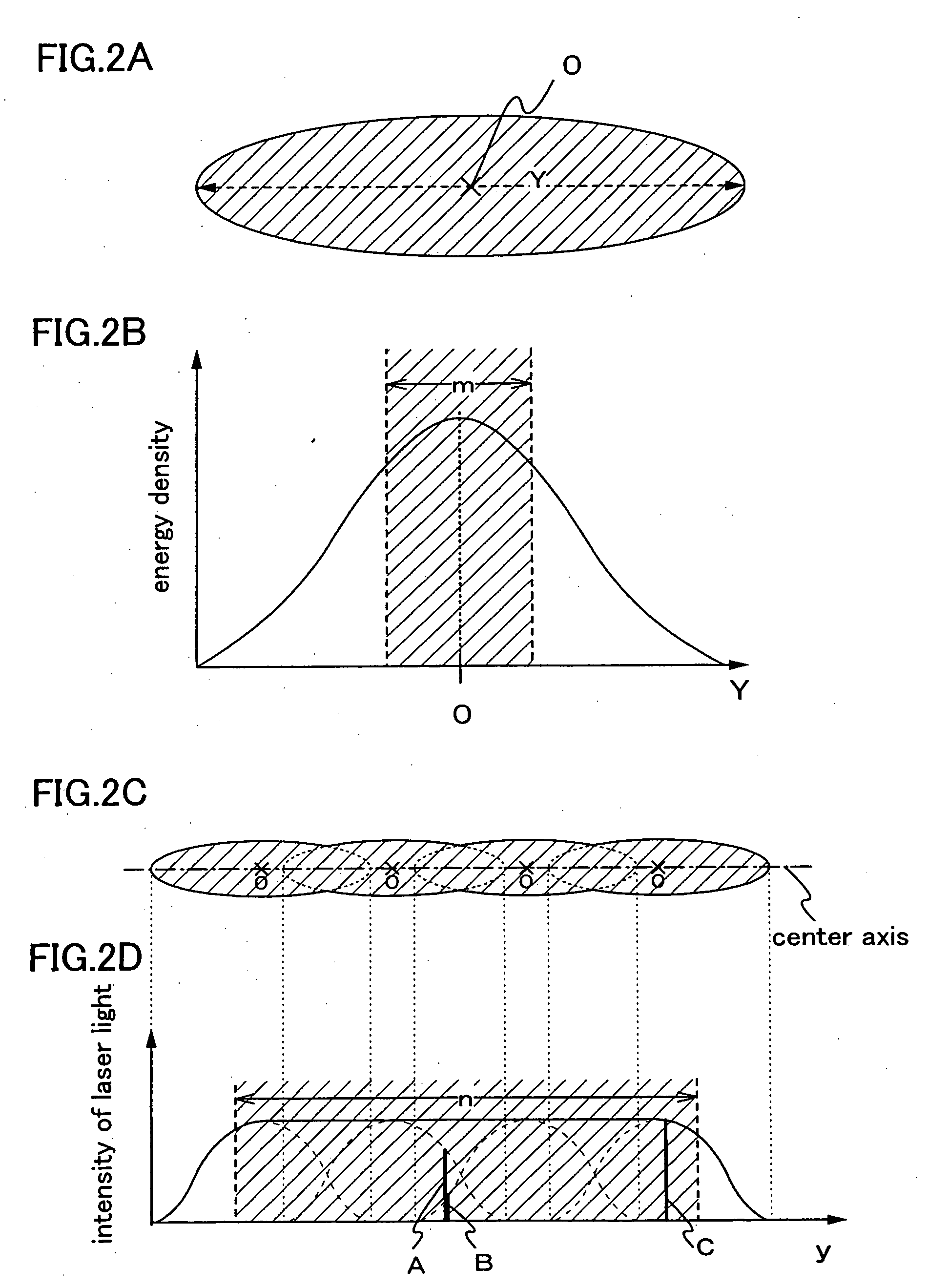
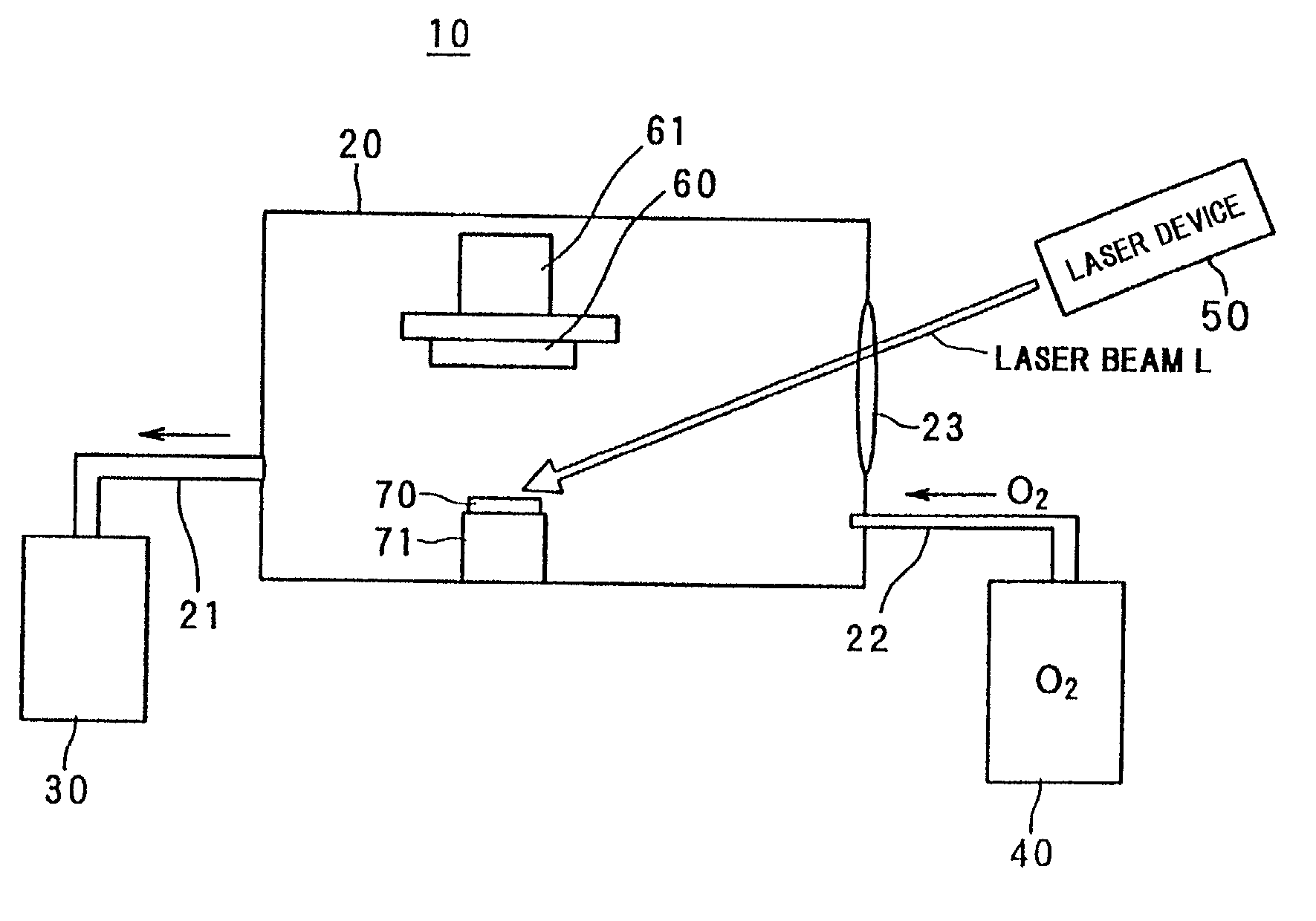
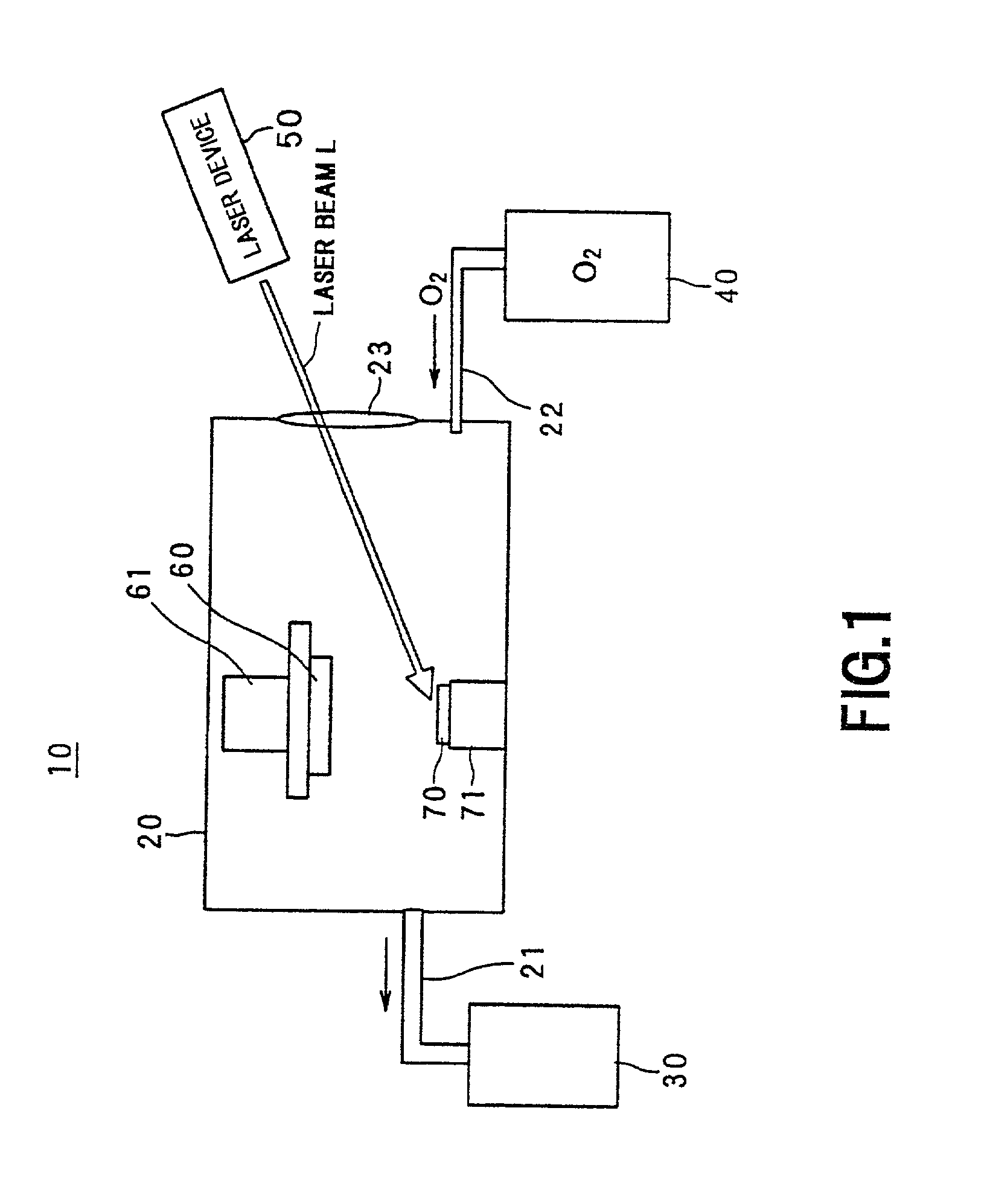
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
222 results about "Laser energy density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
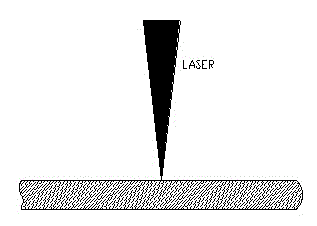
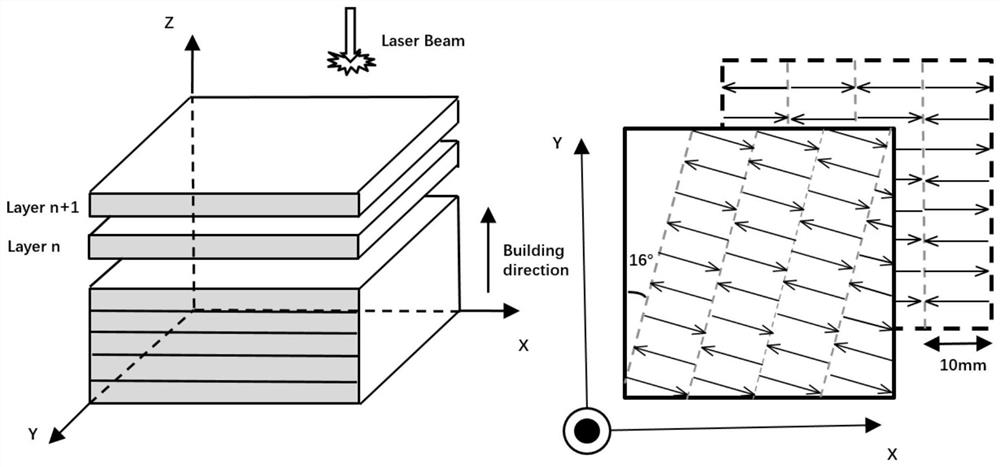
Laser energy density is considered a key factor that affects the properties of as-built parts fabricated by SLM processing. The widely used volume based energy density E (J/mm3) is defined in equation (1), where P is laser power (W), v is scan speed (mm/s), h is hatch spacing (mm) and. t is layer thickness (mm) [1].
