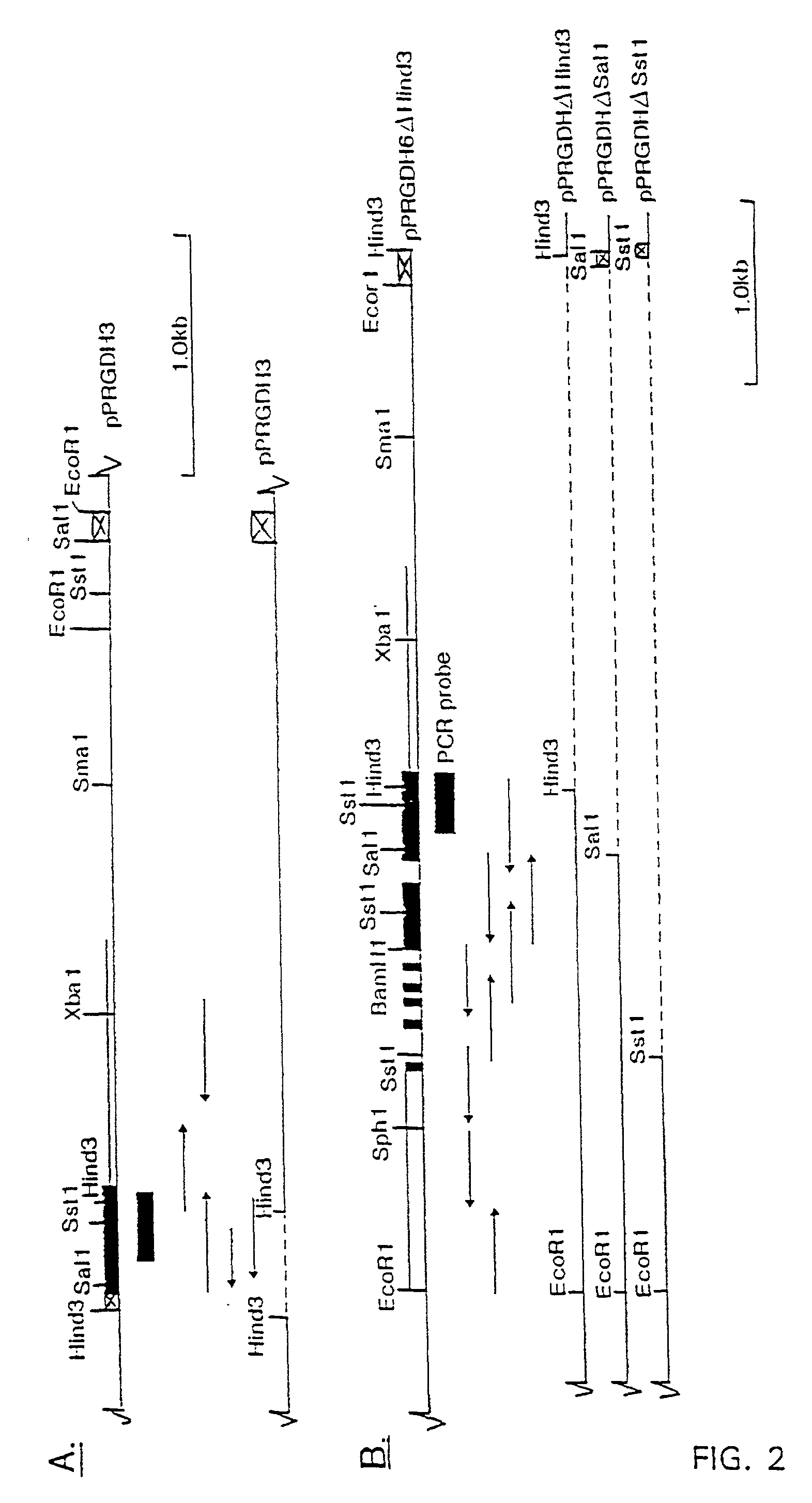
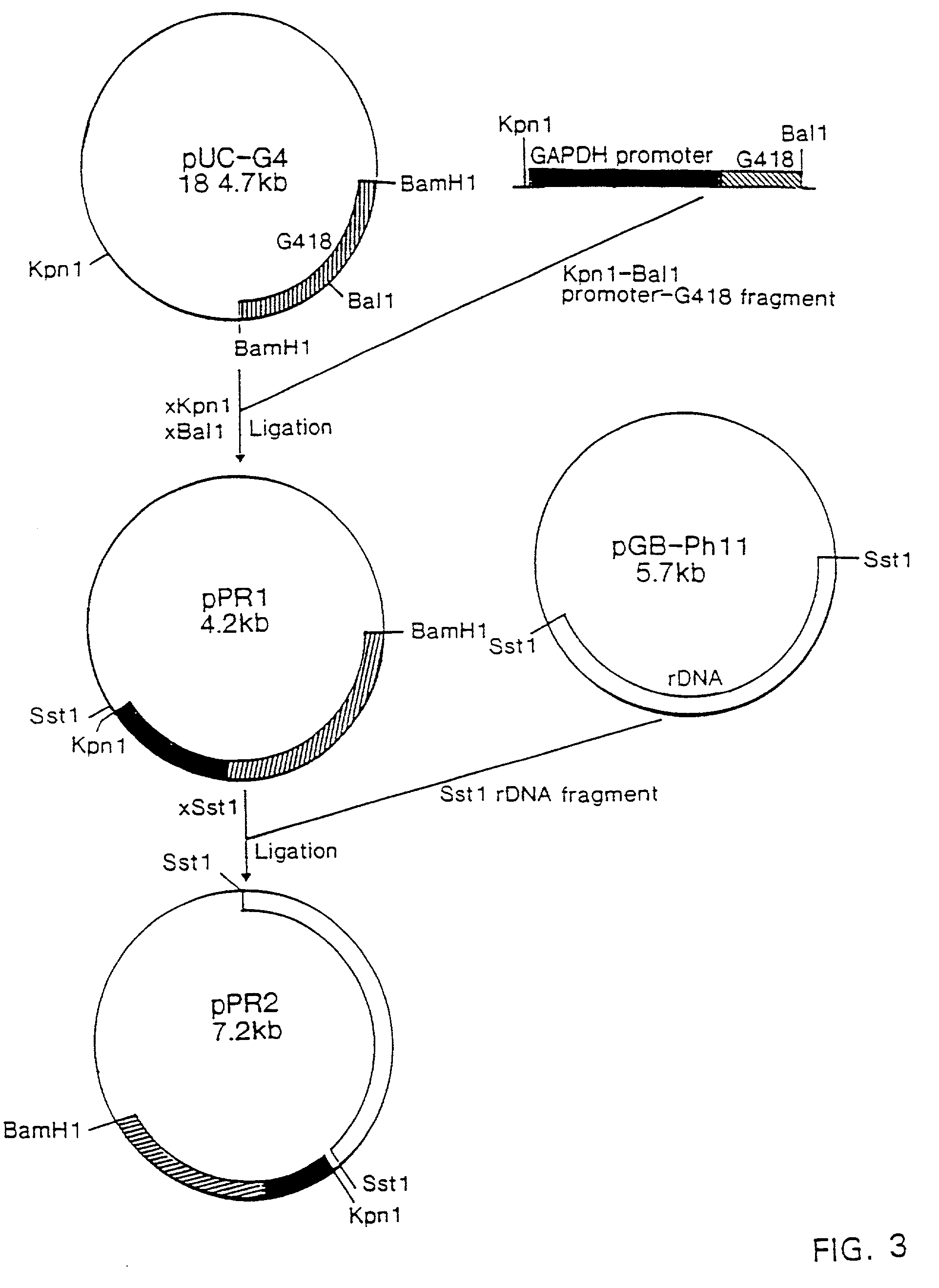
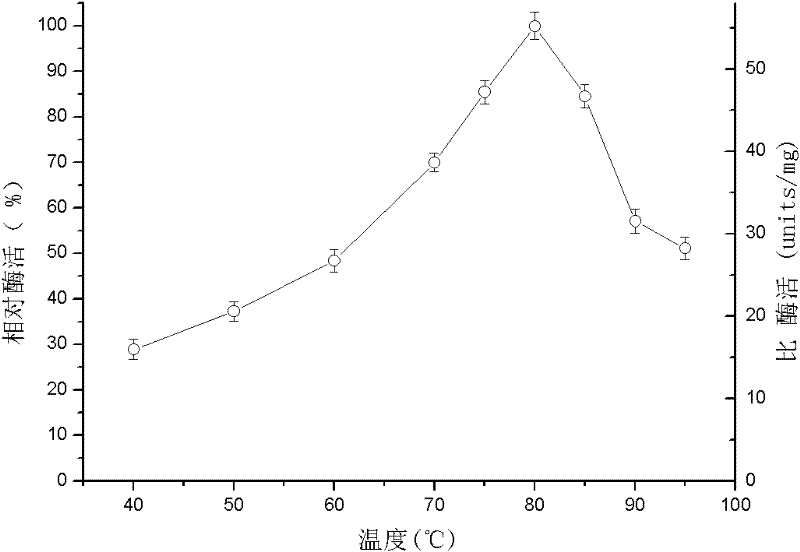
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Isomerase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalysis of the geometric or structural changes within one molecule. Isomerase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 5. [ISBN:0198506732]
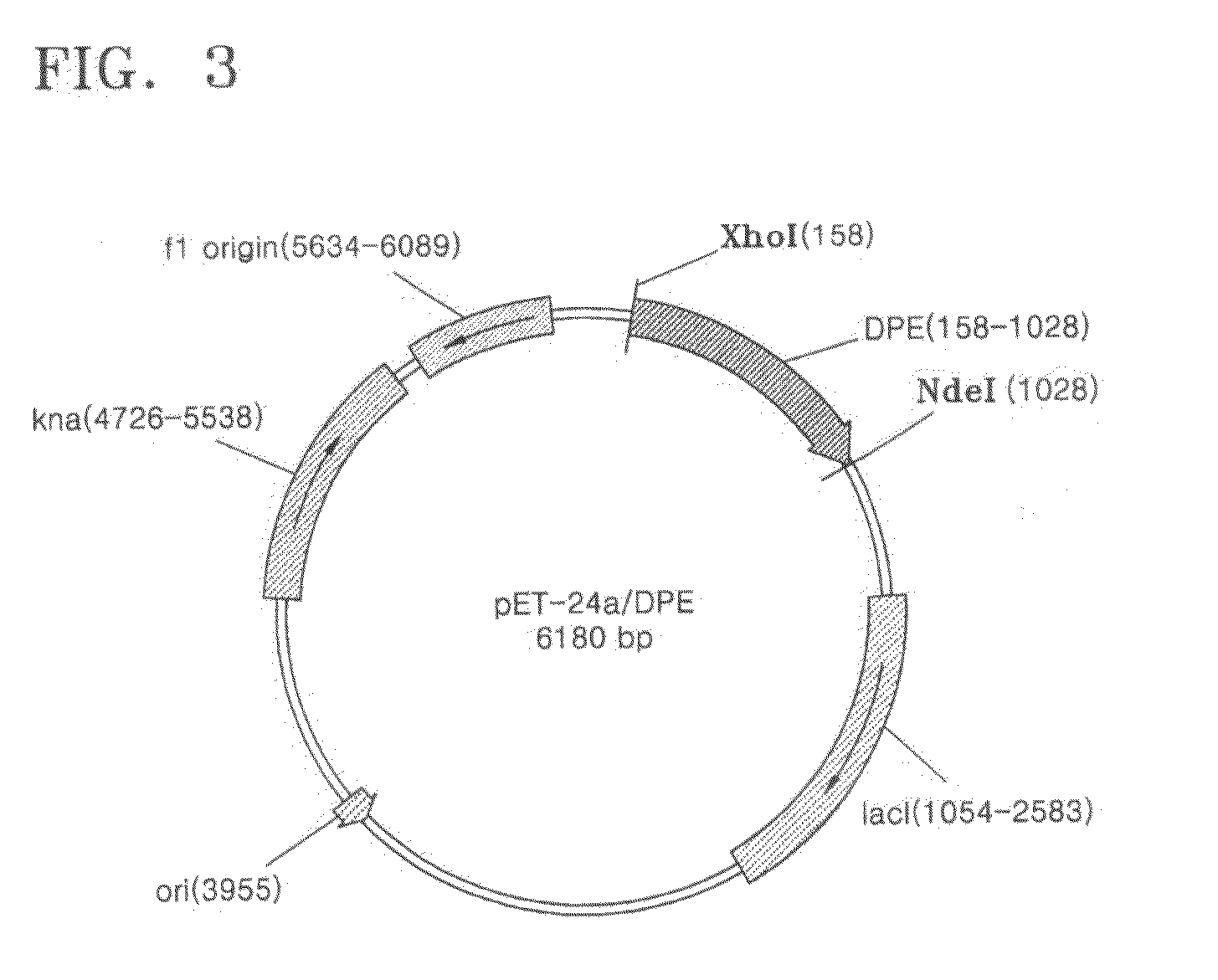
D-psicose production method by D-psicose epimerase
ActiveUS8030035B2Improve production yieldLow production costIsomerasesFermentationIsomerase activityEnzyme
Provided is a method of producing D-psicose using a D-psicose epimerase derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Provided are a protein having an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 and having a psicose 3-epimerase activity, a gene encoding the protein, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene, and a method of producing D-psicose by reacting the protein produced on a mass scale with D-fructose. The method of producing D-psicose is an environmentally friendly method using a new enzyme, in which an inexpensive substrate is used, and the activity of the enzyme can be retained for a prolonged time period. Thus, the method can be efficiently used for the mass production of D-psicose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
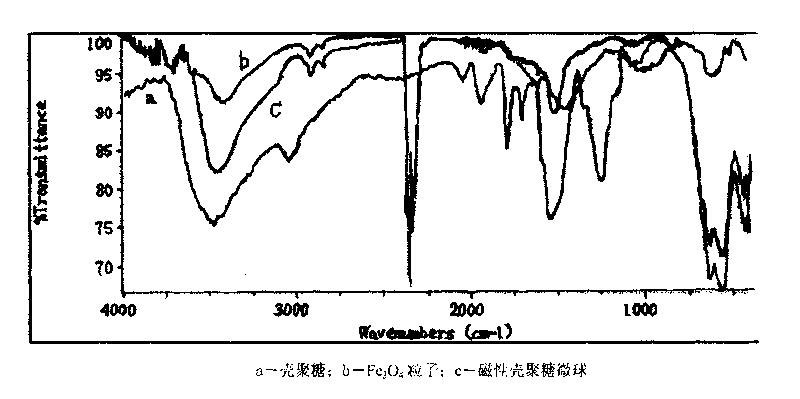
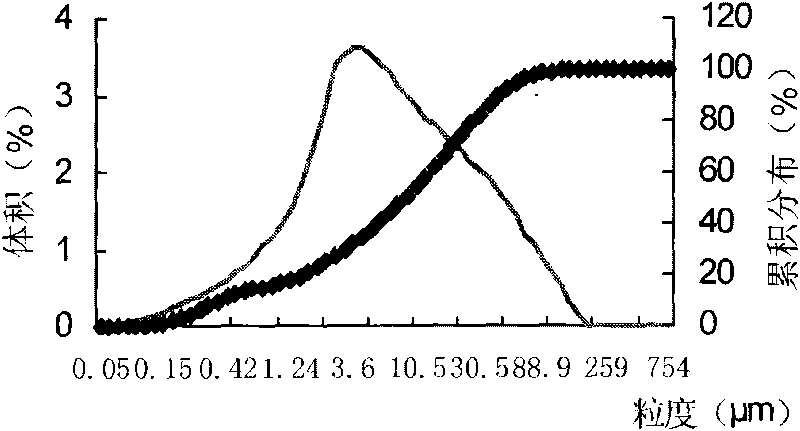
Method for preparing immobilized glucose isomerase with composite magnetic chitosan microballoon spheres
InactiveCN101748113AImprove efficiencyQuality improvementOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierPhosphateMicrosphere
The invention relates to a method for preparing immobilized glucose isomerase with composite magnetic chitosan microballoon spheres, which comprises the steps of: adding polyethylene glycol into FeCl2 and FeCl3, dissolving, regulating pH of solution to 8 to 10 with ammonia water, washing, filtering, freezing and drying in vacuum to obtain Fe3O4 magnetic nuclei, dissolving chitosan powder in acetic acid to carry out ultrasonic dispersion to prepare chitosan solution, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion and stirring on emulsifying agents and the Fe3O4 magnetic nuclei, crosslinking 1 to 5% glutaric dialdehyde at 2000 r / min, stirring, washing, filtering, freezing and drying in vacuum to obtain composite magnetic chitosan microballoon spheres, soaking the composite magnetic chitosan microballoon spheres with phosphate buffer pH of which is 7.0 to 7.8, filtering, adding glucose isomerase diluted by buffer, vibrating, taking out the glucose isomerase, putting the glucose isomerase in a refrigerator for one night, pouring off supernate, precipitating, washing, and filtering to obtain the immobilized glucose isomerase. In the invention, the glucose isomerase activity recovery ratio of which can reach more than 80% is immobilized by the composite magnetic chitosan, and has high service efficiency, reusability and low cost.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant materials for carotenoid production
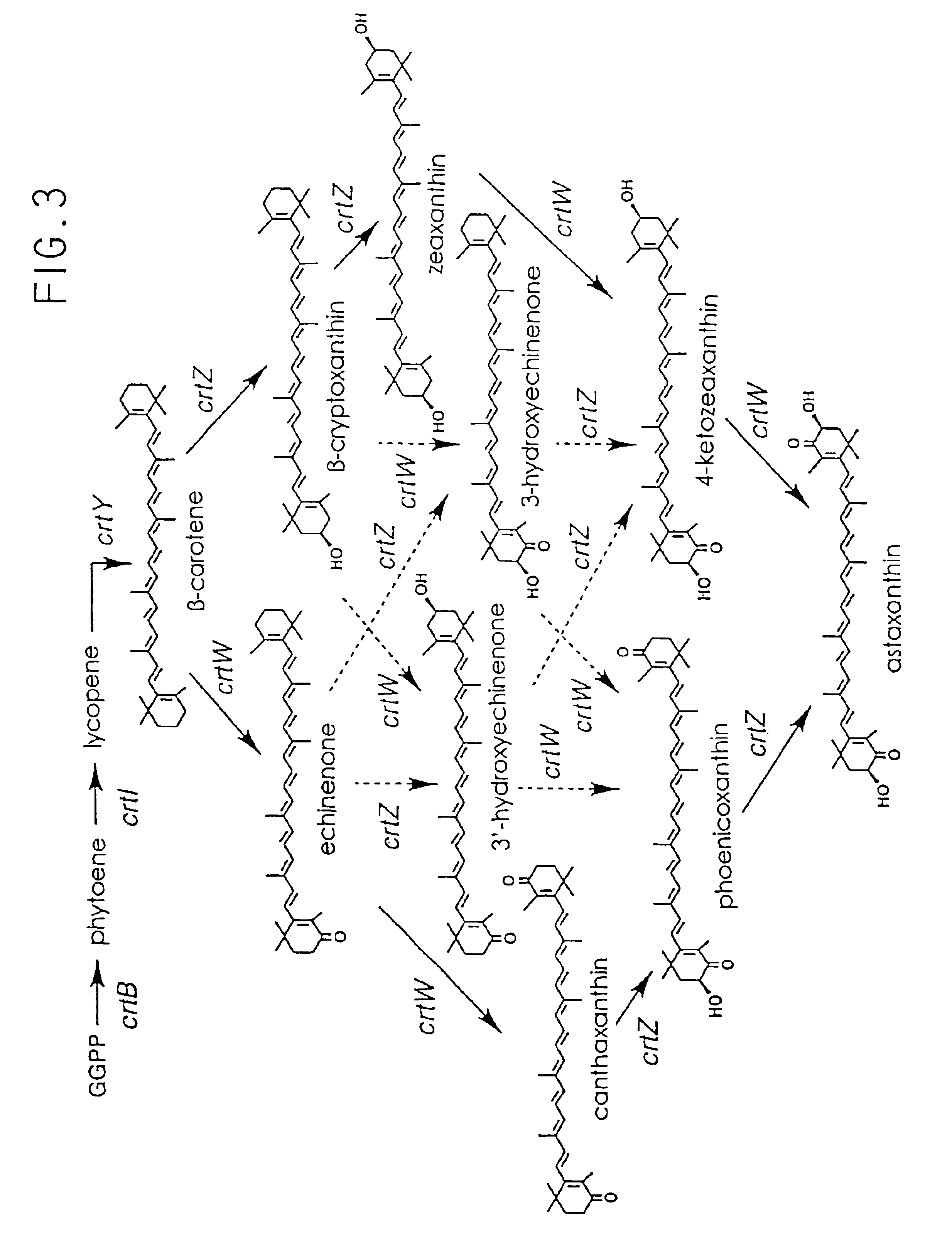
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the amino acid sequences depicted in any one of SEQIDNOs: 24 to 50. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided, preferably wherein said enzyme has an activity selected from isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase activity, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase activity, phytoene synthase activity, phytoene desaturase activity and lycopene cyclase activity, still more preferably those coding for an enzyme having an amino acid sequence selected from the one represented by SEQIDNO: 13, SEQIDNO: 15, SEQIDNO: 17, SEQIDNO: 19, SEQIDNO: 21 or SEQIDNO: 23. Further embodiments concern vectors, transformed host organisms, methods for making proteins and / or carotenoids, such as astaxanthin, and methods for isolating highly expressed promoters from Phaffa.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Glucose isomerase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN102443578ASolve technical problemsSignificant technological progressMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesBiotechnologyHalf-life
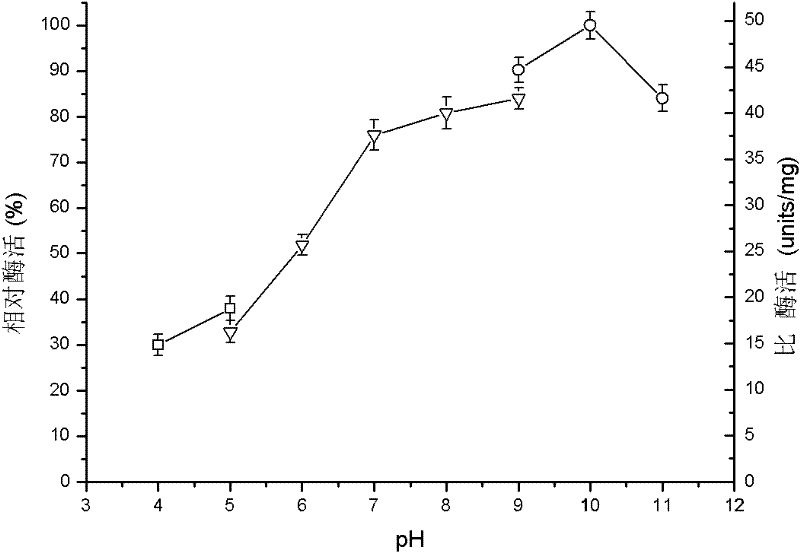
