Clean metallurgic comprehensive utilization method of iron vitriol slags
A technology of jarosite slag and jarosite, which is applied in the field of metallurgical hazardous solid waste treatment, can solve the problems of low recovery rate of silver and lead, high cost, inevitable iron dissolution, etc., to solve serious pollution problems, good environmental benefits and economical Benefits, the effect of reducing energy consumption and material consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
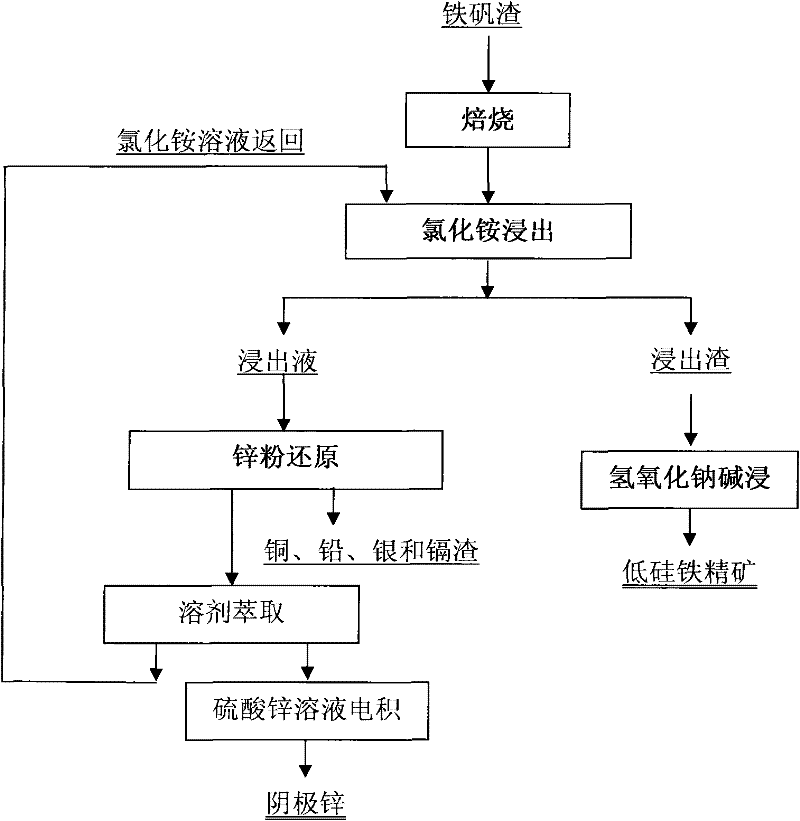
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
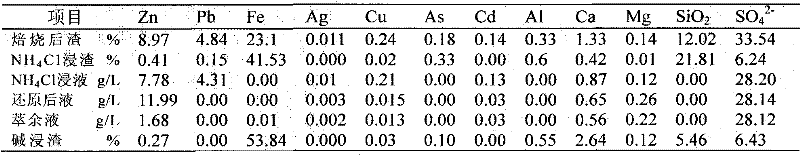
[0035] The jarosite slag was calcined at 650°C for 1 h, and its composition after firing is shown in the first line of Table 2.
[0036] The chemical composition of each operation gained slag among the table 2. embodiment 1
[0037]
[0038] With NH at a molar concentration of 6M 4 Cl and 1M NH 4 The OH solution selectively leached the roasted jarosite slag under the condition of a liquid-solid ratio (mL / g) of 10:1. The composition of the obtained leaching residue was shown in the second row of Table 2, and the composition of the leachate was shown in the third row of Table 2. As shown in the row, the leaching rate of zinc reaches 97.5%, the leaching rate of copper reaches 95.4%, the leaching rate of silver and cadmium reaches 100%, and the leaching rate of lead reaches 93.3%; Fe and As hardly leach;
[0039] Stir the leaching solution and zinc powder with 1.3 times the total molar number of copper, lead, cadmium and silver in the ammonium chloride leaching solution at 50...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The jarosite slag was calcined at 600°C for 2 hours, and its composition after firing is shown in the first line of Table 3.
[0044] The chemical composition of each process gained slag in the table 3. embodiment 2
[0045]
[0046] With NH at a molar concentration of 5M 4 Cl and 0.6M NH 4 The OH solution selectively leaches the roasted jarosite slag under the condition of a liquid-solid ratio of 10:1. The composition of the obtained leaching residue is shown in the second row of Table 3, and the composition of the leachate is shown in the third row of Table 3, wherein Zinc leaching rate is 96.0%, copper leaching rate is 83.7%, silver leaching rate is 80.5%, cadmium leaching rate is 100%, lead leaching rate reaches 90.2%, Fe and As hardly leaching;
[0047] Stir the leaching solution and zinc powder with 1.5 times the total molar number of copper, lead, cadmium and silver in the ammonium chloride leaching solution at 40°C for 60 minutes. The recovery rate can rea...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The solution shown in the first column of Table 4 was subjected to a zinc powder reduction experiment with the addition of 2.0 times the molar ratio of the required reducing elements. The reaction temperature was 50°C and the time was 1 hour. After the reduction, the solution composition was as shown in Table 4 As shown in the column, the recovery rate of the reduction process is as shown in the third column of Table 4.
[0052] The recovery rate of chemical components before and after reduction among table 4. embodiment 3
[0053]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com