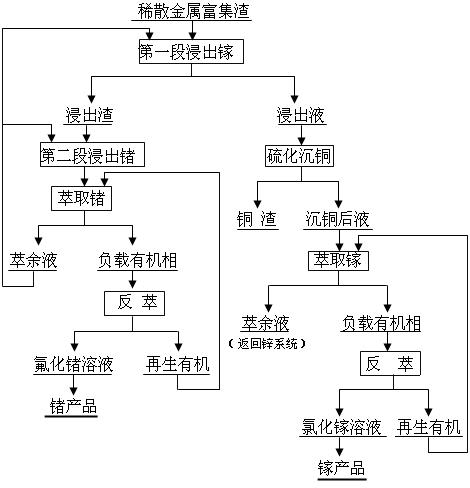
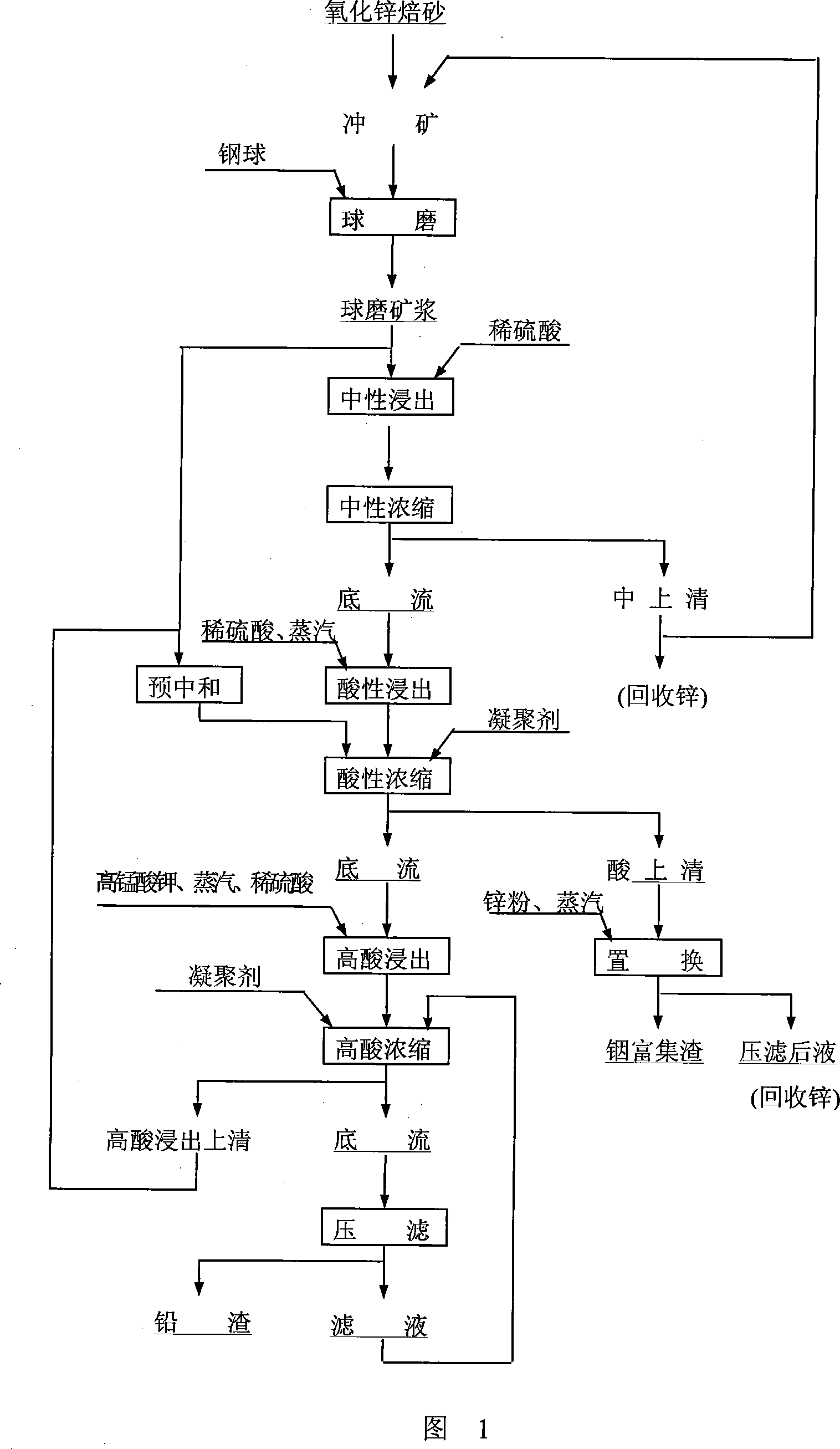
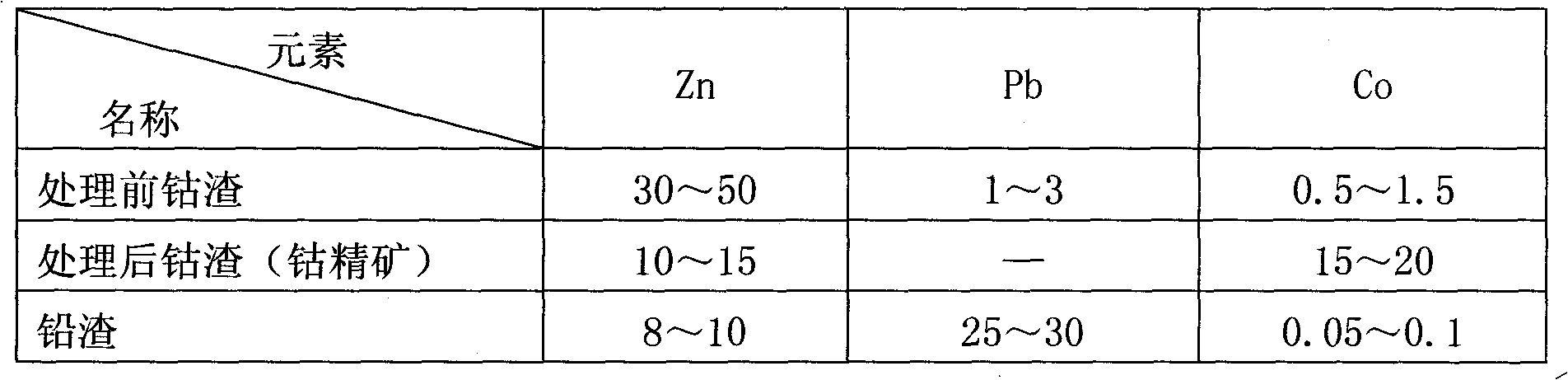Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
659 results about "Zinc smelting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zinc smelting is the process of converting zinc concentrates (ores that contain zinc) into pure zinc. Zinc smelting has historically been more difficult than the smelting of other metals, e.g. iron, because in contrast, zinc has a low boiling point. At temperatures typically used for smelting metals, zinc is a gas that will escape from a furnace with the flue gas and be lost, unless specific measures are taken to prevent it.
Rotary hearth furnace and method for treating lead and zinc smelting slag
ActiveCN105671328ASolve the problem that cannot be comprehensively recycledAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementIndiumSulfur
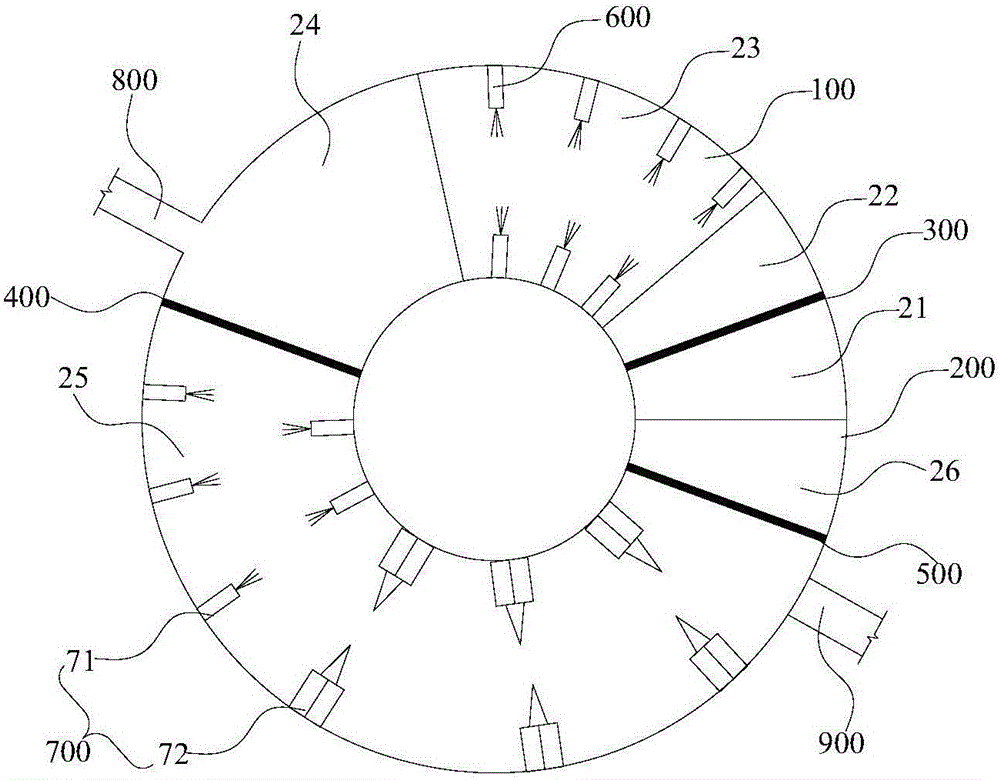
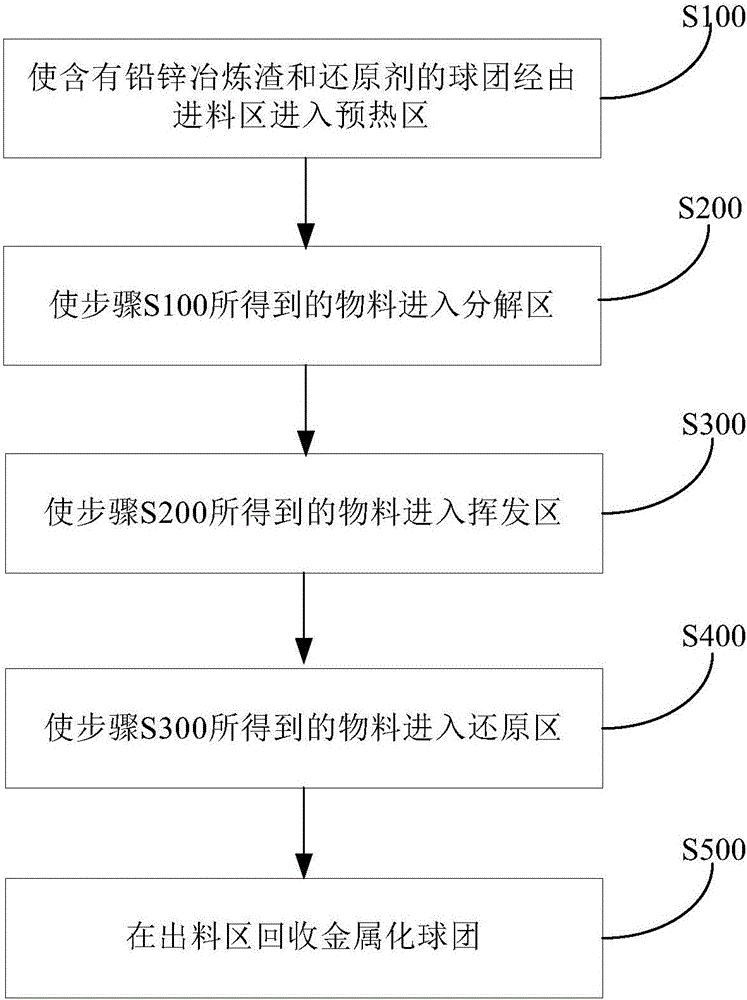
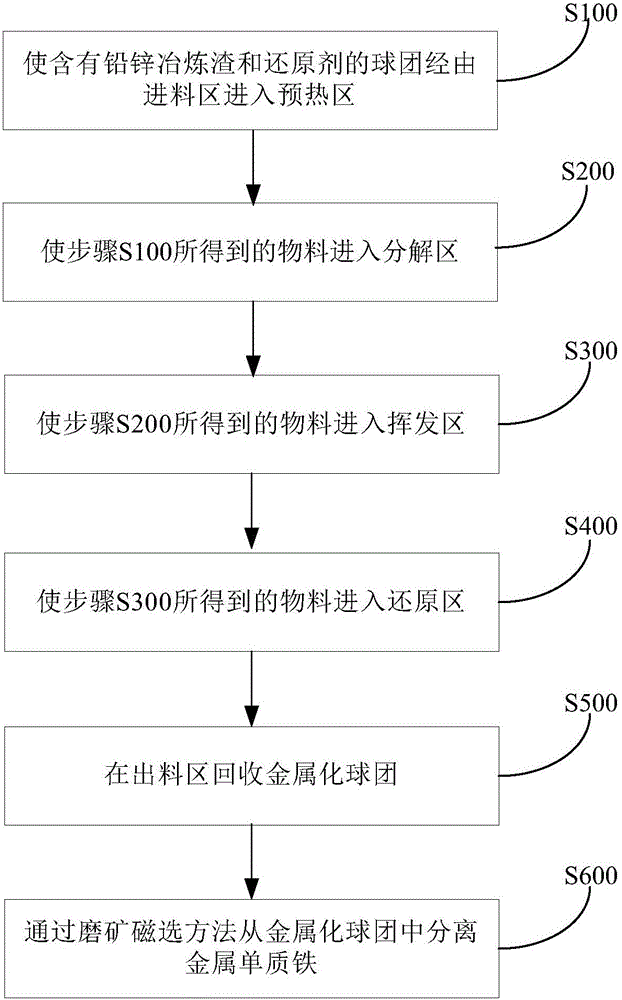
The invention discloses a rotary hearth furnace and method for treating lead and zinc smelting slag. The rotary hearth furnace comprises a rotatable furnace bottom, an annular hearth, a first partition, a second partition, a third partition, a first heating unit and a second heating unit. A smelting space is defined in the annular hearth, and the smelting space is divided into a feeding area, a preheating area, a decomposing area, a volatizing area, a reducing area and a discharging area in sequence according to the entering areas of materials in the circumferential direction of the annular hearth. The first partition is arranged between the feeding area and the preheating area. The second partition is arranged between the volatizing area and the reducing area. The third partition is arranged between the reducing area and the discharging area. The first heating unit is arranged in the decomposing area. The second heating unit is arranged in the reducing area. The rotary hearth furnace can solve the problem that valuable elements in lead and zinc smelting slag in the prior art cannot be comprehensively recycled, and in addition, valuable elements such as iron, lead, zinc, indium and sulfur in the lead and zinc smelting slag can be recycled in the same device.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Method for preparing microcrystalline glass from hazardous solid wastes
