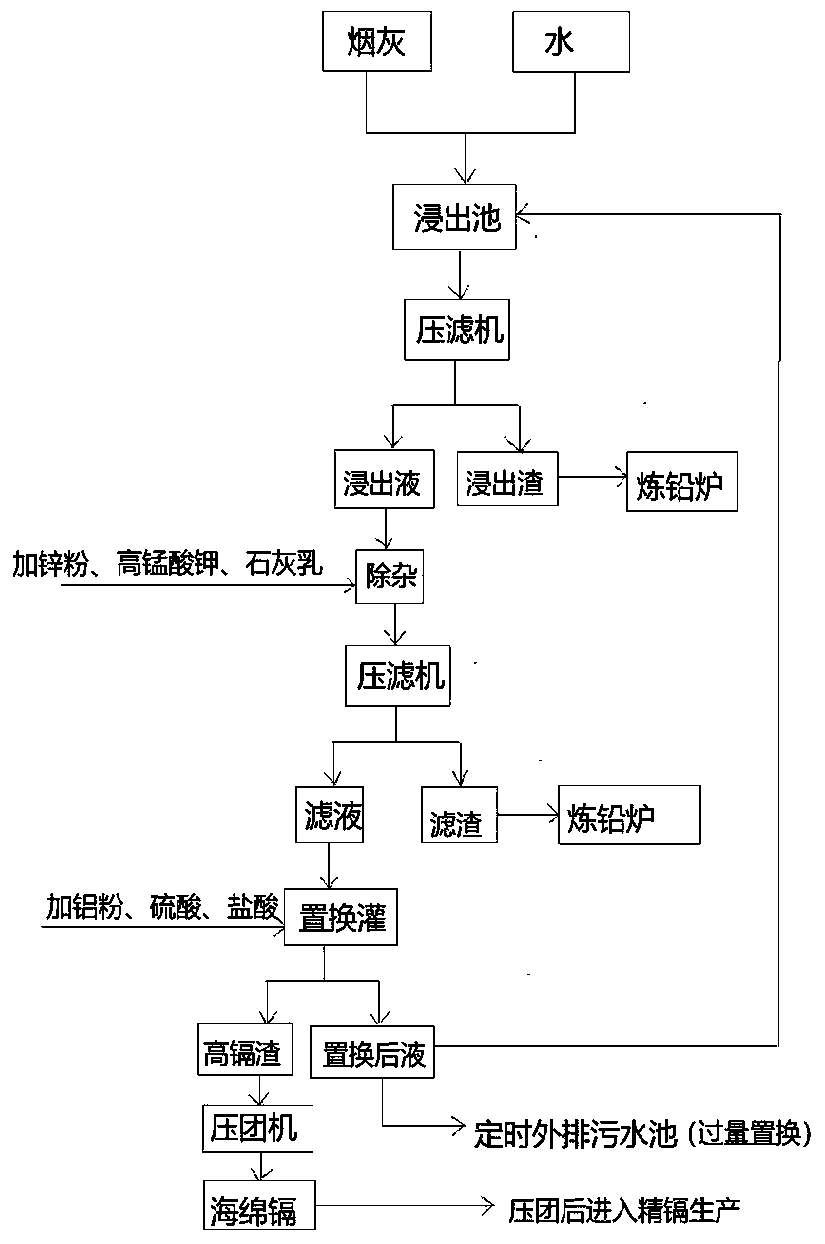
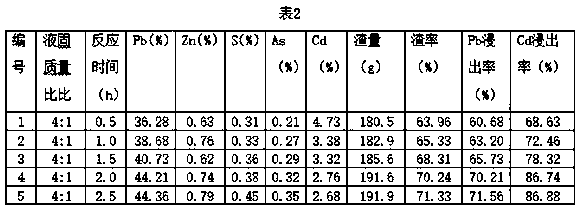
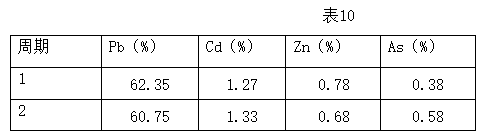
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70 results about "Cadmia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In alchemy, cadmia (Latin for cadmium) is an oxide of zinc (tutty) which collects on the sides of furnaces where copper or brass was smelted, and zinc sublimed. The term is also applied to an ore of cobalt.
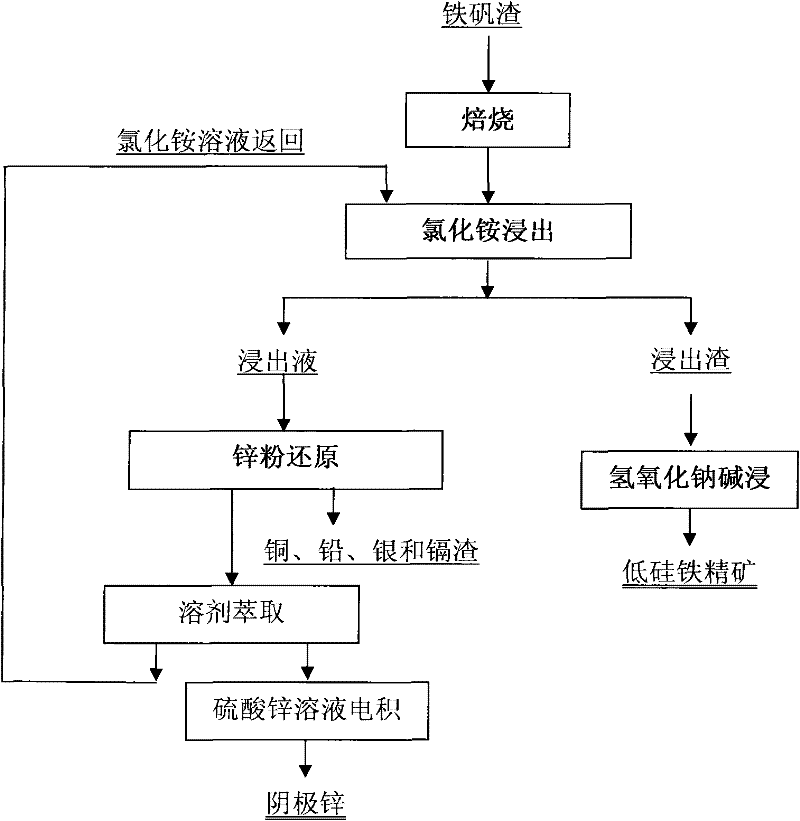
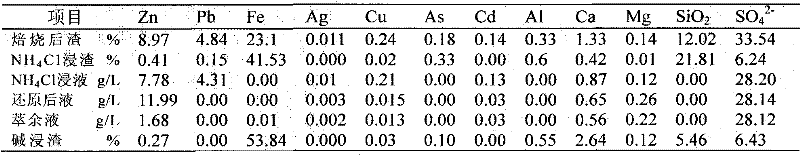
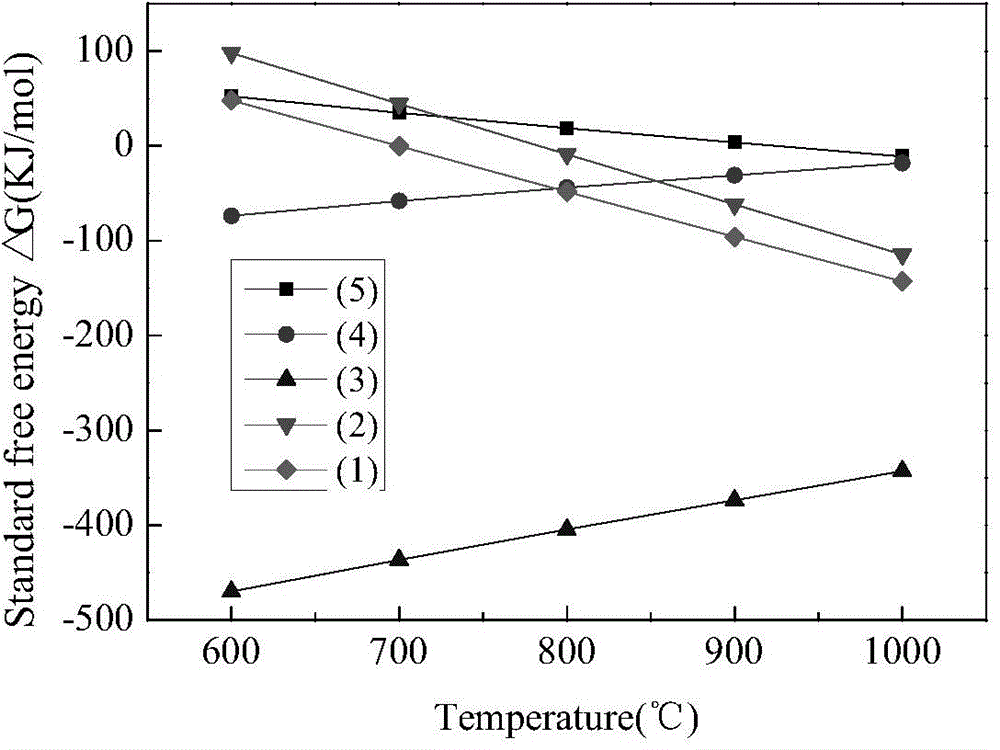
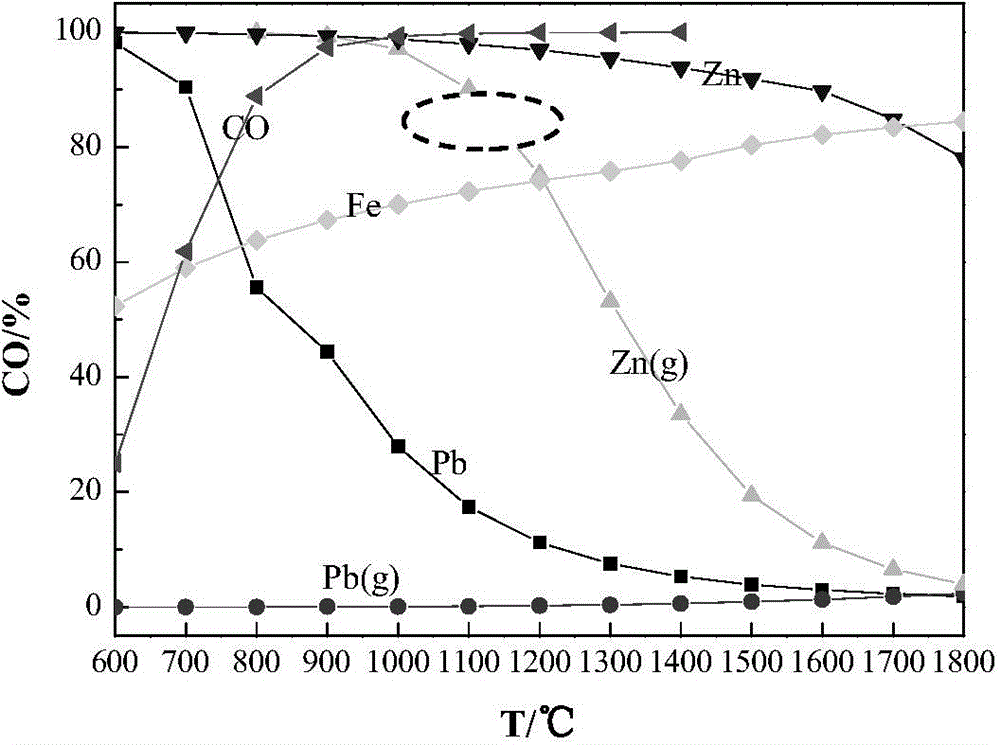
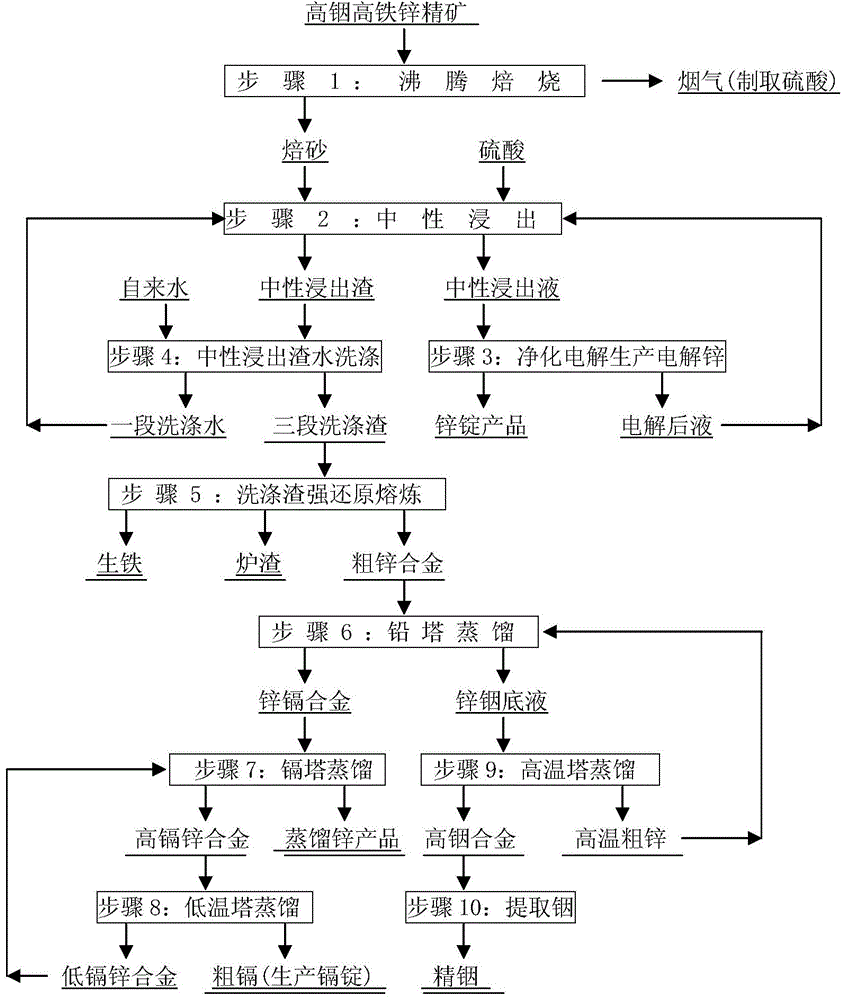
Clean metallurgic comprehensive utilization method of iron vitriol slags
InactiveCN102443701AImprove pollutionReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementFerrosiliconPollution
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Comprehensive recycling technique of valuable elements in smelting soot
InactiveCN102517449AAdaptableHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSecondary loss
The invention provides a comprehensive recycling technique of valuable elements in smelting soot, which comprises the steps of: adding sulfuric acid in the smelting soot to pulpify the same, leaching for twice, and filter pressing the smelting soot to form lead-silver-bismuth slag; smelting, casting, electrolyzing, refining and reducing and smelting the lead-silver-bismuth slag in a converter to obtain rough lead, copper matte, pure bismuth and silver-zinc slag; adding cupric hydroxide in the supernatant to deposit arsenic, depositing the copper in the copper arsenate slag with deposited arsenic to form copper-arsenic solution, concentrating, crystallizing, dissolving and separating the solution to obtain white arsenic and cupric sulfate solution; performing twice electrodeposition treatments on the copper-zinc-cadmium solution with deposited arsenic to respectively obtain electrolytic copper and black copper, sequentially adding zinc oxide and zinc powder to perform deacidification, high-temperature copper removal and low-temperature