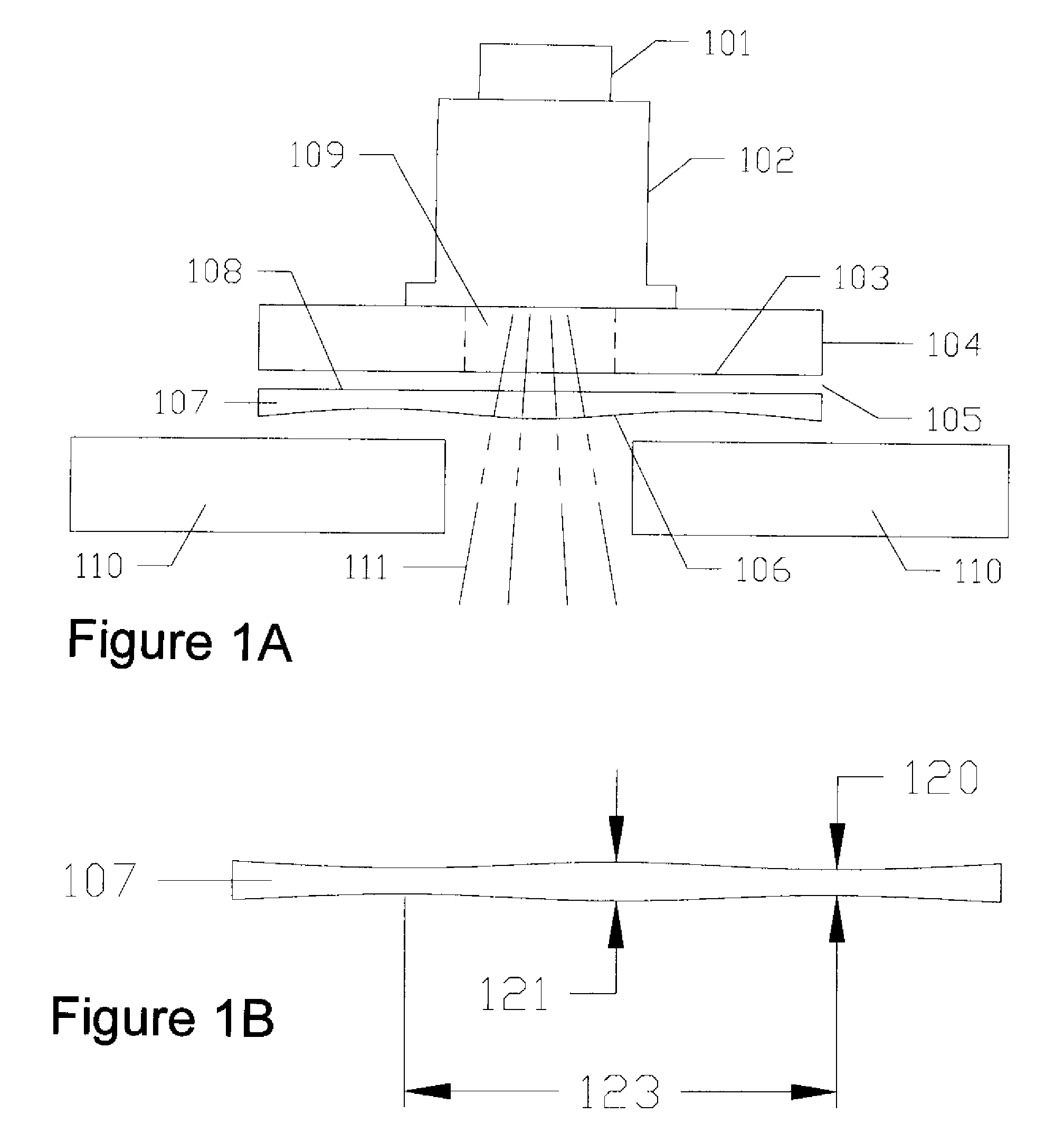
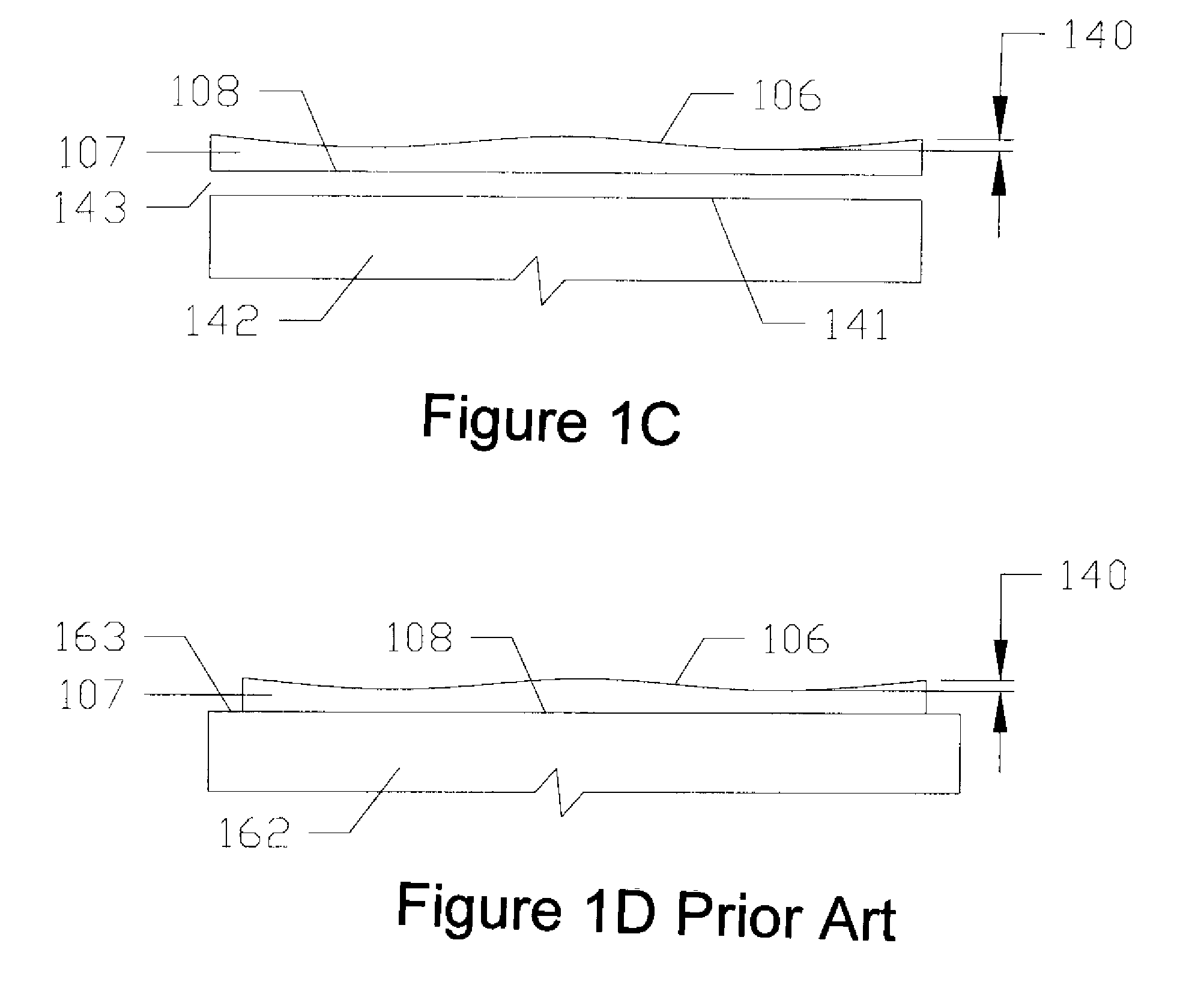
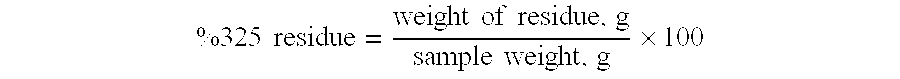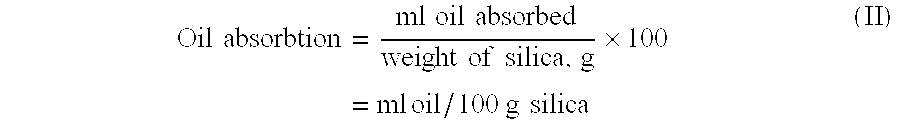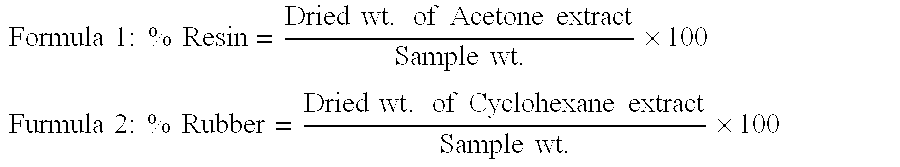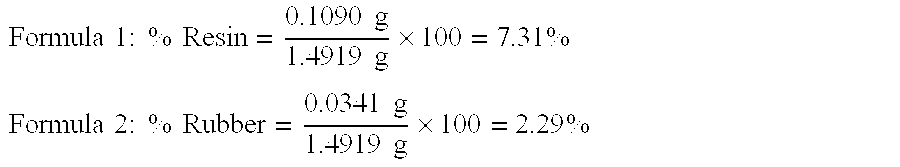Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11727results about "Gas current separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
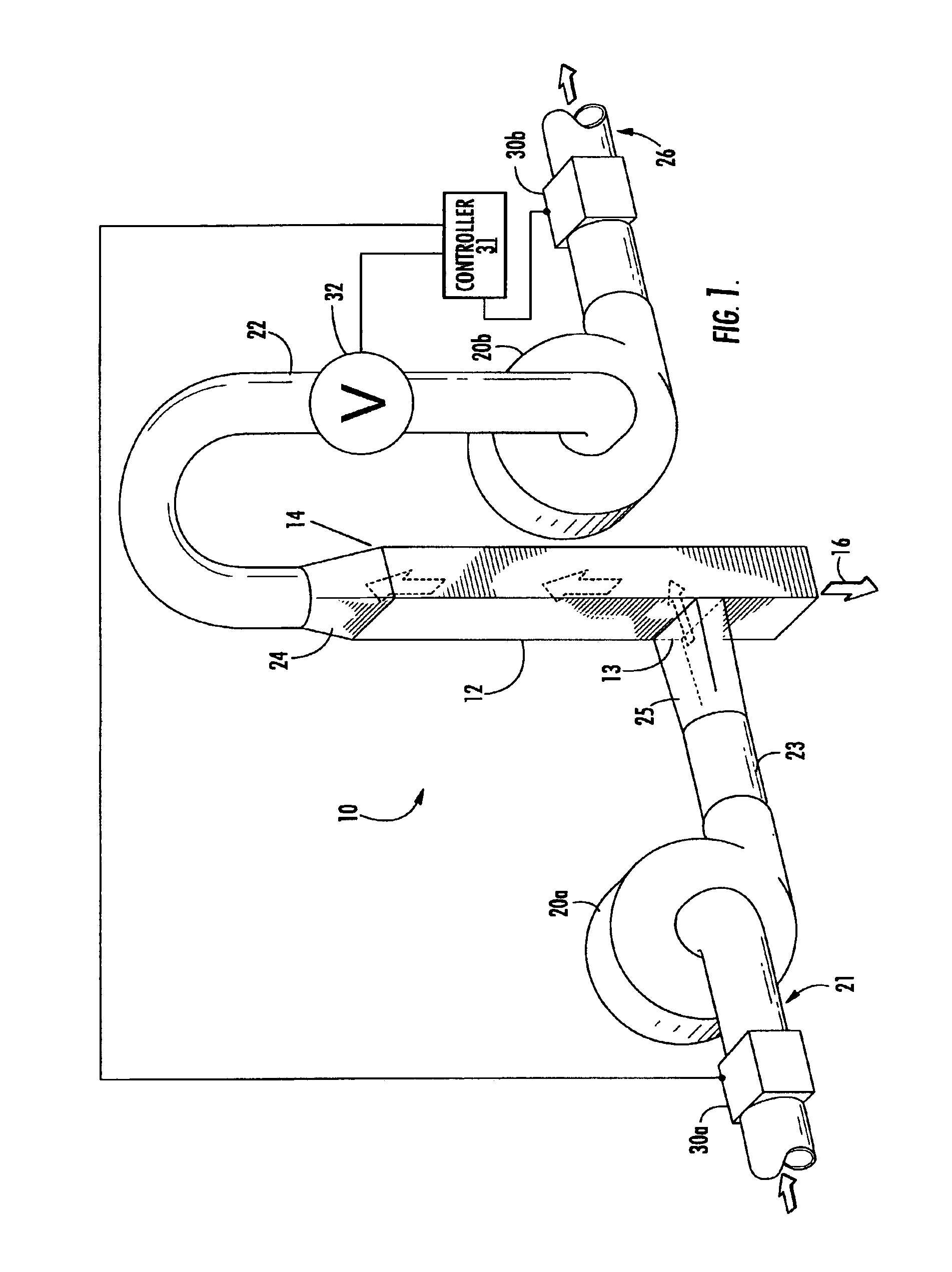
Methods and devices for continuous sampling of airborne particles using a regenerative surface
InactiveUS20040232052A1Increase volume of materialImprove concentrationFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringAtmospheric sciences
Airborne particles are impacted on a collection surface, analyzed, and then the collection surface is regenerated. Thus, the same collection surface can be used in numerous cycles. The analysis can be focused on one or more properties of interest, such as the concentration of airborne biologicals. Sensors based on regenerative collection surfaces may be incorporated in many networks for applications such as building automation.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Non-contact porous air bearing and glass flattening device
Thin substrates, such as flat glass panels, are levitated on a porous media air bearing creating a pressurized film of air and preloaded against the air film by negative pressure areas. The pressure can be distributed most uniformly across the pressure areas by defusing the pressure through a porous medium. Such a bearing can be used for glass flattening by holding the glass such that the unevenness is migrated to the side opposite the side to be worked on.
