Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101 results about "Motor commands" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Motor command Defines a rotational or linear motor using an element on a selected part. You use motor features to help you observe how a set of under-constrained parts will move relative to the part you define as a motor.
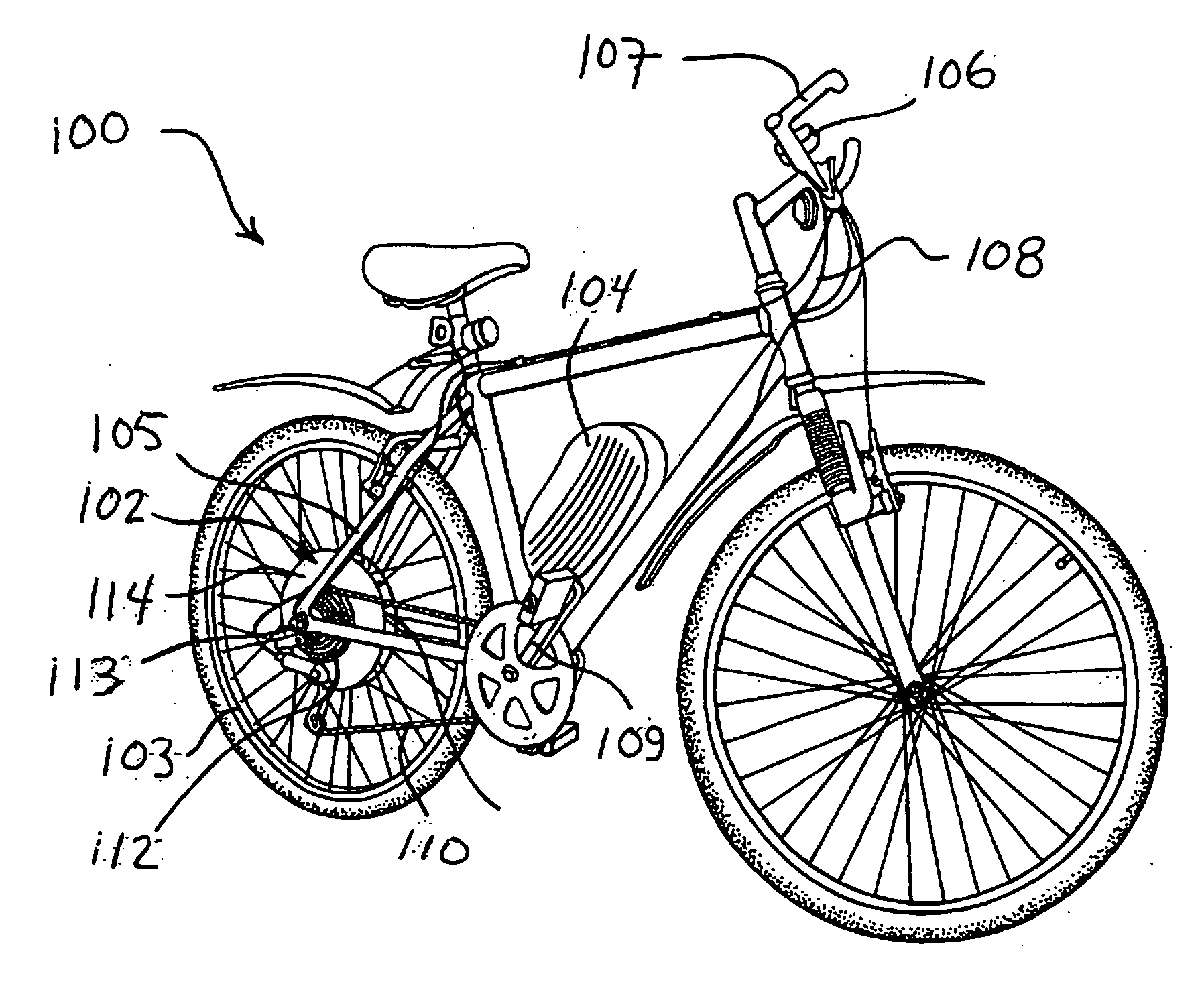
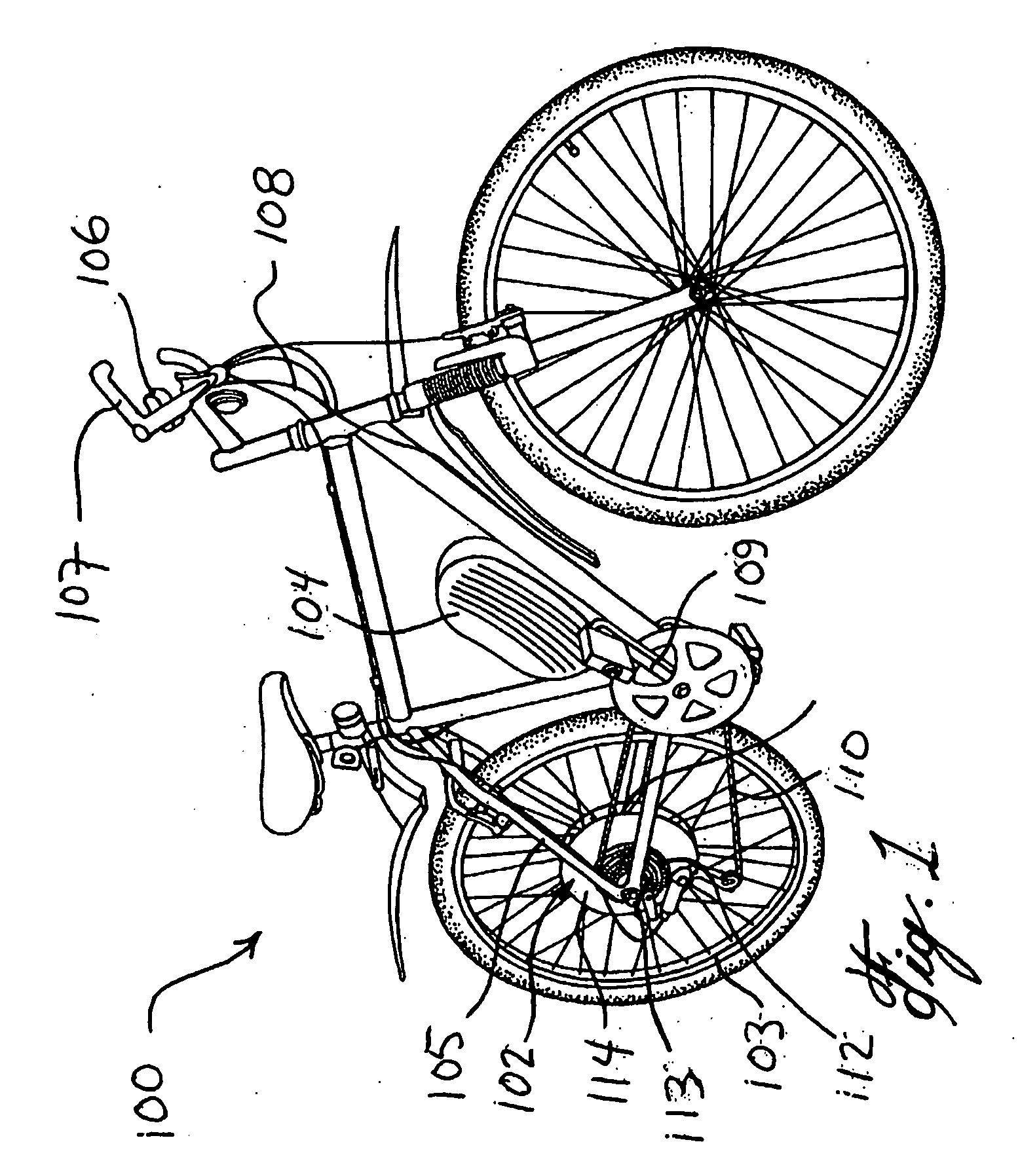
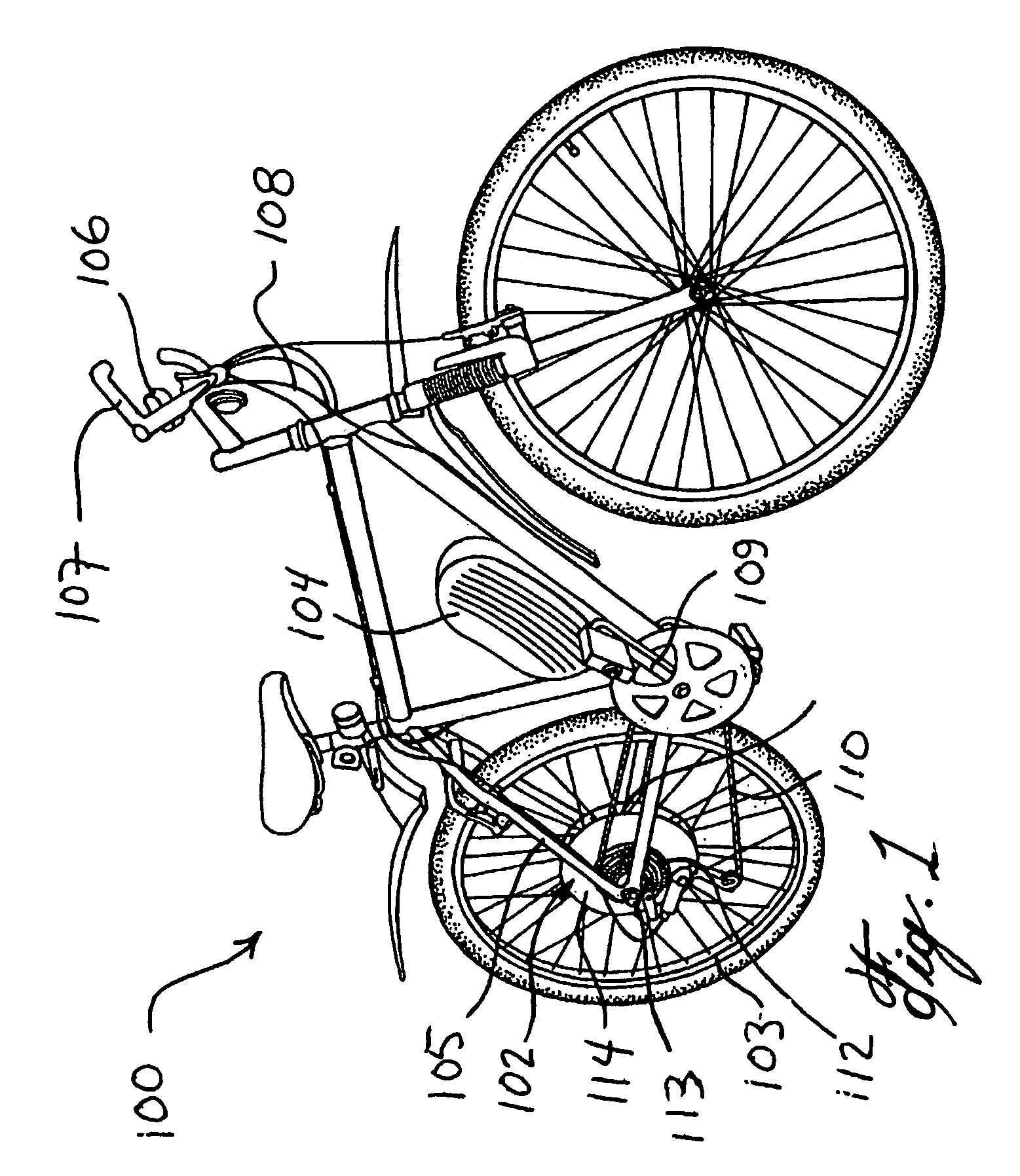
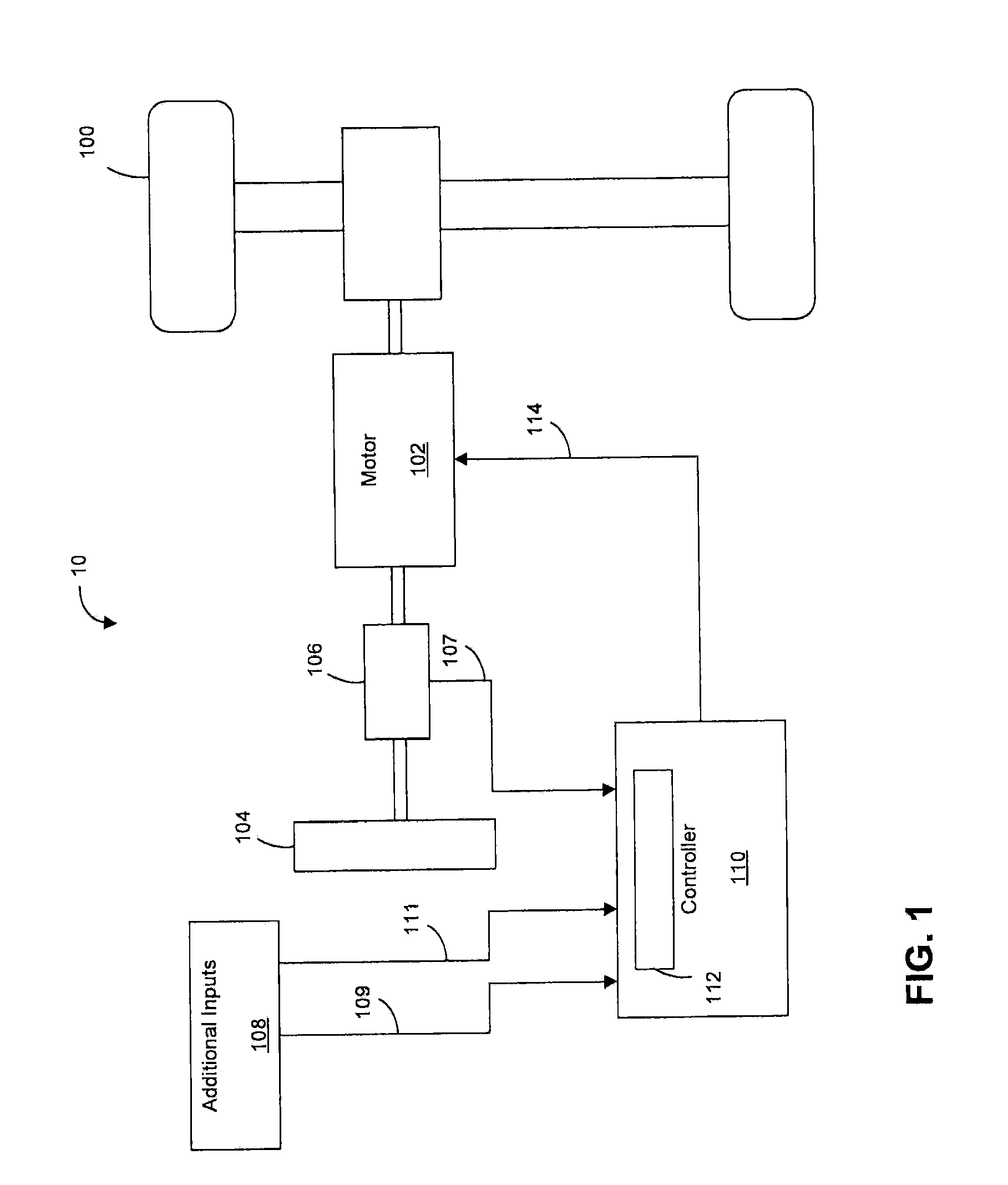
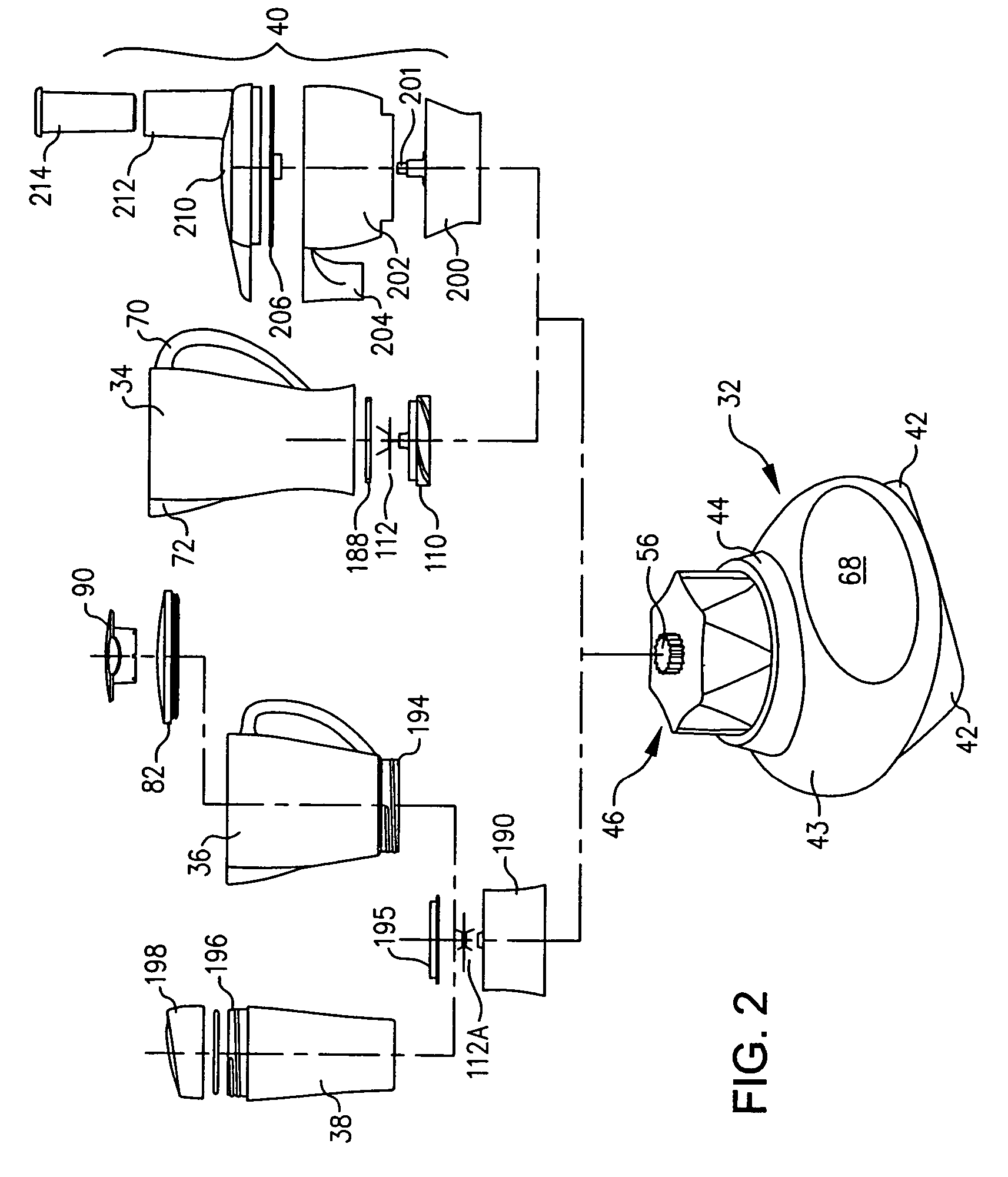
Energy Management System for Motor-Assisted User-Propelled Vehicles
InactiveUS20080071436A1Battery energy to longerComfortable rideVehicle testingVehicle fittingsUser inputMotor commands
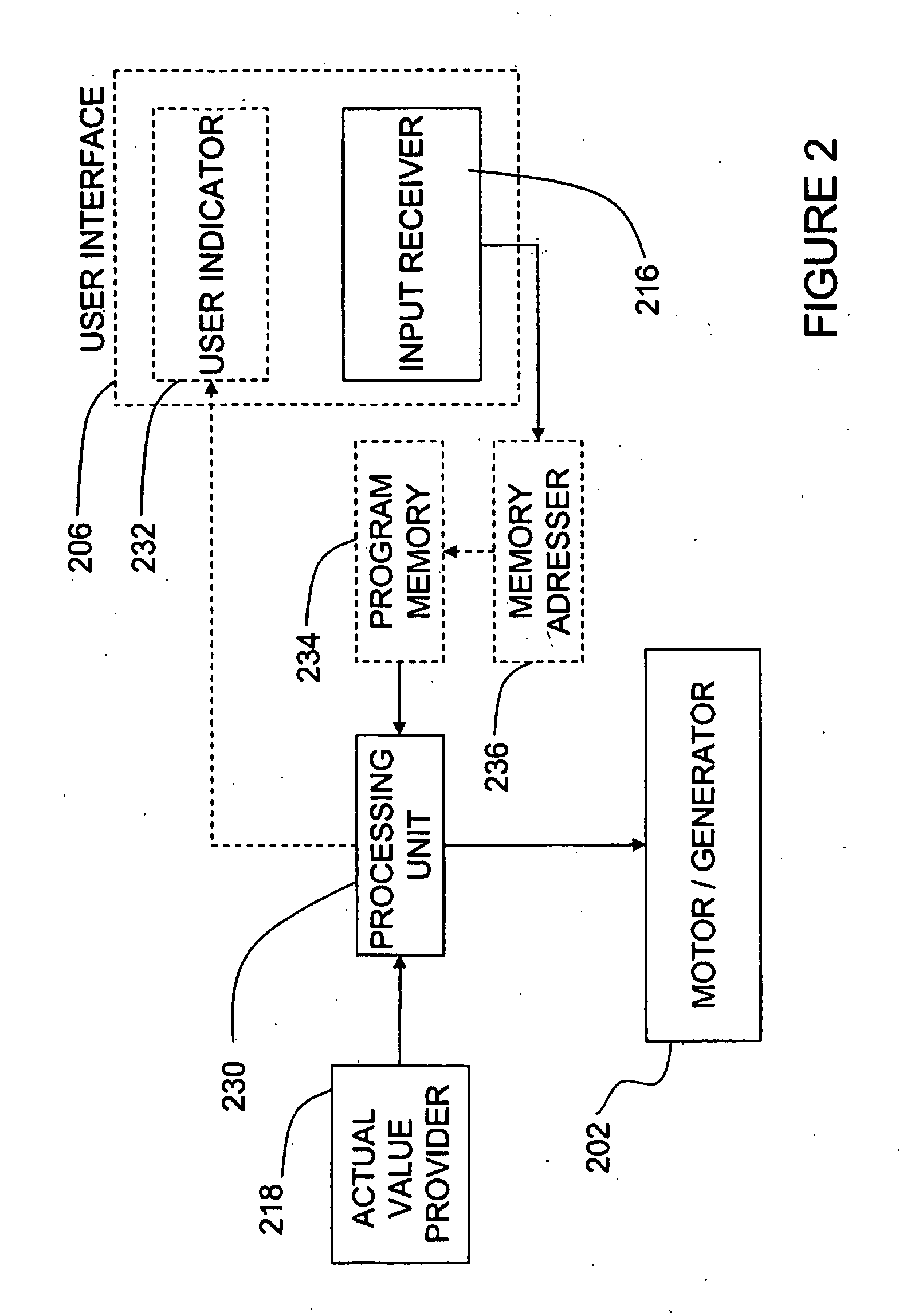
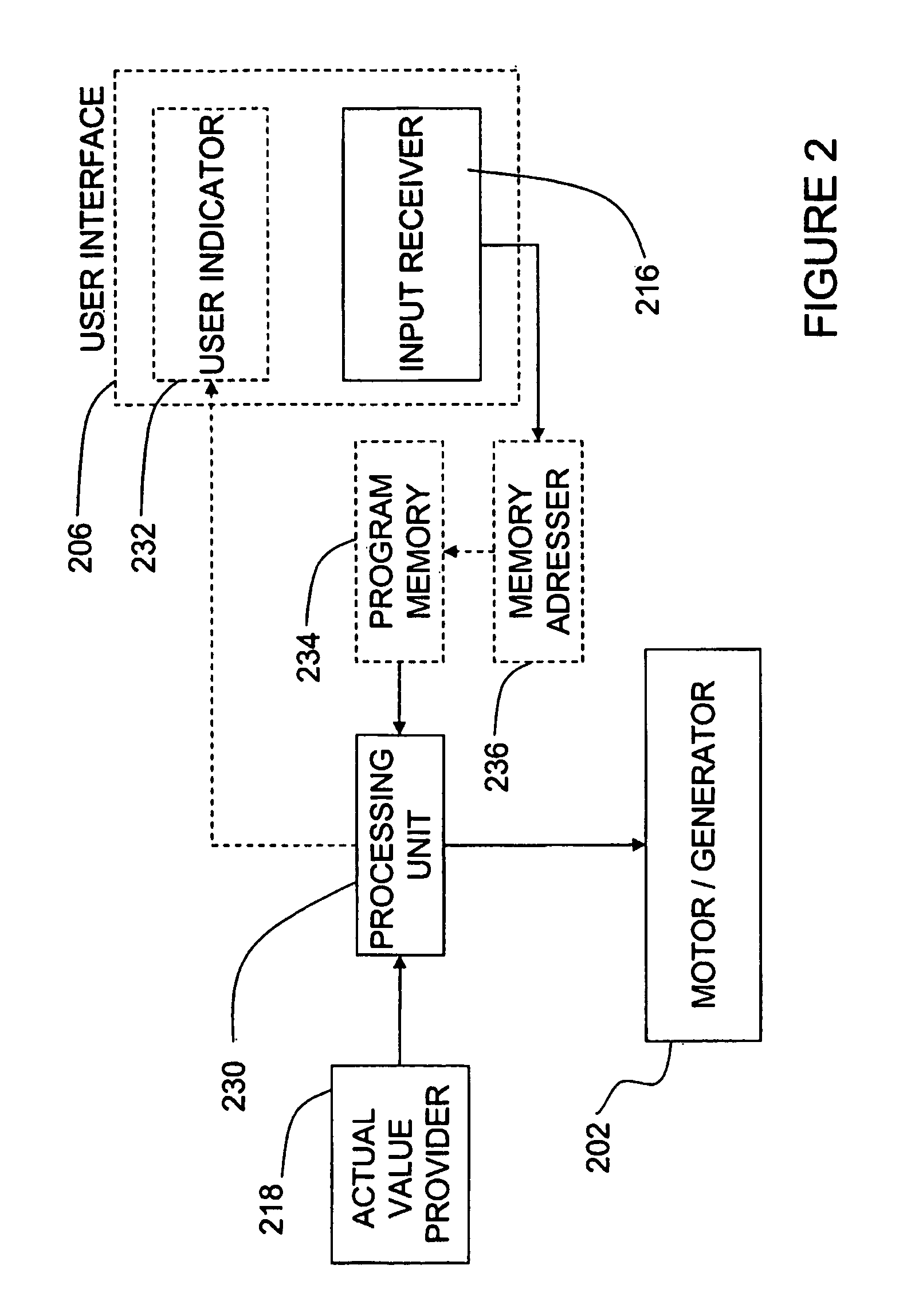
An energy management system for a motor-assisted user-propelled vehicle comprising a motor capable of assisting in propelling the vehicle and a rechargeable power supply for supplying energy to the motor. The system comprises: a user input for providing a desired value for each of at least one control parameter related to the user; a sensor for each control parameter for obtaining an actual value of the control parameter; a value comparator for receiving the desired value and the actual value of each control parameter and comparing them to generate a comparison signal for each control parameter; a command generator for generating a motor command using at least one comparison signal; and a motor controller for operating the motor, using the motor command, either to assist in propelling the vehicle, or act to recharge the power supply, in a way to bring the actual value closer to the desired value.
