Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
216 results about "Recombineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Recombineering (recombination-mediated genetic engineering) is a genetic and molecular biology technique based on homologous recombination systems, as opposed to the older/more common method of using restriction enzymes and ligases to combine DNA sequences in a specified order. Recombineering is widely used for bacterial genetics, in the generation of target vectors for making a conditional mouse knockout, and for modifying DNA of any source often contained on a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), among other applications.
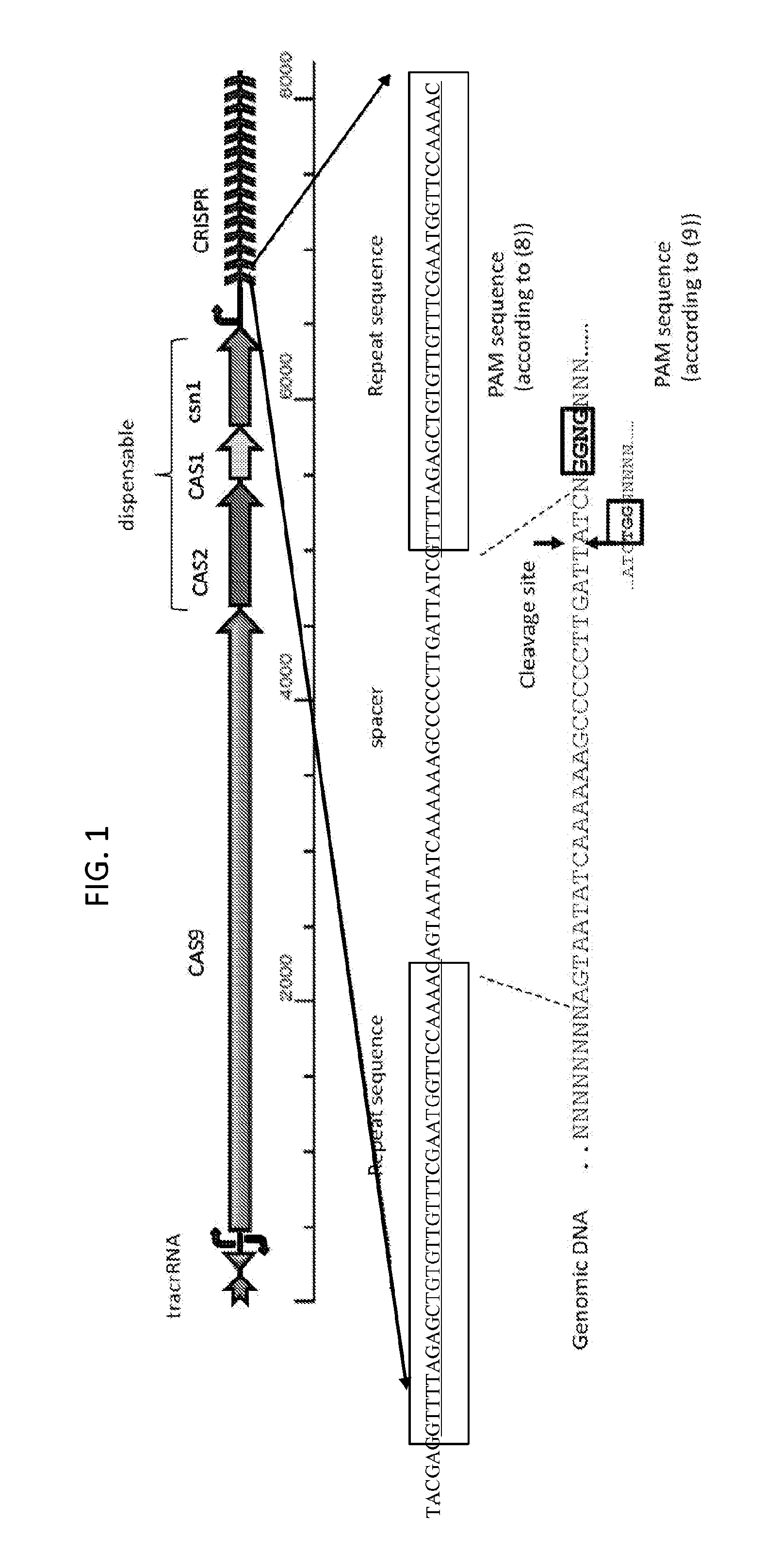
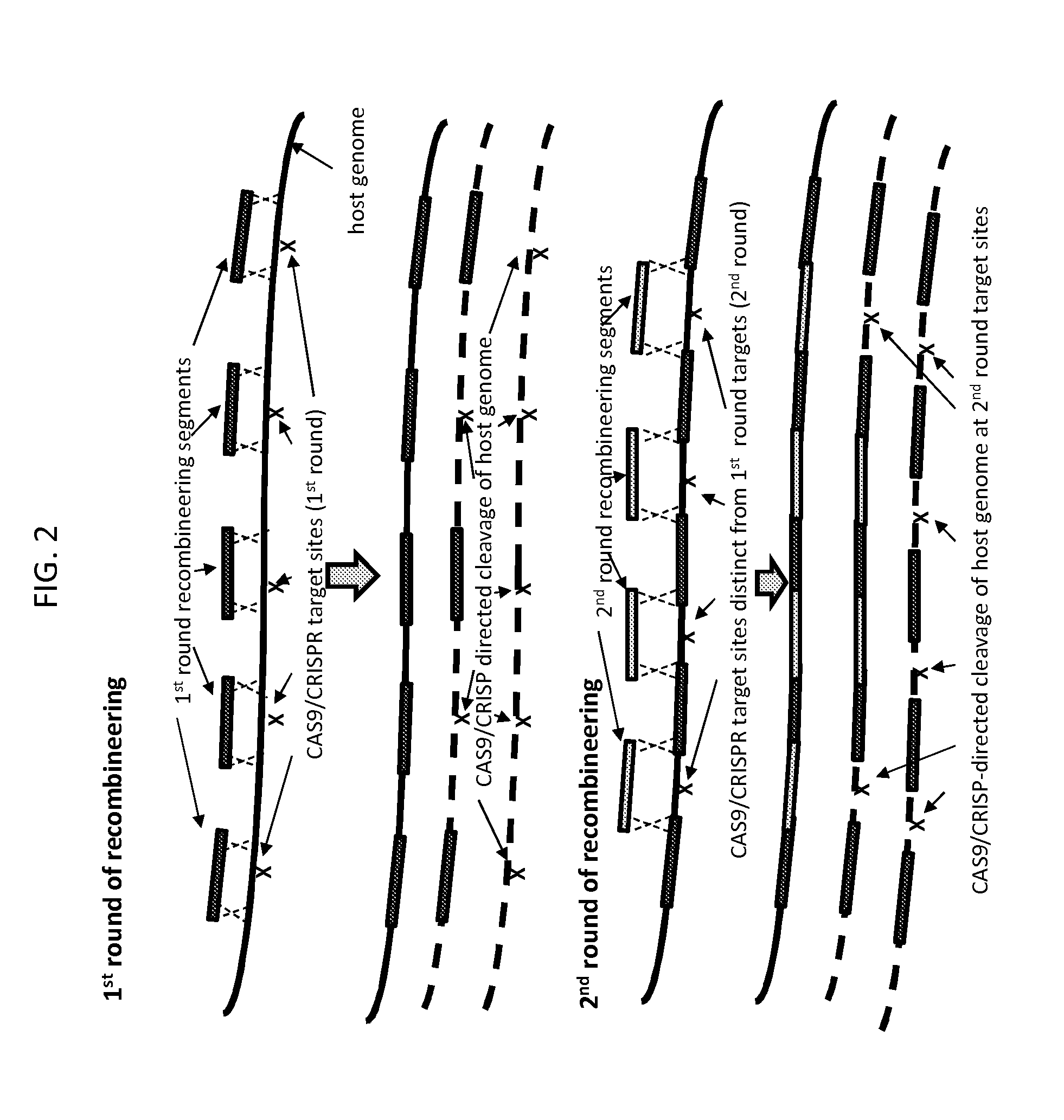
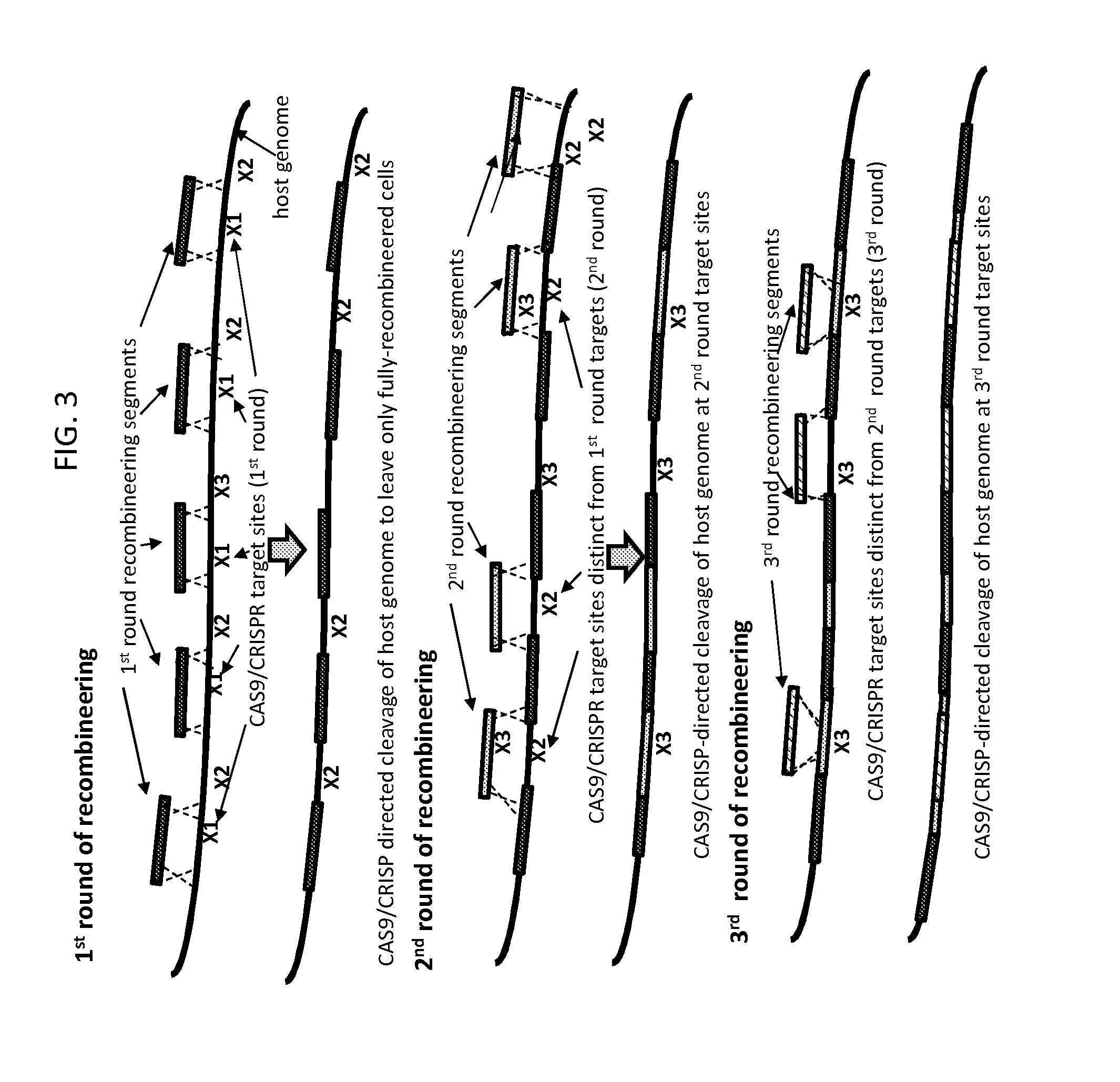
Methods of in vivo engineering of large sequences using multiple crispr/cas selections of recombineering events
ActiveUS20160024529A1Eliminate generationMinimize the numberBacteriaHydrolasesIn vivoHost cell filopodium
The present invention provides a method for making a large nucleic acid having a defined sequence in vivo. The method combines recombineering techniques with a CRISPR / Cas system to permit multiple insertions of defined sequences into a target nucleic acid at one time, double stranded cleavage of target nucleic acids in which the defined sequences were not successfully inserted, and selection of successful recombinant cells. The method further includes repeating the process one or more times, using a successful recombinant from one round as the host cell for the next round.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Recombinant expression of proteins from secretory cell lines
InactiveUS6194176B1Increase productionIncrease secretionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousHigh level expression
Owner:BETAGENE +1
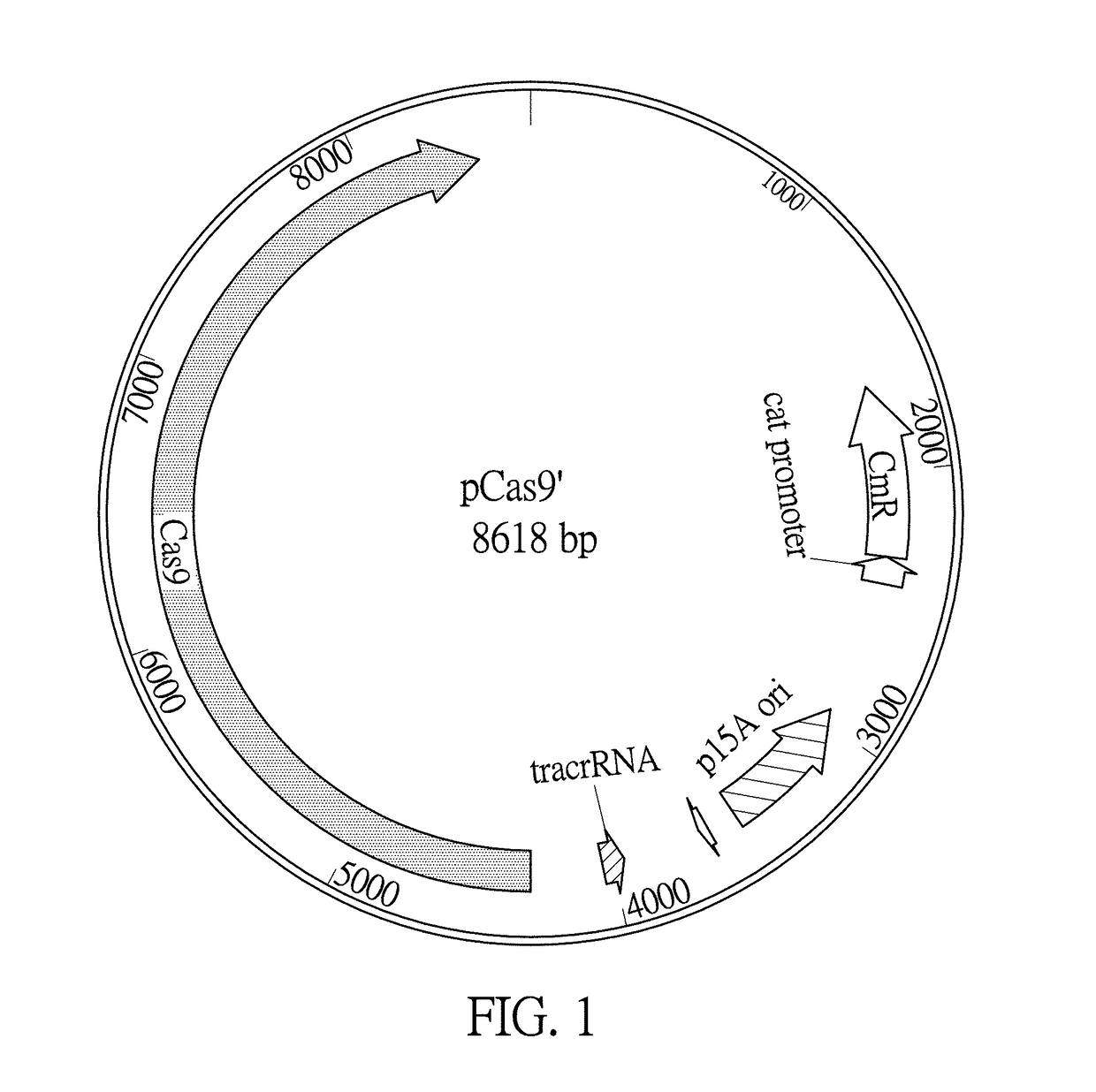
Cas9 plasmid, genome editing system and method of escherichia coli
ActiveUS20170226522A1Improve efficiencyImprove fidelityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliGenome editing
A Cas9 expression plasmid, a genome editing system and a genome editing method for Escherichia coli are provided. The Cas9 expression plasmid includes a tracrRNA sequence, a Cas9 gene and a chloramphenicol resistance gene (CmR). The Cas9 expression plasmid is applied to CRISPR / Cas-coulped λ-red recombineering system for editing genomes of E. coli with high efficiency.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Lactococcus promoters and uses thereof
ActiveUS8759088B2Increase the number ofHigh expressionBiocideBacteriaHeterologousFusion Protein Expression
The invention is in the field of molecular biology, and relates to recombinant engineering and protein expression. More in particular, the invention relates to nucleic acids for recombinant expression of proteins comprising sequences derived from Lactococcus and useful as promoters. The invention further relates to vectors comprising the nucleic acids and host cells transformed therewith. The invention also covers the use of host cells comprising the nucleic acids or vectors for expressing heterologous or homologous proteins; and also for delivery, especially therapeutic delivery, of the said proteins to subjects.
Owner:INTREXON ACTOBIOTICS NV
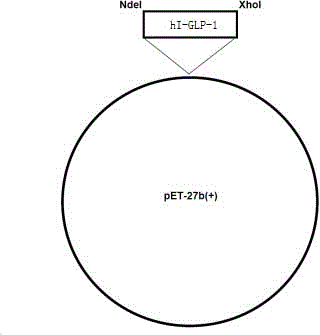
Preparation method of liraglutide intermediate polypeptide
The invention belongs to the technical field of polypeptide preparation and relates to a preparation method of a liraglutide intermediate GLP-1(7-37). The preparation method utilizes a genetic recombination technology. Compared with chemical synthesis, the preparation method reduces impurities and improves purity and a yield. The preparation method comprises the following steps of introducing plasmids with hI-GLP-1(7-37) gene sequences into cells of escherichia coli by a gene engineering method to construct recombinant engineering bacteria, carrying out fermentation induction to obtain a hI-GLP-1(7-37) expression fusion protein, and carrying out renaturation, digestion conversion and separation purification to obtain GLP-1(7-37).
Owner:JIANGSU WANBANG BIOPHARMLS +1
High-expression semeglutide precursor recombinant engineering bacterium and construction method thereof
ActiveCN113502296AHigh industrial application valueSuitable for high density fermentationBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliRestriction Enzyme Cut Site
