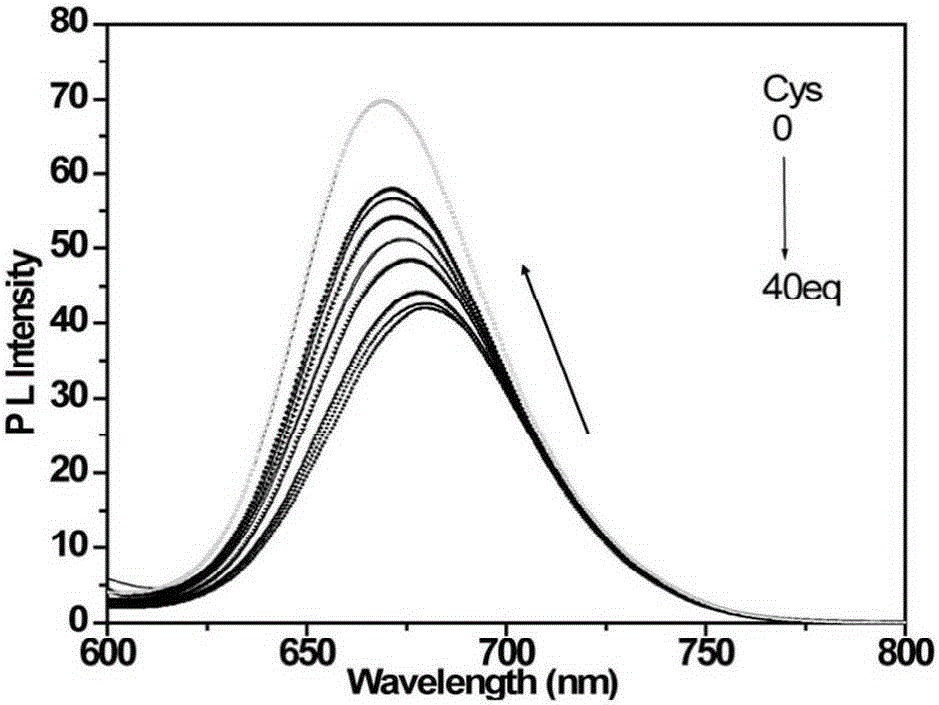
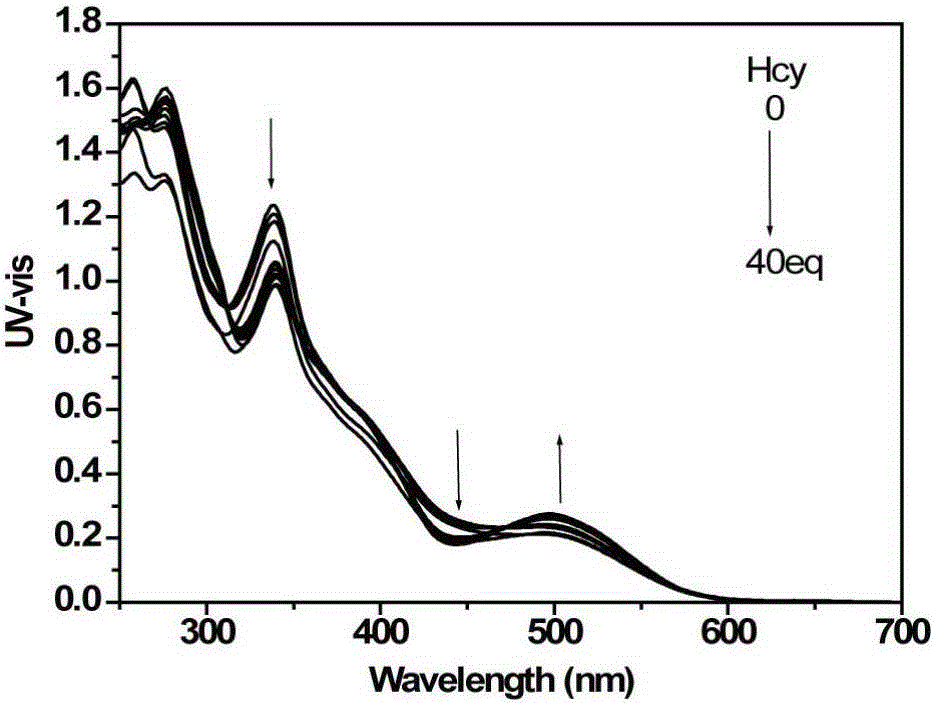
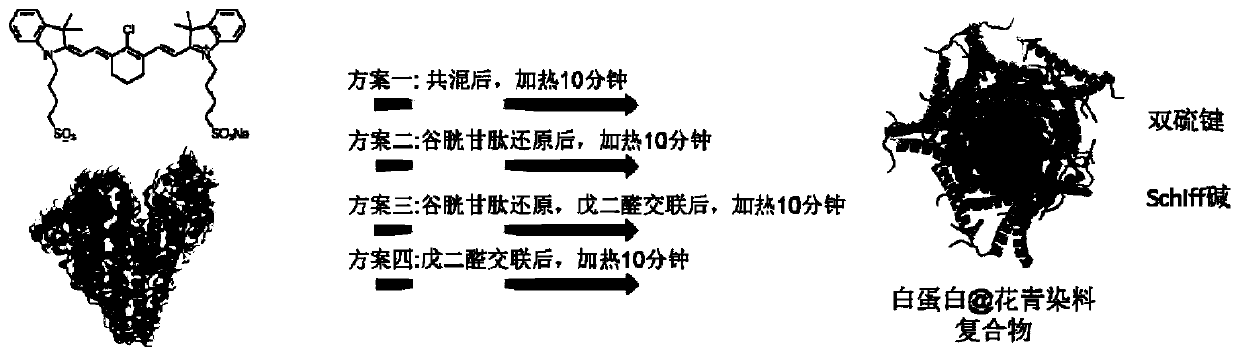
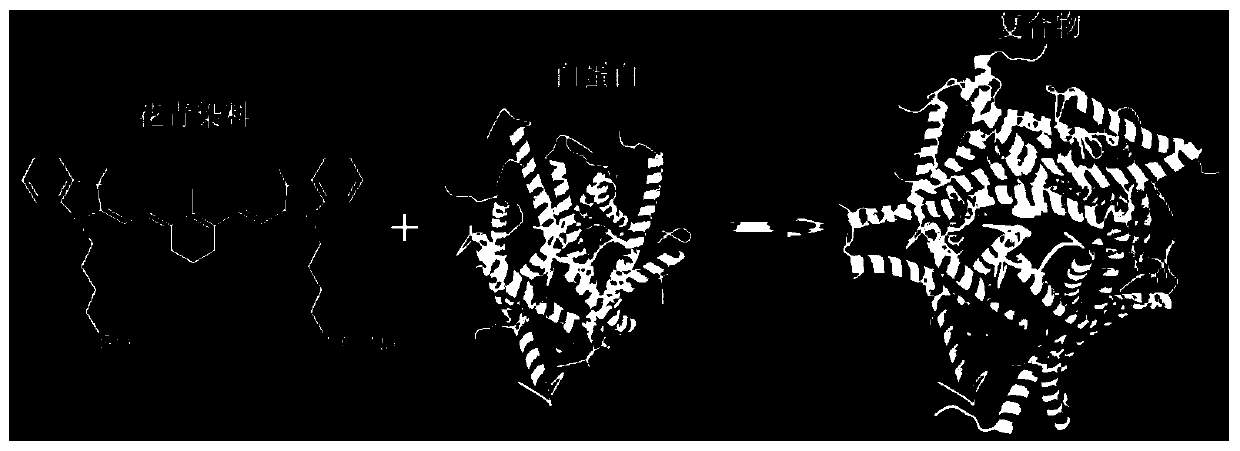
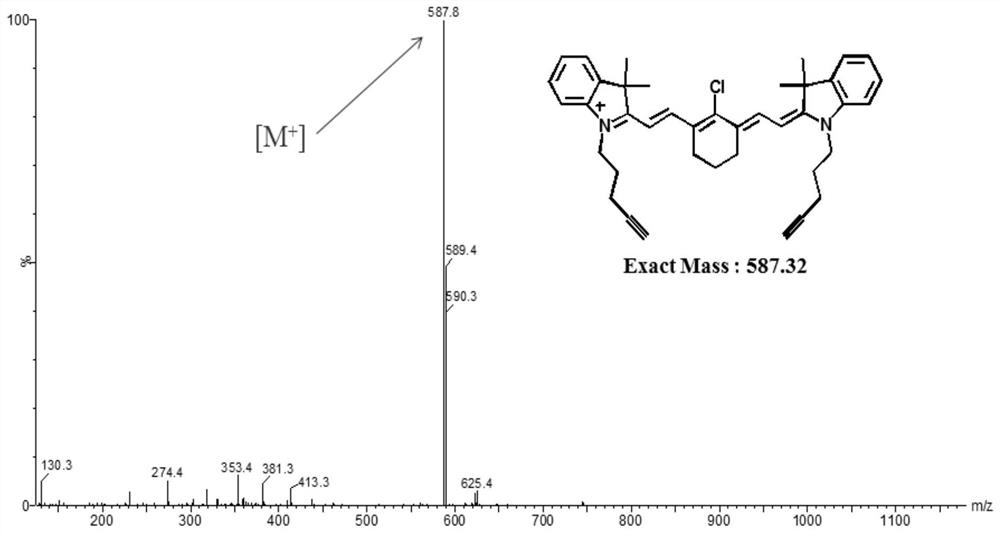
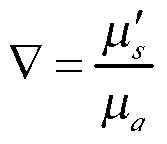Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "In vivo fluorescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
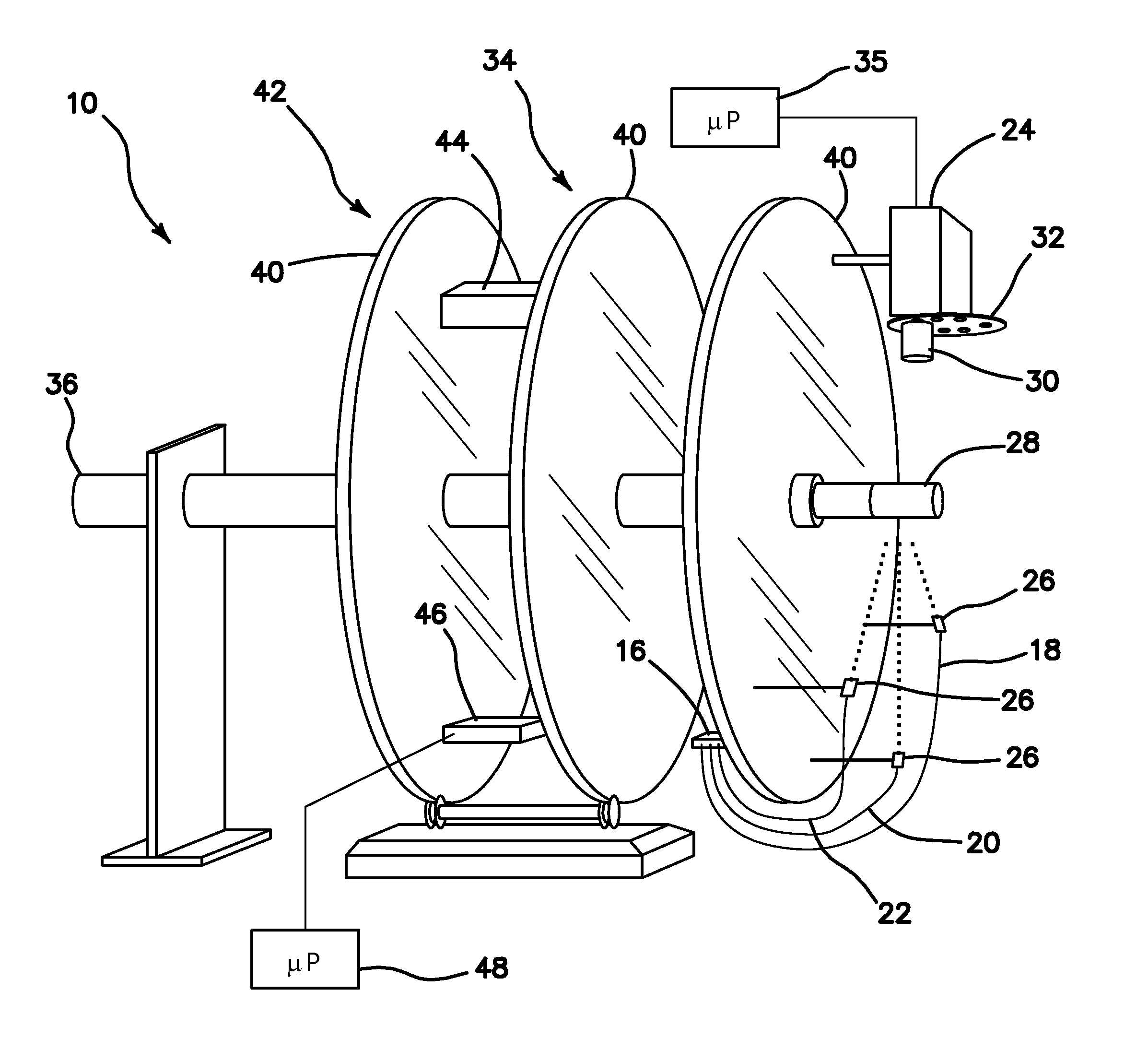
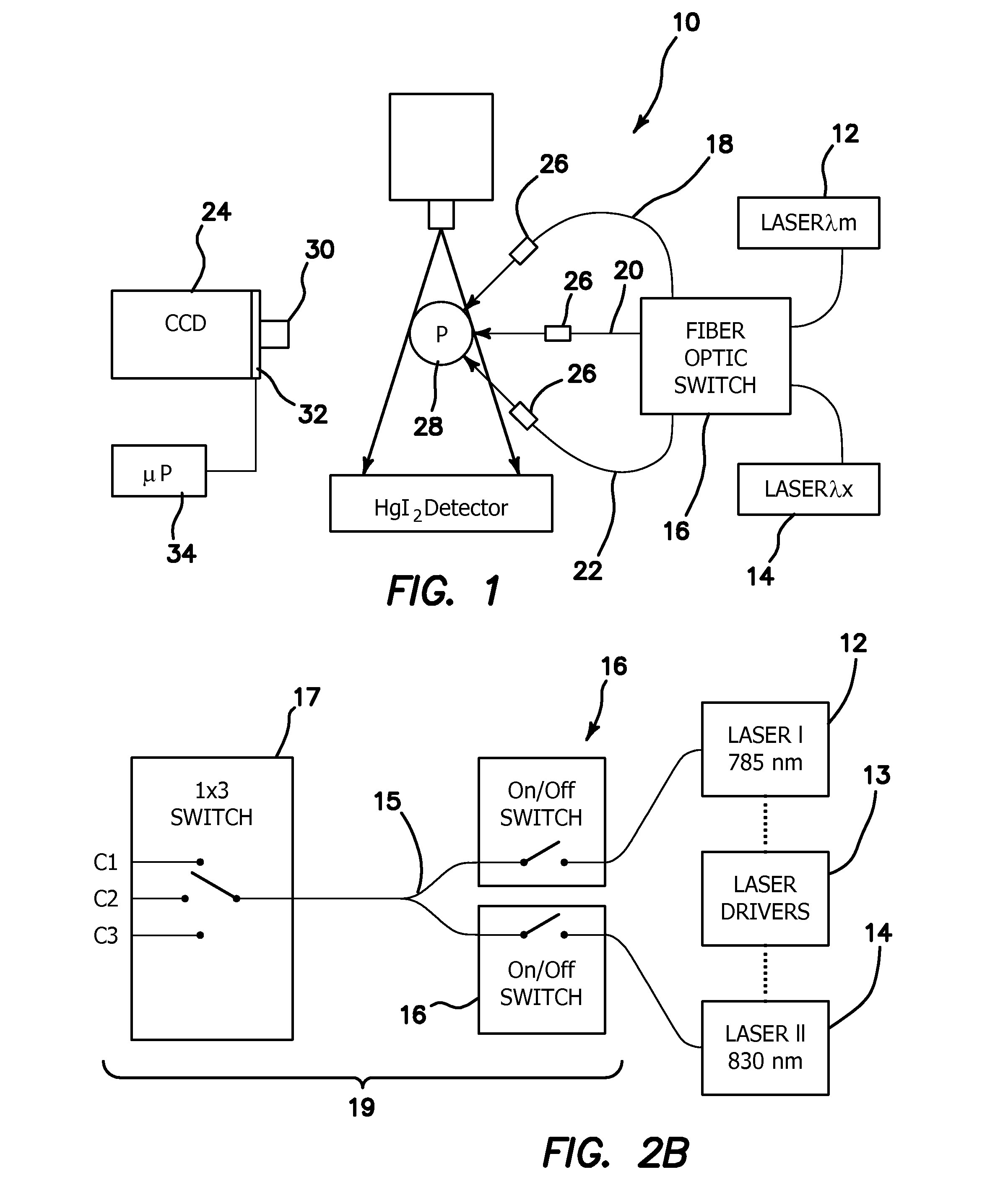
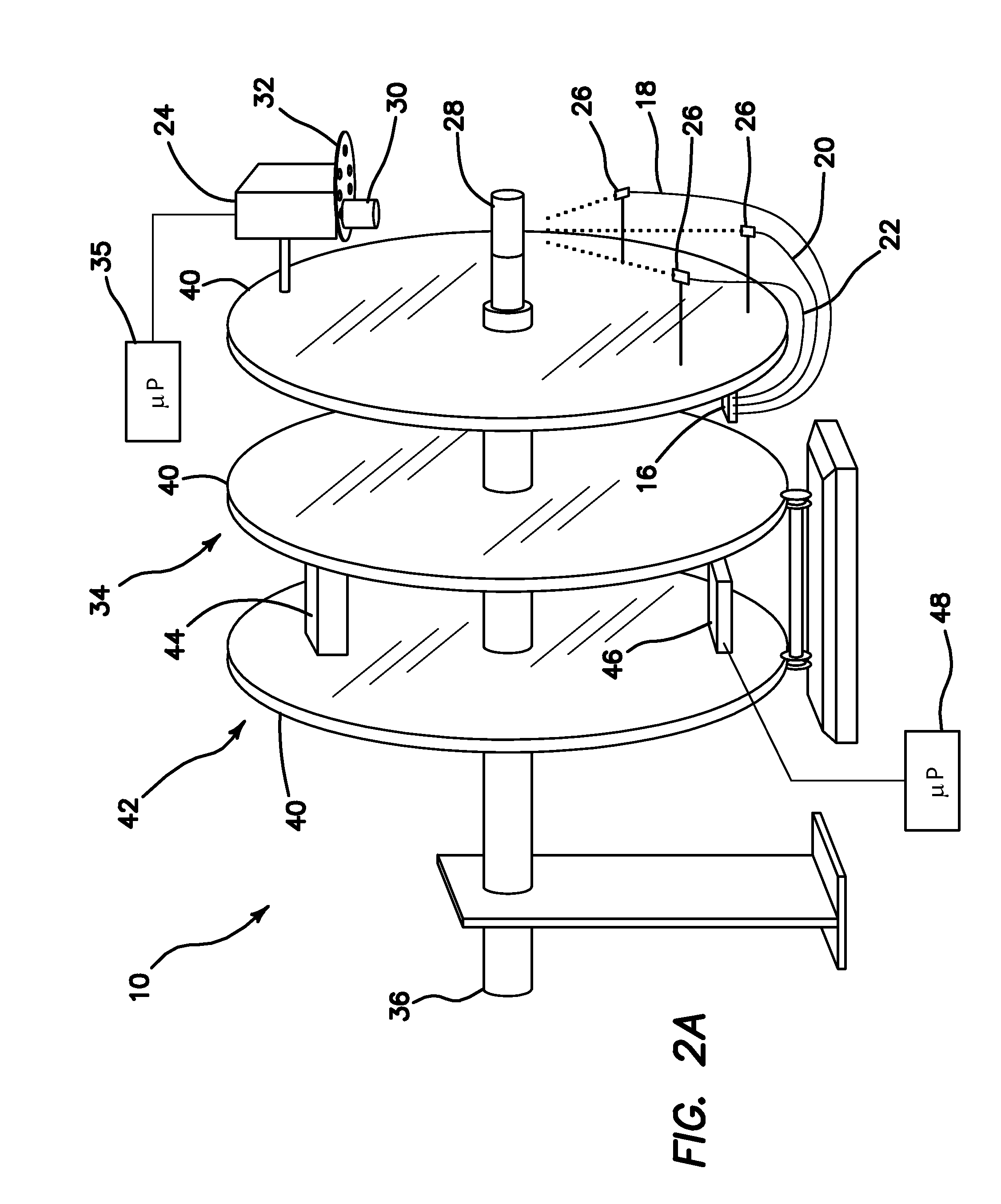