Owner:9141 7030 QUEBEC +2
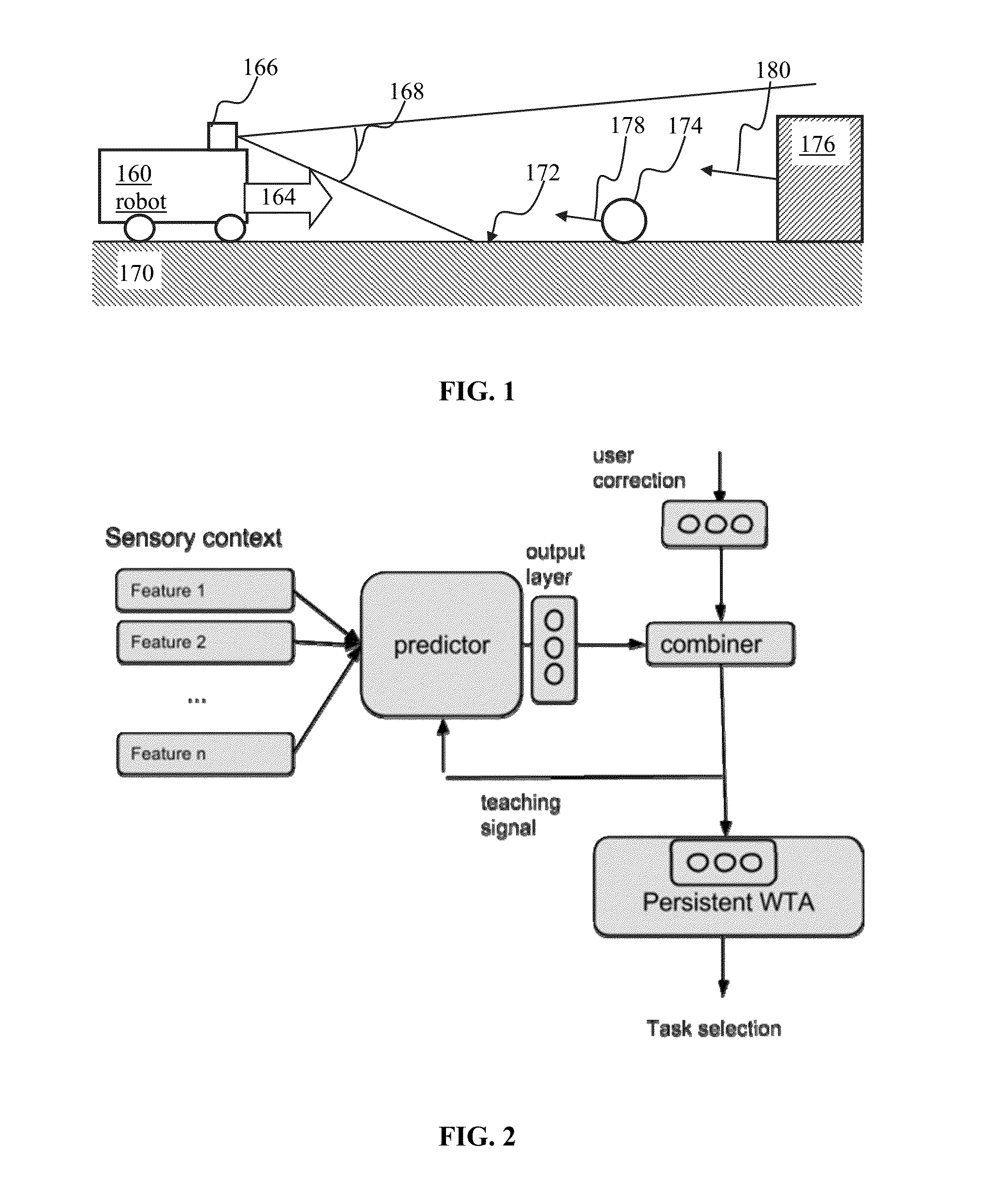
Apparatus and methods for training of robots
ActiveUS20160096272A1Programme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processVision basedCharacteristic space
A random k-nearest neighbors (RKNN) approach may be used for regression / classification model wherein the input includes the k closest training examples in the feature space. The RKNN process may utilize video images as input in order to predict motor command for controlling navigation of a robot. In some implementations of robotic vision based navigation, the input space may be highly dimensional and highly redundant. When visual inputs are augmented with data of another modality that is characterized by fewer dimensions (e.g., audio), the visual data may overwhelm lower-dimension data. The RKNN process may partition available data into subsets comprising a given number of samples from the lower-dimension data. Outputs associated with individual subsets may be combined (e.g., averaged). Selection of number of neighbors, subset size and / or number of subsets may be used to trade-off between speed and accuracy of the prediction.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
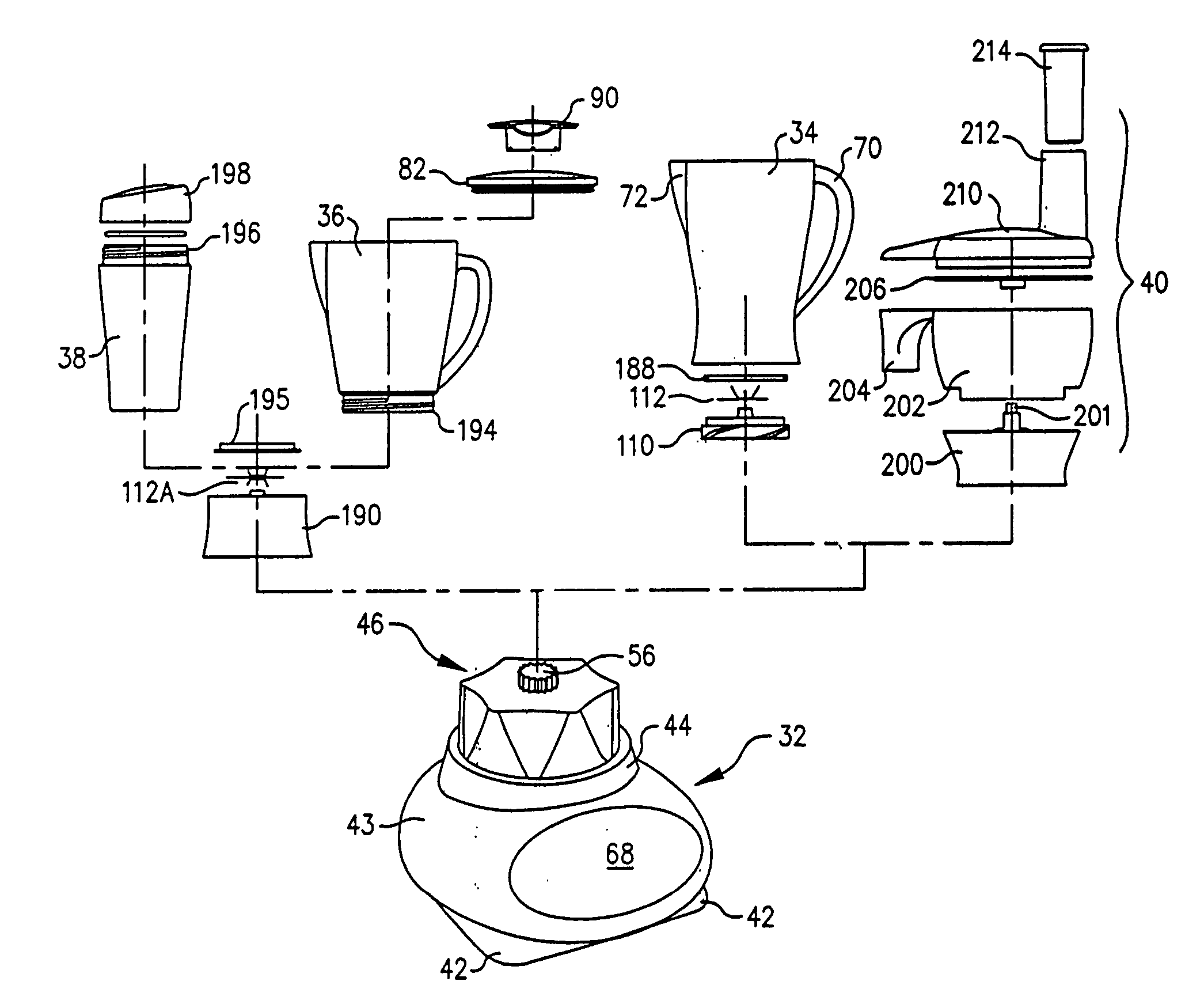
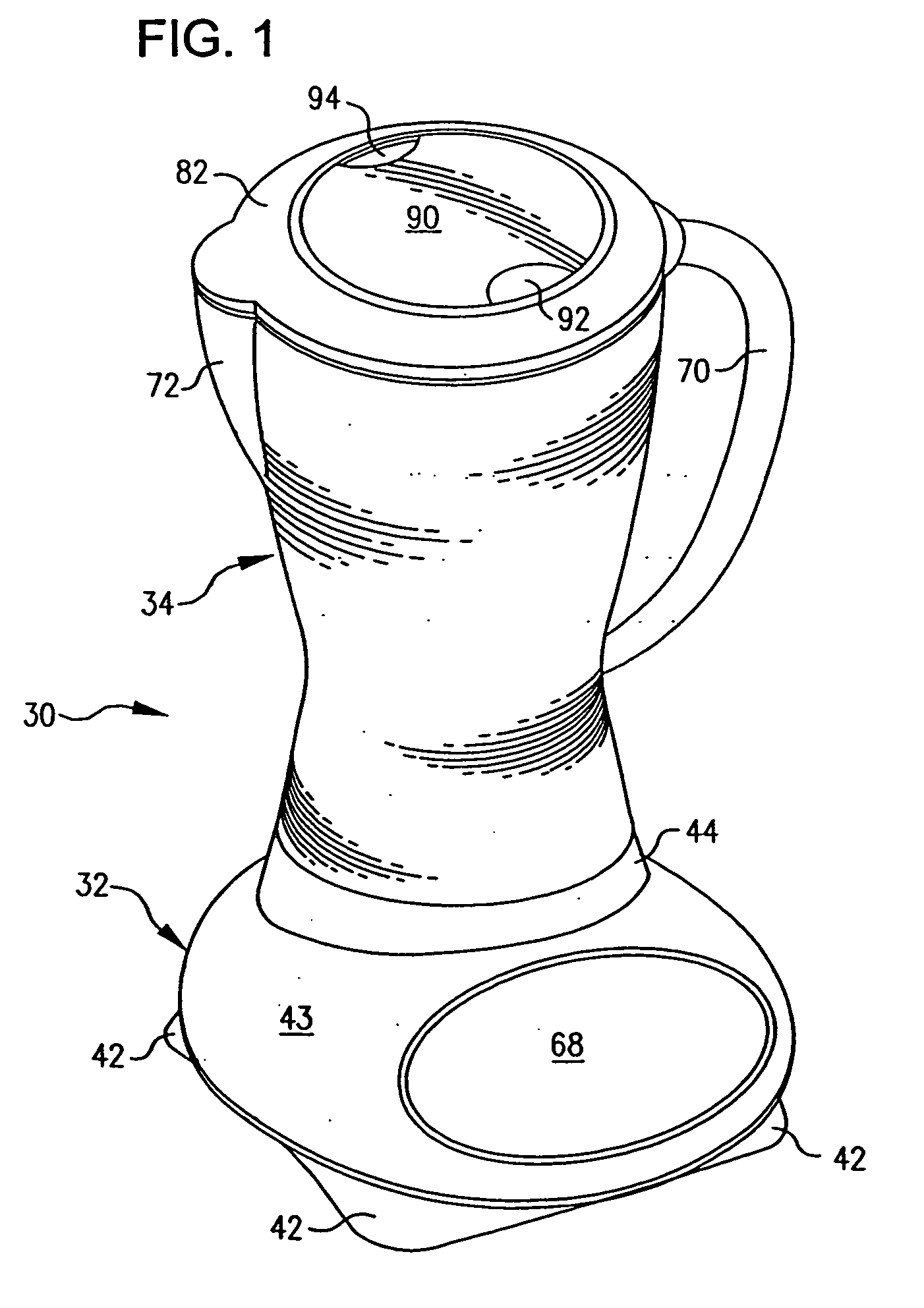
Blender base with food processor capabilities
InactiveUS20050068846A1Avoid vibrationImprove stabilityGas current separationTransportation and packagingMicrocontrollerLiquid-crystal display
A blender base that may be used with a food processor container, a blender container, and a single use beverage container. The blender container includes a novel blade unit having a food processor-style blade and blender type blades. Programs with preprogrammed motor commands for desired operations are stored in memory and may be selected by a user on a user interface. The user interface may include a liquid crystal display, or function switches and light emitting diodes. Upon selection of a particular pre-defined function, the microcontroller retrieves the appropriate program from the read only memory and specifies the preprogrammed motor commands to accomplish the selected function.
Owner:WULF JOHN DOUGLAS +5
Stabilizing unintentional muscle movements
A system and method for stabilizing unintentional muscle movements are disclosed. In a first aspect, a non-contact sensing system comprises a stabilization unit, at least one non-contact position sensor coupled to the stabilization unit, and a processing unit coupled to the at least one non-contact position sensor, wherein the processing unit transmits motion commands to the stabilization unit to cancel unintentional muscle movements. In a second aspect, the method comprises a processing unit of a non-contact sensing system receiving position data of a stabilization unit that is detected by at least one non-contact position sensor and filtering the position data to identify the unintentional muscle movements. The method includes modeling the position data to create a system model and determining motor commands based upon the system model to cancel the unintentional muscle movements.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
Energy management system for motor-assisted user-propelled vehicles
InactiveUS7706935B2Battery energy to longerComfortable rideVehicle testingVehicle fittingsUser inputMotor commands
