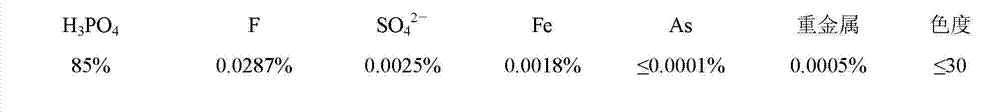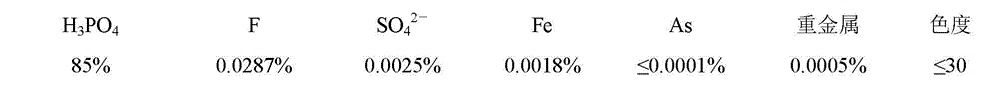Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46results about How to "Low Sulfate Content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of preparing electronic grade nickel carbonate by sodium carbonate deposition
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of electron-grade nickel carbonate through sedimenting sodium carbonate, which is characterized by the following: adopting soluble nickel salt as nickel source and sodium carbonate as sediment; co-flowing nickel salt solution and sodium carbonate solution; controlling pH value, temperature and aging condition; washing; drying; washing again; drying again; grinding into product.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED +1
Method for treating nickel-containing laterite by microwave reducing roasting-hematite precipitation conversion method
InactiveCN101392321AFast heatingImprove energy efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementSulfate radicalsSlurry
The invention relates to a method for processing laterite ore comprising nickel by means of microwave reduction roasting-hematite deposit transformation, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: (1) a carbonaceous reducing agent is added into the laterite ore, and heated for 5min to 20min under microwave radiation after even blending so as to obtain laterite ore calcine; and (2) the laterite ore calcine is leached in a high-pressure container. The concentration of ore slurry leached is 10 percent to 30 percent, and the ore slurry is fed into oxygen-enriched air or pure oxygen to carry out oxidation leaching reaction. Nickel cobalt in the laterite ore enters the leached liquid, with iron transformed to hematite deposit. The method consumes less acid, with the leaching temperature greatly lower than that of the existing high-pressure acid leaching method, thereby being favorable to the decrease in manufacturing cost of leaching equipment; simultaneously, the scale in equipment is greatly decreased, the content of sulfate radical in the leaching residue is accordingly lowered, thus being favorable to the comprehensive utilization of the leaching residue.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Preparation method of low-solidification-temperature agarose
The invention discloses a preparation method of low-solidification-temperature agarose. The preparation method includes the following steps that 1, agarose is dissolved in deionized water to prepare an agarose solution; 2, the agarose solution is naturally cooled to 60-83 DEG C, and then a sodium hydroxide solution of sodium borohydride is added into the agarose solution for a reduction reaction; 3, a sodium hydroxide solution is added for alkalization treatment; 4, rapid cooling is carried out, and oxirane is slowly dripped with stirring for a derivatization reaction; 5, heating is carried out, and an acetic acid solution is dripped with stirring to regulate the pH value of the solution; 6, hot isopropanol is added with stirring for alcohol precipitation fractionation; 7, filtering, smashing and washing are carried out several times to obtain a filter cake; 8, after drying, smashing and screening, low-solidification-temperature agarose is obtained. According to the preparation method, common agarose is subjected to chemical modification and fractionation purification, and prepared agarose has the advantages of being low in solidification temperature and melting temperature, high in jelly strength and the like and is an ideal biological material for DNA separation and extraction.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Method for reducing content of sulfate radicals in rare earth hydrate
ActiveCN105621471AReduce contentSimple processRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesButanedioic acidSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a method for reducing the content of sulfate radicals in rare earth hydrate. The method comprises the following steps: adding sulfate radical-containing rare earth hydrate into a coordination solution containing one or more organic matters in malic acid, acetylacetone, lactic acid, acetic acid, butanedioic acid, glycolic acid and malonic acid, wherein the pH value of the coordination solution is 7-10; and then performing solid-liquid separation, water-washing and drying to obtain rare earth hydrate with the sulfate radical content less than 0.5%. According to the method, sulfate ions are removed with a method for competitive coordination with sulfate radicals; a process is simple and easy to control; a desulfurization effect is remarkable; and the organic matters entering rare earth hydrate can be removed in a roasting manner, so that the purity of a rare earth oxide product is not influenced finally.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
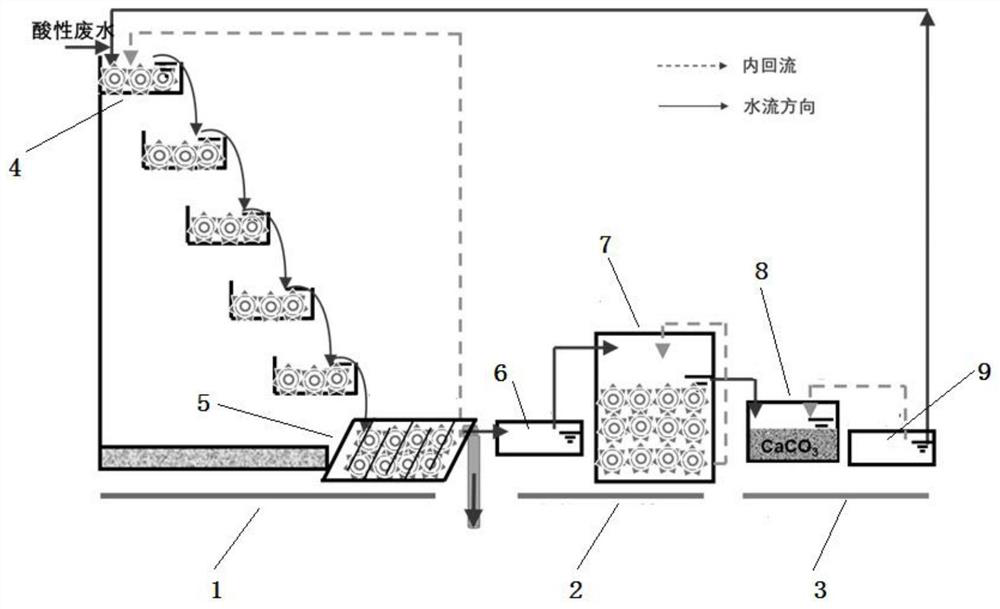
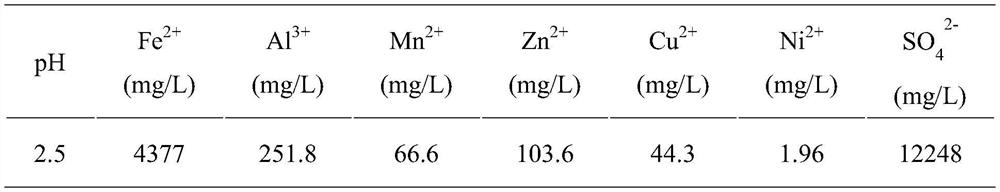
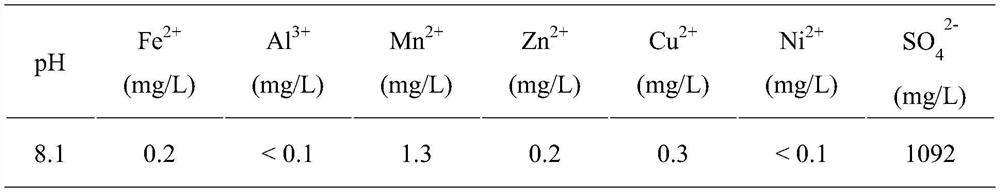
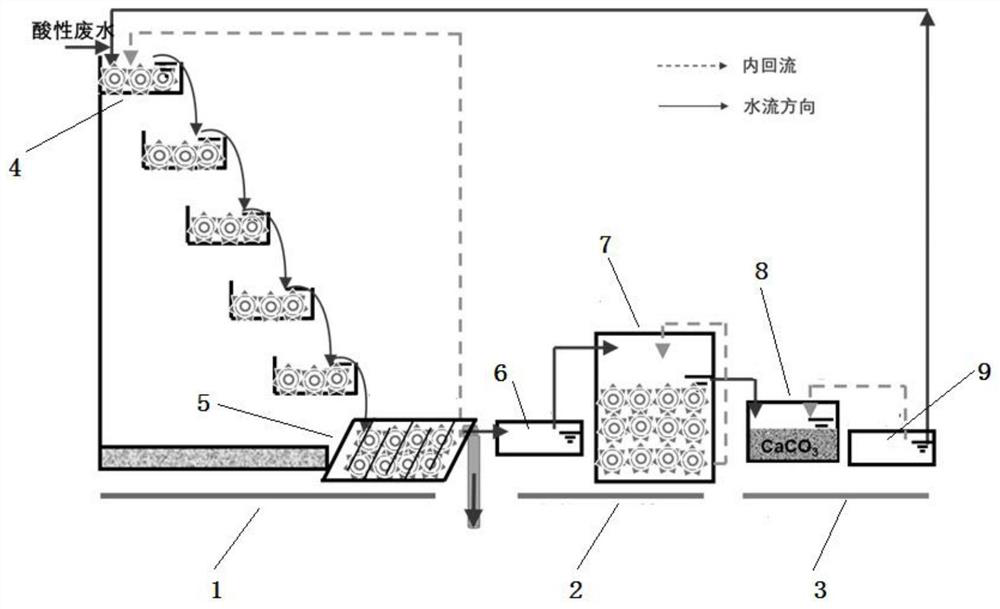
Method for biologically treating acidic mine wastewater and recovering iron ions and system thereof
ActiveCN111620444AReduce metal ionsLow Sulfate ContentWaste water treatment from quariesTreatment using aerobic processesWastewaterBiomineralization