The invention discloses a method for preparing microcrystalline glass by taking hazardous solid wastes which are hazardous solids for short. The method is characterized by taking heavy metals in the hazardous solids as nucleating agents, mixing, fusing, rolling, nucleating, crystallizing and annealing to obtain the microcrystalline glass. The method has the advantages that the heavy metal elements in waste incineration ash, stainless steel slag, stainless steel acid pickling sludge, electroplating sludge, chromium slag, lead-zinc smelting slag and coal ash can be stably solidified; the pollution is avoided; meanwhile, high-additional-value microcrystalline glass is prepared; the harmless high-value application of the hazardous solids is realized; and the method has remarkable environmental and economic benefits and wide market prospects.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
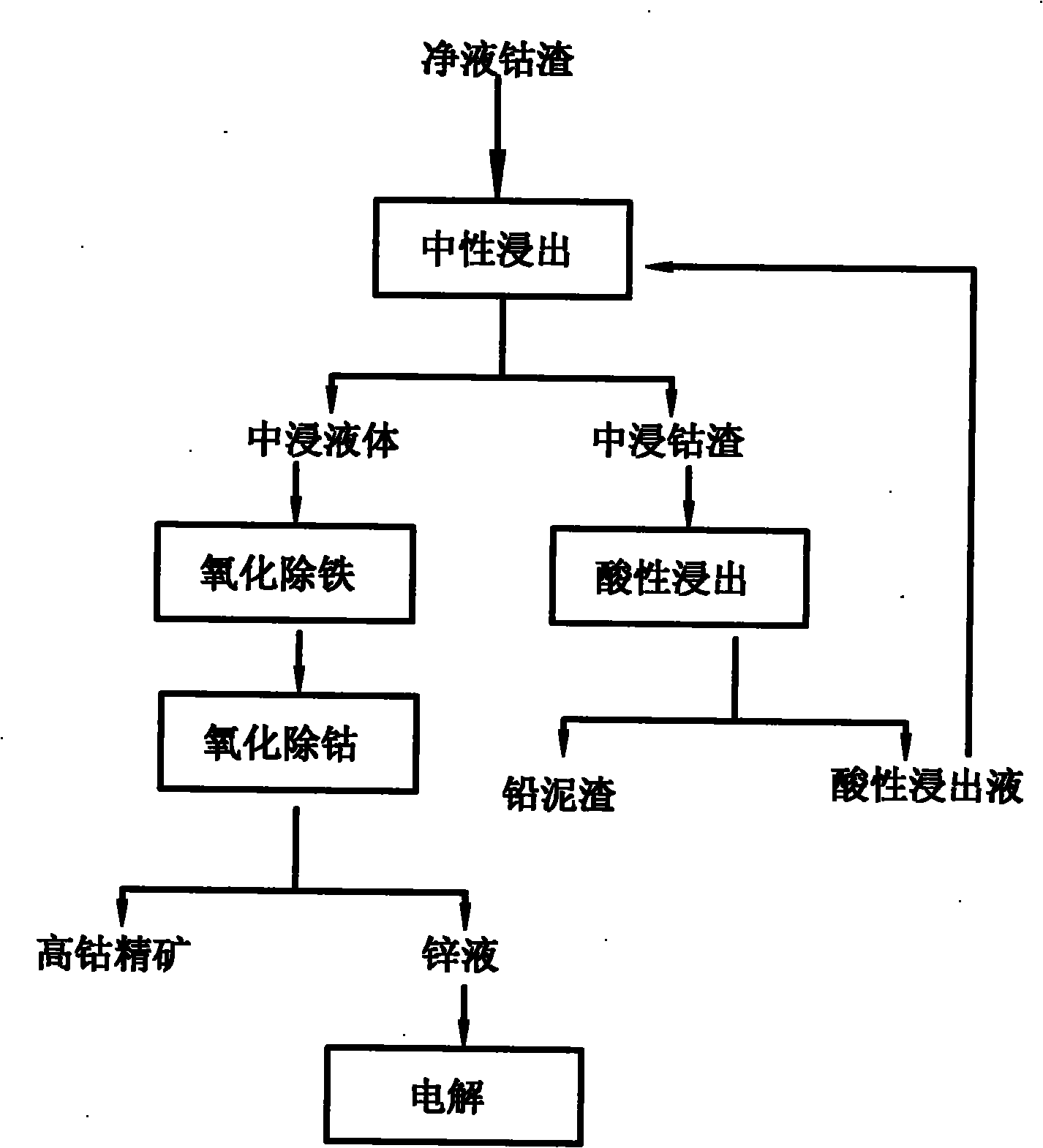
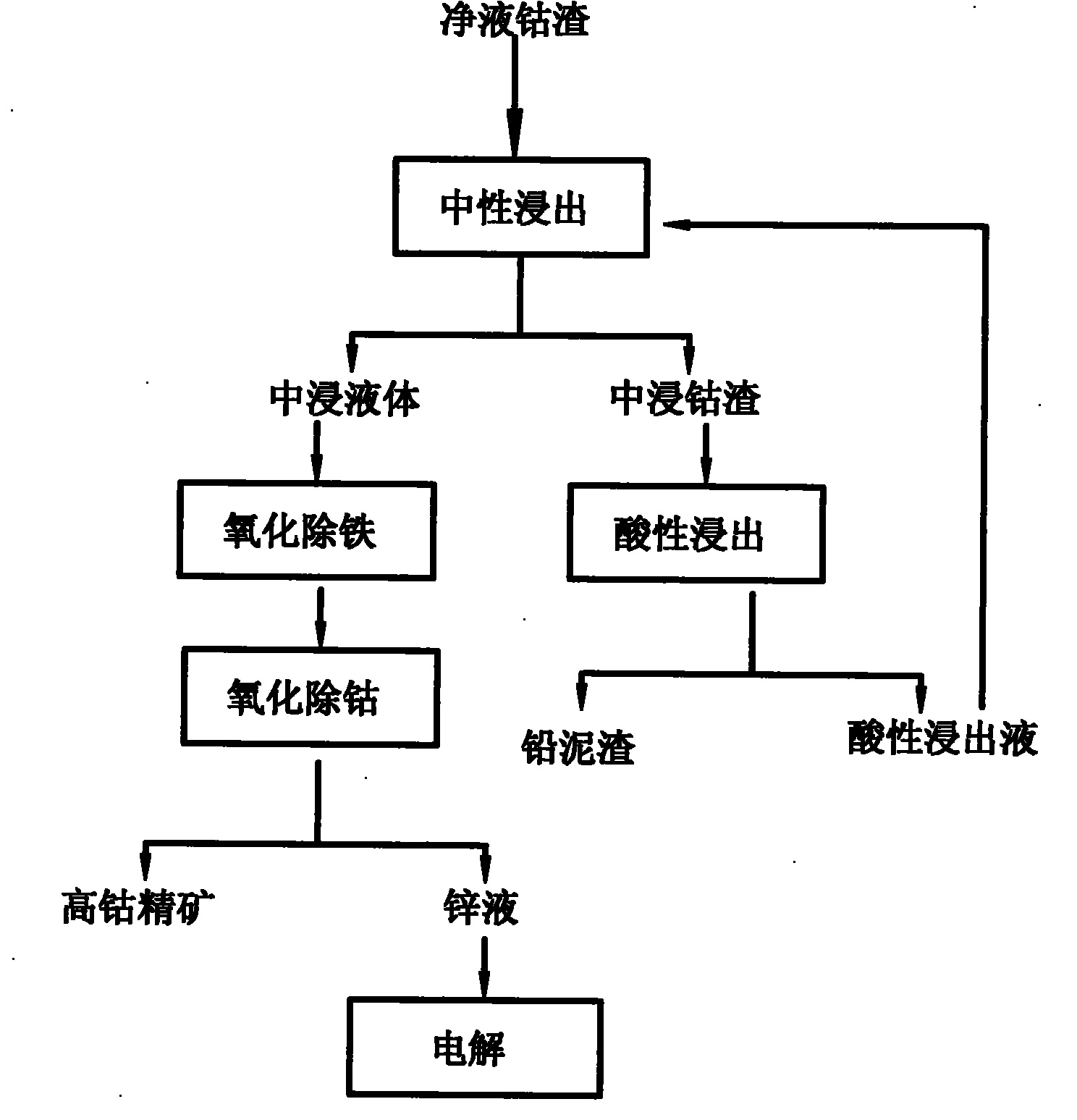
Wet separation method for valuable metals in purified liquid cobalt slags of wet zinc smelting system
ActiveCN101838736AReduce pollutionAchieve effective useProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionZinc smelting
The invention relates to a wet separation method for valuable metals in purified liquid cobalt slags of a wet zinc smelting system, which comprises the processes of neutral leaching of cobalt slags, acid leaching of the cobalt slag, removal of iron in neutrally leached liquid, removal of cobalt in the neutrally leached liquid and the like and concretely comprises the following steps: firstly, sieving and crushing the purified liquid cobalt slags in the wet zinc smelting process; carrying out segmented leaching in a sulfuric acid system; separating leached ore pulp to obtain lead slags; treating impurities in the leached liquid; and adding oxidant into the treated leached liquid for separating Fe and Co to obtain high cobalt concentrate with the cobalt content more than 15%, wherein the high cobalt concentrate can be used as a cobalt smelting raw material to be sold. The invention can effectively recover the valuable metals such as cobalt, zinc, lead and the like in the purified liquid cobalt slags, outputs the lead slags, the high cobalt concentrate and electrolytic zinc, realizes the effective utilization of waste slags, solves the problem of treatment of the waste slags in the wet zinc smelting process, and achieves the purpose of comprehensively recycling resources.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG ZINC IND