Optical instrument and technique for cancer diagnosis using in-vivo fluorescence emission of test tissue
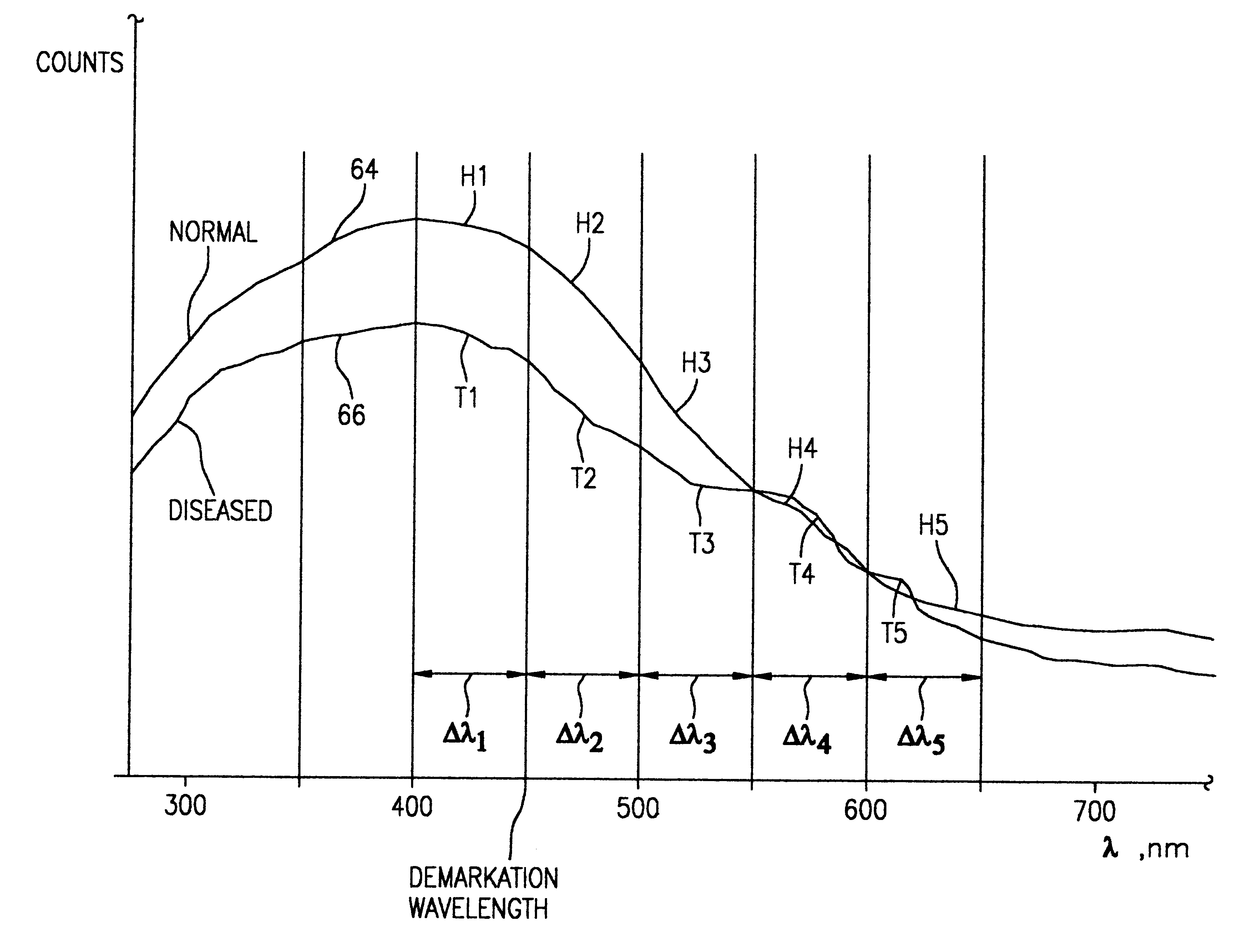
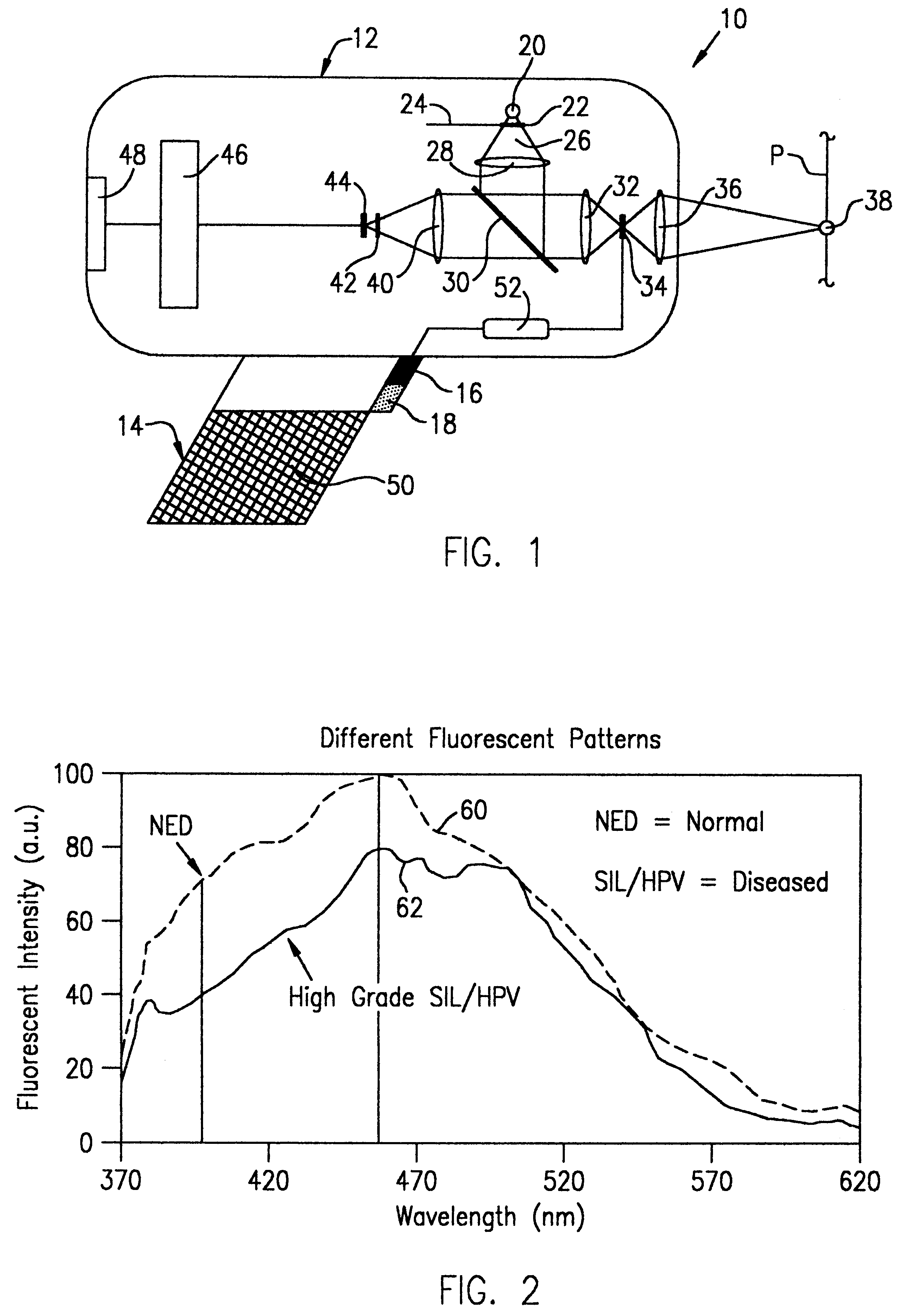
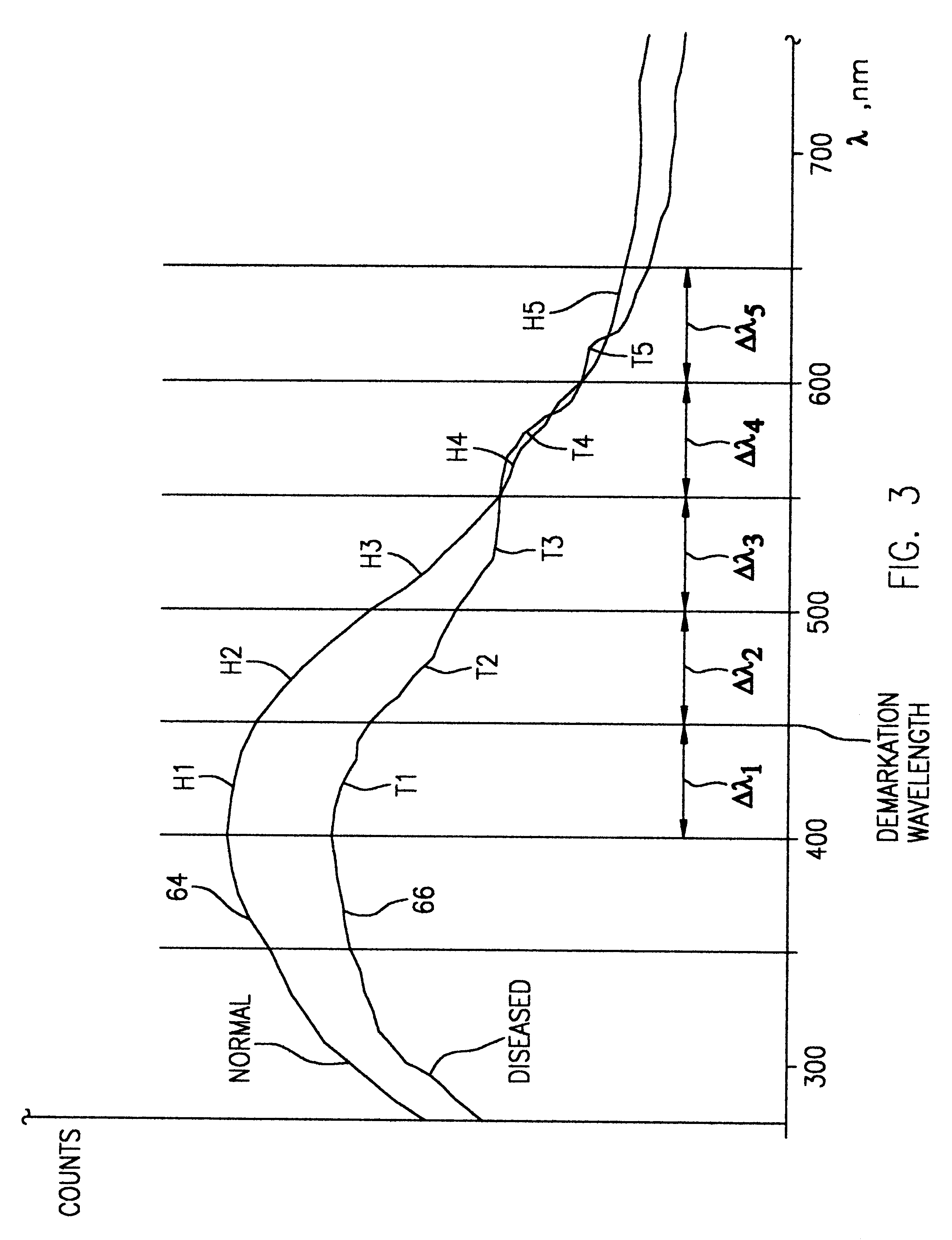
A hand-held, small, lightweight instrument is disclosed that contains a light source capable of producing radiant energy in the spectral range between approximately 370 and approximately 410 nm, and an optical direction system for irradiating a target tissue by producing an illuminated spot thereon. A