Quick high-flexibility manufacturing method for ceramic circuit board
ActiveCN103188877AImprove bindingImprove thermal conductivityPrinted circuit manufactureLaser beam welding apparatusChemical platingChemical reaction
A quick high-flexibility manufacturing method for a ceramic circuit board comprises the following steps: irradiating laser on the surface of a ceramic matrix, and controlling the energy density of the laser to reach above the fracture threshold of the chemical bond of the compound containing active ions, so that chemical reaction occurs on the surface of the ceramic matrix, an active substance is separated out to serve as a chemical plating catalytic source, and the active substrate generated by the reaction and the matrix form chemical metallurgical bonding, wherein different laser sources are selected aiming at different ceramic materials according to the chemical bond energy of the ceramic material components, and the laser energy is controlled to reach the ceramic modified threshold by controlling the average power of laser output, pulse repetition frequency, scanning speed, defocusing amount, space between scanning line and scanning times; and the ceramic matrix modified by the laser is placed into a chemical plating solution to perform plating to form a metal coating. The surface of the ceramic is modified by the laser, so that a metal conductive layer and the matrix form chemical metallurgical bonding, the bonding force of the circuit board is greatly increased, and the heat-conducting property and the electric property are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNSHINE LASER & ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Method For Fabricating Thin Films
InactiveUS20090246530A1Small particle sizeEasily realizedLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge heatingSheet filmAlloy
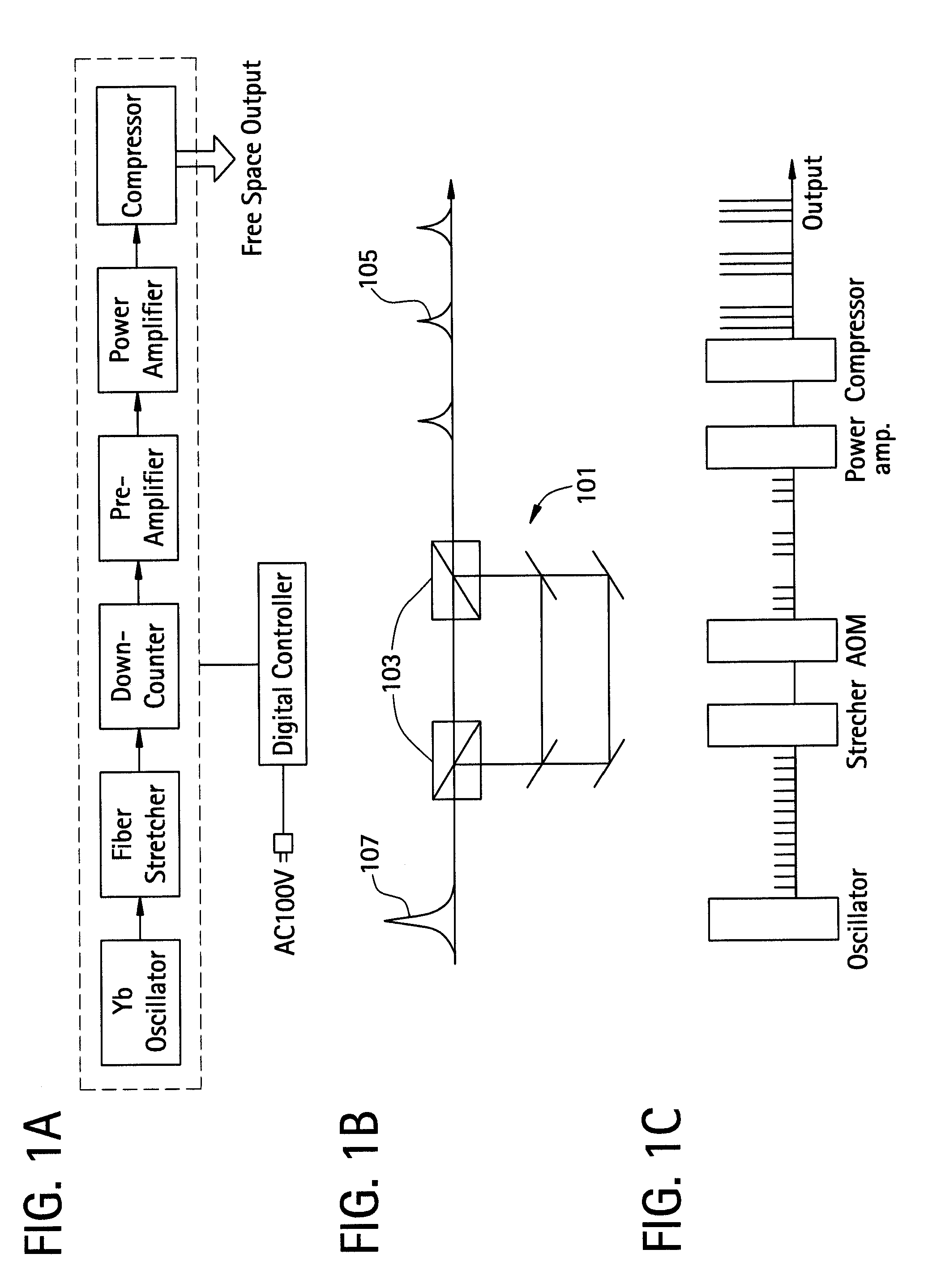
A method of pulsed laser deposition (PLD) capable of continuously tuning formed-film morphology from that of a nanoparticle aggregate to a smooth thin film free of particles and droplets. The materials that can be synthesized using various embodiments of the invention include, but are not limited to, metals, alloys, metal oxides, and semiconductors. In various embodiments a ‘burst’ mode of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation and deposition is provided. Tuning of the film morphology is achieved by controlling the burst-mode parameters such as the number of pulses and the time-spacing between the pulses within each burst, the burst repetition rate, and the laser fluence. The system includes an ultrashort pulsed laser, an optical system for delivering a focused onto the target surface with an appropriate energy density, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Ultraviolet method of embedding structures in photocerams
InactiveUS6932933B2Fast batch processingEasy to controlDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusUltravioletVolumetric Mass Density
A laser direct write method creates true three dimensional structures within photocerams using an focused pulsed ultraviolet laser with a wavelength in a weakly absorbing region of the photoceram material. A critical dose of focused laser UV light selectively exposes embedded volumes of the material for subsequent selective etching. The photoceram material exposure is nonlinear with the laser fluence and the critical dose depends on the square of the per shot fluence and the number of pulses. The laser light is focused to a focal depth for selective volumetric exposure of the material within a focal volume within the remaining collateral volumes that is critically dosed for selecting etching and batch fabrication of highly defined embedded structures.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
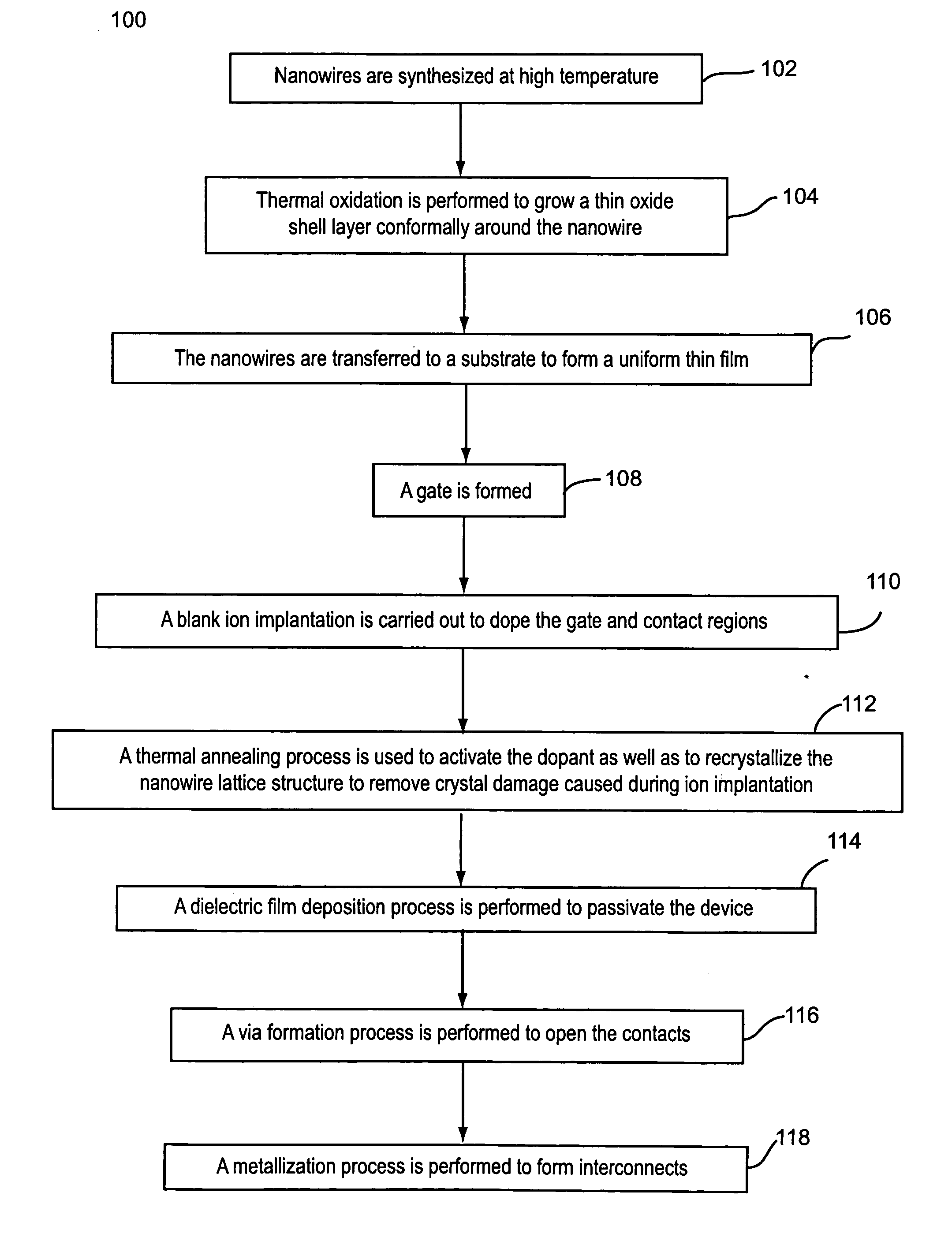
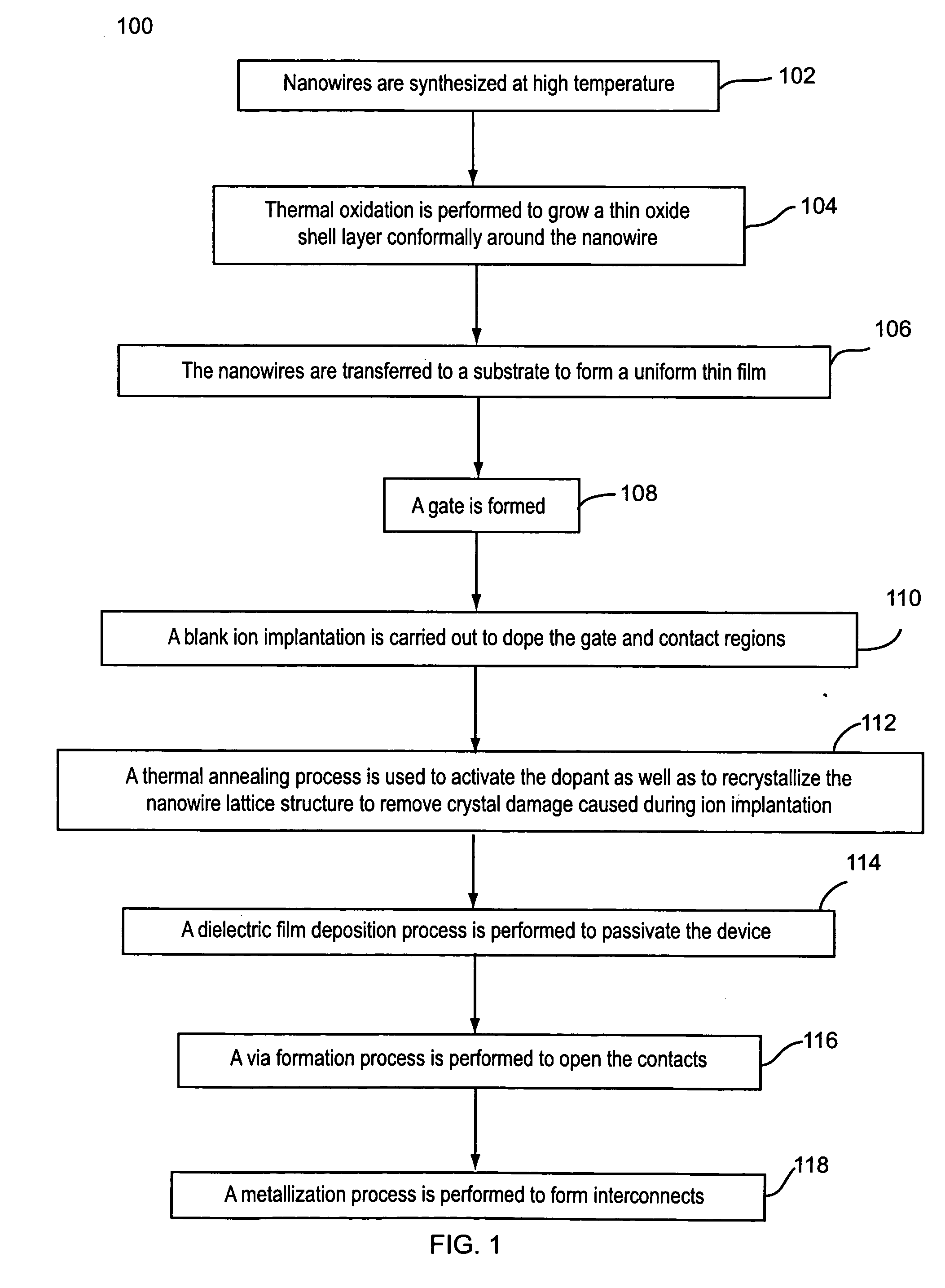
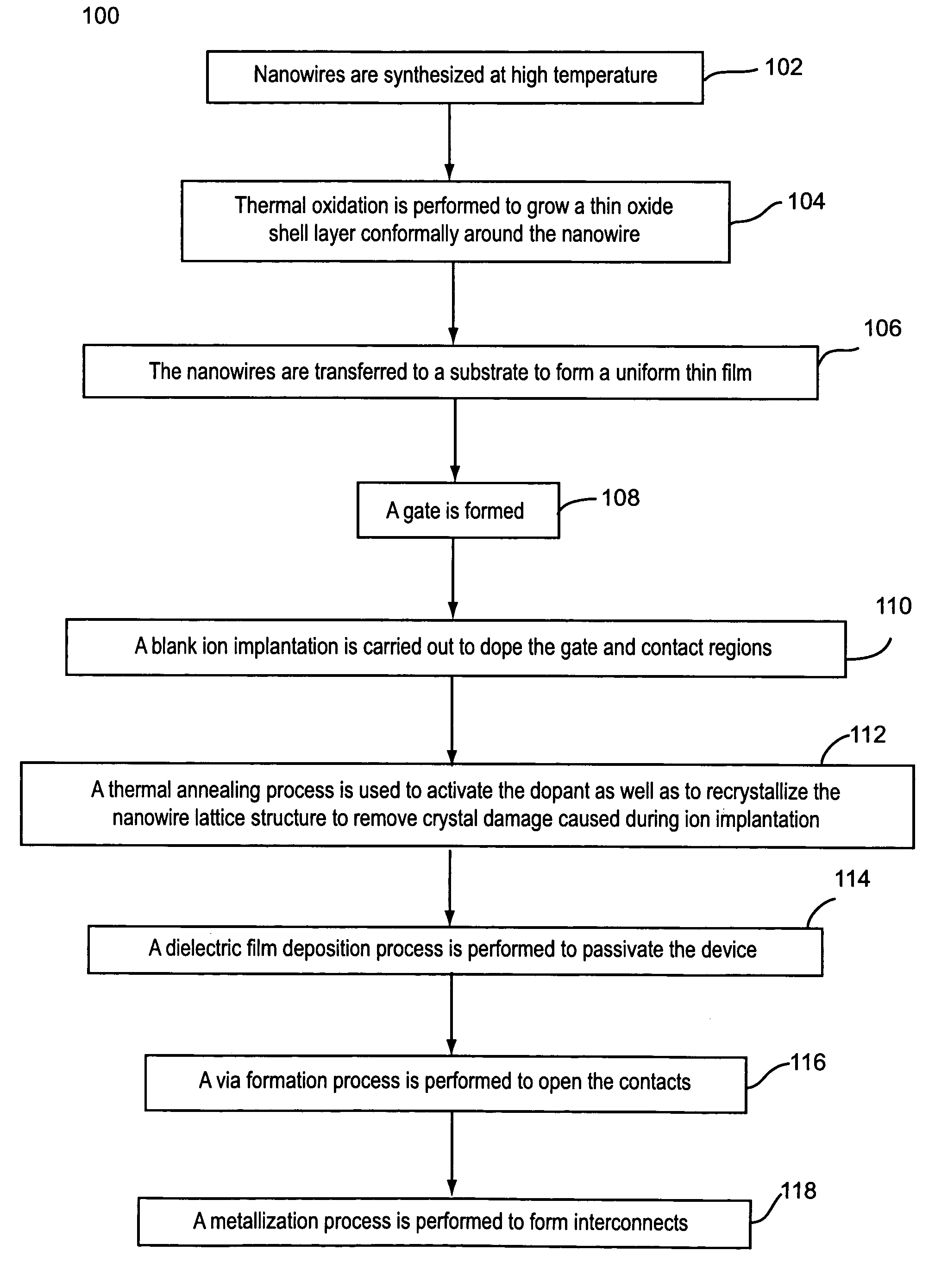
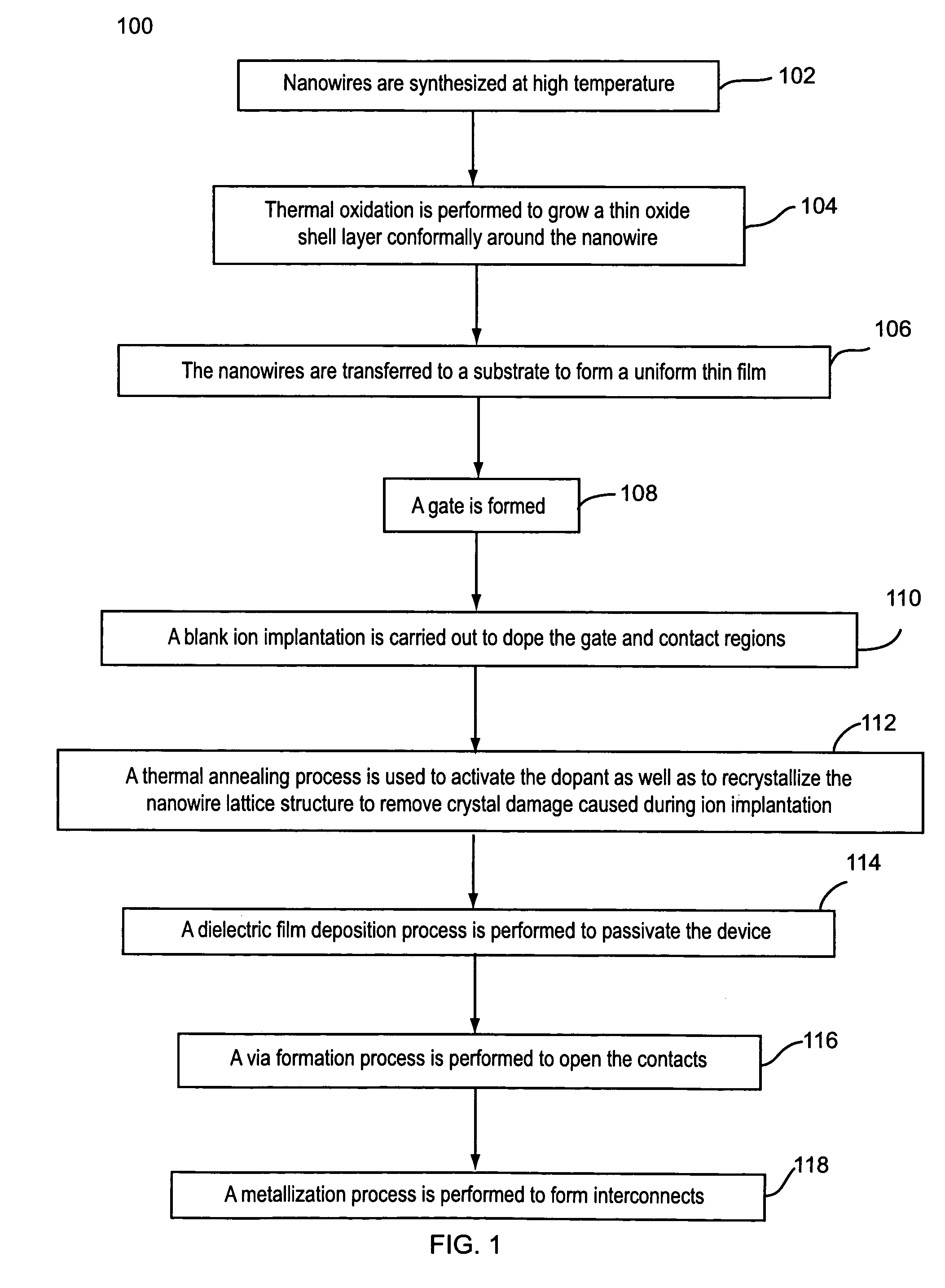
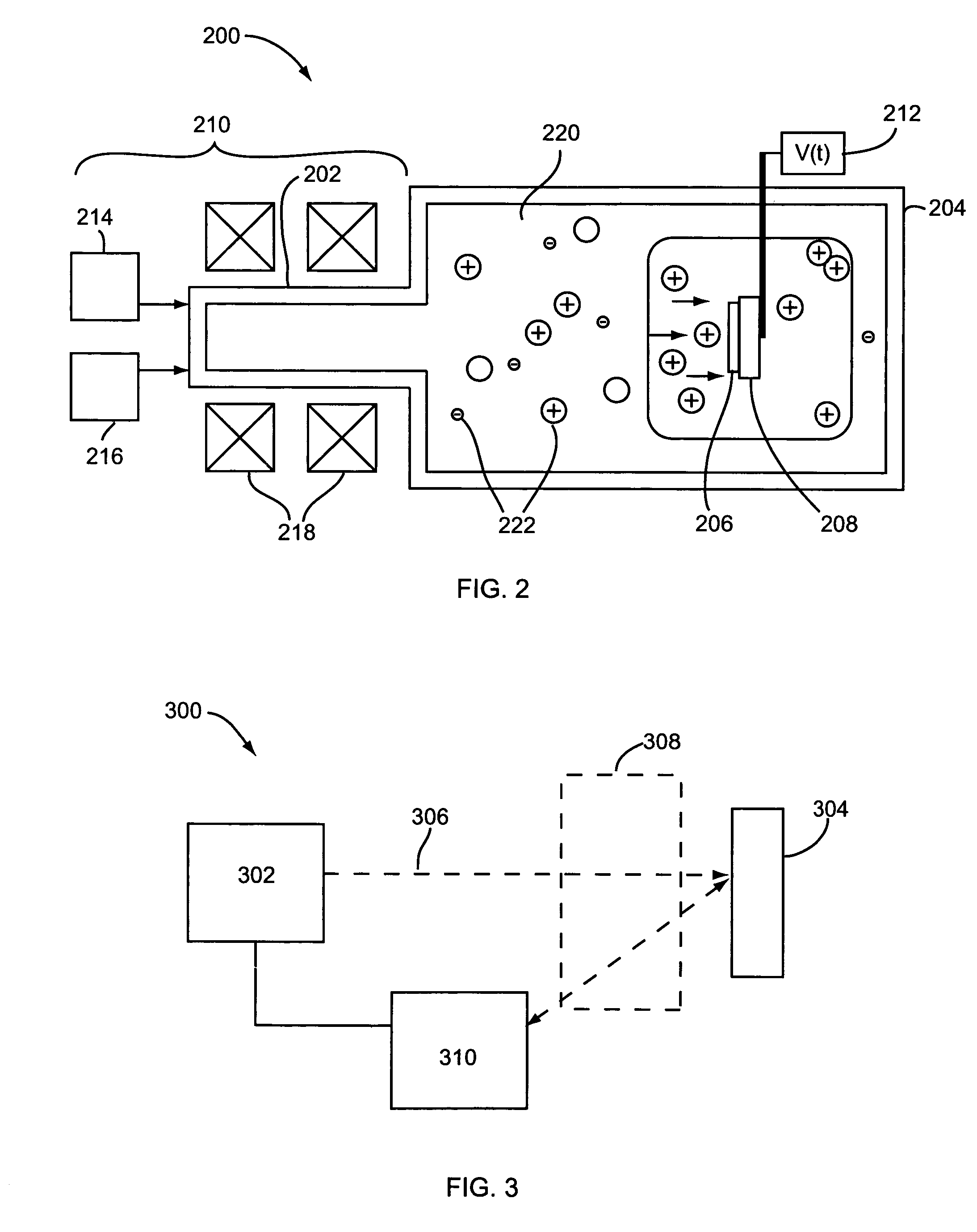
Contact doping and annealing systems and processes for nanowire thin films
InactiveUS20060234519A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanowireVolumetric Mass Density
Embodiments of the present invention are provided for improved contact doping and annealing systems and processes. In embodiments, a plasma ion immersion implantation (PIII) process is used for contact doping of nanowires and other nanoelement based thin film devices. According to further embodiments of the present invention, pulsed laser annealing using laser energy at relatively low laser fluences below about 100 mJ / cm2 (e.g., less than about 50 mJ / cm2, e.g., between about 2 and 18 mJ / cm2) is used to anneal nanowire and other nanoelement-based devices on substrates, such as low temperature flexible substrates, e.g., plastic substrates.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Femtosecond laser processing device and method for rapid deep etching of silicon carbide
ActiveCN110385521AFast etch qualityImprove etch qualityLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingLaser processing
The invention discloses a femtosecond laser processing device and method for rapid deep etching of silicon carbide. The femtosecond laser processing device mainly comprises a laser source module, a laser motion module, a shaping and focusing module, an auxiliary gas module and a laser etching module. According to the device and method, a focal plane is calibrated, a protection layer is prepared, an etching path is planned, layer-by-layer scanning etching is carried out according to parameter groups, and micro-chips are removed, so that deep etching of silicon carbide is realized. According tothe method, due to the fact that a femtosecond laser is used for processing silicon carbide, factors influencing the etching quality are controlled, namely, the laser energy density, the light spot overlapping rate and the line overlapping rate, and therefore silicon carbide is subjected to rapid and high-quality deep etching in a layer-by-layer scanning manner and a continuous feeding processingmanner according to the planned etching path.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Laser dissipation spot path, two-color and three-color laser source