The invention discloses a glucose isomerase mutant and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of enzyme genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, a high temperature glucose isomerase gene (NCBI coding: CP000088) is obtained from total DNA of thermobifida fusca, and after site-directed mutagenesis, high efficiency expression of the glucose isomerase gene with a high conversion rate is realized, with the plasmid pT7-7 or a vector that can express glucose isomerase as an expression vector and E. coli BL21 (DE3) or a bacterial strain that can express glucose isomerase as an expression host; the glucose isomerase gene has altogether 1158 nucleotide and encodes 385 amino acids; expression plasmid is constructed in the invention, glucose isomerase is expressed through conversion of bacteria or yeast, and an obtained recombinase mutant has activity of glucose isomerase and has a conversion rate of 60% at a temperature of 70 DEG C, 7% higher than the conversion rate of a parent; optimum temperature of the recombinant glucose isomerase is 80 DEG C, an optimum pH is 10, and the half life of the recombinant glucose isomerase at a temperature of 70 DEG C is no less than 30 h. The recombinant glucose isomerase is particularly applicable to production of F55 high-fructose syrup in the industry of foodstuffs.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods of producing carotenoids using DNA molecules encoding isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase
InactiveUS6821749B1Reduce the amount of solutionIncrease volumeSugar derivativesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
The production of carotenoid is accomplished using a DNA molecule that encodes a polypeptide as obtained from Haematococcus pluvialis, Phaffia rhodozyma, or Saccharomyces cerevisiae, having isopentonyl pyrophosphate (IPP) isomerase activity, or DNA molecule having a nucleotide sequence that hybridizes thereto. In particular, one can introduce such a DNA molecule into a carotenoid-producing microorganism, culture the microorganism thus transformed, and then obtain carotenoids in the culture broth and cells.
Owner:KIRIN HOLDINGS KK
Clone, expression and biological activity of stingray caudal spine cyclophilin A gene
InactiveCN1428348AGood application prospectHigh industrial development valueSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA libraryEscherichia coli
The present invention utilizes the construction of dasytis akajei caudal spine cDNA library and DNA sequencing and designs the primer according to the obtained (CyP) EST 3' end and carrier nucleotide sequence, and uses PCR method to screen the dasytis akajei caudal spine cDNA library and clone the cyclophilin A total strength gene. The tength of new gene is 656 bp for coding mature peptide of 167 amino acids, the isoelectric point of the expressed protein is 8.34, and the molecular weight is 18,021 Dalton. The dasytis akajei caudal spine cyclophilin A gene is cloned in the uxA gene 3' tail end of thioredoxing gene fusion expression vector pTRX and the fusion gene meeting reading frame is construcled, said fusion protein is existed in colibacillus, its expression amount can be up to 60 mg / L.
Owner:北京博奥环宇生物技术有限公司
Improved xylose utilization in recombinant zymomonas having increased ribose-5-phosphate activity
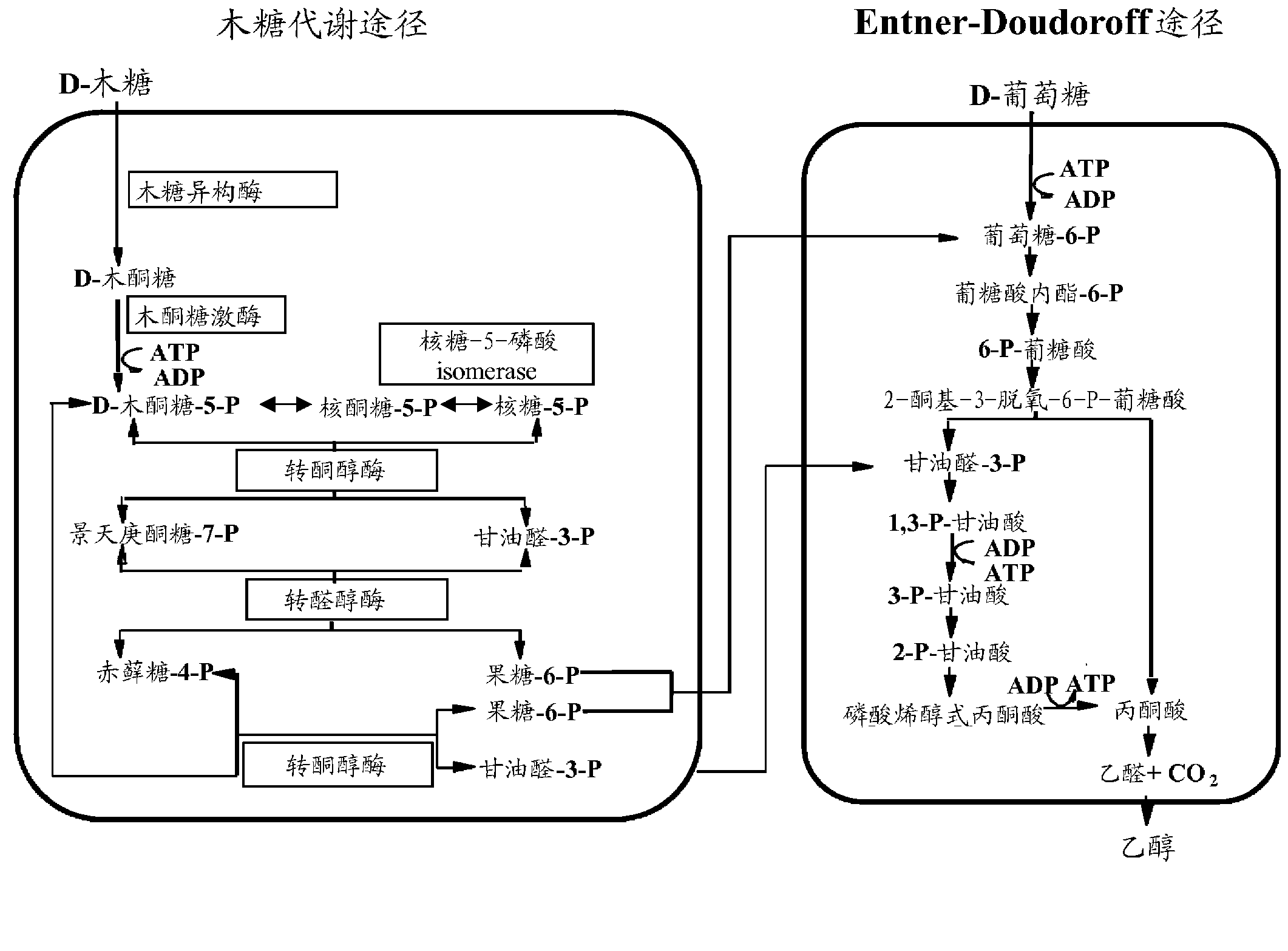
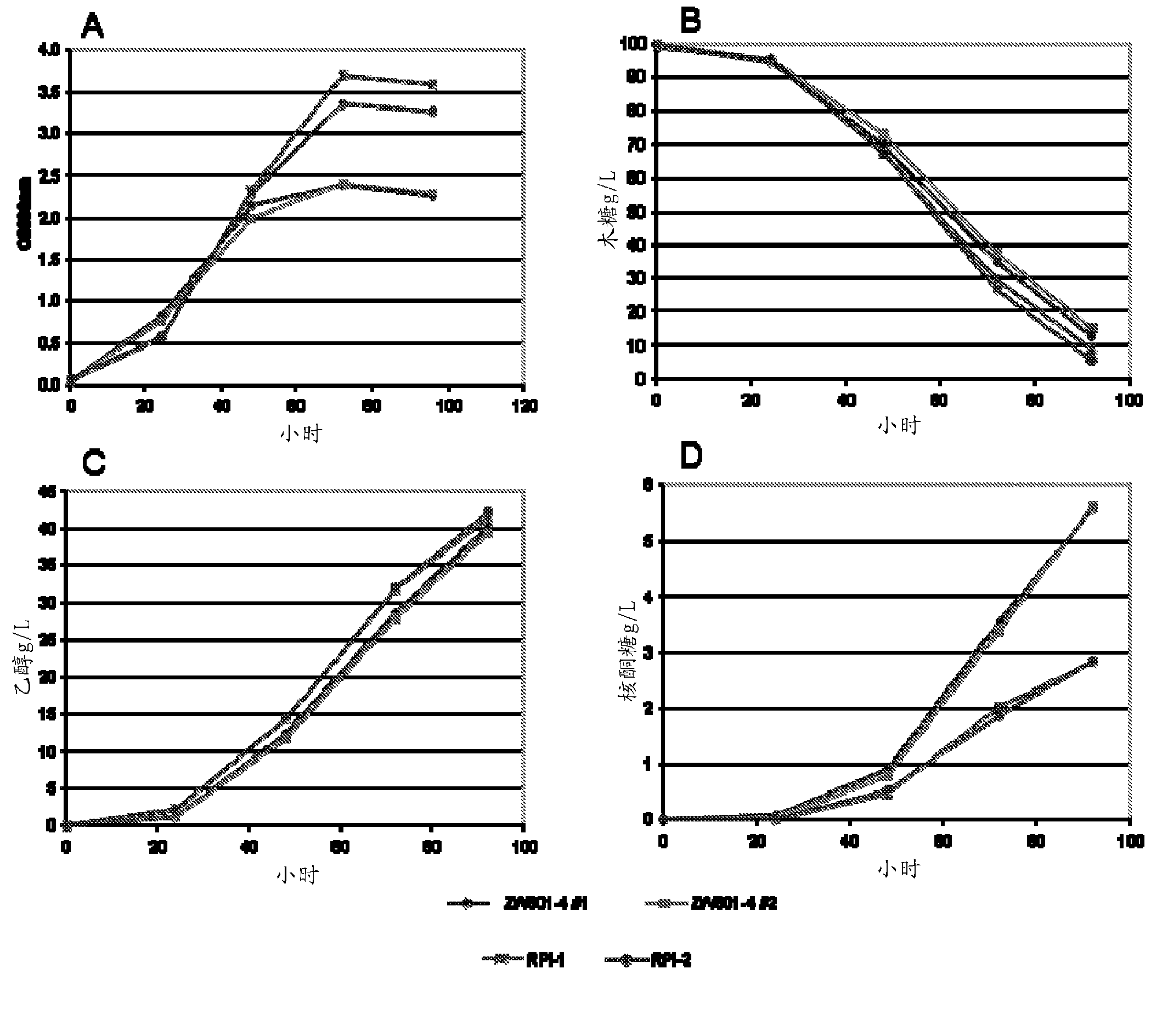
Xylose-utilizing Zymomonas strains studied were found to accumulate ribulose when grown in xylose-containing media. Engineering these strains to increase ribose-5-phosphate isomerase activity led to reduced ribulose accumulation, improved growth, improved xylose utilization, and increased ethanol production.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
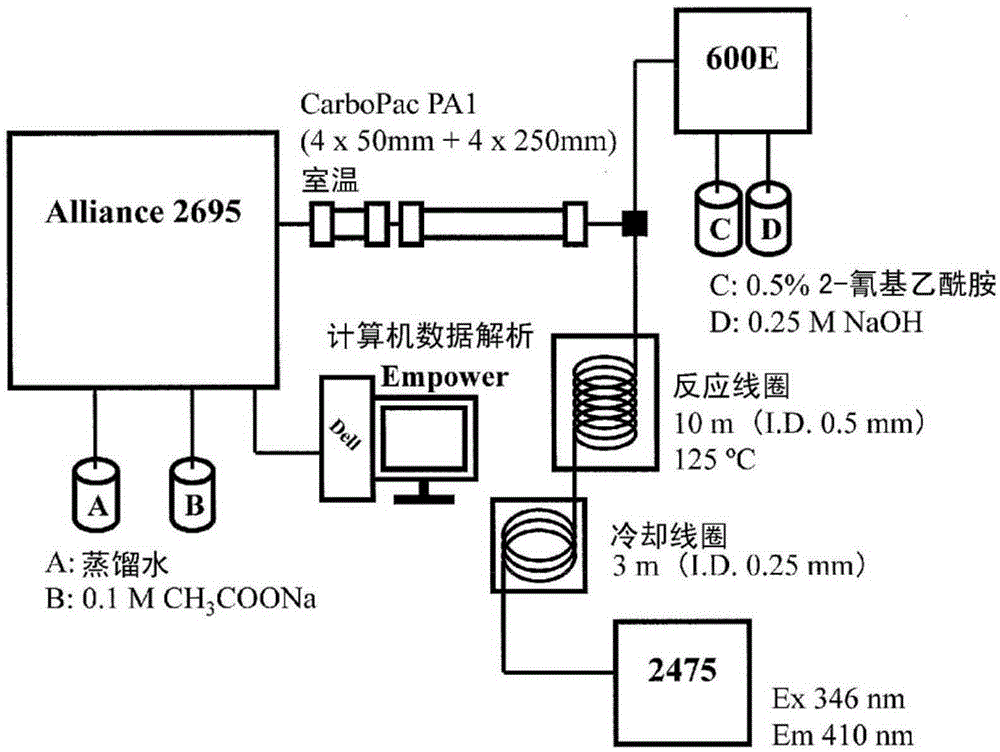
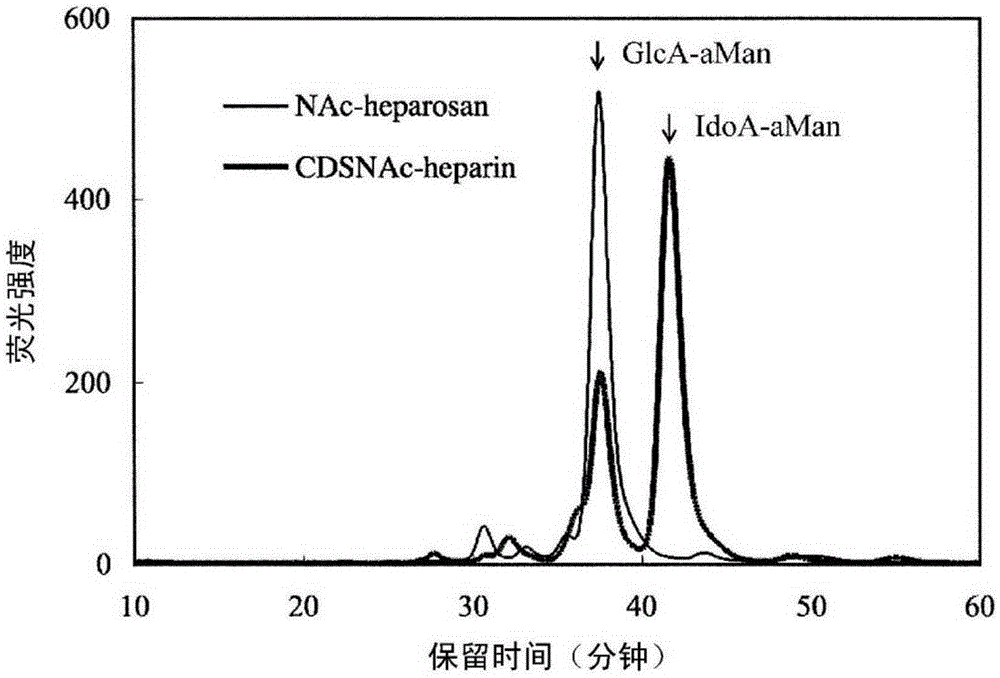
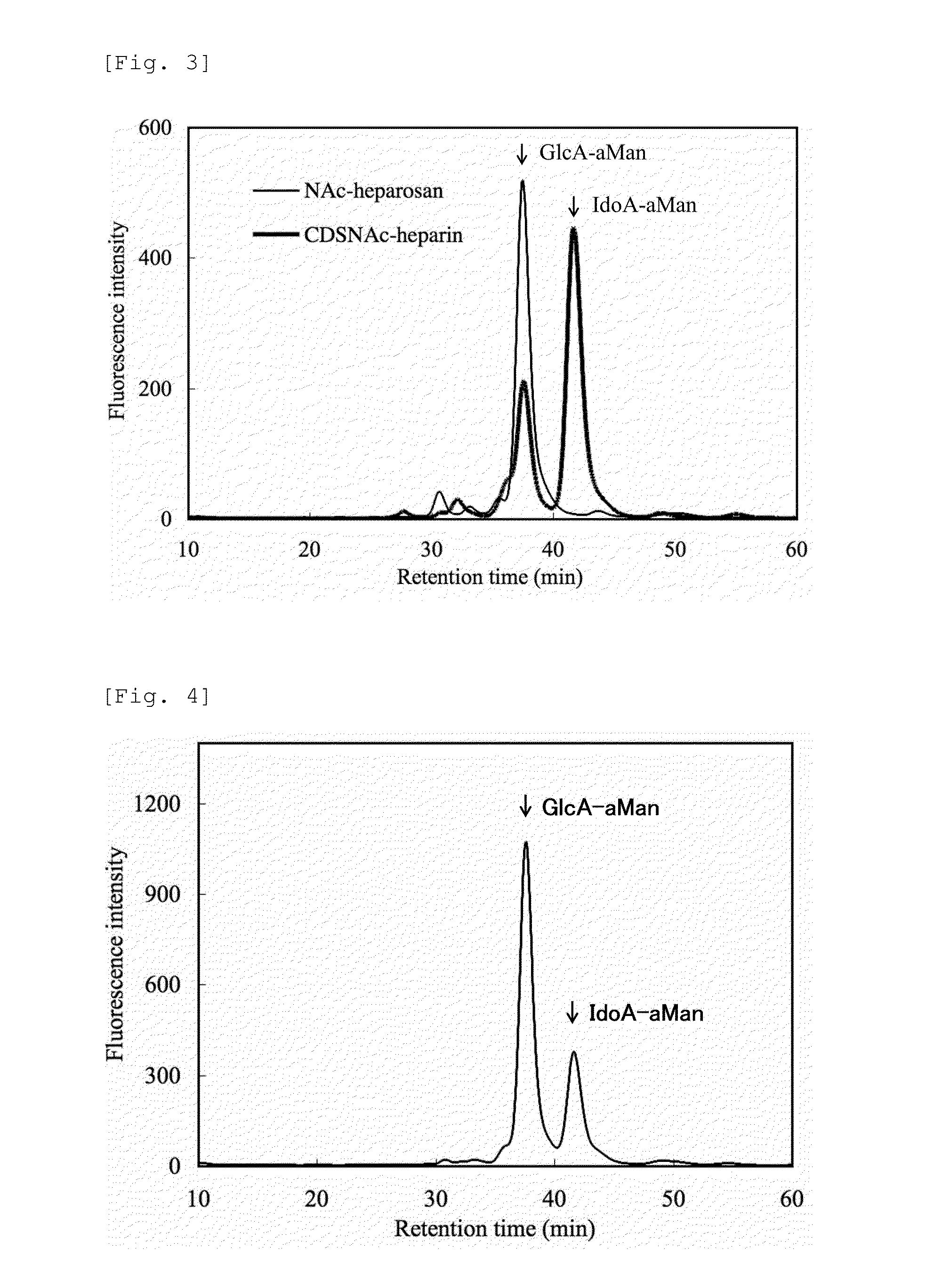
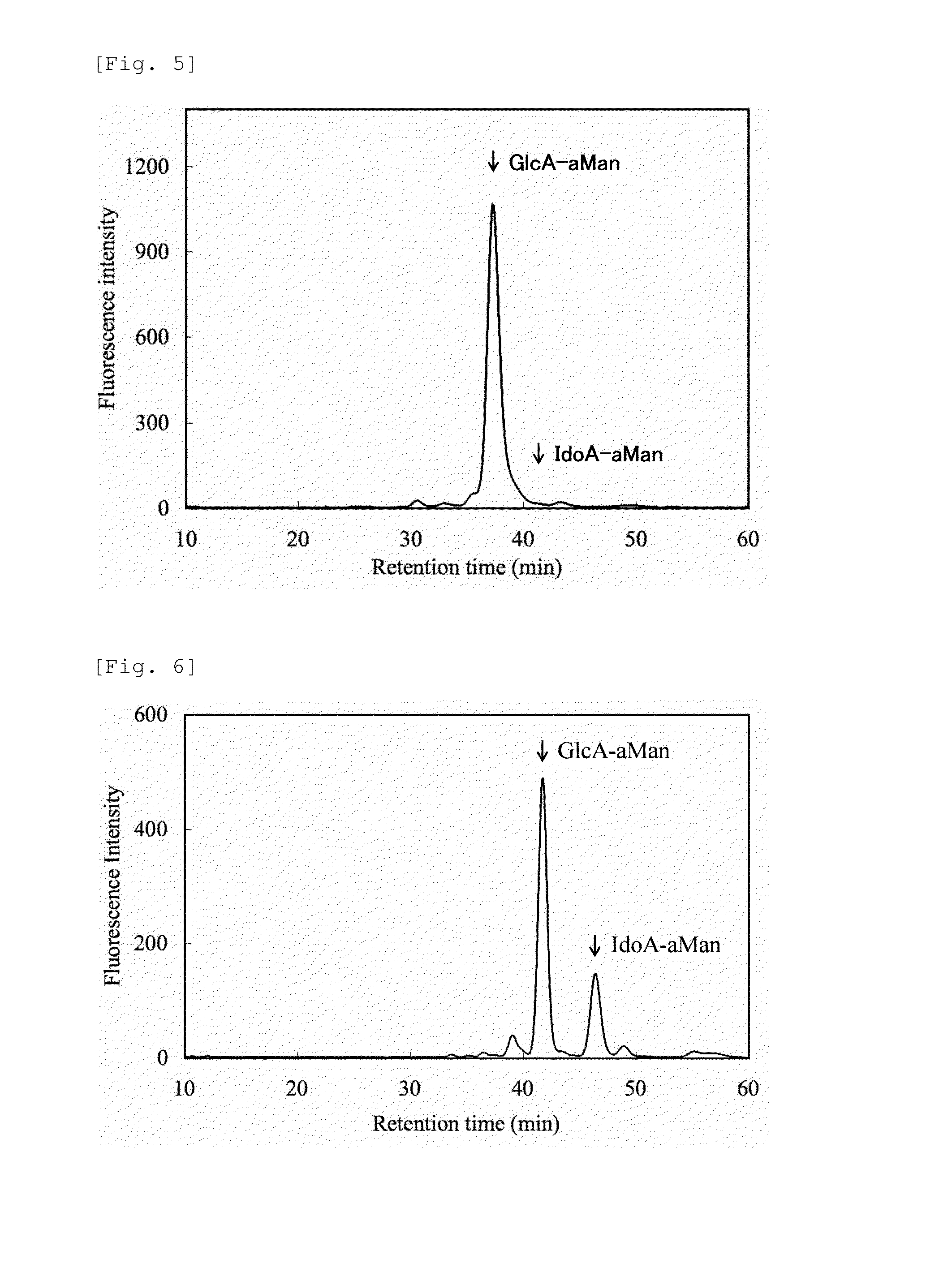
Heparosan-glucuronic acid-5-epimerase, and method for producing polysaccharide using same