An energy management system for a motor-assisted user-propelled vehicle comprising a motor capable of assisting in propelling the vehicle and a rechargeable power supply for supplying energy to the motor. The system comprises: a user input for providing a desired value for each of at least one control parameter related to the user; a sensor for each control parameter for obtaining an actual value of the control parameter; a value comparator for receiving the desired value and the actual value of each control parameter and comparing them to generate a comparison signal for each control parameter; a command generator for generating a motor command using at least one comparison signal; and a motor controller for operating the motor, using the motor command, either to assist in propelling the vehicle, or act to recharge the power supply, in a way to bring the actual value closer to the desired value.
Owner:9141 7030 QUEBEC +2
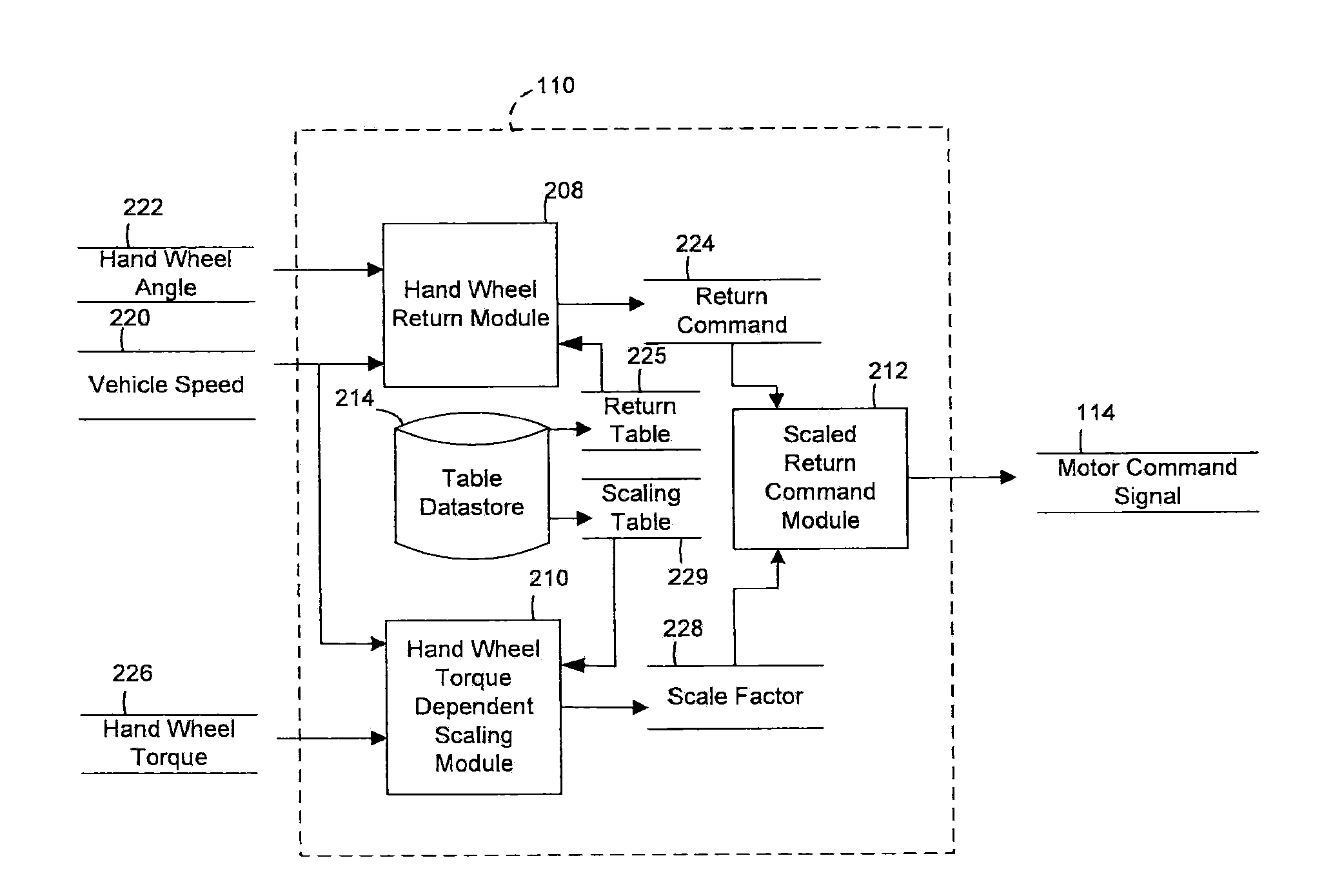
Methods and systems involving return torque
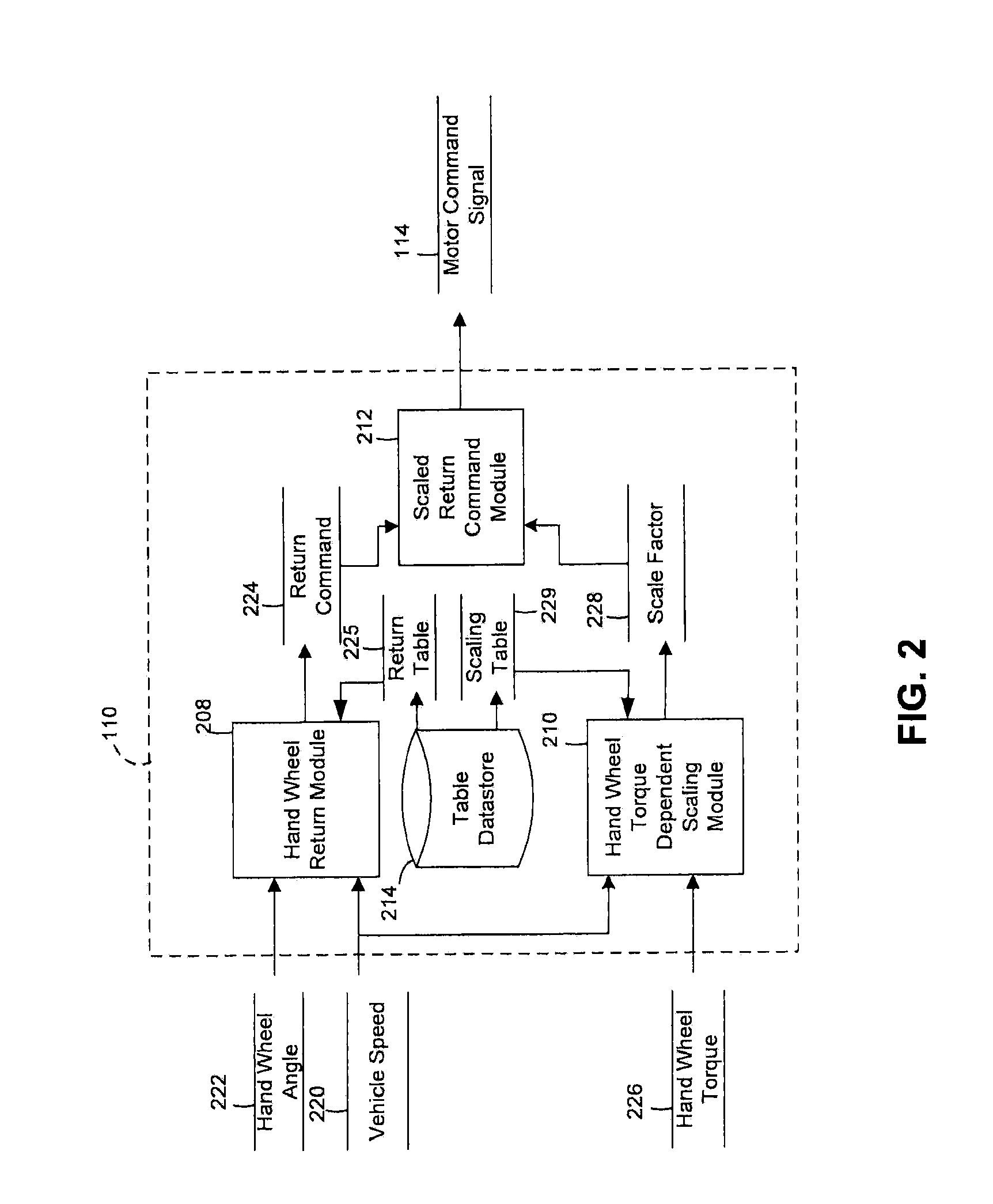
ActiveUS20100286869A1Digital data processing detailsSteering initiationsMotor commandsPower steering
A method of controlling a motor of a power steering system is provided. The method includes: estimating a scale factor based on a vehicle speed and a hand wheel torque; applying the scale factor to a return command; and generating a motor command signal based on the applying the scale factor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
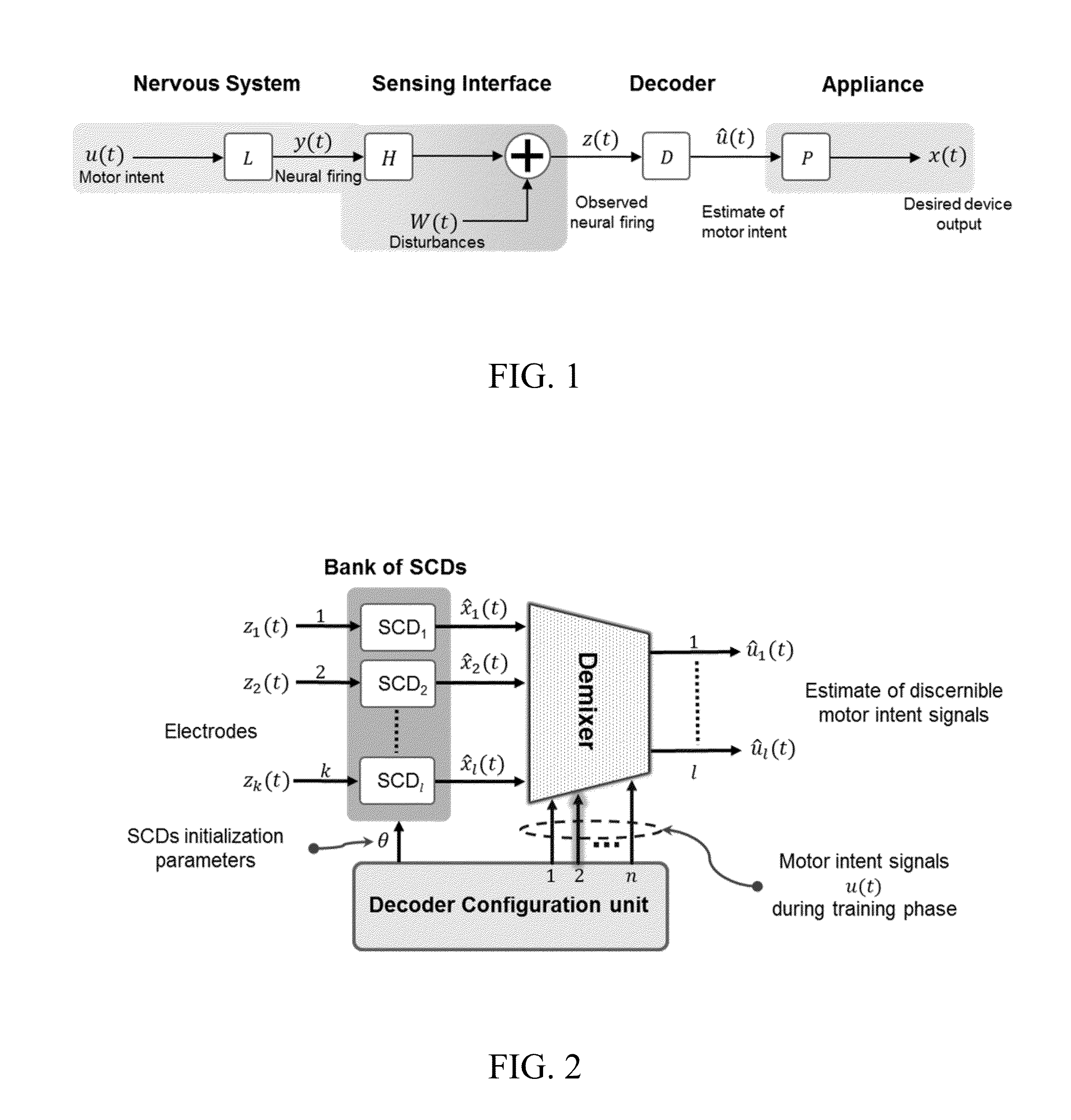
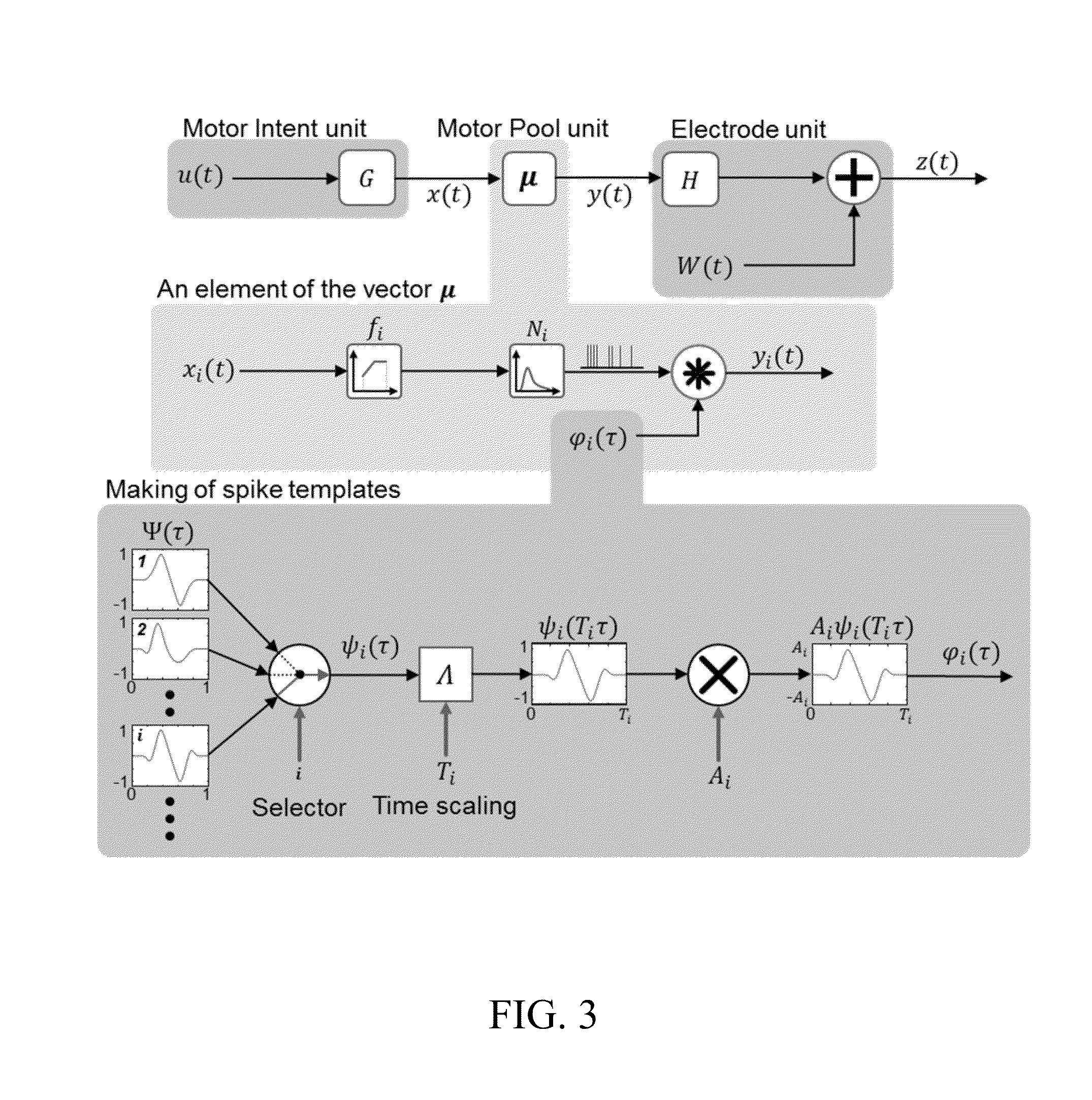
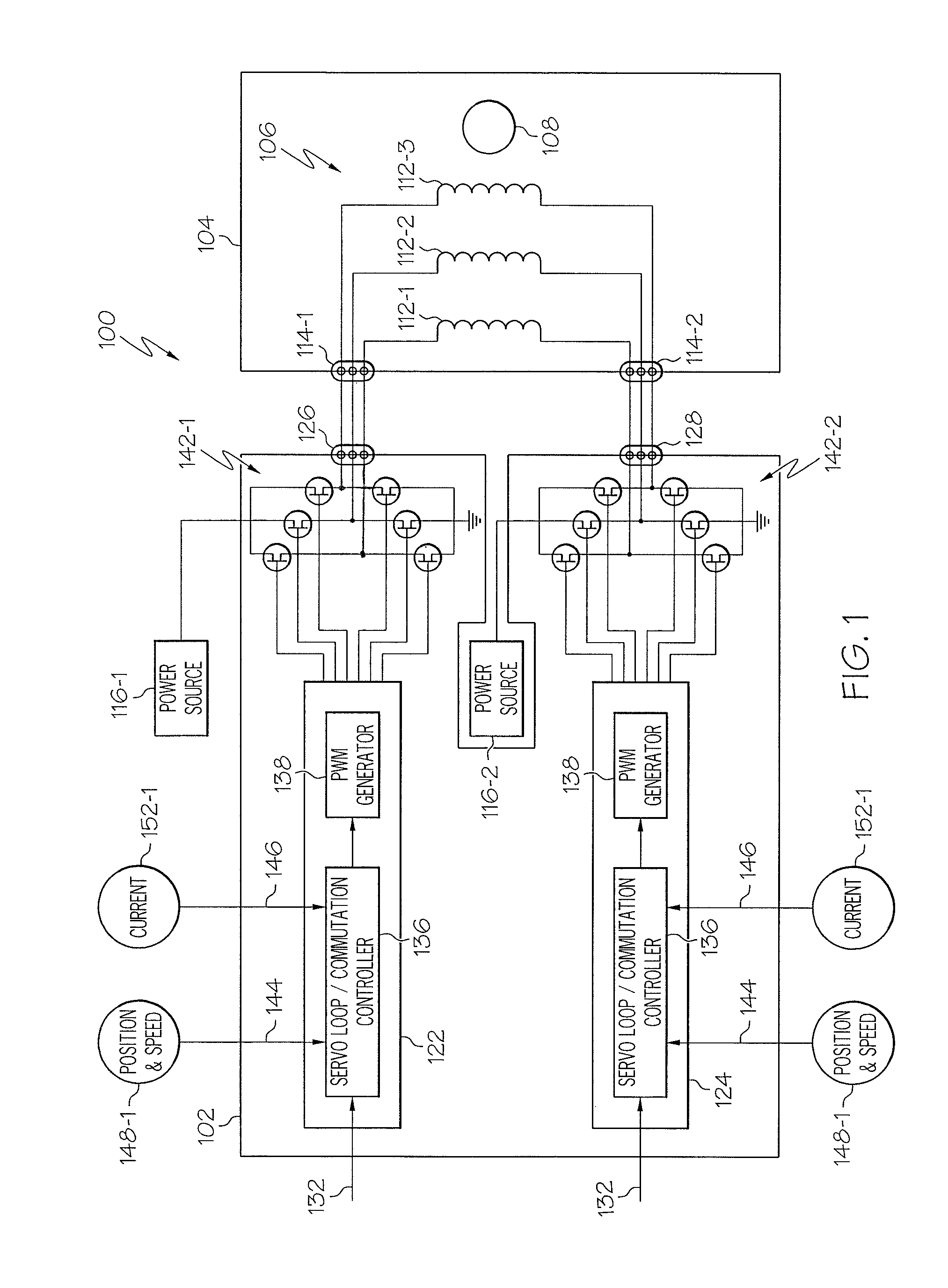
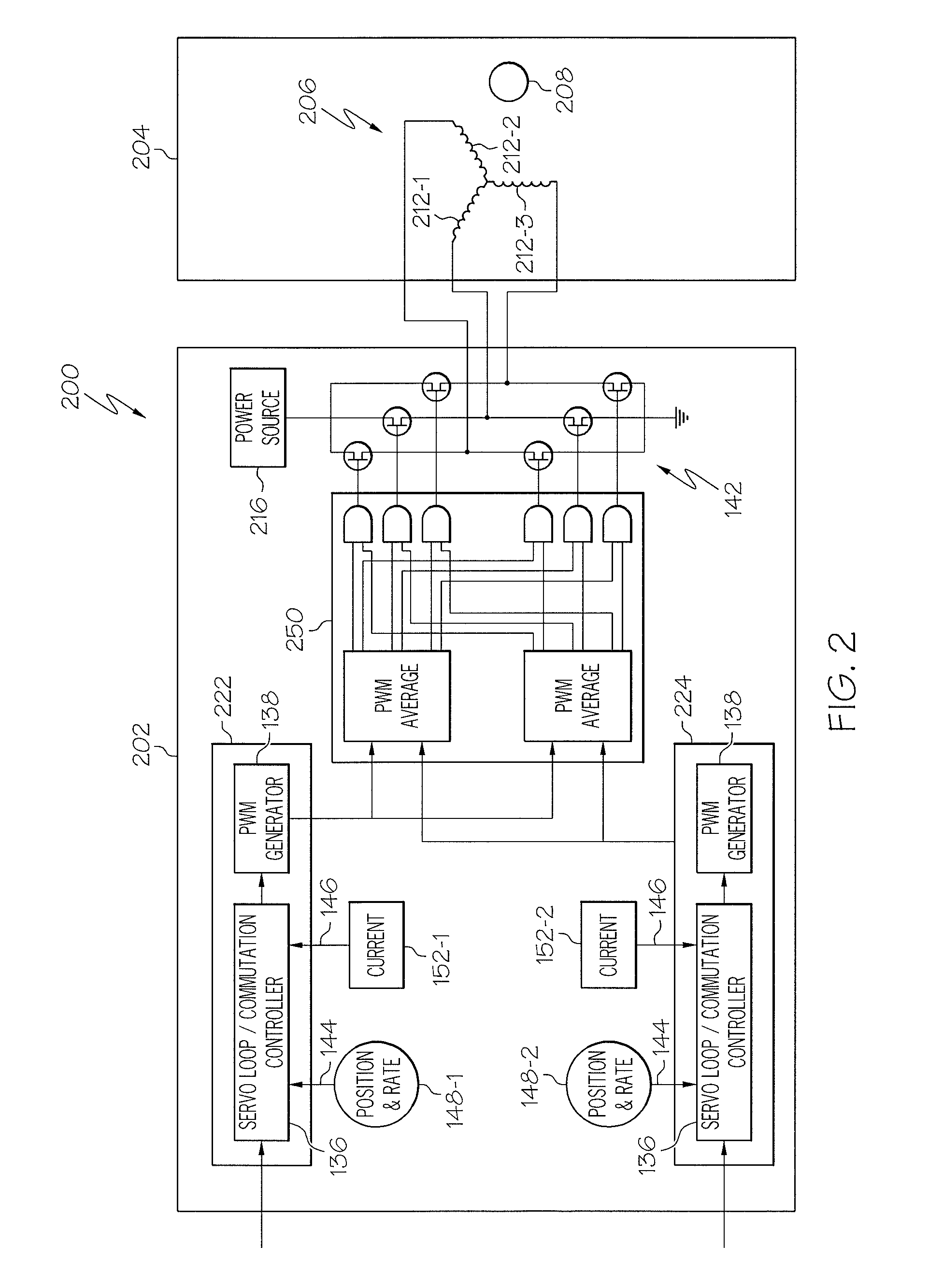
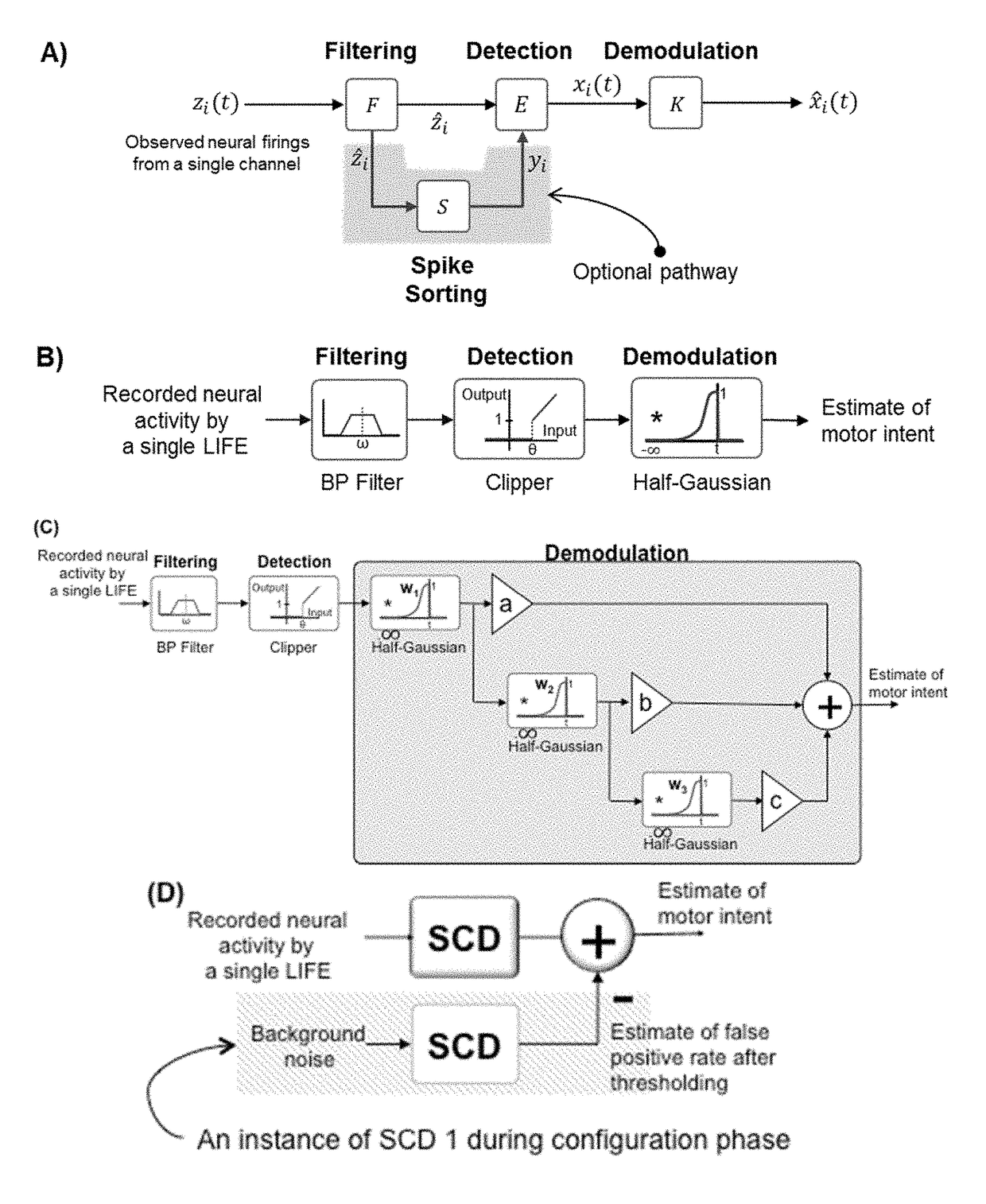
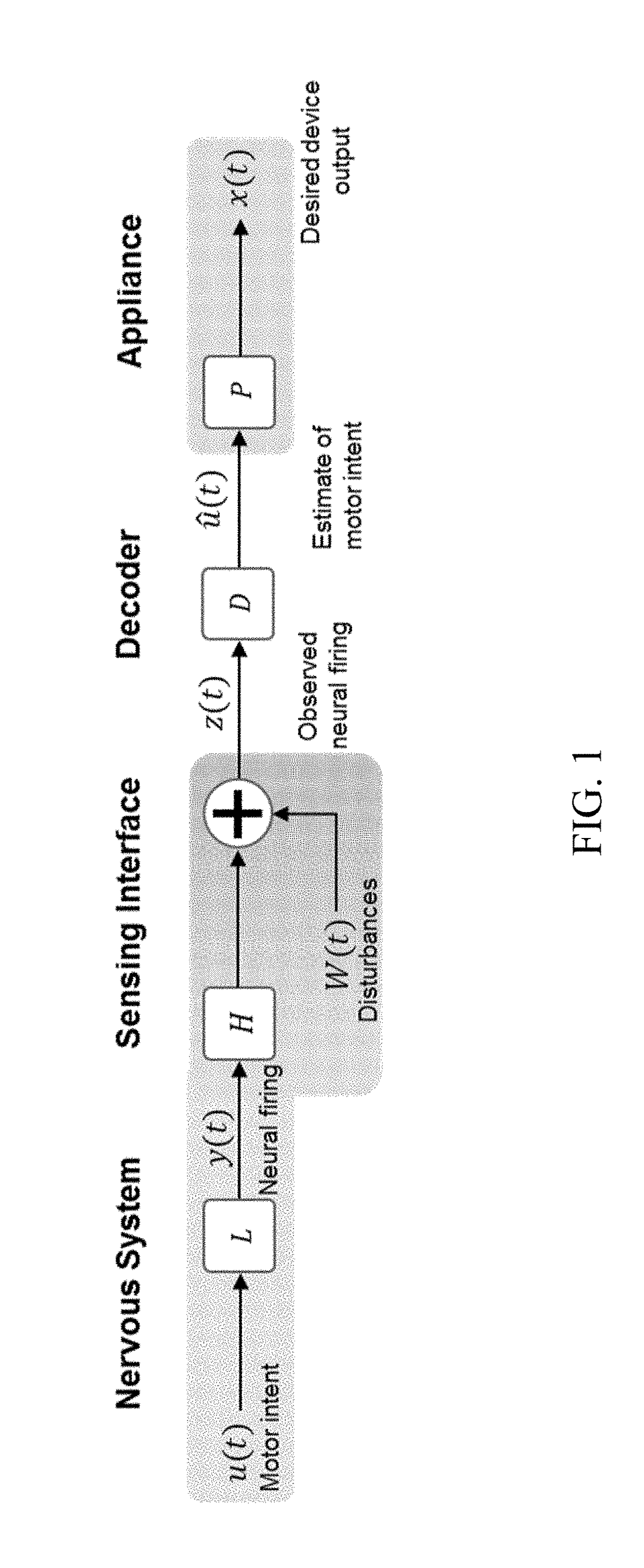
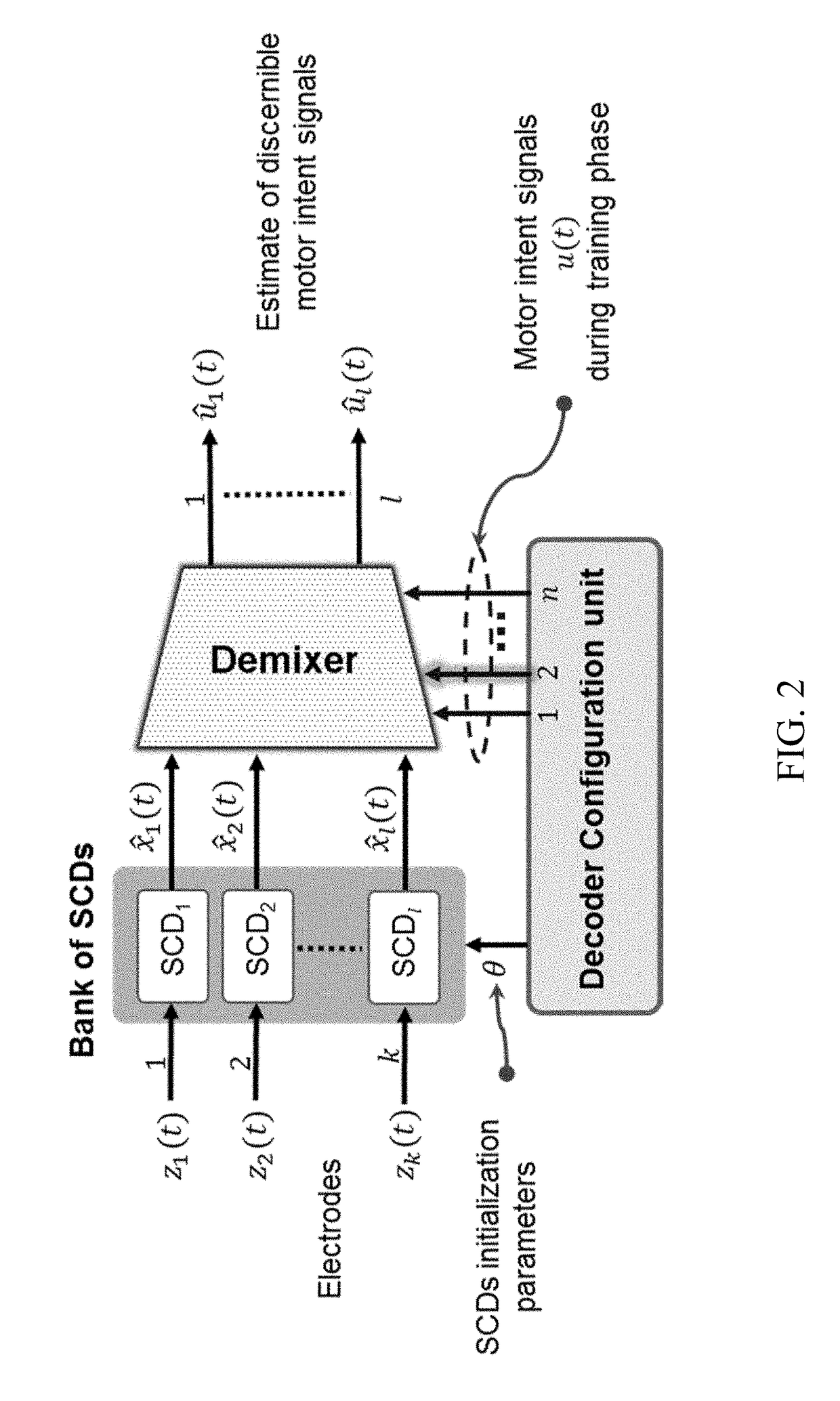
Systems and methods for decoding intended motor commands from recorded neural signals for the control of external devices or to interact in virtual environments
ActiveUS20140330404A1Suppress noiseFaster and efficient transmissionInput/output for user-computer interactionComputer controlAlgorithmMotor commands
Systems and methods for decoding neural and / or electromyographic signals are provided. A system can include at least one single channel decoder. Optionally, the system can include a demixer in operable communication with the single channel decoders. Each single channel decoder can include a filter to attenuate noise and sharpen spikes in the neural and / or electromyographic signals, a detection function to identify spikes, and a demodulator to get a real-time estimate of motor intent.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Electric power steering apparatus
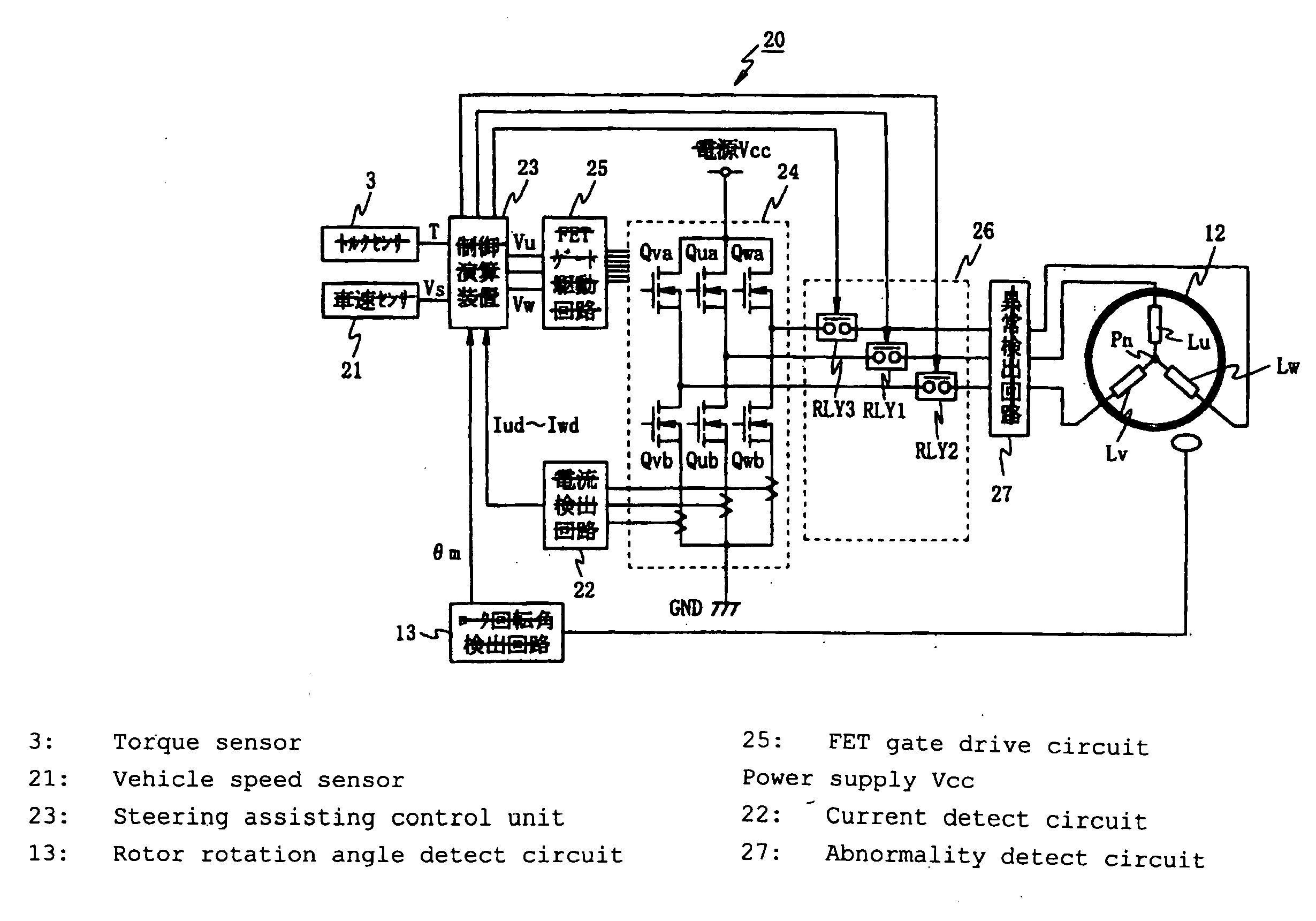
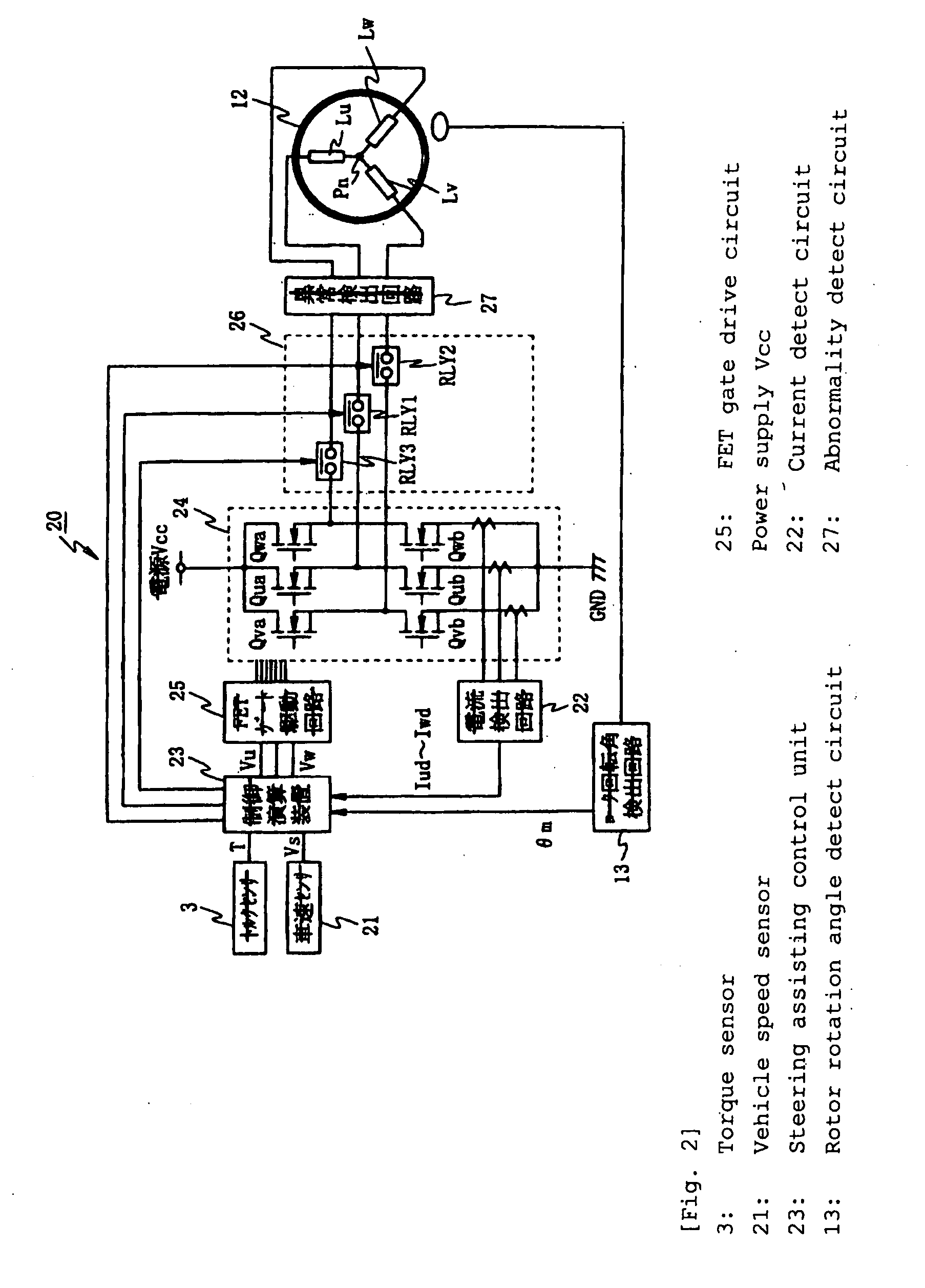
InactiveUS20100017063A1Reduce loadCommutation monitoringDigital data processing detailsPhase currentsElectric power steering
An electric power steering apparatus in which the intensity and directions of drive currents flowing in remaining phases continues motor rotation driving. An abnormality detect unit (27) detects a conduction abnormality in drive systems for the respective phase coils of the 3-phase brushless motor (12). A steering assisting current command value calculating unit (31) calculates a steering assisting current command value. A normal time motor command value calculating unit (33) calculates three phase current command values according to the steering assisting current command value. An abnormal time motor command value calculating unit (34) calculates two phase current command values for using the two remaining phase coils. A command value select portion (35) selects the phase current command values calculated by the normal or abnormal time motor command value calculating unit. A motor control unit (36) drives the electric motor (12) according to the selected phase current command value.