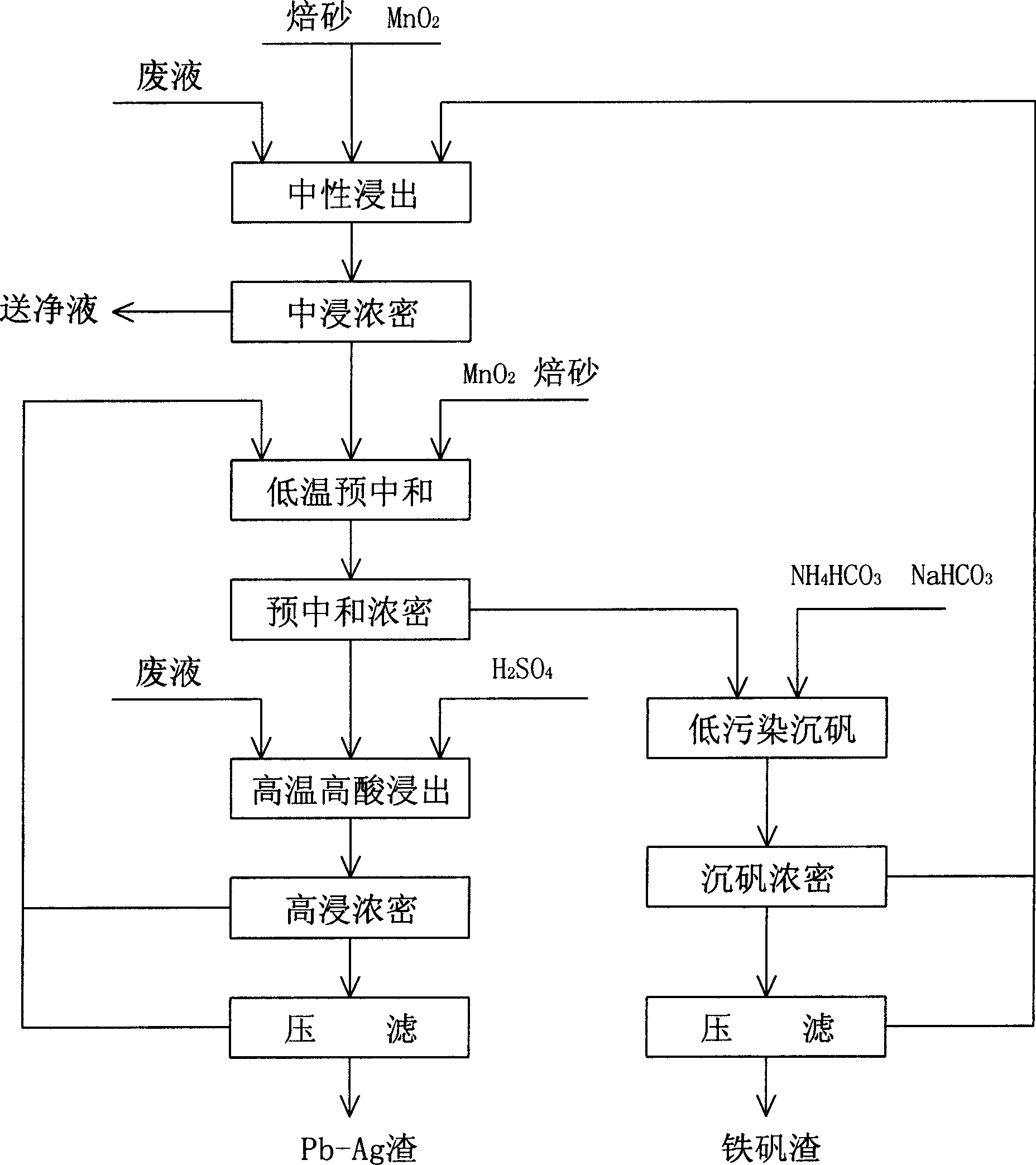
Low pollution vanadium settling iron-removing wet zinc smelting method
ActiveCN1900330AHigh recovery rateReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementAcid concentrationZinc smelting
The present invention discloses a kind of wet zinc smelting process, which includes four main technological steps of neutral leaching, low temperature pre-neutralizing, high temperature high acid concentration leaching, and low pollution vanadium settling and iron removing. Before low pollution vanadium settling and iron removing, the high temperature high acid concentration leaching step has iron leached at most, and the solution composition is regulated in the low temperature pre-neutralizing step for satisfactory iron removing effect during vanadium settling without need of adding neutralizing agent. The technological process is suitable for treating complicated zinc concentrate, and has raised metal recovering rate, strengthened impurity removing capacity, raised ultimate product quality, lowered material and power consumption and reduced pollution.
Owner:CHIFENG ZHONGSE ZINC IND CO LTD +1
Wet zinc metallurgical ultrasound purification method, device and use
InactiveCN101392328AImprove stabilityHas the prospect of industrializationPurification methodsCopper
The invention relates to an ultrasonic purification method for wet zinc smelting, and a device and application thereof. In the ultrasonic purification device for wet zinc smelting, an ultrasonic field produced by ultrasonic waves is adopted to carry out irreversible ultrasonic irradiation to wet zinc smelting solution to be purified, which causes the concentration of ionic impurities to be decreased irreversibly so as to realize the purpose of removing impurities. The application of the method can realize quick purification of required standards, greatly decreases the consumption of zinc powder, directly produces high-quality copper residue, cadmium residue and cobalt residue, and also is applicable to the treatment of the copper-cadmium residue and cobalt-nickel residue produced by wet zinc smelting purification previously.
