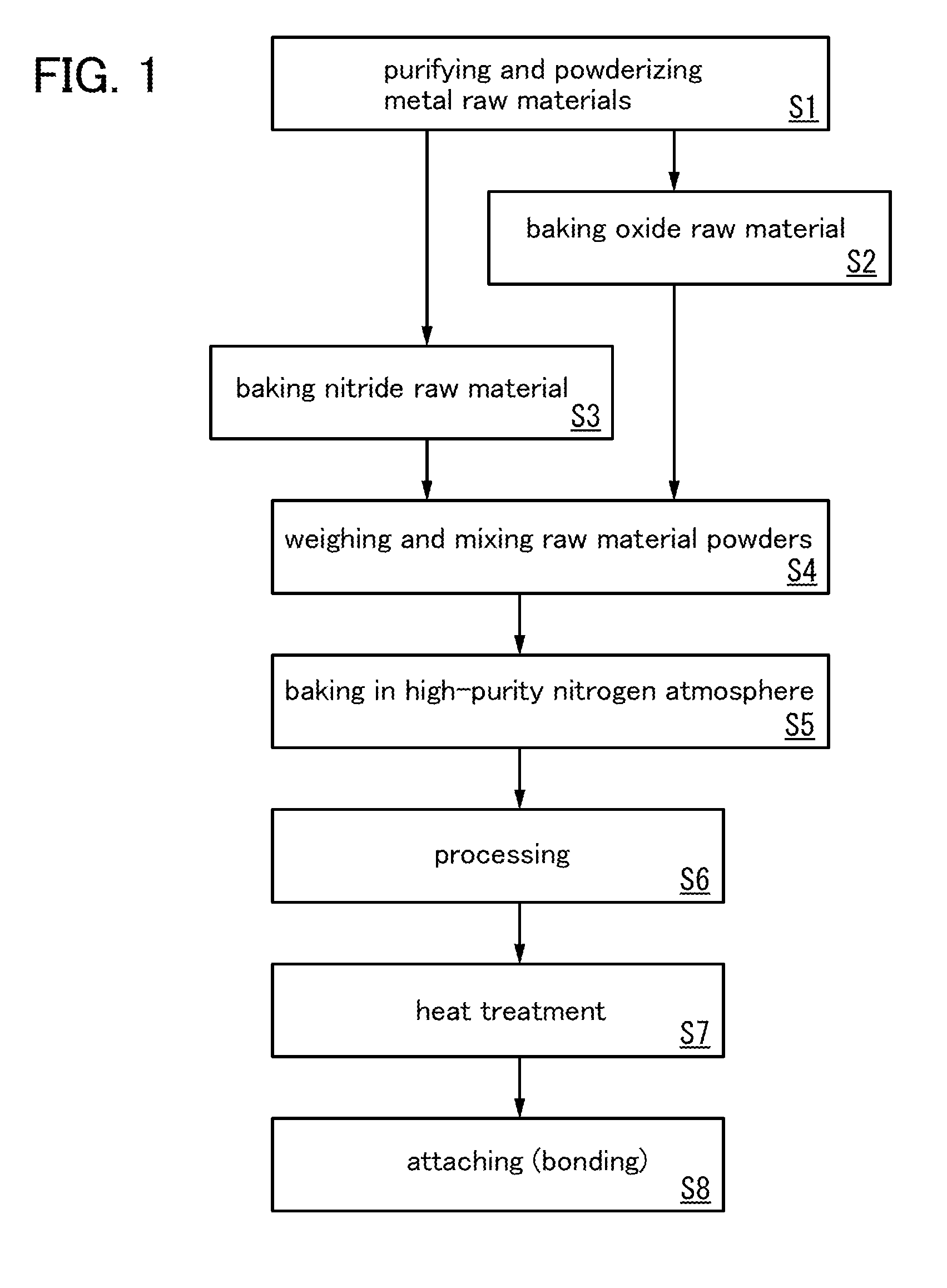
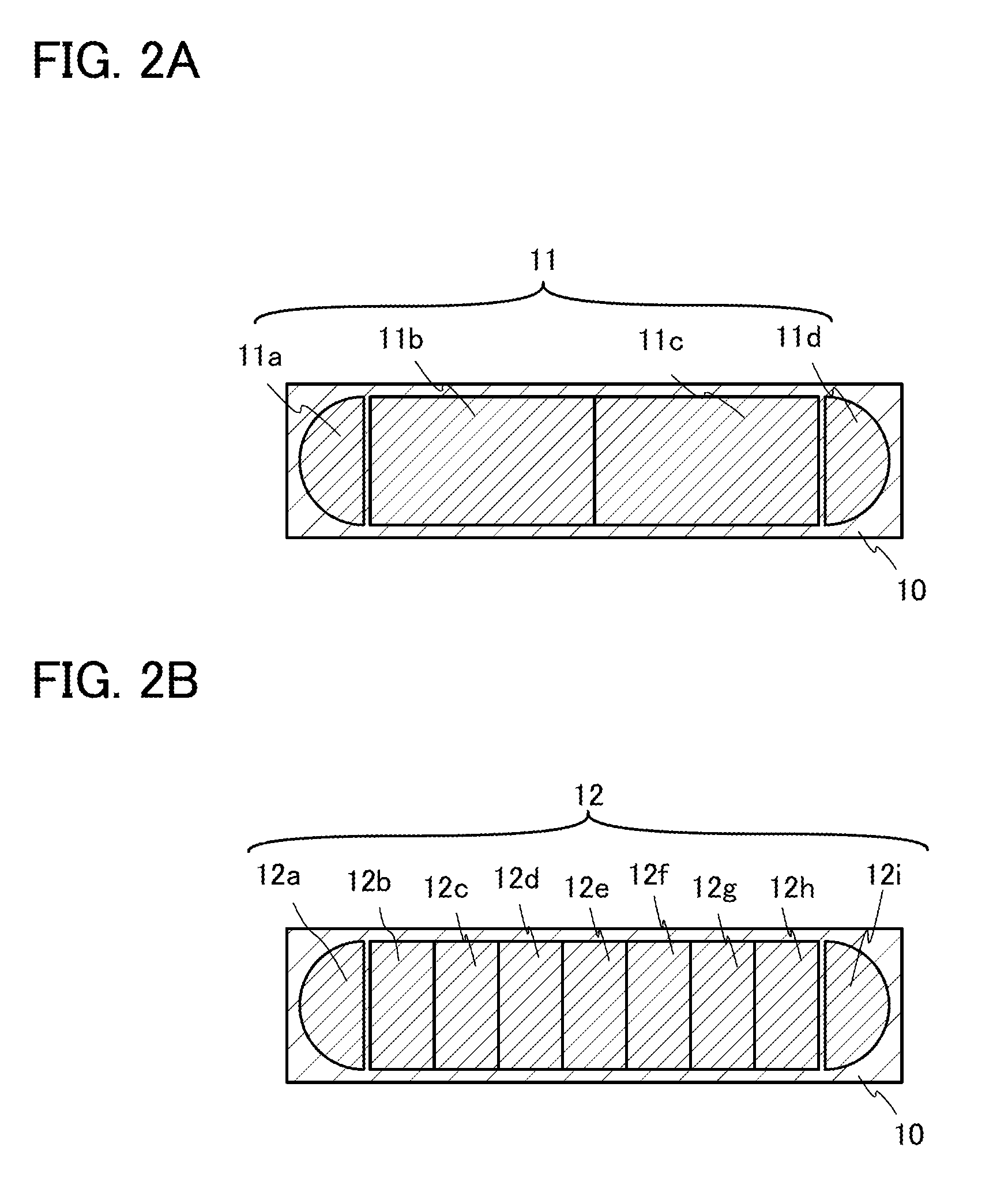
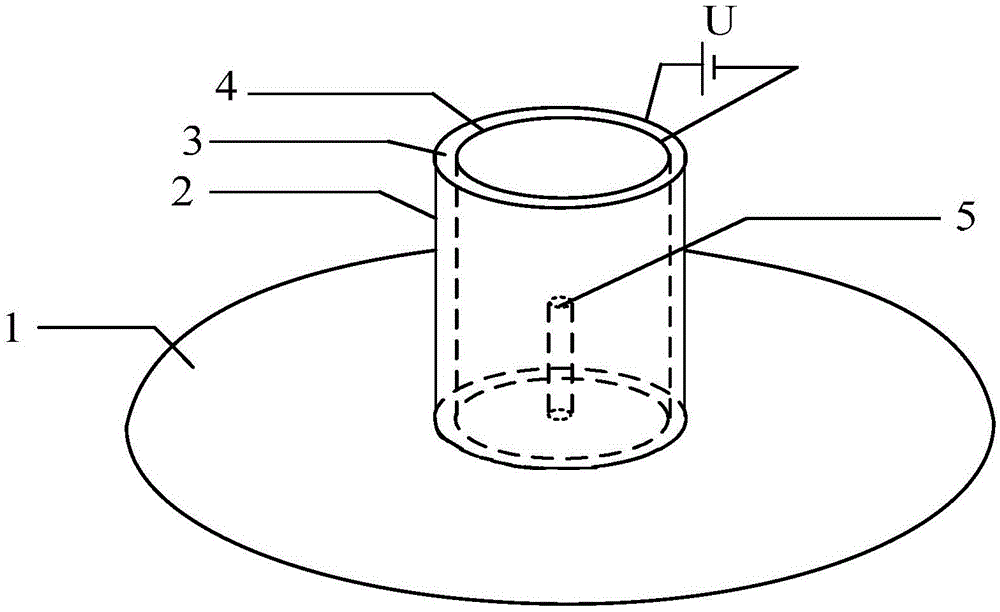
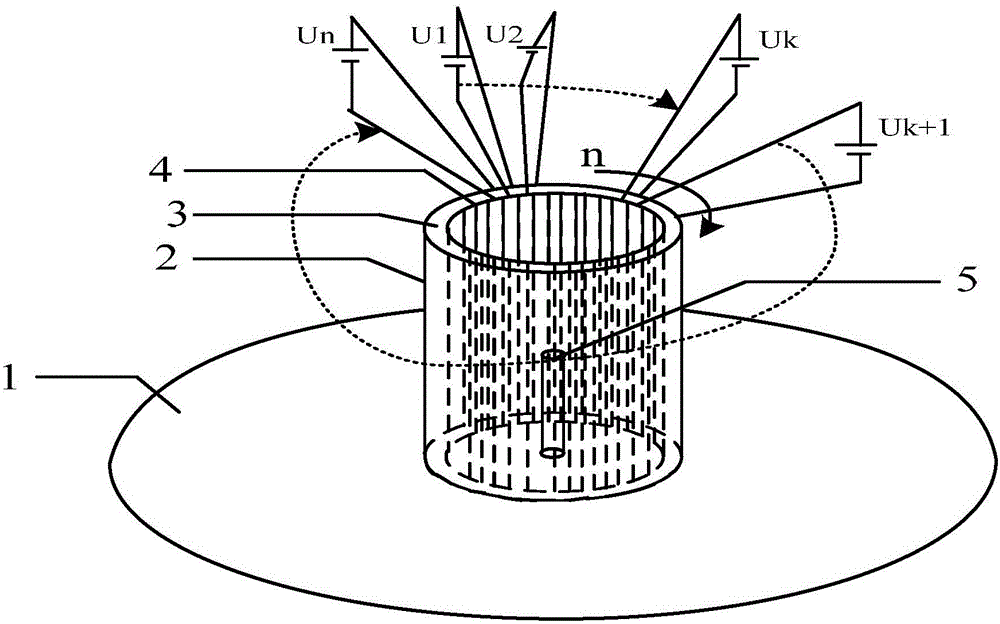
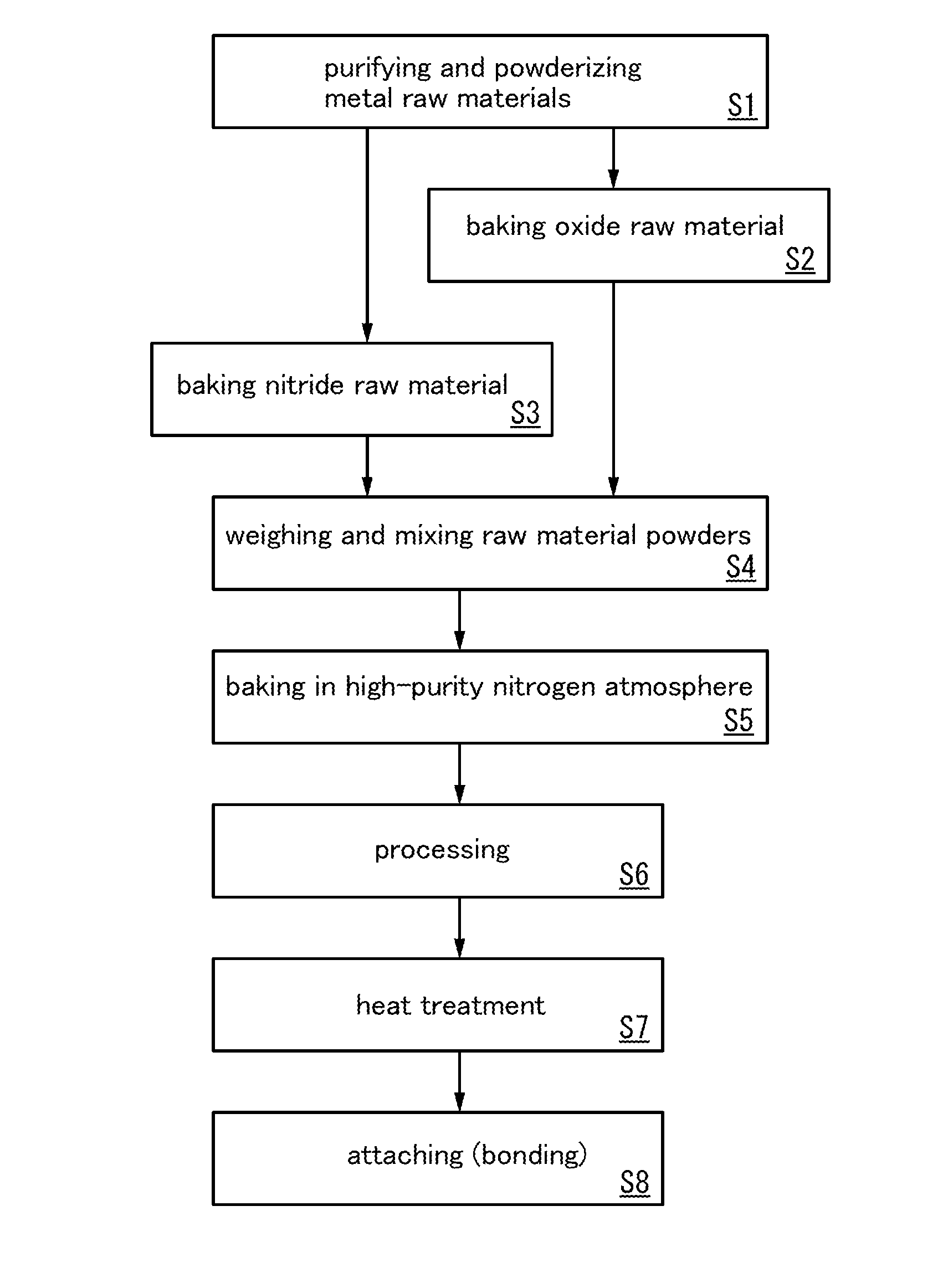
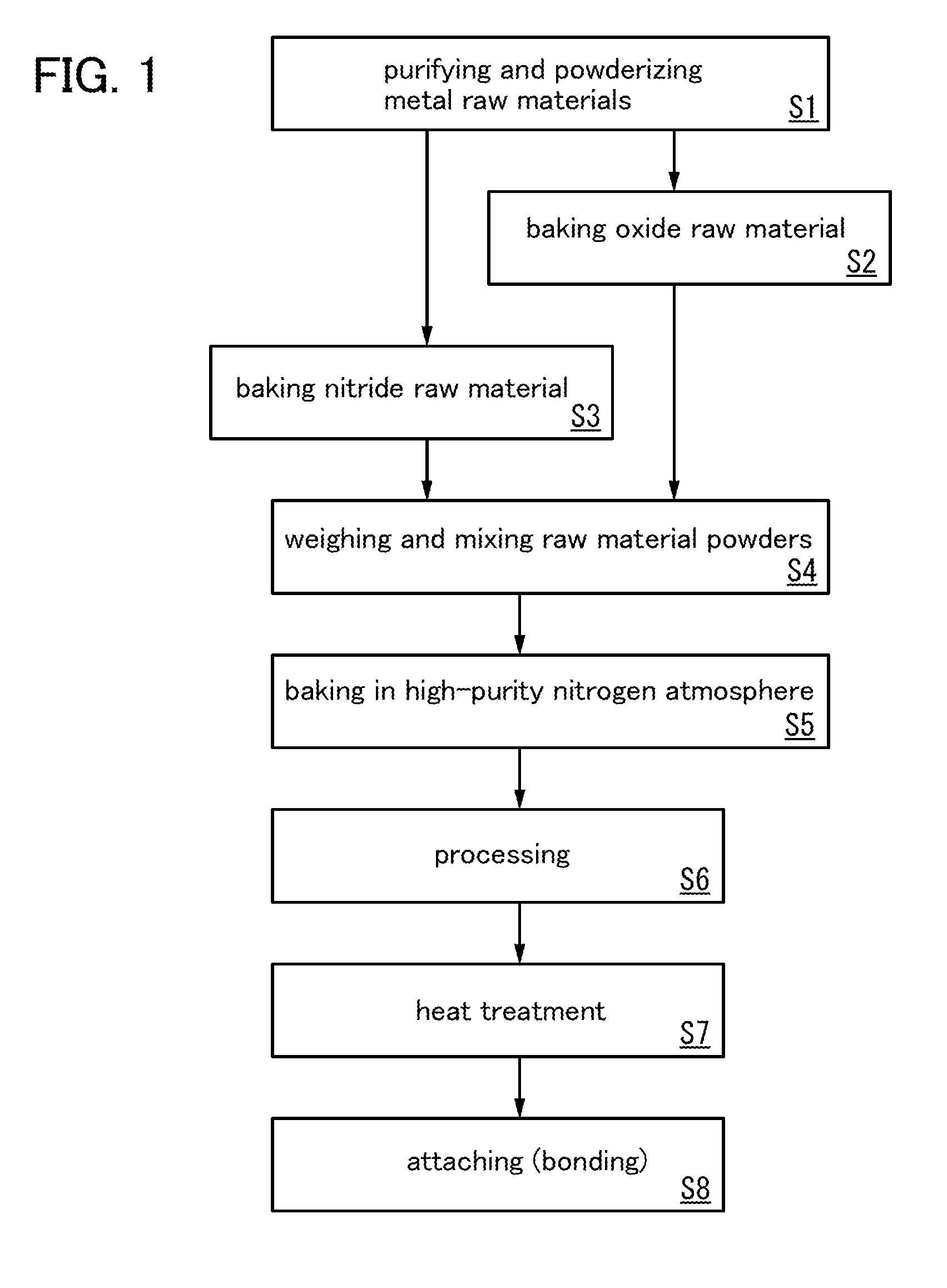
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70results about How to "Increase carrier density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
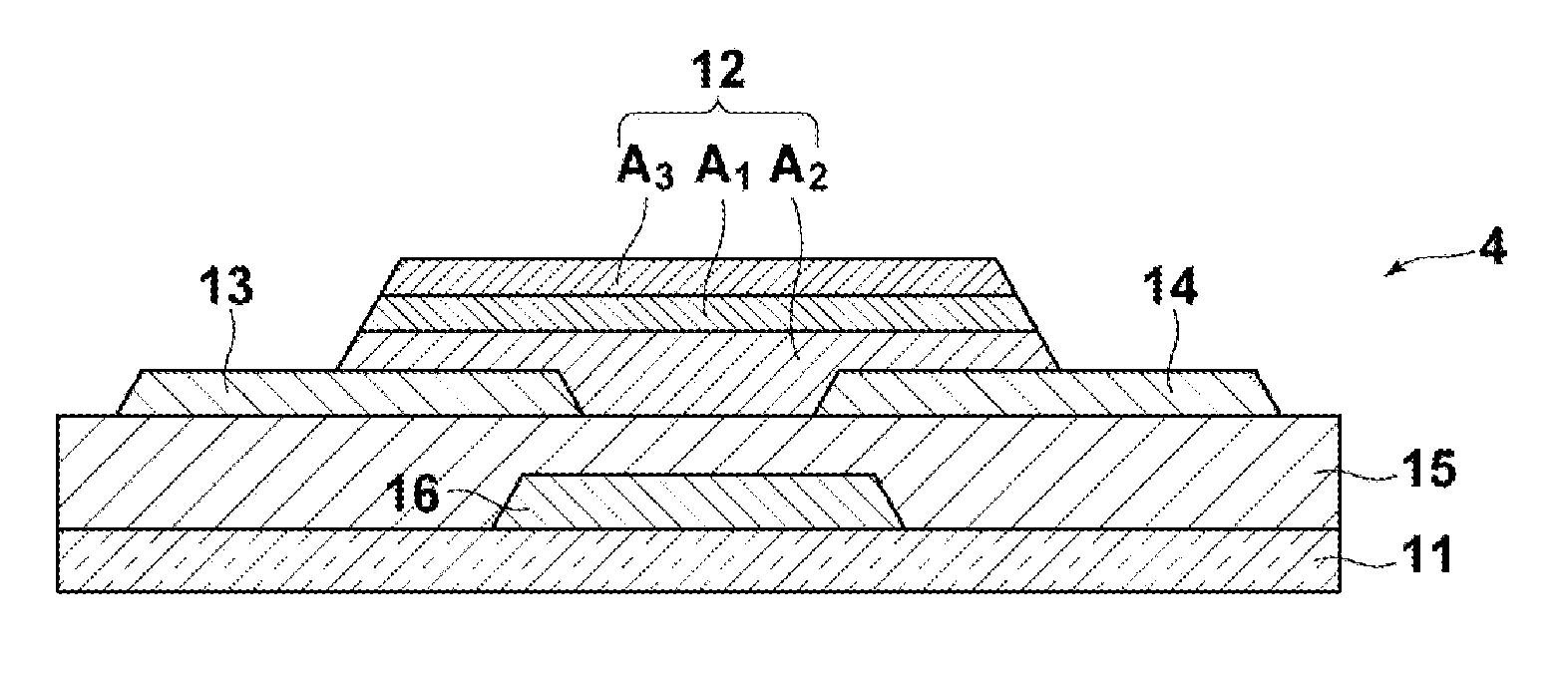
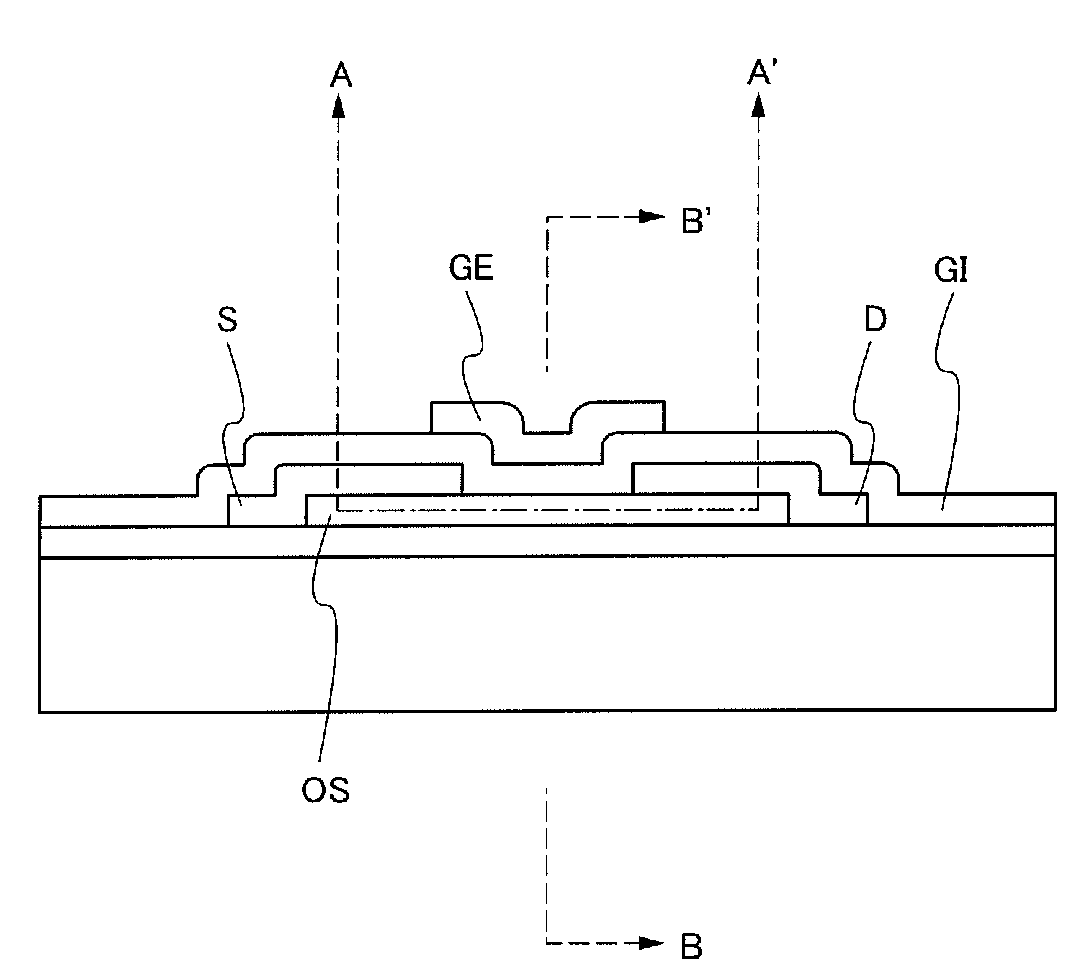
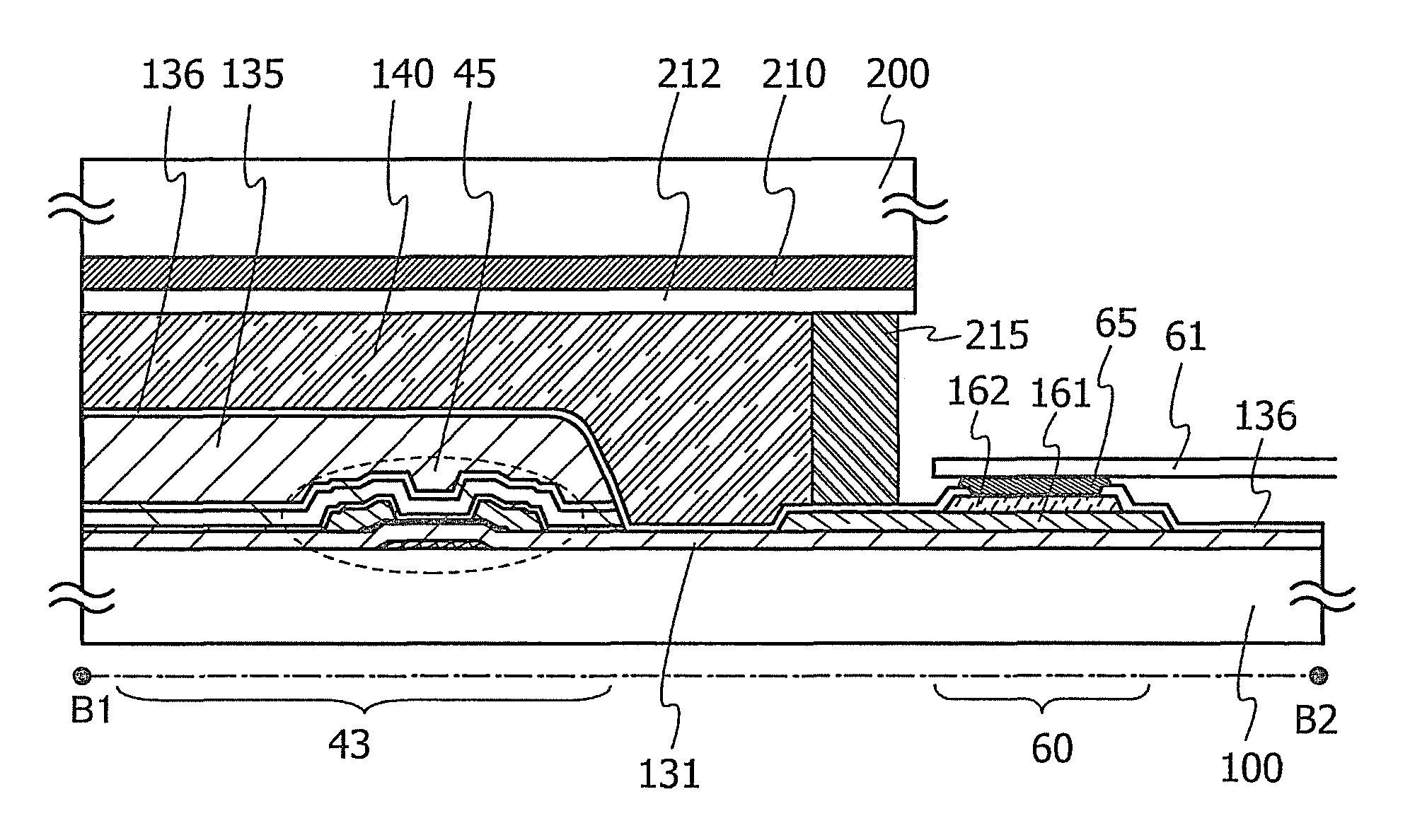
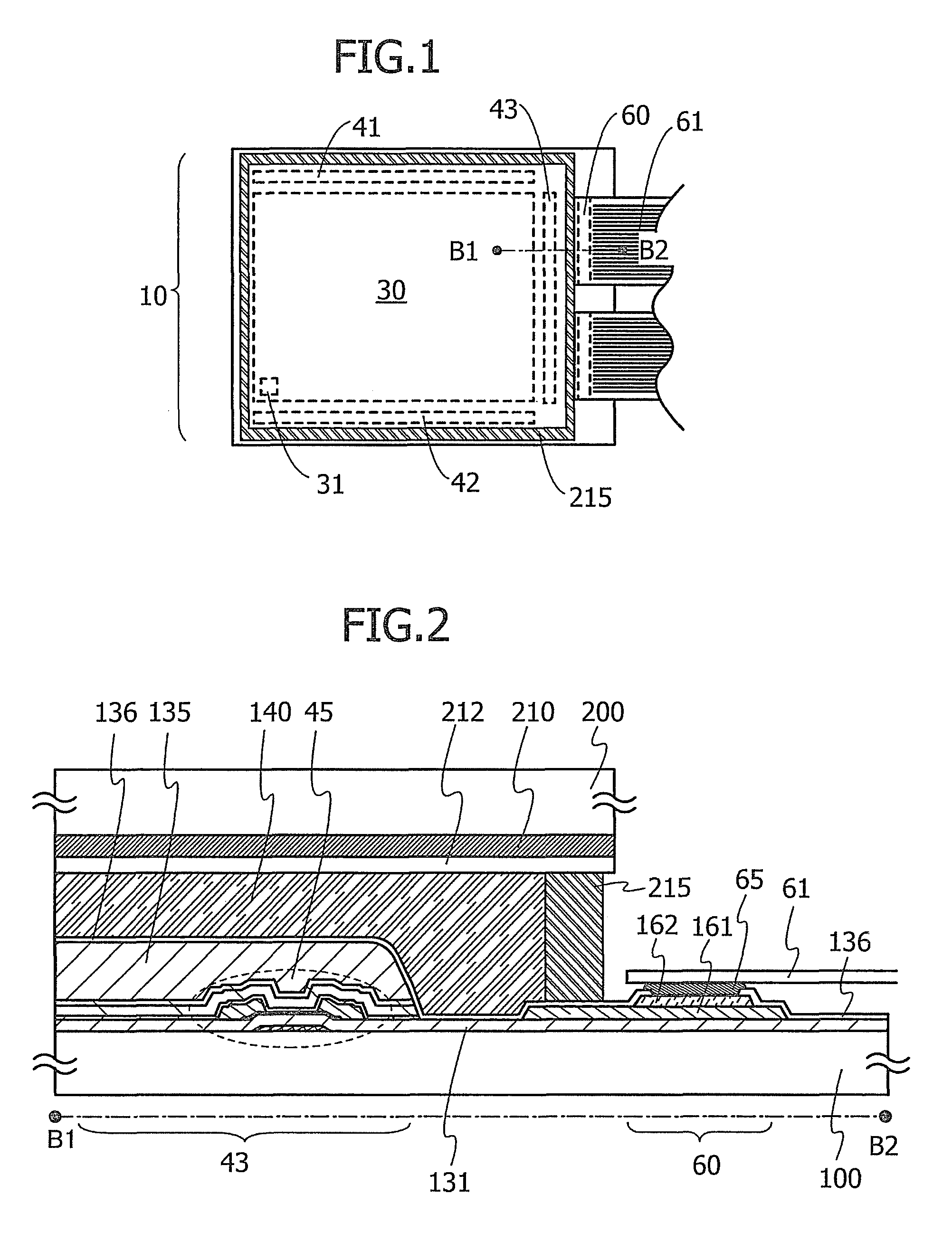
Thin-film transistor, method of producing the same, and devices provided with the same
ActiveUS20110140100A1Low mobilityIncrease carrier densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenSemiconductor
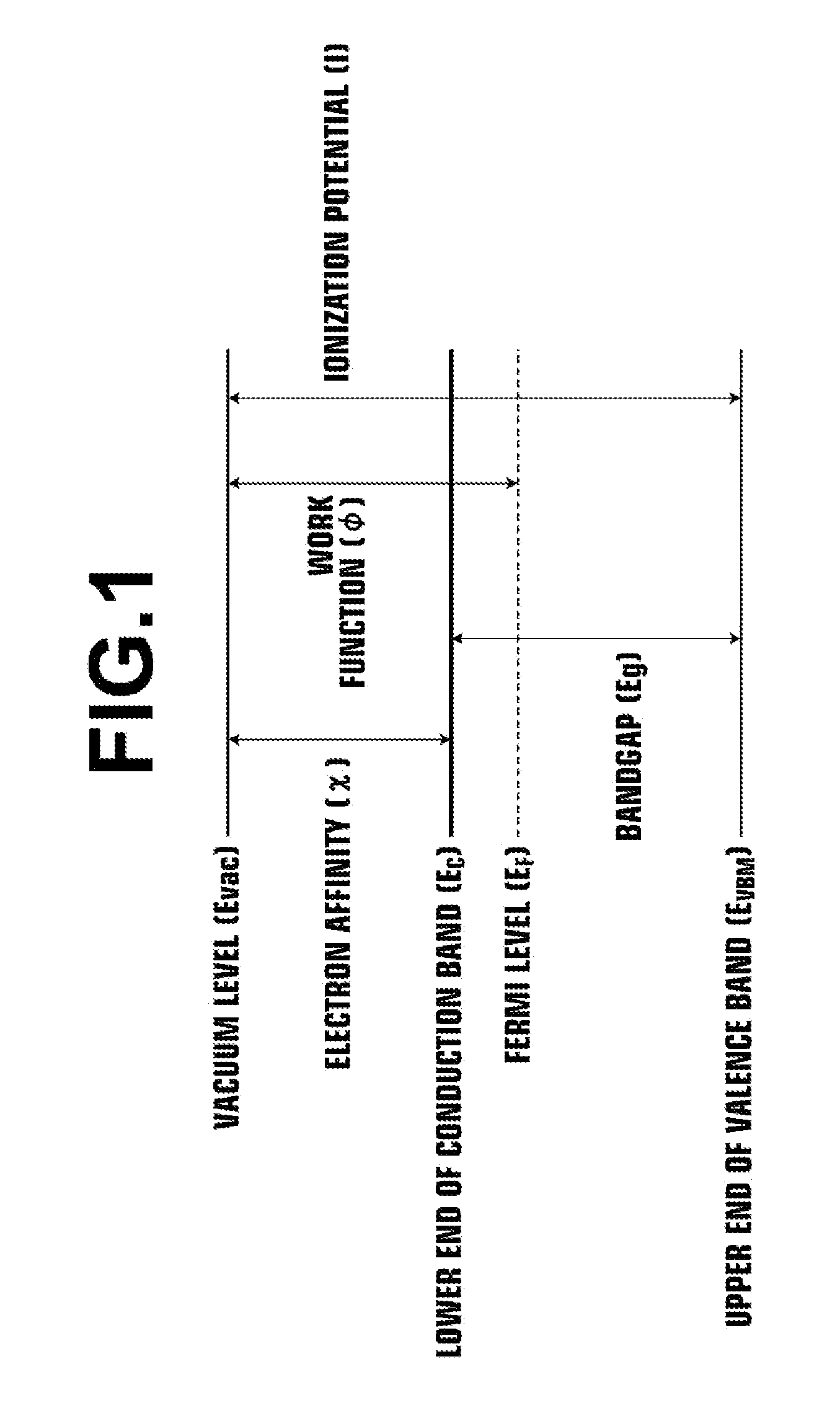
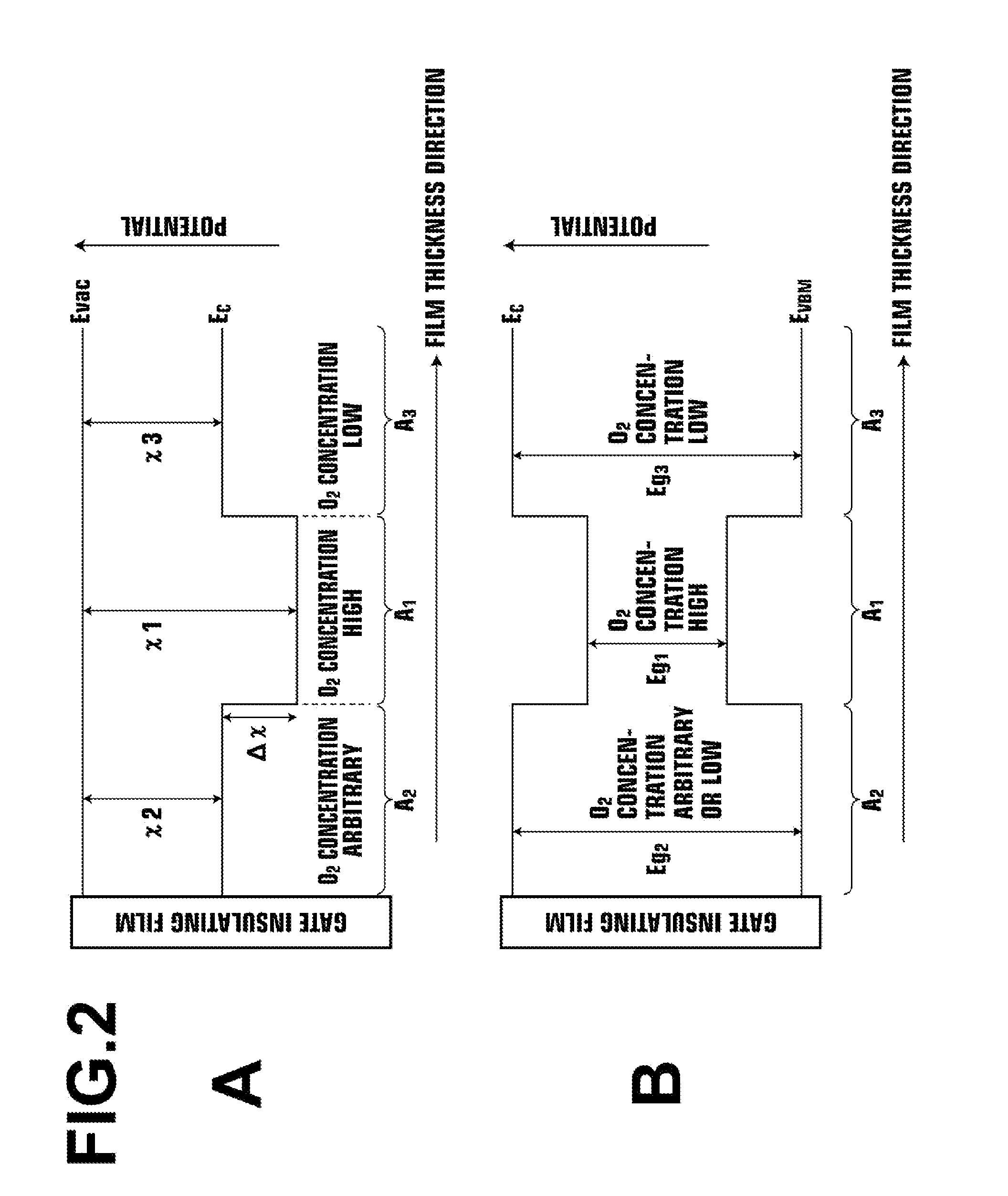
A thin-film transistor including an oxide semiconductor layer is disclosed. The oxide semiconductor layer includes a first area, a second area and a third area forming a well-type potential in the film-thickness direction. The first area forms a well of the well-type potential and has a first electron affinity. The second area is disposed nearer to the gate electrode than the first area and has a second electron affinity smaller than the first electron affinity. The third area is disposed farther from the gate electrode than the first area and has a third electron affinity smaller than the first electron affinity. At least an oxygen concentration at the third area is lower than an oxygen concentration at the first area.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Light emitting element, light emitting device, and electronic device
InactiveUS20070172699A1Reduce failureReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLight emitting deviceElectron
An object of the present invention is to provide a light emitting element which has low driving voltage and can increase lifetime longer than a conventional light emitting element. One feature is to include a plurality of layers which includes a layer containing a light emitting substance between first and second electrodes, in which at least one layer of the plurality of layers contains a carbazole derivative represented by General Formula (1) and a substance having an electron accepting property with respect to the carbazole derivative represented by General Formula (1). By employing this structure, the above object can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Manufacture of silicon-based devices having disordered sulfur-doped surface layers
