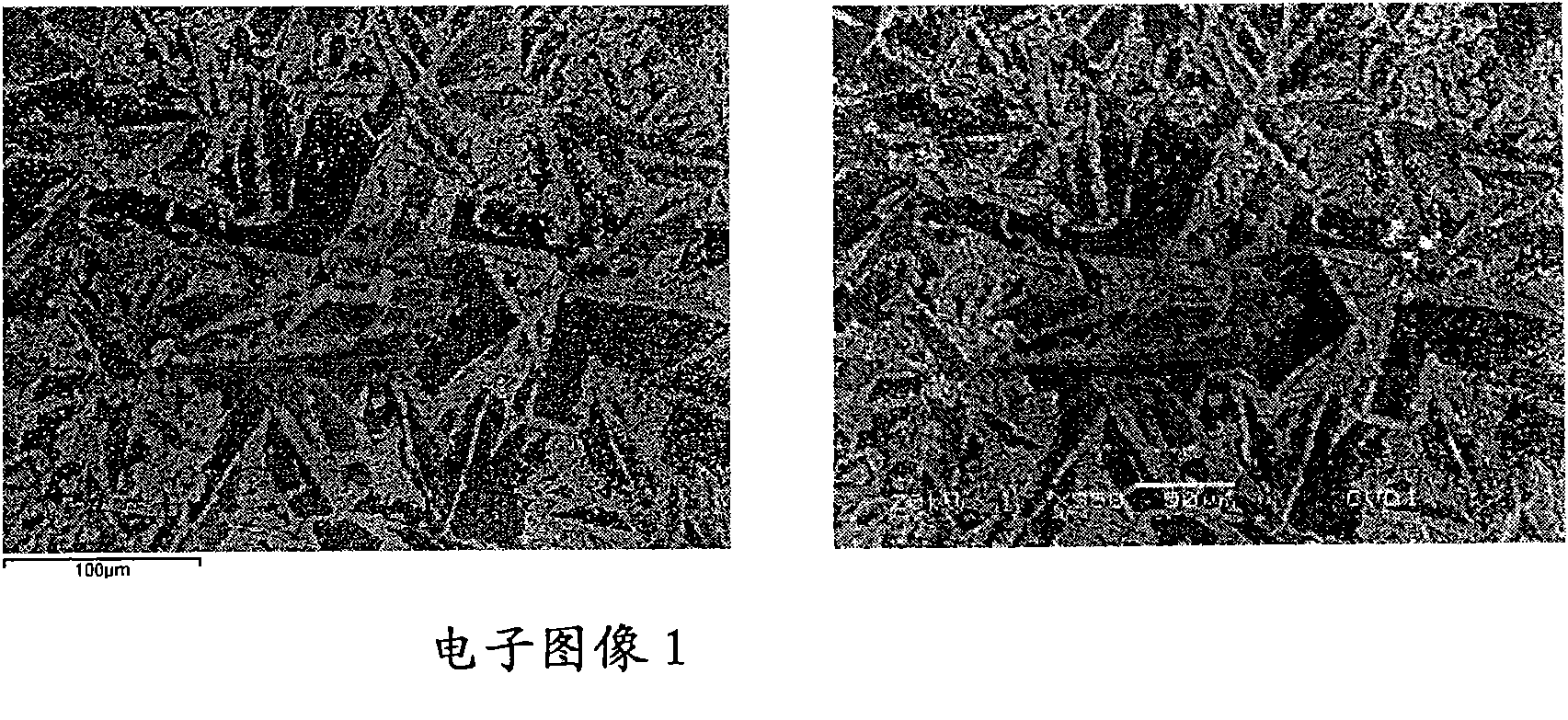
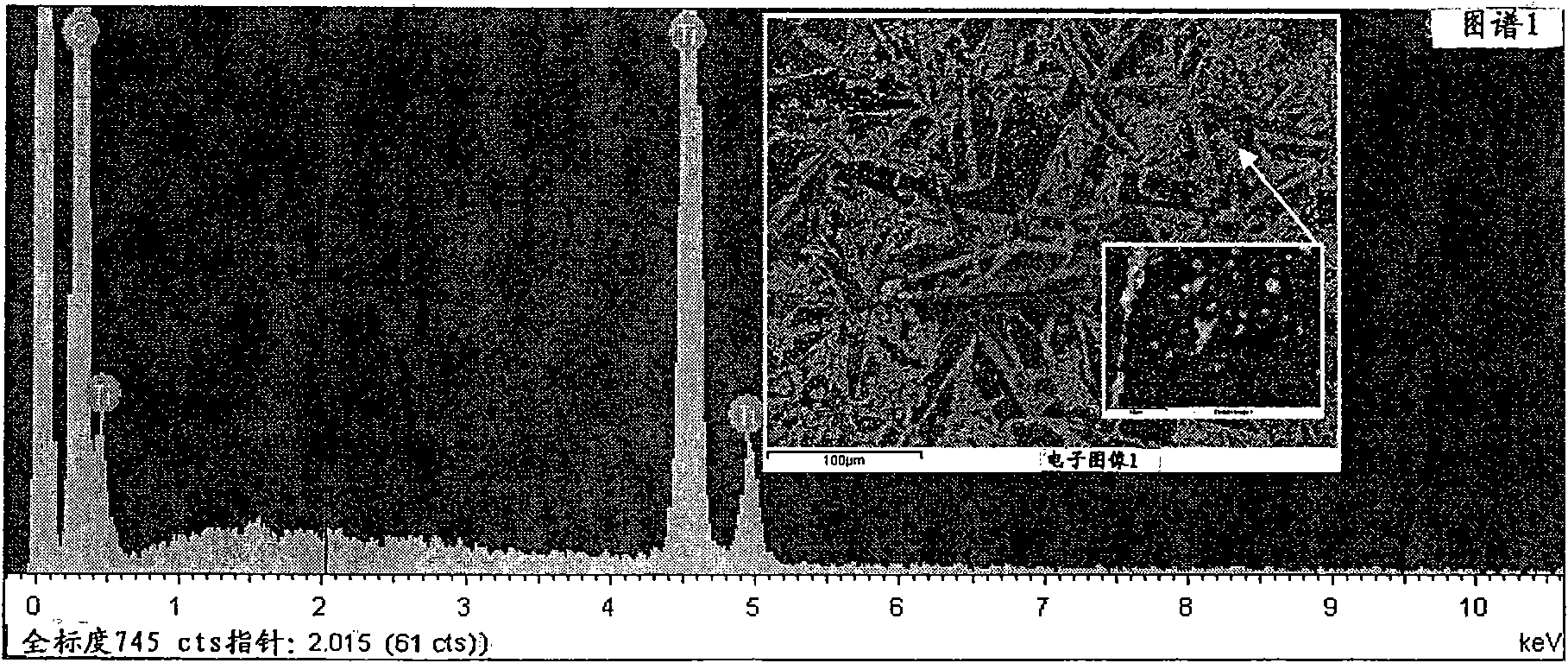
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
322 results about "Diamond substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
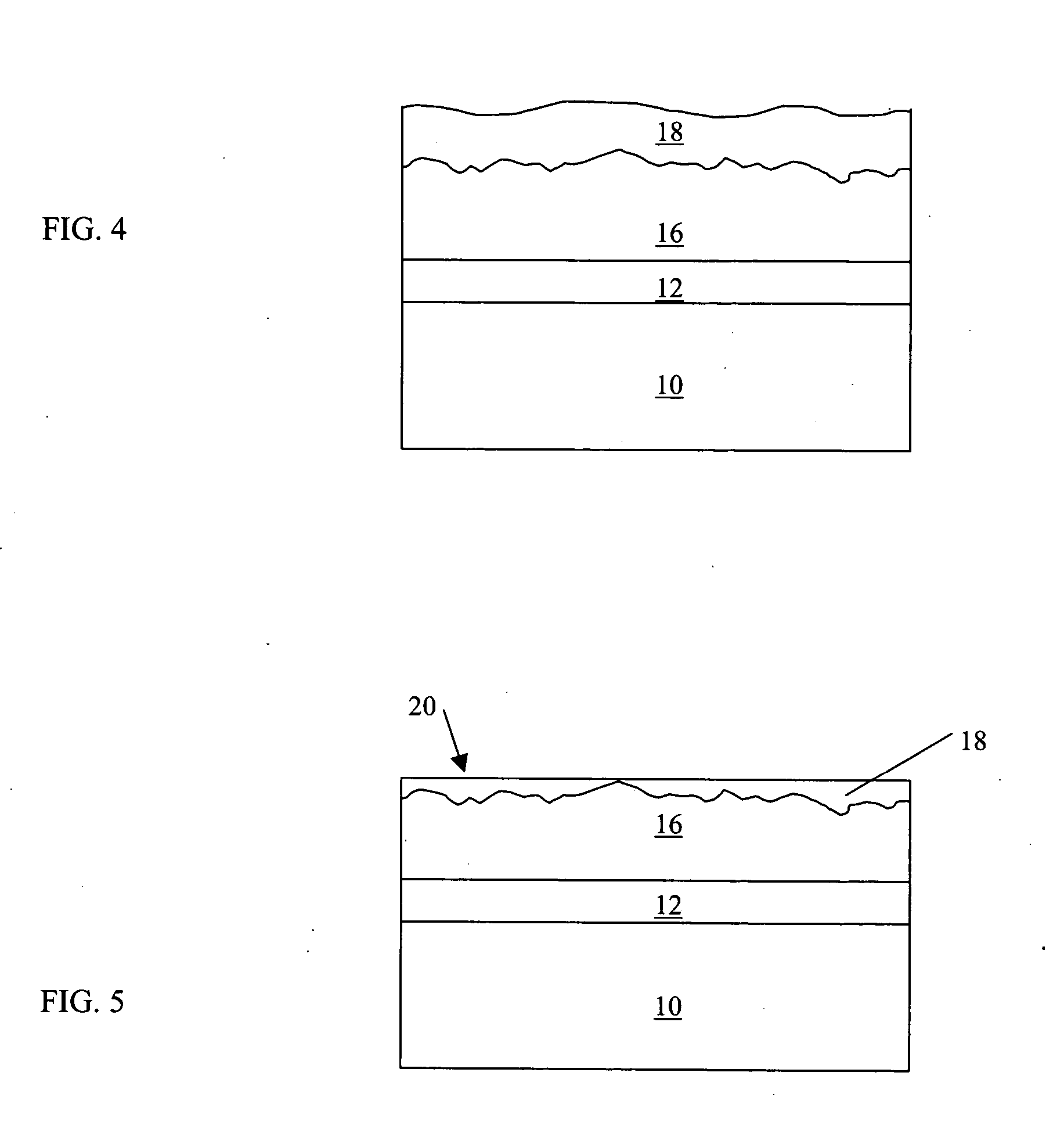
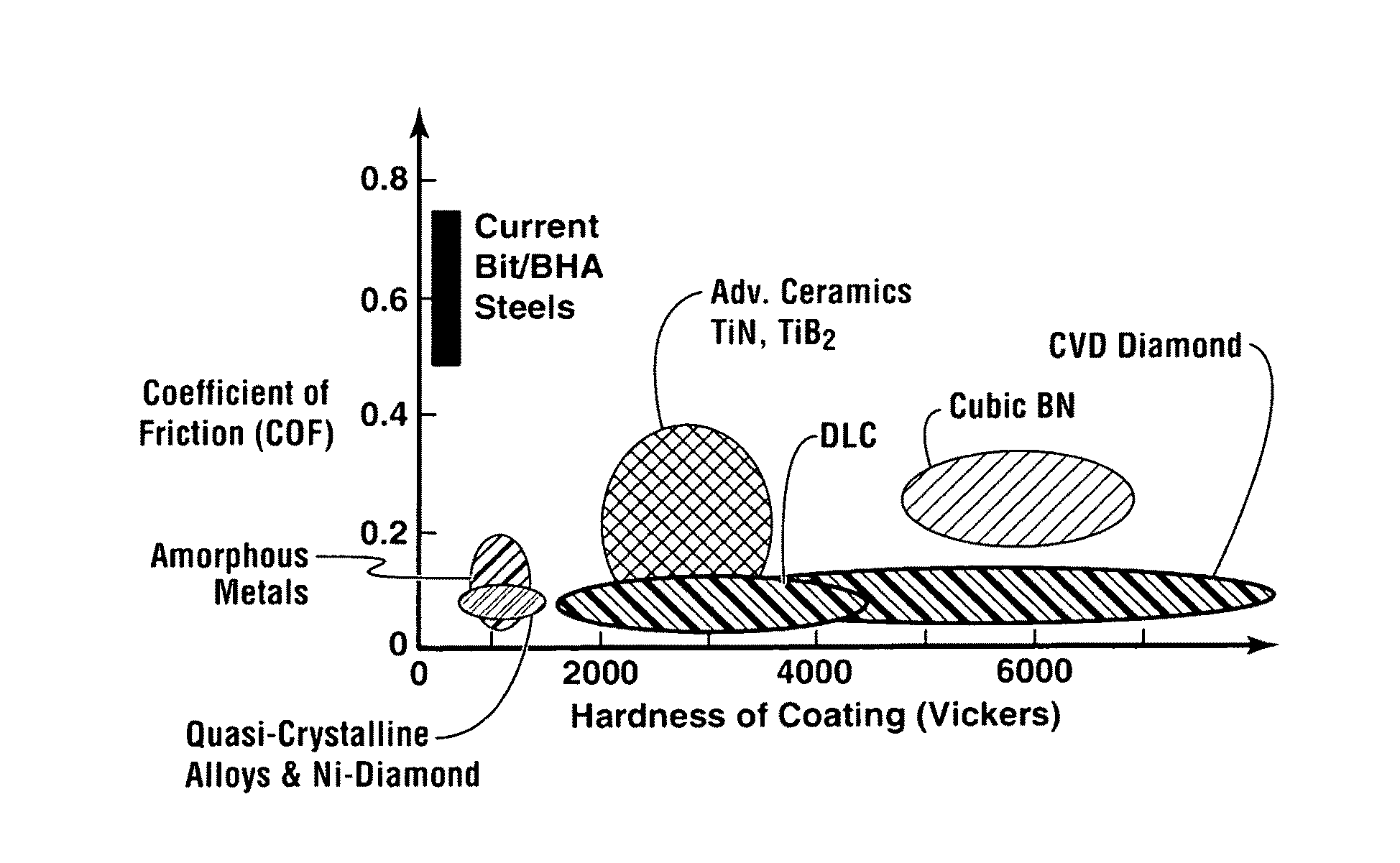
First is surface roughness, as the diamond bond to the tool substrate is a mechanical bond. The second factor is chemical compatibility. Cobalt, which is used as the binder for tungsten carbide, is a deterrent to diamond growth.