Provided are a polypeptide having heparosan-glucuronic acid-5-epimerase activity, and a means for producing a polysaccharide having an isomerized hexuronic acid residue using same. The cDNA library of Achatina fulica is screened, and the DNA that codes for the polypeptide of heparosan-glucuronic acid-5-epimerase, which is an isomerase that acts on a glucuronic acid residue of N-acetylheparosan and / or an iduronic acid residue of completely desulfated and N-acetylated heparin, is obtained. The polypeptide coded by the DNA is expressed in insect cells, and the polypeptide, which has heparosan-glucuronic acid-5-epimerase activity, is obtained. By contacting the polypeptide with N-acetylheparosan or completely desulfated and N-acetylated heparin, a polysaccharide having the isomerized hexuronic acid residue is obtained.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
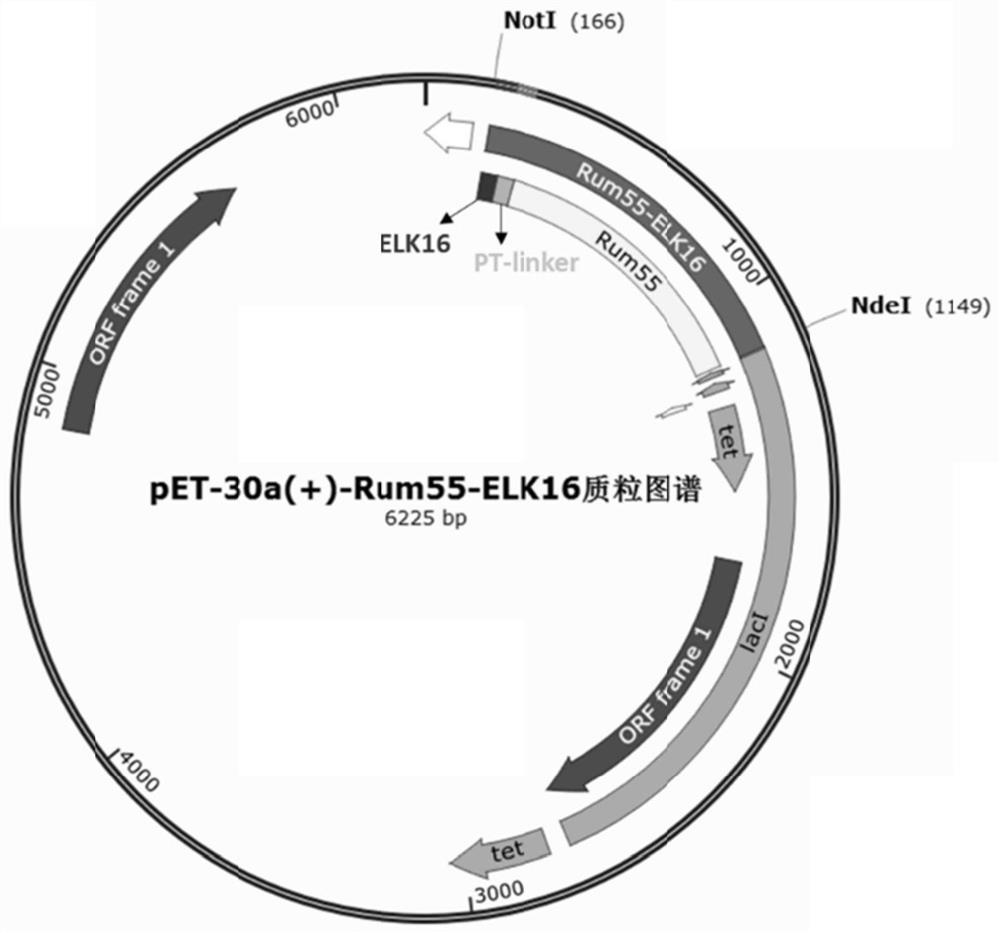
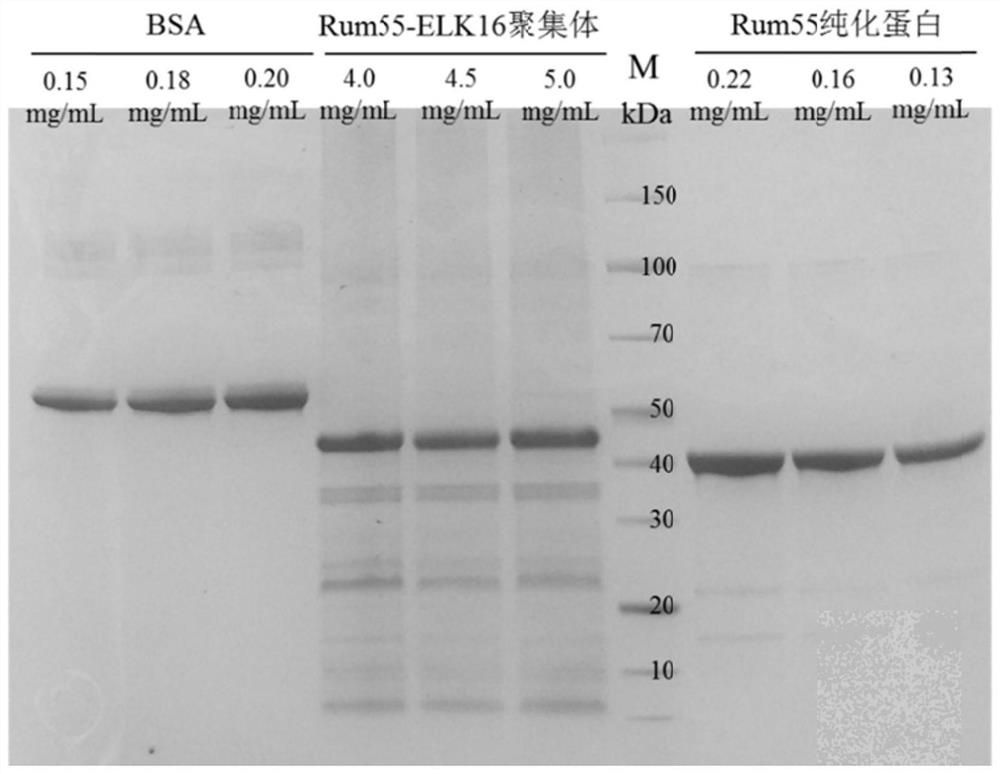
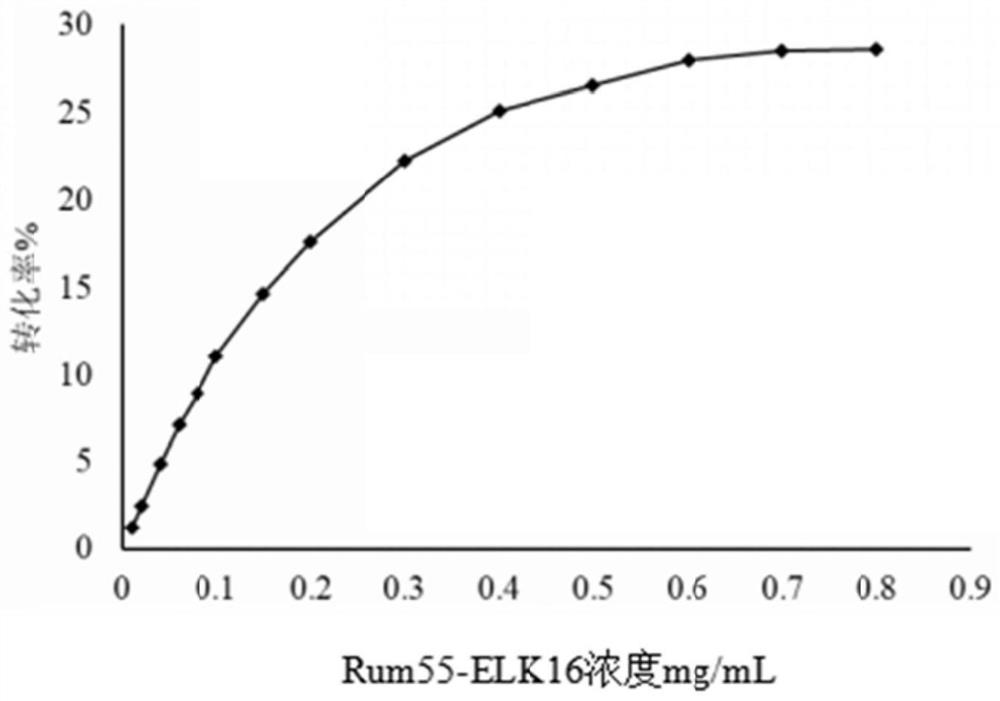
D-psicose-3-epimerase active aggregate as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering, and discloses a D-psicose-3-epimerase active aggregate as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The D-psicose-3-epimerase active aggregate comprises D-psicose-3-epimerase and a self-aggregation oligopeptide, so that the reaction temperature of the D-psicose-3-epimerase can be increased, and the half-life period of the D-psicose-3-epimerase can be prolonged; the dependence on metal ions is obviously reduced; and the reutilization frequency is increased.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative capable of inhibiting activity of DNA topoisomerase, preparation method and application of quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative
PendingCN110551072AHas inhibitory activityStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryQuinoxalineStaphylococcus aureus
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemistry, and particularly relates to a quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative capable of inhibiting the activity of DNA topoisomerase, a preparationmethod and application of the quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative. 4,5,-difluoro-2-nitroaniline is used as a raw material for synthesis of the quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative, the quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative reacts with sodium hypochlorite under catalysis of a basic catalyst, namely sodium hydroxide, and 5,6-difluoro-N-benzofuroxan is obtained; and then the quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxidederivative reacts with different substrates in Beirut reaction and substitution reaction, and a series of the quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative is obtained. According to the quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative, the preparation method and application of the quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivative, quinoxoline-N1,N4-dioxide has good bacteriostatic activity to previously reported gram-negative bacteria, and also had good bacteriostatic activity to actinobacilluspleuropneumoniae and gram-positive bacteria such as staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pneumoniae.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing recombinant glycoproteins with high sialic acid content
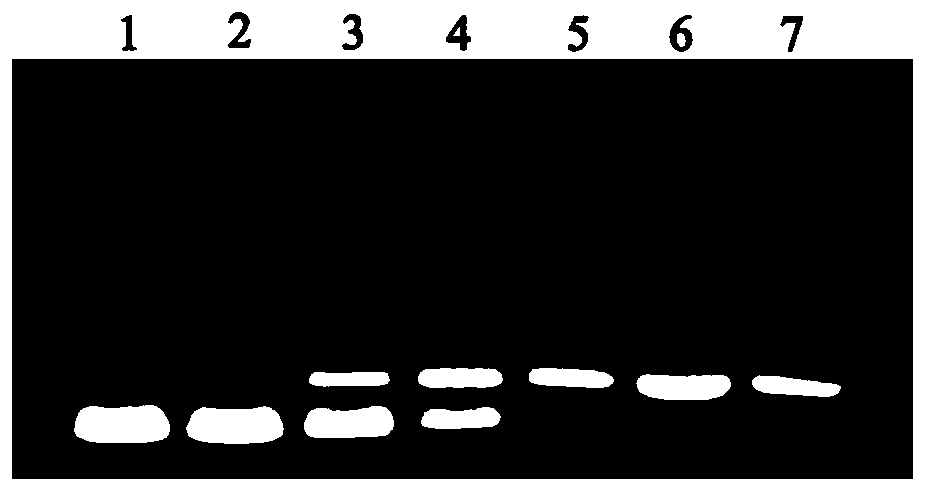
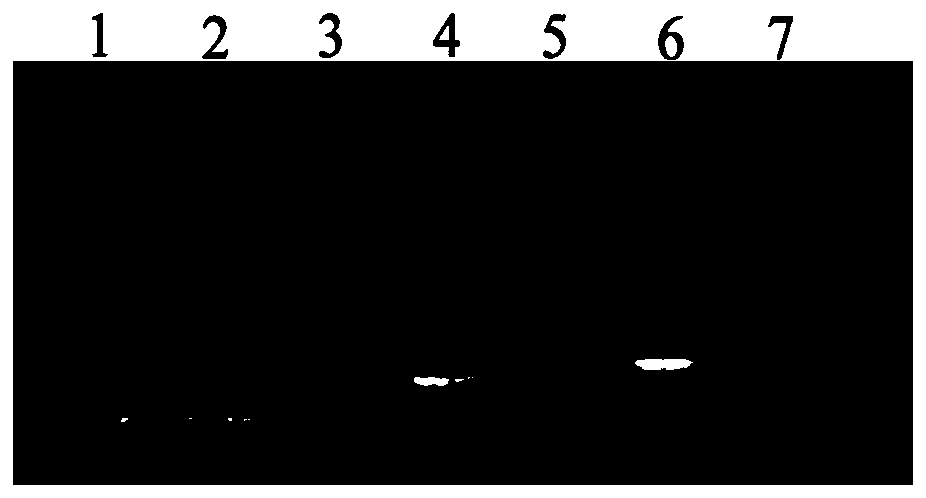
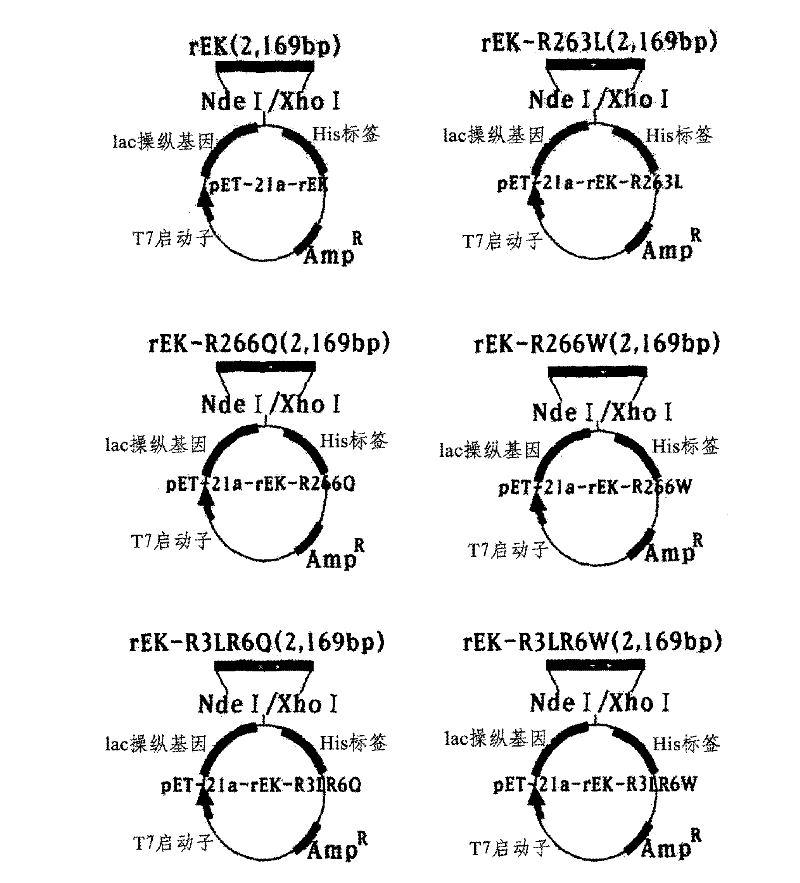
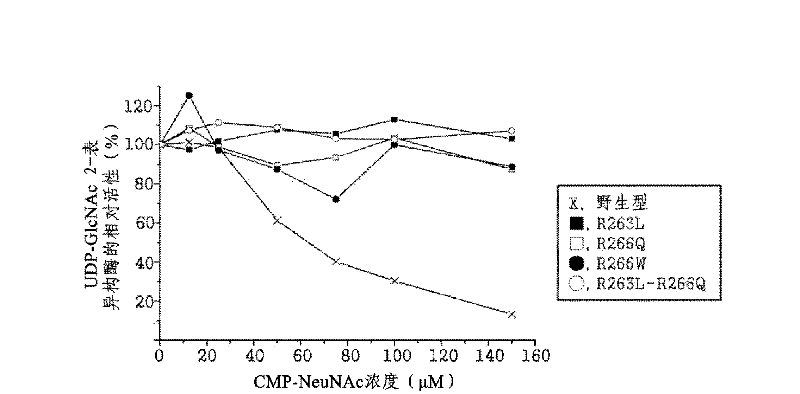
ActiveCN102482674AIncreased sialic acid contentThrombopoietinCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsArginineTert-leucine
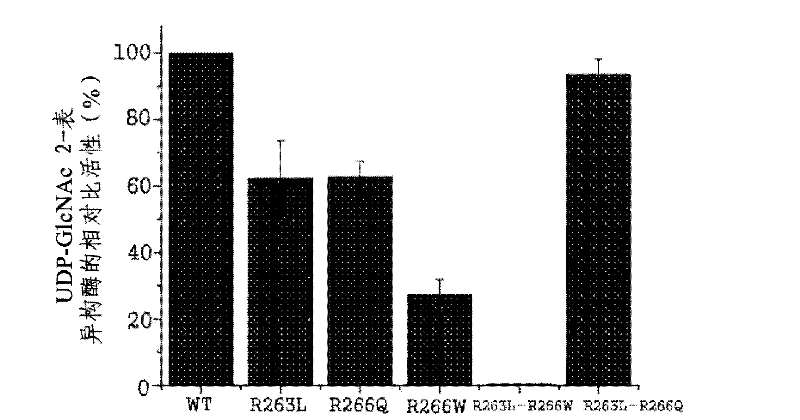
The present disclosure relates to a method for preparing recombinant glycoproteins with high sialic acid content. More specifically, for UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase / ManNAc kinase (GNE / MNK) enzyme where point mutation was induced by substituting arginine at position 263 by leucine only or by further substituting arginine at position 266 by glutamine, epimerase activity is constantly maintained, and overexpressed cells thereof experience an increase in intracellular cytidine monophosphate (CMP)-sialic acid content, irrespective of CMP-sialic acid concentration.,Particularly, since in an glycoprotein(such as, erythropoietin and thrombopoietin)-producing host cell where point mutationinduced GNE / MNK, human alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase and a CMP-sialic acid transporter gene are simultaneously overexpressed, intracellular content of CMP-sialic acid and sialic acid in glycoprotein increases in cells, overexpression in a host cell producing a sialylated recombinant glycoprotein the three genes above may be useful for preparing glycoprotein with increased sialic acid content.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Fat-soluble glabridin compound whitening agent and application thereof