Owner:XINGMIN TECH ZHUZHOU
Method for separating zinc, fluorine and chlorine from fluorine- and chlorine-containing zinc sulfate solution
InactiveCN102021336ALow impurity contentAchieve separationZinc sulfidesProcess efficiency improvementPhosphateKerosene
The invention relates to a method for separating zinc, fluorine and chlorine from fluorine- and chlorine-containing zinc sulfate solution, in particular to a method for separating zinc, fluorine and chlorine from fluorine- and chlorine-containing secondary zinc resource Sulfuric acid leaching solution. In the method, during solution pretreatment, zinc powder and calcium oxide are added into the fluorine- and chlorine-containing zinc sulfate solution; during extraction, di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate is adopted as an extracting agent and kerosene is adopted as a diluent to prepare an organic phase with certain concentration, the organic phase is mixed with the pretreated solution for extraction, zinc in a water phase is transferred into the organic phase, fluoride ions and chloride ions are remained in the water phase, and the separation of the zinc, fluorine and chlorine is realized; and during back extraction, sulfuric acid solution serves as a back washing agent, the zinc-containing loaded organic phase is mixed for back extraction, the zinc in the loaded organic phase is transferred into the water phase again, zinc sulfate solution is obtained and the organic phase is subjected to impurity removal and recycled. The zinc, fluorine and chlorine separation efficiency is over 95 percent, and the obtained zinc sulfate solution has high purity and can be combined into a purification flow of the traditional zinc smelting. The method has the advantages that: the cost is low, the method is easy to operate, the efficiency is high, and the continuous production can be realized.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
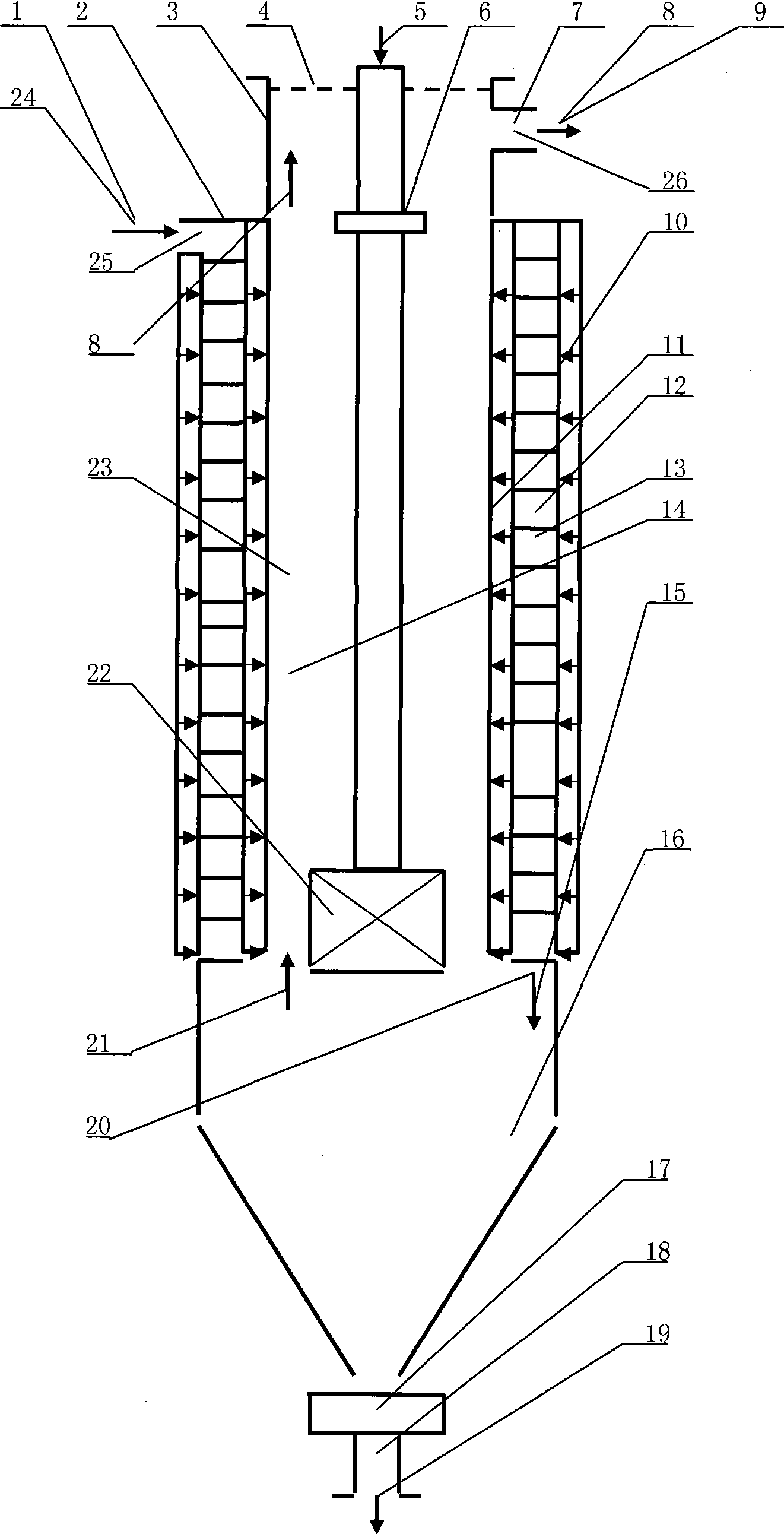
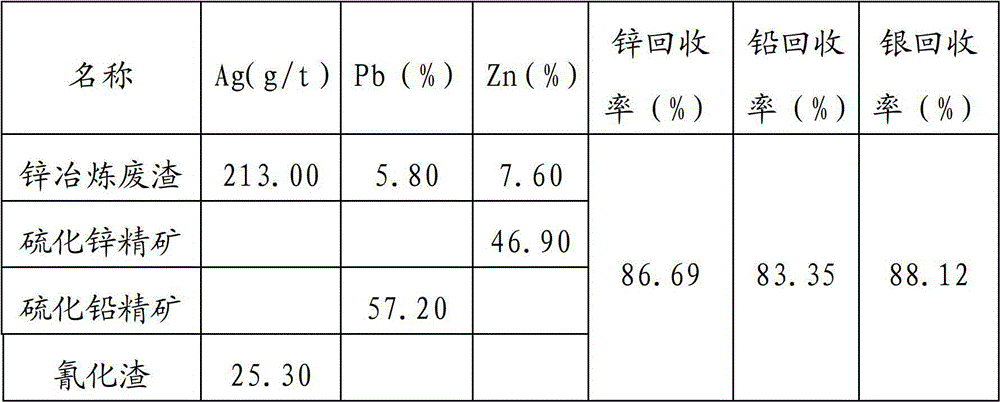
Method for comprehensively recovering zinc, lead and silver from waste residues generated in zinc smelting
ActiveCN102719675ARealize resource utilizationInnovative treatment processProcess efficiency improvementSocial benefitsZinc smelting
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively recovering zinc, lead and silver from waste residues generated in zinc smelting. The method comprises process steps of conducting acid leaching and zinc leaching by sections, removing impurities by using pickle liquor, leaching lead with alkali section by section, vulcanizing settled lead from alkali leaching liquid, cyaniding leached silver by alkali leaching residues and replacing zinc powders to extract silver through a leaching agent. According to the method, zinc, lead and silver in the waste residues generated by smelting zinc are effectively and comprehensively recovered, not only can resources of waste residues generated by smelting zinc be comprehensively utilized, also the processing process of residues generated by smelting zinc is innovated, the cost and expense are reduced, the economical benefits of enterprises are improved, and reat environment-friendly and social benefits are also created.
Owner:SHANDONG GUODA GOLD
Method for preparing activated zinc oxide by utilizing high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process
The invention relates to a method for preparing activated zinc oxide by utilizing a high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process, which belongs to the field of inorganic chemical industry and secondary resource recovery. The method comprises the following technical processes in sequence as follows: leaching, purifying, ammonia distillation, washing, dry crushing, calcining and the like. According to the method for preparing the activated zinc oxide by utilizing the high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process, by taking high-arsenic-antimony secondary zinc oxide generated in a lead and zinc smelting process as a raw material, selective leaching is performed by adding ammonia water and ammonium bicarbonate; then, two-stage purification and deeppurification are performed by ferrous salt, hydrogen peroxide, sulfide and zinc powder; and the ammonia water is recycled and valued metal waste residues are comprehensively recovered. The method forpreparing the activated zinc oxide by utilizing the high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process has strong adaptability on zinc-contained materials and is capable of treating various complicated zinc-contained resources. The method for preparing the activated zinc oxide by utilizing the high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process has the advantages of short flow, production process closed cycle, convenience in operation, low energy consumption, excellent product quality, high economic benefits, low pollution, high comprehensive recovery capacityand the like, and is suitable for industrial production and popularization.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Flash smelting method and device for zinc sulfide concentrates and materials containing lead and zinc
InactiveCN103382527AMeet the requirements of smeltingTo meet the heat required for reductionEnvironmental resistanceResource utilization
The invention discloses a flash smelting method and a device for zinc sulfide concentrates and materials containing lead and zinc. The flash smelting method for the zinc sulfide concentrates and the materials containing the lead and the zinc comprises mixing the dry powder materials containing lead and zinc in proportion and spraying the mixed materials and oxygen into a smelting device from the top of a reaction tower; the smelting device is formed by three portions namely a reaction tower area, a reducing area and a clarification area which are provided with communicated bottoms; materials containing zinc achieve a oxidation sweetening reaction in the air above the reaction tower to generate into high zinc slag melt with an appropriate melting point of minus 1200 DEG C and fall into the reaction tower area; the liquid form high zinc slag melt enters into the reducing area; zinc in the high zinc slag melt is performed reduction to generate zinc steam to be collected; lead is performed reduction to be metallic lead; precious metal such as golden, silver and the like of raw materials are gathered to be precipitated at the bottom of a melt pond and discharged through a lead discharging opening. Slags which are performed reduction are discharged through a slag discharging opening, fuming processing is abandoned or further performed according to the content of the lead and the zinc. The flash smelting method and the device for the zinc sulfide concentrates and the materials containing the lead and the zinc have the advantages of being short in process, strong in material adaptability, low in energy consumption, environmentally friendly, high in resource utilization efficiency, significant for technology progress of a lead and zinc smelting industry and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for extracting metal indium from waste residues generated from lead and zinc smelting
InactiveCN101660054AHigh recovery rateHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementIndiumWastewater
The invention provides a method for extracting metal indium from waste residues generated from lead and zinc smelting. The method is implemented by the following steps: carrying out low-temperature and low-acid leaching on the waste residues generated from the lead and zinc smelting, and removing acid-soluble metals from the waste residues; then carrying out high-temperature and high-acid leachingto obtain indium; and obtaining the metal indium after extraction, re-extraction, reduction and refining. The method has relatively short process flow and low production cost, generates a great amount of byproducts, can comprehensively recover and recycle waste water and the waste residues, is not only good for environmental protection, but also realizes cyclic and comprehensive resource use. Thetotal recovery rate of the metal indium is 70-80%, and the recovery rate of high-purity metal indium is up to 99.995%.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Zinc smelting technology
ActiveCN103540765AImprove leaching rateHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementMagnetic separationNon magneticCalcination
The invention discloses a zinc smelting technology. The zinc smelting technology comprises the following step that high-iron sphalerite concentrate is subjected to calcination, neutral leaching and low-acid leaching; zinc ferrite is separated from the low-grade leaching residues by a magnetic separator and the non-magnetic leaching residues are further treated by high-acid leaching; and the zinc ferrite is decomposed into ferroferric oxide and zinc oxide by reduction roasting, and the ferroferric oxide and the zinc oxide are used respectively as a magnetic seed and a neutralizer used in a leachate magnetofluid iron-removal technology. Through combination of a wet method and a fire method, a zinc leaching rate and a lead and silver recovery rate are improved, and the calcinations of the zinc ferrite are used in the magnetofluid iron-removal technology so that an iron-removal technology cost is effectively reduced and iron residues are pure, have high iron content and are conducive to iron residue comprehensive utilization. The zinc smelting technology can efficiently prepare high-quality zinc leachate, utilize agents having wide sources and a low cost, prepare a very-low iron-content zinc leachate, greatly improve the efficiency of the zinc wet method smelting technology, basically prevent a valuable metal loss and promote resource comprehensive utilization.