Owner:NEW WAY MACHINE COMPONENTS
Spiral Microchannel Particle Separators, Straight Microchannel Particle Separators, and Continuous Particle Separator and Detector Systems
A spiral microchannel particle separator includes an inlet for receiving a solution containing particles, at least two outlets, and a microchannel arranged in a plurality of loops. Particles within a solution flowing through the spiral microchannel experience a lift force FL and a Dean drag force FD. The spiral radius of curvature R and the hydraulic diameter Dh of the spiral microchannel are such that for a flow rate U of the solution, the lift force FL and a Dean drag force FD are approximately equal and act in opposite directions for particles of a first size. The particles of the first size are focused in a single stream located at an equilibrium position near an inner wall of the microchannel. In another embodiment, a straight microchannel particle separator separates particles by modulating shear rates via high aspect ratios that focuses particles of a first size along two first walls.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
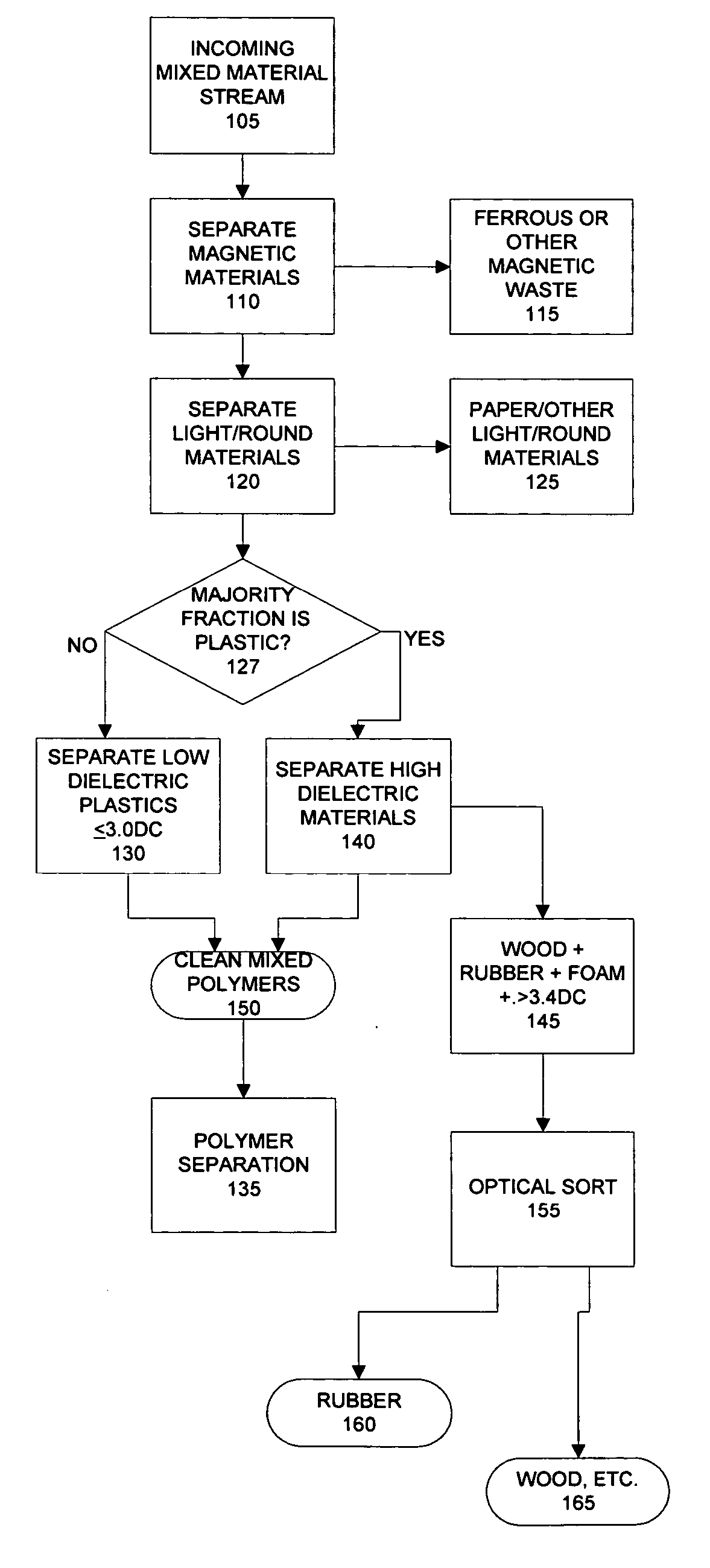
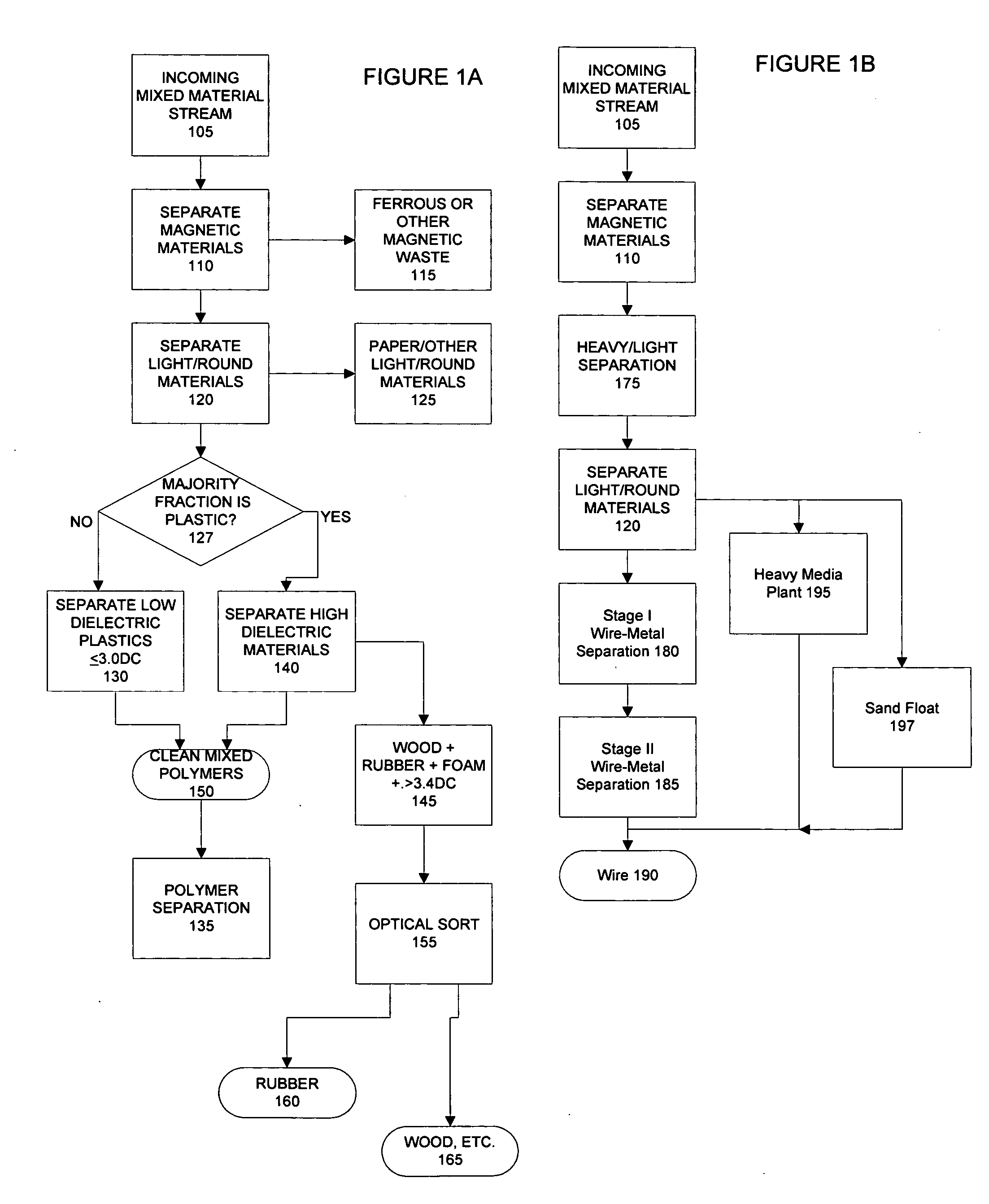
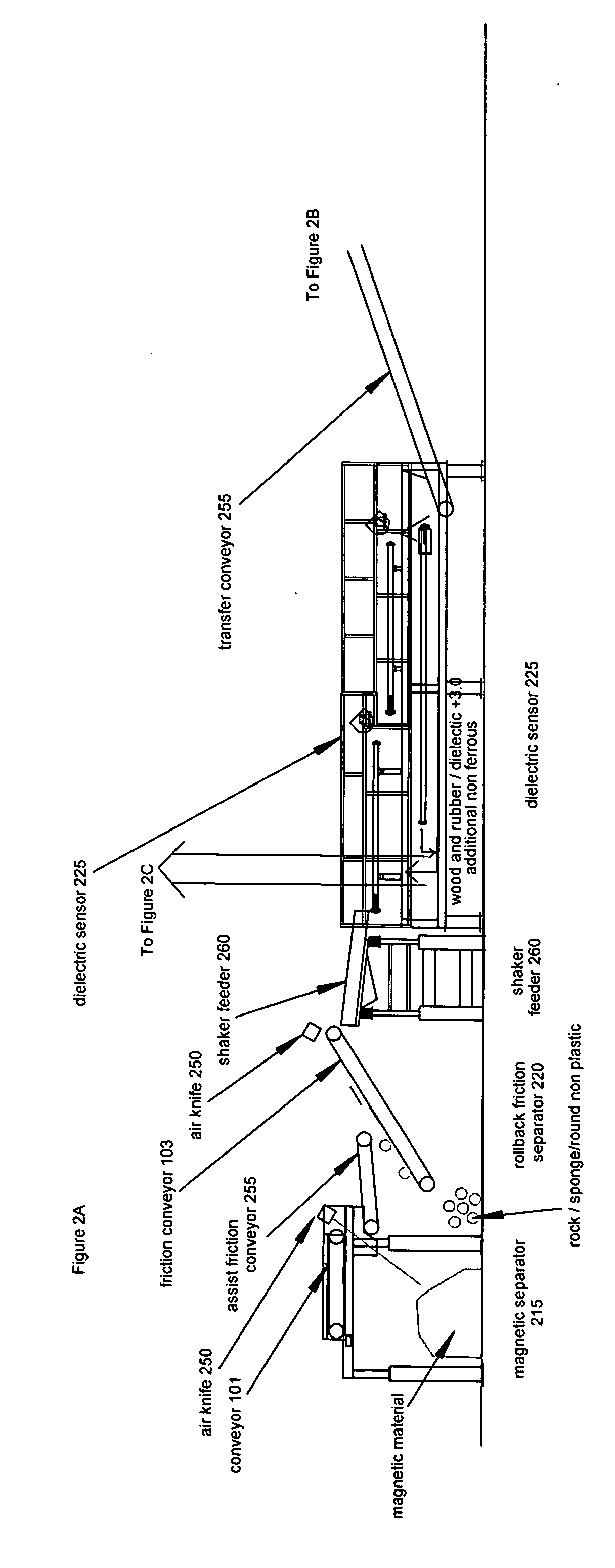
Dissimilar materials sorting process, system and apparata
InactiveUS20070187299A1Improve uniformityUnified operationGas current separationSolid waste disposalElectricityMagnetic separator
An automated system for sorting dissimilar materials, and in particular for sorting plastics from other materials and for sorting different types of plastics from one another comprises, depending upon the embodiment, combinations of a sizing mechanism, a friction separation, an air separator, a magnetic separator, a dielectric sensor sortation bed, shaker screening, a ballistic separator, an inductive sensor sortation system and a float / sink tank. The dielectric sensor sortation system may be either analog or digital, depending upon the particular implementation. One or more float / sink tanks can be used, depending upon the embodiment, each with a media of a different specific gravity. The media may be water, or water plus a compound such as calcium chloride. In addition, multiples of the same general type of module can be used for particular configurations. A heavy media system or a sand float process can be used either alternatively or additionally.
Owner:VALERIO THOMAS A
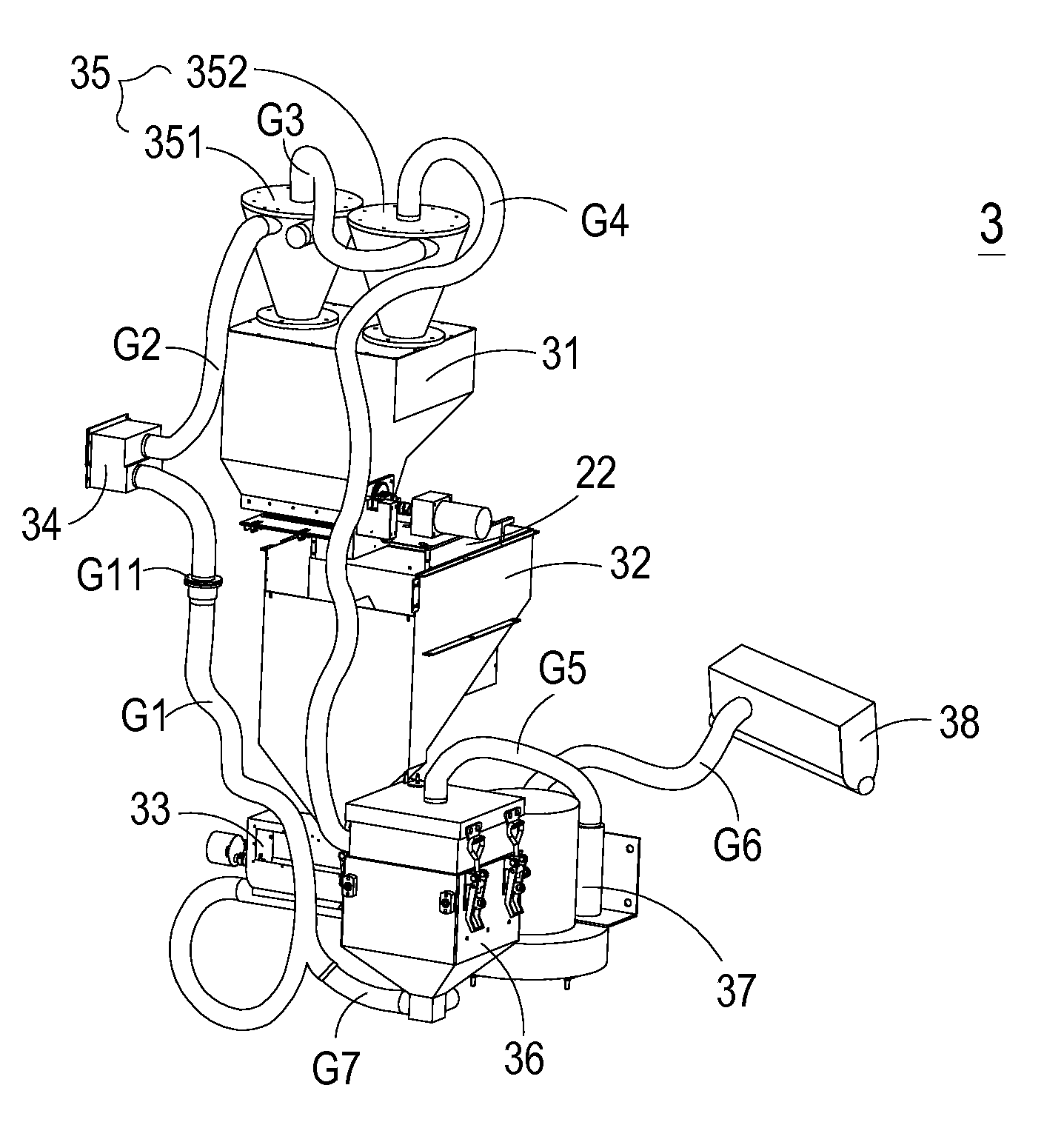
Powder recycling system
ActiveUS20150298397A1More user-friendlyCost-effectiveAdditive manufacturing apparatusGas current separationParticulatesPressure generation
A powder recycling system includes a powder feeder, a remaining powder collector, a bridge breaker, a block powder filter, a cyclone separator, a particulate filter cleaner, an air pressure generation device and an electrostatic precipitator. The powder feeder provides a construction powder to a construction platform. The remaining powder collector for collects the remaining powder. The cyclone separator is used to separate the large-size powdery particles and the small-size powdery particles of the remaining powder from each other through a rotating gaseous stream. The large-size powdery particles fall down to the powder feeder due to gravity, and the small-size powdery particles of the remaining powder is removed from the rotating gaseous stream and transmitted to the particulate filter cleaner. After the small-size powdery particles of the remaining powder are filtered by the particulate filter cleaner, the suspended small-size powdery particles are transmitted to the electrostatic precipitator.
Owner:MICROJET TECH
Blender base with food processor capabilities
InactiveUS20050068846A1Avoid vibrationImprove stabilityGas current separationTransportation and packagingMicrocontrollerLiquid-crystal display
A blender base that may be used with a food processor container, a blender container, and a single use beverage container. The blender container includes a novel blade unit having a food processor-style blade and blender type blades. Programs with preprogrammed motor commands for desired operations are stored in memory and may be selected by a user on a user interface. The user interface may include a liquid crystal display, or function switches and light emitting diodes. Upon selection of a particular pre-defined function, the microcontroller retrieves the appropriate program from the read only memory and specifies the preprogrammed motor commands to accomplish the selected function.