InactiveCN105137610ASolve light decayReduce accumulationProjectorsColor television detailsDiffusionOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a laser dissipation spot path, which is used for receiving a laser emergent light, and comprises a beam shrinking lens group arranged on the laser emergent light path and a diffusion sheet, wherein the beam shrinking lens group comprises a first beam shrinking lens and a second beam shrinking lens, and the diffusion sheet is located between the first beam shrinking lens and the second beam shrinking lens. Through arranging the diffusion sheet between the first beam shrinking lens and the second beam shrinking lens, the area of a laser spot received on the diffusion sheet can be increased, the received laser energy density is reduced, a dust or particle accumulation phenomenon on the diffusion sheet is lessened, a decay phenomenon is lessened, and the laser source service life can be prolonged. The invention also discloses a two-color laser source and a three-color laser source by using the above laser dissipation spot path.
Owner:HISENSE
Method for fabricating thin films
A method of ultrashort pulsed laser deposition (PLD) capable of continuously tuning formed-film morphology from that of a nanoparticle aggregate to a smooth thin film completely free of particles and droplets. The materials that can be synthesized using various embodiments of the invention include, but are not limited to, metals, alloys, metal oxides, and semiconductors. A ‘burst’ mode of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation and deposition is provided, where each ‘burst’ contains a train of laser pulses. Tuning of the film morphology is achieved by controlling the burst-mode parameters such as the number of pulses and the time-spacing between the pulses within each burst, the burst repetition rate, and the laser fluence. The system includes an ultrashort pulsed laser, an optical setup for delivering the laser beam such that the beam is focused onto the target surface with an appropriate average energy density (fluence), and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Laser ablation method for patterning a thin film layer
InactiveUS20050231105A1Increase energy densityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDielectricFluorescence
Owner:IFIRE IP CORP
3D projection type photocuring 3D printing machine
The invention discloses a 3D projection type photocuring 3D printing machine which comprises a 3D projection system, a resin box and a laser device controlled by a computer. The 3D projection system is composed of an x-y scanning galvanometer and a galvanometer in the Z axis direction. The resin box is made of a material with the transparent periphery. Photosensitive resin is poured into the resin box in advance. A three-dimensional model is spliced into a two-dimensional face pattern in the Z axis direction according to the molding accuracy. Lasers are controlled by the computer to pass through the Z-axis focusing galvanometer and x-y scanning galvanometer, and a three-dimensional image is formed in the liquid photosensitive resin. The energy density of the laser focus is the highest so that the photosensitive resin can be cured, and due to the fact that the laser energy density of other regions is low, the photosensitive resin still keeps in a liquid state. Through irradiation, the required three-dimensional model is cured in the liquid. Different from an existing layer-by-layer scanning and curing manner, the molding speed is increased greatly, and the molding size depends on the scanning range of the scanning galvanometer.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Contact doping and annealing systems and processes for nanowire thin films
Embodiments of the present invention are provided for improved contact doping and annealing systems and processes. In embodiments, a plasma ion immersion implantation (PIII) process is used for contact doping of nanowires and other nanoelement based thin film devices. According to further embodiments of the present invention, pulsed laser annealing using laser energy at relatively low laser fluences below about 100 mJ / cm2 (e.g., less than about 50 mJ / cm2, e.g., between about 2 and 18 mJ / cm2) is used to anneal nanowire and other nanoelement-based devices on substrates, such as low temperature flexible substrates, e.g., plastic substrates.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
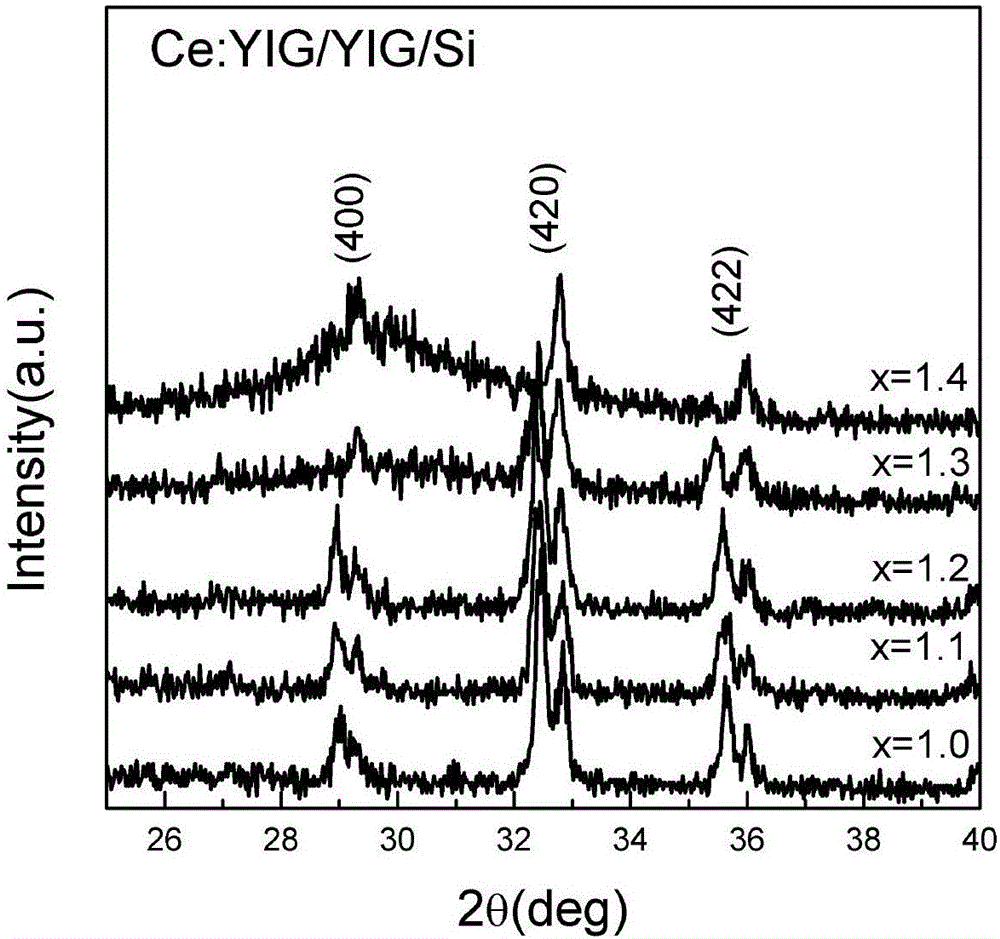
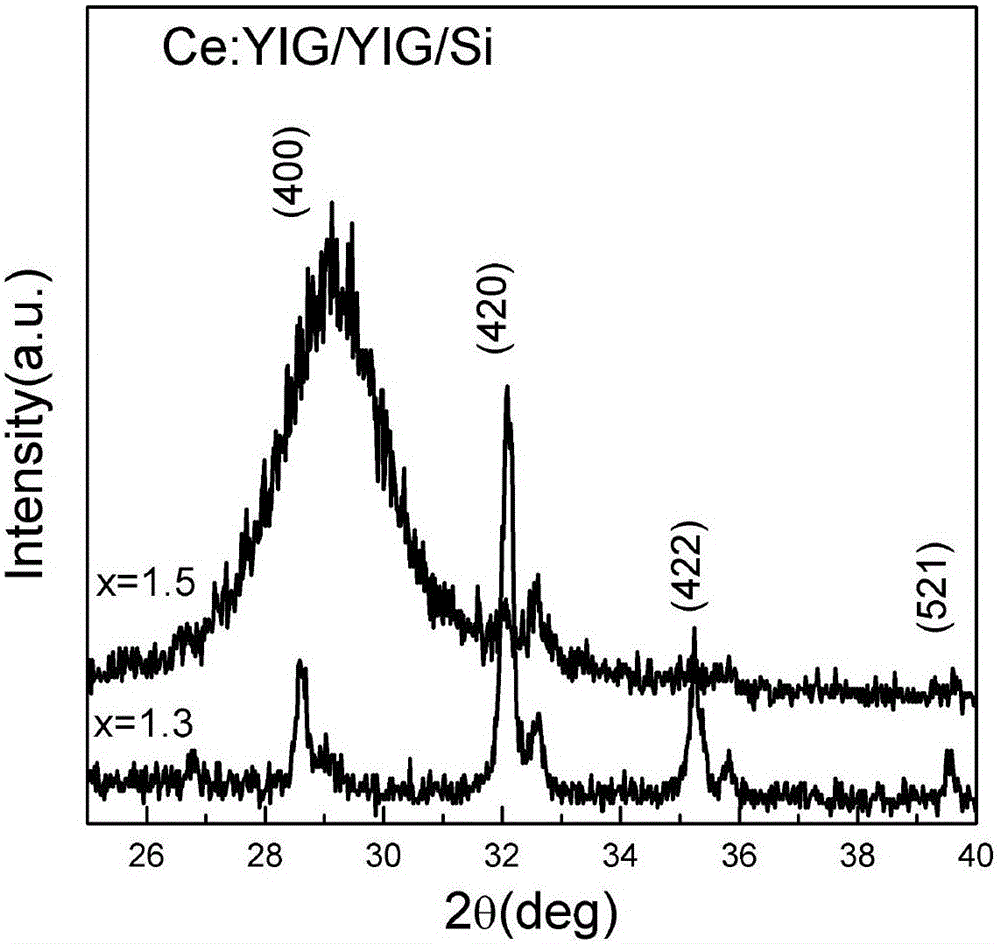
Preparation method for directly growing highly-doped yttrium iron garnet film on silicon
ActiveCN105714379AEnhanced magneto-optical performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsDeposition temperatureRare earth
The invention belongs to the technical field of production of magnetic oxide films, and particularly relates to a preparation method for directly growing a highly-doped yttrium iron garnet film on silicon. The laser energy density in the growth process of a rare earth-doped yttrium iron garnet film is changed from 1.8 J / cm<2> to 4.0 J / cm<2>, the film deposition temperature is changed from 400 DEG C to 850 DEG C, and the film deposition air pressure is changed from 1 mTorr to 20 mTorr, so that the rare earth doping concentration in the yttrium iron garnet film growing on a silicon substrate is improved from 33% to 50%, the Faraday optical constant of the material in photo-communication 1550 nm wavelengths is improved from 2800 degrees / cm to 6000 degrees / cm, and the magneto-optical property of the material is greatly enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
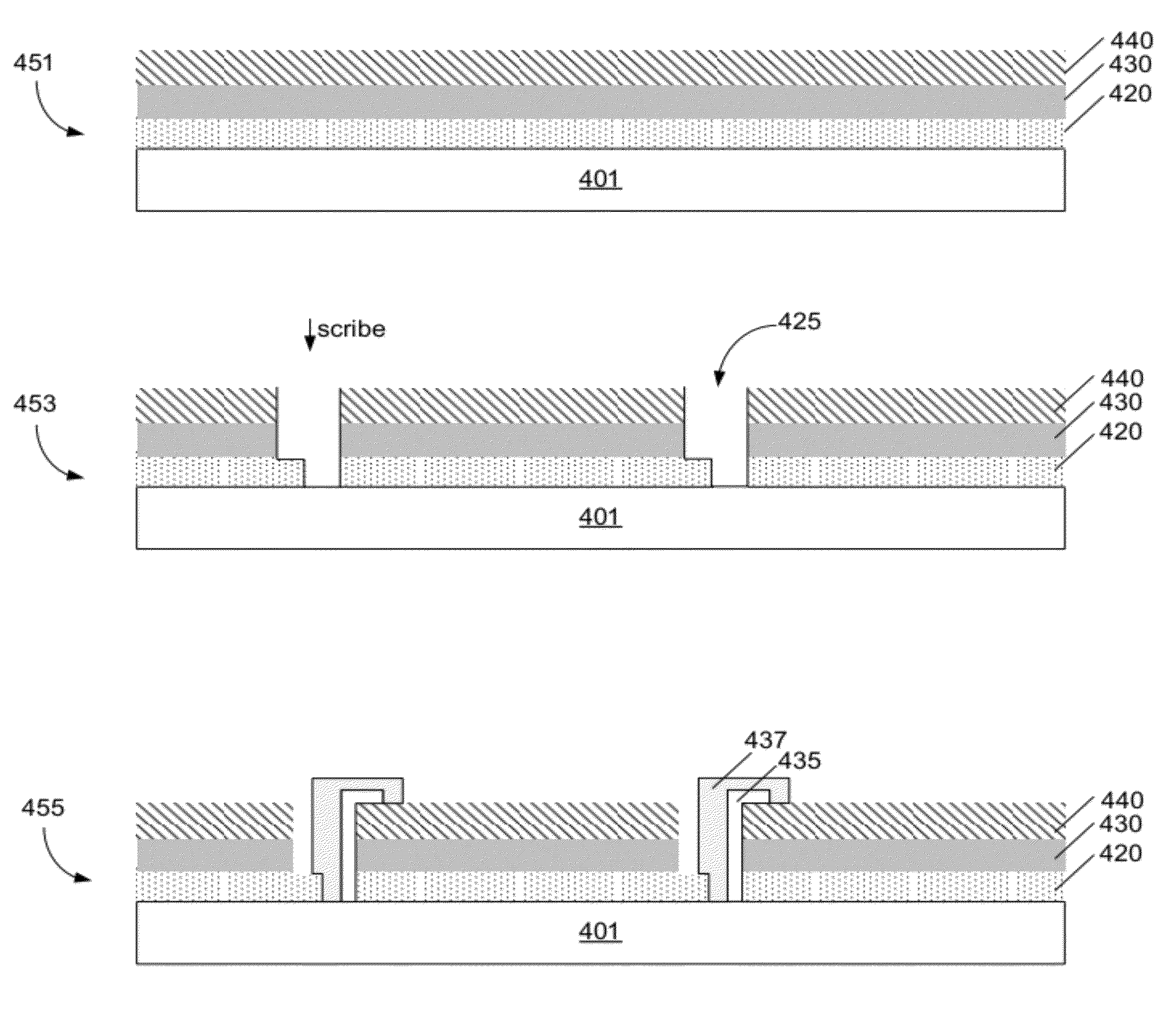
Ablative scribing of solar cell structures
InactiveUS20120094425A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationMedicineLaser scribing
Provided herein are improved methods of laser scribing photovoltaic structures to form monolithically integrated photovoltaic modules. The methods involve forming P1, P2 or P3 scribes by an ablative scribing mechanism having low melting, and in certain embodiments, substantially no melting. In certain embodiments, the methods involve generating an ablation shockwave at an interface of the film to be removed and the underlying layer. The film is then removed by mechanical shock. According to various embodiments, the ablation shockwave is generated by using a laser beam having a wavelength providing an optical penetration depth on the order of the film thickness and a minimum threshold intensity. In some embodiments, photovoltaic materials can be scribed using picosecond pulse widths and certain wavelength and laser fluence levels.