Owner:CHANGSHA HASKY ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH DEV CO LTD
Micro-electrolysis method for lead and zinc smelting waste water
InactiveCN101928085ASimple processEasy to handleWaste water treatment from metallurgical processWater/sewage treatmentElectrolysisTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a method for treating smelting waste water, in particular to a micro-electrolysis method for lead and zinc smelting waste water, which belongs to the technical field of environment protection. The method comprises the following steps of: pretreating lead and zinc smelting acid waste water and feeding the pretreated waste water into an iron carbon bed for reacting, wherein the mass ratio of scrap iron to active carbon is 0.5-3:1; recycling most of heavy metal pollutants by performing a micro-electrolysis reaction, wherein a pH value is increased; adjusting the pH to be between 7.5 and 9.5 and generating a flocculating constituent from Fe<2+> and Fe<3+> generated in a previous reaction; precipitating and removing remaining heavy metal ions together with arsenic and fluorine pollutants by adsorption, flocculation and co-precipitation; and recycling supernatant serving as industrial water. The method has the advantages of good treatment effect on the lead and zinc smelting waste water, low cost and capability of recycling heavy metal resources and reusing treating water.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for removing chlorine from solution of zinc sulfate
The invention discloses a method for chlorine from solution of zinc sulfate, which mainly comprises the following: 1, a step of extraction, in which tributylamine is used as an extractant, kerosene or para-octanol is used as diluent, clear liquid of zinc sulfate is mixed with an organic phase for extraction, and chlorine in a water phase is transferred to an organic phase; 2, a step of back extraction, in which back extraction is performed by using ammonia water or solution of sodium hydroxide, chlorine in the organic phase is retransferred to the water phase, and the organic phase is recycled; 3, a step of organic phase regeneration, in which 5 to 10 percent solution of sodium hydroxide is mixed with the organic phase which ages after being used for a certain period of time in a ratio of 1:0.9 to 1:2.5, and the mixture is stirred by an electromagnetic siterr at a high speed for 8 to 15 minutes for regenerating the organic phase; and 4, a step of deoiling, in which raffinate is subjected to active carbon absorption or ultrasonic demulsification so as to remove the organic phase in the raffinate. In the invention, the organic phase and the raffinate can be used circularly, the dechlorination rate is over 85 percent, the electrolytic operation environment is improved, the process flow is simple, and the method can be used for dechlorinating solution of zinc sulfate from wet-method zinc smelting plants and can also be used for dechlorinating wastewater.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
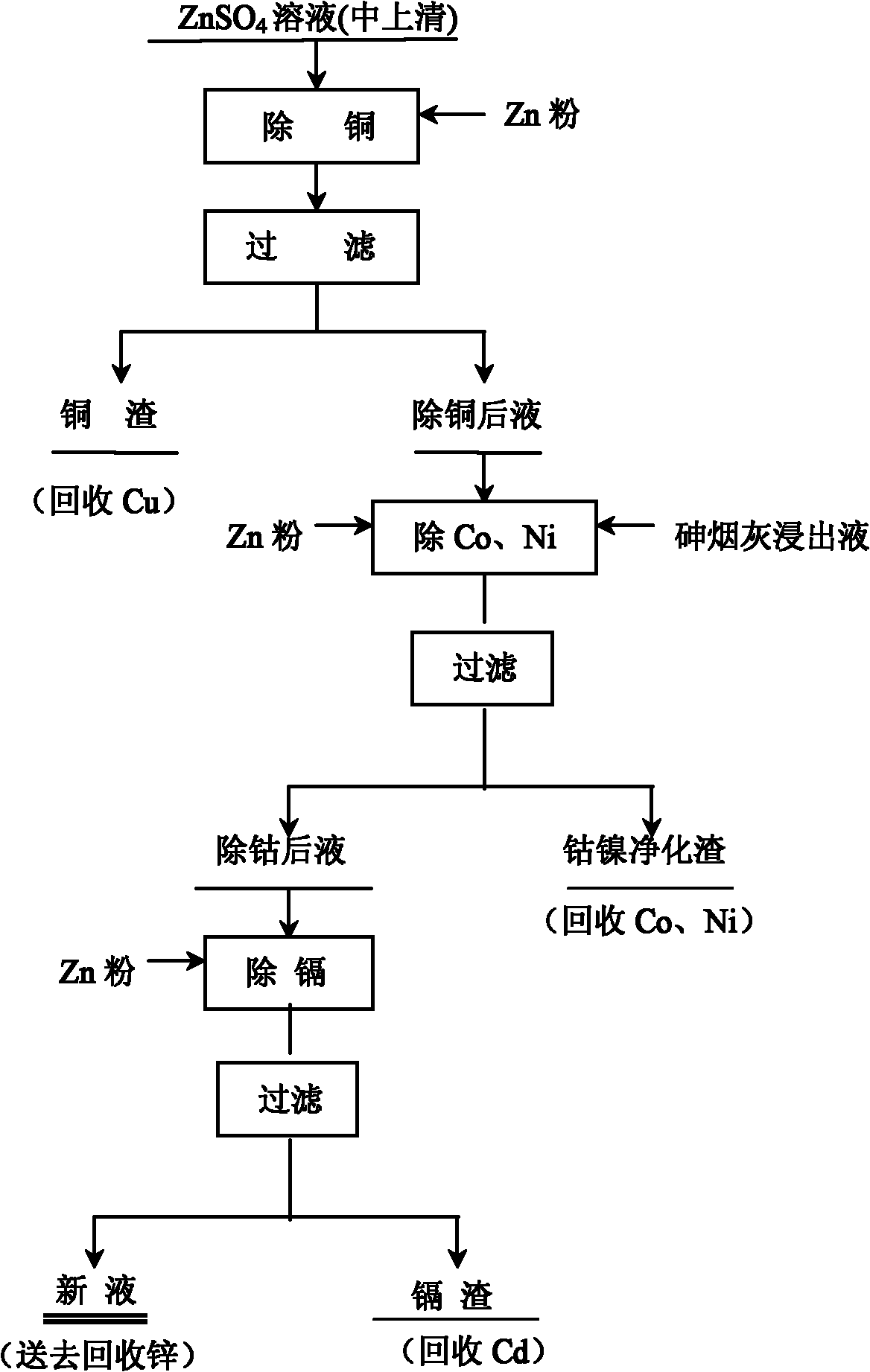
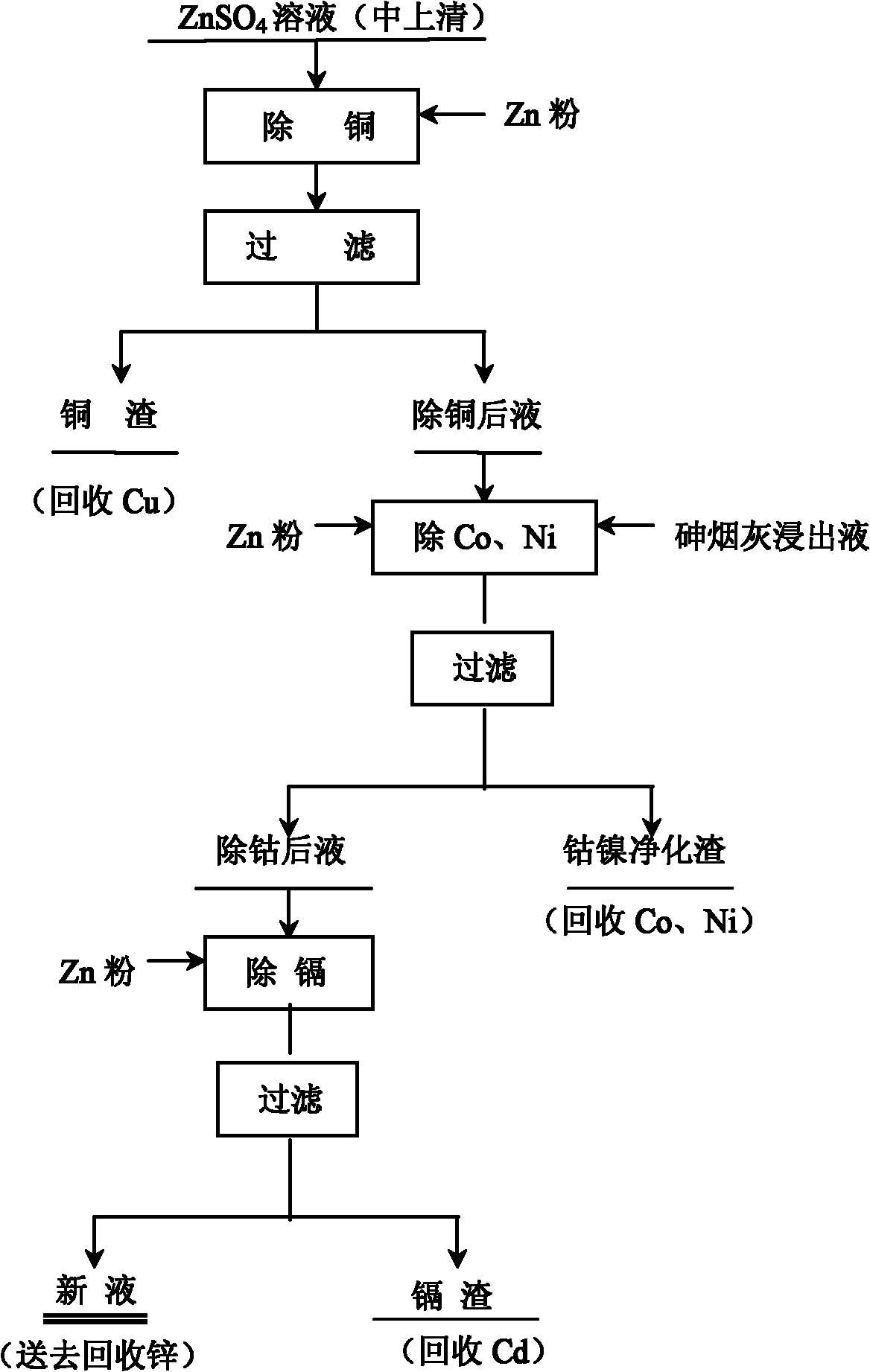
Method for purifying zinc sulfate solution and removing cobalt by using arsenic ash lixivium
ActiveCN101994005ASolve the pollution of the environmentAvoid the Cons of PollutionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSulfate
The invention discloses a method for purifying a zinc sulfate solution and removing cobalt by using arsenic ash lixivium. The invention aims at providing a method for purifying the zinc sulfate solution and removing the cobalt by using the arsenic ash lixivium, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: A, adding zinc powder to remove copper: adding the zinc powder in a ZnSO4 solution to remove the copper, filtering to obtain copper residue and a copper-removed solution, controlling the copper content of the copper-removed solution to 150-300mg / L; B, removing cobalt and nickel: adding the zinc powder and arsenic ash lixivium into the copper-removed solution obtained in the step A to remove the cobalt and the nickel, filtering to obtain a cobalt-removed solution and cobalt and nickel purified residue; and C, removing cadmium: adding the zinc powder into the cobalt-removed solution obtained in the step B to remove the cadmium, stirring and filtering to obtain a new solution, recovering zinc from the new solution and recovering the cadmium from the cadmium residue . The invention is mainly used for purifying the zinc sulfate solution and removing the cobalt in a wet-process zinc-smelting plant.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
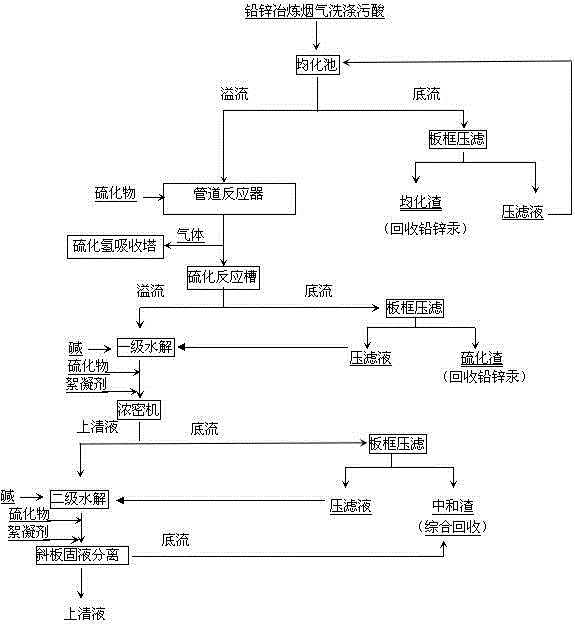
Technology for removing thallium with lead and zinc smelting flue gas washing waste acid water
InactiveCN104445733AGuaranteed deep removalRealize deep purificationWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from gaseous effluentsFiltrationIon
The invention discloses a technology for removing thallium with lead and zinc smelting flue gas washing waste acid water. The technology comprises the steps of settling the flue gas washing waste acid water in an equalizing tank, adding sulfide into the equalized waste acid water to remove most mercury, then carrying out primary treatment, regulating a pH (potential of hydrogen) value of the waste acid water after mercury is removed, adding sulfide and a flocculant in sequence for press filtration, then carrying out secondary treatment, regulating the pH value of primary supernatant purified water to 11, adding sulfide and the flocculant in sequence, and removing thallium and heavy metal ions in depth via inclined plate settling. After the technology is employed, a thallium content in the lead and zinc smelting flue gas washing waste acid water is decreased to be less than or equal to 0.000005g / L, and the technology for removing the thallium is effective and strong in industrial applicability.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Autoclaved phosphogypsum brick and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101684675AQuality improvementHigh strengthConstruction materialSolid waste managementBrickPhosphogypsum
The invention discloses an autoclaved phosphogypsum brick completely prepared by industrial waste residues and a method for preparing the same and belongs to the technical field of construction materials. The autoclaved phosphogypsum brick is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 60 to 80 parts of phosphogypsum, 3.9 to 7.8 parts of neutralization modifying agent, 15 to 30 parts of activated admixture, 1 to 2 parts of cementing aggregate, 0.1 to 0.2 part of exciting agent and 10 to 15 parts of water, wherein the neutralization modifying agent is carbide slag or lime slag;the activated admixture is one or more of zinc smelting granulated slag, fluidized bed furnace fire coal slag and grate furnace fire coal slag; the cementing aggregate is construction sand; and the exciting agent is glauber salt or sodium sulfate. The compressive strength of the autoclaved phosphogypsum brick disclosed in the invention reaches 15 to 20MPa.
