Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73results about How to "Etching precision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
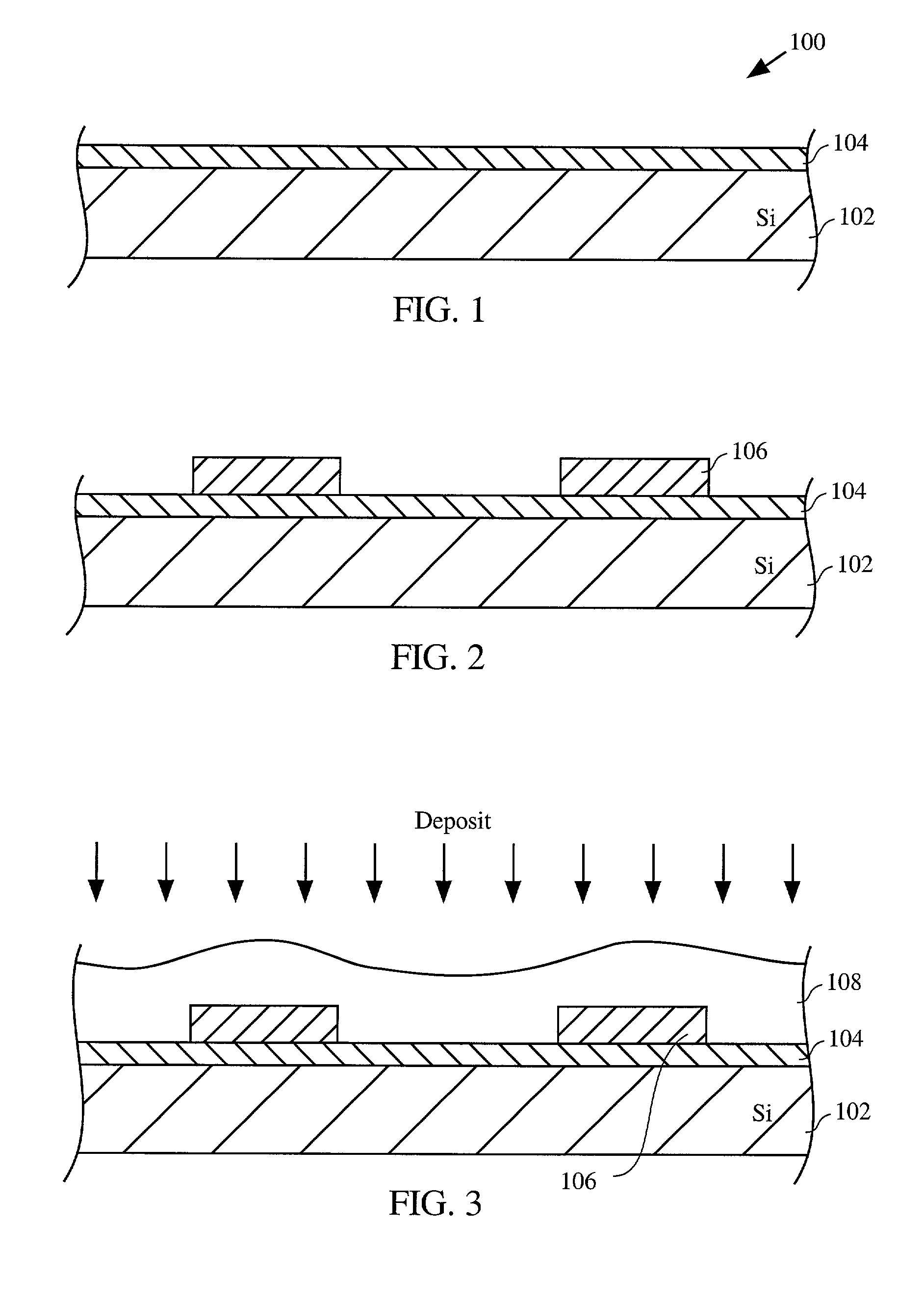
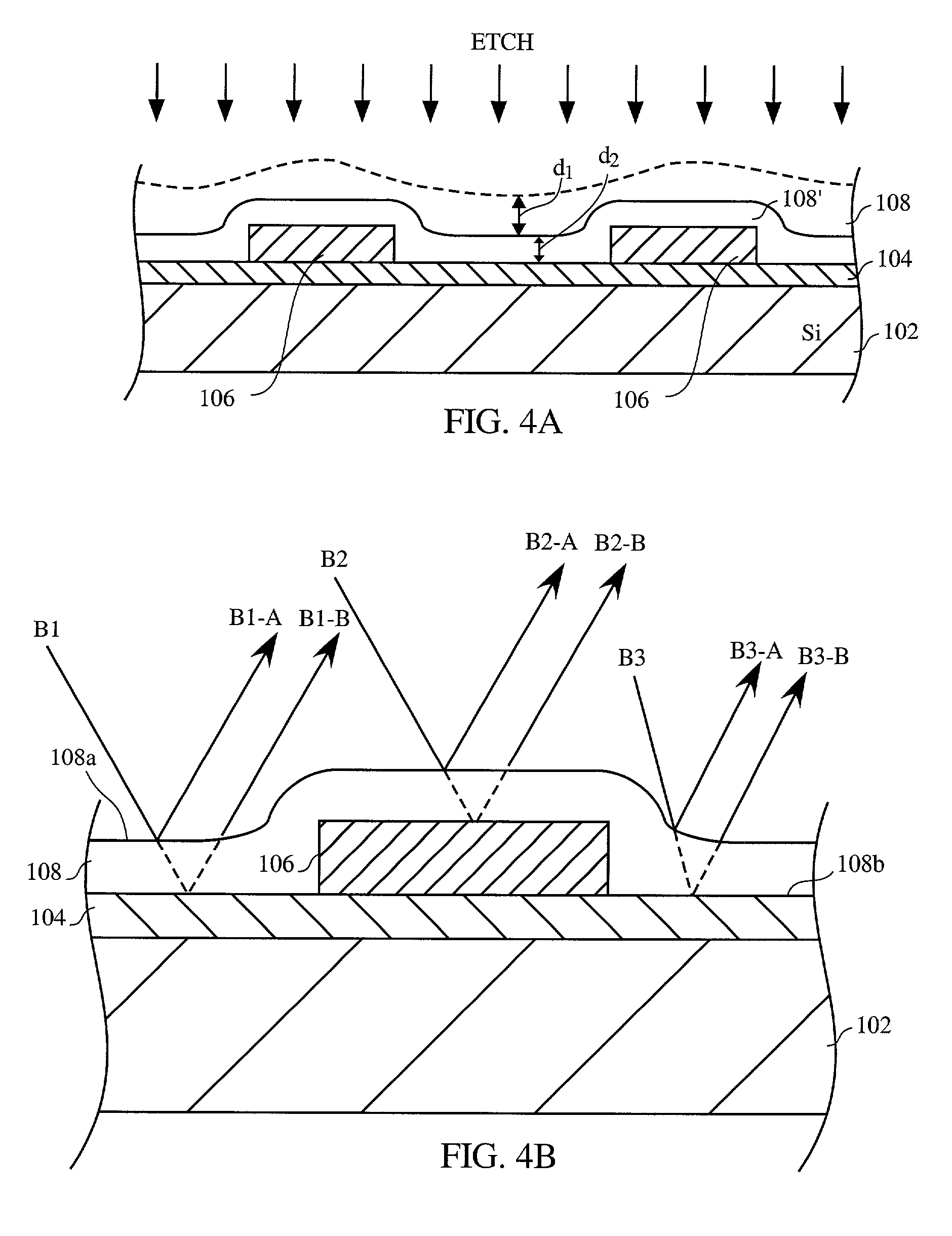
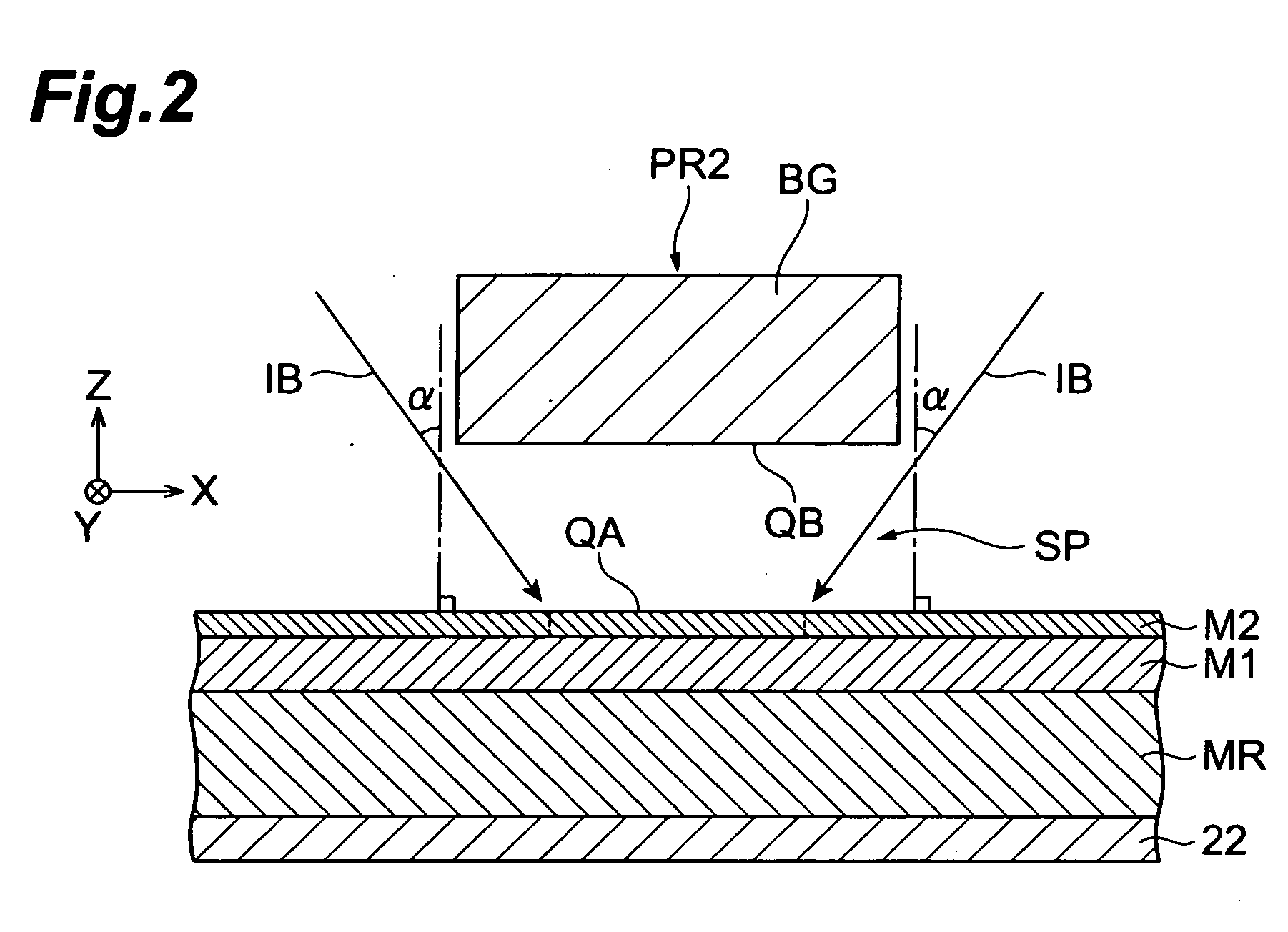
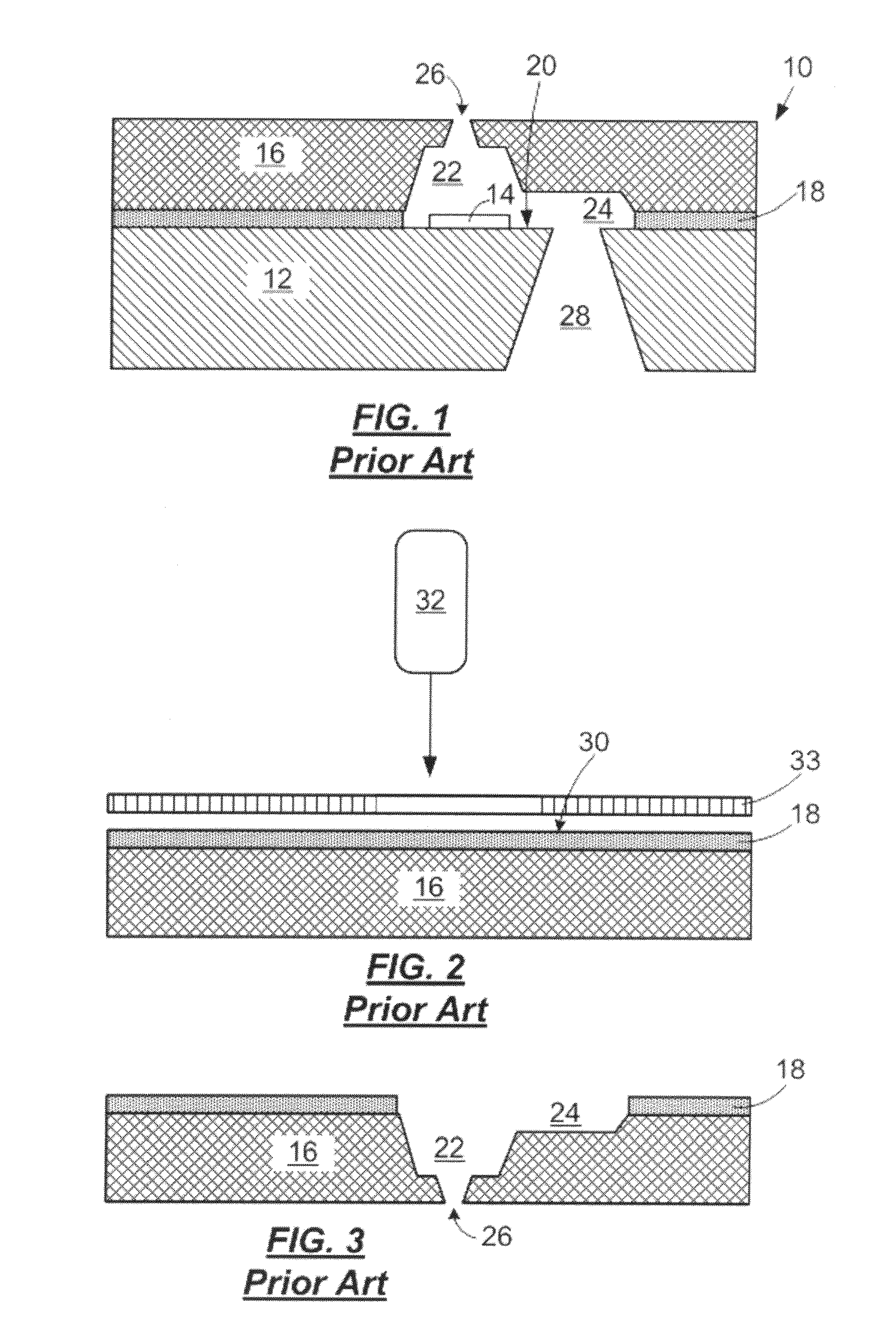
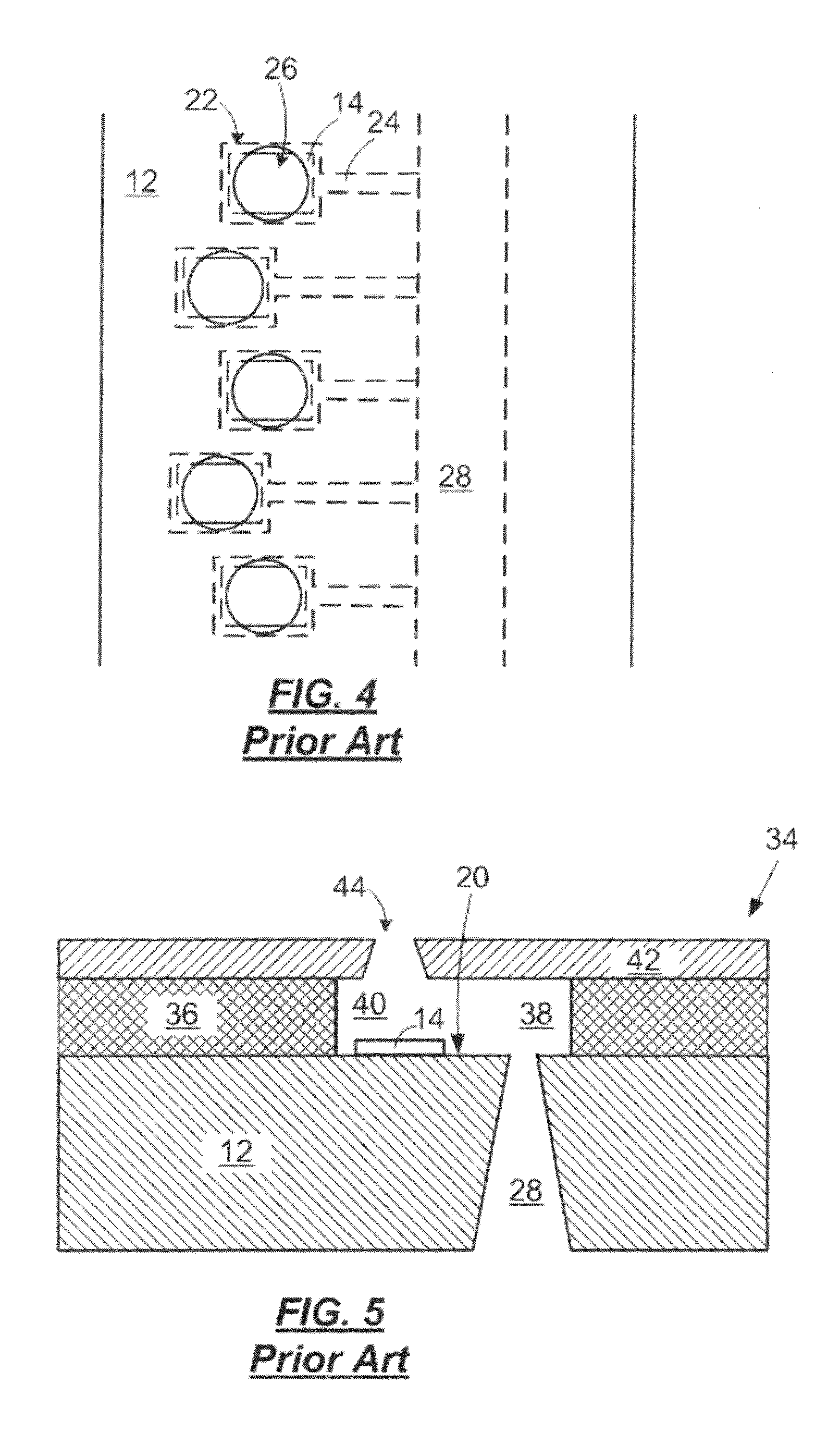
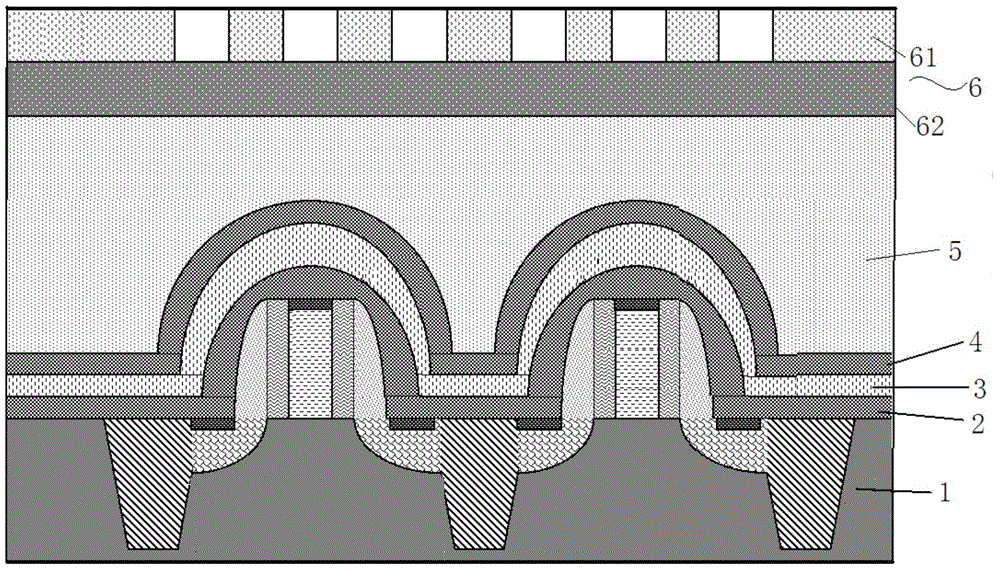
Tempered glass and method for producing same
InactiveUS20140170380A1Efficiently provideImprove surface qualityRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMetallurgyCompression stress
A tempered glass of the present invention is a tempered glass having a compression stress layer in a surface thereof, the tempered glass comprising, as a glass composition in terms of mol %, 45 to 75% of SiO2, 3 to 15% of Al2O3, 0 to 12% of Li2O, 0.3 to 20% of Na2O, 0 to 10% of K2O, and 1 to 15% of MgO+CaO, and having a molar ratio (Al2O3+Na2O+P2O5) / SiO2 of 0.1 to 1, a molar ratio (B2O3+Na2O) / SiO2 of 0.1 to 1, a molar ratio P2O5 / SiO2 of 0 to 1, a molar ratio Al2O3 / SiO2 of 0.01 to 1, and a molar ratio Na2O / Al2O3 of 0.1 to 5, characterized in that the surface or an end surface of the tempered glass is etched after tempering treatment.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Dielectric recording medium, and method of and apparatus for producing the same
InactiveUS6841220B2Remove electric charge on the recording surface rapidlyImprove abilitiesNanoinformaticsFerroelectric carrier recordingSingle crystalOptoelectronics
The dielectric recording medium is provided with a dielectric material, a conductive thin film, and a substrate. The conductive thin film and the substrate are bonded by a resin adhesive. The dielectric material is constructed of a ferroelectric single crystal having a uniform thickness, and its one surface is used for a recording and / or reproducing surface, on the order of mm on a side and about 5000 Å thick. The conductive thin film, about 1000 to 2000 Å thick, is placed on a surrounding portion and a back surface of the recording and / or reproducing surface of the dielectric material. The substrate is intended to preserve the thin dielectric material and maintain the planarity, and concave portions are formed on the adhesive surface. The concave portions absorb excessive resin adhesive when the dielectric material is bonded onto the substrate, which makes the adhesive surface uniform and flat.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
In situ Etching of inorganic dielectric anti-reflective coating from a substrate
InactiveUS6103632AImprove etch selectivityEtching precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingComputational physics