cadmium removal treatments to obtain sponge cadmium, smelting the sponge cadmium to obtain rough cadmium, concentrating and crystallizing the zinc sulfate solution to obtain heptahydrate zinc sulfate. The comprehensive recycling technique provided by the invention has the advantages of improving the recovery of multiple metals, having extensive treatment raw materials, low production cost and high economic benefit, and avoiding the secondary pollution of decentralized processing and secondary loss of valuable metals.
Owner:SHANDONG FANGYUAN NON FERROUS METAL TECH SERVICE
Improved hot galvanizing method of iron handicraft or furniture
InactiveCN103668030ANo over-cleaning phenomenonImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesEthylenediamineThiourea
The invention relates to an improved hot galvanizing method of an iron handicraft or furniture. The method comprises the following steps: (1) uncoiling and degreasing a workpiece; (2) removing dust; (3) washing; (4) assisting plating; (5) baking; (6) galvanizing by dipping; (7) settling; (8) passivating; (9) cooling. In the method, a degreasant is changed into acidity and is composed of a sulfuric acid solution, OP-10 and di-o-tolyl-thiourea. Thus, a washing procedure can be saved; a water resource and the degreasant can be saved; the workpiece does not generate an over-cleaning phenomenon; a pickling solution is composed of a hydrochloric acid solution, phosphoric acid, alkylphenol ethoxylates, lauryl sodium sulfate and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, so that the pickling speed is improved, formation of acid mist and use of a complexing agent can be restricted, reduction of cadmia in galvanizing zinc is facilitated, the malleability of a zinc coating on the surface of the work-piece is improved, proper temperature and event are adopted in the subsequent galvanizing by dipping, and the thickness and the stability of the zinc coating at the surface of the workpiece are ensured. Thus, the improved hot galvanizing method is a method which is simple and convenient for operation and good in galvanized effect.
