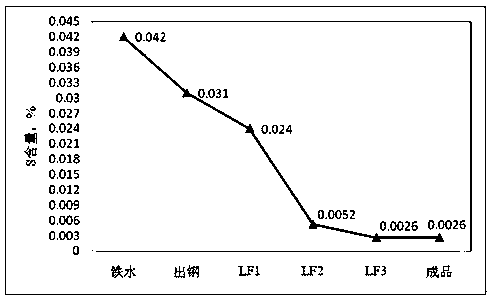
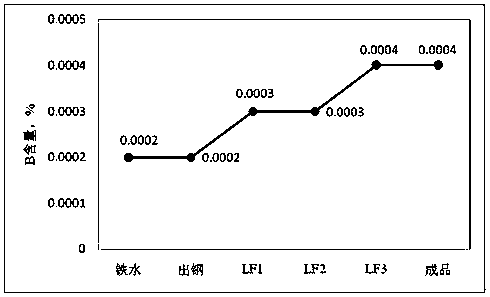
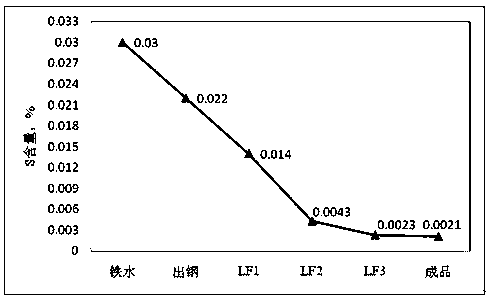
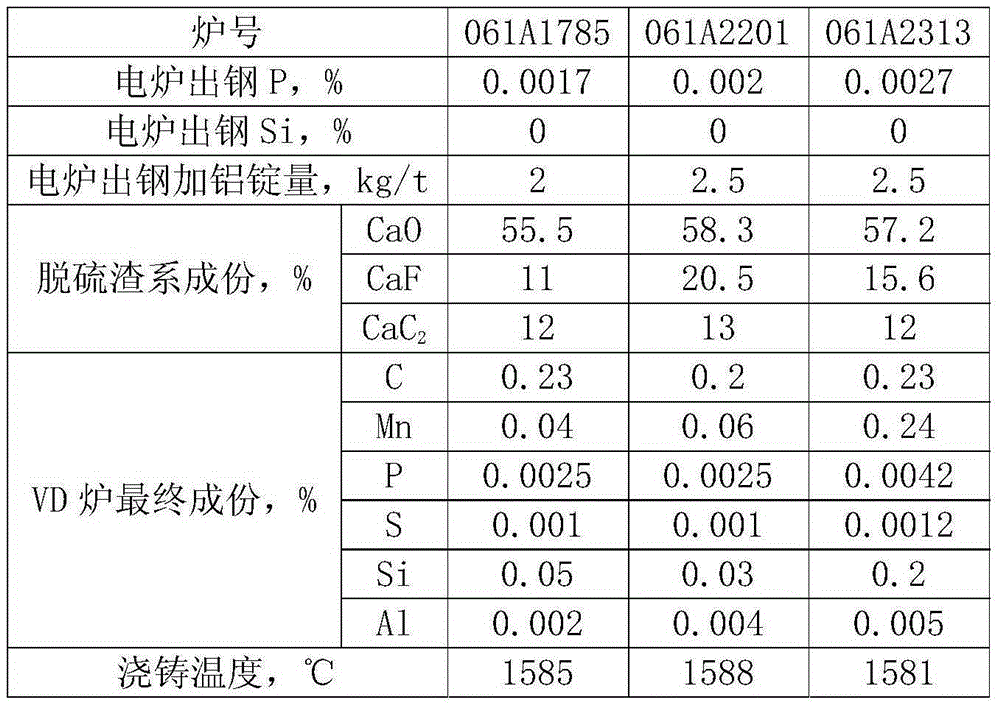
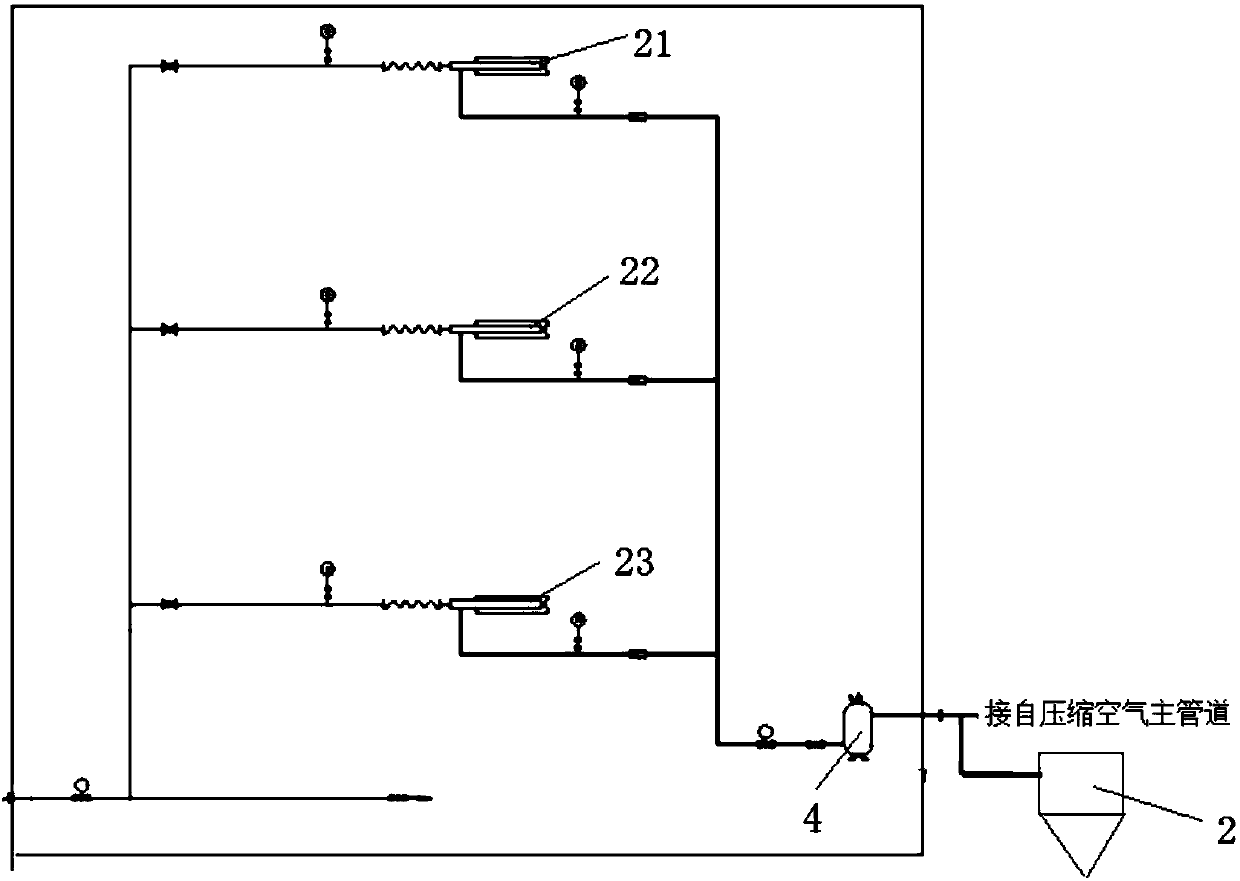
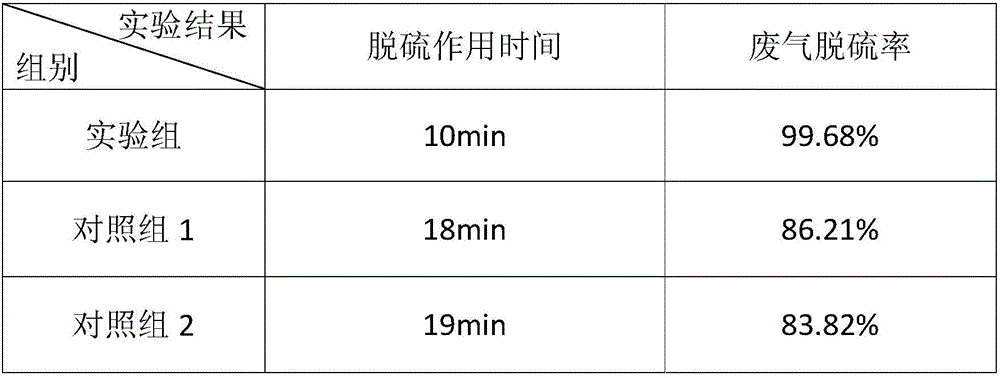
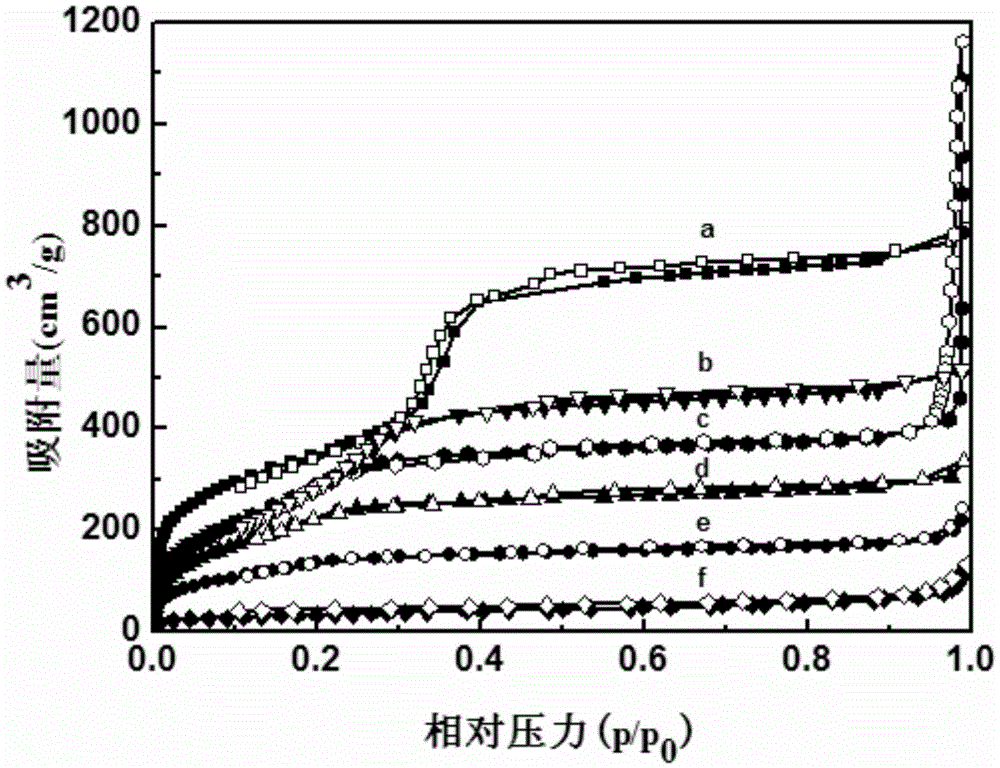
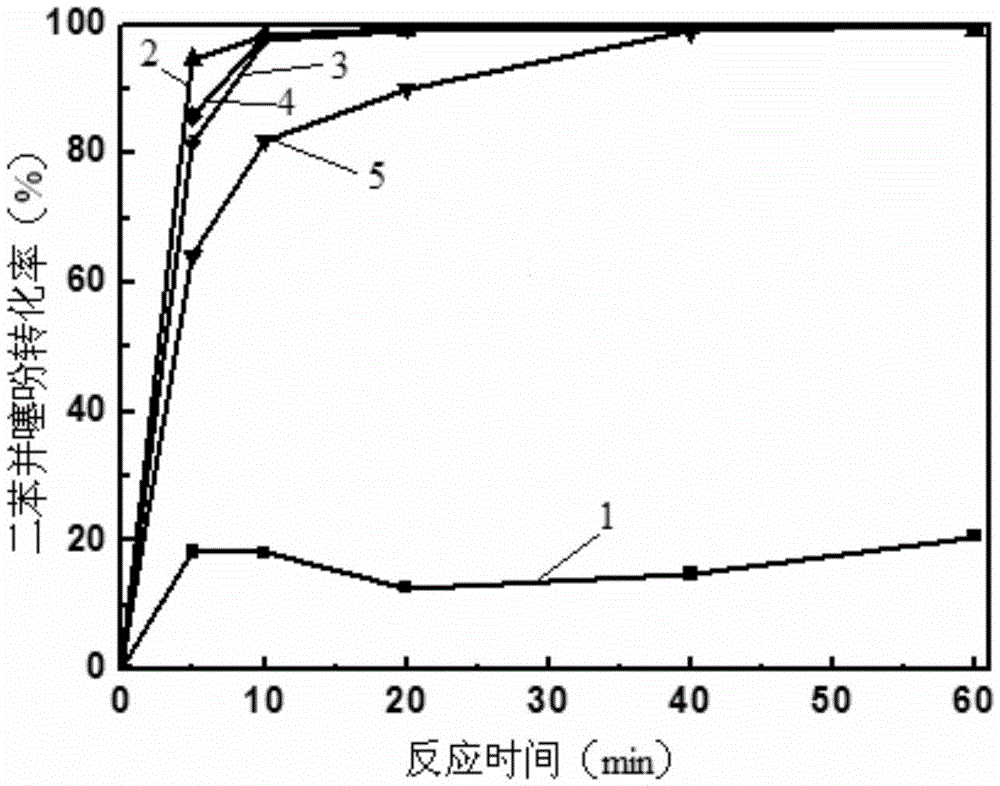
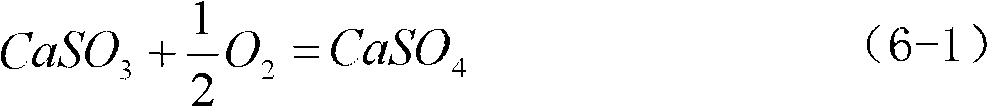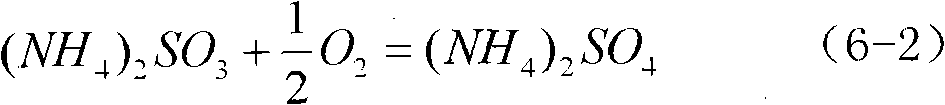Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
121results about How to "Fast desulfurization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Convertor tapping washing fining furnace fast desulfurization method
The invention relates to a method for rapidly desulfurizing a slag washing and refining furnace for converter tapping, which belongs to the steelmaking technical field and is used to solve the problem that the converter tapping is rapidly refined and desulfurized. The method comprises two steps of steel ladles slag-washing and LF refining and is characterized in that pre-melted slag and white lime 3-5Kg / t are added according to the ratio of 7-12Kg / t in the step of the steel ladles slag-washing, the pre-melted slag is added according to the ratio of 3-5Kg / t in the step of LF refining, and fluxing medium is added according to the following ratio: lime 3-5Kg / t, calcium carbide 2-4Kg / t and ferrosilicon powder 2-4Kg / t, the components of the pre-melted slag is combined according to following weight units: CaO 46-52, Al2O3 38-45, CaF2 5-7, SiO2<=10, Fe2O3 <=2, H2O<= 0.5, and the pre-melted slag melting point <=1350DEG C. The invention can increase the rear furnace slug washing of a high converter under the condition that aluminum is added to deoxidize in refining and refining slag is rapidly produced under the weak oxidation condition, and the requirements for producing low sulphur steel are satisfied.
Owner:HANSTEEL
Rapid desulfurization refining method for ladle furnace
The invention discloses a rapid desulfurization refining method for a ladle furnace (LF). The method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing desulfurization refining in the LF, wherein the LF treatment starting temperature is between 1,570 and 1,605 DEG C; 2) after a ladle argon blowing device of the LF is turned on, blowing argon from the bottom of the ladle; 3) after finishing adjusting the temperature, inserting a desulfurization powder spraying gun into a molten steel liquid for spraying a desulfurizing agent; 4) after finishing spraying powder, switching the spraying gun to a functional stage of blowing the argon, blowing the argon from the top, simultaneously blowing