Owner:WULF JOHN DOUGLAS +5
Apparatus and method of enhancing the quality of high-moisture materials and separating and concentrating organic and/or non-organic material contained therein
ActiveUS20080201980A1Processed evenly and quicklySignificant environmental benefitsDrying solid materials with heatSolid fuel pretreatmentParticulatesFluidized bed drying
The present invention harvests and utilizes fluidized bed drying technology and waste heat streams augmented by other available heat sources to dry feedstock or fuel. This method is useful in many industries, including coal-fired power plants. Coal is dried using the present invention before it goes to coal pulverizers and on to the furnace / boiler arrangement to improve boiler efficiency and reduce emissions. This is all completed in a low-temperature, open-air system. Also included is an apparatus for segregating particulate by density and / or size including a fluidizing bed having a particulate receiving inlet for receiving particulate to be fluidized. This is useful for segregating contaminants like sulfur and mercury from the product stream.
Owner:RAINBOW ENERGY CENT LLC
Granules, tablets and granulation
ActiveUS20080111269A1Quick cureEasy to assemblePowder deliveryElectrostatic separationMaterials scienceAirflow
The invention provides, inter alia, a method for producing granules from a powder, characterized in that a low compaction force is applied to the powder to produce a compacted mass comprising a mixture of fine particles and granules and separating fine particles from the granules by entraining the fine particles in a gas stream. Also provided are apparatus for use in the process and tablets formed by compression of the resultant granules.
Owner:ATACAMA LABS OY
Cutter assembly for a grinder pump
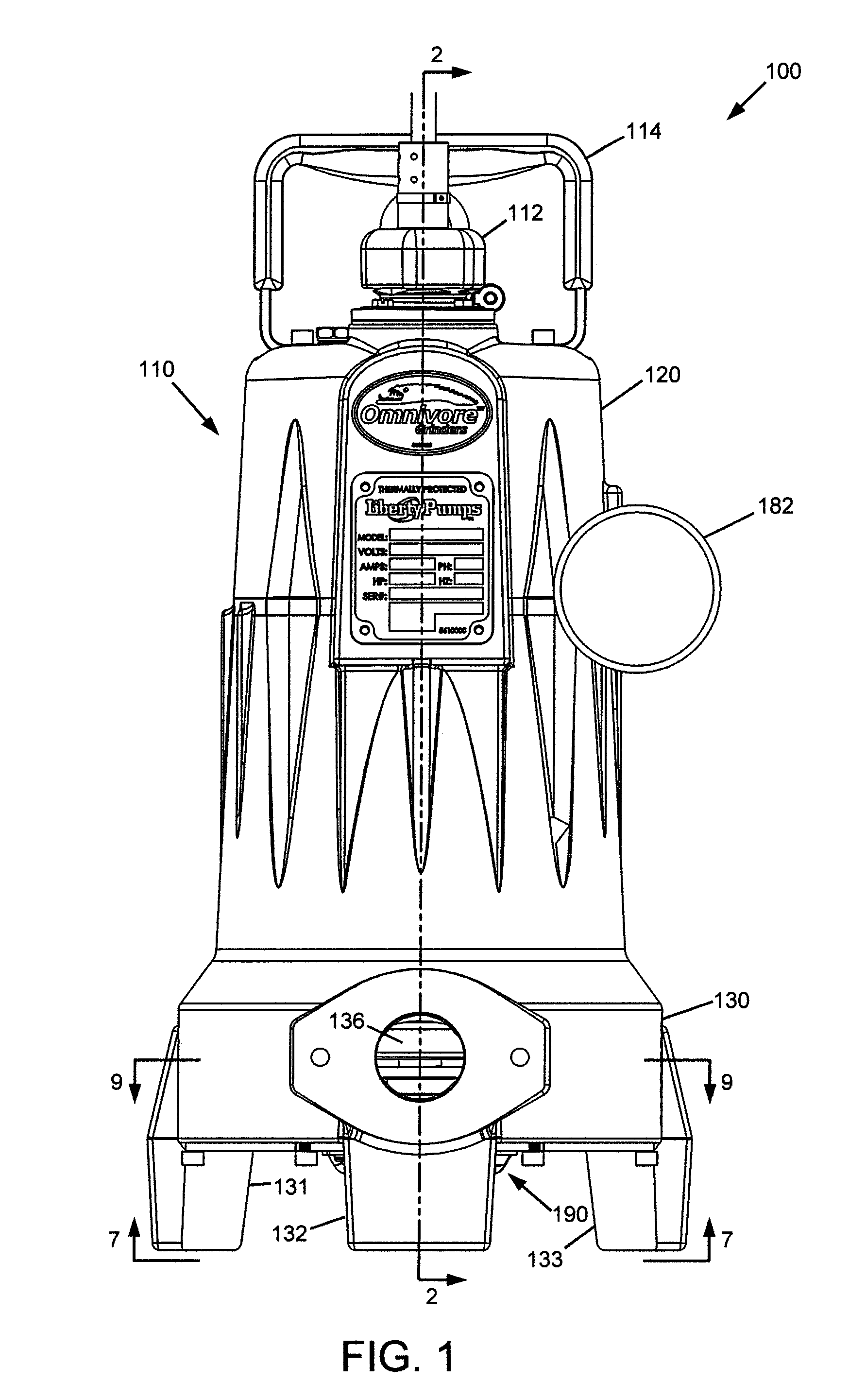
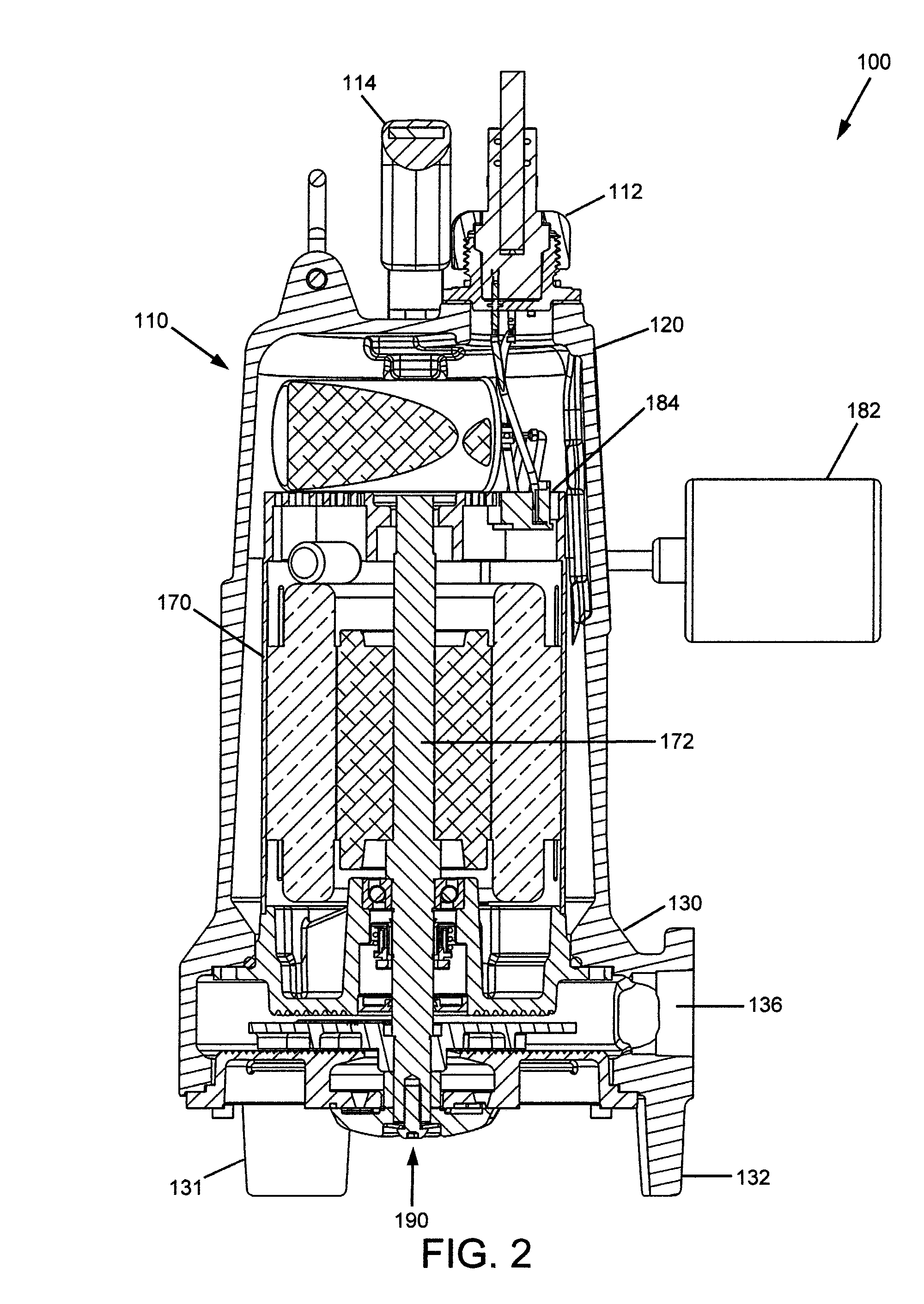
A cutting assembly for a grinder pump comprised of a rotary cutter rotatable against an opposing plate cutter. The cutting edges of the plate cutter include a plurality of V-slice cutting teeth, which create bridging spaces to pinch material which is being sucked in to ports and begin cutting along the V-slice and then for cut material to pass through and onward into the volute of the pump. The rotary cutter has a ground edge with a rake angle which shears the gathered material in cooperation with the cutting edges of the plate cutter. A grinder pump including the cutter assembly is also disclosed.
Owner:LIBERTY PUMPS
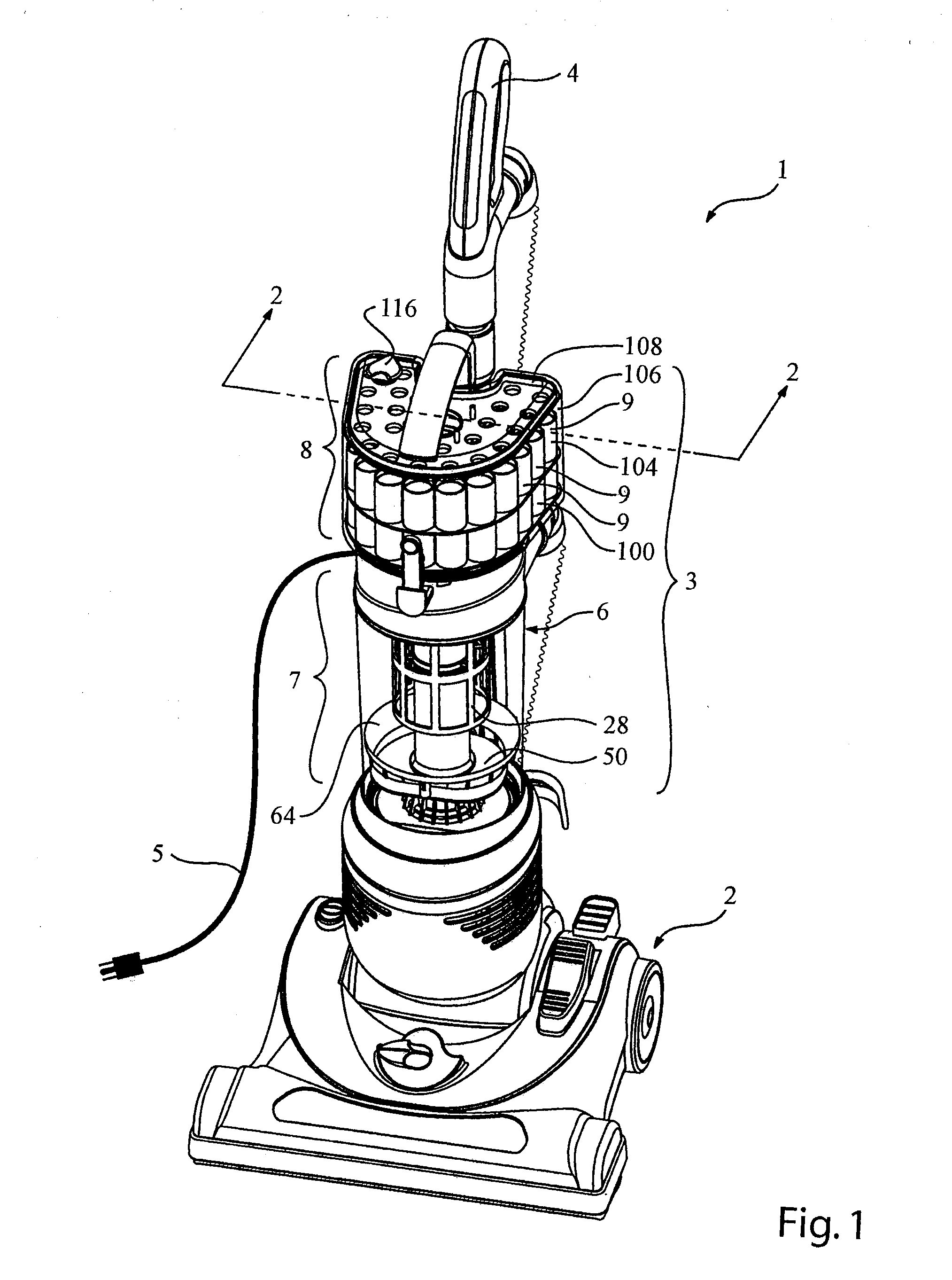
Vacuum cleaner with a removable screen
InactiveUS20070209334A1Improve efficiencyGrowth inhibitionCleaning filter meansCombination devicesSurface cleaningEngineering
A surface cleaning apparatus comprises a dirt inlet, a handle, a cyclone separator having an outer wall, a top, a fluid inlet downstream from the dirt air inlet and a fluid outlet, a screen positioned around the fluid outlet such that fluid exiting the cyclone separator passes through the screen and the screen is removable through the top of the cyclone separator, and, a fluid flow motor.
Owner:G B D
Automatic debris separation system
InactiveUS6883667B1Easy to process directlyReduce environmental impactGas current separationThreshers
The invention is an automatic debris separation system for effecting air separation of fragmented materials, such as size-reduced fiber feedstocks derived from textile wastes. The system uses high-velocity air within an elutriation assembly to efficiently remove ferrous and non-ferrous metal debris from recyclable polymer fibers. In particular, the system may employ automatic process control strategies to vary airflow within the elutriation assembly in process-controlled response to measured metal contamination, thereby ensuring that post-separation metal contamination is maintained at or below an upper contamination limit.