Owner:SICHUAN HONGDA
Method for recovering cobalt in cobalt-containing waste residues from zinc smelting
InactiveCN101974691AEasy to separateEasy to recycleProcess efficiency improvementSulfate zincManganese
The invention relates to a method for recovering cobalt, and the like in cobalt-containing waste residues from zinc smelting, solving the technical problems of providing the method for recovering the cobalt, and the like in the cobalt-containing waste residues from zinc smelting, which has the advantages of high enrichment ratio and good cobalt precipitation effect, recovers and utilizes valuable metals such as the cobalt, and the like in the cobalt-containing waste residues from zinc smelting with lowest cost and realizes the purpose of comprehensively utilizing the cobalt-containing waste residues from zinc smelting with high value. The method for recovering the cobalt, and the like in the cobalt-containing waste residues from zinc smelting is characterized by comprising the following steps of: taking the cobalt-containing waste residues from zinc smelting as a raw material; carrying out process flows of ball milling, leaching, filter pressing lead slags, removing iron and manganese, filter pressing iron and manganese slags, precipitating the cobalt and filter pressing cobalt slags; and obtaining the cobalt raw material with the cobalt content larger than 30 percent in the cobalt-containing waste residues from zinc smelting, thereby realizing efficient separation of metals, such as the cobalt, zinc, nickel, cadmium, and the like and completely solving the problem of difficult separation of the cobalt, the zinc, the nickel, the cadmium, and the like of the prior art. The method can be also used for separating out the lead slags with the lead content larger than 30 percent, cadmium sponge used for producing refined cadmium, nickel slags with the nickel content larger than 10 percent and a zinc sulfate solution.
Owner:BAIYIN NONFERROUS GROUP
Cleansing and cobalt-removing method for zinc smelting leachate and scavenging agent used therein
ActiveCN103526021ALow costNo secondary pollutionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionActivated carbon
The invention discloses a cleansing and cobalt-removing method for zinc smelting leachate. The method comprises the following three stages of cleansing: in the first stage of cleansing, zinc dust is employed for removal of copper and cadmium, and cadmium content is less than 0.01 g / L after the first stage of cleansing; in the second stage of cleansing, zinc dust and copper sulphate are employed to remove arsenic and antimony, and the contents of arsenic and antimony after the second stage of cleansing are less than 0.00015 g / L and less than 0.00015 g / L, respectively; and in the third stage of cleansing, a scavenging agent, an activator and active carbon are utilized to further remove residual cadmium and most Co, the contents of cadmium and cobalt after the third stage of cleansing are less than 0.001 g / L and less than 0.0004 g / L, respectively, and active carbon is used to absorb removed cadmium so as to obtain cobalt slag. According to the method, through combination of the specific scavenging agent, scavenging temperature, scavenging time and the like, consumption of zinc dust is substantially reduced by more than 55%, removed Co is hard to redissolve, a high Co removal rate is obtained, and low cost is realized. Furthermore, the invention discloses the scavenging agent used in the method.
Owner:南丹县吉朗铟业有限公司
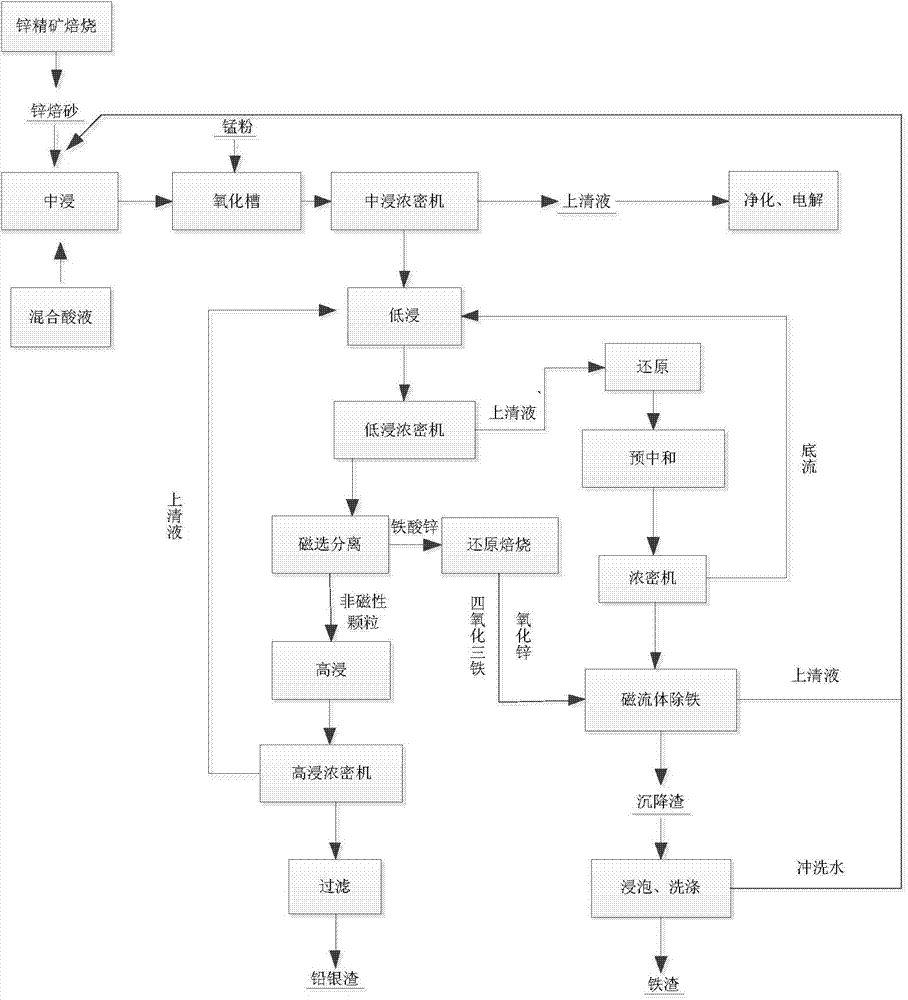
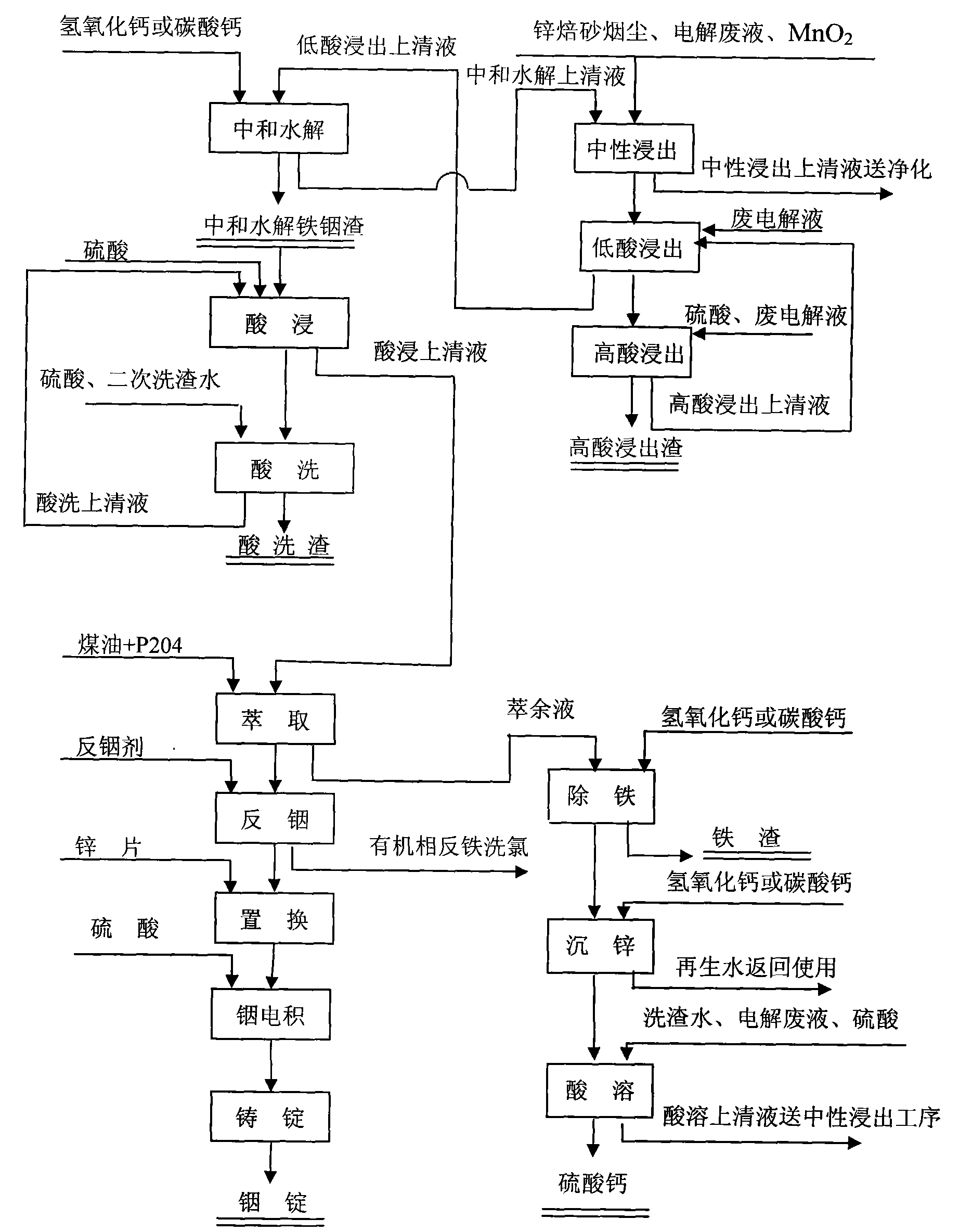
Zinc smelting process by neutralization and hydrolysis iron removal method
InactiveCN101629246AReduce processShort processProcess efficiency improvementCalcium hydroxideIndium
The invention relates to a nonferrous metal smelting technology, in particular to a zinc smelting process by a neutralization and hydrolysis iron removal method for smelting zinc and indium from zinc roasting-sand smoke dust. The zinc smelting process comprises the following working procedures: A. leaching a working section comprising a neutral leaching working procedure, a weak acid leaching working procedure and a strong acid leaching working procedure: delivering the supernatant obtained after neutral leaching to the purifying and the electrodeposit working procedure for extracting zinc; and B. a neutralization and hydrolysis working procedure: delivering the supernatant obtained after weak acid leaching to the neutralization and hydrolysis working procedure, adding in calcium hydroxide or calcium carbonate for neutralizing hydrolysis for iron removal, and returning the supernatant obtained after neutralization and hydrolysis to the neutral leaching working procedure, wherein the iron residues obtained after neutralization and hydrolysis are piled when no indium is included, and when the iron residues obtained after neutralization and hydrolysis are iron residues including indium, the iron residues are delivered to the pickling working procedure, and the supernatant obtained after pickling is delivered to a traditional centrifugal-extraction indium-extracting system for indium extraction. The invention shortens the process flow of the zinc metallurgy (including indium extracting), invents a method for removing iron at normal temperature and comprehensively recycling the zinc and indium without coal consumption at normal temperature, achieves the purposes of saving energy, reducing consumption, reducing the zinc and indium production cost and having good impurity cleaning effect and also provides a process flow simply following the traditional process.