Owner:MIASOLE
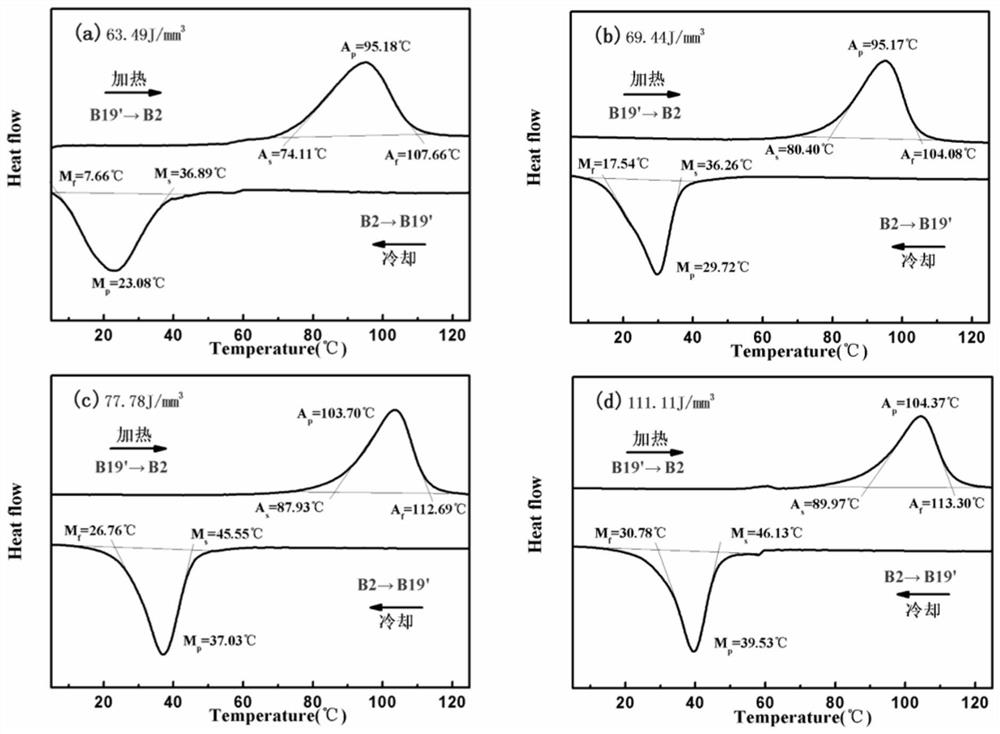
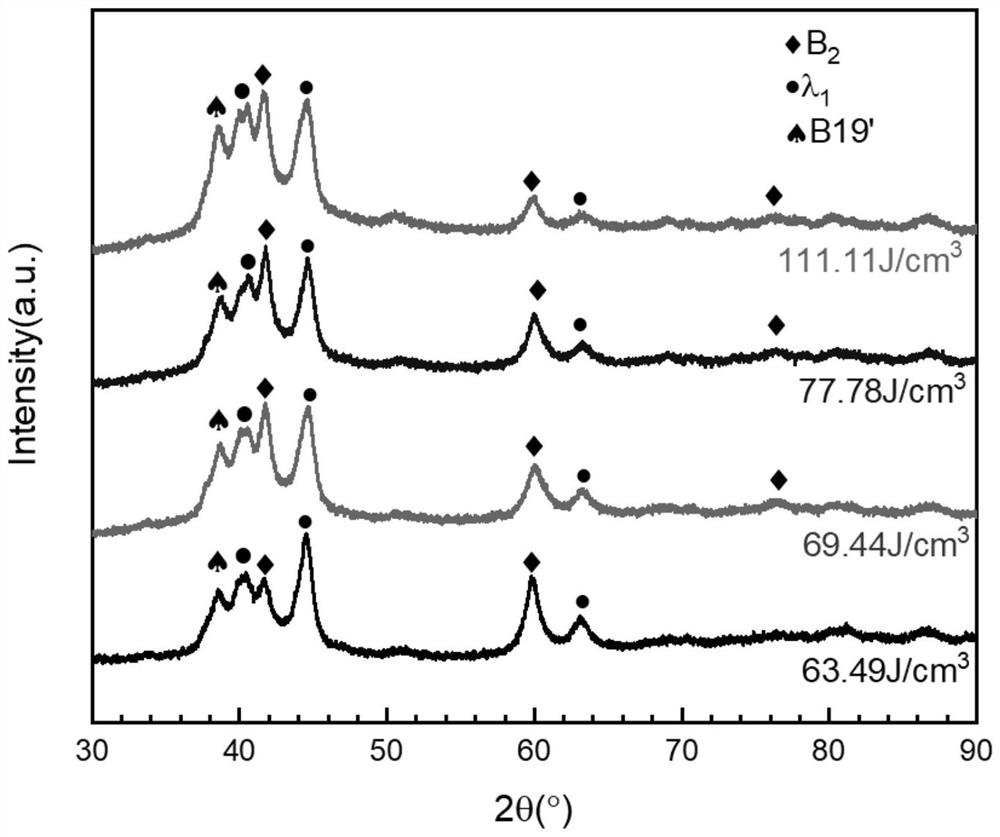
4D printing method of nickel-titanium-based ternary shape memory alloy
InactiveCN111842888AHas shape memory effectRaise the transition temperatureAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingBinary alloy
The invention belongs to the technical field of 4D printing additive manufacturing, and discloses a 4D printing method of a nickel-titanium-based ternary shape memory alloy. The 4D printing method ischaracterized in that a selective laser melting technology is adopted for printing gas atomized prefabricated NiTiZr ternary alloy powder, and a component obtained through printing has the shape memory function; and the laser energy density is changed by changing the technological parameters adopted in the selective laser melting technology, and therefore the changes of the structure and performance of the printed piece are regulated and controlled. According to the 4D printing method, the ternary component Zr is introduced into an existing nickel-titanium binary alloy, the martensite phase transformation temperature is obviously increased, the selective laser melting technology is adopted for forming, and complex parts uniform in structure and high in density can be obtained while the excellent shape memory performance and mechanical performance are guaranteed.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
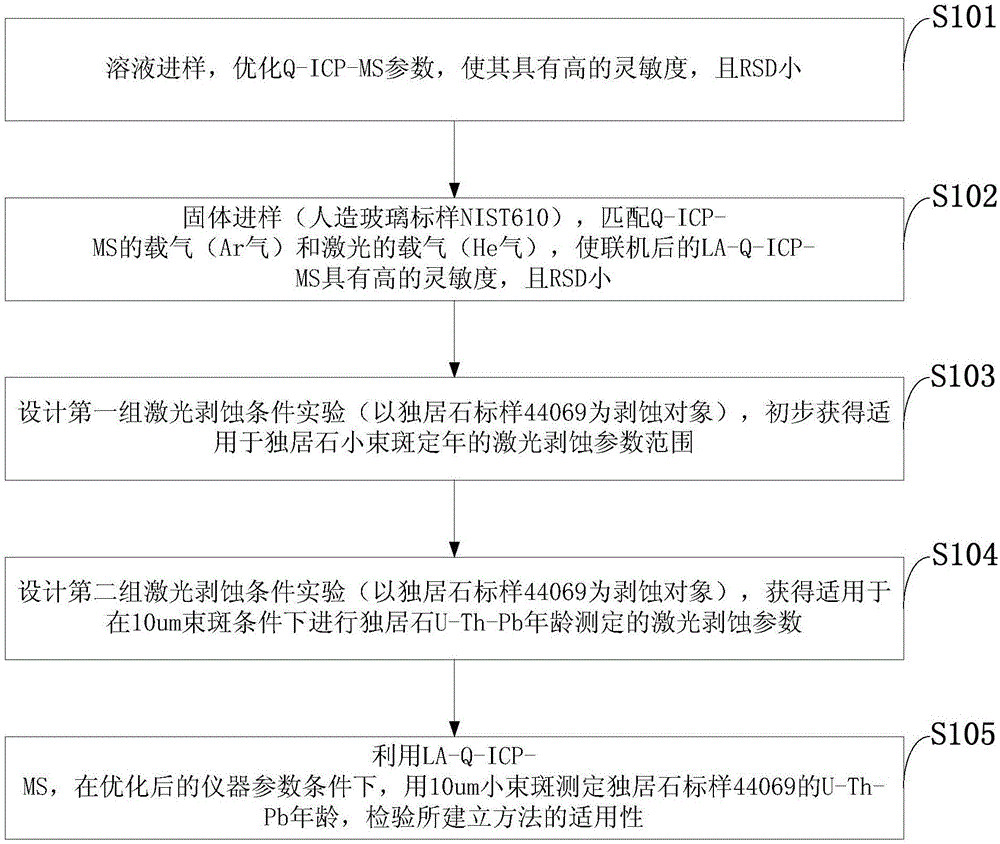
Monazite 10-micron small-beam-spot LA-Q-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb age determination method
ActiveCN106124606AIncreased Elemental Response StrengthGuarantee optimal detection statusMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRelative standard deviationMass analyzer
The invention discloses a monazite 10-micron small-beam-spot LA-Q-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb age determination method. The method includes the steps that a standard solution sample with the concentration of 1 ppb is directly led into a four-level-rod inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer, the instrument parameters are optimized, the response strength of <205>T1 is larger than 200,000 cps / ppb, the relative standard deviation is 1% to 2%, the double charges are smaller than 1.5%, and the yield of oxidation is smaller than 1%; an artificial glass NTSI 610 solid standard sample is led into the four-level-rod inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer in a laser ablation mode, carrier gas of a laser and carrier gas of the four-level-rod inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer are matched, and counting of <238>U reaches the maximum; a monazite standard sample 44069 is led into the four-level-rod inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer in a laser ablation mode, the density of laser energy is 3 J / cm<2>, the impulse frequency is 4 Hz, and the age of monazite U-Th-Pb is determined through a 10-micron small laser beam spot. By means of the method, the space resolution ratio of monazite LA-Q-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb age determination is increased, and the testing requirement of monazite is met.
Owner:XIAN CENT OF GEOLOGICAL SURVEY CGS
Preparation method of high-accuracy ceramic printed circuit board
ActiveCN104105353AReduce widthImprove edge qualityPrinted circuit manufactureChemical platingHeat-affected zone
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-accuracy ceramic printed circuit board. The preparation method comprises the steps of radiating laser on the surface of a ceramic substrate covered with a palladium ion solid film, controlling the energy density of the laser to reach above a modified threshold of the substrate, allowing a V-shaped microgroove structure to be formed on the surface of the ceramic substrate, allowing a palladium ion in a microgroove to be reduced to an atom state, bonding the palladium ion with an oxygen atom at a high temperature to form palladium oxide with very high chemical stability, forming firm metallurgical bonding with the substrate, allowing the structure on the surface of the substrate in a heat affected zone of the laser not to be changed, and only allowing the palladium ion to be reduced to metal palladium. Metal palladium in the heat affected zone is selectively removed by the chemical cleaning step; palladium oxide in the microgroove structure is left as an active center of catalytic chemical plating reaction; and then a high-accuracy conducting circuit can be obtained by implementing chemical plating. According to the preparation method, the conducting circuit can be quickly prepared on the surface of the ceramic substrate; the preparation method has no special requirement for a material of the substrate; and the obtained conducting circuit is high in accuracy, good in conductivity and high in binding force.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
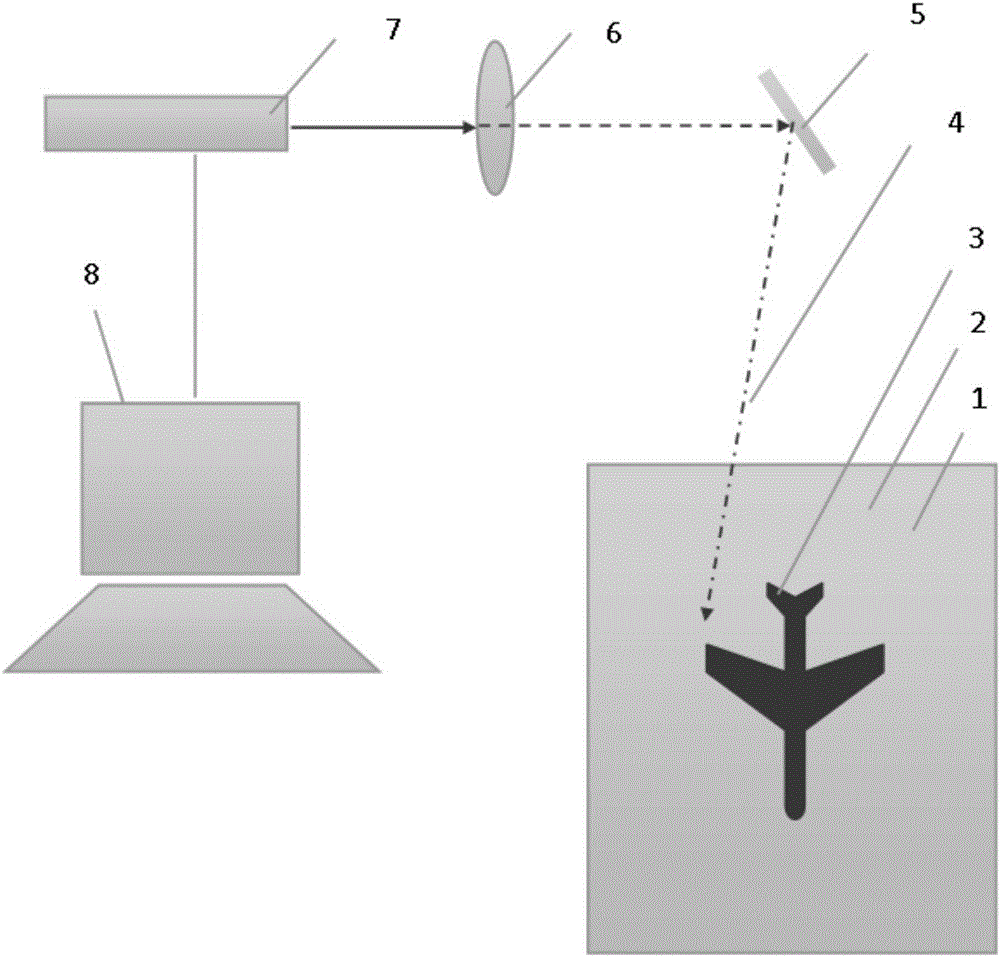
Laser irradiating apparatus and method of manufacturing semiconductor apparatus
InactiveUS20070059949A1Decrease depression and projectionFlat surfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusLaser lightOxygen
First laser light is irradiated (energy density of 400 to 500 mj / cm2) to a semiconductor film 102 in an atmosphere containing oxygen in order to obtain a semiconductor film 102b having large depressions and projections on the surface. Then, an oxidized film 105a formed by the irradiation of the first laser light is removed. After that, an inert gas with an oxygen density of 10 ppm or below is blown thereto, and, at the same time, second laser light is irradiated thereto (the energy density is higher than that of the irradiation of the first laser light). Thus, the surface of the semiconductor film 102b is flattened, and a semiconductor film 102c having fewer depressions and projections on the surface can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser irradiation method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060009016A1Reduce energy densitySufficient energySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusLaser lightVolumetric Mass Density
