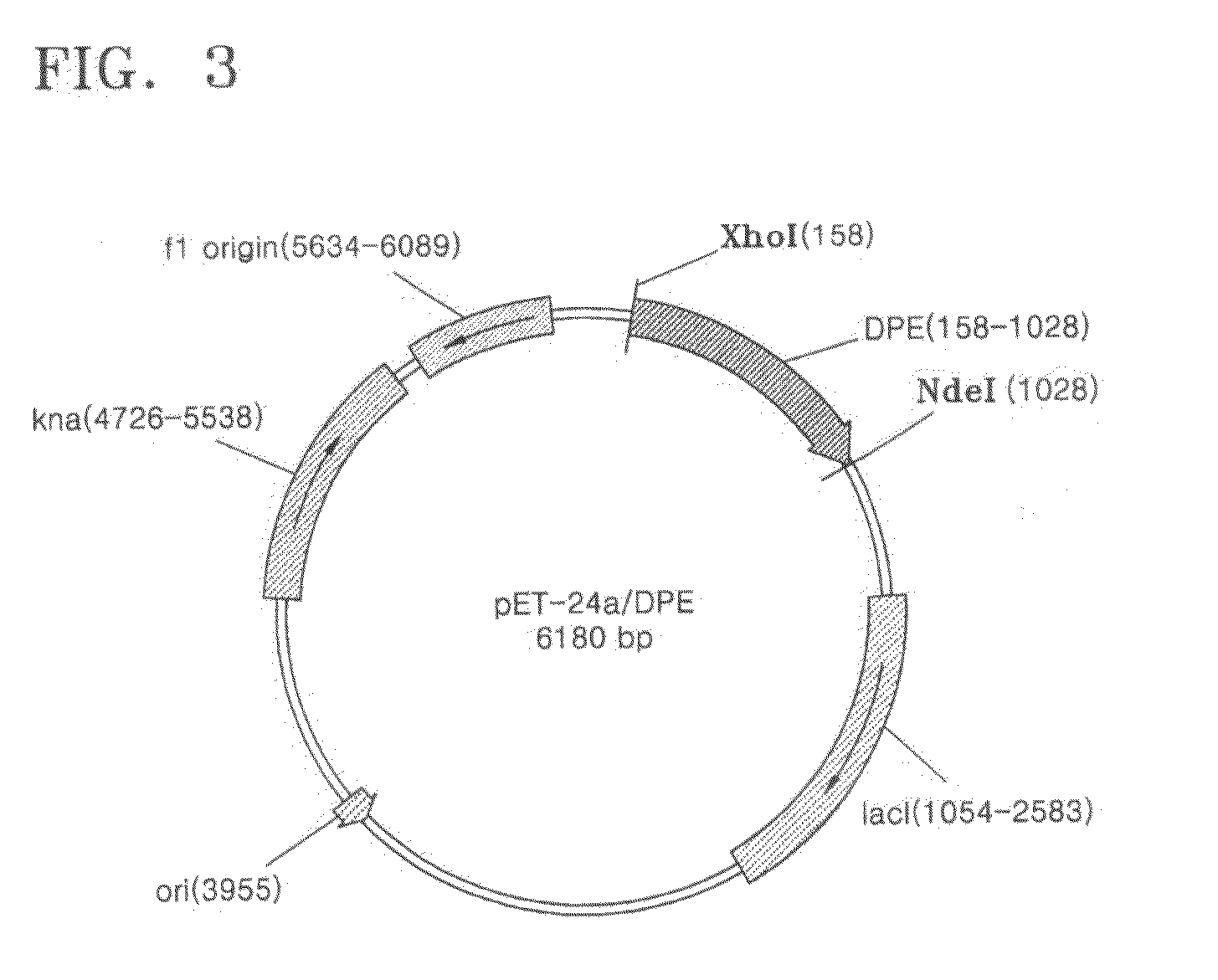
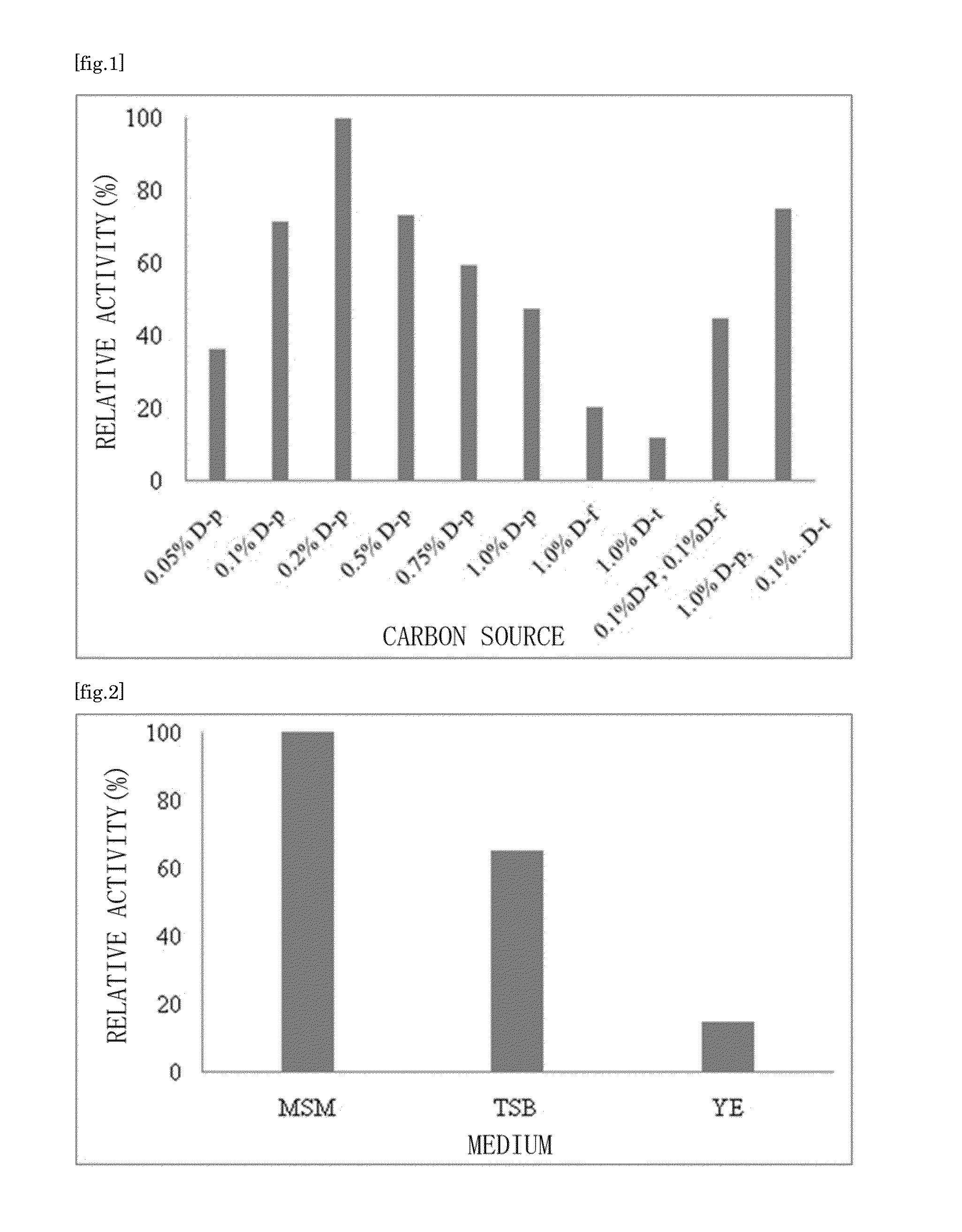
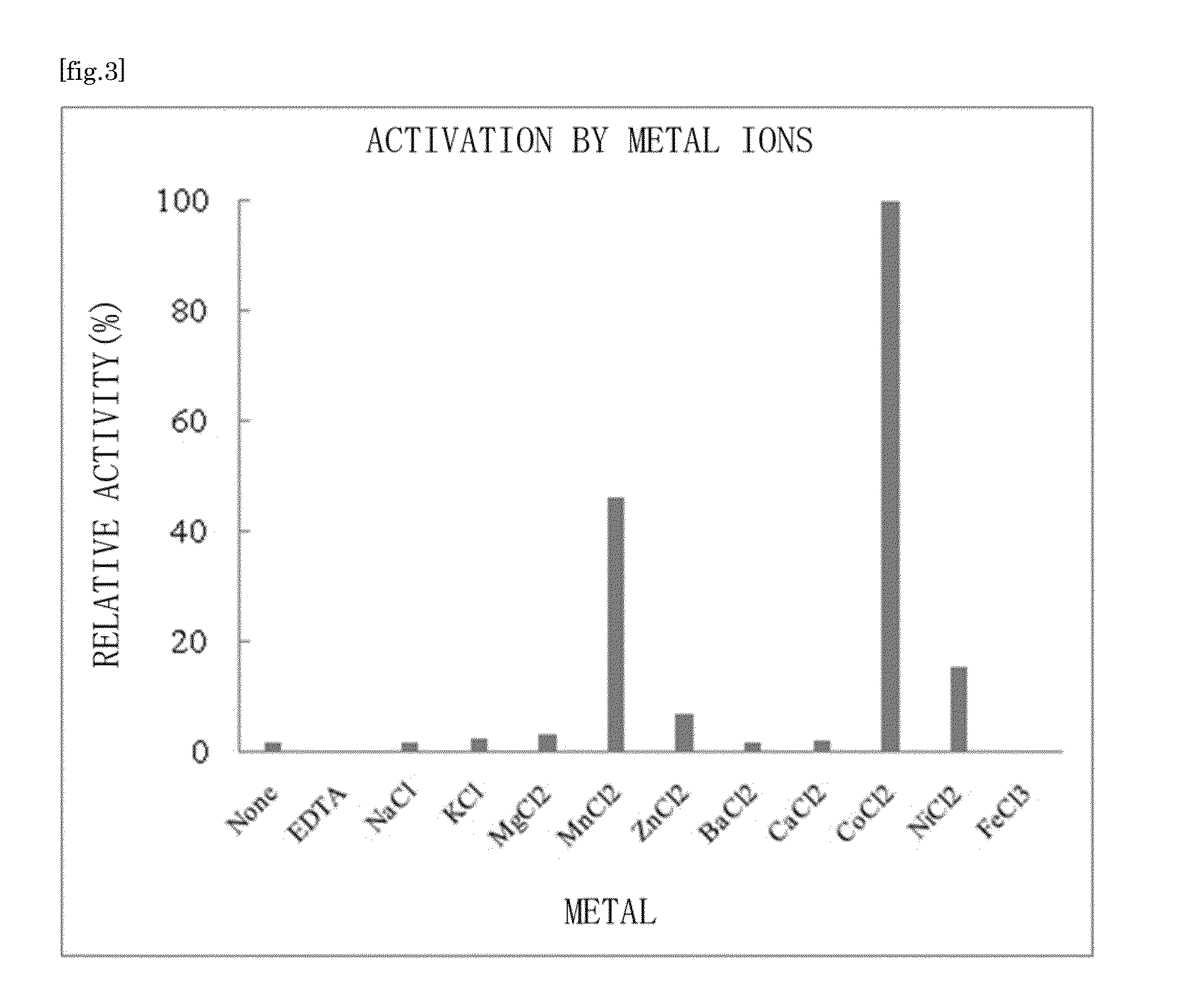
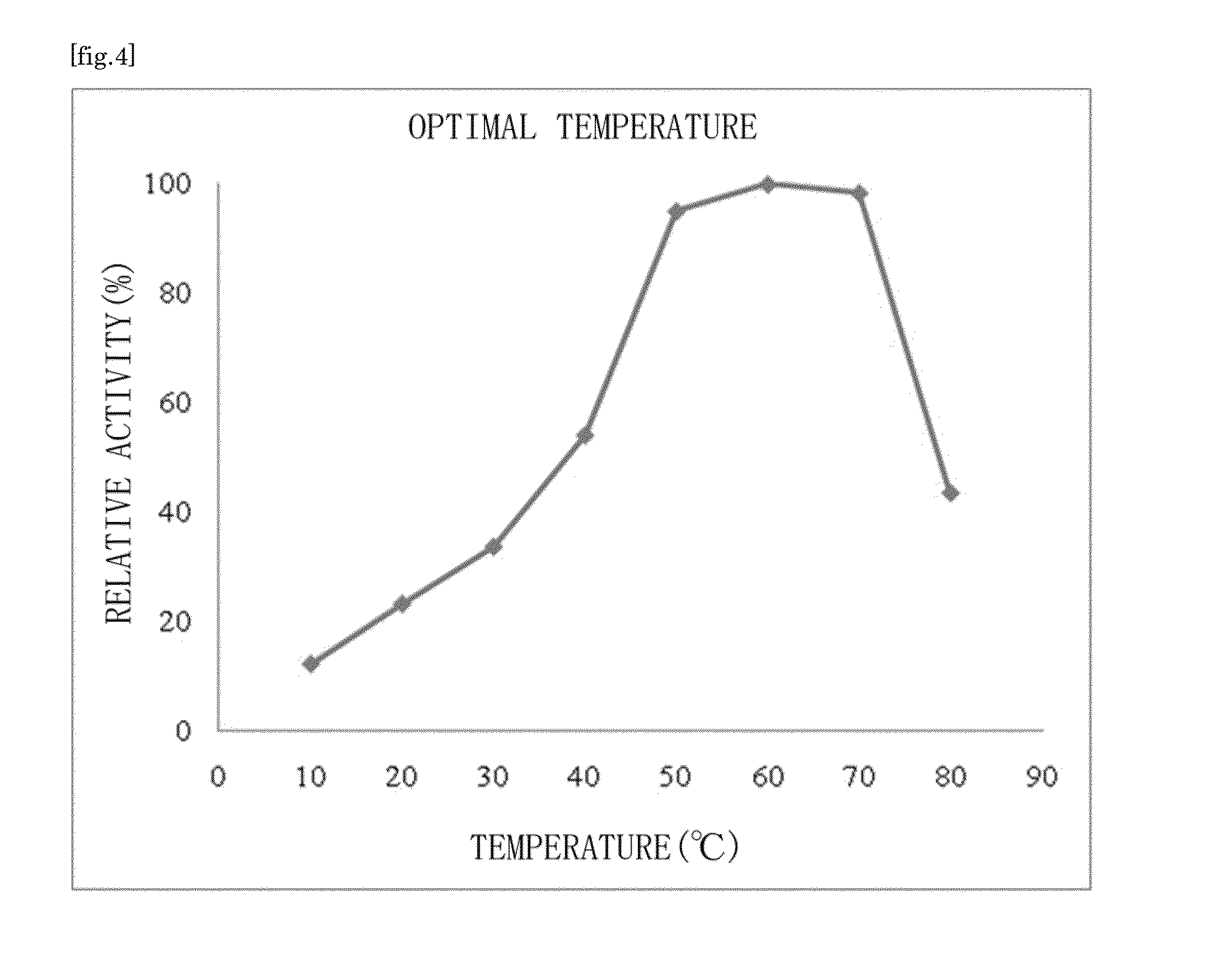
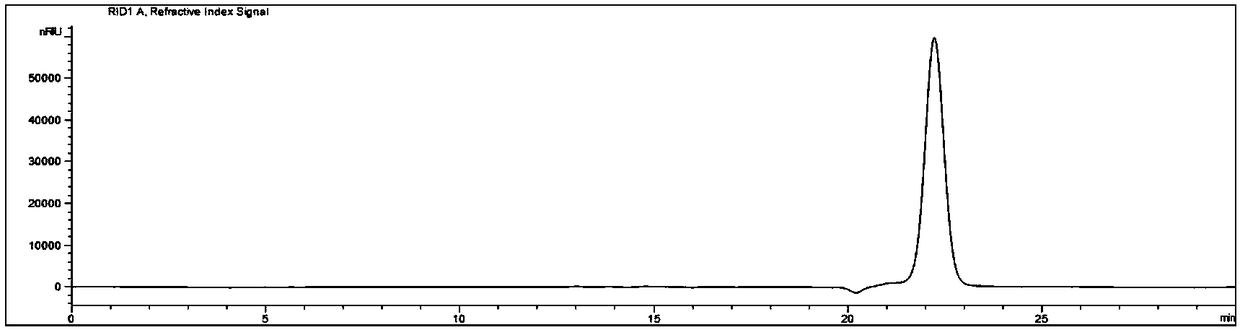
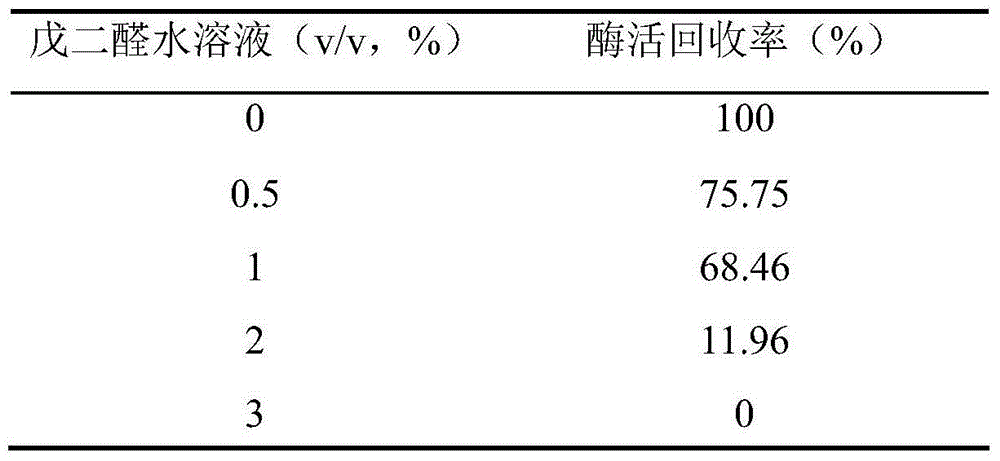
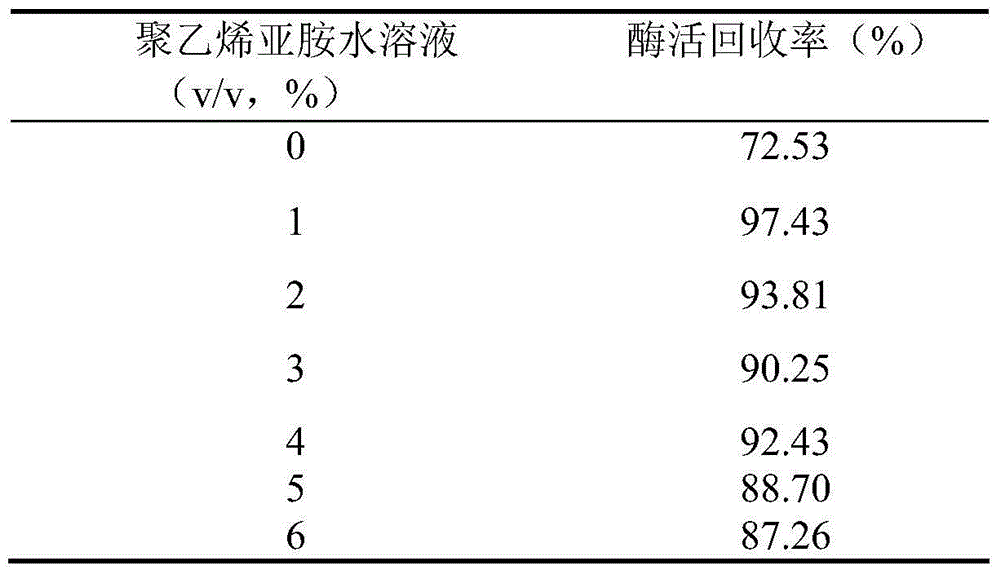
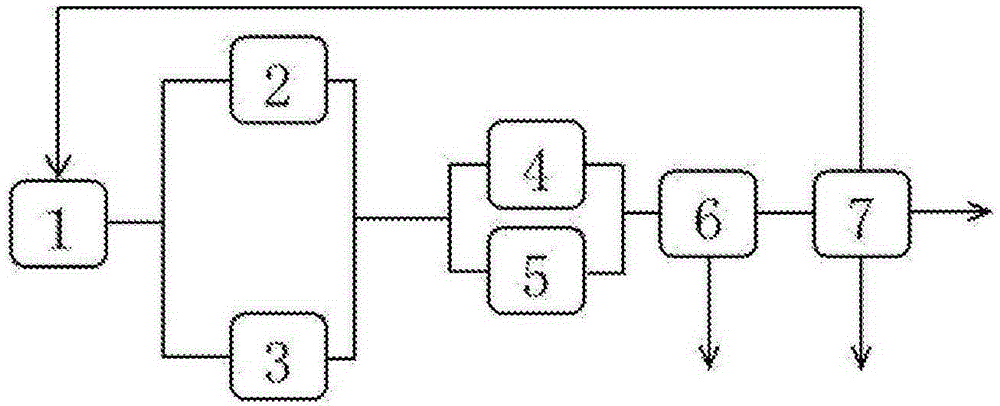
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
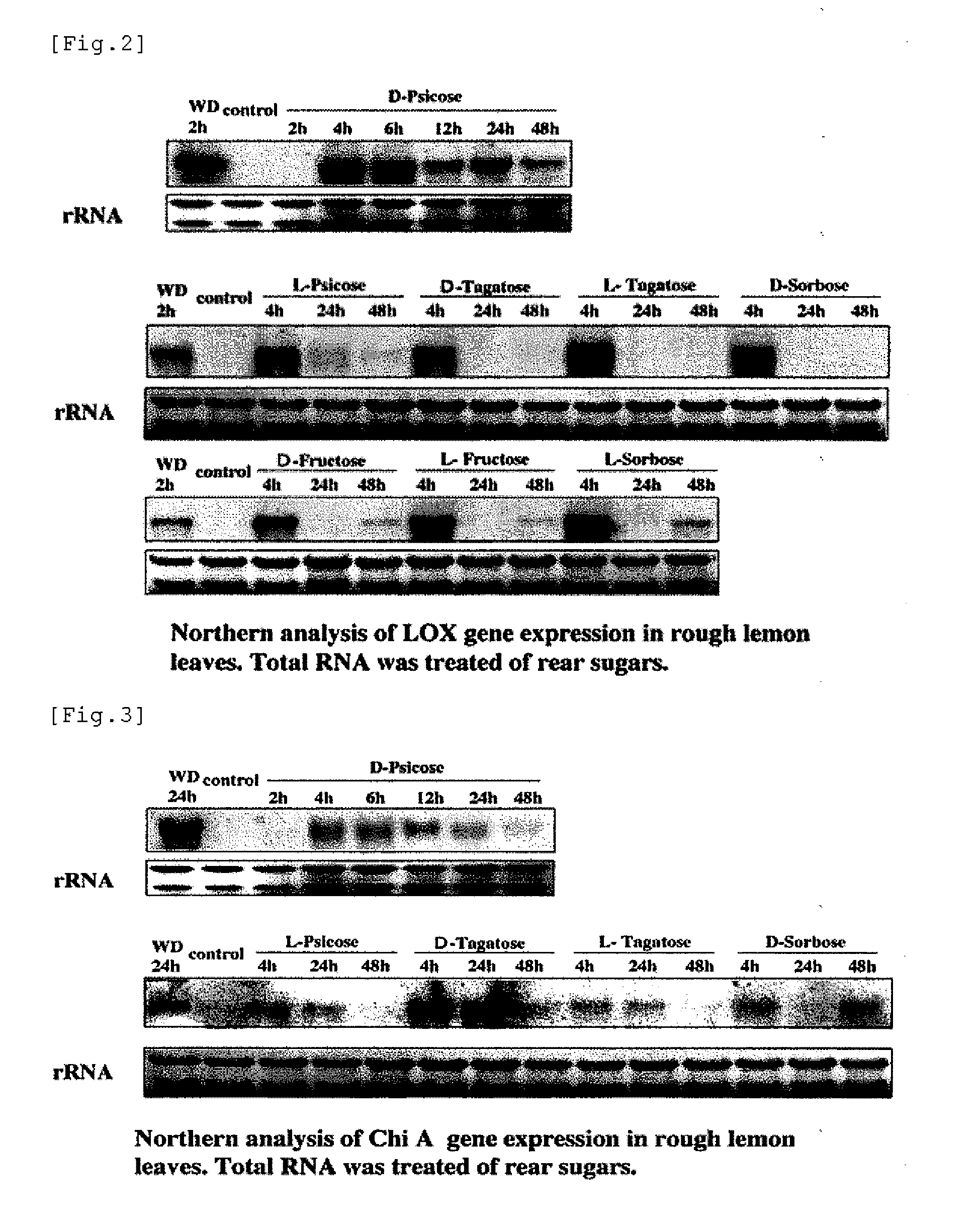
115 results about "D fructose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
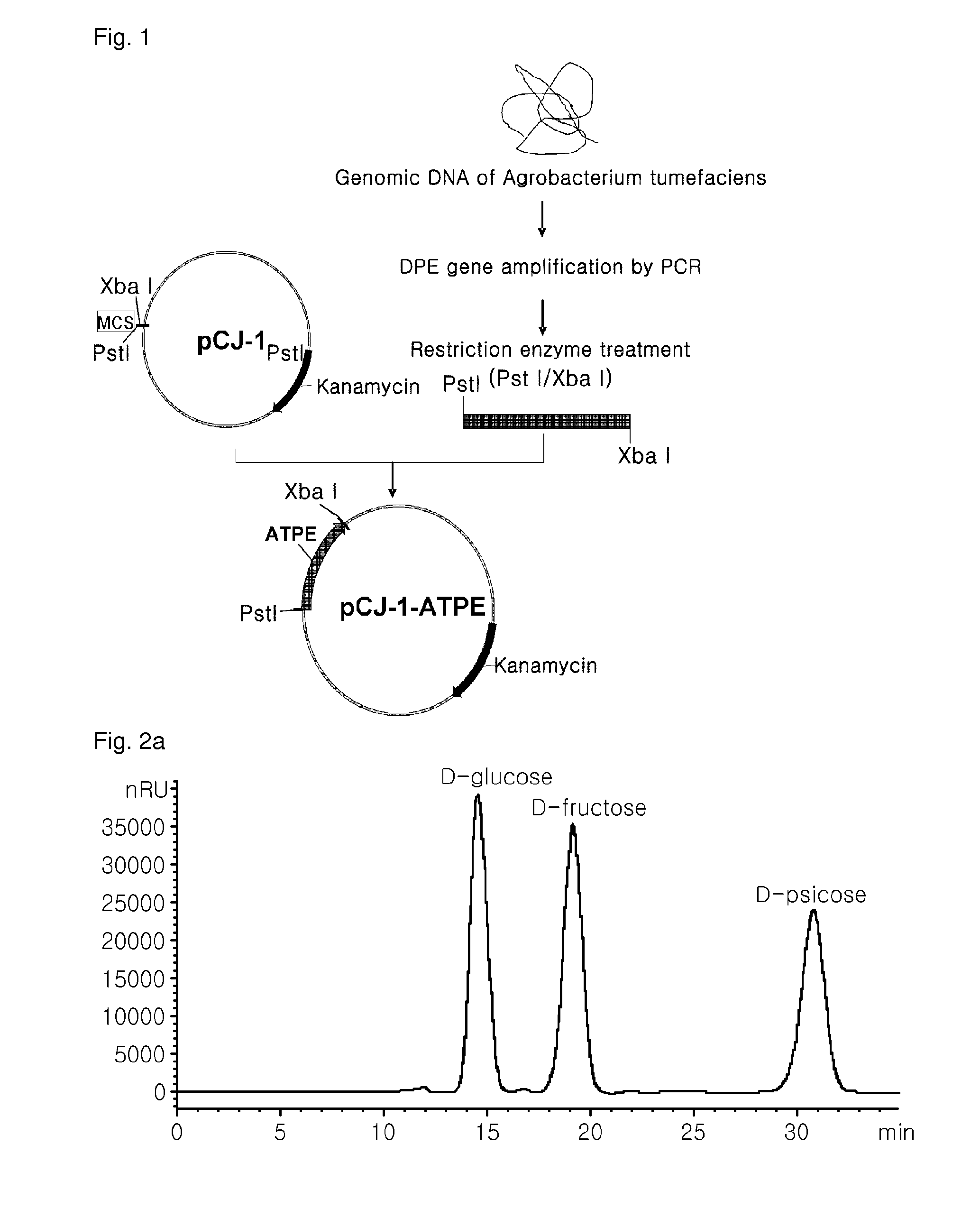
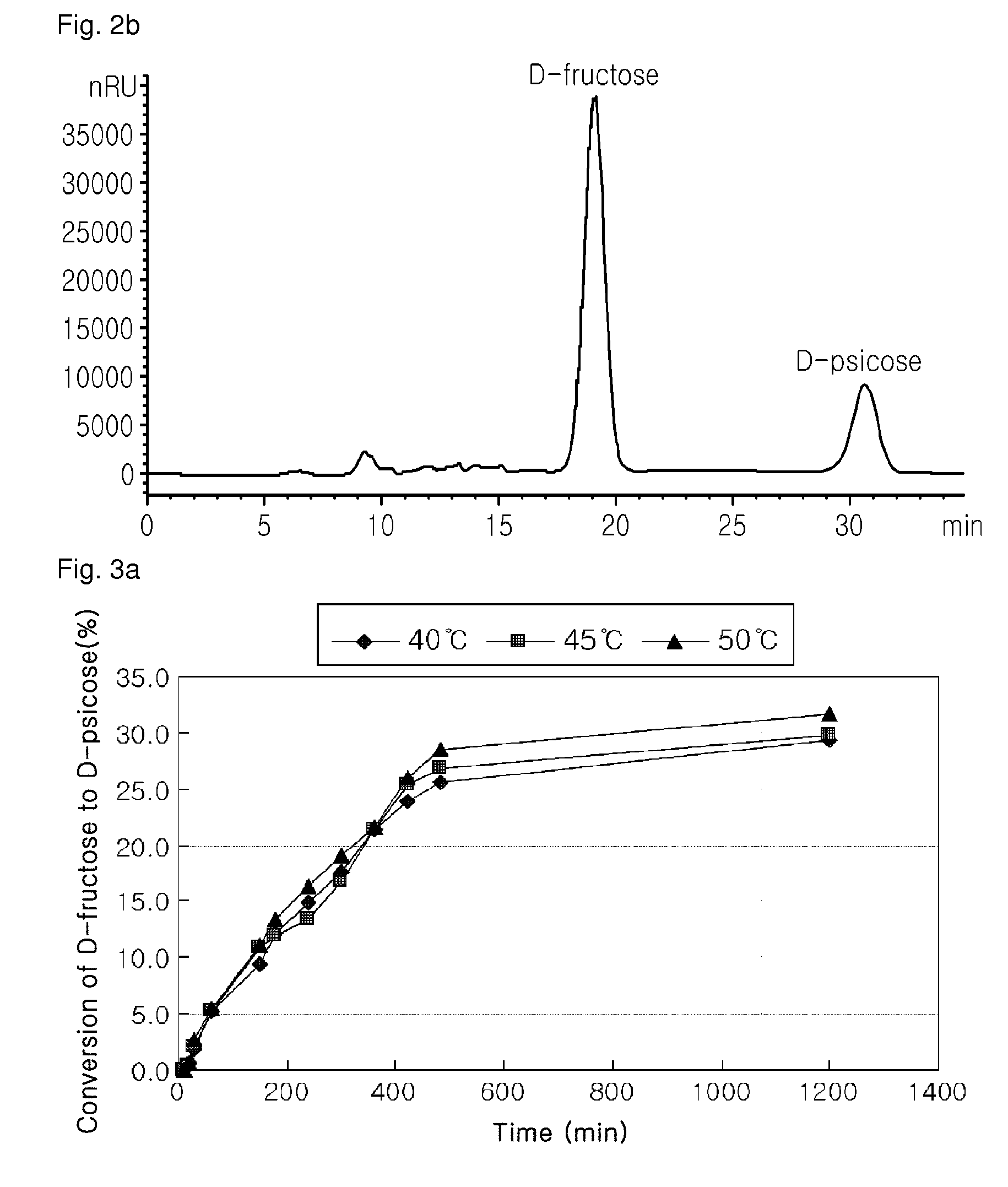
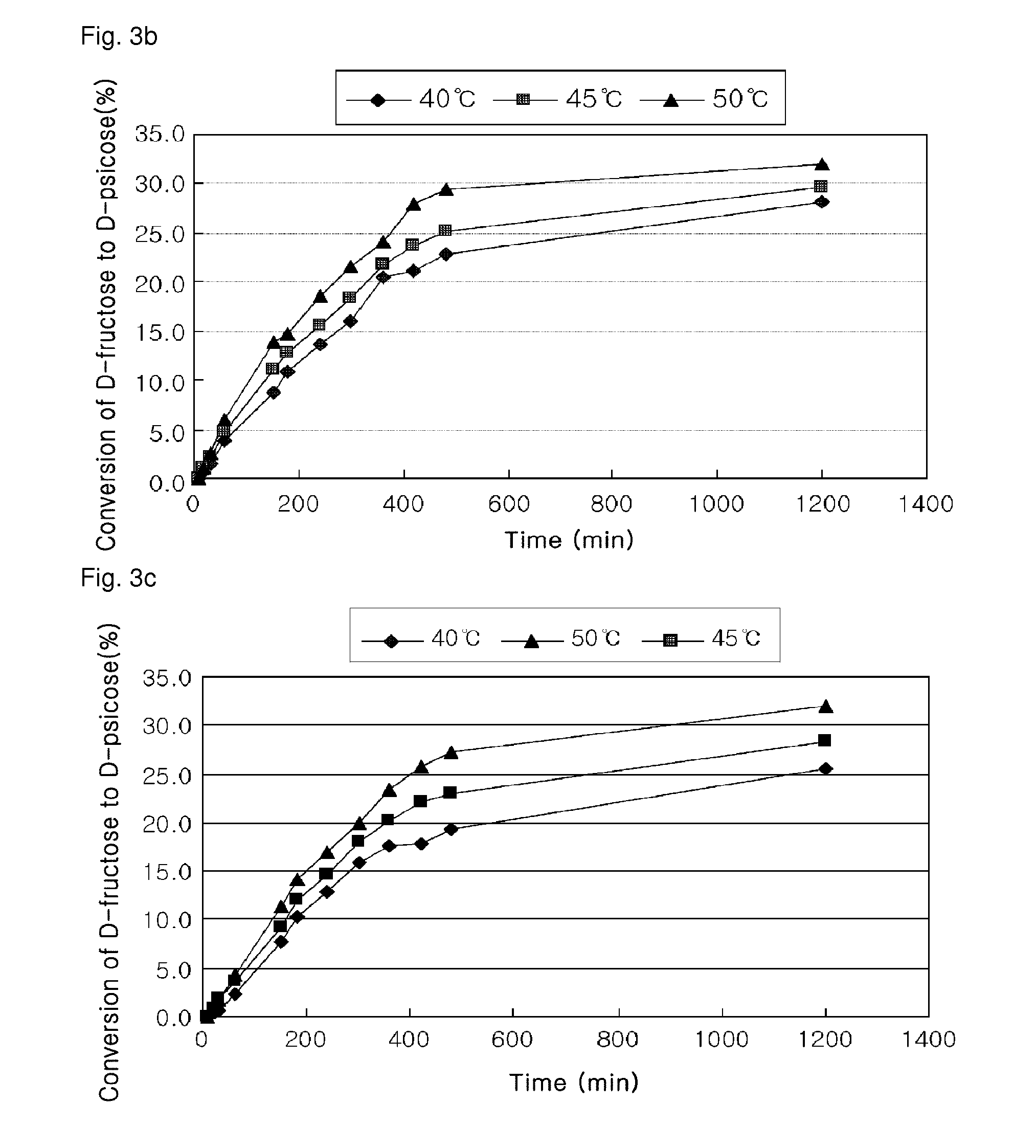
D-psicose production method by D-psicose epimerase
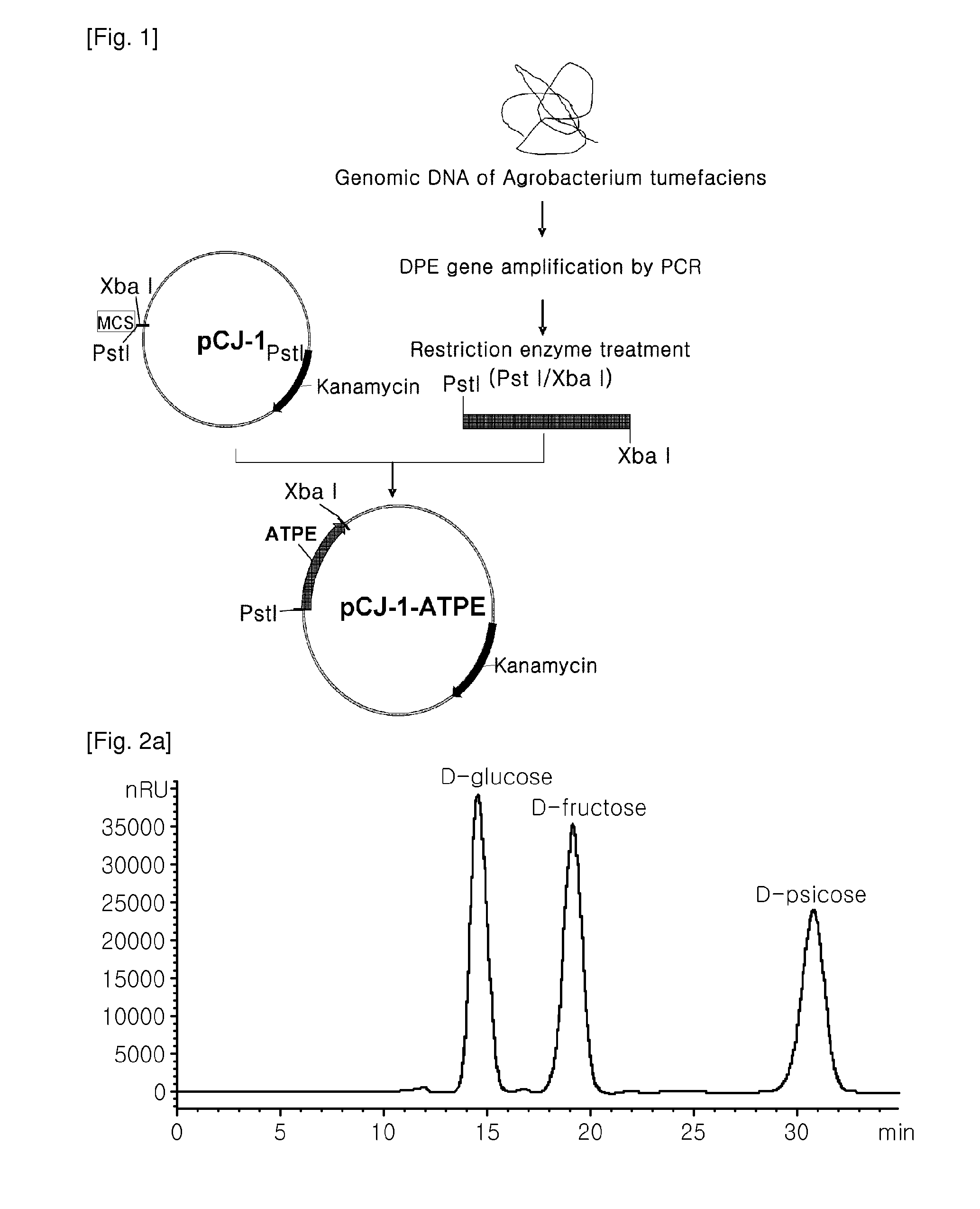
ActiveUS8030035B2Improve production yieldLow production costIsomerasesFermentationIsomerase activityEnzyme
Provided is a method of producing D-psicose using a D-psicose epimerase derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Provided are a protein having an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 and having a psicose 3-epimerase activity, a gene encoding the protein, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, and a method of producing D-psicose by reacting the protein produced on a mass scale with D-fructose. The method of producing D-psicose is an environmentally friendly method using a new enzyme, in which an inexpensive substrate is used, and the activity of the enzyme can be retained for a prolonged time period. Thus, the method can be efficiently used for the mass production of D-psicose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Ketose 3-epimerase produced by arthrobacter globiformis
There are provided a highly safe epimerase usable in food industry, and a method for producing a ketose. The epimerase is a ketose 3-epimerase obtainable from a microorganism of the genus Arthrobacter, and having the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 of the Sequence Listing, and (1) substrate specificity whereby a D- or L-ketose is epimerized at position 3 to produce a corresponding D- or L-ketose, and (2) the highest substrate specificity for D-fructose and D-psicose among D- and L-ketoses. The ketose 3-epimerase is also represented by SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4 of the Sequence Listing, and epimerizes a D- or L-ketose at position 3 to produce a corresponding D- or L-ketose.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD +1