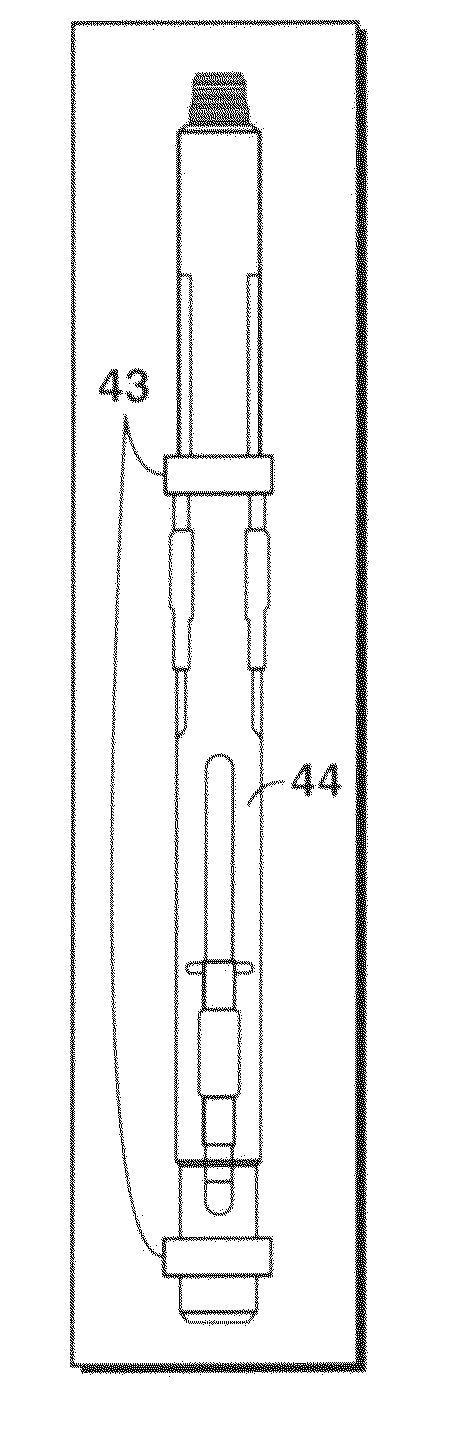
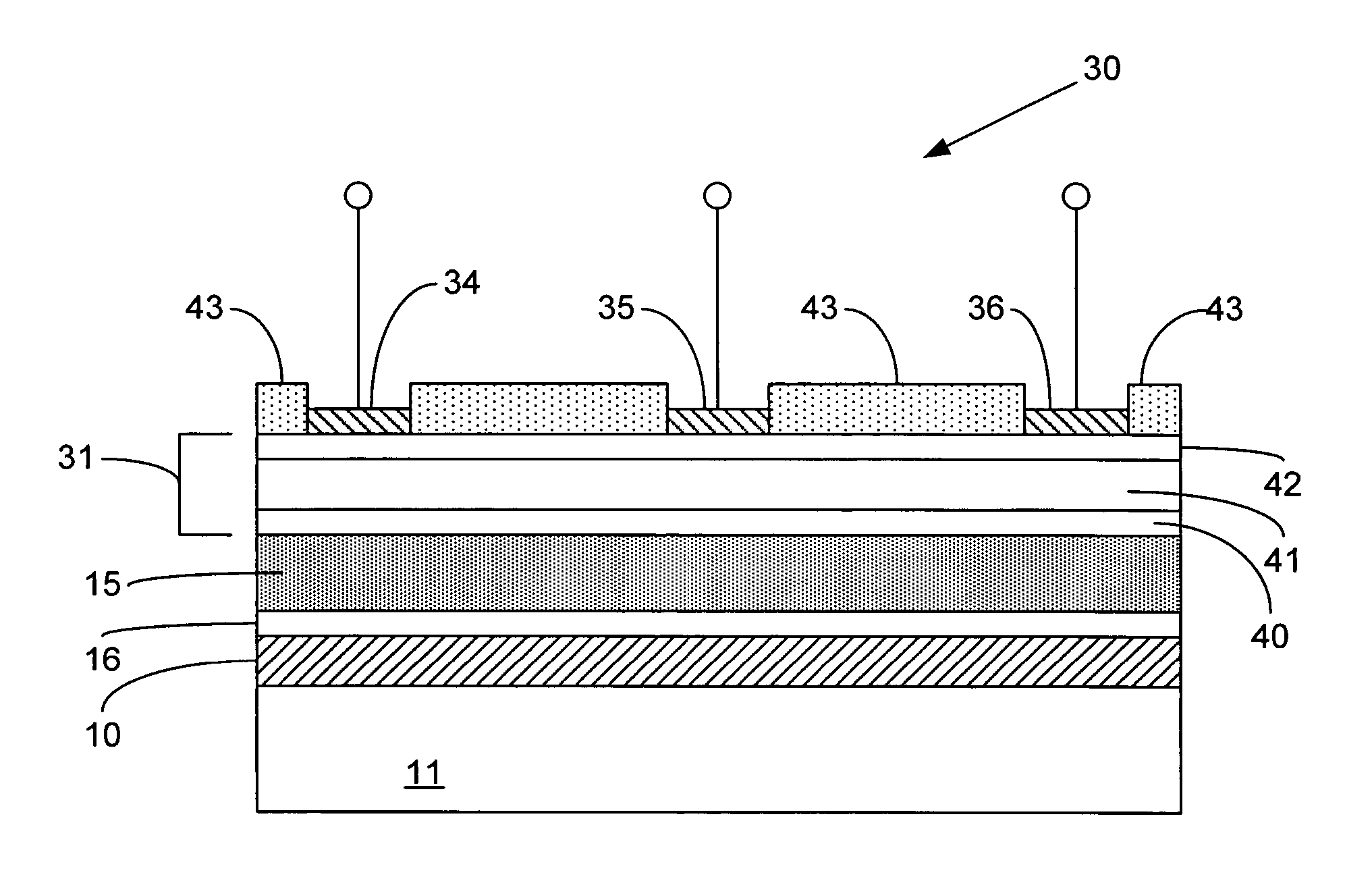
Coated sleeved oil and gas well production devices
Provided are coated sleeved oil and gas well production devices and methods of making and using such coated sleeved devices. In one form, the coated sleeved oil and gas well production device includes an oil and gas well production device including one or more bodies and one or more sleeves proximal to the outer or inner surface of the one or more bodies, and a coating on at least a portion of the inner sleeve surface, outer sleeve surface, or a combination thereof, wherein the coating is chosen from an amorphous alloy, a heat-treated electroless or electro plated based nickel-phosphorous composite with a phosphorous content greater than 12 wt %, graphite, MoS2, WS2, a fullerene based composite, a boride based cermet, a quasicrystalline material, a diamond based material, diamond-like-carbon (DLC), boron nitride, and combinations thereof. The coated sleeved oil and gas well production devices may provide for reduced friction, wear, erosion, corrosion, and deposits for well construction, completion and production of oil and gas.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Silicon Carbide on Diamond Substrates and Related Devices and Methods
ActiveUS20050164482A1Improve thermal conductivityReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
A method of forming a high-power, high-frequency device in wide bandgap semiconductor materials with reduced junction temperature, higher power density during operation and improved reliability at a rated power density is disclosed, along with resulting semiconductor structures and devices. The method includes adding a layer of diamond to a silicon carbide wafer to increase the thermal conductivity of the resulting composite wafer, thereafter reducing the thickness of the silicon carbide portion of the composite wafer while retaining sufficient thickness of silicon carbide to support epitaxial growth thereon, preparing the silicon carbide surface of the composite wafer for epitaxial growth thereon, and adding a Group III nitride heterostructure to the prepared silicon carbide face of the wafer.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Diamond anode
ActiveUS7359487B1Avoid damageImprove cooling effectX-ray tube laminated targetsX-ray tube anode coolingOptoelectronicsMaterials science
According to one aspect of the invention a robust anode structure and methods of making and using said structure to produce ionizing radiation are disclosed. An ionizing radiation producing layer is bonded to the target side of a highly conductive diamond substrate, by a metal carbide layer. The metal carbide layers improves the strength and durability of the bond, thus improving heat removal from the anode surface and reducing the risk of delaminating the ionizing radiation producing layer, thus reducing degradation and extending the anode's life. A smoothing dopant is alloyed into the radiation producing layer to facilitate keeping the layer surface smooth, thus improving the quality of the x-ray beam emitted from the anode. In an embodiment, the heat sink comprises a metal carbide skeleton cemented diamond material. In another embodiment, the heat sink is bonded to the diamond substrate structure in a high temperature reactive brazing process.
Owner:NOVA MEASURING INSTRUMENTS INC
Method for manufacturing a display device with low temperature diamond coatings
InactiveUS20060017055A1Increase powerEasy to operateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
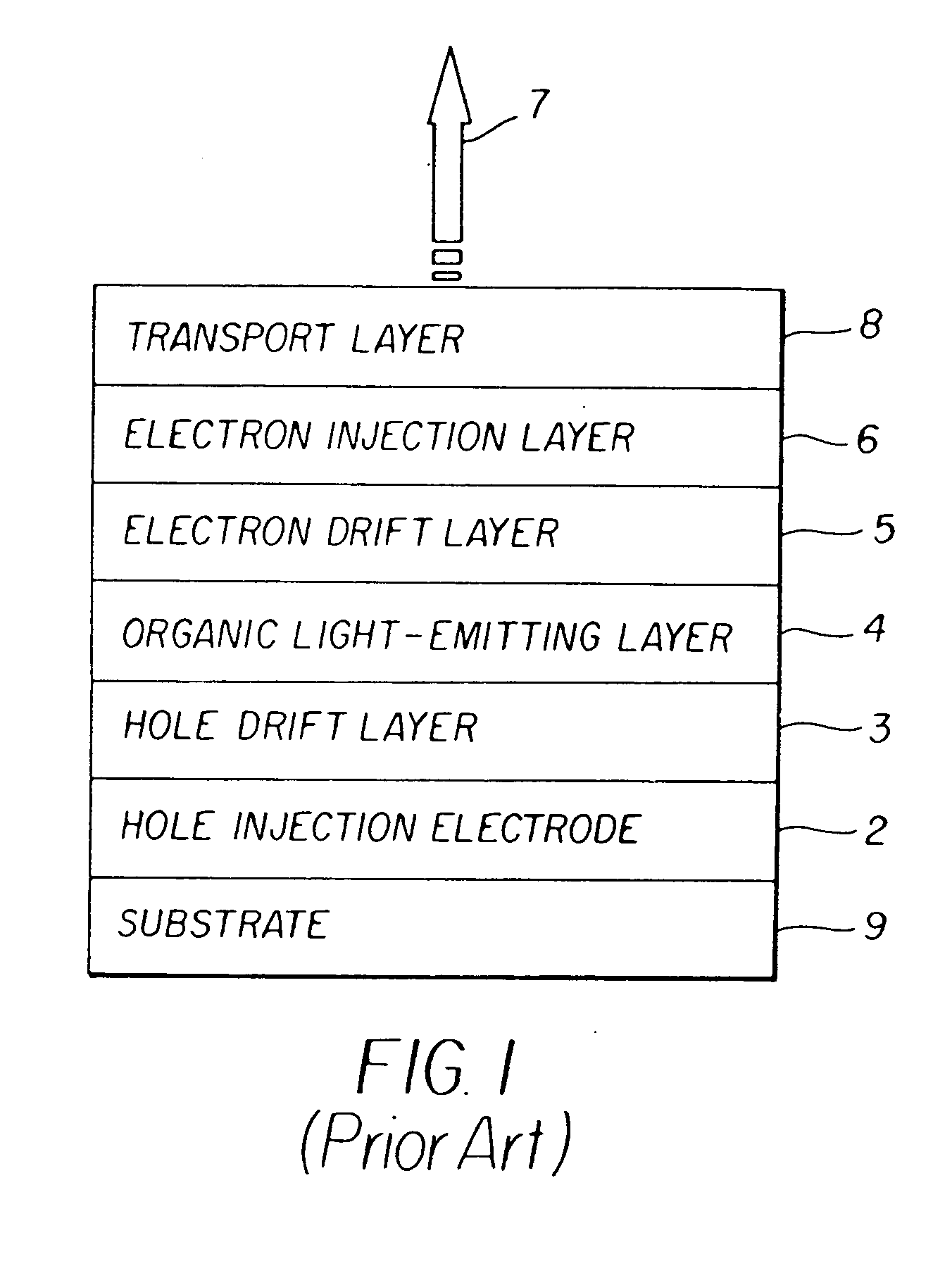
A display device with multiple low temperature diamond coatings, including a substrate as a base; an anode layer residing on the diamond substrate for emitting holes; a hole drift layer that includes a doped diamond coating residing on the anode layer; an emissive layer for emitting light and residing on the hole drift layer. The display device also includes an electron transport layer that includes a doped diamond coating residing on the light emitting layer; a cathode layer, residing on the electron transport layer, for emitting electrons that will drift towards the light emitting layer; and a diamond coated encapsulation layer for sealing the display device from atmospheric moisture; wherein the multiple low temperature diamond coatings are all formed below 750° C. on the display device.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Structured anode X-ray source for X-ray microscopy
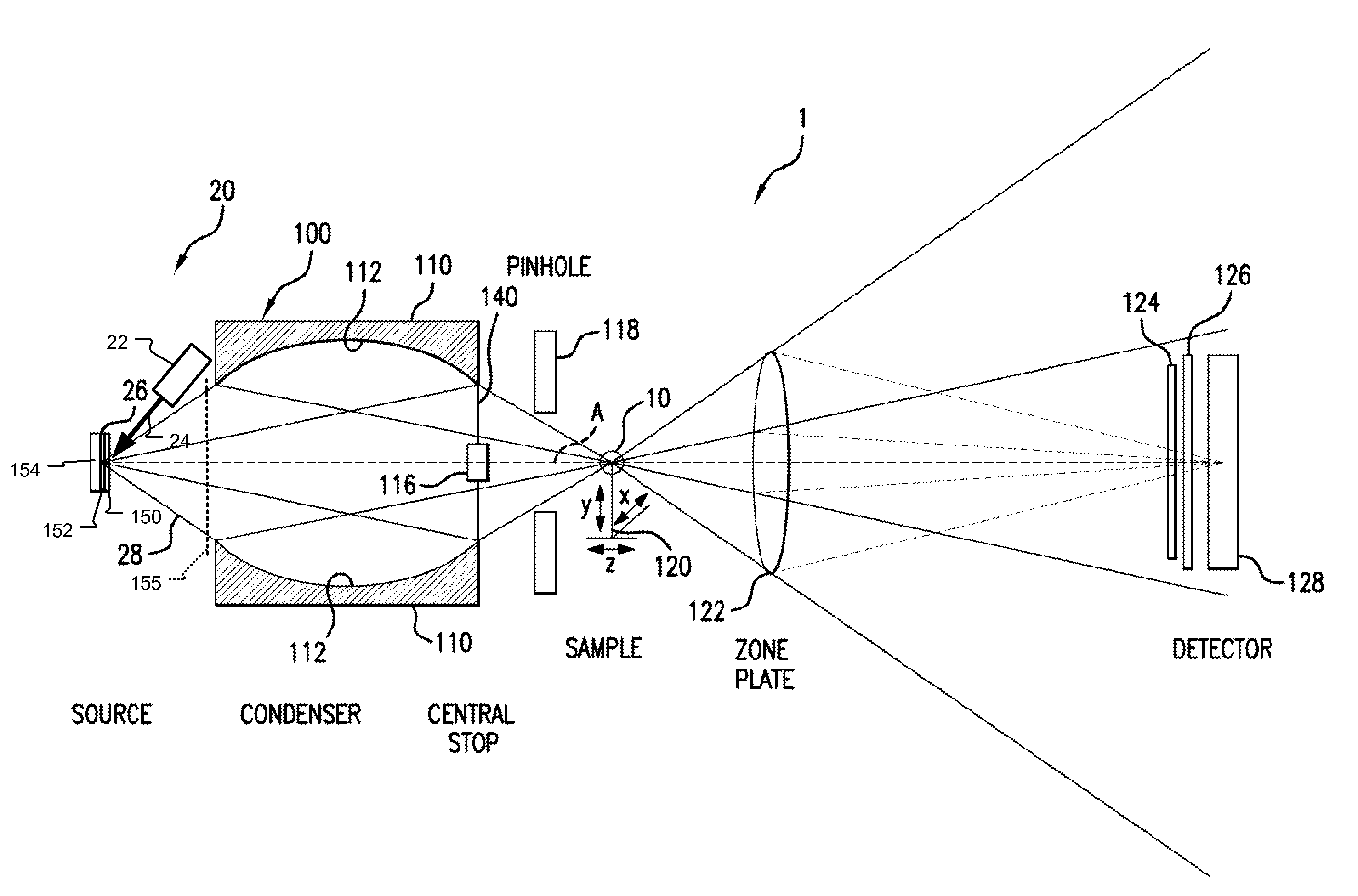
ActiveUS7443953B1Improve performanceImprove thermal performanceX-ray tube laminated targetsX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyX-ray
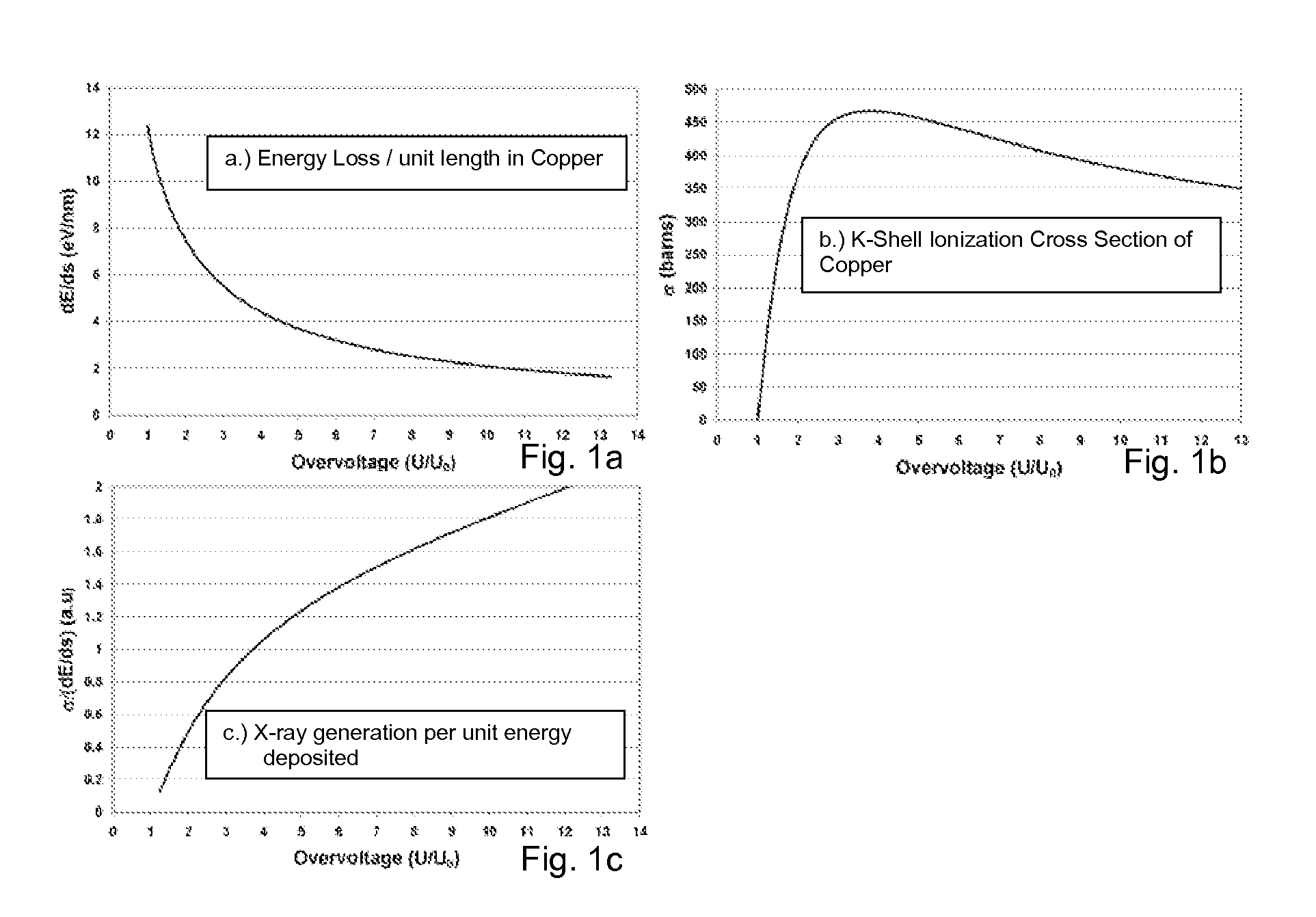
An x-ray source comprises a structured anode that has a thin top layer made of the desired target material and a thick bottom layer made of low atomic number and low density materials with good thermal properties. In one example, the anode comprises a layer of copper with an optimal thickness deposited on a layer of beryllium or diamond substrate. This structured target design allows for the use of efficient high energy electrons for generation of characteristic x-rays per unit energy deposited in the top layer and the use of the bottom layer as a thermal sink. This anode design can be applied to substantially increase the brightness of stationary, rotating anode or other electron bombardment-based sources where brightness is defined as number of x-rays per unit area and unit solid angle emitted by a source and is a key figure of merit parameter for a source.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Silicon carbide on diamond substrates and related devices and methods