Owner:TIANJIN BIAODIAN METAL HANDICRAFT CO LTD
Cadmia reduction smelting method for the preparation of low-phosphorus iron
ActiveCN104911365ARestoredAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingPollutant emissions
The present invention discloses a cadmia reduction smelting method for the preparation of low-phosphorus iron. The method is as below: adding a slagging constituent into cadmia and roasting in an oxidizing atmosphere; then adding a reducing agent and conducting reduction smelting under an inert atmosphere; reducing the lead and zinc in the slag, volatilizing and entering into dust collection; and stratifying the slag phase to obtain pig iron and slag. The method reaches iron recovery of 84%, and obtains a pig iron product; and the iron grade is no less than 92.65%, contains 0.03% of lead, 0.001% of zinc and 0.06% of phosphorus, and reaches superfine class standards of the national steel-making pig iron. The invention can effectively recycle iron in cadmia, the pig iron product has low content of phosphorus, lead and zinc; the process is short, discharges few pollutants, and recycles lead and zinc, has good economic and environmental meaning.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
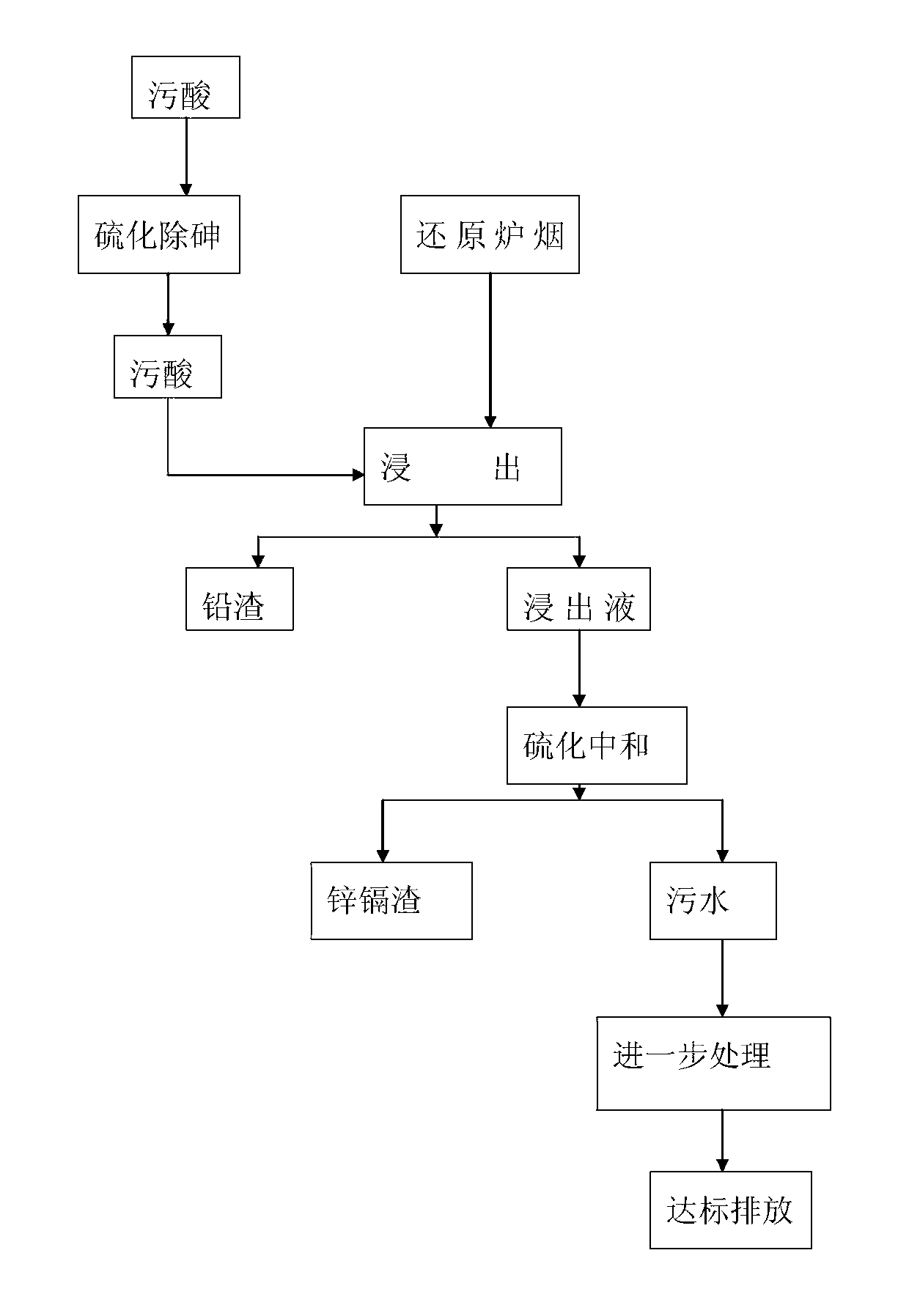
Process for recovering lead, zinc and cadmium in soot on recovery section in process of treating waste acid generated in lead smelting
InactiveCN102994764ALow running costAvoid harmProcess efficiency improvementLead smeltingNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention relates to the field of nonferrous metal smelting and particularly relates to a process for recovering lead, zinc and cadmium in soot on a recovery section in the process of treating waste acid generated in lead smelting. The soot of a reduction furnace is subjected to a leaching reaction by using arsenic sulfide removal waste acid in the lead smelting industry to generate lead slag to be recovered, and then, the leaching agent is continued to be neutralized by using sodium sulphide and sodium hydroxide to generate high-grade zinc and cadmium slag to be recovered. According to the invention, the waste acid is used for separating the lead, zinc and cadmium in the soot of the reduction furnace for lead smelting, so that the operation cost is low; the problem of production operation damage caused by circulated accumulation of the zinc and cadmium in lead smelting is solved and the pressure of a lead smelting system is relieved under the condition of low cost; and the lead slag which is low in arsenic content and suitable for being treated by a lead system and the zinc and cadmium slag which is suitable for being treated by a zinc system can be generated, and meanwhile, the waste acid is also treated, so that not only is the treatment cost of the waste acid reduced, but also the treatment difficulty is lowered.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG GOLD & LEAD
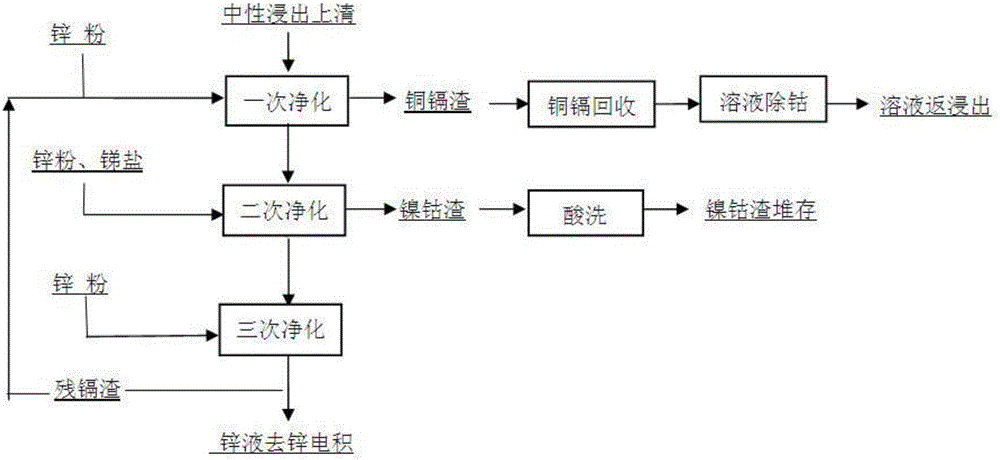
Method for comprehensively recovering zinc nickel cadmium from copper cadmium residues
InactiveCN106435213AAvoid leachingAchieve removalProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionNickel cadmium
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively recovering zinc nickel cadmium from copper cadmium residues. The method is characterized by including the steps: A leaching and purifying: simultaneously leaching and purifying the copper cadmium residues and filtering the copper cadmium residues to obtain leach liquor; B primary cadmium settling: adding zinc powder into the leach liquor in the step A to obtain primarily cadmium settled liquor and a sponge cadmium product; C secondary cadmium settling: adding substitute zinc powder into the primarily cadmium settled liquor in the step B to obtain secondarily cadmium settled liquor and crude cadmium; D zinc ingot production: performing 'extraction-washing-back extraction-electrodeposition-casting' procedures for the secondarily cadmium settled liquor obtained by the step C to produce a zinc ingot product; E nickel hydroxide neutralization and precipitation: precipitating and neutralizing nickel in zinc extraction raffinate obtained in the step D to obtain a nickel hydroxide product. The method is simple in process, low in cost and high in metal recovery rate, has the advantages of short process cycle, high efficiency and easiness in realizing automation and continuity, and is a clean pollution-free production process.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
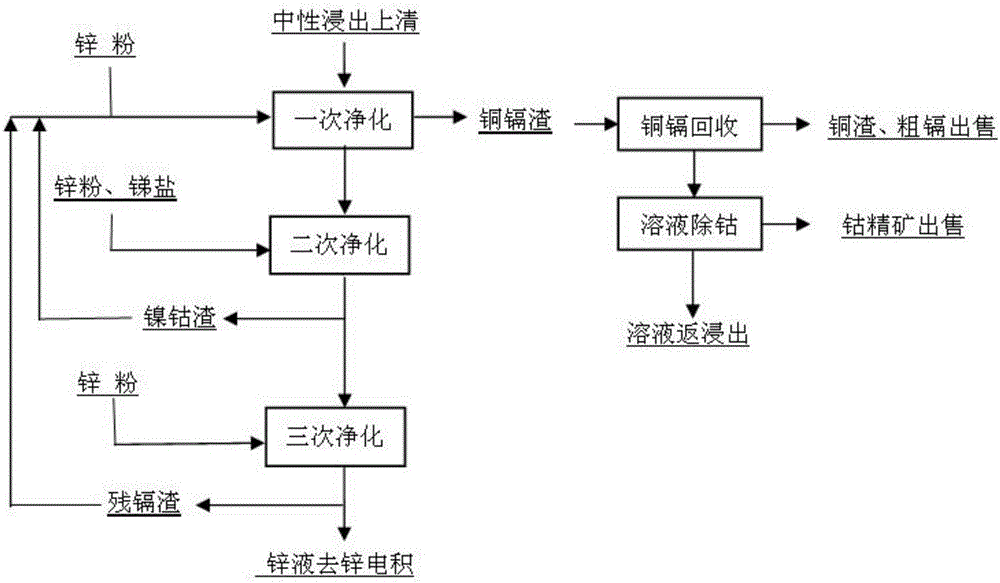
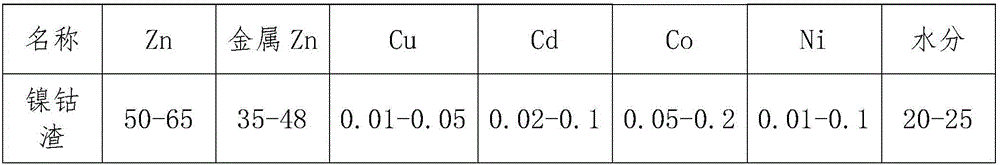
Recycling method for zinc smelting nickel and cobalt slag
InactiveCN106244813AReduce consumptionLow costPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsCopperZinc smelting
Provided is a recycling method for zinc smelting nickel and cobalt slag. The method comprises the steps that nickel and cobalt slag which is produced through three-section reverse antimony and two-section purification production is added to be subjected to one-section purification after being pulpified; copper and cadmium are removed in one-section purification by zinc powder remaining in the nickel and cobalt slag, copper cadmium cobalt slag is formed by the used slag, and then nickel and cobalt slag is not produced any more through purification. The copper cadmium cobalt slag is recycled by cadmium and is leached to separate copper and cadmium, the content of cobalt in the solution is 150-1000 mg / l, and the solution is returned back to a main system after the cobalt is recycled by an organic reagent. According to the recycling method, consumption of purification zinc powder is lowered by fully utilizing zinc powder remaining in the nickel and cobalt slag; a new way is developed for recycling of dangerous solid waste, like the nickel and cobalt slag, produced in wet zinc smelting; the technological process of cadmium recycling production is simplified, production operation is simple, and no precedent reports exist at home and abroad.