The invention provides recombinant escherichia coli capable of efficiently expressing a semeglutide precursor. Two different leader peptides and enterokinase restriction enzyme cutting sites are designed and added at the front end of a semeglutide precursor to construct a fusion polypeptide structure, a coding gene of the optimized polypeptide structure is inserted into a pET-30a(+) expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector, the recombinant expression vector is transformed into escherichia coli BL21(DE3), and the recombinant engineering bacterium capable of stably and highly expressing the simeglutide precursor is obtained. The recombinant engineering bacterium disclosed by the invention not only can stably and highly express the semeglutide precursor, but also is particularly suitable for a high-density fermentation method, and the expression quantity of a target protein can be further improved.
Owner:BEIJING HUIZHIHENG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Escherichia coli strain for recombined engineering
InactiveCN101633901AWill not harmNo distractionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
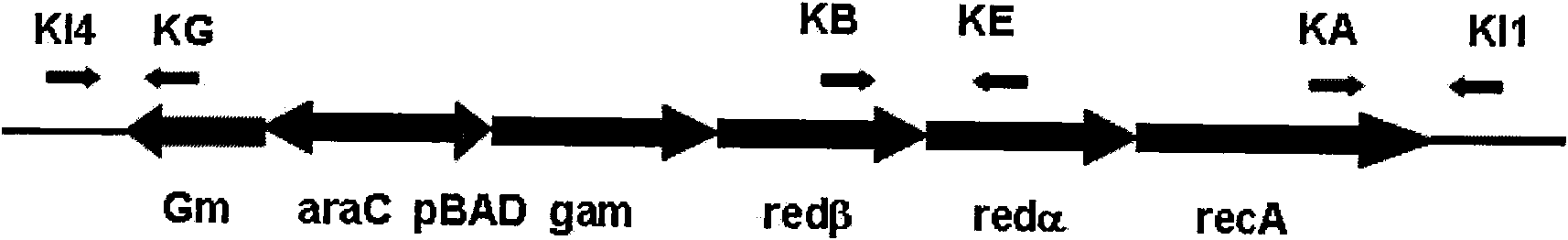
The invention relates to escherichia coli CGMCC NO.3192 for recombined engineering and a variant thereof. The strain is obtained by integrating gene segments subjected to the recombined engineering, i.e. a regulatory gene araC of the Arabinose ara operon from the escherichia coli, a promoter pBAD of the Arabinose ara operon from the escherichia coli, recombined enzyme genes red alpha, red alpha beta and gam from a gamma bacteriophage, a gene recA and gentamicin resistance gene (Gm) from the escherichia coli, into an endA gene area of a gene group of the escherichia coli DH10B, wherein red alpha, red alpha beta, gam and recA are driven by pBAD induced by arabinose. The recombined enzyme can catalyze homologous recombination among DNA short segments to finish the recombined engineering. The length of the DNA segment is about 50 base pairs. The invention has convenient operation of carrying out the recombined engineering by the strain and high recombined efficiency, thereby becoming the universal strain for the recombined engineering.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Glutamate decarboxylase mutant and application thereof in preparation of gamma-aminobutyric acid
ActiveCN111635898AImprove catalytic performanceIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseWild type
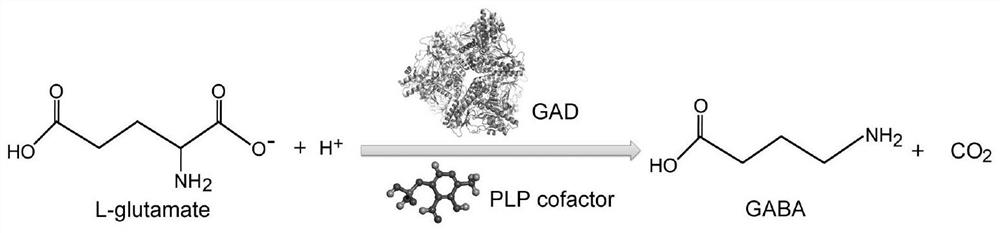
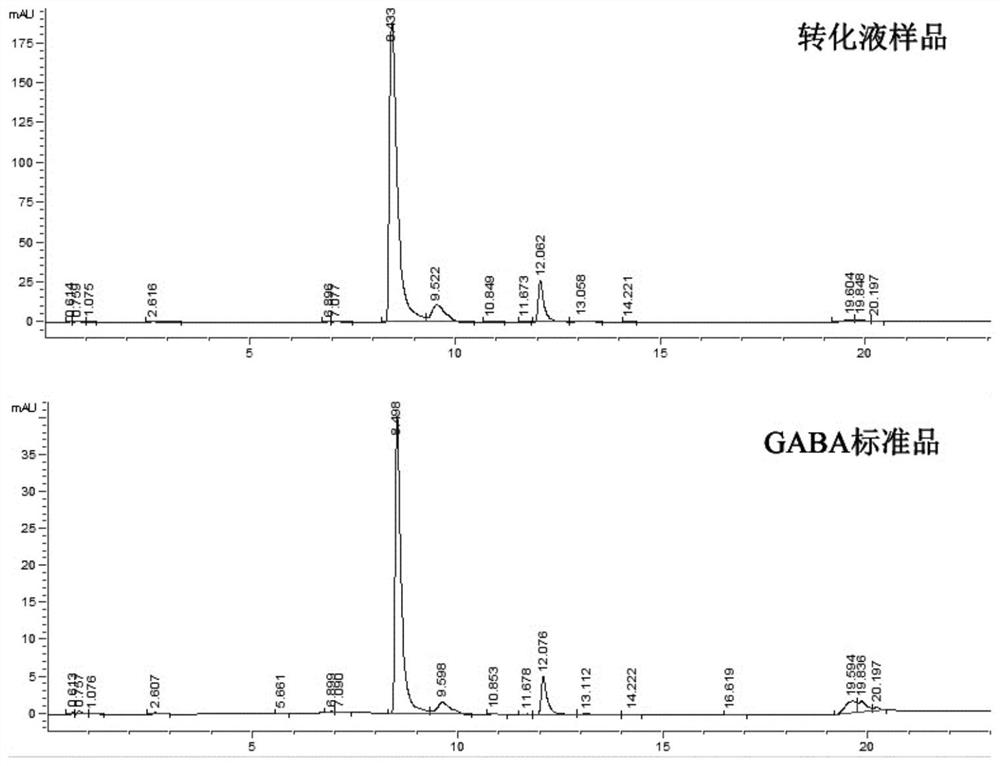
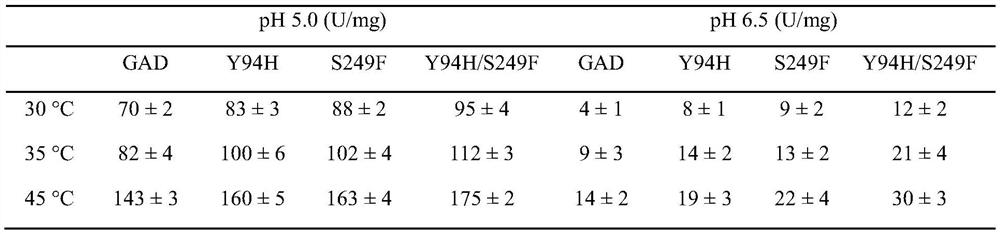
The invention discloses a glutamate decarboxylase mutant with improved enzyme activity and application thereof. The glutamate decarboxylase coding gene from bacillus megatherium is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis, and the catalytic performance of the obtained mutant is obviously improved compared with that of a wild type mutant. A recombinant engineering strain is constructed on the basis of the mutant, gamma-aminobutyric acid is prepared by taking a large amount of fermentation product L-glutamic acid as a substrate through a whole-cell catalysis method, the maximum yield of gamma-aminobutyric acid reaches 625.6 g / L, the molar conversion rate in a catalytic system is close to 100%, and no by-product is produced. The glutamate decarboxylase mutant disclosed by the invention has a very wide application prospect in efficient production and preparation of gamma-aminobutyric acid.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Carbonyl reductase expressed recombination engineering bacterium and application thereof
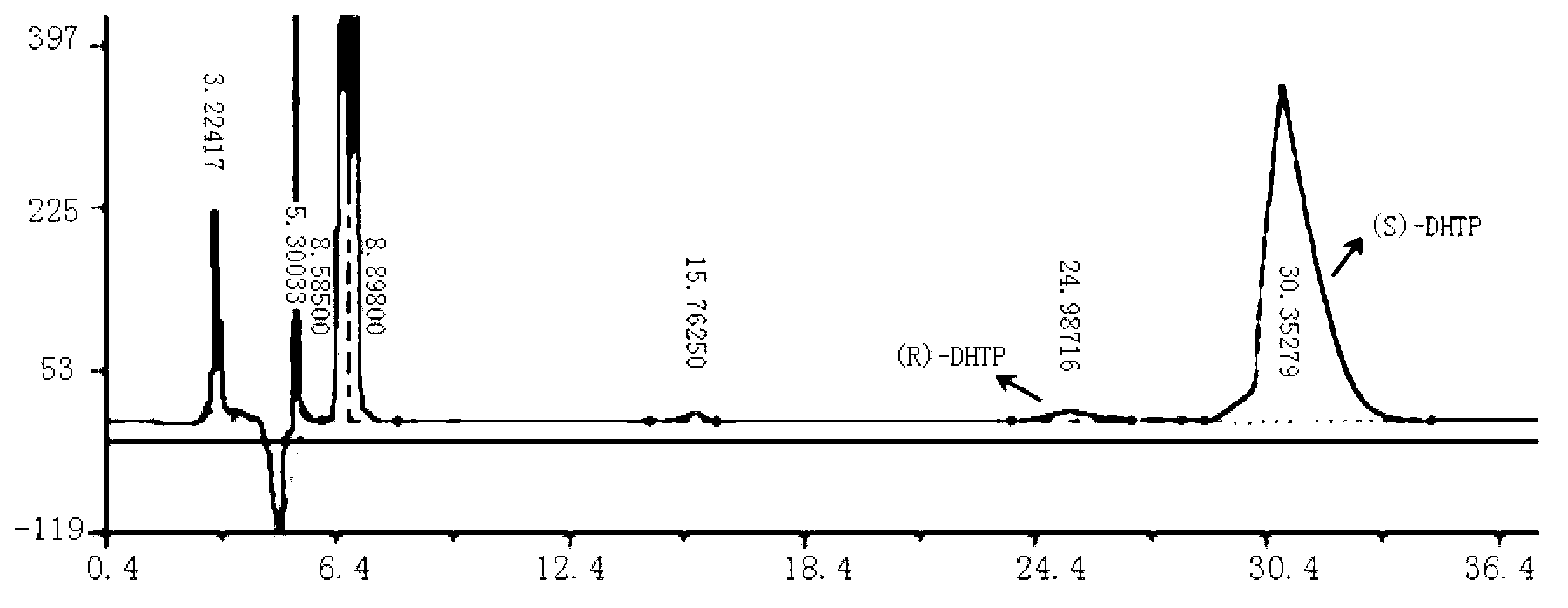
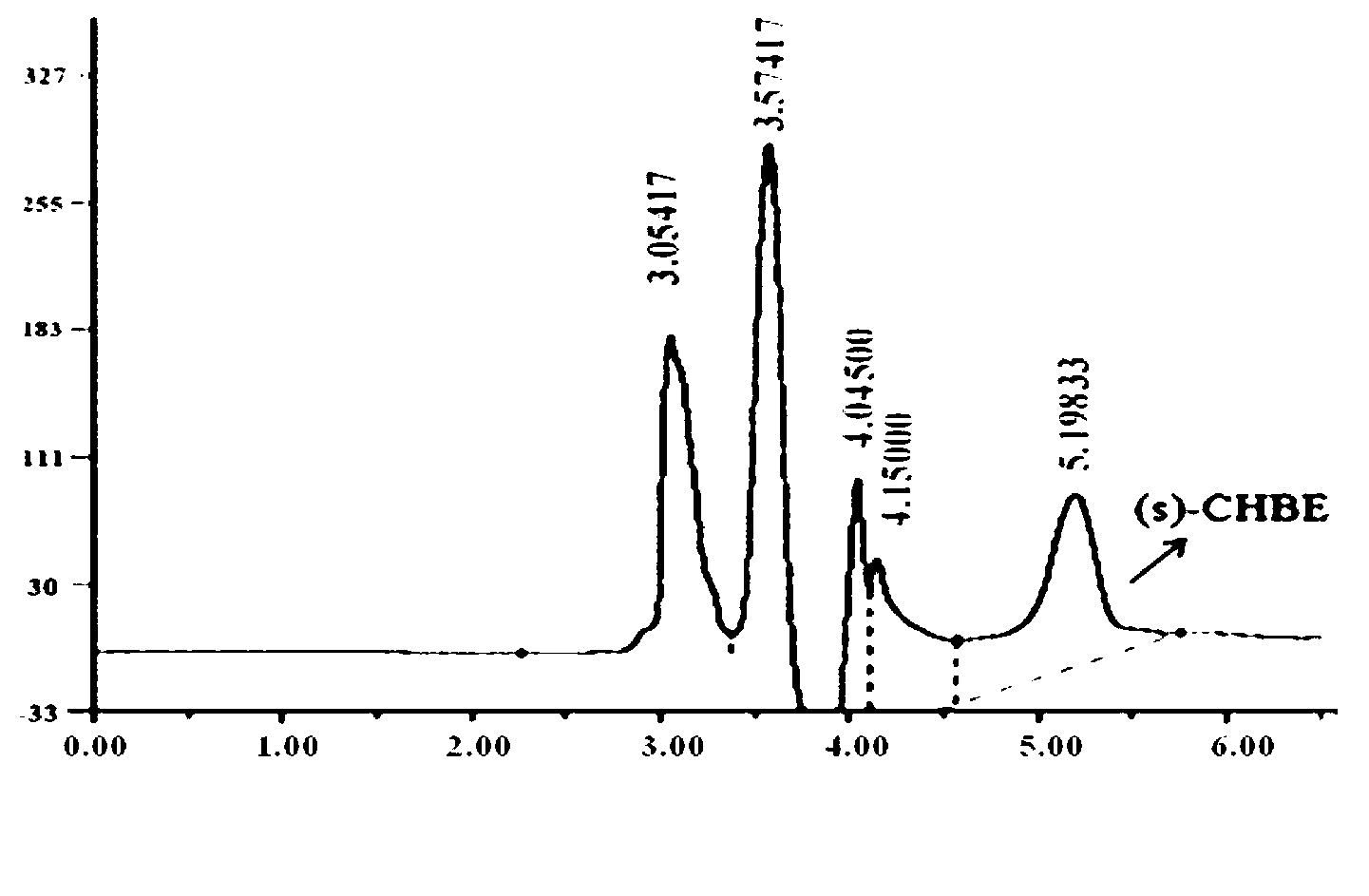
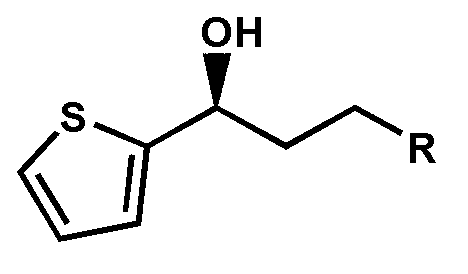
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase expressed recombination engineering bacterium and application thereof. The engineering bacterium comprises a host cell and a recombinant vector transferred into the host cell, wherein the recombinant vector consists of an original vector and a target gene connected into the original vector, the host cell is Escherichiacoli Rosetta (DE3), the target gene is a carbonyl reductase gene, and the base sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. According to the recombination engineering bacterium, the expression level of a carbonyl reductase is high, bacterial cells which are prepared through induced culture are used for converting N,N-dimethyl-3-oxy-3-(2-thienyl)-l-propylamine hydrochloride into (S)-N,N-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl)-l-propylamine or converting 4-chloroethyl acetoacetate into (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyethyl butyrate, and the two products are higher in both optical purity and conversion rate.