The invention provides a method and a system for biologically treating acidic mine wastewater and simultaneously recovering iron ions. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out biomineralization on the acidic mine wastewater by acidophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria, carrying out cyclic biological reduction treatment by acidophilic iron-reducing bacteria, introducing the wastewater into an alkali regulating tank, circularly regulating the pH value, and circulating an effluent to a biomineralization treatment unit for cyclic treatment; and (2) after reaction for a period of time,leading the wastewater out from the tail end of the water collecting tank and can be subsequently connected with a lime neutralization treatment system, and recycling jarosite minerals or schwertmannite minerals in the biological mineralization unit. The screened bacteria are indigenous strains existing in the actual mine environment and can be completely suitable for mine wastewater treatment. According to the invention, the precipitation amount of iron in the acid wastewater is increased by adopting circular treatment, and the mine wastewater can completely reach the standard by subsequentlyconnecting lime for neutralizing treatment.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
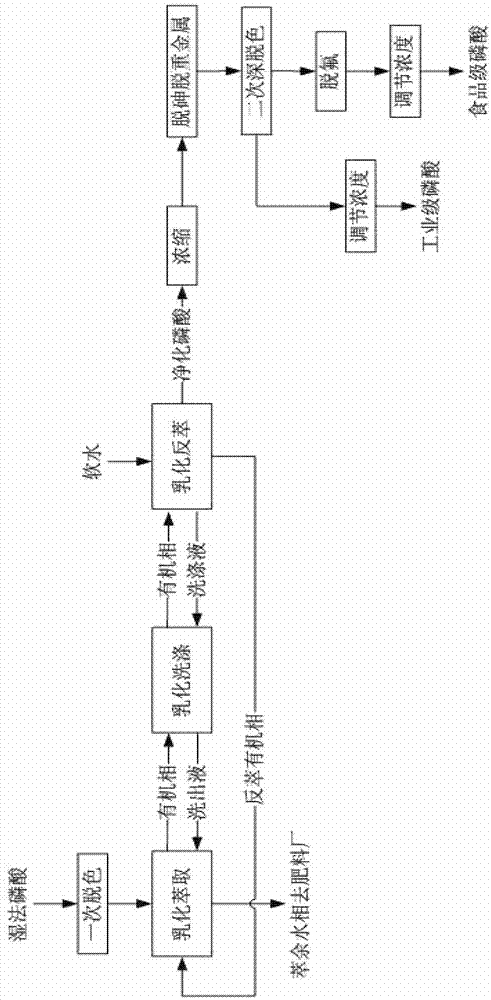
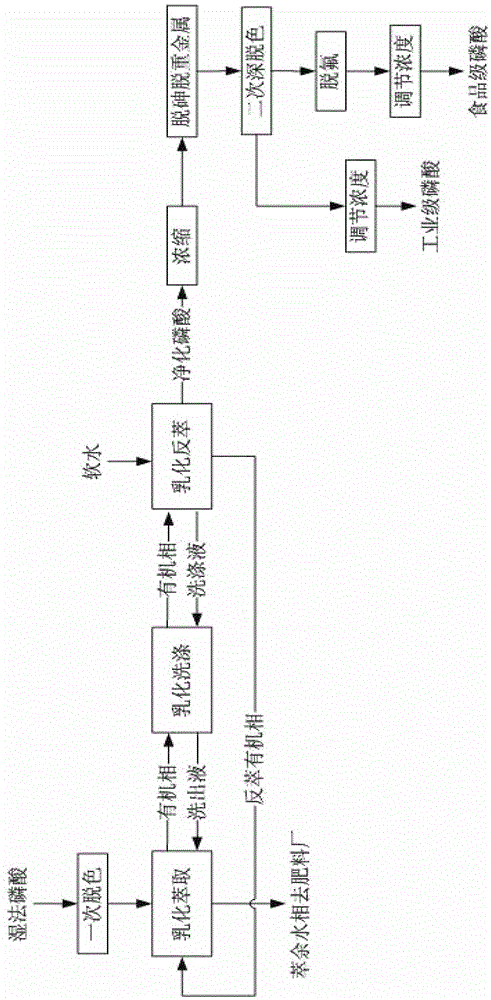
Method for preparing industrial-grade and food-grade phosphoric acid by emulsification, extraction and purification wet method
ActiveCN102730661AHigh recovery rateShorten the production cyclePhosphorus compoundsPhosphoric acidTechnical grade
The invention provides a method for preparing industrial-grade phosphoric acid by an emulsification, extraction and purification wet method. The method comprises the sequential process steps of primary de-coloring, emulsification and extraction, emulsification and washing, emulsification and reverse extraction, concentration, dearsenification and heavy metal removing, secondary deep de-coloring and concentration adjustment. A method for food-grade phosphoric acid by the emulsification, extraction and purification wet method comprises the sequential process steps of primary de-coloring, emulsification and extraction, emulsification and washing, emulsification and reverse extraction, concentration, dearsenification and heavy metal removing, secondary deep de-coloring, defluorination and concentration adjustment. The emulsification and extraction step comprises the following steps of: agitating at normal pressure and at a temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 10-60 seconds at the speed of 500-3000 r / min; and agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 60-240 seconds at the speed of 120-220 r / min; the emulsification and washing step comprises the following steps of: agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 10-60 seconds at the speed of 500-3000 r / min; and agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 60-240 seconds at the speed of 120-220 r / min; and the emulsification and reverse extraction step comprises the following steps of: agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 10-60 seconds at the speed of 500-3000 r / min; and agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 60-240 seconds at the speed of 120-220 r / min.
Owner:SICHUAN JINGCUI CHEM TECH
Production process for extracting agar from ahnfeltia plicata
The invention discloses a production process for extracting agar from ahnfeltia plicata. The production process is implemented by the following steps of: 1, washing and drying ahnfeltia plicata frond in the air; 2, soaking the frond by using alkali liquor; 3, filtering, and washing the frond with clean water; 4, adding distilled water into the frond and performing primary colloid extraction underincreased pressure; 5, filtering a mixed liquor to obtain filtrate and filter residue; 6, adding activated carbon into the filtrate for decoloring while hot; 7, filtering while hot, cooling the filtrate to obtain a colloid, and treating the colloid to form primary agar; 8, adding the alkali liquor into the frond, namely the filtrate residue, and performing secondary colloid extraction under the increased pressure; 9, filtering the secondarily extracted-mixed solution to obtain the filtrate and the filtrate residue; and 10, cooling the filtrate to obtain the colloid; and treating the colloid to obtain secondary agar. The agar extracted from the ahnfeltia plicata has various good performance indicators; a low-alkali pressurization process is utilized; the method is simple and easy to implement; the utilization value of the ahnfeltia plicata is improved; and good economic benefit is expected to obtain.
Owner:FUJIAN GOLD SWALLOW OCEAN BIOTECH +1
Method for preparing agar with low sulfate radical content
The invention discloses a method for preparing agar with low sulfate radical content. The method comprises the following steps: 1, alkali treatment, namely adding a NaOH solution into agar, conducting a water bath for 2-10 hours at 50-90 DEG C, and washing to be neutral with water; 2, cation exchange resin treatment, namely dissolving with water, adding cation exchange resin into the agar liquid, reacting for 5-60 minutes at 50-80 DEG C, filtering and removing resin with nylon cloth after the reaction is completed to obtain an agar solution; 3, EDTA-Na2 treatment, namely adding an EDTA-Na2 solution having a concentration of 5-7g / L into the agar solution prepared in the step 2, regulating the pH to be 8-10, and reacting for 1-4 hours at 50-70 DEG C; and 4, washing and drying, namely freezing the agar solution in a refrigerator after the reaction is completed and the agar solution is solidified, unfreezing in a warm water bath, washing, drying and grinding to obtain an agar product with low sulfate radical content. Compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantages of low raw material cost, low sulfate radical content in the agar product, no complicated equipment and simple operation.