Owner:JIANGXI COPPER
Preparation method of high-purity indium
ActiveCN102839391AReduce contentAvoid it happening againPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisIndium
The invention relates to a preparation method of high-purity indium. The preparation method comprises the following steps: an acid leaching step of leaching the material indium to dilute sulphuric acid, so as to remove oxide on the surface of the material indium; a measuring step of getting the material indium out of the dilute sulphuric acid, cleaning and drying the material indium, and measuring the impurities and content in the material indium by a photometer, wherein the impurities include copper, tin, arsenic, zinc, thallium, lead, iron, cadmium and aluminium; a smelting and impurity-removing step of smelting the impurity-removed material indium and removing the impurity of tin, thallium and cadmium. According to the preparation method of the high-purity indium, firstly, the impurities of tin, thallium and cadmium, which are difficult to electrolyze and of which chemical potentials close to that of indium, are smelted to reduce the content of the tin, the thallium and the cadmium; and then the content of copper, tin, arsenic, zinc, thallium, lead, iron, cadmium, aluminium and the like are further reduced by secondary electrolysation, so that the high-purity indium achieves the purity of more than 5N, thereby satisfying the usage requirements; and moreover, the preparation method is simple to operate, and is capable of preventing the poisonous gas from polluting the environment.
Owner:广西德邦科技有限公司
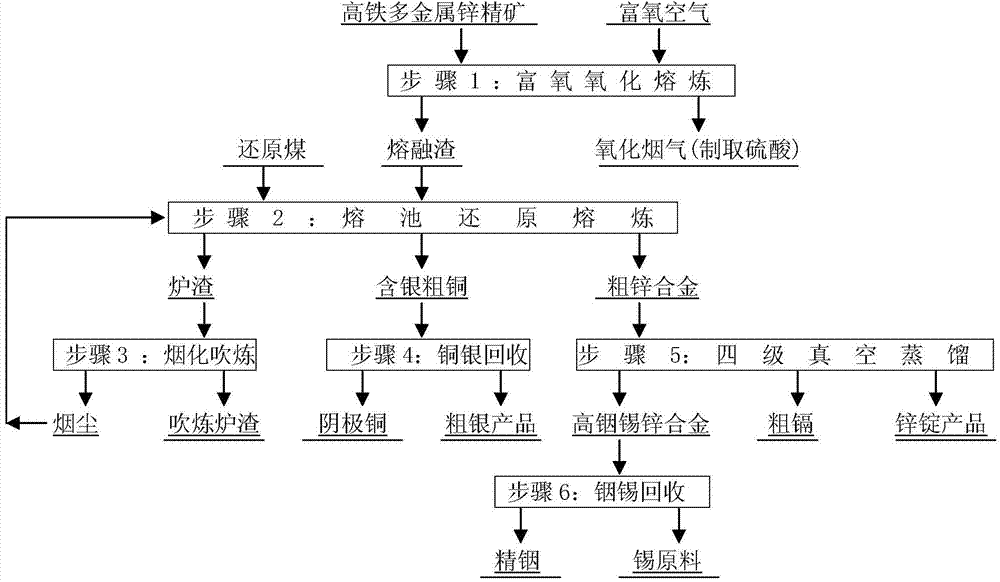
Smelting method of high-iron multi-metal zinc concentrate
ActiveCN103695663AReduce lossesEfficient recyclingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementIndiumDistillation
The invention relates to a smelting method of a high-iron multi-metal zinc concentrate. The method comprises the following steps: performing oxygen-enrichment oxidation melting on a zinc concentrate containing 14% to 20% of Fe, 0.03% to 0.10% of In, 0.2% to 0.6% of Cu, 0.2% to 0.6% of Cd, 0.005% to 0.02% of Ag, 0.1% to 0.2% of Sn and 40% to 50% of Zn so as to generate an oxidized flue gas and molten slags; preparing the oxidized flue gas into sulfuric acid; performing reduction smelting on the molten slags in a smelting pool so as to generate a crude zinc alloy, crude copper containing silver and slags; blowing the slags so as to obtain smoke dust and blown slags; returning the smoke dust to be subjected to reduction smelting; selling the blown slags in a market; extracting the copper and the silver from the crude copper containing silver; and performing four-stage distillation on the crude zinc alloy entering an electric-heating graphite vacuum furnace so as to generate a pyrogenic distilled zinc product, a crude cadmium product and a high-indium-tin zinc alloy which is used for extracting indium and tin. The method is reasonable in process, good in comprehensive recovery, high in production efficiency, low in production cost and clean and environmentally friendly in production process.
Owner:LAIBIN CHINA TIN SMELTING
Method for removing copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt out of zinc sulfate solution through one step
The invention discloses a method for removing copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt out of a zinc sulfate solution through one step. The method comprises the steps that manganese metal powder and / or manganese-based alloy powder are / is added into the zinc sulfate solution containing copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt, wherein the temperature of the zinc sulfate solution ranges from 45 DEG C to 70 DEG C, and the pH of the zinc sulfate solution is larger than 4.0; and stirring is carried out for a reaction, after the reaction is finished, filtering separation is carried out, and the zinc sulfate solution with the contents of copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt all lower than 0.8 ppm is obtained. According to the method, copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt can be efficiently removed out of the zinc sulfate solution through one step at the same time, no impurities endangering zinc electrolyzing are introduced, the technological process is simple and low in cost, no complex and special equipment is needed, and good industrial application prospects are achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Eutectic alloy for spraying electronic component and its making method
The invention provides a eutectic alloy for electronic element surface spray coating and its preparing method. The alloy consists of Sn, Zn, Pb, Cu, and Bi or Cd and is prepared by smelting in proportion. The preparing process comprises: preparing the materials according to the proportion, smelting, cast forming, hot extrusion, and bright drawing. In the invention, the lead is replaced with Bi or / and Cd and Sb, which can reduce the lead pollution.
Owner:李建仲
Zinc doped sodium-based leadless piezoelectric ceramic synthesized at low-temperature and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101318819ALower sintering temperatureImprove performancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesMole fractionPotassium sodium
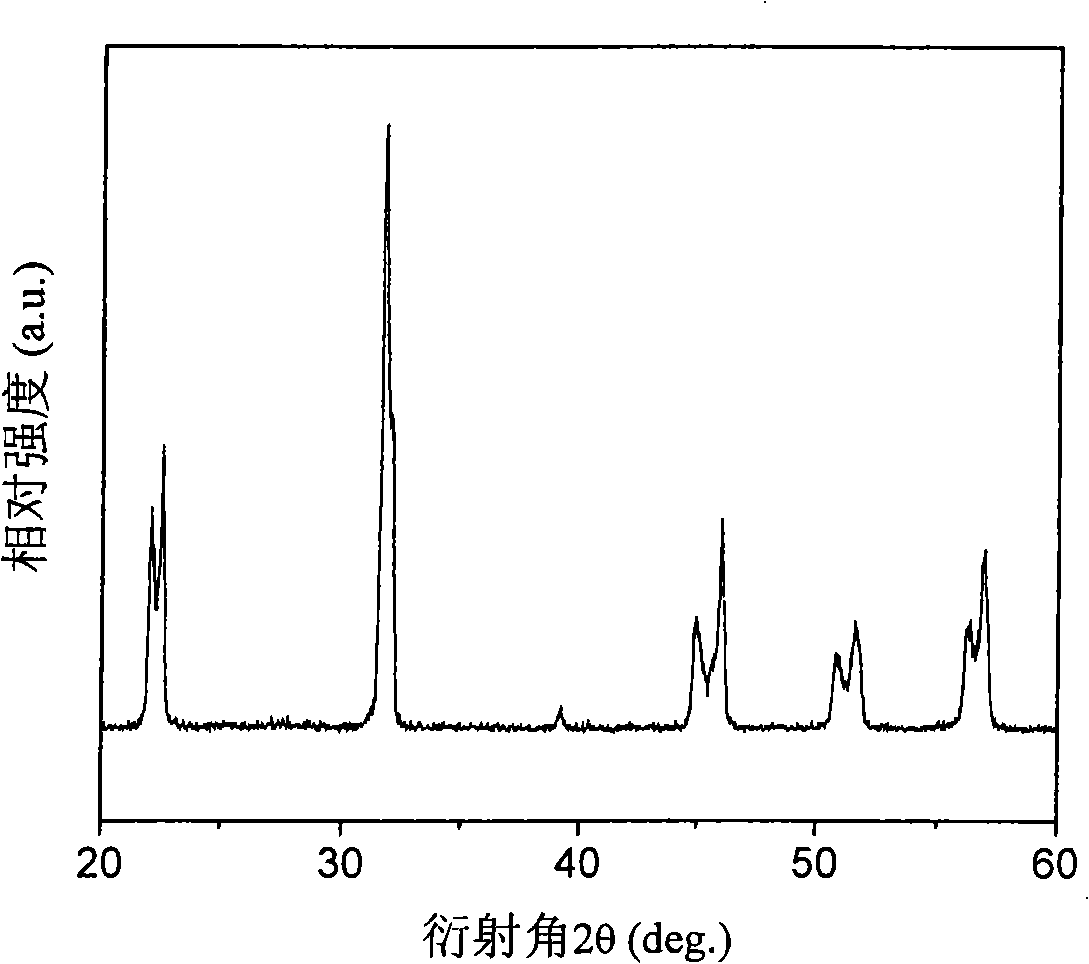
The invention provides a zinc-doped potassium sodium niobate based lead free piezoelectric ceramic material synthesized at a low temperature, belonging to the environment-friendly functional ceramic material field. The composition is (1-x)(NaaKbLic)NbO3+xZnO, wherein, a(1-x), b(1-x), c(1-x) and x respectively represent the molar fraction of components of Na, K, Li and Zn, a is more than or equal to 0.20 and less than or equal to 0.80, b is more than or equal to 0.20 and less than or equal to 0.80, c is more than or equal to 0.00 and less than or equal to 0.30, and x is more than or equal to 0.00 and less than or equal to 0.30. The preparation method comprises the process steps of weighing raw materials, mixing, baking, forming, sintering, baking silver and polarizing, etc. The material has the advantages that the sintering temperature of the potassium sodium niobate based lead free piezoelectric ceramics is effectively reduced by doping ZnO, ZnCO3 or alkali cadmia, and the potassium sodium niobate based lead free piezoelectric ceramic sample with good performance is synthesized at a low temperature of between 900 and 1,200 DEG C.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Treatment method of wet method zinc smelting by-products
InactiveCN101824541AAchieve separationSimple post-processingProcess efficiency improvementCadmium sulfateOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a treatment method of wet method zinc smelting by-products, which comprises the following steps: firstly, using a sulfuric acid solution for leaching heat treated copper-cadmium slag or copper-rich slag; then, using an organic solvent extraction method for extracting copper and cadmium at the same time from leach liquor to obtain copper-cadmium-rich organic phase zinc-sulfate-containing faffinate; using sulphuric acid for carrying out back extraction on the copper-cadmium-rich organic phase to obtain a mixed solution of copper sulfate and cadmium sulfate; then, adding a proper amount of organic precipitant into the mixed solution to obtain a mixture of organic precipitates of the copper and the cadmium; separating and washing the copper and cadmium precipitates; and adding a reducing agent solution for carrying out reduction reaction to respectively obtain sheet type copper powder and organic cadmium products. The invention realizes the value adding utilization of wet method zinc smelting by-products, reduces the treatment cost of the zinc smelting by-products, and reaches the goals of discharge reduction and yield improvement.