The present invention is embodied in a method and apparatus for etching dielectric layers and inorganic ARC's without the need for removing the substrate being processed from the processing chamber and without the need for intervening processing steps such as chamber cleaning operations (in situ process). A layer and / or a multi-layer film deposited on a substrate, such as silicon, is located within a processing chamber. The substrate has a base, an underlying layer above the base, an overlying layer above the underlying layer, and a top dielectric anti-reflective coating (DARC) layer formed on the overlying layer. In the preferred method, first, the DARC layer and the overlying layer is etched by a first process gas. Next, the underlying layer is etched by a second process gas.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dielectric recording medium, and method of and apparatus for producing the same
InactiveUS20050098532A1Remove electric charge on the recording surface rapidlyImprove abilitiesDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsSingle crystalResin adhesive
The dielectric recording medium is provided with a dielectric material, a conductive thin film, and a substrate. The conductive thin film and the substrate are bonded by a resin adhesive. The dielectric material is constructed of a ferroelectric single crystal having a uniform thickness, and its one surface is used for a recording and / or reproducing surface, on the order of mm on a side and about 5000 Å thick. The conductive thin film, about 1000 to 2000 Å thick, is placed on a surrounding portion and a back surface of the recording and / or reproducing surface of the dielectric material. The substrate is intended to preserve the thin dielectric material and maintain the planarity, and concave portions are formed on the adhesive surface. The concave portions absorb excessive resin adhesive when the dielectric material is bonded onto the substrate, which makes the adhesive surface uniform and flat.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
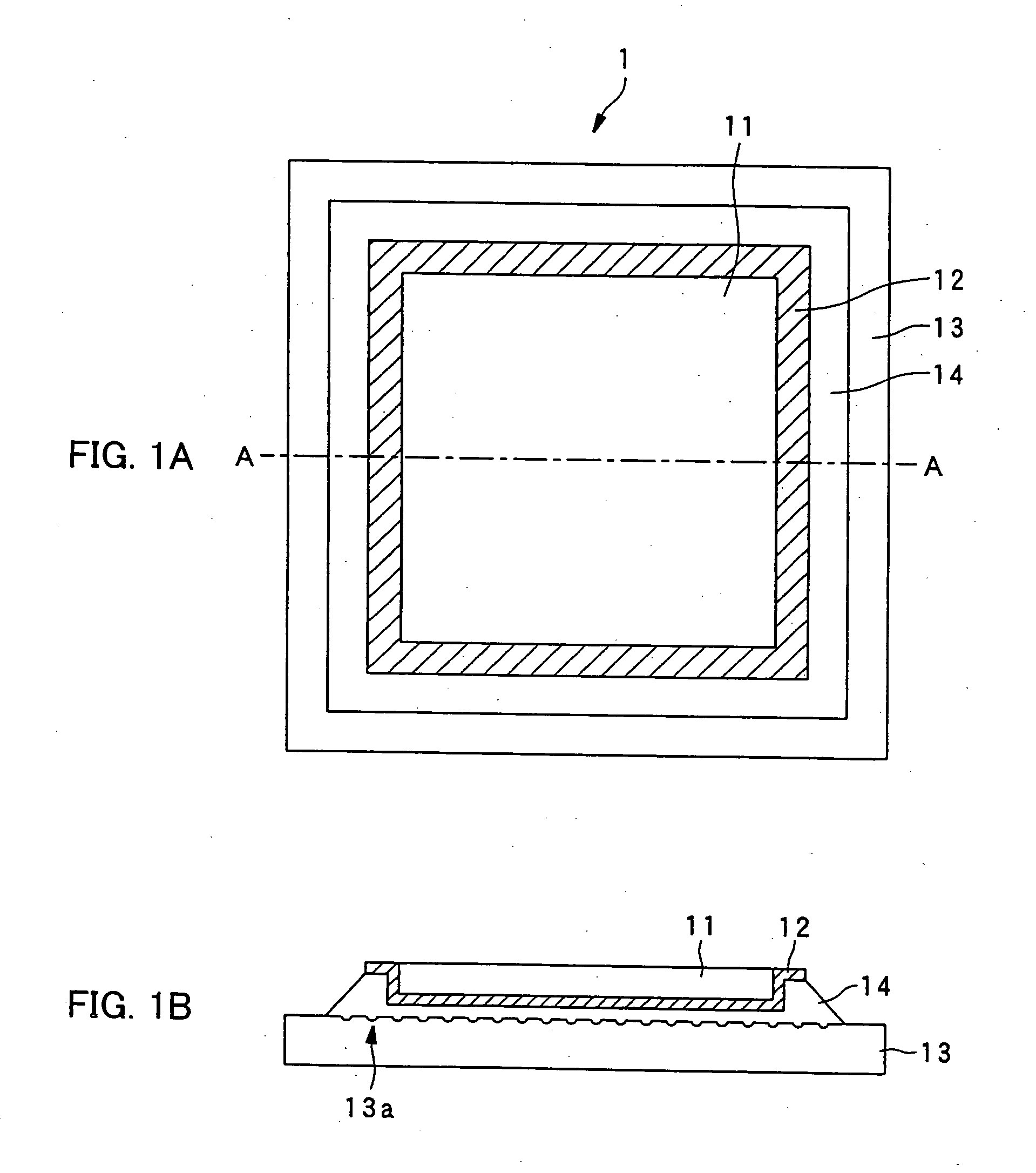
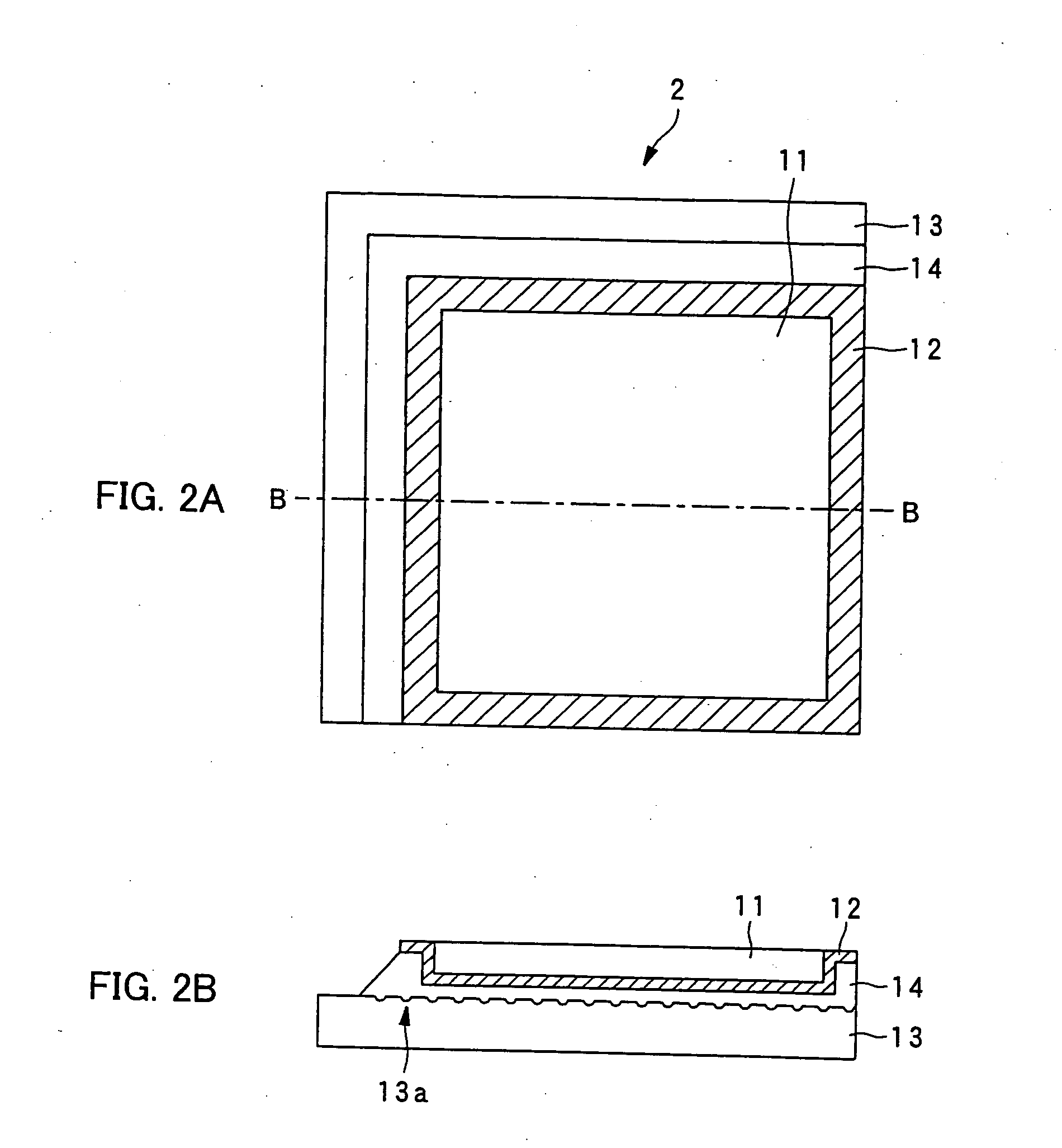
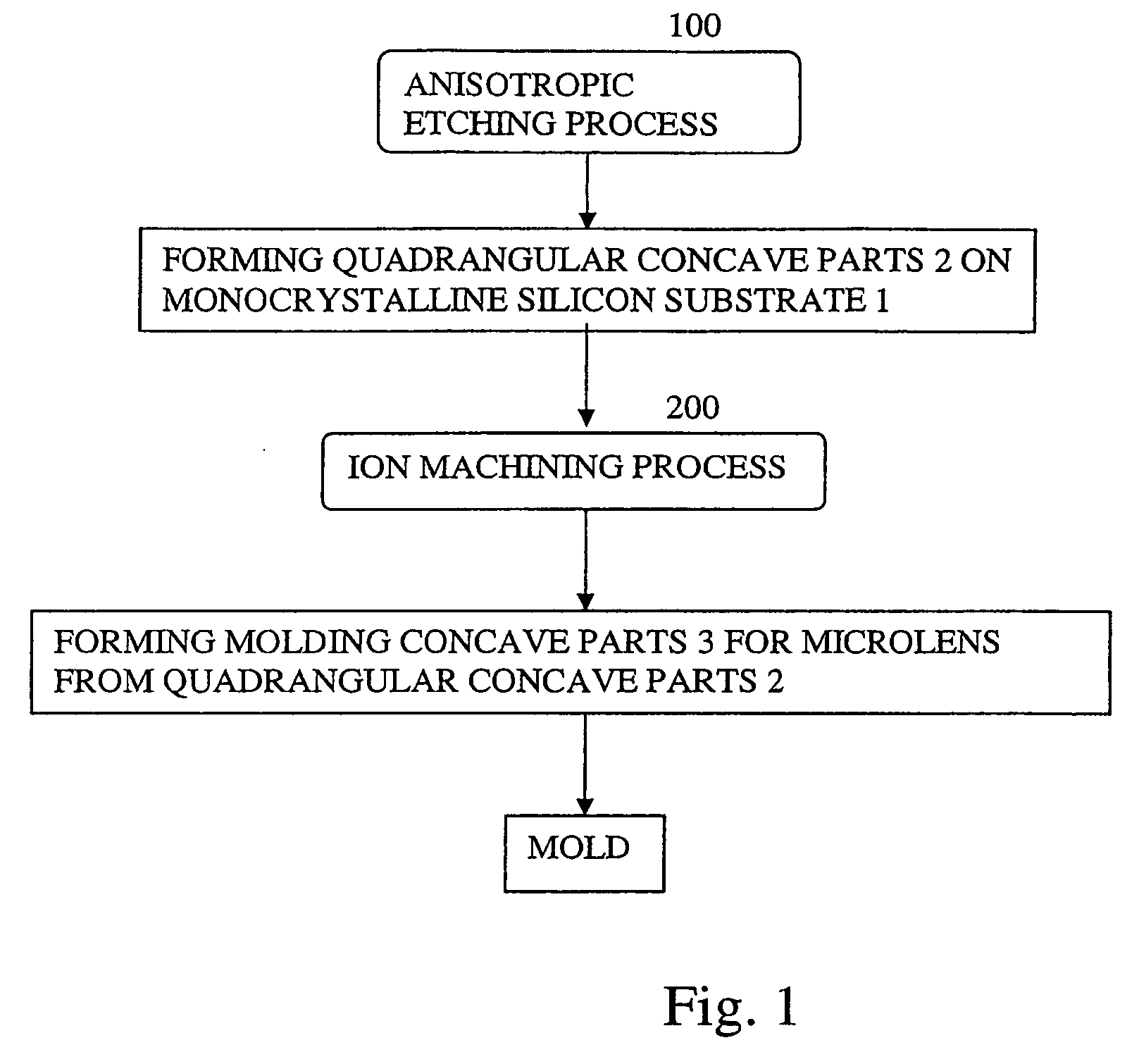
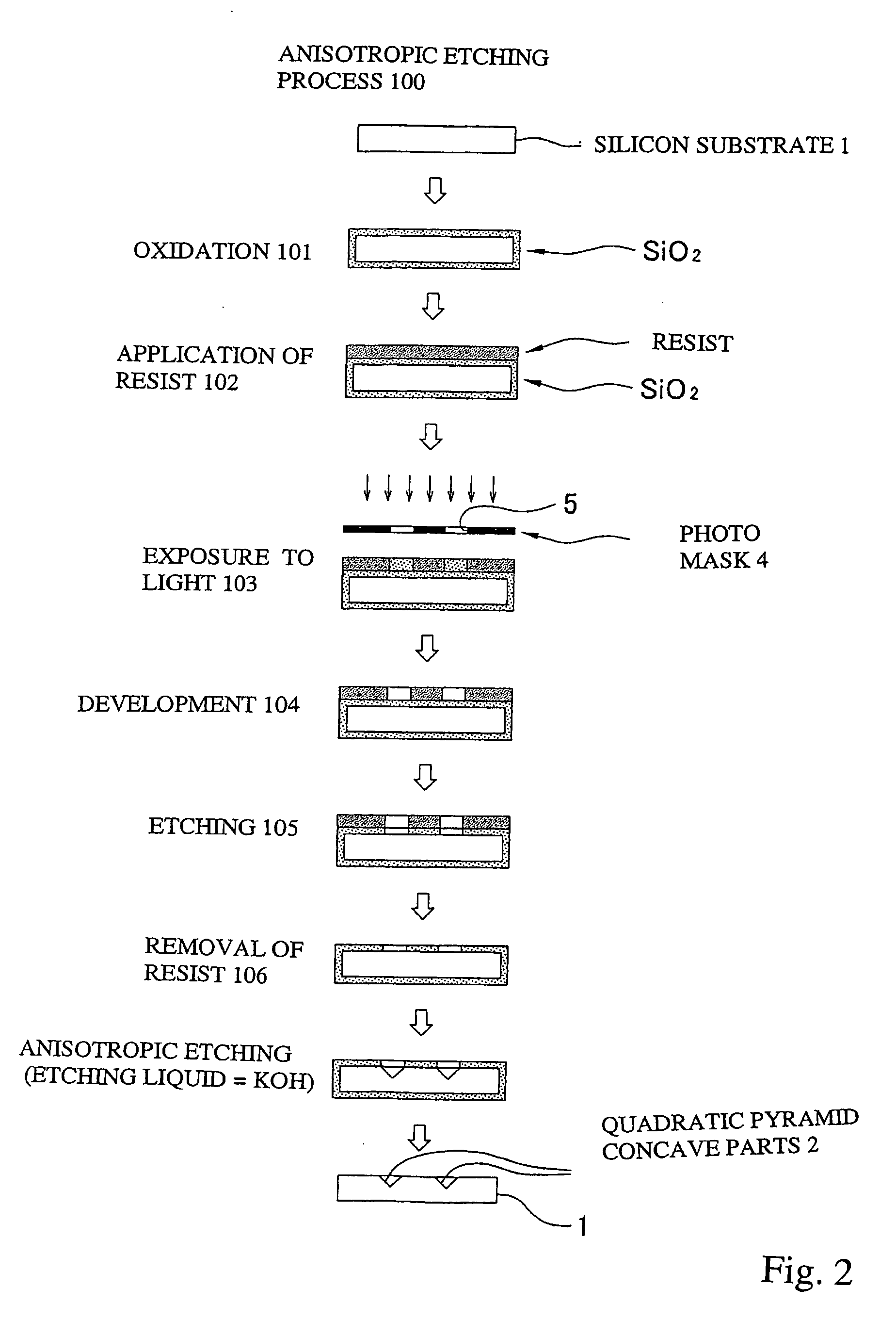
Mold for microlens and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20090194666A1Reduce material costsLow costDecorative surface effectsOptical articlesAnisotropic etchingMicro lens array
A mold for producing microlenses or a microlens array is produced by sequentially carrying out an etching step of forming quadrangular pyramid concave parts on a single crystal silicon substrate by anisotropic etching and an ion etching step of forming molding concave parts with spherical or cylindrical surface parts from the quadrangular pyramid concave parts.