Owner:NINGBO MENOVO PHARMA +1
Gene for coding glutamine dipeptide biosynthetic enzyme and application thereof
ActiveCN106754985AImprove conversion efficiencyResolve separabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDipeptide
The invention discloses a gene for coding a glutamine dipeptide biosynthetic enzyme and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses an amino acid sequence coded by the gene, and provides a recombinant vector containing the gene, recombinant escherichia coli, and a method for performing biotransformation to synthesize the glutamine dipeptide by using the gene. The gene and the application of a recombinant bacterial strain of the gene have the advantages of high mol conversion rate, high reaction speed, easy separation, low cost and the like. In the synthesis method, the maximum mol conversion rate of the glutamine dipeptide can reach 83.3 percent; meanwhile, the thalli can be applied to the catalytic synthesis of the glutamine dipeptide again after the circulation recovery; in addition, the catalytic activity is stable. Therefore high market competitive power and application values are realized; a foundation is laid for the industrial production of the glutamine dipeptide.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
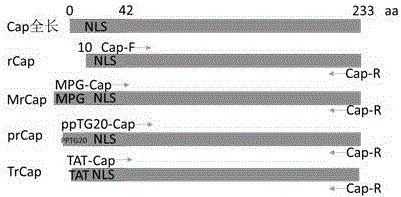
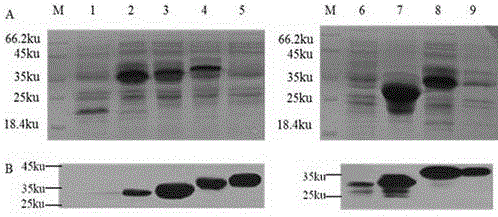
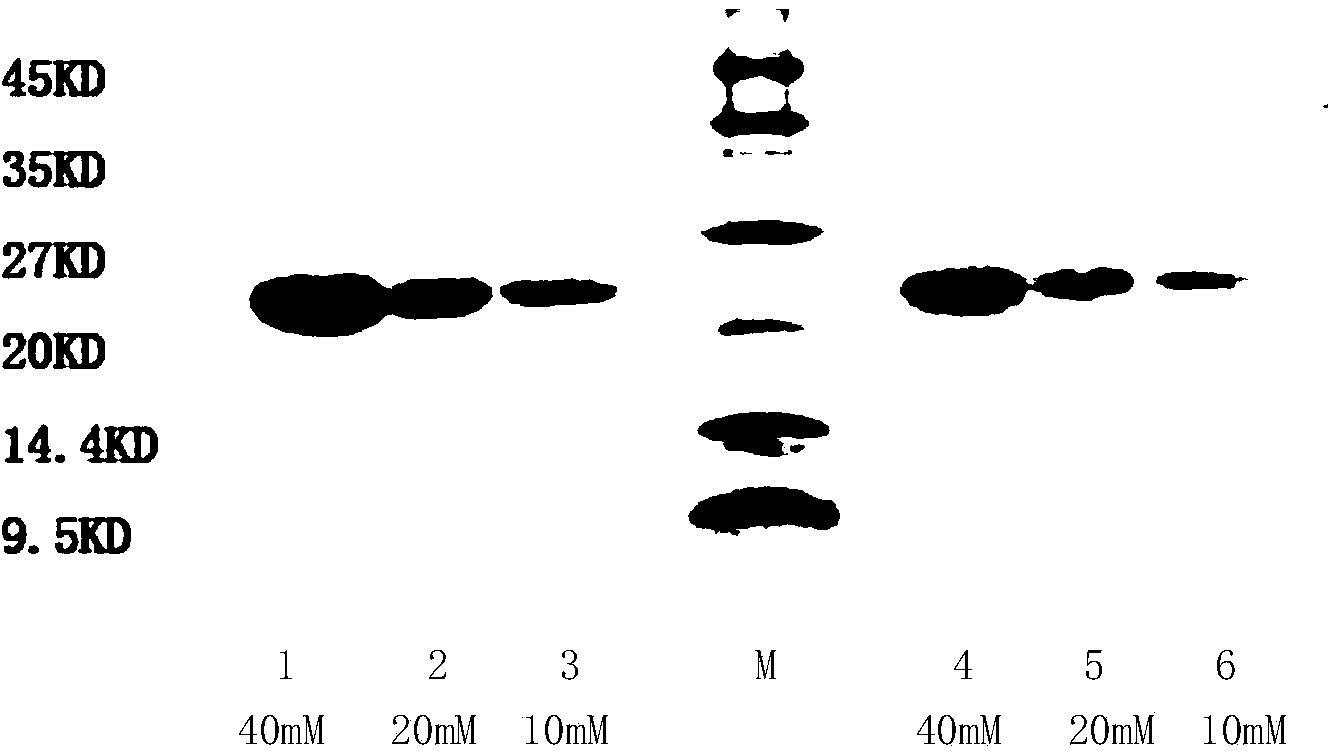
Gene encoding recombinant porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein and application thereof
The present invention provides a gene encoding a recombinant porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein and application thereof. The present invention aims to obtain a soluble recombinant PCV2 Cap protein, and adopts a PCR method for fusion of MPG and NLS partially deleted Cap protein N-terminal gene to construct a new gene; and then the new gene is cloned into an E. coli expression vector pET28a to obtain a recombinant plasmid; the recombinant plasmid is transformed into E. coli BL21 to obtain recombinant engineering bacteria; the recombinant engineering bacteria is subjected to induced expression by IPTG to obtain the soluble recombinant PCV2 Cap protein. SDS-PAGE and Western-blot identification shows that most of the recombinant protein MrCap is present in the bacterial lysis supernatant and is soluble; and the recombinant protein MrCap has high immunogenicity and immunoreactivity, and lays foundation for the development of a PCV2 antibody detection kit and subunit vaccines.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Recombinant engineering bacteria for efficiently expressing human growth hormone, construction method and application
ActiveCN103882015AEfficient secretionGood secretory expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPeptideToxin
The invention discloses recombinant engineering bacteria for efficiently expressing human growth hormone (hGH), a construction method and an application and provides an escherichia coli operon for expressing recombinant hGH, an expression plasmid containing an operon sequence and engineering bacteria QJSW-SZ01 (CGMCC No:7258) used for secretory expression of the recombinant hGH and obtained by transformation of the expression plasmid containing the operon. The recombinant engineering bacteria are characterized in that a coding sequence of a signal peptide of an escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin is changed, and rare codons of escherichia coli in the coding sequence are mutated so as to avoid formation of a secondary structure; meanwhile, an amino acid is altered on the terminal of the coding sequence so that the coding sequence is more beneficial to guidance of secretory expression of hGH; the signal peptide, an escherichia coli alkaline phosphatsae promoter (phoA promoter) and an escherichia coli T7 terminator are combined to be used as an expression control element so that the recombinant hGH is efficiently secretory-expressed in the escherichia coli in a soluble form. The recombinant engineering bacteria lay the foundation of finally developing a low-cost hGH pharmaceutical product.