Owner:FUJIAN PROVINCE LVQI FOOD COLLOID
Production method of natural-color anti-rusting body paper
InactiveCN107724167AIncrease productionReduce energy consumptionChemical/chemomechanical pulpPaper-making machinesSulfatePapermaking
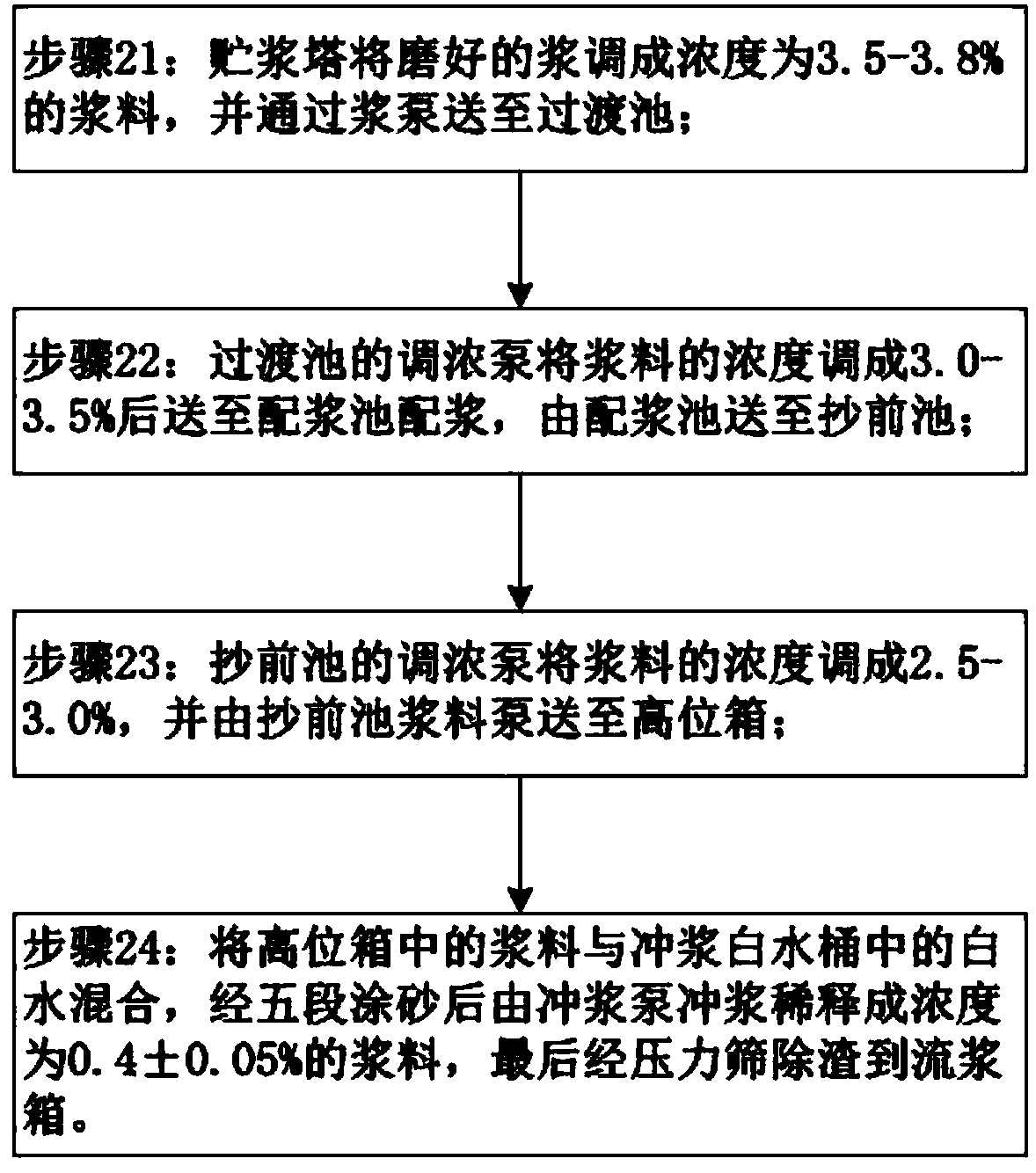
The invention discloses a production method of natural-color anti-rusting body paper. The production method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing natural-color sulfate softwood pulp with sulfite wood pulp, adding pure water, and carrying out pulping; (2) sequentially blending the pulp by virtue of a pulp storage tower, a transition tank, a pre-papermaking tank and a high-level tank, mixing theblended pulp with white water, removing residues by virtue of a sand filter and a sucking-moving roll, and finally, conveying the pulp to a flow pulp tank; (3) uniformly distributing the pulp to a net by virtue of the flow pulp tank, dehydrating by virtue of a net part, so as to obtain a wet paper blank; (4) sucking and moving the wet paper blank to coarse cotton cloth by virtue of the sucking-moving roll, and carrying out three squeezing dehydration processes, so as to obtain wet paper; (5) introducing the wet paper to a drying part by virtue of a paper introducing rope, drying, and introducing the wet paper to a reeling part, discharging the wet paper from the roll while reaching a specified roll diameter after parameters are qualified; and (6) re-reeling the wet paper into a specifiedspecification by virtue of a re-reeling machine after discharging. The natural-color anti-rusting body paper produced by virtue of the production method is high in yield, low in energy consumption, good in water-absorbing quality, high in strength, stable in moisture and uniform in thickness.
Owner:TAIZHOU XINYUAN ELECTRICAL EQUIP
Method for preparing industrial-grade and food-grade phosphoric acid by emulsification extraction and purification of wet-process phosphoric acid
ActiveCN102730661BHigh recovery rateShorten the production cyclePhosphorus compoundsEmulsionPhosphoric acid
The invention provides a method for preparing industrial-grade phosphoric acid by an emulsification, extraction and purification wet method. The method comprises the sequential process steps of primary de-coloring, emulsification and extraction, emulsification and washing, emulsification and reverse extraction, concentration, dearsenification and heavy metal removing, secondary deep de-coloring and concentration adjustment. A method for food-grade phosphoric acid by the emulsification, extraction and purification wet method comprises the sequential process steps of primary de-coloring, emulsification and extraction, emulsification and washing, emulsification and reverse extraction, concentration, dearsenification and heavy metal removing, secondary deep de-coloring, defluorination and concentration adjustment. The emulsification and extraction step comprises the following steps of: agitating at normal pressure and at a temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 10-60 seconds at the speed of 500-3000 r / min; and agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 60-240 seconds at the speed of 120-220 r / min; the emulsification and washing step comprises the following steps of: agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 10-60 seconds at the speed of 500-3000 r / min; and agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 60-240 seconds at the speed of 120-220 r / min; and the emulsification and reverse extraction step comprises the following steps of: agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 10-60 seconds at the speed of 500-3000 r / min; and agitating at the normal pressure and at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C for 60-240 seconds at the speed of 120-220 r / min.
Owner:成都富鼎鑫瑞科技股份有限公司
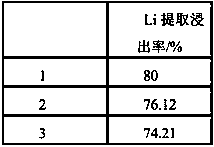
Method for extracting lithium sulfate from lepidolite
ActiveCN110395751ATake advantage ofReduce the amount requiredLithium sulfates/sulfitesLithium sulfatePotassium sulfate
A method for extracting lithium sulfate from lepidolite is disclosed. The method adopts the lepidolite as a raw material and a roasting manner, and includes steps of crushing, material mixing, dryingand roasting stabilizer adding, and the like. The raw material and auxiliary materials are mixed, and the mixture is roasted in a rotary kiln device to achieve lithium sulfate extraction. During lepidolite roasting, a recovered by-product salt is added in place of potassium sulfate, a roasting additive that is ferric oxide powder is added during roasting so that the ferric oxide powder reacts andis bonded with silica in the lepidolite raw material, a stabilizer function is achieved, and a raw material phenomenon and an inner kiln blockage phenomenon are avoided, thus increasing utilization rates of lithium and lithium salts such as lithium sulfate extracted from the lepidolite. The production process is simple.
Owner:江西南氏锂电新材料有限公司
Production process for extracting agar from ahnfeltia plicata
The invention discloses a production process for extracting agar from ahnfeltia plicata. The production process is implemented by the following steps of: 1, washing and drying ahnfeltia plicata frond in the air; 2, soaking the frond by using alkali liquor; 3, filtering, and washing the frond with clean water; 4, adding distilled water into the frond and performing primary colloid extraction underincreased pressure; 5, filtering a mixed liquor to obtain filtrate and filter residue; 6, adding activated carbon into the filtrate for decoloring while hot; 7, filtering while hot, cooling the filtrate to obtain a colloid, and treating the colloid to form primary agar; 8, adding the alkali liquor into the frond, namely the filtrate residue, and performing secondary colloid extraction under the increased pressure; 9, filtering the secondarily extracted-mixed solution to obtain the filtrate and the filtrate residue; and 10, cooling the filtrate to obtain the colloid; and treating the colloid to obtain secondary agar. The agar extracted from the ahnfeltia plicata has various good performance indicators; a low-alkali pressurization process is utilized; the method is simple and easy to implement; the utilization value of the ahnfeltia plicata is improved; and good economic benefit is expected to obtain.