Owner:NSK LTD
Vehicle Stability And Steerability Control Via Electronic Torque Distribution
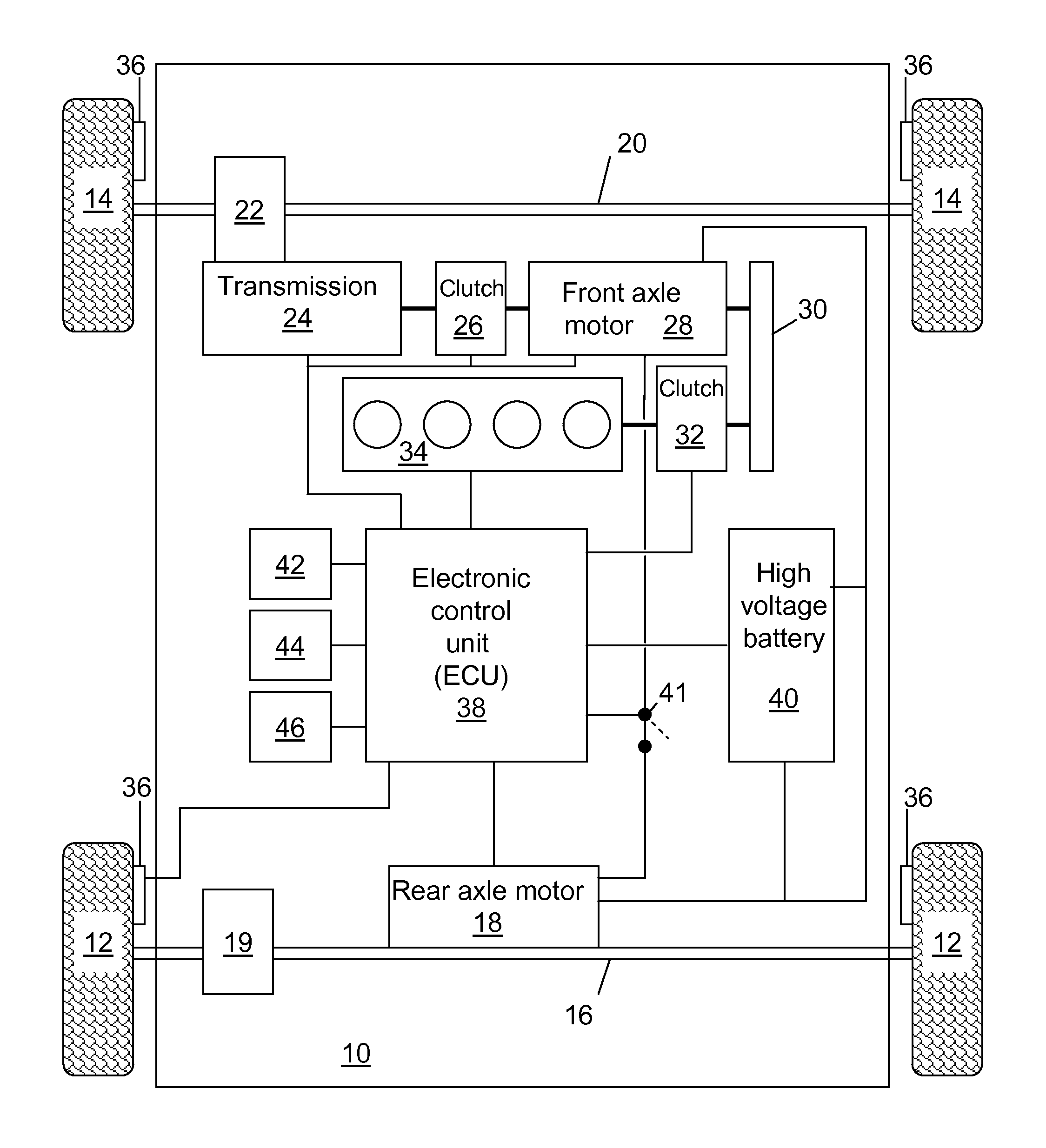
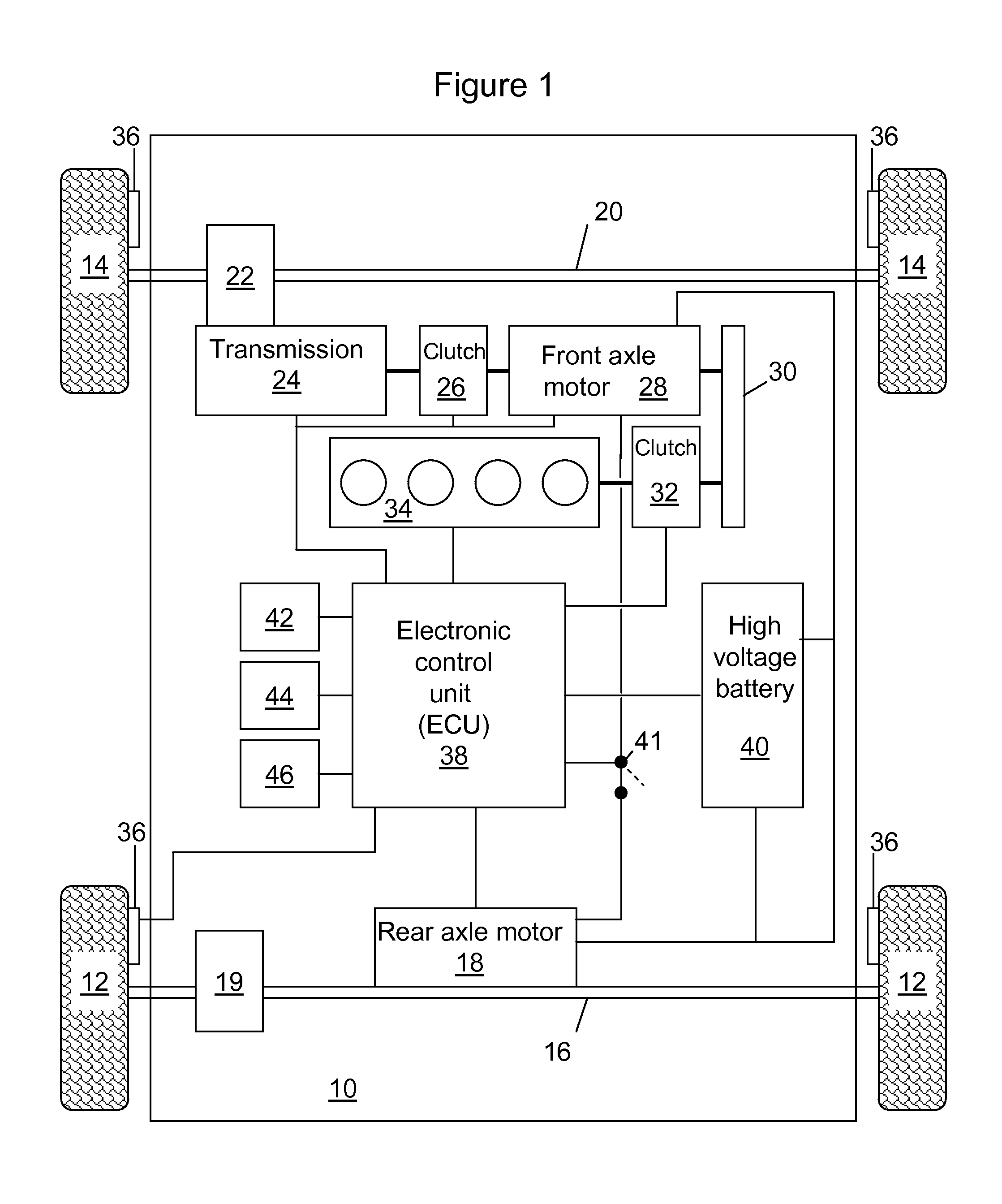
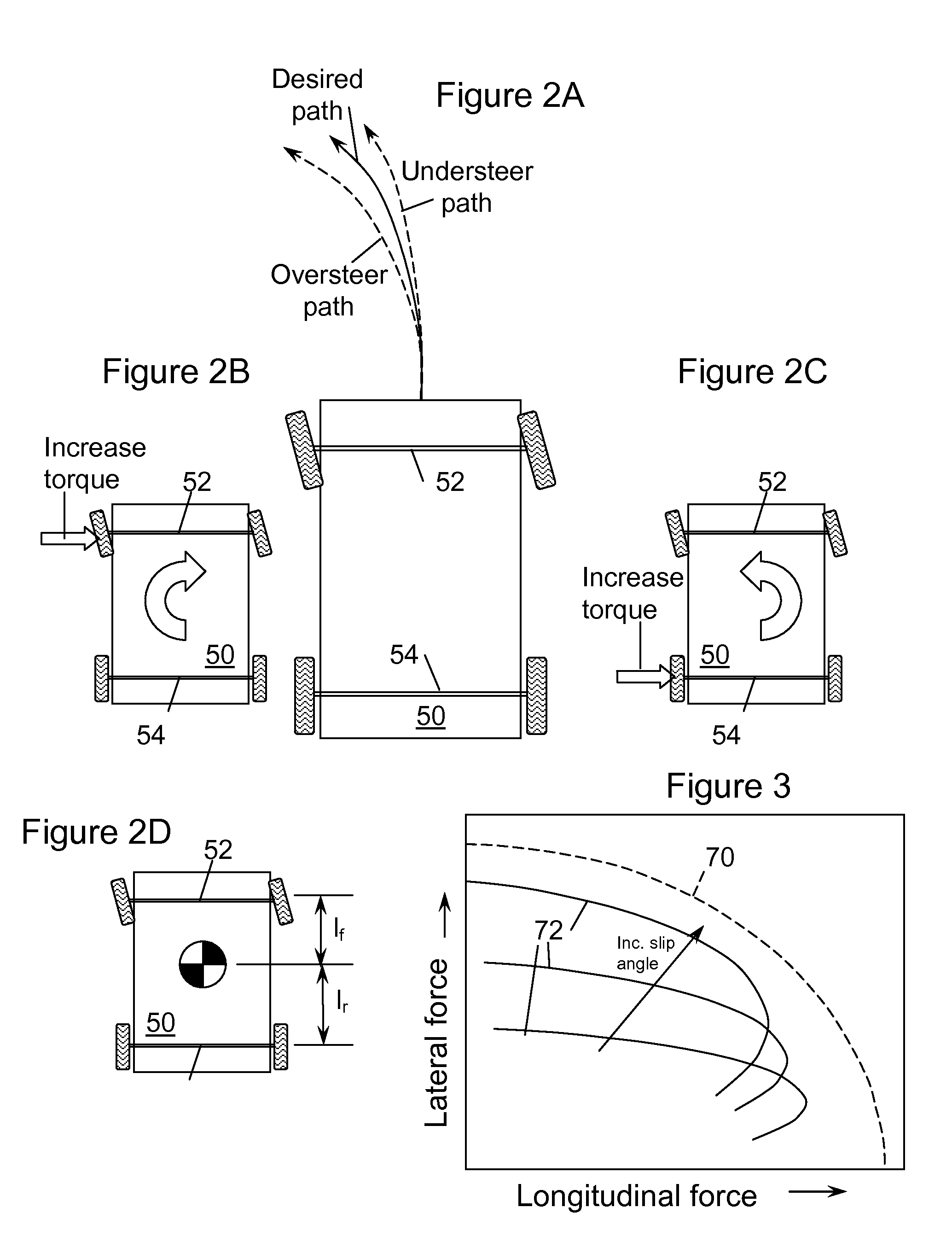
ActiveUS20110257826A1Reduce electrical energyIncrease torqueVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesElectric machineMotor commands
A system for distributing propulsion to front and rear axles of a vehicle includes: a front axle motor coupled to the front axle and a rear axle motor coupled to the rear axle. An electronic control unit (ECU) electronically coupled to the motors commands the rear axle motor to increase torque supplied to the rear axle during understeer and commands the front axle motor to increase torque supplied to the front axle during oversteer. A method to distribute propulsion to front and rear axles of a vehicle includes estimating actual yaw rate, estimating desired yaw rate, providing electrical energy to the front axle motor during oversteer, and providing electrical energy to the rear axle motor during understeer. Additionally, electrical energy may be extracted from the rear axle motor during oversteer and electrical energy may be extracted from the front axle motor during understeer.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Blender base with food processor capabilities
InactiveUS7520659B2Avoid vibrationImprove stabilityElectric motor controlOther chemical processesMicrocontrollerLiquid-crystal display
Owner:SUNBEAN PROD INC
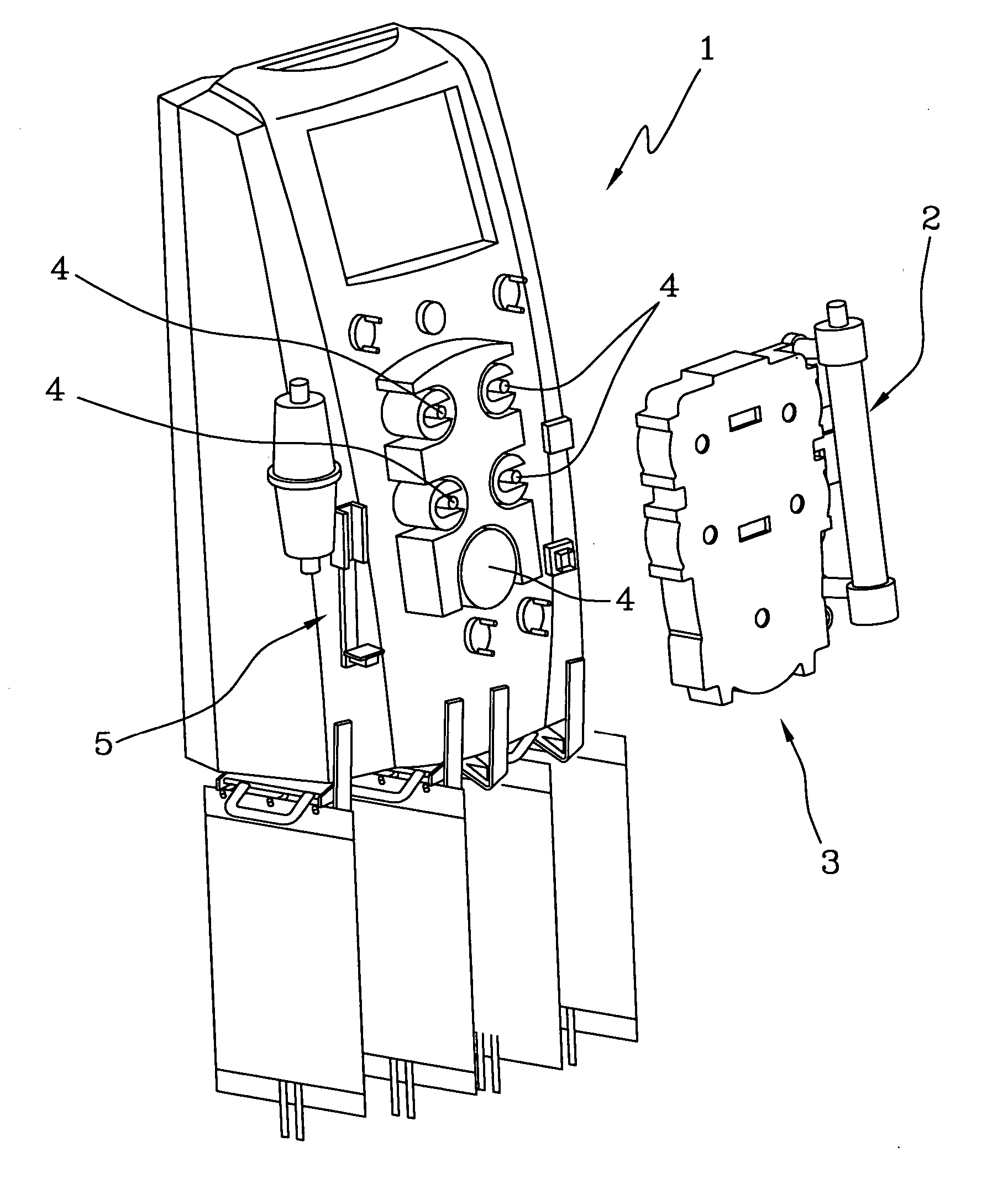
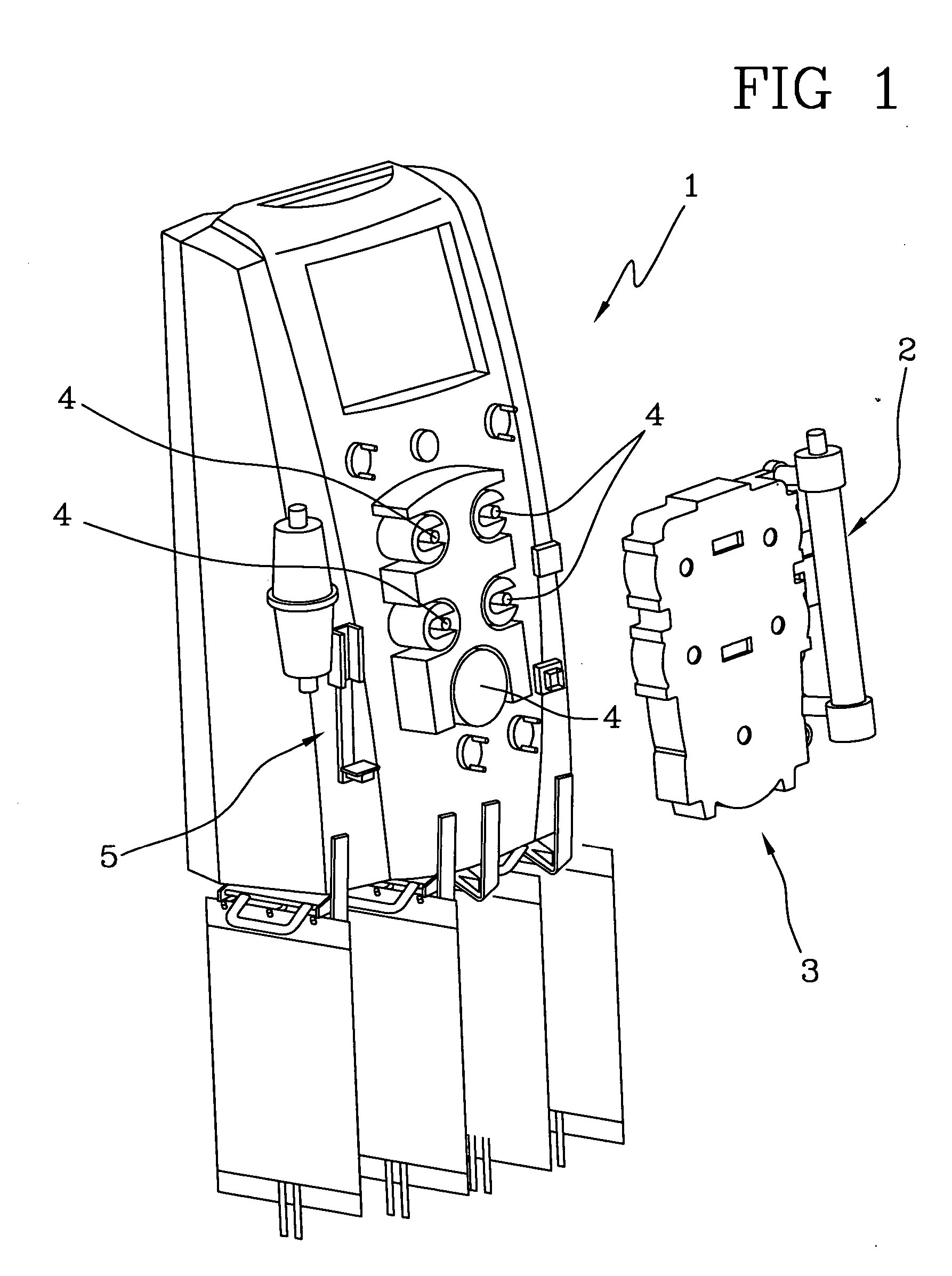
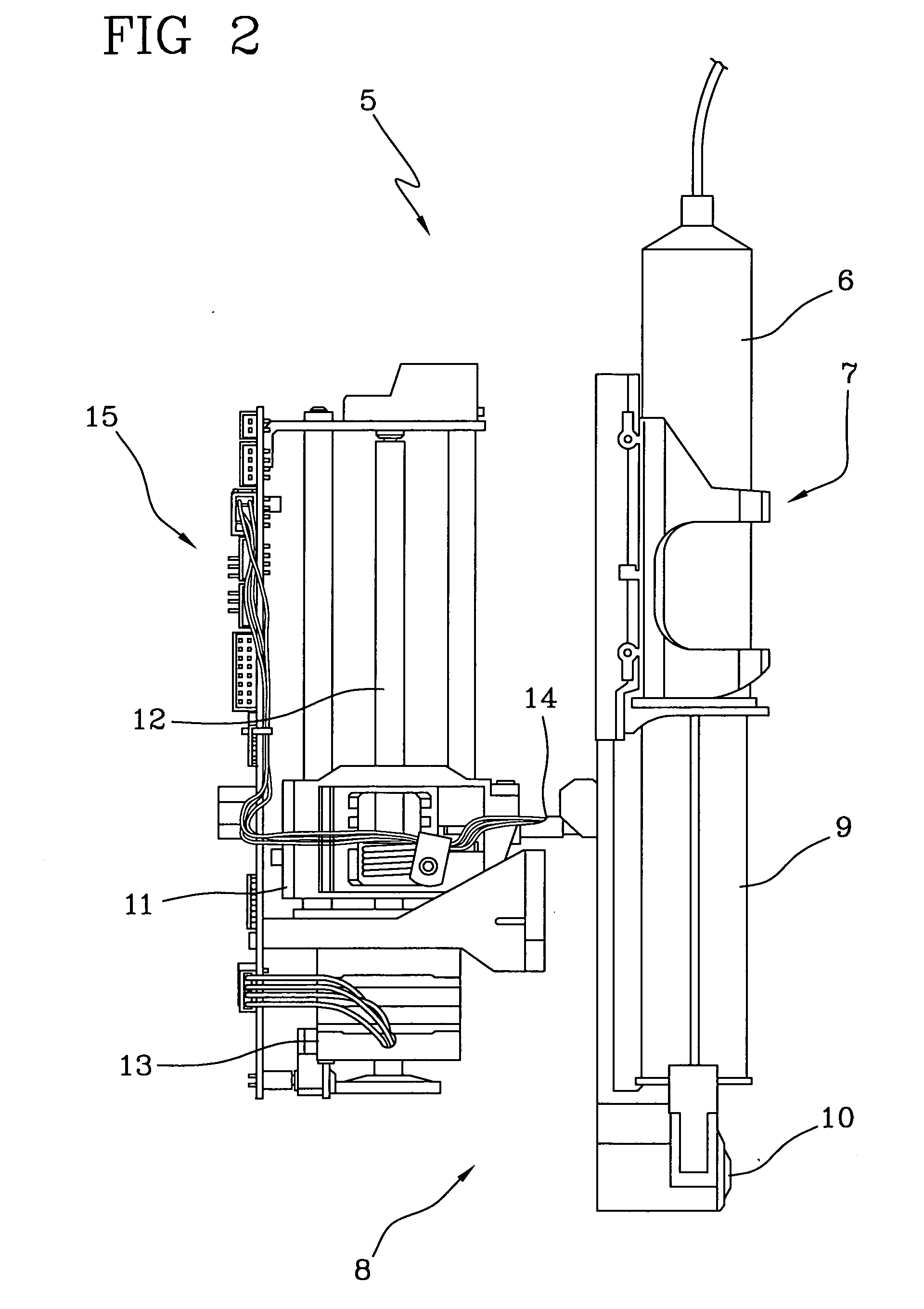
Infusion device for medical fluids
ActiveUS20050234382A1Economical and simpleHighly reliable and very preciseOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsMedicineAnticoagulant
An infusion device comprises a pusher for a plunger of a syringe containing a liquid to be infused. A load cell measures the push force. An encoder associated to a motor commanding the pusher measures the displacement of the pusher. A controller signals an alarm when the ratio between the variation of the push force and the displacement exceeds a predetermined threshold. The device, which serves for infusing an anticoagulant into an extracorporeal blood circuit in a dialysis apparatus, is able to signal an onset of an anomalous situation of lack of infusion in good time.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
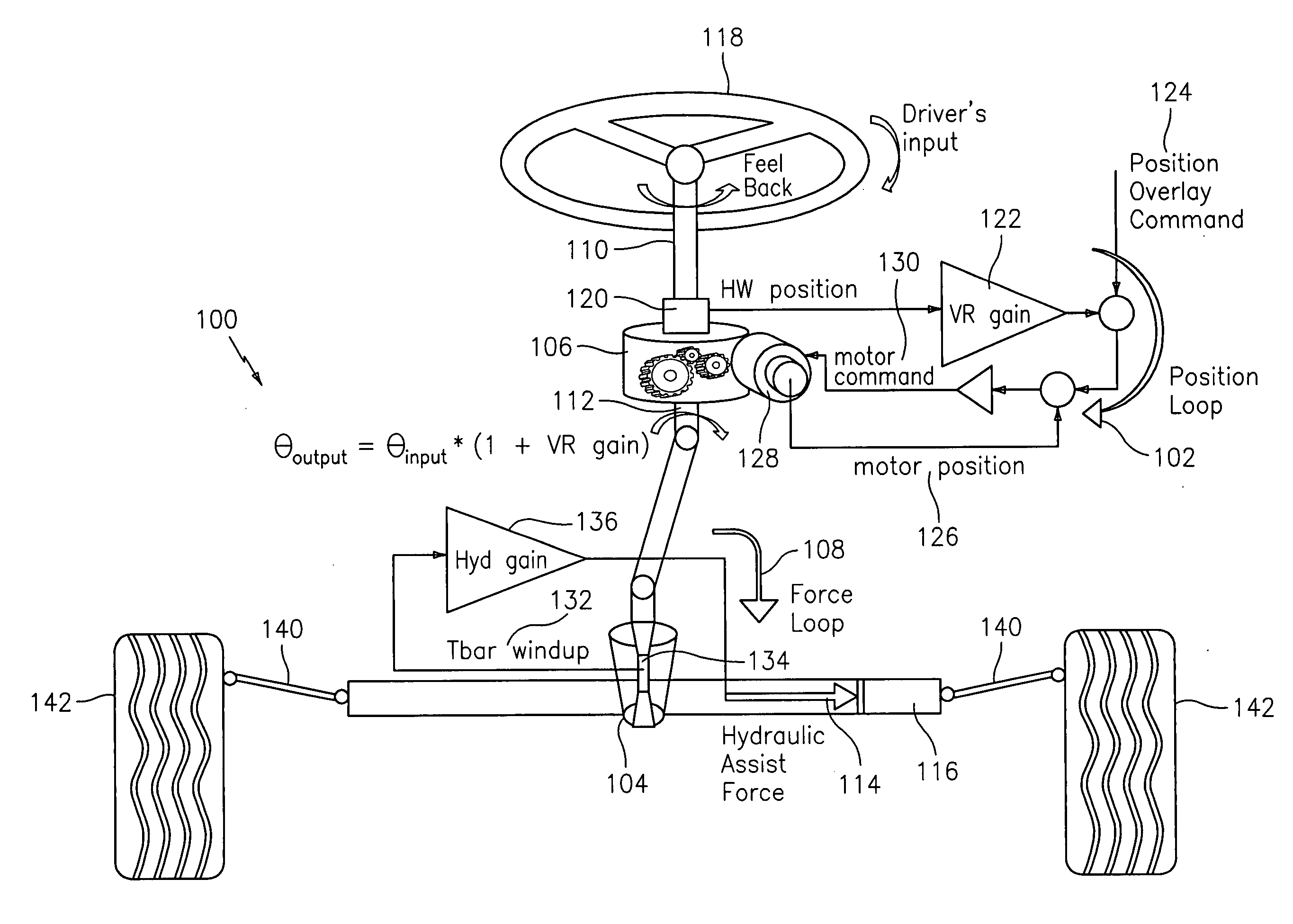
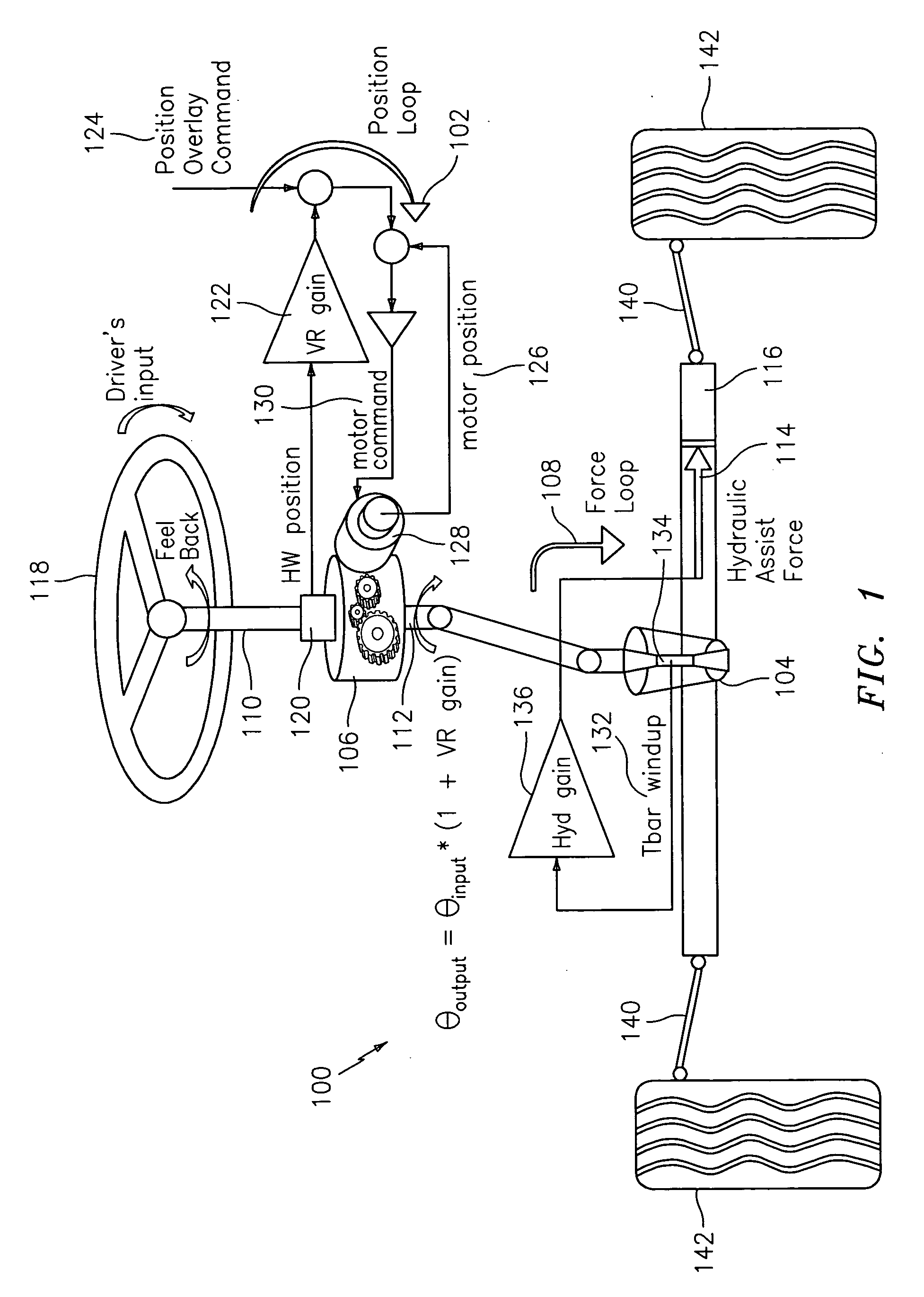
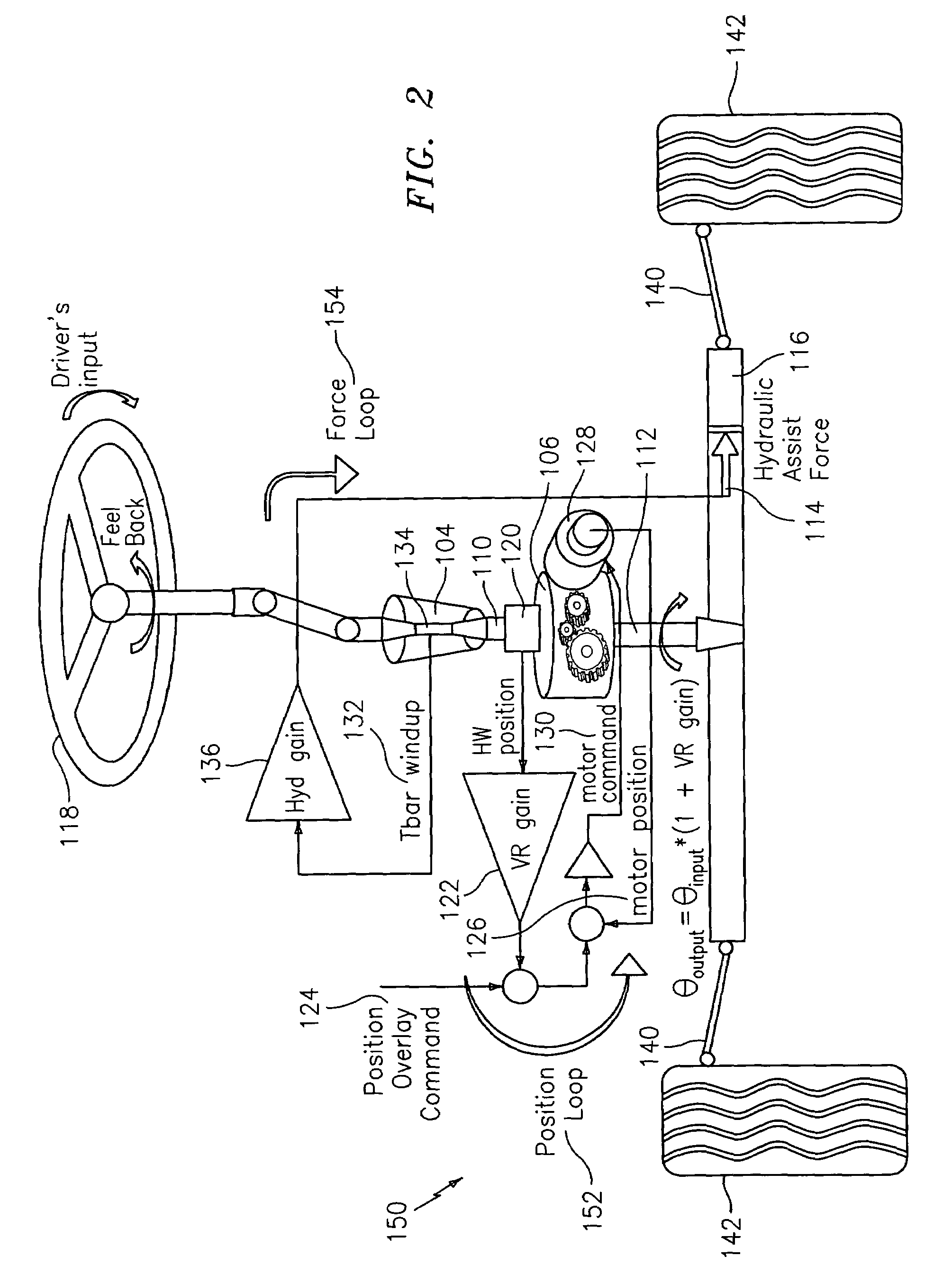
Force and position control for active front steering
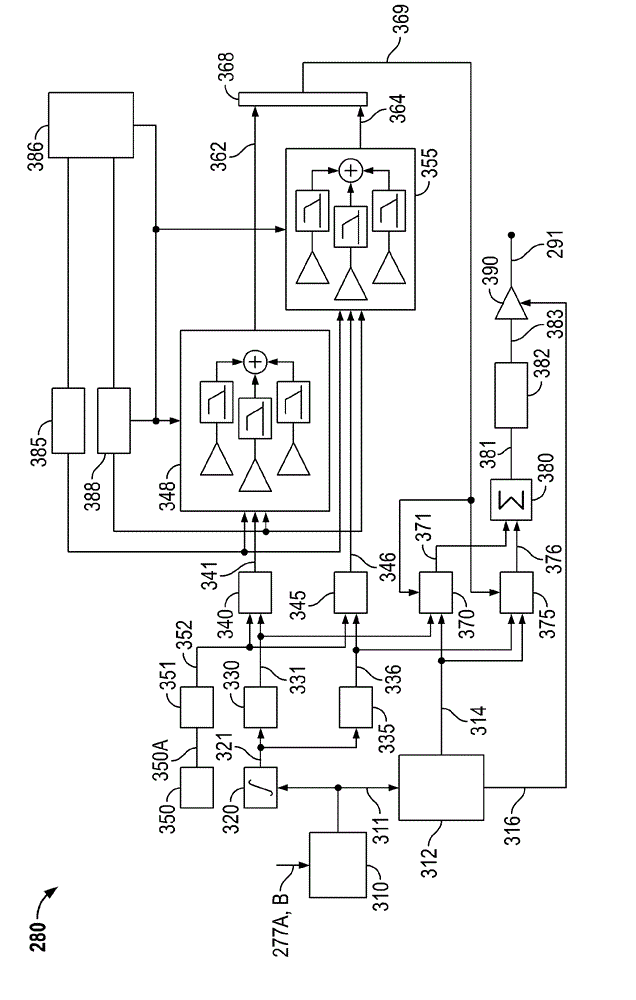
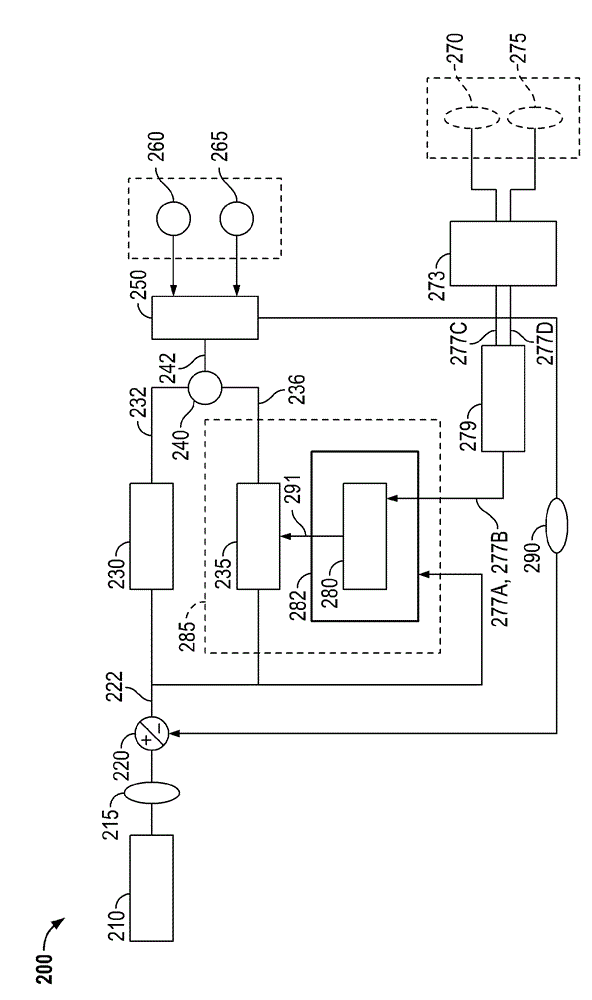
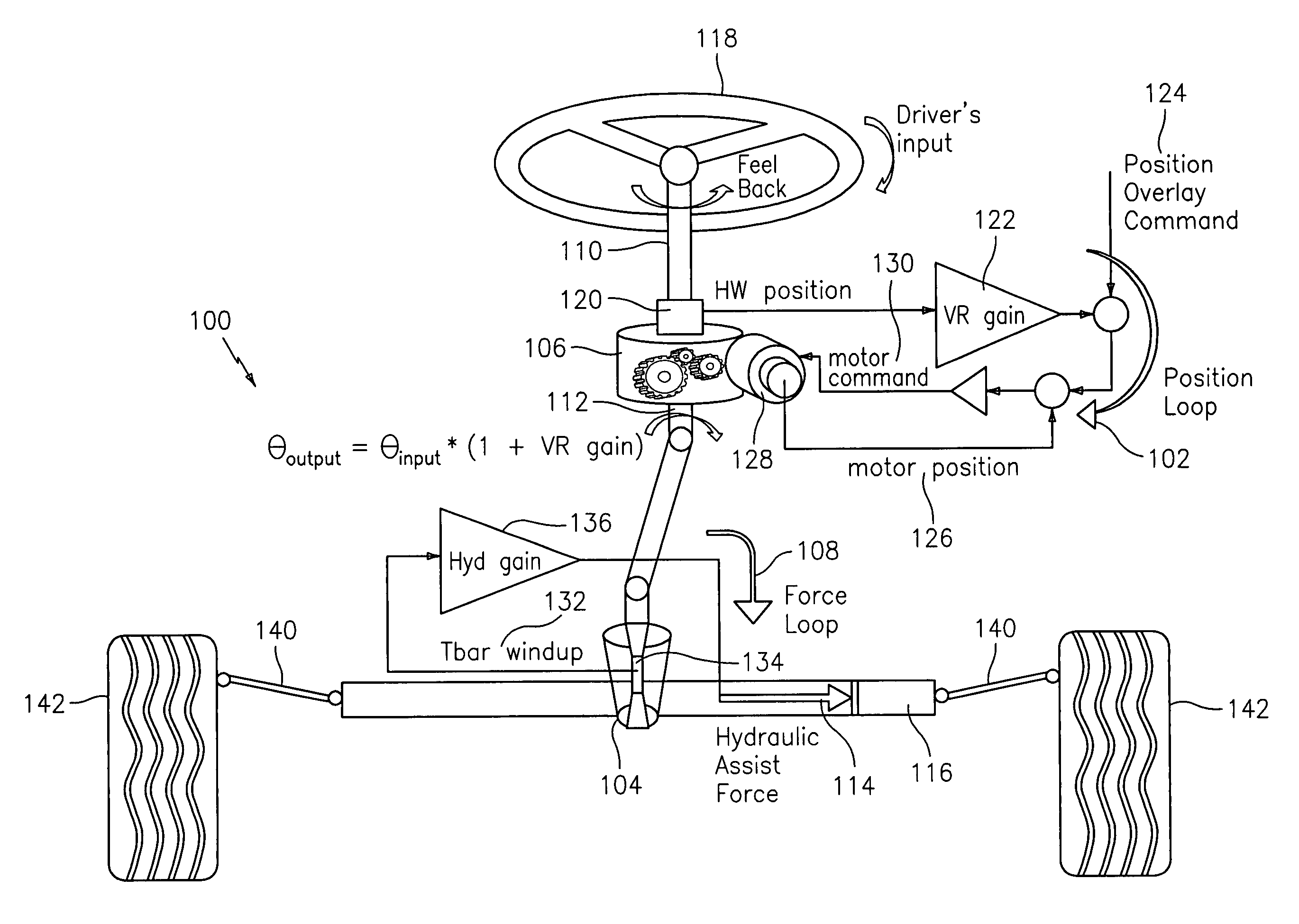
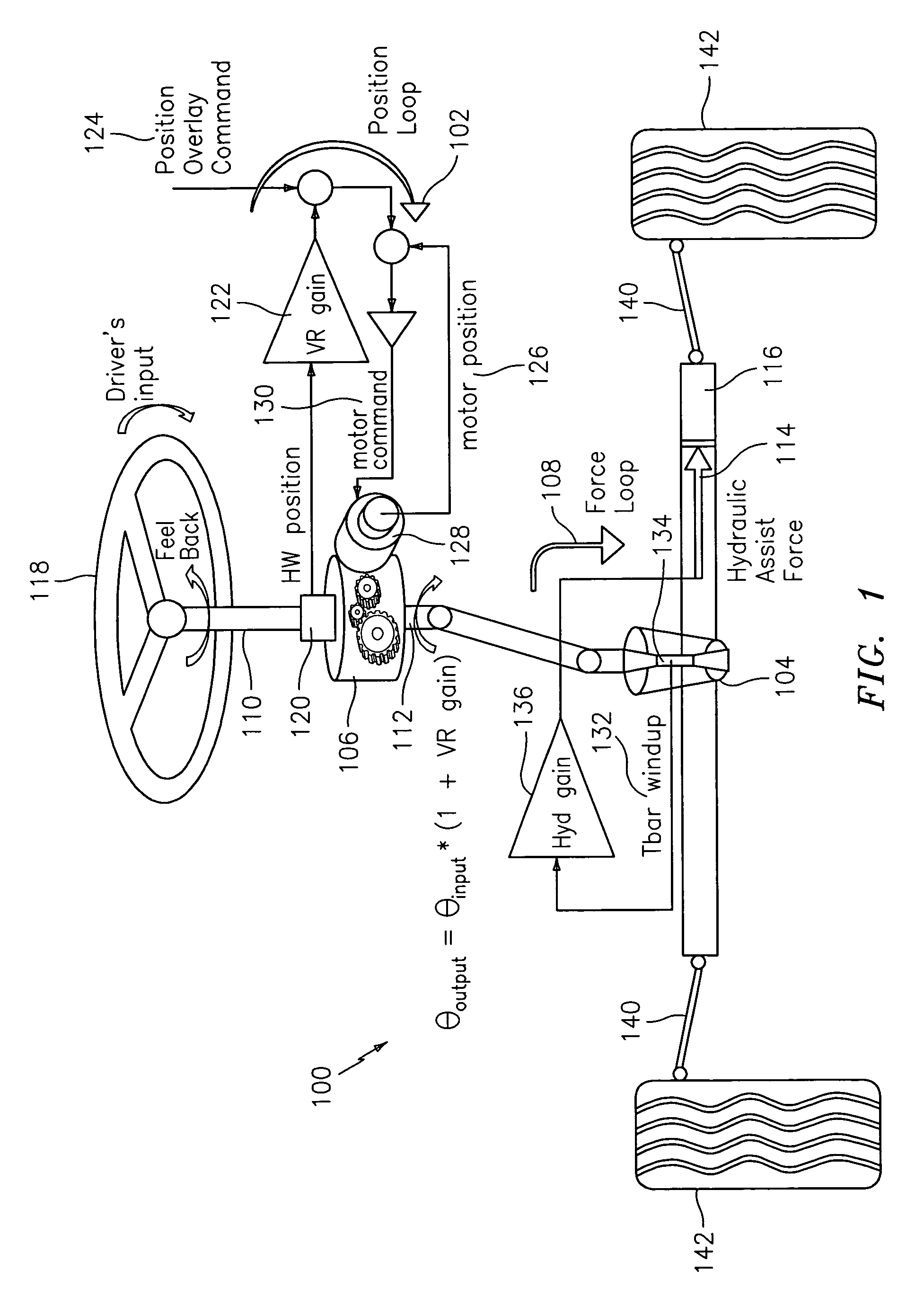
A steering system with reduced coupling between a position overlay unit and a torque overlay unit may include a remote valve assembly for controlling a hydraulic assist force or an electric motor for providing torque overlay and electric assist to a rack of a rack and pinion steering system. In one embodiment, the position overlay unit may provide the assist force and the torque overlay unit may provide a motor command signal to the motor of a differential positioned on a steering shaft. In another embodiment, the position overlay unit may provide the motor command signal and the torque overlay unit may provide the assist force. In either embodiment, the position overlay unit may include variable ratio gain that uses a position signal to output a variable ratio command.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Arrangement for autonomous mobile network nodes to organize a wireless mobile network based on detected physical and logical changes
InactiveUS8527457B2Autonomous decision making processDigital data processing detailsComputer networkWireless mesh network
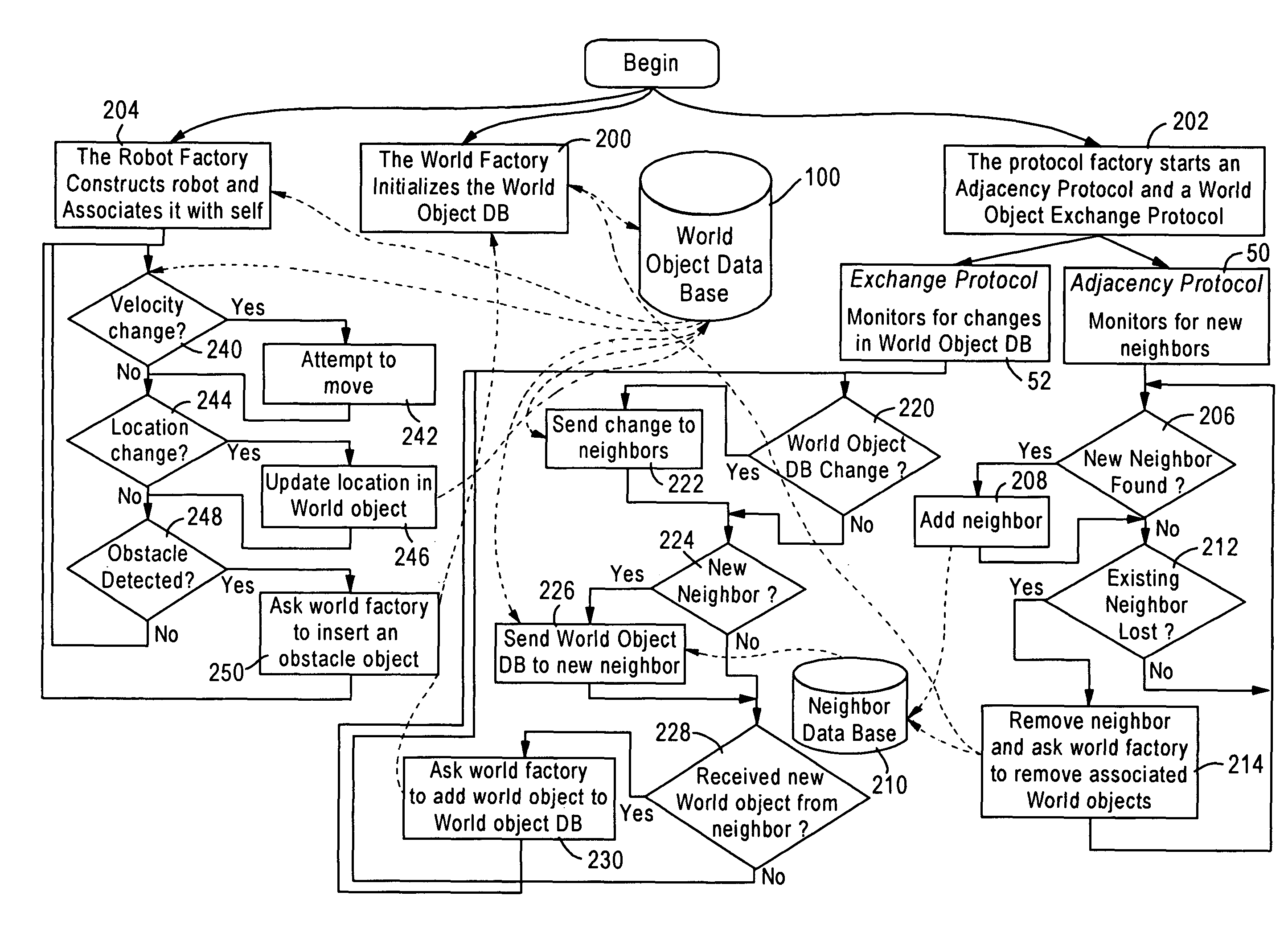
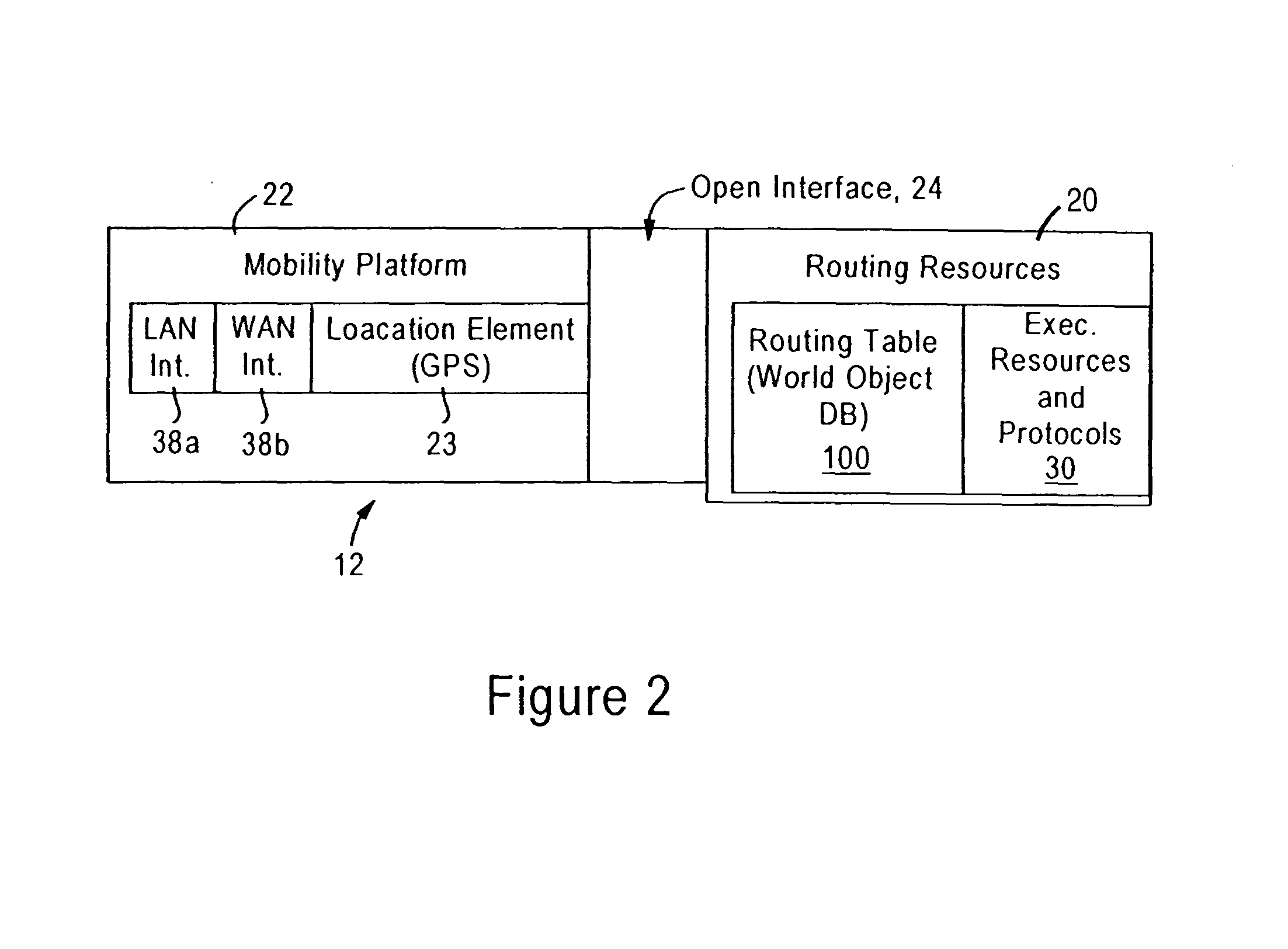
An autonomous wireless mobile network is established between mobile nodes configured as wireless autonomous robotic mobile access points. Each mobile node includes a mobility platform, an executable routing resource, and a standardized interface. The mobility platform is configured for supplying sensor data from attached physical sensors, and responding to motor commands from the standardized interface. The standardized interface is configured for converting each sensor datum into a corresponding sensor object, and converting received movement directives into the respective motor commands. The executable routing resource is configured for maintaining a database of world objects representing attributes within an infosphere established by the wireless mobile network based on the sensor objects and received network objects. The executable routing resource also is configured for generating the received movement directives and executing network decisions based on periodic evaluation of the world database, and exchanging the world objects with other mobile nodes.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Joint-space impedance control for tendon-driven manipulators