ActiveCN108498412ASimple recipeGood whitening effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsQuinoneWhitening Agents
The invention discloses a fat-soluble glabridin compound whitening agent and application of the agent in cosmetics. The compound whitening agent is prepared from the following active ingredients in byweight percent: 30-50 percent of glycyrrhiza glabra extract, 10-30 percent of tetrahydroxychalcone, 10-30 percent of ubiquinone and 10-30 percent of an endothelin antagonist. The compound whitening agent has main whitening action mechanisms of inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase, inhibiting the activity of DOPA chrome tautomerase and obstructing indole-5,6-quinone polymerization, so that melanogenesis can be obstructed, differentiation of melanophores can be reduced, and the aims of whitening skin, lightening spots and improving dark skin color can be achieved. The compound whitening agenthas a simple and practical formula and a good whitening and spot-lightening effect, is environmentally friendly and safe since natural products are adopted, is mild and nonirritant in use, and can overcome the defect in an existing whitening agent.
Owner:亿利耐雀生物科技有限公司
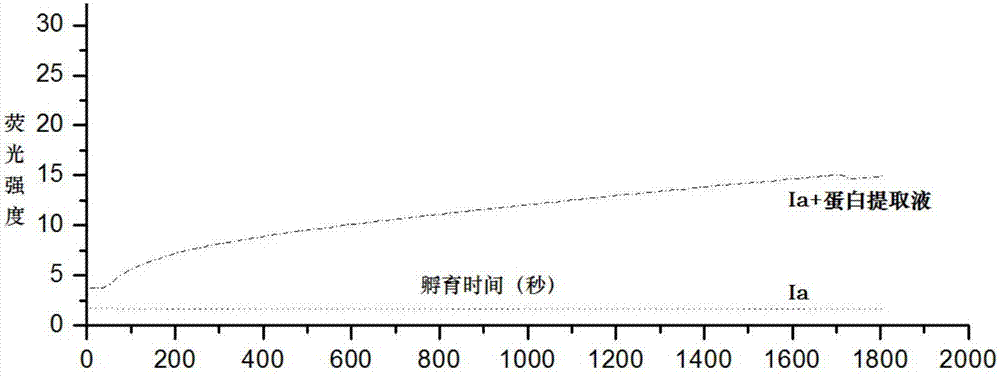
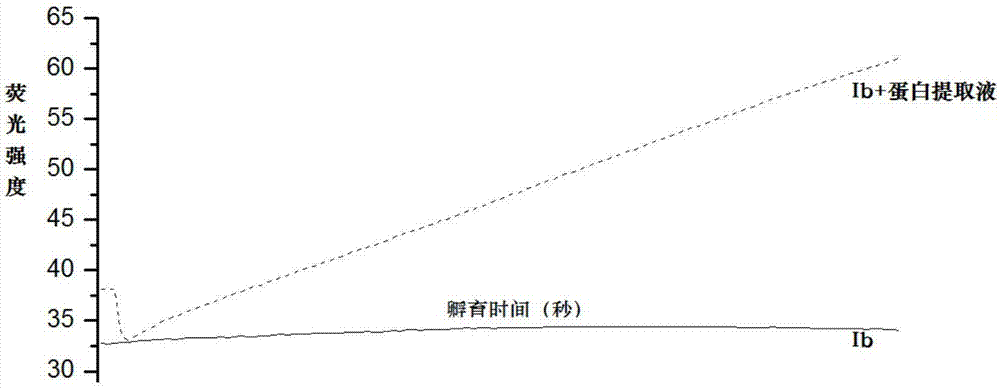
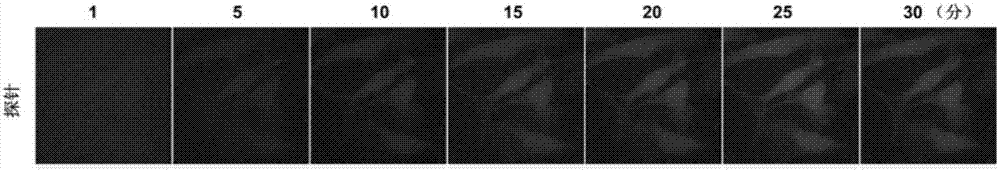
Fluorescent probe for detecting activity of proline isomerase and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107312068AImprove stabilityLong-term storage and useMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsIsomerase activityTissue Protein Extraction
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for detecting the activity of proline isomerase. The probe produces weaker fluorescence in a physiological environment, can specifically produce configuration inversion under the catalytic action of the proline isomerase to generate a fluorescent signal enhanced product. Therefore, the probe can be used for active evaluation of the proline isomerase, can be applied to detection of the activity of proline isomerase in a cell or tissue protein extraction solution and detection of the activity of proline isomerase in living cells. The fluorescent probe has the following advantages that the probe is good in stability and can be saved and used for a long time; a detection method is simple, the probe is added in a detection system, incubation is performed for 10 minutes, fluorescence intensity is measured, and a result can be given out without assistance of other reagents; in-vivo detection of the activity of the proline isomerase in the living cells can be achieved, other reported methods can be only used for a cell homogenization solution. The specific structure of the probe is shown in Figures (shown in the description).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
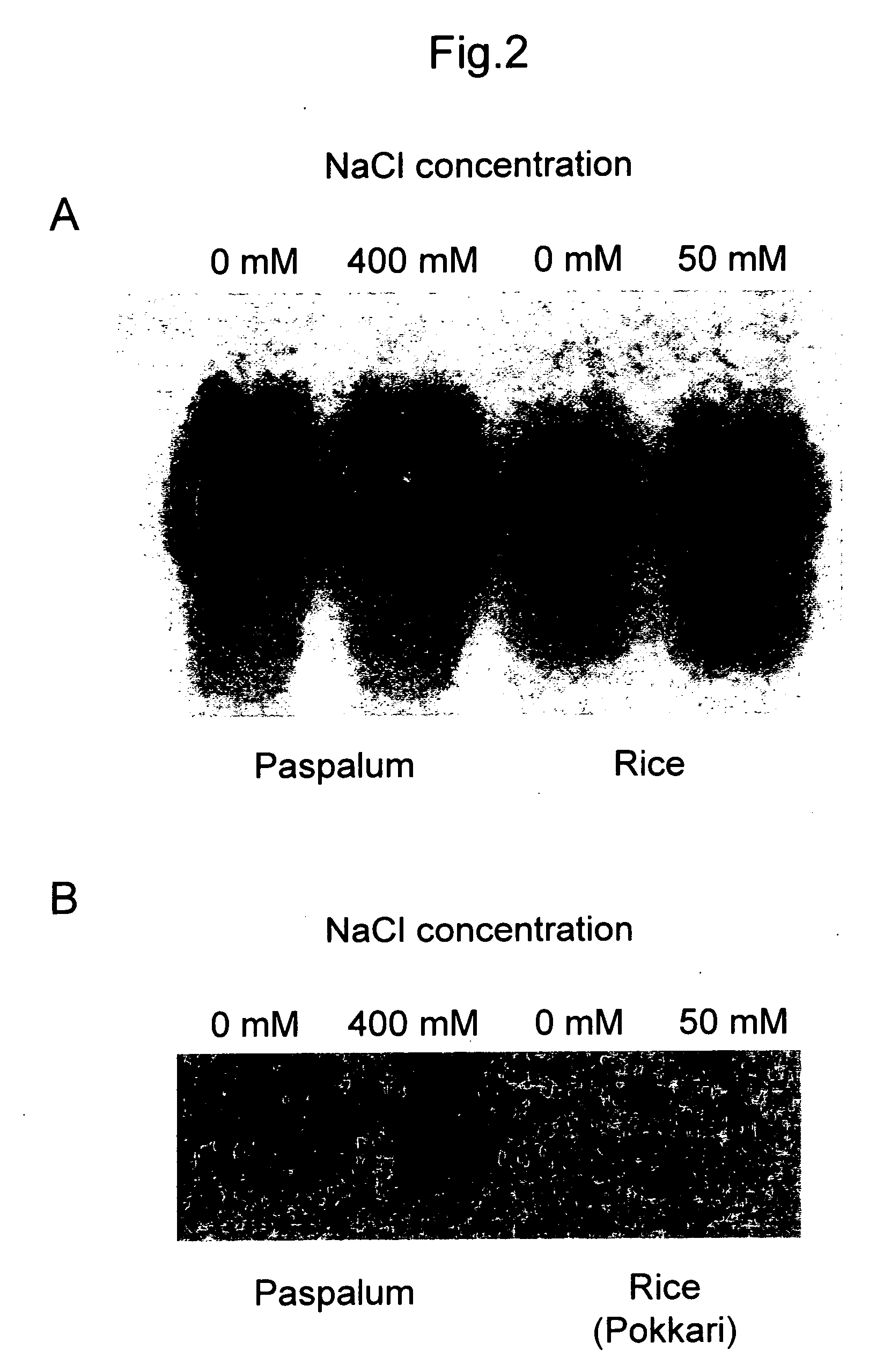
Gene capable of imparting salt stress resistance
This invention provides a novel gene that can impart salt stress tolerance to plants for a long period of time and salt stress tolerant transgenic plants to which such gene has been introduced. Such novel gene encodes the following protein (a), (b), or (c), and such salt stress tolerant transgenic plant has such gene introduced therein: (a) a protein consisting of the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 in the Sequence Listing; (b) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence derived from the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 in the Sequence Listing by deletion, substitution, or addition of one or several amino acid residues and having activity of imparting salt stress tolerance to plants; or (c) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence derived from the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 in the Sequence Listing by deletion, substitution, or addition of one or several amino acid residues and having UDP-glucose 4-epimerase activity.
