stable product quality and good product safety and the like.
Owner:XINGJIA BIO ENG CO LTD
Corrosive for original austenite grain boundary of superhigh strength alloy structure steel and display method of original austenite grain boundary
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallographic structure observation, and particularly relates to a display method for an original austenite grain boundary of superhigh strength alloy structure D6AE steel. A corrosive for the austenite grain boundary of the superhigh strength alloy structure steel comprises the following components in parts by weight: 4.5 to 5.5 parts of picric acid, 7.5 to 8.5 parts of fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether, 1.8 to 2.8 parts of ammonium cupric chloride, 100 parts of water and 6.6 to 8.1 parts of hydrogen peroxide. By the adoption of the corrosive disclosed by the invention, crystalline grains of original austenite of the superhigh strength alloy structure D6AE steel can be displayed clearly, and thus the problem that the original austenite grain boundary of the D6AE steel is difficult to display is solved.
Owner:成都积微物联集团股份有限公司
Method for preparing strong-hydrophilicity PET membrane
InactiveCN105435651AStrong anti-pollutionLow priceMembranesSemi-permeable membranesTetrachloroethaneCompanion animal
A disclosed method for preparing a strong-hydrophilicity PET membrane comprises the following steps: a, dissolving stannous chloride, cupric chloride or calcium chloride into an acetone solution, so as to obtain a doping solution; b, adding nanometer silicon dioxide into deionized water, performing ultrasonic dispersing, then adding a silane coupling agent under stirring condition, and adjusting pH value of the solution with a hydrochloric acid, so as to obtain a modified nanometer silicon dioxide solution; c, adding a PET particle into a mixed solvent of tetrachloroethane and phenol, heating to completely dissolve PET particle, and then adding the doping solution obtained in the steps a, so as to prepare a PET membrane forming solution, and dropwise adding the PET film forming solution to a glass slide, and then putting in a vacuum baker for drying, so as to obtain a blended membrane; and d, immersing the blended membrane obtained in the step c in the modified nanometer silicon dioxide solution obtained in the step b, and taking out and naturally drying in air after immersion is finished, so as to obtain the strong-hydrophilicity PET membrane. The prepared strong-hydrophilicity PET membrane possesses strong anti-pollution capability and possesses relatively good application prospect in the fields of water processing industry and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
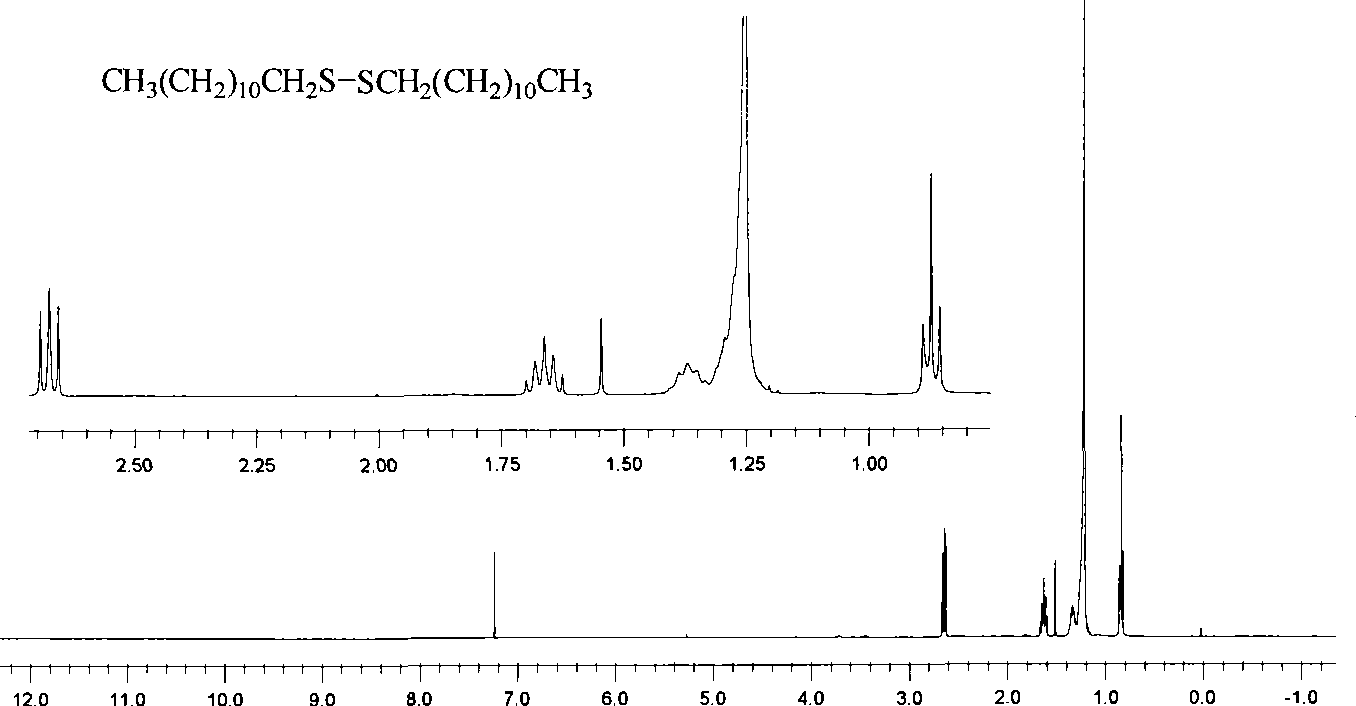
Preparation of symmetrical disulfide bond-bearing compound