A system and method for controlling tendon-driven manipulators that provide a closed-loop control of joint torques or joint impedances without inducing dynamic coupling between joints. The method includes calculating tendon reference positions or motor commands by projecting a torque error into tendon position space using a single linear operation. The method calculates this torque error using sensed tendon tensions and a reference torque and internal tension. The method can be used to control joint impedance by calculating the reference torque based on a joint position error. The method limits minimum and maximum tendon tensions by projecting the torque error into the tendon tension space and then projecting ii back into joint space.
Owner:NASA +1
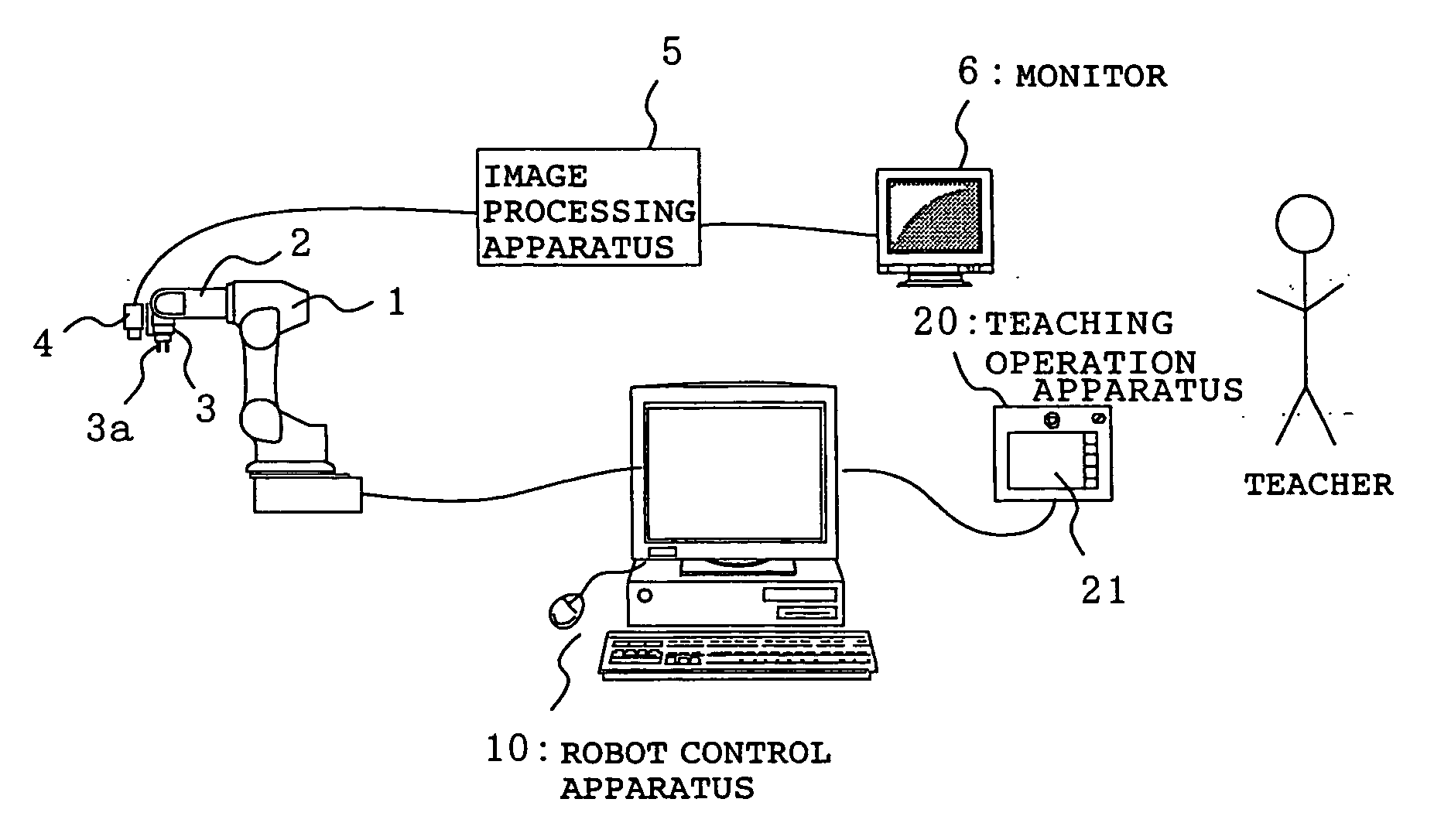
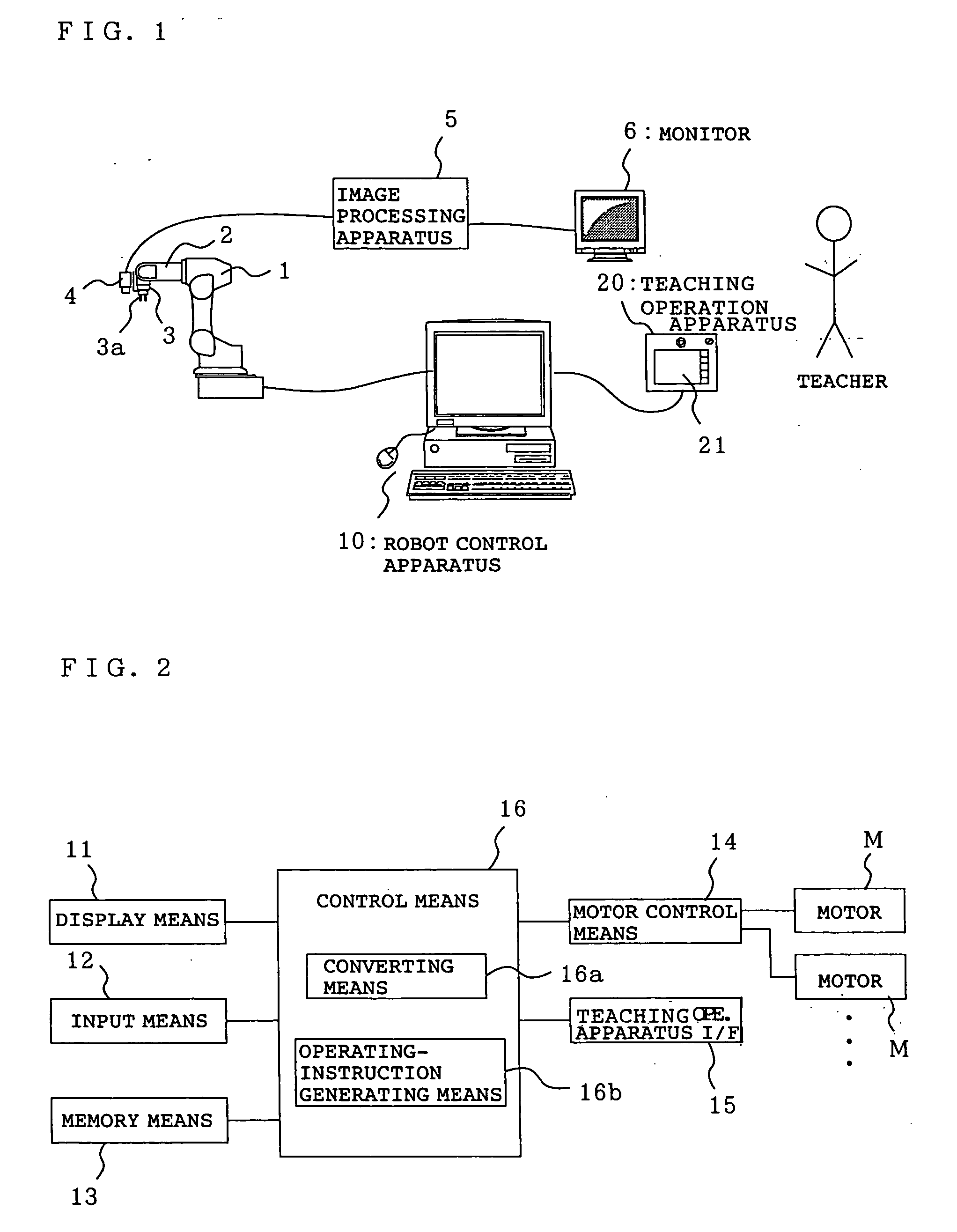
Motion control apparatus for teaching robot position, robot-position teaching apparatus, motion control method for teaching robot position, robot-position teaching method, and motion control program for teaching robot-position
InactiveUS20060229766A1Reduce the burden onImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsMotion vectorElectric machine
A motion control apparatus for teaching a robot position includes an operating unit that inputs an operating command to a robot on a camera coordinate system having, as a reference, an image capturing screen displayed on the monitor, a converting unit that generates a motion vector on the camera coordinate system for moving the robot from the current position to the next moving position in accordance with the operating command on the camera coordinate system input from the operating unit and converts the motion vector on the camera coordinate system into a motion vector on a robot coordinate system, an operating-instruction generating unit that generates a motor instructing value to be given to a motor arranged at a joint of the robot 1 based on the motion vector on the robot coordinate system obtained by the converting unit, and a motor control unit that controls the motor arranged at the joint of the robot in accordance with the motor instructing value generated by the operating-instruction generating unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Dual lane control of a permanent magnet brushless motor using non-trapezoidal commutation control
InactiveUS20090128072A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlBrushless motorsPermanent magnet rotor
A motor control system and method implements non-trapezoidal motor control and meets established “fail passive” regulatory guidelines. In particular, a system and method of controlling a multi-phase brushless motor that includes a multi-pole permanent magnet rotor, and an individual, electrically isolated stator winding associated with each phase that includes a first terminal and a second terminal. A motor command is supplied to a motor control. The motor control is configured such that the first terminal of each stator winding is selectively coupled to a power source at a first duty cycle, and the second terminal of each stator winding is selectively coupled to a power source asynchronously with the first terminal of each stator winding at a second duty cycle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method, system and device for reducing steering wheel vibrations in electric steering system
The invention relates to a method, a system and a device for reducing steering wheel vibrations in an electric steering system. Specifically, methods and systems are provided for suppressing steering wheel vibrations generated by periodic disturbances in a vehicle steering system. An exemplary method to reduce the steering wheel vibrations caused by periodic disturbances comprises determining a total torque attributable to the periodic disturbances in the steering system, determining a desired amount of suppression of the vibrations on the steering wheel, determining an offset torque based on the total torque and the desired amount of suppression, and generating a motor command signal in a manner that is influenced by the offset torque. The motor control command signal is provided for an electric motor which is combined with the steering wheel and / or vehicle tires, and the motor control command signal affects the torque applied by the motor in order to assist the steering of the vehicle tires from the steering wheel in such a way that the vibrations conveyed to the steering wheel attenuates the desired amount.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