Strain and method for preparing D-allulose by microbial transformation of D-levulose
ActiveCN101177672AImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial transformationFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a strain for producing D-piscose by using microorganism to transform D-fructose and a preparation method thereof, pertaining to food biotechnology field. The invention relates to a strain of spherical Rhodobacter sphaeroides SK011 screened from bottom mud of a fish-pond with the preservation number, CCTCC NO: M 207185, and the preparation method that the spherical Rhodobacter sphaeroides SK011 is used for transforming the D-fructose and producing the D-piscose through culture and fermentation. The invention adopts the SK011 as the strain and a fermentation culture medium which consists of carbon and nitrogen sources, inducer and inorganic salt; the obtained strain is further treated, so as to obtain cell biocatalyst; then by using the D-fructose as a substrate to do bio-transformation, the D-piscose is prepared. Under optimum conditions during the fermentation culture, fermenting solution or free cells or permeability cells or frozen dry powder or solidified cells thereof are used for transforming the D-fructose for 0.5 to 4.8 hours, and the content of the D-piscose in the transformation solution is 2 to 50g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Immobilization of psicose-epimerase and a method of producing D-psicose using the same
The present invention relates to a method of successively producing D-psicose from D-fructose or D-glucose by using a psicose-epimerase derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens which is expressed in a food safety form.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
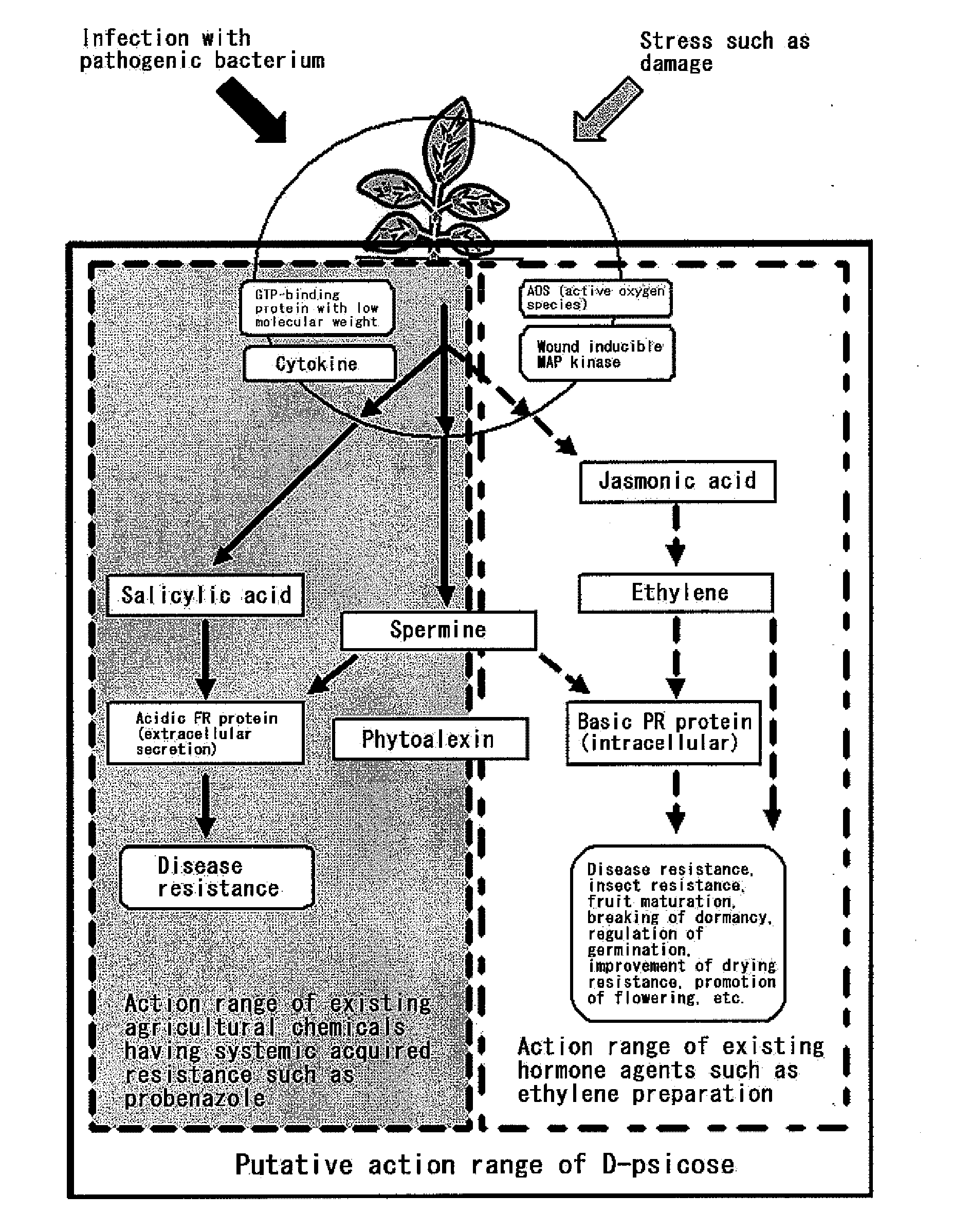
Utilization of Rare Sugars in Plant or Microorganism
InactiveUS20080182752A1Low toxicityEasy to degradePlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant hormoneGrowth retardant