the argon from the bottom of the ladle, and performing strong stirring desulfurization operation; 5) alloying, namely after desulfurization is finished, lifting the desulfurization powder spraying gun, adjusting a ladle bottom blowing flow, and performing alloy configuration to meet a target requirement on final components of a steel grade; and 6) after finishing adjusting components, performing soft stirring operation, measuring the temperature, sampling, and turning off the ladle argon blowing device to finish treating. The method realizes rapid desulfurization of the LF, and can shorten an overall melting cycle and improve the number of continuous casting furnaces and production efficiency.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Technology for removing hydrogen sulfide in gas at room temperature
ActiveCN101766946AImprove the degree of purificationOvercome the disadvantage of high consumptionGas treatmentDispersed particle separationRoom temperatureProduct gas
The invention relates to a wet desulphurization method for removing hydrogen sulfide in gas at room temperature. The method comprises the following steps: 1. contacting gas containing hydrogen sulfide with suspending liquid containing desulfurizer in a desulphurization reactor to react; 2. sending the reacted suspending liquid to a regenerative reactor, wherein the suspending liquid is obtained from the step 1 and contains waste agent which is generated through desulfuration by using desulfurizer, regenerating the waste agent by using gas containing oxygen; and 3. sending the regenerated suspending liquid with desulfurizer which is obtained from the step 2 to the desulphurization reactor in the step 1, and contacting with hydrogen sulfide. The method for removing hydrogen sulfide in gas at room temperature of the invention has the advantages that the process is simple, the operation is performed under room temperature and normal pressure, the desulphurizing rate is high and the cost is low.
Owner:BEIJING SJ ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION & NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
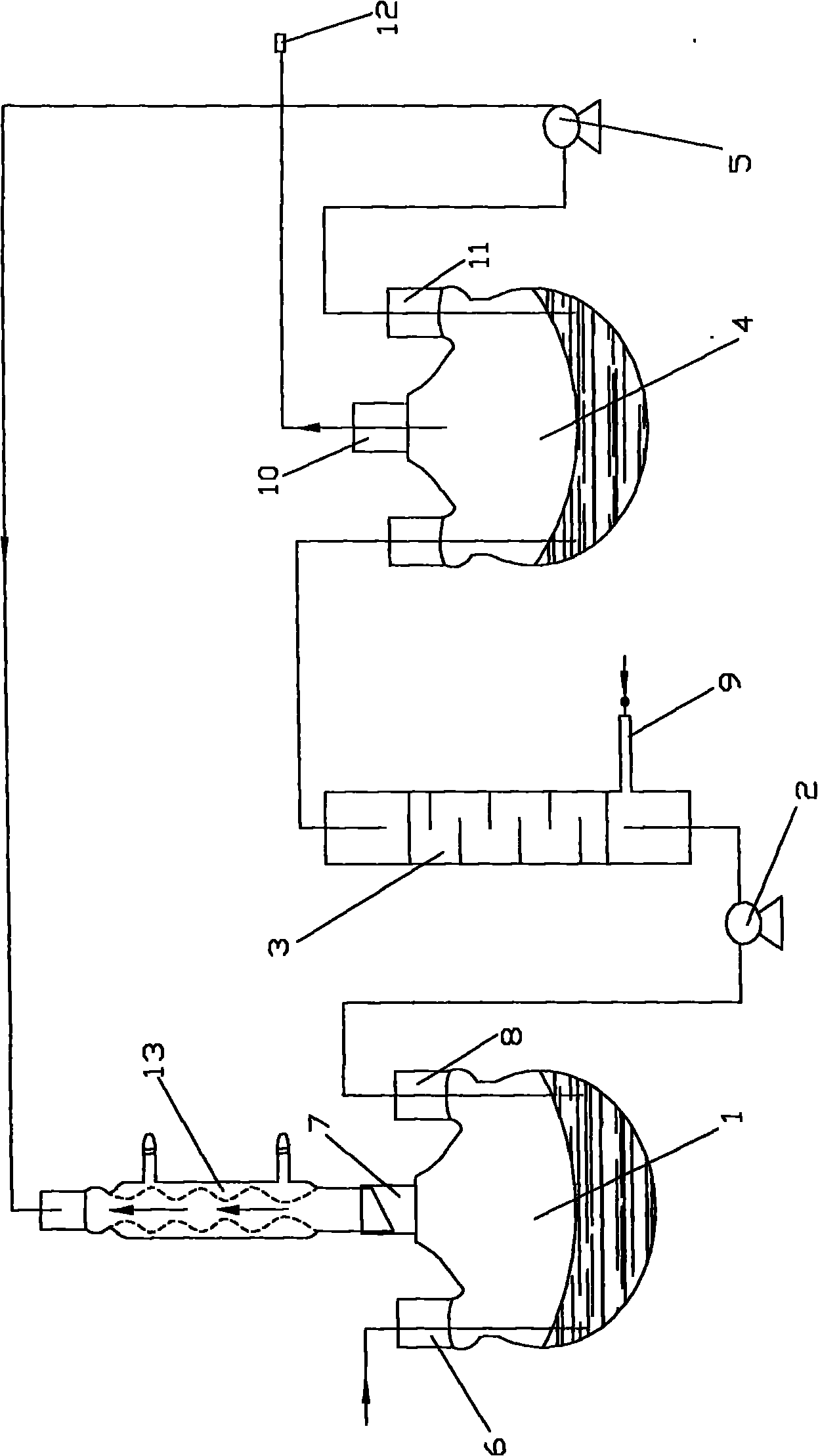
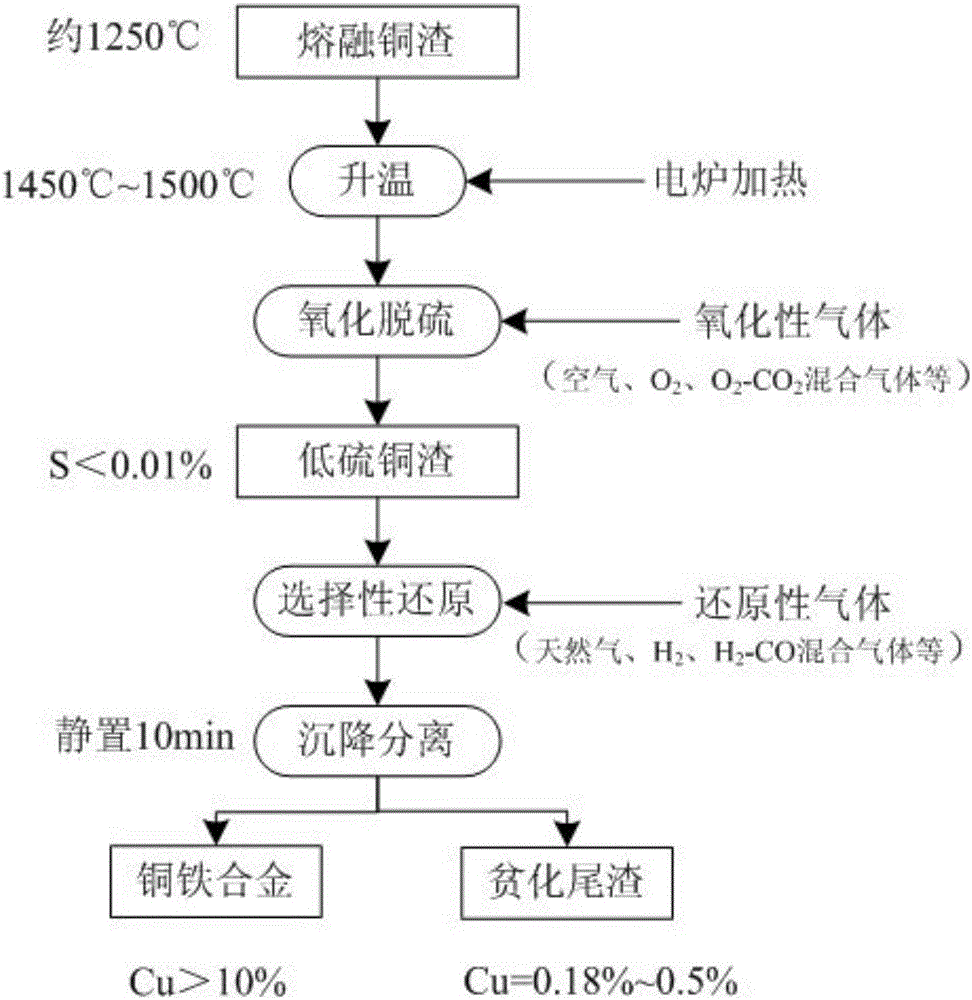
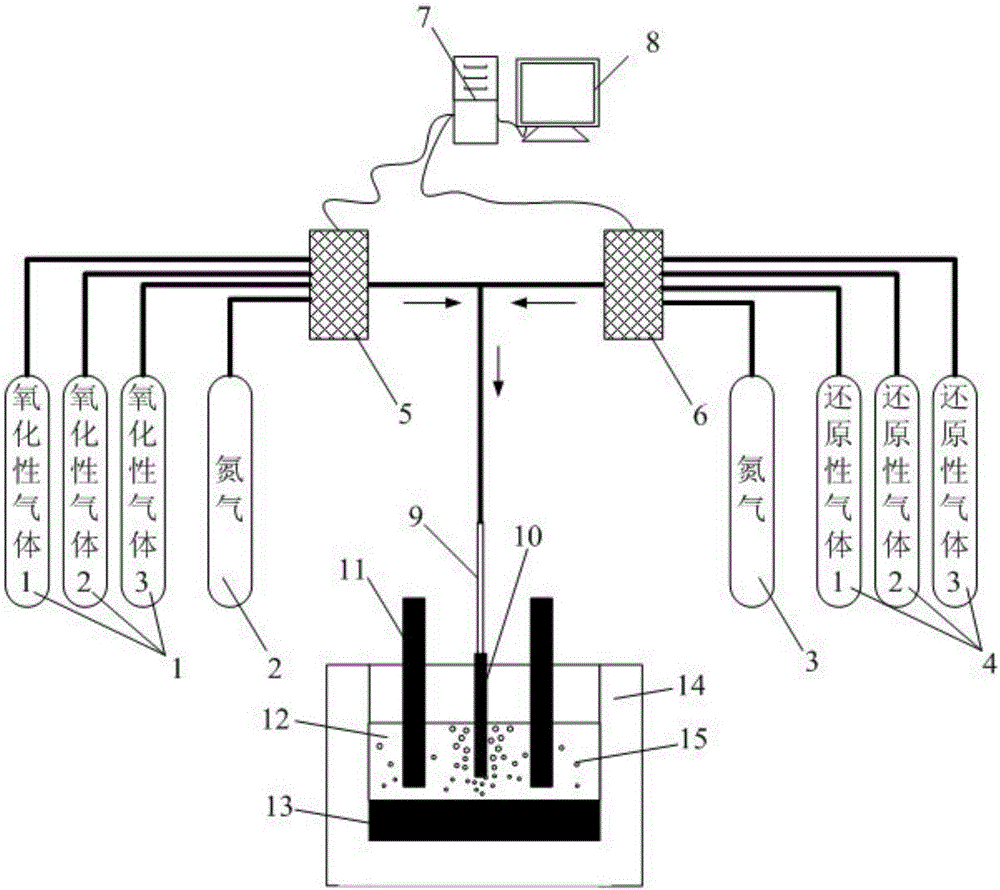
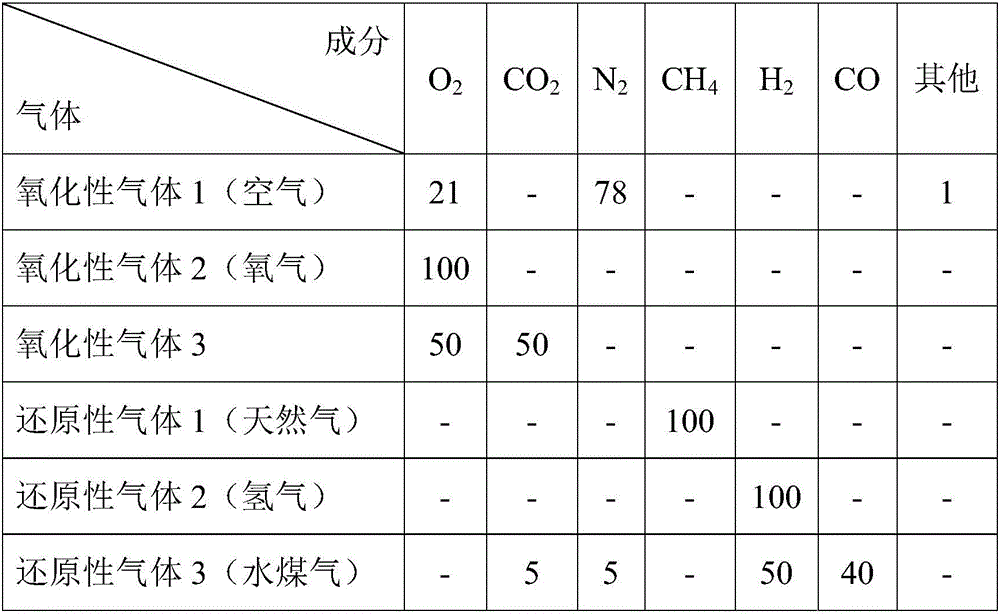
Method for realizing deep depletion on copper slag through multielement gas substep injection
ActiveCN106756062ARealize deep depletionComprehensive depletion results are excellentRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesLow copperMaterials science