Owner:WELLMAN PLASTICS RECYCLING
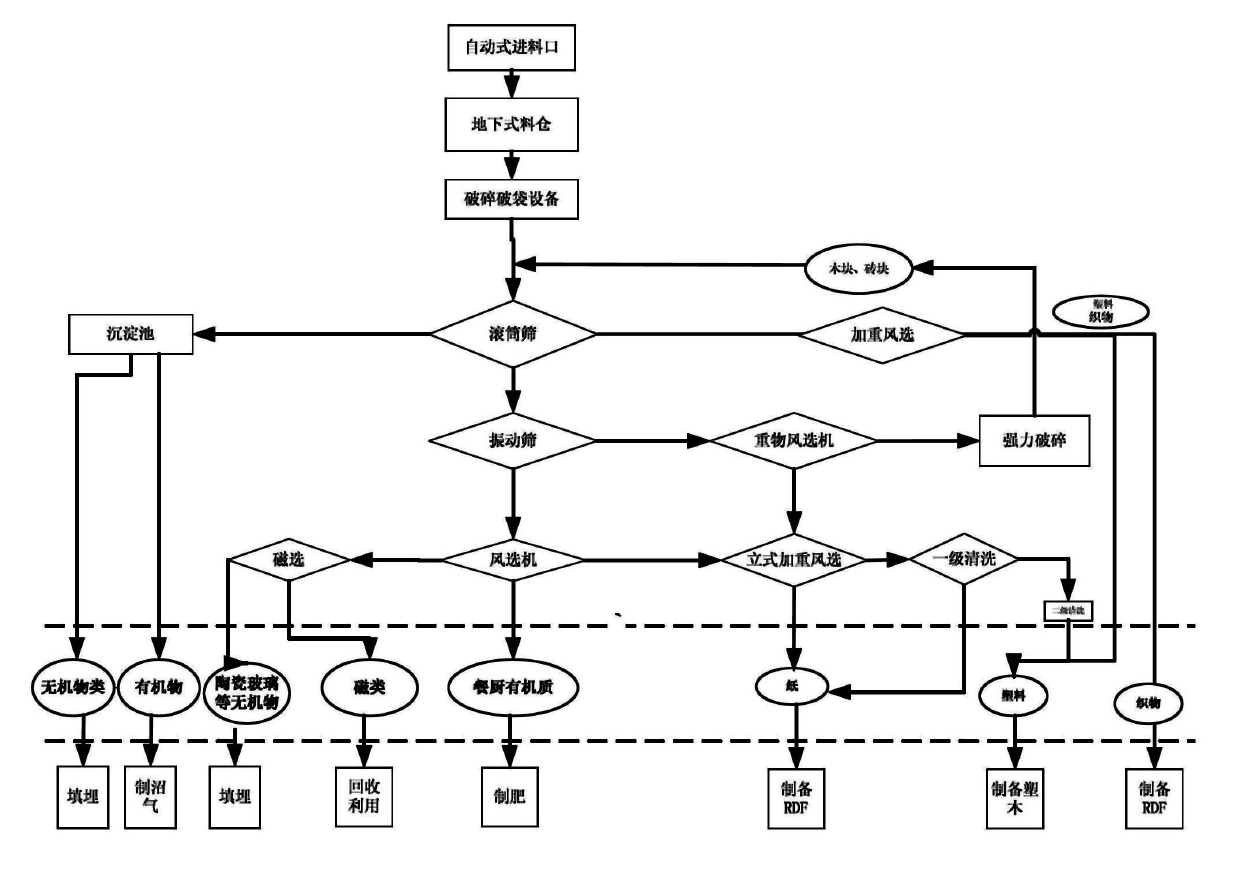
Method for sorting and comprehensively using urban mixed garbage
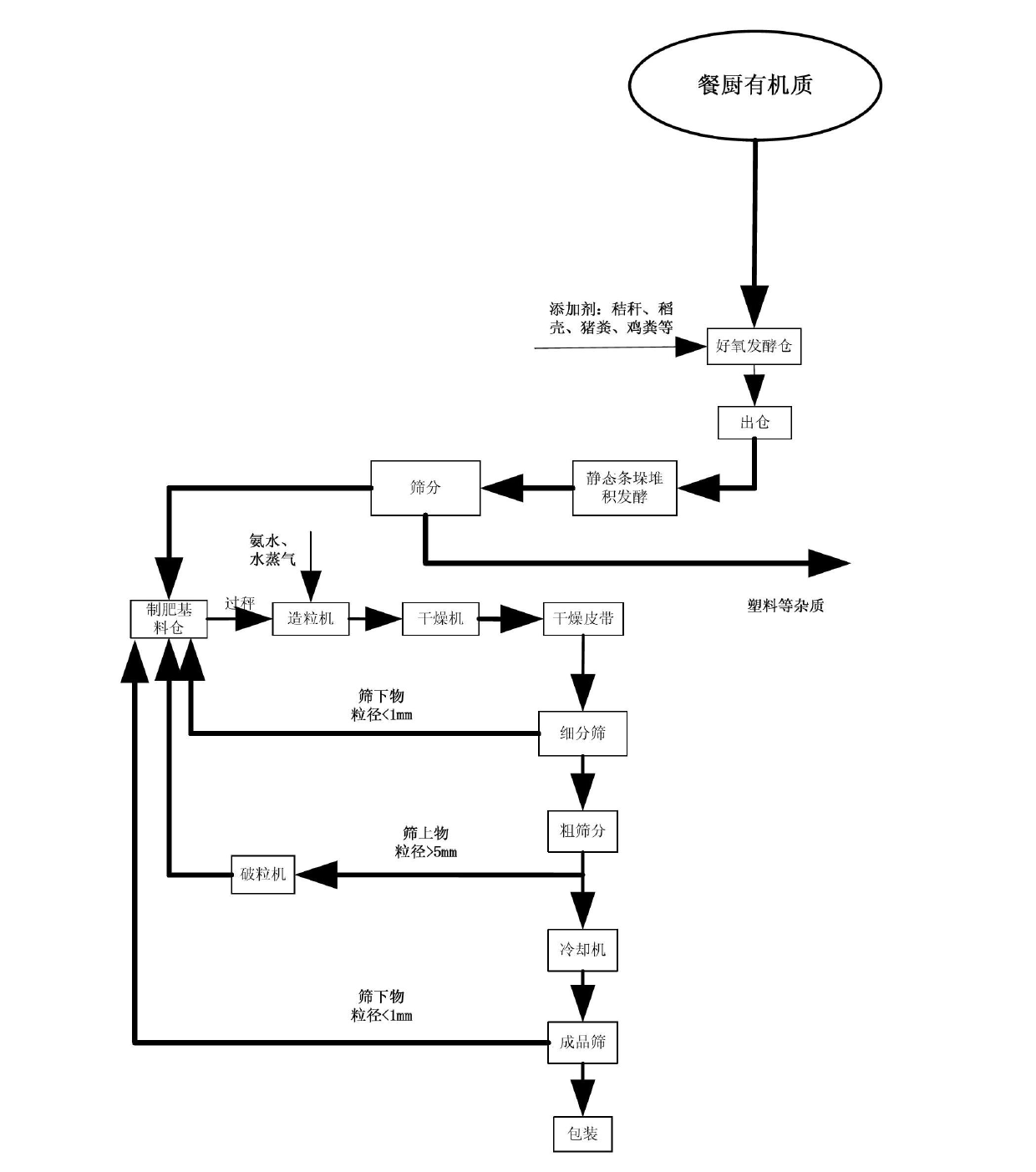
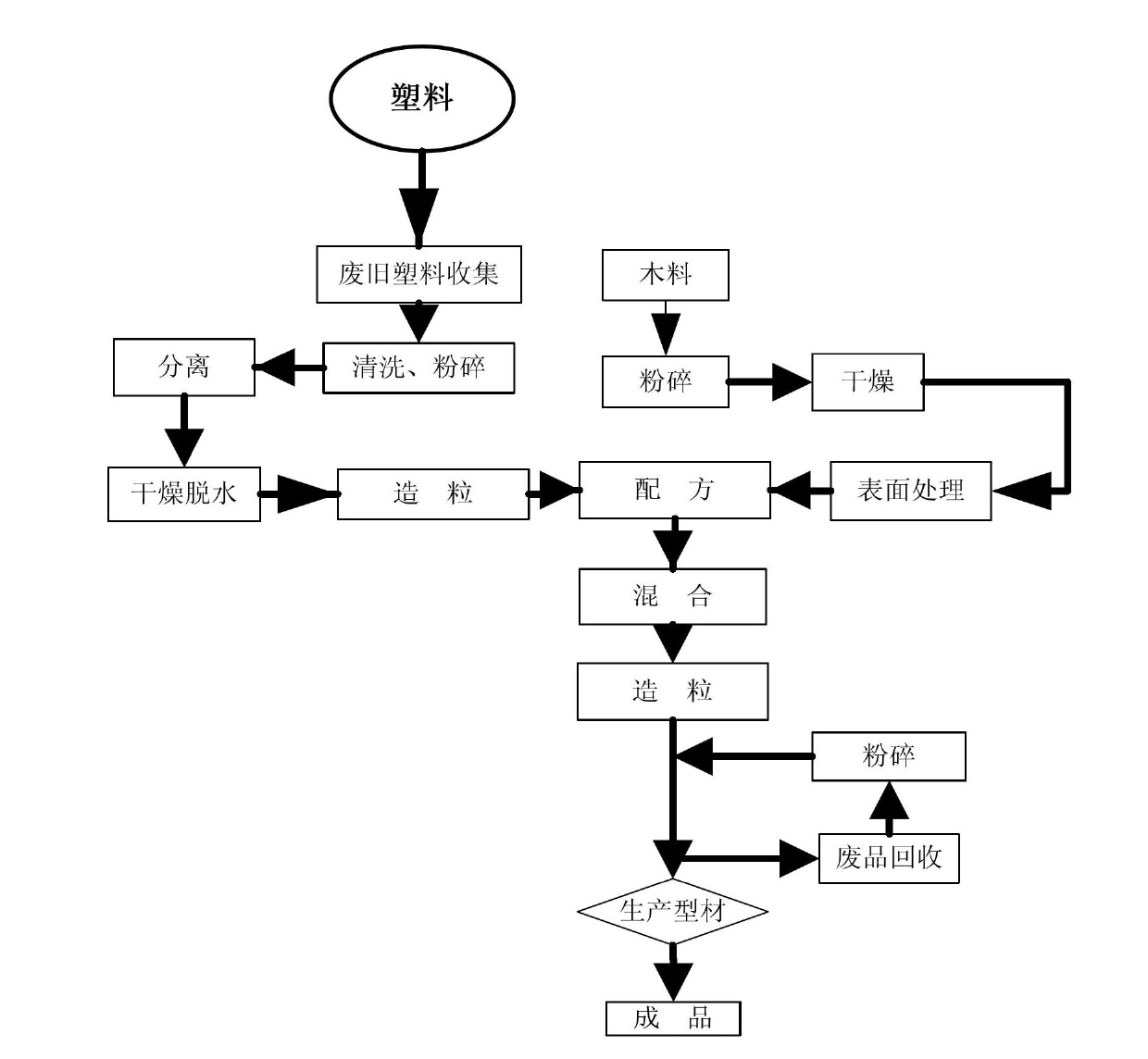
InactiveCN102671928AStructural innovationRealize full mechanizationBio-organic fraction processingSolid waste disposalRefuse-derived fuelPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a method for sorting and comprehensively using urban mixed garbage. The method comprises the following steps: 1) allowing the urban mixed garbage to enter a feed bin through a feeding hole, discharging, and introducing into crushing and bag breaking equipment; 2) breaking garbage bags and crushing block garbage by using the crushing and bag breaking equipment; 3) feeding the garbage subjected to crushing and bag breaking into a two-stage rotary screen, screening out dust of which the grain size is less than 3mm, and picking out strip substances; and 4) feeding the mixed garbage into a vibration screen, separating inorganic cakes, large-sheet plastics and paper from an oversize material by using a heavy winnowing machine, and winnowing heavy substances, light substances and intermediate substances from an undersized material in a double-wind chamber multifunctional winnowing machine. Sorting equipment is effectively combined, so that the mixed garbage is efficiently sorted and recycled; and the sorted paper and textiles, plastics and kitchen organics are respectively used for preparing garbage derived fuel, plastic wood and fertilizers.
Owner:SICHUAN CRUN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENERGY TECH CO LTD +1
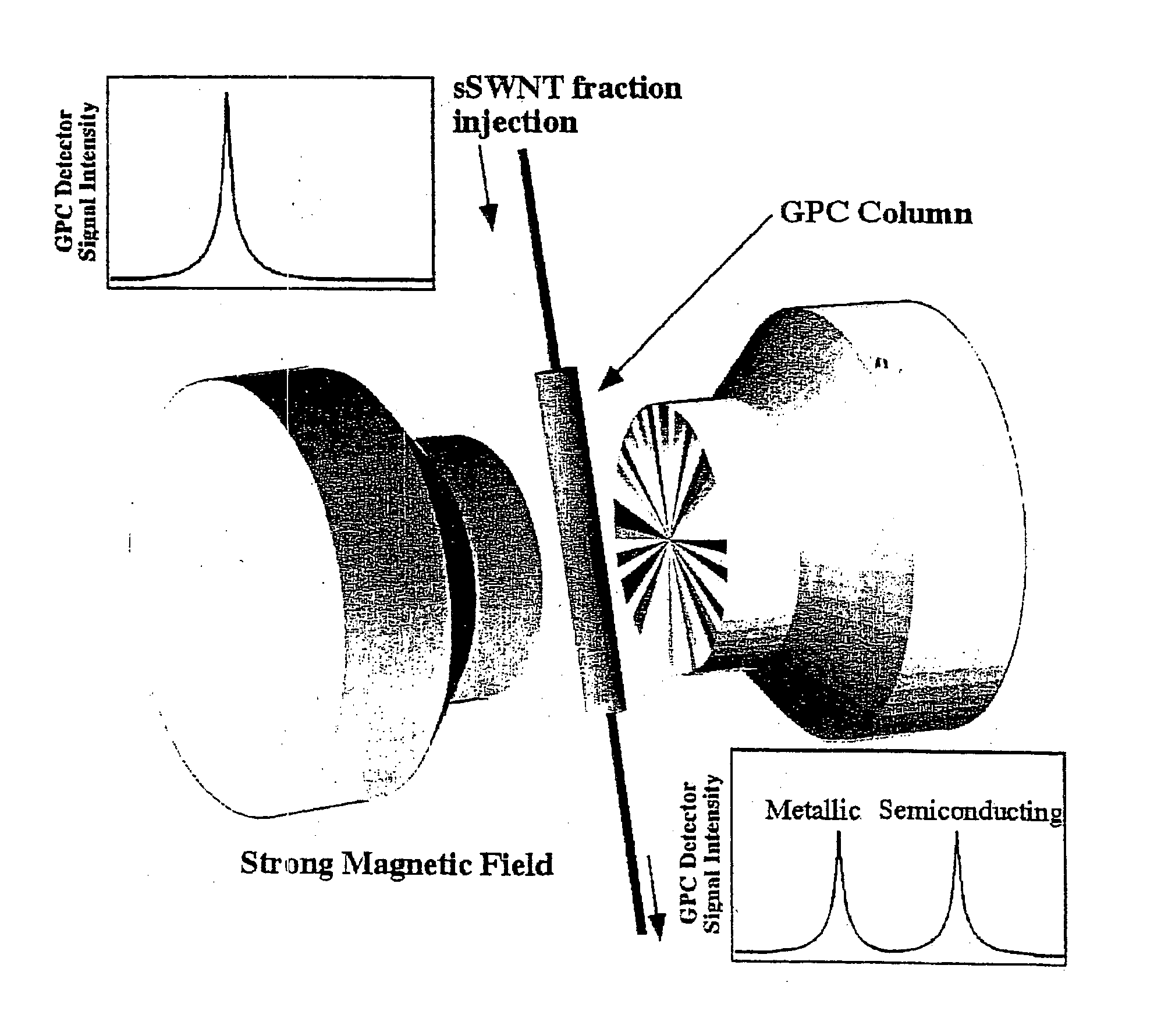
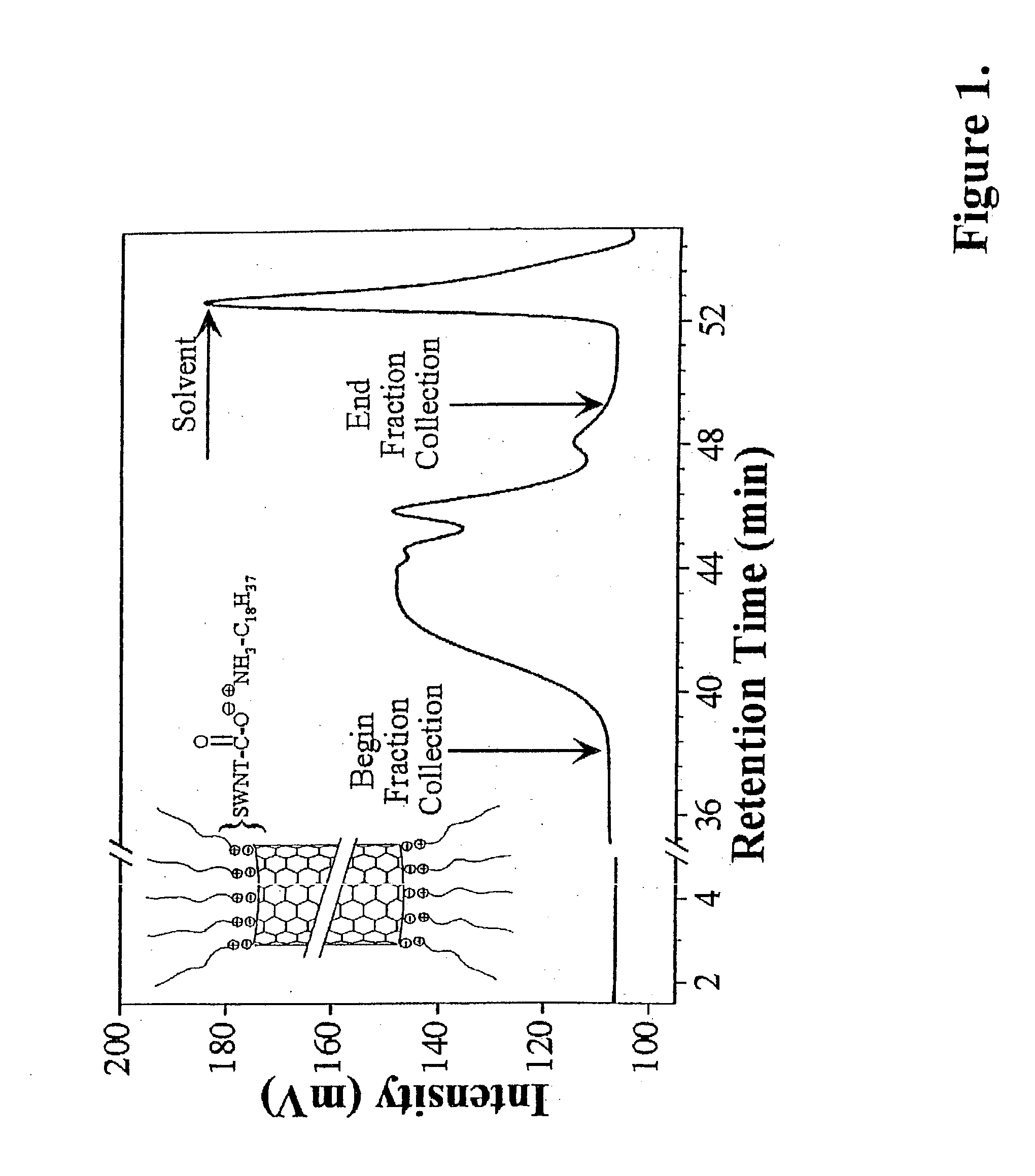
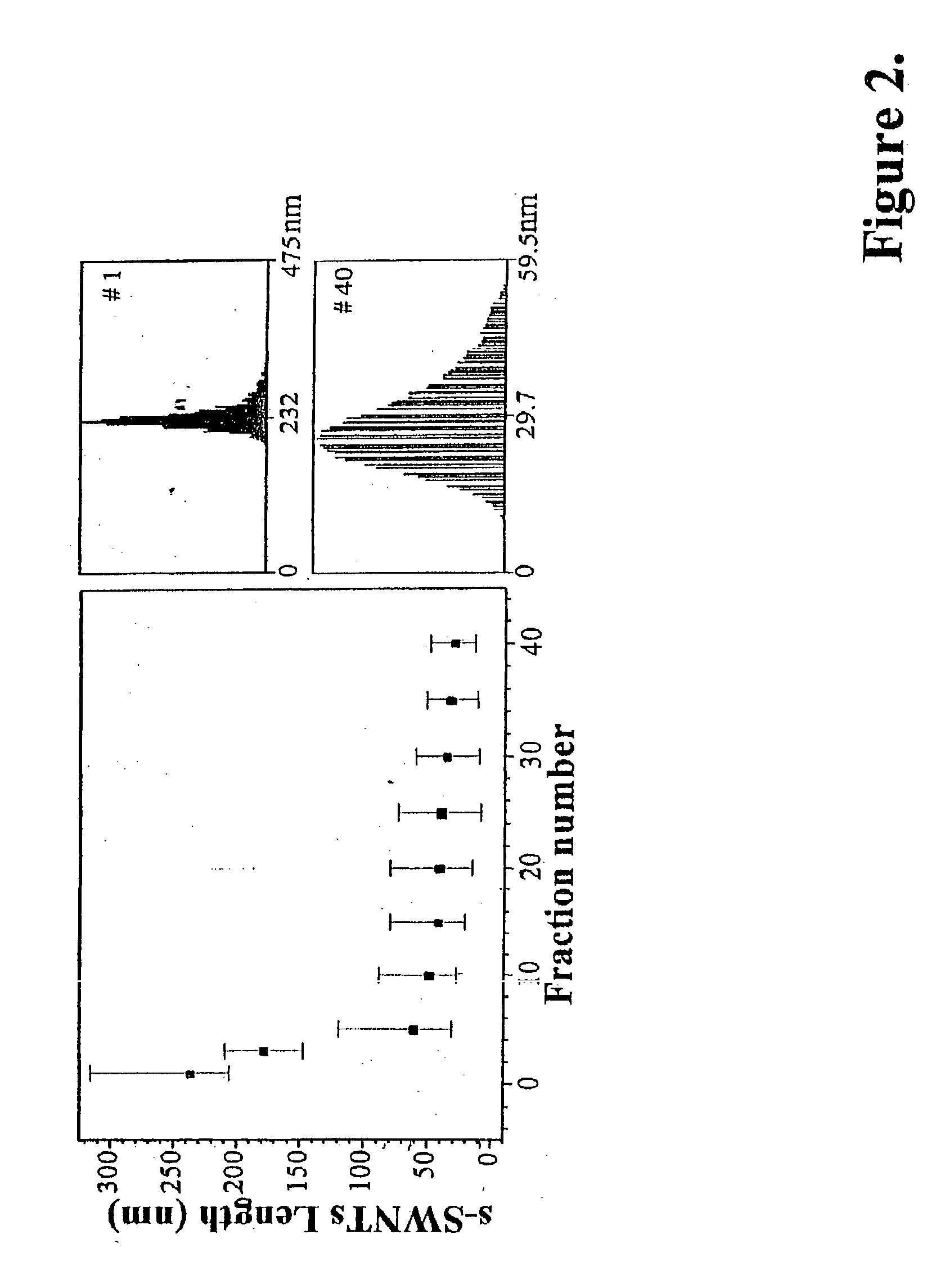
Separation of single wall carbon nanotubes
ActiveUS20030168385A1Good solubilization effectImproved size fractionationSievingMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductorNanotube
A method has been developed for the post-synthesis separation of nanotubes by size and / or type. Solubilized, functionalized nanotubes are passed over a GPC column such that length-separated fractions are collected. These length-separated fractions can then further be separated by diameter or type. Particularly useful are methods for separating nanotubes into metallic and semiconducting fractions.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