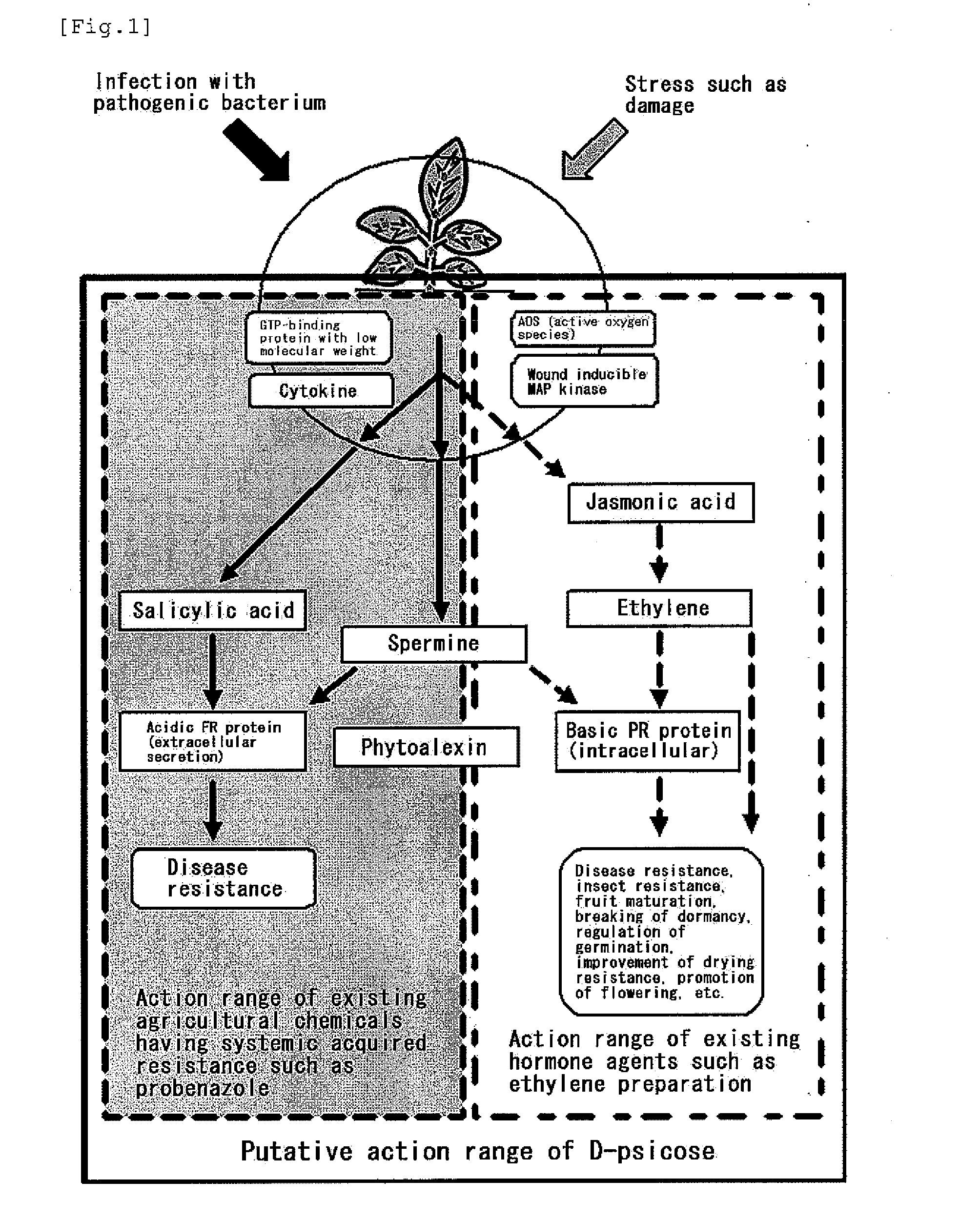
[OBJECT] To provide an agricultural chemical and the like with the use of an effect of inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant. To provide a growth inhibitor of not only a plant pathogenic bacterium but also a harmful microorganism.[MEANS FOR RESOLUTION] Utilization of a rare sugar for inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant or inhibiting the growth of a microorganism. Utilization thereof as an agricultural chemical with the use of the effect of inducing systemic acquired resistance in a plant, a plant disease inhibitor, an inducer of a plant growth regulatory factor (i.e., an inducer of plant hormone-like actions consisting of disease resistance, insect resistance, fruit maturation, breaking of dormancy, regulation of germination, drying resistance, and other than this, resistance to environmental stresses such as low temperature resistance, high temperature resistance, salt resistance and heavy metal resistance and promotion of flowering) and a microorganism growth inhibitor. The rare sugar is an aldose (D-allose, D-altrose or L-galactose) or a ketose (D-psicose or a mixture of D-psicose and D-fructose).
Owner:KAGAWA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of carbon quantum dots based on chemical reaction of fructose and sodium hydroxide
InactiveCN102942924AHigh fluorescence intensityEasy to operateLuminescent compositionsChemical reactionUltraviolet lights
The invention provides a preparation method of carbon quantum dots based on a chemical reaction of fructose and sodium hydroxide, and belongs to the technical field of nanomaterials. The method comprises a first step of preparing a D-fructose solution; a second step of preparing a sodium hydroxide solution; a third step of mixing the D-fructose solution with sodium hydroxide solution; and a fourth step of standing the mixed solution to obtain a carbon quantum dot solution. The preparation method is simple and economic, is easy to operate, and has extremely low energy consumption. The prepared carbon quantum dots have high fluorescent intensity, can transform ultraviolet light to green visible light, have no biological toxicity and no pollutions to the environment, and have great application potentiality in in improving conversion efficiency of solar cells and in the fields of biological labels, biological medicine and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Immobilization of psicose-epimerase and a method of producing d-psicose using the same