The invention provides a method for realizing deep depletion on copper slag through multielement gas substep injection. The method fully utilizes waste heat of molten copper slag, copper matte is converted into oxide through gasification desulphurization, then selective reduction is carried out to obtain copper iron alloy with higher copper content, the problem of copper slag depletion in a smelting process is solved, and low-sulfur low-copper depletion slag is produced, so that conditions are created for a follow-up iron extracting process, and the deep depletion on the copper slag is realized; the traditional matte-producing depletion process is abandoned, but a gasification desulphurization process is firstly carried out for converting the copper matte into the oxide, then the oxide is subjected to selective reduction by virtue of a reducing agent, so that a copper-iron alloy phase is obtained. Operation is simple, adaptability is strong, the method can be realized by modifying the original electric furnace, nickel slag similar to the copper slag in properties can be treated, and metal elements such as Cu, Ni, Co and Fe can be comprehensively recycled.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
KR (knotted reactor) powder spraying, stirring and desulfurizing device and method
InactiveCN102676741AThe desulfurization cycle is shortenedReduced desulfurization working timeGranularityEngineering
The invention relates to a KR (knotted reactor) powder spraying, stirring and desulfurizing device. The KR powder spraying, stirring and desulfurizing device comprises a stirring head and a driving device for controlling the stirring head to act, wherein the driving device comprises a connecting rod linked with the stirring head, a lifting device for driving the connecting rod to move up and down and a stirring motor for driving the connecting rod to rotate. The KR powder spraying, stirring and desulfurizing device is characterized by further comprising a feeding system and a high-pressure gas source, wherein a through hole for introducing high-pressure inert gas and desulfurizing agents is formed on the stirring head, and an inlet of the through hole is communicated with a desulfurizing agent outlet and a high-pressure gas source outlet of the feeding system. The invention further relates to a method for desulfurizing molten iron by using the KR powder spraying, stirring and desulfurizing device. By using the device, efficient, fast and precise desulfurization can be realized, and the effects of reducing the requirements for granularity of desulfurizing agents, reducing the temperature drop and reducing the loss of the stirring head can be achieved.