InactiveUS20080044943A1Increase carrier densityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface layerSulfur
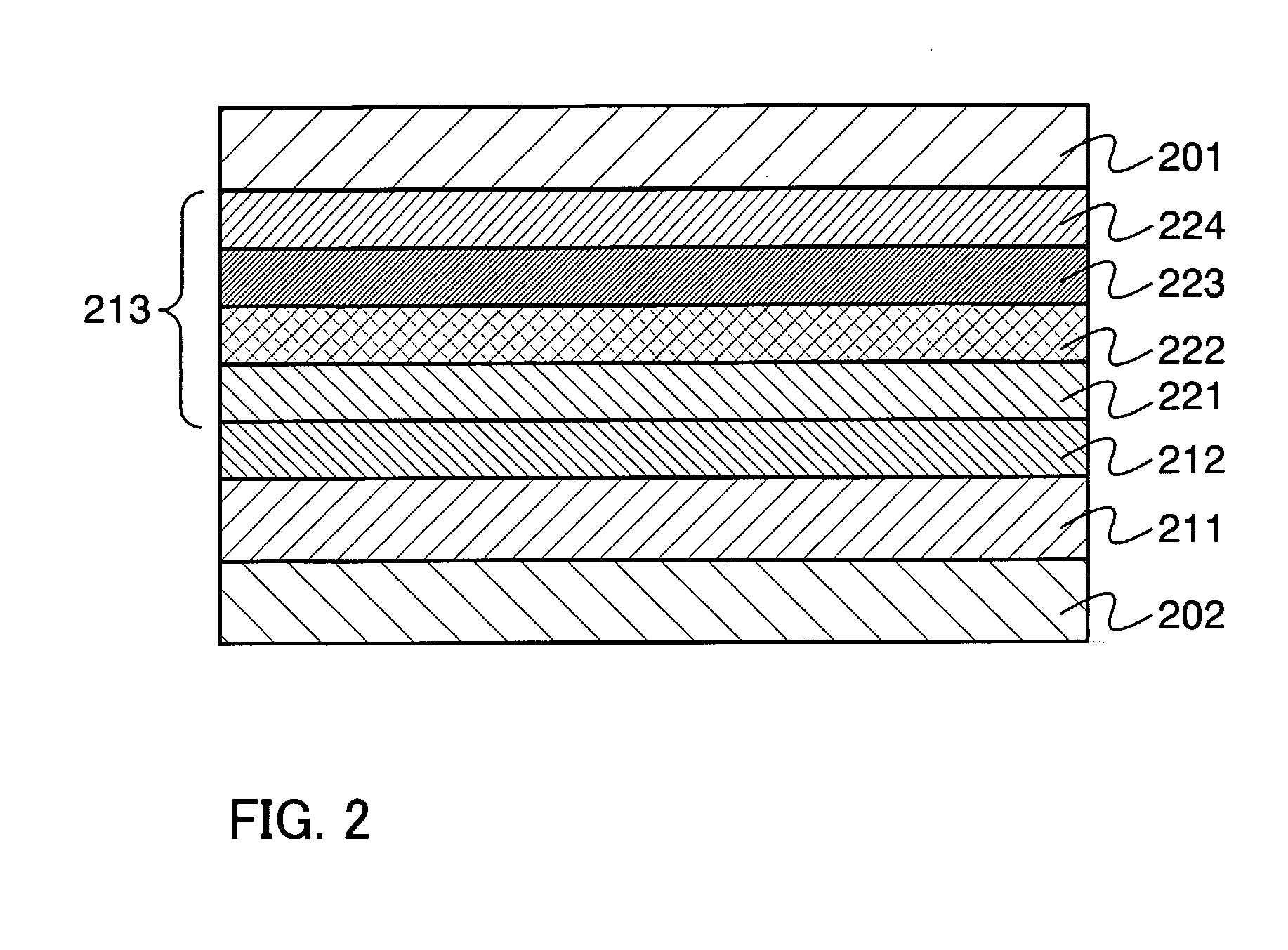
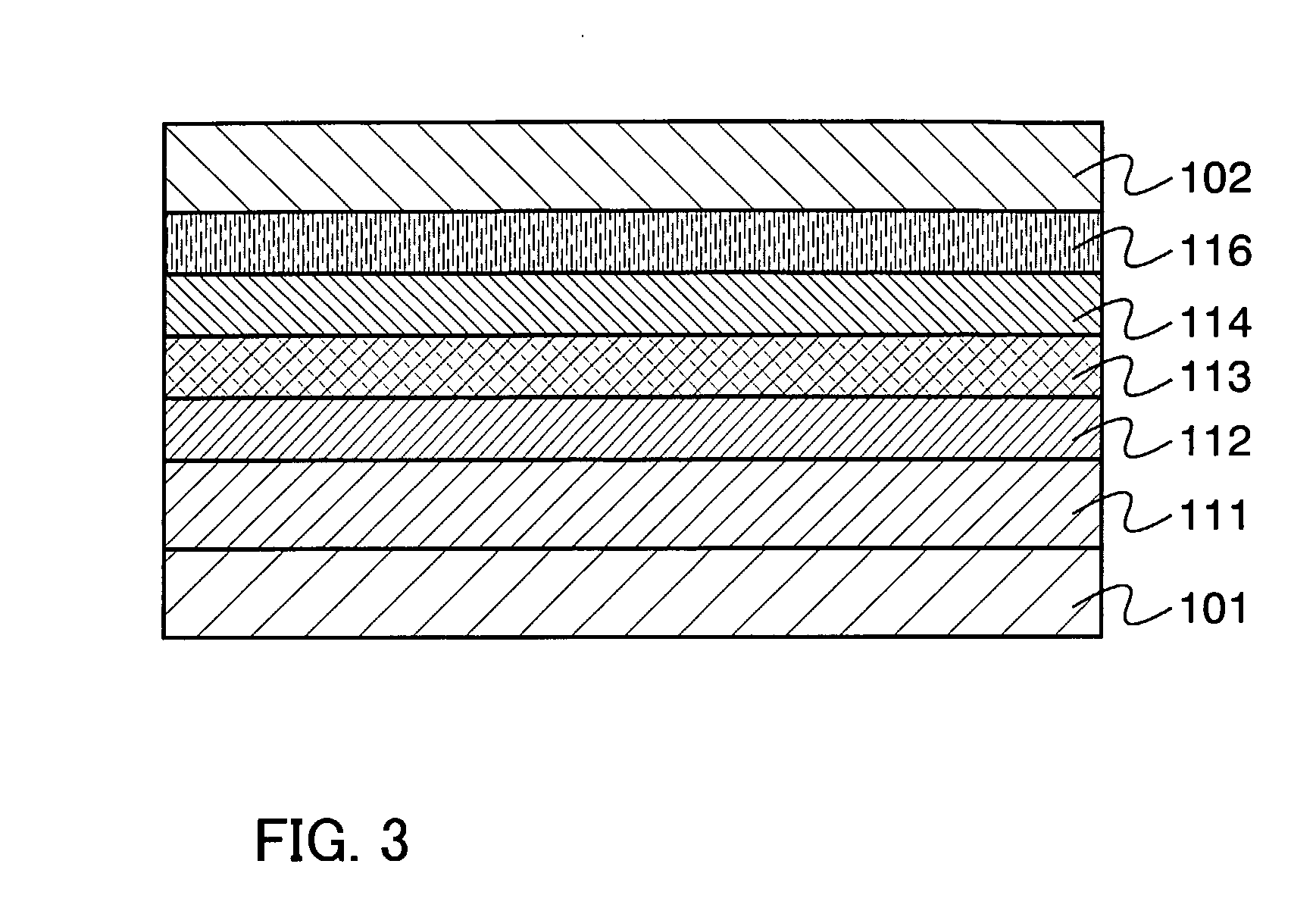
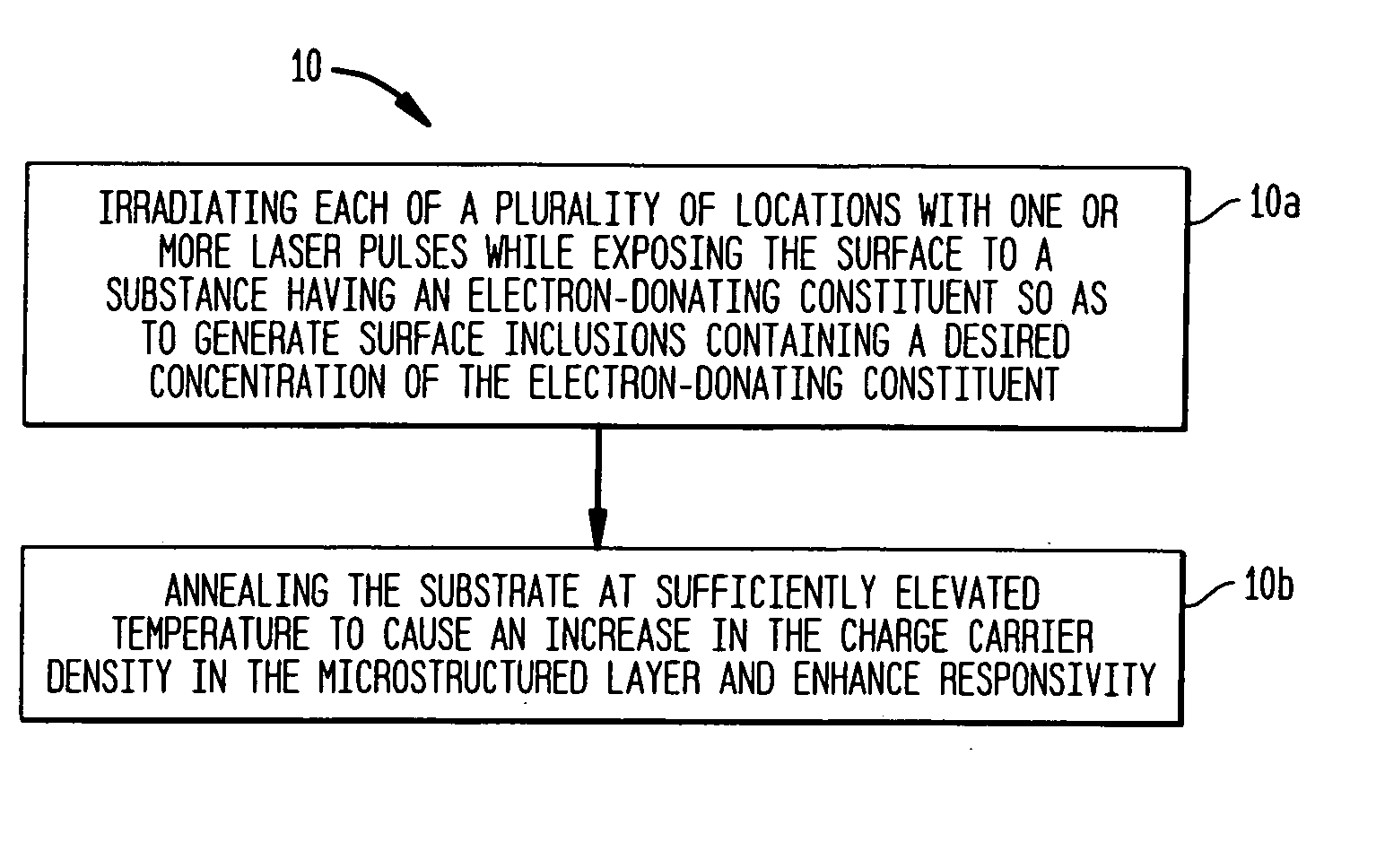
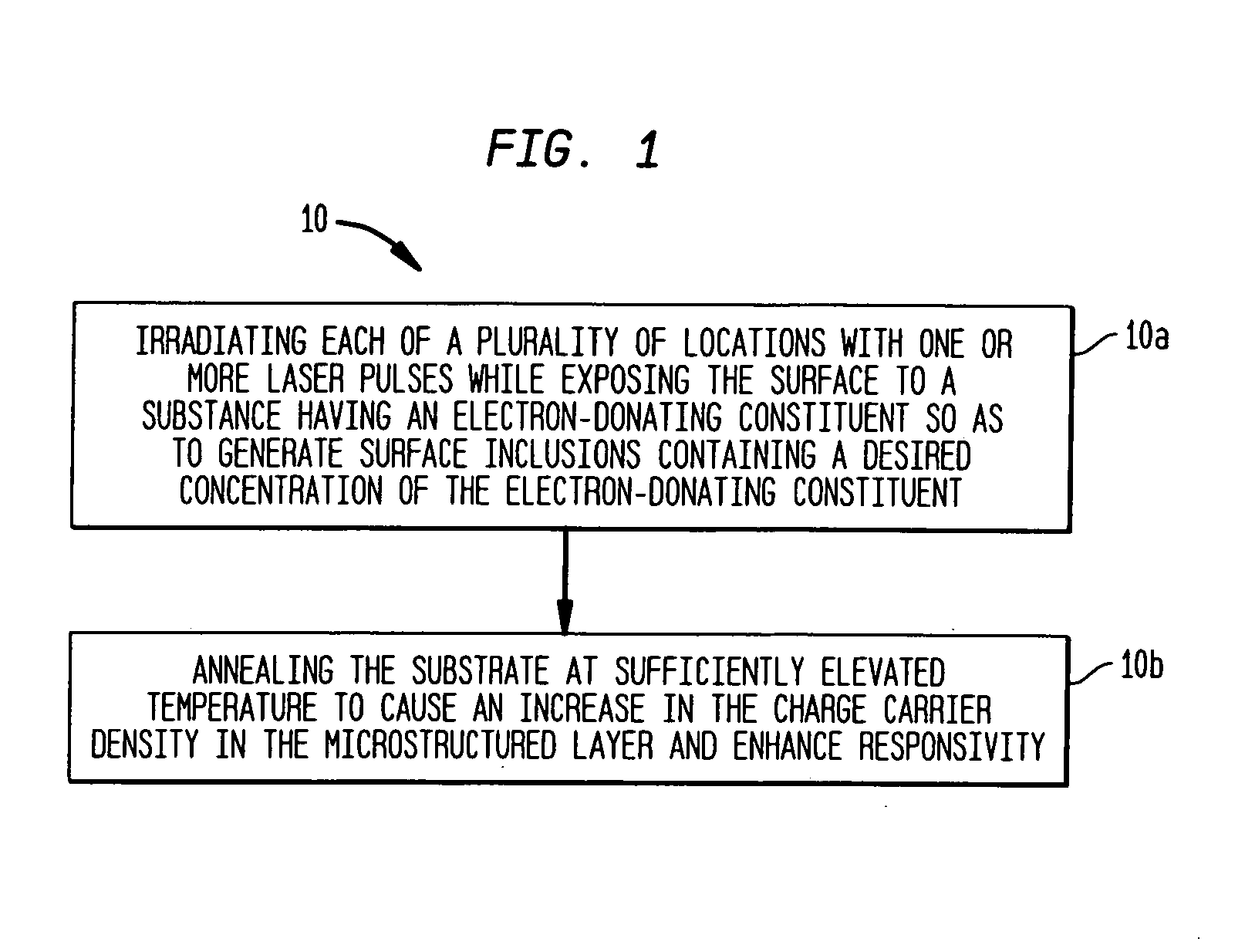
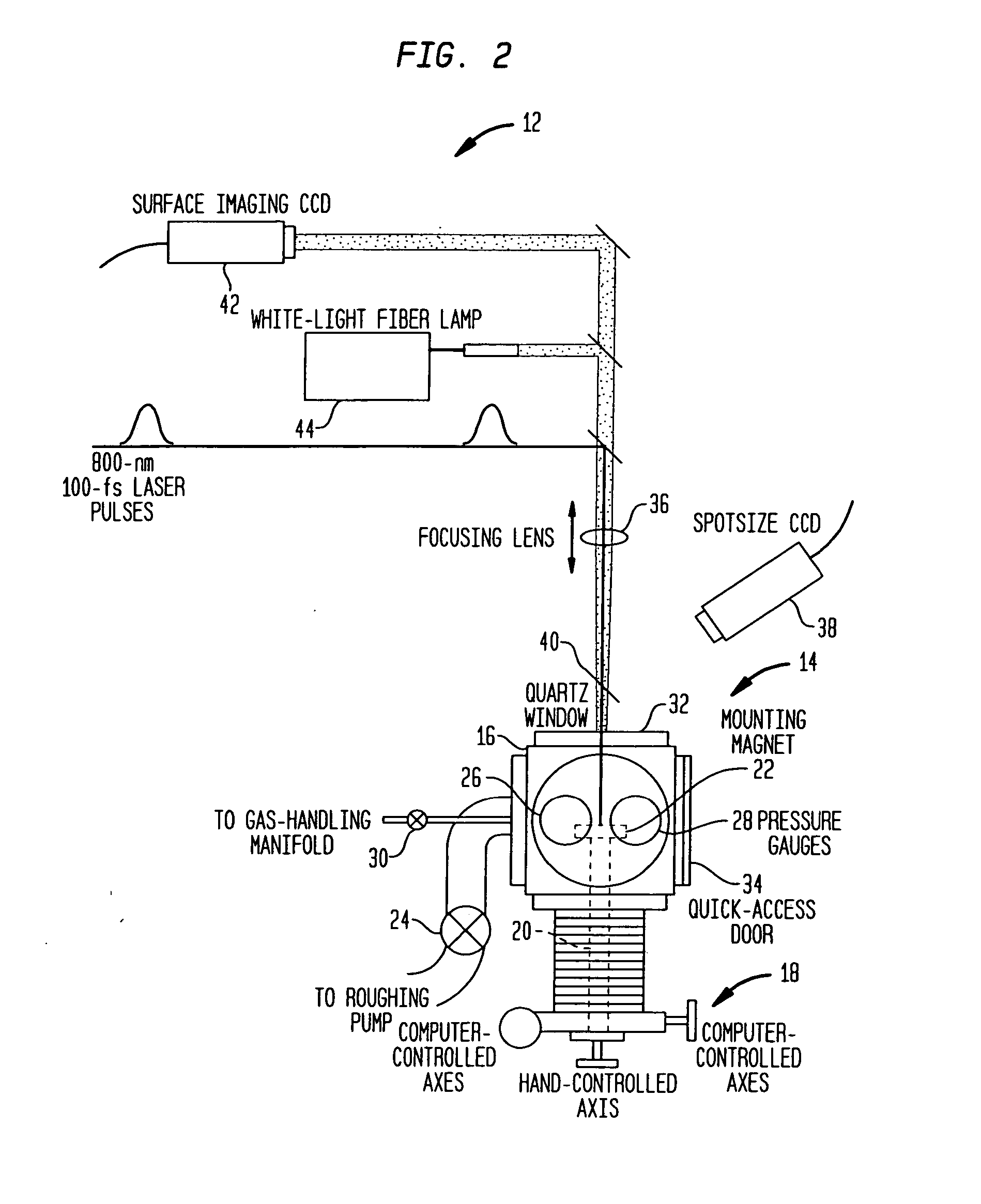
The present invention provides methods of fabricating a radiation-absorbing semiconductor wafer by irradiating at least one surface location of a silicon substrate, e.g., an n-doped crystalline silicon, by a plurality of temporally short laser pulses, e.g., femtosecond pulses, while exposing that location to a substance, e.g., SF6, having an electron-donating constituent so as to generate a substantially disordered surface layer (i.e., a microstructured layer) that incorporates a concentration of that electron-donating constituent, e.g., sulfur. The substrate is also annealed at an elevated temperature and for a duration selected to enhance the charge carrier density in the surface layer. For example, the substrate can be annealed at a temperature in a range of about 700 K to about 900 K.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Gate stack for high performance sub-micron CMOS devices
InactiveUS6894357B2Increased drive current capabilityMinimize the effect of parasitic capacitanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceDielectric
A new method is provided for the creation of sub-micron gate electrode structures. A high-k dielectric is used for the gate dielectric, providing increased inversion carrier density without having to resort to aggressive scaling of the thickness of the gate dielectric while at the same time preventing excessive gate leakage current from occurring. Further, air-gap spacers are formed over a stacked gate structure. The gate structure consists of pre-doped polysilicon of polysilicon-germanium, thus maintaining superior control over channel inversion carriers. The vertical field between the gate structure and the channel region of the gate is maximized by the high-k gate dielectric, capacitive coupling between the source / drain regions of the structure and the gate electrode is minimized by the gate spacers that contain an air gap.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Sputtering target and manufacturing method thereof, and transistor