The invention discloses a method for preparing symmetrical compounds containing disulfide bonds. The method comprises: firstly, taking thioalcohol or phenylsulfhydrate as a raw material, utilizing metal alkyl compounds to seize reactive hydrogen on the thioalcohol or the phenylsulfhydrate at a temperature of between 60 DEG C below zero and 80 DEG C below zero and obtaining sulfur anions; secondly, using anhydrous cupric chloride for oxidation coupling to generate the disulfide bond; and thirdly, purifying reaction products and obtaining the symmetrical compounds containing the disulfide bonds. The preparation method has high yield and low cost, is simple and easy to obtain the adopted raw material, and is an effective path for preparing the symmetrical compounds containing the disulfide bonds.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Chemical copper plating solution and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103422078ADoes not affect responseRapid responseLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical platingCopper plating
The invention provides a chemical plating solution and a preparation method thereof. The chemical plating solution comprises cupric chloride, vanillin, a complexing agent, a stabilizing agent, a reducing agent and a surfactant. The content of the cupric chloride is 5-10 g / L. The content of the vanillin is 1-5 g / L. According to the chemical plating solution, the cupric chloride with strong permeability is utilized to provide bivalent copper ions and utilized as a source of deposited copper. In addition, the chemical plating solution comprises the vanillin, and the vanillin and the cupric chloride form a stable complex, thereby protecting plating from being oxidized and assuring the quality of the plating.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
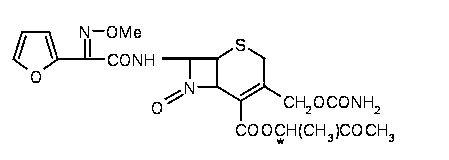
Preparation method of cefuroxime axetil
The invention discloses a preparation method of cefuroxime axetil. The method comprises the following steps: completely dissolving cefuroxime acid in dimethylformamide, and carrying out esterification reaction with 1-bromethylacetate under the catalytic action of cupric chloride; and hydrolyzing with ethyl acetate and sodium chloride solution, extracting, carrying out vacuum distillation, crystallizing with cyclohexane, carrying out vacuum filtration, and drying to obtain high-purity cefuroxime axetil. The cupric chloride, which has the advantages of no toxicity, no harm and high catalytic efficiency, is preferably used as the catalyst; the cyclohexane for crystallization is easy to recover and reutilize, thereby lowering the production cost; and meanwhile, the method has the advantages of mild and controllable reaction conditions, short production cycle and lower energy consumption, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:GUANGDONG LIGUO PHARMACY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com