Owner:FUJIAN GOLD SWALLOW OCEAN BIOTECH +1
Complex preventing and controlling process and technology for coal solid waste sulfur contamination
InactiveCN101053871AReduce sulfur contentAvoid sulfur pollutionSolid waste disposalSulfurCircular economy
According to circulating economic principle, sulphur pollution problem in coal gangue can be solved by using alkalescence of waste fly ash. A columnar eluviation method is adopted to resolve the sulphur pollution problem of the coal gangue and reduce pollution to soil and water body caused by coal gangue sulfuration through a different proportion process of the fly ash and the coal gangue. Leachate PH value can be increased, leachate salt ion concentration and sulphur emersion quantity can be reduced efficiently by proportion treatment in such a way that: based on the same volume, the coal gangue with different particle diameter matches with fly ash to form two layers (20cm coal gangue, and 20cm fly ash disposed on lower layer), and to form four layers(the coal gangue and the fly ash are spaced with each other to form 4 layers, each of which has thickness of 10cm, and the fly ash is disposed on the lowest layer). According to the sulphur pollution control effect, the two layers proportion 20cm thickness fly ash treatment is superior to four layers proportion 10cm thickness fly ash treatment, and contribution rate of the fly ash for controlling sulphur pollution of the leachate can reach 64%, which shows that the fly ash has better application potential for treating sulphur pollution problem of coal gangue.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
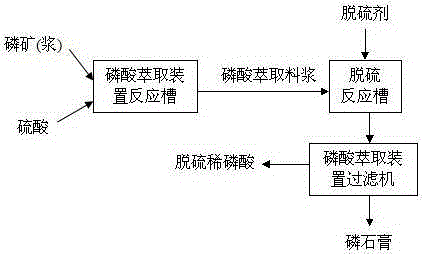
A method for reducing sulfate radical content in dihydrate dilute phosphoric acid
ActiveCN103754850BShort reaction timeImprove responsePhosphorus compoundsO-Phosphoric AcidSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a method for reducing the content of sulfate radicals in dihydric dilute phosphoric acid, which is characterized in that a desulfurizer is added to wet-process phosphoric acid extraction slurry, mixed and stirred, and mixed and reacted at 60-80°C for 5-30 minutes. Then the mixed slurry is sent to the filter of the phosphoric acid extraction device for filtration, and the diluted phosphoric acid with a sulfate mass percentage content of less than 1.2% is obtained by filtration; The mass ratio of sulfate radicals in the medium is 0.35-0.50:1. The present invention solves the problem of high sulfate content in the dilute phosphoric acid of the dihydrate method, and is beneficial to the use of the dihydrate method phosphoric acid in the production of high-nutrient ammonium phosphate fertilizer, feed grade phosphate, industrial grade ammonium phosphate and phosphoric acid purification products. Simple, short desulfurization reaction time, good desulfurization effect and low desulfurization cost.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
A method and system for biologically treating acid mine wastewater while recovering iron ions
ActiveCN111620444BLow Sulfate ContentEasy to trainWaste water treatment from quariesTreatment using aerobic processesWastewaterBiomineralization
The invention provides a method and system for biologically treating acidic mine wastewater while recovering iron ions. The method comprises: (1) Biomineralizing the acidic mine wastewater by acidophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria, then performing circular biological reduction treatment by acidophilic iron-reducing bacteria, and then entering an alkali adjustment tank to circulate and adjust pH, and then the effluent is circulated to biomineralization treatment (2) After a period of reaction, the waste water is drawn out from the end of the sump, which can be connected to the lime neutralization treatment system, and jarosite minerals or Shi's minerals can be recovered in the biomineralization unit. The bacteria screened by the invention are indigenous strains existing in the actual mine environment, and can be fully applied to the treatment of mine wastewater. The invention adopts circulation treatment to increase the precipitation amount of iron in the acid waste water, and is subsequently connected with lime neutralization treatment, so that the mine waste water can fully meet the standard.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Treatment method of lead-zinc smelting waste acid
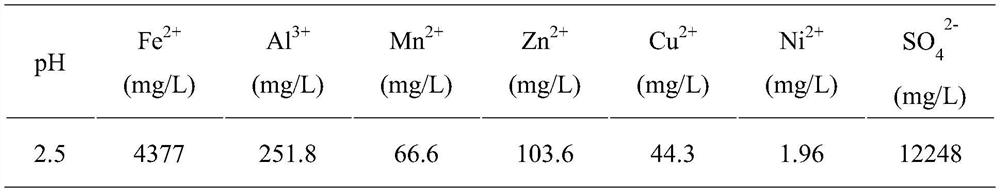
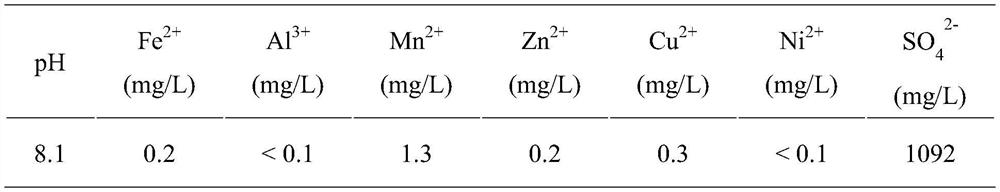
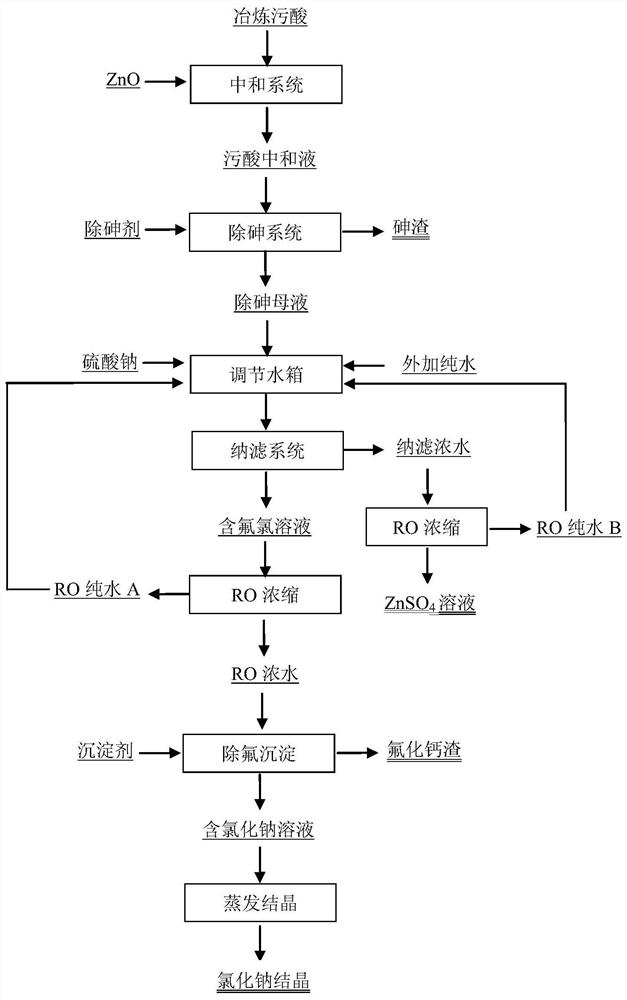
ActiveCN111661950AImprove the separation effect of nanofiltrationLow costZinc sulatesWaste water treatment from metallurgical processEngineeringSodium sulfate
The invention provides a treatment method of lead-zinc smelting waste acid. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding ZnO into the smelting waste acid, and carrying out a neutralization reaction to obtain a neutralized waste acid solution; (2) adding an arsenic removal agent into the neutralized waste acid solution, carrying out an arsenic removal reaction, and filtering after the reaction is completed to obtain arsenic slag and an arsenic-removed mother liquor; (3) mixing the arsenic-removed mother liquor with sodium sulfate and pure water, and carrying out nanofiltration to obtainnanofiltered concentrated water and a fluorine-containing chlorine solution; (4) carrying out RO concentration on the fluorine-containing chlorine solution to obtain RO pure water and RO concentratedwater; and (5) adding a precipitant into the RO concentrated water, and carrying out a defluorination precipitation reaction and solid-liquid separation to obtain a sodium chloride-containing solution and calcium fluoride slag. The treatment method provided by the invention is simple and safe in operation management, can effectively reduce the operation energy consumption and the treatment cost,can recover sulfuric acid in the waste acid at the same time, and ensures that the water quality index of the waste acid reaches the standard and is discharged.