Owner:ZENITH STEEL GROUP CORP
Refined-smelting ladle furnace carbon control deep desulphurization method for ultra-low-carbon steel production
ActiveCN101323896ASolve the problem of adding CShorten desulfurization treatment timeProcess efficiency improvementAlkalinitySulfur
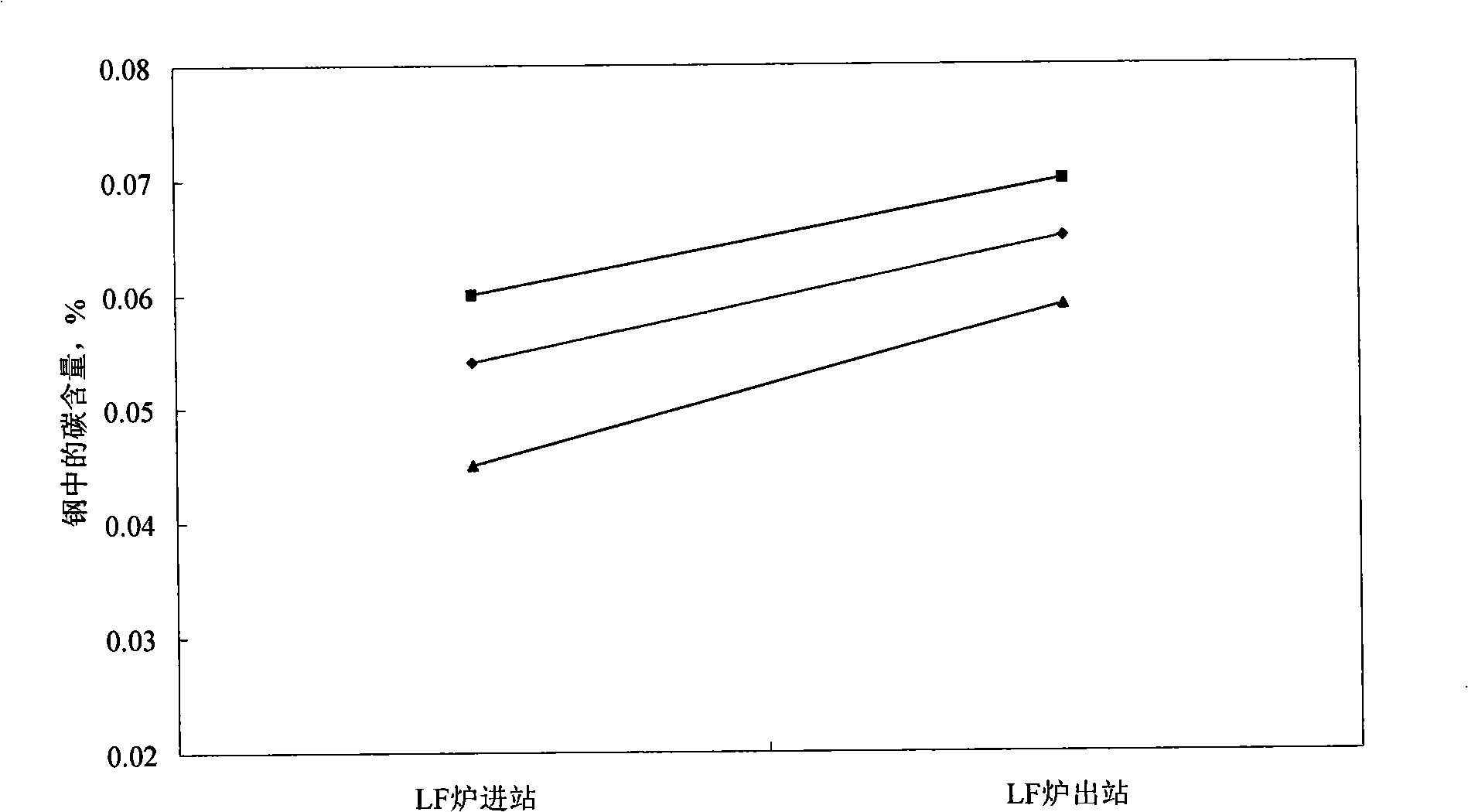
The invention discloses a method for controlling carbon and deep desulphurization by a refined-smelting ladle furnace in the production of extreme low carbon steel, pertaining to the technical field of ladle refining. The technology of the invention is that the amount of roughing slag of a converter is controlled and the thickness of the slag is 30 mm to 60mm; the temperature of molten steel in an LF furnace ranges from 1590 DEG C to 1640 DEG C and the content of Al in the steel is equal to 0.05 percent to 0.09 percent; 6 to 12 kg / ton of refining slag with high basicity and 0.4 to 1.0 kg / ton of Al granules are added; the flow of bottom-blowing argon gas is controlled during the rapid deep desulphurization refining process. On the condition that no electrode is available, argon gas with mass flow of 6 to 8NL / (min question mark t) is adopted for melting slag. After slag melting, the electrode is arranged to control the flow of argon gas to 4.8-6NL / (min question mark t) and carbon pickup of the molten steel occurs; when the refining is completed, the oxidizability of steel slag (FeO+MnO) is required to be less than or equal to 1.0 percent and the weight percentage of alkalinity of (CaO) / (SiO2) is equal to 5.5 to 8.0. The method of the invention has the advantages of solving the problem of carbon pickup during the refining in the LF furnace and controlling the weight percentage of carbon increment within 0.015 percent, thereby realizing rapid deep desulphurization with the content of sulfur[S] which is less than or equal to 0.0010 percent after desulphurization, and shortening the smelting time of the LF furnace.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Method for activating high-sulfur bauxite by means of low-temperature roasting desulfurization method
ActiveCN102897812ALow costReduce energy consumptionDispersed particle separationAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationRed mudFluidized bed
The invention relates to a method for activating high-sulfur bauxite by means of a low-temperature roasting desulfurization method. The method which carries out oxidative desulfurization roasting on bauxite with 1 to 5 wt percent of sulfur content so that the bauxite can become material applicable to the Bayer process production of alumina is characterized in that the oxidative desulfurization temperature is controlled between 500 DEG C and 600 DEG C. More specifically, in a fluidized bed roaster or a rotary kiln, hot air which is 650 DEG C to 900 DEG C is utilized to heat dry-ground mineral powder. Not only is the sulfur content in the processed mineral powder decreased to be less than 0.5 percent, but also the organic matters in the mineral are completely oxidized to be decomposed, and meanwhile, because the roasting temperature is low, activated alumina can be prevented from being transformed to become over-stable. When the roasted bauxite is used in Bayer digestion, the digestion performance is improved, and the digestion rate of alumina is higher than 93 percent. After limestone suspension is cyclically sprayed or red mud suspension is sprayed to desulfurize the tail gas containing SO2 produced by oxidative desulfurization, the SO2 content can be decreased to be less than 300mg / m3, and thereby the tail gas comes up to the emission standard.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
High-efficiency deep desulfurization active carbon and preparation method thereof
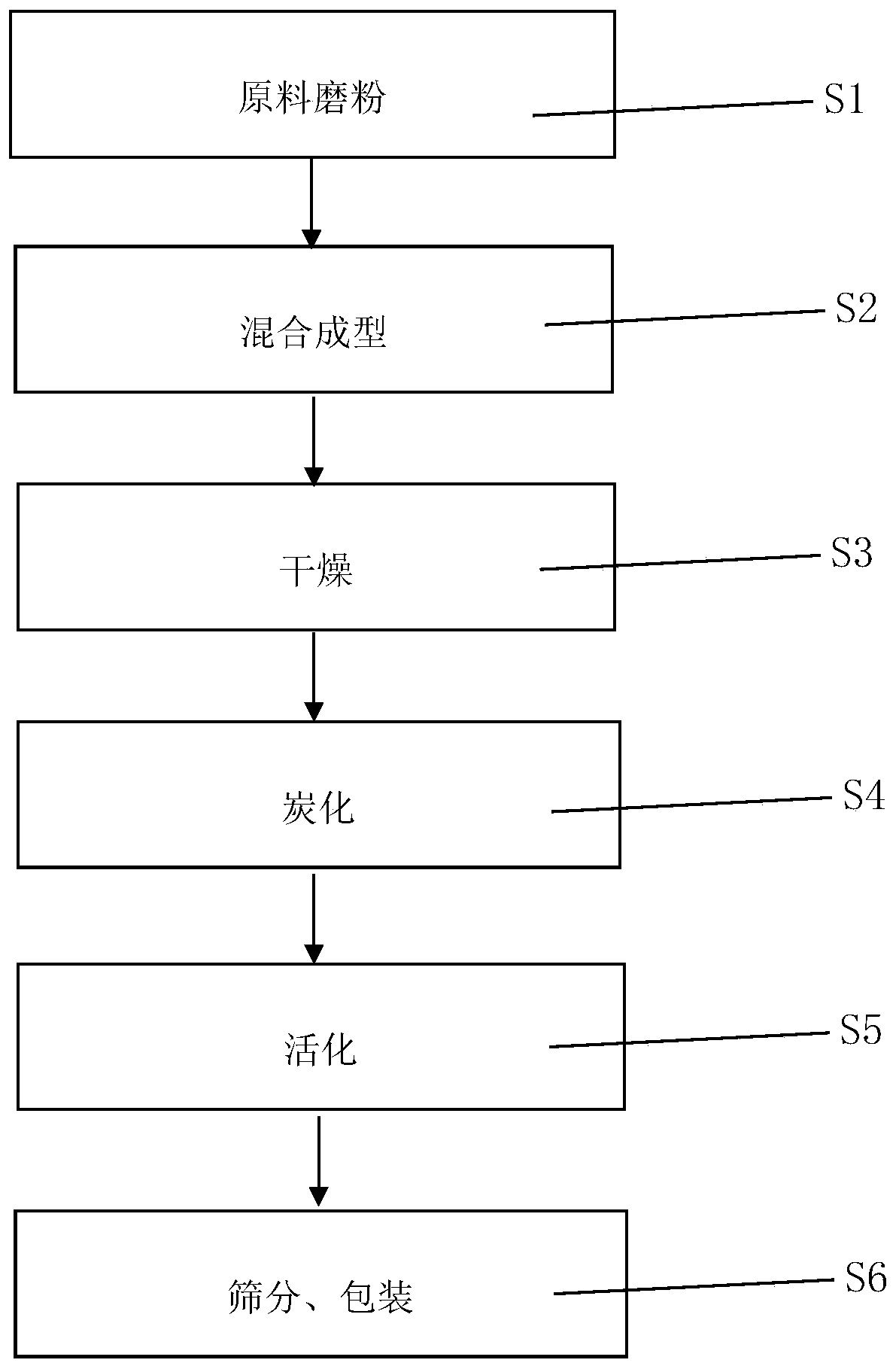
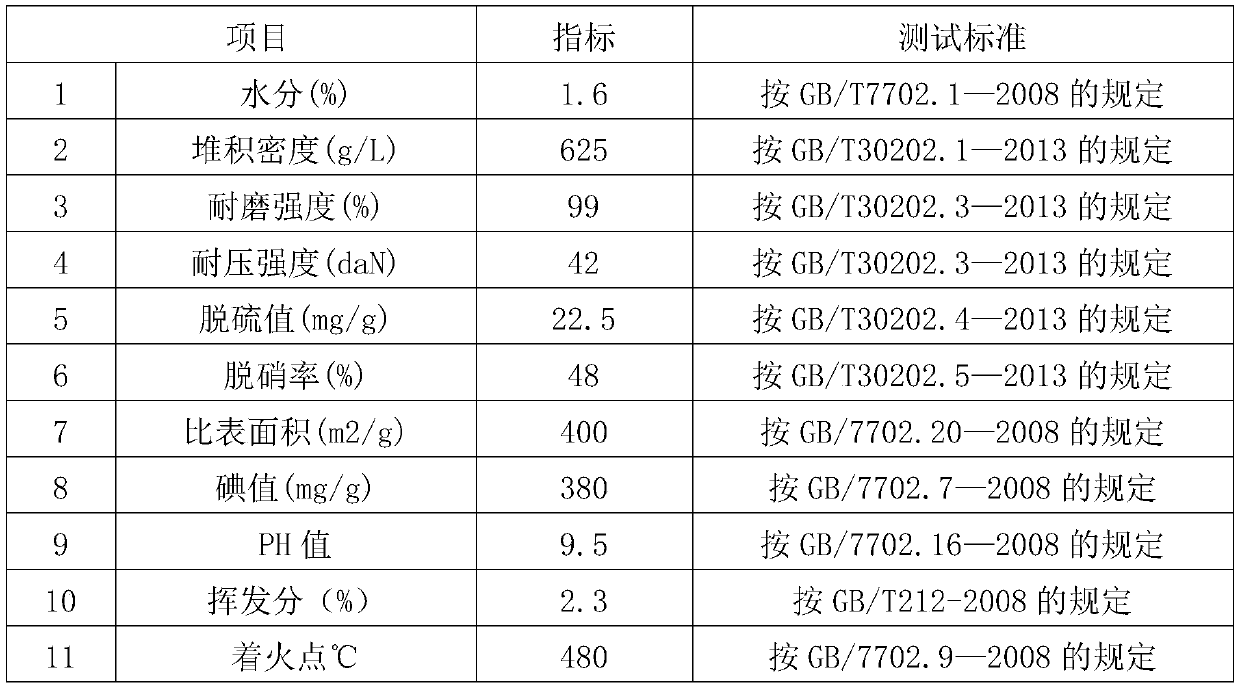
ActiveCN104667872AHigh sulfur capacityFast desulfurizationOther chemical processesActive agentFiltration
The invention discloses high-efficiency deep desulfurization active carbon and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of modified active carbon materials. The high-efficiency deep desulfurization active carbon is prepared through the steps of by adopting coal or a coconut shell as raw materials, crushing, screening, then adding a coal tar adhesive for extrusion forming, and calcining at 750-950 DEG C to form primary active carbon; carrying out dipping treatment on the primary active carbon, uniformly loading a hydroxide active agent and a cyclodextrin assistant active agent, carrying out secondary high-temperature calcination in the presence of excessive heat water vapors to obtain a high-efficiency desulfurization active carbon product. The active carbon prepared through the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high sulphur capacity, high desulfurization speed, long usage period, high strength, good abrasion resistance, good material permeability, no dust and the like, can not only be used for the large-scale deep desulfurization and purification of petrochemical products such as fuel oil, natural gas, gas, liquid hydrocarbon and synthetic ammonia, but also be used for the fields of pharmaceutical gas sterilization, solution filtration and purification, solvent recovery, water purification, gas purification and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHUHAI ACTIVATED CARBON CO LTD
Method for producing ultralow-sulfur steel under high vacuum
InactiveCN102787209AImprove slag capacityImprove quality pass rateManufacturing convertersAlkalinityMolten steel
The invention provides a method for producing an ultralow-sulfur steel under high vacuum, the sulfur content of steel discharged by a converter can be controlled below 0.010%; during the LF furnace refine treatment process, the sulfur content can be controlled at 0.005-0.007%, the slag alkalinity in the later stage can be controlled between 2.0-4.5, thereby a CaO-MgO-Al2O3-CaF slag system is formed, the total slag amount can be controlled at 8.5-10kg / ton steel, the argon flow during the whole process is 150-250N1 / min; and a VD furnace high vacuum treatment is carried out by using argon with a flow of 450-550N1 / min for mixing. Thereby the molten slag equivalent of slag can be enhanced, great flip of a molten steel surface can be avoided, the addition of the molten steel nitrogen absorption and impurities can be minimized, rapid operation during desulphurization process can be promoted, the sulfur content of the finished product can be controlled below 0.005%, and nitrogen content of the finished product can be controlled below 25ppm, and the qualified rate of ultralow-sulfur steel production can be increased.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Alkaline modified activated carbon desulfurizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103691394AFast desulfurizationImprove efficiencyOther chemical processesActivated carbonCost savings