Owner:吉林省奇健生物技术有限公司
Fusion protein of tumor blood vessel targeted polypeptide and tissue factor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102153653AImprove anti-tumor effectGrowth inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsFermentationBlood vessel
The invention provides the expression and the purification of a recombinant fusion protein, particularly a fusion protein of the tumor blood vessel targeted polypeptide and tissue factor and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the fusion protein of the tumor blood vessel targeted polypeptide and tissue factor comprises the following steps: designing primers, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) to amplify an recombinant gene of the fusion protein EG3287-tTF, guiding the recombinant gene of the fusion protein EG3287-tTF into a carrier, guiding a recombinant carrier into a host cell, constructing a recombinant engineering bacteria for expressing the fusion protein EG3287-tTF, fermenting to culture, and separating and purifying fermentation liquor to obtain the fusion protein of the tumor blood vessel targeted polypeptide and tissue factor. The targeted antitumor fusion protein EG3287-tTF is constructed, a novel tTF derivative with the antitumor advantage of the tTF and the targeting effect is obtained, the antitumor effect of the tTF is improved, and a foundation is laid to the development of a novel medicament for the targeted therapy of the tumor blood vessel.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for producing L-tyrosine recombinant engineering bacteria and application of recombinant engineering bacteria
InactiveCN107916245AEase of industrial productionEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention provides a method for producing L-tyrosine recombinant engineering bacteria and application of the recombinant engineering bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: taking escherichia coli SyBE-002447 as a starting strain and integrating total chemical synthesis modules Plac-aroG-tyrA-aroE and Ptrc-pps-tkt-glk respectively, so as to construct a chassis strain SyBE-22002 ofL-tyrosine; then integrally inserting a total chemical synthesis module Ptacs-hpaBC-ldh into a nupG downstream position on a chromosome, so as to obtain a strain SyBE-22011. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the problem that antibiotics and an induction agent isopropyl-beta-D-thiopyrangalactoside need to be added in a fermentation process is solved, and the L-tyrosine and tanshinolcan be efficiently produced; a downstream separation and purification process is simplified and the industrial production cost is reduced; pollution, caused by the antibiotics and the induction agent, to the environment is avoided and the economic benefits are improved.
Owner:THE FRONTIER TECH RES INST OF TIANJIN UNIV
Nitrilase mutant and application thereof in preparation of nicotinic acid
ActiveCN106148310AEfficient productionExpansion of microbial resourcesBacteriaHydrolasesWater bathsBacterial strain
The invention discloses a nitrilase mutant and application thereof in preparation of nicotinic acid. The mutant can be used for mutating phenylalanine at position 168 of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 into valine and serine at position 192 into phenylalanine. A wet cell obtained by induced expression of a recombinant bacterial strain containing an itrilase mutant encoding gene is used as an enzyme source, 3-cyanopyridine is used as a reaction substrate, and a PBS buffer with pH of 7.0 is used as a reaction medium to form a reaction system, a reaction is carried out in a 40 DEG C water bath, and the nicotinic acid is obtained after the reaction is finished.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Trichoderma biocontrol recombinant engineering bacteria for efficiently expressing chitinase coding gene and Beta-1,3-glucanase coding gene as well as application thereof
InactiveCN101724573AImprove the ability to antagonize pathogenic bacteriaBiocideFungiTrichodermaPot plant
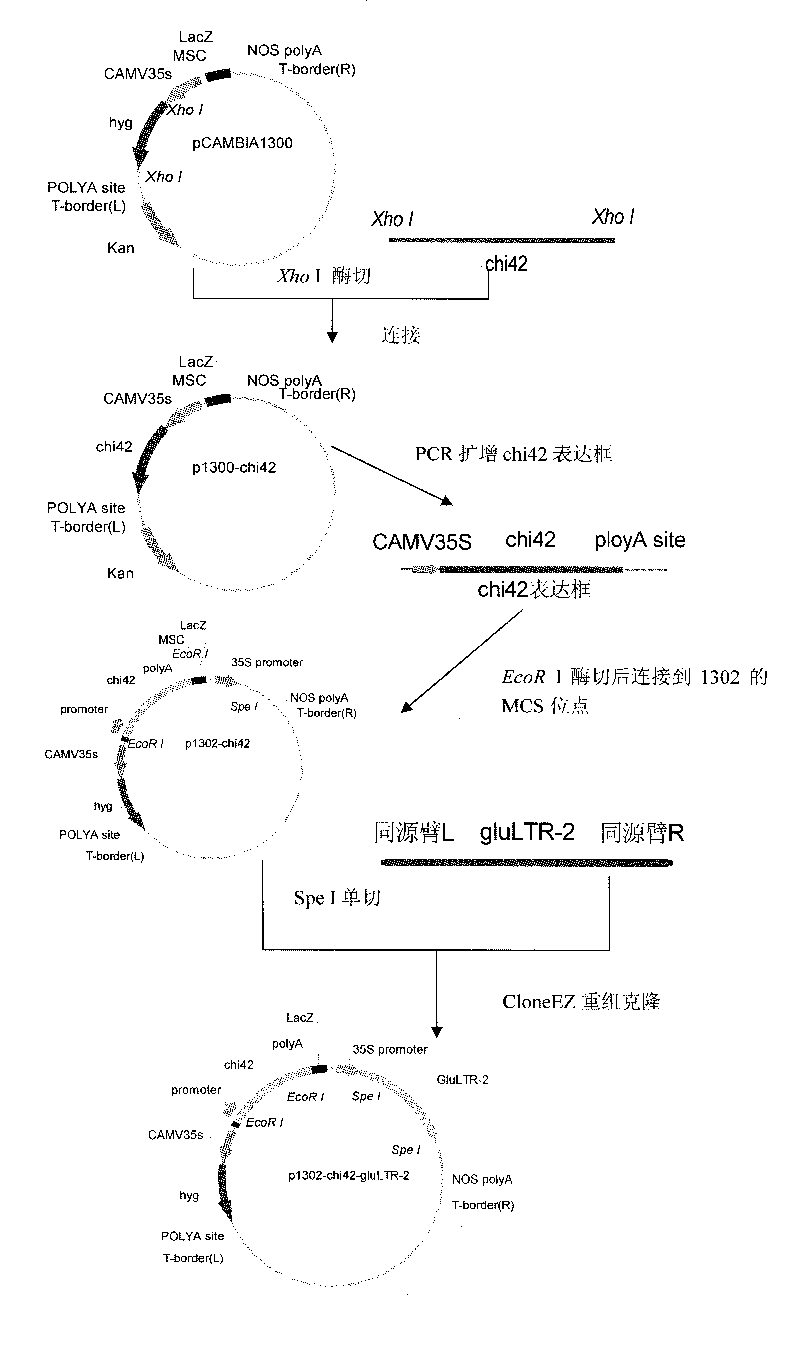