The present invention relates to a method of successively producing D-psicose from D-fructose or D-glucose by using a psicose-epimerase derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens which is expressed in a food safety form.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Preparation method of carbon quantum dots based on atmospheric pressure micro-plasma technology
InactiveCN102942170AHigh fluorescence intensityEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyNano-carbonSodium bicarbonatePhosphate
The invention provides a preparation method of carbon quantum dots based on atmospheric pressure micro-plasma technology. The method comprises a first step of preparing a D-fructose solution; a second step of preparing a solution of sodium hydroxide, or sodium bicarbonate potassium or dihydrogen phosphate; a third step of mixing the D-fructose solution with the solution of sodium hydroxide, or sodium bicarbonate potassium or dihydrogen phosphate; and a fourth step of performing atmospheric pressure micro-plasma electro discharge treatment on the mixed solution to obtain a carbon quantum dot solution. The preparation method is simple and economic, is easy to operate, and has extremely low energy consumption. The prepared carbon quantum dots have high fluorescent intensity, can transform ultraviolet light to blue visible light, have no biological toxicity and no pollutions to the environment, and have great application potentiality in improving conversion efficiency of solar cells and in the fields of biological labels, biological medicine and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for efficiently preparing D-psicose 3-epimerase and use of D-psicose 3-epimerase
InactiveCN107723307ALow costHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsozymePsicose
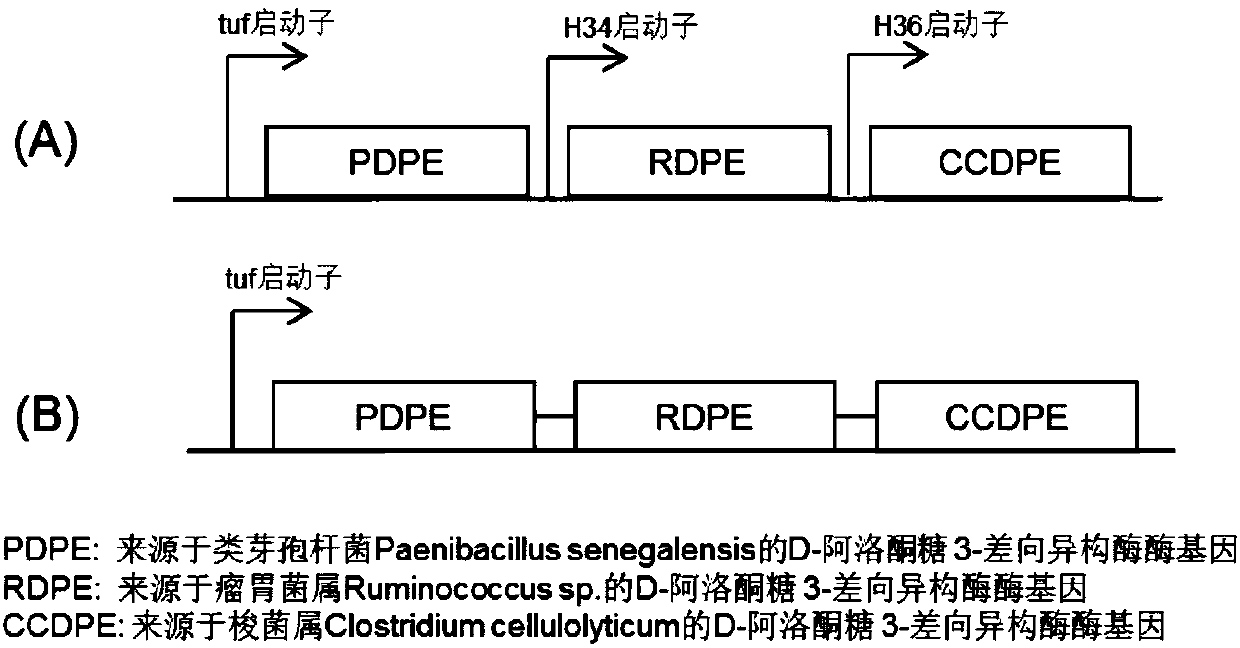