ActiveUS7033912B2Improve thermal conductivityReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Diamond hard coating of ferrous substrates
The present invention relates to hard coating of ferrous metal substrates using a laser beam with diamond particles in a metal matrix produced from precursor powders of metals which bond to the diamond particles and to the ferrous substrate. The hard coating is particularly useful for white iron castings for pumps ( 200 ) used in piping tar sand and water mixtures.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
Homogeneous epitaxial lateral growth method for diamond
InactiveCN104651928AReduce dislocation densityQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesMicro structureSingle crystal
The invention discloses a homogeneous epitaxial lateral growth method for diamond. The method comprises the following steps: 1, depositing a mask layer on the bottom surface of a monocrystal diamond substrate; 2, patterning the surface, deposited with the mask layer, of the substrate, thus forming the substrate with a patterned surface, wherein the patterned surface of the substrate is divided into a homogeneous epitaxial growth area and a lateral growth area; and 3, carrying out homogeneous epitaxial diamond growth in the homogeneous epitaxial growth area, and carrying out lateral diamond growth in the lateral growth area. By combining with the lateral growth method, an existing homogeneous epitaxial growth technique of monocrystal diamond is improved; a monocrystal diamond film which is low in dislocation density, high in quality and smooth in surface can effectively grow; the difficulty in epitaxial growth of the monocrystal diamond film for an electronic device is reduced; the film quality is improved; and meanwhile, the technique can be applied to control over the growth structure of the monocrystal diamond film, so as to obtain a monocrystal diamond micro-structure required by MEMS and the like.
Owner:王宏兴
Coated diamond
InactiveCN101680076APrevent proliferationOther chemical processesVacuum evaporation coatingCarbideMetal
The invention relates to a coated diamond comprising a diamond substrate; a primary carbided layer of a carbide forming element; a secondary layer of a high melting point metal selected from W, Mo, Cr, Ni, Ta, Au, Pt, Pd or any combination or alloy thereof, the secondary layer being substantially free of carbide forming element from the primary layer; and an overcoat of Ag, Ni, Cu, Au, Pd, Pt, Rh,Os, Ir, Re, any combination or alloy thereof, the metal of the secondary layer being different to the metal of the overcoat. The invention further relates to methods for producing such coated diamonds and abrasive-containing tools including such coated diamonds.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Method of fabricating n-type semiconductor diamond, and semiconductor diamond
InactiveUS20050202665A1Increase carrier densityEfficient dopingPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesSingle crystalNon doped
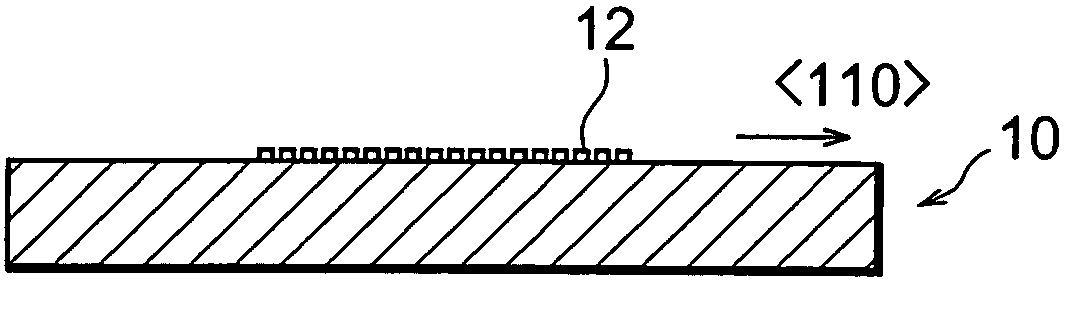
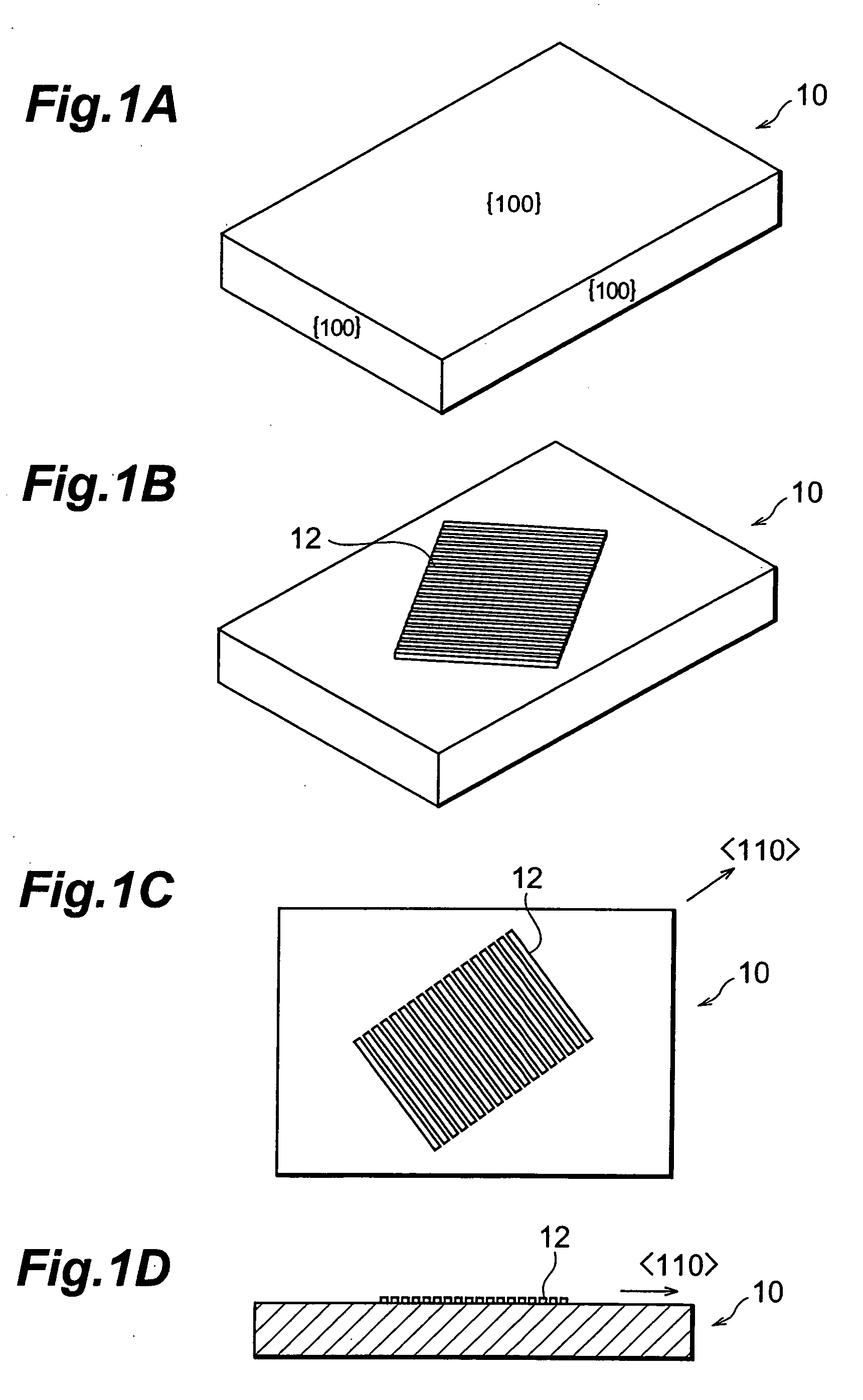
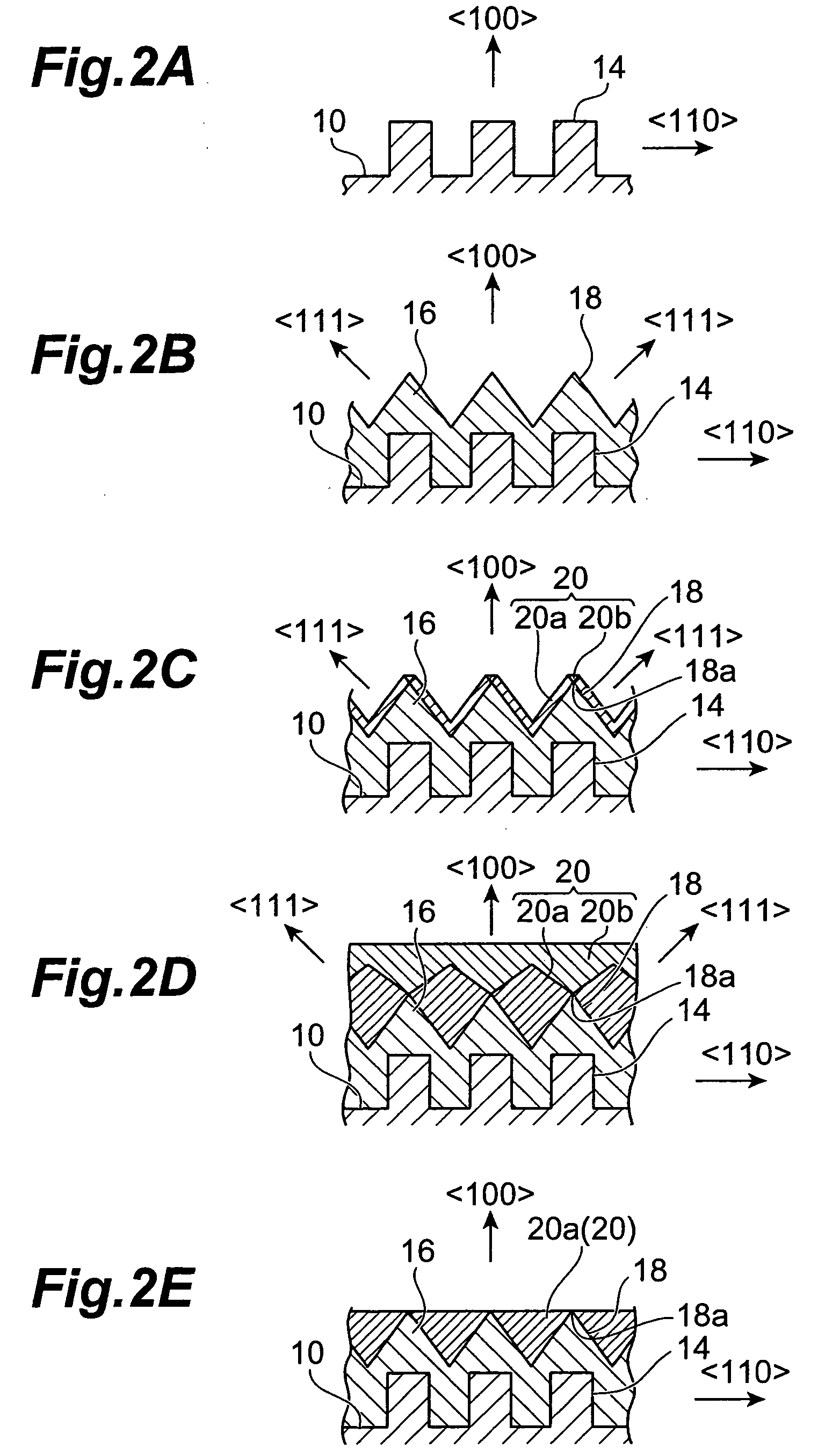
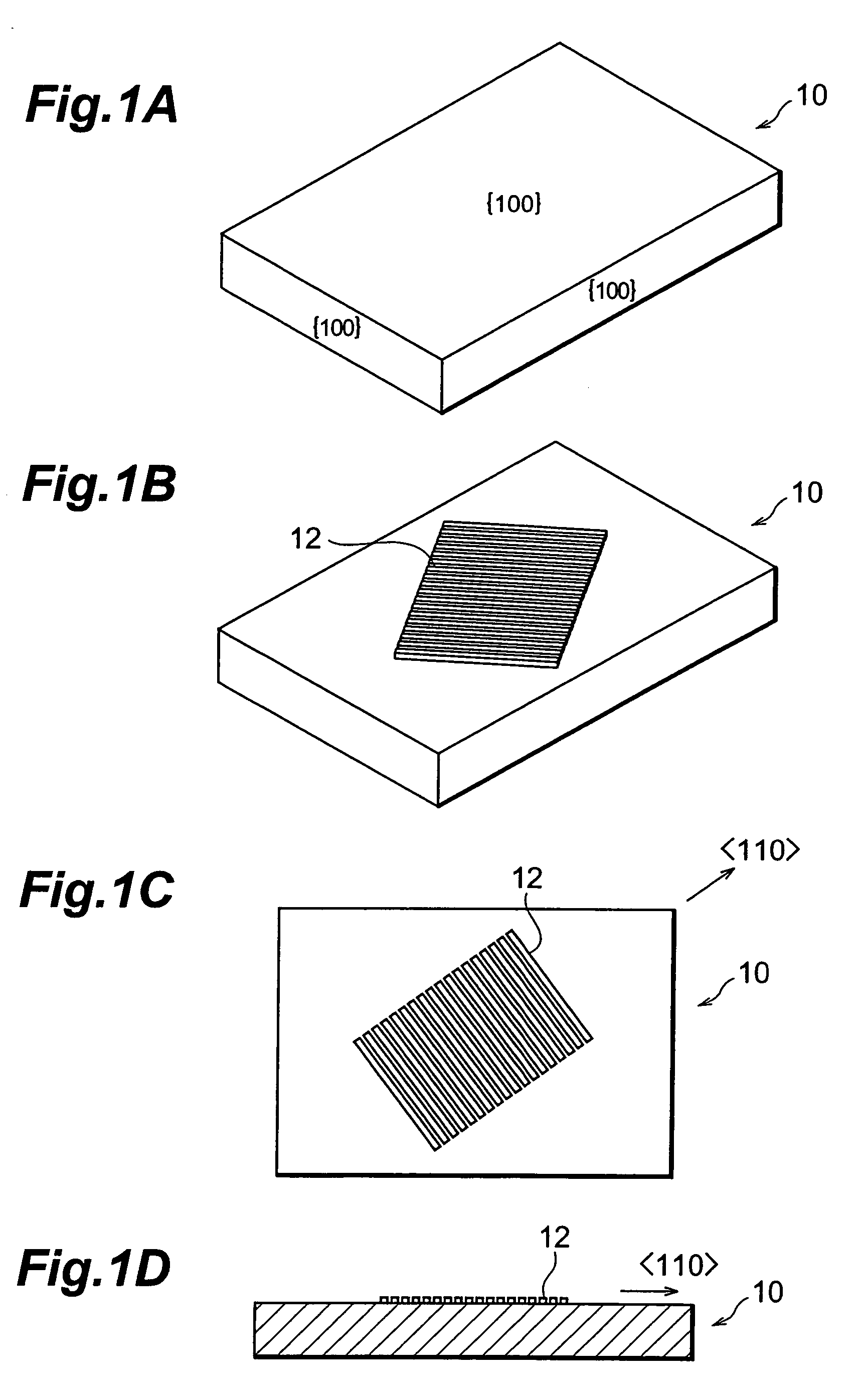
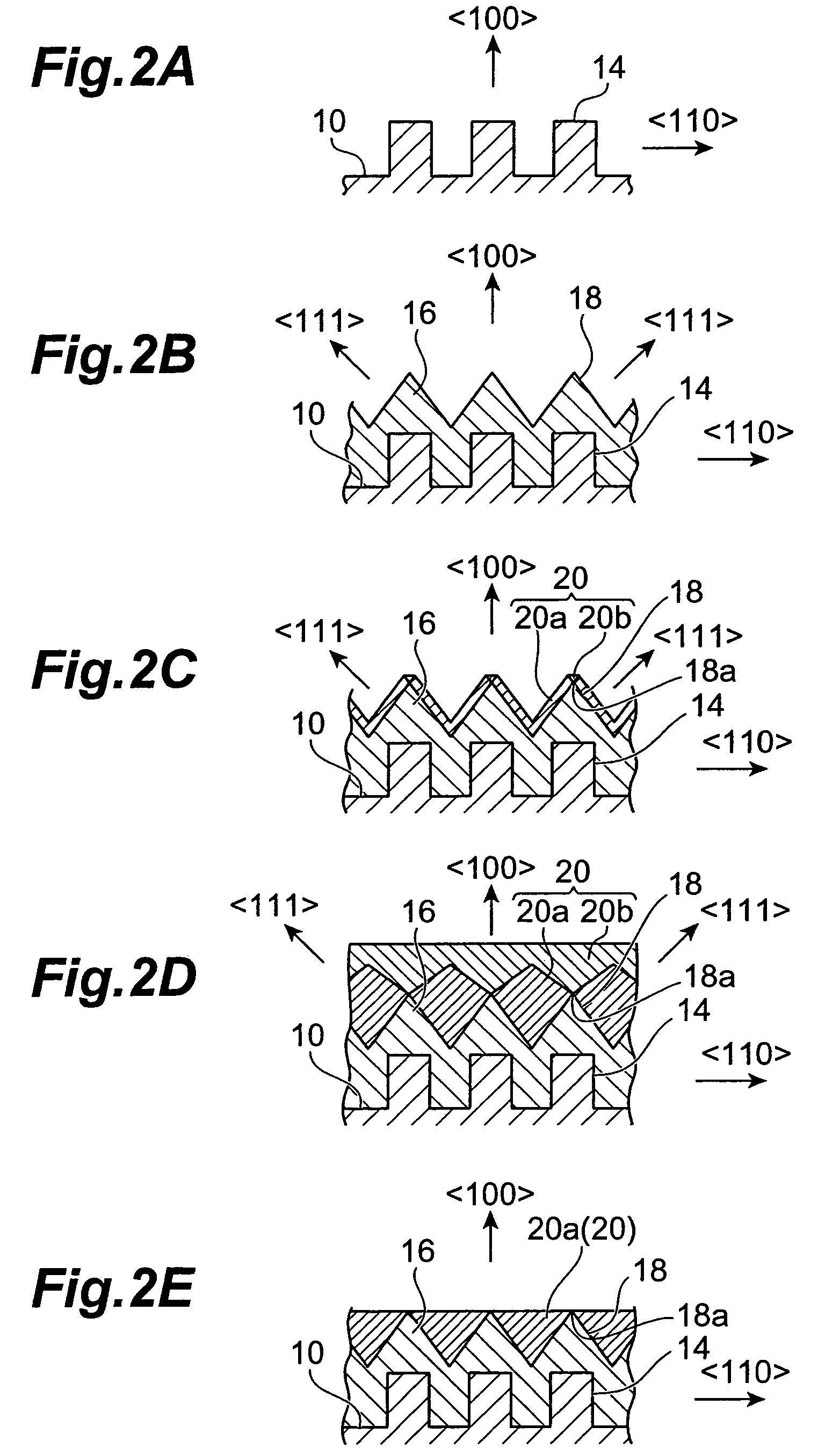
An n-type diamond epitaxial layer 20 is formed by processing a single-crystalline {100} diamond substrate 10 so as to form a {111} plane, and subsequently by causing diamond to epitaxially grow while n-doping the diamond {111} plane. Further, a combination of the n-type semiconductor diamond, p-type semiconductor diamond, and non-doped diamond, obtained in the above-described way, as well as the use of p-type single-crystalline {100} diamond substrate allow for a pn junction type, a pnp junction type, an npn junction type and a pin junction type semiconductor diamond to be obtained.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method for Producing Diamond Having Acicular Projection Array Structure on Surface thereof, Diamond Material, Electrode and Electronic Device
InactiveUS20090258255A1Higher negative electron affinity electronImprove emission effectElectrode manufacturing processesDecorative surface effectsPt elementElectron
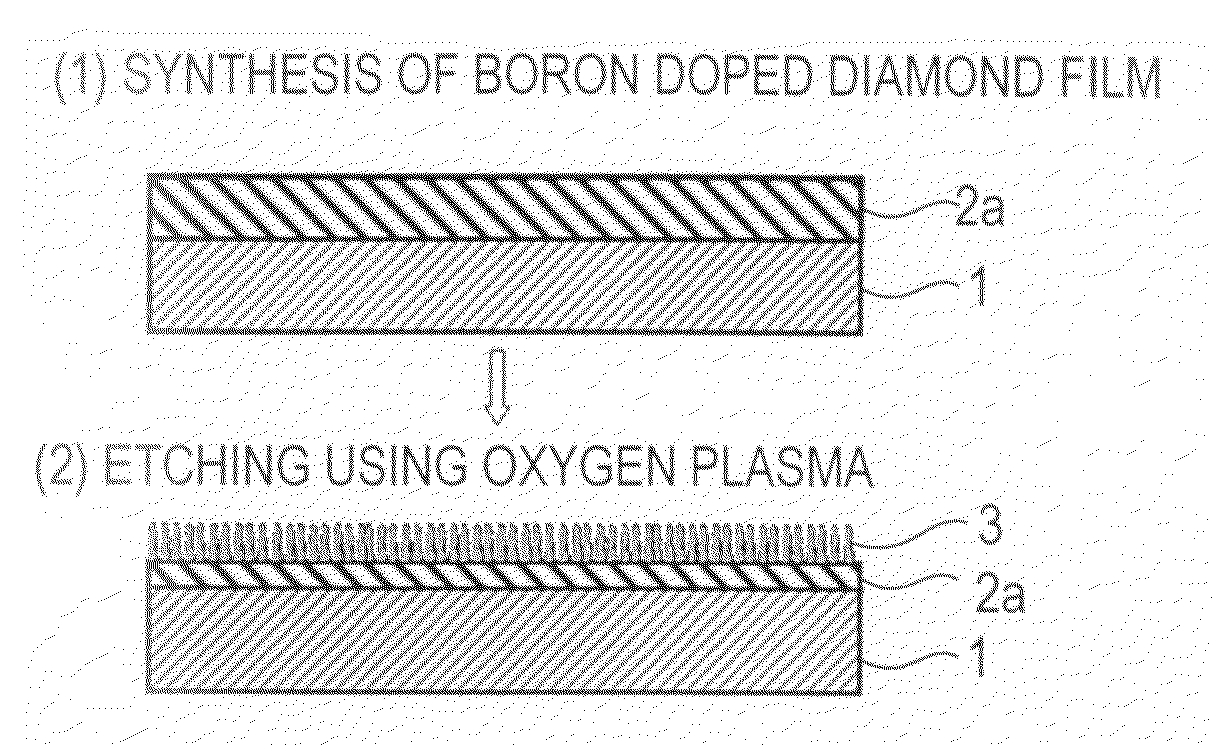
A method for producing a diamond having an acicular projection array structure on a surface thereof comprises the step of forming the acicular projection array structure on a surface of a diamond base material by treating the surface of the diamond base material by dry etching using oxygen gas. At least one dopant selected among boron (B), nitrogen (N), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), phosphorus (P), sulfur (S), copper (Cu), arsenic (As), molybdenum (Mo), platinum (Pt) and gold (Au) is doped with a concentration of 1×1019 atoms / cm3 and more at least in a region near the surface of the diamond base material.
Owner:CENTRAL JAPAN RAILWAY COMPANY
Diamond substrate-based gallium nitride high-electron-mobility transistor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106783998AEpitaxial growth controlImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricCooking & baking
