Method for removing copper, cadmium, nickel and cobalt out of zinc sulfate solution through one step
A zinc sulfate solution and removal technology, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy zinc, can solve the problems of long purification process, high purification cost, low utilization rate, etc., and achieve the effects of high reduction potential, high purification efficiency and high utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Measure 1.6L of iron removal solution (Zn: 142g / L, Cu: 318mg / L, Cd: 533mg / L, Ni: 15.4mg / L, Co: 13.8mg / L, pH=5.15) in a 2L beaker, Start stirring and heat up to 55°C, then add 160-mesh manganese-copper alloy powder (Mn: 92%, Cu: 8%) according to 3.5 times the total mass of copper and cadmium, and keep it warm for 90 minutes to complete the reaction, vacuum filter and collect Filtrate and filter residue. The concentrations of copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel in the obtained filtrate are 0.11, 0.16, 0.45 and 0.24mg / L respectively, and the removal rates are all over 98%, which can meet the requirements of the zinc electrolysis process.
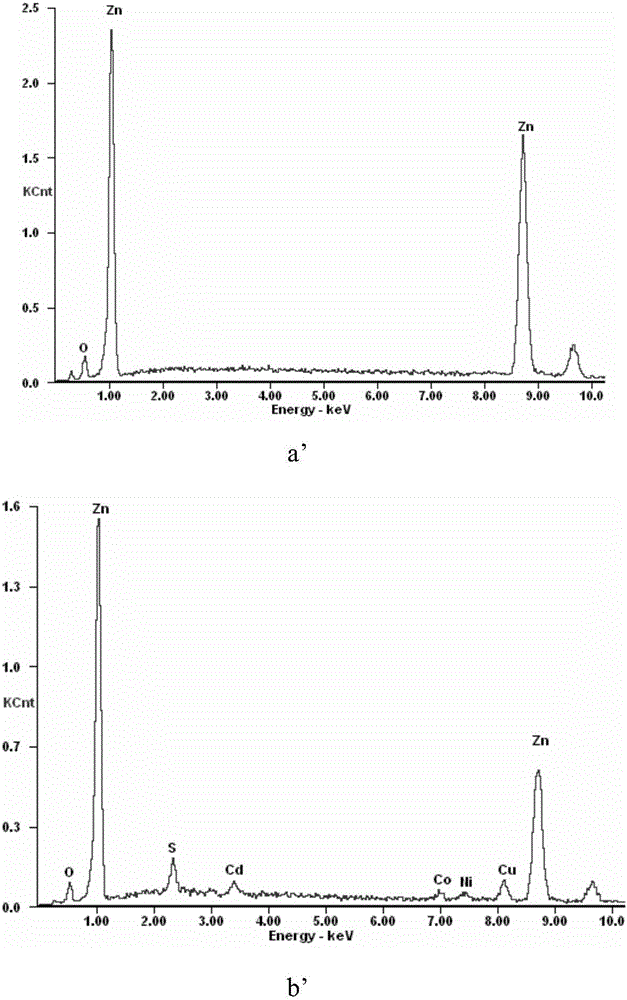
[0034] The microscopic morphology and EDS analysis results of manganese-copper alloy powder before and after impurity removal are as follows: figure 1 Shown: by figure 1 a and figure 1 b It can be seen that the morphology of manganese-copper alloy powder has changed greatly before and after impurity removal, from dense particles on the...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Measure 1.6L of iron removal solution (Zn: 142g / L, Cu: 318mg / L, Cd: 533mg / L, Ni: 15.4mg / L, Co: 13.8mg / L, pH=5.15) in a 2L beaker, Start stirring and heat up to 65°C, then add 110-mesh metal manganese powder (Mn:99%) according to 4 times the total mass of copper and cadmium, and keep the reaction for 90 minutes to complete the reaction, vacuum filter and collect the filtrate and filter residue. The concentrations of copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel in the obtained filtrate are 0.23, 0.21, 0.41 and 0.29 mg / L respectively, and the removal rates are all over 98%, which can meet the requirements of the zinc electrolysis process.
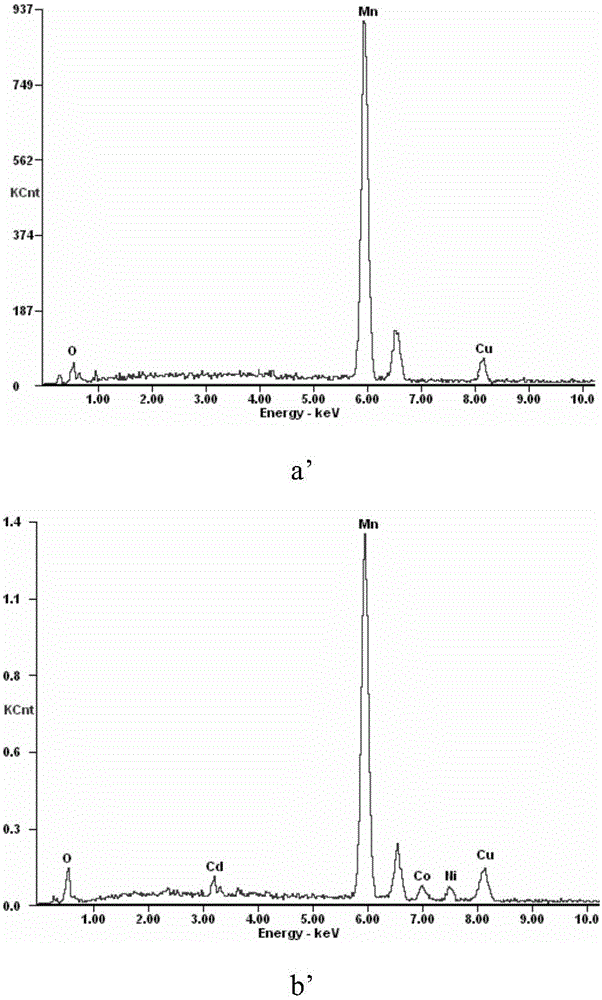
[0037] The microscopic morphology and EDS analysis results of metal manganese powder before and after impurity removal are as follows: figure 2 Shown: by figure 2 a and figure 2 b. It can be seen that the morphology of metal manganese powder has changed greatly before and after impurity removal, from irregular particles with dense surface to...
Embodiment 3
[0039]Measure 1.6L of iron removal solution (Zn: 142g / L, Cu: 318mg / L, Cd: 533mg / L, Ni: 15.4mg / L, Co: 13.8mg / L, pH=5.15) in a 2L beaker, Start stirring and heat up to 50°C, then add 200-mesh manganese-copper alloy powder (Mn: 98%) according to 5 times the total mass of copper and cadmium, and keep the reaction for 140 minutes to complete the reaction. Vacuum filtration and collect the filtrate and filter residue. The concentrations of copper, cadmium, cobalt and nickel in the obtained filtrate are 0.18, 0.14, 0.27 and 0.15 mg / L respectively, and the removal rates are all over 98%, which can meet the requirements of the zinc electrolysis process.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com