The invention discloses a method for efficiently preparing D-psicose 3-epimerase and a use of the D-psicose 3-epimerase and provides a method for efficiently preparing an enzyme catalyst for catalyzing the same reaction through isozyme combined expression. The method utilizes corynebacterium glutamicum as a host cell to construct a recombinant strain expressed by plasmid dissociation and chromosomal integration, measures D-fructose catalytic efficiency, improves enzyme catalytic efficiency by 2-4 times than that of single expression of D-psicose 3-epimerase through combined expression and hasa conversion ratio of 29% when 70% of fructose is a substrate. The method improves D-psicose production efficiency and is suitable for industrial production of D-psicose. The invention also disclosesa novel use of the D-psicose 3-epimerase in psicose synthesis. The enzyme is derived from Paenibacillus senegalensis, has catalytic activity of about 25 U / mg and can be used to convert D-fructose intoD-psicose.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
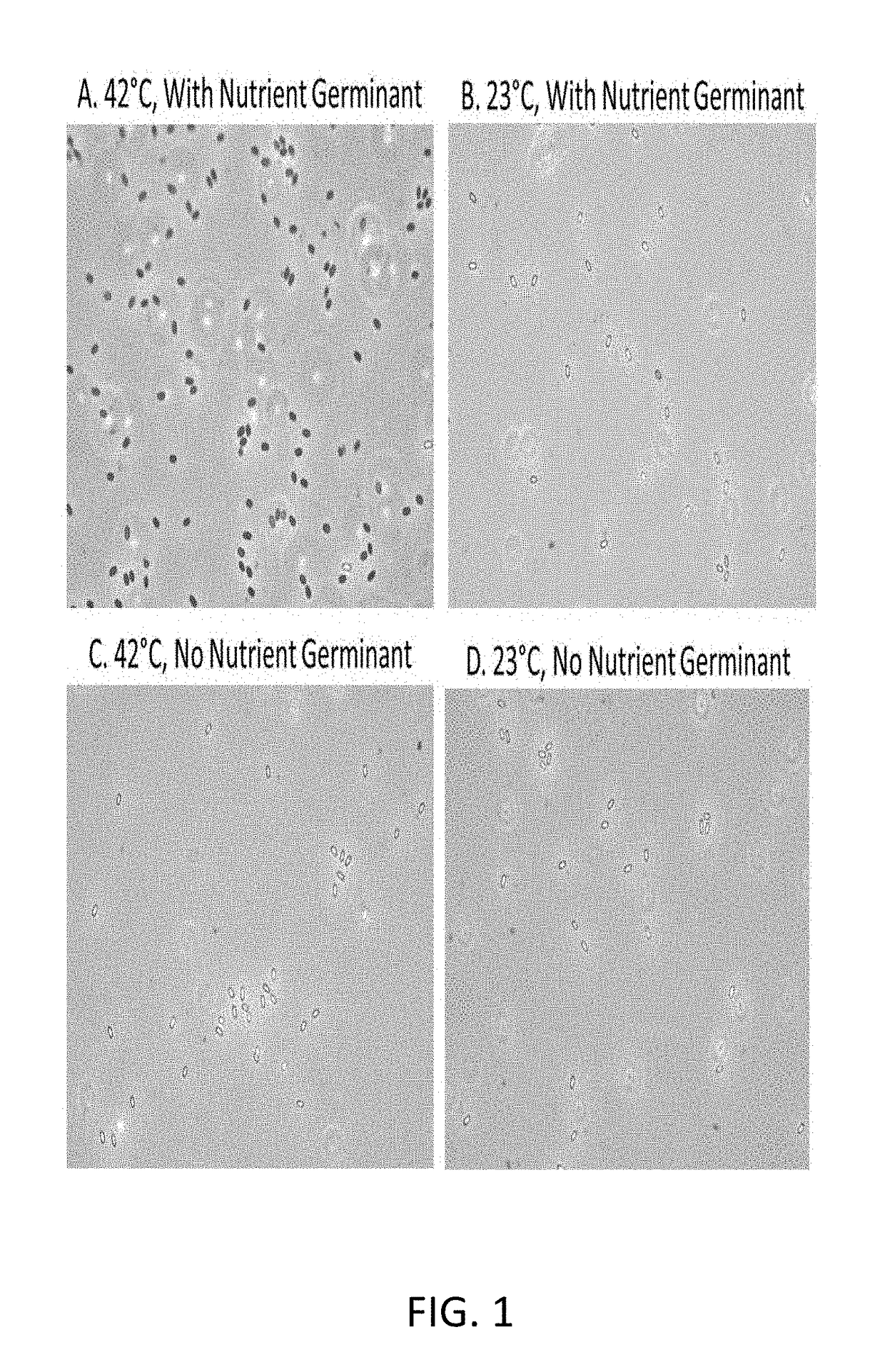
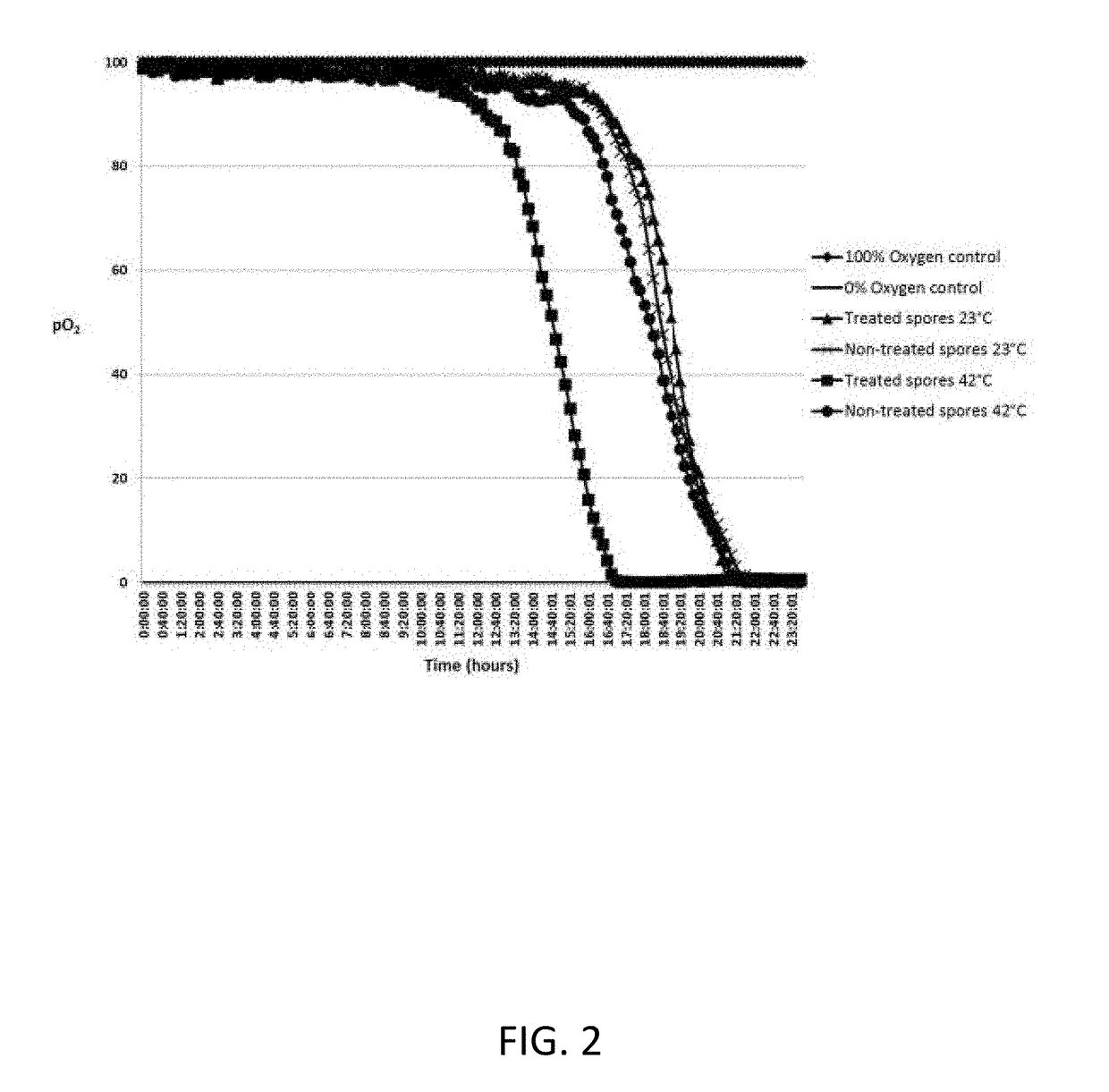
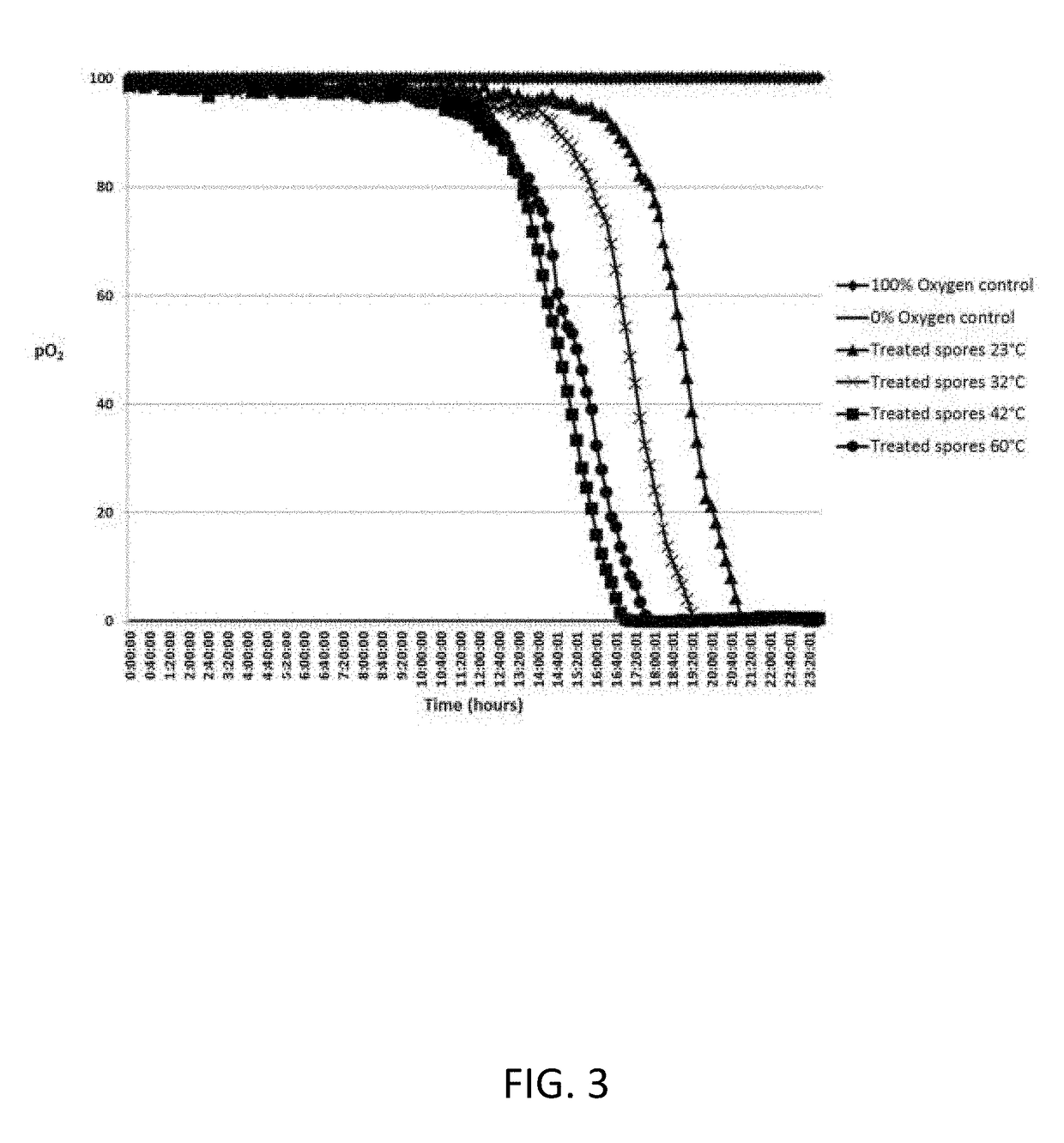
Nutrient Rich Germinant Composition and Spore Incubation Method
ActiveUS20170281696A1Easy and fast mixingLow costBacteriaInorganic non-active ingredientsSpore germinationD-Glucose
A nutrient-germinant composition to aid in spore germination and a method for increased spore germination efficiency. The composition comprises L-amino acids, D-glucose and / or D-fructose, a phosphate buffer, an industrial preservative, and may include bacteria spores or they may be separately combined for germination. The method comprises providing a nutrient-germinant composition and bacteria spores, preferably of one or more Bacillus species, and heating to a preferred elevated temperature range of 41° C. to 44° C. for an incubation period of around 2 to 60 minutes. The nutrient-germinant composition is preferably in a concentrated liquid form that is diluted just prior to initiating the germination / incubation method at the point of use. The method may also include dispensing a germinated spore solution to a point-of-use / consumption, such as animal feed, water, or bedding, or a wastewater system or drain.