Owner:杨志杰
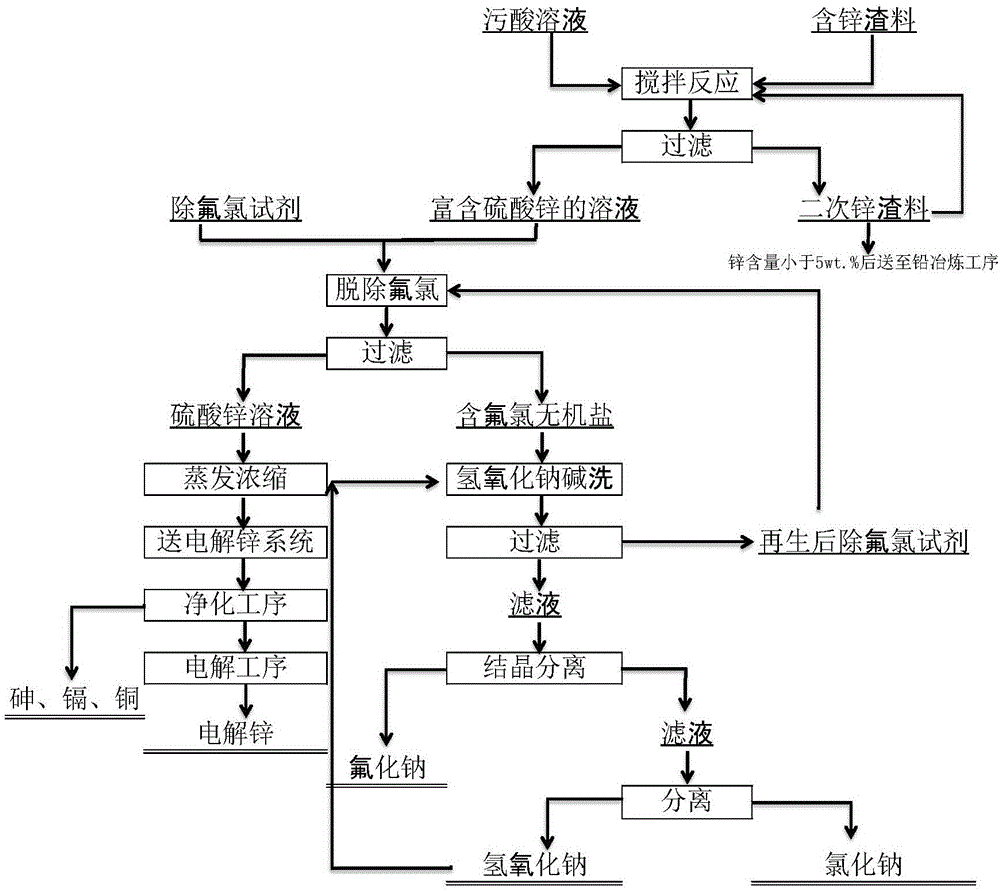
Comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues
ActiveCN105861844AEfficient separation and recoveryWon't break the balanceProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
Disclosed is a comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues. The zinc-containing residues generated in the zinc smelting production process serve as an acidic wastewater neutralizer. Liquid obtained after neutralization is subjected to fluorine and chlorine removal and concentrated to meet the requirements for a zinc sulfate solution of a zinc system, and then directly enters the electrolytic zinc system. Valuable metal such as arsenic, cadmium and copper in the acidic wastewater is recycled through an impurity purification procedure of the zinc system. The zinc-containing residues are subjected to a neutralization step to be recycled and fed into a lead extraction procedure after being enriched with lead, silver and other metal. The filter residues with fluorine and chlorine removed are regenerated with a sodium hydroxide solution, the residues obtained after regeneration can be used for the fluorine and chlorine removal procedure repeatedly, and sodium fluoride, sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide in the liquid obtained after regeneration are separated and recycled through efficient evaporative crystallization. The comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues is based on an existing zinc hydrometallurgy system, the balance of original materials in the system is maintained, and an additional heavy metal impurity purification procedure is not added. The comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues is short in process, low in cost, high in valuable metal recycling rate, free of discharging of secondary waste residues and waste water and good in comprehensive economical benefit.
Owner:湖南麓云达环境科技有限公司
Method for removing arsenic and antimony from zinc smelting leach liquor
InactiveCN103911512AEfficient use ofStable physical and chemical propertiesProcess efficiency improvementIndium metalPregnant leach solution
The invention discloses a method for removing arsenic and antimony from zinc smelting leach liquor, and relates to a method for removing arsenic and antimony from a solution produced during zinc smelting by purifying. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: comprehensively recovering valuable components of zinc, indium, iron and the like by purifying in an arsenic and antimony removing process consisting of pre-reduction, neutralization of precipitated indium and a hematite process under the condition that zinc smelting low-acid leach liquor is taken as a raw material; turning high-valence iron into low-valence iron by taking zinc concentrate, zinc sulfite, sulfur dioxide and the like as reducing agents in the low-acid leach liquor, wherein the content of high-valence iron (Fe<3+>) in the reduced liquor is lower than 2g / L; performing two-stage neutralization by using lime, limestone, secondary zinc oxide, calcined sand and zinc oxide to regulate the pH value of reduced liquor to 4.0-5.4 in order to enrich indium precipitate; and removing arsenic and antimony from indium-precipitated liquor to fulfill the aim of efficiently cleaning and purifying the solution. The method has the advantages of high indium metal recovery rate, high arsenic and antimony removing rates, small residue amount, stable performance and environmental friendliness.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
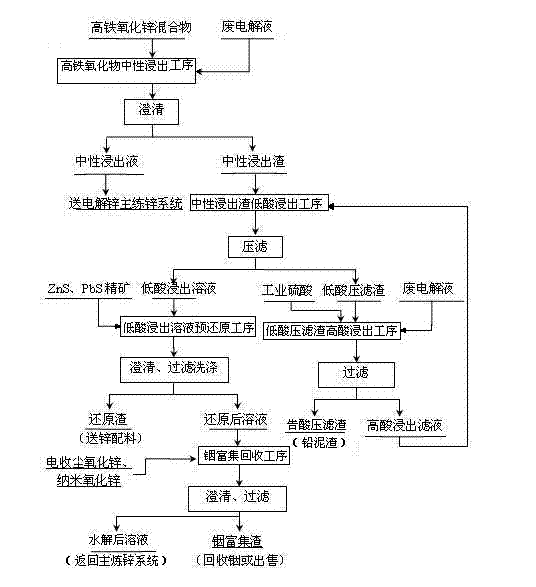
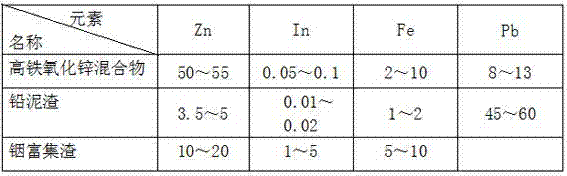
Method for recovering zinc, indium, iron, and lead from high-iron zinc oxide mixture smelted with zinc
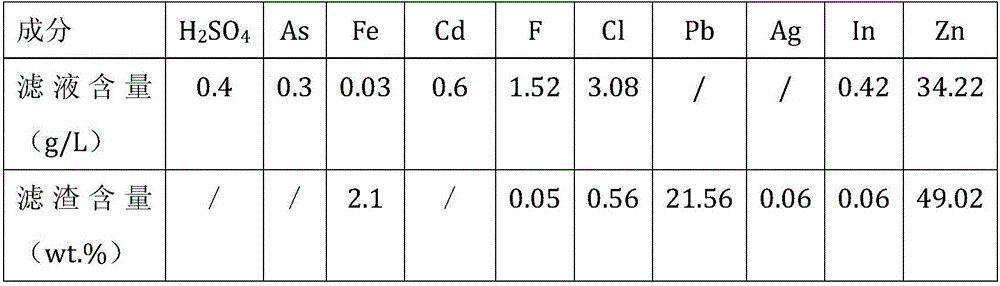
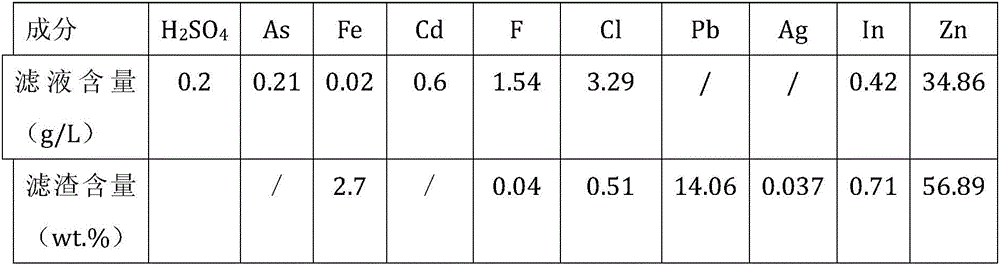
ActiveCN103667720ASolve processing problemsReduce the amount addedProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionElectrolysis
The invention relates to the field of metal smelting, particularly to a method for recovering zinc, indium, iron, and lead from a high-iron zinc oxide mixture smelted with zinc. The method comprises the following processes: a high-iron zinc oxide mixture neutral leaching process, a neutral leaching residue low acid leaching process, a low acid pressure filter residue peracid leaching process, a low acid leaching liquid prereduction process, and a indium enrichment recycling process; valuable metals are comprehensively recovered from the high-iron zinc oxide mixture; a generated neutral leaching liquid is adopted by a main zinc smelting system to generate electrolytic zinc; a hydrolyzing filter liquor generated from the indium enrichment recycling process contains relatively rich ferrous ions; the hydrolyzing filter liquor is adopted by the main system for removing impurities and generating high-grade indium enrichment residues; therefore, the high-iron zinc oxide mixture is effectively recycled, the problem of high-iron zinc oxide mixture treatment is solved, capability of comprehensive utilization of metal resources is increased, so that resources are comprehensively recycled, and environment protection is facilitated; the method has relatively good economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG ZINC IND
Method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from zinc smelting slag
InactiveCN103710544AAchieving simultaneous enrichmentAchieve recyclingReverberatory furnaceBlast furnace detailsChemical industryIndium
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from zinc smelting slag, belonging to the technical fields of metallurgy and chemical industry. The method comprises the following steps: proportioning blast furnace slag, iron alum slag and lead silver slag in a mass ratio of (1-2):(2-4):1, mixing, briquetting and drying; smelting the briquette, coke and a fluxing agent in a mass ratio of (4-8):(0.5-2):1 in a matting furnace at 1050-1400 DEG C; collecting dust from matting furnace gas to obtain indium-rich zinc oxide smoke dust; and settling the fused mass while keeping temperature at 1000-1400 DEG C to obtain lead copper matte and harmless furnace slag. The method implements synchronous enrichment and recovery of valuable elements in the zinc smelting slag by the one-step smelting process, and has the characteristics of simple technical process, high comprehensive recovery rate of valuable metals, high cleanness and high efficiency.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH TECH IND SALES MANAGEMENT
Technology for zinc wet-process clean smelting and resource comprehensive recycling
InactiveCN102978391AEnhanced leaching processHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementIndiumElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of zinc smelting of the nonferrous metal smelting industry, in particular relates to a technology for valuable metal comprehensive recycling and iron element separating and concentrating during a zinc clean smelting process. Zinc calcine which is produced through calcinating zinc concentrate is separated out through neutral leaching and low-acid leaching and is then fed into a wet-process reinforced leaching system to separate acid soluble metals from insoluble substances; the separated zinc and soluble impurity-containing liquid enters a valuable metal separating and concentrating system to separate out indium, gallium, germanium and the like, the separated valuable metal sludge enters a special recycling system; and the liquid enters a zinc and iron separating system to completely separate out zinc and iron, iron is output in a high-grade iron ore concentrate mode, zinc enters the next process in a zinc sulfate mode, and the liquid enters an electrolyzing system after deep purification to output metal zinc. The technology has high metal zinc recovery rate, good valuable metal comprehensive recycling effect, a good environment-friendly effect and high iron content of hematite sludge, the hematite sludge can be treated to be used as a raw material for smelting iron, so that 'non-sludge' smelting is realized, and the smelting process is compact.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG ZINC IND
Synchronous fluorine-calcium removal treatment process for reverse osmosis concentrated liquor of waste water from lead-zinc smelting