The invention discloses a diamond substrate-based gallium nitride high-electron-mobility transistor and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of firstly cleaning a silicon carbide-based gallium nitride wafer and the surface of a temporary slide; coating the front surface of the temporary slide with an adhesive material as a bonding material and putting the adhesive material on a hot plate for baking; oppositely bonding the silicon carbide-based gallium nitride wafer and the front surface of the temporary slide; carrying out thinning polishing and etching on a silicon carbide substrate of the silicon carbide-based gallium nitride wafer to remove the residual silicon carbide substrate; cleaning the surface of a gallium nitride epitaxial layer employing the temporary slide as a support; growing a layer of dielectric on the outer surface of the gallium nitride epitaxial layer employing the temporary slide as the support; carrying out epitaxial growth of a polycrystalline diamond substrate on the gallium nitride epitaxial layer employing the temporary slide as the support and automatically separating a diamond-based gallium nitride wafer from the temporary slide; and preparing the high-electron-mobility transistor on the diamond-based gallium nitride wafer. The limitation that original epitaxial growth is very difficult is broken, and epitaxial growth of diamond on gallium nitride can be relatively well controlled.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Mosaic diamond substrates
InactiveUS20070036896A1Provides adequateQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsHigh pressureCarbon source
The present invention provides methods of forming high quality diamond bodies under high pressure, and the diamond bodies produced by such methods. In one aspect, a method may include for joining together a plurality of diamond segments to form a diamond body. The method may include placing the plurality of diamond segments in close proximity under high pressure in association with a molten catalyst and a carbon source, and maintaining the plurality of diamond segments under high pressure in the molten catalyst until the plurality of diamond segments have joined into a single diamond body.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Method of manufacturing diamond substrates
InactiveUS20070034147A1Suitable for useEnhanced electrical breakdown propertyAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthPolycrystalline diamondOptoelectronics
A tiled array of diamond plates, which is suitable for wafer scale processing, for example, in the manufacture of electronic or other device structures on the diamond plates. The diamond plates are fixed to a support layer, preferably a polycrystalline diamond support layer, in a substantially planar arrangement such that at least one of the major surfaces of the respective fixed diamond plates defines a fabrication surface that is exposed for further processing. The support layer may be a backing layer, in which case only one of the major faces of the diamond substrate is exposed for further processing, or may extend between respective diamond substrates such that both major surfaces are exposed for further processing.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Graphene on Diamond Devices and Associated Methods
Graphene layers and associated methods are disclosed. In one aspect, for example, a method of making graphene on a diamond substrate is provided. Such a method can include applying a layer of a metal to a crystallographic face of the diamond substrate, and heating the diamond substrate under vacuum to convert a portion of the diamond substrate at the crystallographic face into graphene. In another aspect, the layer of metal is applied only on diamond substrate faces having a same crystallographic orientation. In yet another aspect, the layer of metal is applied to only a single crystallographic face of the diamond substrate. Additionally, in one aspect, converting the portion of the diamond substrate at the crystallographic face into graphene includes converting the portion of the diamond substrate by a martensitic transformation.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
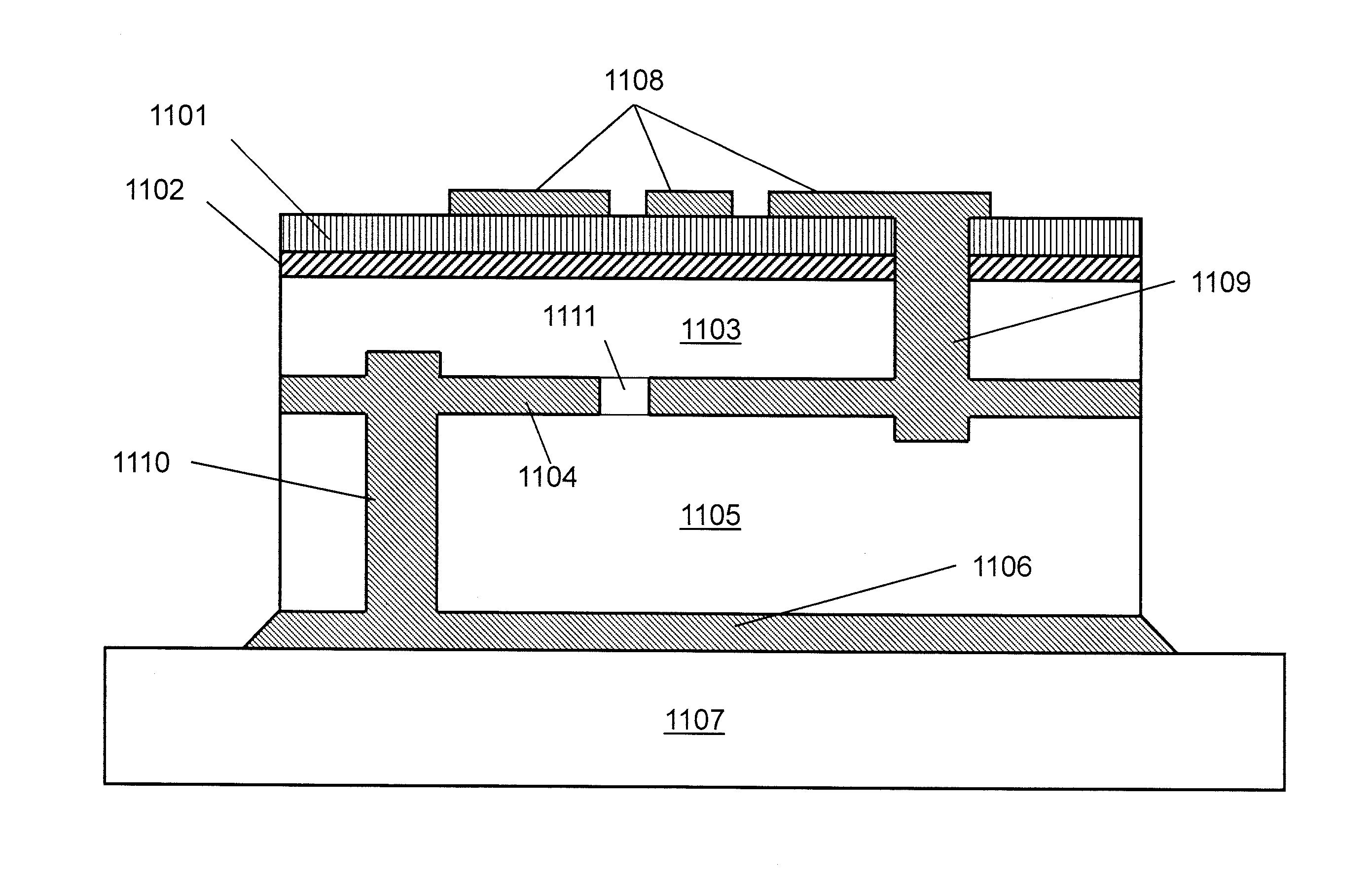
Diamond substrate formation for electronic assemblies
InactiveUS20060073640A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phasePorous layer
Electronic assemblies and methods for forming assemblies including a diamond substrate are described. One embodiment includes providing a diamond support and forming a porous layer of SiO2 on the diamond support. A diamond layer is formed by chemical vapor deposition on the porous layer so that the porous layer is between the diamond support and the diamond layer. A polycrystalline silicon layer is formed on the diamond layer. The polycrystalline silicon layer is polished to form a planarized surface. A semiconductor layer is coupled to the polysilicon layer. After coupling the semiconductor layer to the polysilicon layer, the diamond support is detached from the diamond layer by breaking the porous layer. The semiconductor layer on the diamond layer substrate is then further processed to form a semiconductor device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Two-dimensional expansion method for CVD monocrystal diamond
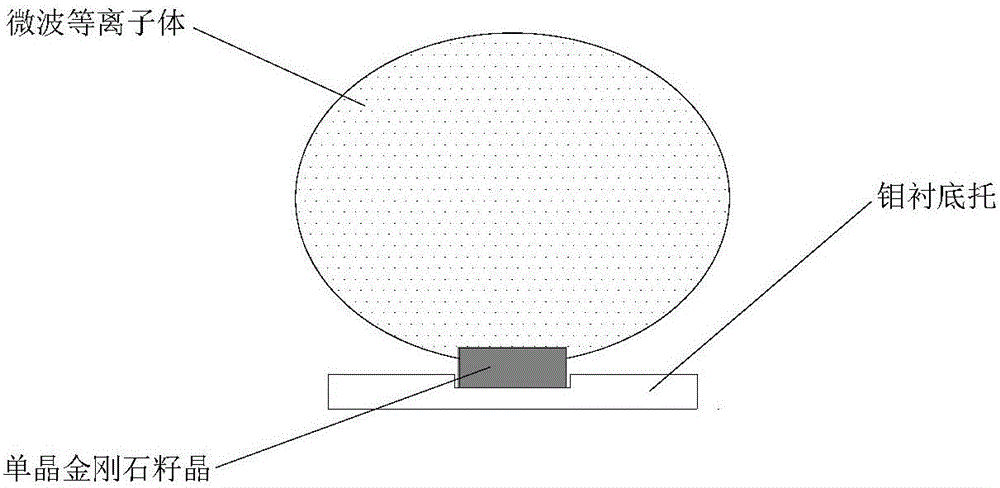
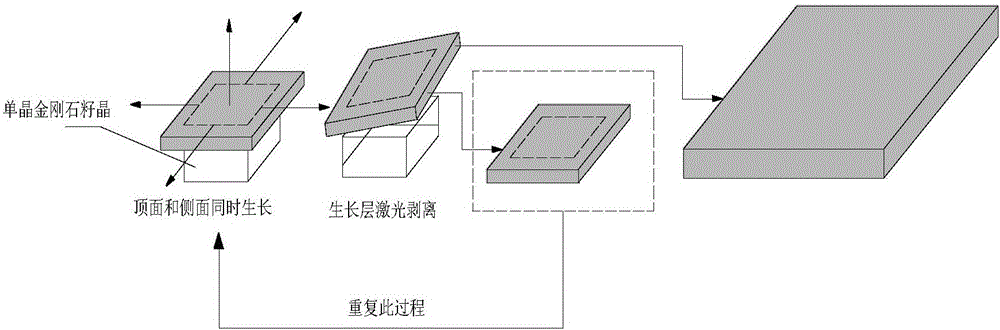
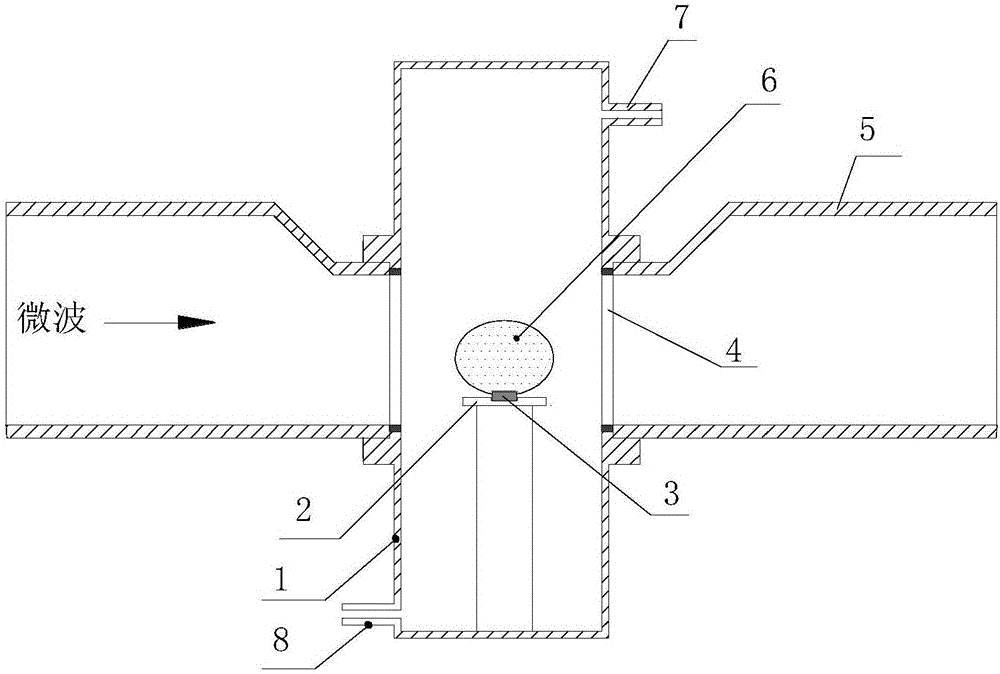
InactiveCN106012003ASmall sizePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesVacuum pumpSeed crystal
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for a monocrystal diamond material, especially to a two-dimensional expansion method for CVD monocrystal diamond. The two-dimensional expansion method is characterized by comprising the following steps: a, placing a seed crystal of monocrystal diamond into a substrate support with a hole in the center so as to allow the seed crystal of monocrystal diamond to be exposed, wherein the substrate support is made of metal molybdenum; b, putting the substrate support with the seed crystal of monocrystal diamond into a deposition chamber and carrying out vacuum-pumping on the deposition chamber; c, generating plasma by using a microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition method, i.e., introducing hydrogen and methane into the deposition chamber, adjusting gas flow, microwave power and air pressure and allowing gas in the deposition chamber to absorb microwave energy and excite and generate plasma, thereby allowing monocrystal diamond to grow on a top surface and four side surfaces at the same time and realizing two-dimensional expansion of monocrystal diamond; and d, carrying out peeling so as to obtain large-size monocrystal diamond. The method realizes two-dimensional growth of monocrystal diamond on a monocrystal diamond substrate via the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition method, so the size of monocrystal diamond is enlarged.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Diamond-base double-layer insulated gate dielectric field effect transistor and a preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104992974ASuppress leakage currentReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricMicrowave
The invention discloses a diamond-base double-layer insulated gate dielectric field effect transistor (FET) and a preparation method thereof. The FET comprises a diamond substrate, a monocrystalline diamond epitaxial film, a conductive channel, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a first insulated gate dielectric layer, a second insulated gate dielectric layer, and a gate electrode. The diamond substrate is equipped with a layer of amonocrystalline diamond epitaxial film. The monocrystalline diamond epitaxial film is provided with the source electrode and the drain electrode. The conductive channel is formed in the monocrystalline diamond epitaxial film between the source electrode and the drain electrode. The first insulated gate dielectric layer covers the conductive channel between the source electrode and the drain electrode, and a part of the source electrode and the drain electrode. The second insulated gate dielectric layer is arranged on the first insulated gate dielectric layer. The gate electrode is arranged on the second insulated gate dielectric layer. The double-layer insulated gate dielectric structure effectively improves the DC and microwave characteristics of the FET.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Coated sleeved oil and gas well production devices
Provided are coated sleeved oil and gas well production devices and methods of making and using such coated sleeved devices. In one form, the coated sleeved oil and gas well production device includes an oil and gas well production device including one or more bodies and one or more sleeves proximal to the outer or inner surface of the one or more bodies, and a coating on at least a portion of the inner sleeve surface, outer sleeve surface, or a combination thereof, wherein the coating is chosen from an amorphous alloy, a heat-treated electroless or electro plated based nickel-phosphorous composite with a phosphorous content greater than 12 wt %, graphite, MoS2, WS2, a fullerene based composite, a boride based cermet, a quasicrystalline material, a diamond based material, diamond-like-carbon (DLC), boron nitride, and combinations thereof. The coated sleeved oil and gas well production devices may provide for reduced friction, wear, erosion, corrosion, and deposits for well construction, completion and production of oil and gas.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Diamond substrate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060213428A1Easy to handleQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsWafering
The present invention provides a manufacturing method for a large-scale diamond substrate and a substrate produced by the method suitable for semiconductor lithography processing and large-scale optical parts, semiconductor materials, thermal-release substrate, semiconductor wafer processing, and back-feed devices, and others. The manufacturing method for a diamond substrate of the present invention comprises: the mounting step of preparing a substrate having a main face comprising a first region which is a concave and having a second region which surrounds the first region, and mounting, on the first region, a single crystalline diamond seed substrate having a plate thickness thicker than the concave depth of the first region; a connecting step of forming a CVD diamond layer from the single crystalline diamond seed substrate using a chemical vapor deposition, and mutually connecting by forming a CVD diamond layer on the second region at the same time; and a polishing step of polishing to substantially flatten both the CVD diamond layers on the single crystalline diamond seed substrate and on the second region by mechanically polishing.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Growth method of high-quality high-speed monocrystal diamond film
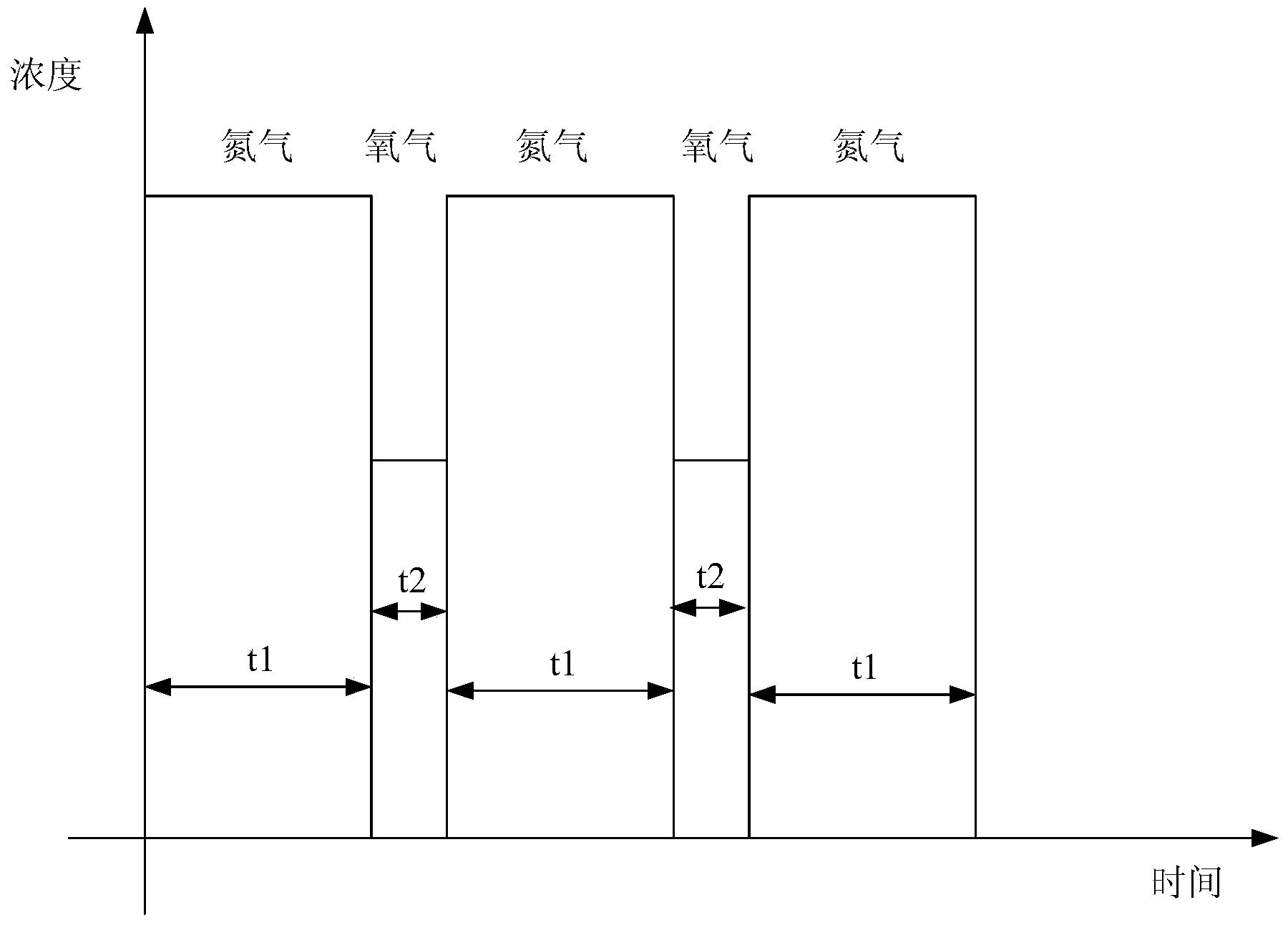
ActiveCN103710748AImprove film forming speedQuality assurancePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSingle crystalNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a growth method of a high-quality high-speed monocrystal diamond film. The growth method comprises the following step: growing the monocrystal diamond film under a condition with a fixed growth temperature on the surface of a monocrystal diamond substrate placed in a deposition cavity by a microwave plasma gas-phase deposition method, wherein reaction gases including methane, a hydrogen gas, a nitrogen gas and an oxygen gas are introduced into the deposition cavity, and an introduction mode of the nitrogen gas and the oxygen gas is an alternative introduction mode. The growth method disclosed by the invention solves technical problems that application of the monocrystal diamond film in the fields such as scientific research, optics, semiconductors and processing is limited as the color of the monocrystal diamond film grown in the prior art changes and is even changed into deeply brown, and crystal quality of the film is worsened.