An objective of the present invention is to provide a laser crystallizing method capable of suppressing a thermal damage on a substrate as well as enhancing a substrate processing efficiency, and a laser irradiation apparatus using the laser crystallizing method. Laser lights oscillated from plural laser oscillating apparatuses are synthesized into one laser light and in a scanning direction of the laser light thus obtained, areas having an energy density lower than a predetermined level are cut with a slit. With the above construction, an average value of laser light energy densities can be increased in the scanning direction. Therefore, laser light irradiation time per area can be suppressed and in addition, a heat quantity applied to an object to be processed can be increased in total. Accordingly, a crystallinity of a semiconductor film can be increased while preventing the substrate from being excessively heated.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for forming porous film, insulating film for semiconductor element, and method for forming such insulating film
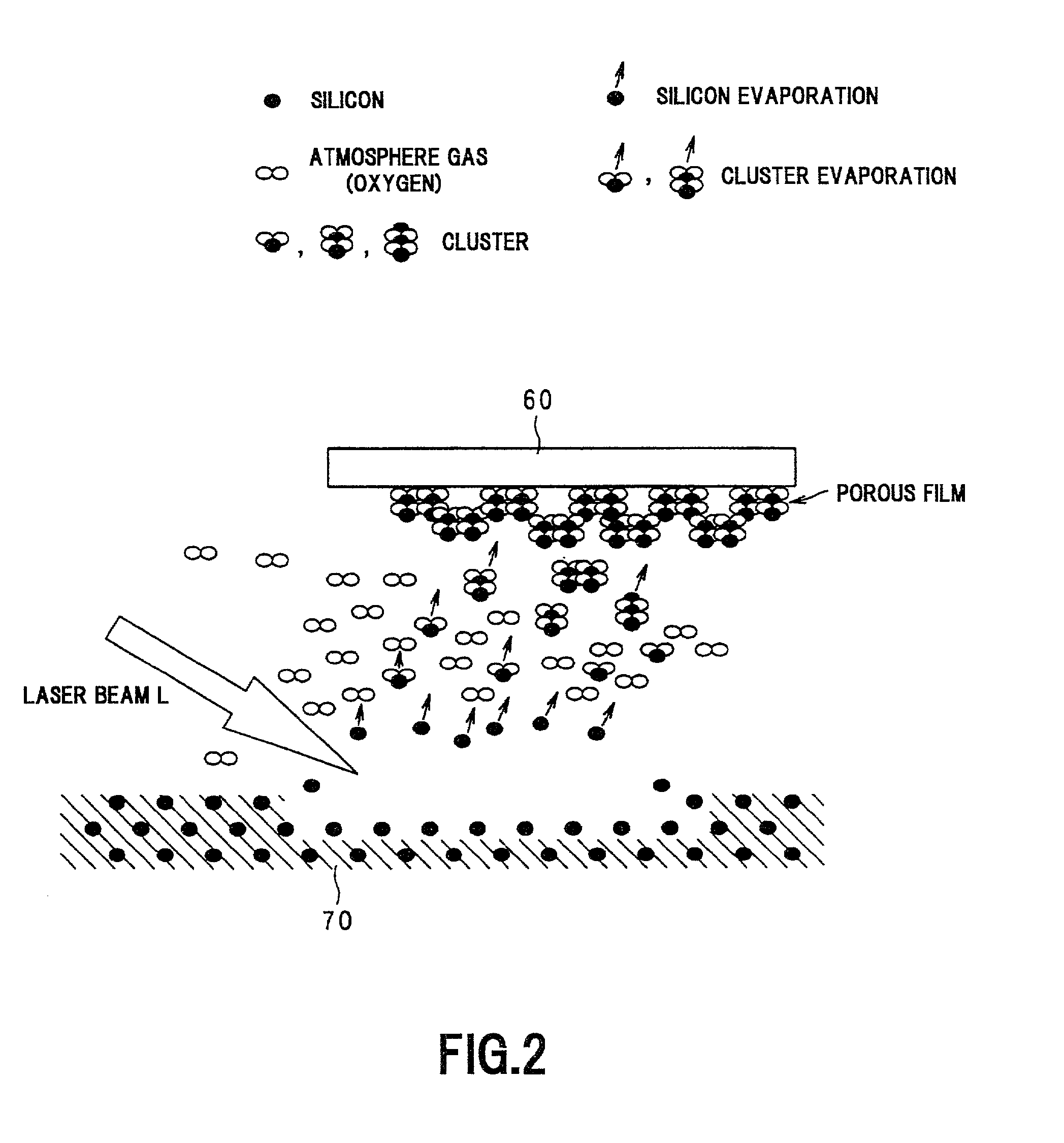
InactiveUS20020031917A1Low costWell formedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGas phaseVolumetric Mass Density
When laser ablation is implemented with respect to a target comprising silicon in an atmosphere containing oxygen, Si constituting the target is ejected from the laser irradiated portion thereof. The ejected Si collides with oxygen, which is the atmosphere gas, and reacts therewith in a gas phase forming clusters composed of SiO2 or SiOx, or silicon (Si) and oxygen, and containing pores with a size of several nanometers. The clusters adhere to the substrate, thereby forming a porous film composed of Si and oxygen and containing pores on the substrate. Furthermore, an insulating film for a semiconductor element is formed to have a multilayer structure in which an aggregate is deposited on the substrate and then a dense film is formed. When the insulating film is formed, the aggregate is produced by implementing laser ablation under a pressure of 1 Kpa, for example. Then, a pressure transition from this 1 KPa to 10 Pa, for example, is caused and a dense film is formed by implementing laser ablation under this pressure of this 10 Pa by adjusting a parameter (for example, laser energy density) other than pressure. The thickness of each layer in the multilayer structure composed of the aggregate and dense film and the thickness ratio of the layers is adjusted by adjusting the number of times the target is irradiated with the laser beam.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
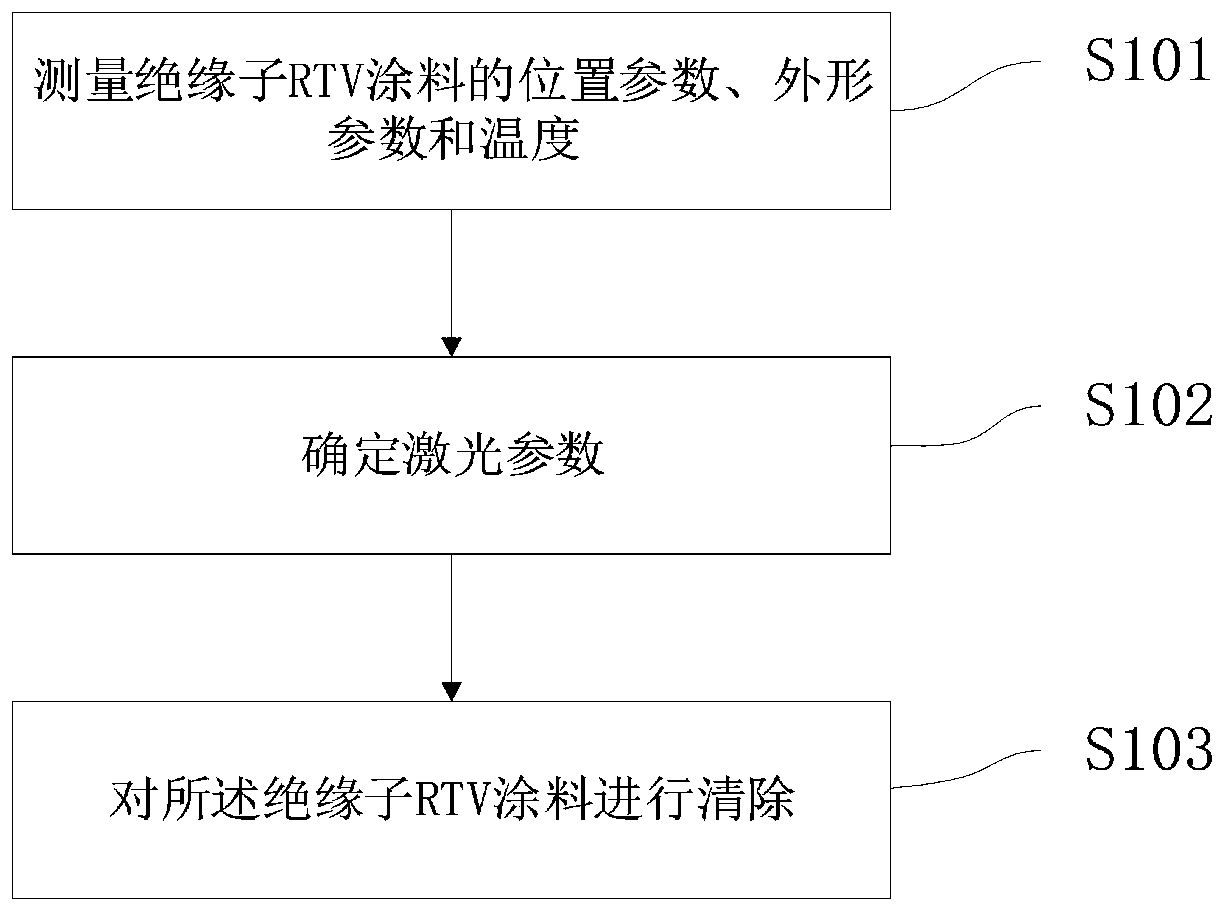
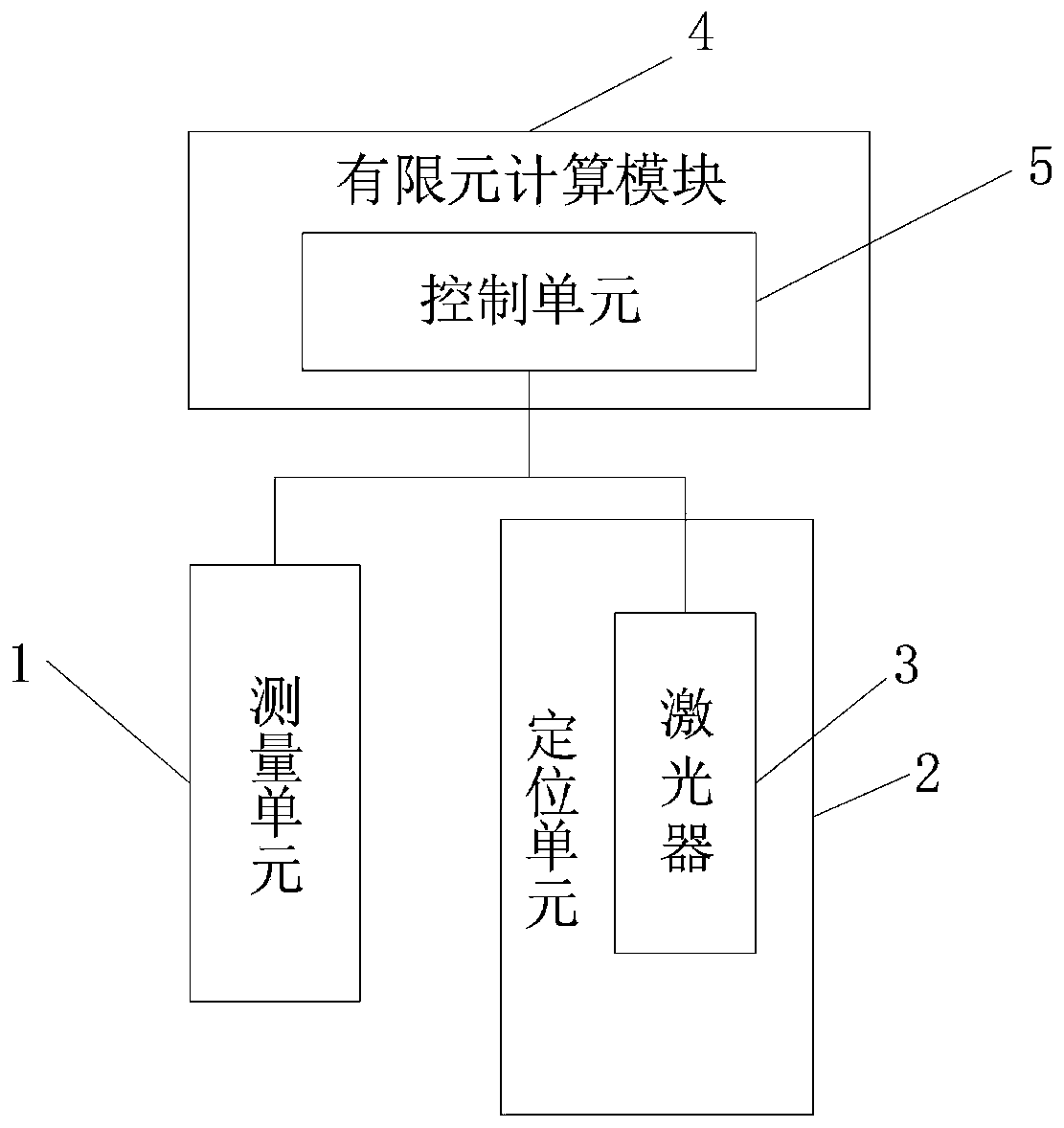
Laser cleaning method and device for insulator RTV coating
ActiveCN109848141AImprove cleaning efficiencyAvoid damageCleaning processes and apparatusEnvironmental resistanceSurface cleaning
The invention provides a laser cleaning method for an insulator RTV coating. The method comprises the following steps that 1, position parameters, appearance parameters and temperature of the insulator RTV coating are measured; 2, laser parameters are determined; and 3, the insulator RTV coating is removed. The laser is used for treating the surface of the RTV coating, the laser is directly actedon pollutants without mechanical contact, and the pollutants are directly gasified, ablated and photodecomposed, so that the high degree of mechanization is realized, the damage to the substrate can be effectively avoided, the surface form of the substrate can be controlled and changed, and a novel surface cleaning technology with relatively high working efficiency is achieved. It can be seen thatnon-contact cleaning and long-distance cleaning of the laser cleaning method for the insulator RTV coating have the characteristics of environmental protection and energy conservation, and the cleaning efficiency and effect can be obviously improved in the aspect of maintenance and use; and meanwhile, the laser cleaning method can effectively avoid damaging the substrate, accurately adjust the laser energy density, and effectively protect the substrate while improving the cleaning efficiency of the RTV coating.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Preparation process of amorphous silicon film solar battery based on laser etched and crystallized optical film layer
InactiveCN101882652AShort recovery timeLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesOptical thin filmSolar battery
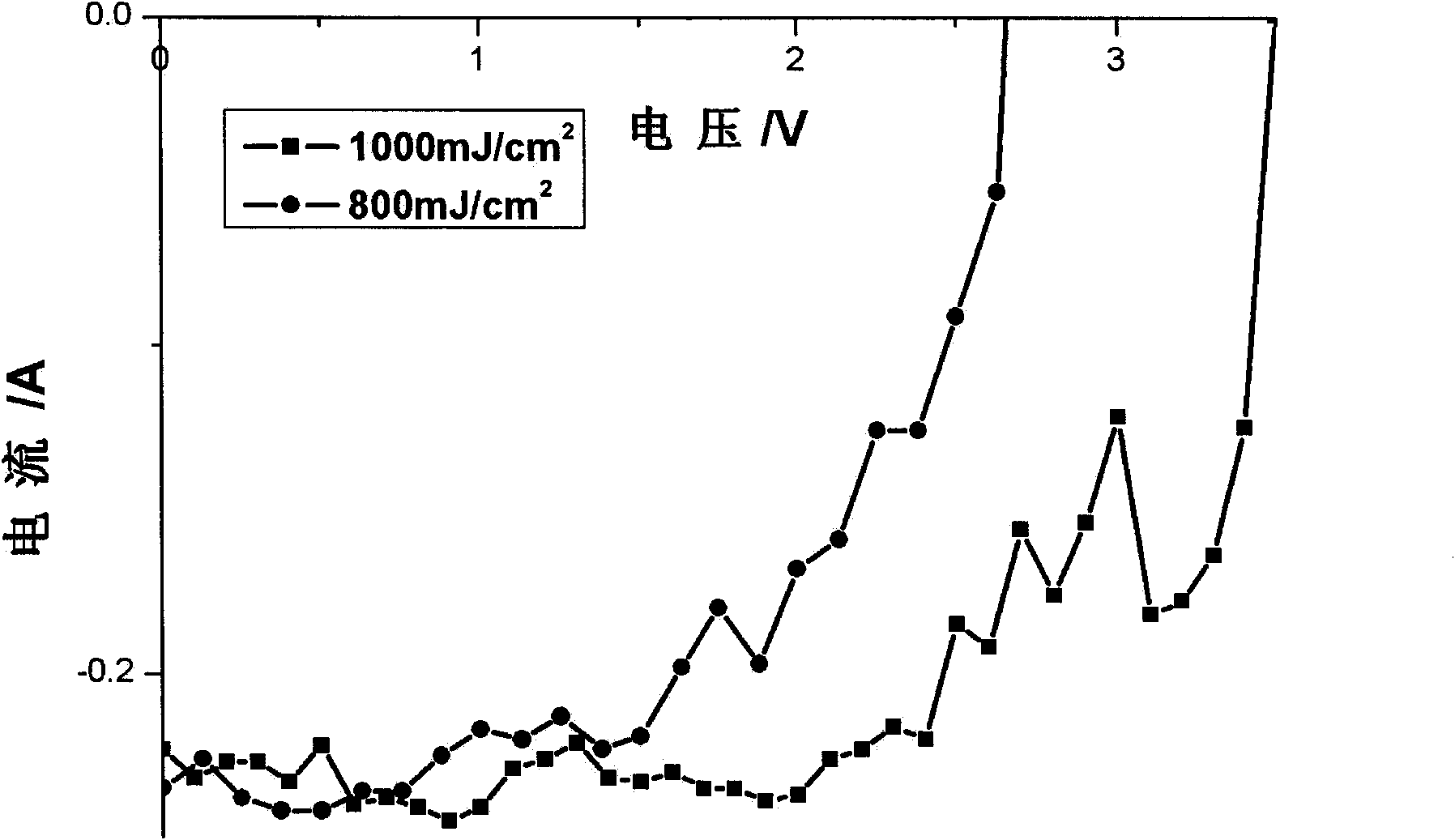
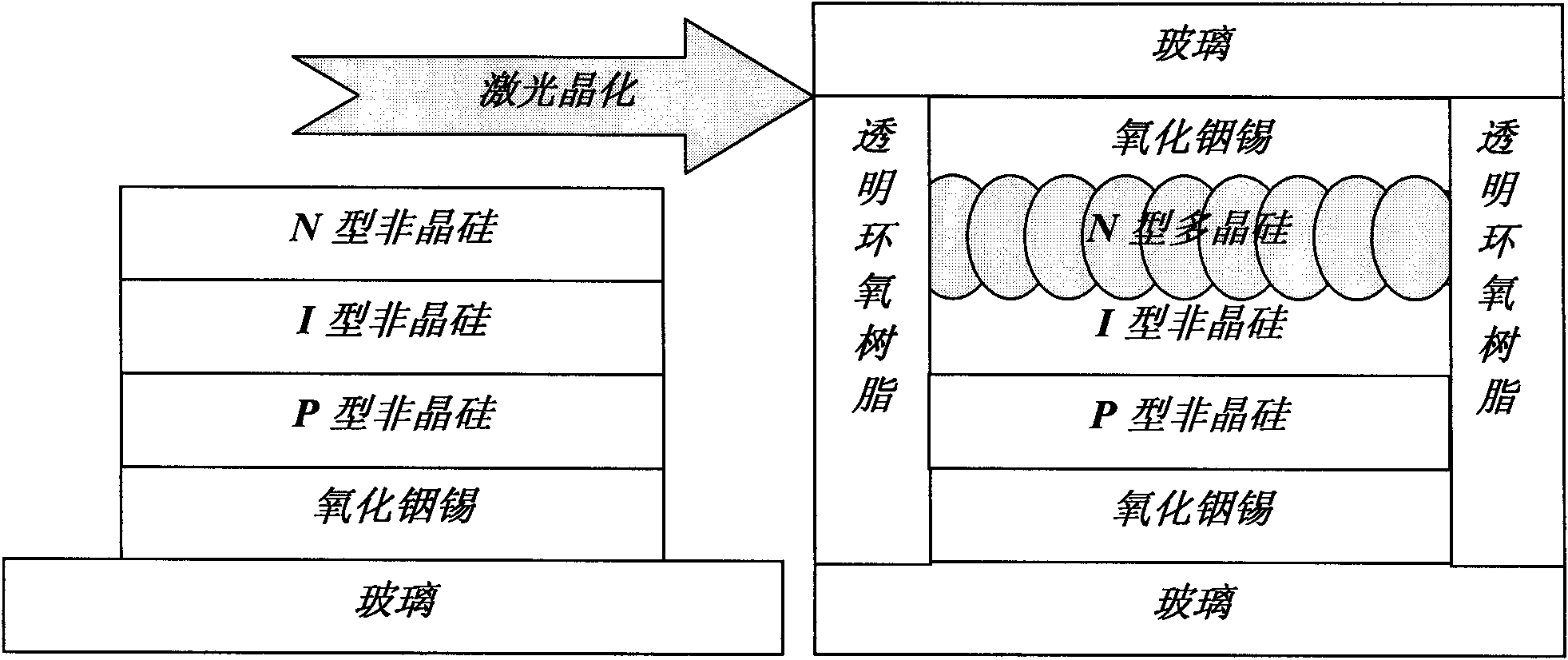