InactiveUS20110114944A1Improve reliabilityReduce the presence of impuritiesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHydrogenHydrogen atom
One object is to provide a deposition technique for forming an oxide semiconductor film. By forming an oxide semiconductor film using a sputtering target including a sintered body of a metal oxide whose concentration of hydrogen contained is low, for example, lower than 1×1016 atoms / cm3, the oxide semiconductor film contains a small amount of impurities such as a compound containing hydrogen typified by H2O or a hydrogen atom. In addition, this oxide semiconductor film is used as an active layer of a transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
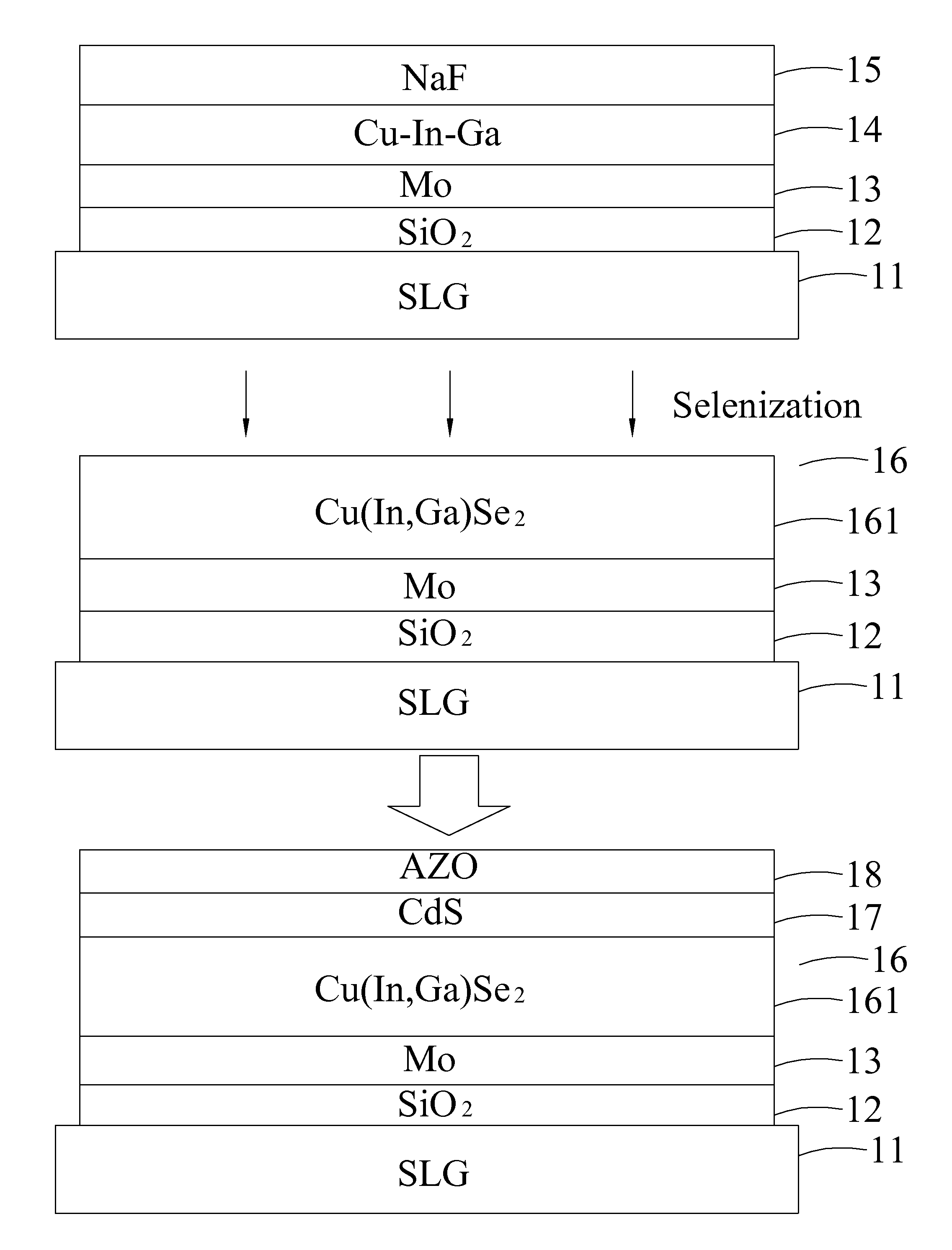
Thin-film solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20120132281A1Effectively control contentReduce grain boundaryFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffusion barrierMetal
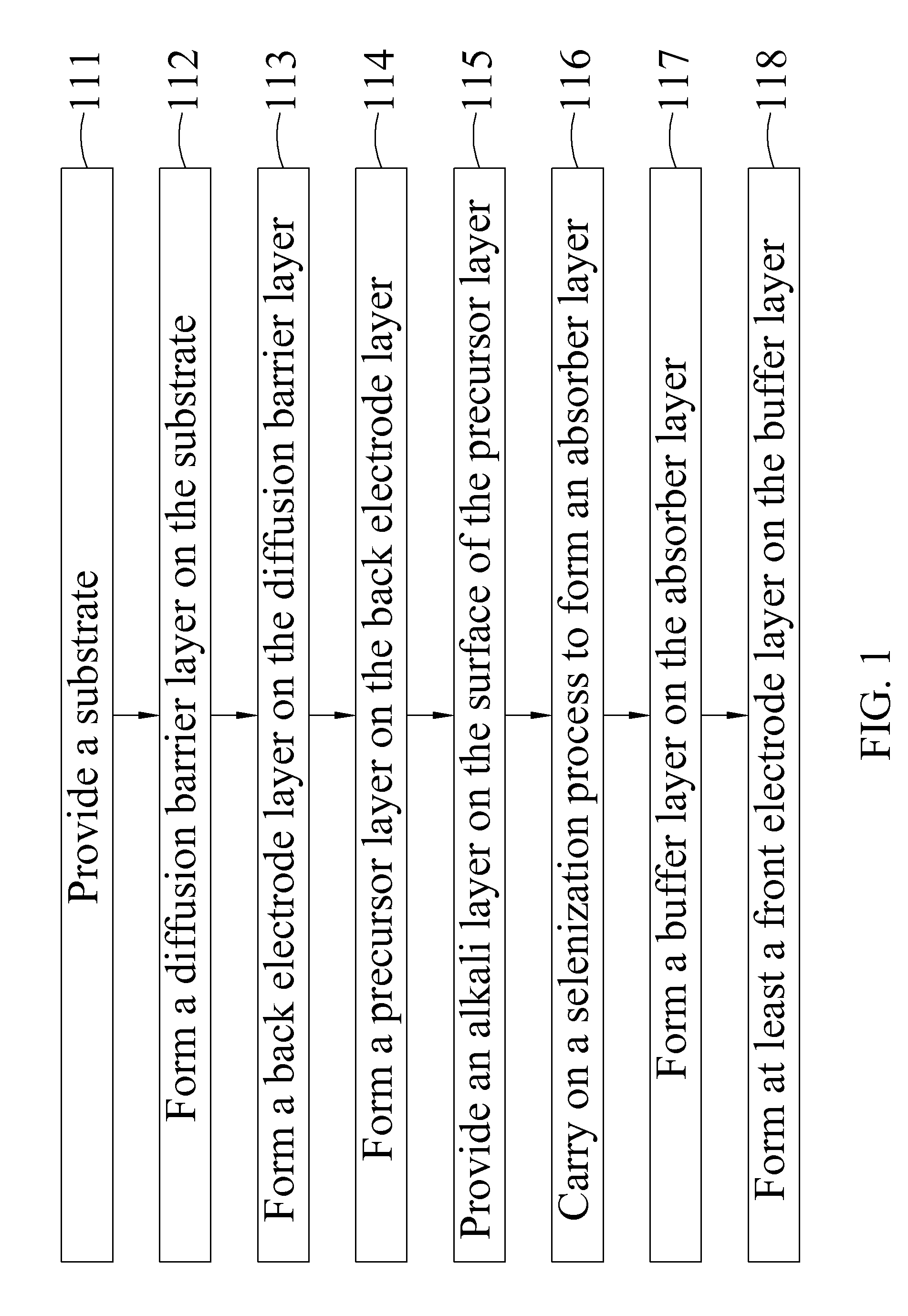
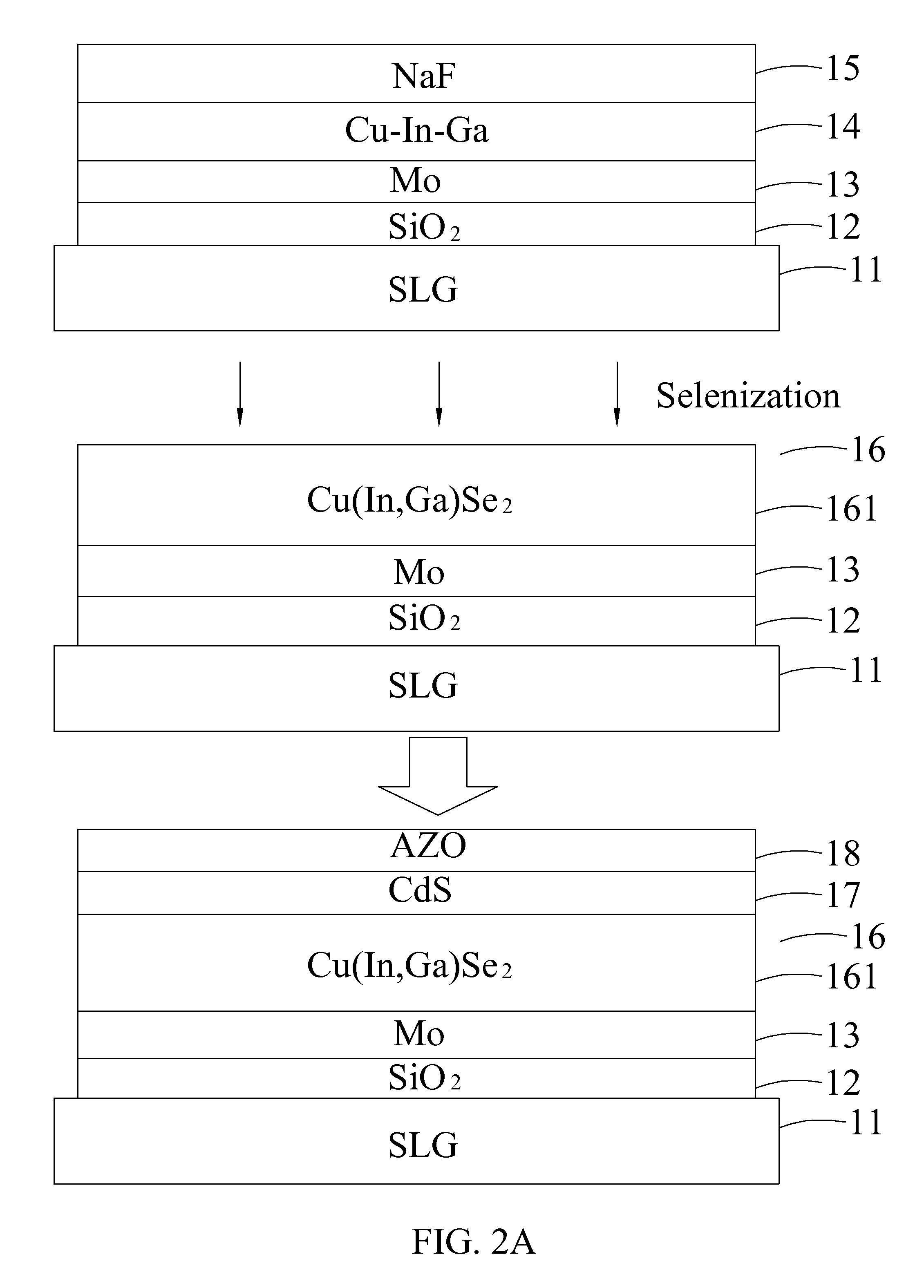
A thin-film solar cell and a manufacturing method thereof are disclosed. The method of manufacturing the thin-film solar cell includes the steps of providing a substrate; forming a diffusion barrier layer on the substrate; forming a back electrode layer on the diffusion barrier layer; forming a precursor layer on the back electrode layer, and the precursor layer including at least Cu, In and Ga; providing an alkali layer on an upper surface of the precursor layer, and the alkali layer being formed of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, or an alkali metal compound; providing a selenization process for the precursor layer and the alkali layer to form an absorber layer, such that an atomic percentage concentration of the alkali metal in the absorber layer is ranged between 0.01%˜10%; forming at least a buffer layer on the absorber layer; and forming at least a front electrode layer on the buffer layer.