collection system is provided for receiving and directing fluorescent emissions in the frequency range between 450 and 700 nm returned from the target area to a detector. A processing system is used to determine the state of the tissue by using at least two and up to five spectral bands, preferably each being larger than 45 nm. Pairs of ratios of fluorescent intensities are compared to identify cancerous cells. An alphanumeric, false-color image and / or audio signal is immediately provided to inform a user of the state of the tissue.
Owner:WOLFE WILLIAM L
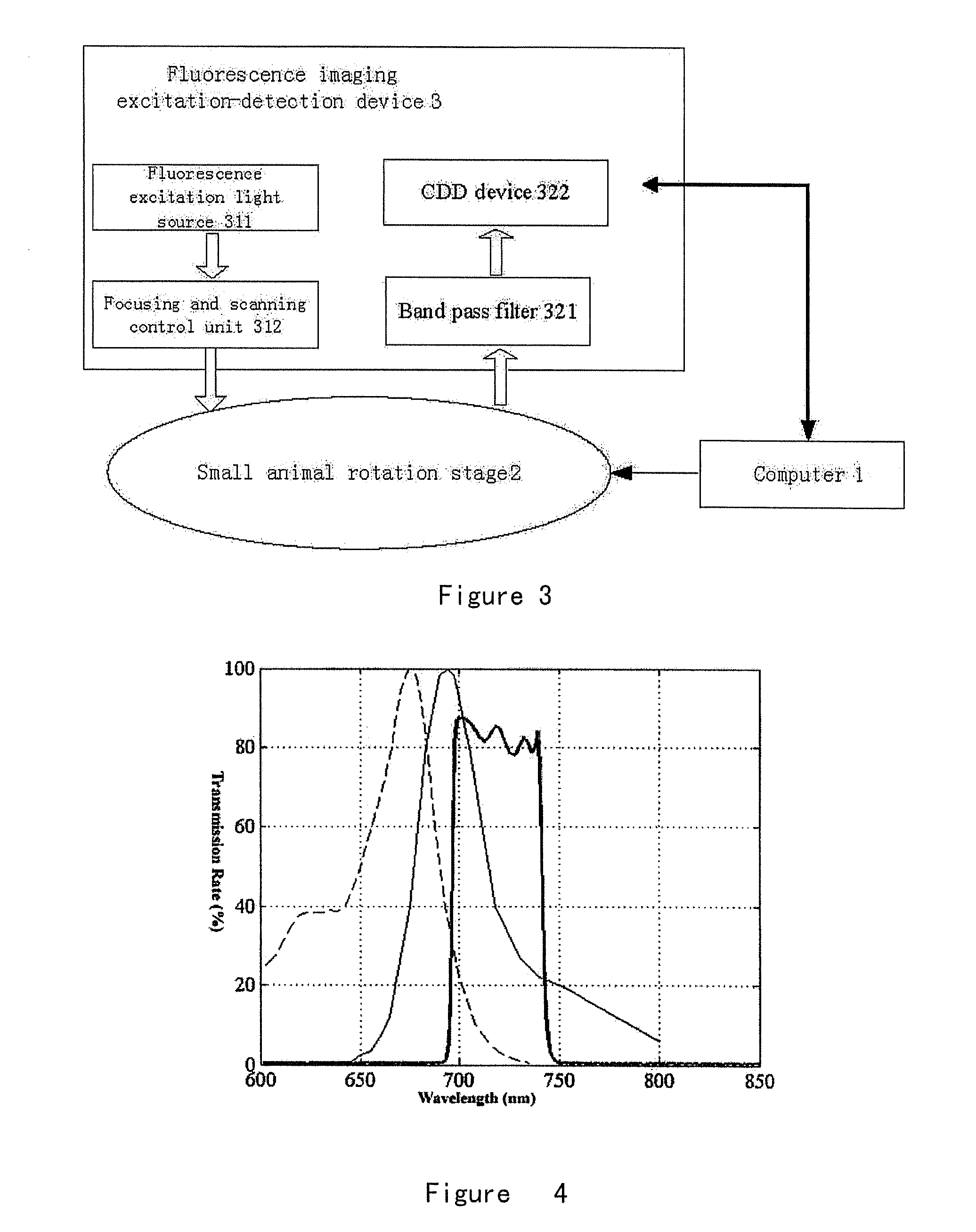
Dynamic Sampling System and Method for In Vivo Fluorescent Molecular Imaging
InactiveUS20090018451A1High throughput imaging technologyStable imaging techniqueMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using tomographySmall animalMolecular imaging
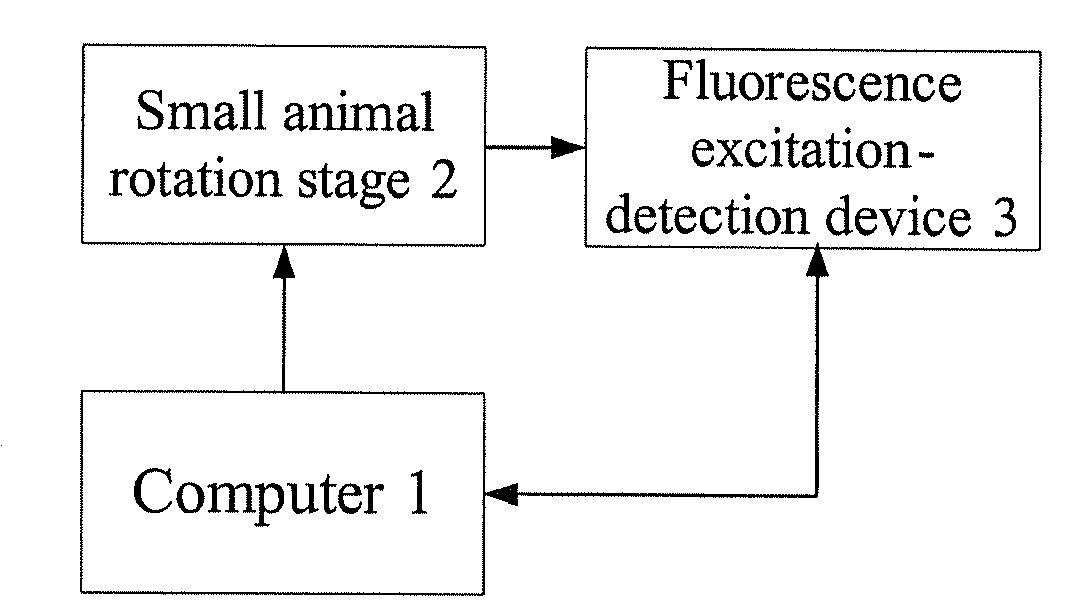
A dynamic dada sampling system and method is disclosed for in vivo small animal fluorescence molecular imaging and dual-modality