The invention discloses trichoderma biocontrol recombinant engineering bacteria for efficiently expressing chitinase and Beta-1,3-glucanase genes derived from trichoderma as well as application thereof. The recombinant bacterial strain is the recombinant engineering bacteria which are acquired by converting trichoderma viride LTR-2 with plant disease biocontrol function from a T-DNA derived carrier which is mediated by agrobacterium and contains the chitinase code gene chi42 derived from the trichoderma and the Beta-1,3-glucanase coding gene glultr-2. The recombinant bacteria can stably express the chitinase code gene chi42 and the Beta-1,3-glucanase coding gene glultr-2 in a PDA culture medium; and a pot plant experiment indicates that the recombinant engineering bacteria have more effective prevention and control effects to vegetable botrytis and wheat sharp eyespot compared with glutamicum LTR-2.
Owner:BIOTECH CENT OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Efficient gene knockout method of pseudomonas putida KT2440
The invention relates to a method for performing gene knockout on pseudomonas putida KT2440 by a recombinant engineering measure. The method comprises the following specific steps of: amplifying through an overlapped-extension polymerase chain reaction so as to obtain a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragment of which both sides are provided with target genes to be knocked, the upstream and downstream are provided with homologous genes of about 500 base pairs and the middle is provided with a kanamycin resistance gene; electrically transforming the DNA fragment into a pseudomonas putida KT2440 electro-transformation competent cell which is expressed by toluic acid induction recombinase with the final concentration of 2mM; and replacing the target genes by the kanamycin resistance gene through homologous recombination between homologous fragments of a recombinase mediate so as to directly obtain a mutant strain from which target genes are knocked. The method is simple and convenient and can become a genetic operating measure of an environmental microorganism, namely pseudomonas putida KT2440 which has important application value in the aspects of organic compound biodegradation and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High-yield engineering bacterium of nicomycin x component and its application
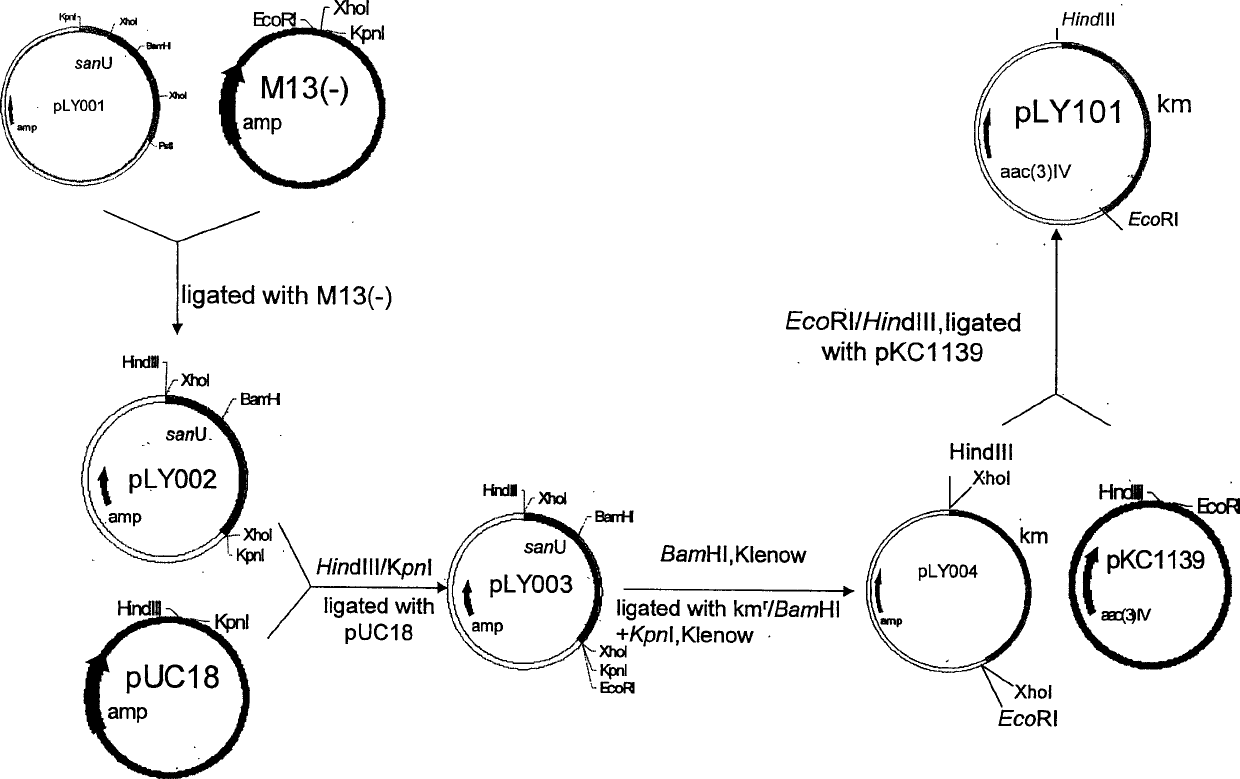
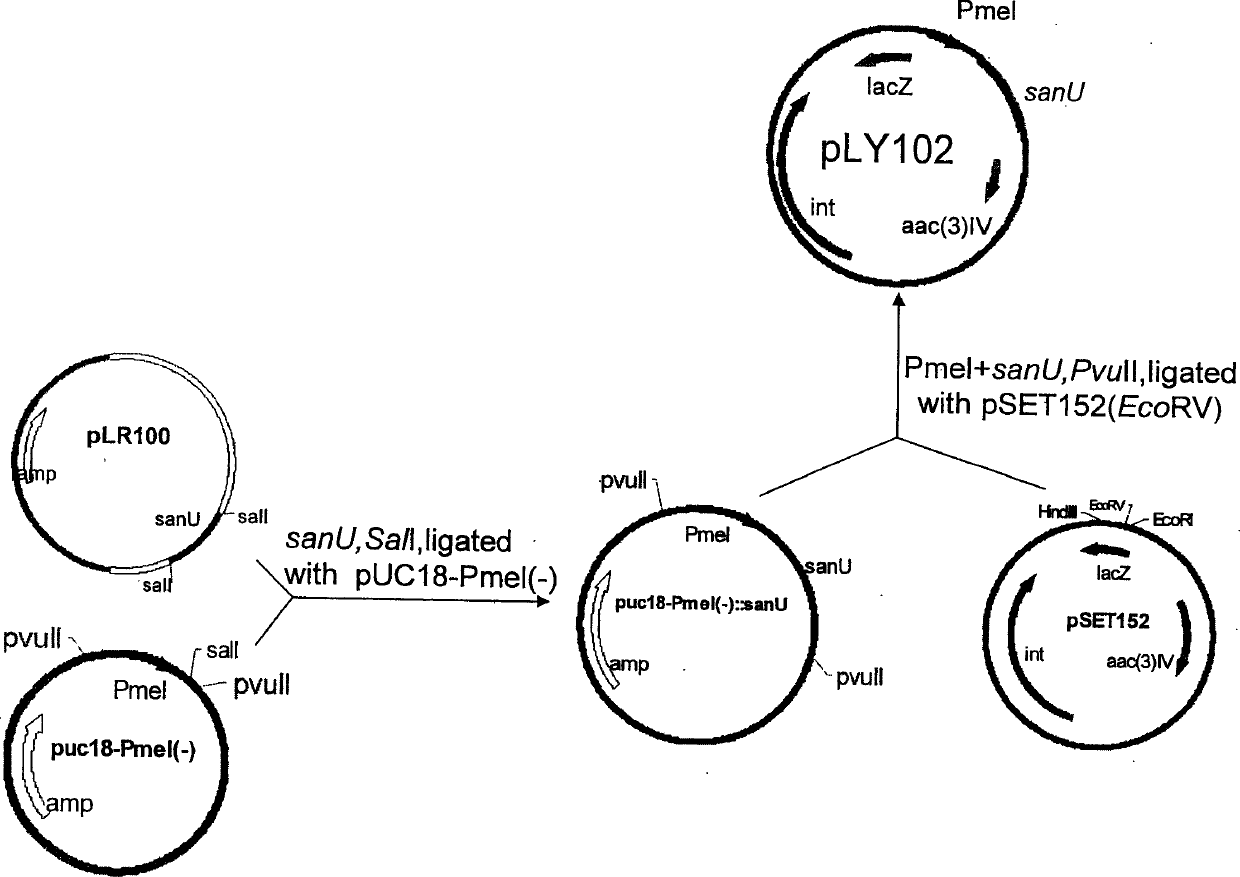
The present invention belongs to the field of antibiotic gene engineering, and is especially the process of cloning nicomycin biological synthetic gene sanU from one strain of Streptomyces ansochromogenes 7100 CGMCC 4.321; connecting the synthetic gene sanU with promoter of melanin biosynthetic structure gene, cloning onto the polycloning site of integrative single-copy plamid, transforming wild Streptomyces ansochromogenes 7100 CGMCC 4.321 protoplast to obtain nicomycin X component of the recombinant engineering bacterium in the yield 2 times higher than wild strain. The high-yield engineering bacterium may be used in preparing antiseptic medicines.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Expressing and purifying method of recombinant human-derived LECT2 protein in Pichia pastoris
ActiveCN102559739AHigh purityChemotactic activityFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionLECT2 gene
The invention discloses an expressing and purifying method of a recombinant human-derived LECT2 protein in Pichia pastoris, and the method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: inserting an artificially synthesized human-derived LECT2 gene into an extracellular expression vector pPICZalphaA to construct a recombinant expression plasmid; carrying out enzyme digestion and linearization, then carrying out electric shock, and introducing the recombinant expression plasmid to Pichia pastoris X33 to obtain a recombinant engineering gene; carrying out shake flask fermentation and methanol induction to realize secretory expression of the recombinant human-derived LECT2 protein; and then, purifying by utilizing column chromatography to prepare the recombinant human-derived LECT2 protein with the purity of over 95%. The expressing and purifying method of the recombinant human-derived LECT2 protein in Pichia pastoris has the advantages that the secretory expressing and purifying method of the recombinant human-derived LECT2 protein in Pichia pastoris is firstly proposed, a great number of recombinant human-derived LECT2 proteins with high activity are expressed by using the Pichia pastoris, and the expressing and purifying method has the advantages of stability, high yield, high activity and the like and can be used for pharmacy and diagnosis detection.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Engineering strain for producing beta-elemene and application of engineering strain