Owner:NCH CORP
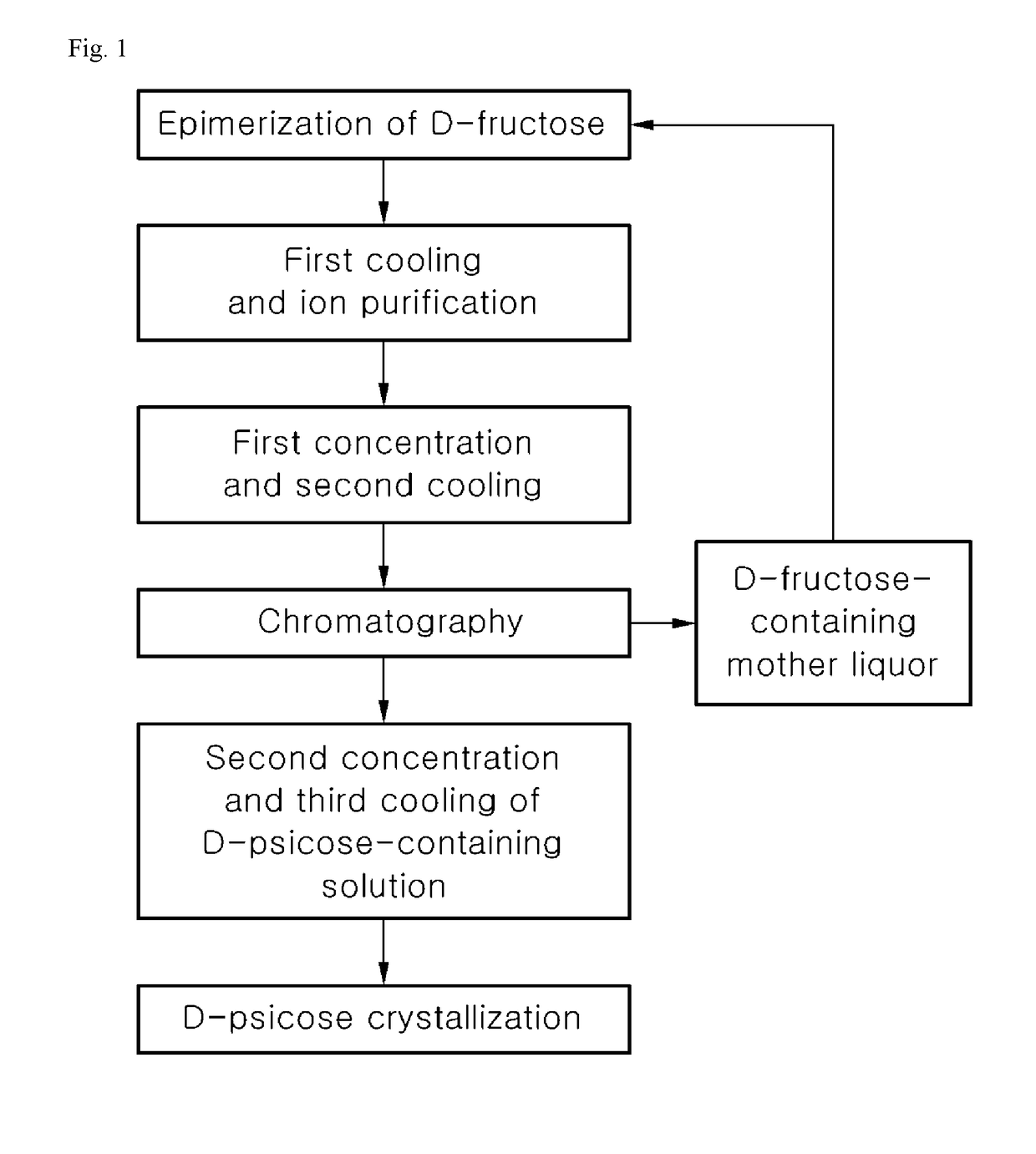
Method of producing high purity d-psicose
ActiveUS20180327796A1Prevent thermal deformationHigh yieldCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersChromatographic separationD fructose
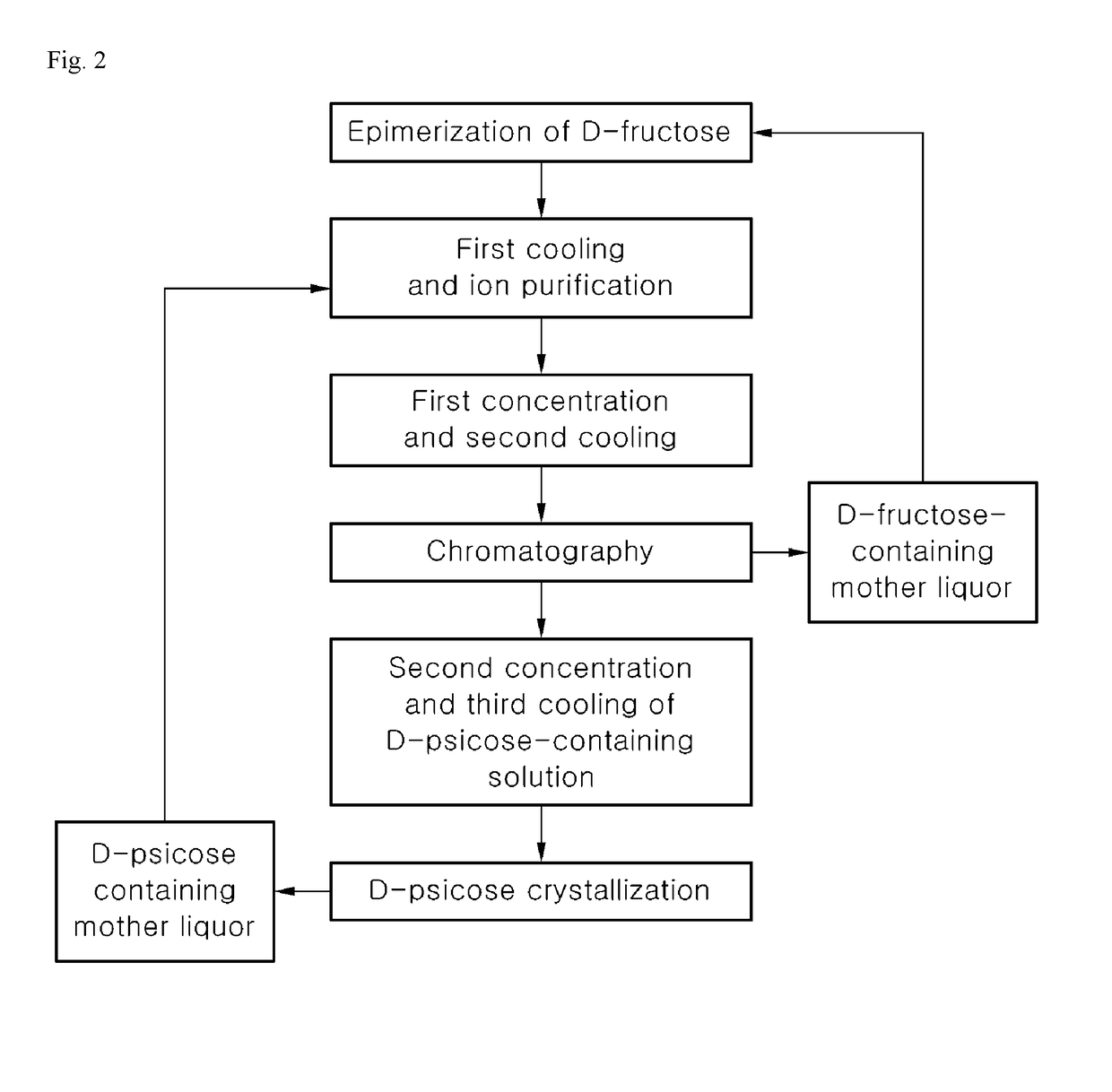
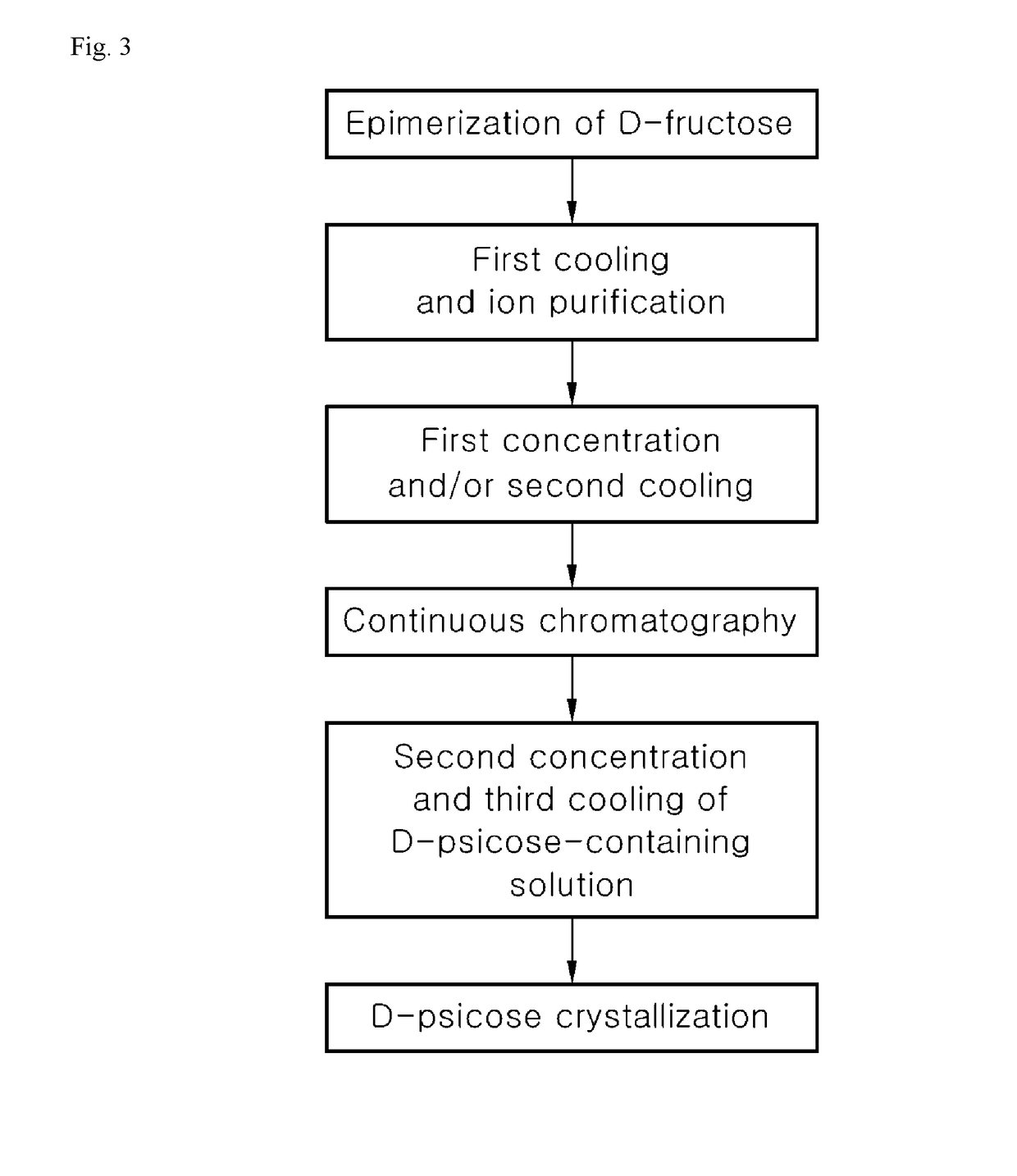
Disclosed herein is a method of producing D-psicose. The method of producing D-psicose includes subjecting D-fructose to D-psicose epimerization to produce a D-psicose-containing solution, subjecting the D-psicose-containing solution to first cooling and ion purification, subjecting the purified D-psicose-containing solution to first concentration and second cooling, subjecting the D-psicose-containing solution, which has been subjected to first concentration and second cooling, to chromatography to obtain a D-fructose-containing mother liquor and a D-psicose-containing separated solution, and subjecting the D-psicose-containing separated solution to second concentration and third cooling to obtain D-psicose crystals, wherein the D-fructose-containing mother liquor produced by chromatography is reused in the D-psicose epimerization.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for preparing D-fructose through isomerization of D-glucose
InactiveCN105837643ANo toxicityHigh yieldSugar derivativesMolecular sieve catalystsIsomerizationD-Glucose
The invention provides a method for preparing D-fructose through isomerization of D-glucose .The method includes the following processing steps that firstly, adding D-glucose, solvent and a catalyst into a high-pressure reaction kettle to form a reaction system, wherein the mass concentration of D-glucose is 0.1-99%, and the mass ratio of the catalyst to D-glucose is 0.01-10; secondly, conducting reaction for 0.01-100 hours under the protection of inert gas at a temperature of 20-400 DEG C, and conducting separation and purification after reaction ends to prepare D-fructose .The method has the advantages that the applied catalyst is low in price, easy to obtain, free of toxin, environmentally friendly and high in product yield .