Owner:TAKAMOTO KIICHI
Suface procesing method by blowing submicron particles
InactiveUS20010007808A1Improve the mixing effectEffective maintenanceLiquid surface applicatorsPropellersMaterials scienceAirflow
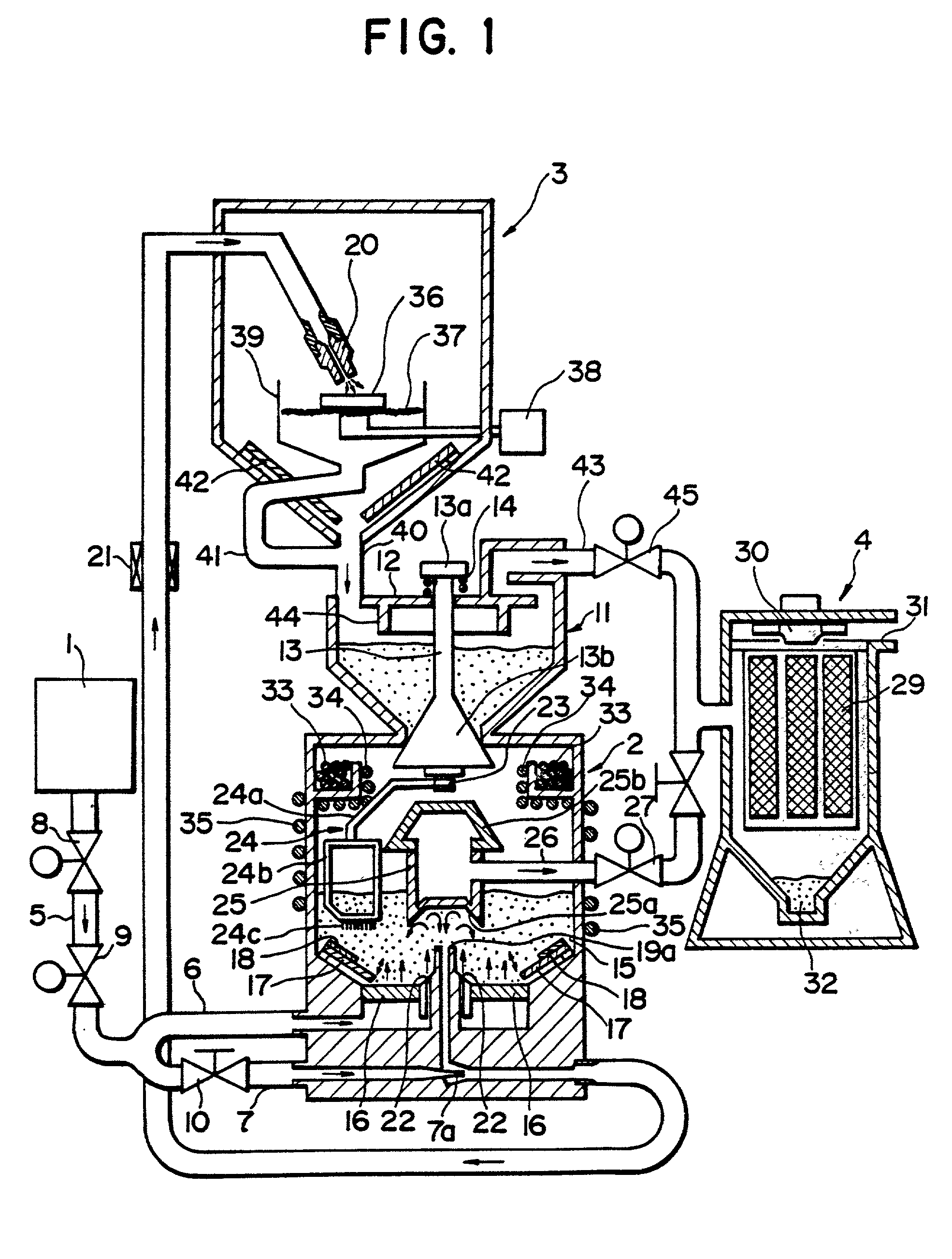
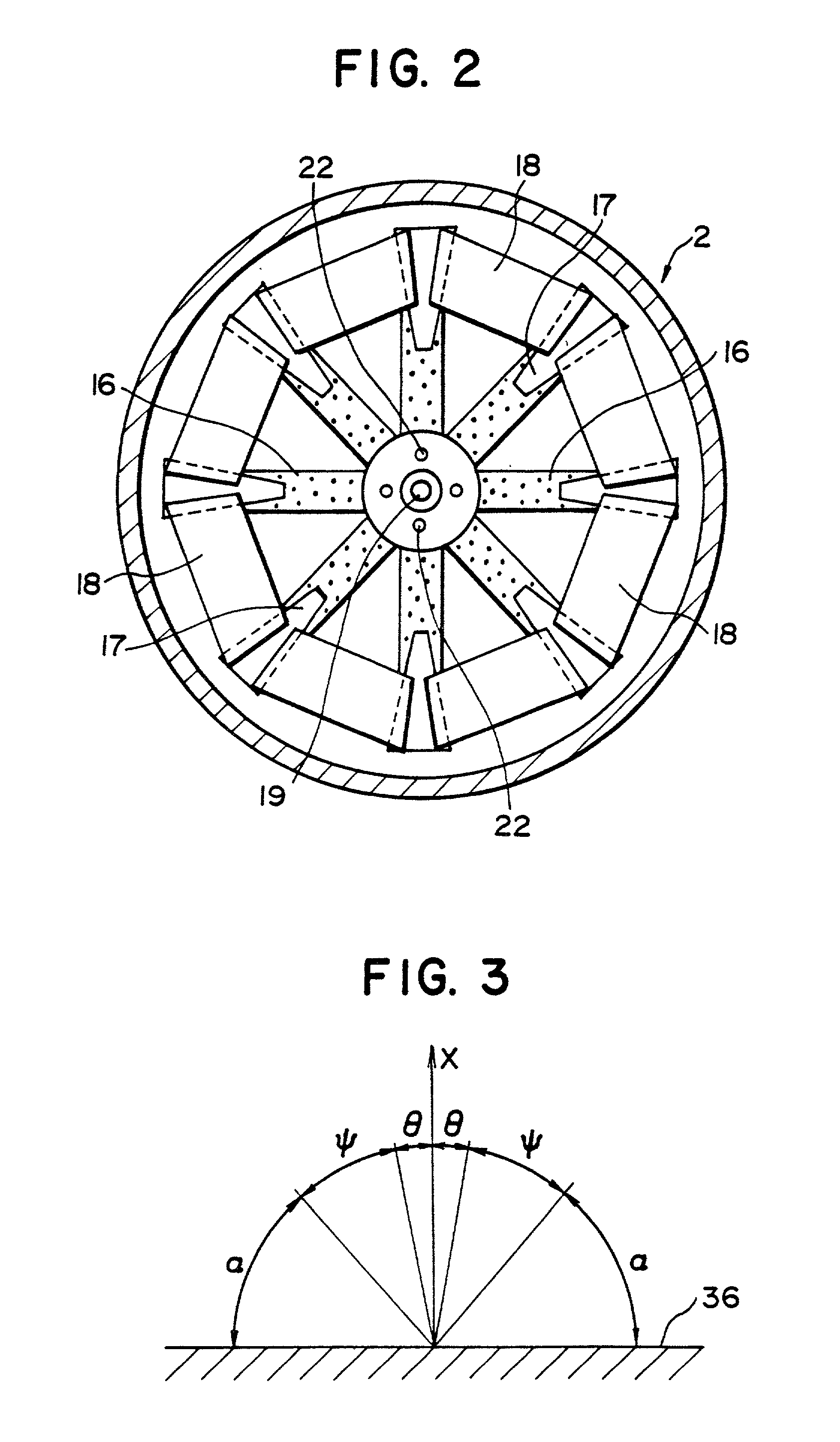
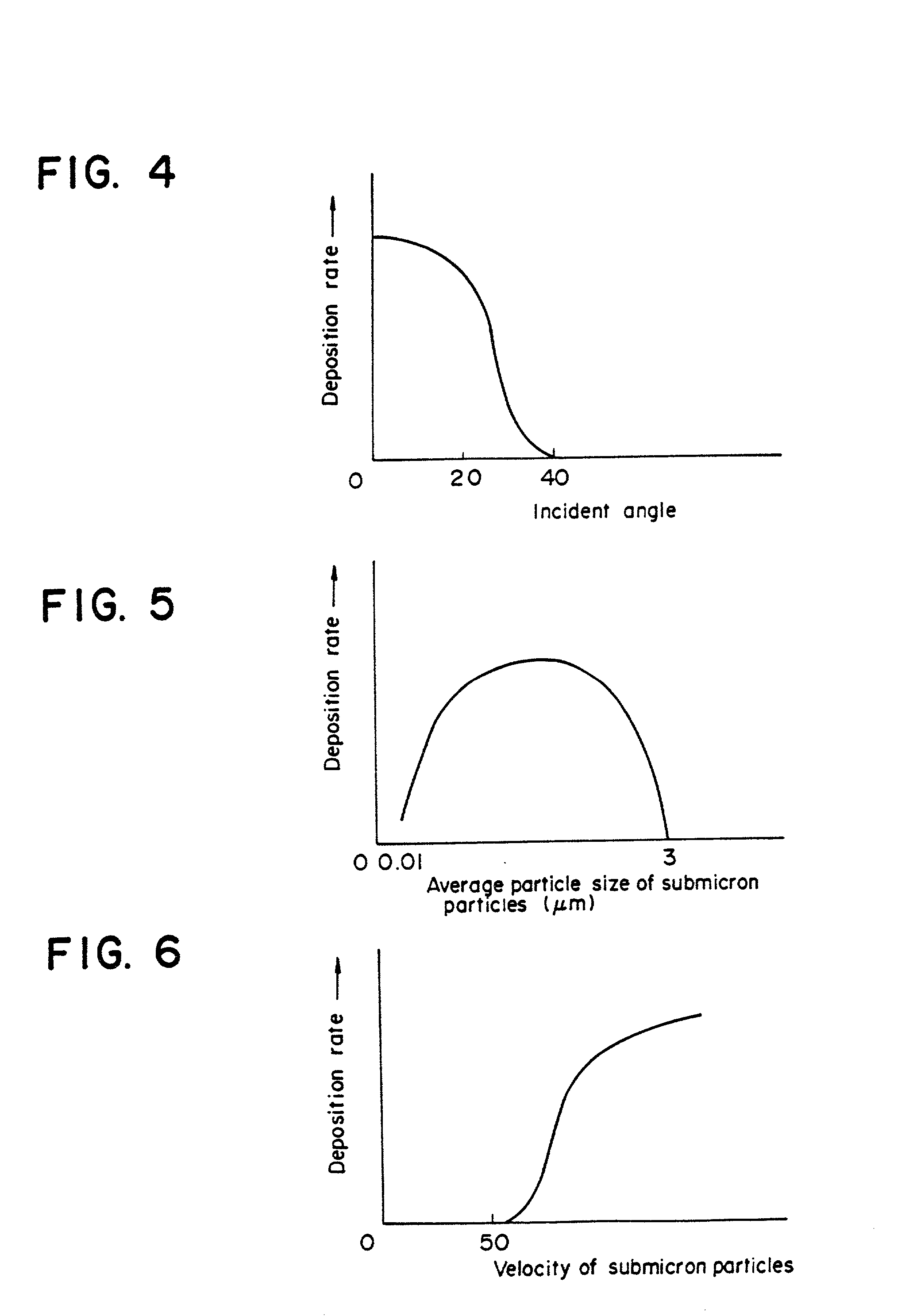
A surface processing method by blowing submicron particles is disclosed, in which submicron particles are blown against a surface of a work to deposit a layer of the material of the particles on a surface of the work, or etching the surface of the work. The processing method uses blowing air stream containing submicron particles having average particles size ranging between 0.01 and 3.0 mum. The deposition or etching is effected depending on an incident angle of the particles to the surface of work. According to the method deposition of the material can be effected with very high deposition rate and in case of etching very smooth etched surface is obtained.
Owner:MISHIMA AKIO +1
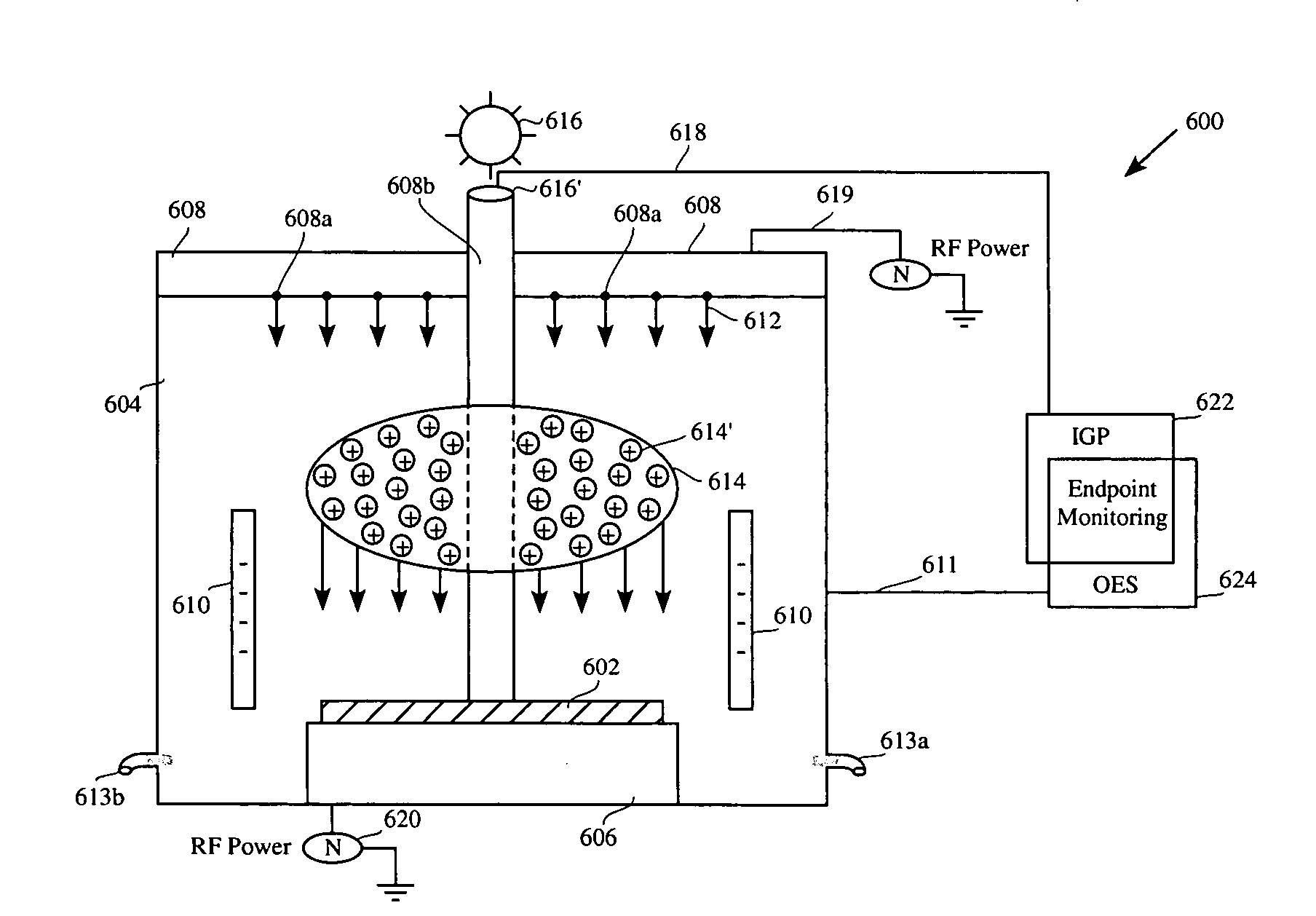
Method and apparatus for nitride spacer etch process implementing in situ interferometry endpoint detection and non-interferometry endpoint monitoring
InactiveUS6977184B1Reduce defectsImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTerminal pointInterferometry
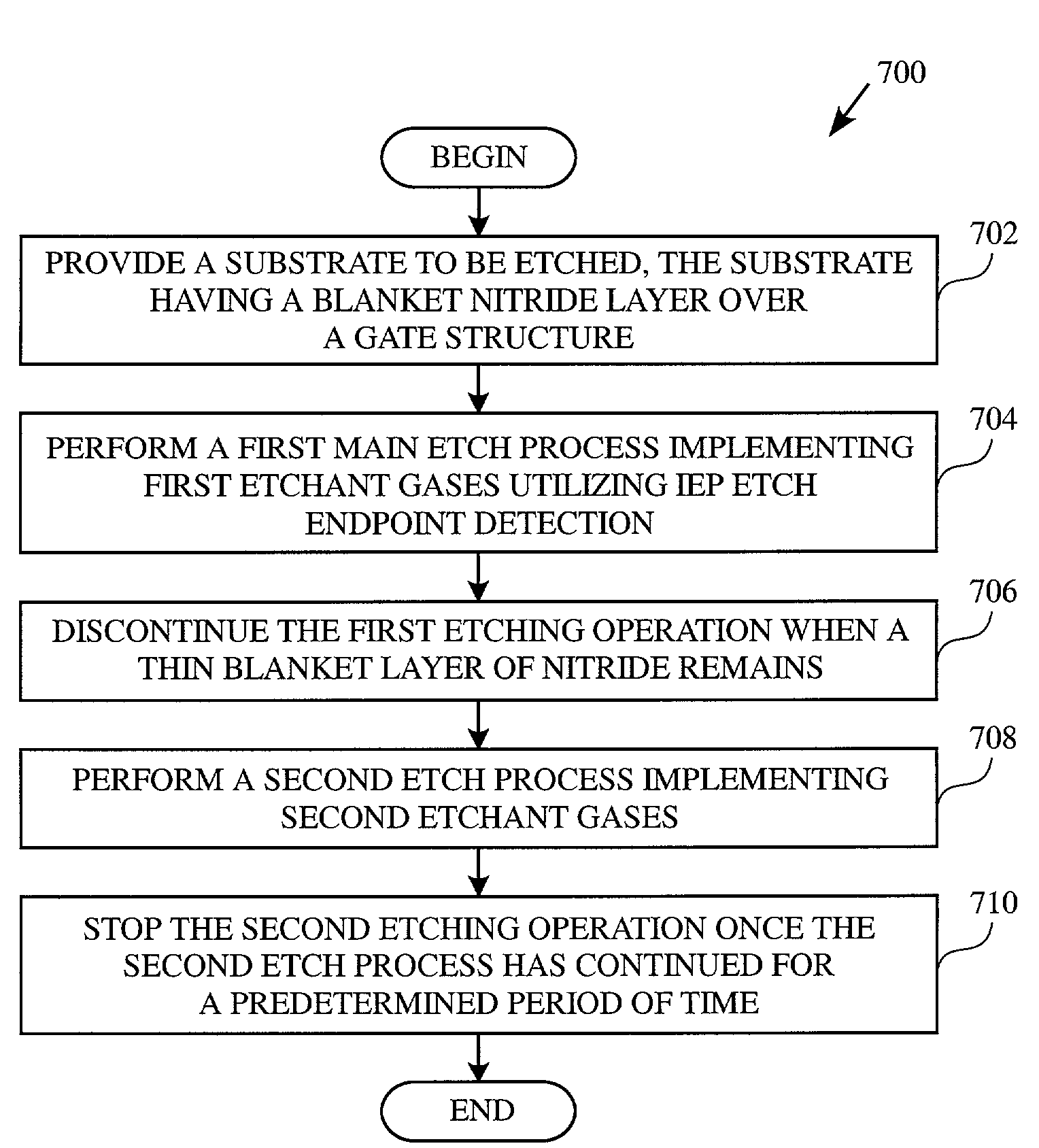
A method for fabricating a spacer of a gate structure is provided. The method performing a first etch process implementing a first etchant gas. The first etch process is configured to implement an interferometry endpoint (IEP) detection method to detect a removal of a portion of a spacer layer having a specific thickness from over the surface of the substrate, thus leaving a thin spacer layer. The method further includes performing a second etch process for a predetermined period of time implementing a second etchant gas. The second etch process is configured to remove the thin spacer layer, leaving the spacer for the gate structure.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
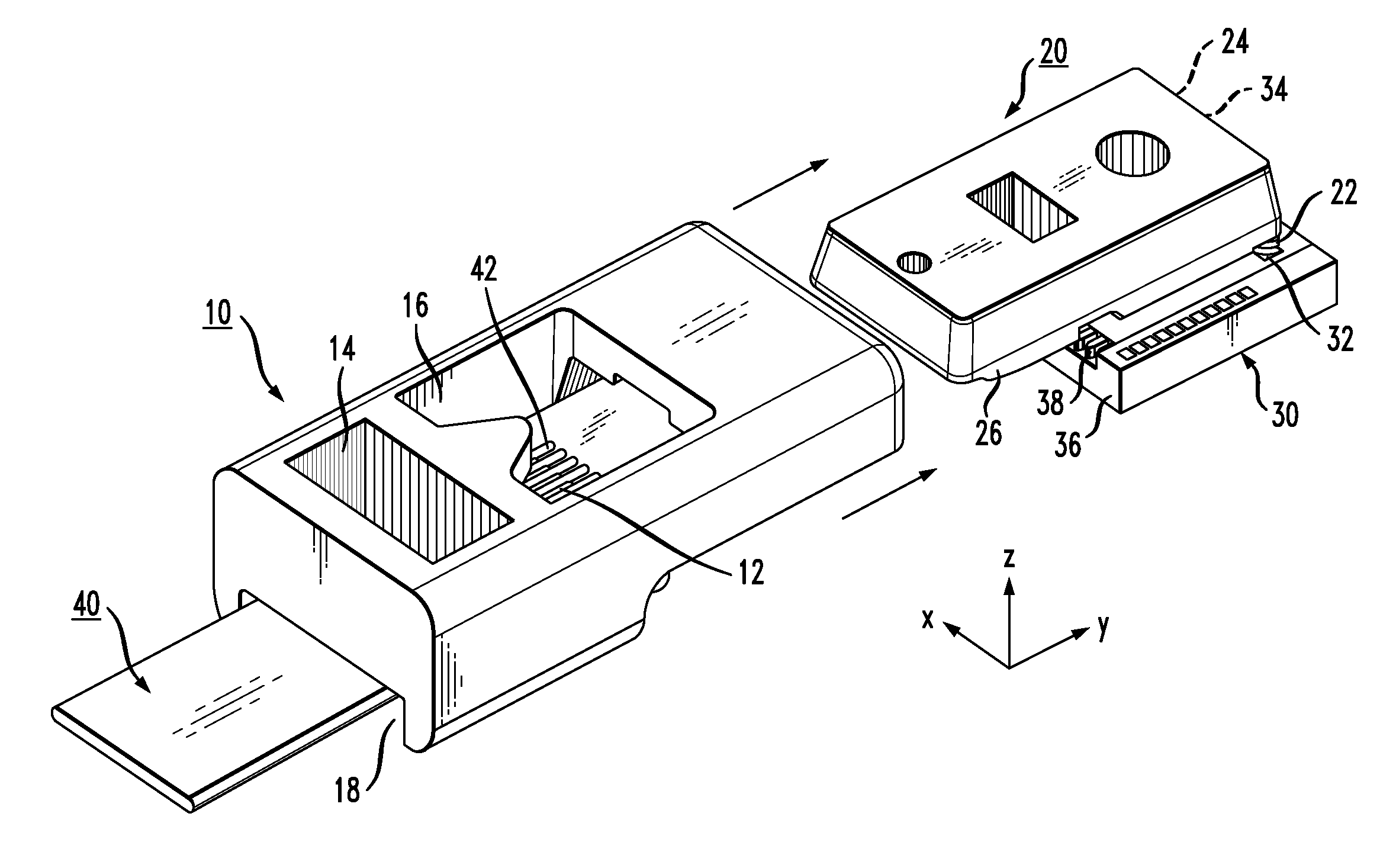
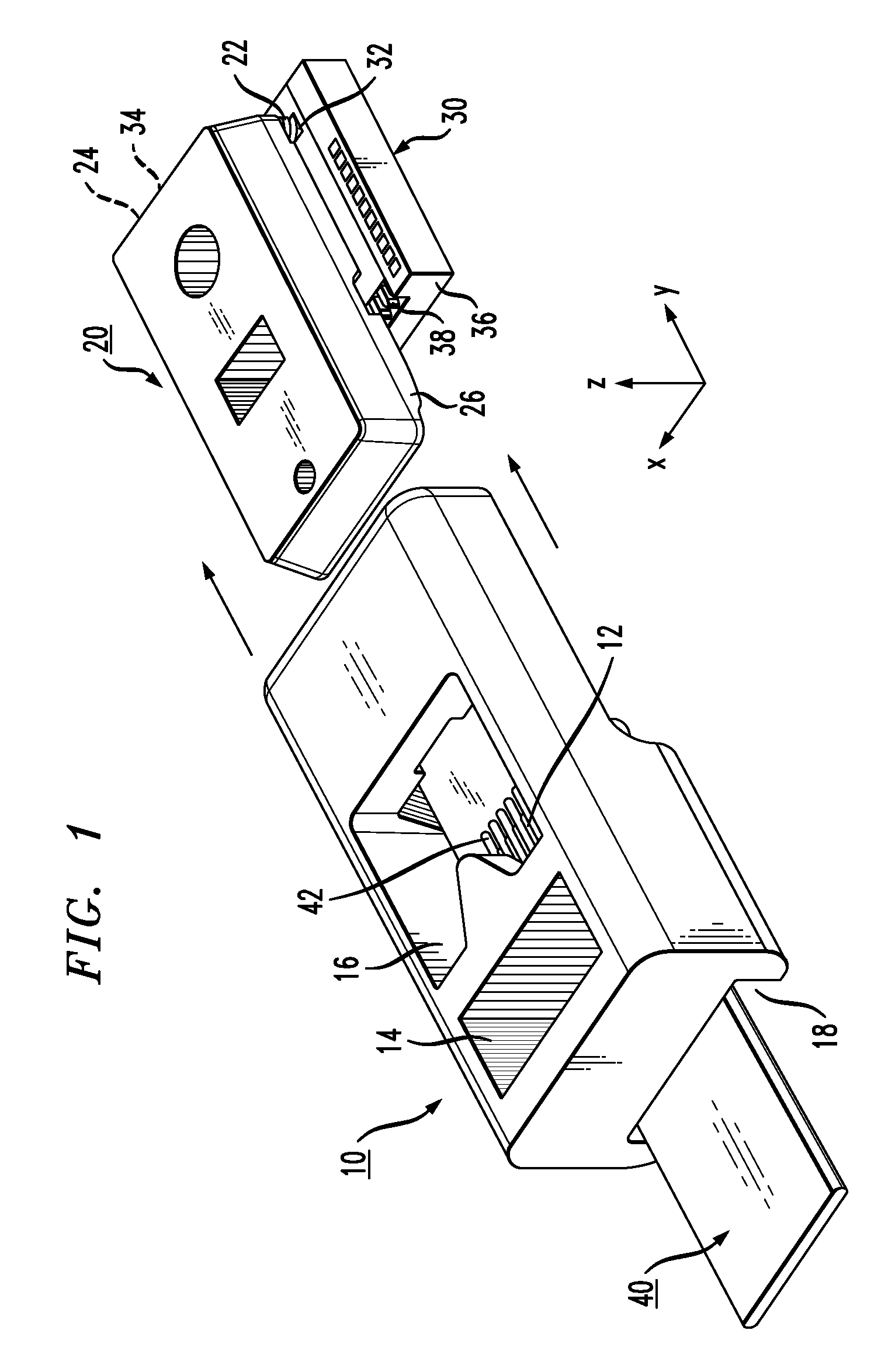
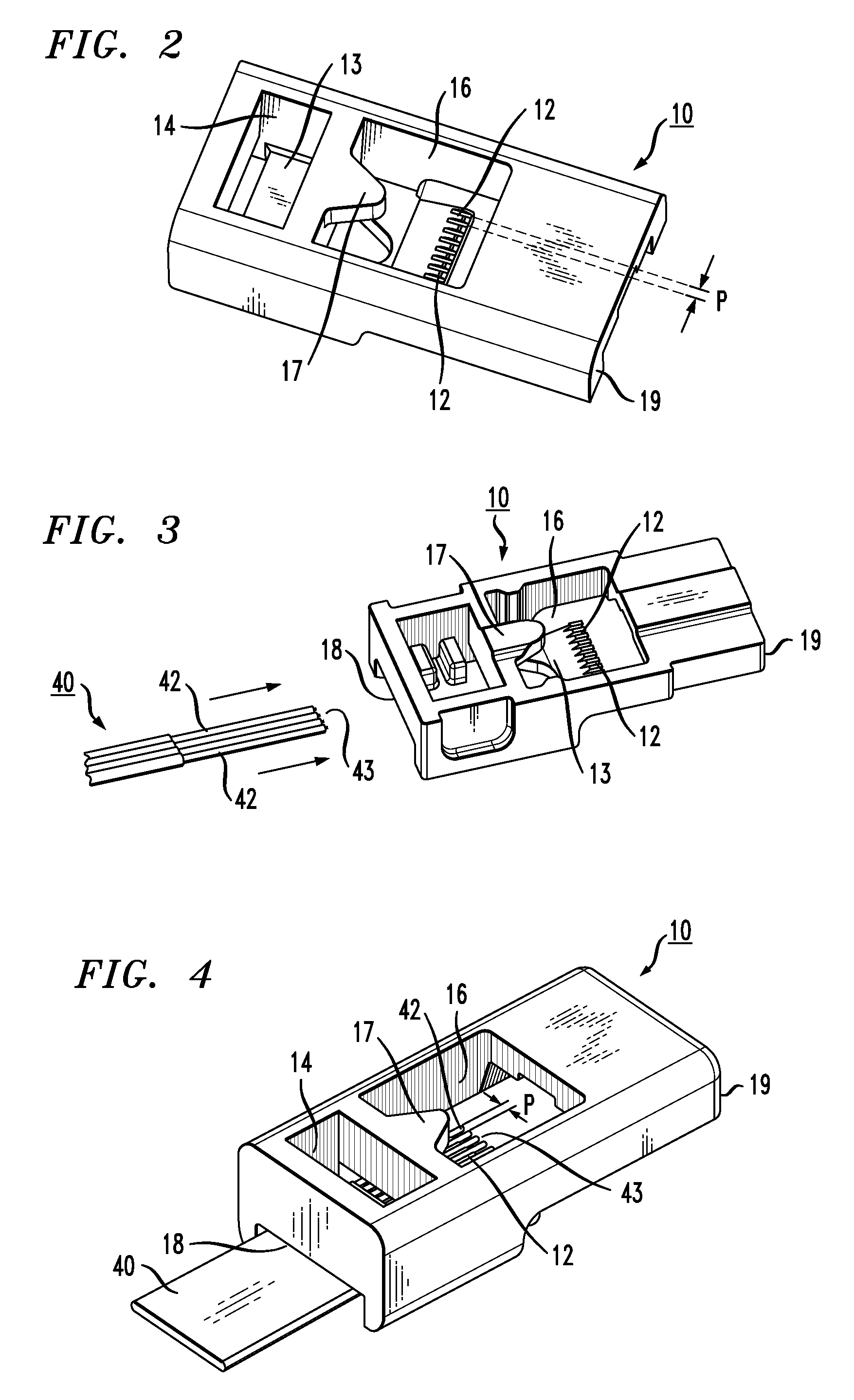
Multi-fiber interface to photonic subassembly
A multiple piecepart alignment and attachment configuration for mating a fiber array (or even a single fiber) with a silicon photonic subassembly utilizes ever-tightening alignment tolerances to align the fiber array with a similar array of waveguides (or other devices) formed within the photonic subassembly. A box-shaped fiber holder is formed to include a plurality of grooves within its bottom interior surface to initially support the fiber array. A separate piecepart in the form of a lid is mated to, and aligned with, the silicon photonic subassembly. The lid is formed to include registration features on its underside that fit into alignment detents formed in the top surface of the silicon photonic subassembly upon attachment. The lid also includes a number of grooves formed on its underside that will capture the top surface of the fibers as the fiber holder is slide into place over the lid. The grooves within the lid function to tighten the pitch of the fiber array and ultimately control the lateral and vertical alignment between the fiber array and the subassembly. The subassembly is also formed to include etched channels along the endface (the channels aligned with optical waveguides / devices in the substrate) to mate with the fiber holder, where the optical fibers are ultimately positioned within the channels so as to be in alignment with the optical waveguides / devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for nitride spacer etch process implementing in situ interferometry endpoint detection and non-interferometry endpoint monitoring