The invention relates to a preparation process of a novel amorphous silicon film solar battery based on a laser etched and crystallized optical film layer, which belongs to the technical field of inorganic material solar device preparation. An optical film comprises an antireflective film, a transmission increasing film, a reflection increasing film and the like, and the invention achieves the reflection increasing and transmission increasing functions of a modulation optical film layer mainly by controlling the grain size. The method comprises the following steps of: depositing three layers of amorphous silicon (a-Si) films respectively in a P type, an I type and an N type on indium tin oxide (ITO) conductive glass by a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) method, and then irradiating the surface of a sample by using frequency-doubled Nd YAG laser with the wavelength of 532nm to realize the conversion of an N type layer from amorphous silicon to a polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si) optical film layer. The polycrystalline silicon grain size of the crystallized optical film layer is controlled by changing the laser energy density to regulate the photoelectric conversion efficiency. The inorganic material solar energy of the invention can be applied to solar automobile film glass and building film glass curtain walls.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Penetrating type laser welding method of solar cell bus bars
PendingCN109986205AImprove heating efficiencySimplify the welding processLaser beam welding apparatusBeam expanderSurface layer
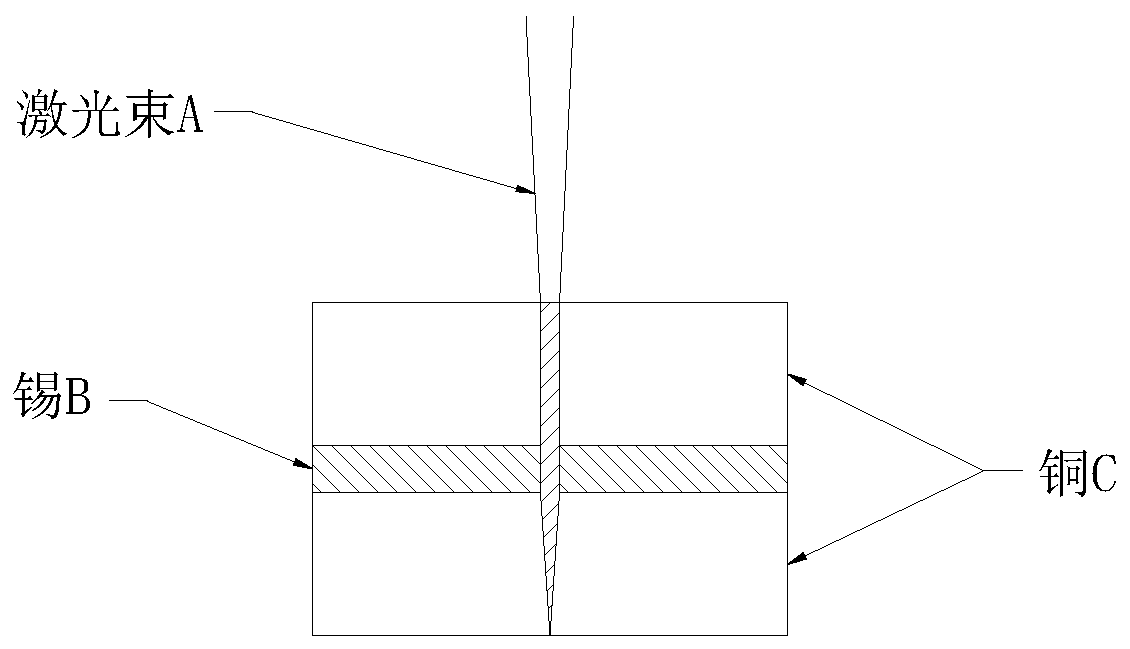
The invention relates to a penetrating type laser welding method of solar cell bus bars. The method comprises the following steps: outputting a laser beam through a pulse laser device, carrying out beam expansion control on diameter of the laser beam through a beam expander, focusing the laser beam subjected to beam expansion on a welding sample through a laser welding head, and enabling the laserwelding head to horizontally move up and down to adjust the size of a laser focal point and a laser welding spot; applying pre-pressure to a position near an area to be welded through a pre-pressingmechanism to enable two layers of welding strips to be in full contact with each other; receiving thermal radiation reflection laser in the welding process through a temperature feedback system, collecting a welding thermal radiation laser beam and converting the welding thermal radiation laser beam into temperature information, and calibrating the temperature of the welded area; enabling a visualimage system to move up and down to adjust a visual image focal point and identifying position information of the welding sample; focusing pulse laser on the welding strips, forming extremely high laser energy density in an action area, directly gasifying tin on the surface layers and copper on the inner sides of the welding strips, forming cavities in the materials and enabling the materials tobe tightly occluded with each other, and directly carrying out fusion welding of copper layers of the two layers of welding strips. The welding quality is high.
Owner:江阴德龙能源设备有限公司
Optical film defect laser damage threshold test method
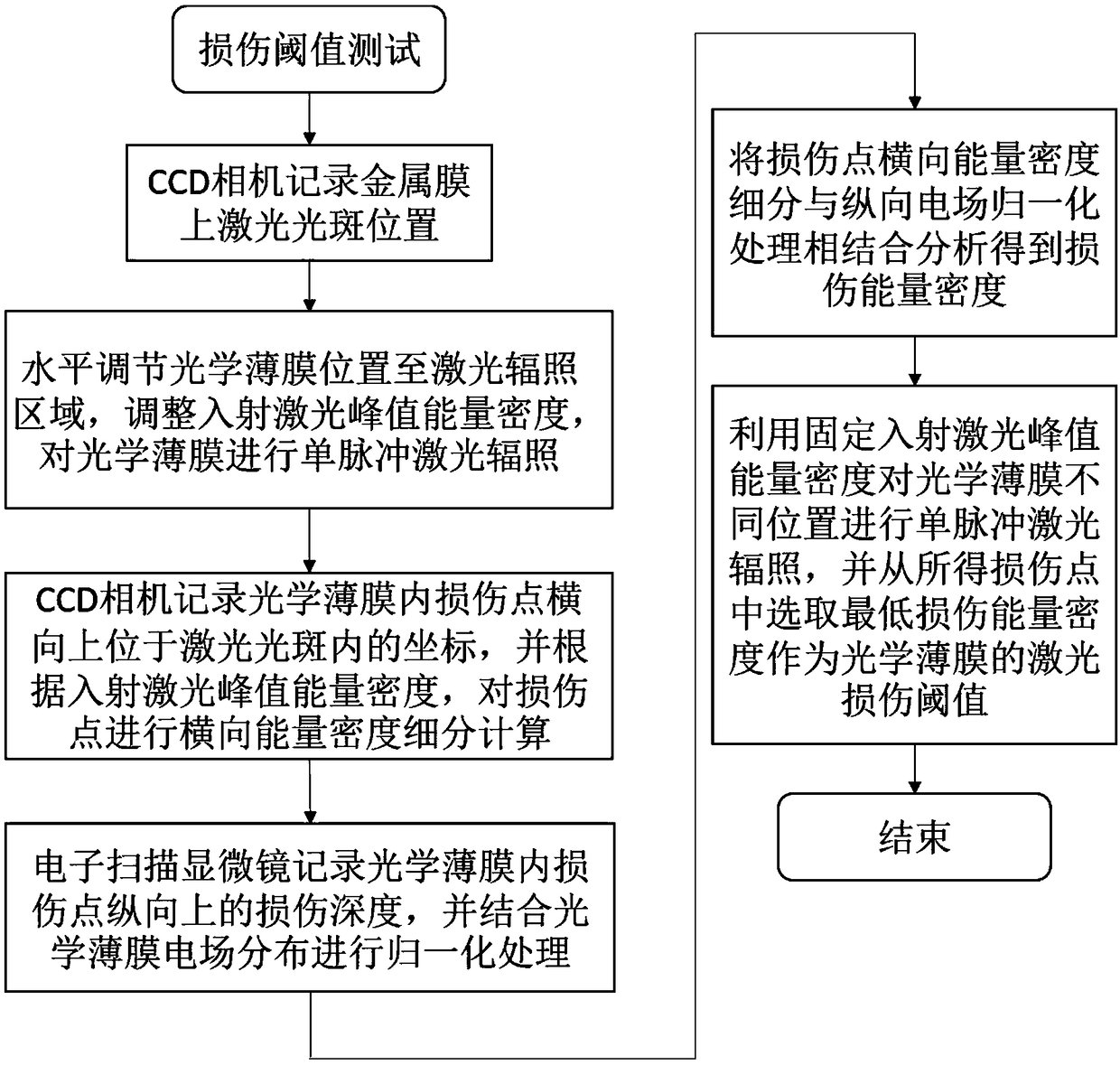
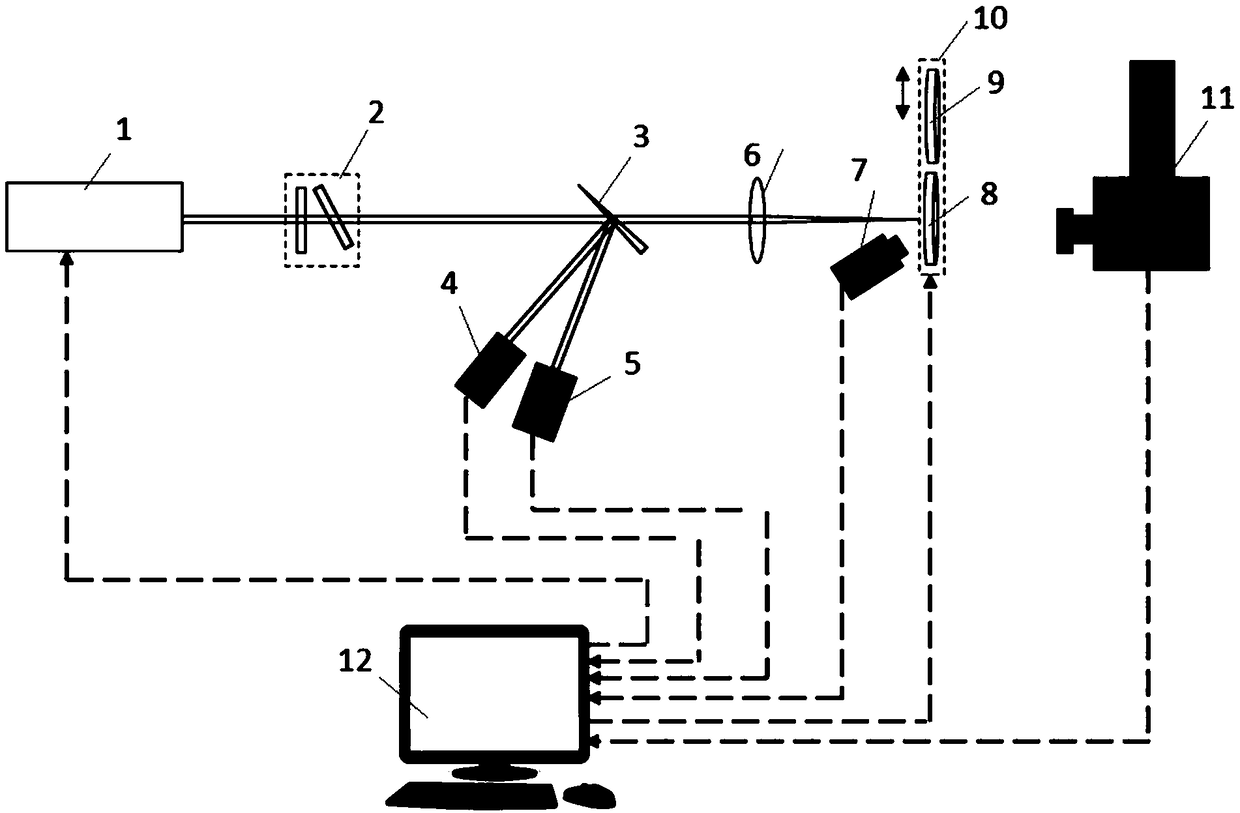
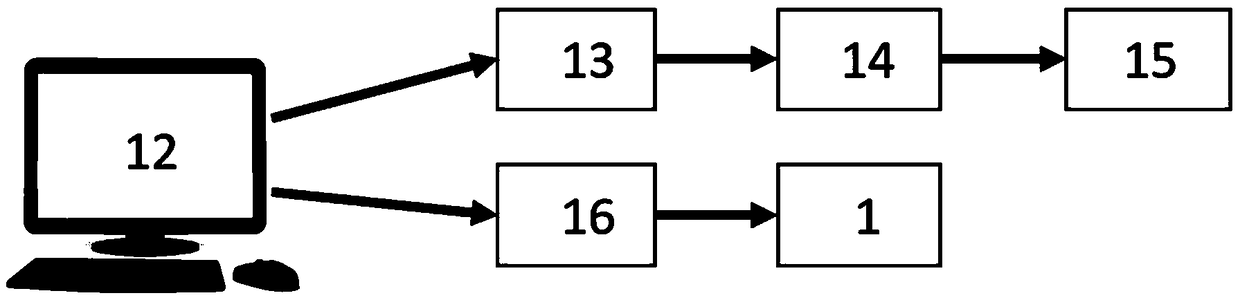
ActiveCN109374264AImprove test accuracyImprove applicabilityTesting optical propertiesBeam splitterScanning electron microscope
The invention discloses an optical film defect laser damage threshold test method. According to the method, after a laser beam passes through an attenuator and arrives at a beam splitter, and the laser beam in the transmission direction of the beam splitter passes through a focusing lens and arrives at a metal film; a CCD camera records a spot position where the laser irradiates on the surface ofthe metal film and a laser damage point coordinate where the laser irradiates on the surface of the optical film; and a scanning electron microscope records the longitudinal depth position of the defect damage point of the optical film in the irradiation of the laser and completes a defect damage point lateral energy density subdivision and longitudinal electric field normalization processing-combined analysis. In an optical film defect laser damage threshold test in the prior art, randomly-distributed defect damage points and laser energy density of Gaussian distribution in a laser spot are considered to be uniformly-distributed damage points and laser energy density equivalently, and influence on the defect damage point caused by the electric field distribution of the optical film is ignored, and as a result, many problems are brought about, while with the optical film defect laser damage threshold test method of the invention adopted, the above problems can be solved, and test accuracy can be improved.
Owner:中国工程物理研究院上海激光等离子体研究所
Laser ablation method for patterning a thin film layer
InactiveUS6838038B2Increase energy densityLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesDielectricFluorescence
The invention relates to a laser ablation method for patterning thin film layers for thick dielectric electroluminescent displays without substantial ablation of or damage to any other layers. Typically, the thin film layers are phosphor layers. The laser ablation method for patterning a thin film phosphor layer of a thick dielectric electroluminescent display includes selecting a wavelength of laser radiation, a laser pulse length, a laser energy density and a sufficient number of laser pulses to pattern the thin film phosphor layer without substantial ablation of or damage to other layers, whereby the wavelength of laser radiation is such that the laser radiation is substantially absorbed by the thin film phosphor layer with minimal absorption by other layers, the laser pulse length is sufficiently short that during the duration of the laser pulse there is minimal heat flow from the thin film phosphor layer to other layers, and the laser energy density and the sufficient number of laser pulses is sufficiently high that energy is deposited in the thin film phosphor layer, whereby the entire thickness of at least a portion of the thin film phosphor layer is ablated.