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Cordyceps militaris liquid culture medium and culture method of cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN105039467AIncrease contentEasy extractionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCulture mediumsLiquid culture
The invention relates to a cordyceps militaris liquid culture medium which comprises the following components: 1-3 g / L of KH2PO4, 1-3 g / L of MgSO4, 5-20 g / L of a nitrogen source, 200-500 g / L of potatoes, 8-15 g / L of D-fructose, 20-50 g / L of agar, 10-25 g / L of basic amino acid, 8-20 g / L of acidic amino acid, and 30-50 g / L of silkworm chrysalis meal. The liquid culture medium provided by the invention uses D-fructose as a carbon source; basic amino acid and acidic amino acid are added to the culture medium; the yield of the cordyceps militaris cultured by using the liquid culture medium is remarkably improved, and the production of cordycepin in the cordyceps militaris is also improved; the production cycle is short; the follow-up extraction and separation of cordycepin are convenient; the cordyceps militaris liquid culture medium is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:中山鼎晟生物科技有限公司
Inulin soya-bean milk beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103120219AImprove rheological propertiesImprove featuresMilk substitutesFood scienceFermentationSoya bean
The invention discloses an inulin soya-bean milk beverage and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of food processing. The inulin soya-bean milk beverage disclosed by the invention mainly consists of the following components in parts by weight: 80-120 parts of soya-bean milk, 2-20 parts of inulin, 1-5 parts of honey and 0.1-0.4 parts of a stabilizer, wherein the inulin, which is also called as synanthrin, is linear straight-chain polysaccharide formed by D-fructose through key jointing of beta (1 to 2), the tail end of the inulin is provided with a glucose residue, and the degree of polymerization is 2-60. The inulin, as a soluble dietary fiber different from a starch structure, can selectively promote the growth of colon probiotics and improve the health condition of a host. The inulin soya-bean milk beverage disclosed by the invention is white, is exquisite and smooth in mouth feel, has a low caloric value and can promote the growth of human colon probiotics, inhibit toxic fermentation products, promote the absorption of mineral materials such as calcium, magnesium and iron and improve the physiological functions such as immunity of the organism.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
D-psicose 3-epimerase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency
ActiveCN108018278AHigh catalytic efficiencyIncreased relative enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPsicoseMutant enzyme
The invention discloses a D-psicose 3-epimerase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The Dorea sp. DPEase mutant enzyme A38E / G105A keepsthe optimal catalytic conditions. Under the optimal catalytic conditions, the relative enzyme activity of the enzyme for catalytic conversion of D-fructose as a substrate into D-psicose is improved by38.6%. The discovery has an important research value for the industrial production of D-psicose.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Coumarins compound containing aryl boric acid and application thereof in detection of sugar
InactiveCN102887914AGood water solubilityEliminate distractionsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceDolichol
The invention relates to a coumarins compound containing aryl boric acid and an application of the coumarins compound containing aryl boric acid in detection of sugar, wherein a novel fluorescent molecular probe utilizes the property of combining aryl boric acid with polybasic alcohol; the spectrums of the compound before and after a reaction with sugar are evidently changed such that the compound has higher detection sensitivity to D-fructose and D-sorbitol; the emission wavelength reaches 620 nm and is located in a red light area; the compound provided by the invention is suitable for detecting the content of the sugar in an organism.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel D-allulose 3-epimerase and application thereof
ActiveCN109306347AImprove conversion rateImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThermal stability
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and in particular relates to novel D-allulose 3-epimerase, DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) for encoding the novel D-allulose 3-epimerase, an expression vector and a transformant containing the DNA and application of the enzyme to production of D-allulose. The D-allulose 3-epimerase is derived from thermoacidophile mesoaciditoga lauensis of a deep-sea spring and has relatively high conversion rate and thermal stability when being used for converting D-fructose into the D-allulose.
Owner:JILIN COFCO BIOCHEM +1
Immobilization method for cells containing glucose isomerase
ActiveCN104962546AImmobilization method is simpleMeet the use requirementsMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesEscherichia coliGenetic engineering
The invention discloses an immobilization method for cells containing glucose isomerase. The immobilization method comprises the following steps of adding wet bacteria obtained by performing fermented culture on a recombinant genetic engineering strain containing glucose isomerase genes in buffer liquor so as to obtain bacterial suspension; adding a carrier in the bacterial suspension; uniformly stirring the bacterial suspension; adding polyethyleneimine and glutaraldehyde to perform crosslinking; filtering the bacterial suspension after performing stirring crosslinking on the bacterial suspension for 1-2 hours at the temperature of 0-30 DEG C; washing filter cakes by using distilled water; extruding the filter cakes into long strips by using an axial extruder; airing the long strips at room temperature; and smashing the long strips into granules so as to obtain immobilized glucose isomerase cells containing the glucose isomerase. The immobilization method has the advantages that the cost of an immobilization material is low, the method is easy to operate and high in mechanical strength, the immobilization material is stable at high temperature, prepared recombinant escherichia coli whole cells for producing the glucose isomerase in an immobilization manner can be used for catalyzing D-glucose to produce D-fructose at high temperature, the conversion rate is 54% at the temperature of 85 DEG C, after being repeatedly used ten times, the cells still have enzyme activity which is higher than 90%, and the industrial application prospect is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Sweetener composition, method for manufacturing same and use thereof
InactiveCN105163603ALow costIncrease sweetnessOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsDiseaseRare sugar
The present invention provides a novel sweetener, which is free from a risk of diseases caused by the intake of isomerized sugars and overcomes problems encountered in the course of producing a rare sugar-containing syrup or disadvantages in taste, a method for manufacturing the same, and a use thereof. A method for manufacturing a sweetener composition, said method comprising: treating sucrose with an acid and / or an enzyme under specific conditions to thereby efficiently decompose sucrose into glucose and fructose; and then isomerizing the obtained mixture using an alkali and / or an enzyme under specific conditions in such a manner as to allow the resultant isomerized product to contain D-psicose mainly as a rare sugar so that the product comprises, at a specific composition ratio, sucrose, D-glucose, D-fructose and rare sugar(s) at least containing D-psicose, or the product comprises, at a specific composition ratio, D-glucose, D-fructose and rare sugar(s) at least containing D-psicose.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD
Method of separating D-fructose and D-psicose by using simulated moving bed
ActiveCN109232675AReduce usageHigh puritySugar derivativesFermentationNanoparticleSimulated moving bed
The invention discloses a method of separating D-fructose and D-psicose by using a simulated moving bed. The method comprises the following steps of: step (1) converting D-psicose, to be specific, converting the D-fructose into the D-psicose by using immobilized D-psicose epimerase nanoparticles, thereby obtaining a mixed sugar solution; step (2) pretreating the mixed sugar solution, to be specific, carrying out decolorizing pretreatment on the mixed sugar solution; and step (3) separating by using the sequential simulated moving bed, to be specific, separating the pretreated mixed sugar solution according to the specific separation parameters of the sequential simulated moving bed to obtain the D-psicose solution and the D-fructose solution, wherein the purity of the D-psicose solution isgreater than or equal to 99%, the recovery rate of the D-psicose solution is greater than or equal to 95%, the purity of the D-fructose solution is greater than or equal to 99%, and the recovery rateof the D-psicose solution is greater than or equal to 90%. In summary, the method has the beneficial effects that the purity and recovery rate of the separated products are high, the sequential simulated moving bed is used for replacing a traditional simulated bed, and the number of chromatographic columns used and the production cost are reduced.
Owner:陕西省生物农业研究所 +1
Strain capable of producing D-mannose isomerase and method for producing D-mannose isomerase by using same
InactiveCN104774794AEfficient productionSuitable for mass productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas tolaasiiMicrobiology
The invention provides a strain capable of producing D-mannose isomerase and a method for producing D-mannose isomerase by using the same, belonging to the food biotechnical field. The invention provides a pseudomonas sp. SK27.016 screened from rotted juicy peach and collected at China Center for Type Culture Collection with a collection number of CCTCC NO.M2014411 and further provides a method for producing D-mannose isomerase through fermentation by using the strain. The method comprises the following steps: (a) fermenting the strain in a fermentation culture medium to obtain the thalli of pseudomonas sp. SK27.016; (b) converting D-fructose by using intracellular D-mannose isomerase produced by pseudomonas sp. SK27.016 to produce D-mannose; and (c) separating and purifying D-mannose. According to the method, D-mannose isomerase produced by the strain is used for efficiently producing D-mannose from D-fructose; therefore, the method is suitable for mass production and a new method is provided for enzyme-method industrial preparation of D-mannose.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-purity SiC ceramic prepared through normal-pressure solid-phase sintering and preparing method thereof
The invention relates to a high-purity SiC ceramic prepared through normal-pressure solid-phase sintering and a preparing method thereof. The preparing method of the high-purity SiC ceramic comprisesthe steps of 1, adding alpha-SiC powder and an aqueous solution containing a sintering aid into a solvent, and mixing the materials to obtain SiC slurry, wherein the sintering aid comprises a source Band a source C, the source B is boric acid, and the source C is selected from at least one of D-fructose and glucose; 2, drying and forming the obtained SiC slurry to obtain an SiC blank; 3, conducting vacuum debinding on the obtained SiC blank, putting the SiC blank in an inert atmosphere, and conducting sintering for 30-120 minutes at 2,050-2,250 DEG C to obtain the high-purity SiC ceramic, wherein the addition amount of the element B in the source B accounts for 0.1-1 wt% of the mass of the alpha-SiC powder, and the addition amount of the element C in the source C does not exceed 5 wt% ofthe mass of the alpha-SiC powder.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
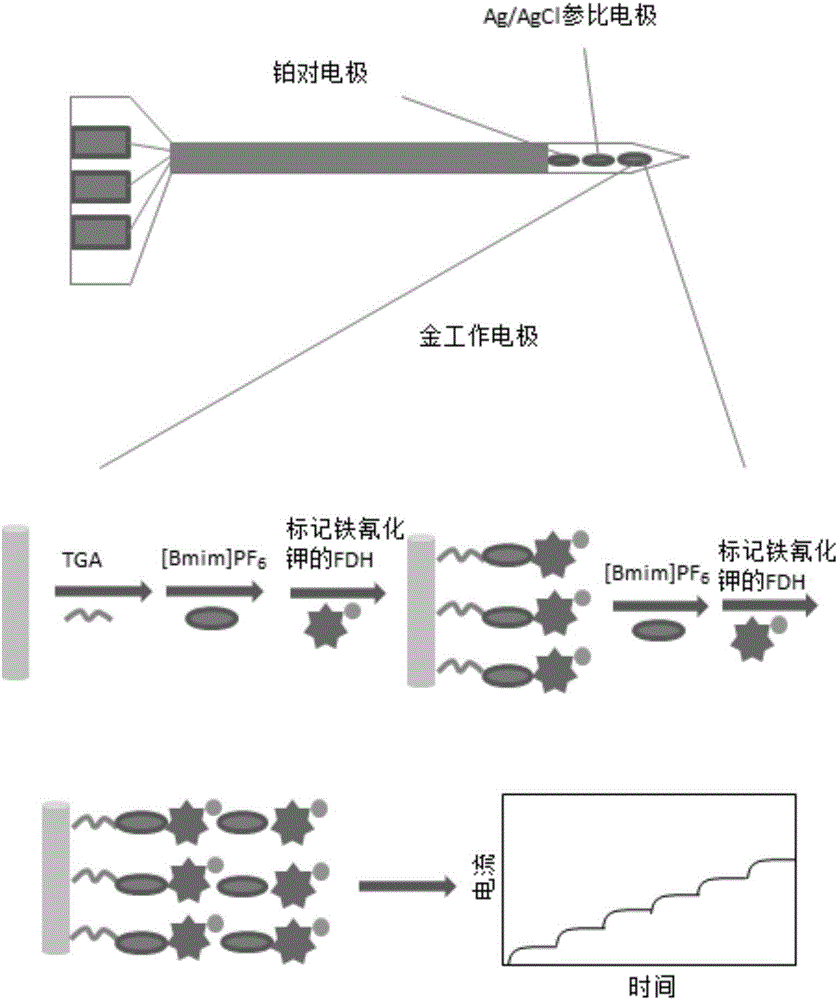
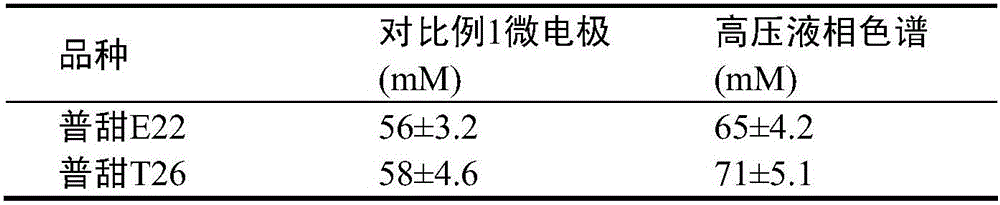
A microelectrode biosensor for in-situ real-time monitoring of the fructose content of a plant and applications thereof
ActiveCN106525939ANo physical damageFructose content understandingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPotassium ferricyanide5-keto-D-fructose
The invention relates to the technical field of microelectrode biological sensing, and particularly discloses a microelectrode biosensor for in-situ real-time monitoring of the fructose content of a plant. According to the microelectrode biosensor, mercaptoacetic acid is assembled onto a work electrode through a drip coating method, then an ionic liquid [Bmim]PF6 is adsorbed to further modify a mixture of fructose dehydrogenase and a potassium ferricyanide medium micromolecule, then the process is repeated to achieve a multilayer modified work electrode of the ionic liquid and the fructose dehydrogenase, the fructose dehydrogenase can catalyze 5-keto-D-fructose generation from D-fructose, and real-time dynamic responses of the enzyme to fructose changes are recorded through chronoamperometry. Through application of the microelectrode biosensor, in-situ real-time monitoring of the fructose content of the plant can be achieved, a tested sample is free of substantial damage, an obtained data result can reflect content changes of fructose in the plant in real time and dynamically, and practical application and operation are simple and convenient and easy to master.