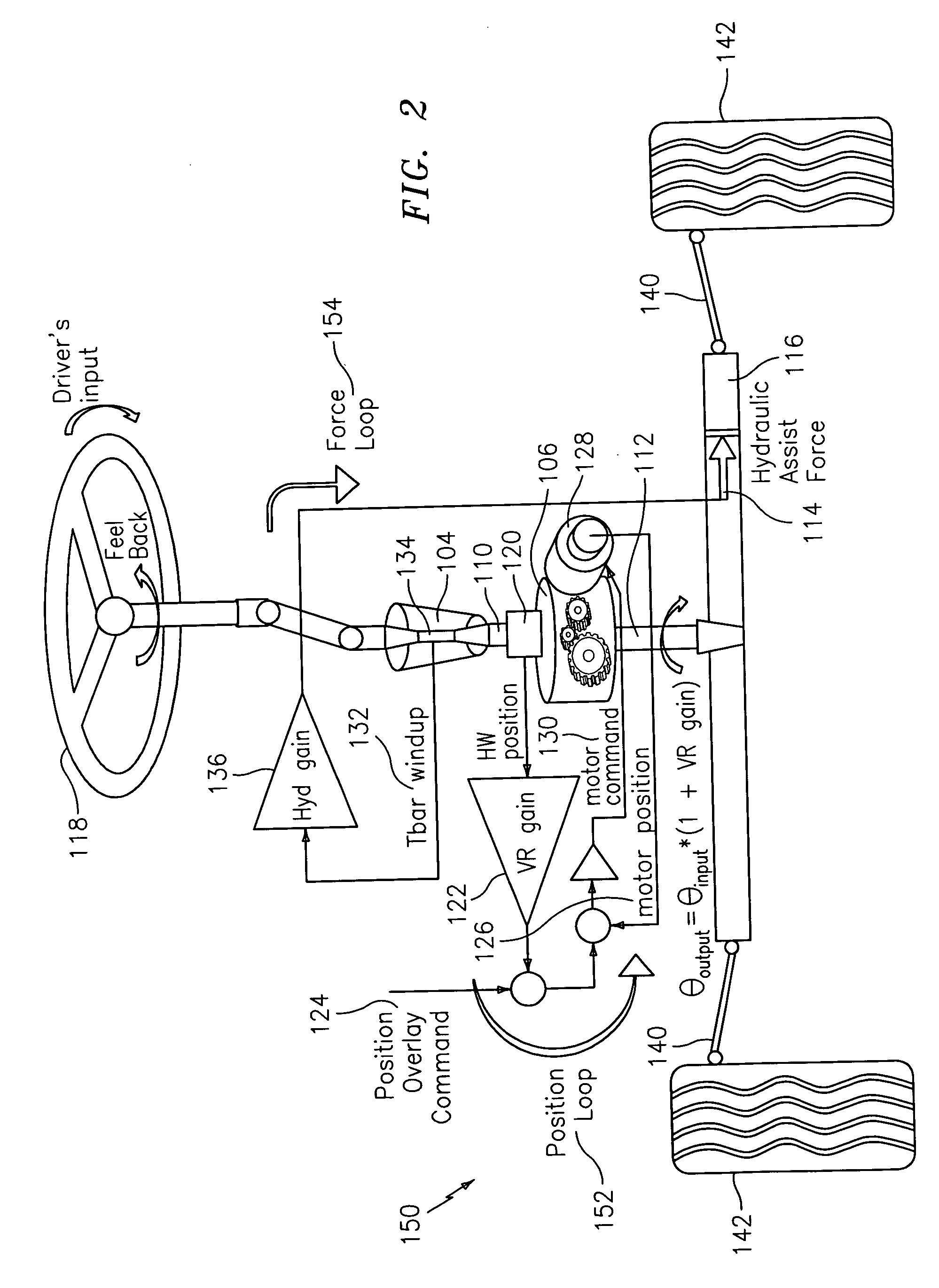
Force and position control for active front steering
A steering system with reduced coupling between a position overlay unit and a torque overlay unit may include a remote valve assembly for controlling a hydraulic assist force or an electric motor for providing torque overlay and electric assist to a rack of a rack and pinion steering system. In one embodiment, the position overlay unit may provide the assist force and the torque overlay unit may provide a motor command signal to the motor of a differential positioned on a steering shaft. In another embodiment, the position overlay unit may provide the motor command signal and the torque overlay unit may provide the assist force. In either embodiment, the position overlay unit may include variable ratio gain that uses a position signal to output a variable ratio command.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Vehicular steering control apparatus
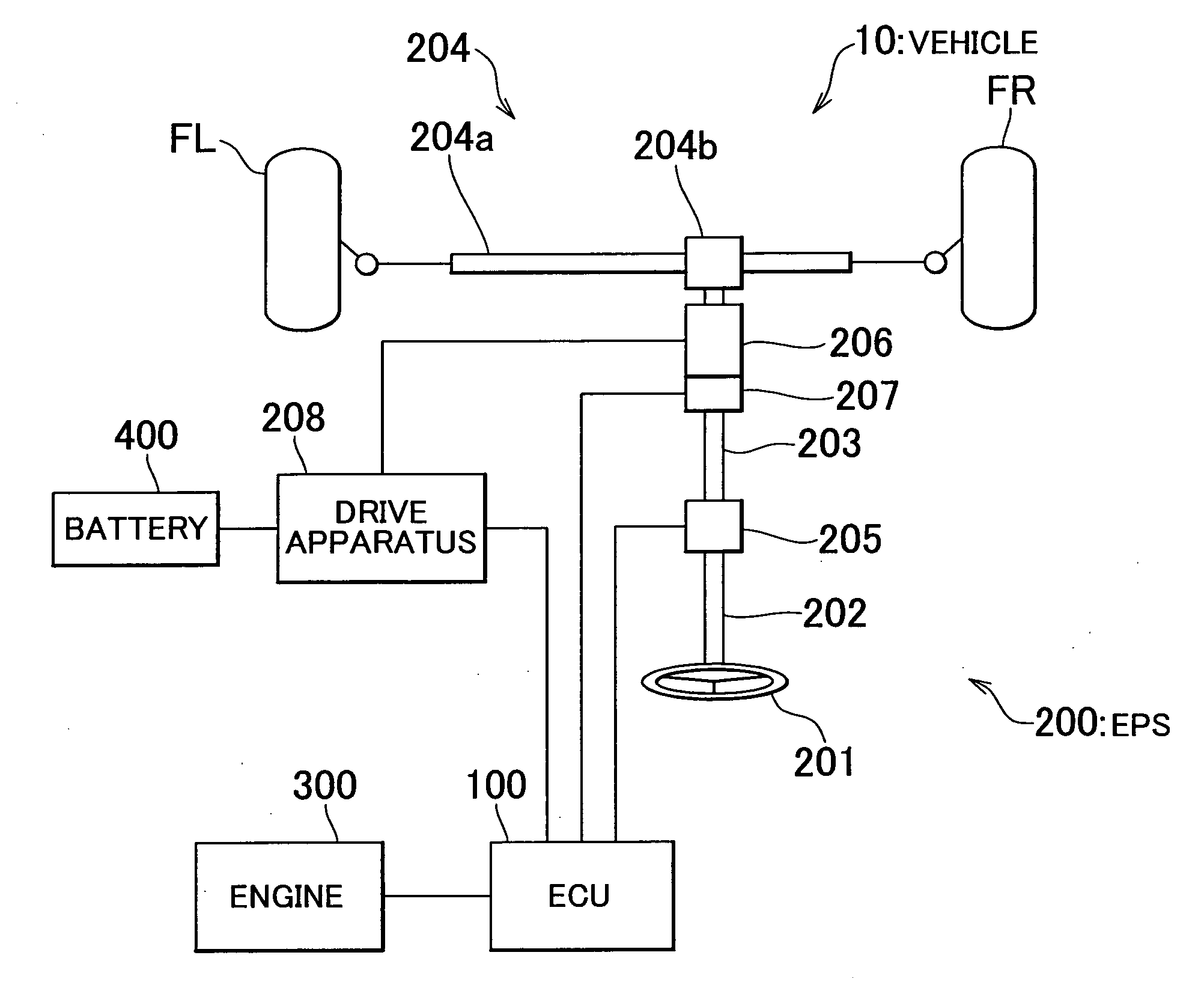
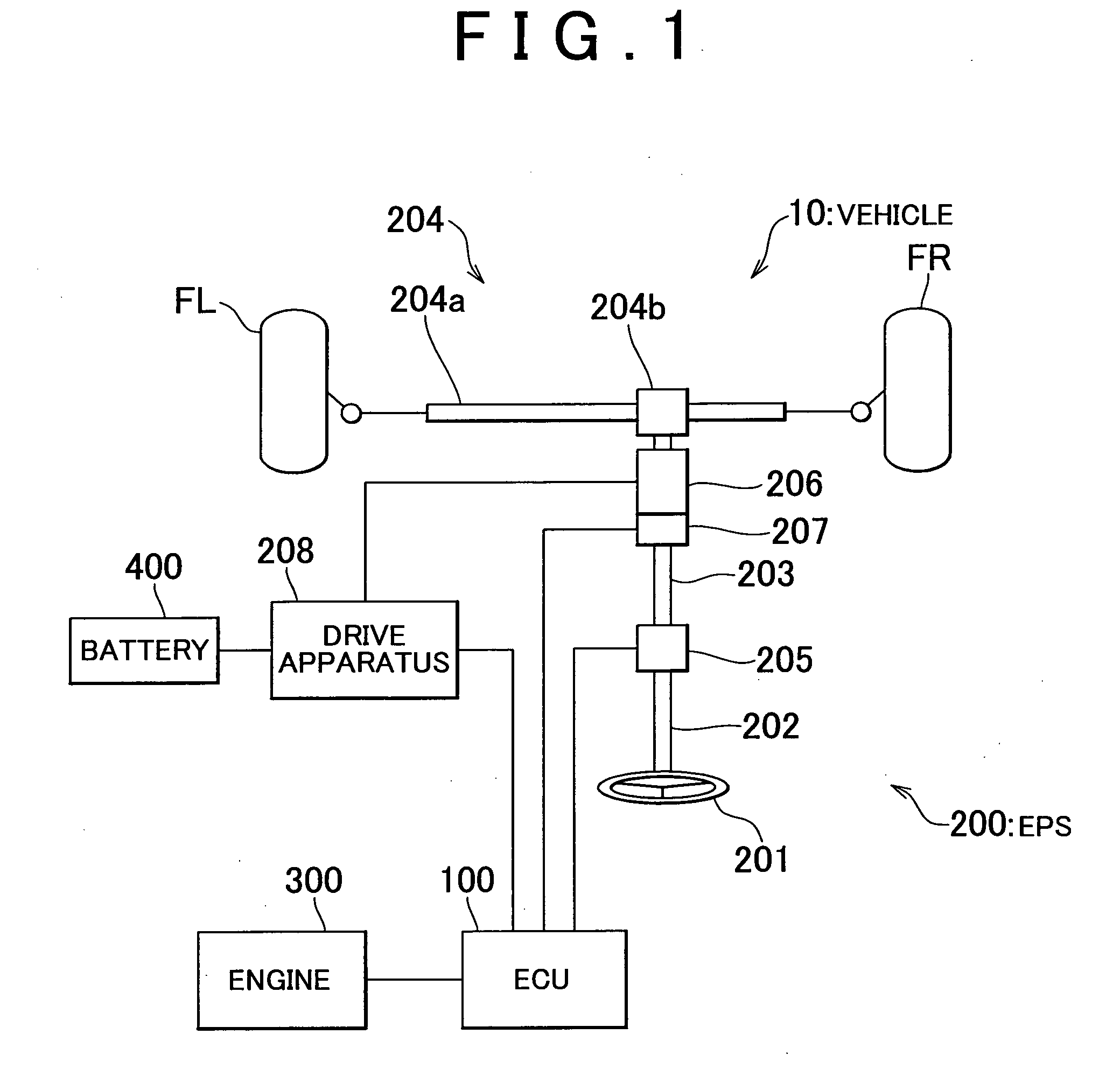
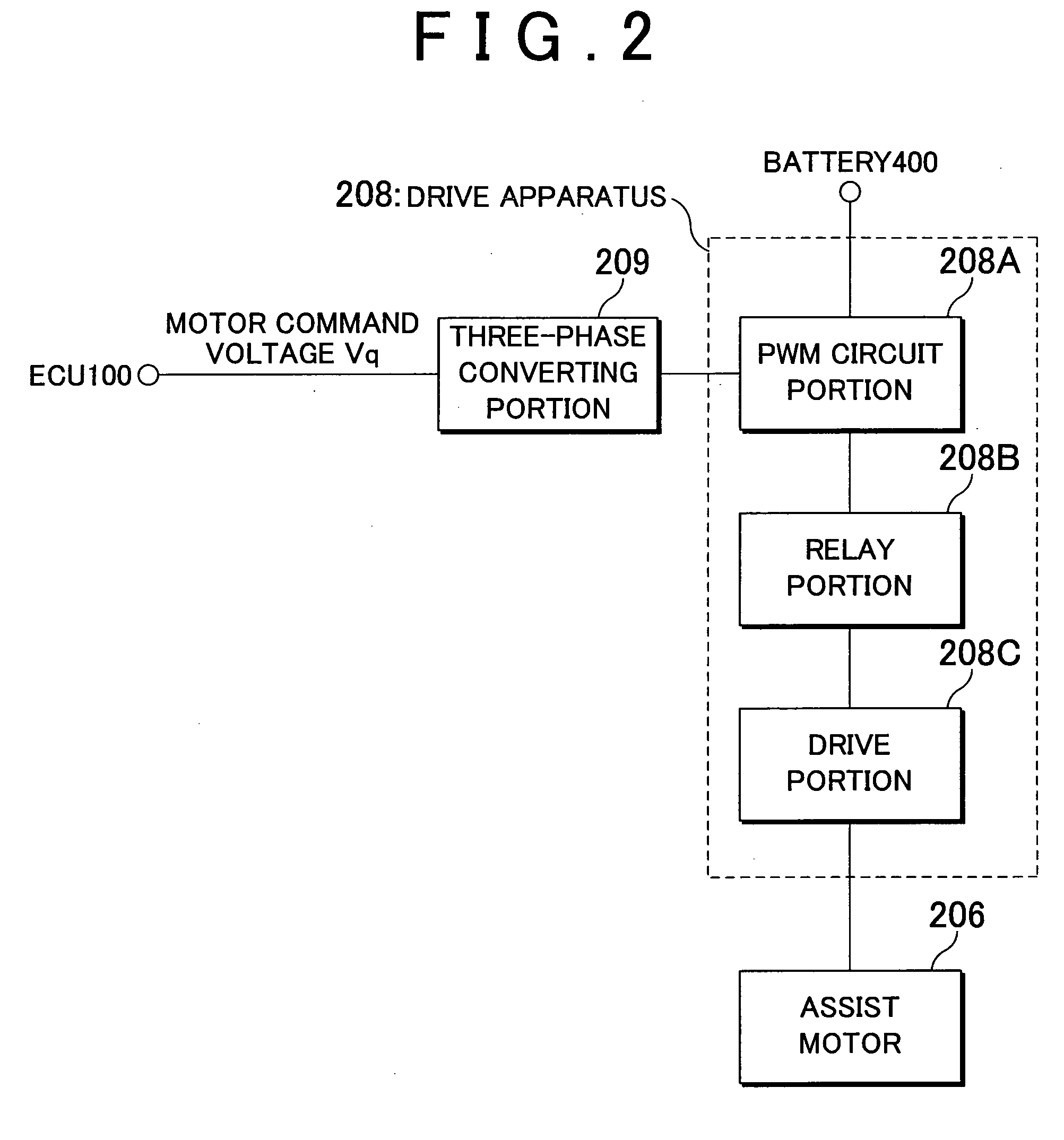
InactiveUS20110010052A1Suppressing decrease in handlingSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsControl powerElectric machinery
An ECU executes steering control in a vehicle including an electronic control power steering apparatus. In the steering control, it is determined that an assist motor is in a power generating state when a motor rotation speed ω which is the rotation speed of the assist motor is greater than an upper limit rotation speed ω1 set according to a motor command voltage Vq that is the driving voltage of the assist motor. When the assist motor is in the power generating state, the ECU interrupts the supply of current to the assist motor by controlling a relay portion of a drive apparatus that drives the assist motor so that it is open, thereby reducing the amount of power that is generated to zero. Also, when returning to an assist possible state, assist torque Tm is changed gradually with zero as the initial value in order to prevent it from changing suddenly.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
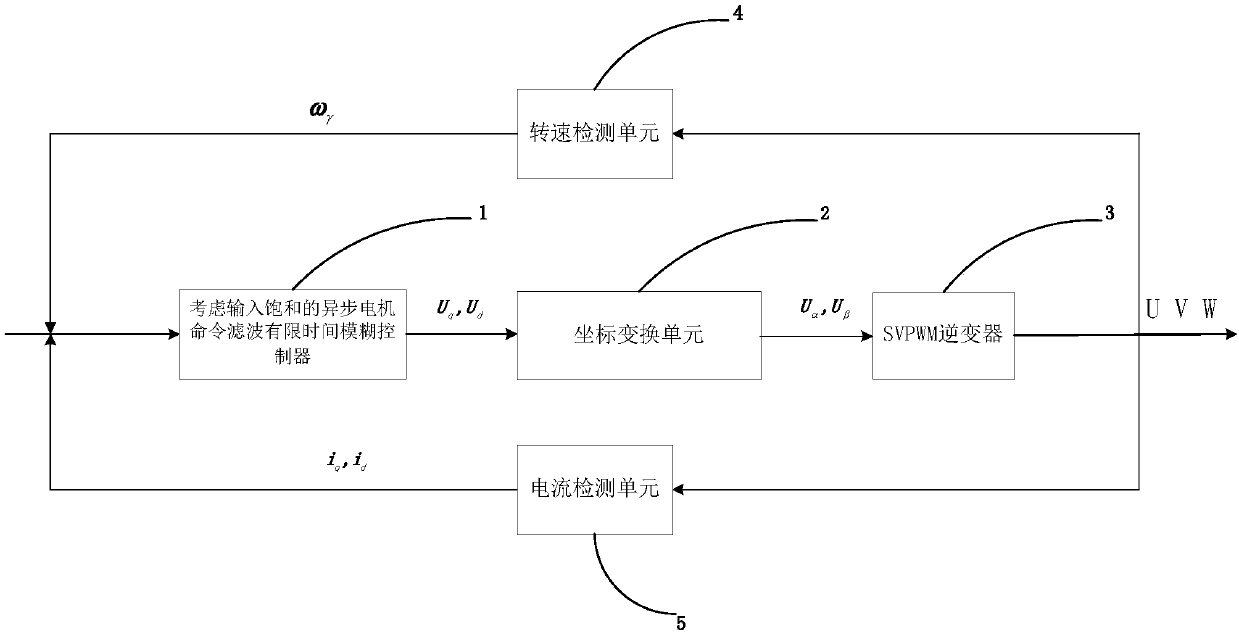
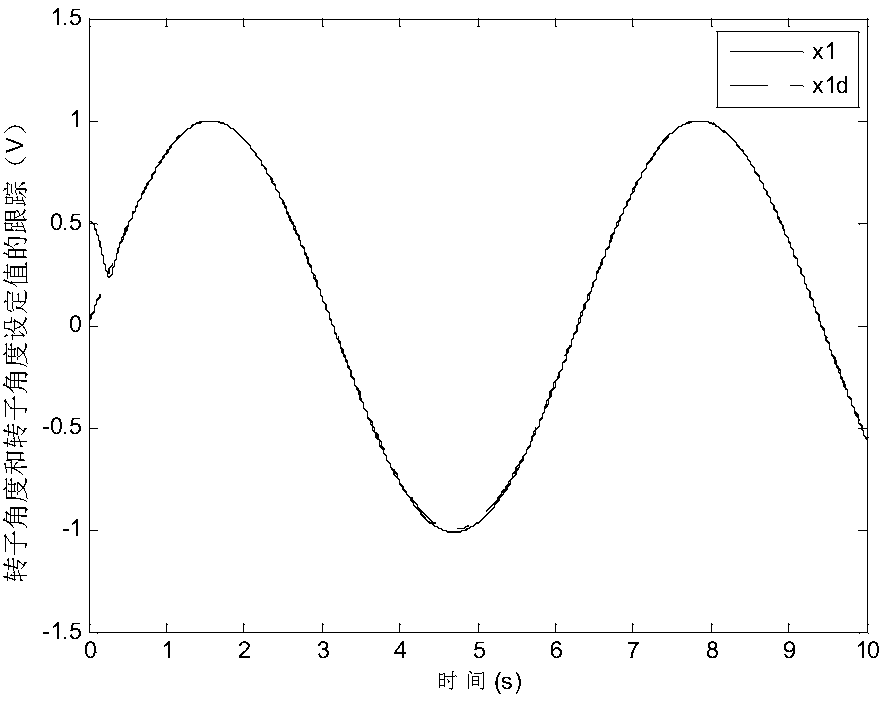
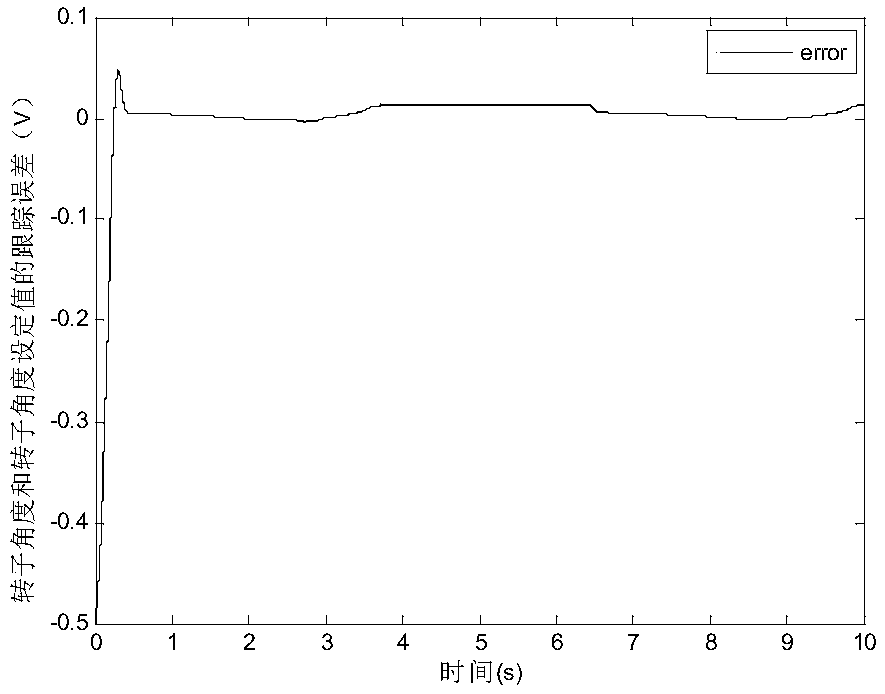
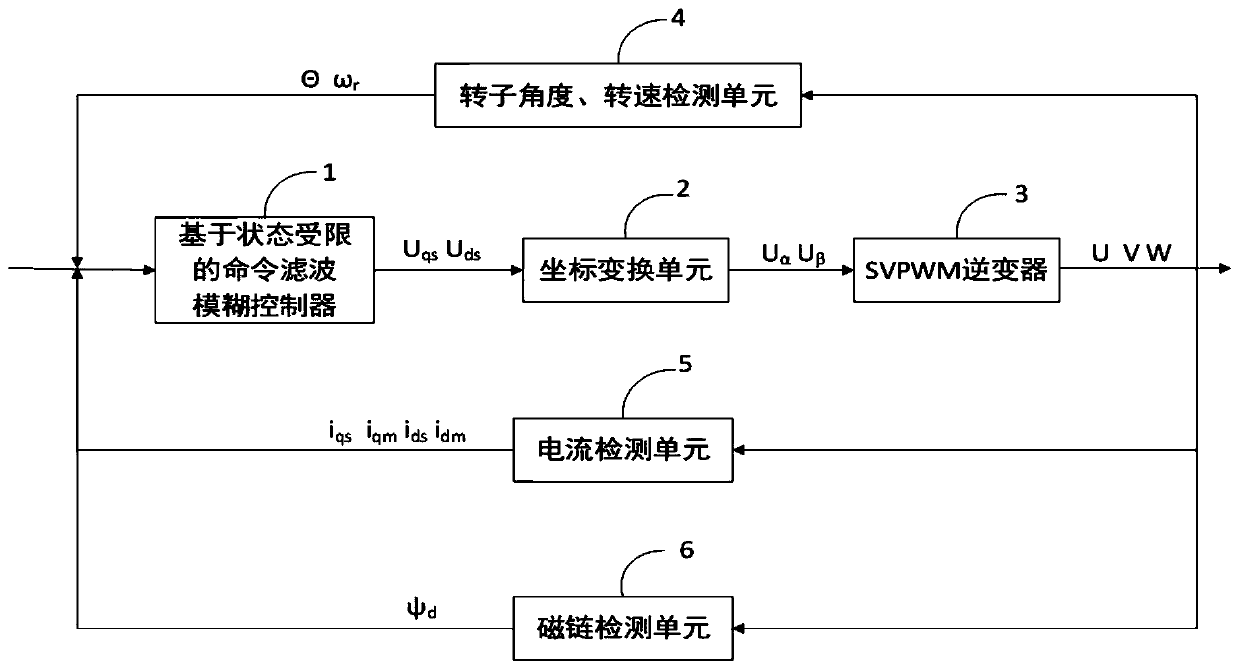
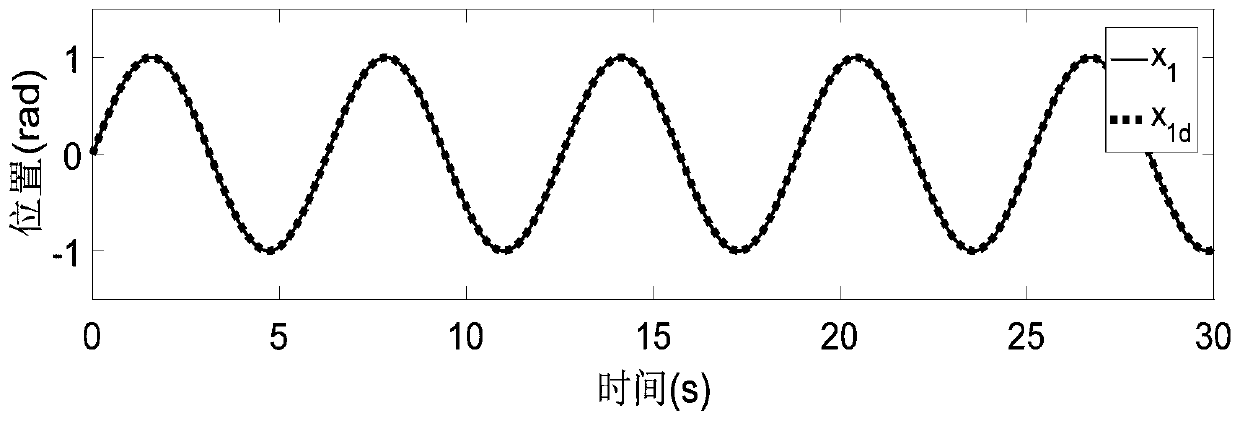
Input saturation considered asynchronous motor command filter finite time fuzzy control method
The invention discloses an input saturation considered asynchronous motor command filter finite time fuzzy control method. Aiming at nonlinear problems of a motor driving and control system, a fuzzy logic system is adopted for approximation to a nonlinear function in the system, a command filter technique is introduced into a traditional backstepping design method, errors generated in filtering are reduced through introduction of a compensation mechanism, the problem of computation explosion caused by continuous derivation in traditional backstepping control is successfully solved, and control precision is improved. Small system stable tracking errors and short dynamic responding time under finite time control are realized, system convergence rate is increased, and interference rejection capability is improved. Under the condition of consideration of input saturation, bounded parameters of a closed-loop system can be guaranteed, and convergence of tracking errors of the system into a sufficiently small origin neighborhood in finite time can be guaranteed as well.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
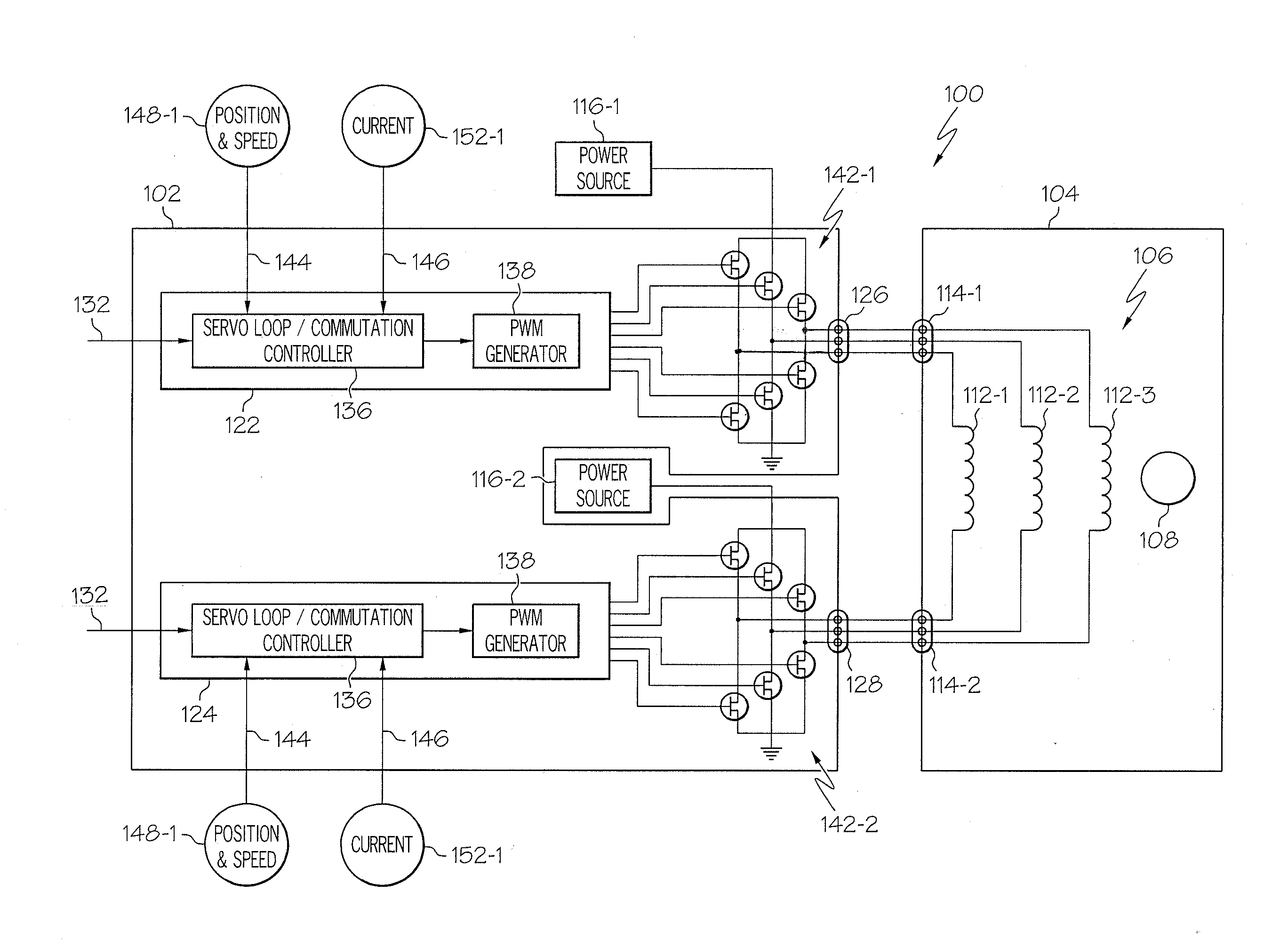
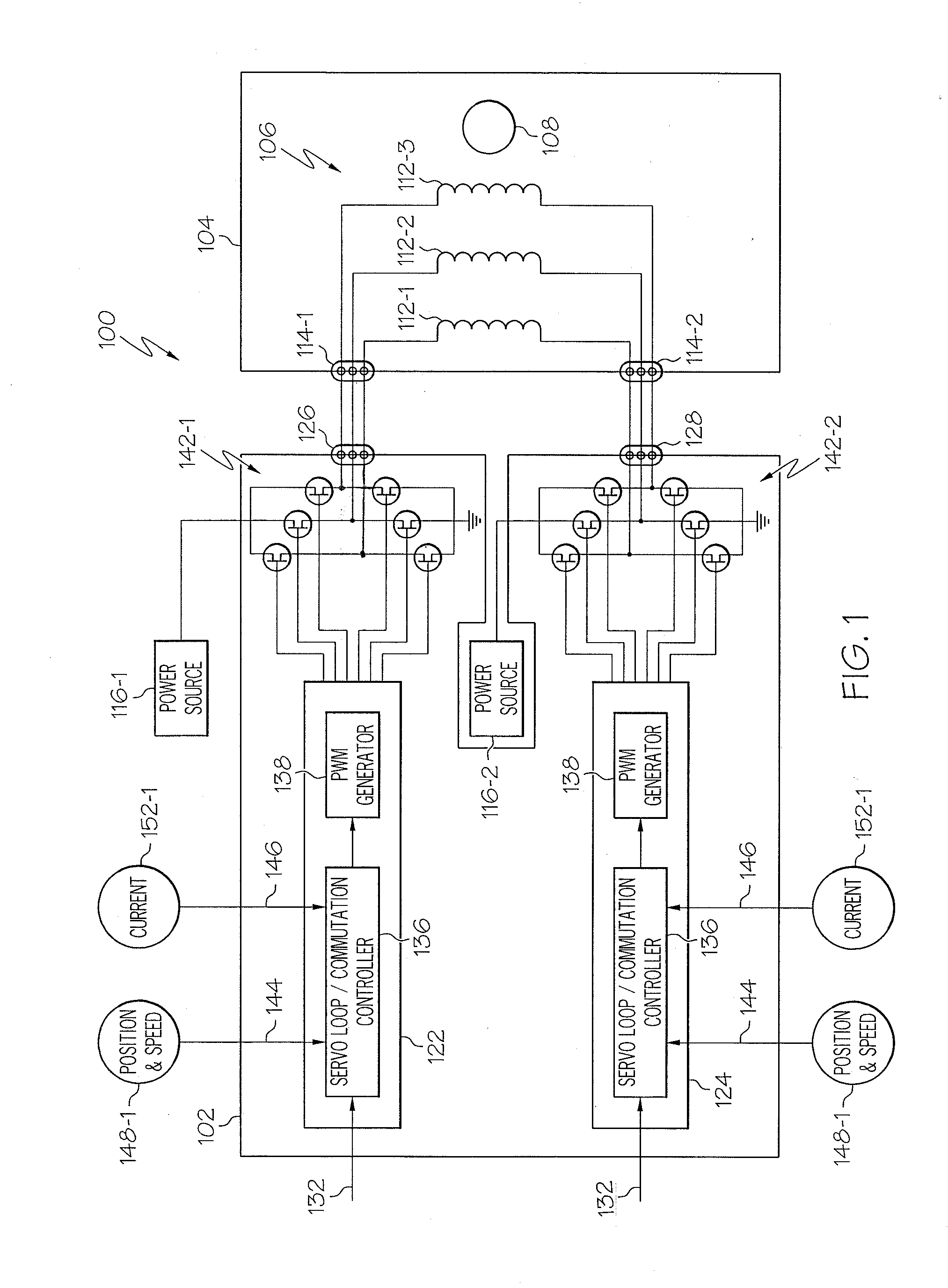
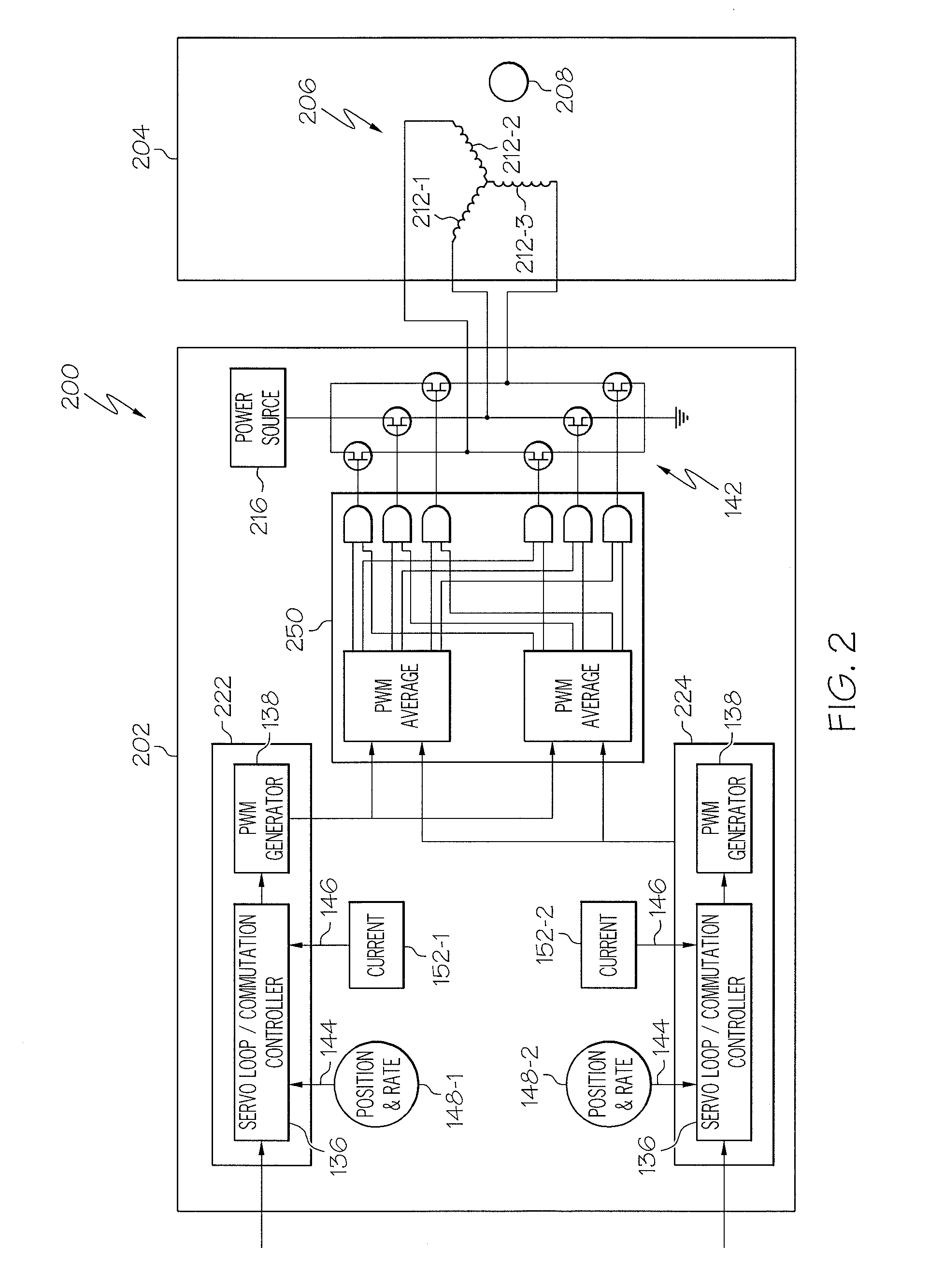
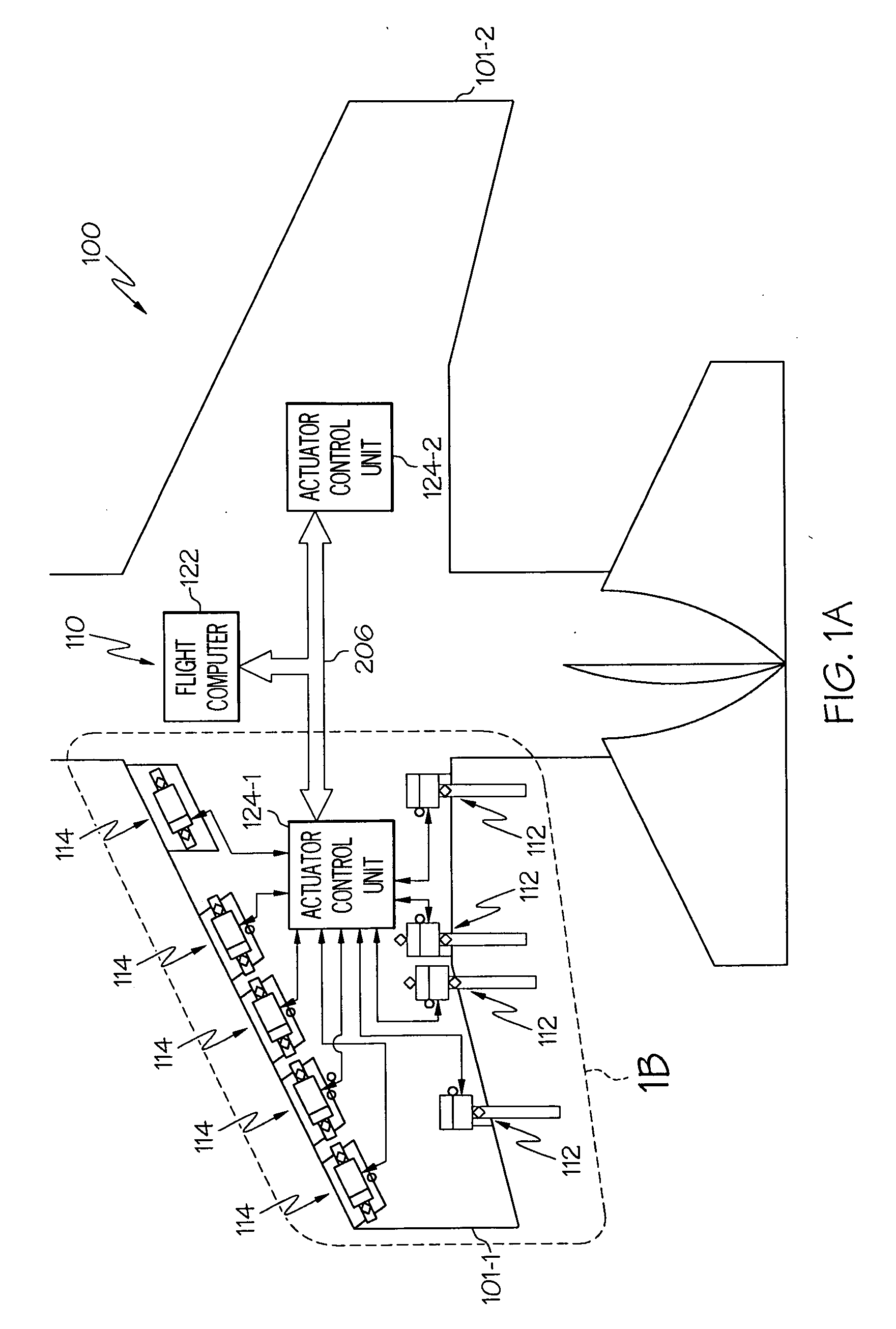
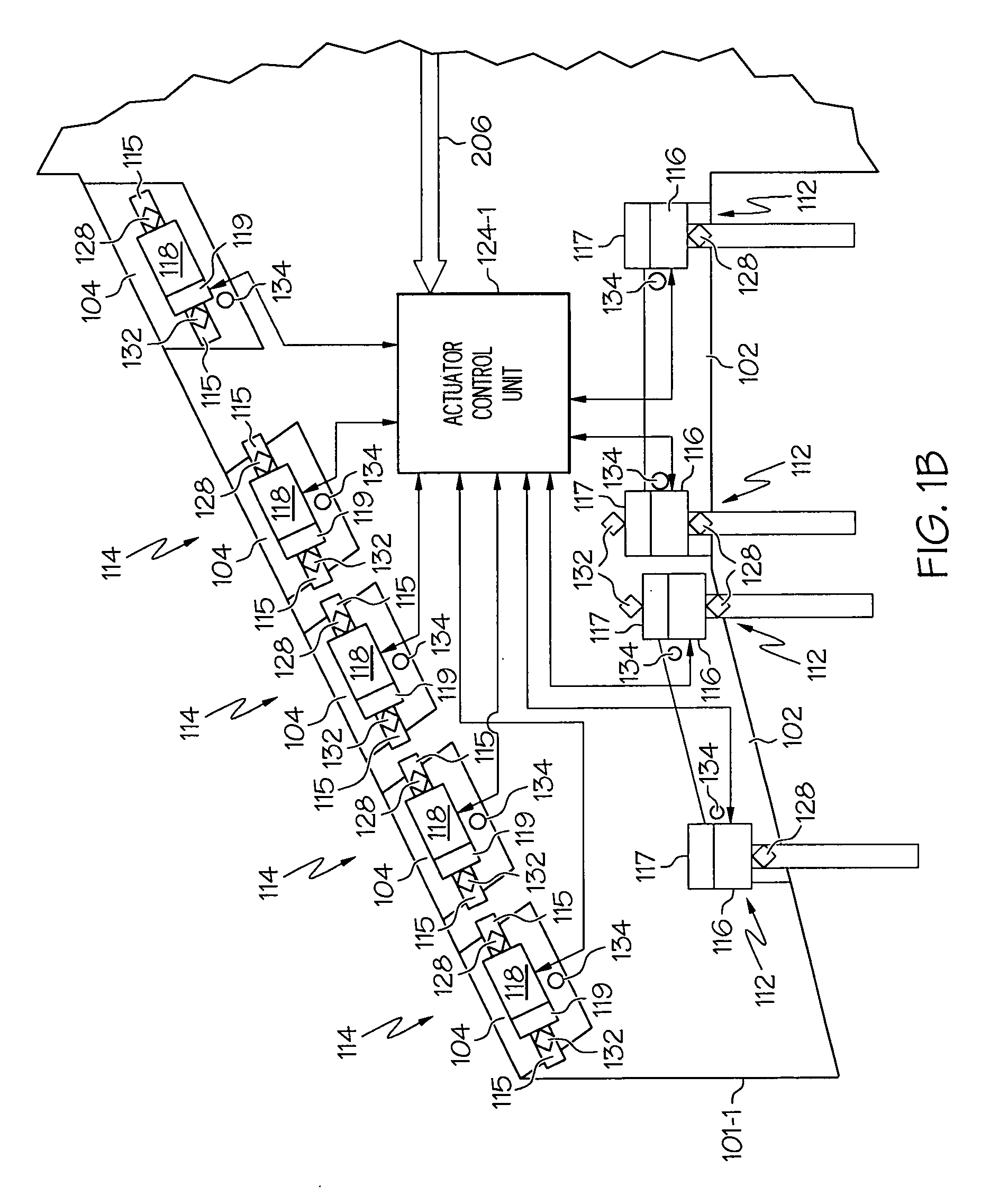
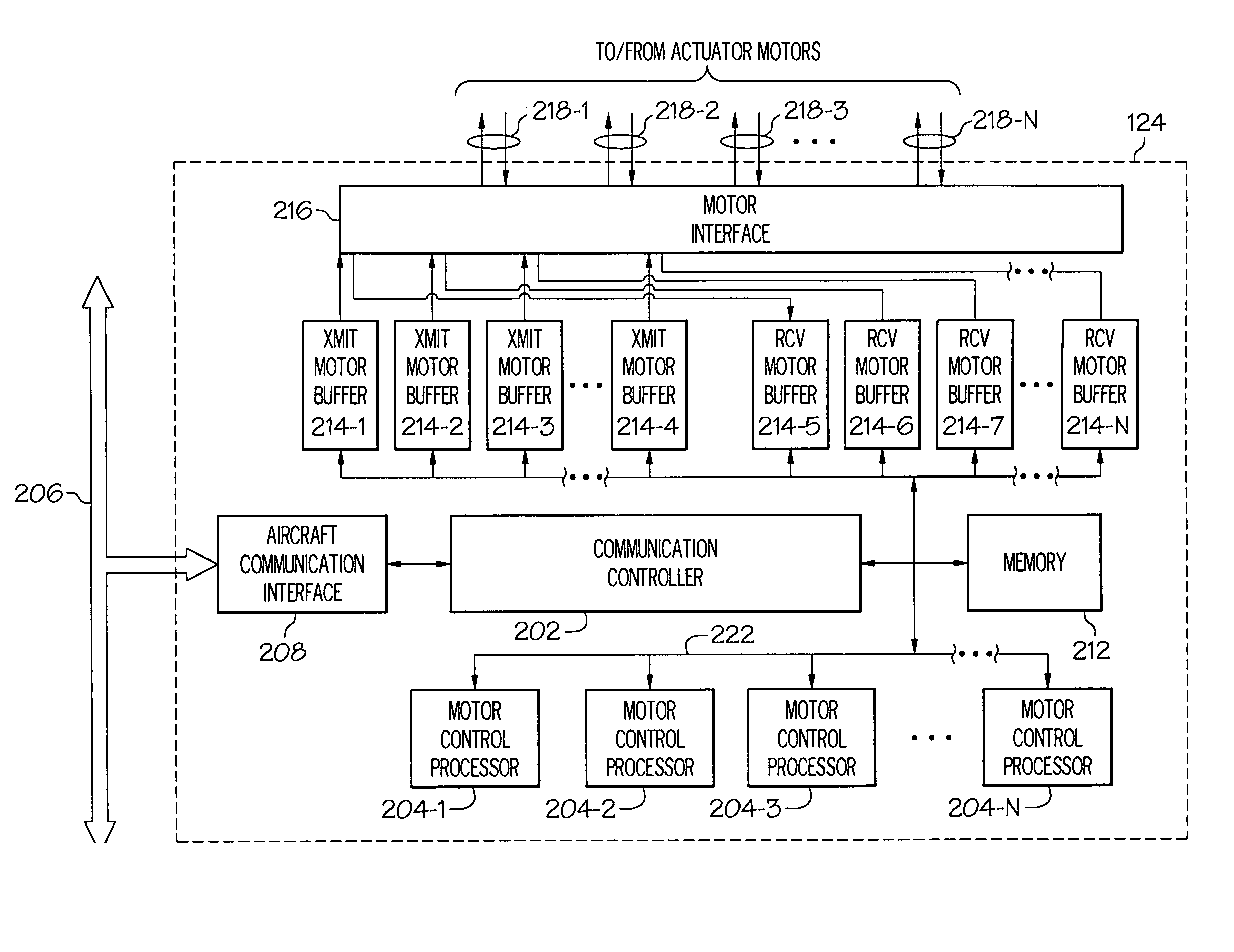
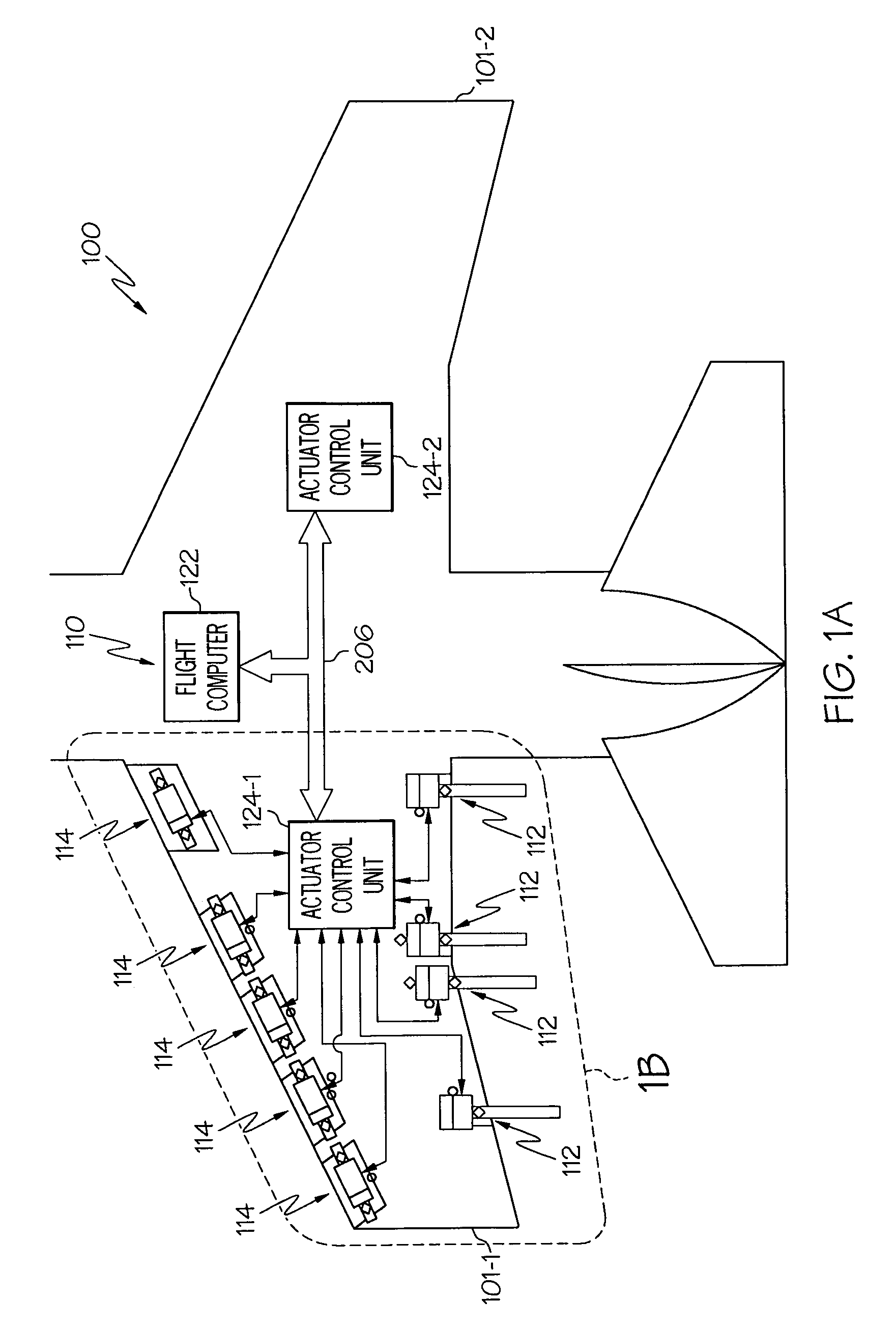
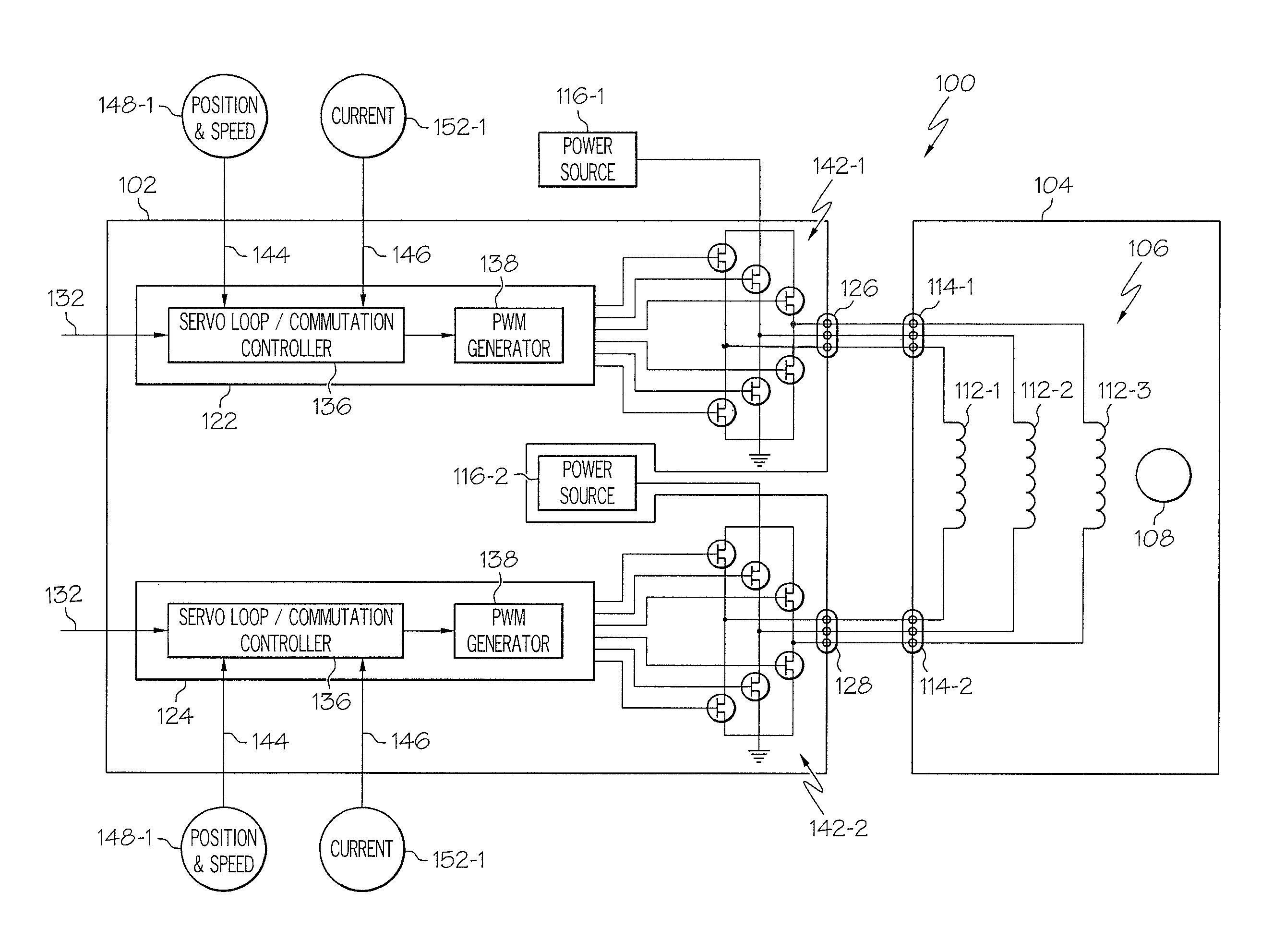
Motor control architecture for simultaneously controlling multiple motors
A motor control architecture is provided that simultaneously controls multiple motors. The motor control system includes memory, a plurality of motor control processors, and a communication controller. The motor control processors are each responsive to control signals supplied from the communication controller to selectively retrieve system commands and motor positions from the memory, to generate motor commands, and to supply the generated motor commands to the memory. The communication controller selectively receives system commands and transmits the received system commands to the memory, selectively supplies the command signals to selected ones of the motor control processors, selectively receives motor positions from a plurality of motors, selectively transmits motor positions to the memory, selectively retrieves generated motor commands supplied to the memory, and selectively transmits the retrieved motor commands.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Motor control architecture for simultaneously controlling multiple motors