Owner:西安德盟特半导体科技有限公司
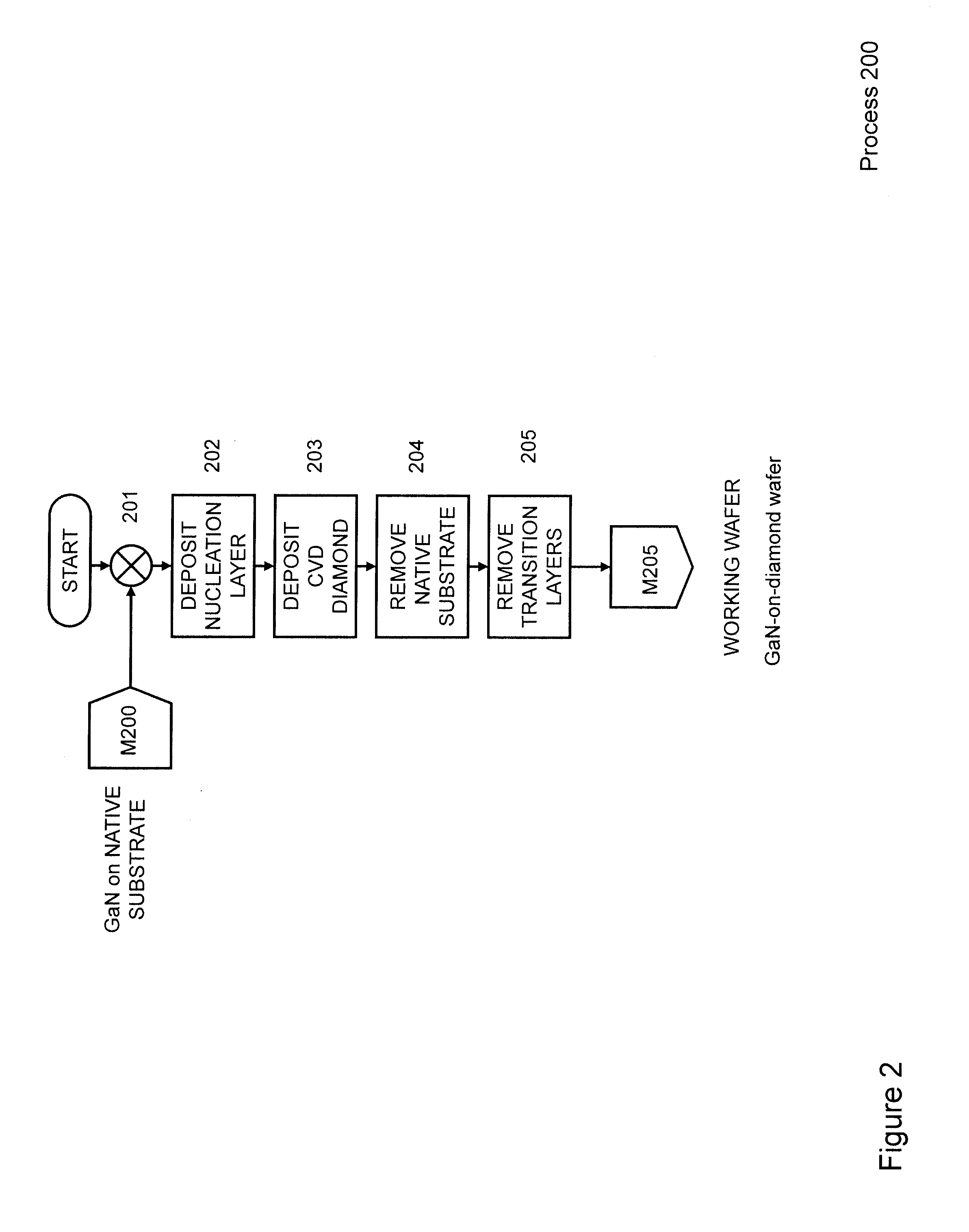
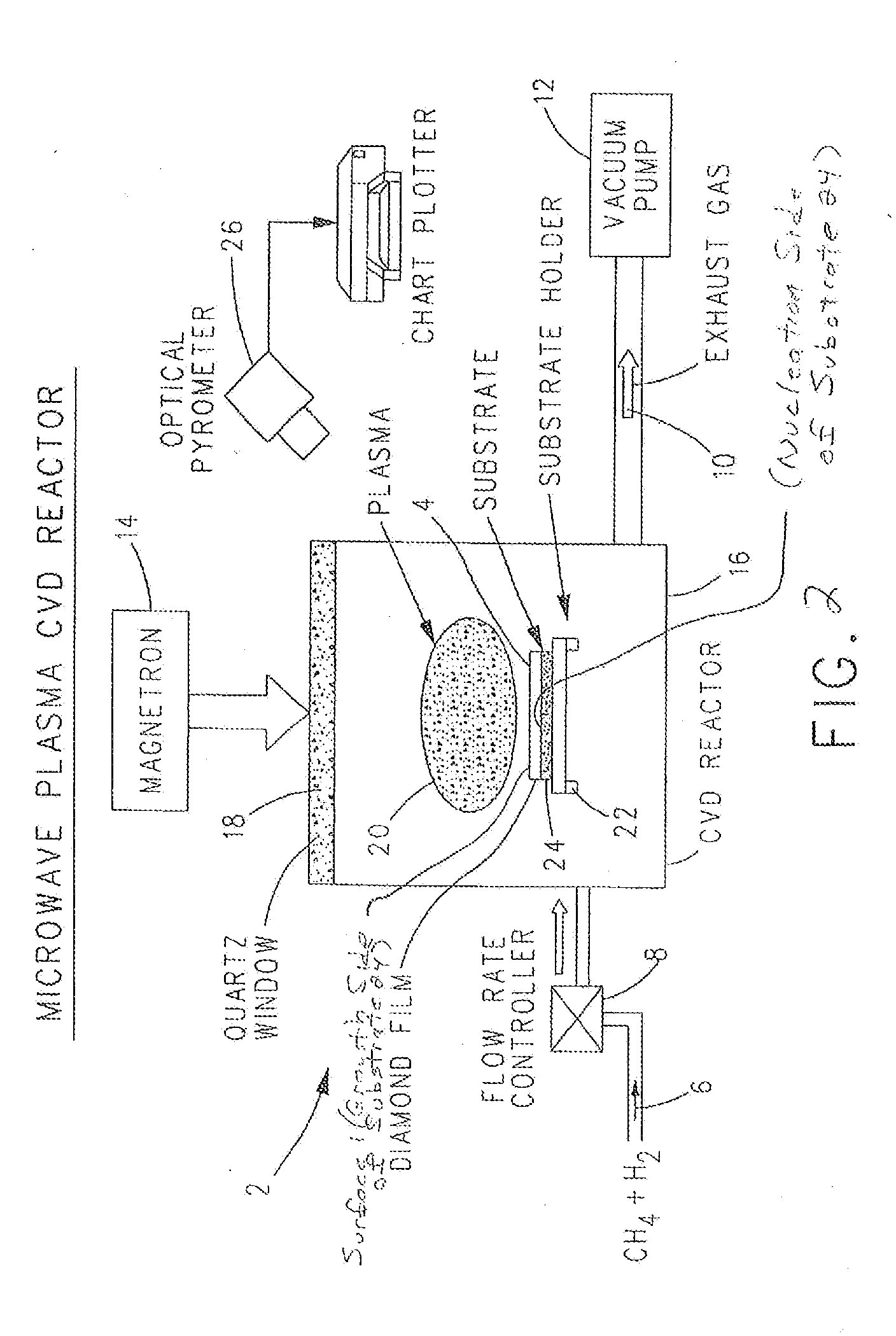
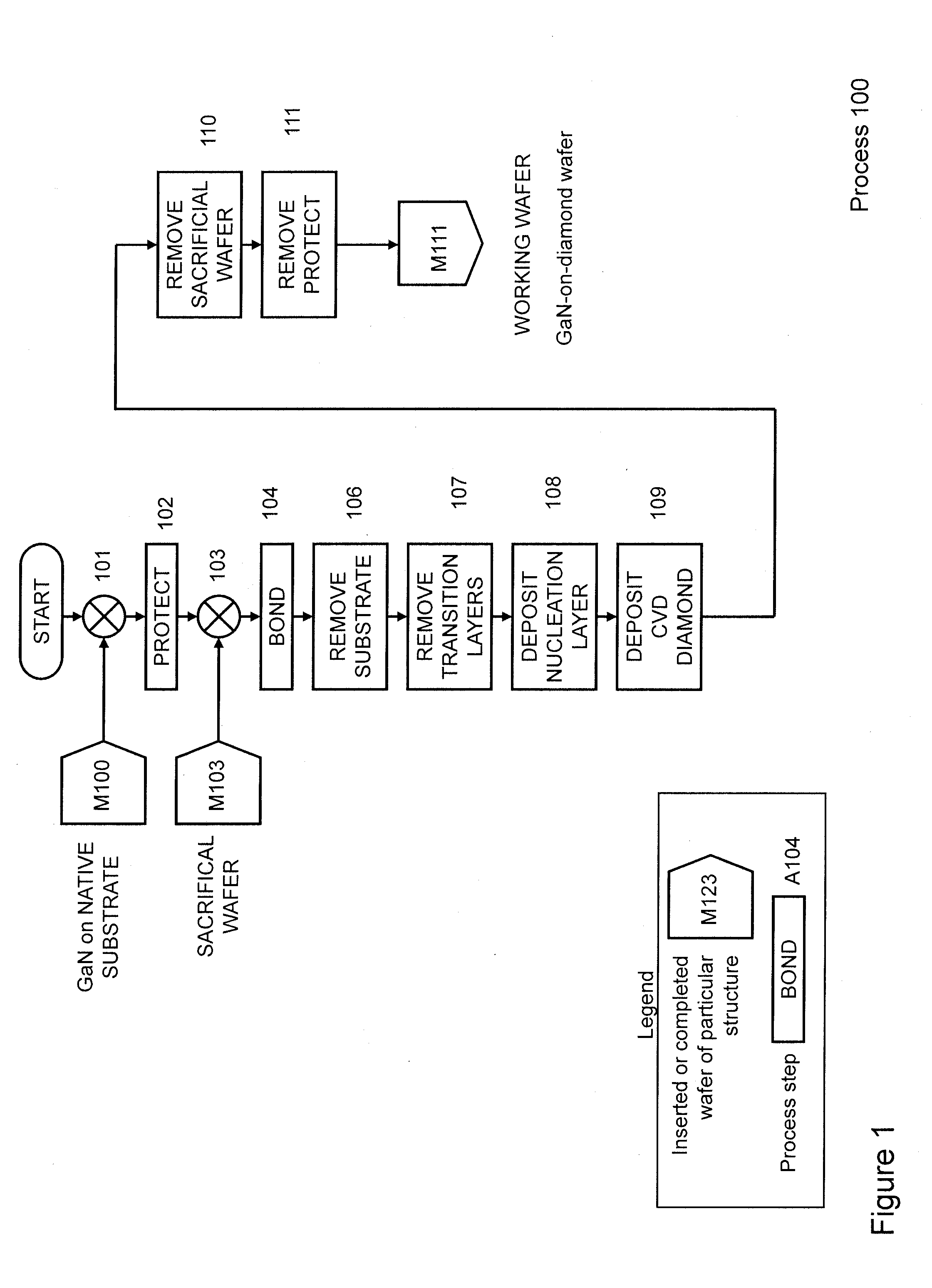
Gallium-nitride-on-diamond wafers and manufacturing equipment and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS9359693B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWide gap semiconductorsGallium nitride
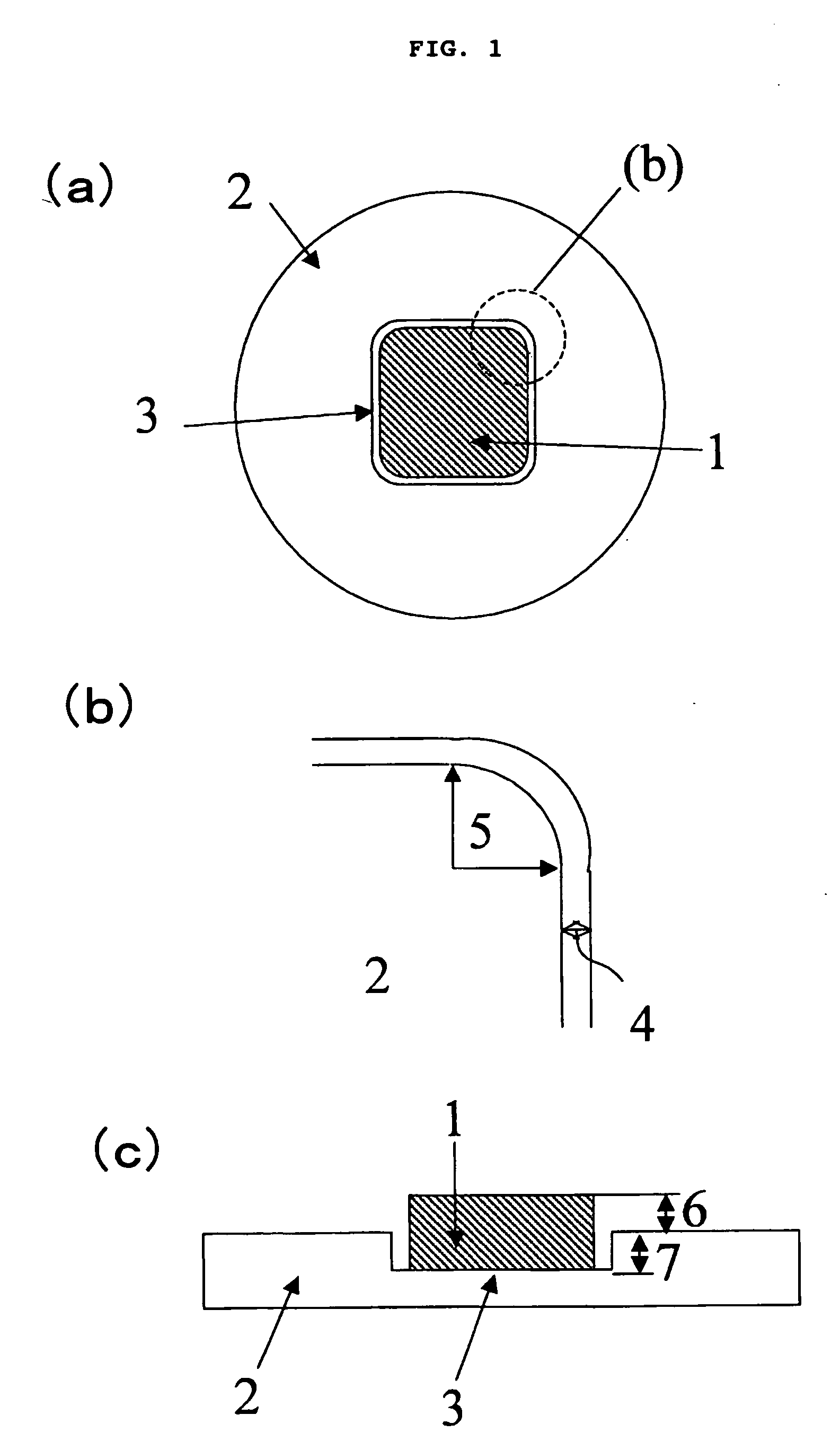
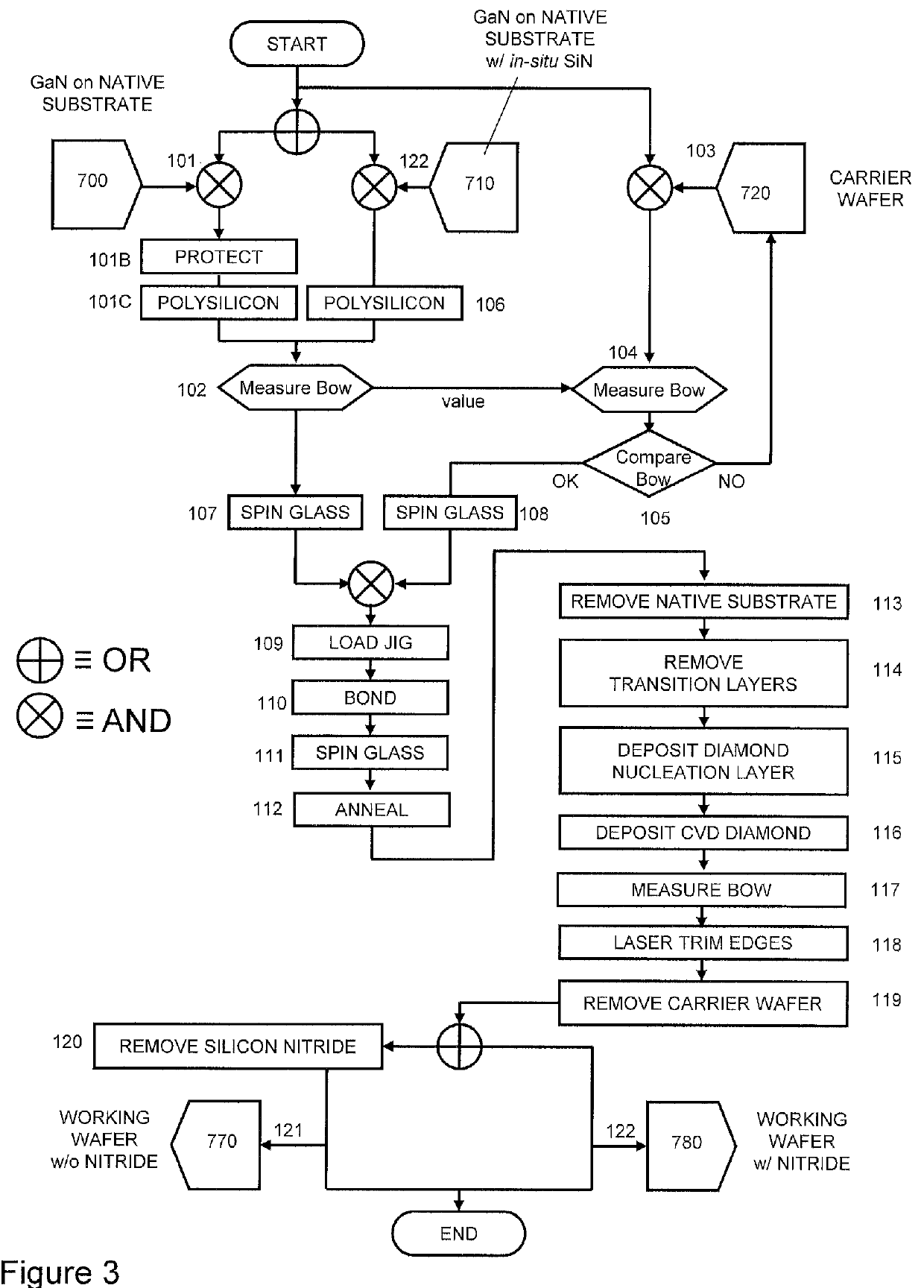
A method for integrating wide-gap semiconductors, and specifically, gallium nitride epilayers, with synthetic diamond substrates is disclosed. Diamond substrates are created by depositing synthetic diamond onto a nucleating layer deposited or formed on a layered structure that comprises at least one layer of gallium nitride. Methods for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers with low bow and high crystalline quality are disclosed along with preferred choices for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers and chips tailored to specific applications.