Owner:湖南中金岭南康盟环保科技有限公司
Production process of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid methyl ester
ActiveCN110590868AAvoid demandReduce wasteSugar derivativesChemical industryEsterification reaction2-keto-L-gulonic acid
The invention discloses a method for continuously producing 2-keto-L-gulonic acid methyl ester by taking 2-keto-L-gulonic acid as a raw material. A plurality of heat exchangers are connected in seriesto form a feeding heat exchanger; the back of the feeding heat exchanger is connected to a tubular reactor to form an esterification reaction device; a material outlet of the tubular reactor is connected to a thermal medium inlet of a primary heat exchanger formed by combining the first M heat exchangers of the feeding heat exchanger; a thermal medium outlet of the primary heat exchanger of the feeding heat exchanger is used as a discharging port of equipment for producing the 2-keto-L-gulonic acid methyl ester; and a secondary heat exchanger formed by combining the last N heat exchangers ofthe feeding heat exchanger adopts an external heat source. The production method comprises the following steps: blending, heating and continuous esterifying. The method has the beneficial effects that: the reaction time is remarkably shortened, the energy consumption is reduced, the workload of workers is reduced, the use amount of sulfuric acid is remarkably reduced, byproducts are reduced, the product quality is further improved, the use amount of conversion reaction alkali can be further reduced, the production cost can be further reduced, and the like.
Owner:石药集团维生药业(石家庄)有限公司
Method for preparing agarose
ActiveCN112094363AAvoid degradationReduce intermediate production linksColloidal particleAnalytical chemistry
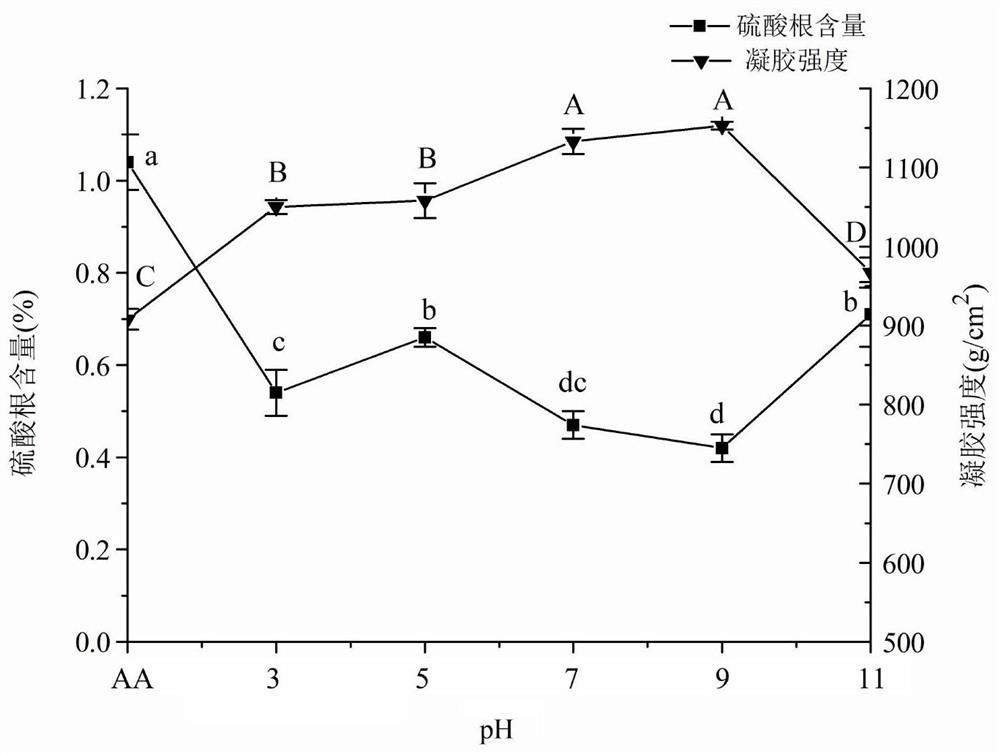
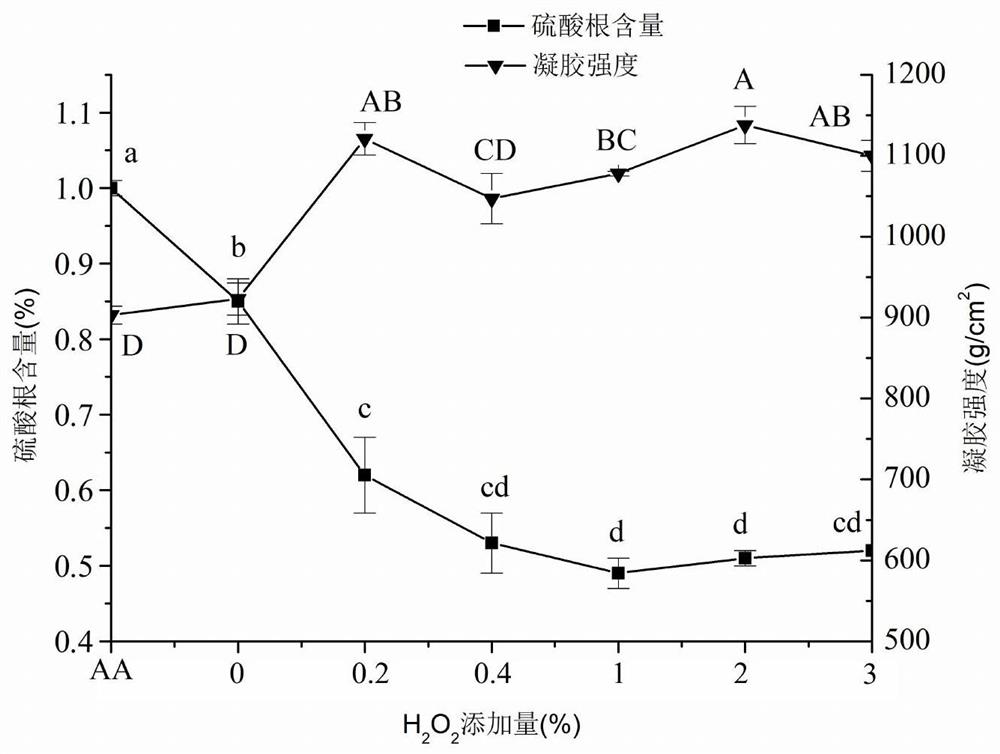
The invention relates to a method for preparing agarose. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning gracilaria, and carrying out alkali treatment, acidification treatment, bleaching treatment,gelatin boiling, filtration, cooling and solidification to obtain colloid; stirring and crushing the colloid; and adding water into the crushed colloid, heating, adjusting the pH value, adding an H2O2 solution for reaction, filtering, washing and repeatedly washing until no H2O2 is left in the colloidal particle sample and the pH value of the washing liquid is 7 after the reaction is finished, and freezing, dehydrating, drying and crushing the sample to obtain the agarose. According to the method, the content of sulfuric acid groups of agar can be remarkably reduced, the gel strength is improved, the electroendosmosis is remarkably reduced, the commercially available agarose index requirement is met, the reaction time is short, and the method is environmentally friendly.