Owner:IFIRE IP CORP
Preparation method of aluminum alloy surface composite coating layer
InactiveCN104005019ALow melting pointReduce dilutionMetallic material coating processesHigh power lasersAbsorption rate
The invention discloses a preparation method of an aluminum alloy surface composite coating layer, and belongs to the laser processing technical field. An NiCrAl / TiC nano coating layer is prepared on the surface of an aluminum alloy through melting covering by using a CO2 high-power laser device; a nano powder has small particle size and large specific surface area, and surface atoms are in an unstable state, so that a melting point is relatively low, the absorption rate on CO2 laser is relatively large, the laser energy density required in the melting covering process is also relatively small, and thus the dilution rate of the coating layer on a substrate can be guaranteed to be relatively small. The interior of the melting-covered layer prepared by the method is free of cracks, pores and other defects; and the prepared laser melting-covered coating layer is suitable for the remanufacturing technical fields such as surface modification and repairing of aluminum alloy engines and other structural parts, can greatly improve the usability of the aluminum alloy structural parts, prolongs the service life, and achieves great economic benefits.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A double-light source laser annealing device and method
InactiveCN101217109AHelp delayLow densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicron scaleLaser light
The invention discloses a dual-light source laser annealing device and a method, which pertains to the semiconductor manufacturing equipment and technical scope. The dual-light source laser annealing device comprises a laser light source for annealing, light sources which have the wavelength of sub-micron to micron scale and are used for auxiliary heating, an optical lens system and a wafer carrier. The processing method is that the oblique incidence of the auxiliary heating light beams reaches the surface of a substrate wafer, and the pre-heating is carried out at the substrate surface before the formal laser annealing, so as to improve the adverse effects of the thermal stress on the annealing and the wafer surface appearance. On the other hand, as the processing of pre-heating, a great number of phonons are introduced to a superficial surface layer of the substrate wafer, the existence of the phonons can be conductive to the relaxation of carrier energy and obtain better annealing effect, so the temperature raise of a crystal lattice and the annealing process of the wafer can be completed in a shorter time, and the more shallow ultra-shallow junction can also be obtained. Due to the pre-heating of the crystal lattice, the laser energy density which is needed by the laser annealing is also reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of nanoparticle linear array resistor
ActiveCN108648890AEasy transferAchieving controllable equipmentResistor manufactureMicro nanoFemtosecond pulsed laser
The invention provides a preparation method of a nanoparticle linear array resistor. The preparation method comprises the steps: a prepared sample is obtained; the prepared sample is put on a three-dimensional micro displacement platform; femtosecond pulse laser passes through an optical path system to transmit a quartz slide to be focused on the surface of a gold film; a PC controls the three-dimensional micro displacement platform to move in the directions of a Y axis and a Z axis; the gold film is subjected to ablation by the focused laser to form plasma spray in a constraint space; the spayed gold nanoparticles are received by the covered glass, and the gold nanoparticle linear array resistor is obtained on the glass surface; and the morphology features of the gold nanoparticle lineararray resistor are represented. The method is based on a femtosecond laser micro-nano processing platform and is combination with a laser induced backward transfer technology; by controlling femtosecond pulse laser energy density, scanning speed and processing number of branches, the linear array resistor formed by the gold nanoparticles is prepared; and the gold nanoparticle morphology features of different processing parameters are represented by a scanning electron microscope and an atomic force microscope.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for evaluating repetitive frequency laser damage resistance of optical thin film
ActiveCN101526461ASimple test methodWeather/light/corrosion resistanceScattering properties measurementsProbability curvePeak value