Owner:NEXPOWER TECH
Method of fabricating n-type semiconductor diamond, and semiconductor diamond
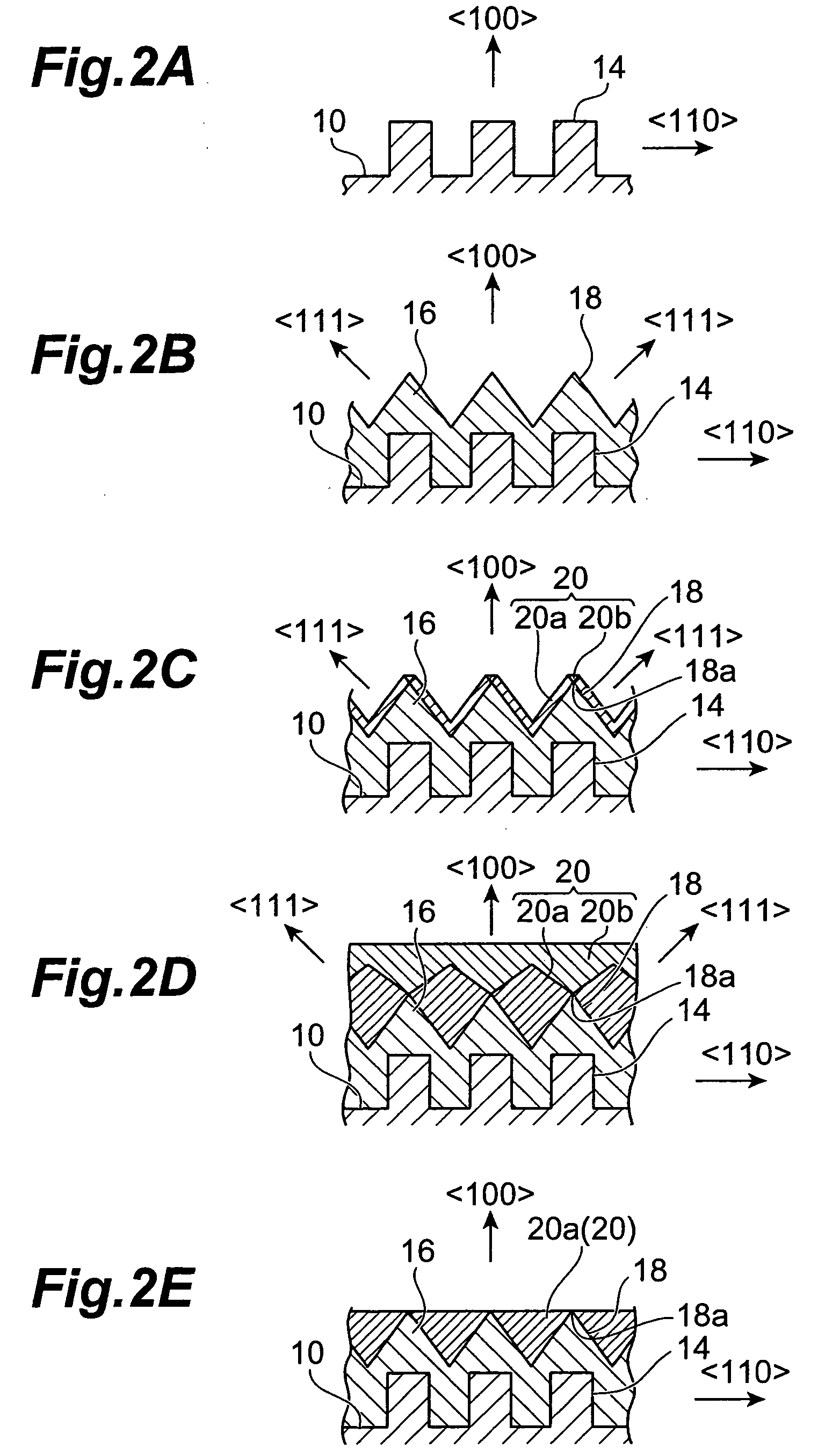
InactiveUS20050202665A1Increase carrier densityEfficient dopingPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesSingle crystalNon doped
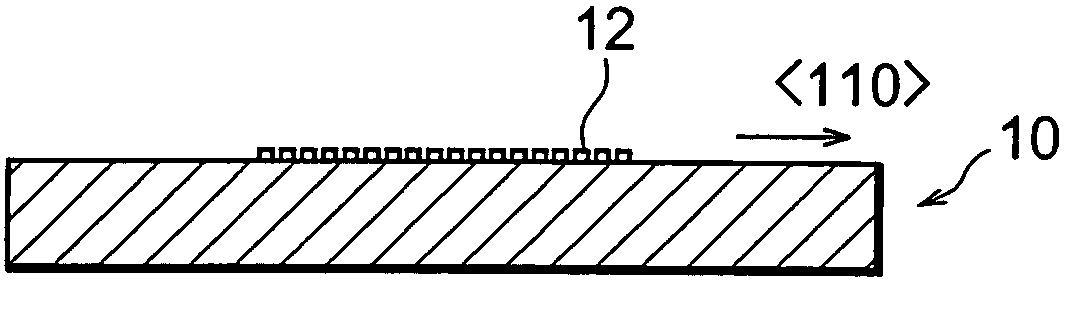
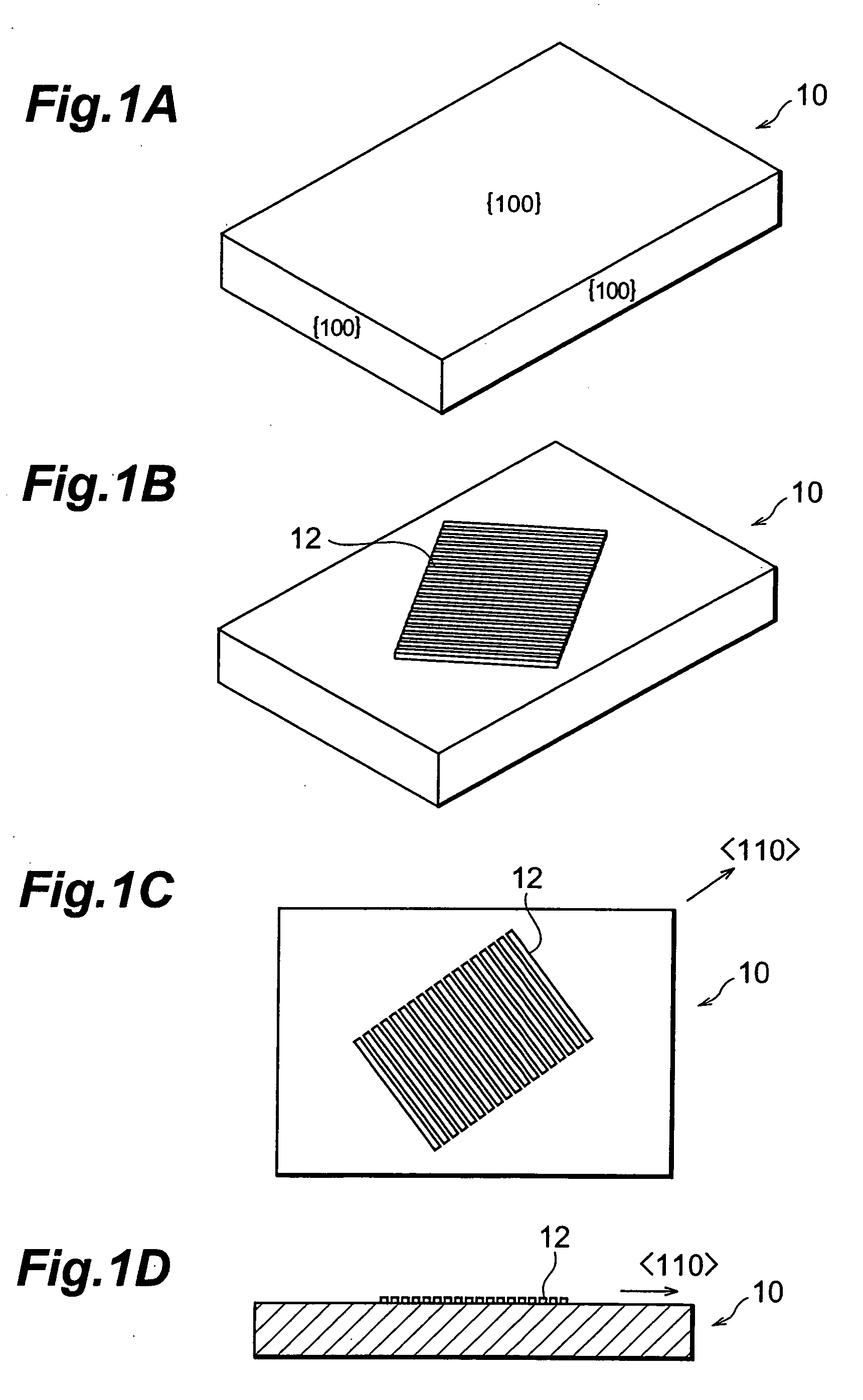
An n-type diamond epitaxial layer 20 is formed by processing a single-crystalline {100} diamond substrate 10 so as to form a {111} plane, and subsequently by causing diamond to epitaxially grow while n-doping the diamond {111} plane. Further, a combination of the n-type semiconductor diamond, p-type semiconductor diamond, and non-doped diamond, obtained in the above-described way, as well as the use of p-type single-crystalline {100} diamond substrate allow for a pn junction type, a pnp junction type, an npn junction type and a pin junction type semiconductor diamond to be obtained.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Sputtering target and manufacturing method thereof, and transistor
InactiveUS8492862B2Increase computing speedEasy to makeElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingHydrogen atomHydrogen
One object is to provide a deposition technique for forming an oxide semiconductor film. By forming an oxide semiconductor film using a sputtering target including a sintered body of a metal oxide whose concentration of hydrogen contained is low, for example, lower than 1×1016 atoms / cm3, the oxide semiconductor film contains a small amount of impurities such as a compound containing hydrogen typified by H2O or a hydrogen atom. In addition, this oxide semiconductor film is used as an active layer of a transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Dispersoid having metal-oxygen bonds, metal oxide film, and monomolecular film
InactiveUS20060239902A1Good dispersionFlat surfaceLiquid surface applicatorsSilicaChemistryOrganic inorganic
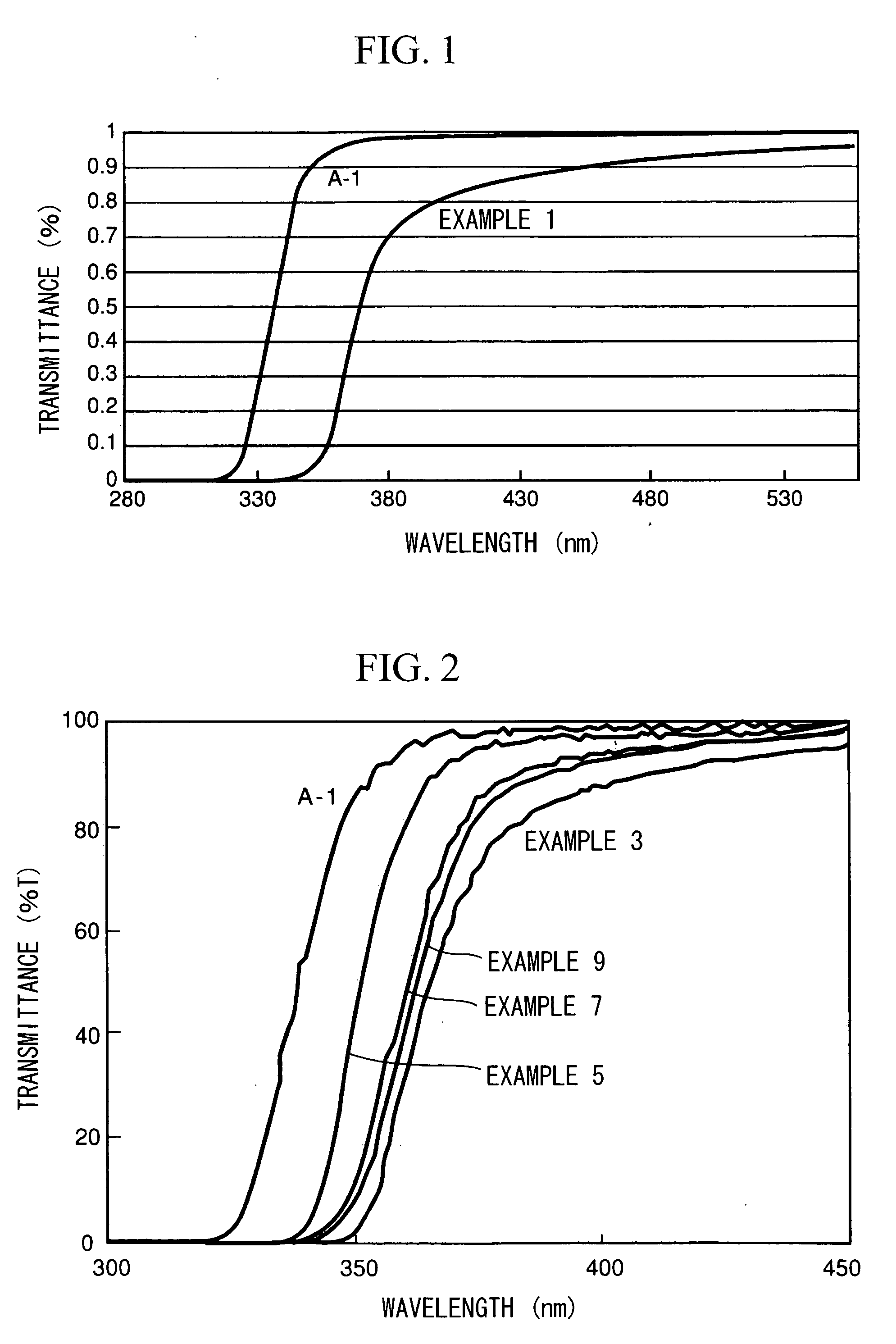
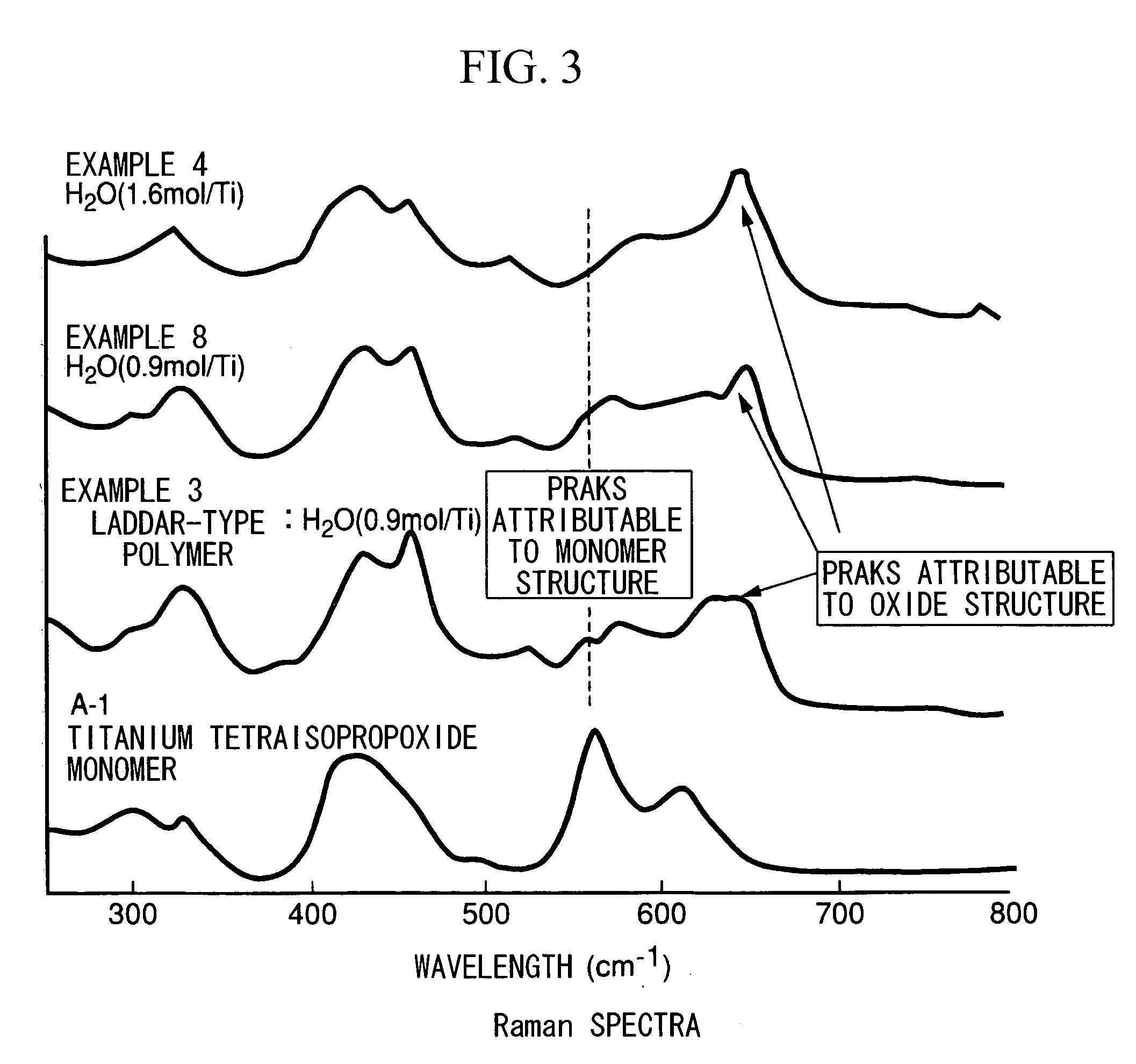
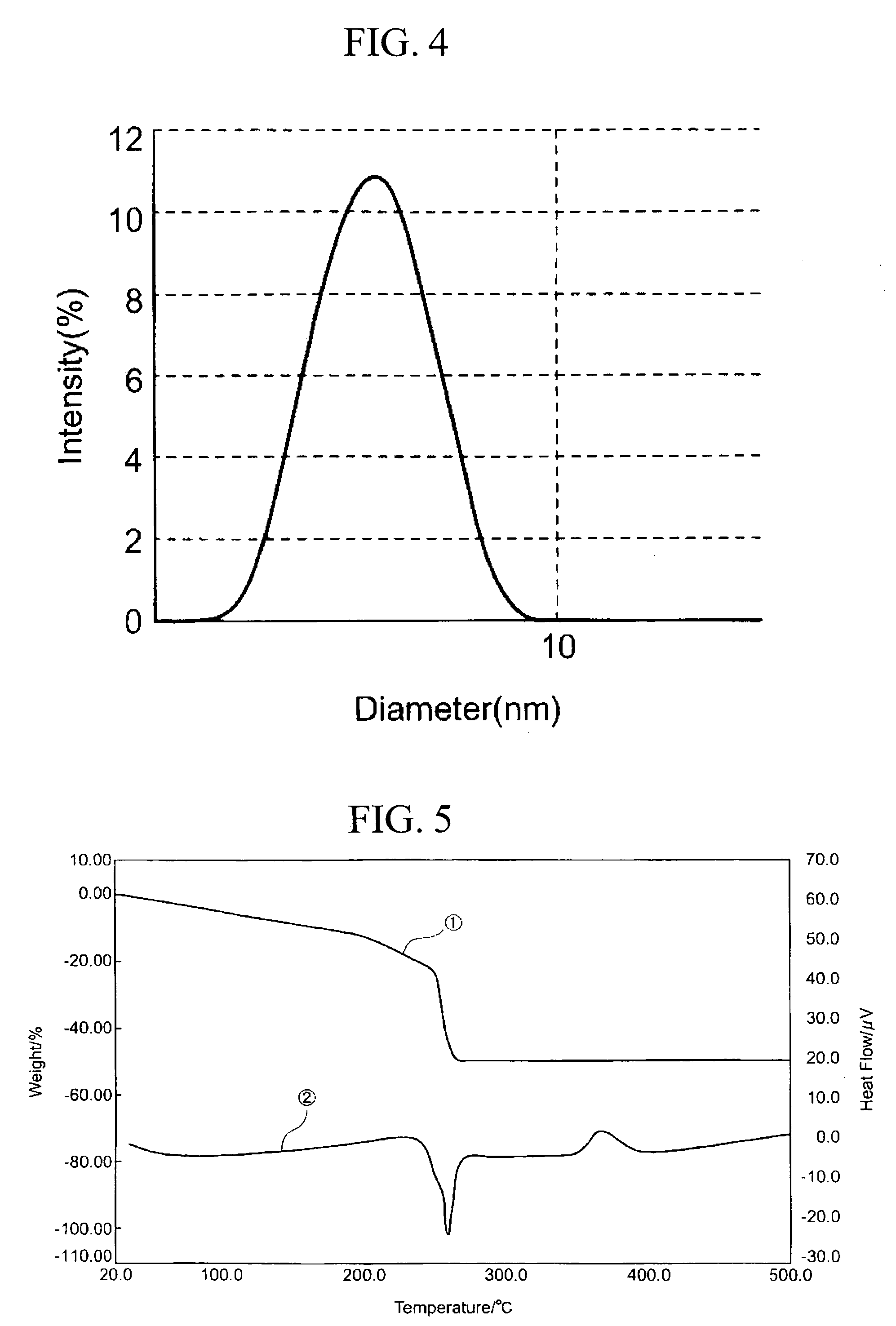
The invention provides dispersoids having metal-oxygen groups which are suitable for the production of metal oxide thin-films at a low temperature of 200° C. or below and for the production of homogeneous organic-inorganic hybrid materials. The invention also provides metal oxide thin-films and organic-inorganic hybrid materials endowed with various capabilities, particularly organic-inorganic hybrid materials having a high refractive index and high transparency. Use is made of a dispersoid having metal-oxygen bonds which is obtained by mixing a metal compound having at least three hydrolyzable groups with at least 0.5 mole but less than 2 moles of water per mole of the metal compound in an organic solvent, in the absence of an acid, a base and / or a dispersion stabilizer, and at a temperature at or below the temperature at which the metal compound begins to hydrolyze, then raising the temperature to at least the temperature at which hydrolysis begins.