InactiveUS20060040415A1Reduce defectsImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDual stageMonitoring system
An in situ dual-stage etch endpoint detection system is disclosed. The system includes an etch chamber, an interferometry endpoint monitoring system, and a non-IEP endpoint monitoring system. The etch chamber includes an electrostatic chuck (ESC), a top electrode, and a bottom electrode. The ESC is designed to support a wafer having a spacer layer formed over a gate structure. The interferometry endpoint (IEP) monitoring system is designed to monitor an interference photon beam reflected by the top of spacer layer and the reflection beam on interface of bottom of spacer during a first etch operation. The non-IEP endpoint monitoring system monitors a second etch operation by monitoring an etch time. A first etch operation implementing the IEP monitoring system is discontinued, leaving a thin spacer layer to be etched during the second etch operation.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Semiconductor wafer etching method
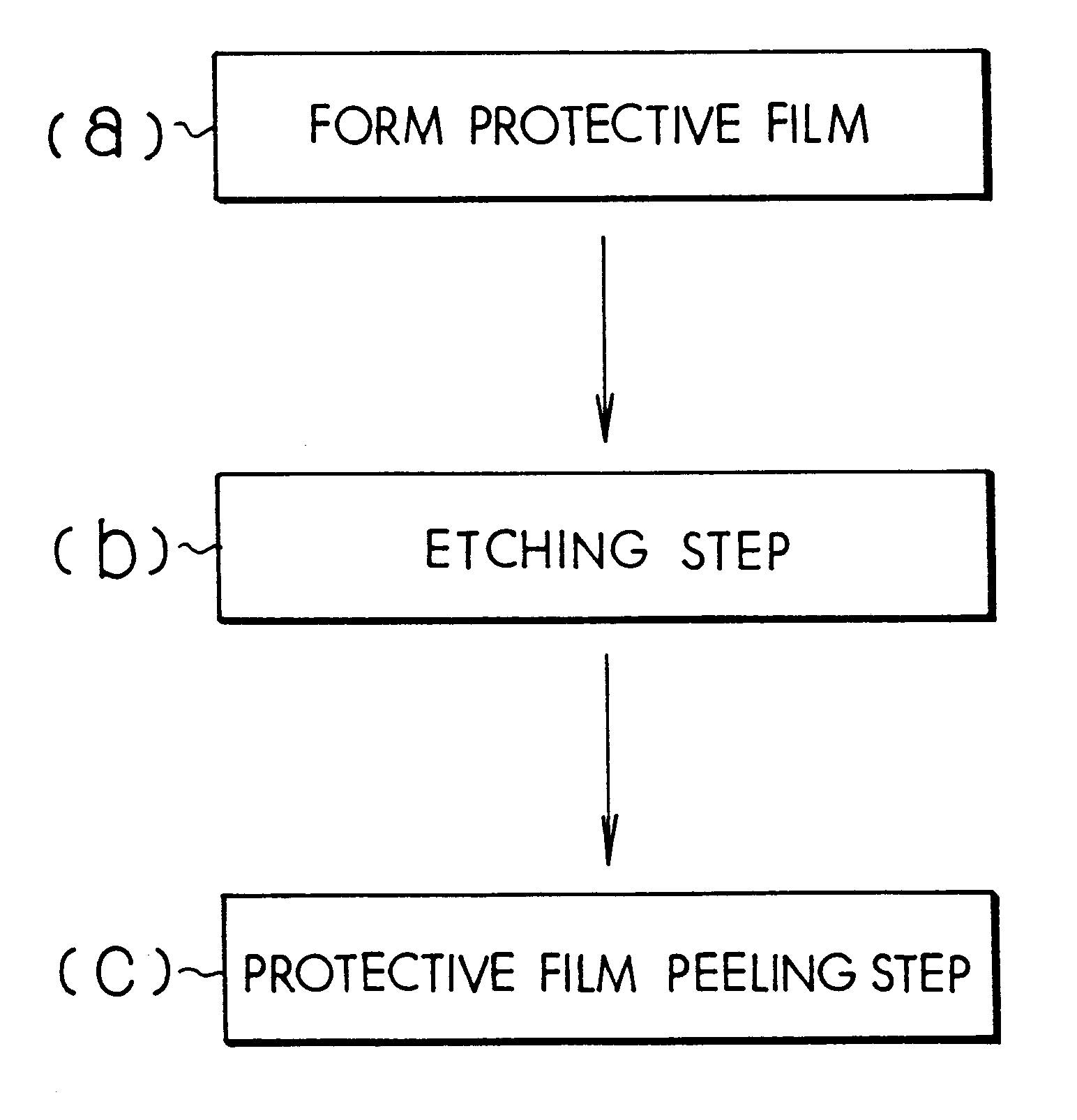
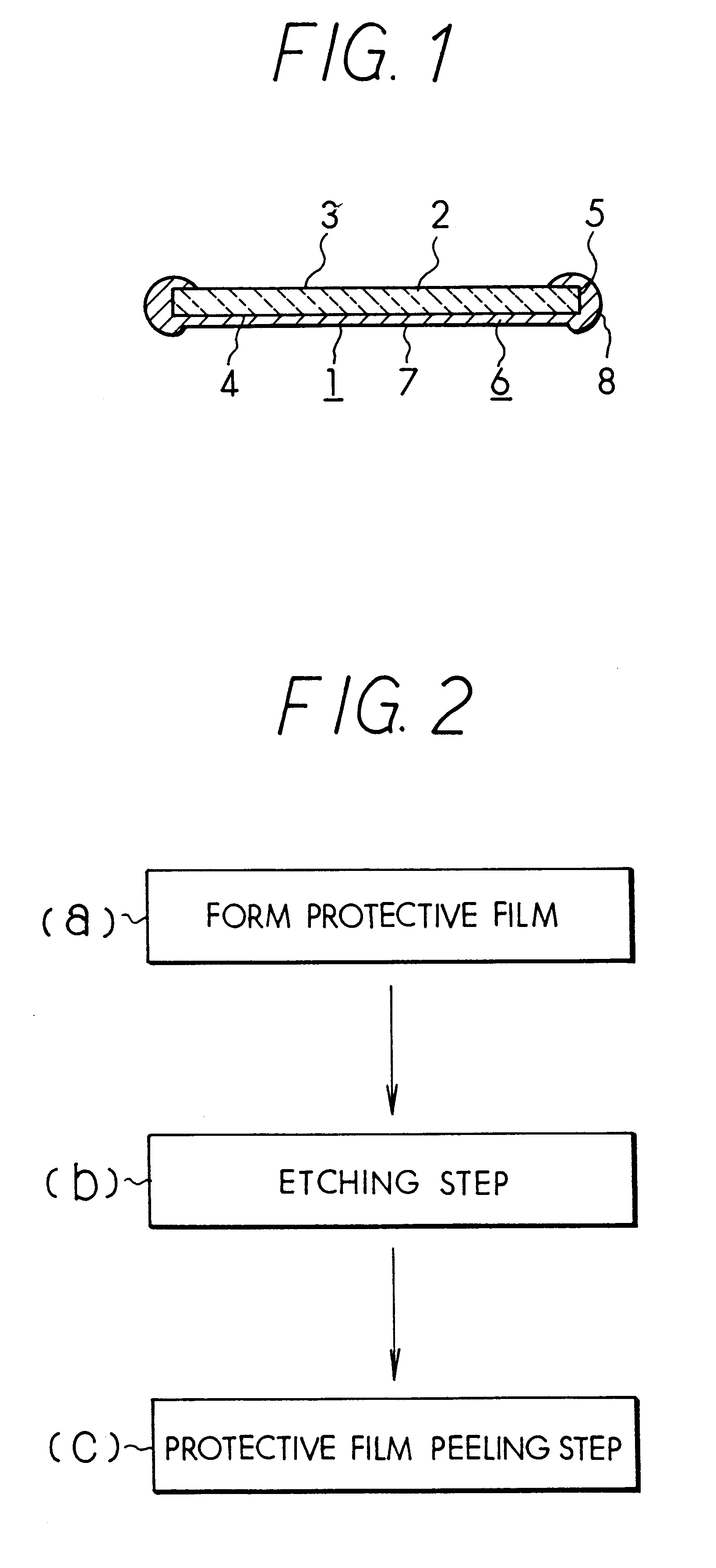
InactiveUS6251542B1Etching precisionSufficiently peeled and cleanedDecorative surface effectsElectrostatic cleaningSolventEtching
A semiconductor wafer etching method is disclosed that allows etching without use of restricted ozone-destroying solvents such as trichloroethane or fluorocarbons. This method involves forming a protective film of silicon resin or alkali resistant resin on a semiconductor wafer. Then, a surface region of the wafer not covered by the protective film is etched. Finally, the protective film is peeled from the semiconductor wafer without damaging the wafer or employing solvents harmful to the environment.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Composite material used in making printed wiring boards
InactiveUS6548153B2Reduce thicknessEtching precisionInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementPrinted circuit secondary treatmentMaterials scienceMicro particles
A composite material for use in making printed wiring boards comprising a carrier having releasable conductive fine particles on its surface. The composite is laminated to a substrate with the conductive fine particles facing the substrate and the carrier removed, leaving the surface of the conductive fine particles exposed. Printed wiring is formed using the conductive fine particles as its base, thus providing improved peel strength and permitting formation of fine wiring lines and spaces.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
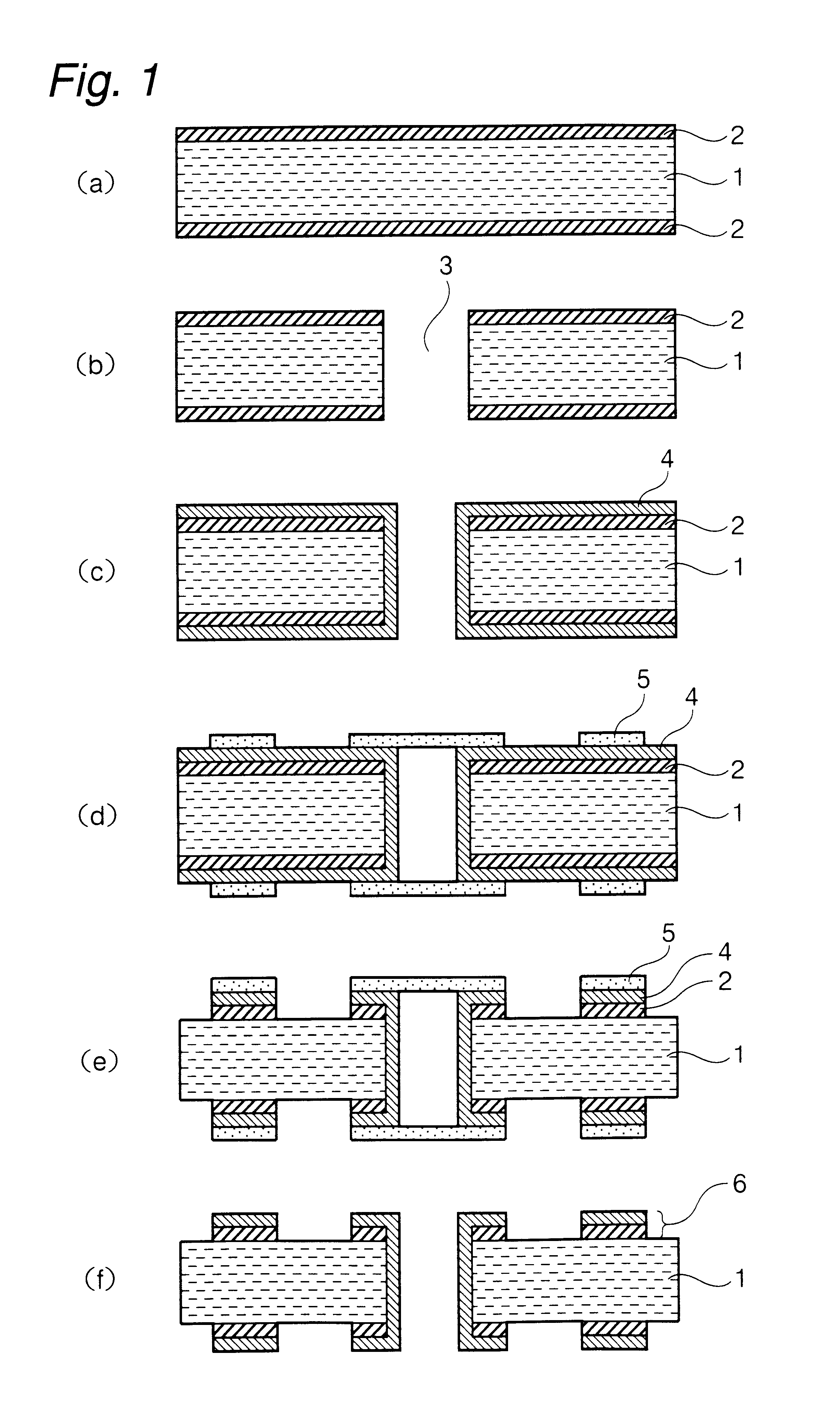
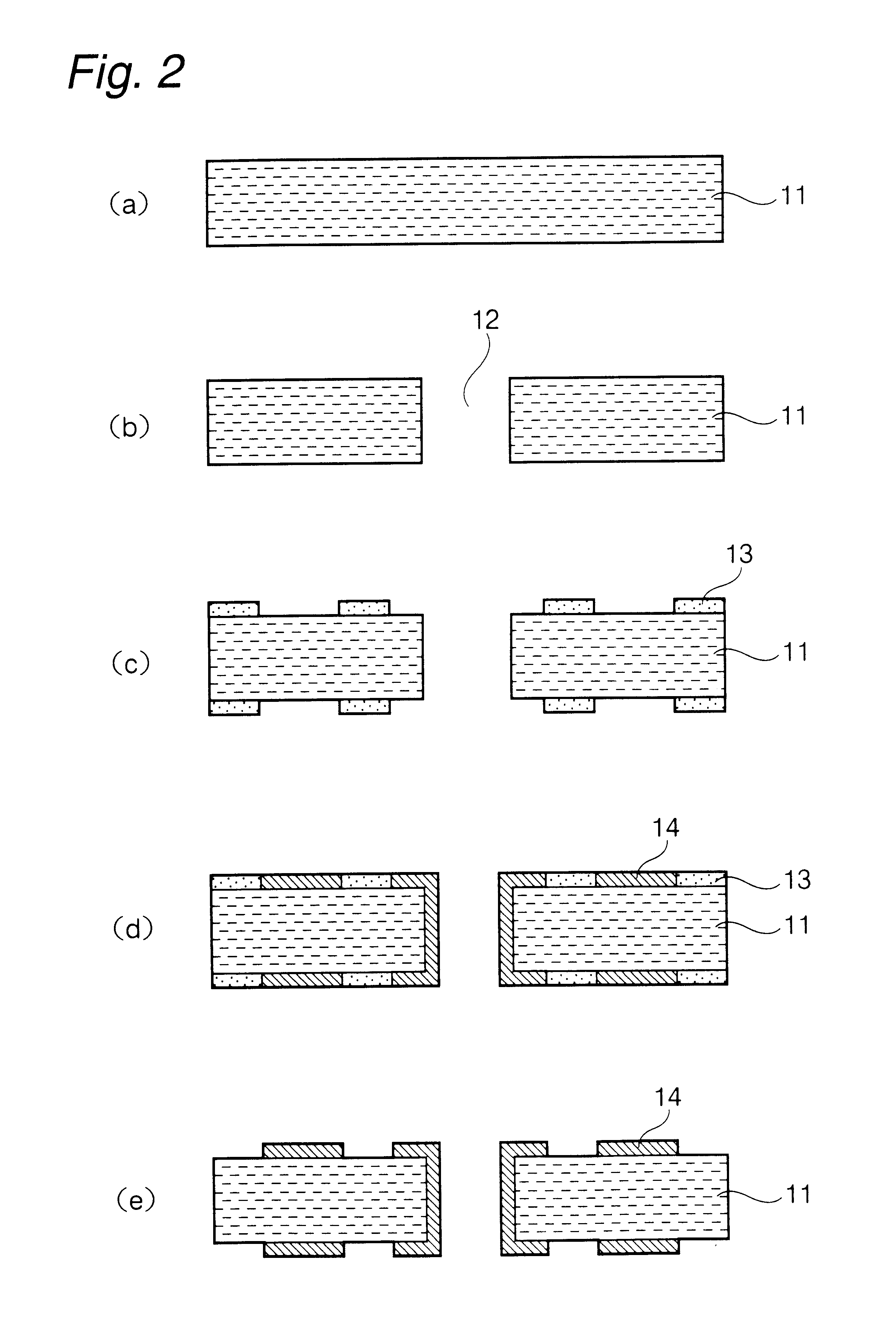
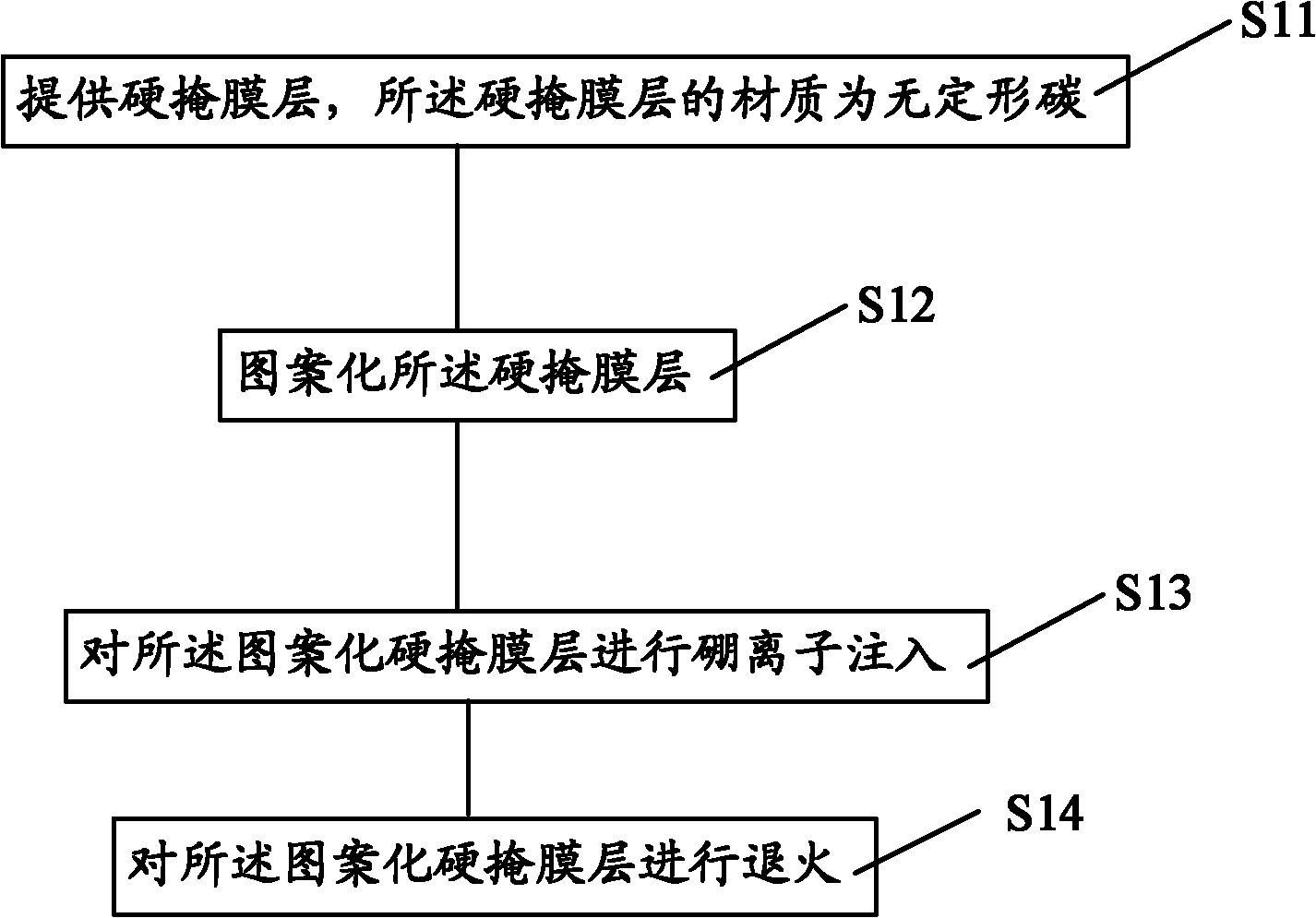
Amorphous carbon processing method and etching method by adopting amorphous carbon as hard mask
ActiveCN103021838AAccurate etching processBoron dosage range is unlimitedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous carbonSemiconductor