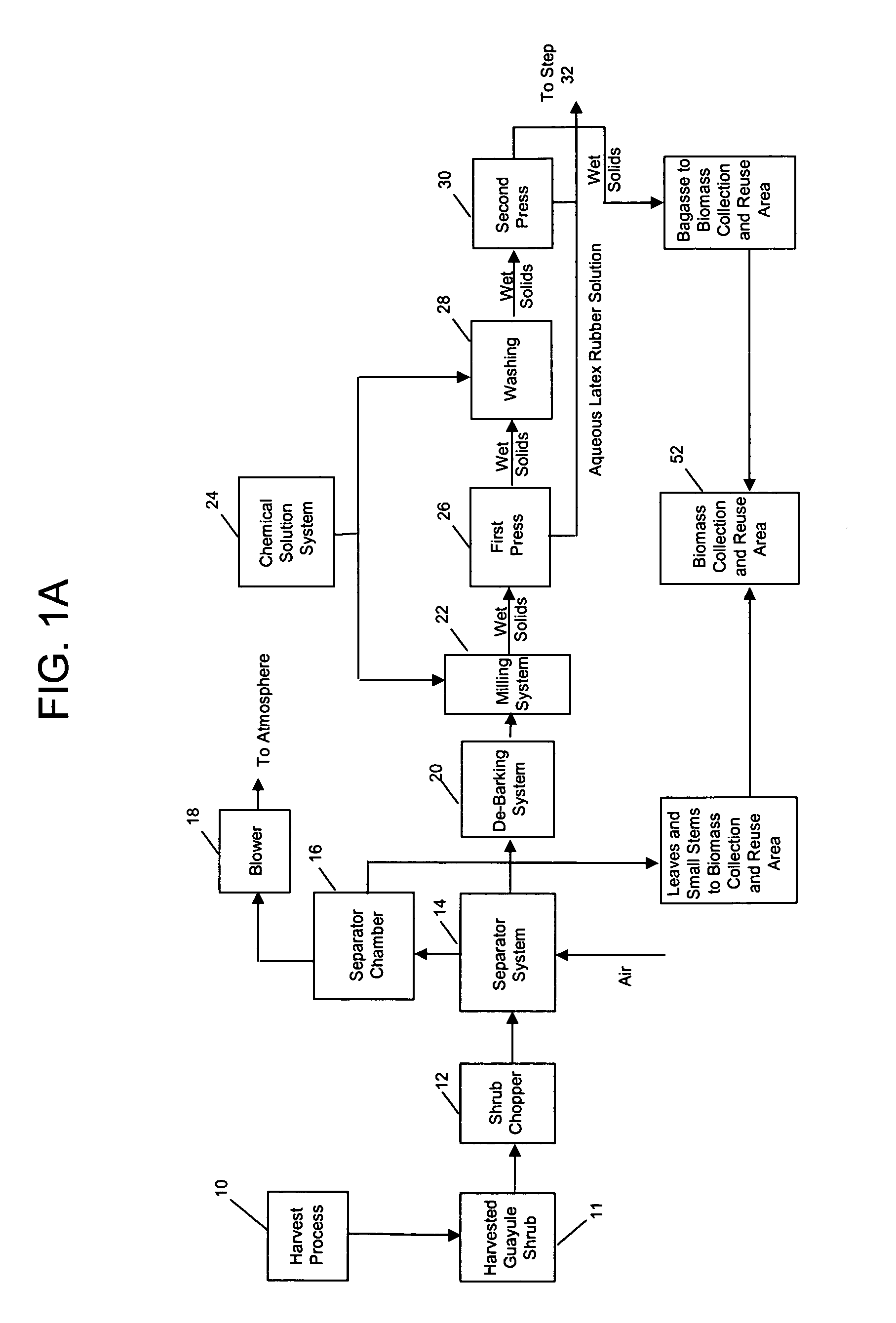
Biopolymer extraction from plant materials
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for the extraction of high molecular weight biopolymers from plants. Specifically, invention described herein relates to the commercial processing of plant material, including that from desert plants native to the southwestern United States and Mexico, such as the guayule plant (Parthenium argentatum), for the extraction of biopolymers, including natural rubbers. More specifically, the invention relates to laboratory to commercial scale extraction of high molecular weight biopolymers from plant materials including the chemical and mechanical processing of the plants and purification of the extracted biopolymer.
Owner:YULEX LLC
Method of creating ultra-fine particles of materials using a high-pressure mill
Owner:CORNERSTONE TECH
Non-contact porous air bearing and glass flattening device
Owner:NEW WAY MACHINE COMPONENTS
Classified silica for improved cleaning and abrasion in dentifrices
InactiveUS20060140878A1Improve uniformityPrecision cleaningCosmetic preparationsSilicaToothpastePhysical chemistry
A method of making precipitated silica abrasive compositions having excellent cleaning performance and lower abrasiveness with post-reactor sizing of the abrasive particles being performed via air classification techniques is provided. By targeting a specific particle size range, it has been determined that higher pellicle film cleaning levels may be achieved without also increasing the dentin abrasion properties of the silica products themselves. As a result, dentifrices including such classified abrasive silica products, and exhibiting particularly desirable cleaning benefits, can be provided for improved tooth polishing, whitening, and the like, without deleteriously affecting the hard tooth surfaces. Also encompassed within this invention also are products of this selective process scheme and dentifrices containing such classified silica products.