molecular imaging. The system comprises a computer, a rotation stage for animal suspension driven by a motor, and a fluorescence excitation-detection apparatus. The fluorescence excitation-detection apparatus comprises a fluorescence excitation module and a fluorescence detection module. The CCD device of the fluorescence detection module is connected to a computer through an interface controller. The motor is connected to a computer through RS232 interface. The process of dynamic data acquisition is as follows: a fluorescent probe is injected into a small animal in order to target specific cells or tissues; a small animal is vertically hung on a rotation stage after anesthesia; the fluorescence imaging detection module acquires the emitting light continuously. The present invention can provide 360 degree imaging quickly, efficiently, and non-invasively.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Luminogens for biological applications
A compound comprises a donor and an acceptor, wherein at least one donor ( "D" ) and at least one acceptor ( "A" ) may be arranged in an order of D-A; D-A-D; A-D-A; D-D-A-D-D; A-A-D-A-A; D-A-D-A-D; and A-D-A-D-A. The compound may be selected from the group consisting of: MTPE-TP, MTPE-TT, TPE-TPA-TT, PTZ-BT-TPA, NPB-TQ, TPE-TQ-A, MTPE-BTSe, DCDPP-2TPA, DCDPP-2TPA4M, DCDP-2TPA, DCDP-2TPA4M, TTS, ROpen-DTE-TPECM, and RClosed-DTE-TPECM. The compound may be used as a probe and may be functionalized with special targeted groups to image biological species. As non-limiting