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and Device for Controlling a Robot
InactiveUS20090018696A1Programme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsMotor commandsControl theory
A robot controller including a multitude of simultaneously functioning robot controller units. Each robot controller unit is adapted to receive an input signal, receive top-down information, execute an internal process or dynamics, store at least one representation, send top-down information, issue motor commands wherein each motor command has a priority. The robot controller selects one or several motor commands issued by one or several units based on their priority. Each robot controller unit may read representations stored in other robot controller units.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
Cooled motor
InactiveUS20120274256A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlMotor speedMotor commands
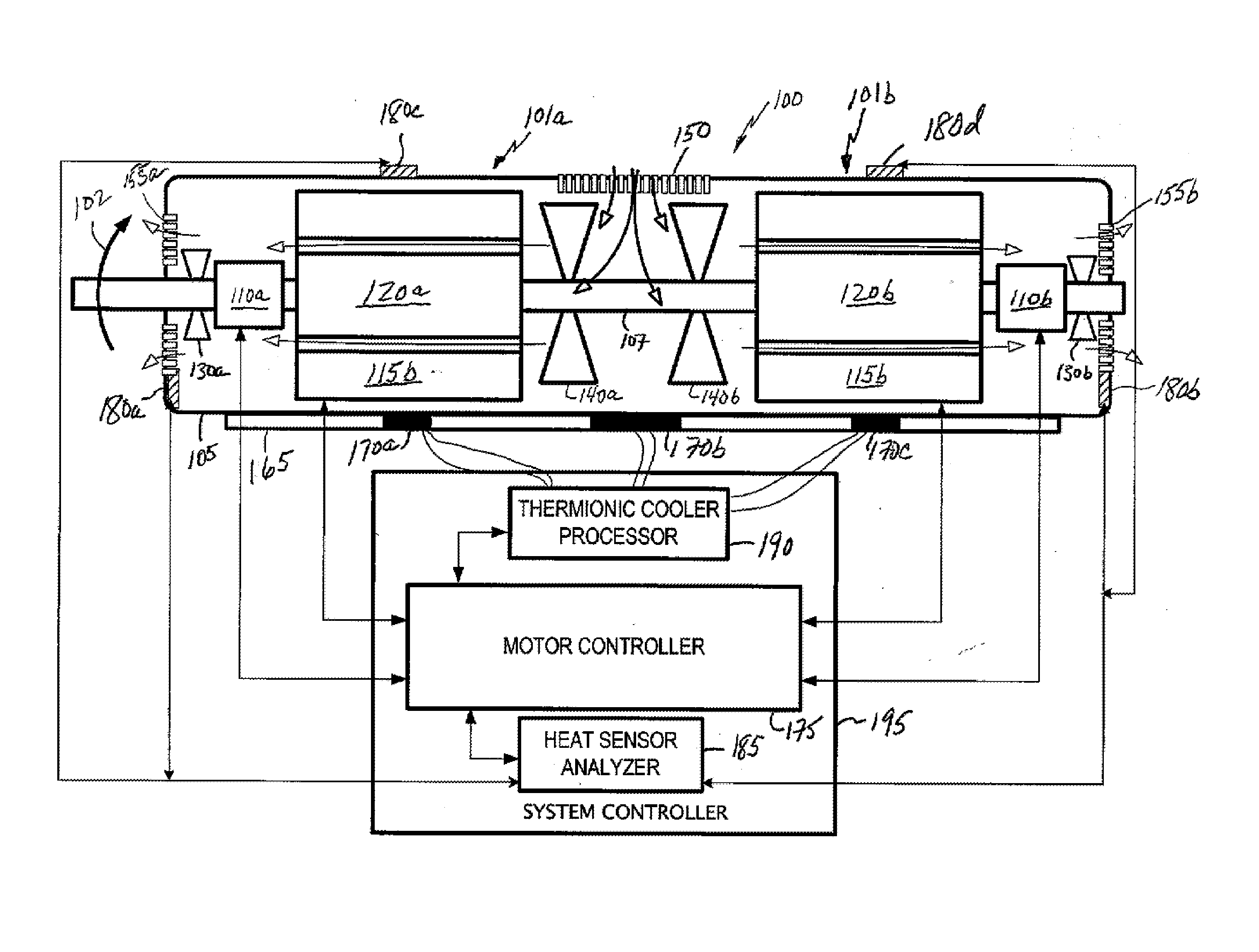
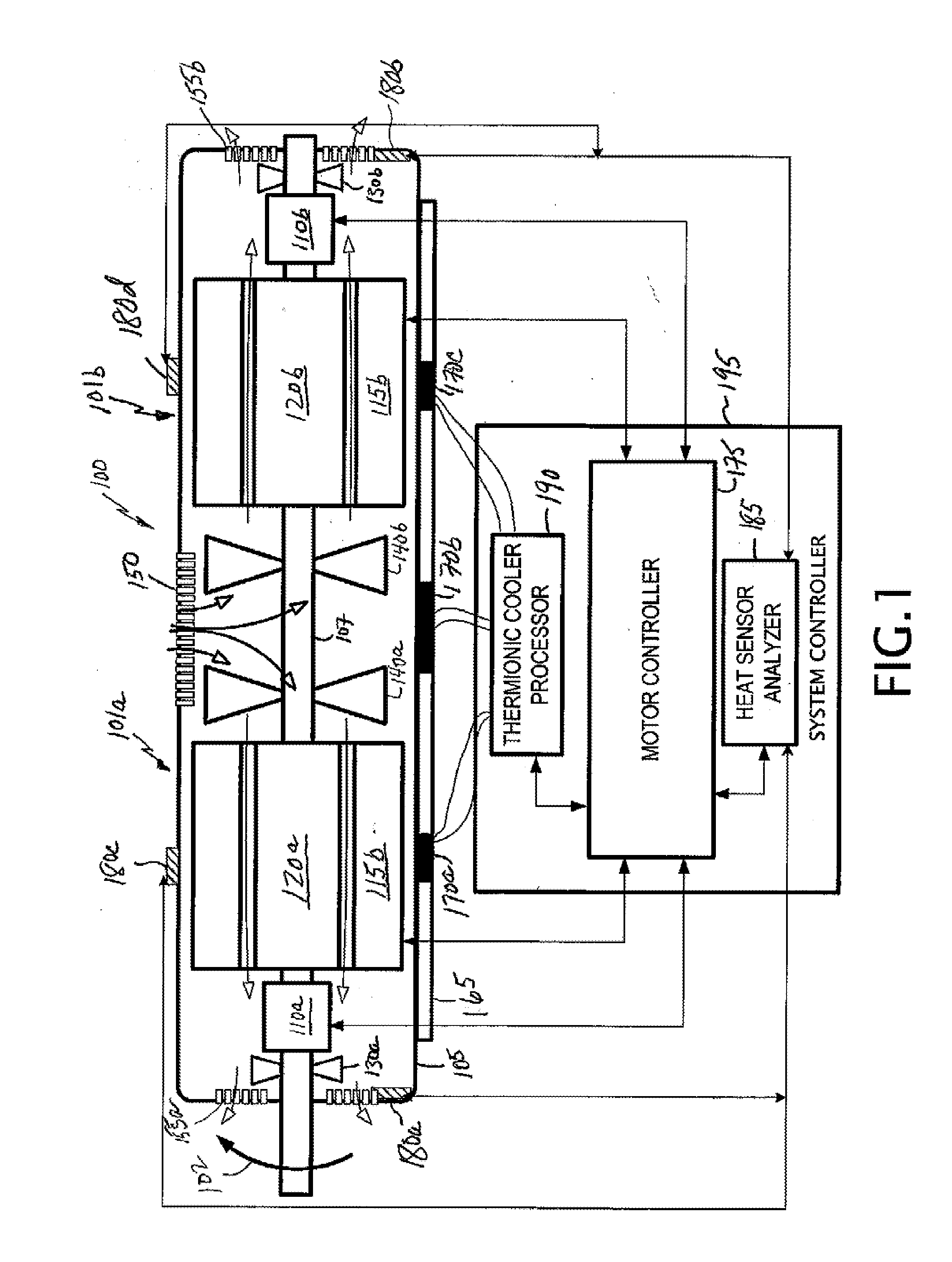
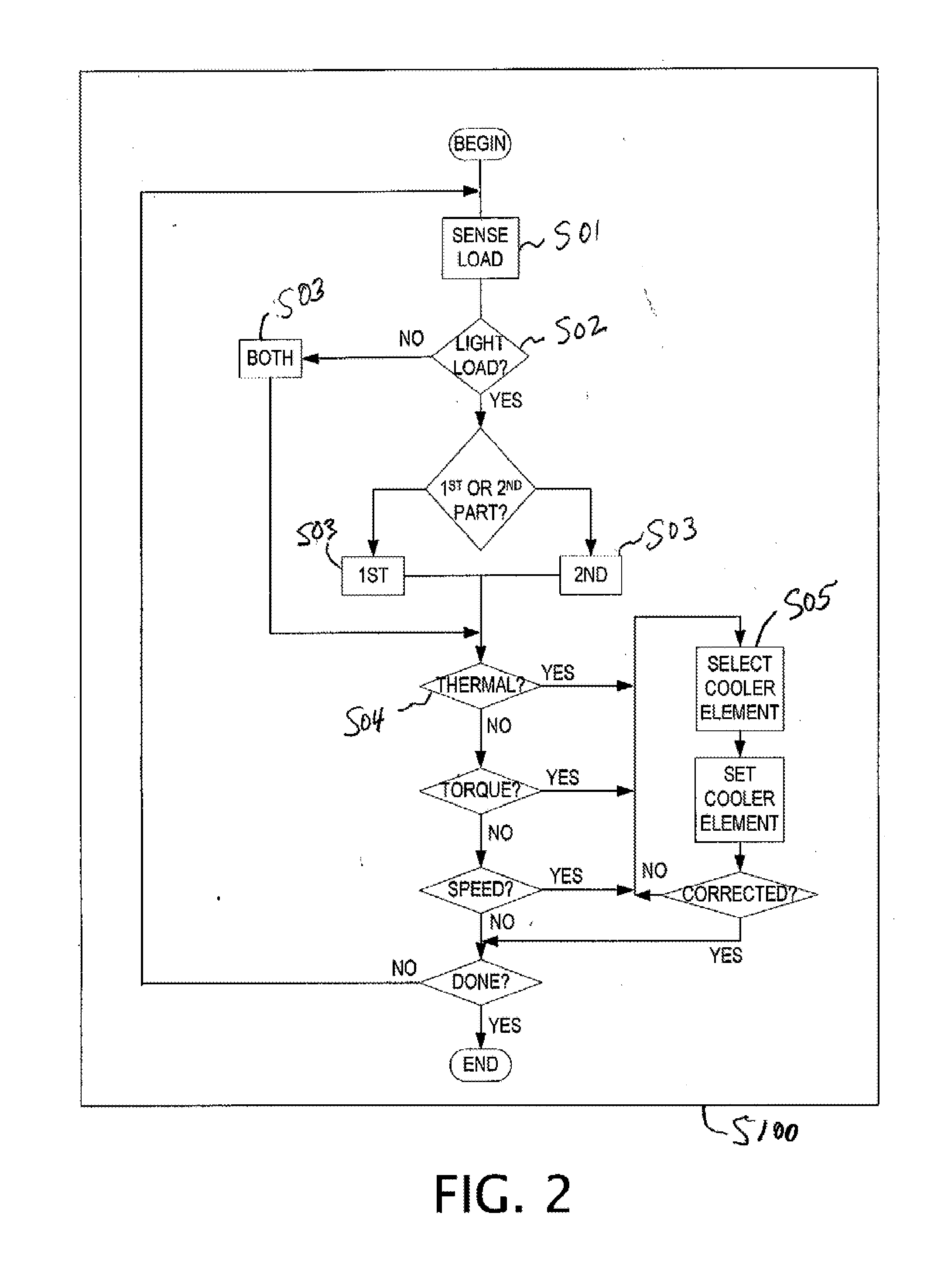
A motor having a first portion configured to turn in a forward direction, a second portion coaxially mirrors the first portion; and a central fan between the first and second portions, and forcing air through the portions. A thermoelectric cooler element, thermally coupled to the portion is configured to cool the motor. A motor controller is electrically coupled to the first and second portions, and operates a portion in response to a condition sensed by the motor controller. The condition sensed by the motor controller is a motor torque, a motor speed, a motor casing temperature, or a zoned motor casing temperature. A method includes detecting a motor operational command; selecting a motor operational state using motor portion responsive to the motor command; sensing a heating state of a motor portion; and providing a cooling state to the motor portion responsive to the heating state.
Owner:AURORA OFFICE EQUIP
Dual lane control of a permanent magnet brushless motor using non-trapezoidal commutation control
InactiveUS8084972B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersBrushless motorsPermanent magnet rotor
A motor control system and method implements non-trapezoidal motor control and meets established “fail passive” regulatory guidelines. In particular, a system and method of controlling a multi-phase brushless motor that includes a multi-pole permanent magnet rotor, and an individual, electrically isolated stator winding associated with each phase that includes a first terminal and a second terminal. A motor command is supplied to a motor control. The motor control is configured such that the first terminal of each stator winding is selectively coupled to a power source at a first duty cycle, and the second terminal of each stator winding is selectively coupled to a power source asynchronously with the first terminal of each stator winding at a second duty cycle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Systems and methods for decoding intended motor commands from recorded neural signals for the control of external devices or to interact in virtual environments
Systems and methods for decoding neural and / or electromyographic signals are provided. A system can include at least one single channel decoder. Optionally, the system can include a demixer in operable communication with the single channel decoders. Each single channel decoder can include a filter to attenuate noise and sharpen spikes in the neural and / or electromyographic signals, a detection function to identify spikes, and a demodulator to get a real-time estimate of motor intent.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Two-way control method for eliminating imaging rotation of scanning imaging system
The invention discloses a two-way control method for eliminating imaging rotation of a scanning imaging system, relates to the technical field of imaging, and solves the problems that the existing imaging rotation elimination methods using mechanical linkage or combination of a servo motor and the mechanical linkage results in low transmission accuracy, or meanwhile strictly coordinated movement of a scanning mirror and a rotation eliminating mechanism is hard to achieve by adopting the servo motor to drive to eliminate the imaging rotation. The two-way control method includes steps of adopting a single motor command tracking controller to receive a rotation command of the scanning mirror, and controlling rotation of a scanning mirror servo motor and a rotation eliminating mechanism servo motor respectively; adopting a torque estimator to estimate equivalent driving torques acted on a motor shafting by the single motor command tracking controller to provide torque information for a four-channel two-way controller. According to the arrangement, positions and torques between two servo systems of the scanning mirror servo motor and the rotation eliminating mechanism servo motor are mix-controlled to realize electrical linkages of the same. Besides, coordinated movement performance between the scanning mirror and the rotation eliminating mechanism in a servo motor rotation eliminating system is improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for controlling operation of car sunroof