Owner:SHANGHAI OPM BIOSCI CO LTD
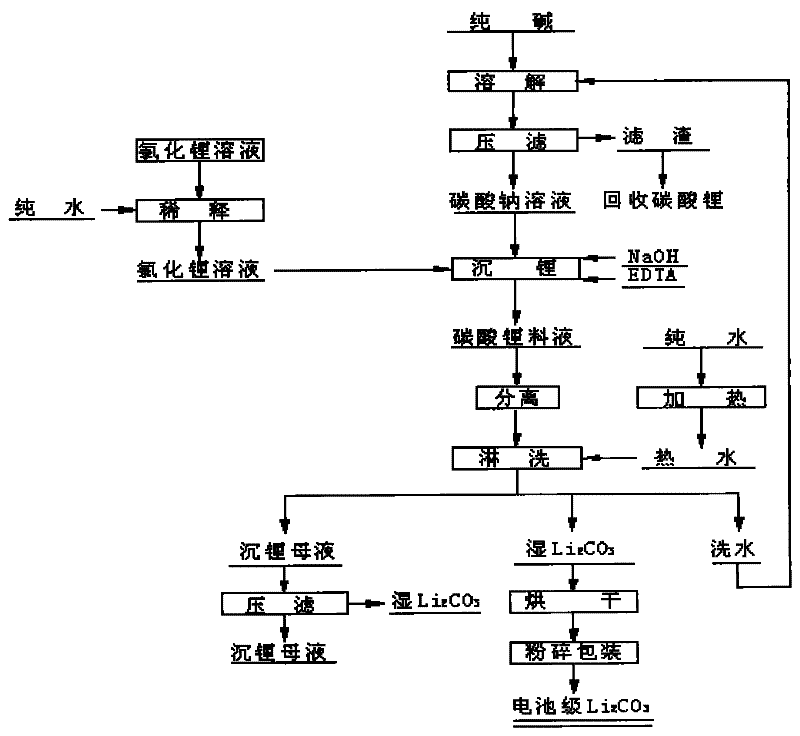
Method for preparing battery level lithium carbonate by using lithium chloride solution
ActiveCN101609888BLow Sulfate ContentQuality improvementElectrode manufacturing processesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesLithium chlorideSulfate radicals
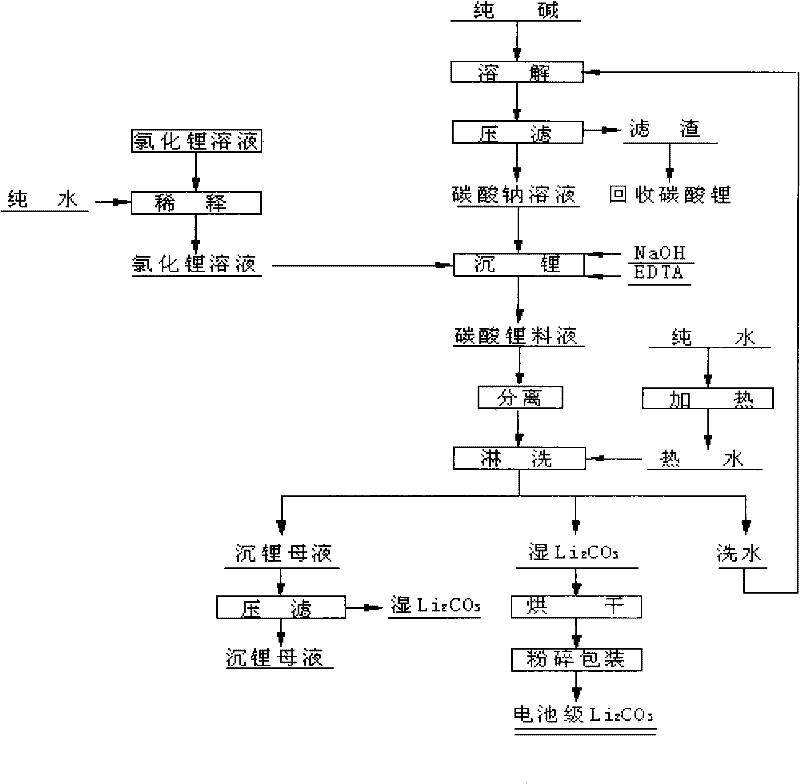
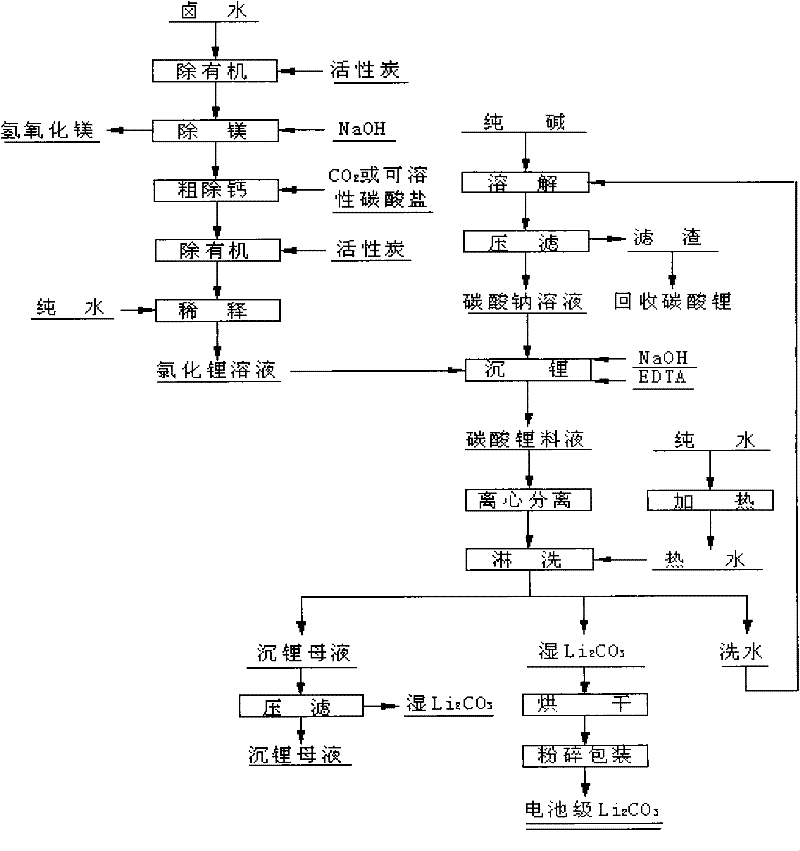
The invention provides a method for preparing battery level lithium carbonate by using lithium chloride solution. The method includes the steps of the dilution of lithium chloride solution, lithium sedimentation in sodium carbonate, the separation of lithium carbonate, washing, drying, grinding and packing. The method is simple in technology, easy in operation and low in production cost, and the obtained product, namely, battery level lithium carbonate, has the advantages of low sulfate radical content, stable quality, high utilization rate of resources and suitability for the production and application of lithium ion battery raw materials, and has extensive market prospect, as well as favorable economic and social benefit.
Owner:GANFENG LITHIUM CO LTD
Power plant circulating cooling water waste water treatment method and system
InactiveCN108203181ALow Sulfate ContentTargetedWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMultistage water/sewage treatmentIonChemistry
The invention relates to a power plant circulating cooling water waste water treatment method and system, the method comprises the steps that sodium aluminate and a calcareous material are added to waste water, and the sodium aluminate and the calcareous material are in complexation with sulfate radicals in the waste water to produce sulfate precipitate; the clear liquid obtained through complexation is subjected to former stage film filtration treatment; the fresh water obtained after former stage film filtration treatment is subjected to aeration treatment, and calcium ions and aluminium ions dissolved in the fresh water are promoted to form calcium carbonate precipitate and aluminium hydroxide precipitate respectively; the fresh water obtained after aeration treatment is subjected to later stage film filtration treatment, and at least residual sulfate radicals are retained. According to the power plant circulating cooling water waste water treatment method and system, a manner of combining the chemical reaction and the physical action is adopted, the high concentration sulfate radicals in the circulating cooling water waste water can be selectively removed, the content of the sulfate radicals in the circulating cooling water waste water is effectively reduced, and the method and the system have the advantages of high efficiency and high pertinency; the quality of the treatedwaste water is excellent, the waste water can be reused in a plurality of links of the production technology, and the reuse rate of the circulating cooling water is improved remarkably.
Owner:武汉天空蓝环保科技有限公司
A method for producing diethylene glycol isophthalate-5-sodium sulfonate from concentrate of three monomer process wastewater
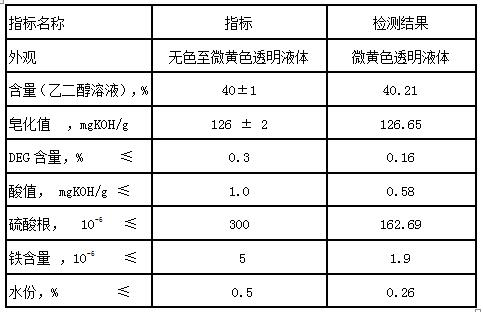
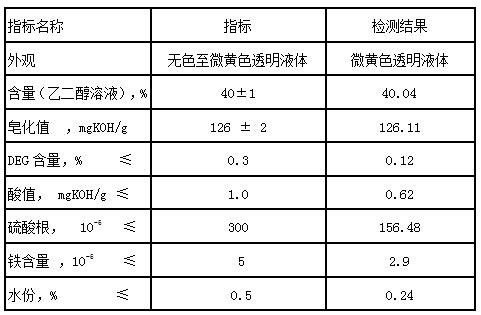
ActiveCN109336791BLow Sulfate ContentGood lookingSulfonic acids salts preparationSulfonateSulfate radicals
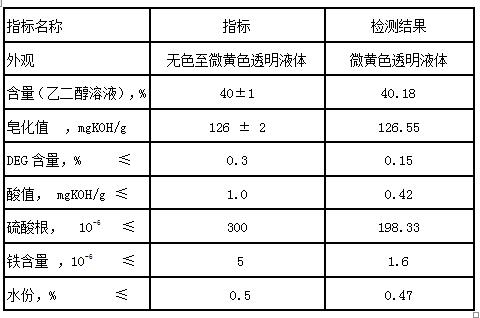
The invention provides a method for producing sodium isophthalate-5-sulfonate diethylene glycol ester (SIPE) from the three-monomer process wastewater concentrate, which is characterized in that: the method includes dissolving, filtering, and SIPE synthesis. The SIPE solution prepared by the present invention has low sulfate content, and the sulfate content is 156.48-231.47ppm; the SIPE solution prepared by the present invention has good appearance, high purity, and less impurity content; the appearance is a slightly yellow transparent liquid, and the purity is 94.33-95.1 % (LC), DEG content is 0.12‑0.28%. The reaction temperature of the present invention is low, the reaction temperatures of the first stage and the second stage are respectively 170-180°C and 185-195°C, and the synthesis reaction time is 4.8-5.2h.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Treatment method of cellulose ethanol waste water
InactiveCN108911364AReduce COD valueReduce ammonia nitrogen contentWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesOxygenSide reaction
The invention discloses a treatment method of cellulose ethanol waste water. The treatment method of the cellulose ethanol waste water comprises the following steps: pretreating the cellulose ethanolwaste water, performing the two-phase anaerobic-aerobic comprehensive treatment and electrochemical oxidation further treatment. By adopting the treatment method of the cellulose ethanol waste water,the COD value, the ammonium and nitrogen content and the sulfate content of the cellulose ethanol waste water can be greatly reduced, the content of side reaction products such as furan rings, furfural, formic acid, levulinic acid and the like, solids such as cellulose, lignin, semi-cellulose and the like as well as inorganic salts in the in the cellulose ethanol waste water can be reduced to be alevel not influencing the long-time operation and successful implementation of the waste water biochemical treatment system, the operation cost is low, the design is ingenious, and easy in maintenance can be achieved.