Owner:TAISEI CORP +1
Eggplant chalcone isomerase SmCHI protein and coding gene thereof
ActiveCN104745561AGood anti-oxidant health effectImprove qualityIsomerasesFermentationGenetic engineeringChalcone isomerase
The invention discloses eggplant chalcone isomerase SmCHI protein and a coding gene thereof. The protein comprises (a) protein consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3; or (b) protein derived from the amino acid sequence in (a), which is substituted, lost or added by one or more amino acids and has the activity of eggplant chalcone isomerase. The cDNA and gDNA of the coding gene respectively have base sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2; and the gene is expressed in roots, stems, leaves, flowers, peels and pulp, and has the expression quantity in peels remarkably higher than that in other tissues. Under stress of low temperature, the expression quantity of the gene reaches the maximal value in 48 hours, which is 3.65 times that of an unprocessed gene. The eggplant chalcone isomerase SmCHI protein and the coding gene thereof provide a theoretical basis for improving plant quality by utilizing the genetic engineering technology to obtain high oxidation resistance medicines or foods in the future, thereby having great application values.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hexulose phosphate isomerase and gene coding said isomerase
There are provided a DNA coding for phosphohexuloisomerase, which is a protein defined in the following (A) or (B), and a method for producing the enzyme: (A) a protein having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 shown in Sequence Listing, (B) a protein having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 shown in Sequence Listing including substitution, deletion, insertion or addition of one or several amino acid residues and having phosphohexulose isomerase activity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
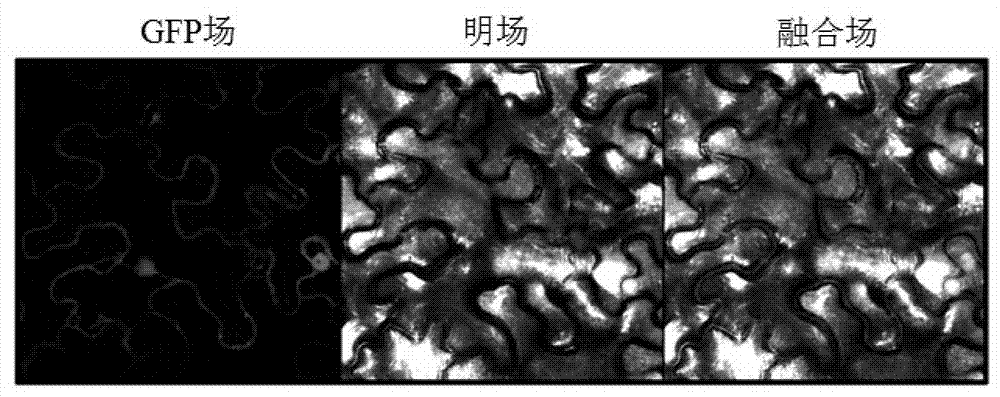
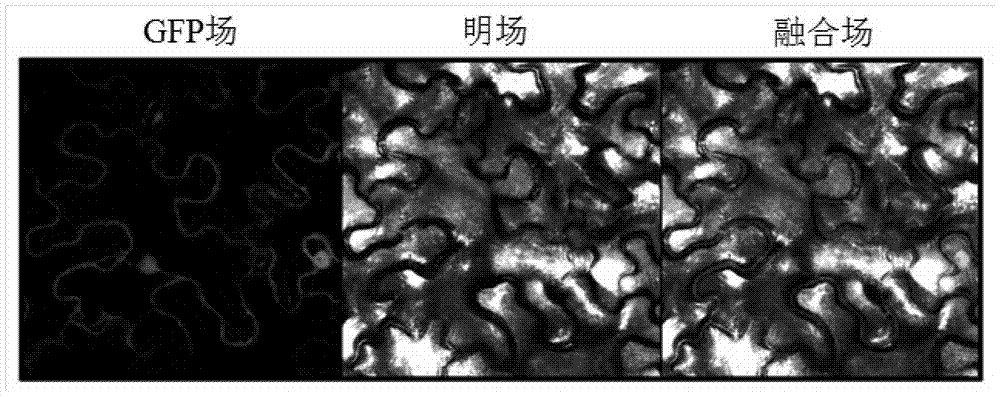
Intracellular analysing and detecting method of peptidyl-propyl-cis/trans isomerase activity
InactiveCN1473939ALong-term useDetermine activityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingIsomerizationFluorescence
The present invention belongs to biotechnology, and the intracellular analysis and detection process of peptidyl-propyl-cis / trans isomerase activity includes constructing fusion gene through fusion of protein or polypeptide, which contains X-Pro bond and realizes correct folding via cis / trans isomerization under PPIases catalysis, with green fluorescent protein (GFP); expressing fusion protein; fluorescent observation of the green fluorescence of GFP; and indicating and analyzing the activity of PPIases inside microbe, plant and animal cell. The said process may be used in PPIases activity detection inside live cell, and the GFP fluorescence may be observed directly with fluorescent microscope to determine intracellular PPIases activity simply, flexibly and intuitively. The cell introduced into fusion gene may be used directly as the type culture for relevant PPIases research and the type culture may be proliferated and propagated via microbe and cell culturing process for long termuse.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
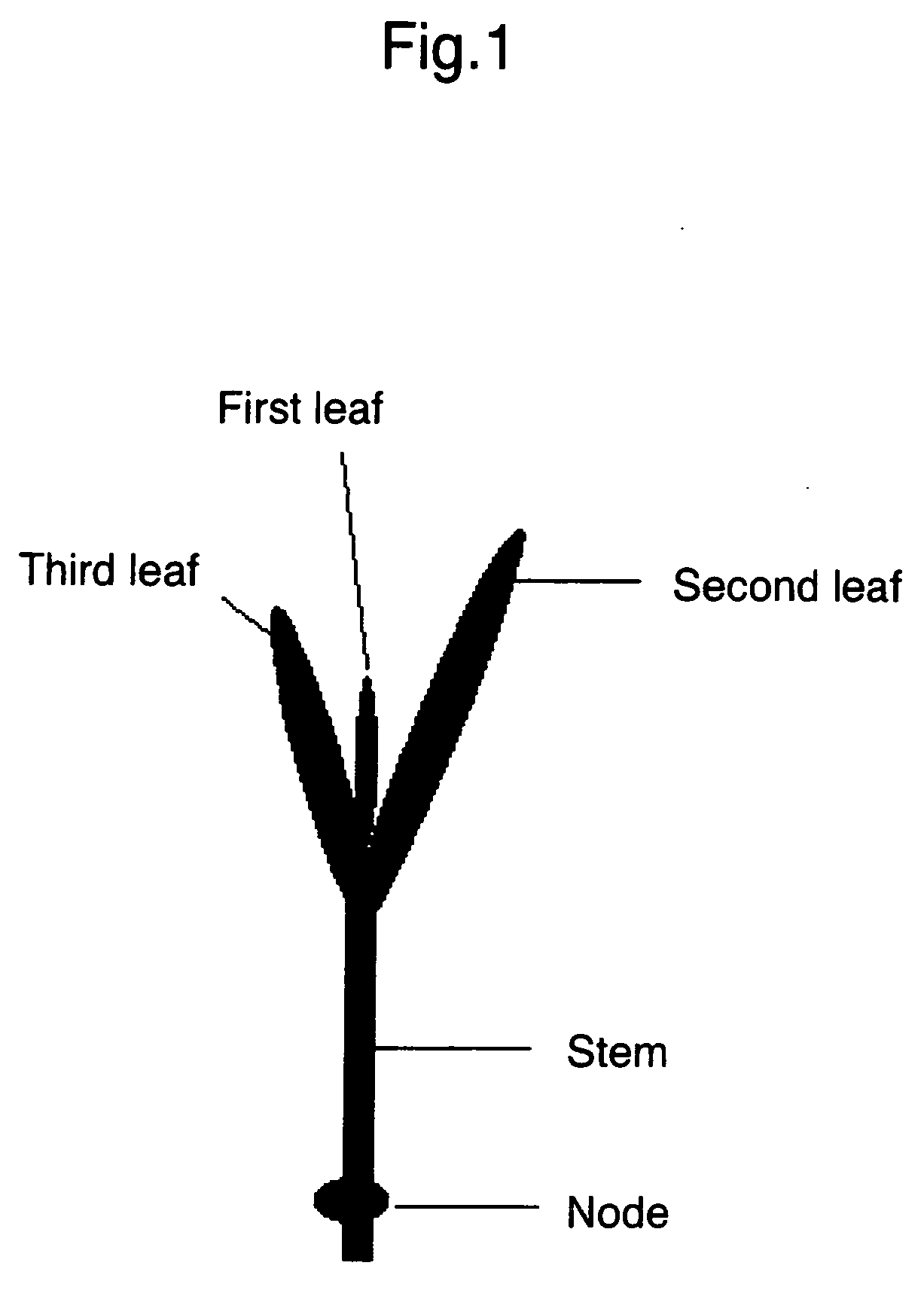
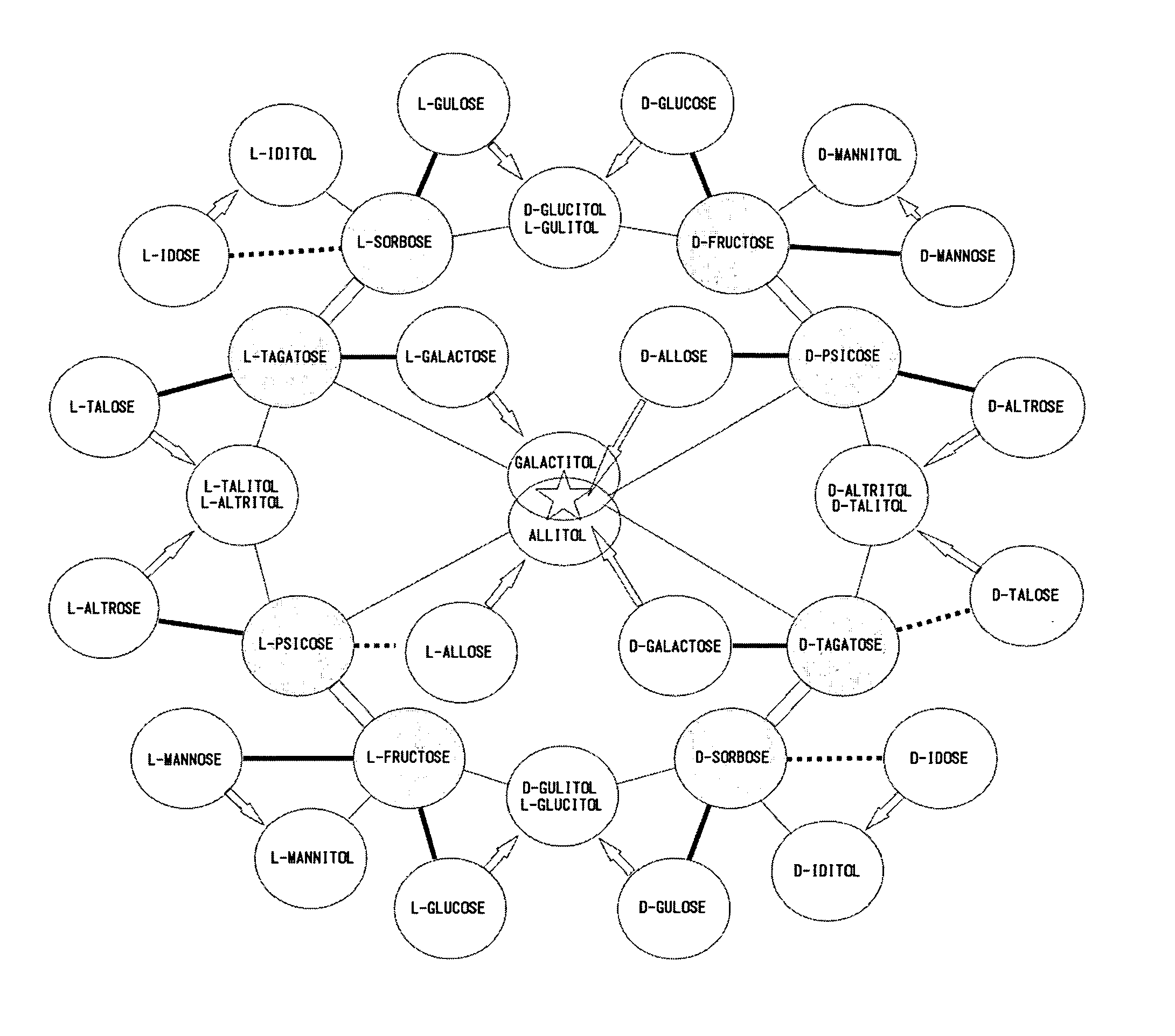
Gene sequence of l-rhamnose isomerase having new catalytic function and use thereof
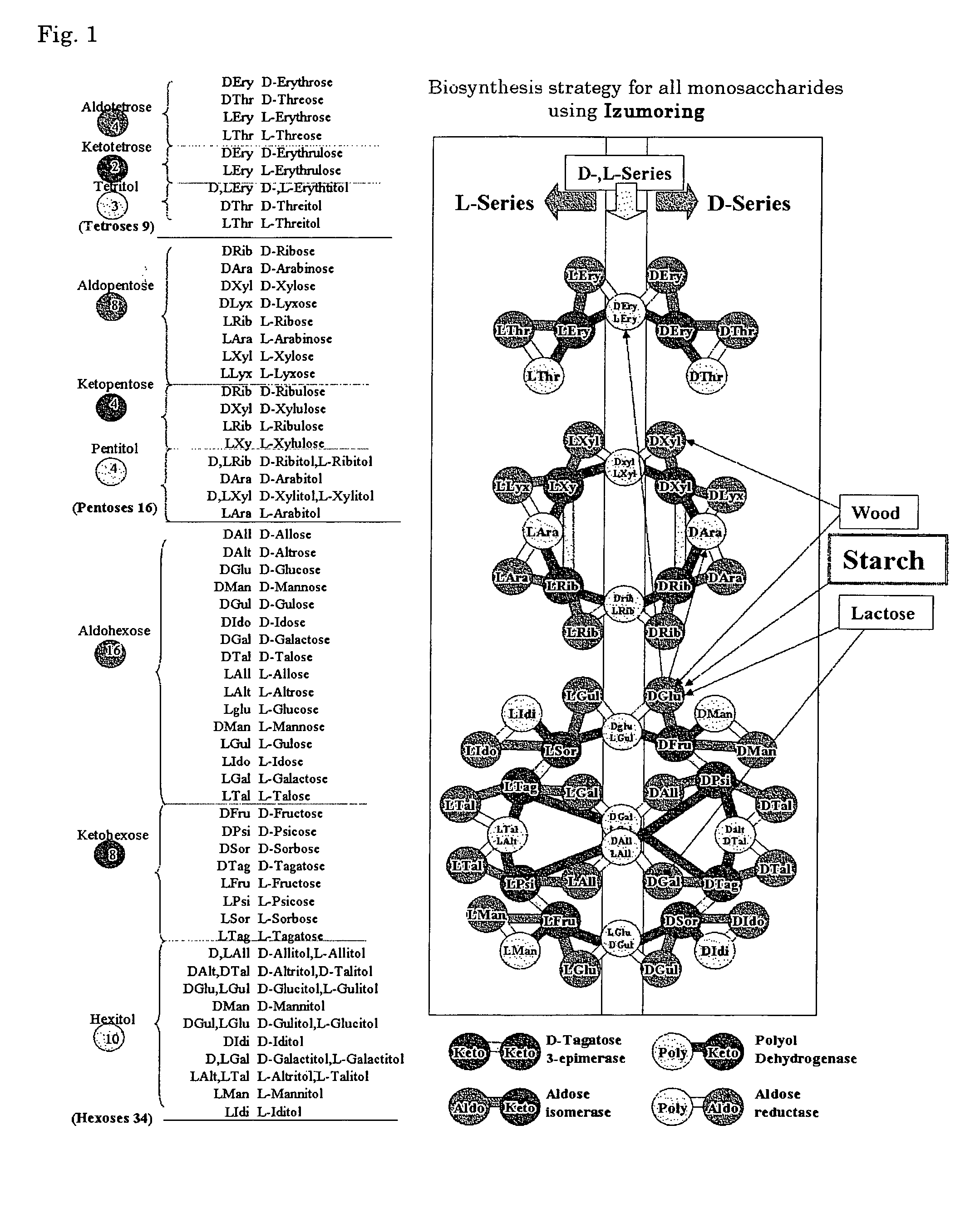
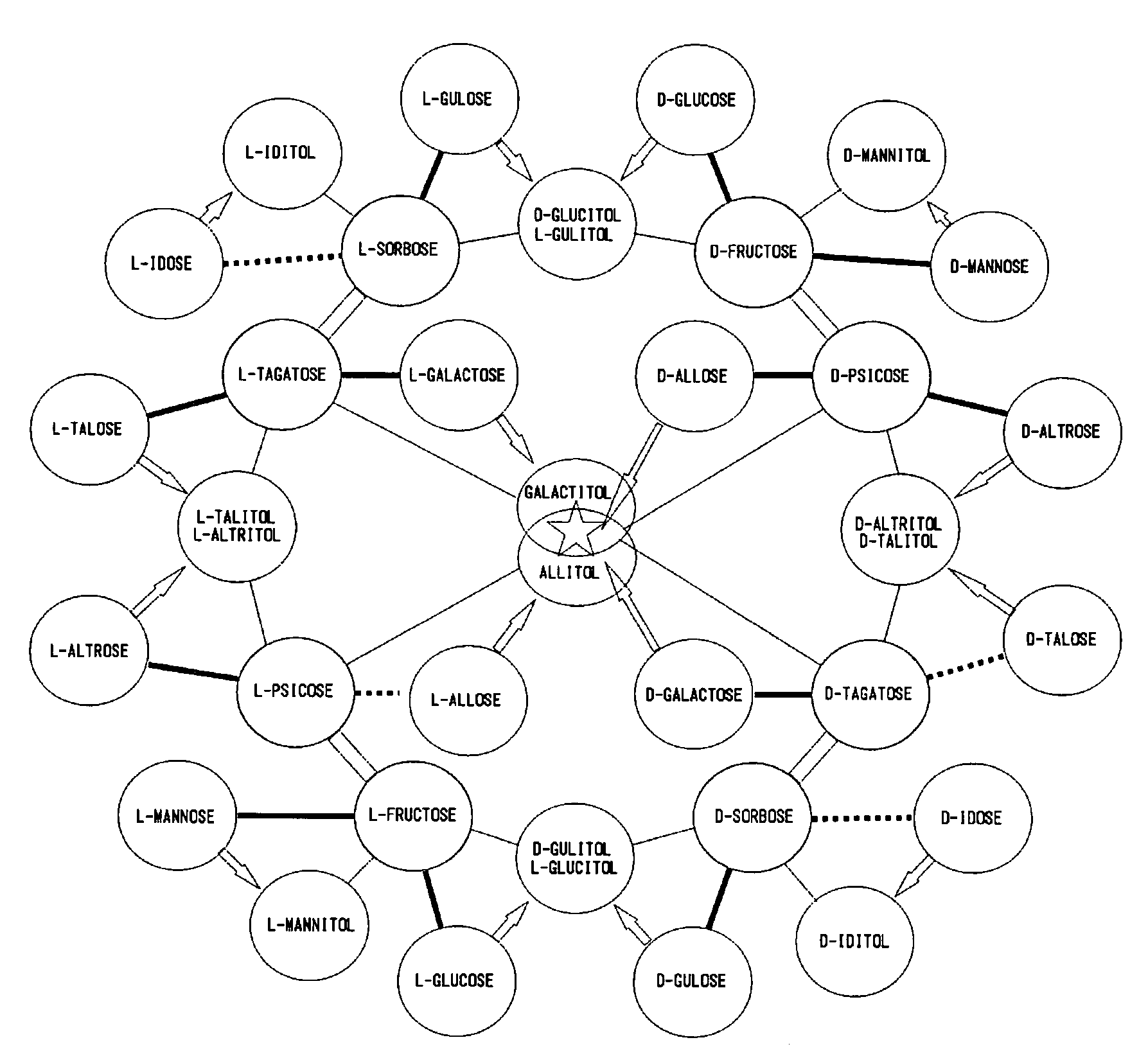
In the rare sugar strategy of Izumoring (FIG. 1), it is intended to establish a reaction system of producing rare sugars of many types by acquiring an isomerase which acts on various rare aldoses and, therefore, is most efficient in producing various rare ketoses. A DNA encoding the following protein (a) or (b). The above-mentioned DNA which is L-rhamnose isomerase derived from Pseudomonas stutzerii. A protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2. A process for producing a recombinant protein characterized by culturing a host cell containing an expression system that can express the above-mentioned protein in a medium and collecting a recombinant protein having an L-rhamnose isomerase activity from the thus obtained culture. A method of applying FIG. 1 to the production of a rare sugar characterized in that the location of a target rare sugar in the overall picture of monosaccharides is understood and thus the optimum production pathway on which the above protein is allowed to act is designed.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD
Sequence of Thermotolerant L-Rhamnose Isomerase Gene and Use of the Same
InactiveUS20090004694A1Reduce pollutionIncrease working temperatureSugar derivativesMicroorganismsIsomerizationHeat stability
[PROBLEMS] To provide the sequence of a thermotolerant L-rhamnose isomerase gene. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] A DNA comprising the base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1. A protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2. A protein originating in Bacillus pallidus strain 14a (FERM AP-20172) and having an L-rhamnose isomerase activity. A protein having an L-rhamnose isomerase activity which is specified as having the following characteristics: optimum temperature and working temperature: showing the maximum enzymatic activity at 80° C. (the optimum temperature) and working temperature ranging from 30 to 80° C.; heat stability: concerning the effect of temperature on the enzymatic activity, being stable at up to 50° C. in the case of heating for 1 hour; and catalyzing the isomerization from D-psicose to D-allose. A method of producing D-allose which comprises treating a solution containing D-psicose with the above protein having the L-rhamnose isomerase activity as a catalyst at 35 to 80° C. to thereby convert D-psicose into D-allose.
Owner:IZUMORING +1
Transferases, epimerases, polynucleotides encoding these and uses thereof
ActiveUS9157088B2High activityIncrease contentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIsomerase activityNucleotide
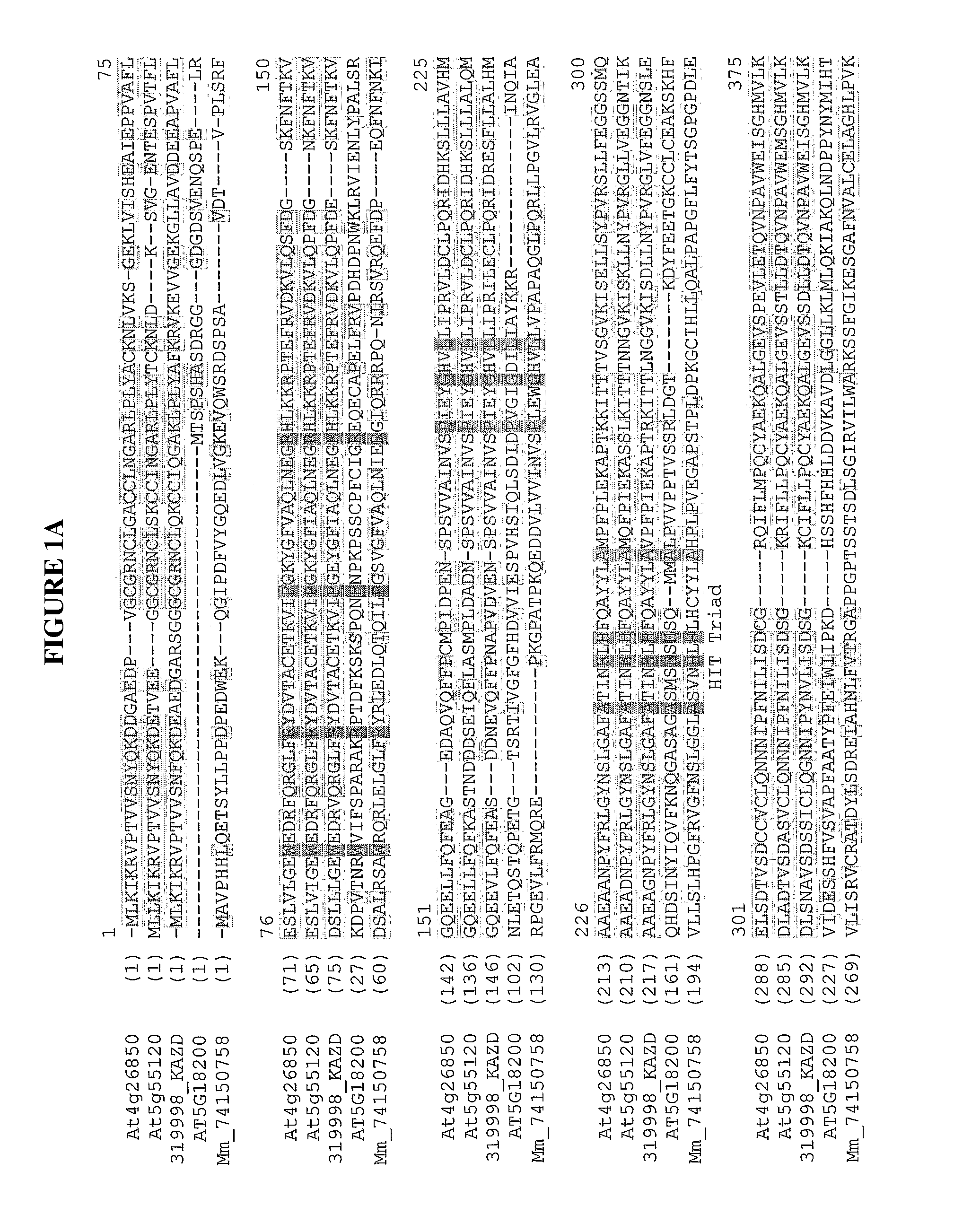
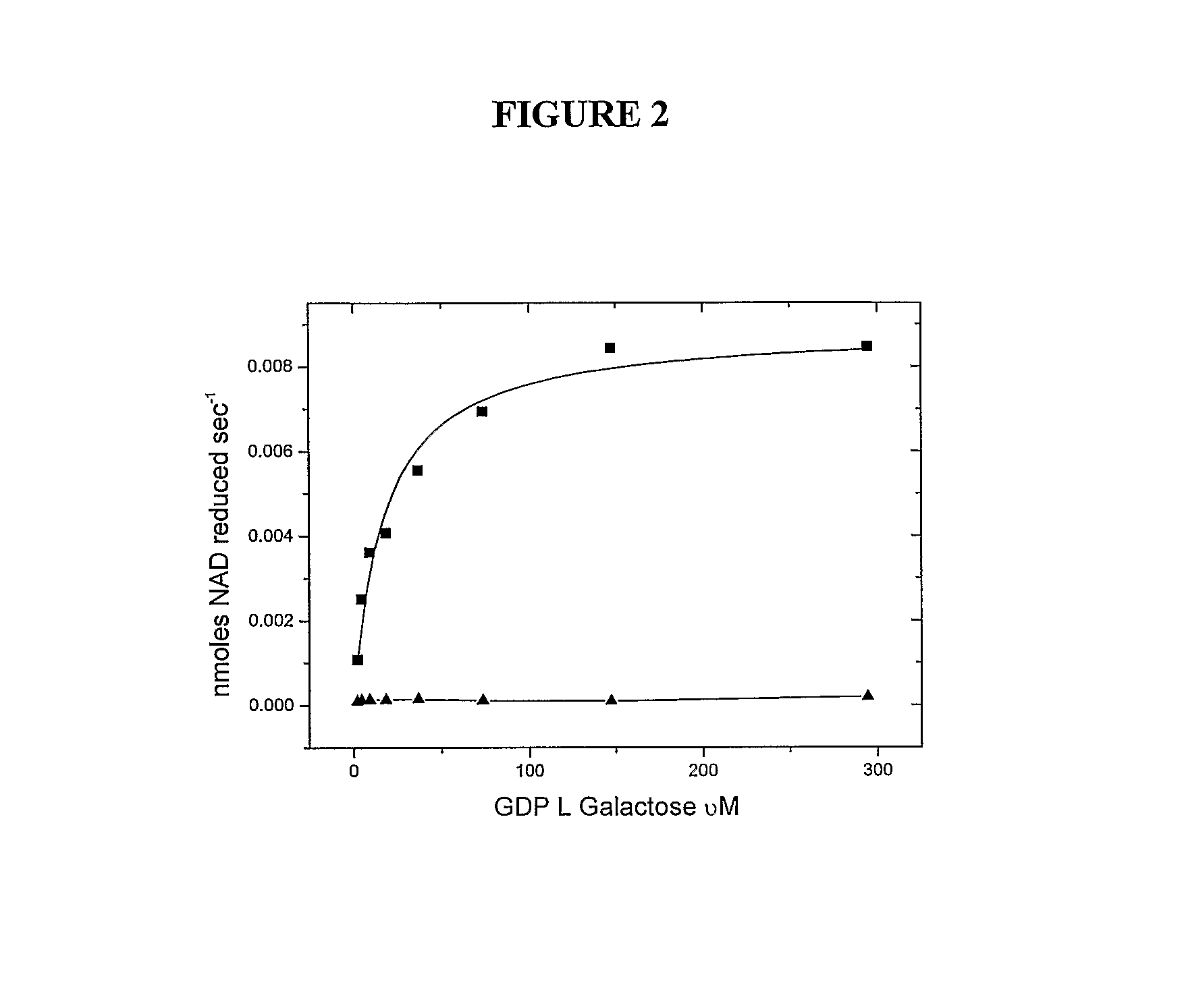
The invention provides compositions and methods for modulating GDP-L-Galactose Guanyltransferase (also known as GDP-L-Galactose phosphorylase) activity; and / or GDP-D-Mannose epimerase activity; and / or ascorbate content in plants. The invention provides plants and plant cells with increased GDP-L-Galactose Guanyltransferase activity; and / or GDP-D-Mannose epimerase activity. The invention provides plants and plant cells with increased ascorbate content as a result of: over-expression of GDP-L-Galactose Guanyltransferase; over-expression of GDP-D-Mannose epimerase; or in particular over-expression of a combination of GDP-L-Galactose Guanyltransferase and GDP-D-Mannose epimerase.
Owner:THE NEW ZEALAND INST FOR PLANT & FOOD RES LTD
Heparosan-glucuronic acid-5-epimerase, and method for producing polysaccharide using same
To provide a polypeptide having heparosan-glucuronate 5-epimerase activity, whereby means for producing a polysaccharide in which hexuronic acid residues has been epimerized is provided. Through screening of Achatina fulica cDNA library, a DNA encoding a polypeptide of heparosan-glucuronate 5-epimerase is obtained. The epimerase acts on glucuronic acid residues of N-acetyl heparosan and / or iduronic acid residues of completely desulfated N-acetylated heparin. The polypeptide encoded by the DNA is expressed by insect cells, to thereby yield the polypeptide having heparosan-glucuronate 5-epimerase activity. By bringing the polypeptide into contact with N-acetyl heparosan or completely desulfated N-acetylated heparin, a polysaccharide in which hexuronic acid residues has been epimerized is yielded.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
New peptides having antimicrobial activity and new enzyme capable of converting l-configured residue in d-configured amino acid in a peptide
ActiveUS20180346526A1Increase productionImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismIsomerase activity
The present invention relates to a new class of peptides having antibacterial activity and presenting D-amino acids and their uses. It also relates to a new enzyme presenting a peptide epimerase activity in vitro and in vivo, thereby being useful for modifying peptides in order to change the amino acid configuration from L to D.