The invention provides a method of processing the amorphous carbon which serves as a hard mask. The method comprises the steps of: providing a hard mask layer which is made of amorphous carbon; patterning the hard mask layer; and conducting boron ion injection on the patterned hard mask layer. The invention further provides an etching method by adopting amorphous carbon as the hard mask, and comprises the steps of: providing a semiconductor substrate, forming an aligned mark and substrate patterns on the semiconductor substrate, wherein a layer to be etched is arranged at the uppermost layer; depositing the hard mask layer on the layer to be etched, wherein the hard mask layer is made of the amorphous carbon; detecting the aligned mark through the amorphous carbon so as to align patterns on a mask edition to the substrate patterns; patterning the hard mask layer; conducting boron ion injection on the patterned hard mask layer to form a new patterned hard mask layer; and etching the layer to be etched by taking the new patterned hard mask layer as a mask. According to the technical scheme, the problems that boron doping amount is limited when the to-be-etched layer is etched and the process requirement is high when the hard mask layer is removed can be solved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Method for efficiently producing high-precision multistep microlens array
ActiveCN104237983AImprove production efficiencyLow costPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusMicro lens arrayComputer science
The invention relates to a method for efficiently producing a high-precision multistep microlens array. The method includes that the step array to be produced is divided into multiple groups including a first group and a second group, the first group and the second group are connected end to end, and steps of each group are continuous in depth; the steps of the first group and the second group are synchronously produced to form two groups of steps identical in corresponding depth; the steps in the second group are integrally etched by certain depth and form the step array continuous in depth with the steps in the first group. By the method, the steps in different groups are created synchronously, so that producing efficiency is greatly improved, and cost is saved.
Owner:中航凯迈上海红外科技有限公司
Chemical method for etching insulating-film for flexible printed circuit, and etching solution
An etching liquid for preparing the insulating film of flexible PCB is prepared from the solution of potassium (or sodium or lithium) hydroxide (5-40%), C2-C6 unitary (or binary or ternery) alcohol or C2-C6 alcoholamine (or dialcoholamine) (10-70%), potassium (or sodium or lithium) carbonate (0-1.5%) and water (25-60%). Its chemical etching process is also disclosed.
Owner:AKM ELECTRONICS INDAL PANYU
Wide bandgap semiconductor device construction
InactiveUS7241699B2Improve material etchWide bandgapSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBroadbandWide band
The invention includes methods for precisely and accurately etching layers of wide bandgap semiconductor material. According to one aspect of the invention, the method includes providing a multi-layer laminate including at least a first and second layer of wide bandgap semiconductor material, measuring a first conductance of the first layer of semiconductor material, partially etching the first layer of semiconductor material a first amount, measuring a second conductance of the first layer of semiconductor material etched the first amount, and utilizing the first and second measured conductance to determine a time required to etch the first layer of semiconductor material a second amount.