An alkaline modified activated carbon desulfurizer is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 100-120 parts of activated carbon, 4-5 parts of sodium hydroxide, 30-34 parts of diatomite, 3-4 parts of glass powder, 4-5 parts of silicon dioxide, 8-10 parts of modified attapulgite, and a proper amount of water. According to the invention, with the use of sodium hydroxide, the desulfurization speed is high, and the efficiency is high; diatomite is added as a carrier, which provides good adsorbing effect; with the desulfurizer of the invention, no harmful substance is generated after desulfurization, which is more environment-friendly and safer; the desulfurizer of the invention is easy to regenerate, and the preparation method of the invention is simple in process, suitable for industrial production, and cost-saving.
Owner:BENGBU PIONEER FILTER
Rapid desulfurizing method for smelting ultrapure steel with vacuum induction furnace
The invention discloses a rapid desulfurizing method for smelting ultrapure steel with a vacuum induction furnace, which comprises the following steps of: calculating the weights of a needed steel scrap raw material, various alloys, carbon granules used as an deoxidizing agent and rare earth wires used as a desulfurizing agent according to the component requirement of steel, and weighing the raw materials; then closing a vacuum chamber, and vacuumizing for 3-8 minutes until the vacuum degree of the vacuum chamber reaches 0.05-0.1 Pa; carrying out power transmission on the vacuum induction furnace for melting steel, and adding the carbon granules in a chute to molten steel by batches during the steel melting process; maintaining the vacuum degree of the vacuum chamber at 0.05-0.1 Pa after steel melting, and continuing vacuumizing for 15-20 minutes; stopping vacuumizing, and introducing argon gas to the vacuum chamber until the pressure in the vacuum chamber reaches 500-700 Pa; adding the various alloys to the molten steel for alloying treatment; adding the desulfurizing agent to the molten steel, stirring, oscillating and standing; and pouring to an ingot mold in a vacuum environment while retaining 2-10% of molten steel. Practice proves that the desulfurizing method provided by the invention employs a precipitation method to desulfurize without slag addition or slag generation, generated desulfurized products are removed through precipitation, rapid desulfurization can be realized, the operation is simple and feasible and the cost is low.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Vermiculite modified activated carbon desulfurization agent and its preparation method
InactiveCN103495400AFast desulfurizationLow costOther chemical processesHazardous substanceToxic material
A vermiculite modified activated carbon desulfurization agent is prepared from the following raw materials: by weight, 100-120 parts of activated carbon, 4-5 parts of oleic acid, 13-16 parts of ethylene glycol, 20-30 parts of vermiculite, 10-15 parts of black manganese ore, 4-5 parts of stearic acid, 4-5 parts of zinc oxide, 8-10 parts of modified attapulgite and a proper amount of water. The vermiculite modified activated carbon desulfurization agent has an enhanced adsorption performance and can absorb various harmful substances due to use of the vermiculite; the black manganese ore and the zinc oxide are also added, so that the vermiculite modified activated carbon desulfurization agent can quickly desulphurize and can be recycled, and the vermiculite modified activated carbon desulfurization agent is low in raw material cost, simple in technology and suitable for industrialized production, produces no toxic substances, and is suitable for household, industry, automobile tail gas desulfurization.
Owner:ANHUI PHOENIX INT CO LTD
Ammonium sulphate-limestone method for desulphurization of flue gas
ActiveCN102485324AThorough responseGreat operating flexibilityDispersed particle separationSlagSlurry
The invention provides an ammonium sulphate-limestone method for desulphurization of flue gas, and specifically provides a wet desulphurization method using limestone as a raw material and ammonium sulfate as a process absorbent. The method is as below: 5-40 wt% of ammonium sulfate is used as the process absorbent, and limestone (calcium carbonate) is used as an absorbent; flue gas enters an absorbing tower from a middle part of the absorbing tower, countercurrent contacts with an absorption liquid for mass transfer and leaves from top of the tower; slurry at tower bottom circulates in the absorbing tower; part of the slurry is sent to desulfurized slag dehydration technology water recovery system. The invention has the beneficial effects that the absorbing tower desulphurization speed is accelerated, so that a same tower can process more flue gas; the absorbing tower has large operating elasticity and stable operation with low energy consumption; partial denitration can be realized while desulphurization; desulfurized slag post-treatment operations reserve larger integral utilization space and comprise a calcining operation for recovering sulfur dioxide.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
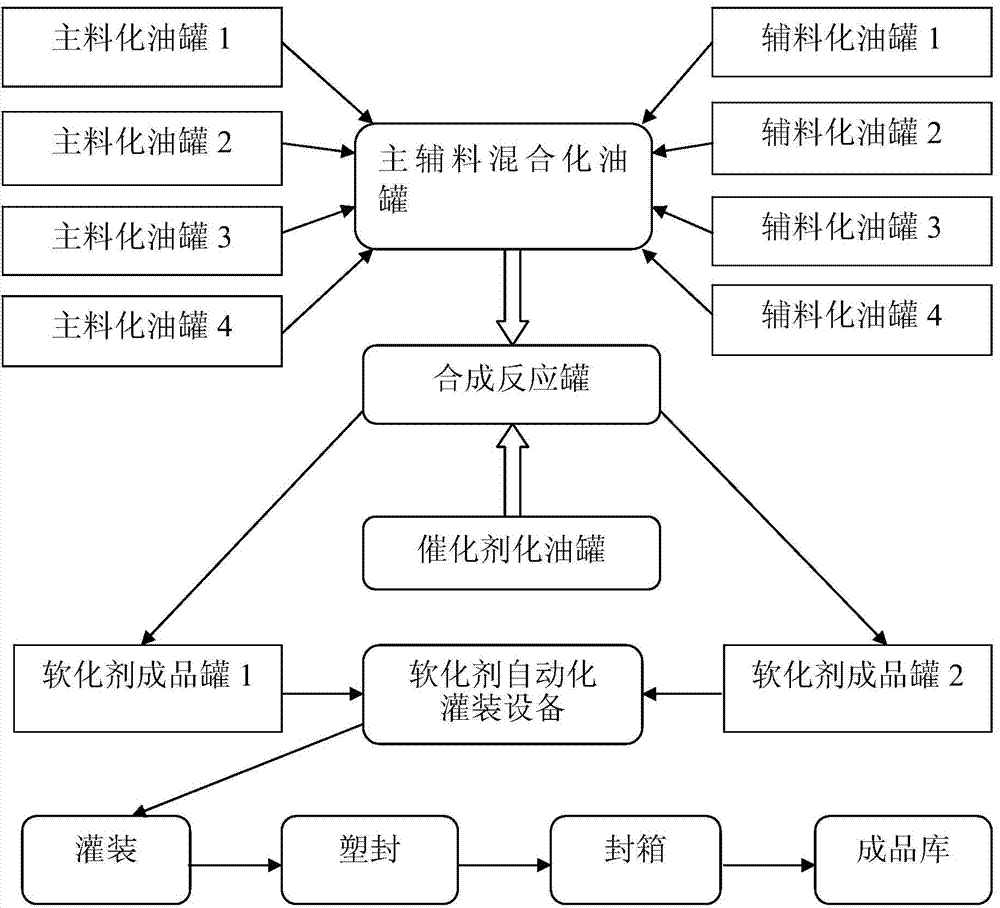
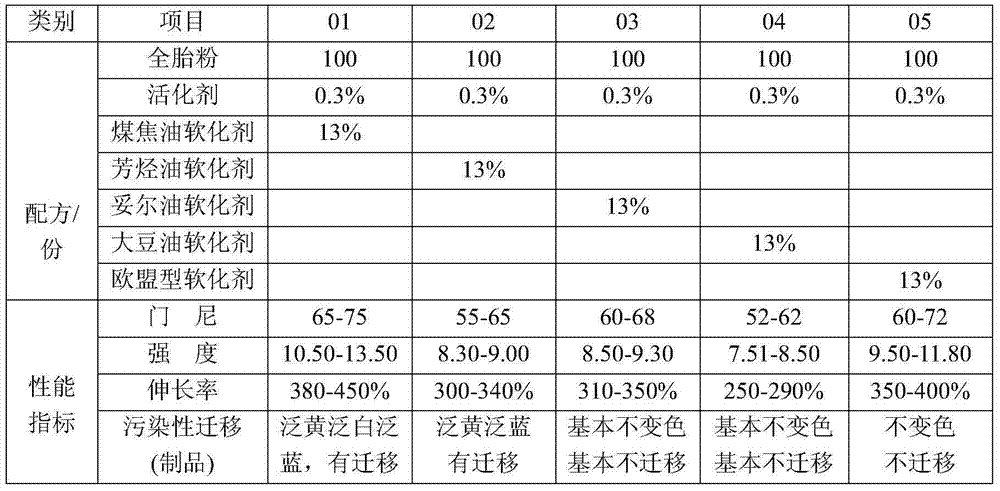
Reclaimed rubber softening agent and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a reclaimed rubber softening agent. The reclaimed rubber softening agent is obtained by reacting a softening agent main material with a softening agent auxiliary in the presence of a catalyst; the softening agent main material comprises a natural vegetable oil ingredient, while the softening agent auxiliary comprises a natural biochemical oil ingredient, and the catalyst is a phthalate; the natural vegetable oil ingredient is a natural vegetable oil and / or natural vegetable oil foots; the natural biochemical oil ingredient is a natural biochemical oil and / or natural biochemical oil foots. The reclaimed rubber softening agent is a composite product prepared by compounding the natural vegetable oil and the biochemical oil and refining the mixed oil under the catalytic action of phthalate. The softening agent passes the PONY test of the international authoritative detection mechanism, meets the requirements of the European Union REACH environmental protection laws and regulations and passes the authentication of China Quality Certification.