Owner:湖南双晟科技信息咨询有限公司
Impurity removal method of electrolytic manganese dioxide
ActiveCN103601246BLow Sulfate ContentImprove discharge performanceElectrolysis componentsManganese oxides/hydroxidesSulfate radicalsElectrolysis
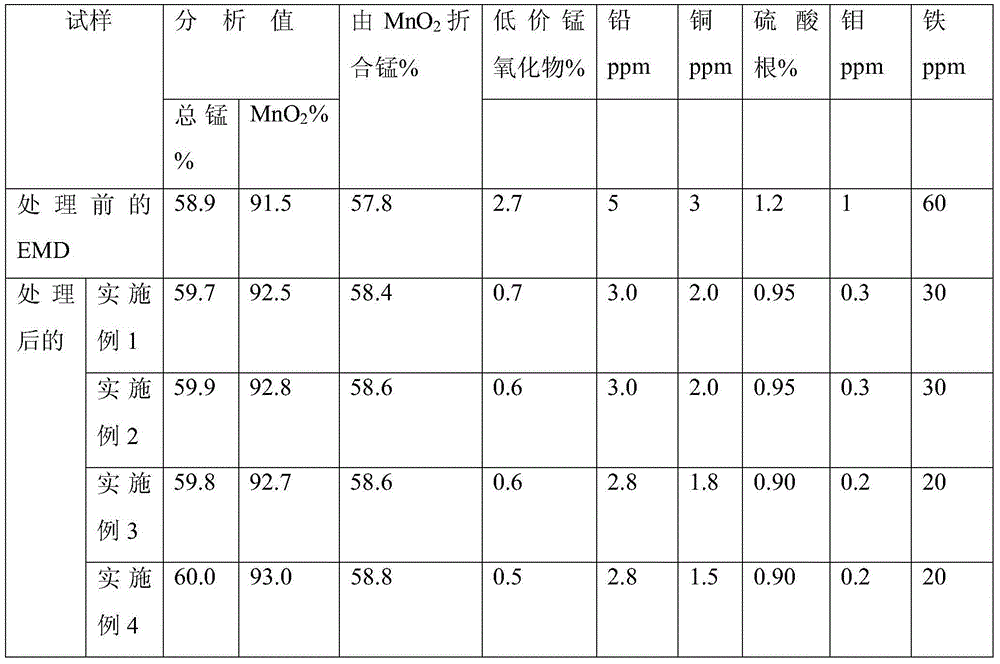
The invention discloses an impurity removal method of electrolytic manganese dioxide. The method comprises the following steps: crushing manganese dioxide falling from anodes, adding dilute sulfuric acid and nitric acid, mixing evenly, sintering the mixture at 200-250 DEG C for 40-50 minutes, cooling the mixture to 70-80 DEG C at a speed of 5-10 DEG C / min, filtering, pickling manganese dioxide left after the filtering treatment by using the dilute sulfuric acid, mixing the pickled manganese dioxide with a small amount of water, heating to 50-70 DEG C through microwave, treating with 30-40 KHz ultrasonic wave for 10-20 minutes, drying, and treating the dry manganese dioxide in a dry magnetic separator for 0.5-2 hours to obtain refined manganese dioxide. The method can be used for not only effectively removing such impurities in the electrolytic manganese dioxide as low-valent manganese oxide, lead, copper, sulfate radical, molybdenum and iron, but also improving the discharge performance of the electrolytic manganese dioxide.
Owner:GUANGXI GUILIU CHEM CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of low solidification temperature agarose
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Application of red algae starch
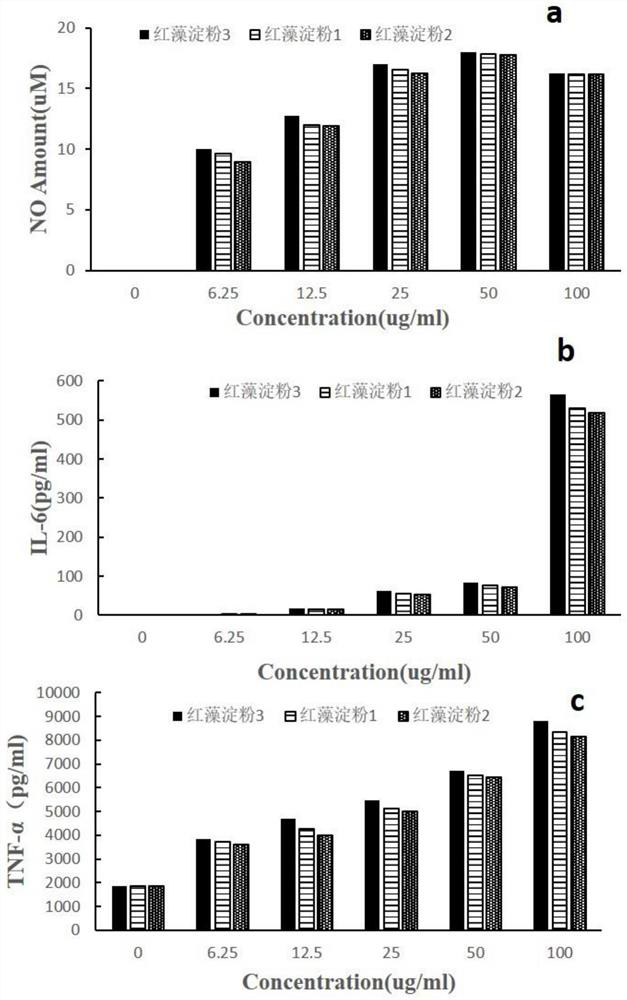
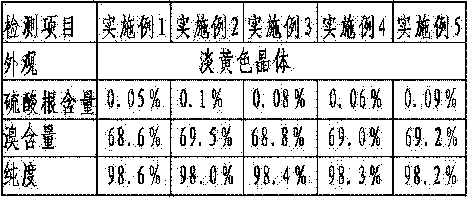
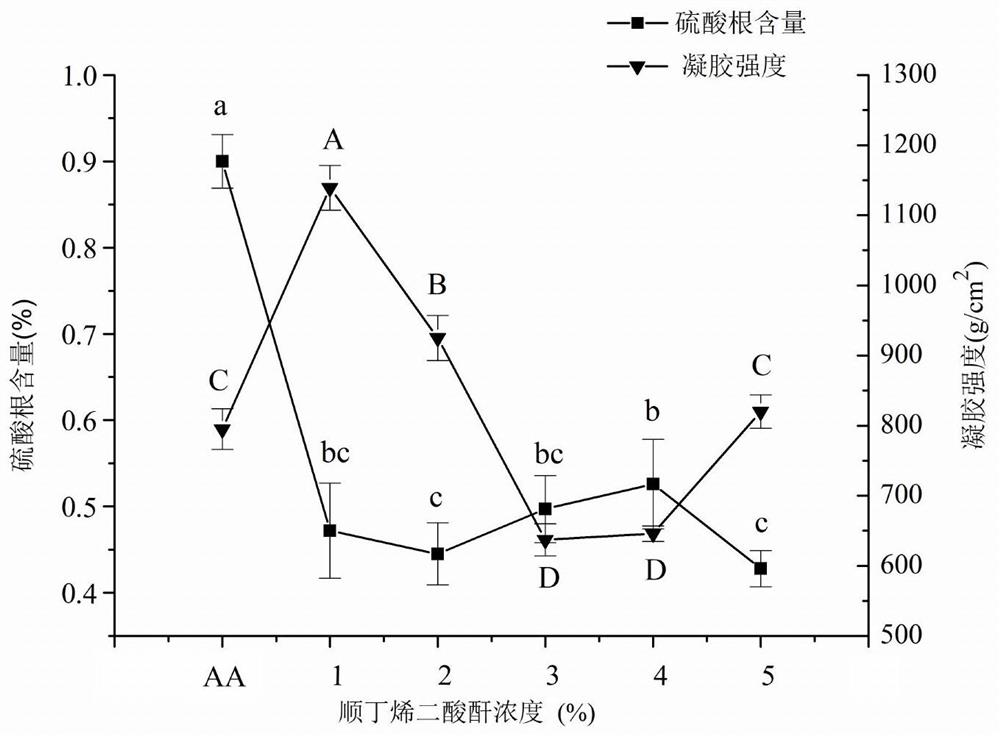
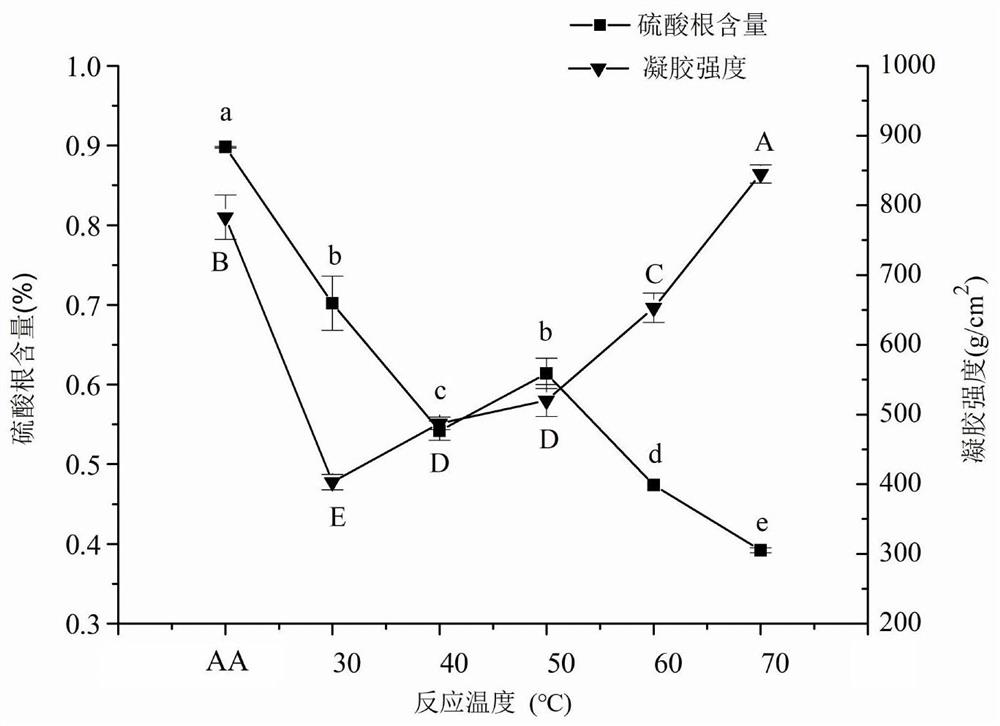
PendingCN114831311AAbundant sources of raw materialsSimple preparation processFood ingredient functionsGlycosidic bondFunctional food
The invention belongs to the technical field of nutritional health-care products, and particularly relates to application of novel red algae starch. The invention relates to application of red algae starch in rapidly improving the glycemic index of a hypoglycemic patient. The sulfate radical content of the red algae starch is lower than 0.1%, the red algae starch is mainly linked by alpha-glucosidic bonds, and the average molecular weight is 1kDa-6KDa. Compared with rice starch, the red algae starch can improve the glycemic index more quickly and has the effects of improving the immunity of the human body and the like, so that the red algae starch is a relatively ideal functional food for patients with hypoglycemia.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for reducing sulfate radical content in rare earth hydroxide
ActiveCN105621471BReduce contentSimple processRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesSulfate radicalsButanedioic acid
The invention discloses a method for reducing the content of sulfate radicals in rare earth hydrate. The method comprises the following steps: adding sulfate radical-containing rare earth hydrate into a coordination solution containing one or more organic matters in malic acid, acetylacetone, lactic acid, acetic acid, butanedioic acid, glycolic acid and malonic acid, wherein the pH value of the coordination solution is 7-10; and then performing solid-liquid separation, water-washing and drying to obtain rare earth hydrate with the sulfate radical content less than 0.5%. According to the method, sulfate ions are removed with a method for competitive coordination with sulfate radicals; a process is simple and easy to control; a desulfurization effect is remarkable; and the organic matters entering rare earth hydrate can be removed in a roasting manner, so that the purity of a rare earth oxide product is not influenced finally.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of preparation method of tetrabromophthalic anhydride
ActiveCN105669620BThe process steps are simpleReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistrySulfate radicalsCentrifugation
The invention relates to a preparation method of tetrabromophthalic anhydride. The preparation method comprises that fuming sulphuric acid, bromine and phthalic anhydride as raw materials undergo a reaction in the presence of a composite catalyst under control of a bromine dropwise addition rate and temperature and a later-stage reaction temperature to produce a product mother liquid, the product mother liquid is subjected to suction filtration, water is added into the filter residue, the filter residues are washed through stirring under control of water washing indexes so that a qualified product is obtained, and the qualified product is subjected to centrifugation and drying so that a finished product is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the characteristics of high product purity and low sulfate radical content.