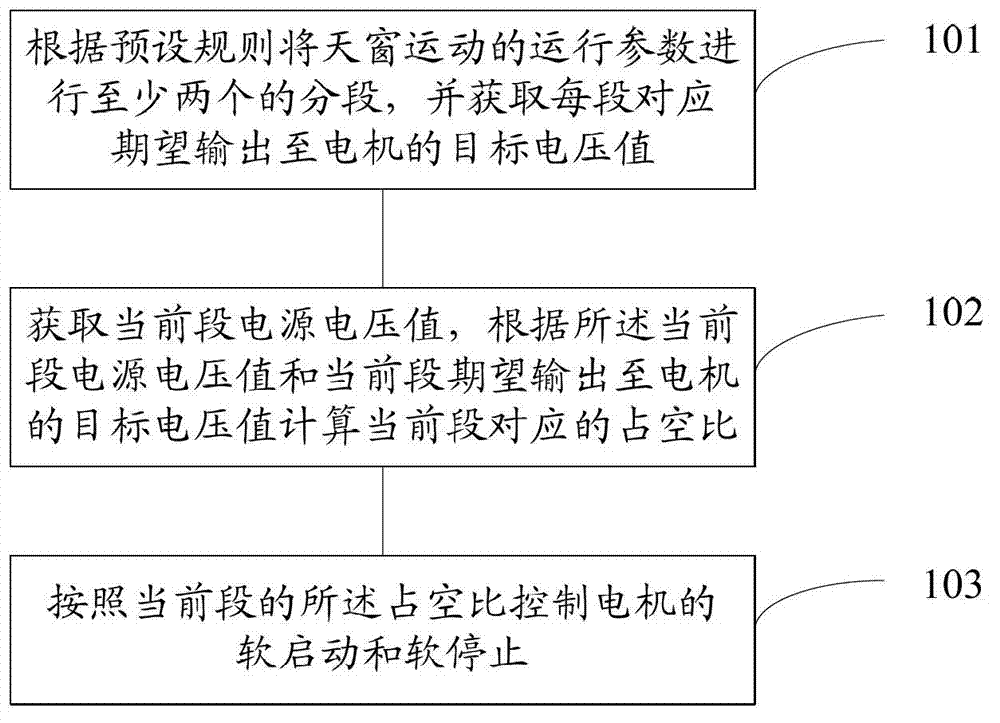
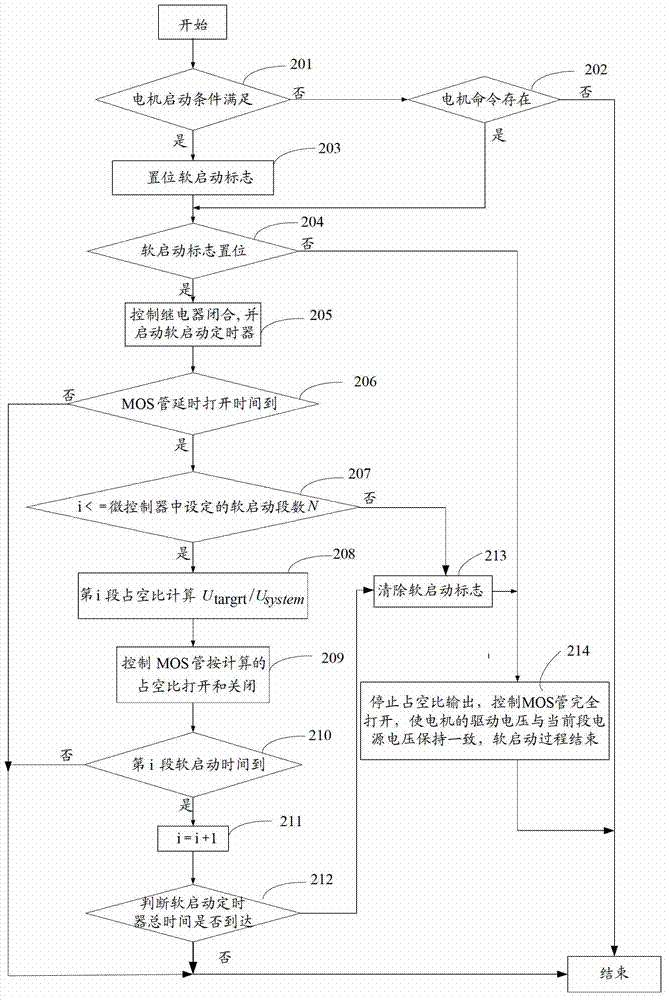
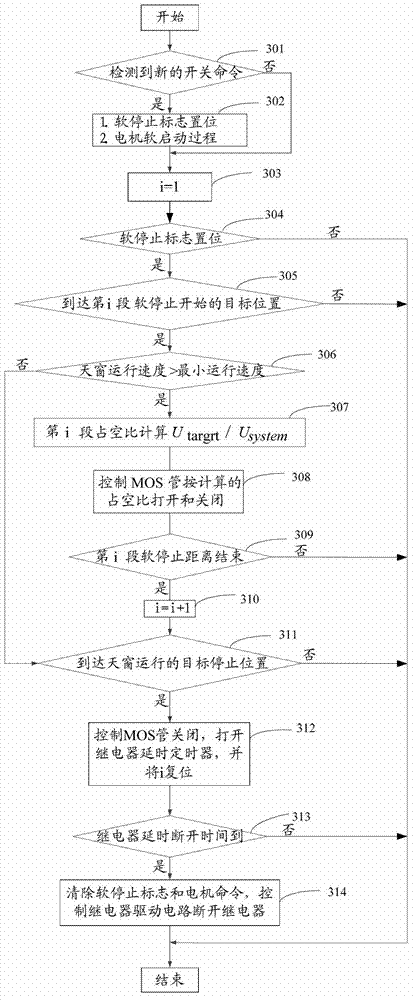
The invention discloses a method and a system for controlling the operation of a car sunroof. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing the operating parameter of the movement of the sunroof into at least two sections according to a preset rule, and obtaining a target voltage value corresponding to each section and expected to be outputted to a motor; obtaining the power voltage value of a current section, calculating the duty ratio corresponding to the current section according to the power voltage value of the current section and the target voltage value of the current section, wherein the target voltage value of the current section is expected to be outputted to the motor; and controlling the soft starting and the soft stopping of the motor according to the duty ratio of the current section. According to the invention, the voltage inputted to the motor is slowly increased or reduced, so that the operation of the sunroof is controlled, and the condition that because of the noise and vibration brought by the sudden starting and stopping of the motor, the comfort reduction of a customer is reduced when the customer takes a car is reduced. Otherwise, during the process of the soft stopping, the target voltage in stopping is reduced because of the multi-time soft stopping method, so that the inertial forward-rushing distance when the motor commands the stopping under various working conditions is effectively controlled, and the position control precision of the stopping of the sunroof is improved.
Owner:BEIJING JINGWEI HIRAIN TECH CO INC
Controller For Machine Tool Including Main Shafts
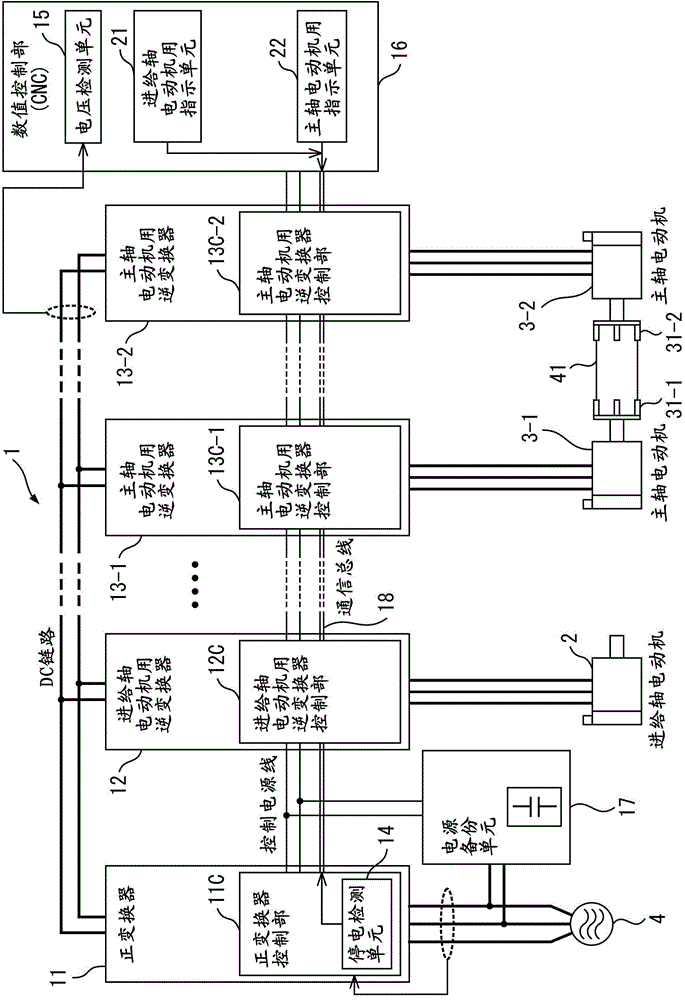
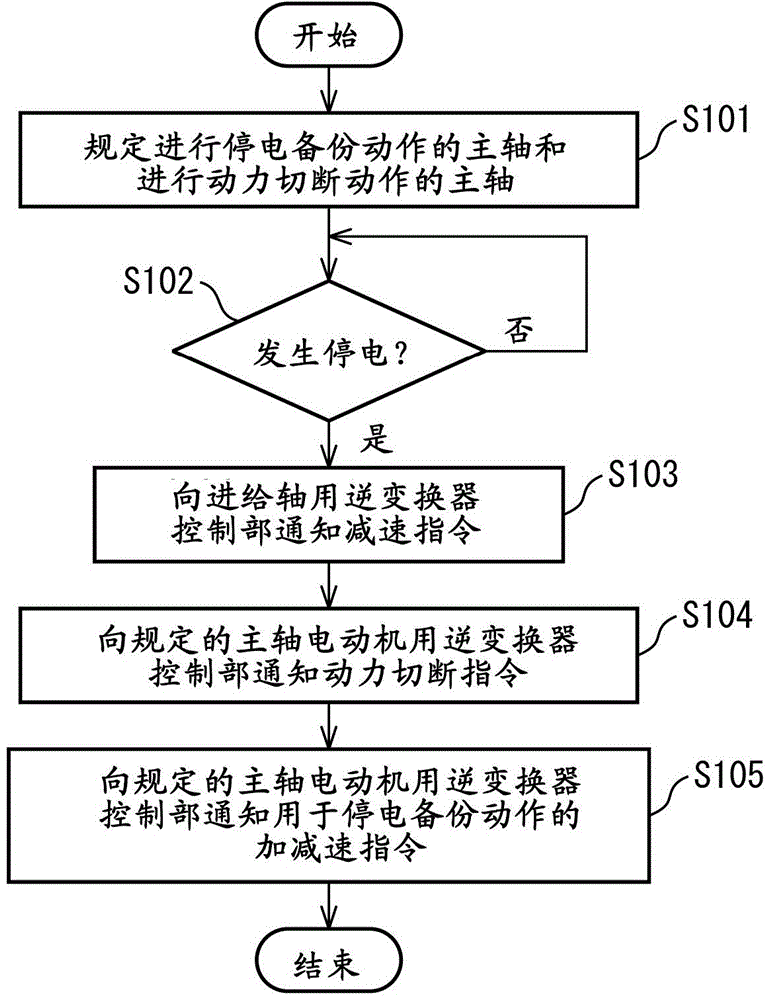
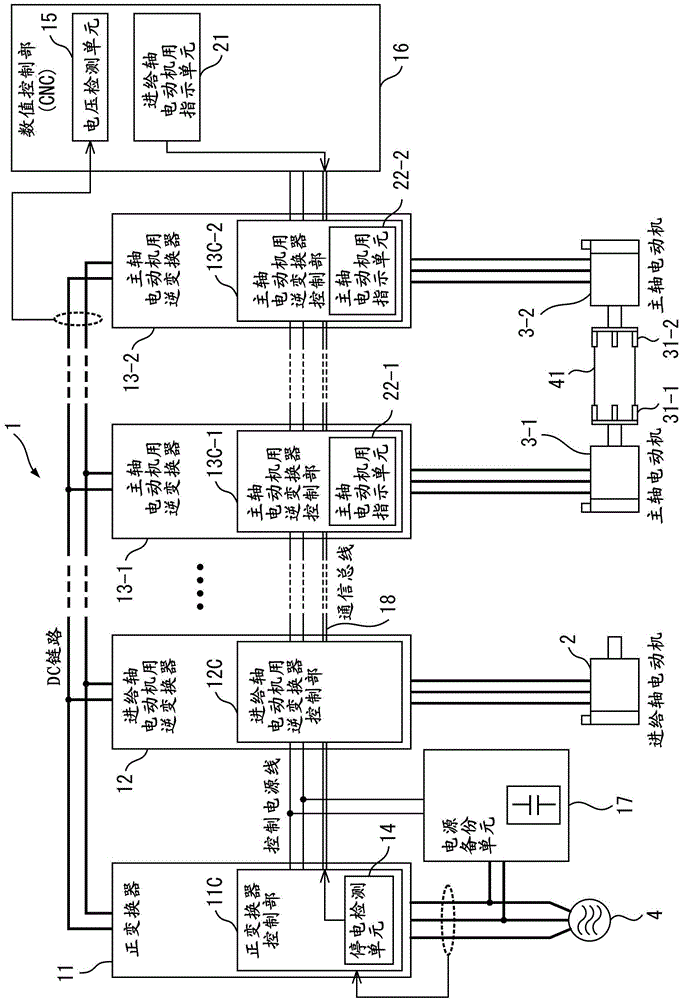
A controller for a machine tool includes a converter converting AC power on the power supply side to DC power, a feed-shaft motor inverter converting DC power on a DC link side and AC power on a feed shaft motor side, first and second main-shaft-motor inverters converting DC power on the DC link side and AC power on first and second main shaft motors side, a power failure detection unit detecting a power failure on the power supply side, a voltage detection unit detecting a DC link voltage value, a feed-shaft-motor command unit outputting a deceleration command to the feed-shaft-motor inverter upon a power failure, and a main-shaft-motor command unit outputting an acceleration / deceleration command to the first main-shaft-motor inverter in accordance with the DC link voltage value and a power shutoff command to the second-main-shaft-motor inverter upon a power failure.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Asynchronous motor command filtering fuzzy control method based on state constraints
ActiveCN110336505AFix security issuesOvercoming the "computational explosion" problemElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlMotor commandsAngular velocity
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor command filtering fuzzy control method based on state constraints. An obstacle Lyapunov function is constructed to ensure that the rotor angular velocity,stator current and other state variables of an asynchronous motor drive system are always within a given state interval. A command filtering technology is introduced to overcome the 'computation explosion' problem which cannot be avoided by the traditional back-stepping method, and a filtering error compensation mechanism is introduced to eliminate the influence of filtering error. A fuzzy logicsystem is adopted to approximate a nonlinear term in the system, and a command filtering fuzzy controller is constructed. In addition, a more accurate model is used in view of the iron loss of the asynchronous motor. The simulation results show that the method not only can achieve an ideal position tracking effect, but also can avoid safety problems caused by the violation of state constraints byconstraining the rotor angular speed, stator current and other state variables within a given constraint interval.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com