Owner:INST NAT DE RECH POUR LAGRICULTURE LALIMENTATION & LENVIRONNEMENT
Indolocarbazole anticancer agents and methods of using same
The present invention relates to anti-tumor compounds, compositions and methods. In particular, the invention relates to indolocarbazole analogues of the following general formulas that inhibit topoisomerase I activity
Owner:ADVANCED LIFE SCI
Methods for obtaining a genetically modified plant or microbe and for increasing oil yield
InactiveUS20150299744A1Improve oil yieldDecrease in triose-phosphate isomerase activityFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteBacteriaMicroorganismIsomerase activity
Methods are provided for obtaining a genetically modified plant, wherein the plant exhibits an increased oil yield relative to a corresponding control plant that is not so genetically modified. The methods comprise genetically modifying a plant progenitor cell to cause a decrease in triose-phosphate isomerase activity and an increase in glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. The methods also comprise culturing the genetically modified plant progenitor cell to obtain the genetically modified plant. Also provided are methods for increasing oil yield, comprising genetically modifying a plant to cause, in at least one oil-producing organ or tissue of the plant, a decrease in triose-phosphate isomerase activity and an increase in glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. The genetic modification is carried out across more than a single generation. The genetically modified plant exhibits an increased oil yield relative to a corresponding control plant. Also provided are similar methods directed to a microbe.
Owner:SIME DARBY MALAYSIA BERHAD
Recombinant materials for carotenoid production
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the amino acid sequences depicted in any one of SEQIDNOs: 24 to 50. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided, preferably wherein said enzyme has an activity selected from isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase activity, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase activity, phytoene synthase activity, phytoene desaturase activity and lycopene cyclase activity, still more preferably those coding for an enzyme having an amino acid sequence selected from the one represented by SEQIDNO: 13, SEQIDNO: 15, SEQIDNO: 17, SEQIDNO: 19, SEQIDNO: 21 or SEQIDNO: 23. Further embodiments concern vectors, transformed host organisms, methods for making proteins and / or carotenoids, such as astaxanthin, and methods for isolating highly expressed promoters from Phaffia.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
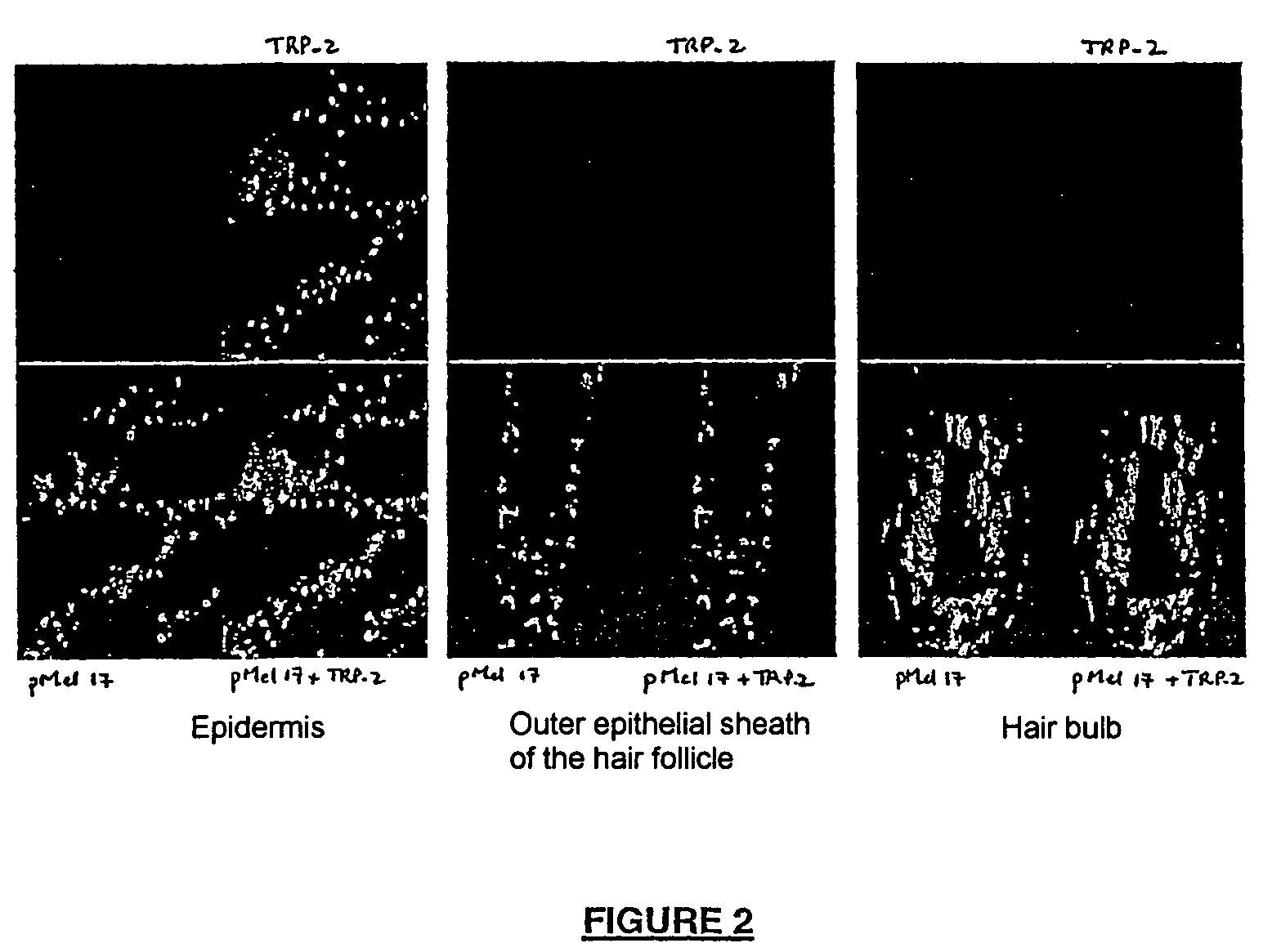
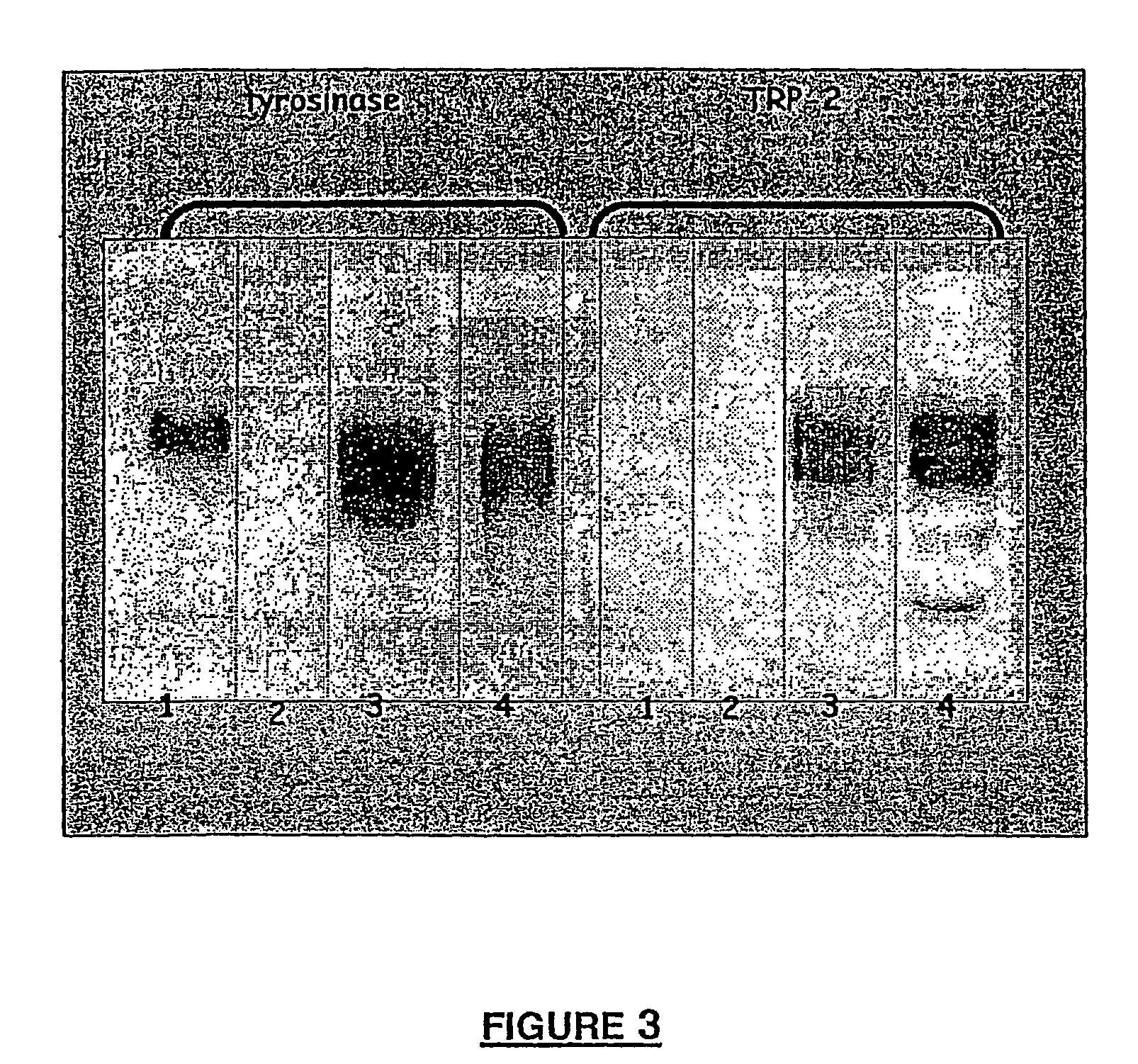
Administration of agents mimicking DOPAchrome tautomerase (TRP-2) activity for protecting hair follicle melanocytes
Agents mimicking DOPAchrome tautomerase activity are administered, notably topically applied, to protect and / or regenerate the melanocytes of hair follicles, to promote the cyclic renewal of the follicular pigmentation unit, to prevent and / or limit and / or arrest the development of canities, and to maintain the natural pigmentation of gray or white head hair and / or body hair.
Owner:LOREAL SA
New improved glucose isomerases
ActiveUS20210180039A1Increased and improved glucose isomerase activityOxidoreductasesIsomerasesCelluloseFructose
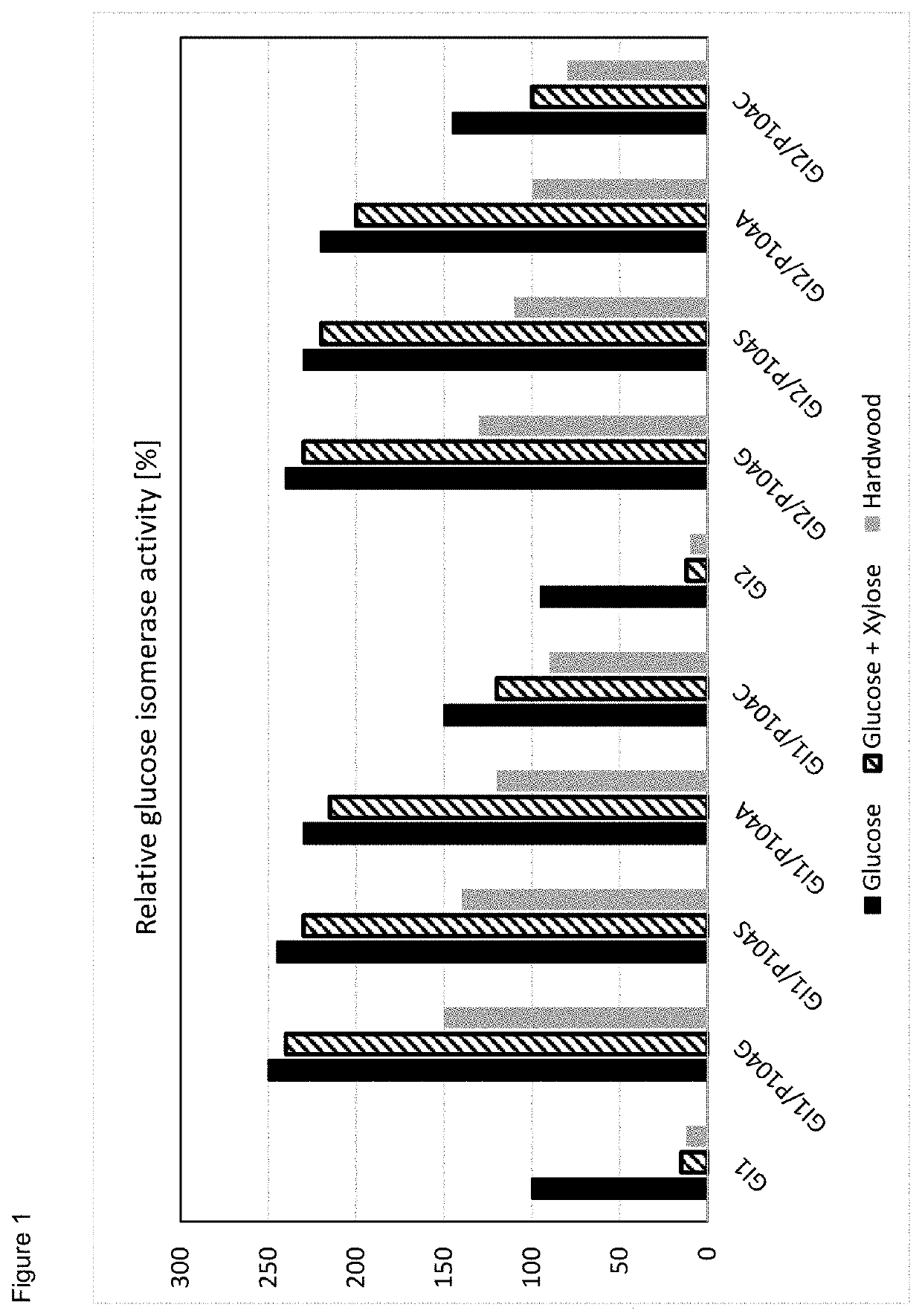
The invention is in the field of enzymology. More in particular, it provides a method for the isomerization of glucose into fructose wherein the glucose is derived from lignocellulosic material. More in particular, the invention provides polypeptides encoding mutant glucose isomerase enzymes with improved glucose isomerase activity as compared to the corresponding wild type enzyme. The disclosed polypeptides are particularly suited for converting glucose to fructose in the presence of xylose.