Owner:AKASH SYST INC
Method of using square-recess embedded substrate support to inhibit growth of polycrystalline diamond
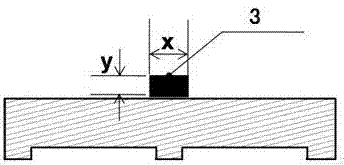
ActiveCN107059120AInhibits edge growthSuppressed edge polycrystallinePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesAlcoholCooling effect
The invention discloses a method of using a square-recess embedded substrate support to inhibit the growth of polycrystalline diamond; the method comprises: manufacturing a substrate support, and making two concentric square recesses in the center of the surface of the substrate support; grinding and polishing the surface of the substrate support and the insides of the recesses; ultrasonically washing with absolute ethyl alcohol, and washing with plasma; ultrasonically washing a monocrystalline diamond substrate with acetate, placing in a substrate support recess, and fitting a growth device; washing a substrate with plasma in the growth device; adding methane to growth monocrystalline diamond. As graphite deposits between the substrate and the substrate support, the lateral sides of the substrate come in contact with the substrate support, substrate edge cooling effect is improved, and temperature uniformity of the whole monocrystalline diamond substrate is optimized, with polycrystalline growth at the edge of the substrate greatly avoided. Experiments discover that it is possible to effectively inhibit the edge polycrystal during the growth of monocrystalline diamond by using the square-recess embedded substrate support, and monocrystalline diamond samples with non-reduced size can be acquired.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST
Method for manufacturing a display device with low temperature diamond coatings
InactiveUS20060189026A1Increase powerLong lastingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
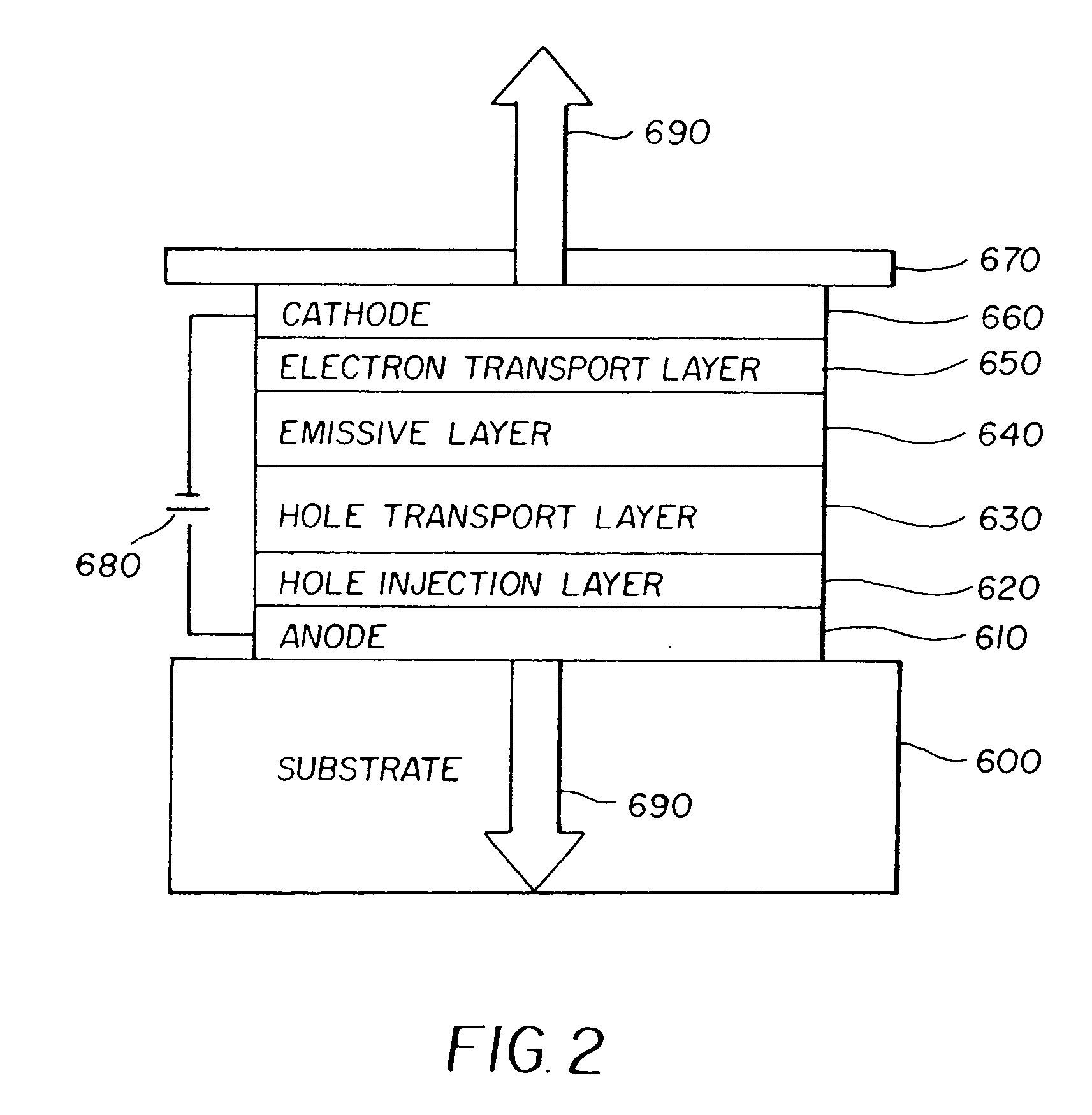
A display device with multiple low temperature diamond coatings, including a substrate as a base; an anode layer residing on the diamond substrate for emitting holes; a hole drift layer that includes a doped diamond coating residing on the anode layer; an emissive layer for emitting light and residing on the hole drift layer. The display device also includes an electron transport layer that includes a doped diamond coating residing on the light emitting layer; a cathode layer, residing on the electron transport layer, for emitting electrons that will drift towards the light emitting layer; and a diamond coated encapsulation layer for sealing the display device from atmospheric moisture; wherein the multiple low temperature diamond coatings are all formed below 750° C. on the display device.
Owner:CROPPER ANDRE D +1
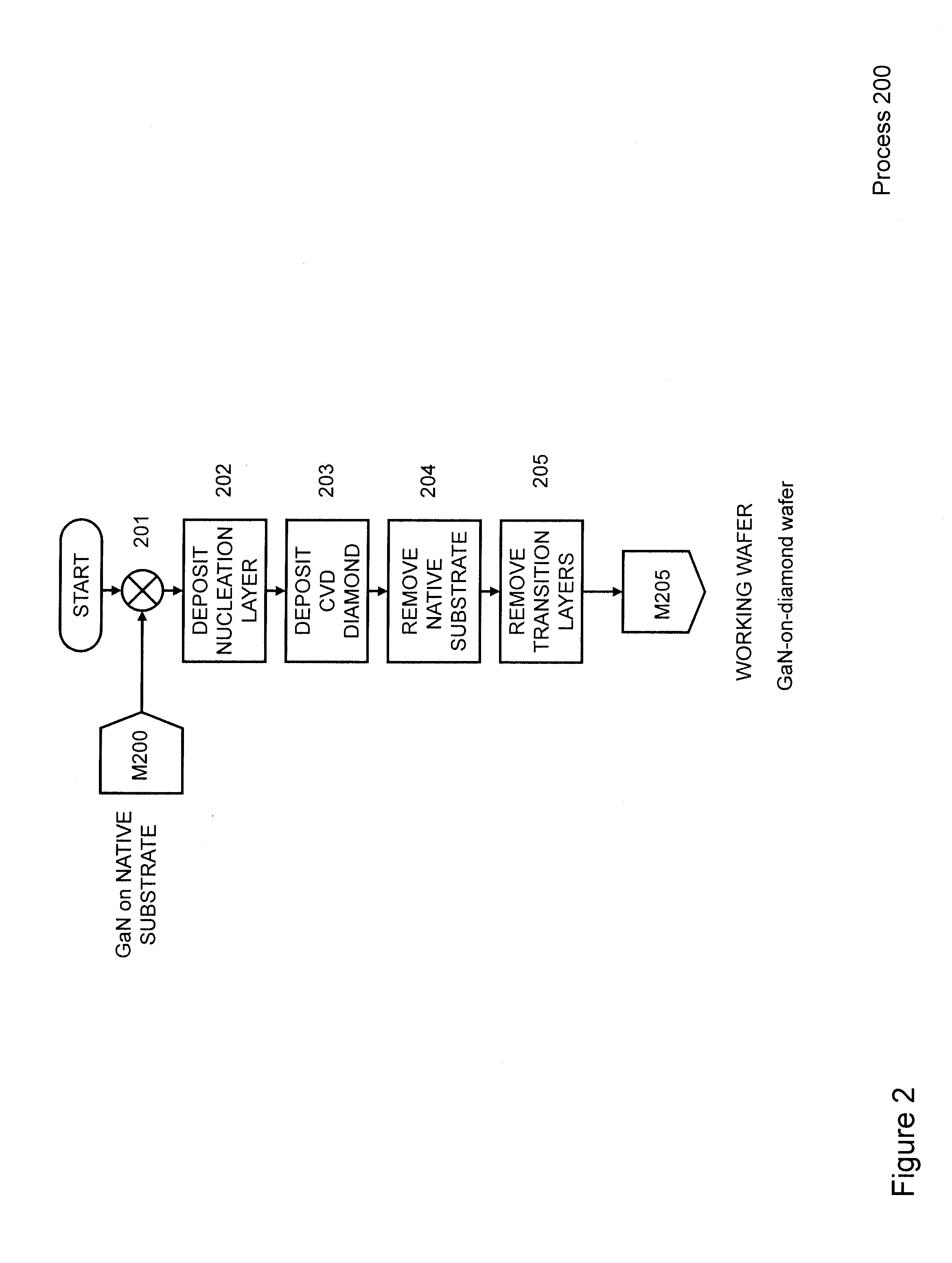
Gallium-nitride-on-diamond wafers and devices, and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS8674405B1Reduce thermal resistanceLower bow of the wafersPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsWide gap semiconductorsGallium nitride
Methods for integrating wide-gap semiconductors, and specifically, gallium nitride epilayers with synthetic diamond substrates are disclosed. Diamond substrates are created by depositing synthetic diamond onto a nucleating layer deposited or formed on a layered structure that comprises at least one layer made out of gallium nitride. Methods for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers with low bow and high crystalline quality are disclosed along with preferred choices for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers and chips tailored to specific applications.