Owner:湖南中海顺达新材料股份有限公司
Method for preparing biomass fuel mainly from fresh chicken manure
ActiveCN106244278AWith water absorption and heat releaseReduce moisture contentBiofuelsSolid fuelsMicroorganismMushroom
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a biomass fuel mainly from fresh chicken manure. The method comprises the following steps: 1) pretreating raw materials; 2) fermentation: mixing fresh chicken manure, mushroom sticks and calcined shell powder, inoculating deodorizing composite microbes and nitrogen fixation-desulfurization composite microbes, and carrying out pile fermentation; 3) naturally drying the fermentation material; and 4) adding tea stems, and carrying out extrusion granulation. The fresh chicken manure is used as the main raw material, the waste mushroom sticks, calcined shell powder and tea stems are used as the auxiliary raw materials, the deodorizing composite microbes and nitrogen fixation-desulfurization composite microbes are added, and the flammability and comprehensive combustion characteristics of the reinforcing material of the composite microbes are fully utilized, thereby preparing the biomass granular fuel which has the advantages of low ignition point, high combustion heat value and high combustion rate. The method can greatly consume chicken manure, and solves the problem of environmental pollution caused by chicken manure. The method provides direction for the recycling of the waste mushroom sticks, shells and tea stems.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENG TECH FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Dolomite-based desulfurizer based on in-situ reduction and preparation thereof
ActiveCN101302576AHigh desulfurization rateImprove desulfurization efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementGranularityDiiron Trioxide
The invention relates to a dolomite matrix desulfurizer based on in-situ reduction and a method for preparing the same. The invention is characterized in that: the dolomite matrix desulfurizer consists of dolime, reducer, self-propagating exothermic agent, reaction promoter and fluorite; the dolime, the reducer, aluminum powders, ferrous iron oxide powders or ferric oxide powders, the reaction promoter and the fluorite are respectively dried for 4 to 20 hours at a temperature of between 120 and 200 DEG C, mixed, grinded by a ball grinding machine till the granularity is less than 200 meshes, then made into particles in a spherical shape or other shapes by a sampling machine at a pressure of between 20 and 50 MPa, thereby preparing the dolomite matrix desulfurizer. The dolomite matrix desulfurizer is adopted for desulphurization reaction, has the advantages of low desulphurization cost, high utilization rate of desulfurizer, high desulphurization rate, no obvious temperature reduction in the desulphurization process, no need of specialized desulphurization equipment, simple operation, etc. and has the desulphurization rate of over 85 percent.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Rail steel refining method
The invention discloses a rail steel refining method. The rail steel refining method includes the steps that in the converter steel tapping process, active lime is adopted for conducting slag washing, and then calcium carbide is adopted for modifying ladle top slag; a modified steel ladle is sent to an LF for conducting slag adjusting, the active lime and the calcium carbide are adopted for refining, adding is carried our two times in the adding process, and the argon flow meets the conditions that the argon flow at the earlier stage ranges from 100 Nl / min to 200 Nl / min, the argon flow at the medium stage ranges from 100 Nl / min to 200 Nl / min, and the argon flow at the later stage ranges from 100 Nl / min to 150 Nl / min. The sulphur content in molten steel obtained after LF processing is smaller than or equal to 0.006%, silica sand is added at the later LF processing stage for reducing the alkalinity of the steel ladle slag, then refining is continuously carried out for an appropriate time, and the steel ladle slag is sent for conducting vacuum processing. The rail steel refining method is suitable for producing high-quality rail steel, and the sulphur content in the steel is smaller than or equal to 0.006%.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Smelting method of low-sulfur and low-boron steel
InactiveCN110423947AReduce carbon contentReduce carryoverProcess efficiency improvementSmelting processAlloy
The invention provides a smelting method of low-sulfur and low-boron steel. The steel comprises, by weight, 0.05%-0.18% of C, 0.10%-0.35% of Si, 1.10%-1.60% of Mn, no more than 0.020% of P, no more than 0.003% of S, 0.010%-0.050% of Nb, 0.008%-0.025% of Ti, no more than 0.30% of Ni, no more than 0.20% of Mo, no more than 0.25% of Cr, no more than 0.0005% of B, and 0.010%-0.050% of Als. The smelting process includes a converter, an LF furnace, an RH furnace and CC. Pretreatment for desulfuration is not needed, the carbon content of steel discharged out of the converter is slightly decreased toreduce molten steel w[B], low-B alloys such as manganese metal and mid-carbon ferromanganese are added, liquid cast waste slag is used, and the quantity of recovered liquid cast slag is controlled, sothat rapid slagging and desulfuration are guaranteed, and the quantity of B dragged into slag is reduced; the LF furnace only adopts aluminum wire deoxidation, and a large quantity of argon is blownfrom the bottom to achieve stirring, so that the probability that boric oxide in the slag is reduced and molten steel enters the slag is lowered while the sulfur content in the molten steel is decreased; and when the sulfur content in the molten steel reaches a required sulfur content, the argon blown from the bottom is regulated to be weak, stirring is conducted to reduce the quantity of added B,and an obtained finished products meets w[S]<=0.003 and w[B]<=0.0005.
Owner:HUNAN VALIN XIANGTAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Desulfurizing smelting method for ultra low sulfur pure iron
Owner:BAOSTEEL SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
Device and method for active carbon flue gas desulphurization and production of dilute sulphuric acid
InactiveCN104607034AContinuous desulfurization operationImprove mass transfer effectDispersed particle separationSulfur compoundsActivated carbonFailure rate
The invention relates to a device and method for active carbon flue gas desulphurization and production of dilute sulphuric acid, and the device is characterized by including a device casing, a foam collecting device located at the upper part of the device casing, an active carbon absorption and elution device located at the middle of the device casing, and a flue gas inlet pipe located at the lower part of the device casing. Spherical active carbon is used as a desulfurization agent, flue gas flows in from the bottom of a the tower, the active carbon is in the fluidized state, spray liquid (dilute sulfuric acid or clear water) and the spherical active carbon are contacted, active carbon desulfurization product sulfuric acid is taken away, and active carbon surface activity is recovered, so that active carbon regeneration rate is also greatly accelerated so as to achieve the continuous operation of flue gas desulfurization. Single column continuous operation is feasible, active carbon filling amount is small, occupation area is small, primary investment is less, and the failure rate is low.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Rapid desulfurizing method for smelting ultrapure steel with vacuum induction furnace
The invention discloses a rapid desulfurizing method for smelting ultrapure steel with a vacuum induction furnace, which comprises the following steps of: calculating the weights of a needed steel scrap raw material, various alloys, carbon granules used as an deoxidizing agent and rare earth wires used as a desulfurizing agent according to the component requirement of steel, and weighing the raw materials; then closing a vacuum chamber, and vacuumizing for 3-8 minutes until the vacuum degree of the vacuum chamber reaches 0.05-0.1 Pa; carrying out power transmission on the vacuum induction furnace for melting steel, and adding the carbon granules in a chute to molten steel by batches during the steel melting process; maintaining the vacuum degree of the vacuum chamber at 0.05-0.1 Pa after steel melting, and continuing vacuumizing for 15-20 minutes; stopping vacuumizing, and introducing argon gas to the vacuum chamber until the pressure in the vacuum chamber reaches 500-700 Pa; adding the various alloys to the molten steel for alloying treatment; adding the desulfurizing agent to the molten steel, stirring, oscillating and standing; and pouring to an ingot mold in a vacuum environment while retaining 2-10% of molten steel. Practice proves that the desulfurizing method provided by the invention employs a precipitation method to desulfurize without slag addition or slag generation, generated desulfurized products are removed through precipitation, rapid desulfurization can be realized, the operation is simple and feasible and the cost is low.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
High-efficiency atomization desulfurization device and method
PendingCN107754591AReduce investmentLow costGas treatmentDispersed particle separationTransfer systemSlurry
The invention discloses a high-efficiency atomization desulfurization device which comprises a lime powder loading and storage system, a lime slurry preparation system, a lime slurry transfer system,a lime slurry storage system, a lime slurry injection system, a desulfurization catalyst storage system and a desulfurization catalyst injection system. The outlet of the lime powder loading and storage system is connected with the inlet of the lime slurry preparation system; the outlet of the lime slurry preparation system is connected with the inlet of the lime slurry storage system through thelime slurry transfer system. The outlet of the lime slurry storage system is connected with the inlet of the lime slurry injection system through the lime slurry transfer system; the outlet of the desulfurization catalyst storage system is connected with the inlet of the desulfurization catalyst injection system. In addition, the invention also discloses a high-efficiency atomization desulfurization method. The high-efficiency atomization desulfurization device has simple structure, low input, low cost, low energy consumption, and desulfurization efficiency of more than 95%; and SO3 is almostcompletely removed.