Owner:河池市津泰资源再生有限公司
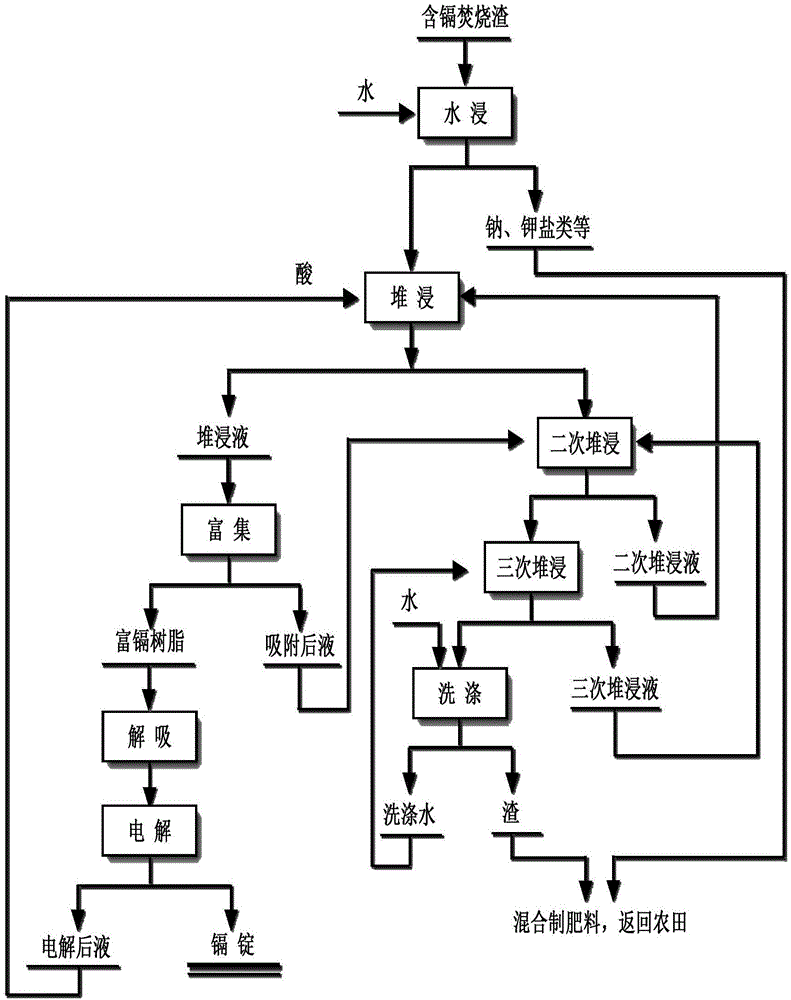
Process for recovering cadmium from cadmium-contained incineration slag
InactiveCN106566930ADisadvantages of Avoiding Landfill DisposalLess investmentPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisDesorption
The invention relates to a process for recovering cadmium from cadmium-contained incineration slag. The process comprises the following steps: water leaching: the cadmium-contained incineration slag is leached by water, so that soluble salt in the cadmium-contained incineration slag is dissolved in the water; and water leaching liquid is obtained, and is separated from the cadmium-contained incineration slag; heap leaching: according to the properties of cadmium in the cadmium-contained incineration slag, sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid or nitric acid is selected for segmented heap leaching, so that cadmium enters heap leaching liquid, and the content of cadmium in the cadmium-contained incineration slag reaches the discharge standard; enrichment: according to the properties of cadmium in the heap leaching liquid, resins are adopted to absorb low-concentration cadmium in the heap leaching liquid; cadmium is enriched in the resins; and absorption post liquid is obtained, and is returned for secondary heap leaching; desorption: the selected cadmium is used for absorbing the resins; and the sulfuric acid is adopted to desorb the absorbed resins at normal temperature to obtain cadmium liquid; and electrolysis: the cadmium liquid is electrolyzed; cadmium ions in solution are separated out on a cathode plate in a cadmium ingot form; and electrolysis post liquid is obtained.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Method for electroplating high-strength corrosion-proof cadmium-tin-titanium alloy on 304 or 316 L stainless steel surface
The invention provides a method for electroplating a protective plating layer of high-strength corrosion-proof cadmium-tin-titanium alloy on a 304 or 316 L stainless steel surface. The corrosion resistance of a plating layer is 6 to 7 times higher than that of a cadmium-plated layer, and the plating layer is uniform and fine and can be matched with cadmium-plated cyanide; after surface pre-treatment and in advanced cadmium-plating, the binding force of a cadmium-tin-titanium alloy plating layer is far more than that of the same kind of cadmium-tin plated alloy and the cadmium-plated layer; the cadmium-tin-titanium plating layer is porous, so that the hydrogen is beneficial for escaping; the cadmium-tin-titanium plating layer has good paintability, weldability, formability and low-hydrogen embrittlement; the whole preparation process is simple, cyanogen-free electroplating is achieved, and the preparation process is safe and environmentally-friendly.
Owner:无锡市恒利弘实业有限公司
Method for recycling zinc, copper and cadmium from zinc hydrometallurgy copper-cadmium residues
InactiveCN107287432AEfficient separationImprove leaching ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisIron removal
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy and particularly relates to a method for recycling zinc, copper and cadmium from zinc hydrometallurgy copper-cadmium residues. According to the method, recycling of the zinc, the copper and the cadmium is completed through the seven steps of oxygen pressure leaching, neutralization iron removal, electrolysis, vacuum distillation, separation, copper-rich residue treatment and electrolysis residual liquor treatment. The whole technological process is short, the amount of waste residues and waste water is small, the environmental pollution is less, and the production cost is low.