Owner:MICROSEMI
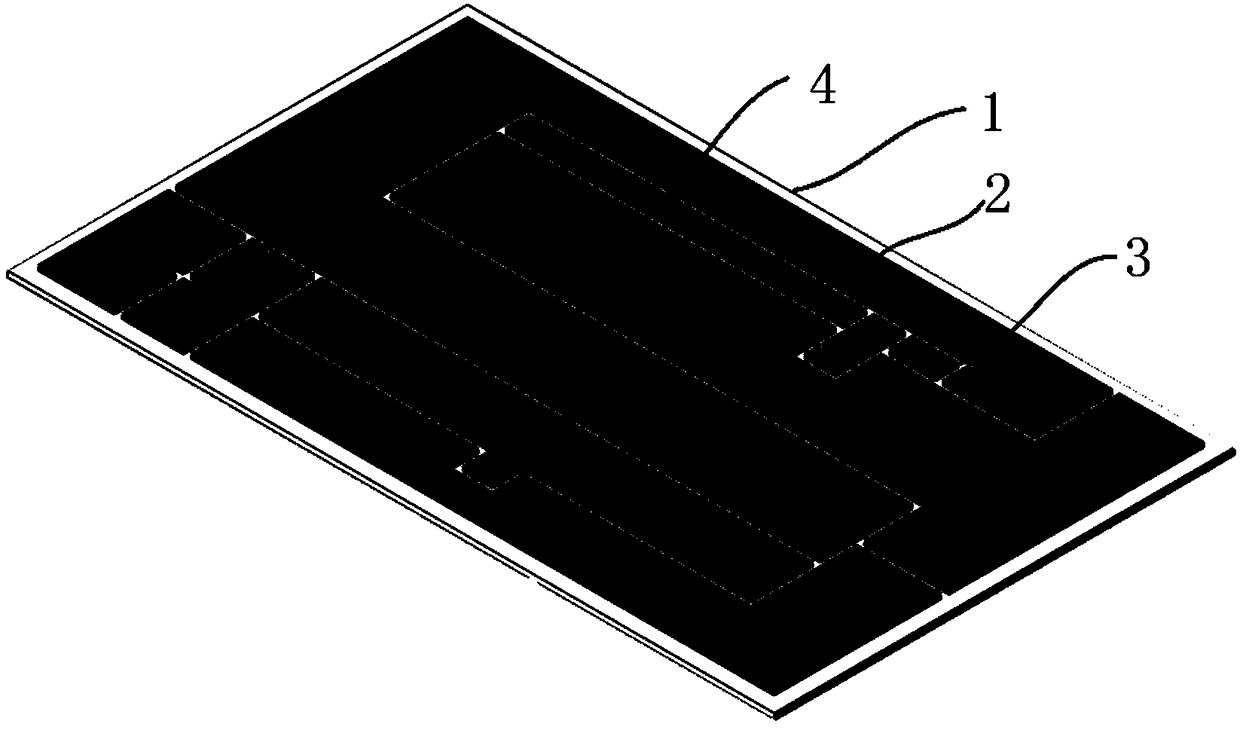
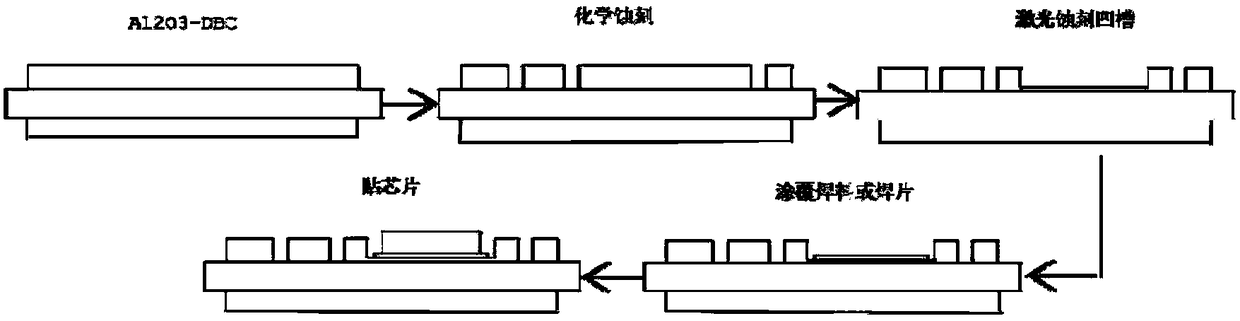
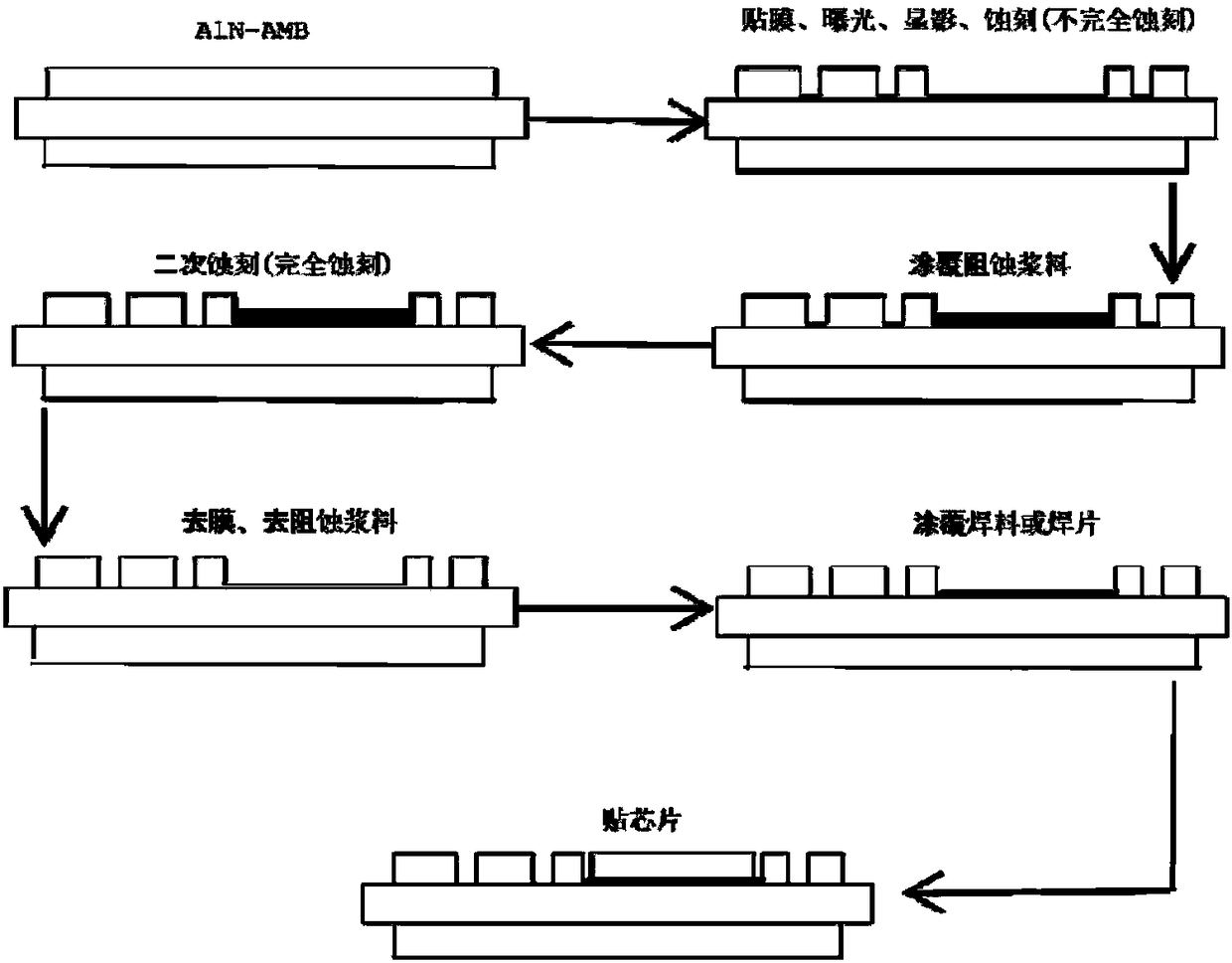
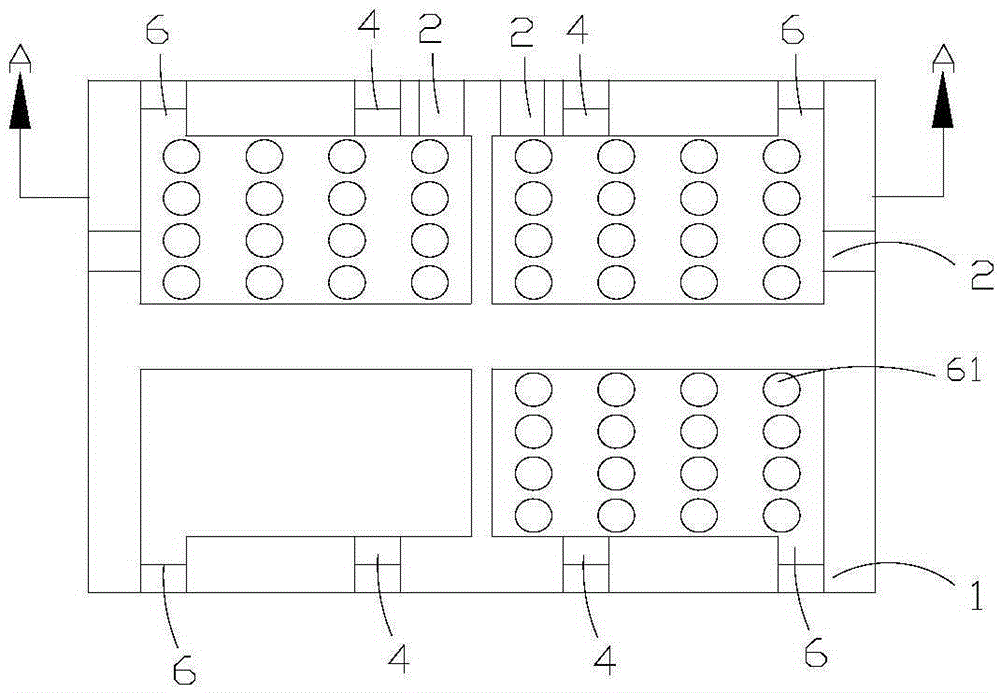
Metalized ceramic substrate, substrate manufacturing method and substrate and chip welding method
PendingCN108615717AFast etchEtching precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal expansionInternal stress
The invention discloses a metalized ceramic substrate, a substrate manufacturing method and a substrate and chip welding method, belongs to the field of a semiconductor device, and specify to the problem of failure of a power electronic device caused by a cracking phenomenon between a chip and a metalized layer, and falling off or cracking of the chip due to frequent impact of cold and hot changesof environment temperature on the metalized ceramic substrate in the prior art. The invention provides the metalized ceramic substrate, the substrate manufacturing method and the substrate and chip welding method; the metalized ceramic substrate comprises a ceramic substrate; a metal layer is arranged on one or two surfaces of the ceramic substrate; a circuit is arranged on the metal layer; a chip groove is formed in a metal layer chip mounting position; and the chip is welded on the chip groove of the manufactured metalized ceramic substrate through a brazing technique. By virtue of the method, internal stress caused by mismatch of thermal expansion coefficients between the metal layer and the chip can be lowered as far as possible, and product reliability is improved.
Owner:井敏
Capacitive humidity sensor and manufacturing method thereof
The present invention specifically discloses a capacitive humidity sensor and a manufacturing method thereof, the capacitive humidity sensor comprises at least a first sensing member, a second sensing member, a third sensing member and a substrate, the sensing members are separately fixedly arranged on the surface of the substrate, the first sensing member comprises a heating electrode layer, an insulating layer, a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer and a moisture sensitive layer; the heating electrode layer of the first sensing member is arranged on the surface of the substrate in an overlaying manner, the insulating layer is arranged on the outer surface of the heating electrode layer in the overlaying manner, and extends to the surface of the substrate, the first electrode layer, the moisture sensitive layer and the second electrode layer are successively arranged on the outer surface of the insulating layer in the overlaying manner in the direction from the substrate to the insulating layer, the surface of the second electrode layer is provided with a through hole communicating the moisture sensitive layer; compared with the first sensing member, the second sensing member and the third sensing member do not include a heating electrode layer, and the surface of a second electrode layer of the third sensing member is not provided with a through hole. The capacitive humidity sensor is simple in structure, various layers are solidly contacted, poor contact or falling-off is less prone to occur, the electrode parasitic resistance can be reduced, and the sensor low temperature performance can be enhanced.
Owner:张绍达
Method of etching magnetoresistive film by using a plurality of metal hard masks
ActiveUS20090110960A1Improve controllabilityEtching precisionDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingResistLower face
This etching method comprises the steps of forming first and second hard masks made of materials different from each other successively on a magnetoresistive film; forming a resist having a lower face opposing a front face of the second hard mask, a space being interposed between the front face and lower face; dry-etching the second hard mask by using the resist as a mask; etching the first hard mask by using the etched second hard mask; and etching the magnetoresistive film by using the first hard mask.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
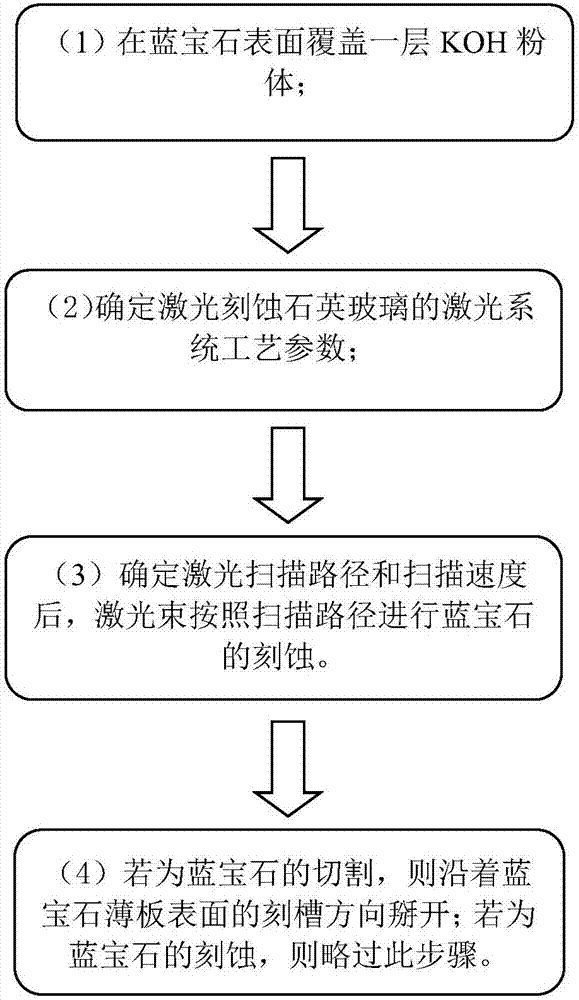
Processing method for etching and cutting sapphire through laser-induced KOH chemical reaction
The invention provides a processing method for etching and cutting sapphire through a laser-induced KOH chemical reaction, and belongs to the field of special processing. The processing method mainlycomprises the following four steps that (1) the surface of the sapphire is uniformly covered with a layer of KOH powder; (2) laser system parameters and process parameters of sapphire laser etching are determined; (3) after the laser scanning path and the scanning speed are determined, etching of the sapphire is conducted by a laser beam according to the scanning path; and (4) if the sapphire is cut, the laser beam is split in the groove etching direction; and if the sapphire is etched, the step is omitted. According to the processing method, two etching methods of fusion KOH corrosion of thesapphire and laser ablation of the sapphire are combined, so that etching with the high etching rate of the sapphire is conducted; based on the processing method, a sapphire thin plate is cut by meansof the crack controlling method; a complex two-dimensional etched groove can be etched on the surface of the sapphire; and due to the fact that the etching mechanism of the processing method is thatsapphire corrosion is mainly achieved through the chemical reaction, the high etching rate under the condition of low crack damage can be achieved, and high-quality linear cutting of the sapphire thinplate can also be realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Molybdenum aluminum molybdenum etching solution
The invention relates to a molybdenum aluminum molybdenum etching solution. Based on a total weight, the molybdenum aluminum molybdenum etching solution comprises: 35-45% of phosphoric acid, 1-3% of nitric acid, 8-12% of glacial acetic acid, 0.5-1.0% of additives and 39-55.5% of deionized water. The additives comprise organic polybasic phosphonic acid substance, amine substance and salt substance.The molybdenum aluminum molybdenum etching solution provided by the invention can meet the customers' requirements for etching angle and etching amount, improves the product's excellent and good rate, at the same time greatly lowers the phosphoric acid content, and reduces the problem of uneven local etching caused by excessive phosphoric acid concentration.