Owner:上海三融环保工程有限公司 +1
Method for producing premelting-type calcium aluminate from electrolytic aluminum waste residue
InactiveCN103966453AQuality improvementExtended service lifeChemical industryProcess efficiency improvementAluminateMelting tank
The invention discloses a method for producing premelting-type calcium aluminate from electrolytic aluminum waste residue. The method comprises the following steps of 1, purifying electrolytic aluminum waste residue, 2, mixing the purified electrolytic aluminum waste residue and lime, 3, putting the raw material into a melting furnace and carrying out melting, 4, discharging the melt product into a high temperature-resistant melting tank and carrying out cooling, and 5, crushing the cooled premelting-type calcium aluminate, carrying out screening and carrying out packaging. The method utilizes electrolytic aluminum waste residue and limestone to prepare the premelting-type calcium aluminate, realizes recycle of waste, is environmentally friendly, saves energy, prevents aluminum resource loss, reduces a calcium aluminate cost and reduces environmental pollution. The calcium aluminate produced by the method has the characteristics of less impurity and uniform and stable components, can be used for the refining process of LF, SKF and VHP and can greatly improve molten steel quality and a ladle service life.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU WHALE SPECIAL MATERIALS
Ecological environment-friendly desulfurizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105833711AFast desulfurizationImprove desulfurization effectGas treatmentDispersed particle separationAluminateSulfolane
The invention discloses an ecological environment-friendly desulfurizer and a preparation method thereof. The ecological environment-friendly desulfurizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 12-16 parts of methyldiethanolamine, 10-12 parts of sulfolane, 12-18 parts of calcium aluminate, 16-20 parts of potassium chloride, 18-20 parts of silver nitrate, 20-22 parts of modified attapulgite, 16-18 parts of fluorite, 10-12 parts of sodium nitrite, 12-18 parts of vanadium pentoxide, 10-16 parts of sodium metaaluminate, 12-14 parts of dimethyl silicon oil, 16-20 parts of zeolite, 12-18 parts of sodium laurate, 10-12 parts of methyldiethanolamine and 12-16 parts of oyster shells. The ecological environment-friendly desulfurizer is green and environment-friendly, rapid in desulfuration speed and good in desulfuration effect.
Owner:张锐
Method for improving weather resistance of decorative base paper titanium dioxide
ActiveCN107500348AReduce concentrationIncrease concentrationTitanium dioxideWeather resistancePotassium
The invention provides a method for improving weather resistance of decorative base paper titanium dioxide, and belongs to the technical field of decorative base paper titanium dioxide. The control is performed through salt treatment and calcination. The method comprises the following steps of A, using bleached slurry as raw materials; adding titanium dioxide sol into the raw materials; controlling the addition to meet the requirement that the proportion of TiO2 in the titanium dioxide sol to TiO2 in metatitanic acid is 2 to 6 percent; performing water washing; diluting the slurry subjected to water washing into 300 to 400g / L TiO2 slurry; B, adding potassium and phosphorus solution with the K2O / P2O5 ratio being 1.3 to 4.0 into the diluted slurry; performing stirring; adding aluminum-containing compound solution according to the Al2O3 to TiO2 proportion being 0.3 to 0.9 percent; performing stirring; C, performing pressurized filtering on the slurry material treated by the step B until the filter cake solid content is 45 to 55 percent; C, roasting the filter cake in the step C for 8 to 10h at the roasting temperature of 200 to 950 DEG C. Through the control on the salt treatment and roasting processes, the primary product weather resistance of the decorative base paper titanium dioxide is improved; the weather resistance of the decorative base paper titanium dioxide is further improved.
Owner:HEBEI MILSON TITANIUM DIOXIDE
Preparation method for Ti/MCM-41 molecular sieve having catalytically oxidizing activity and application thereof
InactiveCN105664998ALow costSimple preparation processMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningMuffle furnaceTitanium
A preparation method and application of a Ti / MCM-41 molecular sieve with catalytic oxidation activity. The invention designs a preparation method and application of a Ti / MCM-41 molecular sieve. The invention aims to solve the problem of low catalytic oxidation desulfurization efficiency of the Ti / MCM-41 molecular sieve prepared by the existing method. Method: 1. Put MCM-41 molecular sieve in a muffle furnace for pretreatment; 2. Disperse organic titanium source evenly in ethanol, then add MCM-41 molecular sieve, perform ultrasonic treatment, then age at room temperature, and then put Stir in an oil bath until water and ethanol are completely volatilized, and finally dry to obtain a white solid; 3. Put the white solid obtained in step 2 in a muffle furnace for calcination to obtain Ti / MCM-41 molecular sieve. The Ti / MCM-41 molecular sieve of the present invention has an excellent catalytic oxidation desulfurization reaction effect at room temperature, and the conversion rate of dibenzothiophene reaches over 97% after the reaction at room temperature for ten minutes.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Novel desulfurization and denitrification activated carbon
PendingCN110255554AImprove featuresImprove removal effectGas treatmentCarbon compoundsHazardous substanceHigh pressure