Owner:贵州省兴安环保科技有限公司
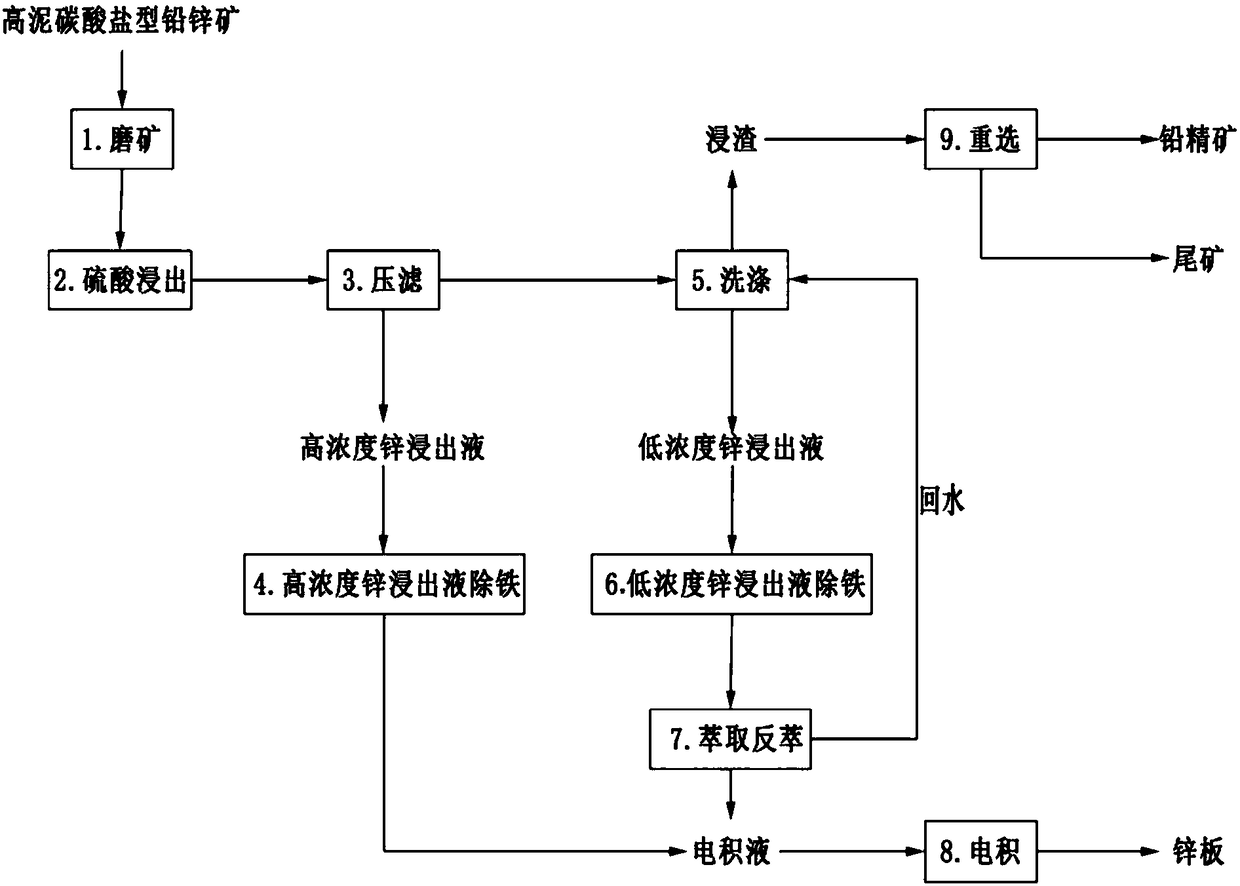
Method of comprehensively recovering lead and zinc in high mud carbonate lead-zinc oxide ores
ActiveCN108239701AReduce pollutionReduce energy consumptionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSmithsoniteVulcanization
The invention relates to a method of comprehensively recovering lead and zinc in high mud carbonate lead-zinc oxide ores by combining beneficiation and smelting to solve the problem that zinc concentrate and lead concrete low in mutual content ratio in high mud carbonate lead-zinc oxide ores cannot be separately obtained by means of conventional vulcanization and sorting processes and the difficulty of comprehensively recovering lead and zinc is great. By means of dissolving difference of smithsonite and cerusite in the same pH region, zinc and lead are dissolved selectively so as to achieve the purpose of comprehensively recovering zinc and lead, high energy consumption of roasting and volatilization is avoided, and meanwhile, pollution of exhaust gas and dust is reduced and the processing flow is shortened.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Method for separating zinc-cadmium-lead alloy materials from copper-cadmium slag and nickel-cobalt slag generated in zinc smelting process
ActiveCN108251651AEasy to separateImprove resource utilizationProcess efficiency improvementAlloyCadmium Cation
The invention discloses a method for separating zinc-cadmium-lead alloy materials from copper-cadmium slag and nickel-cobalt slag generated in a zinc smelting process. The method comprises the following steps that a mixture of the copper-cadmium slag, the nickel-cobalt slag or the copper-cadmium slag and the nickel-cobalt slag are prepared into the coal powder and alkaline-earth metal oxide, the mixture is subjected to vacuum distillation, the distillation pressure is less than 200 Pa, heating is started, the distillation temperature ranges from 900 DEG C to 1200 DEG C, then heat preservationis carried out for 0.5h-10h, the distillate obtained by collecting and distilling contains lead, zinc, and cadmium alloy materials, and the distillation residues are copper, nickel, cobalt and the like. According to the method, the lead, the zinc, the cadmium, the copper and the nickel in the copper-cadmium slag and the nickel-cobalt slag are utilized, the lead in the copper-cadmium slag and the nickel-cobalt slag is realized by the vapor pressure difference of the cobalt at different temperatures, zinc, cadmium, copper, nickel and cobalt, a large amount of lead, zinc and cadmium in the distillation process can be separated, and the residual substances in the distillation residues are copper, nickel and cobalt, so that the preliminary separation of metal in the copper-cadmium slag and thenickel-cobalt slag is realized. The method is convenient to operate, high in energy utilization rate and heating efficiency, safe, sanitary and pollution-free.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Smelting method of high-indium high-iron zinc concentrate
ActiveCN103602806AEfficient recyclingReduce consumption costPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisIndium
The invention relates to a smelting method of high-indium high-iron zinc concentrate, which comprises the following steps: carrying out boiling-bed roasting on high-indium high-iron zinc concentrate, carrying out neutral leaching on the obtained roasted product, and carrying out purifying electrolysis on the neutral leaching solution to produce electrodeposited zinc; washing the neutral leaching slag with countercurrent water, returning the washing water to the neutral leaching preparation solution, carrying out strong-reduction smelting on the washed slag to produce a crude zinc alloy, sending the crude zinc alloy into a lead tower to perform distillation, sending the obtained zinc cadmium alloy into a cadmium tower to perform secondary distillation, carrying out casting cooling on the produced distilled zinc to obtain a zinc ingot product, distilling the high-cadmium zinc alloy in a low-temperature tower, using the obtained crude cadmium for producing a cadmium ingot, and returning the low-cadmium zinc alloy to the cadmium tower for distillation; and distilling the zinc indium bottom solution in a high-temperature tower, returning the produced high-temperature crude zinc to the lead tower for distillation, and carrying out crushing, leaching, extraction, replacement and electrolysis on the high-indium alloy to extract the indium. The method has the advantages of reasonable technique, clean and environment-friendly process, less emission of three wastes, high production efficiency and low production cost.
Owner:LAIBIN CHINA TIN SMELTING
Method for performing wet desulfurization and zinc sulfate recycling through cooperation of copper slag tailings and zinc smelting fly ash