Owner:GROUP4 LABS
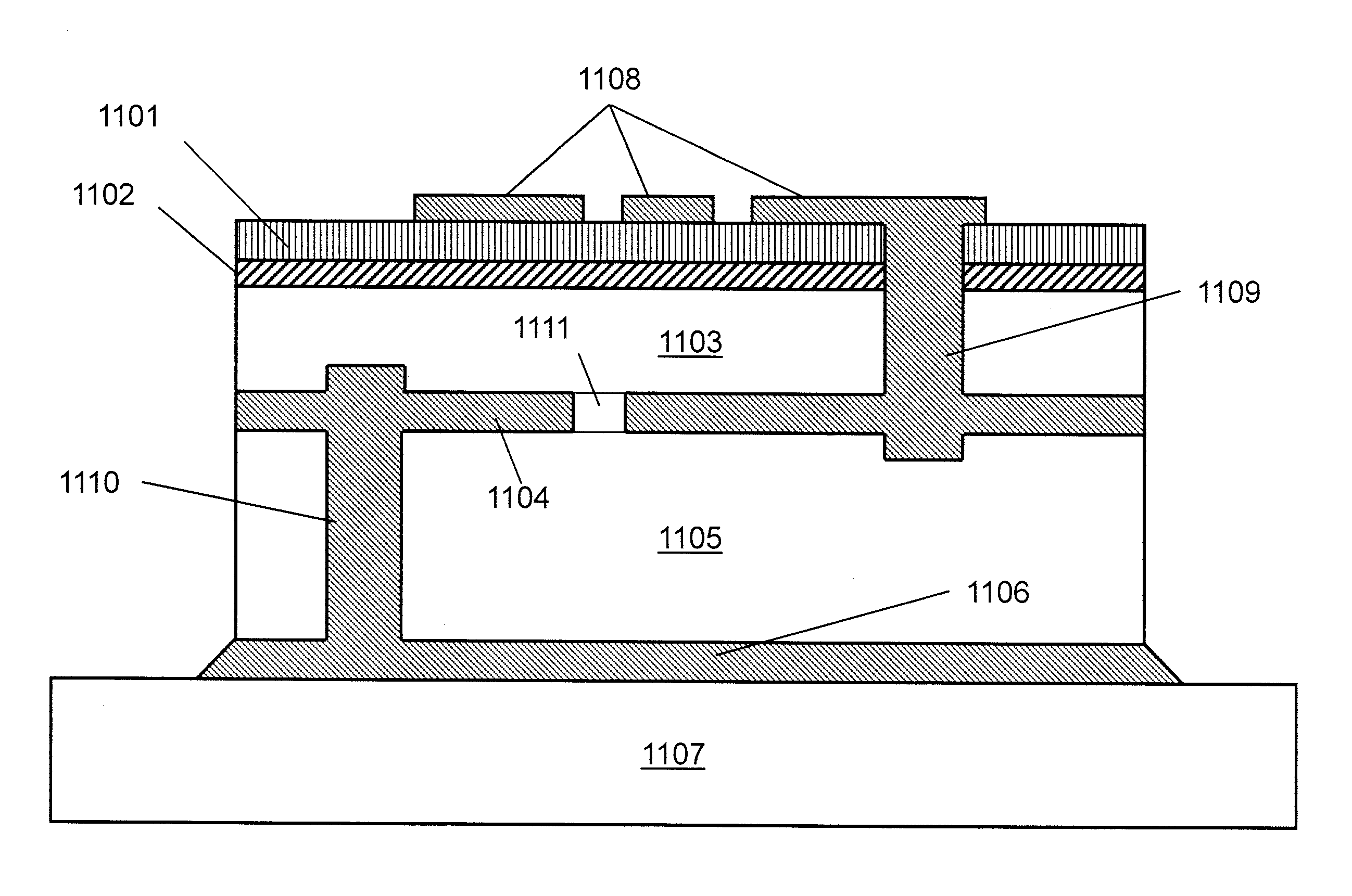
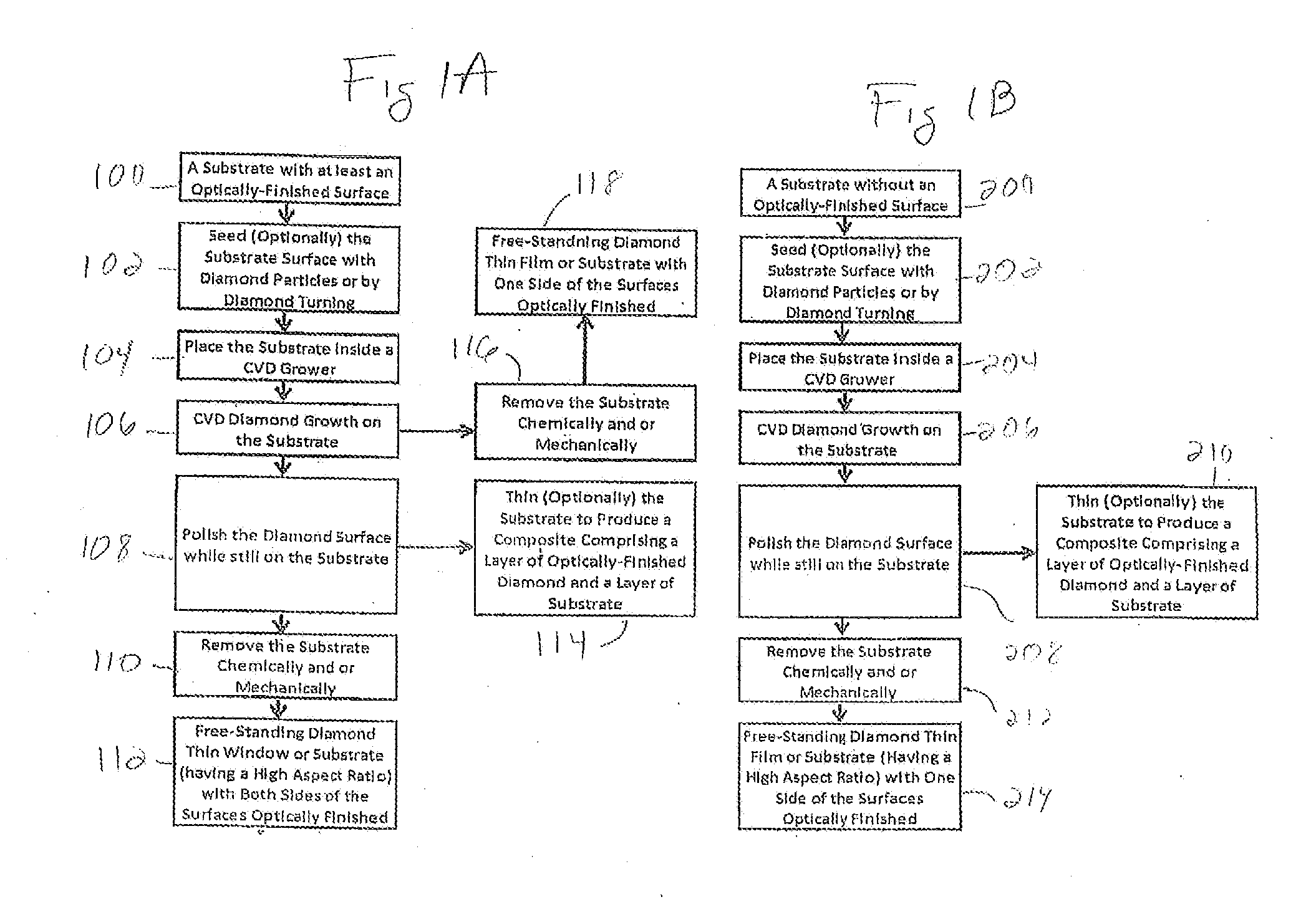
Optically-Finished Thin Diamond Substrate or Window of High Aspect Ratio and a Method of Production Thereof
In a method of forming a diamond film, substrate, or window, a silicon substrate is provided and the diamond film, substrate, or window is CVD grown on a surface of the silicon substrate. The grown diamond film, substrate, or window has an aspect ratio ≧100, wherein the aspect ratio is a ratio of a largest dimension of the diamond film, substrate or window divided by a thickness of the diamond film. The silicon substrate can optionally be removed or separated from the grown diamond film, substrate, or window.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Gallium-nitride-on-diamond wafers and devices, and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20140141595A1Reduce thermal resistanceLower bow of the wafersPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsWaferingWide gap semiconductors
Methods for integrating wide-gap semiconductors, and specifically, gallium nitride epilayers with synthetic diamond substrates are disclosed. Diamond substrates are created by depositing synthetic diamond onto a nucleating layer deposited or formed on a layered structure that comprises at least one layer made out of gallium nitride. Methods for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers with low bow and high crystalline quality are disclosed along with preferred choices for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers and chips tailored to specific applications.
Owner:AKASH SYST INC
Diamond based blue/UV emission source
A diamond based Blue / UV light emitting source is disclosed. The source includes a diamond substrate having a first conductivity type, a first aluminum gallium nitride layer above the diamond substrate having the same conductivity type as the substrate, a bulk or a quantum well structure on the AlGaN layer formed of a plurality of repeating sets of alternating layers selected from among GaN, InGaN, and AlInGaN, a second AlGaN layer on the quantum well or the bulk active layer having the opposite conductivity type as the first AlGaN layer, a contact structure on the second AlGaN layer having the opposite conductivity type from the substrate and the first AlGaN layer, an ohmic contact to the diamond substrate, and an ohmic contact to the contact structure.
Owner:INPHOT
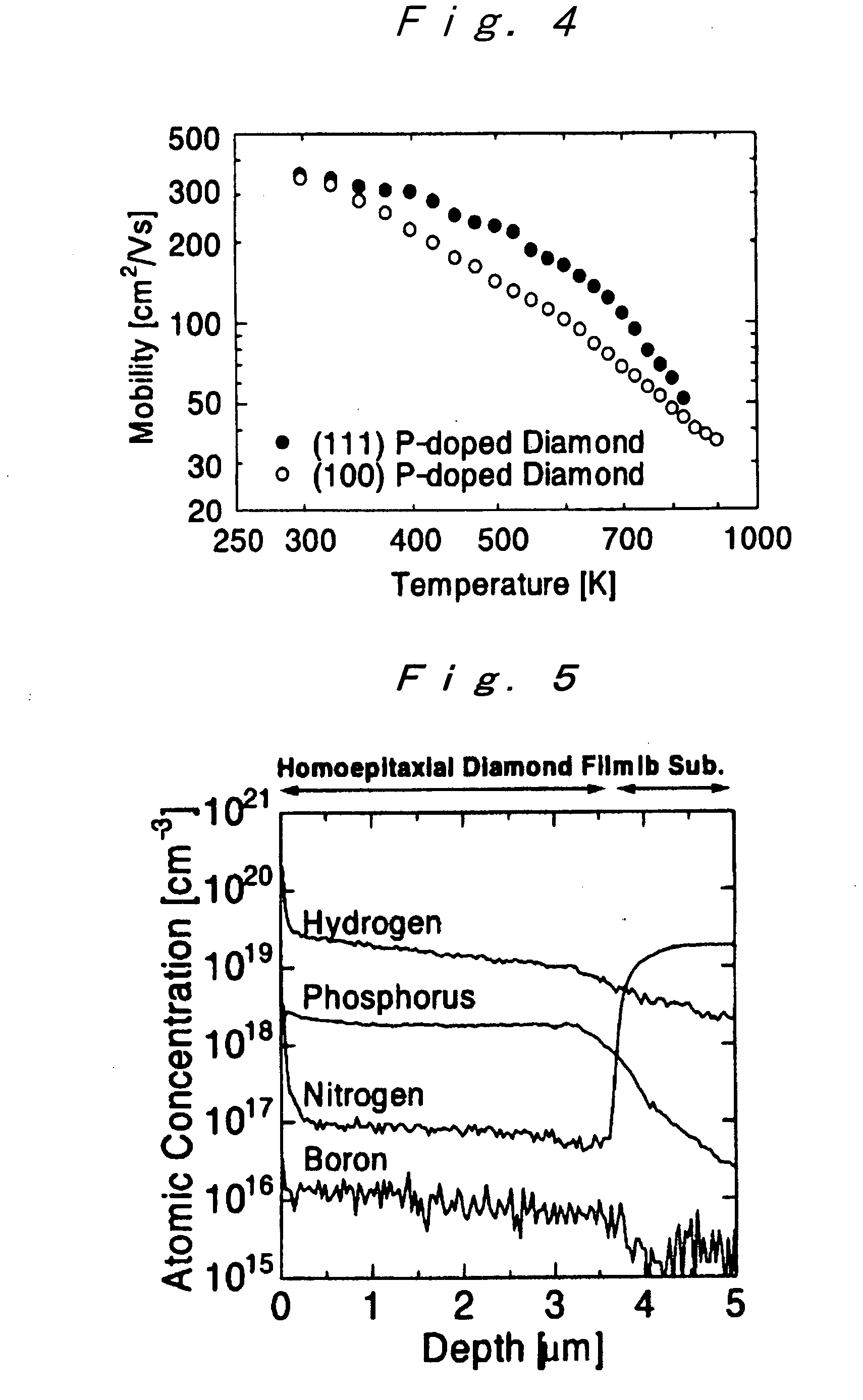
Film of N Type (100) Oriented Single Crystal Diamond Semiconductor Doped with Phosphorous Atoms, and a Method of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080193366A1Enlarging of area and flattening are easyBig impactPolycrystalline material growthUltra-high pressure processesHydrogenHydrogen atom
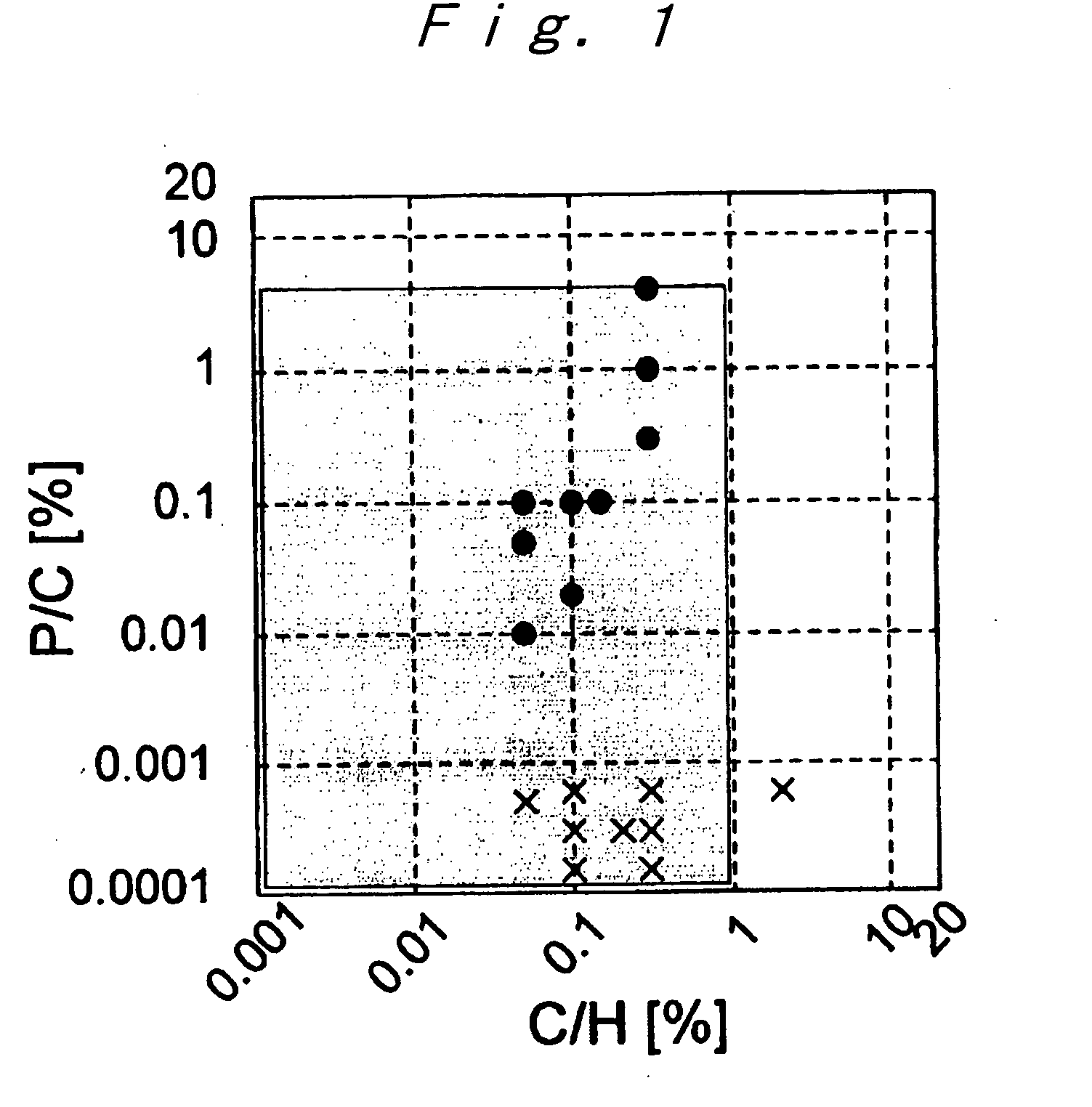
There is provided an n type (100) oriented single crystal diamond semiconductor film into which phosphorus atoms have been doped and a method of producing the same. The n type (100) oriented single crystal diamond semiconductor film, characterized in that (100) oriented diamond is epitaxially grown on a substrate under such conditions that; the diamond substrate (100) oriented diamond, a means for chemical vapor deposition provides hydrogen, hydrocarbon and a phosphorus compound in the plasma vapor phase, the ratio of phosphorus atoms to carbon atoms in the plasma vapor phase is no less than 0.1%, and the ratio of carbon atoms to hydrogen atoms is no less than 0.05%, and the method of producing the same.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Method of fabricating n-type semiconductor diamond, and semiconductor diamond
InactiveUS7172957B2Quality improvementIncrease surface areaPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesSingle crystalNon doped
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com