Owner:J M HUBER CORP
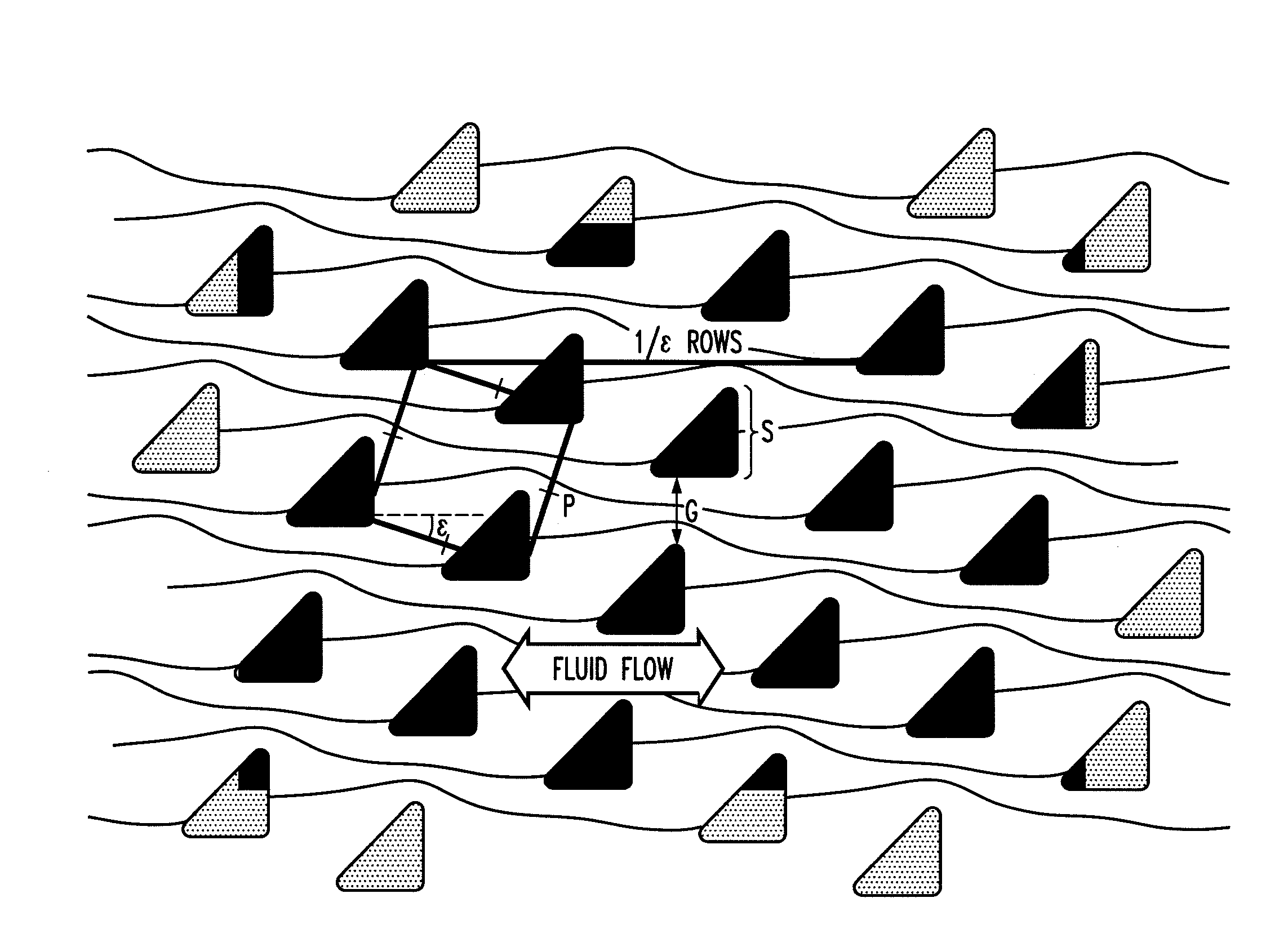
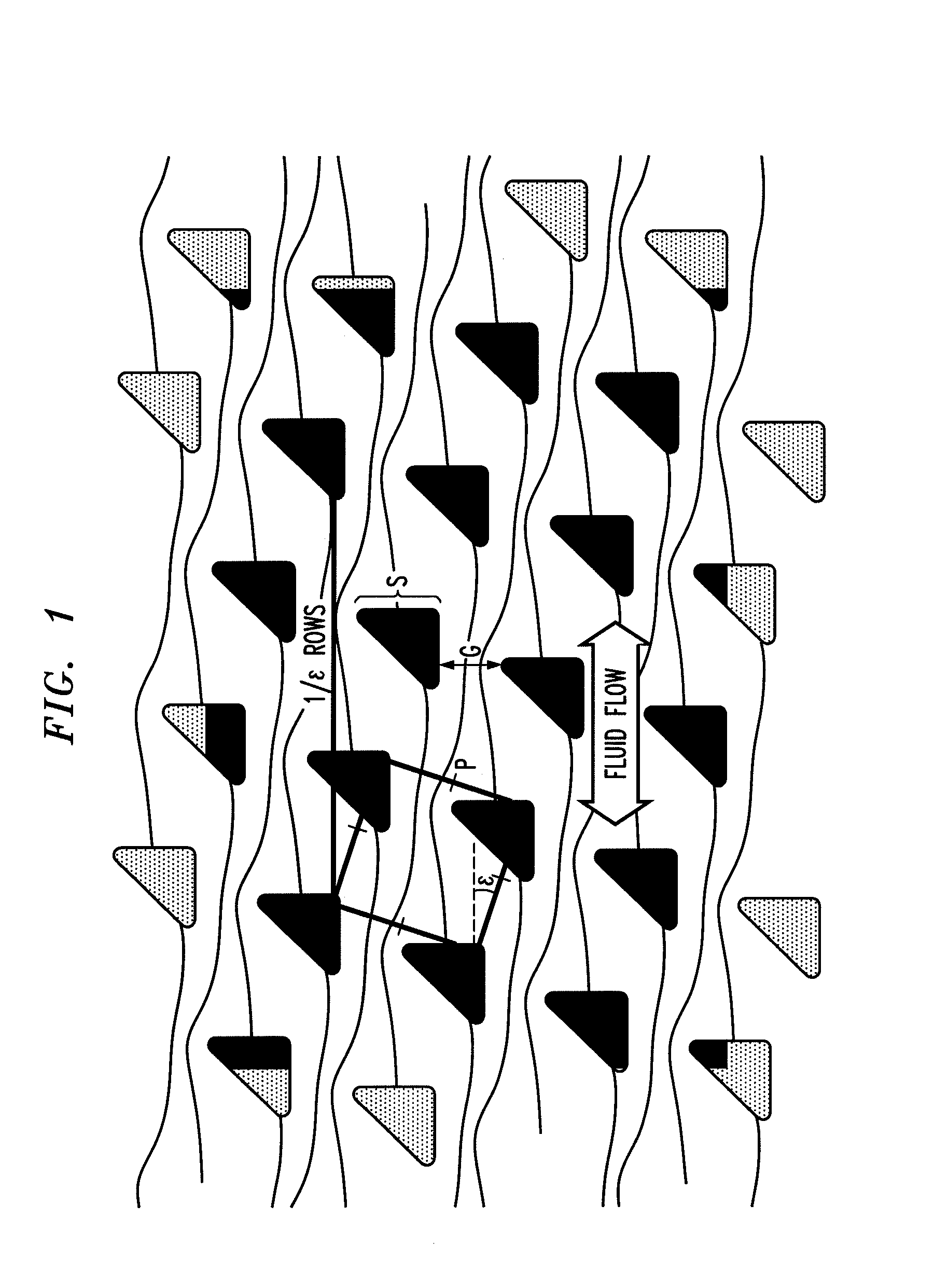
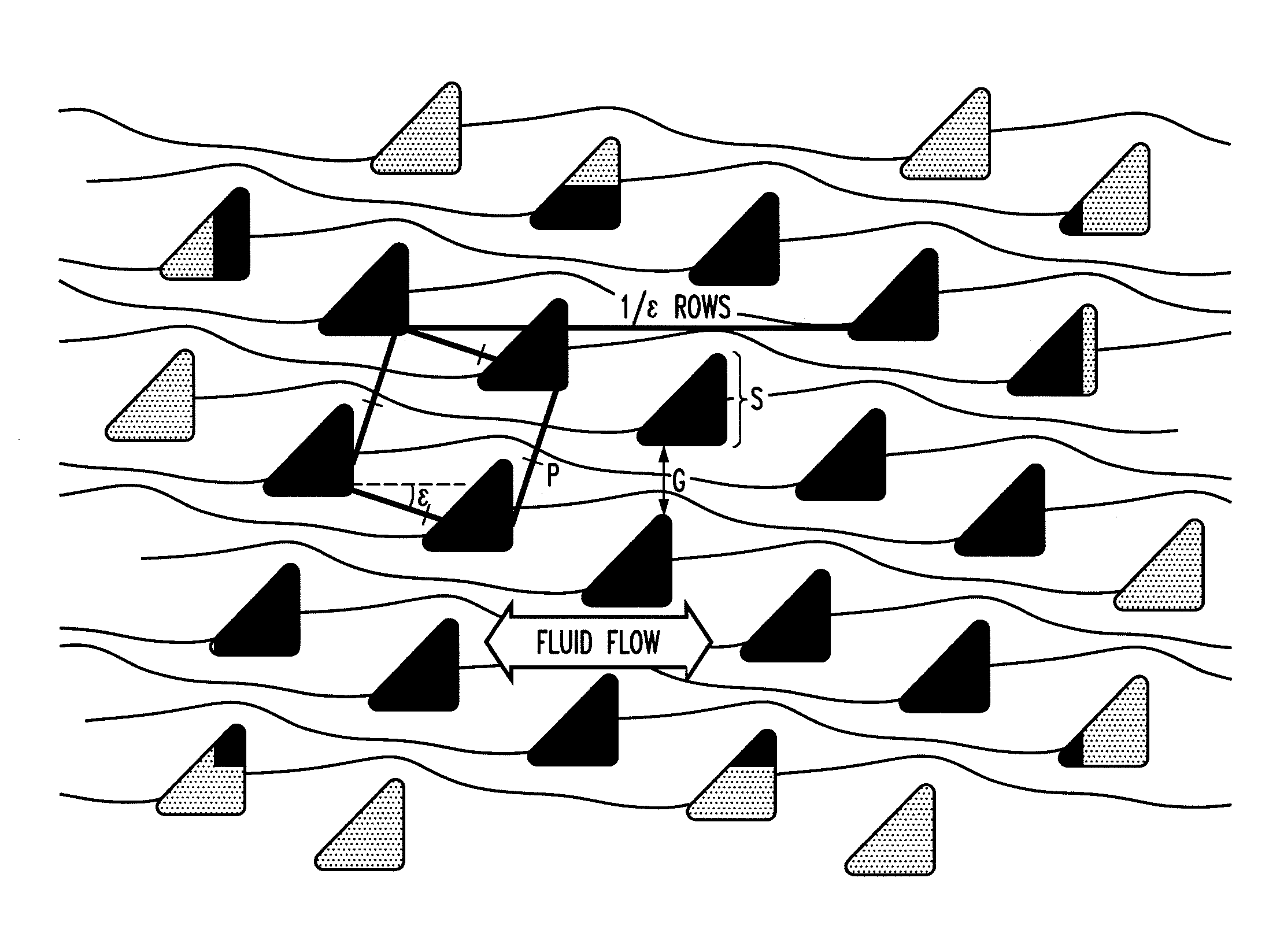
Bump array device having asymmetric gaps for segregation of particles
ActiveUS20100059414A1Easy to operateReduce gapGas current separationComponent separationEngineeringMechanical engineering
The disclosure relates to obstacle array devices (also known as bump array devices) for separating populations of particles by size. Improvements over previous obstacle array devices are realized by causing the fluid velocity profile across gaps between obstacles to be asymmetrical with respect to the plane that bisects the gap and is parallel to the direction of bulk fluid flow. Such asymmetry can be achieved by selecting the shape(s) of the obstacles bounding the gap such that the portions of the obstacles upstream from, downstream from, or bridging the narrowest portion of the gap are asymmetrical with respect to that plane. Improvements are also realized by using obstacles that have sharp edges bounding the gaps. Other improvements are realized by selecting obstacle shapes such that the critical particle dimensions defined by the gaps in two different fluid flow directions differ.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Vacuum cleaner with a moveable divider plate
ActiveUS20070209335A1Improve efficiencyGrowth inhibitionCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentSurface cleaningVacuum cleaner
A surface cleaning apparatus comprises a dirt inlet, a handle, a cyclone separator having an outer wall, a fluid inlet downstream from the dirt air inlet and a fluid outlet, a plate having a cyclone chamber surface and positioned to substantially divide the cyclone separator into a cyclone chamber and a dirt collection chamber, the plate being removably mounted in the cyclone separator, a passage extending between the cyclone chamber and the dirt collection chamber and a fluid flow motor.
Owner:OMACHRON INTPROP
Compact dedusting apparatus
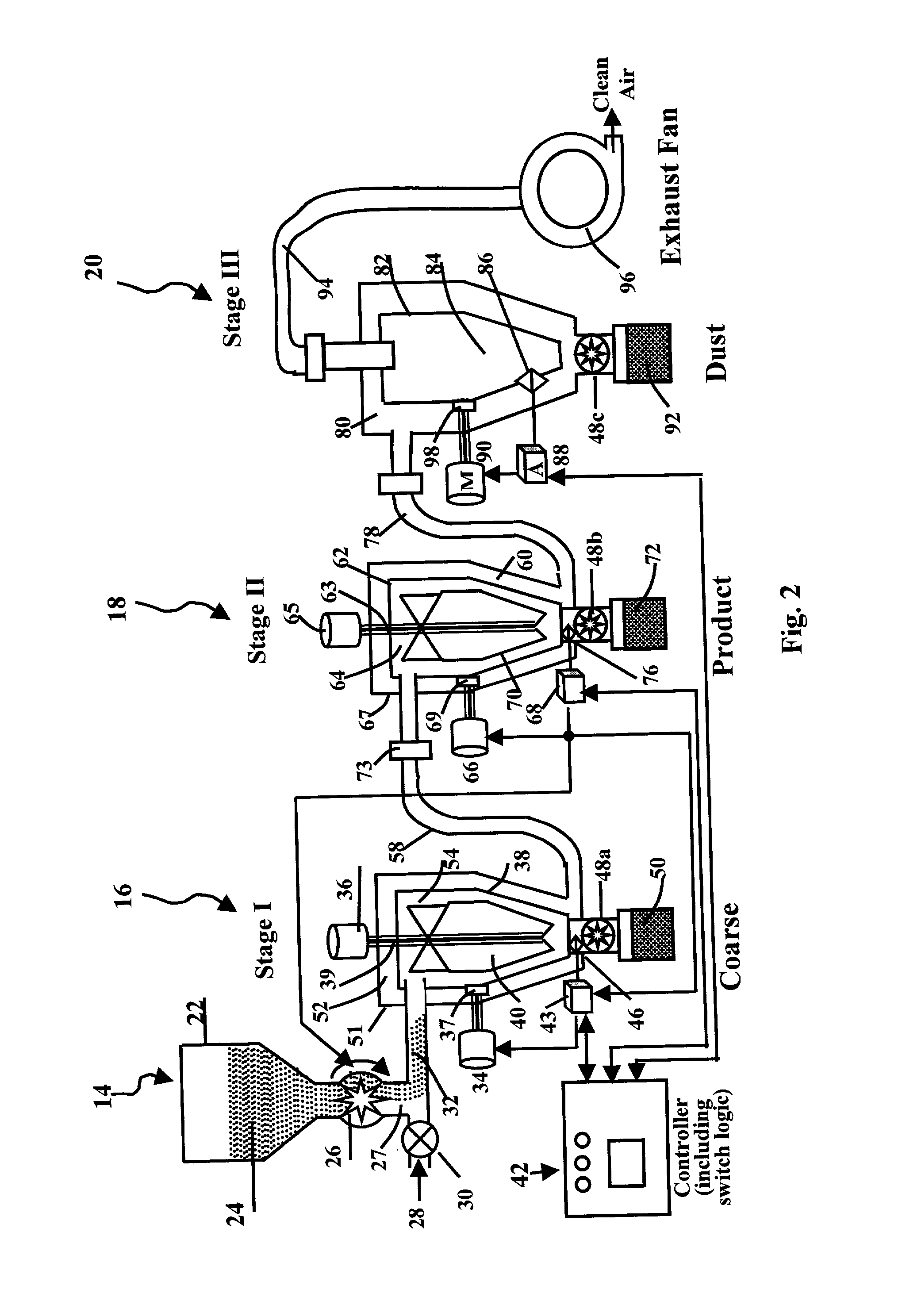
ActiveUS7380670B2Improved airflow characteristicsClean thoroughlyGas current separationMagnetic separationMagnetic fluxDust particles
A compact housing for a dedusting apparatus utilizes a magnetic flux field to disrupt the static charge attracting dust particles to product particles, which along with fluidization and counter current airflow principles that are proven to dislodge dust particles from the product, provides a highly efficient, compact deduster. The housing supports a double wash deck with product flow separated between the back-to-back primary wash decks. A deflector directing the flow of product onto the primary wash decks is provided with an extension that extends parallel to the wash deck to eliminated product bouncing off of the wash deck. The lower air outlets are eliminated, while the upper air outlets are positioned in extensions to the main housing above the product inlet opening. Air flow through the Venturi zone is enhanced by re-directing clean air directly to the backside of the Venturi panels, thereby eliminating the extraneous by-pass boxes.