ActiveCN110090548ASolve the problem of low desulfurization efficiencyImprove desulfurization effectGas treatmentZinc sulatesFerric hydroxideCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a method for performing wet desulfurization and zinc sulfate recycling through the cooperation of copper slag tailings and zinc smelting fly ash, and belongs to the technical field of comprehensive utilization of resources. The method mixes copper slag tailings, zinc smelting fly ash and water to prepare into desulfurization pulp; flue gas is in contact reaction with the pulp; the sulfur dioxide in the flue gas is absorbed into the slurry and is catalyzed and oxidized into sulfuric acid by the oxygen and valuable metal ions in the flue gas; the iron, zinc, manganese, aluminum and other elements in the copper slag tailings and the zinc in the zinc smelting fly ash can be further leached out by the sulfuric acid; the reacted pulp can obtain filter residues and filtrate through filtering; the iron can be precipitated by adding alkali into the filtrate; heavy metal arsenic in the filtrate can be removed through the utilization of the flocculation of ferric hydroxide; the cadmium and lead in the filtrate can be displaced by adding zinc dust; and a product zinc sulfate can be finally obtained by introducing the slurry into a zinc sulfate system after flocculation.The method is simple in operation and low in operation cost; the copper slag tailings and the zinc smelting fly ash can be recycled to remove the sulfur dioxide in the flue gas; and the zinc in the desulphurization slurry can be recycled, so that a zinc sulfate by-product can be obtained.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for leaching zinc from purification copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel slag of zinc hydrometallurgy
InactiveCN105821216AImprove leaching rateShorten the production cycleProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionTime range
The invention relates to the technical field of nonferrous metallurgy, in particular to a method for leaching zinc from purification copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel slag of zinc hydrometallurgy. The method includes the following steps that (1) ore grinding is carried out, wherein the purification copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel slag with the particle size smaller than 2 mm is placed into a ball mill, during control, the rotating speed of the ball mill is 25 r / min, the ore grinding time ranges from 5.00 min to 10.00 min, the pulp density ranges from 45% to 50%, and ore grinding is carried out; (2) agitation leaching is carried out, wherein sulfuric acid and an oxidizing agent with the using amount 0.015 to 0.02 time the mass of the purification copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel slag are mixed into the purification copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel slag processed in the step (1), the liquid-solid ratio (mL / g) is controlled to be 3.5-4.0:1, the leaching temperature ranges from 40 DEG C to 85 DEG C, the leaching time ranges from 60 min to 90 min, the leaching final point pH value ranges from 3.00 to 3.50, then solid-liquid separation is carried out, and leaching liquid and leaching slag which contain zinc are obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method for leaching the zinc from the purification copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel slag of zinc hydrometallurgy has the beneficial effects that the zinc leaching rate is high and reaches more than 99.00wt%; the production period is short, and the leaching time ranges from 60 min to 90 min; and the process is simple, and the processing cost is low.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
Method for removing copper and cadmium from zinc sulfate leachate
ActiveCN108277345ASolve technical problems that are difficult to separateLow costProcess efficiency improvementIron powderSulfate
The invention discloses a method for removing copper and cadmium from zinc sulfate leachate. A middle supernate of a zinc hydrometallurgy production system is taken out, metal lead powder is added, and copper slag and copper removal liquid is obtained after the metal lead power is replaced and filtered; aluminum powder or iron powder is added into the copper removing liquid and filtered so as to obtain high-grade cadmium-sponge and cadmium-removal liquid. The method is short in technological process and low in reagent cost, and impurity copper and cadmium in a zinc sulfate solution are removedstep by step, copper slag, sponge cadmium, the copper and the cadmium are recycled step by step, and the copper slag is sent to the top blowing furnace system, so that comprehensive recovery is realized.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
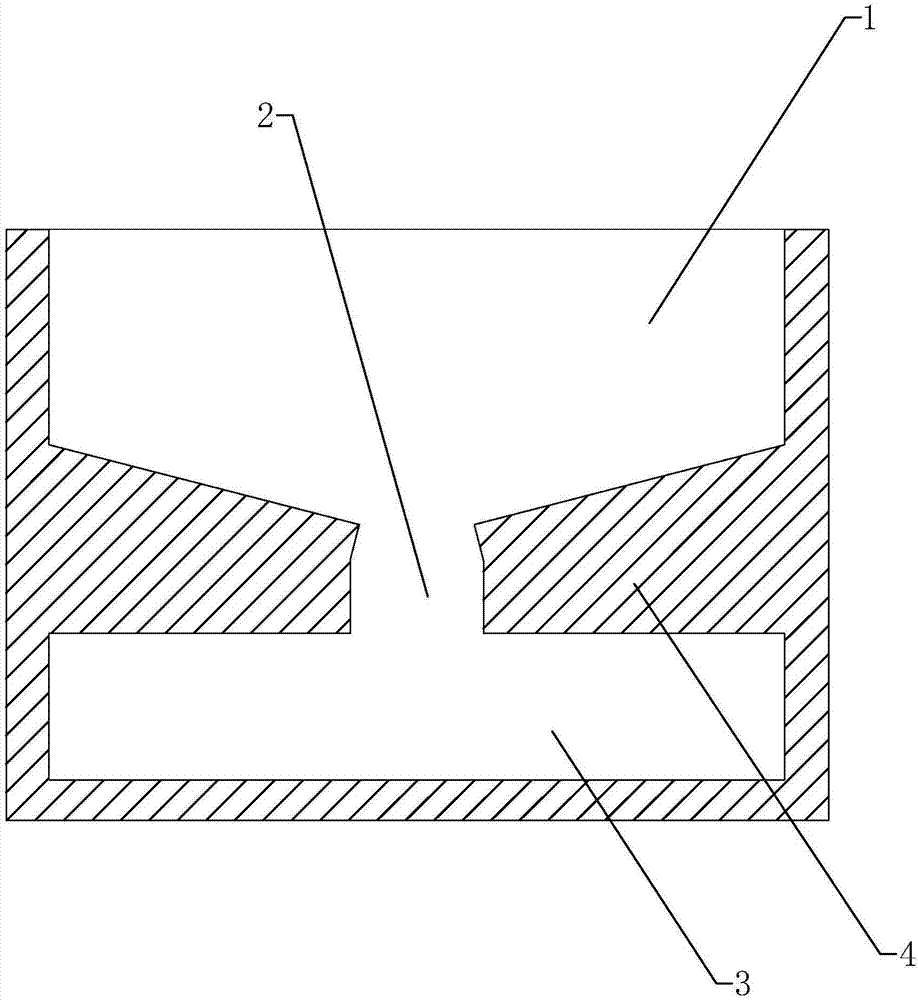
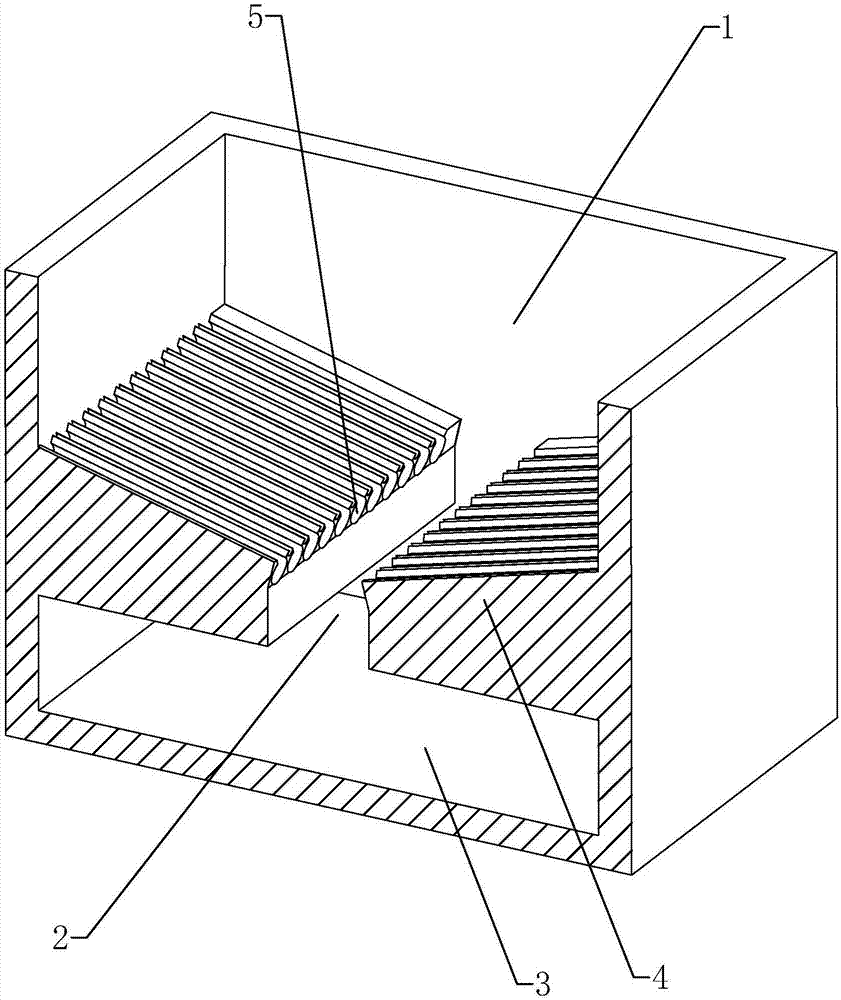
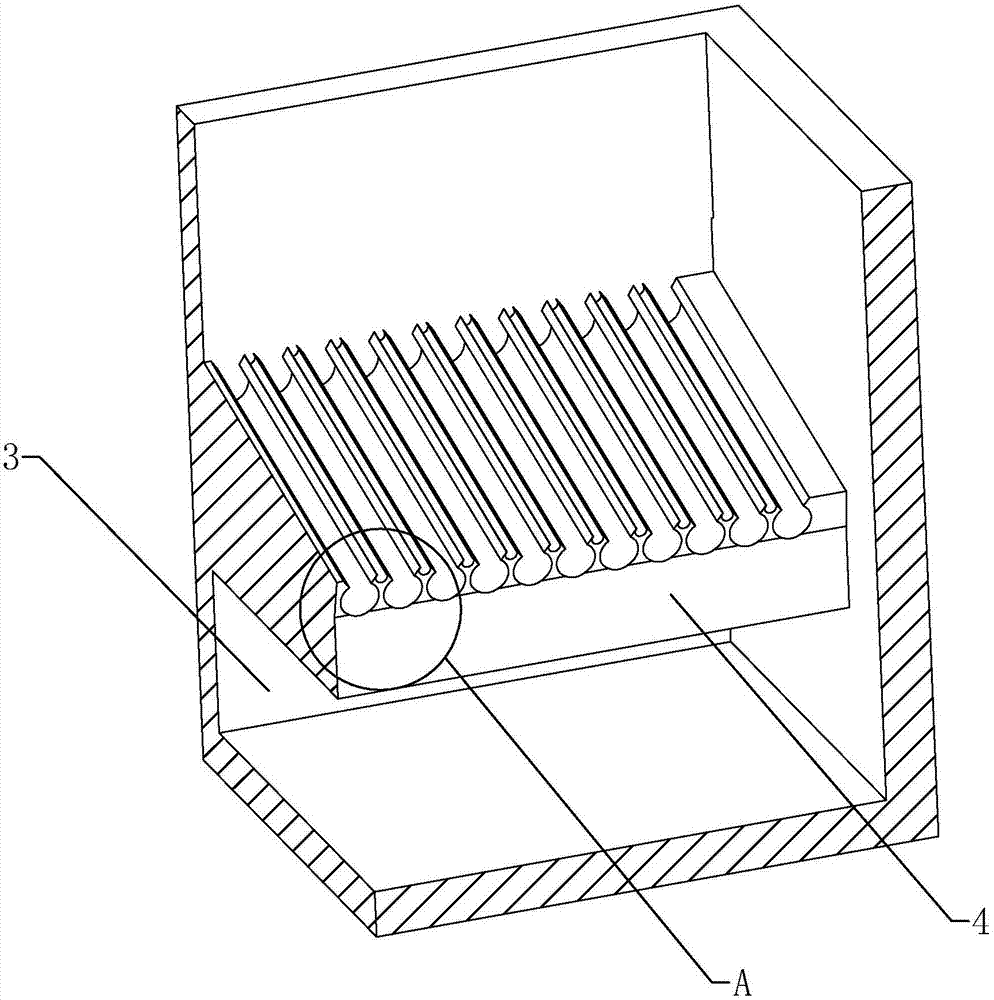
Hot dipping pool for hot galvanizing technology and hot galvanizing technology
ActiveCN107385373AReduce surface defectsReduce oxidationHot-dipping/immersion processesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a hot dipping pool for a hot galvanizing technology and the hot galvanizing technology. The hot dipping pool is internally provided with an adapting part used for adapting cadmia. The adapting part is provided with a plurality of first adapting cavities used for adapting the cadmia. The sections, perpendicular to the direction of the adapting part, of the first adapting cavities are of arch shapes. Openings are formed in the first adapting cavities. The centers of circles of curvature circles of the first adapting cavities at openings are located on the sides, facing the interior of the first adapting cavities, of the first adapting cavities. The hot galvanizing technology comprises the following steps of pickling, rinsing, assistant plating, heat plating, cooling and passivating, and the hot galvanizing technology has the advantages that surface defects of steel components caused by the cadmia are reduced.