ActiveCN104445717ADestroy scale inhibitionEnsure reaction precipitation effectWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processCalcium handlingReverse osmosis
The invention relates to a synchronous fluorine-calcium removal treatment process for the reverse osmosis concentrated liquor of waste water from lead-zinc smelting. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, removing fluorine by virtue of oxidation and precipitation, secondly, removing calcium by precipitating, thirdly, removing fluorine by virtue of adsorption, next, sequentially regenerating activated aluminum oxide, removing fluorine from the generated mixed liquor, removing calcium from the generated mixed liquor and treating the generated mixed liquor, and finally, removing fluorine by precipitating, wherein the precipitation sludge generated in the calcium removal process is gathered and dehydrated by virtue of filter pressing, the water obtained by filter pressing is returned to a reverse osmosis concentrated liquor collecting tank for circular treatment, and the mud cake is subjected to unified disposal. After the oxidization, precipitation and adsorption treatment processes are adopted, the fluorine content and the calcium content of the reverse osmosis concentrated liquor are lower than 3mg / L and 50mg / L, respectively, and the problems of scaling and blockage caused by fluorine ions and calcium ions in the subsequent evaporation and concentration process of the reverse osmosis concentrated liquor are solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHONGJIN LINGNAN NONFEMET COMPANY +1
Combined process for organic solvent extracting zinc and wet zinc refining
ActiveCN1858272AExpand the range of raw materialsNothing producedPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteElectrolysis
The present invention belongs to the field of wet zinc smelting technology, and is one combined technological process of organic solvent extraction of zinc and wet smelting of zinc. The combined technological process includes organic solvent extraction of low grade and high impurity content zinc material, wet zinc smelting, reverse extracting the zinc containing organic phase with the waste electrolyte from wet zinc smelting, returning the reverse extracted liquid to the wet zinc smelting, and returning the reverse extracted organic phase to the organic solvent extraction. The present invention has best utilization of zinc resource and less environmental pollution.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD
Method for producing zinc powder and reclaiming scattered metals indium and germanium by distilling aluminum hard zinc in vacuum
InactiveCN101565779AEfficient use ofPromote environmental protectionProcess efficiency improvementIndiumDistillation
The invention relates to a method for producing zinc powder and reclaiming scattered metals indium and germanium by distilling aluminum hard zinc in vacuum. The method comprises the following steps: adding lumpy aluminum hard zinc slag into a distillation pot placed on a heater, then covering a sealing cover, raising the temperature of the heater, generating zinc vapor when the temperature of the heater reaches a vaporizing temperature point of metal zinc, and cooling the zinc vapor in a condenser provided with a condenser sealing cover and a condenser water jacket from an insulating pipe under the action of negative pressure of a vacuum pump connected with an exhaust pipe to form the zinc powder; and separating residues generated after the zinc distillation is finished in the distillation pot, and further producing zinc salt and indium and germanium metals. The method can effectively utilize wastes, is favorable for environmental protection and resource maximized utilization, and is suitable for fully applying the zinc smelting waste to the production.
Owner:HULUDAO ZINC IND CO LTD
Method for extracting gallium and germanium from zinc smelting slag
InactiveCN102560133AEmission reductionLeave out the baseProcess efficiency improvementWastewaterGallium
The invention relates to a method for extracting gallium and germanium from zinc smelting slag, in particular to a method for wet extraction of gallium and germanium metals from zinc smelting slag. The method is characterized in that: in the extraction process, the zinc smelting slag is subjected to two-stage acid leaching, the gallium is leached out in the first stage, and then the acid leaching slag after the gallium is leached out is subjected to the second-stage acid leaching, so that the germanium is leached out. According to the method, the leaching characteristics of scattered metal enriched slag gallium and germanium and the extraction characteristics of the gallium and the germanium are found in experiments, a process flow that the gallium and the germanium are leached out and extracted by steps to enrich the gallium and the germanium is provided, so that the germanium leaching and extraction form a closed loop, the alkali neutralization work procedure is eliminated, the alkali consumption is eliminated, the acid consumption is reduced, and the wastewater drainage is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Method for extracting germanium from zinc smelting replacement slag
InactiveCN106834695AEliminates leaching effectsImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementMasking agentMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for extracting germanium from zinc smelting replacement slag. According to the method, germanium-containing leachate is obtained through an oxygen pressure acid leaching process; and after an ion masking agent is added into the leachate, tannin is added to enable germanium to settle, tannin germanium sediment is obtained, the tannin germanium sediment is calcined, and then germanium concentrate is obtained. Compared with a traditional process, the method has the beneficial effects that 1, the oxygen pressure acid leaching process is adopted, mixed acid of sulfuric acid and hydrofluoric acid is used as a leaching agent, the leaching influences of silicone and iron on germanium are eliminated, the acidolysis speed is increased by 2 times or above, the leaching rate of germanium is increased, and the leaching rate of germanium reaches 95% or above; 2, by reducing the content of silicone and iron in the germanium leachate, the extraction influences of silicone and iron on germanium are eliminated, the recovery rate of germanium is increased, the quality of the germanium concentrate is improved, the recovery rate of germanium reaches 95% or above, and the mass fraction of germanium in the germanium concentrate is larger than 20%; and 3, the method is short in flow, low in energy consumption, easy to operate and low in production cost, and facilitates industrial production.
Owner:六盘水中联工贸实业有限公司
Method for leaching, enriching and reclaiming indium from lead-zinc smelting by-product zinc oxide
ActiveCN101104884ASolve liquidity problemsSolve the low leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementIndiumStrong acids
The invention discloses a method for leaching, enriching and recovering indium from zinc oxide byproduct in the lead and zinc smelting process. The invention is implemented by the following technical proposal: by using three-step leaching process and adding oxidizing agent in the leached slurry, the problem of low indium leaching rate is solved; intermittent slag feeding mode is used to prevent the over-high acidity due to the leached strong acids and the excessive iron production and thus to avoid the production of indium-conjugated jarosite in the next preneutralization process, which may influence the recovery of indium; the high-acidity solution is neutralized with a neutralizer such as zinc oxide or zinc calcine, so that the problem of high-acidity solution disposal is solved; when the low-acidity and high-acidity leach slurry are fed into the concentration machine, the compound flocculant is added to solve the technical problems of difficulty in settlement clarification of ore slurry, poor fluidity of thickened underflow and serious hardening. With this method, the indium leaching rate is increased up to 70-80 percent and the recovery rates of indium and zinc are also increased. Additionally, the method allows the disposal of lead-containing materials (lead slag) in the lead system and helps to reduce the discharge of waste slag, gas and water, protecting the environment.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com