Owner:PELLETRON CORP
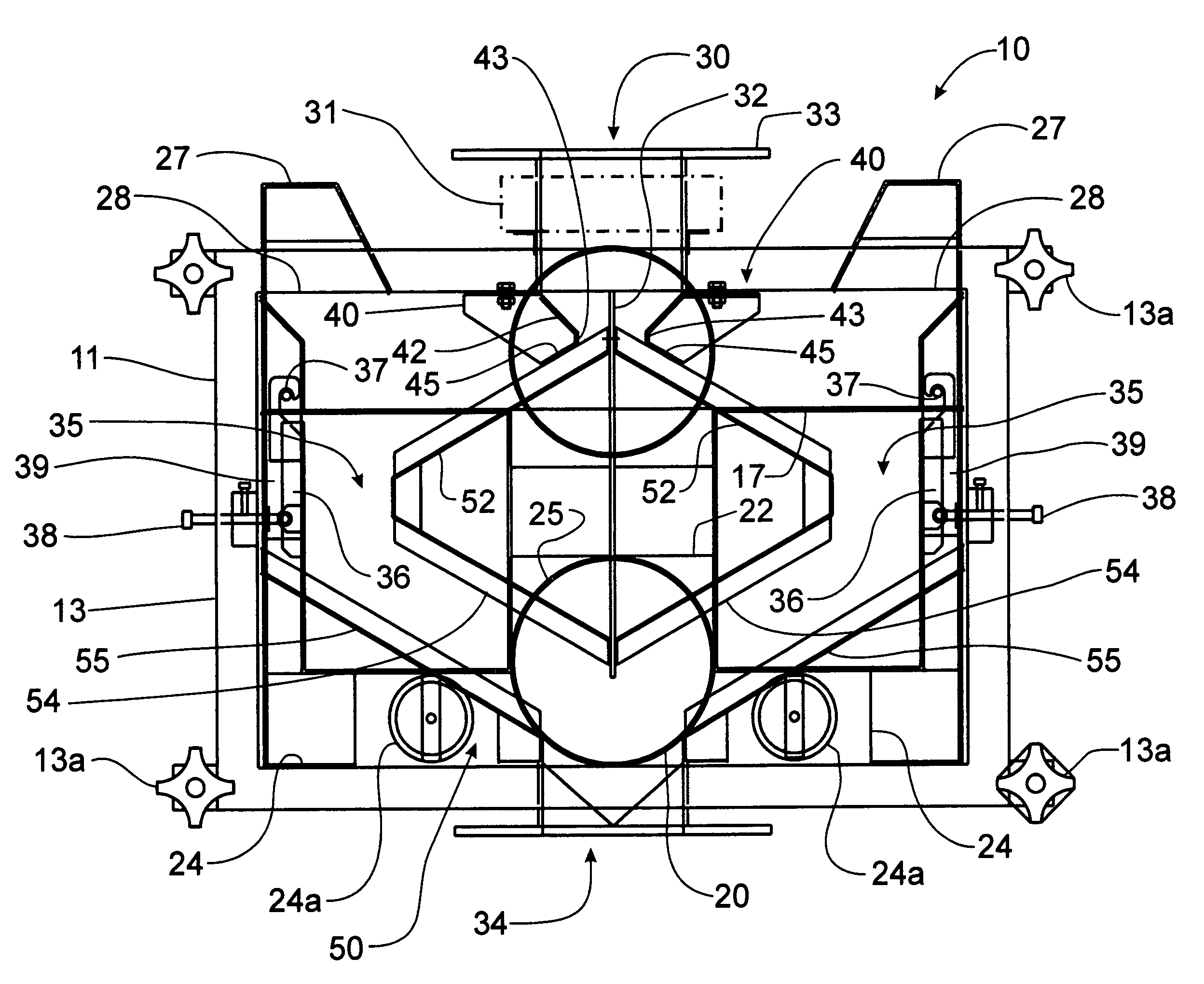
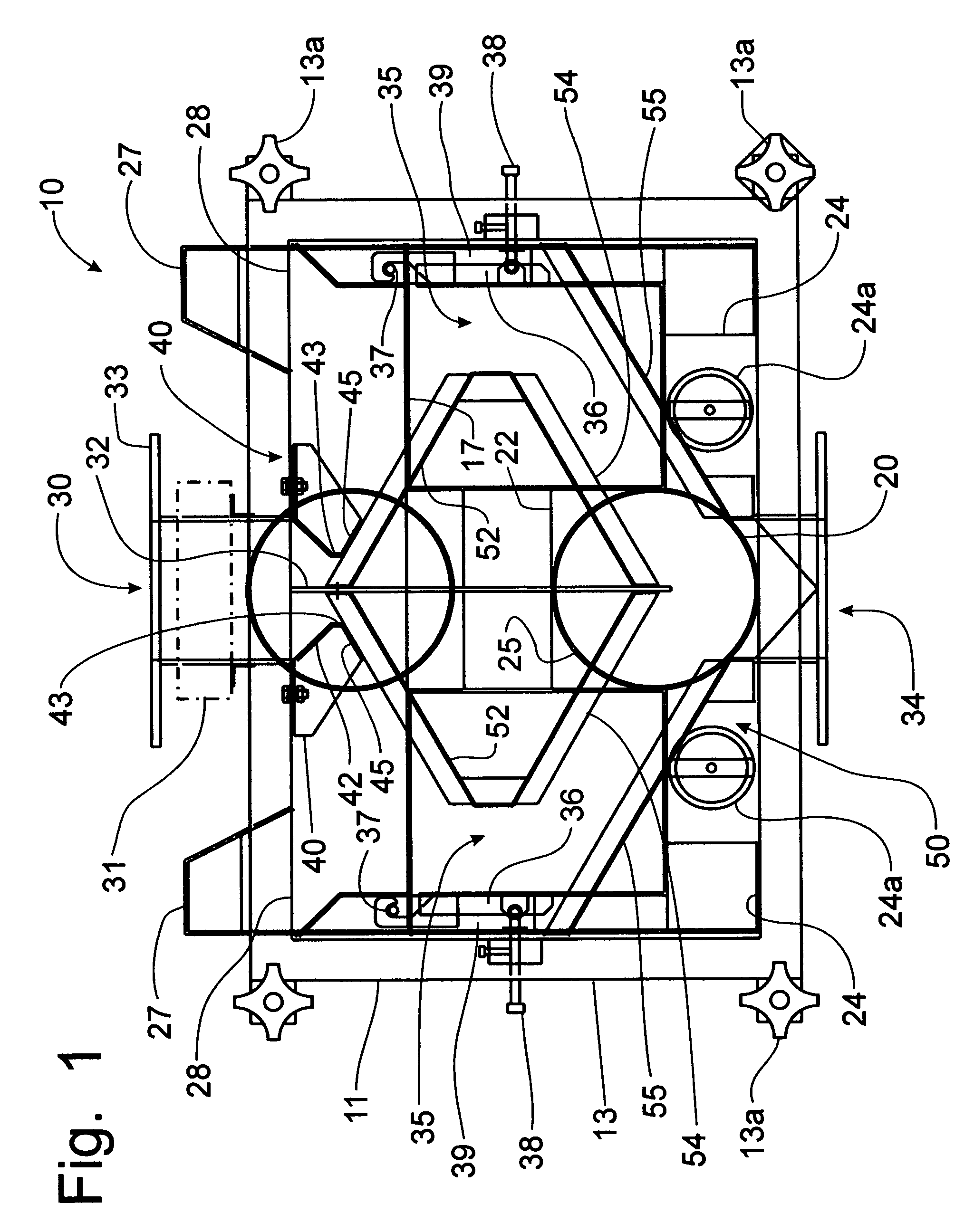
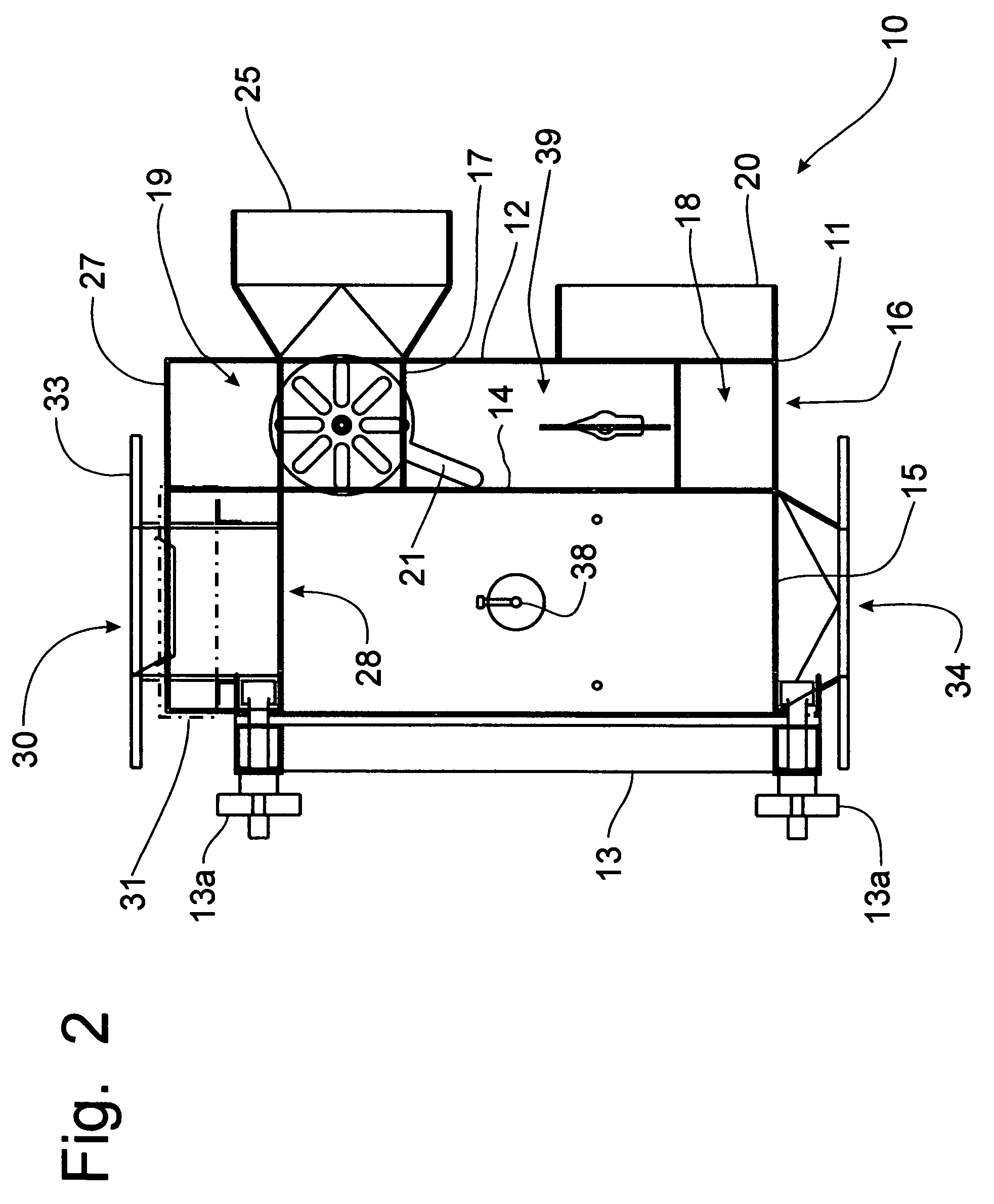
Extraction and fractionation of biopolymers and resins from plant materials
ActiveUS20060106183A1High yieldHigh purityGas current separationSolvent extractionParthenium argentatumBiopolymer
A method for the extraction, separation, fractionation and purification of biopolymers from plant materials using supercritical and / or subcritical solvent extractions is disclosed. Specifically, the process can be used for the separation of resins and rubber from guayule shrub (Parthenium argentatum), and other rubber and / or resin containing plant materials, using supercritical solvent extraction, for example supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. Additionally, polar and / or non-polar co-solvents can be used with supercritical carbon dioxide to enhance the selective extraction of resins and rubbers from the shrub.
Owner:YULEX LLC
Extraction and fractionation of biopolymers and resins from plant materials
ActiveUS7259231B2High yieldHigh purityGas current separationSolvent extractionParthenium argentatumBiopolymer
A method for the extraction, separation, fractionation and purification of biopolymers from plant materials using supercritical and / or subcritical solvent extractions is disclosed. Specifically, the process can be used for the separation of resins and rubber from guayule shrub (Parthenium argentatum), and other rubber and / or resin containing plant materials, using supercritical solvent extraction, for example supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. Additionally, polar and / or non-polar co-solvents can be used with supercritical carbon dioxide to enhance the selective extraction of resins and rubbers from the shrub.
Owner:YULEX LLC
Vacuum cleaner with a plurality of cyclonic cleaning stages
InactiveUS20070209339A1Improve efficiencyAssist in removingCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentCycloneEngineering
A portable appliance comprises a dirt inlet, first and second cyclonic stages wherein each cyclonic stage comprises a plurality of cyclones in parallel and the second cyclonic stage is downstream from the first cyclonic stage and a fluid flow motor.
Owner:OMACHRON INTPROP
Food waste disposer having a variable speed motor
The present invention provides a food waste disposer having an upper food conveying section, a motor section, a central grinding section and a controller. The upper food conveying section includes a housing forming an inlet to receive food waste. The motor section includes a switched reluctance machine having a rotor and a stator. The rotor imparts rotational movement to a rotatable shaft. The central grinding section is disposed between the food conveying section and the motor section. The food conveying section conveys food waste to the grinding section. The grinding section includes a grinding mechanism where a portion of the grinding mechanism is mounted to the rotatable shaft. The controller is electrically connected to the stator to control the switched reluctance machine. The controller is capable of directing rotational movement to the rotatable shaft and the portion of the grinding mechanism mounted to the rotatable shaft. The controller is further capable of maintaining the rotational movement of the rotatable shaft at more than one rotational speed. The present invention also includes methods of operating a variable speed motor in different operational modes such as idle mode and anti-jamming mode.