Owner:NIPPON SODA CO LTD
Strongly correlated oxide field effect element
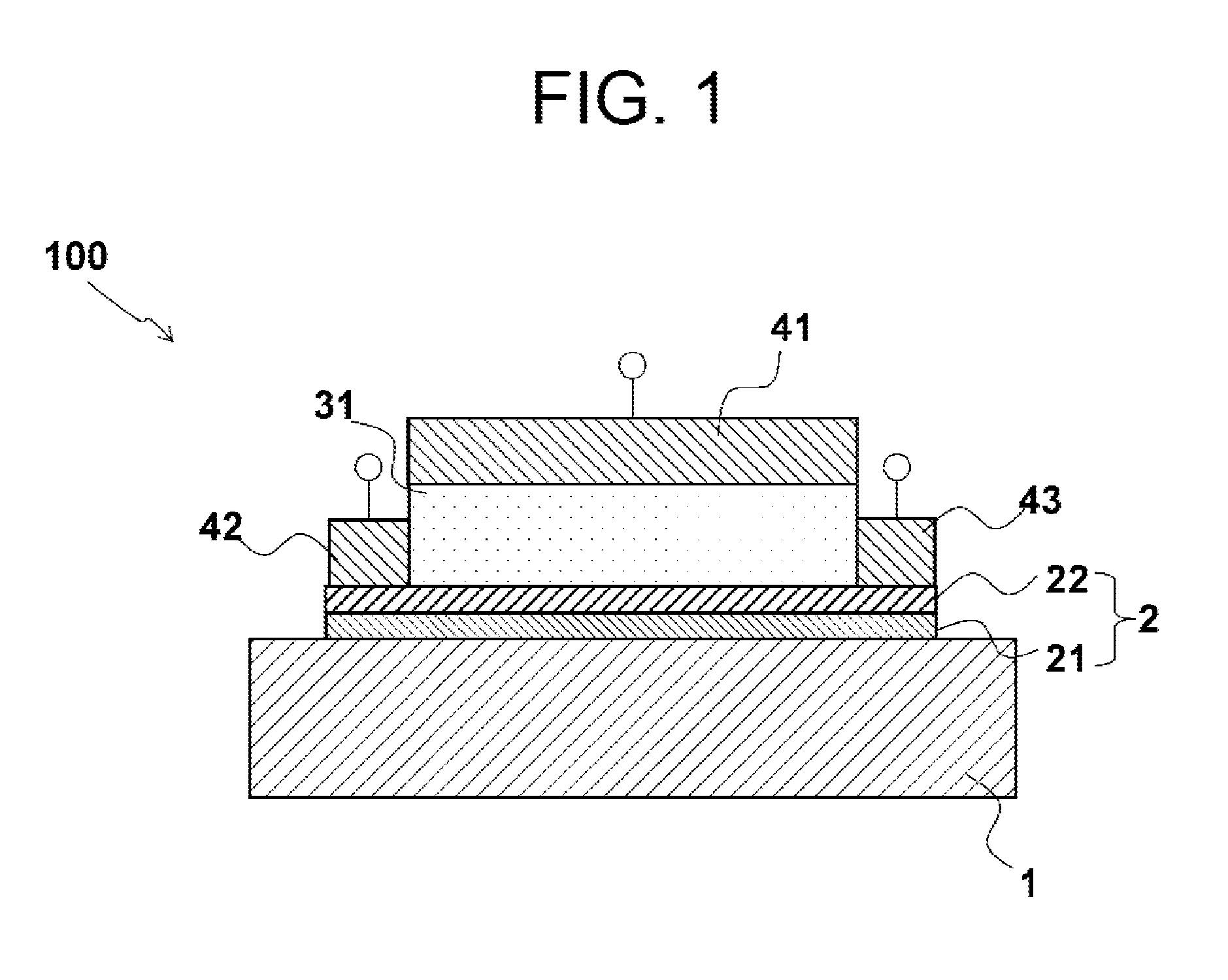
InactiveUS20130200457A1Reduce thicknessGuaranteed functionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCritical thicknessTransition layer
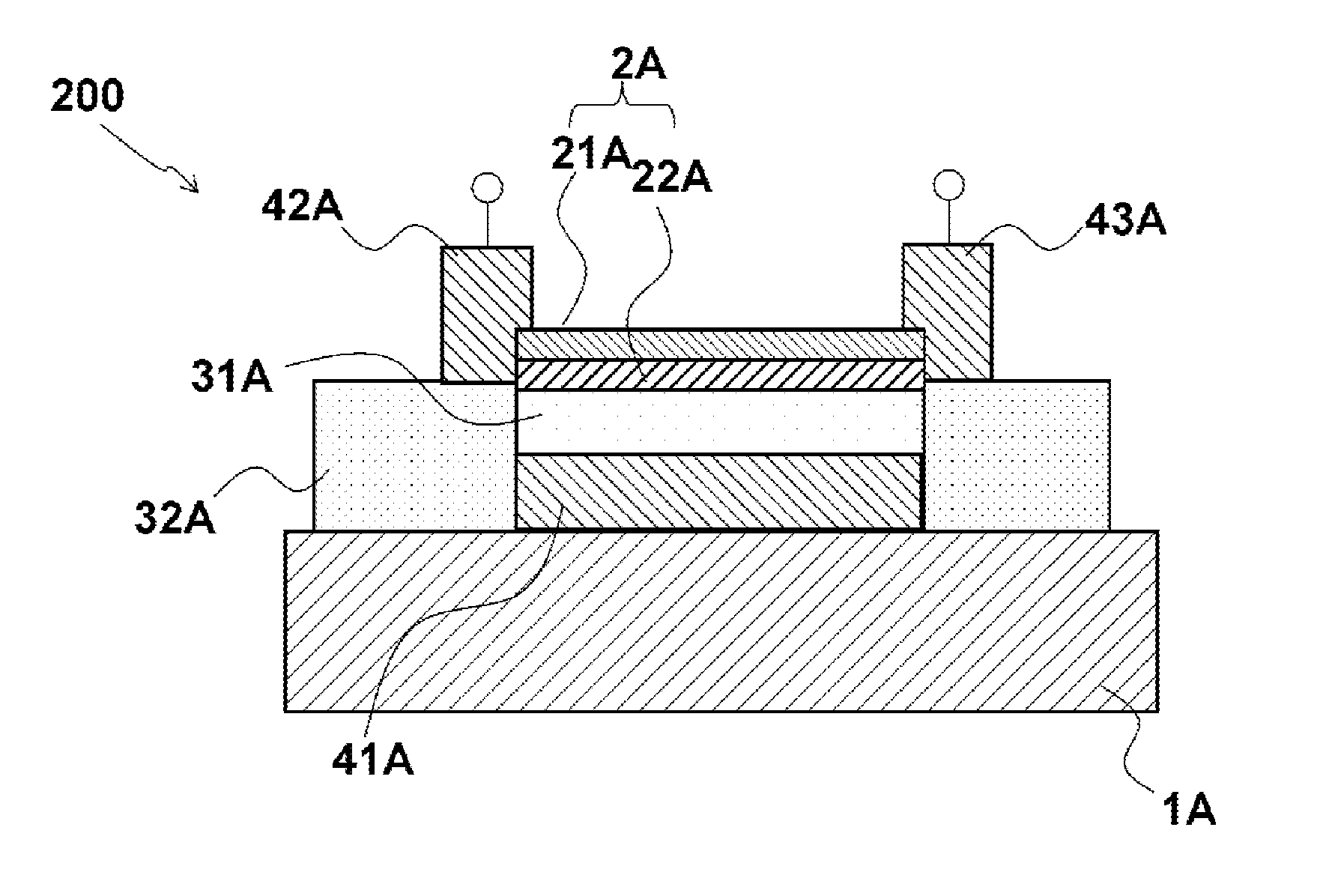
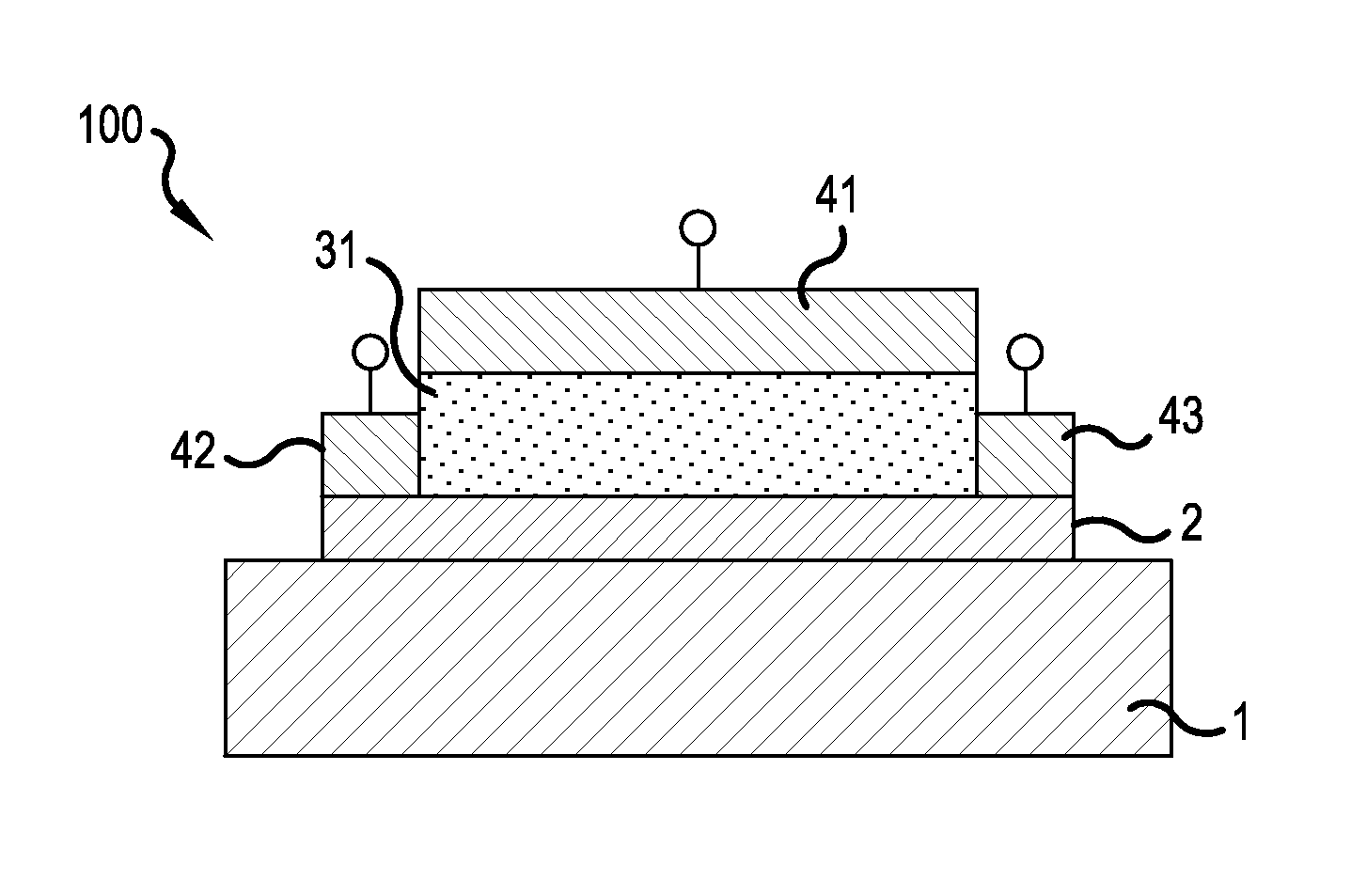
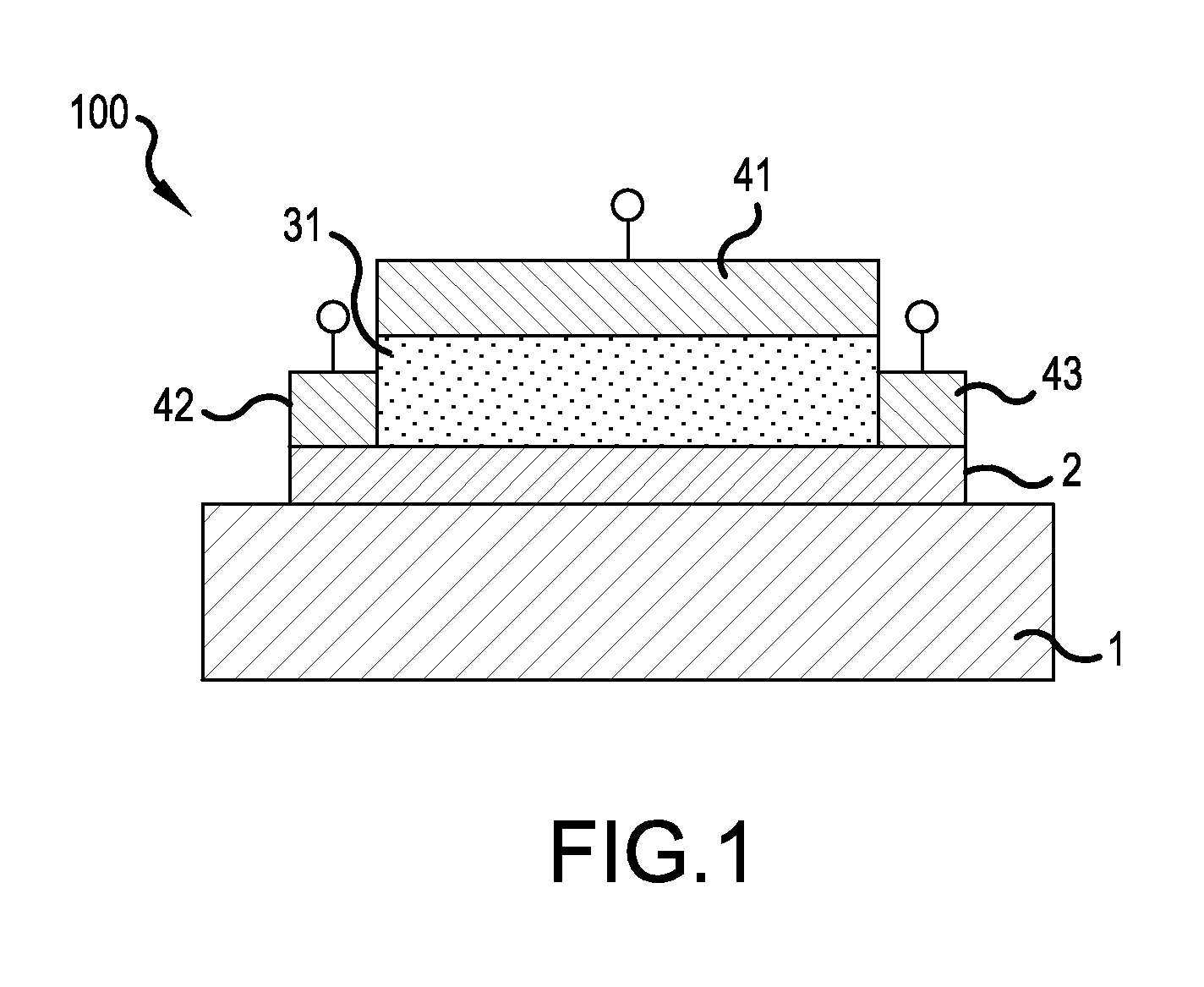
Provided is a strongly correlated oxide field effect element demonstrating a phase transition and a switching function induced by electrical means. The strongly correlated oxide field effect element is a strongly correlated oxide field effect element 100 including a channel layer 2 constituted by a strongly correlated oxide film, a gate electrode 14, a gate insulating layer 31, a source electrode 42, and a drain electrode 43. The channel layer 2 includes an insulator-metal transition layer 22 of a strongly correlated oxide and a metallic state layer 21 of a strongly correlated oxide that are stacked on each other. The thickness t of the channel layer 2, the thickness t1 of the insulator-metal transition layer 22, and the thickness t2 of the metallic state layer 21 satisfy the following relationship with critical thicknesses t1c and t2c for respective metallic phases of the layers: t=t1+t2≧t1c>t2c, where t1<t1c and t2<t2c.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
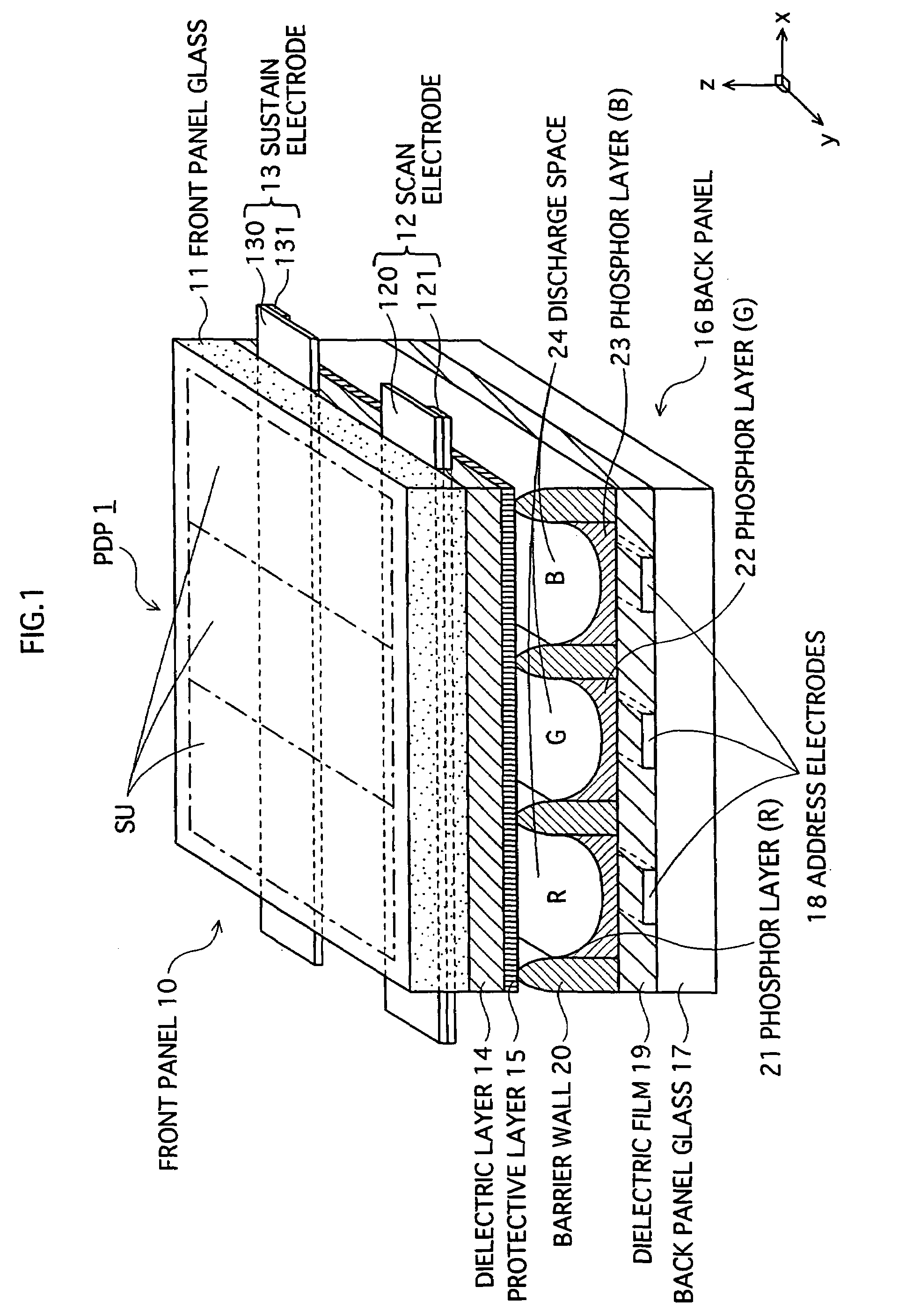
Plasma display panel and method for manaufacturing same
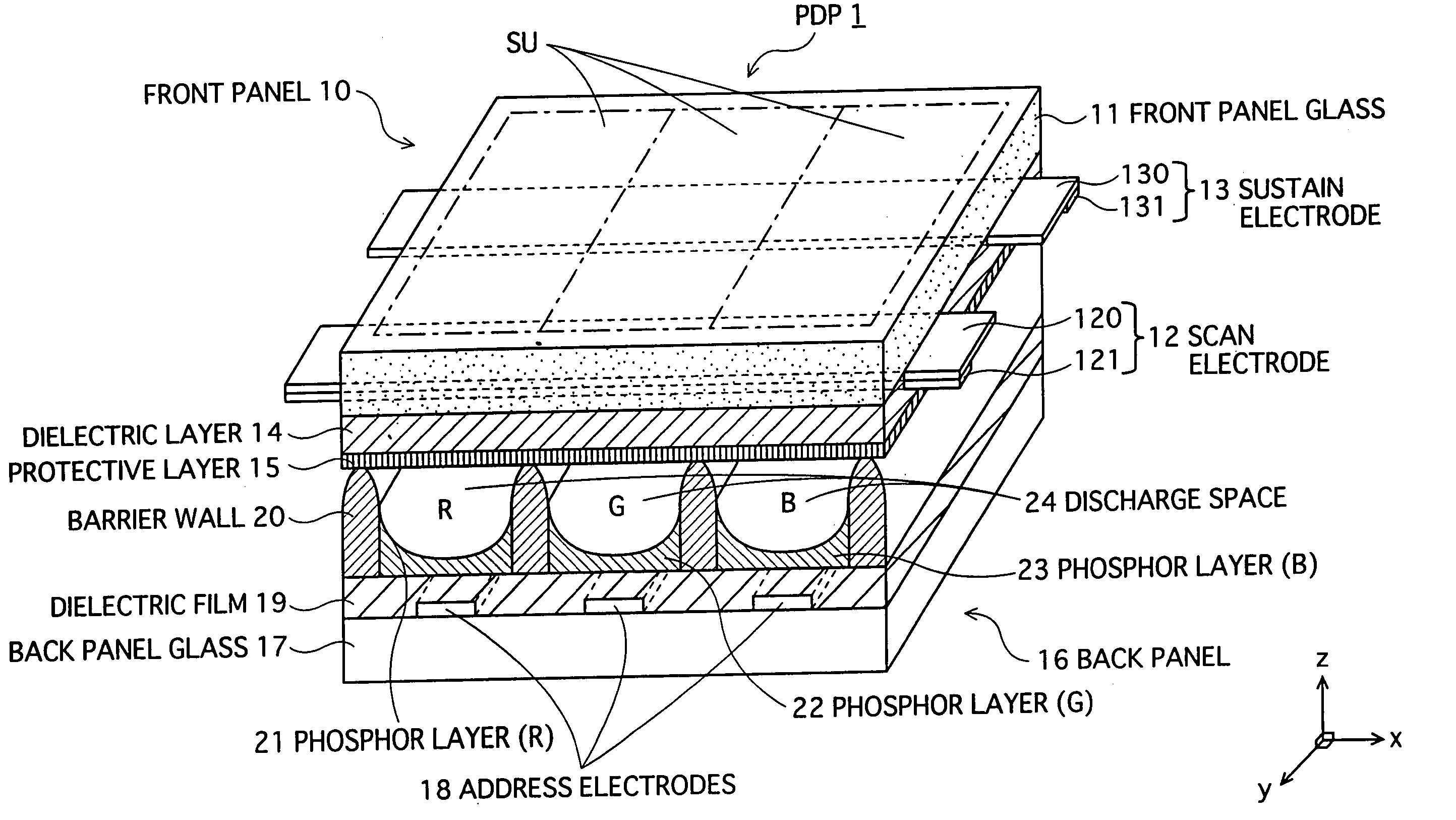
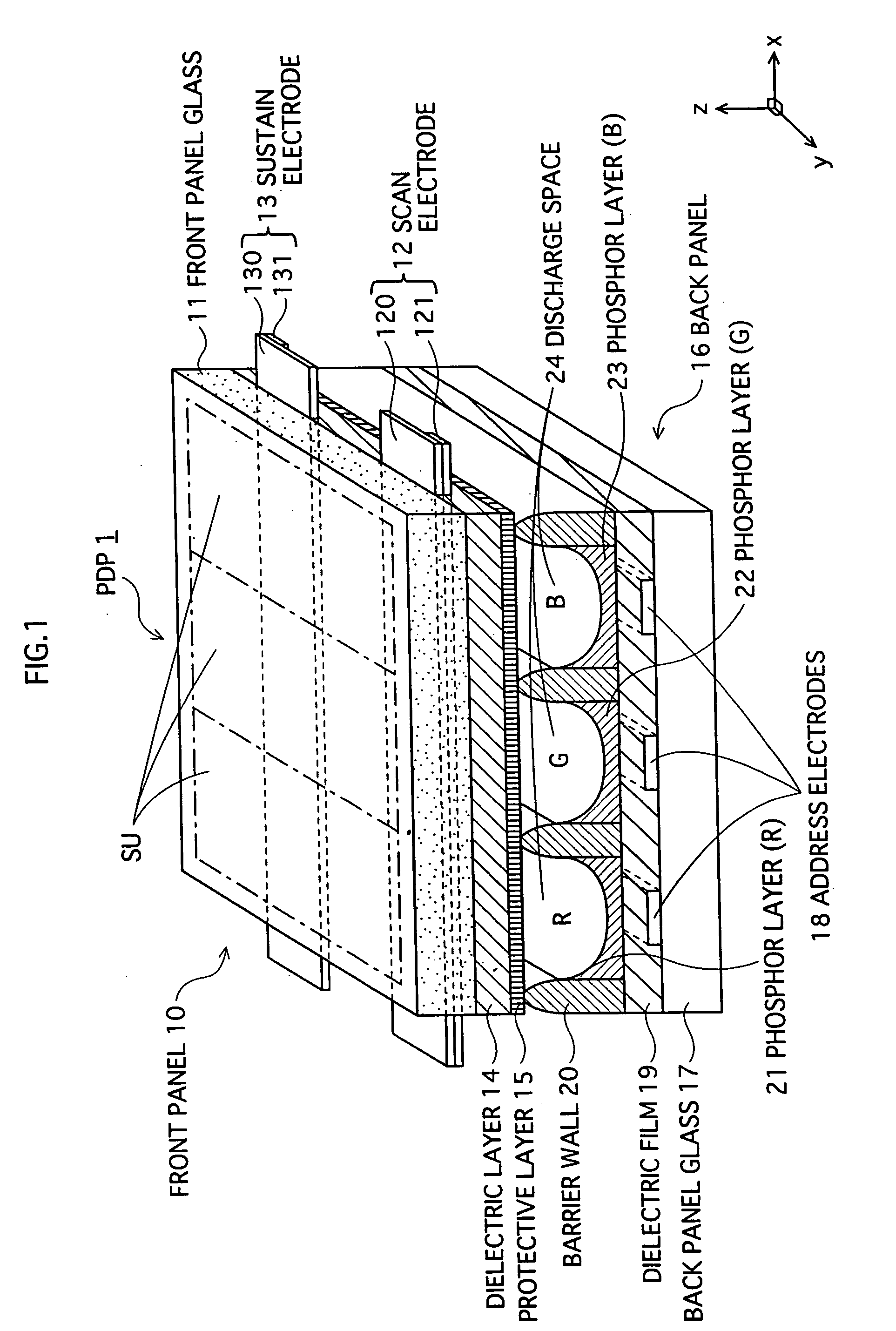
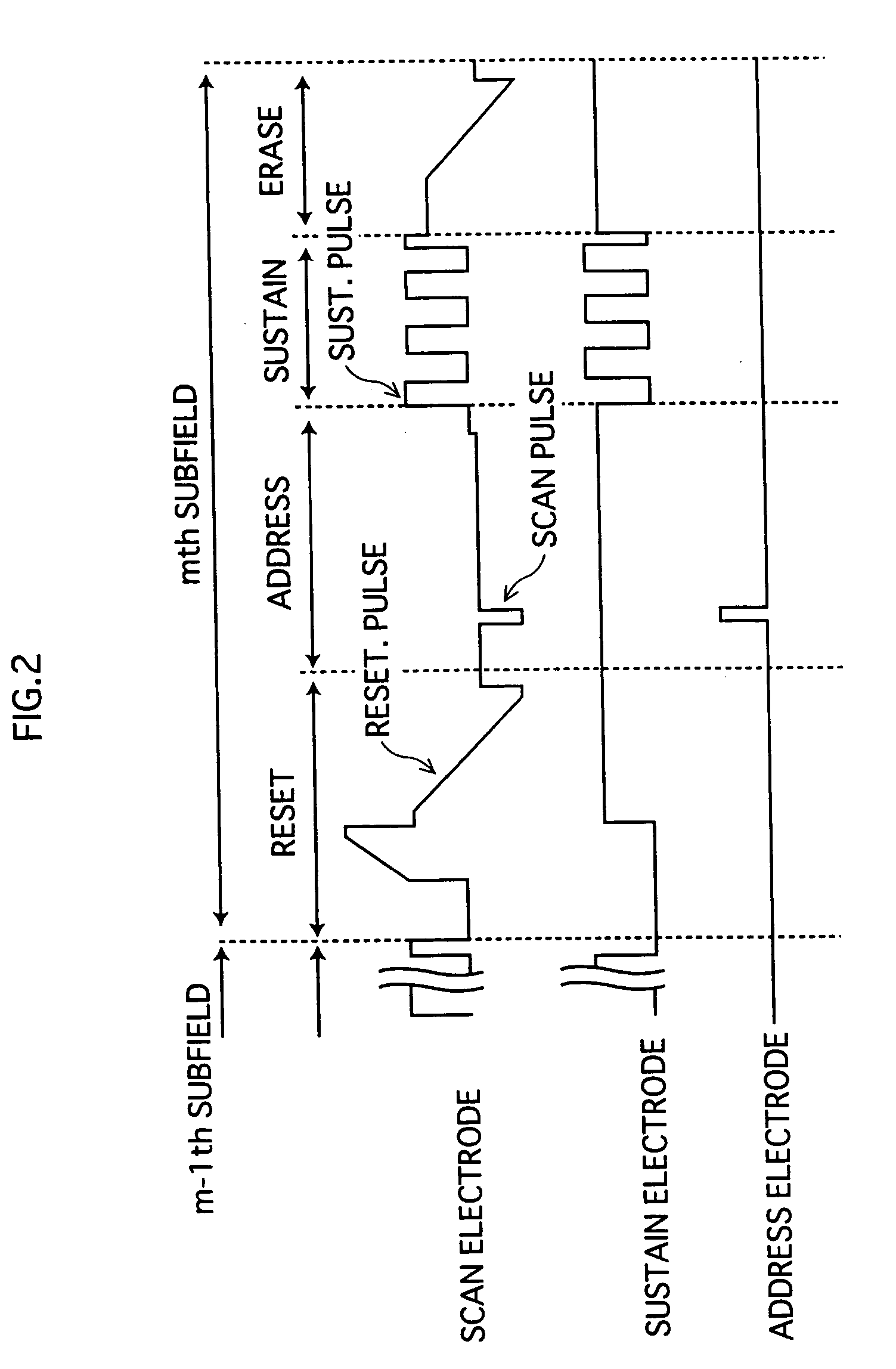
InactiveUS20060012721A1Good secondary electron emission propertyVoltage Vf can be reducedTelevision system detailsAddress electrodesElectronAtomic physics
A plasma display panel in which a first substrate having a protective layer formed thereon opposes a second substrate across a discharge space, with the substrates being sealed around a perimeter thereof. At a surface of the protective layer, first and second materials of different electron emission properties are exposed to the discharge space, with at least one of the materials existing in a dispersed state. The first and second materials may be first and second crystals, and the second crystal may be dispersed throughout the first crystal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Sputtering target and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120056176A1Improve reliabilityReduce the presence of impuritiesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHydrogenAlkaline earth metal
An object is to provide a deposition technique for depositing an oxide semiconductor film. Another object is to provide a method for manufacturing a highly reliable semiconductor element using the oxide semiconductor film. A novel sputtering target obtained by removing an alkali metal, an alkaline earth metal, and hydrogen that are impurities in a sputtering target used for deposition is used, whereby an oxide semiconductor film containing a small amount of those impurities can be deposited.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device and touch panel
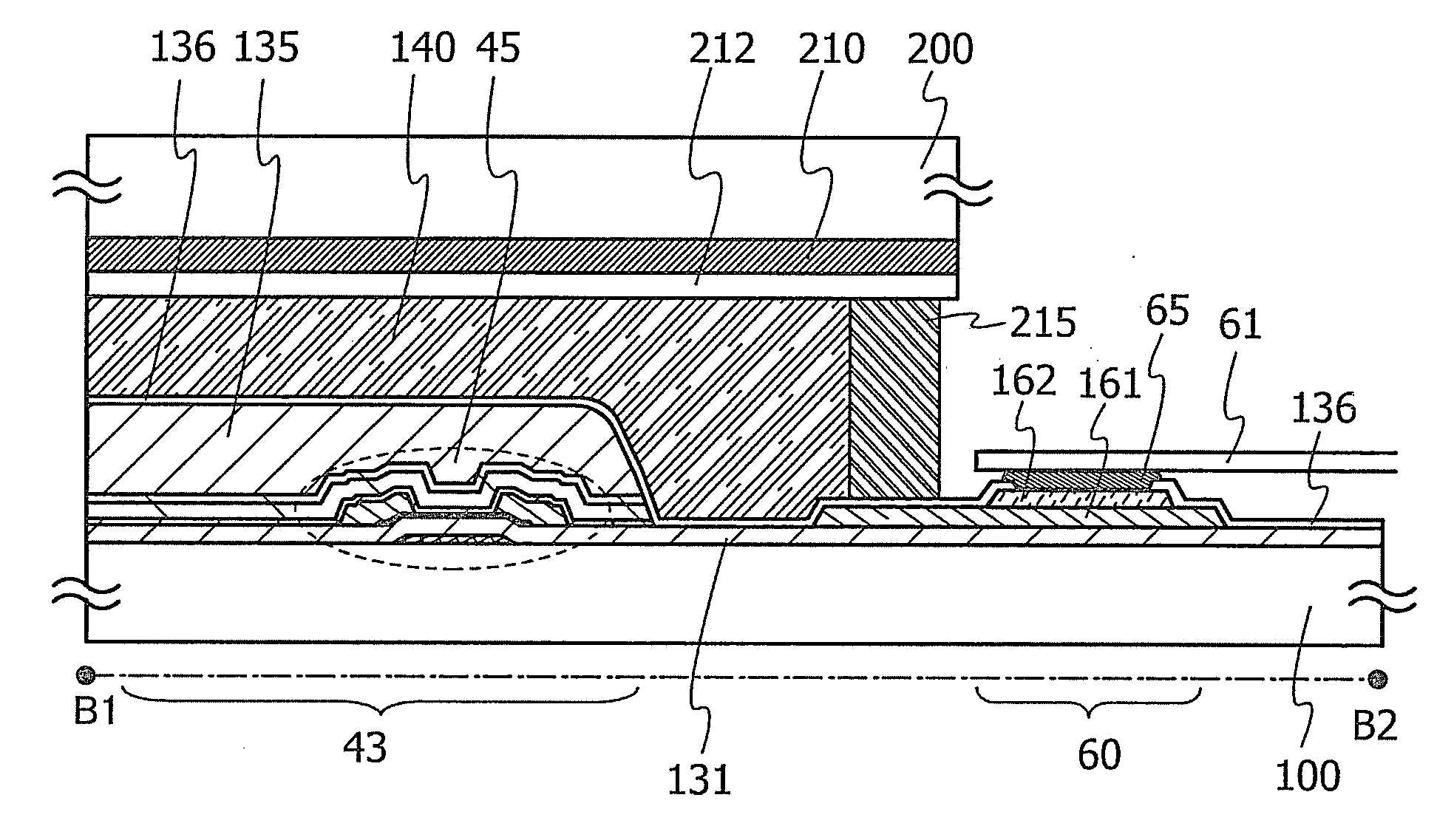
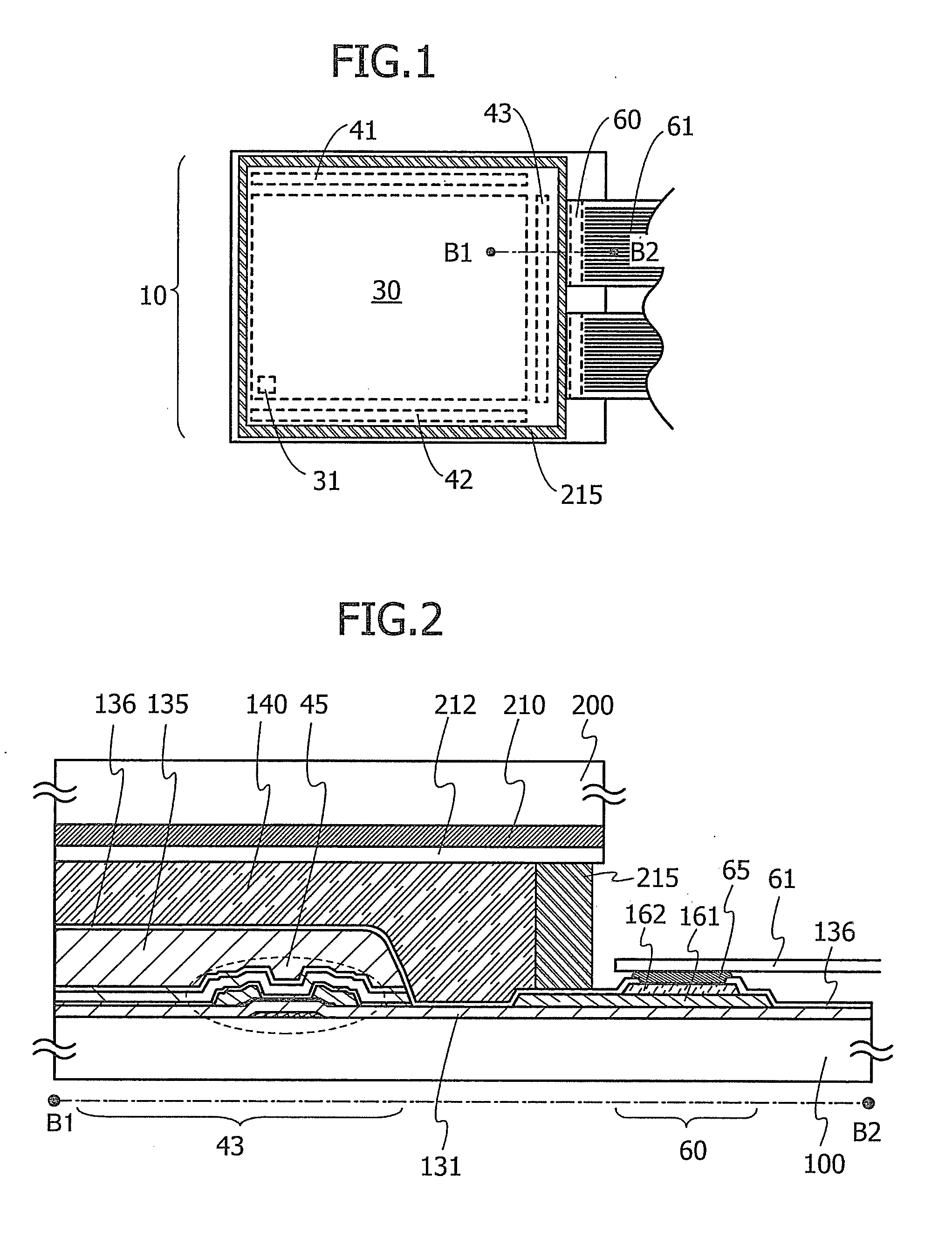
ActiveUS20140104507A1Improve reliabilityIncrease carrier densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsOxide semiconductorTouch panel
A semiconductor layer of a transistor is formed of an oxide semiconductor film including a crystal part. An organic resin film covering the transistor is formed. By treatment such as drying treatment on the organic resin film in a cell process, variations in the threshold voltage of the oxide semiconductor transistor due to moisture can be suppressed. A common electrode faces a pixel electrode. The common electrode and the pixel electrode are formed over the organic resin film with an insulating film provided therebetween. Therefore, a capacitor can be provided to a liquid crystal element if a pixel does not include a wiring for a storage capacitor. An antistatic electrode is provided on the outer side of a color filter substrate and the capacitance between the antistatic electrode and the common electrode is utilized, so that the liquid crystal display device can be used as a touch panel.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Sputtering target, method for manufacturing the same, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120152728A1Reduce concentrationRaise the ratioCellsVacuum evaporation coatingZinc nitrideIndium