InactiveCN110819650AIncrease productionSuitable for industrial productionBacteriaTransferasesChemical synthesisCompetent cell
The invention discloses an engineering strain for producing beta-elemene and an application of the engineering strain. The engineering strain for producing beta-elemene is obtained by simultaneously converting a recombinant plasmid containing a sesquiterpene synthase coding gene XsGAS derived from xanthium sibiricum and a recombinant plasmid containing a phosphate synthase coding gene ERG20 derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae into an E.coli BL21 competent cell for construction. According to the invention, the constructed recombinant engineering bacteria is utilized for fermentation in a terrific broth (TB) culture medium to synthesize beta-elemene, and after carbon source, carbon source concentration, inducer concentration, induction time and induction OD600 are optimized, the yield of beta-elemene reaches 1.17mg / L. Compared with a chemical synthesis method, the application has the advantages that the engineering bacteria provided by invention can efficiently produce beta-elemene without pollution, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
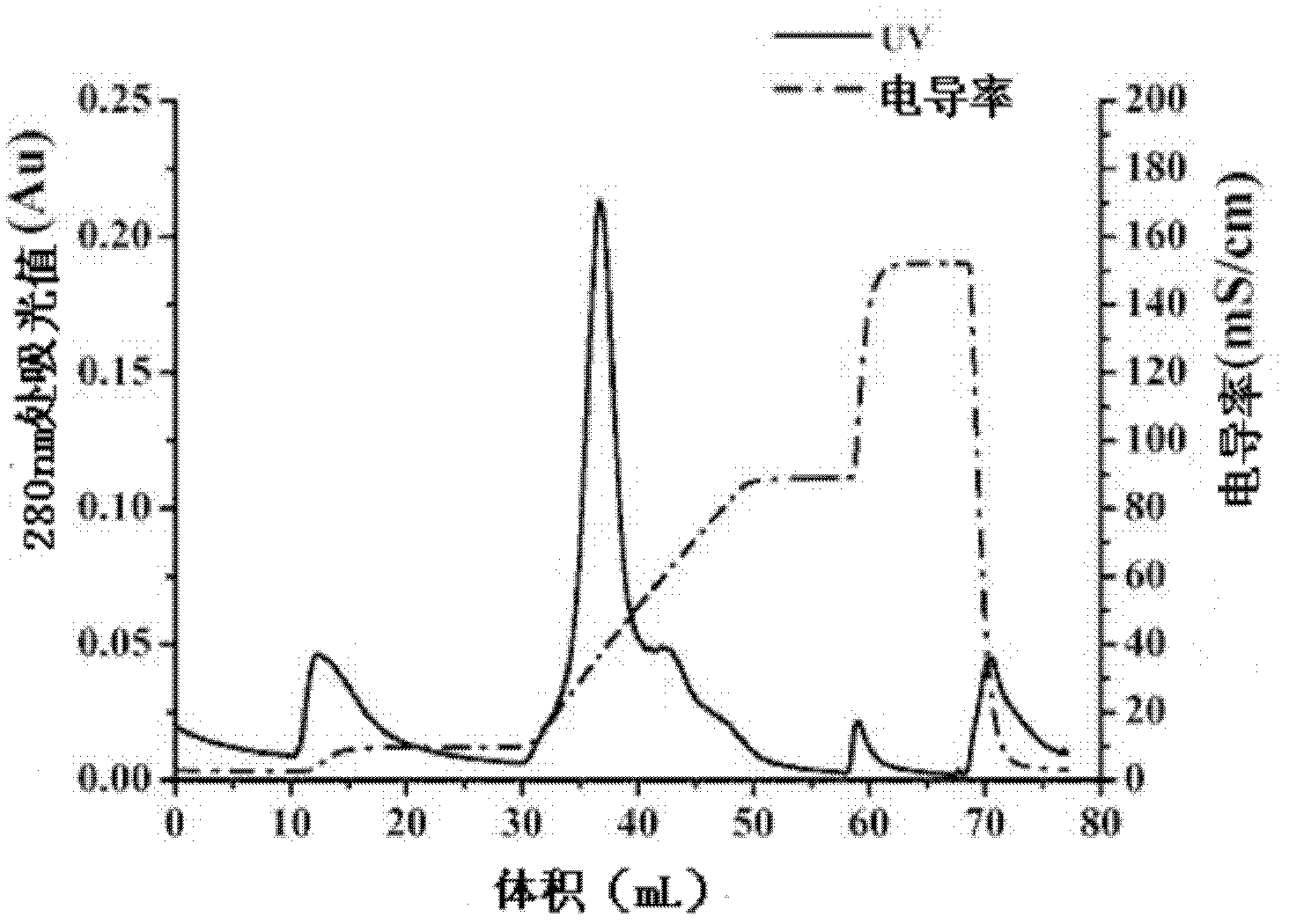
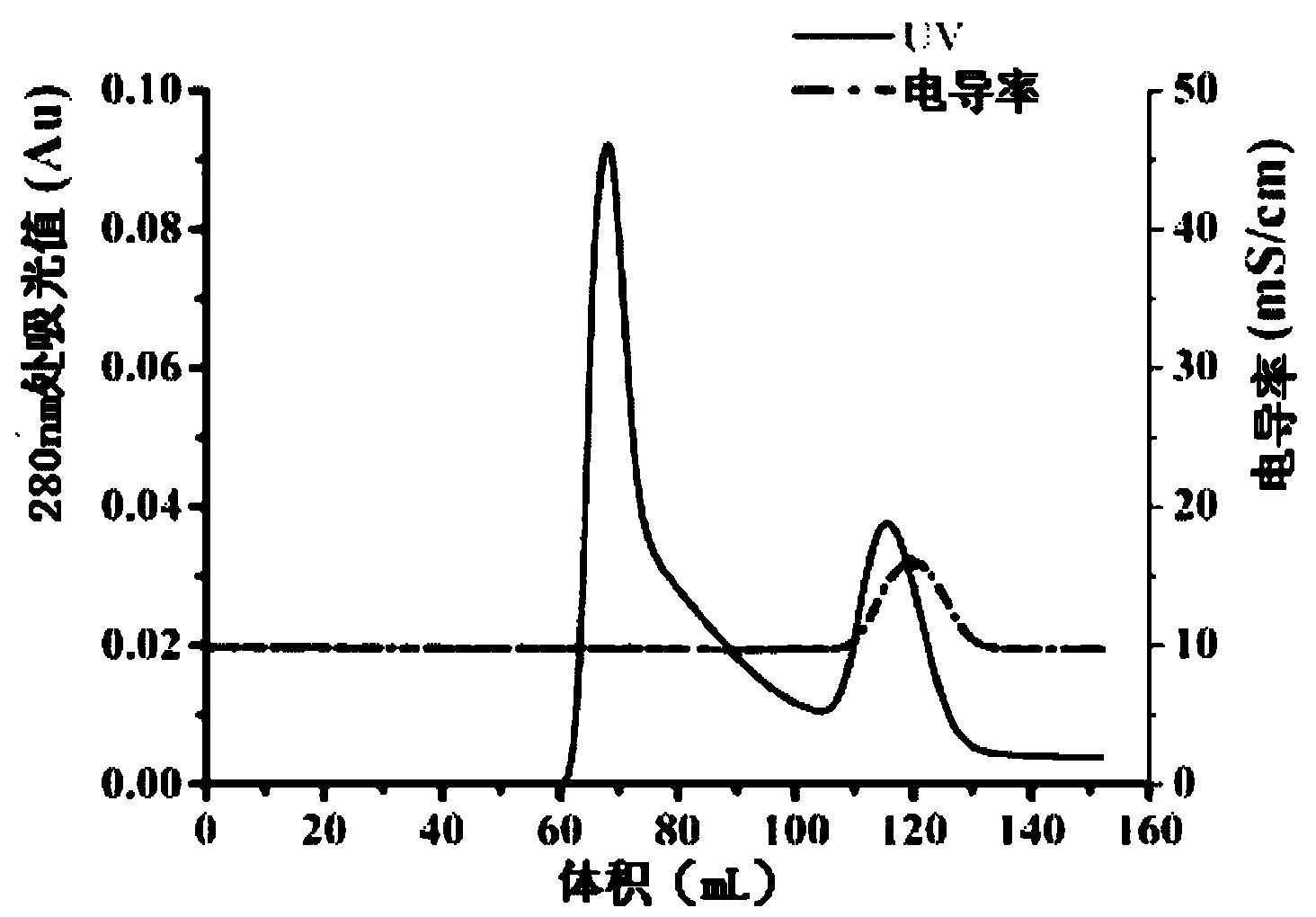
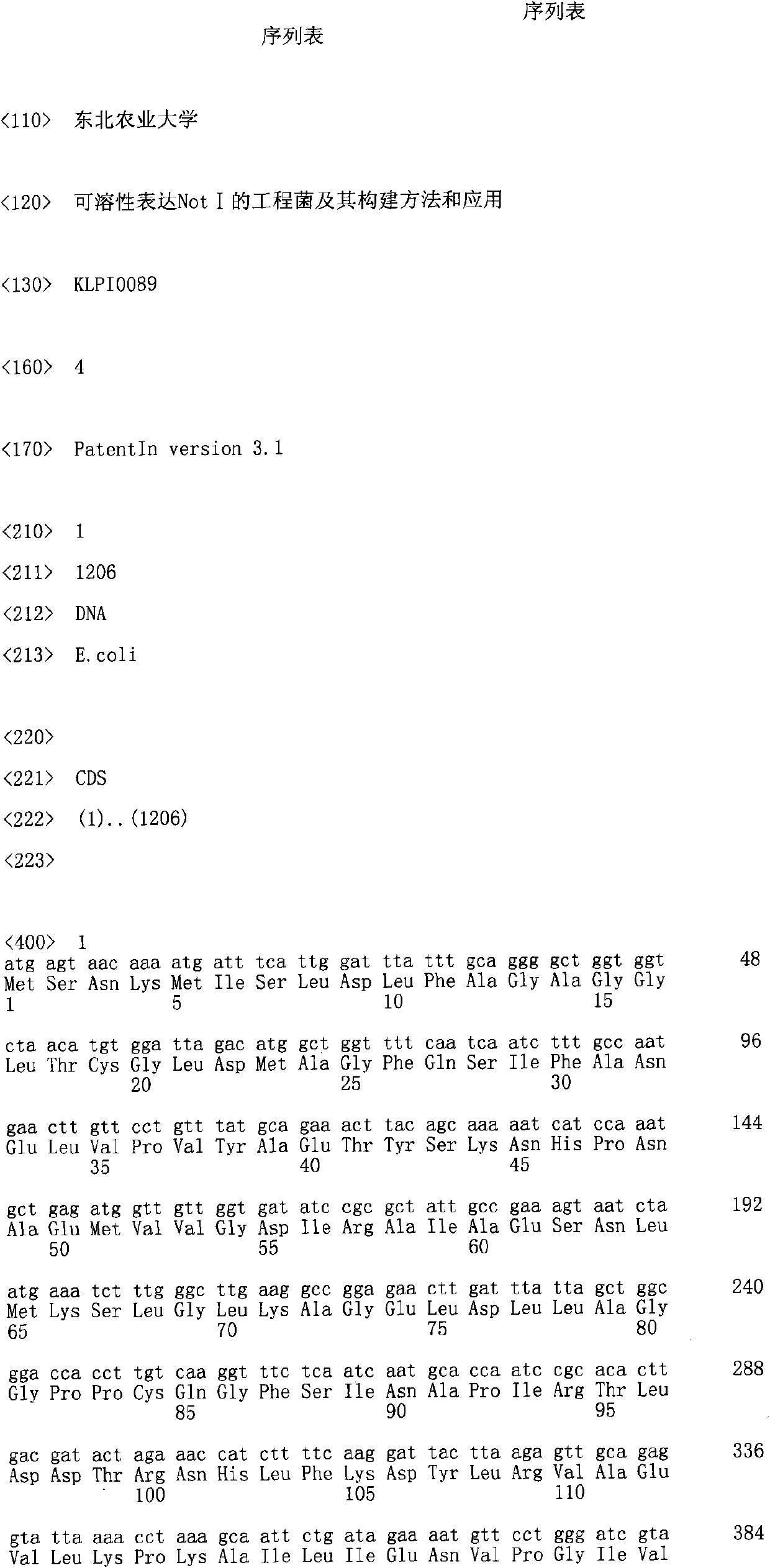
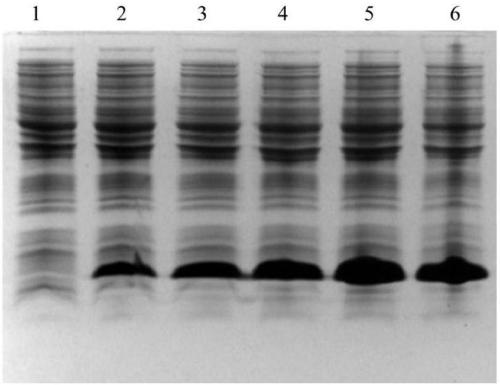
Engineering bacteria of soluble expression Not I, and construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses engineering bacteria of soluble expression Not I, and a construction method and application thereof. The engineering bacteria of the invention comprises methylase Eag I M gene, restriction enzyme Not I gene and escherichia coli (E. coli) ER2566 (mcrC-mrr). After separating and identifying the Not I gene, the invention obtains the engineering bacteria of efficient soluble expression Not I through the reconstruction of the recombinant. In the invention, the Not I restriction enzyme with high purity can be prepared through groping the inducement conditions of recombining the engineering bacteria and optimizing a protein purification process.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Production method of semaglutide precursor
ActiveCN111378027AImprove denatured efficiencyHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a production method of a semaglutide precursor. According to the production method of the semaglutide precursor, a gene recombination technology is adopted, and compared with chemical synthesis, the production method of the semaglutide precursor has the advantages that impurities are reduced, and the purity and a yield are higher; and the production method of the semaglutide precursor comprises the main steps of introducing a plasmid with a tandem expression GLP-1(9-37) gene sequence into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) by means of the gene recombination technology at first to construct recombinant engineering bacteria, conducting high-density fermentation and induction to obtain tandem expression protein which expresses the GLP-1(9-37), and carrying out the steps of degeneration, renaturation, digestion, purification and the like to obtain the semaglutide precursor GLP-1(9-37).
Owner:VONSUN PHARMATECH CO LTD +2
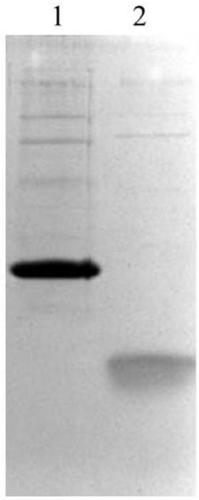
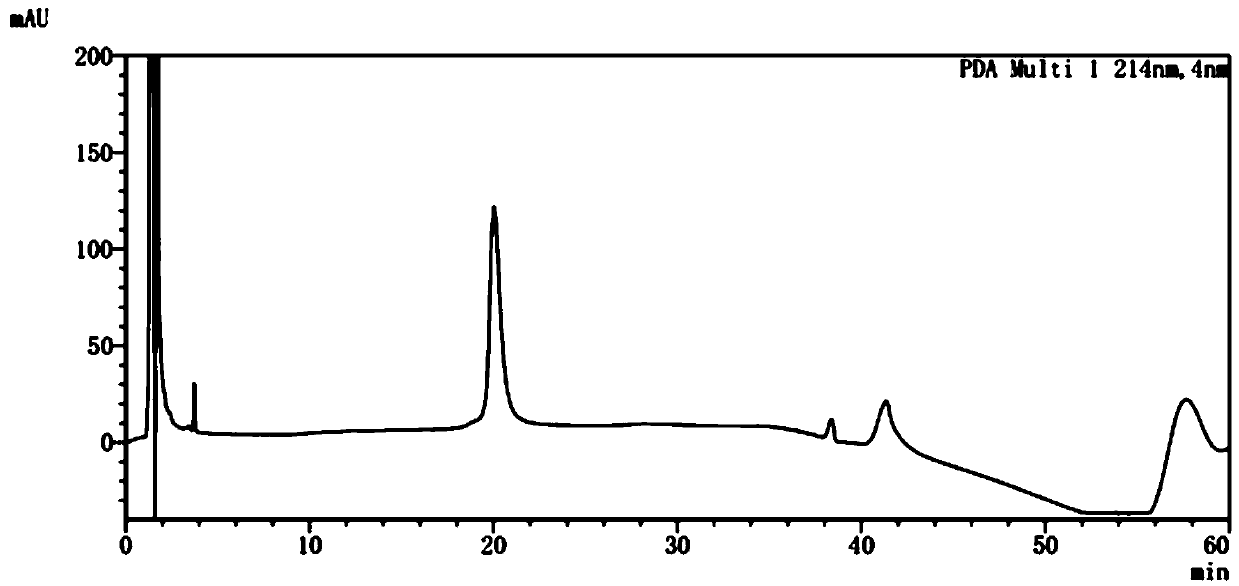
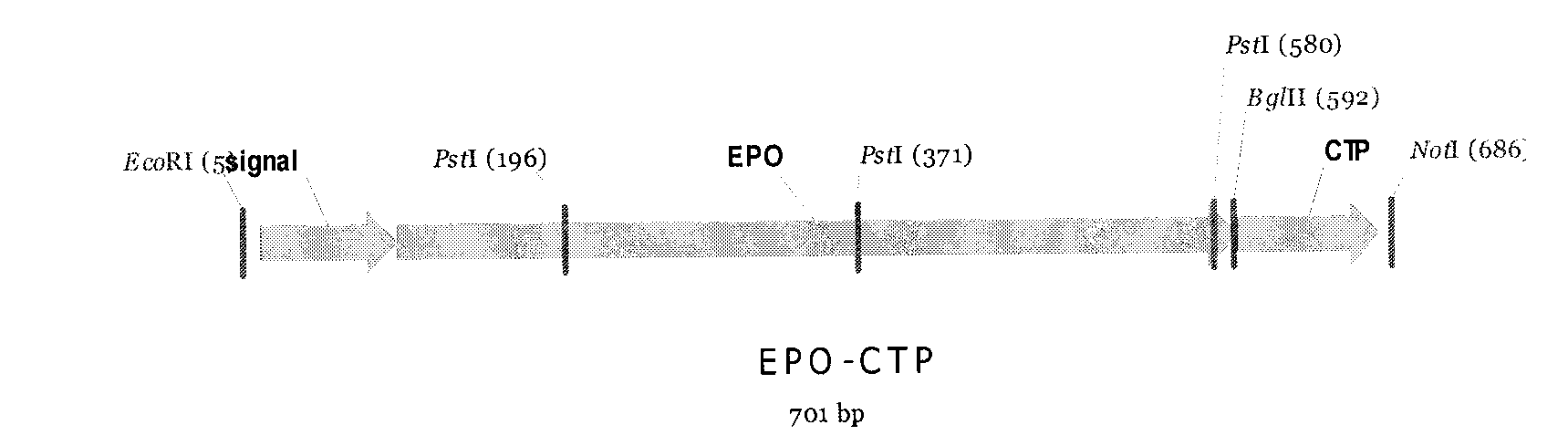
Recombinant human erythropoietin-CTP fusion protein production process and application
ActiveCN102994547AHigh activityHigh purityPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid peptidesPerfusion CultureRenal anemia
The invention discloses a recombinant human erythropoietin-CTP fusion protein production process. The process is characterized in that a microcarrier suspension perfusion culture technology or a serum-free suspension fed-batch culture technology is adopted as a recombinant engineering cell line culture manner. The invention also discloses a recombinant human erythropoietin-CTP fusion protein purifying process. Through optimization, a simple process flow is obtained, such that high-purity and high-activity recombinant human erythropoietin-CTP fusion protein is obtained. The invention also relates to the ticokinetics study of the recombinant human erythropoietin-CTP fusion protein in monkey bodies, and the application of the recombinant human erythropoietin-CTP fusion protein in treating rat renal anemia.