Owner:EMERSON ELECTRIC CO
Polycrystalline silicon and method for production thereof
Polycrystalline silicon of the invention contains: (a) polycrystalline silicon fragments, wherein at least 90% of the fragments have a size from 10 to 40 mm, (b) <15 ppmw of silicon dust particles having particle sizes <400 μm; (c) <14 ppmw of silicon dust particles having particle sizes <50 μm; (d) <10 ppmw of silicon dust particles having particle sizes <10 μm; (e) <3 ppmw of silicon dust particles having particle sizes <1 μm; and (f) surface metal impurities in an amount ≦0.1 ppbw and ≧100 ppbw. A polycrystalline silicon production method of the invention includes fracturing polycrystalline silicon deposited on thin rods in a Siemens reactor into fragments; classifying the fragments by size; and treating the fragments with compressed air or dry ice to remove silicon dust from the fragments without wet chemical cleaning.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
System for separating solids from a fluid stream
InactiveUS7514011B2Easy to transportMaximize impactLiquid separation auxillary apparatusSingle direction vortexSpiral bladeSlurry
Owner:DEL
Bump array device having asymmetric gaps for segregation of particles
ActiveUS8579117B2Easy to operateReduce gapGas current separationComponent separationEngineeringAsymmetry
The disclosure relates to obstacle array devices (also known as bump array devices) for separating populations of particles by size. Improvements over previous obstacle array devices are realized by causing the fluid velocity profile across gaps between obstacles to be asymmetrical with respect to the plane that bisects the gap and is parallel to the direction of bulk fluid flow. Such asymmetry can be achieved by selecting the shape(s) of the obstacles bounding the gap such that the portions of the obstacles upstream from, downstream from, or bridging the narrowest portion of the gap are asymmetrical with respect to that plane. Improvements are also realized by using obstacles that have sharp edges bounding the gaps. Other improvements are realized by selecting obstacle shapes such that the critical particle dimensions defined by the gaps in two different fluid flow directions differ.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF PRINCETON UNIV
Dynamic filtration method and apparatus for separating nano powders
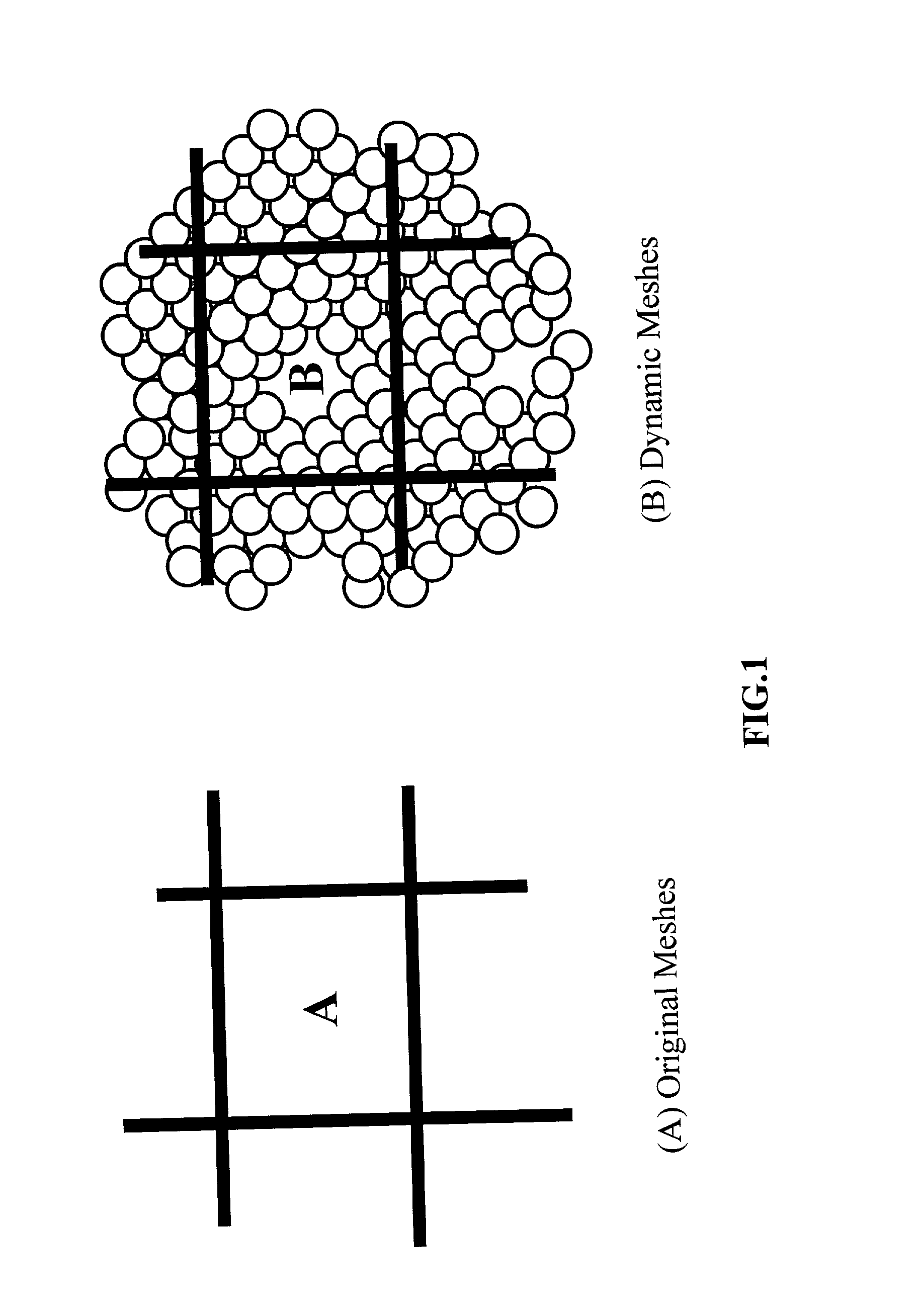
A method and apparatus for separating nanometer-sized particles of a powder. The method includes (a) feeding the powder particles into a pressurized gas stream which carries the particles into a first stage filter device of a multiple-stage separator system; (b) operating the first stage filter device to remove and collect coarse particles and a filter device in at least another stage to remove and collect finer particles of the powder; the filter device having a dynamic filter which is composed of (b1) a mesh of a multiplicity of openings with the opening size at least two times larger than the average size of the particles, (b2) vibration devices or shakers to shake off the particles that may otherwise clog up the mesh openings, (b3) size sensors to measure the sizes of the particles collected by the filter devices, and (b4) a controller to regulate the operations of the shakers and sensors in order to form desired dynamic mesh holes for the purpose of filtering out the coarse particles in the first stage or the finer particles in another stage; and (c) operating a dust collector to exhaust the residual gas, allowing the finest particles of the powder to be separated and collected.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
Process for producing dispersions
InactiveUS6991190B2Simple and economic isolationGas current separationFlow mixersWater vaporAtmosphere
A finely divided, stable dispersion of a solid is produced by: spraying at least two streams of a preliminary dispersion, each through a separate nozzle by pumps, onto a collision point in a reactor chamber enclosed by a reactor housing; passing water vapor through an opening into the reactor chamber so that a vaporous atmosphere consisting mainly of water vapor prevails in the reactor chamber; and removing the finely divided dispersion and a) vapor, b) partially condensed vapor consisting mainly of water or c) a combination of a) and b) from the reactor chamber by excess pressure of an incoming water vapor on the gas inlet side; wherein the solid has an average particle size of from 10 nm to 10 μm.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Apparatus and method for circular vortex air flow material grinding
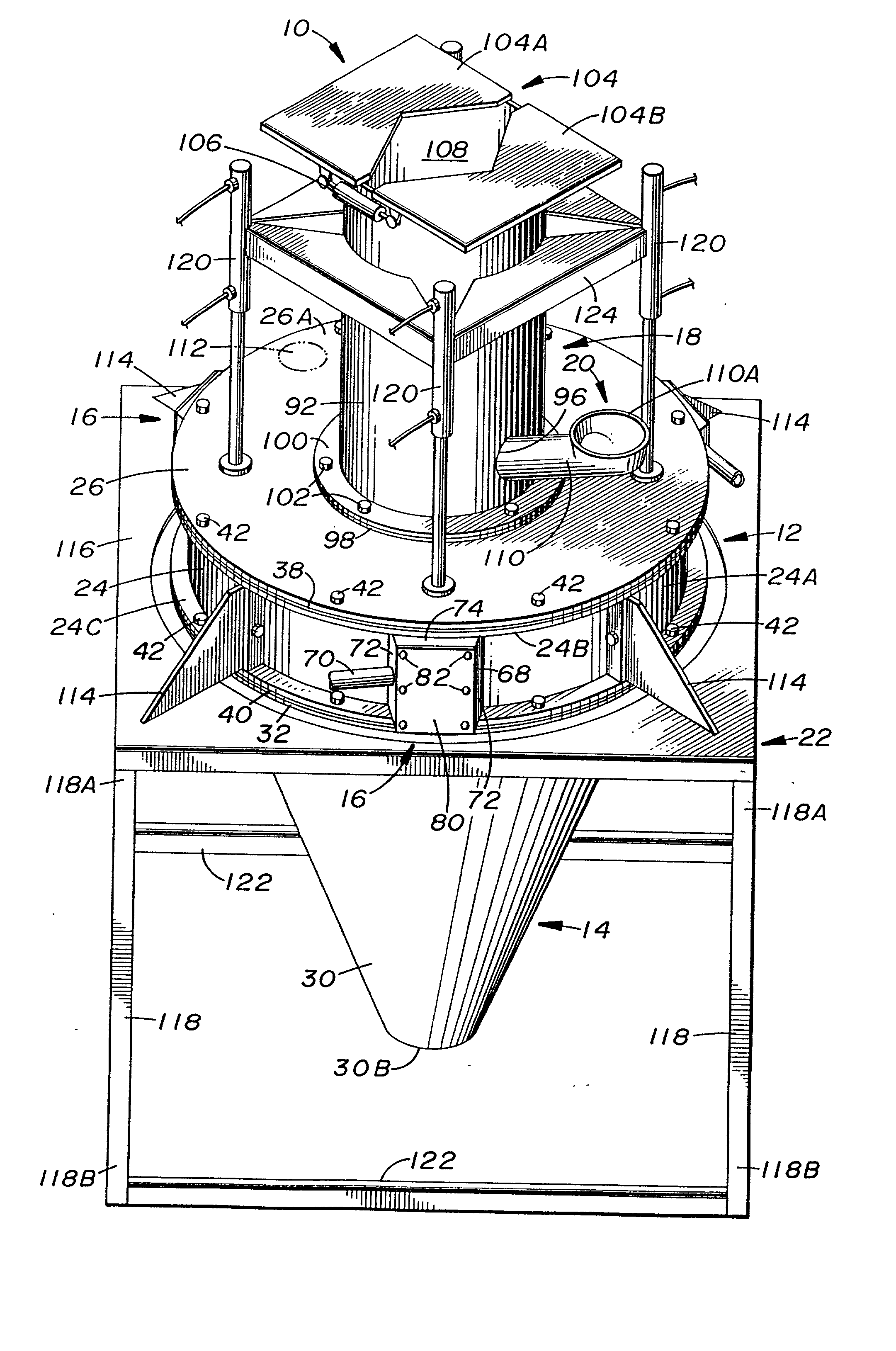
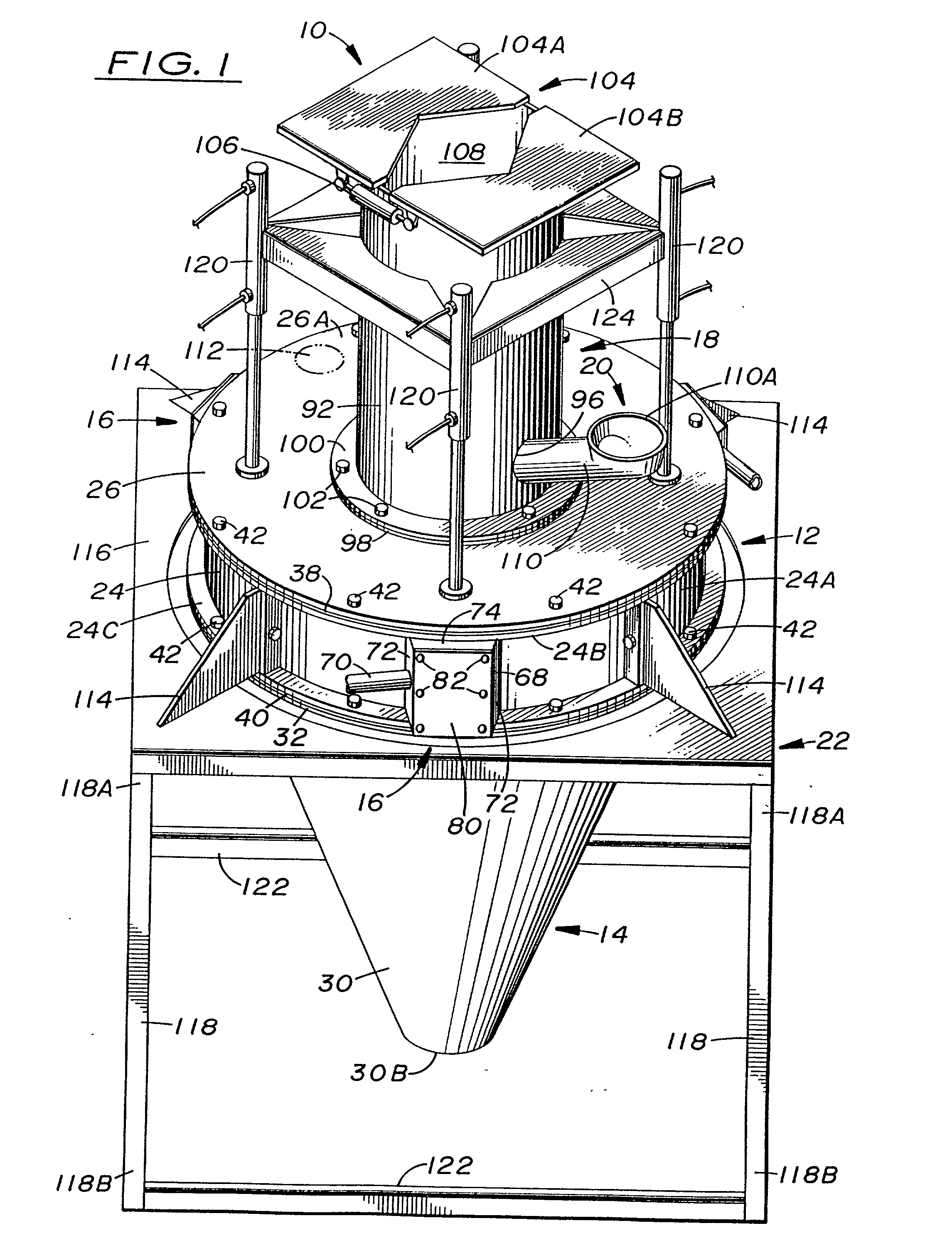
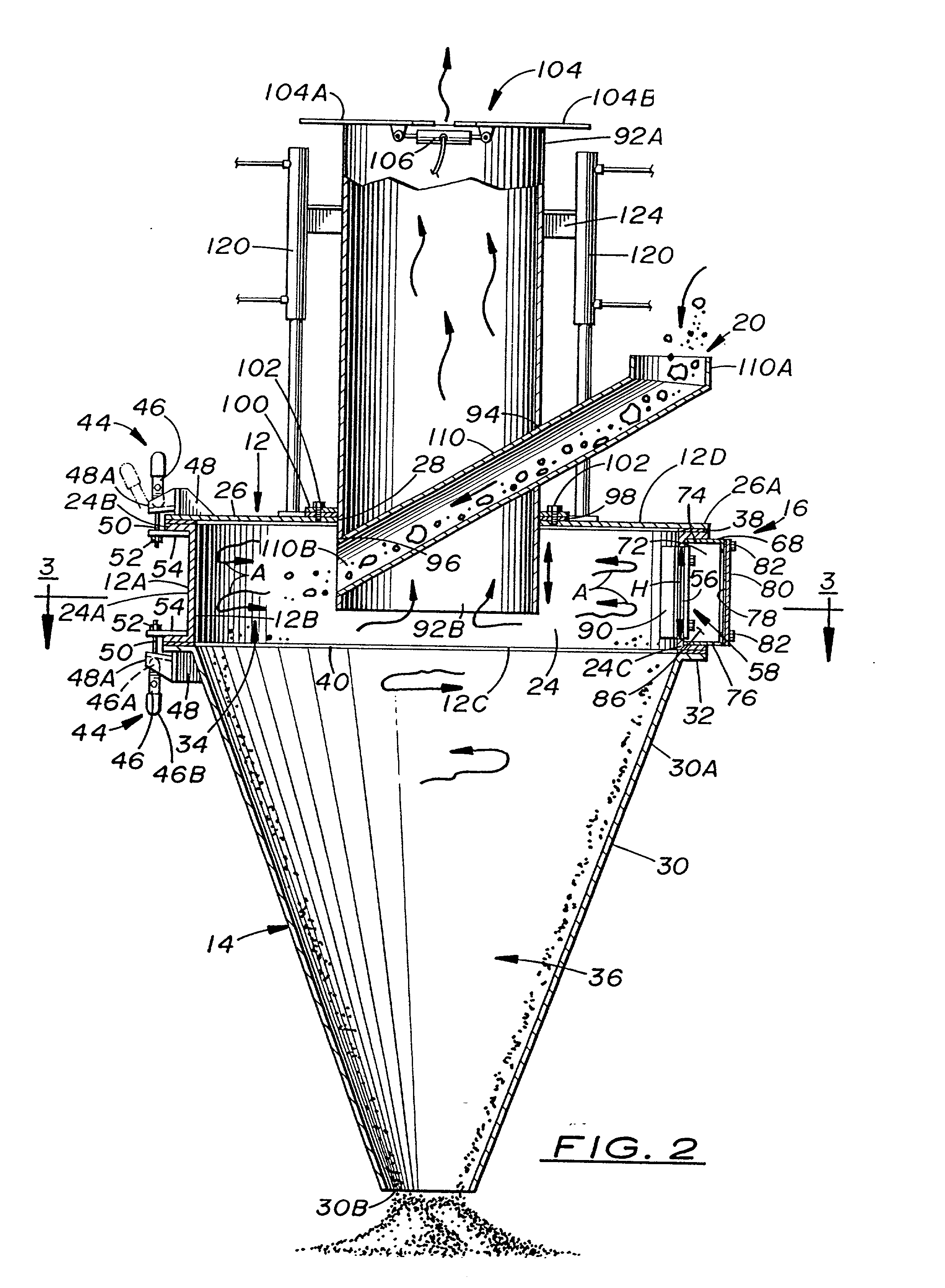
InactiveUS20020027173A1Easy constructionEliminate needGas current separationGrain millingEngineeringAirflow
A material grinding apparatus (10) includes an annular upper enclosure (12) defining an upper chamber (34) into which material to be ground is introduced from above, a conical lower enclosure (14) defining a lower chamber (36) and supported in tandem with the upper enclosure (12), and one or more angled slots (56) defined in the sidewall of the upper enclosure (12) through which compressed air is introduced relatively circumferentially into the upper chamber (34) so as to generate a circular vortex flow of air and material in the upper enclosure (12) for grinding and drying to take place. The air flow is exhausted by a pipe (92) through an upper end of the upper enclosure (12) and the dried ground material is discharged through an open lower end of the lower enclosure (14). The lower enclosure (14) is a downward continuation and extension of the upper enclosure (12) so as not to extend upwardly into nor past the upper chamber (34) thereof.
Owner:VORTEX DEHYDRATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com