A deposition technique for forming an oxynitride film is provided. A highly reliable semiconductor element is manufactured with the use of the oxynitride film. The oxynitride film is formed with the use of a sputtering target including an oxynitride containing indium, gallium, and zinc, which is obtained by sintering a mixture of at least one of indium nitride, gallium nitride, and zinc nitride as a raw material and at least one of indium oxide, gallium oxide, and zinc oxide in a nitrogen atmosphere. In this manner, the oxynitride film can contain nitrogen at a necessary concentration. The oxynitride film can be used for a gate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, or the like of a transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Reconfigurable antenna based on graphene coating
ActiveCN105161832AAchieve broadbandAchieving UWBRadiating elements structural formsDielectricReconfigurable antenna
The invention discloses a reconfigurable antenna based on a graphene coating. The reconfigurable antenna comprises an antenna body which comprises a ground plate and a monopole erected on the ground plate. The antenna body further comprises a dielectric sleeve which is thoroughly through and shaped like a hollow cylinder. The dielectric sleeve is positioned on the group plate and at the outer periphery of the monopole. One of inner and outer side surfaces of the dielectric sleeve is coated with a grapheme coating, and the other is coated with a silicon coating. Each of the graphene coating and the silicon coating is connected with one end of external offset voltage, and a certain gap is reserved between the graphene coating or the silicon coating connected with the anode of the external offset voltage and the ground plate. The external offset voltage is controlled by dividing the graphene coating and the silicon coating into multiple blocks, so that the antenna is enabled to have characteristics of wide band, reconfigurable frequency and / or reconfigurable radiation pattern.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060273329A1High reliabilityLow electric resistanceOptical wave guidanceSolid-state devicesPhysicsBand gap
The semiconductor device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor layer containing plural band gap change thin films in which a band gap is continuously monotonously changed in a laminating direction. Therefore, the present invention provides a semiconductor device having high reliability and low electric resistance.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Plasma display panel and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS7432656B2Improve electron emission performanceReduce voltageAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesElectronPlasma display
A plasma display panel in which a first substrate having a protective layer formed thereon opposes a second substrate across a discharge space, with the substrates being sealed around a perimeter thereof. At a surface of the protective layer, first and second materials of different electron emission properties are exposed to the discharge space, with at least one of the materials existing in a dispersed state. The first and second materials may be first and second crystals, and the second crystal may be dispersed throughout the first crystal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
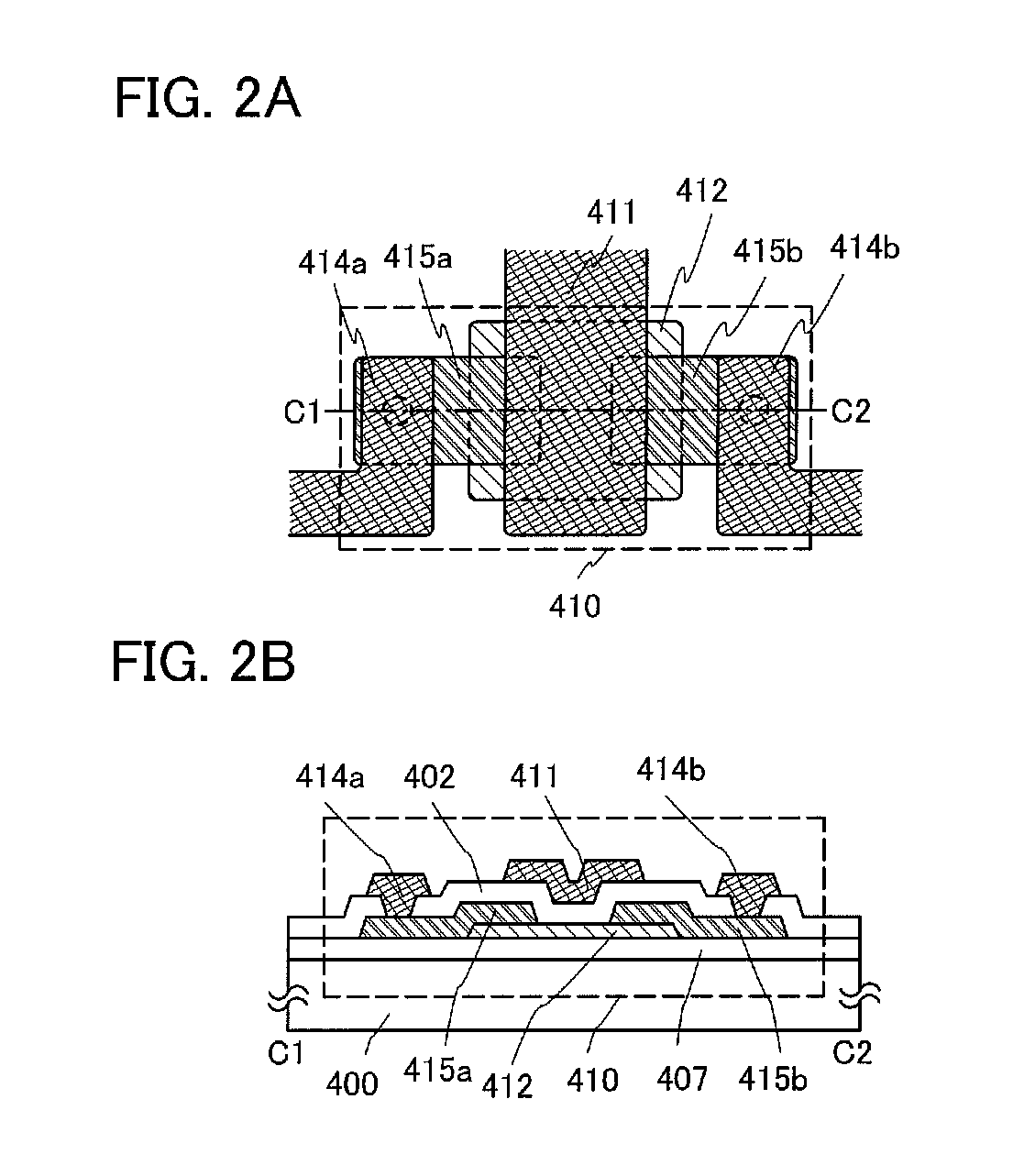
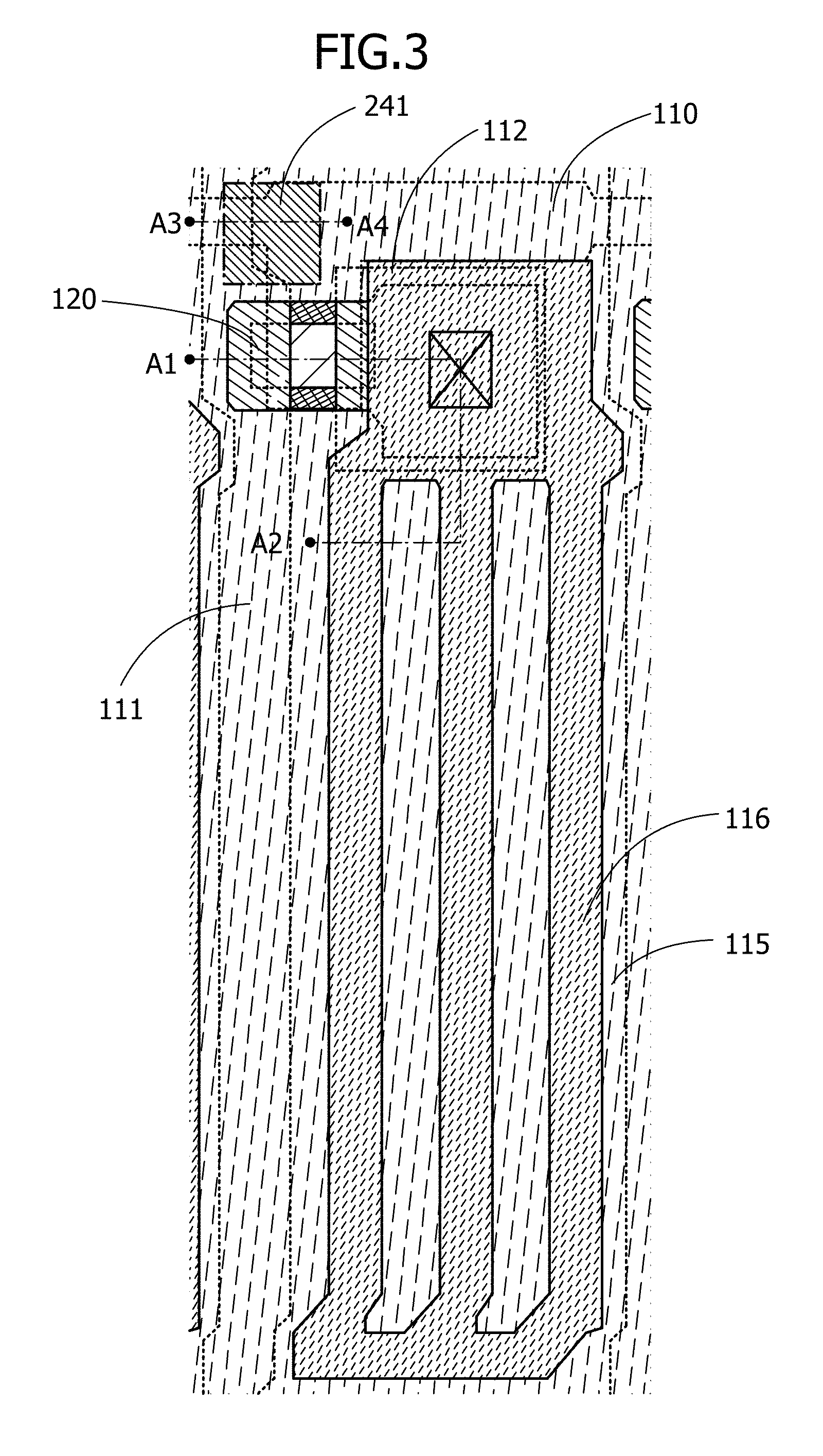
Method of manufacturing thin-film transistor, method of manufacturing organic light-emitting display device including the same, and thin-film transistor and organic light-emitting display device manufactured using the methods
ActiveUS20140312320A1Increase carrier densityTransistorSolid-state devicesOxide semiconductorCharge-carrier density
A method of manufacturing a thin-film transistor includes: forming an oxide semiconductor pattern including a first region and a second region on a substrate; forming an insulation film on the substrate to cover the oxide semiconductor pattern; removing the insulation film on the second region through patterning; increasing carrier density of the first region of the oxide semiconductor pattern through an annealing process; forming a gate electrode on the insulation film so that the gate electrode is insulated from the oxide semiconductor pattern and overlaps the second region; and forming a source electrode and a drain electrode to be insulated from the gate electrode and contact the first region.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Organic semiconductor device and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20050211977A1Increase in carrier densityHigh efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesOrganic semiconductorElectrode Contact
The organic semiconductor device of the present invention includes an organic semiconductor material and a conductive electrode contacting with the organic semiconductor material, wherein a quasi Fermi level of the organic semiconductor material and a Fermi level of the conductive electrode are optimized by using adjustment means, and a junction barrier between the organic semiconductor material and the conductive electrode is controlled.