Owner:NONGXIN TECH BEIJING CO LTD
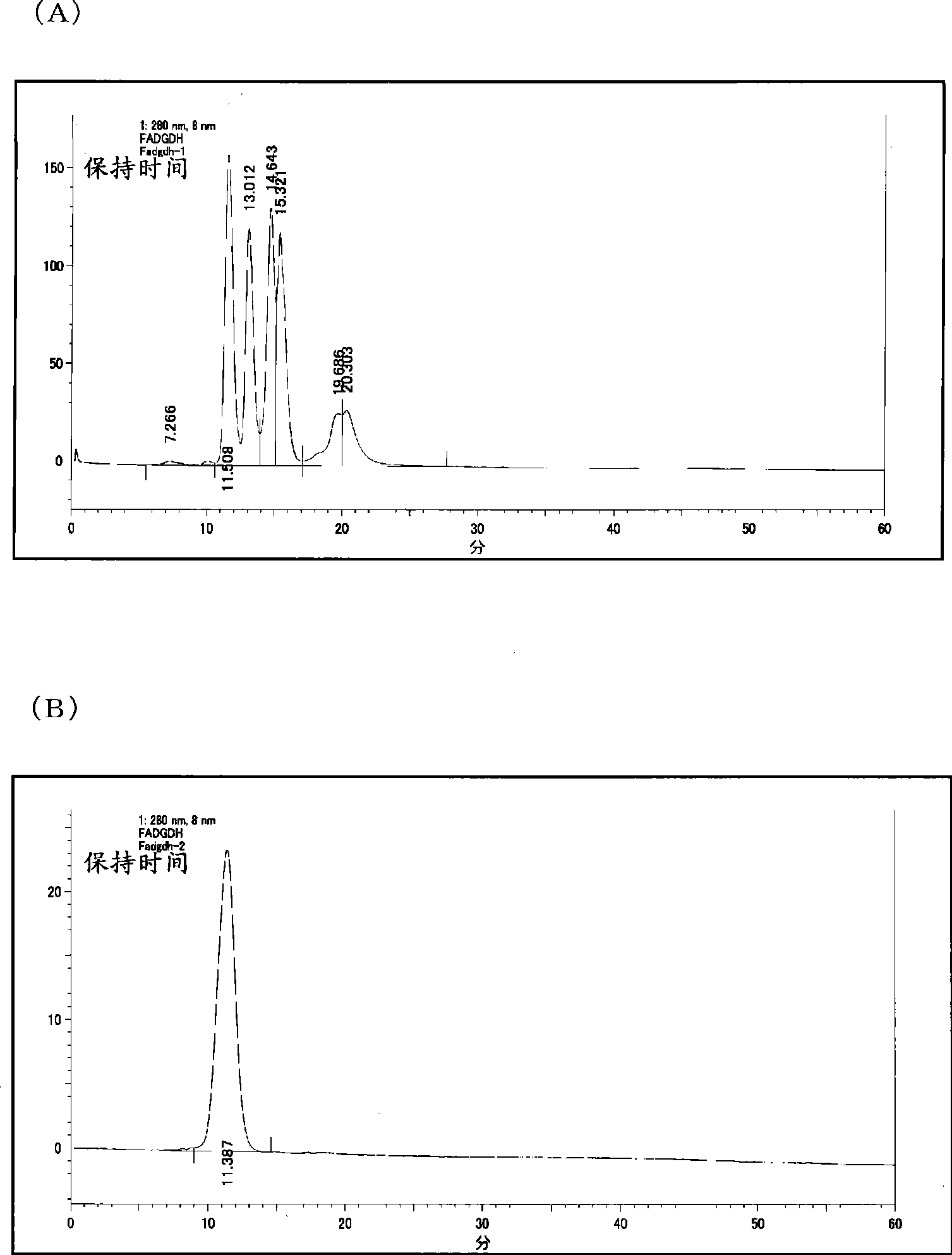
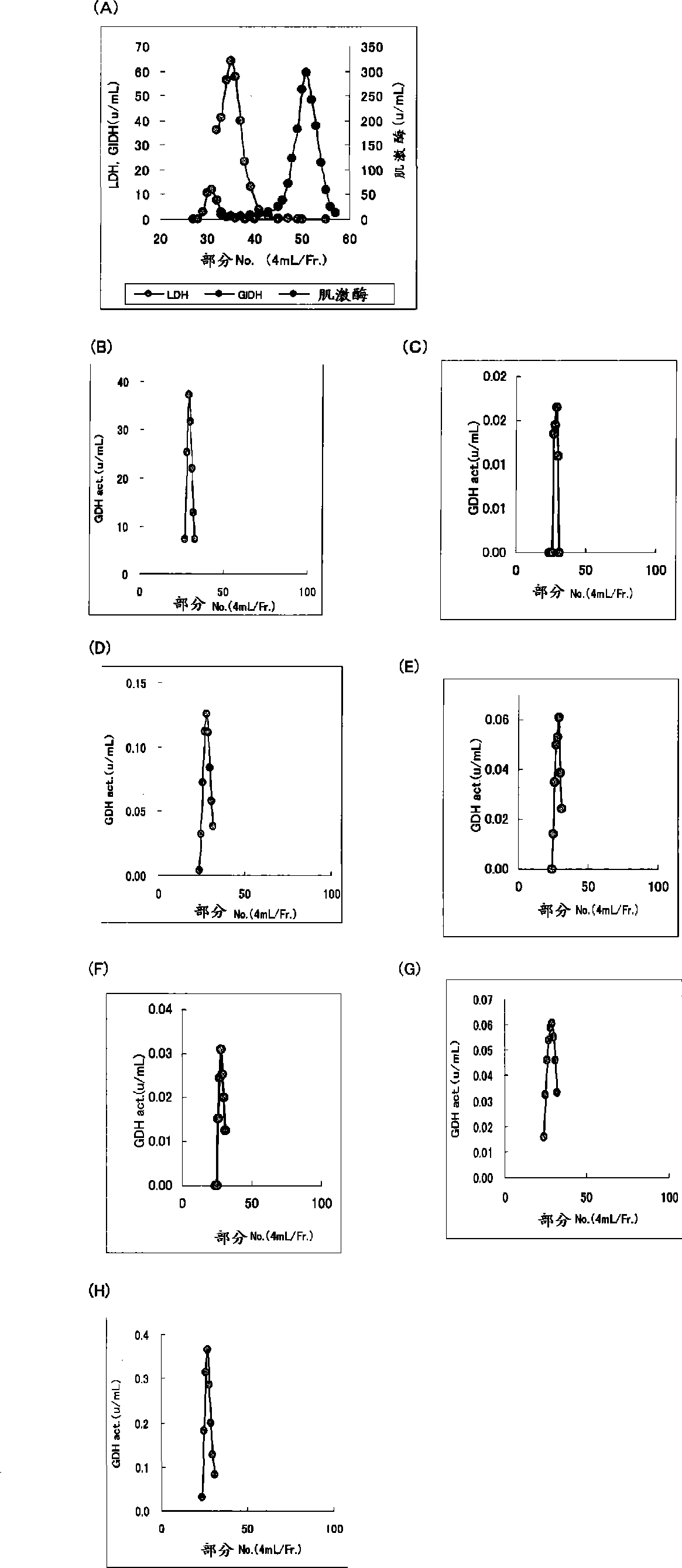
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS8945359B2Good reproducibilityImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConcentrations glucoseMaltose
The invention provides a flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase exhibiting reduced fluctuation of activity depending on temperature environment, and a method for measuring glucose concentration using the flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has the following properties (1) to (3): (1) activity: which exhibits glucose dehydrogenase activity in the presence of an electron acceptor; (2) substrate specificity: which exhibits an activity of 10% or less against maltose, D-galactose, D-fructose, sorbitol, lactose and sucrose when the activity against D-glucose is defined as 100%; and (3) temperature characteristics: which exhibits lower fluctuation of activity in a wide temperature range of 10 to 50° C.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Bacillus pumilus mutant and alkaline proteinase produced from the same by fermenting
The present invention provides one kind of Bacillus pumilus mutant with high yield of alkali protease and the process of fermenting with the strain to prepare alkali protease, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The strain is obtained with Bacillus pumilus strain 1.894 and through ultraviolet mutagenesis and screening. Into wheat bran as main substrate, yeast extract, D-fructose, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and water are added and Bacillus pumilus strain 2080 is inoculated and cultured statically at air condition and 35 deg.c for 48 hr to reach alkali protease producing peak. Then, the culture is leached with Na2CO3 / NaHCO3 buffering solution and filtered to obtain the filtrate as the alkali protease liquid, and the alkali protease liquid is ultrafiltering concentrated or spray dried to obtain the alkali protease powder. The present invention has alkali protease yield up to 15.3 Kilounit / g dry substrate.
Owner:BEIJING UNION UNIVERSITY
Glucose isomerase, gene, vector, engineering bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN106566824AIncrease enzyme activityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsomerizationHigh fructose
The invention discloses a glucose isomerase, a gene, a vector, an engineering bacteria and the application thereof in preparing D-fructose through catalyzing the D-glucose isomerization. The amino acid sequence of the glucose isomerase is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention provides a novel high-temperature-resistant glucose isomerase. The glucose isomerase is higher in enzyme activity (2.42 U / mg) and excellent in thermal stability. At the temperature of 85 DEG C, 20 mM of a manganese salt additive is added and 80% of the initial enzyme activity is still retained even after the temperature is maintained for 48 hours. Therefore, the glucose isomerase has an industrial application potential in the biocatalytic production of high fructose syrup at a high temperature.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Synthetic method of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural doped 2,3-unsaturated glucoside
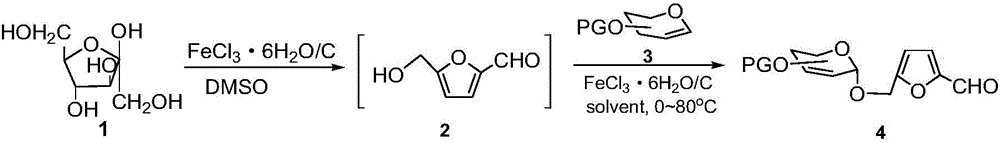
InactiveCN106117283AOmit separationOmit purificationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHydroxymethylfurfuralRearrangement reaction
The invention discloses a synthetic method of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural doped 2,3-unsaturated glucoside. The synthetic method is characterized in that a Ferrier rearrangement reaction is carried out on D-fructose in dimethyl sulfoxide by taking FeCl3 6H2O / C as a catalyst, prepared 5-hydroxymethyl furfural is not separated and is directly used as a receptor in the next Ferrier rearrangement reaction, and a one-pot reaction is carried out on the receptor and 2,3-unsaturated saccharides which are used as a donor to synthetize 2,3-unsaturated glucoside. Compared with the prior art, the synthetic method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that two reactions are used as the one-pot reaction to synthetize the 2,3-unsaturated glucoside, cyclic utilization of the catalyst is up to at least three times, the catalyst still has relative high catalytic activity, the technology is simple, the operation is convenient, the yield is high, the production cost is low, and the synthetic method is an environment-friendly, economical and efficient novel method for synthetizing the 2,3-unsaturated glucoside and has a good application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
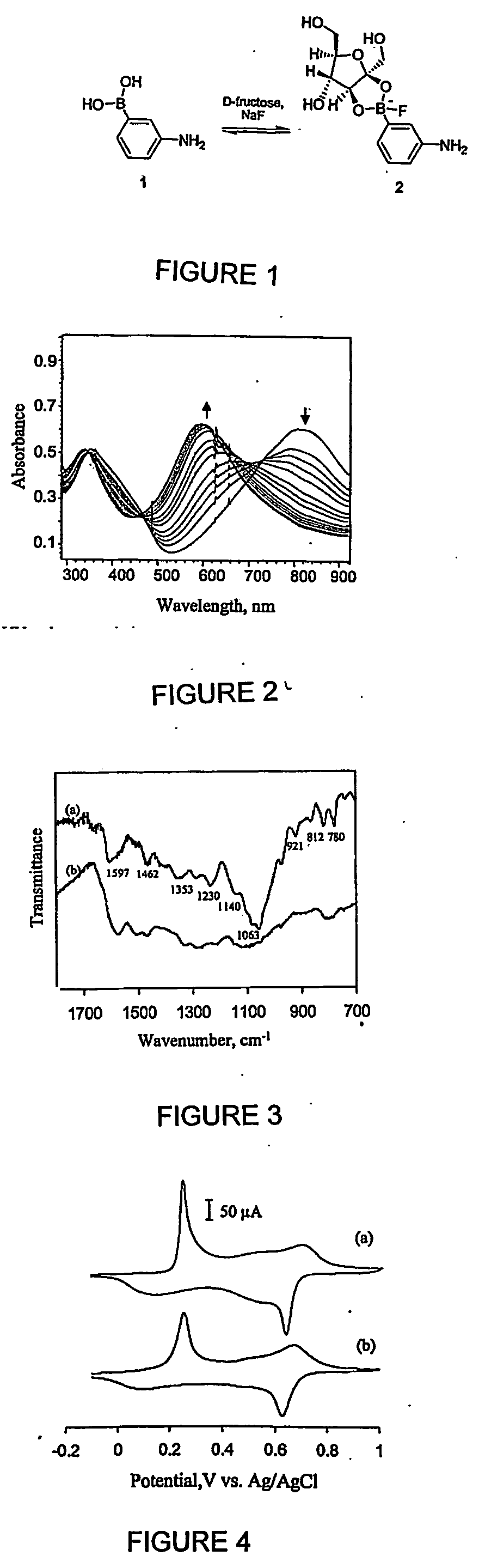
Switchable self-doped polyaniline
A substituted polyaniline whose self-doped state can be controlled via complexation between boronic acid groups along the backbone with D-fructose in the presence of fluoride is described. For the first time, this allows the formation of a water-soluble, self-doped conducting polymer under the polymerization conditions. In turn this facilitates the growth of polyaniline over a wider pH range
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
Flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase
The object is to provide a novel enzyme which enables to determine the glucose level more accurately, a bacterium capable of producing the enzyme, and use of the enzyme. Disclosed is a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase having the following properties (1) to (3):(1) the enzyme has an activity of catalyzing a reaction for oxidizing a hydroxyl group in glucose in the presence of an electron acceptor to produce glucono-delta-lactone; (2) the enzyme has a molecular weight of about 100 kDa as measured by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or about 400 kDa as measured by gel filtration chromatography; and (3) the enzyme is less reactive to maltose, D-fructose, D-mannose and D-galactose. Also disclosed is a microorganism Aspergillus oryzae which can produce the enzyme. Further disclosed are a glucose determination method, a reagent for the determination of glucose, and a kit for the determination of glucose, each utilizing the enzyme.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Glucose isomerase and gene, mutant, engineering bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN104745563AIncrease productionSolve the problem of low optimum reaction temperatureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a glucose isomerase, an encoding gene, a recombinant vector, a genetically engineered bacteria and a mutant thereof and an application of the glucose isomerase and the mutant thereof in preparation of D-fructose for catalyzing D-glucose isomerization. A recombinant escherichia coli capable of efficiently expressing high-temperature resistant glucose isomerase, provided by the invention, solves the problem of low optimal reaction temperature of a common glucose isomerase, is applied to production of the glucose isomerase and has the advantages of high yield, simple process and convenient industrial application; the strain can be directly used for the high fructose syrup production without cell disruption; after finishing fermentation, the total enzyme activity for D-fructose at the temperature of 90 DEG C is 414.3U / g, the conversion rate of D-fructose is 55.4%, the remnant enzyme activity at the temperature of 90 DEG C after storage for 24h is 68% and the equilibrium of reaction is shortened to 1.5h; a good technical support for the large-scale production of the high fructose syrup and for the use of high fructose syrup as an important food additive can be provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com