The invention discloses novel desulfurization and denitrification activated carbon, which mainly comprises pulverized coal, bentonite, aluminum oxide and starch, the weight percentage ratio of the components being 1:(0.08-0.2):(0.01-0.2):(0.01-0.2) correspondingly. A preparation method comprises the following steps: grinding the raw materials according to the mixing ratio, mixing and molding the powders, drying, carbonizing and activating the mixture, and sieving and packaging the mixture to produce the novel desulfurization and denitrification activated carbon. The product has high pressure resistance, impact resistance and wear resistance in actual use; the activated carbon has the advantages of high sulfur dioxide adsorption capacity, high desulfurization speed and obvious desulfurization and denitrification effects, can be repeatedly recycled, and has favorable removal effects on various harmful substances such as SO2, NO, mercury, dioxin, dust and the like and harmful substances such as SO3 which are difficult to remove by the conventional wet process.
Owner:尹金彦
Catalyst for oxidation sweetening of diesel oil and application thereof
InactiveCN101711993AFast desulfurizationImprove efficiencyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRefining with oxygen compoundsCarbon chainOxygen
The invention relates to a catalyst for oxidation sweetening of diesel oil and an application thereof. The catalyst has the expression as QrBmHn[AxMyOz](r+m+n)-; in the expression, Q represents quaternary ammonium salt cations and is constituted by R1R2R3R4N+, R1, R2, R3 and R4 represent saturated alkyls of C1-C20 in which at least one carbon chain length is larger than or equal to 4 carbon atoms; B represents metal cations; H represents hydrogen atoms; A represents one of B, P, As, Si and Al elements; M represents the metal elements W and Mo; and O represents oxygen atoms, wherein r+m+n is equal to or less than 14, r is equal to or less than 10 and equal to or larger than 1, m is equal to or larger than 0 and equal to or less than 3, n is equal to or larger than 0 and equal to or less than 3, x is equal to 1 or 2, y is equal to or larger than 0 and equal to or less than 18, and z is equal to or larger than 34 and equal to or less than 62.The catalyst used for preparing low sulphur diesel mainly comprises the following steps: mixing the catalyst QrBmHn[AxMyOz] (r+m+n), aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution and diesel oil, reacting for 10min-5h under the temperature of 30-60 DEG C, standing or centrifugalizing to recovery the catalyst and obtain the oxidized diesel oil, and removing sulphone and / or sulphone sulfocompound from the oxidized diesel oil by an extracting or distilling method to obtain the low sulphur diesel of the sulphur content is less than 10ppm.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Poly (tetramethylguandium acrylate) aqueous solution desulfurization agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102657999AIncrease profitReduce the impactDispersed particle separationIce waterAntioxidant
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application method of poly (tetramethylguandium acrylate) desulfurization agent. The poly (tetramethylguandium acrylate) desulfurization agent can be used for flue gas desulfurization of a thermal power plant and a metallurgic plant, and has excellent selective absorption for sulfur dioxide as well as good lasting absorption property and multi-time cycle absorption and desorption stability. The desulfurization agent is characterized by comprising the components: poly (tetramethylguandium acrylate), water, antioxidant, corrosion inhibitor and defoaming agent. The preparation method comprises the steps of: adding solvent into a polymerizing pot, then adding initiator into the solvent, slowly heating to 120-140 DEG C when stirring, and dripping acrylic acid within 2-4h at the temperature of 120-140 DEG C; then removing the solvent under pressure reduction, and grinding to obtain polyacrylic acid; adding polyacrylic acid and water into a reaction flask and stirring; controlling the temperature to be 0-5 DEG C by ice-water bath, dripping 1,1,3,3-tetramethyl guanidine, reacting for 1h and then stopping the reaction; and adding right amount of antioxidant, corrosion inhibitor and defoaming agent, and evenly stirring to obtain poly (tetramethylguandium acrylate) aqueous solution, wherein the aqueous solution is the target desulfurization agent product.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Ammonia desulfurization process and desulfurization device thereof
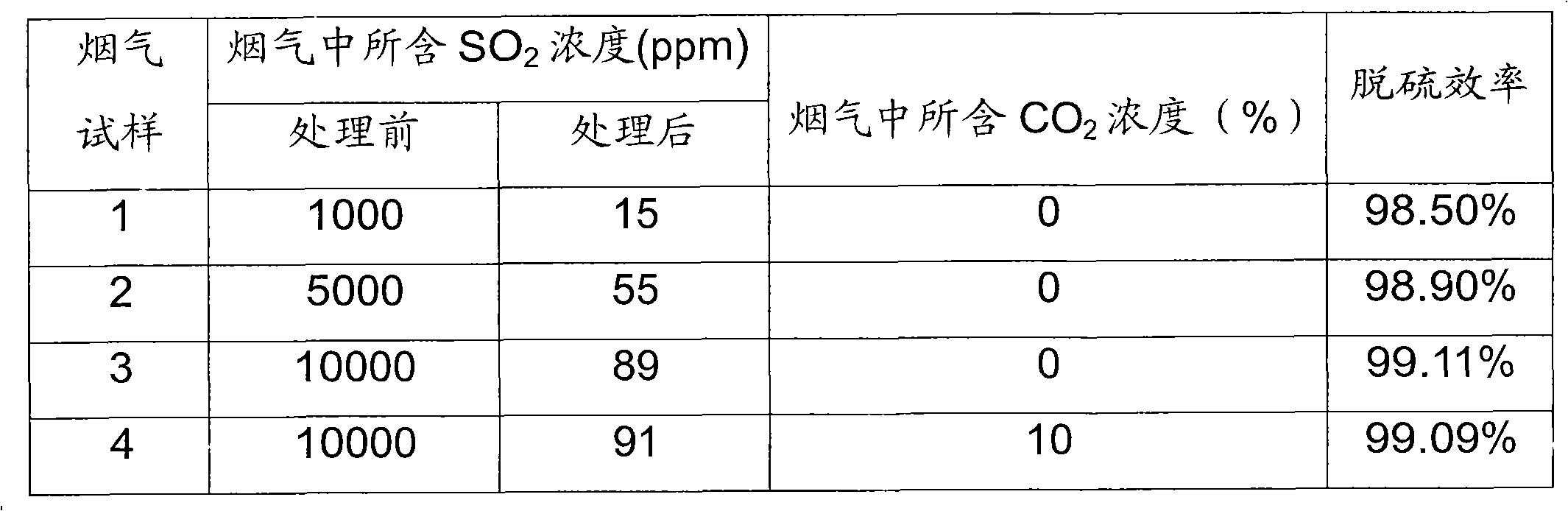
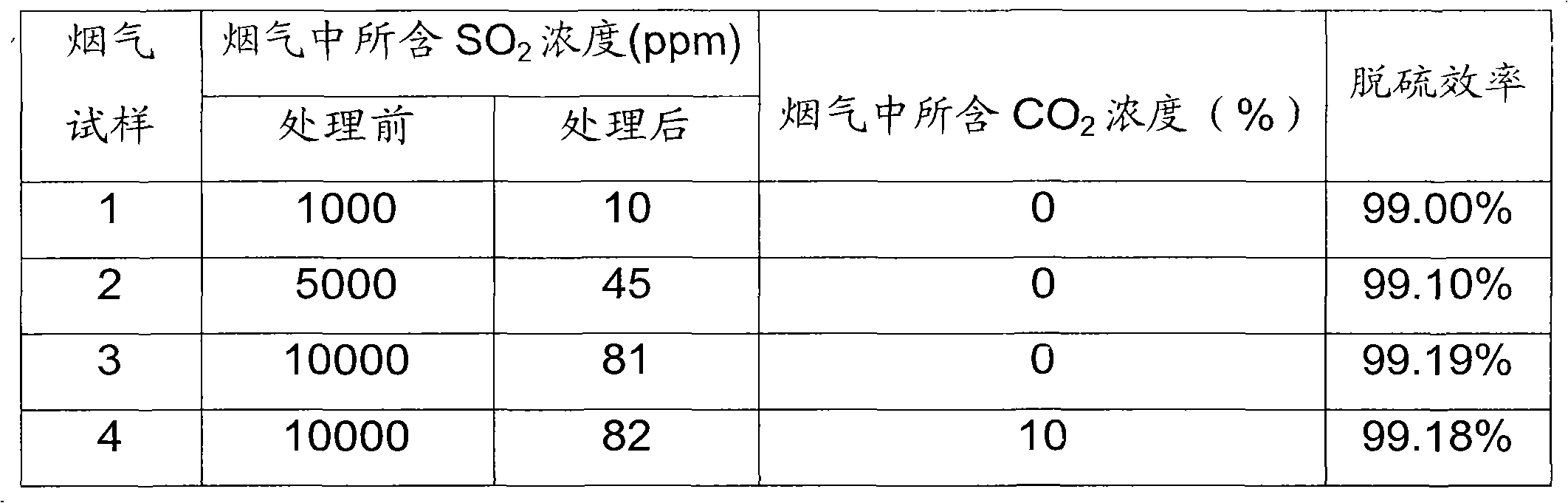
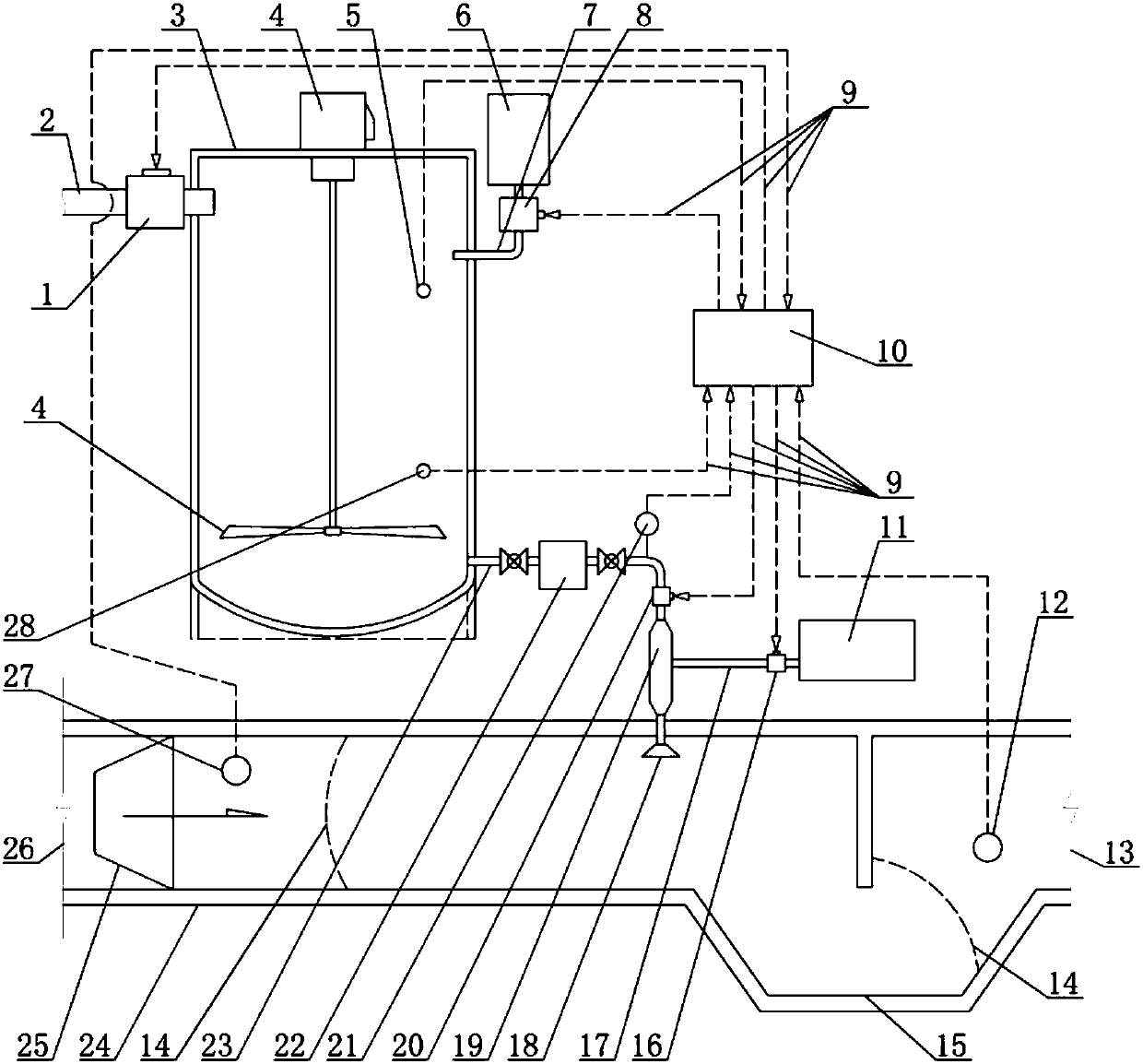
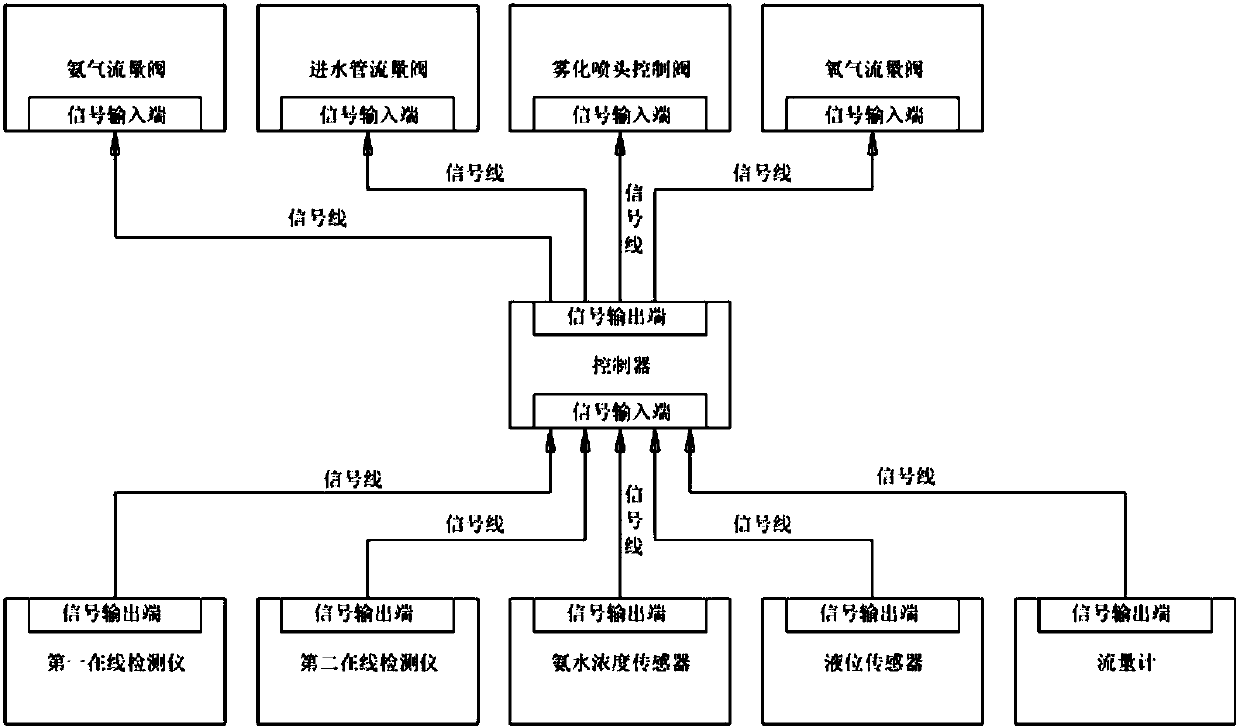
PendingCN108014610AFast oxidationFast desulfurizationGas treatmentDispersed particle separationChemical reactionOxygen tank
The invention provides an ammonia desulfurization process and a desulfurization device. A desulfurizer takes water, ammonia gas and oxygen with the weight ratio being 6:1:0.01 as raw materials, and isconveyed to a desulfurization reaction area in a boiler flue through a power system; the temperature of the desulfurization reaction area is 35 to 150 DEG C; ammonium hydroxide and the oxygen make contact with sulfur dioxide through an atomization nozzle to produce chemical reaction so as to generate ammonium sulfate, and the weight ratio of the ammonium hydroxide and the oxygen to the sulfur dioxide is 1:(1.72 to 1.46); a control system is characterized in that the spray volume of the ammonium hydroxide and the oxygen is automatically controlled by a computer according to collected data; product collection is characterized by adopting a wet process for trapping ammonium sulfate or a dry type gravity method for collecting the ammonium sulfate; the desulfurization device comprises a flue,a liquid storage tank, an oxygen tank, a production collecting device, an online detector, an atomization spray head and the control system. According to the ammonia desulfurization process and the desulfurization device thereof, provided by the invention, desulfurization can be carried out in the boiler flue or a waste gas channel of equipment producing the sulfur dioxide, the desulfurization efficiency and the desulfurization rate are automatically controlled, the reaction speed is fast, a desulfurization effect is good, and the operation cost can be reduced.
Owner:靳新令
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com