Owner:哈药集团股份有限公司 +1
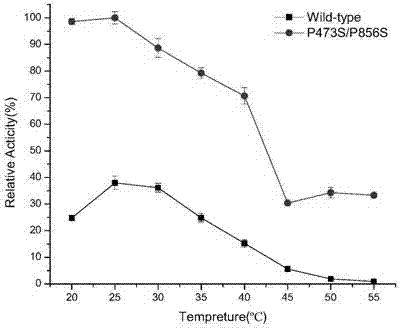
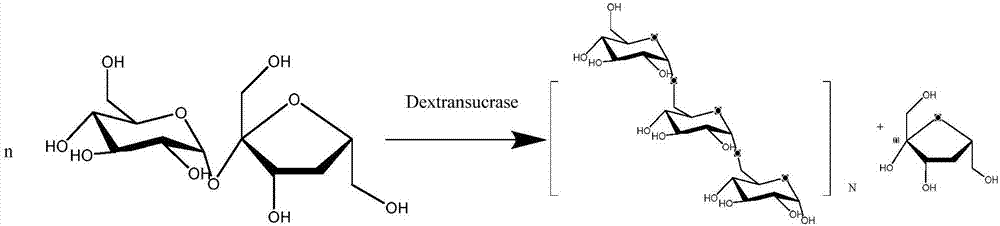
Genetically engineered bacterium for expressing heat resistant type dextransucrase, as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN107201332AIncrease enzyme activitySave production capitalBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for expressing heat resistant type dextransucrase, as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium for expressing the heat resistant type dextransucrase is constructed as follows: a dex-YG gene obtained by cloning is inserted into an expression vector pET28(+)a, so as to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid pET28(+) / dex-YG which is taken as a template; site-directed mutagenesis is performed on a 473-site and a 856-site, heat-resistant double-mutants P473S / P856S with high enzyme activity is obtained after screening, and a recombinant engineered bacterium dex-YG-thMu01 is obtained from the conversion of a host bacterium E.ColiBL21(DE3). The genetically engineered bacterium dex-YG-thMu01 disclosed by the invention have the characteristics of heat resistance and high enzyme activity, and provide a certain basis for application of the genetically engineered bacterium dex-YG-thMu01 to industrial production of the dextransucrase; the productive capital can be saved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
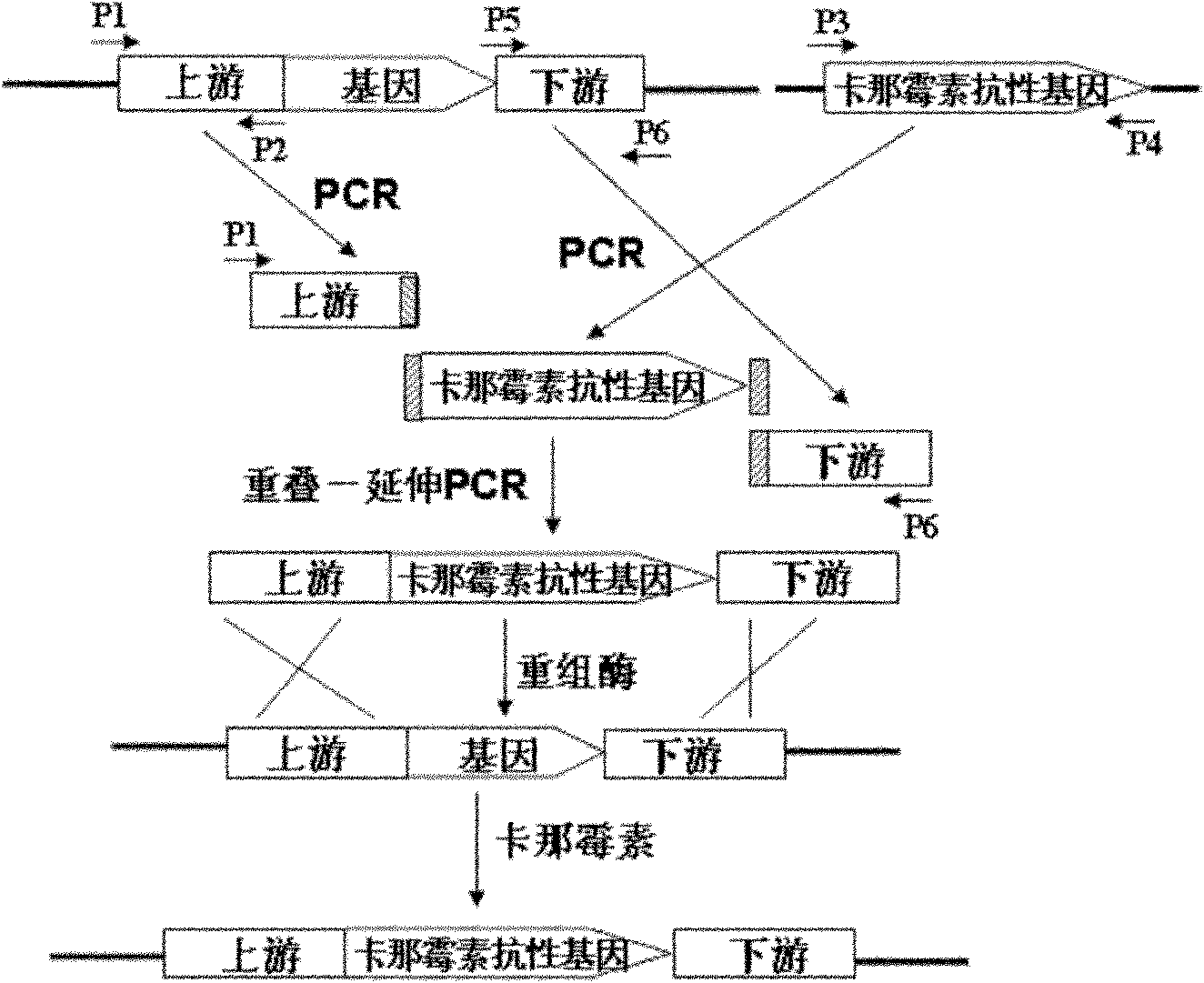
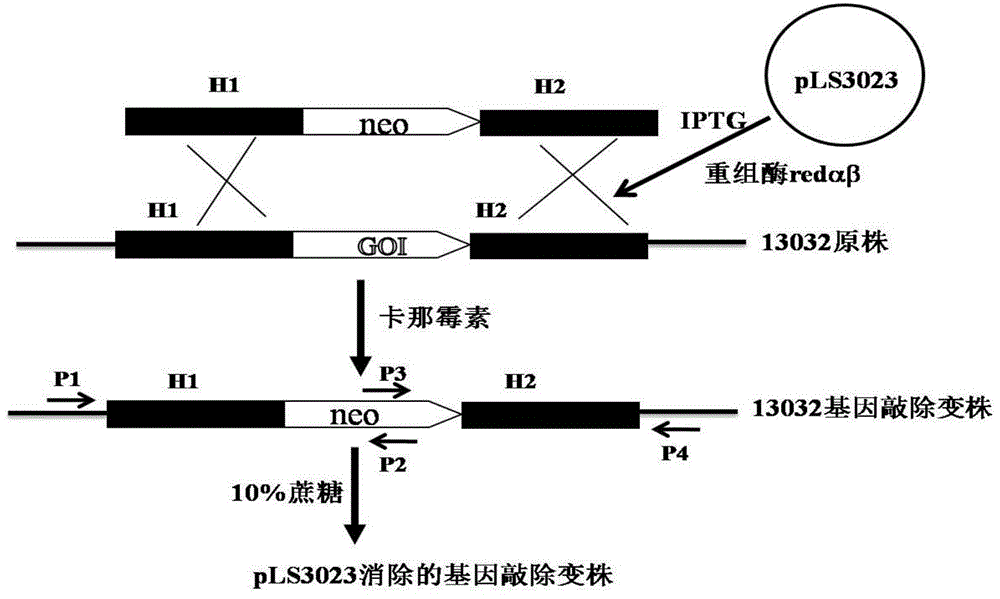
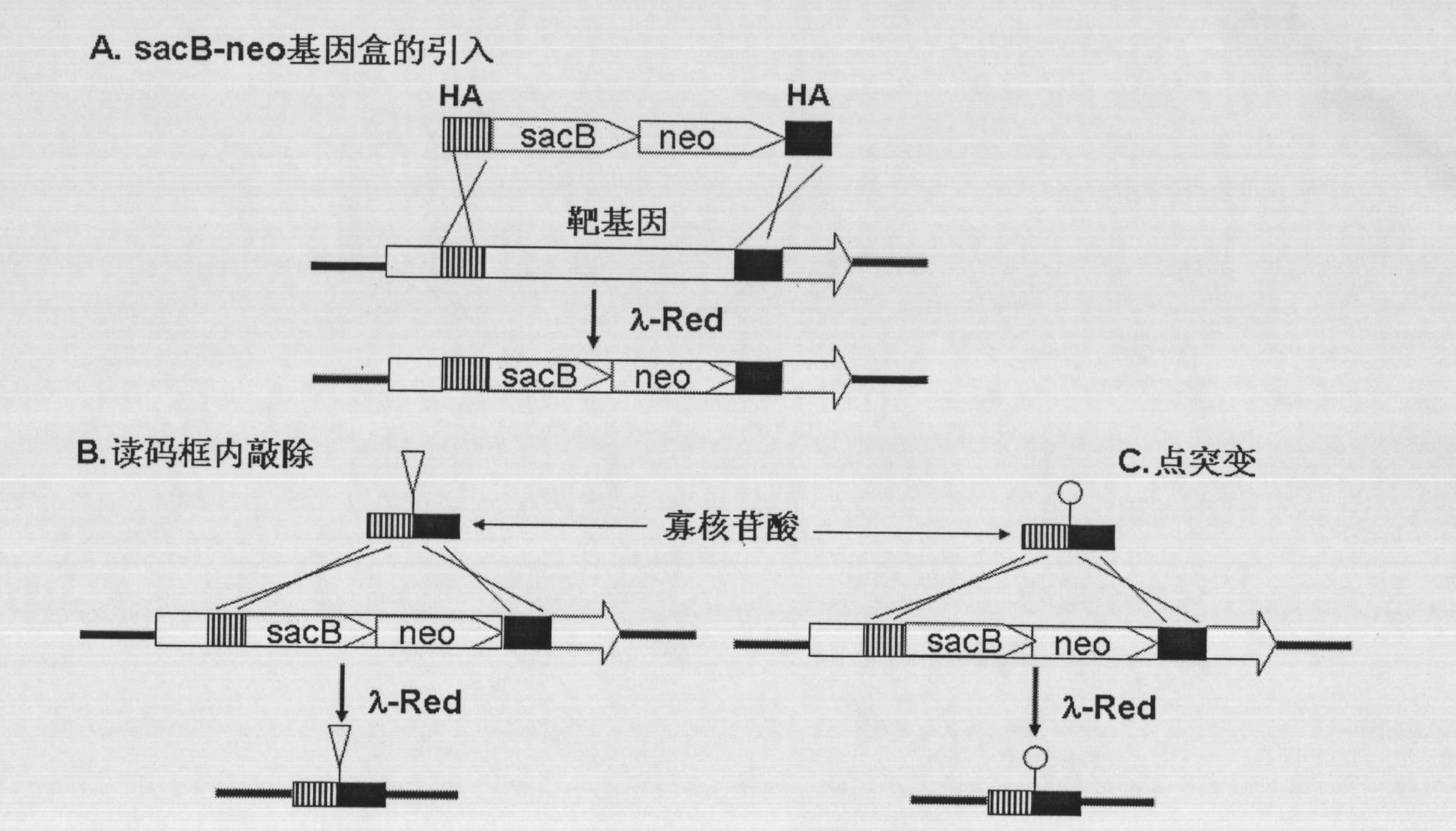
Recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032
InactiveCN104561077AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSaccharumThiogalactosides
The invention relates to a recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. The gene knockout method comprises the following specific implementation steps: obtaining a DNA fragment which is provided with 500-bp homologous sequences on two sides aiming at genes to be knocked out and a kanamycin resistance gene in the middle through a polymerase chain reaction amplification; carrying out electrotransformation on the DNA fragment into a corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 cell in which recombinase is induced to express by isopropyl-Beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside, and enabling the kanamycin resistance gene to replace the target gene through the resistance selection of kanamycin to obtain gene knockout strains; finally, cultivating mutant strains in a solid medium containing cane sugar to eliminate plasmids containing recombinase genes. The gene knockout method adopts simple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and electrotransformation supplemented by the resistance selection of kanamycin, is free of operating steps, such as gene cloning in molecular biology and other certain operating steps, and simple and rapid, and has important application in the aspects of researching gene functions and producing amino acid.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
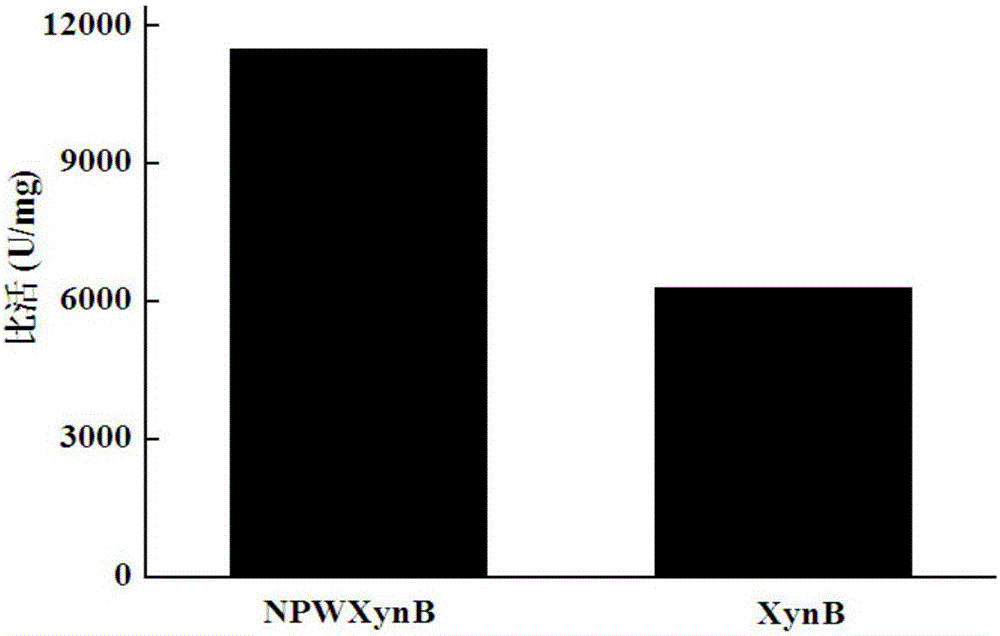
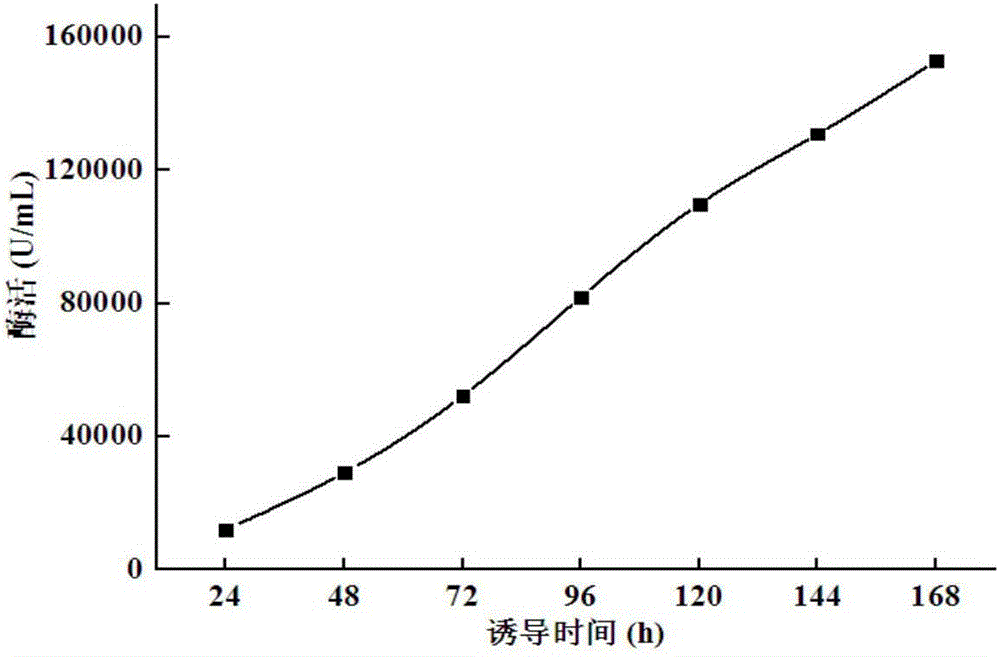
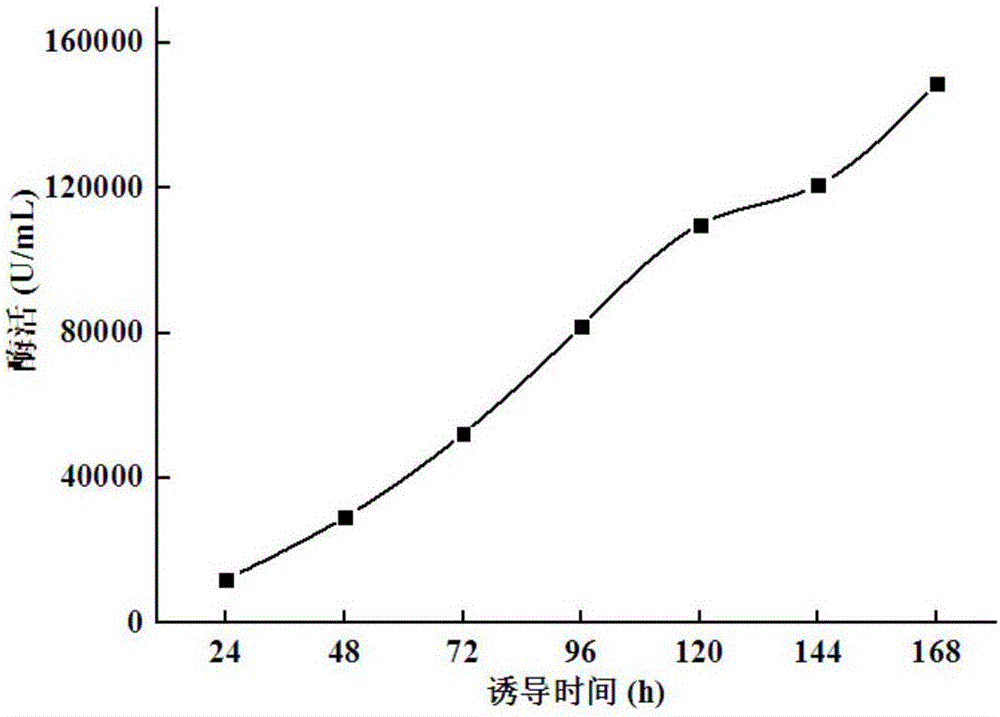
High-specific-activity endo-xylanase NPWXynB, and gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106834255ATaller than aliveReduce the cost of fermentation productionFungiMicroorganism based processesSite-directed mutagenesisRumen
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, particularly a high-specific-activity endo-xylanase NPWXynB, and a gene and application thereof. Orthogenesis and site-directed mutagenesis are utilized to perform molecular modification on endo-xylanase XynB derived from rumen fungus Neocallimastix patriciarum to obtain the high-specific-activity xylanase NPWXynB. In the amino acid sequence, the 58th site Y is substituted by F, the 78th site M is substituted by Y, the 94th site Y is substituted by S, the 143rd site V is substituted by L, the 145th site E is substituted by R, and the 182nd site D is substituted by R. The specific activity of the endo-xylanase mutant NPWXynB provided by the invention is 11500 U / mg under the condition of 37 DEG C, which is enhanced by 82.5% as compared with the specific activity of the original endo-xylanase XynB. The maximum enzyme activity of the NPWXynB-gene-containing recombinant engineering bacterium can reach 153000 U / mL, and the production cost is greatly lowered.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTR BIO TECH
Method for preparing human parathyroid hormone 1-34
InactiveCN102304518APromotes high-yield extracellular accumulationAvoid attackPeptide preparation methodsParathyroid hormonesProtein targetThioredoxin
