Method for cleaning copper electrolyte to remove impurities
A copper electrolyte, purification and impurity removal technology, applied in the direction of electrolysis process, electrolysis components, process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve the problems of high fire refining requirements, side effects of electrolyte, poor purification effect, etc., and achieve the effect of impurity removal Good, the effect of improving economic benefits and reducing the amount of copper
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
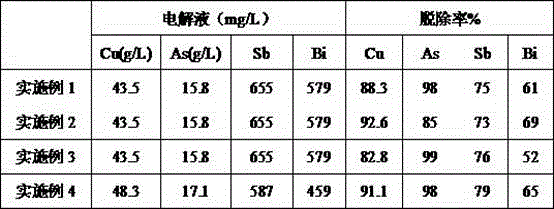
[0029] The treated copper electrolytic waste liquid in this example contains Cu: 43.5 g / L, As: 15.8 g / L, Sb: 655 mg / L, and Bi: 579 mg / L. The treatment process and effect are as follows:
[0030] (1) The molar mass m(Bi):m(As)=1.5:1 Calculate the amount of bismuth-containing precipitation to be added, and add it to the corresponding volume of electrolyte at a temperature of 60℃, and stir for 40min. The precipitation rates of arsenic, antimony and bismuth are 98%, 75% and 61% respectively.
[0031] (2) Alkaline leaching regeneration with bismuth-containing precipitation agent, sodium hydroxide mass concentration 60g / L, volume-mass ratio of alkaline leaching solution and co-precipitate is 5:1 (ml / g), temperature 80℃; time 1.5h. The leaching rate of arsenic is 98%, and antimony and bismuth are basically not leached.
[0032] (3) Electrodecopperize the purified liquid in the electrowinning tank, the electrolyte flow rate is 2m 3 / h. Current density of the first stage 250A / m 2 , The cop...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The treated copper electrolytic waste liquid in this example contains Cu: 43.5 g / L, As: 15.8 g / L, Sb: 655 mg / L, and Bi: 579 mg / L. The treatment process and effect are as follows:
[0035] (1) Mass of mole m(Bi):m(As)=0.8:1 Calculate the amount of bismuth-containing precipitate to be added, and add it to the corresponding volume of electrolyte at a temperature of 70°C and stir for 1h. The precipitation rates of arsenic, antimony and bismuth are 85%, 73% and 69% respectively.
[0036] (2) Alkaline leaching regeneration of bismuth-containing precipitant, sodium hydroxide mass concentration 80g / L, volume-mass ratio of alkaline leaching solution and co-precipitate is 3:1 (ml / g), temperature 75℃; time 2h. The leaching rate of arsenic is 96%, and antimony and bismuth are basically not leached.
[0037] (3) Electrodecopperize the purified liquid in the electrowinning tank, the electrolyte flow rate is 2.2m 3 / h. The first stage current density 260A / m 2 , The copper ion concentratio...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The treated copper electrolytic waste liquid in this example contains Cu: 43.5 g / L, As: 15.8 g / L, Sb: 655 mg / L, and Bi: 579 mg / L. The treatment process and effect are as follows:
[0040] (1) The molar mass m(Bi):m(As)=2:1 Calculate the amount of bismuth-containing precipitate to be added, and add it to the corresponding volume of electrolyte at a temperature of 50°C and stir for 15min. The precipitation rates of arsenic, antimony and bismuth are 99%, 76% and 52% respectively.
[0041] (2) Alkaline leaching regeneration with bismuth-containing precipitant, sodium hydroxide mass concentration 20g / L, volume mass ratio of alkaline leaching solution and co-precipitate is 8:1 (ml / g), temperature 90℃; time 30min. The leaching rate of arsenic is 95%, and antimony and bismuth are basically not leached.
[0042] (3) Electrodecoppering the purified liquid in the electrowinning tank, the electrolyte flow rate is 2.6m 3 / h. Current density of the first stage 220A / m 2 , The copper ion c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com