Owner:METGEN
Method for rapidly measuring activity of epimerase by using circular dichroism spectrum
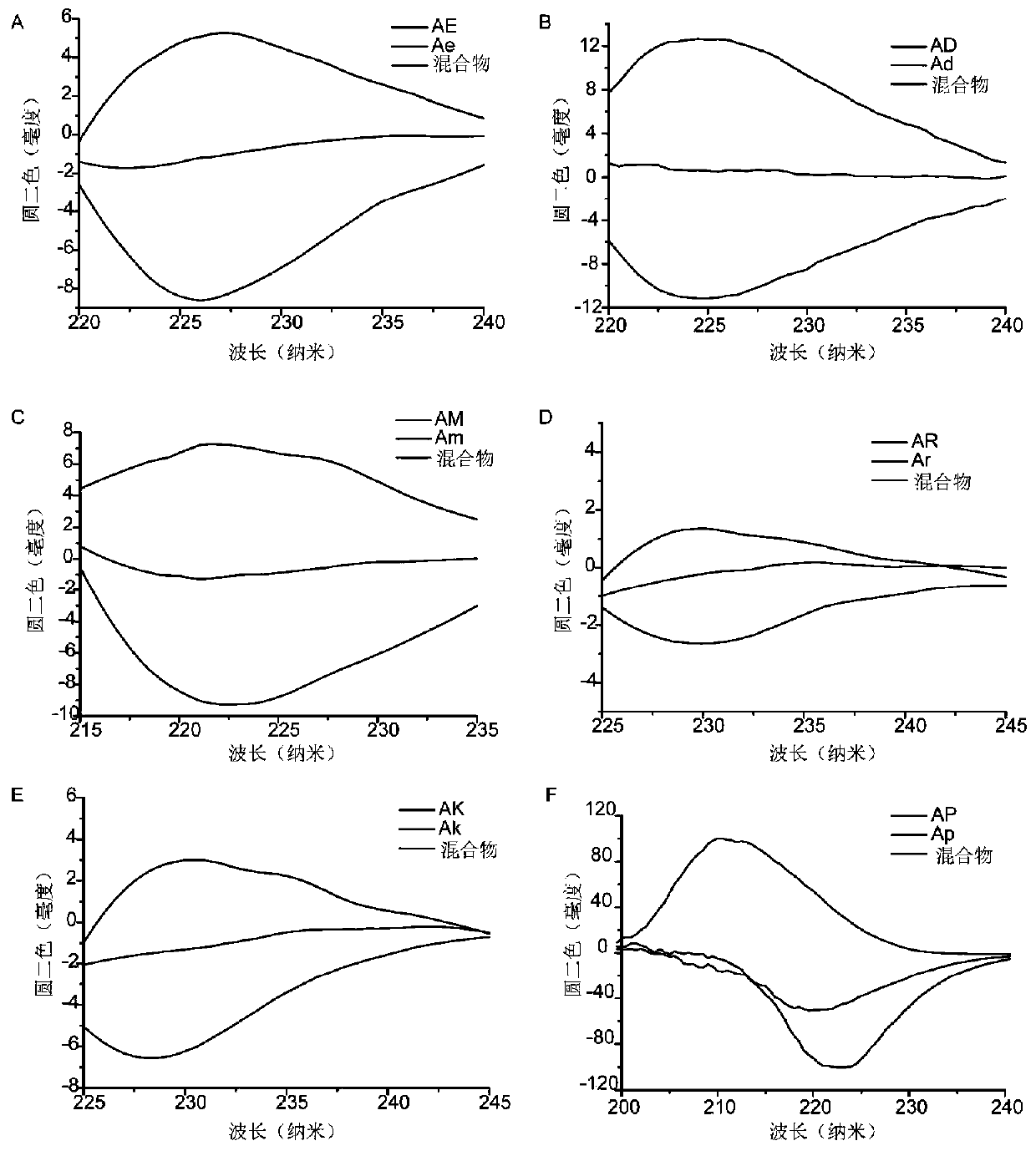
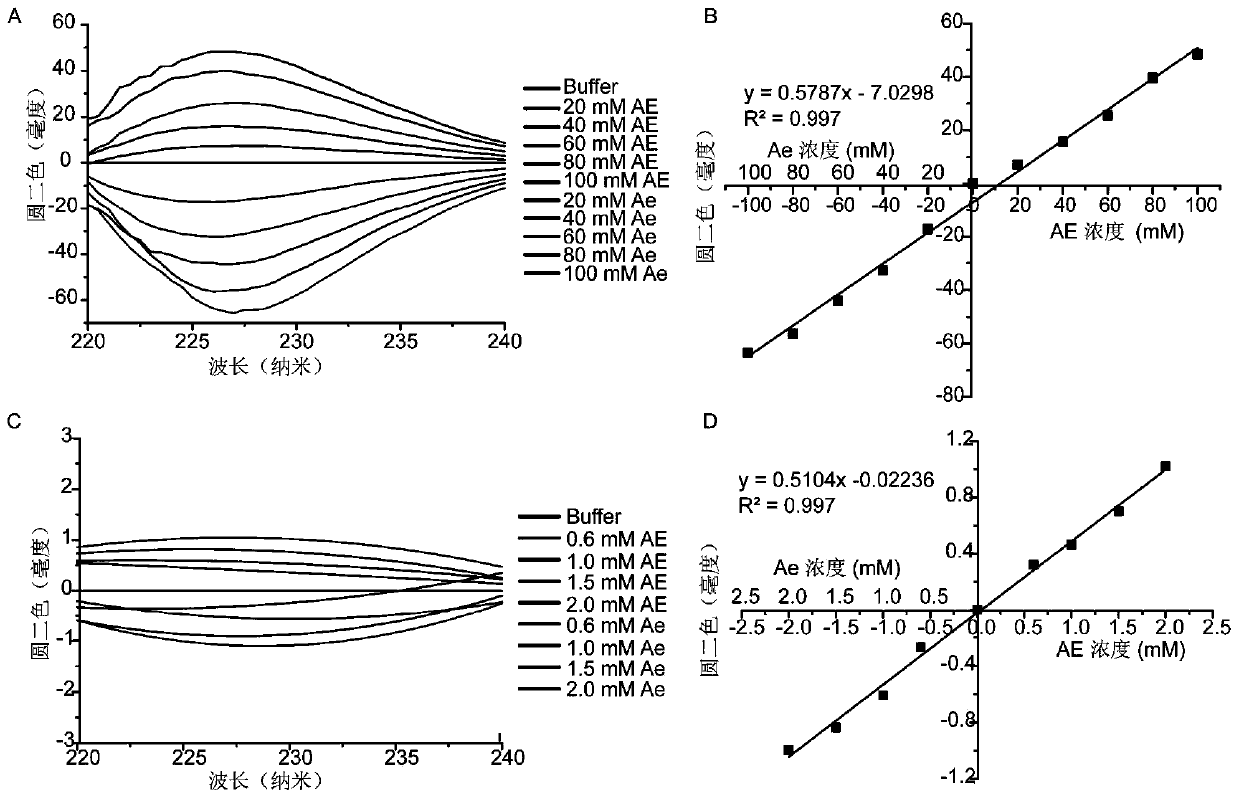
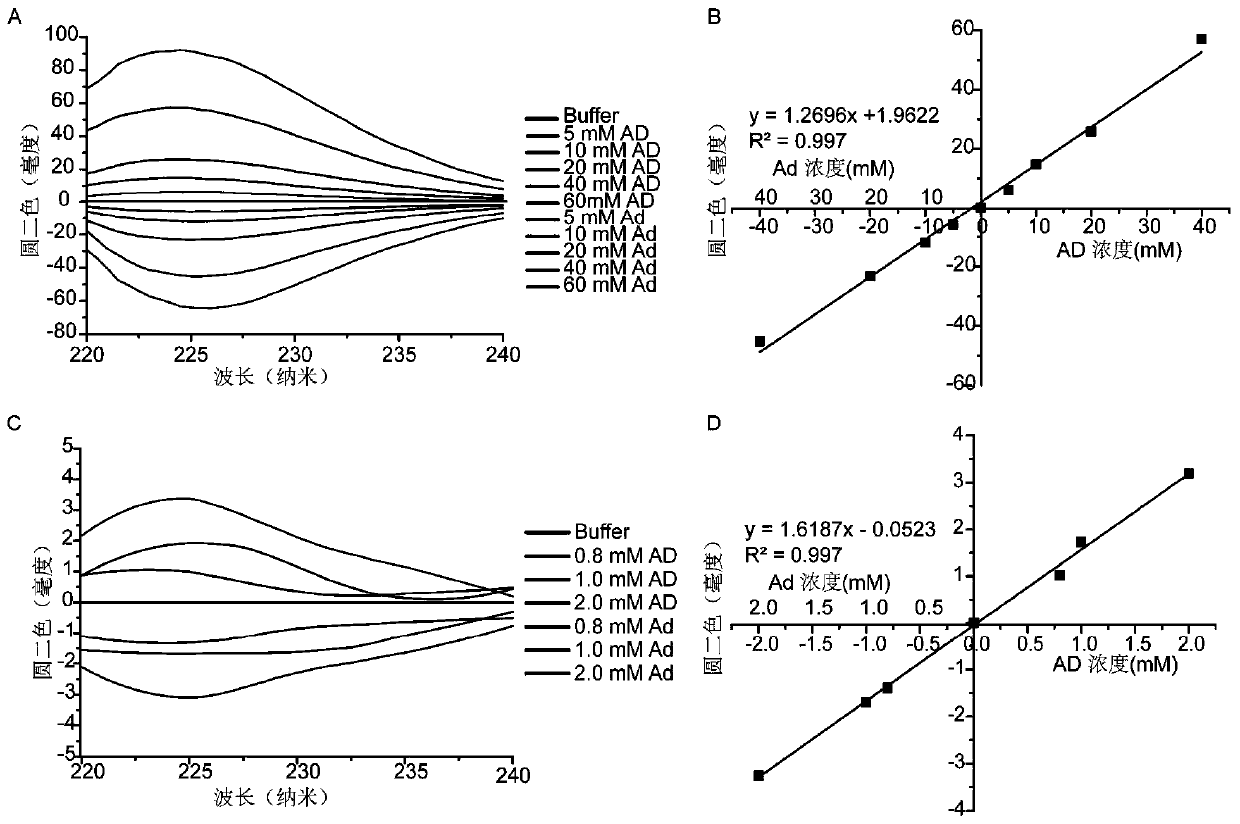
ActiveCN110736705AClear activityRealize quantitative determinationAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionColor/spectral properties measurementsDipeptideIsomerase activity
The invention relates to a method for rapidly measuring the activity of epimerase by using a circular dichroism spectrum. According to the method, epimerase is added into a dipeptide enantiomer initial solution for catalytic reaction; a CD signal intensity change of the dipeptide enantiomer solution before and after the catalytic reaction is detected by using a circular dichroism spectrum; if anychange happens, the epimerase is indicated to have activity; and otherwise, e epimerase is indicated not to have activity. According to the method provided by the invention, no derivative reaction isneeded; the operation is simple, the reproducibility is high, the error range is small, the sensitivity is high, the linear range is wide, and measurement can be carried out continuously, and in-situdetection can be realized. Therefore, a new field is provide for research on chiral recognition.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for producing high yield attenuated Salmonella strains
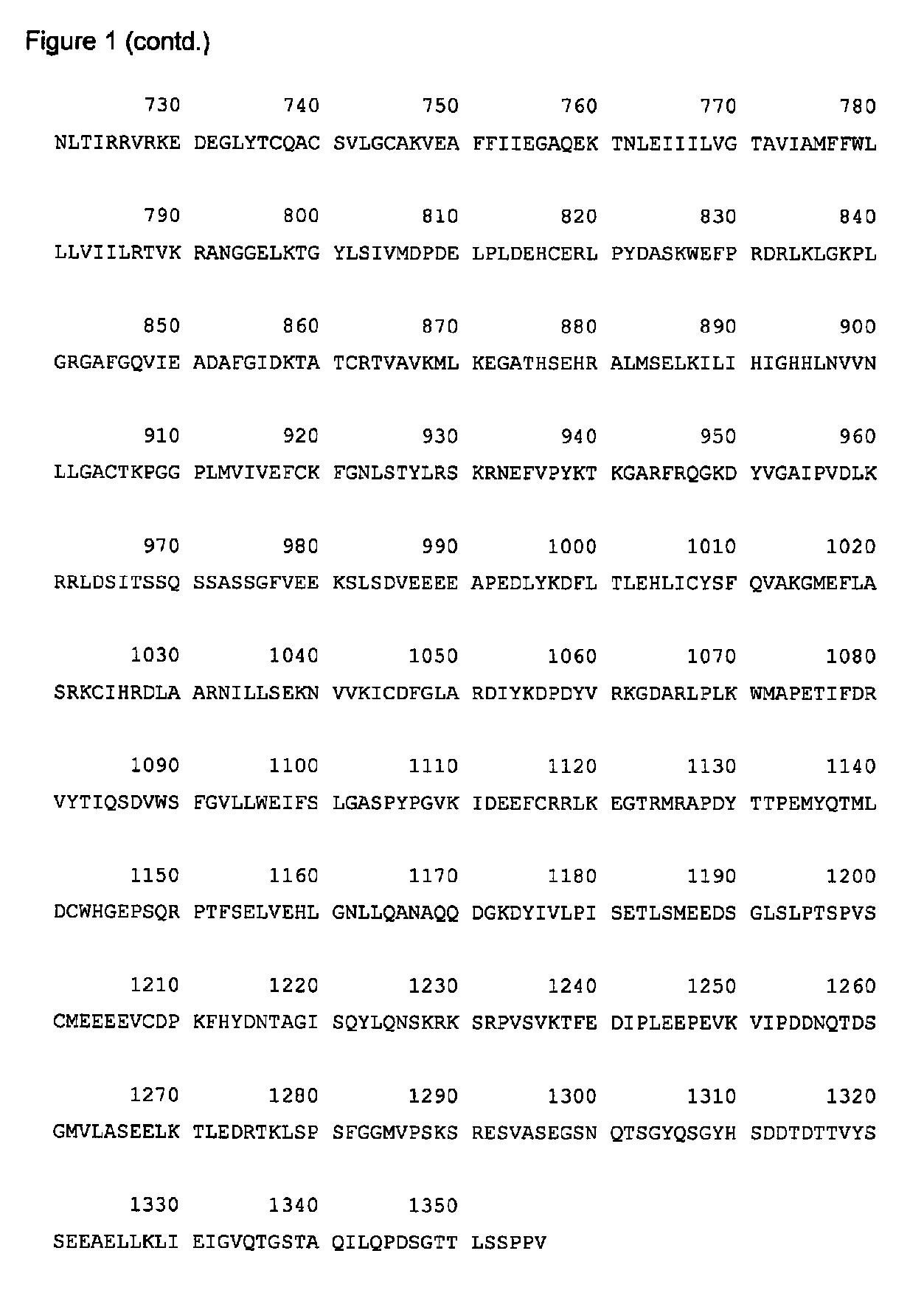
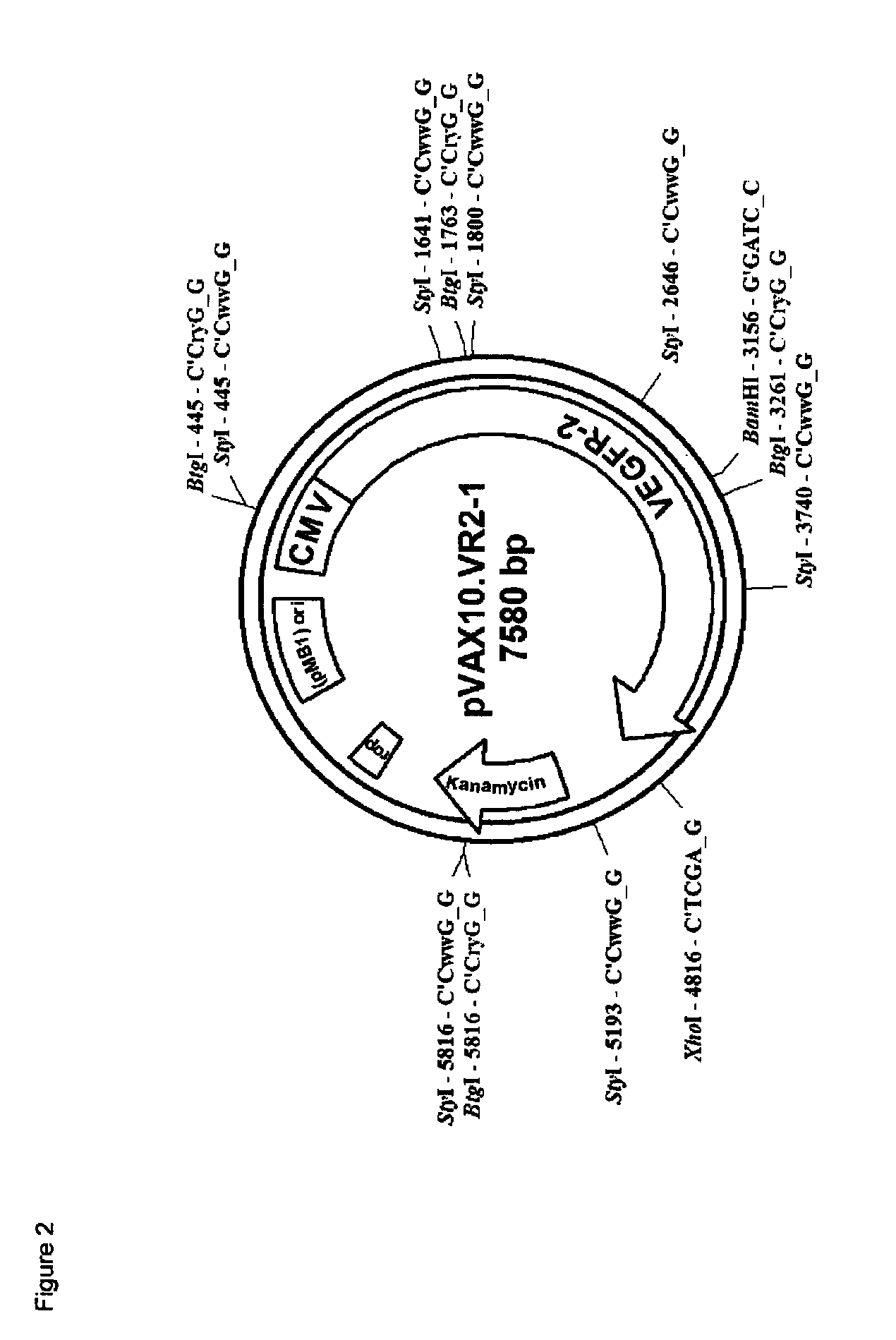
ActiveUS9493738B2High yieldIncreased cell yieldBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementIsomerase activityVEGF receptors
This invention relates to a novel method for growing attenuated mutant Salmonella typhi strains lacking galactose epimerase activity and harboring a recombinant DNA molecule. The method comprises the step of culturing said Salmonella typhi strain without adding glucose to the medium during the fermentation with a starting glucose amount that is depleted before reaching the stationary phase. The invention further relates to attenuated mutant Salmonella typhi strains obtainable by said method and to an attenuated mutant Salmonella typhi strain harboring a recombinant DNA molecule encoding a VEGF receptor protein for use as a vaccine.
Owner:VAXIMM
Eggplant chalcone isomerase smchi protein and its coding gene
ActiveCN104745561BGood anti-oxidant health effectImprove qualityIsomerasesFermentationIsomerase activityPlant quality
The invention discloses eggplant chalcone isomerase SmCHI protein and a coding gene thereof. The protein comprises (a) protein consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3; or (b) protein derived from the amino acid sequence in (a), which is substituted, lost or added by one or more amino acids and has the activity of eggplant chalcone isomerase. The cDNA and gDNA of the coding gene respectively have base sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2; and the gene is expressed in roots, stems, leaves, flowers, peels and pulp, and has the expression quantity in peels remarkably higher than that in other tissues. Under stress of low temperature, the expression quantity of the gene reaches the maximal value in 48 hours, which is 3.65 times that of an unprocessed gene. The eggplant chalcone isomerase SmCHI protein and the coding gene thereof provide a theoretical basis for improving plant quality by utilizing the genetic engineering technology to obtain high oxidation resistance medicines or foods in the future, thereby having great application values.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com