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical engineering, and relates to a method for preparing human parathyroid hormone (1-34) through fermenting and purifying human parathyroid hormone 1-34 recombinant engineering bacteria constructed by a gene engineering method. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: fusing and expressing the genes for coding human parathyroid hormone and a thioredoxin label, and further constructing and finishing genetic engineering bacteria capable of highly expressing human parathyroid hormone; adding IPTG (isopropyl beta D thiogalactopy ranoside) and triton X-100 in the fermentation process by adopting a chemosmosis fermentation technology so as to improve the release of proteins extracellularly in the fermentation process, which is good for the continuous synthesis of proteins, and avoiding the attack of endoproteinase, thus protein high-yield extracellular accumulation is promoted; and simultaneously carrying out heat treatment on a fermentation liquid when the fermentation reaches the final point aiming at the heat stability of thioredoxin fusion, thus initially purified target proteins are directly recycled and obtained from a fermentation liquor supernatant after centrifugation.
Owner:中国科学院上海生命科学研究院湖州工业生物技术中心
Gene for highly expressing nuclease P1 and its application
InactiveCN101654677AHigh phosphodiesterase activityHigh yieldFungiHydrolasesHydrolysatePenicillium citrinum
The invention discloses a gene highly expressing a nuclease P1 and an expression vector and a host cell comprising the gene and an application for the gene. The invention discloses a recombinant pichia yeast CGMCC No.3188 expressing the gene of nuclease P1 produced from Penicillium citrinum and its construction method. The inventive recombinant engineering strain pichia yeast CGMCC No.3188 can highly express Penicillium citrinum nucP gene. The secretion-expressed nuclease P1 has high phosphodiesterase activity, is used for hydrolyzing RNA, has high product yield and little generated impurity and reduces working procedure of downstream separation as well as decreases production cost. The invention uses the recombinant engineering strain pichia yeast CGMCC No.3188 to perform high density fermentation. The enzyme activity is 1.5 times by the wild strains. The acquired recombinase is applied to RNA solution enzymatic hydrolysis, thus, reaching the hydrolysis rate of more than 40% and the acquired hydrolysate by-product is substantially reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Oligonucleotide mediated colibacillary gene knock-out or point mutation method
InactiveCN101812442ANo redundancyAvoid polarity effectsMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliOligonucleotide
The invention relates to a method for carrying out gene knock-out or point mutation on a colibacillary genome by an oligonucleotide mediated recombineering measure. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, integrating a gene box of a cane sugar 6-fructosyltransferase gene and a kanamycin resistance gene containing isogenous arms into a target gene through recombineering; and then, carrying out isogenous recombination on oligonucleotide containing the isogenous arms and the isogenous sequences on the genome through the recombineering to remove the cane sugar 6-fructosyltransferase gene and the kanamycin resistance gene. Thereby, the gene knock-out and point mutation without any basic group redundance are realized. The gene knock-out oligonucleotide design conforms to the basic group sequences of both sides of the target genes, and base groups needing the mutation are introduced in the oligonucleotide by the point mutation oligonucleotide. The invention does not need in-vitro clone and in-vitro realization of some basic group bit mutation or mutation gene transplanting into germ bodies. The method of the invention can provide an effective early-stage operation platform for the industrial production and the research such as genetics, molecular biology, biochemistry and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
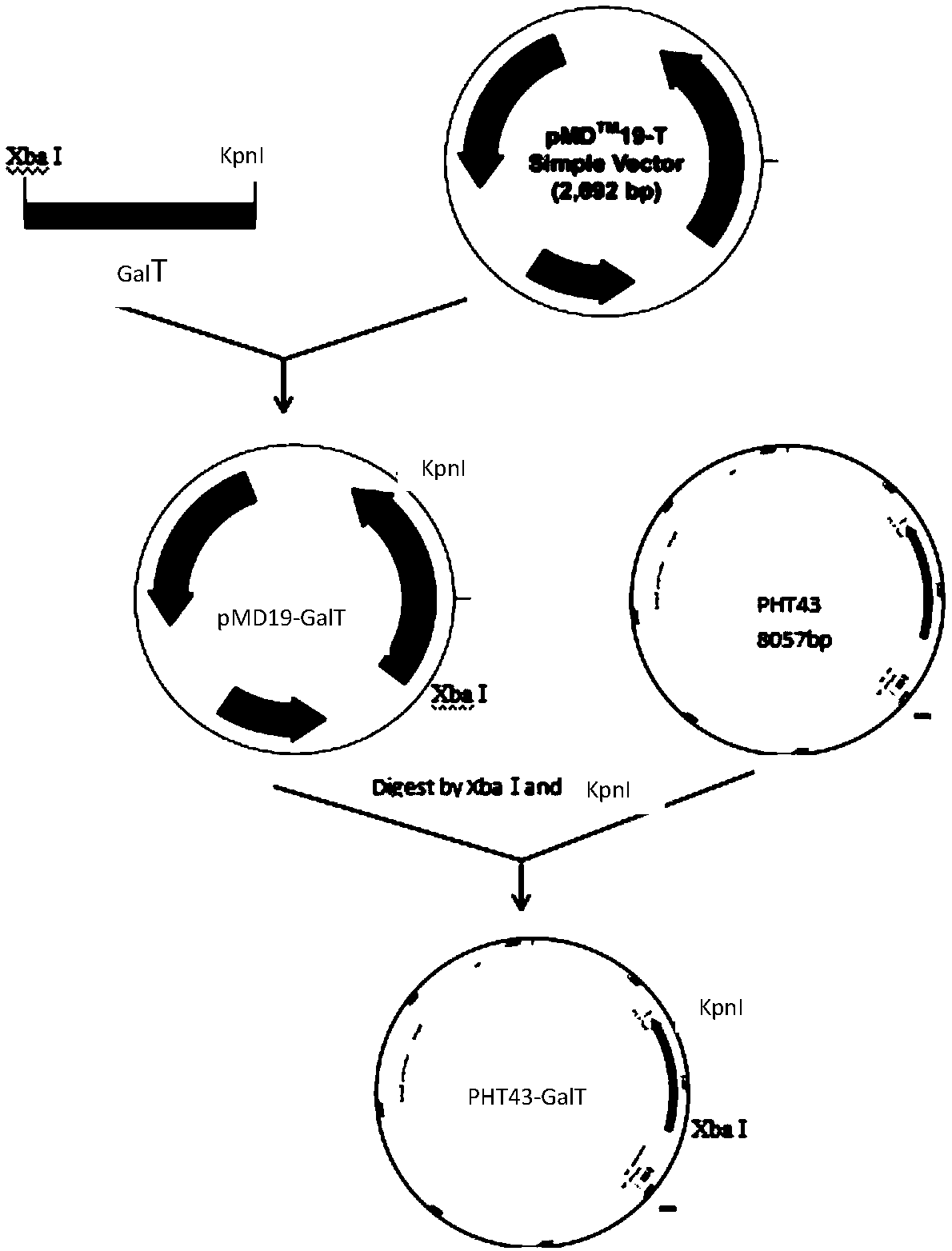
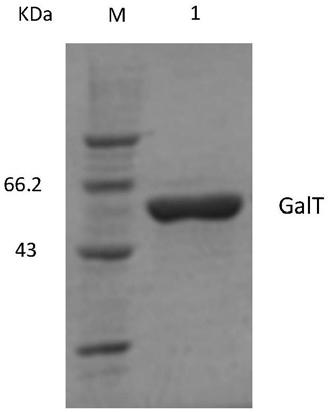
Method for efficient expression preparation of UDP-glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase
ActiveCN109295087AStrong ability to secrete proteinEasy to trainBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyFood industry
The invention relates to a method for efficient expression preparation of UDP-glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase. According to the method, a recombinant expression vector is constructed fromUDP-glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GalT) gene and Bacillus subtilis by using a vector; the recombinant expression vector is transformed into Bacillus subtilis to construct a recombinant engineered strain; the recombinant engineering strain is subjected to induced culture in a liquid culture medium; and the obtained bacterial liquid is subjected to centrifugation, and the supernatant is taken. According to the present invention, the method has advantages of high yield of UDP-glucose-hexose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase, pure protein, easy recovery and purification and simple production operation, provides the convenience in the industrial large-scale production of GalT, further has advantages of yield improving, time saving, labor saving and cost saving, particularly provides the safety assurance in the application of the enzyme in the food industry, and has great significance.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com