Owner:杭州龙耀电力配件有限公司
Method for recycling copper and cadmium from copper and cadmium sediment
The invention discloses a method for recycling copper and cadmium from copper and cadmium sediment, and belongs to the technical field of recycling of by-products of smelting engineering. By the principle that zinc, cadmium and oxides of the zinc and the cadmium in the copper and cadmium sediment are easily dissolved in sulfuric acid but copper is not dissolved in the sulfuric acid, the copper isseparated from the zinc and the cadmium, then metal copper slag with the copper content greater than 65% is produced by washing and filtering, the copper slag is sold as a copper smelting raw material, and thus, the copper and cadmium sediment is utilized effectively, and has high economic benefit. By recycling the copper and cadmium sediment, the stacked and stored copper and cadmium sediment isreduced, and pollution to the environment is relieved.
Owner:BAIYIN NONFERROUS GROUP
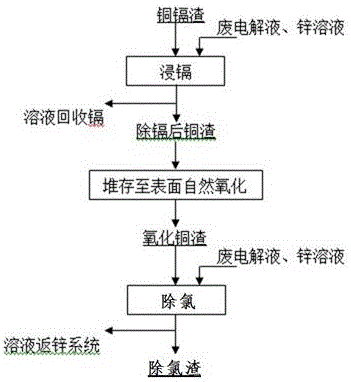
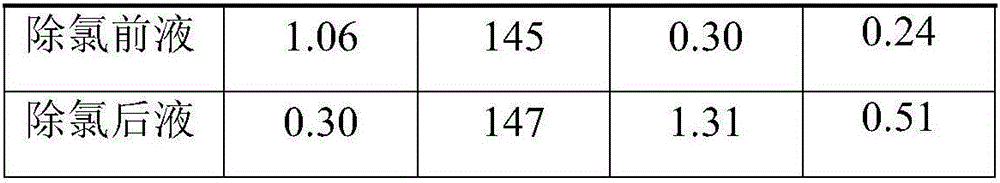
Method for removing chlorine from zinc solution by adopting cadmium removed and surface naturally-oxidized copper slag
InactiveCN106555060AReduce anti-dissolutionLow impurity contentProcess efficiency improvementAutoxidationFiltration
The invention relates to a method for removing a chlorine from zinc solution by adopting cadmium removed and surface naturally-oxidized copper slag, and belongs to the field of zinc wet metallurgy. The method concretely comprises the following steps: 1, leaching cadmium from fresh copper and cadmium slag of the zinc solution in sulfuric acid to obtain cadmium removed copper slag with the Cu content of 15-70% and the Cd content of 0.2-1%; 2, piling up the cadmium removed copper slag until the surface is naturally oxidized and the natural oxidation degree is 5-35%; 3, adjusting the initial sulfuric acid concentration by using a chlorine-containing zinc solution, adding 5-50 kg / m<3> of the oxidized copper slag, and stirring the solution and the oxidized copper slag, wherein a ratio of NCu / NCl is 1.4-2.0, the chlorine removal temperature is controlled to be 30-80 DEG C, and the chlorine removal duration is 0.5-1 h; and 4, carrying out filtration and removal after the reaction ends in order to obtain a chlorine removed zinc solution and chlorine removed slag. The method adopting a prior cadmium removal technology reduces the impurity content of the copper slag, and improves the copper grade of the copper slag; the cadmium removed and surface naturally-oxidized copper slag is adopted to substitute fresh copper slag, so a copper sulfate or oxidized leached copper slag process for preparing a copper sulfate solution is avoided; and the method has the advantages of effective simplification of the process, production cost reduction, and increase of enterprises' economic benefits.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
Method for removing iron through external circulation standing and cooling during continuous hot-dipping of zinc and aluminum
ActiveCN102011081AReduce lossReduce generationHot-dipping/immersion processesSolubilityTemperature difference
The invention discloses a method for removing iron through external circulation standing and cooling during continuous hot-dipping of zinc and aluminum and relates to the technical field of hot-dip galvanizing. The adopted technical scheme is that: a low-temperature standing zinc pot is arranged on the side of a galvanizing zinc pot, zinc-aluminum melt is driven to pass through a pipe to be led out of the galvanizing zinc pot, so that zinc liquid flows into the low-temperature standing zinc pot, and the process of removing the iron in the zinc liquid is performed in the low-temperature standing zinc pot. The low-temperature standing zinc pot is heated by a resistor, and the temperature difference between the low-temperature standing zinc pot and the galvanizing zinc pot is reasonably controlled, the iron in the zinc-aluminum melt is separated out in the low-temperature standing zinc pot through standing and cooling by using different solubility of iron at different temperatures and density difference between iron-containing cadmia and the zinc-aluminum melt, and the iron-containing cadmia is generated and settled at the bottom of the zinc-aluminum melt; and the zinc-aluminum melt which is subjected to standing and purification passes through a pipe connected with the galvanizing zinc pot to flow back into the galvanizing zinc pot so as to finish the process for removing the iron from the zinc-aluminum melt. The method can be used in and out of the line of hot-dipping of zinc and aluminum, so that the content of the iron in the zinc liquid in the galvanizing zinc pot can be reduced obviously, the quality of coating is improved and the waste of the zinc and aluminum is reduced.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Wet treatment method for recycling copper and zinc in bismuth middlings
ActiveCN109913647AAchieve separationAdaptablePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisFiltration
The invention relates to a wet treatment method for recycling copper and zinc in bismuth middlings. The wet treatment method comprises the steps that the bismuth middlings are subjected to wet grinding into powder in which minus 160 mesh-powder occupies 98%, the powder and diluted zinc electrolysis effluent are subjected to slurrying, preimpregnation and filtration, and filtrate of which the finalacidity is 20 g / L to 30 g / L and filter residues are obtained; the filter residues are subjected to high-temperature roasting desulfuration into oxides, bismuth oxides and bismuth concentrate are subjected to mixing and smelting into raw bismuth; after pH of the filtrate is adjusted to 1.5 to 2.0, filtrate is subjected to 3-grade counter-current extraction, 2-grade washing and 2-grade reverse extraction through 20%+80%N902 kerosene, a copper sulfate solution is obtained, the copper sulfate solution enters a copper electrodeposition system, and 99.9% cathode copper is separated at a cathode; copper extraction raffinate is neutralized, iron is removed, impurity elements like copper and cadmium are removed from zinc powder, a liquid is extracted and purified through 40%+60%P204 kerosene, anda zinc sulfate solution is obtained through 4-grade counter-current extraction, 3-grade washing and 3-grade reverse extraction; and oil in the zinc sulfate solution is absorbed through a degreaser, and the zinc sulfate solution is introduced into a zinc electrodeposition system to be subjected to zinc electrodeposition. According to the wet treatment method, material consumption is low, the automation degree is high, waste water, wastes and waste residues are not generated during the production process, and a pollution-free clean technology is adopted.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
Method for recycling cadmium metal from dust of lead-smelting bottom-blowing furnace
InactiveCN108913910AImprove leaching rateWorkmanship is feasibleProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionLead smelting
The invention provides a method for recycling cadmium metal from dust of a lead-smelting bottom-blowing furnace, which can be used for treating the ash of the bottom-blowing furnace and displacing with aluminum powder to recycle cadmium. The method for recycling the cadmium metal from the dust of the lead-smelting bottom-blowing furnace comprises the following steps: (1) a leaching procedure: carrying out water immersion on the ash of the lead-smelting bottom-blowing furnace and enabling a Cd compound to enter a liquid phase; enriching compounds including Pb, As and the like which are not dissolved in water in leaching residues; then separating to obtain a leaching solution and the leaching residues; (2) a displacement procedure: taking out the leaching solution and regulating the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) of a mixed solution of sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid to 2.0 to 2.5; heating to 103 to 105 DEG C; displacing with the aluminum powder with the granularity of 140 to 200 meshes,so as to obtain high-cadmium residues and a displaced solution.
Owner:河南金利金铅集团有限公司
Smelting method of high-iron multi-metal zinc concentrate
ActiveCN103695663BReduce lossesEfficient recyclingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementIndiumDistillation
The invention relates to a smelting method of a high-iron multi-metal zinc concentrate. The method comprises the following steps: performing oxygen-enrichment oxidation melting on a zinc concentrate containing 14% to 20% of Fe, 0.03% to 0.10% of In, 0.2% to 0.6% of Cu, 0.2% to 0.6% of Cd, 0.005% to 0.02% of Ag, 0.1% to 0.2% of Sn and 40% to 50% of Zn so as to generate an oxidized flue gas and molten slags; preparing the oxidized flue gas into sulfuric acid; performing reduction smelting on the molten slags in a smelting pool so as to generate a crude zinc alloy, crude copper containing silver and slags; blowing the slags so as to obtain smoke dust and blown slags; returning the smoke dust to be subjected to reduction smelting; selling the blown slags in a market; extracting the copper and the silver from the crude copper containing silver; and performing four-stage distillation on the crude zinc alloy entering an electric-heating graphite vacuum furnace so as to generate a pyrogenic distilled zinc product, a crude cadmium product and a high-indium-tin zinc alloy which is used for extracting indium and tin. The method is reasonable in process, good in comprehensive recovery, high in production efficiency, low in production cost and clean and environmentally friendly in production process.
Owner:LAIBIN CHINA TIN SMELTING
Recycling method for nickel in nickel-cadmium-zinc slag
InactiveCN105331821AEasy to separateHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementNickel cadmiumIngot
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com