Owner:CANON KK
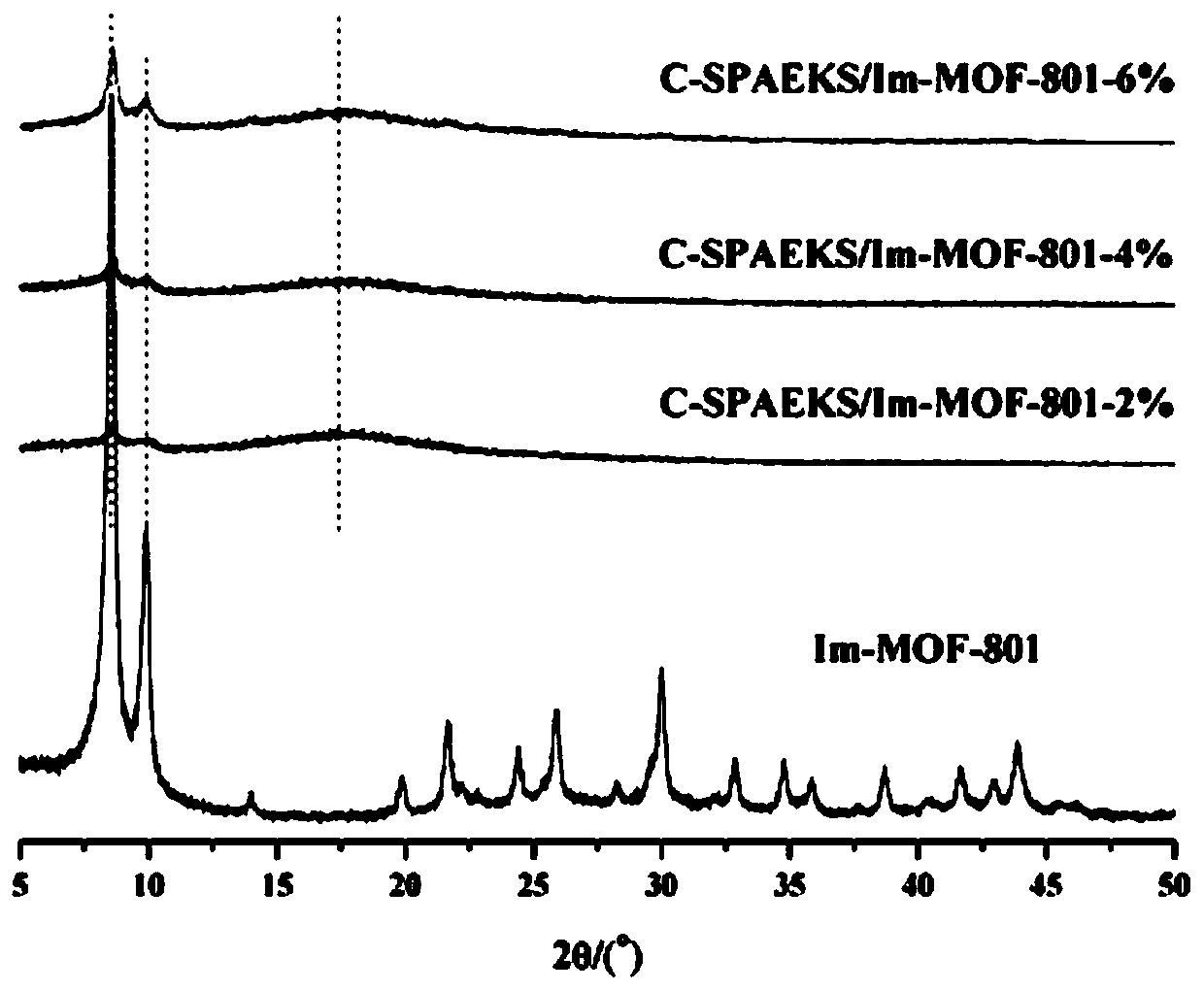
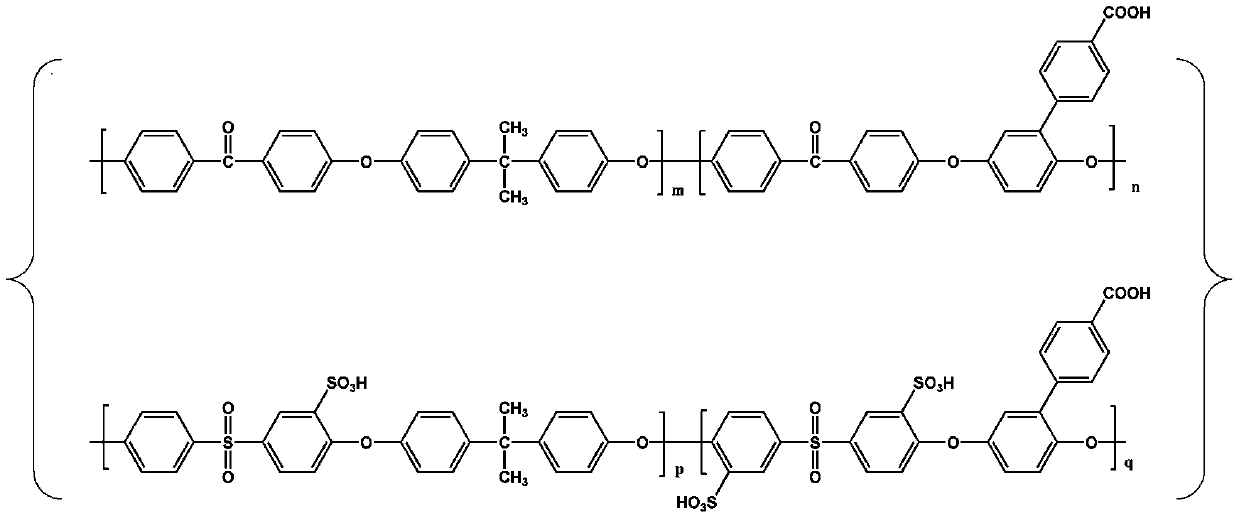
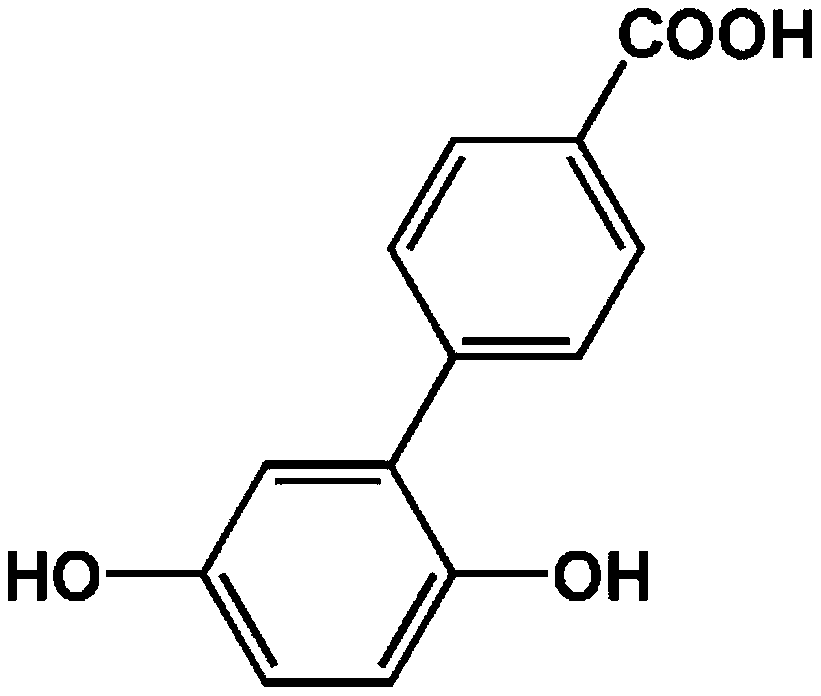
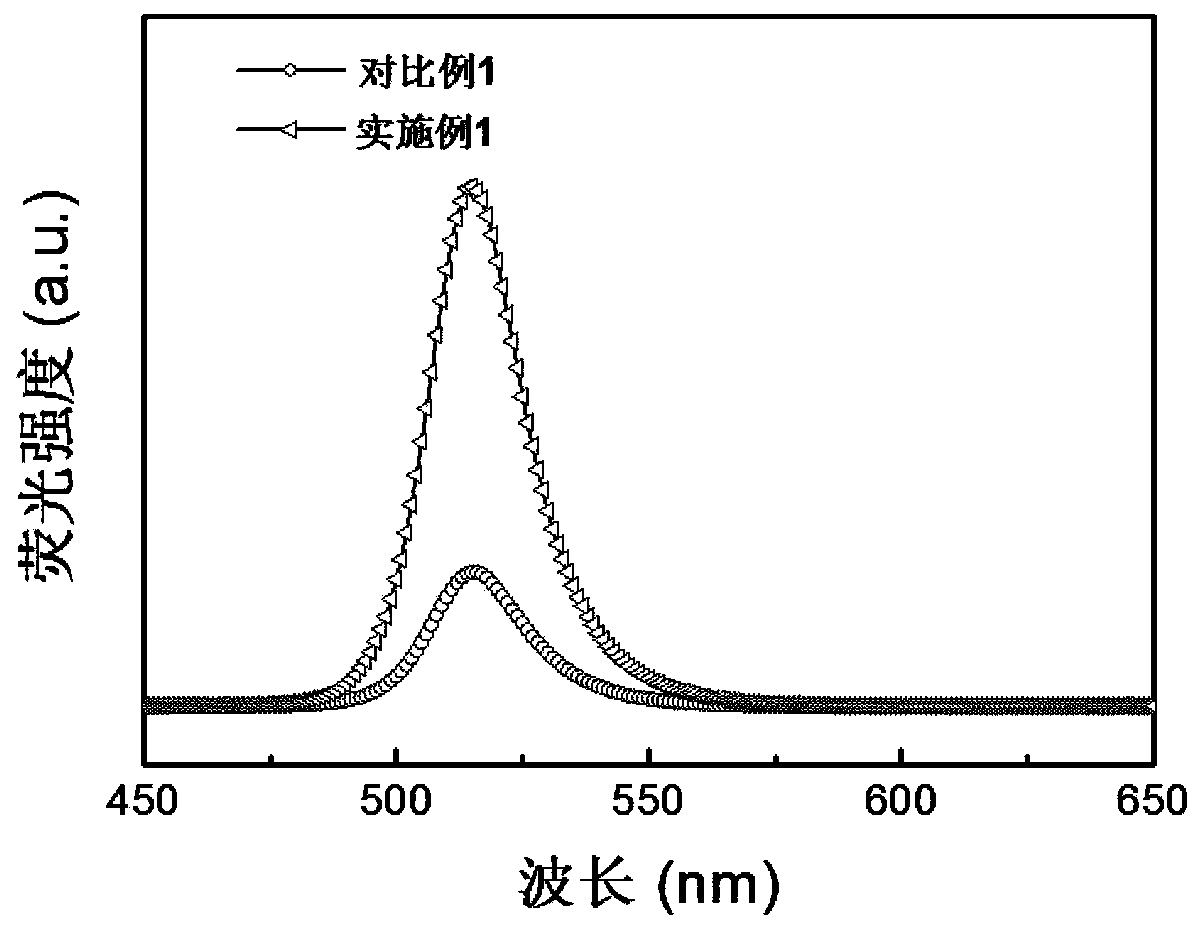
Organic-inorganic composite membrane based on carboxyl-containing sulfonated polyaryletherketone sulfone and Im-MOF-801 and preparation method of organic-inorganic composite membrane
ActiveCN110492158AImprove proton exchange conductivityIncrease carrier densityFuel cellsMetal-organic frameworkSolvent
The invention discloses an organic-inorganic composite membrane based on carboxyl-containing sulfonated polyaryletherketone sulfone and Im-MOF-801 and a preparation method of the organic-inorganic composite membrane. The invention belongs to the field of polymer chemistry and proton exchange membrane fuel cells. The exchange composite membrane takes carboxyl-containing sulfonated polyaryletherketone sulfone as a matrix and takes a metal organic framework Im-MOF-801 containing coordinated imidazole as a filler, the Im-MOF-801 filler contains a carboxyl functional group and is connected with a main chain of a matrix polymer through a hydrogen bond, and the composite membrane is prepared through a solution blending method. According to the method, the carboxyl-containing sulfonated polyaryletherketone sulfone is prepared by utilizing nucleophilic polycondensation reaction, the coordination imidazole-containing Im-MOF-801 is prepared by utilizing solvothermal reaction, and the organic-inorganic composite proton exchange membrane is prepared by utilizing the solution blending method. The maximum proton conductivity of the organic-inorganic composite proton exchange membrane at 90 DEG Ccan reach 0.128 Scm-1.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Low-roll-off quasi-two-dimensional perovskite light emitting diode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111192971ASolve the problem of serious efficiency roll-offImprove luminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron holeElectron transporting layer
The invention discloses a low-roll-off quasi-two-dimensional perovskite light-emitting diode and a preparation method thereof. The low-roll-off quasi-two-dimensional perovskite light-emitting diode issequentially provided with a cathode, a hole transport layer, a hole transport layer and light-emitting layer interface modification layer, a perovskite light-emitting layer, a light-emitting layer and electron transport interface modification layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injection layer and an anode from bottom to top. By modifying the interface of the hole transport layer andthe perovskite light-emitting layer, the hole injection barrier between the hole layer and the light-emitting layer is reduced, the hole injection efficiency is improved, the hole layer can be prevented from quenching the perovskite layer, and the light-emitting efficiency of the perovskite layer is improved. The interface of the perovskite light-emitting layer and the electron transport layer isalso modified, so that the defect state of the perovskite surface can be passivated, the film quality of the light-emitting layer is improved, non-radiative recombination is inhibited, and the light-emitting efficiency of the device is further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
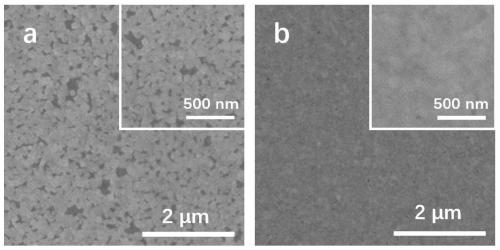
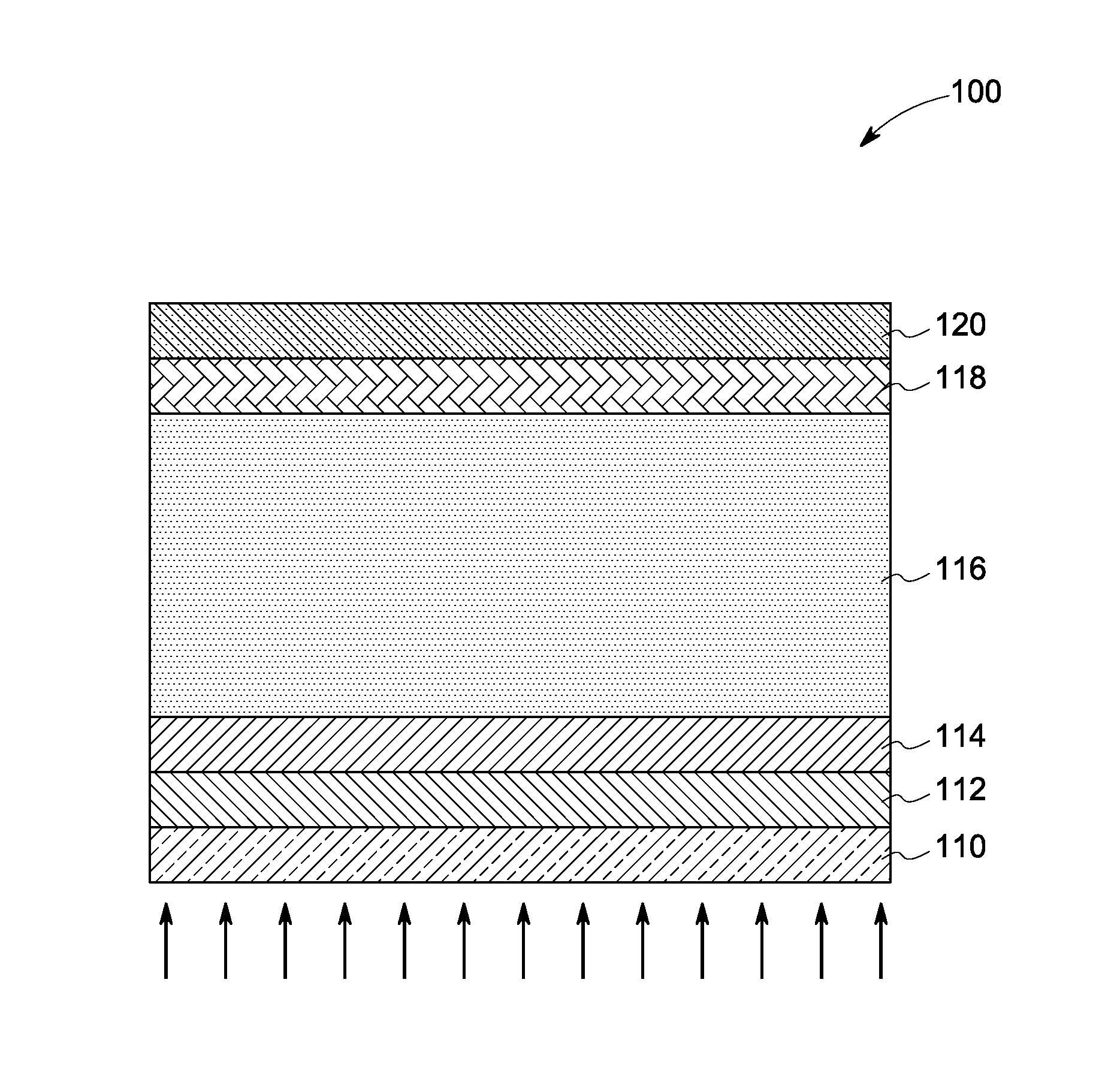
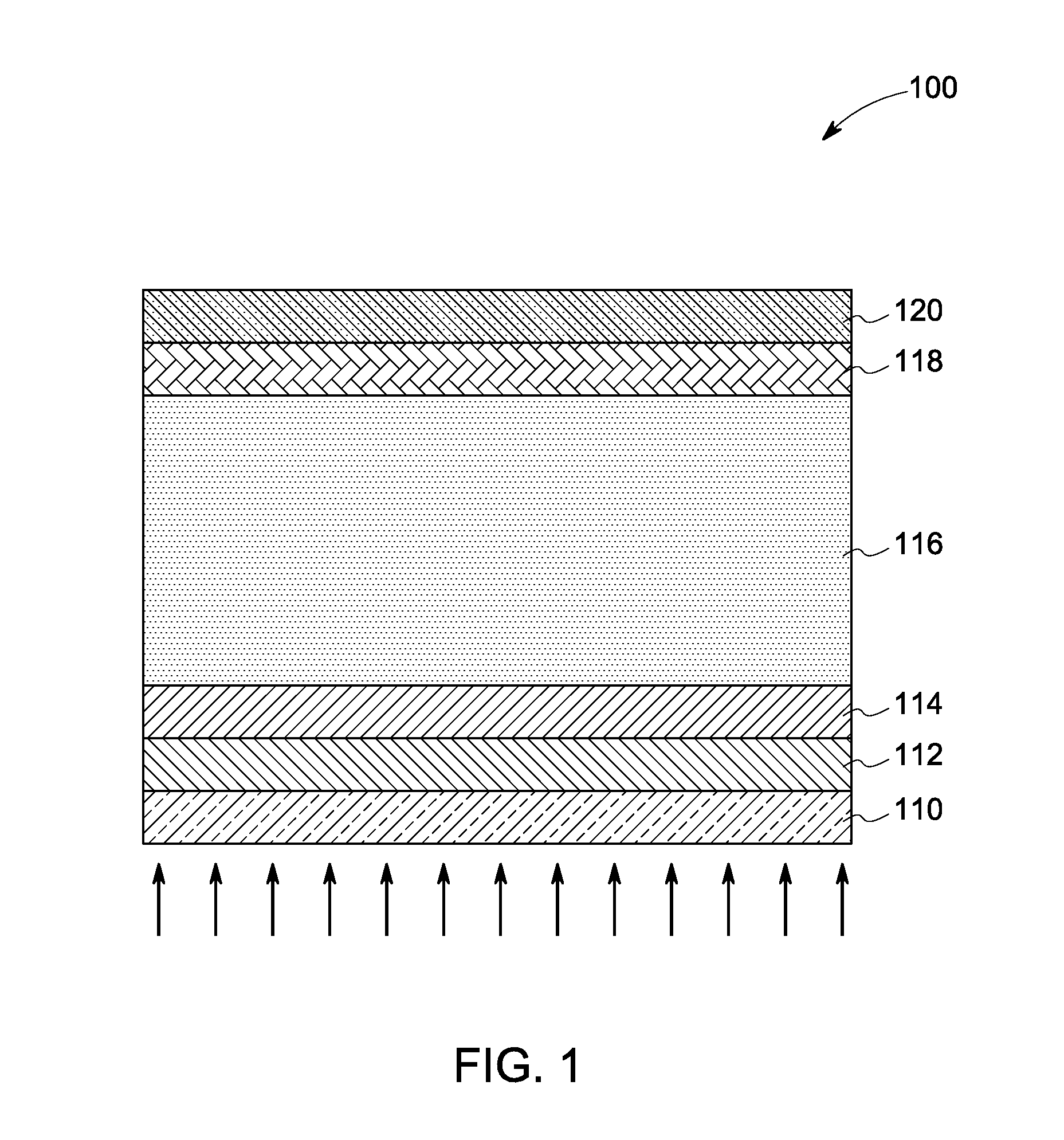
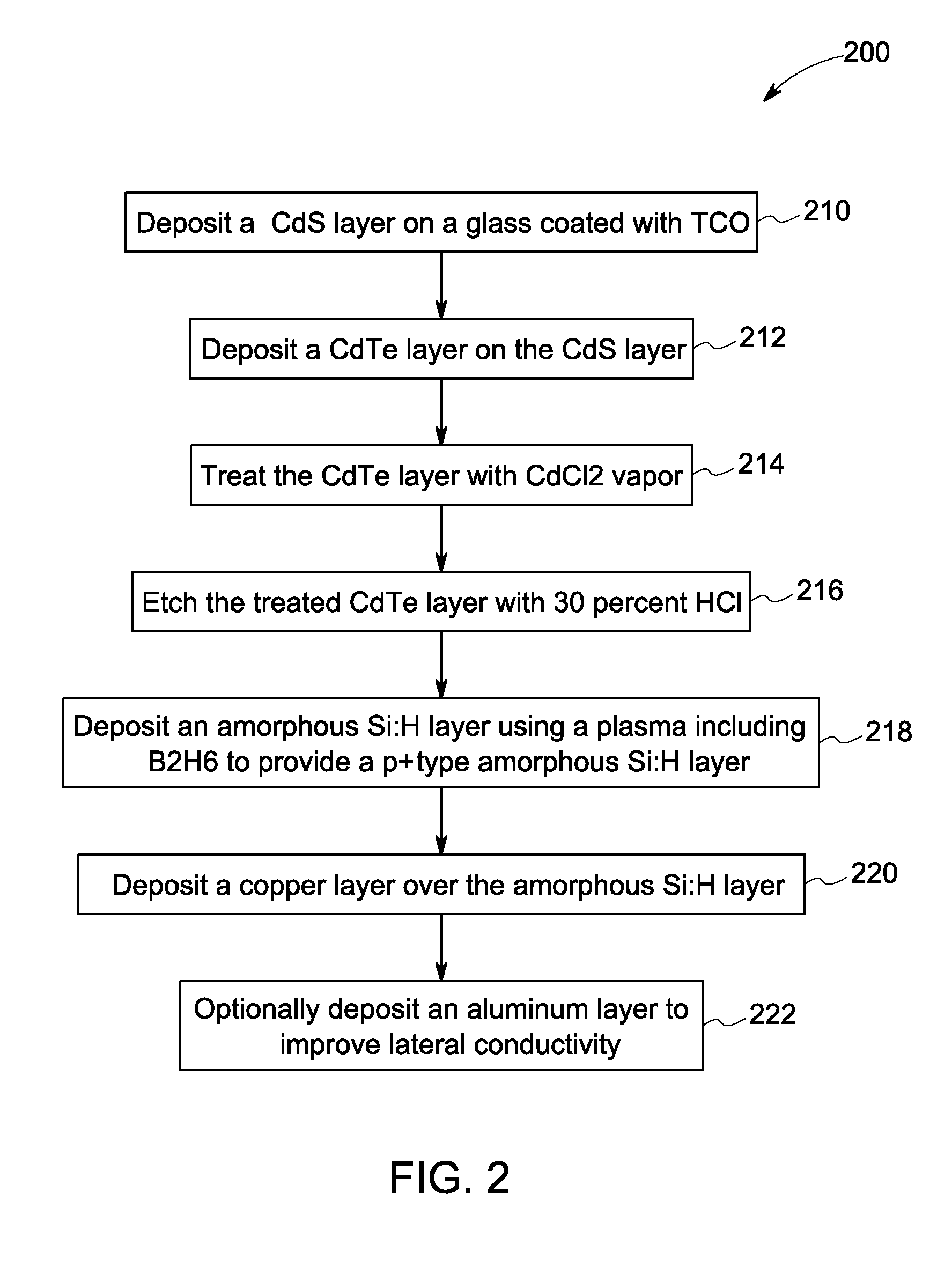
Layer for thin film photovoltaics and a solar cell made therefrom
InactiveUS20110100447A1Increase carrier densityHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationCharge carrierSolar cell
A photovoltaic device is provided. The photovoltaic device comprises an absorber layer comprising a p-type semiconductor, wherein at least one layer is disposed over the absorber layer. The at least one layer is a semiconductor having a higher carrier density than the carrier density of the absorber layer. The at least one layer comprises silicon. The at least one layer comprises a p+-type semiconductor. The absorber layer is substantially free of silicon. A method of forming the photovoltaic device is provided.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Sputtering target, method for manufacturing the same, manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS8894825B2Reduce concentrationRaise the ratioCellsVacuum evaporation coatingZinc nitrideIndium
A deposition technique for forming an oxynitride film is provided. A highly reliable semiconductor element is manufactured with the use of the oxynitride film. The oxynitride film is formed with the use of a sputtering target including an oxynitride containing indium, gallium, and zinc, which is obtained by sintering a mixture of at least one of indium nitride, gallium nitride, and zinc nitride as a raw material and at least one of indium oxide, gallium oxide, and zinc oxide in a nitrogen atmosphere. In this manner, the oxynitride film can contain nitrogen at a necessary concentration. The oxynitride film can be used for a gate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, or the like of a transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Strongly correlated nonvolatile memory element
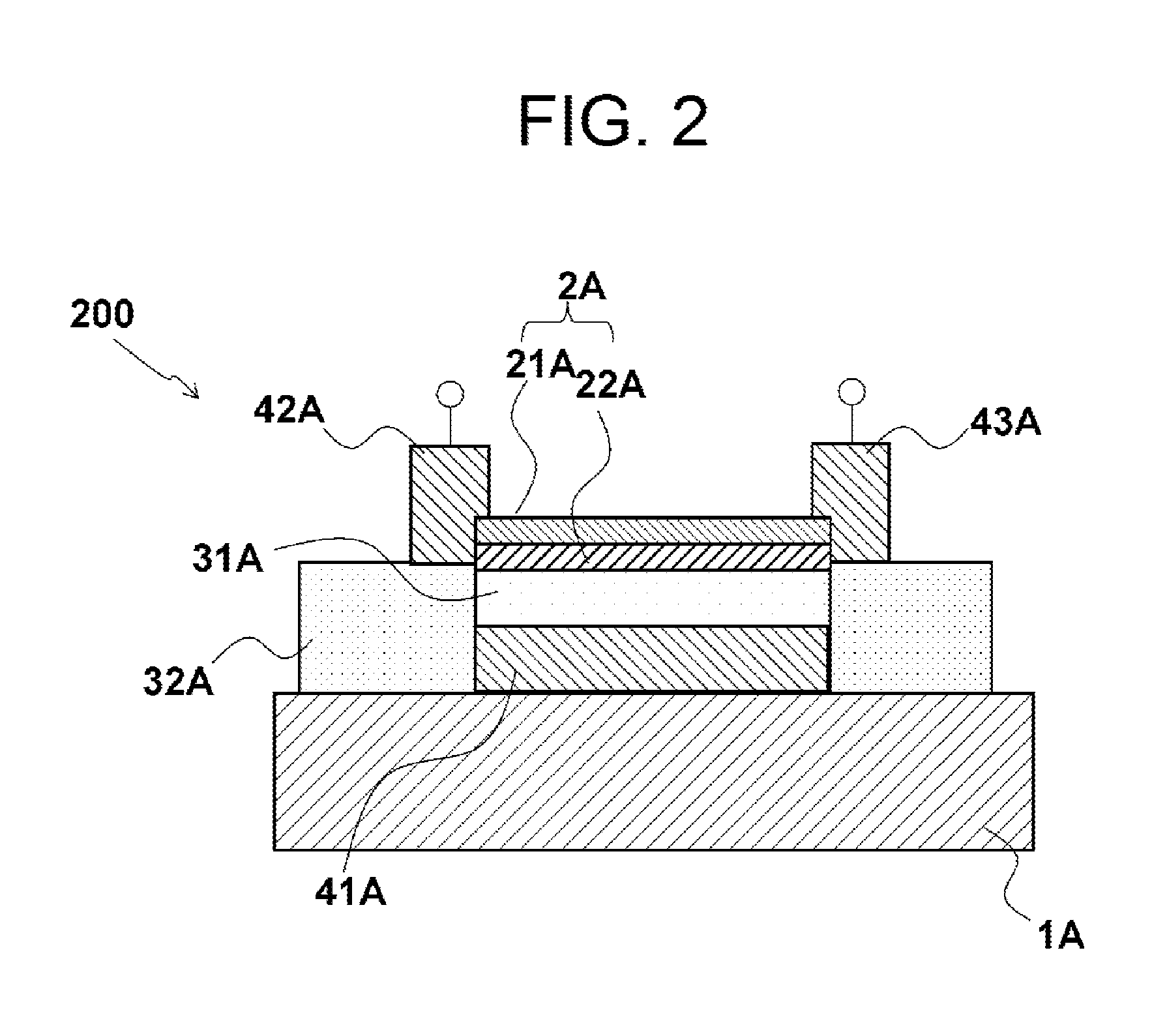
InactiveUS20140209850A1Giant resistance changeIncrease carrier densitySolid-state devicesDigital storagePhysicsEngineering
In aspects of the invention, a strongly correlated nonvolatile memory element is provided which exhibits phase transitions and nonvolatile switching functions through electrical means. In an aspect of the invention, a strongly correlated nonvolatile memory element is provided including, on a substrate, a channel layer, a gate electrode, a gate insulator, a source electrode, and a drain electrode. The channel layer includes a strongly correlated oxide thin film, and is formed of a perovskite type manganite which exhibits a charge-ordered phase or an orbital-ordered phase; the gate insulator is formed in contact with at least a portion of a surface or interface of the channel layer and is sandwiched between the channel layer and the gate electrode, and the source electrode and drain electrode are formed in contact with at least a portion of the channel layer.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Ultraviolet-transparent conductive film and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6897560B2Effective transparent conductivityReduce distanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDopantUltraviolet
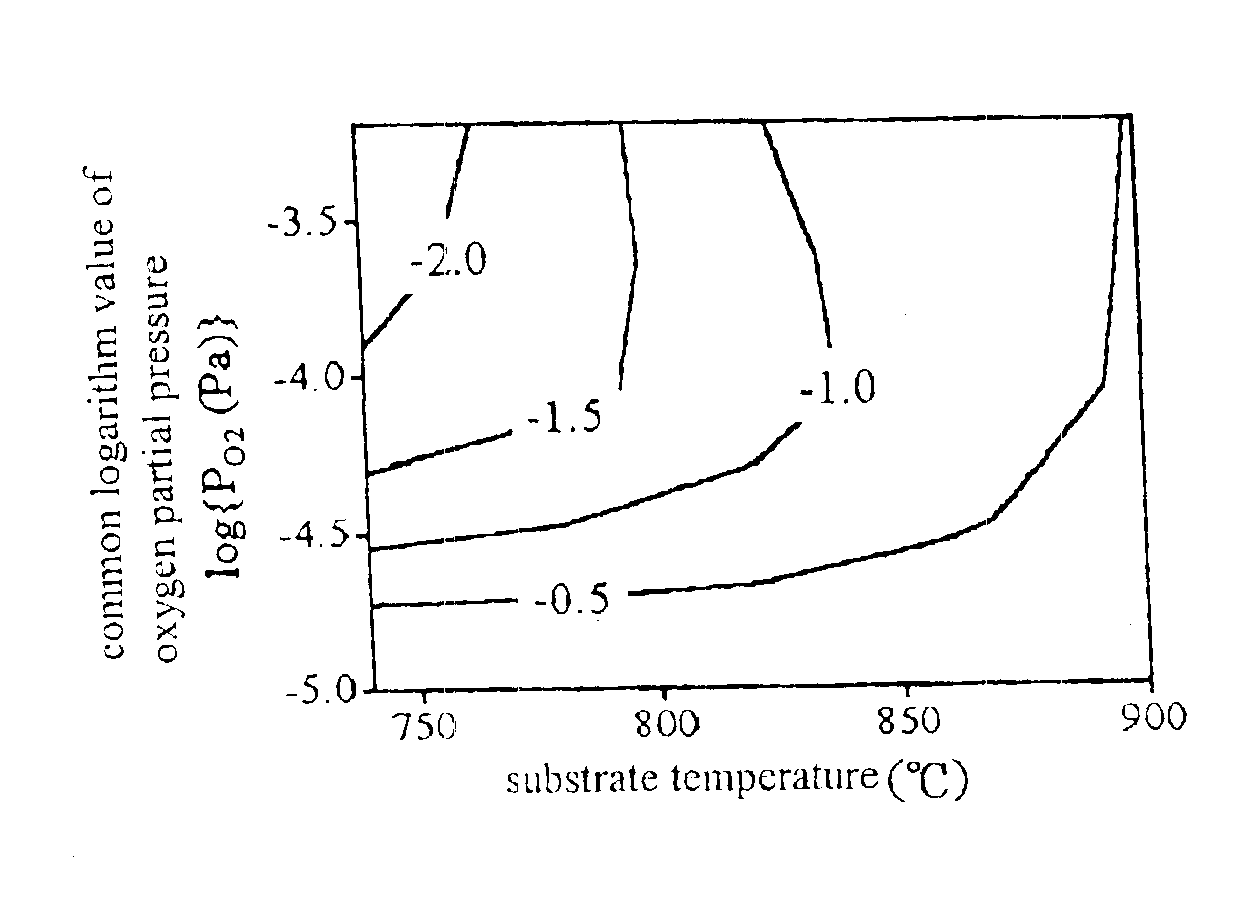
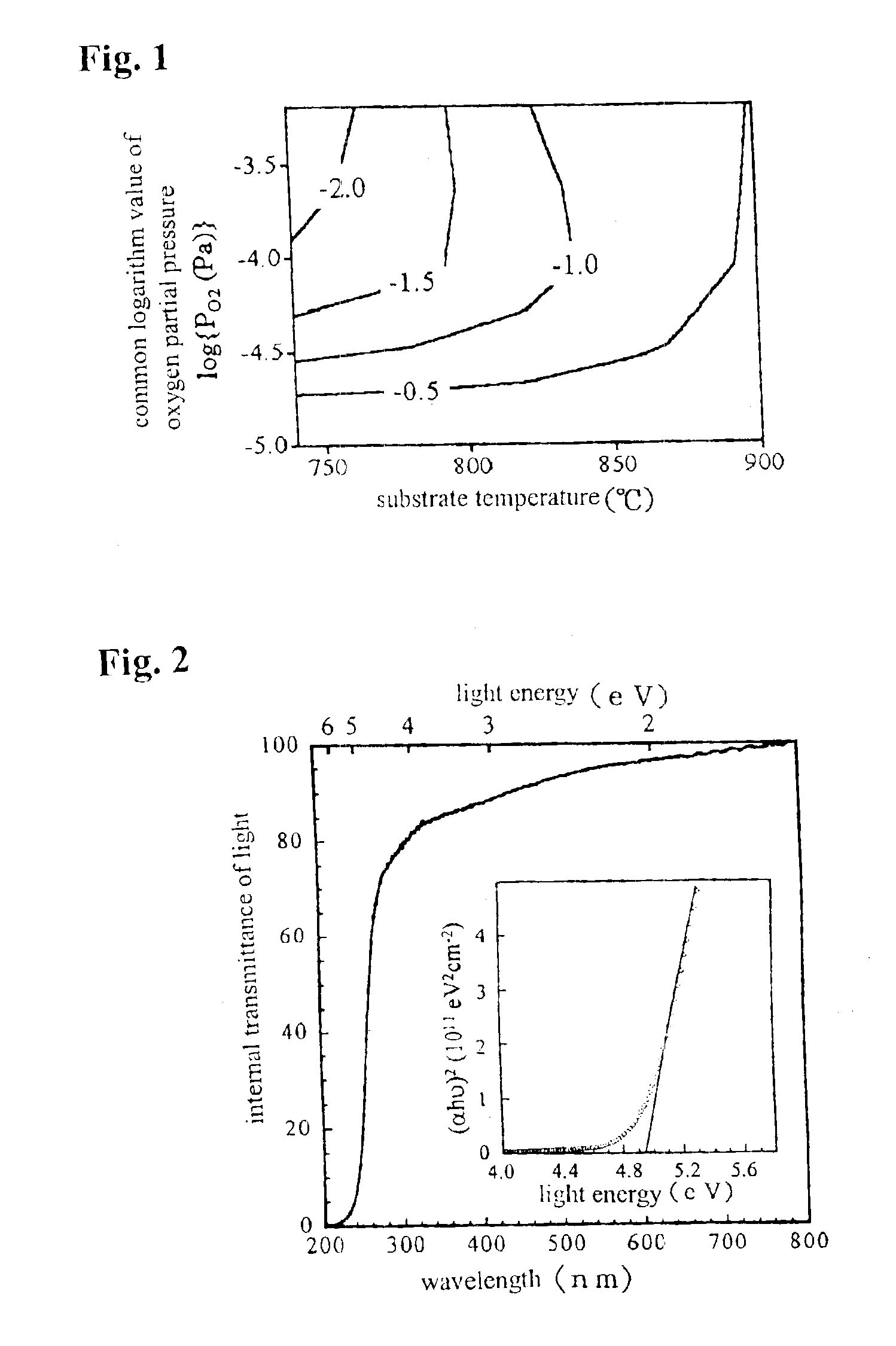
The present invention provides an ultraviolet-transparent conductive film comprising a Ga2O3 crystal. The film has a transparency in the wavelength range of 240 to 800 nm, or 240 to 400 nm, and an electric conductivity induced by an oxygen deficiency or dopant in the Ga2O3 crystal. The dopant includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of the Sn, Ge, Si, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo and W. The ultraviolet-transparent conductive film is formed through either one of a pulsed-laser deposition method, sputtering method, CVD method and MBE method, under the conditions with a substrate temperature of 600 to 1500° C. and an oxygen partial pressure of 0 to 1 Pa.