The invention provides a method for evaluating repetitive frequency laser damage resistance of an optical thin film. The method comprises the following steps: irradiating different test points of a thin film sample to be tested with a series of sequence laser pulse with a certain energy density, determining and recording a damage state of each test point, and calculating small damage probability at the energy density; repeatedly changing the energy density of the laser to irradiate different test points of the thin film sample to be tested, determining and recording the damage probability of each test point, and respectively calculating the small damage probability at each energy density; respectively taking the energy density and the small damage probability as a horizontal coordinate and a longitudinal coordinate to draw a change curve of the small damage probability with the laser energy density, and evaluating the repetitive frequency laser damage resistance of the optical thin film at the energy density corresponding to a damage probability peak value of the probability curve. The energy density is higher, the repetitive frequency laser damage resistance of the optical thin film is better. The method helps simplify and practice methods for evaluating the repetitive frequency laser damage resistance of optical films.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for graphene-316L stainless steel based on selective laser melting
ActiveCN112453395AHigh yield strengthHigh tensile strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingSS - Stainless steel
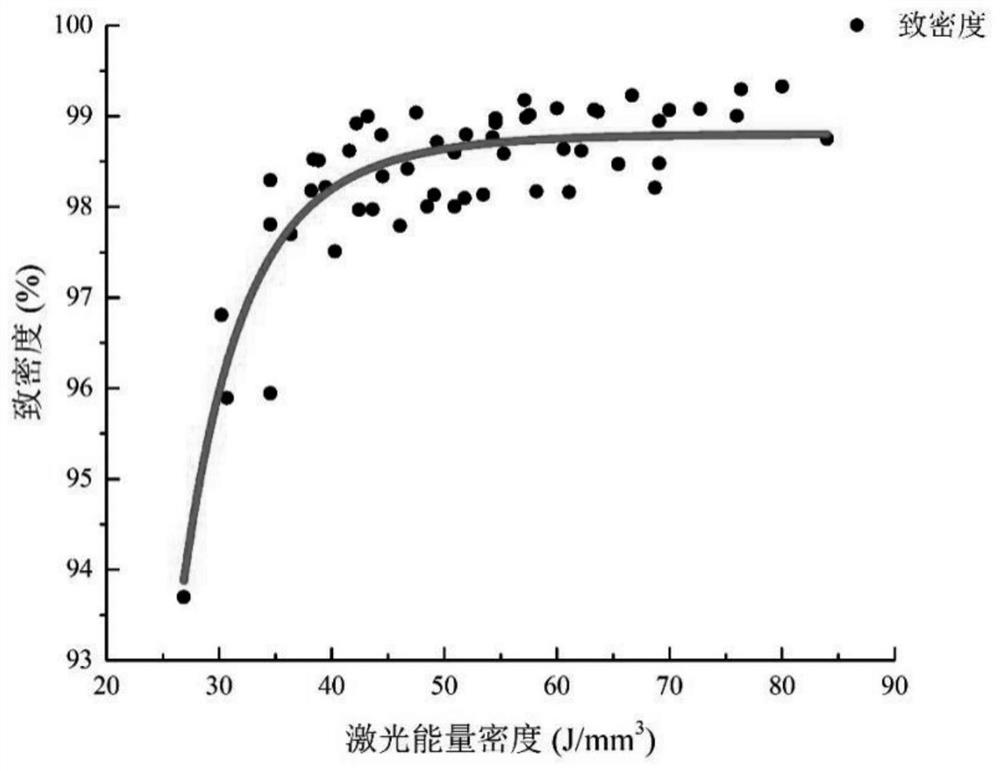
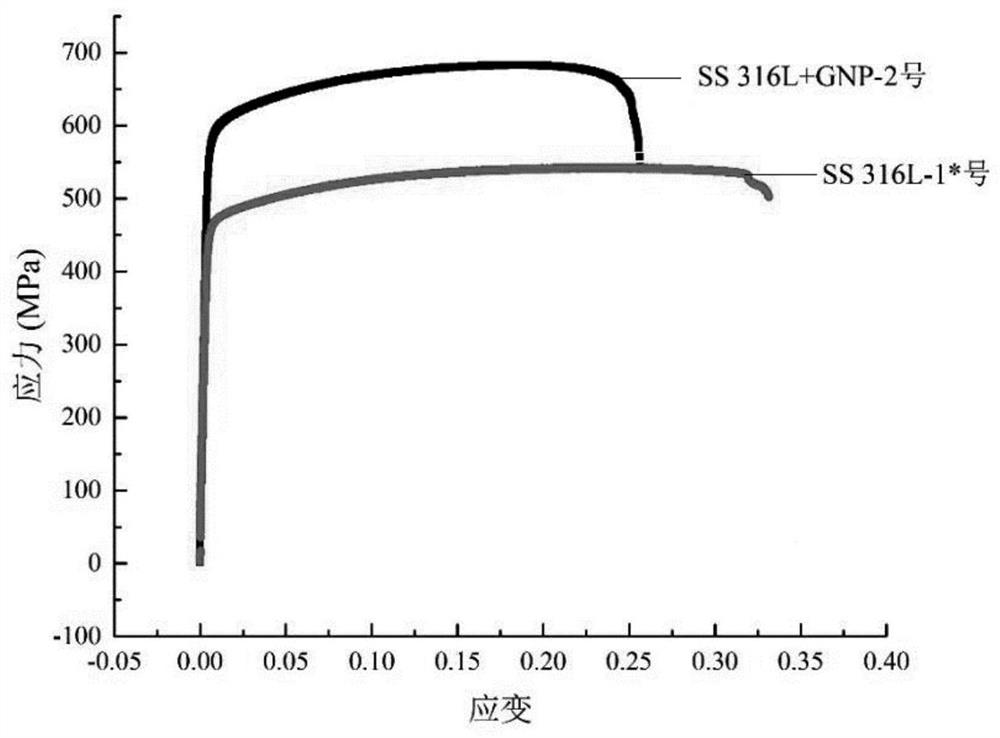
The invention discloses a preparation method for graphene-316L stainless steel based on selective laser melting. The preparation method comprises the following steps that graphene powder and 316L powder are mixed to obtain 316L and graphene mixed powder; then, the mixed powder is subjected to selective laser melting block forming, the optimal technological parameters are obtained through analysisof density, mechanical properties, electrochemical corrosion and metallographic and microcosmic appearance, the exposure time is 100 microseconds, the dot pitch is 50 micrometers, the power is 210 W,the laser energy density is 49.35 J / mm < 3 >, and compared with pure 316L stainless steel, the graphene / 316 L stainless steel sample under the optimal technological parameters has the advantages thatthe yield strength is improved by 28%, the tensile strength is improved by 26%, and the corrosion resistance is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Control of crystal grain size of polysilicon film and detecting method thereof
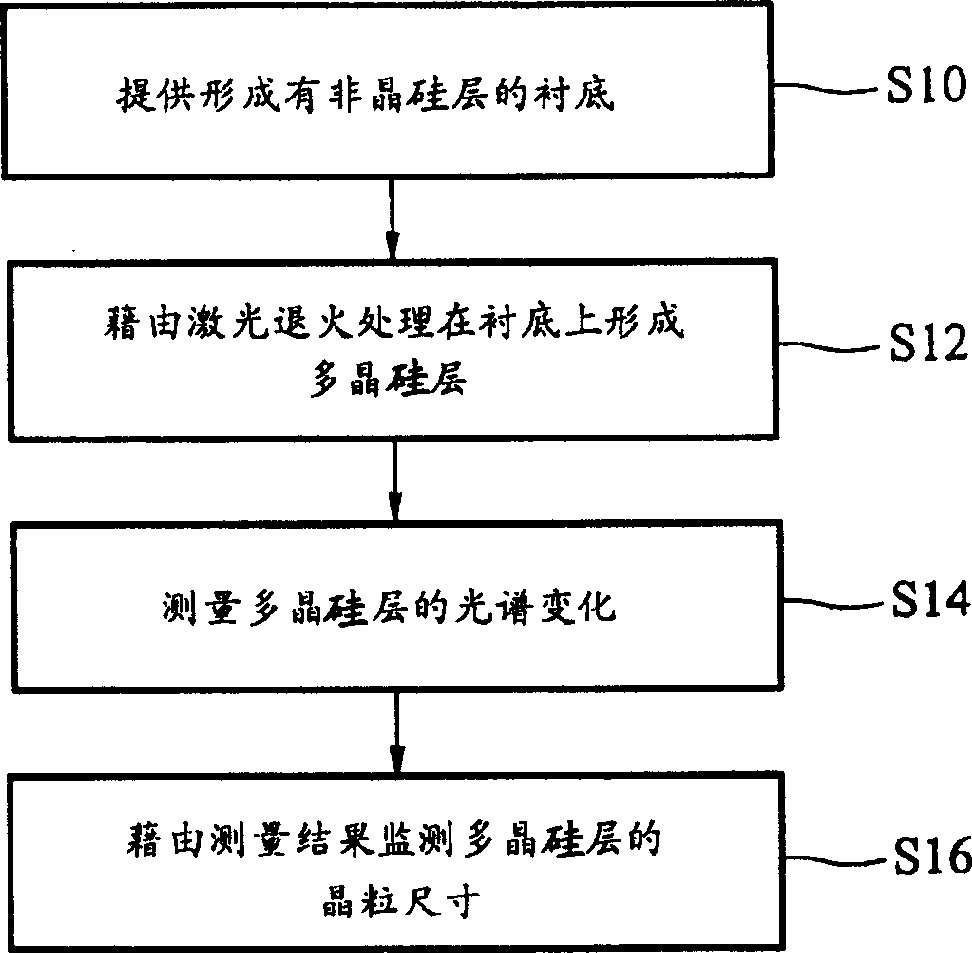
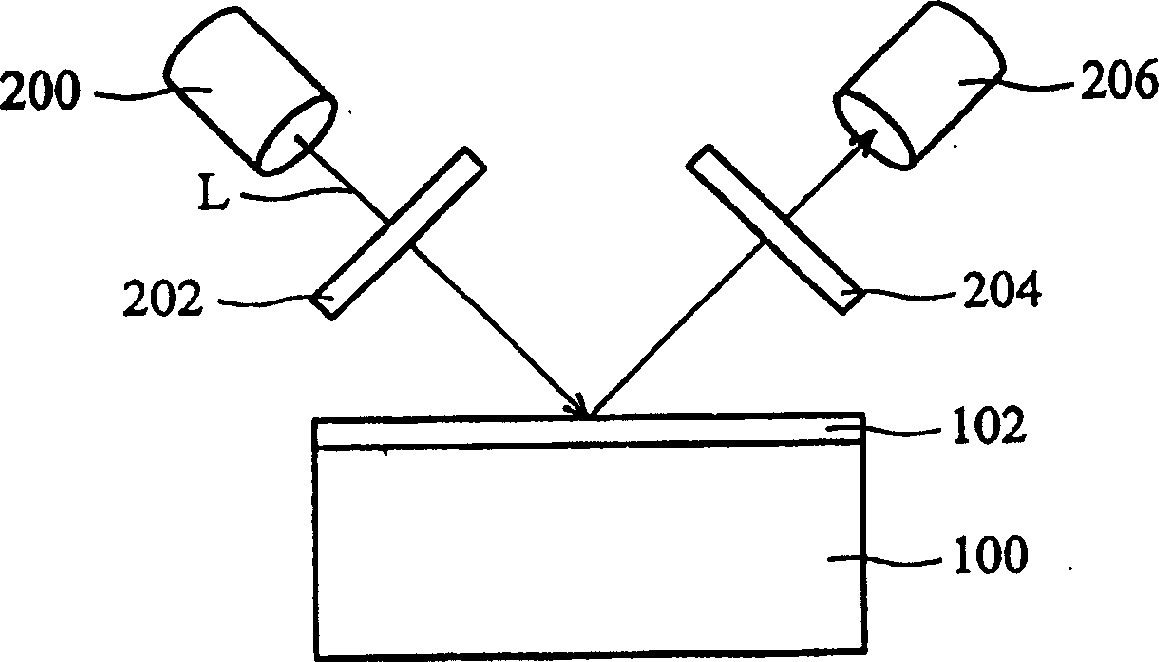
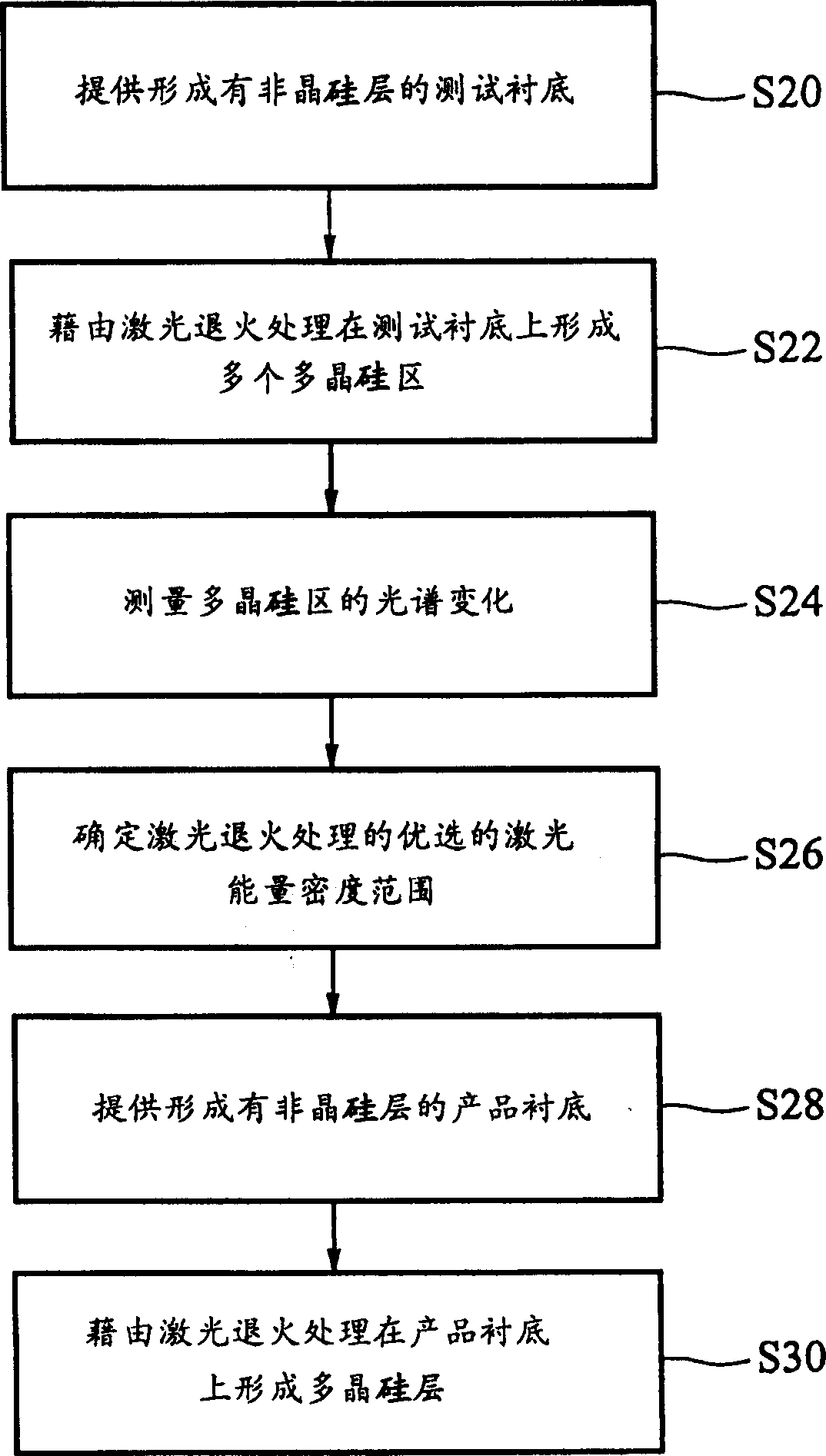
InactiveCN1501465AAccurate detectionQuick checkSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansLighting spectrumCrystalline silicon
The invention discloses a polycrystalline silicon thin film crystal particle size control and detecting method comprising, providing a first substrate covered by a first non-crystalline silicon layer, implementing annealing treatment to the first non-crystalline silicon layer using laser rays of dissimilar energy density to form a plurality of first polycrystalline silicon areas, measuring the light spectrum change of each first polycrystalline silicon area with a finite photon energy range, providing a second substrate covered by a second non-crystalline silicon layer, implementing annealing treatment to the first non-crystalline silicon layer using the above laser energy density to obtain largest polycrystalline silicon crystal particle dimension, and detecting its crystal particle dimension using an elliptical instrument.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
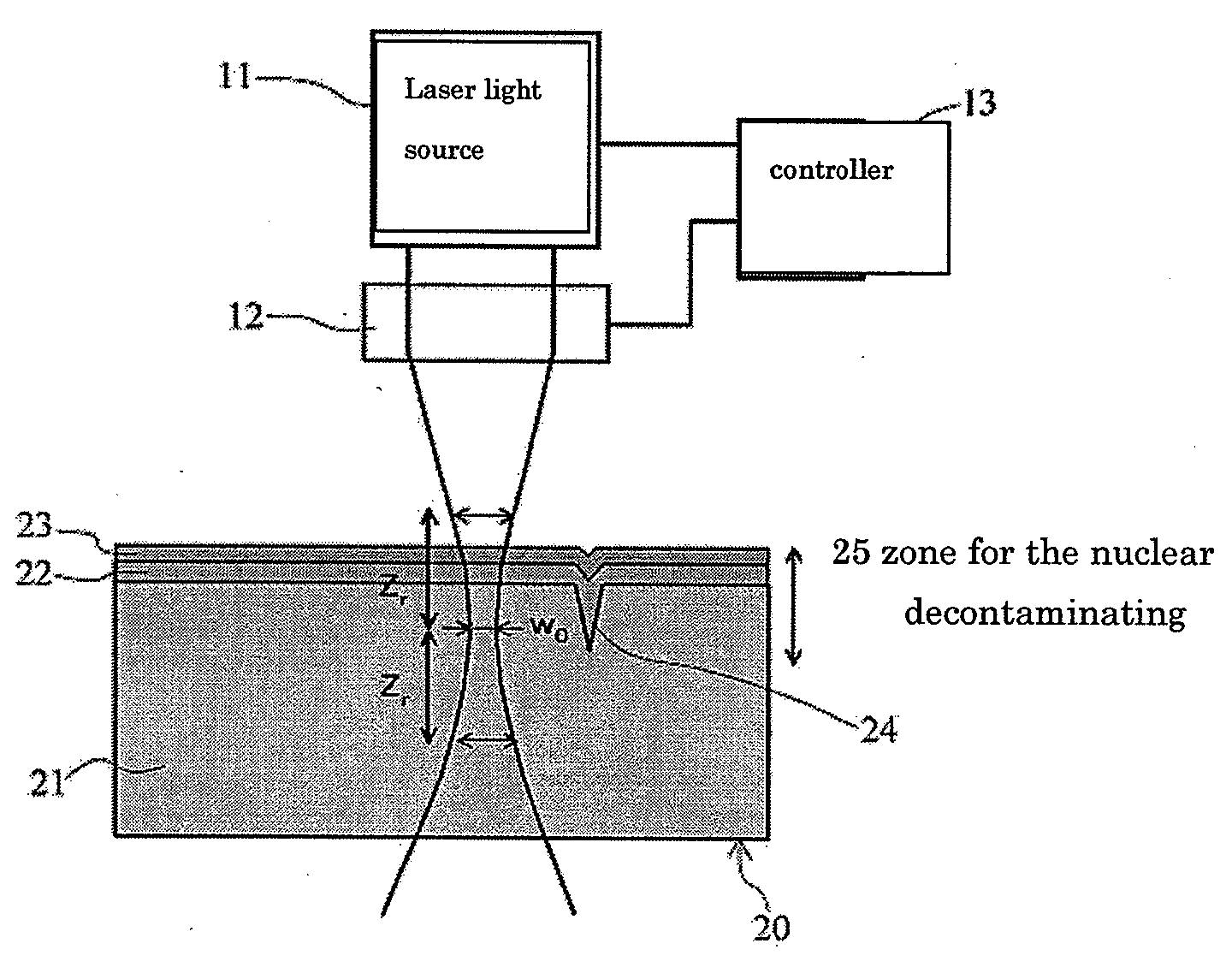
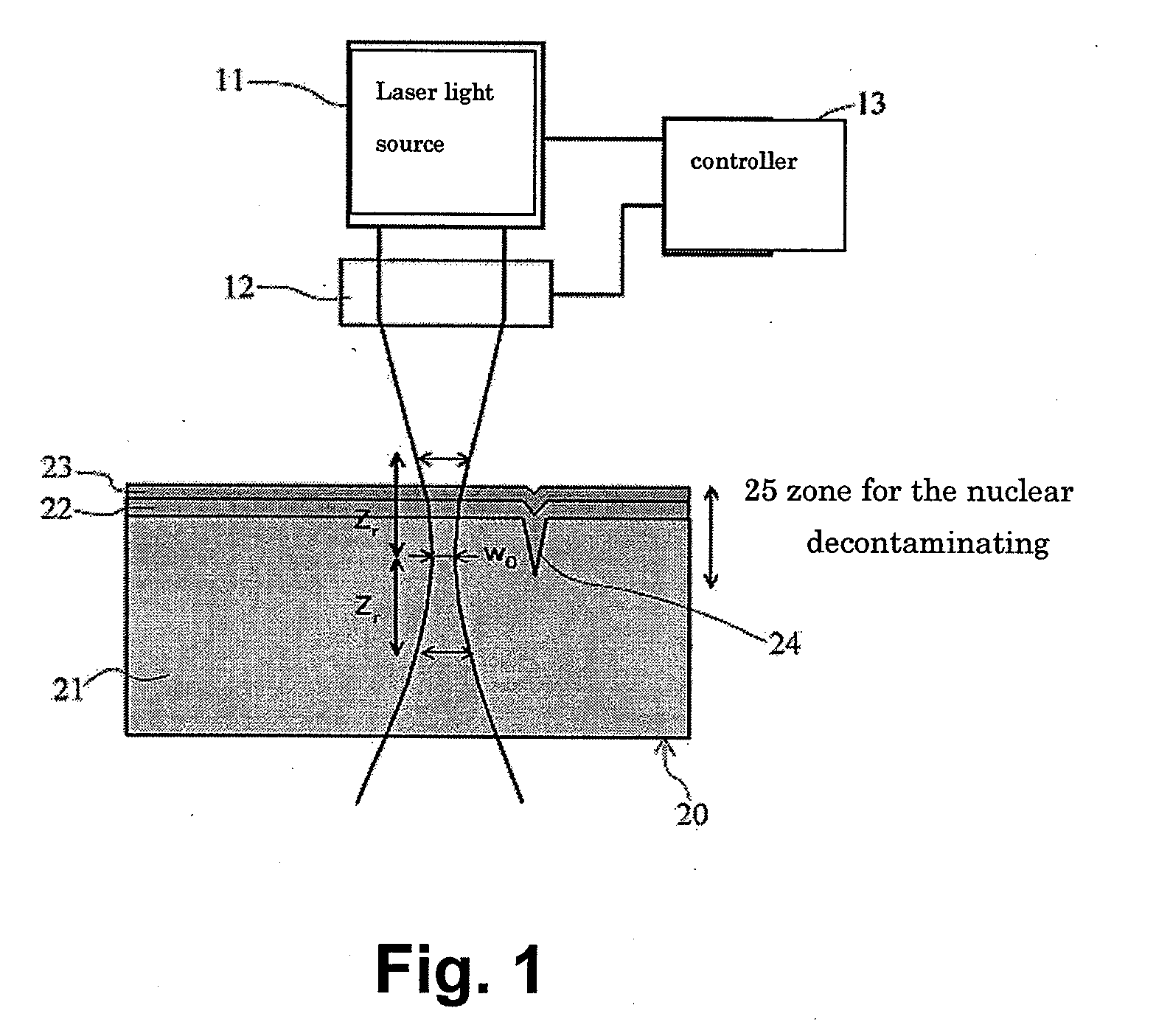
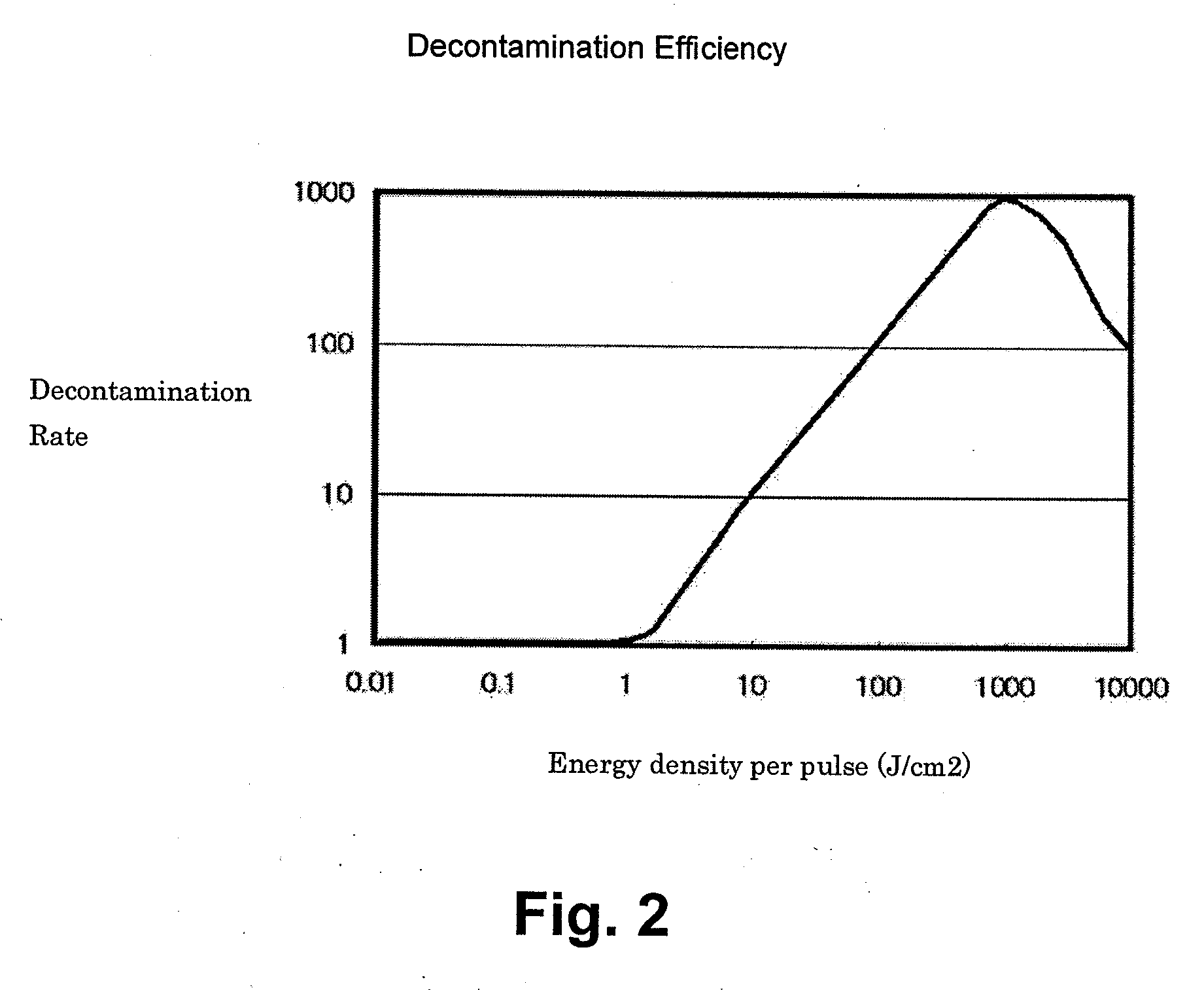
Nuclear decontamination device and a method of decontaminating radioactive materials
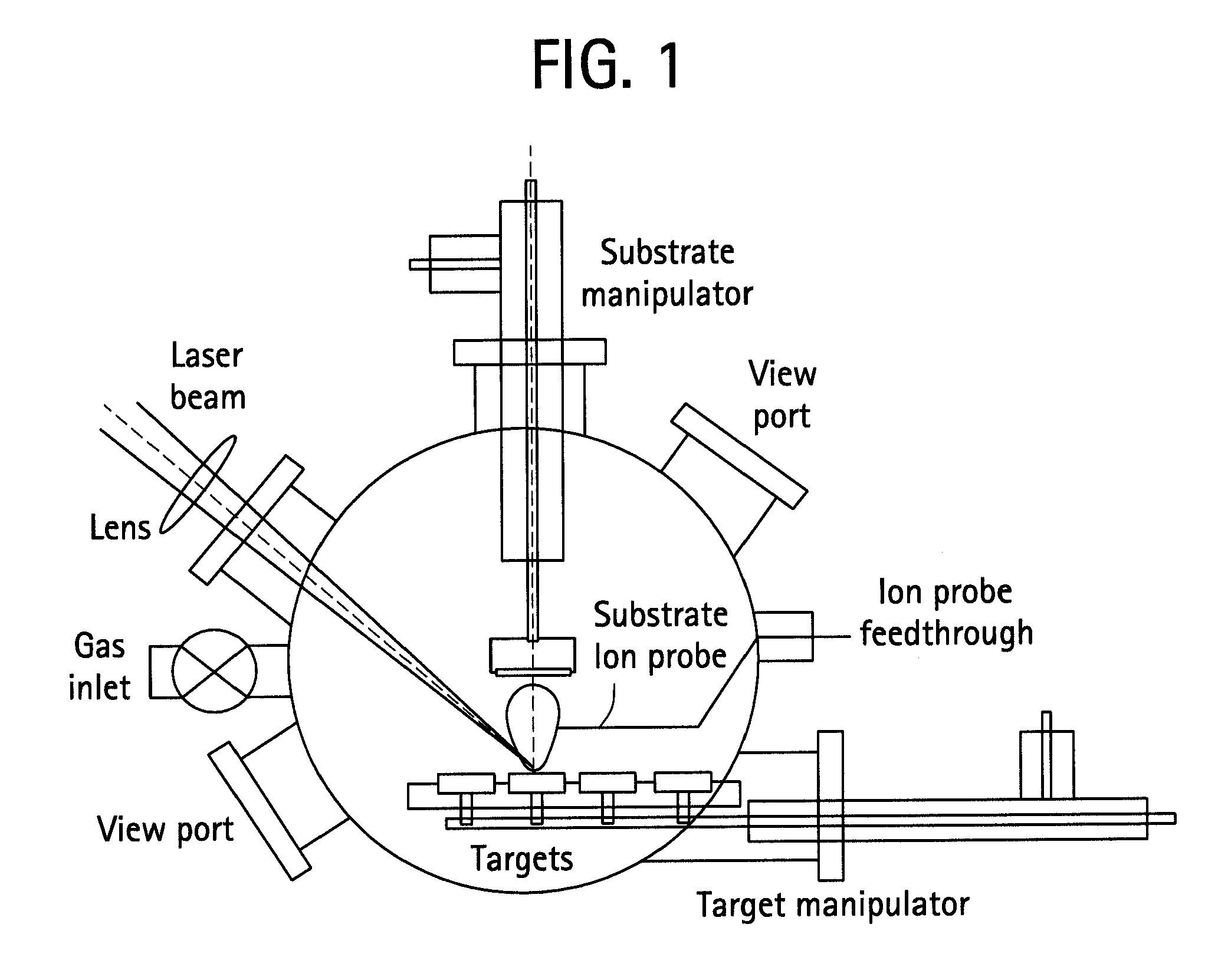
InactiveUS20100269851A1Effective decontaminationElectrostatic cleaningRadioactive decontaminationRadioactive agentVolumetric Mass Density
This is an efficient nuclear decontamination device using the laser light to remove the radioactive substance from the polluted parts of the radioactive object sample in the nuclear devices and facilities. In the nuclear decontamination device, the laser source (11) of the oscillator and amplifier system is used to irradiate on the surface (20) of the decontamination object sample through the condensing optics (12). The controller (13) optimizes the laser energy density on the surface by using both of the laser sources (11) and condensing optics (12). In the optimization, the energy density per pulse is controlled by optics system (12) of condensing within the range of 1 J / cm2-1000 J / cm2 in the surface of the decontamination object sample (20). Minimum beam spot size and Rayleigh length are chosen to keep the energy density per pulse in the above-mentioned range of the energy density.
Owner:MINEHARA EISUKE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com