Owner:SHENZHEN CAPCHEM TECH CO LTD
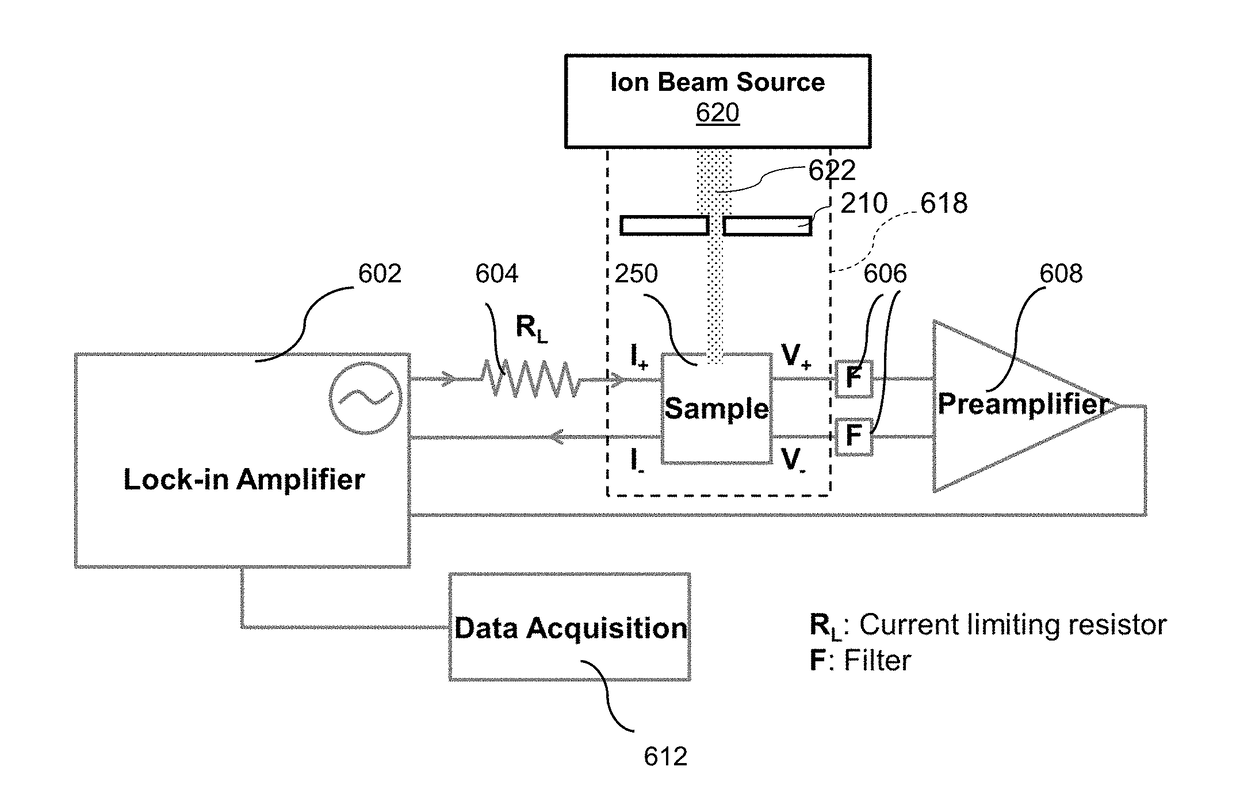
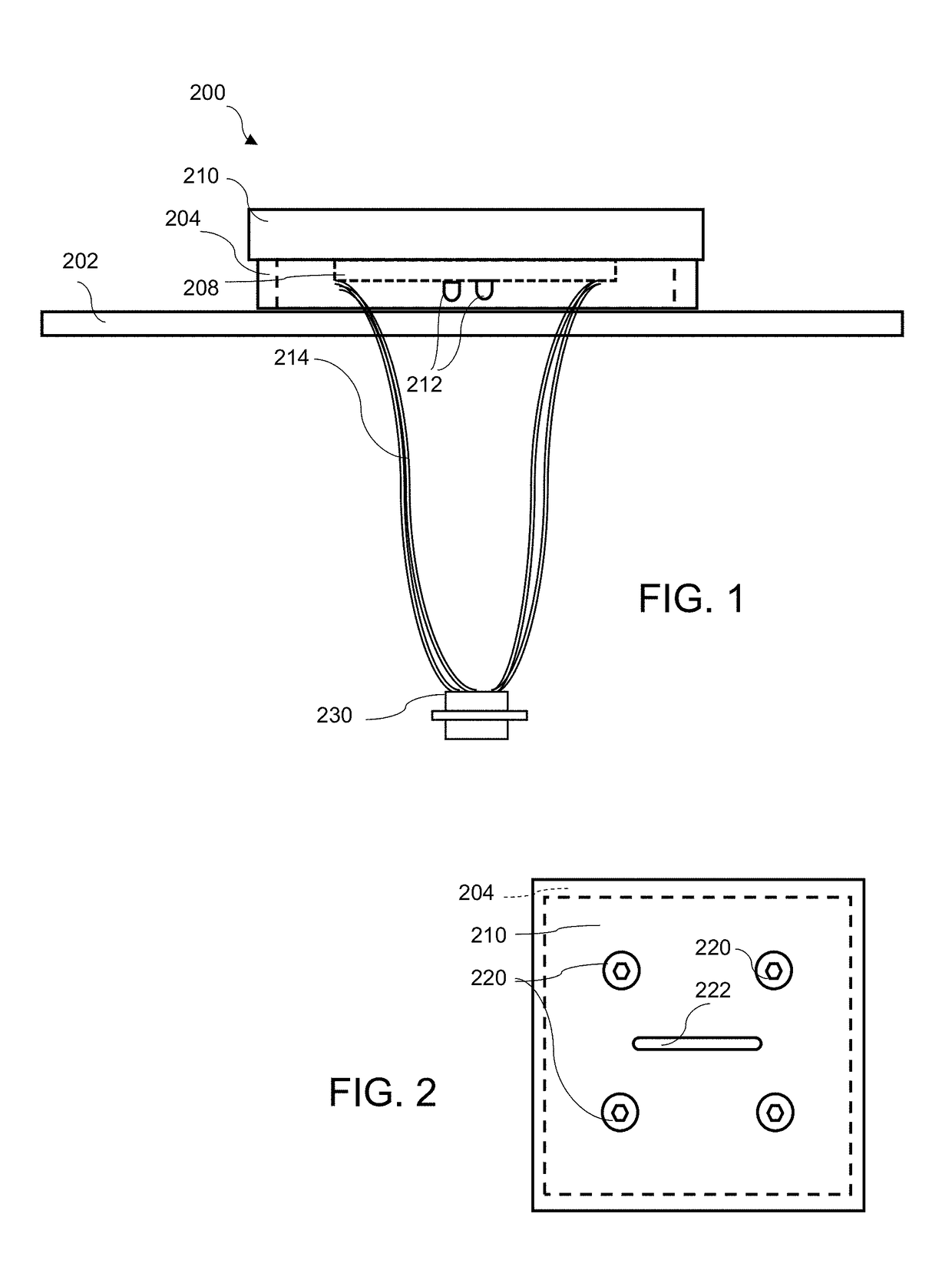
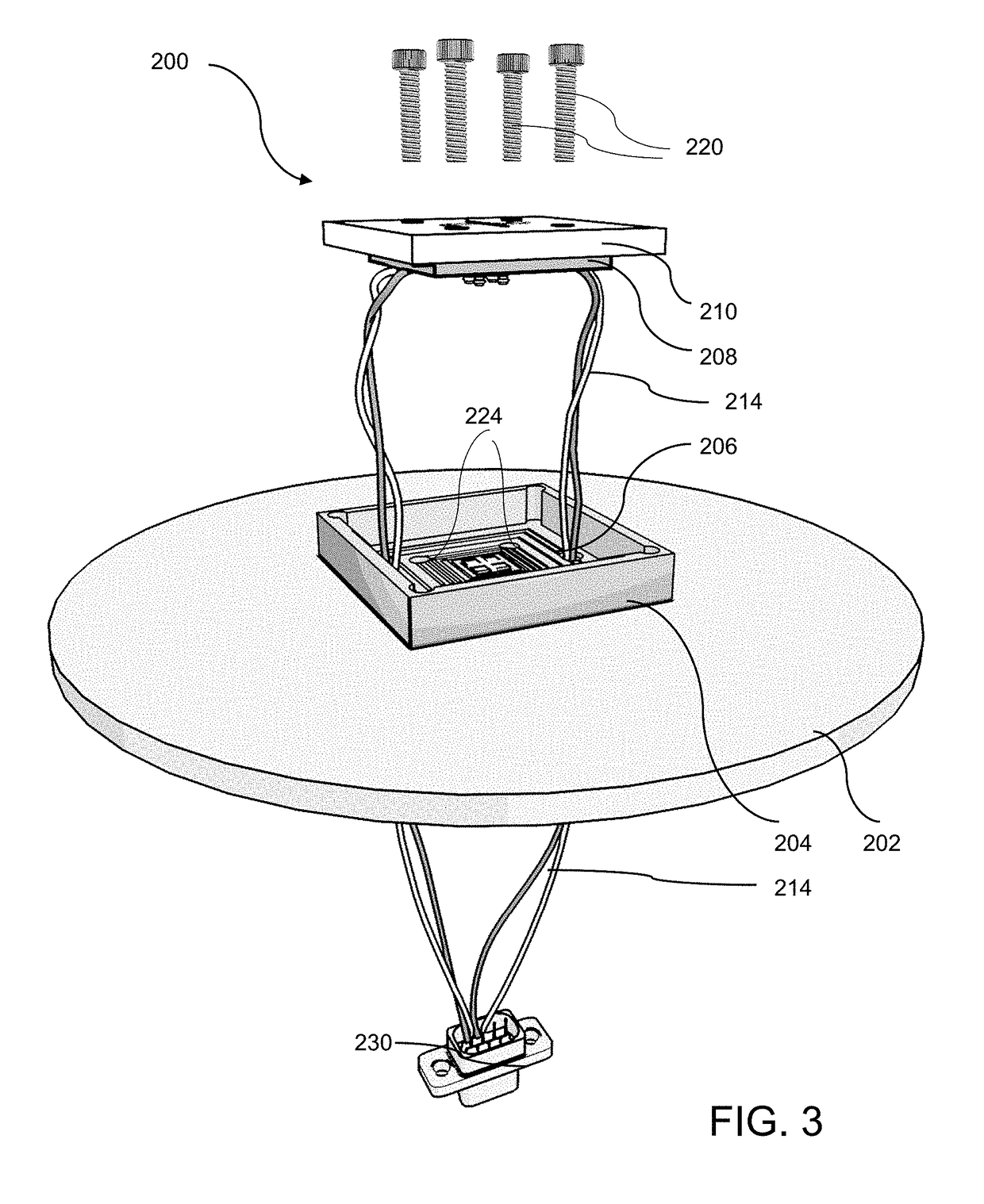
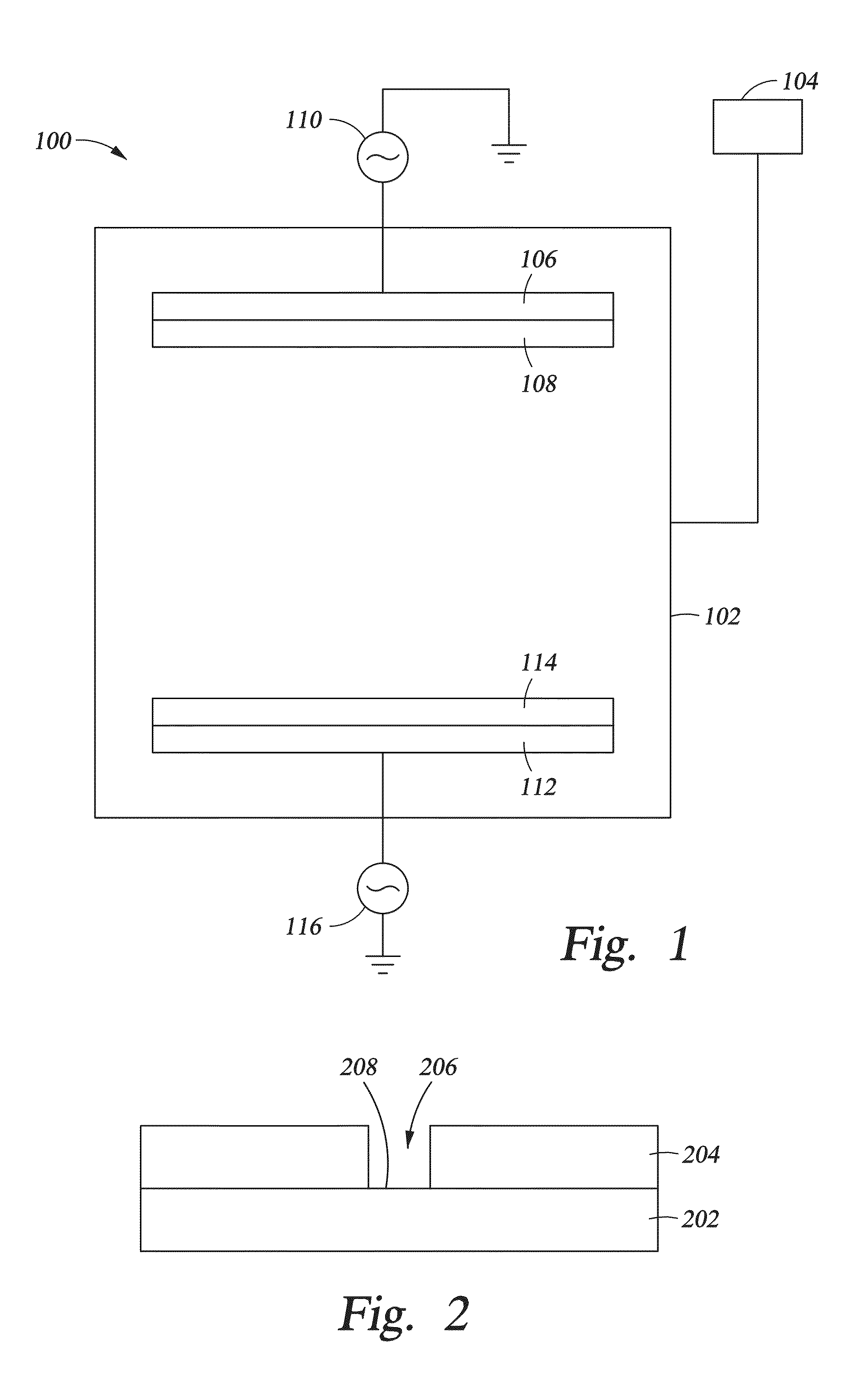
Ion beam mill etch depth monitoring with nanometer-scale resolution
ActiveUS20180053626A1Easy to operateStop preciseSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesElectricityPower flow
A method for measuring conductance of a material real-time during etching / milling includes providing a fixture having a socket for receiving the material. The socket is attached to a printed circuit board (PCB) mounted on one side of a plate that has at least one opening for providing ion beam access to the material sample. Conductive probes extend from the other side of the PCB to contact and span a target area of the material. A measurement circuit in electrical communication with the probes measures the voltage produced when a current is applied across the material sample to measure changes in electrical properties of the sample over time.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of Etching Polymeric Materials Suitable for Making Micro-Fluid Ejection Heads and Micro-Fluid Ejection Heads Relating Thereto
A micro-fluid ejection head structure, methods for making micro-fluid ejection head structures, and methods for etching polymeric nozzle plates. One such micro-fluid ejection head structuring includes a substrate having a plurality of fluid ejection actuators. A thick film layer is attached adjacent the substrate. The thick film layer has a fluid chamber and a fluid flow channel capable of providing fluid to the fluid chamber. A polymeric nozzle plate is attached adjacent the thick film layer. The polymeric nozzle plate includes a nozzle capable of being in fluid communication with one or more of the fluid flow chambers. The nozzle is a plasma etched nozzle defined by a photoresist mask layer.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Semiconductor contact hole etching method
InactiveCN104465502AReduce lossImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideSemiconductor
The invention relates to a semiconductor contact hole etching method achieved through a sandwich structure. The method includes the steps of providing a substrate, wherein a plurality of electric conduction structures are formed on the substrate; forming a first SiN layer covering the substrate and the electric conduction structures on the substrate; forming an SiO2 layer on the first SiN layer; forming a second SiN layer on the SiO2 layer; forming an ILD layer of the SiO2 layer on the second SiN layer through deposition; flattening the ILD layer and forming an ILD cap layer on the surface of the ILD layer, wherein the ILD cap layer sequentially comprises a photoetching adhesive layer and an anti-reflection coating from top to bottom; forming a contact hole pattern in the photoetching adhesive layer; conducting etching through the contact hole pattern so that all the electric conduction structures and source / drain electrodes located on the two sides of the electric conduction structures can be exposed. The method has the advantages that the adoption of the single-medium SiN or double-layer media is avoided, and the number of silicon oxides on the surface of the substrate and the number of consumed STI layers are decreased.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Product and method for protecting metal during etching
InactiveUS20050082254A1Good etchingSacrificing quality and precisionDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusResistMaterials science
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for etching the interior of a mold. In one implementation of the invention the interior of a mold is coated with an acid-resistant material. A photosensitive laminate is partially exposed to light, with only those areas that are to be etched being exposed. The laminate is subsequently developed to remove that portion of the laminate that has been exposed. This removed portion corresponds to the portion of the mold that is to be etched. After development the laminate is positioned in the interior of the mold over the acid-resistant coating, and then portions of the acid-resistant material are abrasively removed. The laminate is lightly wetted in some implementations in order to make it more flexible and stretchable, thereby allowing it to more readily conform to the interior surface of the mold. The intact portions of the photosensitive laminate (those portions that were not exposed to the light) provide protection to the acid-resist material, while the developed and removed portions of the photosensitive laminate provide little or no protection.
Owner:IKONICS CORP
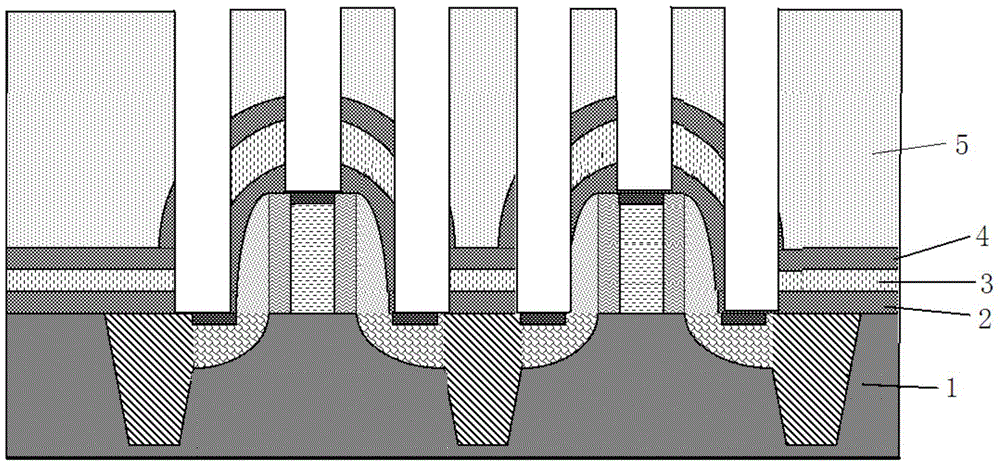
Manufacturing method of three-dimensional memory
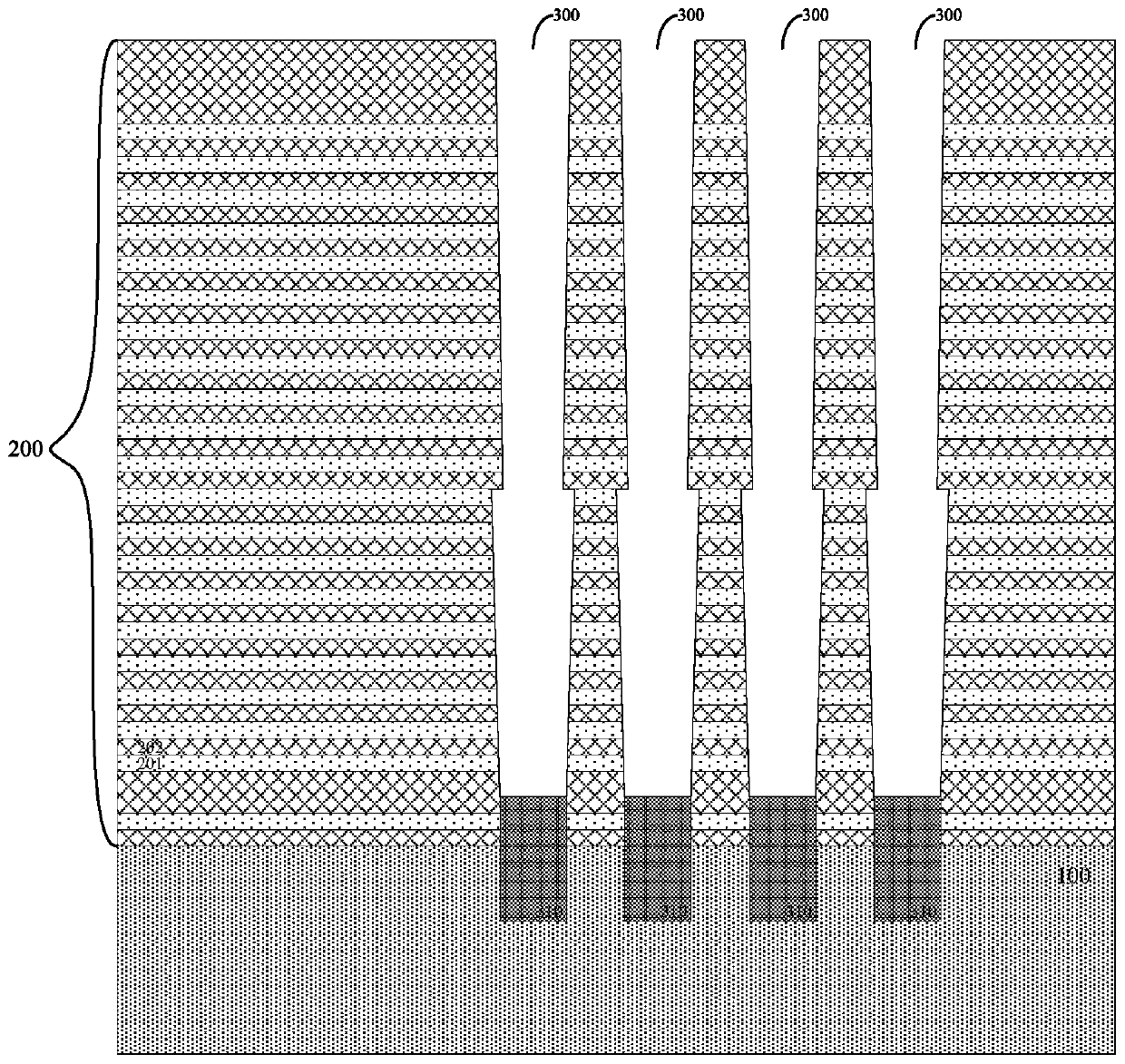
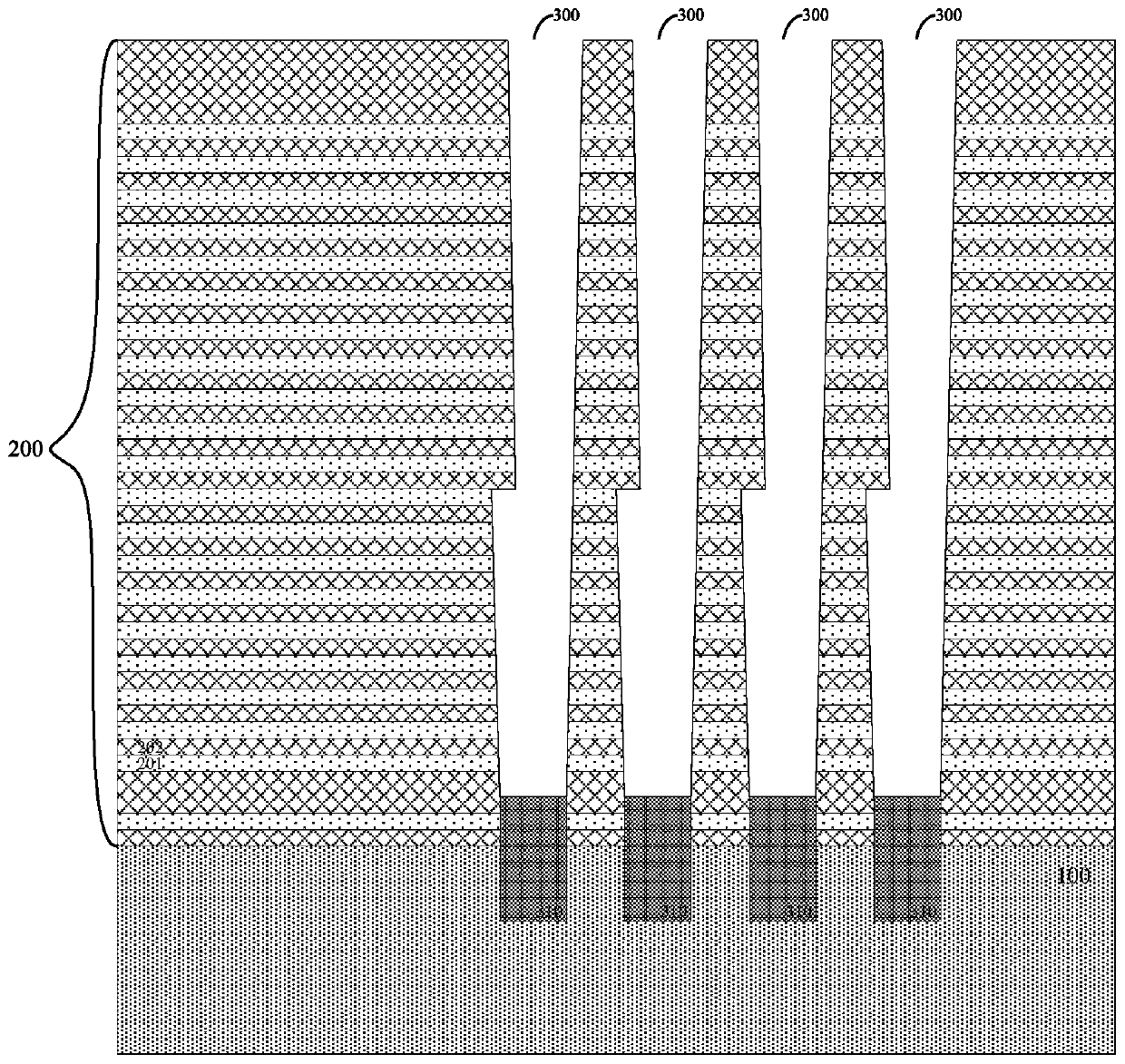
ActiveCN110544695AThe appearance is as expectedIncreased Efficiency of Etch StepsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringProtection layer
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a three-dimensional memory. The method specifically comprises the steps: providing a substrate, wherein a channel through hole penetrating through a whole stacking layer in the height direction of the substrate is formed in the stacking layer on the substrate, a silicon epitaxial structure is formed at the bottom of the channel through hole, and a first oxide layer, a nitride layer, a second oxide layer and a protective layer are sequentially formed on the side wall of the channel through hole and the upper surface of the silicon epitaxial structure; etching the protective layer on the upper surface of the silicon epitaxial structure to form a notch exposing the second oxide layer; etching the second oxide layer through the gap by adopting afirst wet process; etching the nitride layer by adopting a second wet process; and etching the first oxide layer by using a third wet process to expose the silicon epitaxial structure, wherein the first wet process and the third wet process employ the same corrosive agent, which is different from the corrosive agent used in the second wet process. According to the manufacturing method provided bythe invention, the channel through hole bottom structure which does not influence surrounding devices can be formed so as to ensure good electrical characteristic performance of the devices.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