Owner:HOYA CORP +1
Liquid crystal display device and touch panel
ActiveUS9366896B2Increase carrier densityCharacteristic variesNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceElectrical battery
A semiconductor layer of a transistor is formed of an oxide semiconductor film including a crystal part. An organic resin film covering the transistor is formed. By treatment such as drying treatment on the organic resin film in a cell process, variations in the threshold voltage of the oxide semiconductor transistor due to moisture can be suppressed. A common electrode faces a pixel electrode. The common electrode and the pixel electrode are formed over the organic resin film with an insulating film provided therebetween. Therefore, a capacitor can be provided to a liquid crystal element if a pixel does not include a wiring for a storage capacitor. An antistatic electrode is provided on the outer side of a color filter substrate and the capacitance between the antistatic electrode and the common electrode is utilized, so that the liquid crystal display device can be used as a touch panel.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Preparation technology for graphene conductive printing ink
The invention provides a preparation technology for graphene conductive printing ink and relates to the technical field of conductive materials. The preparation technology comprises the following steps of performing pretreatment on flake graphite, performing sealing oxidization on potassium perchlorate, adding the obtained graphene oxide in deionized water, performing ultrasonic vibration stripping, and performing low-temperature evaporation after stripping to obtain a uniformly dispersed brown graphene oxide solution; slowly dropwise adding ammonium hydroxide in an ethanol solution of silvernitrate, regulating a pH value of a system to be 9 to obtain a silver ammonia solution, and preparing a graphene-loaded nanometer silver conductive material by utilizing the silver ammonia solution; and mixing and adding raw materials in a high-speed shearing dispersion machine, adding an adhesive and an additive after high-speed shearing dispersion, performing continuous high-speed shearing dispersion, removing large-particle impurities with a filter membrane with a certain aperture, and performing split charging. The graphene conductive printing ink provided by the invention has good printability; and an ink layer after printing has various excellent properties of low electrical resistivity, low curing temperature, stable conductivity, good conductivity and the like and has a very largemarket application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN ANDGEM GRAPHENE TECH CO LTD
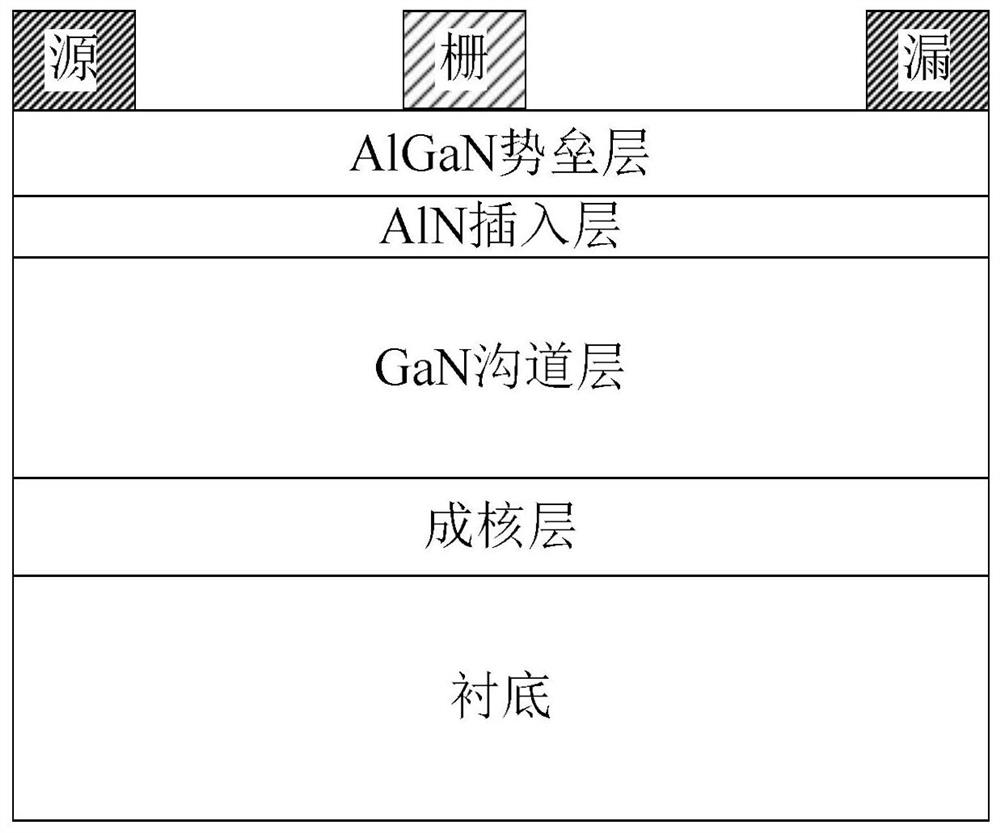
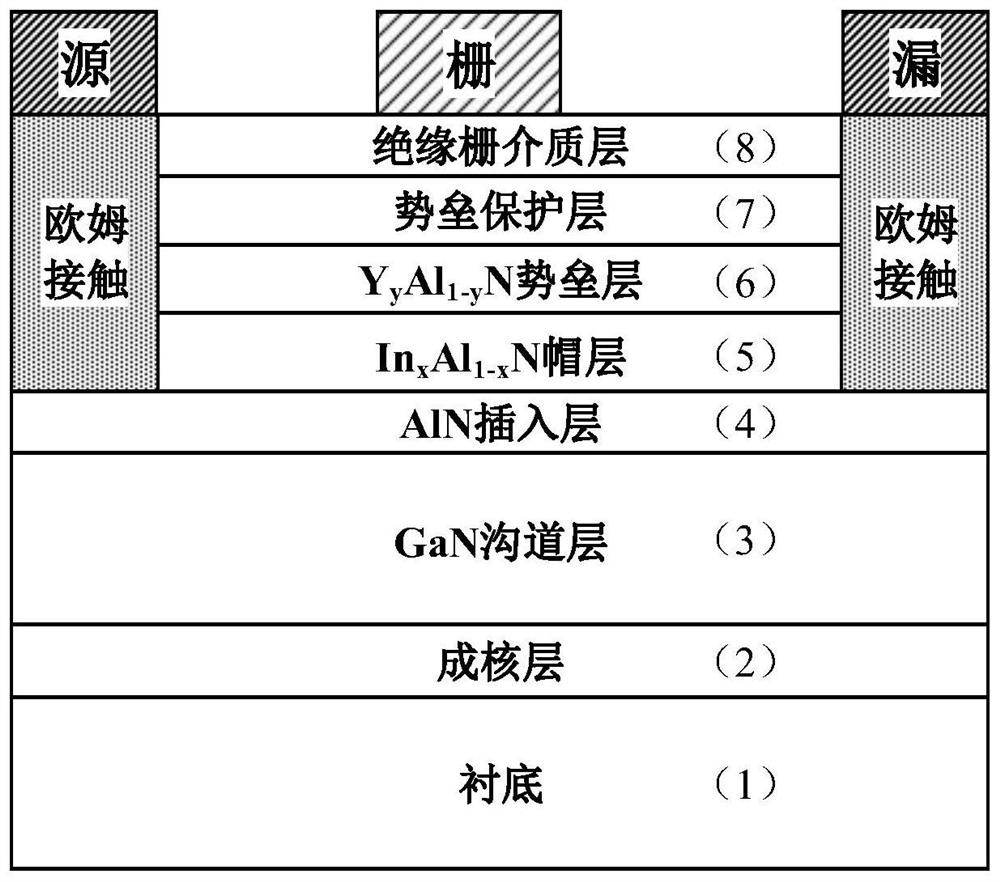
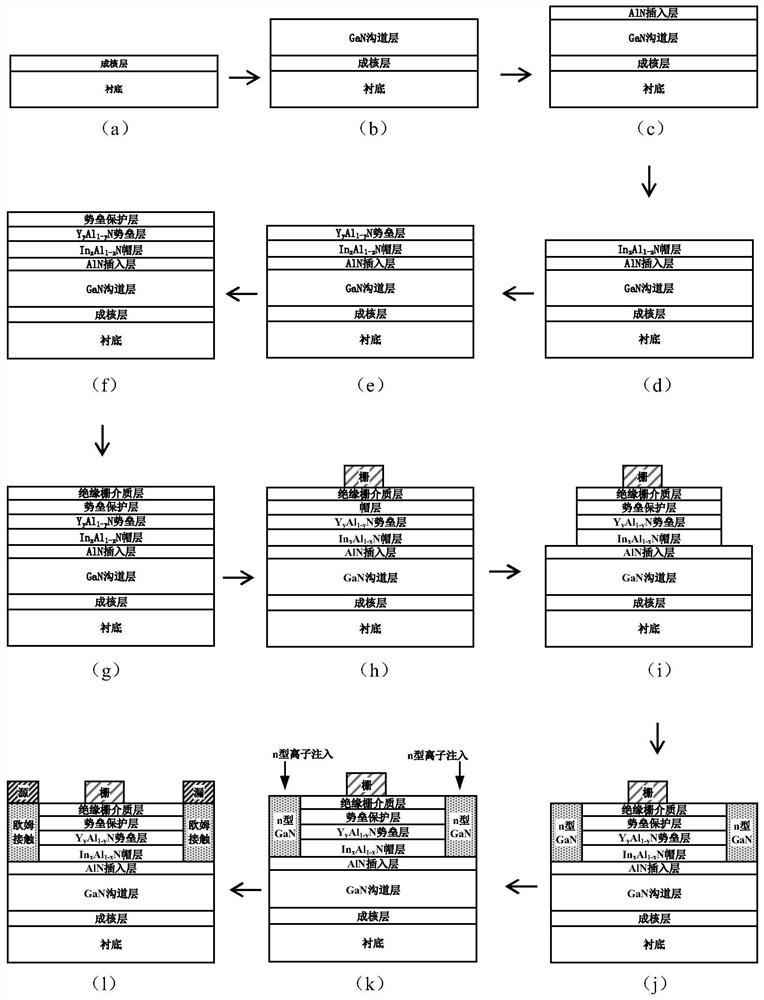
YAlN/GaN high-electron-mobility transistor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN112736131AEffective protectionImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricOhmic contact
The invention relates to a YAlN / GaN high-electron-mobility transistor and a manufacturing method thereof, and mainly solves the problems of low working frequency and high material dislocation density of an existing nitride microwave power device. The transistor comprises a substrate, a nucleating layer, a GaN channel layer, an AlN insertion layer and a YAlN barrier layer from bottom to top, wherein an InAlN cap layer is arranged between the insertion layer and the barrier layer; a barrier protection layer and an insulated gate dielectric layer are sequentially arranged at the upper part of the barrier layer, and ohmic contact regions for manufacturing a source electrode and a drain electrode are arranged on two sides from the InAlN cap layer to the insulated gate dielectric layer. A nucleating layer, a GaN channel layer, an AlN insertion layer and an InAlN cap layer in the structure are grown by adopting MOCVD; and the YAlN barrier layer and the barrier protection layer are grown by adopting MBE. The material is high in polarization intensity, high in device working frequency, high in reliability, simple in manufacturing process and high in consistency, and can be used for a high-frequency microwave power amplifier and a microwave millimeter wave integrated circuit.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
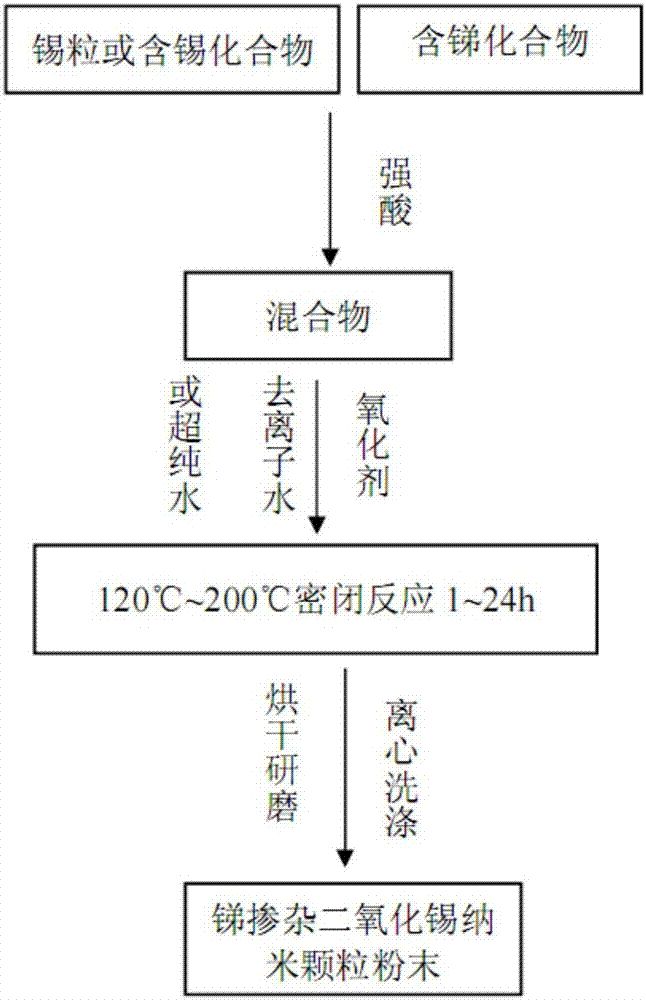
Preparation method of ultrafine high-purity antimony-doped tin oxide nanometer powder
InactiveCN107473263AWell mixedHigh purityMaterial nanotechnologyAntimony oxides/hydroxides/oxyacidsPrillLow emissivity
The invention relates to the field of nanomaterial synthesis, and discloses a preparation method for ultrafine high-purity antimony-doped tin oxide nanopowder, which comprises the following steps: taking tin particles or tin-containing compounds, antimony-containing compounds, adding strong acid, and then adding oxidizing agent and deionization Water or ultrapure water is then transferred to a closed reaction kettle, reacted at 120°C-200°C for 1-24h, cooled to room temperature, centrifuged and washed until neutral, dried, and ground to obtain antimony-doped tin dioxide nanoparticle powder. No anion impurity is introduced in the preparation process of the present invention, which ensures high purity of the prepared nanoparticles. The invention is easy to dope accurately and according to the amount, and solves the technical problems in the prior art that the doping is uneven, the particles contain anion impurities, and the particles are easy to agglomerate; the nano particles synthesized by the invention have high purity, small particle size and are easy to disperse. The coated glass prepared by the nano particles of the invention has high visible light transmittance, has the function of blocking infrared rays, and has low resistance, and can be applied to low-radiation glass and transparent conductive glass.
Owner:杭州聚力氢能科技有限公司
Semiconductor laser, electronic apparatus, and method of driving semiconductor laser
ActiveUS20190173262A1Increase injection carrier densityIncrease resistanceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsElectrical conductorSemiconductor package
In a semiconductor laser according to an embodiment of the present disclosure, a ridge part has a structure in which a plurality of gain regions and a plurality of Q-switch regions are each disposed alternately with each of separation regions being interposed therebetween in an extending direction of the ridge part. The separation regions each have a separation groove that separates from each other, by a space, the gain region and the Q-switch region adjacent to each other. The separation groove has a bottom surface at a position, in a second semiconductor layer, higher than a part corresponding to a foot of each of both sides of the ridge part.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com