Owner:WEIFANG XINYANG CHEM CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of high-quality agarose
The invention discloses a method for separating and preparing high-quality agarose from agar in combination with a flocculation method. The method comprises the following steps: preparing an agar solution of a certain concentration, heating and dissolving; preparing a solution of polyaluminum chloride and polyacrylamide with a suitable concentration; keeping warm in a water bath at 40-100°C for a period of time; Add a certain volume of polyaluminum chloride solution and stir for a certain period of time; add a certain volume of polyacrylamide solution and stir for a certain period of time in the above reaction solution; filter, remove the filter residue, and collect the filtrate; The gel was freeze-dehydrated, washed, dried, and crushed to obtain agarose. The preparation method used in the present invention is to remove sulfur agar and pigment in the agarose solution through the combined use of polyaluminum chloride inorganic cationic flocculant and polyacrylamide cationic flocculant, which has good gel performance and can reach the fields of molecular biology and the like. Requirements for high-quality agarose.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing agarose
ActiveCN111995699AReduce intermediate production linksShorten the production cycleAlcoholColloidal particle
The invention relates to a method for preparing agarose. The method comprises the following steps of: cleaning gracilaria, and carrying out alkali treatment, acidification treatment, bleaching treatment, colloid boiling, filtration, cooling and solidification to obtain colloid; stirring and crushing the colloid; and adding water into the crushed colloid, heating, adjusting the pH value, slowly dropwise adding a maleic anhydride ethanol solution for reaction, performing filtering after finishing the reaction, alternately washing the colloidal particle sample by using absolute ethyl alcohol anddeionized water, repeatedly washing the sample until the pH value of the washing solution is neutral, and freezing, dehydrating, drying and crushing the colloidal particle sample to obtain agarose. According to the method, the content of sulfuric acid groups of agar can be remarkably reduced, the jelly strength is improved, the electroendosmosis is remarkably reduced, the index requirements of thecommercially available agarose is met, the reaction time is short, and the method is environmentally friendly.
Owner:SHANGHAI OPM BIOSCI CO LTD
Phosphoric acid desulfurization method applied to the production process of feed grade calcium hydrogen phosphate
ActiveCN105905876BAchieve pre-concentrationLow Sulfate ContentPhosphorus compoundsCycloneHydrogen phosphate
The invention discloses a phosphoric acid desulphurization method used in a feed grade calcium hydrogen phosphate production technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adding phosphate rocks to phosphoric acid to carry out pre-extraction and desulphurization; 2, conveying a slurry obtained after a complete reaction to a cyclone, and carrying out solid-liquid separation; 3, allowing cyclone underflow to enter an extraction tank after the solid-liquid separation, extracting the cyclone underflow, allowing an overflowing slurry to enter a settlement device, and settling the overflowing slurry; and 4, allowing a clear liquid obtained after settlement to enter a defluorination process, allowing a thick slurry obtained after settlement to enter the extraction tank, extracting the thick slurry, and circulating step 2 to step 4. The method has the advantages of ingenious design, stable thick slurry volume and denseness, no influences of re-extraction of the desulphurized thick slurry on the slurry filtering effect, low cost, satisfactory improvement of the contradiction of phosphoric acid desulphurization and the filtering effect, and realization of depth desulphurization.
Owner:SICHUAN MIANZHU PANLONG MINERALS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com