Pvd aln film with oxygen doping for a low etch rate hardmask film
ActiveUS20130296158A1Smoother featureEtching precisionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEtching rateCrystallite
The present invention generally relates to a doped aluminum nitride hardmask and a method of making a doped aluminum nitride hardmask. By adding a small amount of dopant, such as oxygen, when forming the aluminum nitride hardmask, the wet etch rate of the hardmask can be significantly reduced. Additionally, due to the presence of the dopant, the grain size of the hardmask is reduced compared to a non-doped aluminum nitride hardmask. The reduced grain size leads to smoother features in the hardmask which leads to more precise etching of the underlying layer when utilizing the hardmask.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Etching method
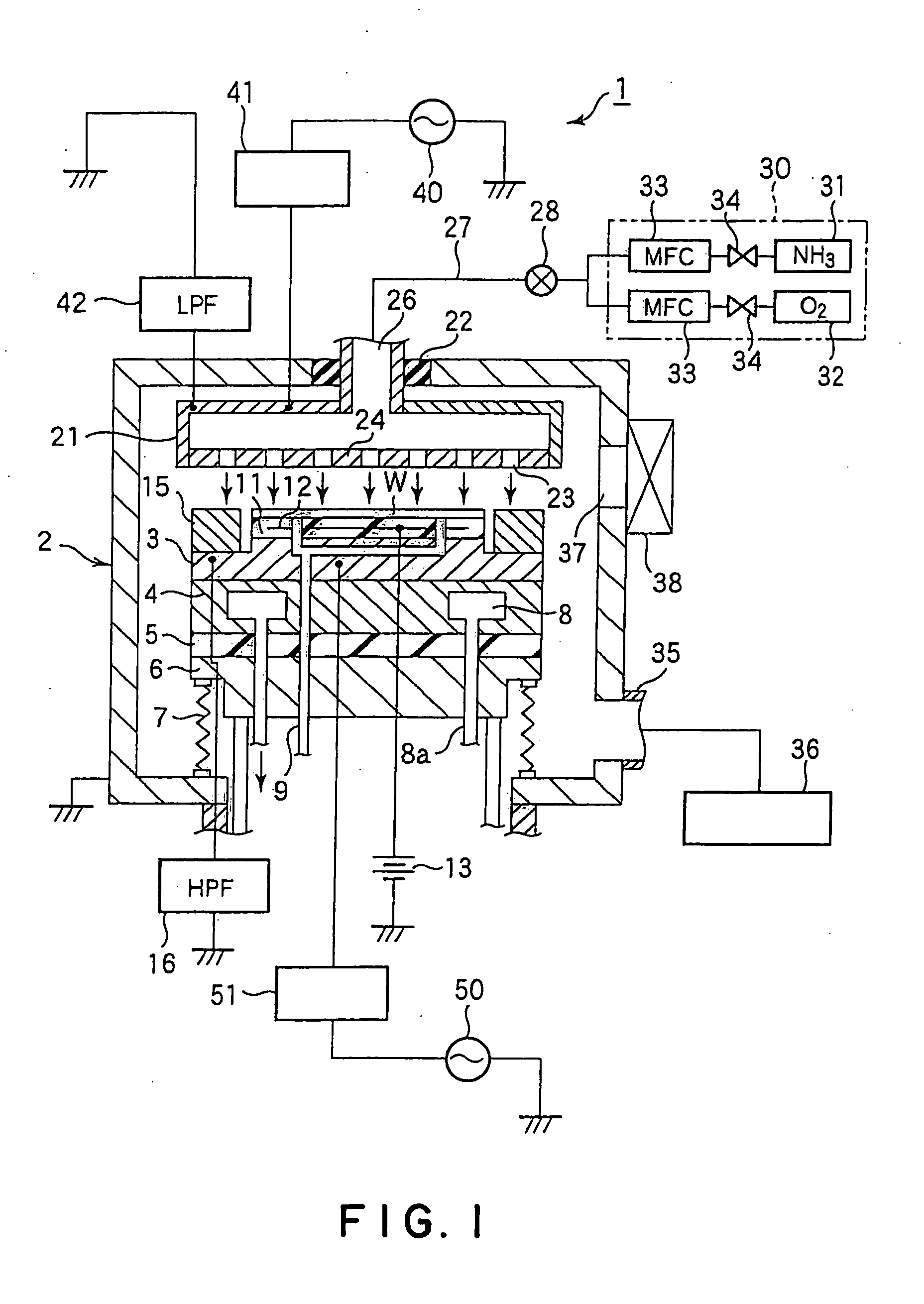
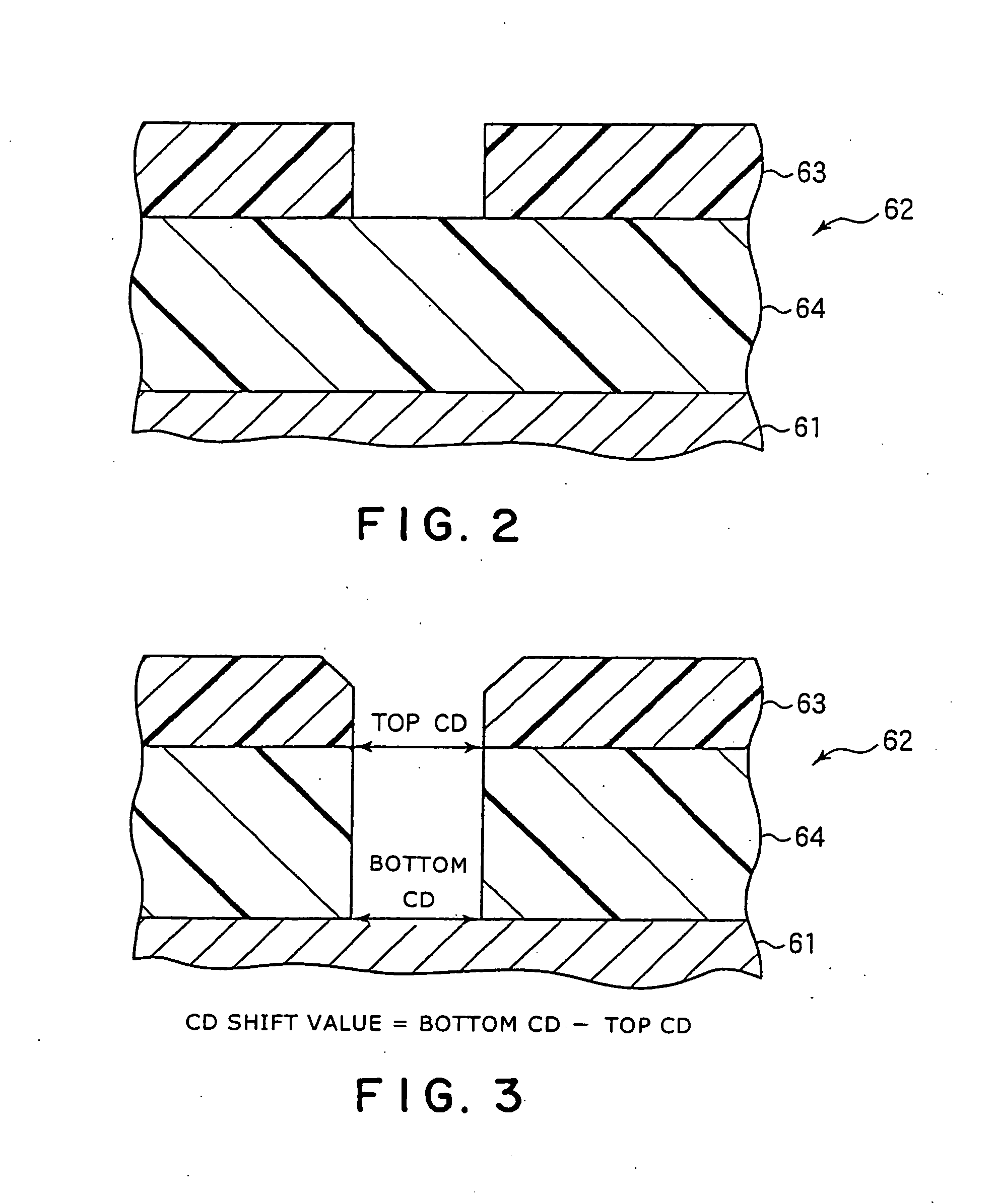
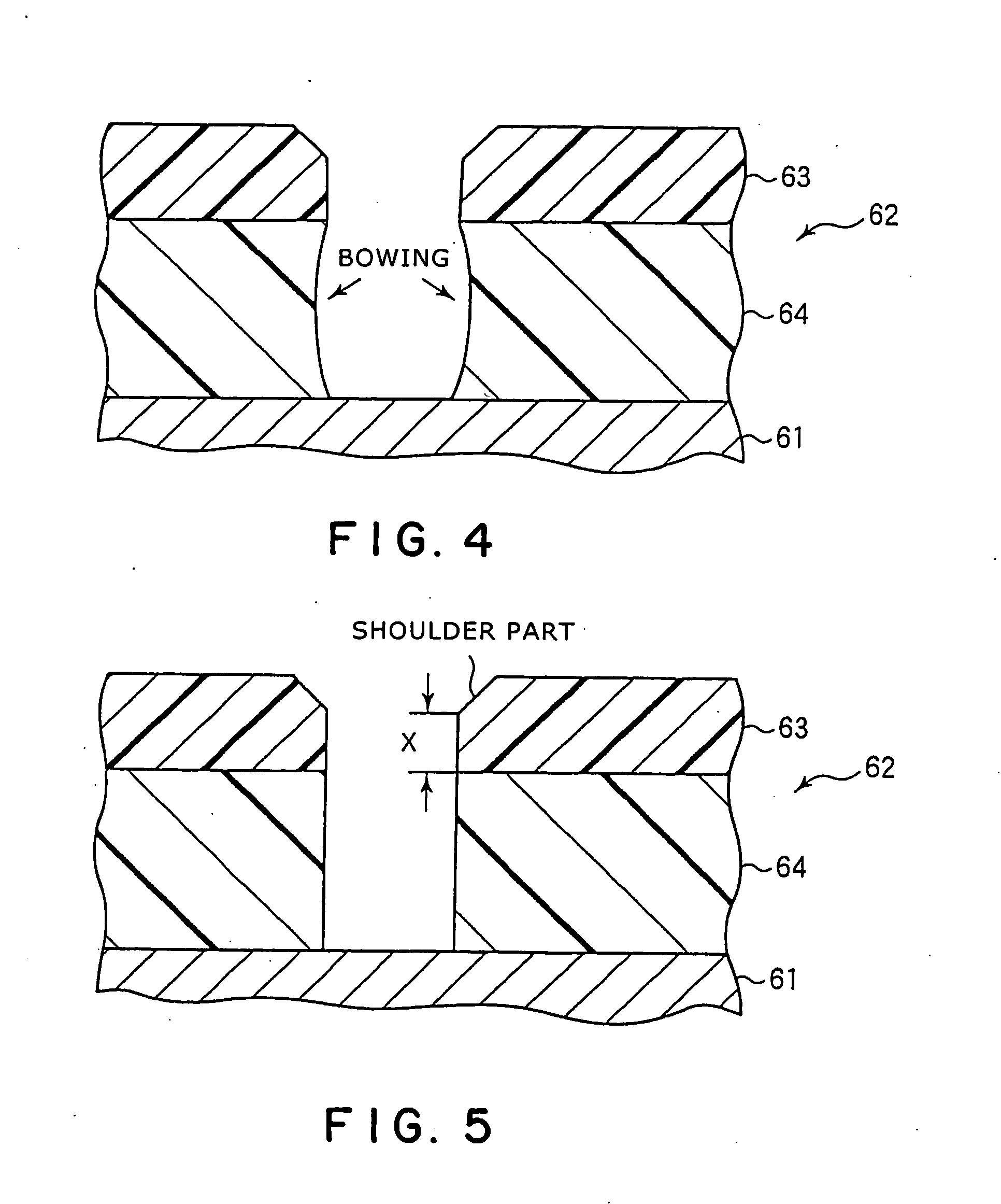
InactiveUS20060118517A1Etching precisionSatisfactory selectivityVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsEtchingSurface layer
The present invention is a method of etching a lower layer film (64) of an organic material formed on a surface layer (61) of a substrate, using an upper layer film (63) of an Si-containing organic material as a mask. A mixed gas containing an NH3 gas and an O2 gas is supplied into the processing vessel as an etching gas, so as to perform etching by a plasma of the etching gas. When the etching gas is supplied into the processing vessel, a CD shift value of etching can be controlled by adjusting a flow ratio of O2 gas to the NH3 gas. Specifically, a satisfactory CD shift value can be obtained when the flow ratio is from 0.5 to 20%, and preferably, 5 to 10%.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Manufacture method for flip-chip and bare chip assembly
InactiveCN107204294AImprove packaging yieldImprove package reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTangential stressCopper
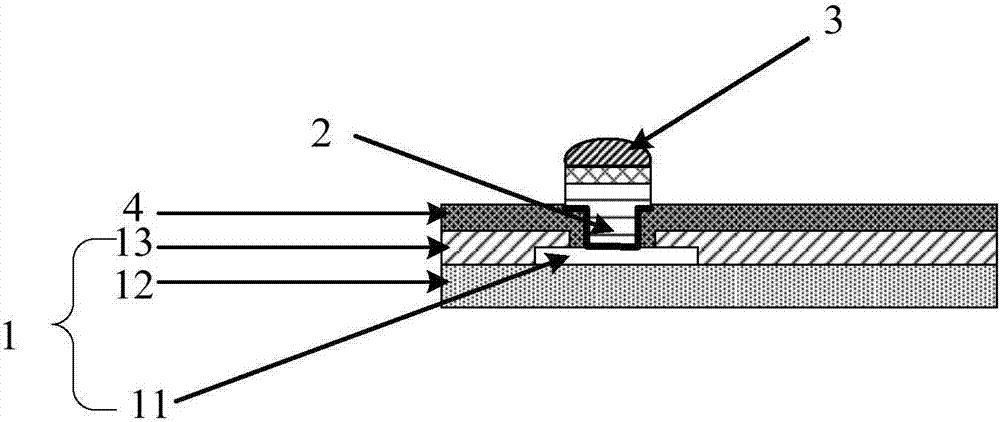
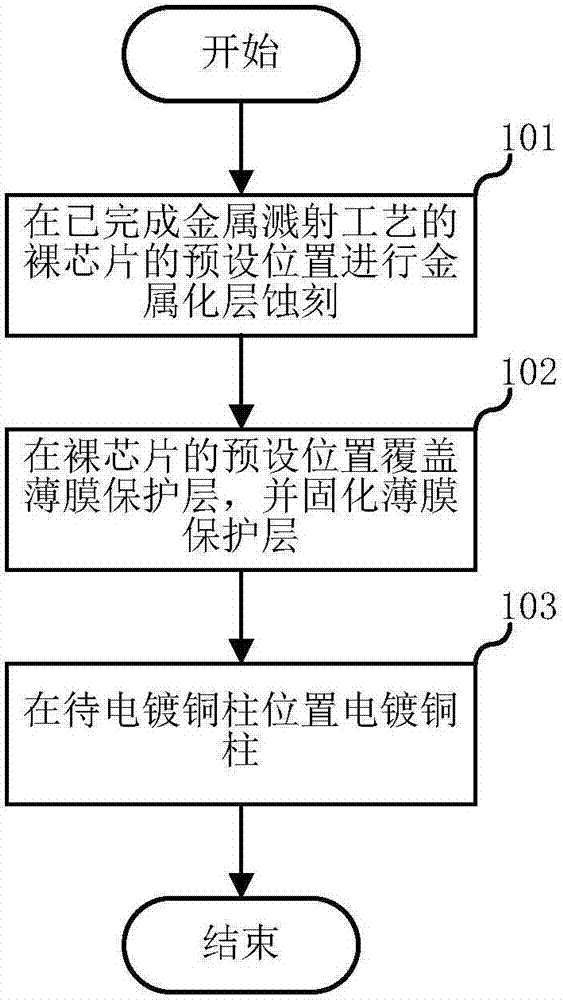
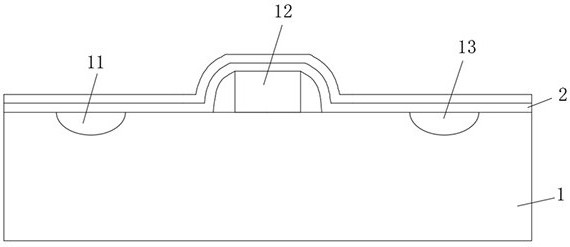
The invention relates to the semiconductor field and discloses a manufacture method for a flip-chip and a bare chip assembly. The manufacture method comprises steps of performing metallization layer etching on a preset position of a bare chip on which metal spurting technology is finished, wherein the preset position is an area beyond a position of a copper column to be electroplated on the bare chip, covering a film protection layer in the preset position of the bare chip and hardening the film protection layer, and electroplating the copper column in the position of the copper column to be electroplated. Through the arrangement, the manufacture method and the bare chip assembly add an extra protection layer on the bare chip in the prior art, which effectively alleviates a potential damage on the copper column which is caused by a tangential stress around the copper column, enhances protection on the flip-chip copper column protection and improves packaging yield rate and reliability.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH +1
Preparation method of semiconductor structure
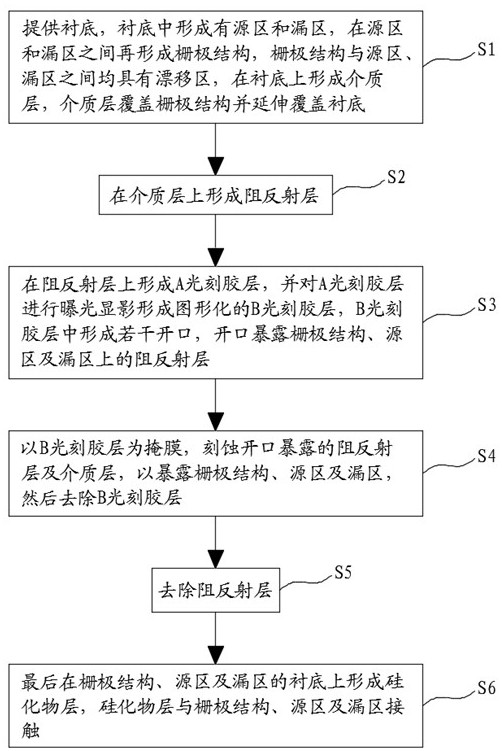
ActiveCN113284808AAvoid the problem of defects or even being strippedEtching precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureEngineering
The invention relates to the field of preparation of semiconductor elements, and particularly discloses a preparation method of a semiconductor structure, which comprises the following steps: firstly, forming a dielectric layer on a substrate, forming a reflection-resistant layer on the dielectric layer, forming an A photoresist layer on the reflection-resistant layer, and exposing and developing the A photoresist layer. Under the effect of thereflection-resistant layer, the arc-shaped part of the dielectric layer at the gate structure does not reflect light, so that the problem that the patterned photoresist layer generates defects and is even stripped off is avoided, then the opening is etched, the reflection-resistant layer is removed, and finally the silicide layer is formed. the processing device is adopted to remove the anti-reflection layer, the processing device comprises a fixing shaft, a clamping mechanism, a loading tray and an adjusting mechanism, the clamping mechanism is used for clamping the loading tray, elements are loaded in the loading tray, and the adjusting mechanism is used for adjusting the clamping mechanism to intermittently and sequentially enter and exit from a dissolving tank, a flushing tank and a drying mechanism. The reflection-resistant layer layer on the element is dissolved, washed and dried, and automatic machining is achieved.
Owner:江苏茂硕新材料科技有限公司
Test method for semiconductor array device
ActiveCN106646179AAchieve electrical characteristicsAvoid damageElectrical measurement instrument detailsIndividual semiconductor device testingSemiconductorSemiconductor device
The invention relates to a test method for a semiconductor array device. The test method comprises: a to-be-tested semiconductor array device is processed and a tungsten plug layer is exposed; etching is carried out above a gate conducting layer of the to-be-tested semiconductor array device at a preset interval until the gate conducting layer is exposed; the etched parts are filled with conducting media to form attached contact points; and nano probes that should be in contact with gate contact points are in contact with the attached contact points and electrical characteristic testing of a semiconductor unit within a preset attached contact range is carried out. The method has the following beneficial effects: for semiconductor units, corresponding to drain contact points and source contact points that are not arranged at a testing machine bench with gate contact points simultaneously, attached contact points in conduction with gates are added near the semiconductor units, so that the attached contact points, the drain contact points and the source contact points corresponding to the semiconductor units can be arranged at the testing machine bench simultaneously, so that the electrical characteristic of the semiconductor unit can be tested by using the nano probe testing instrument.
Owner:WUHAN XINXIN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com