examples, the compound maybe used in cellular cytoplasms or tissue imaging, blood vessel imaging, in vivo fluorescence imaging, brain vascular imaging, sentinel lymph node mapping, and tumor imaging, and the compound may be used as a photoacoustic agent.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
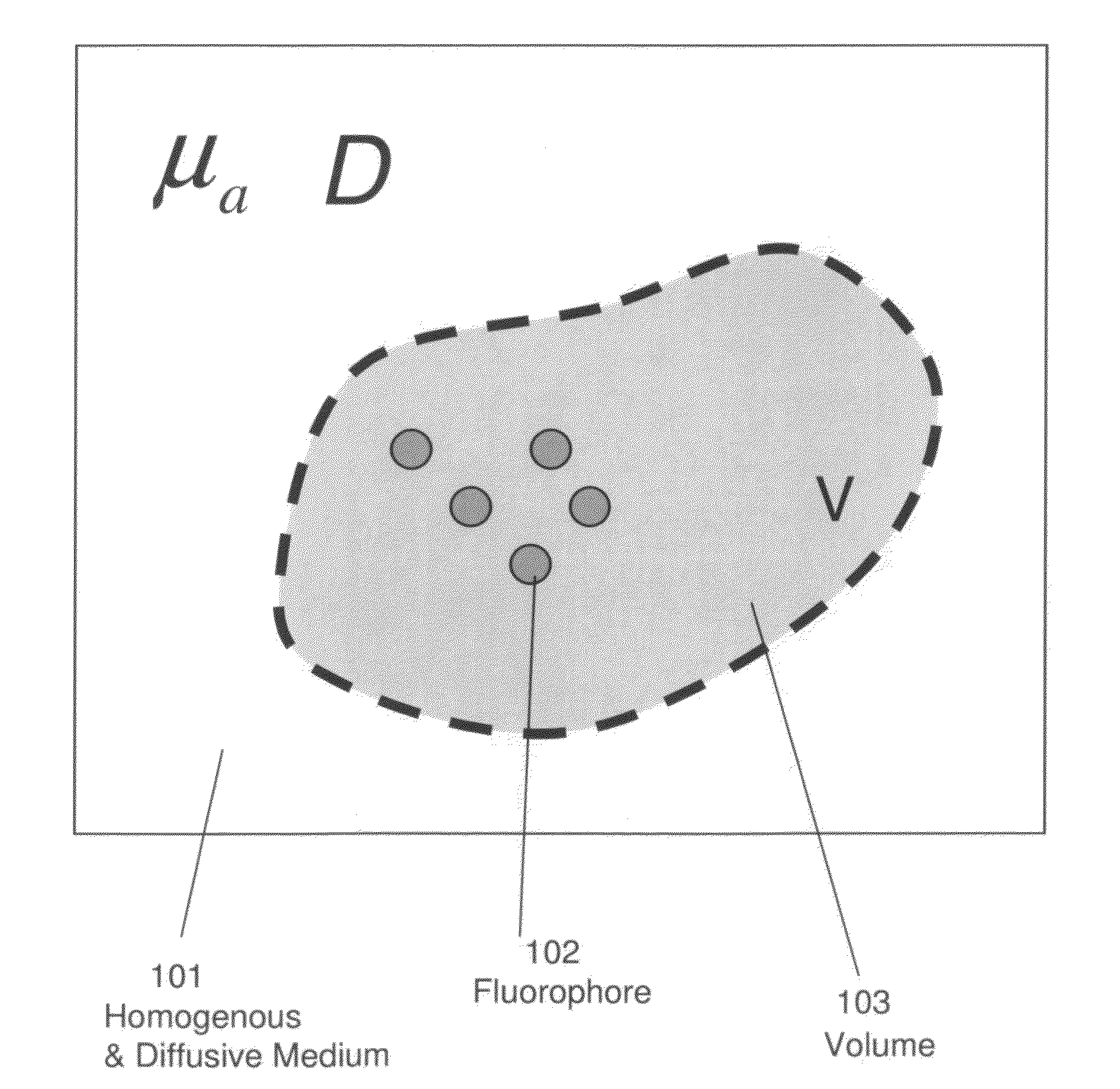
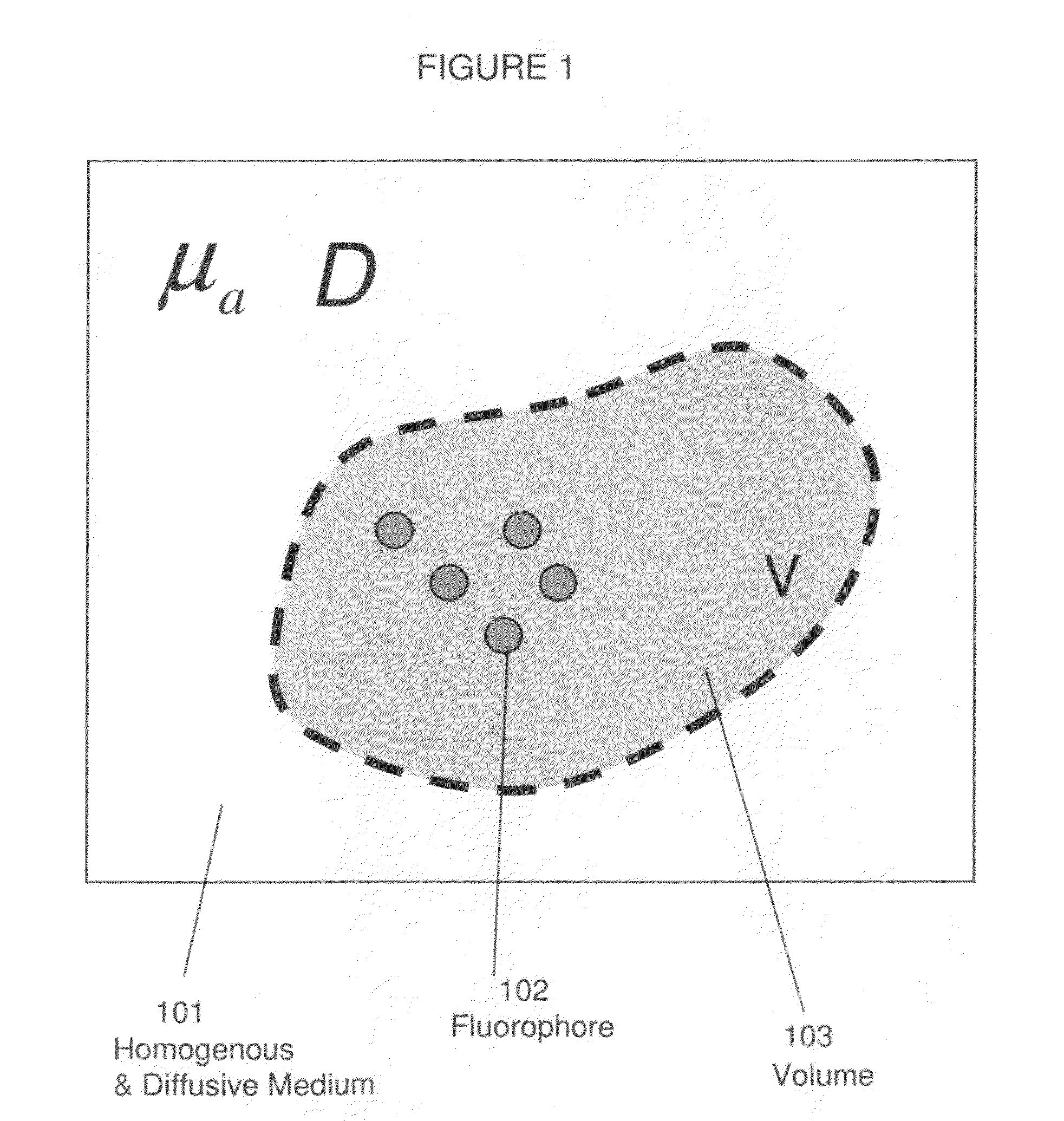
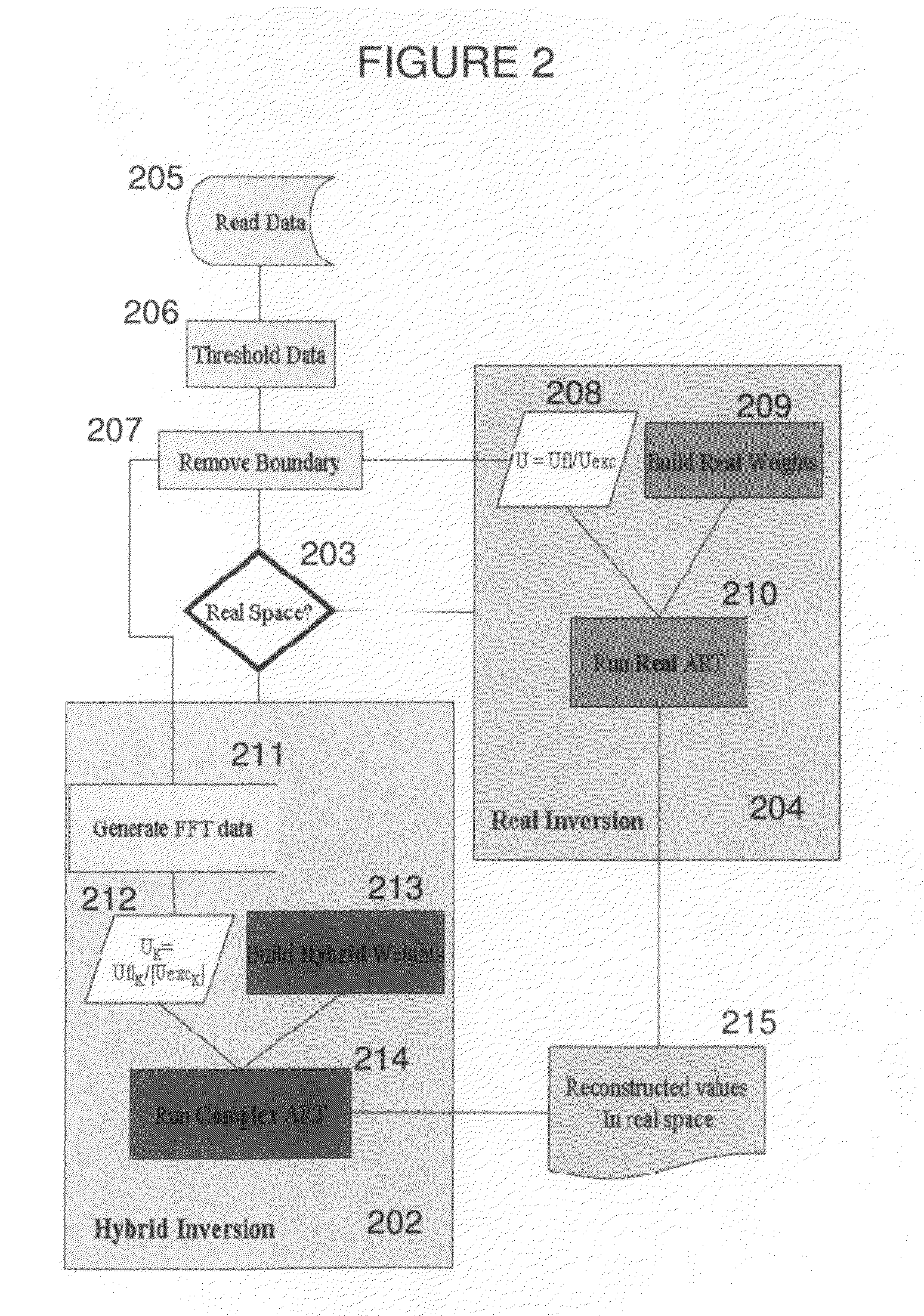
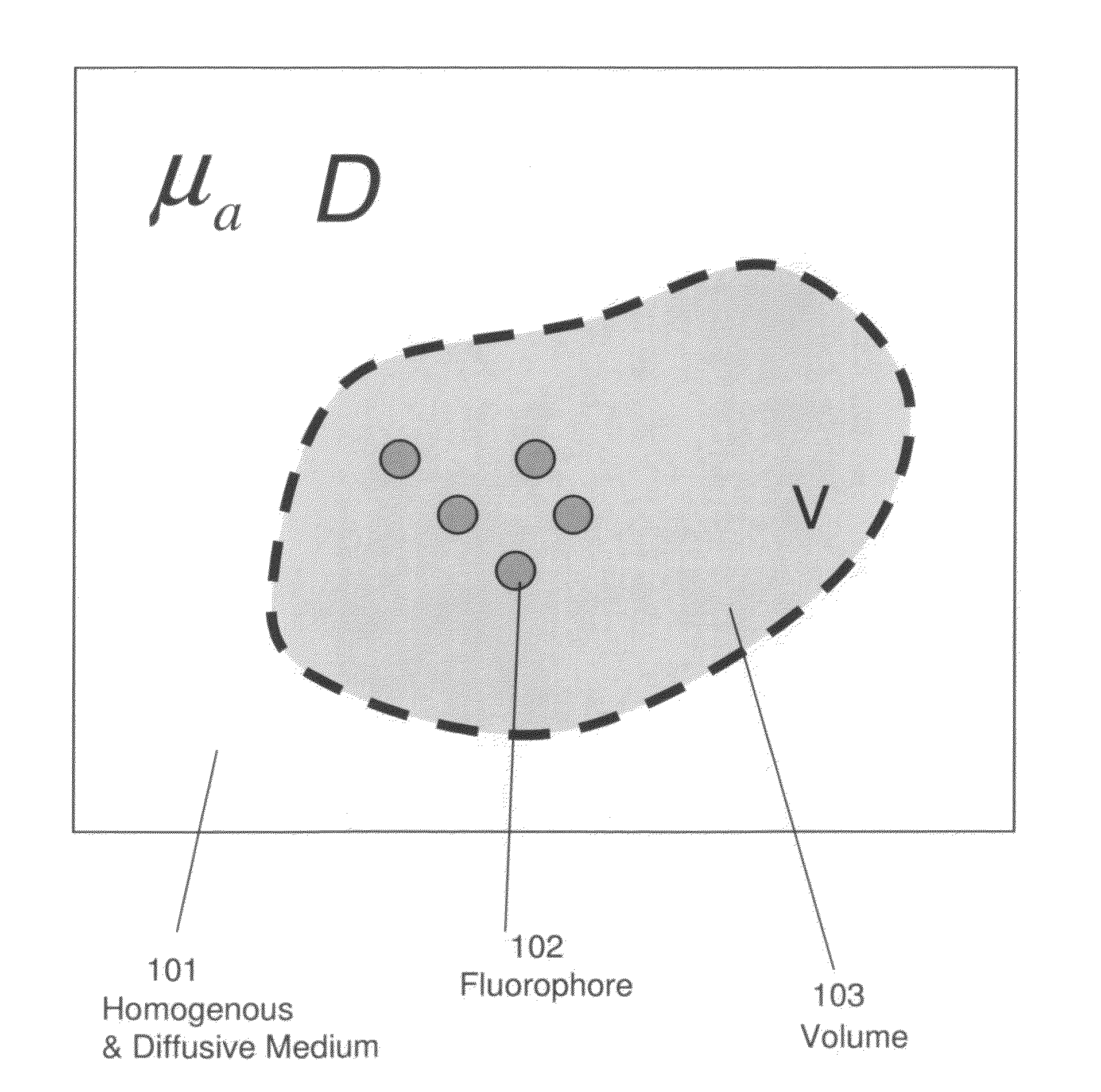
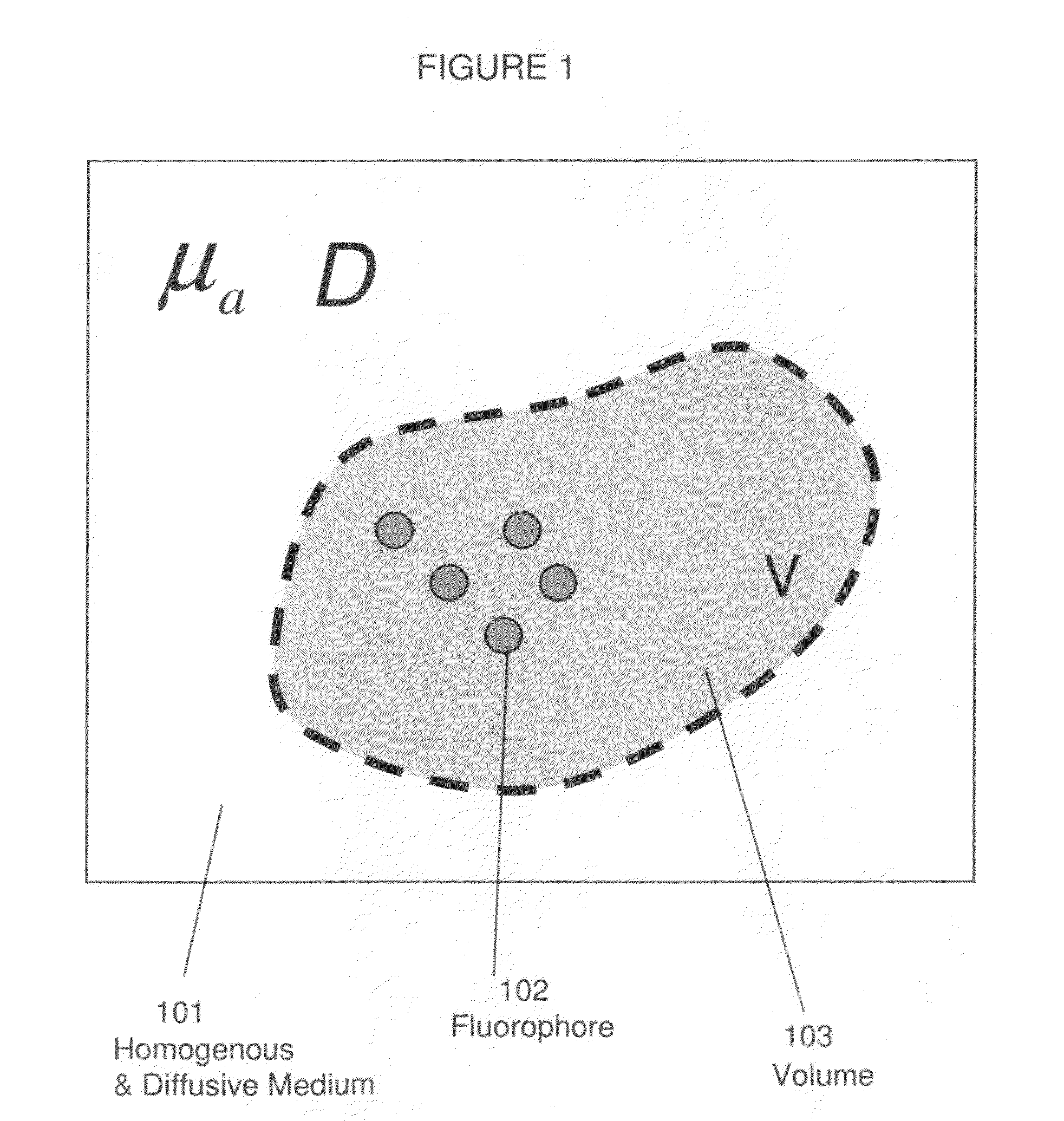
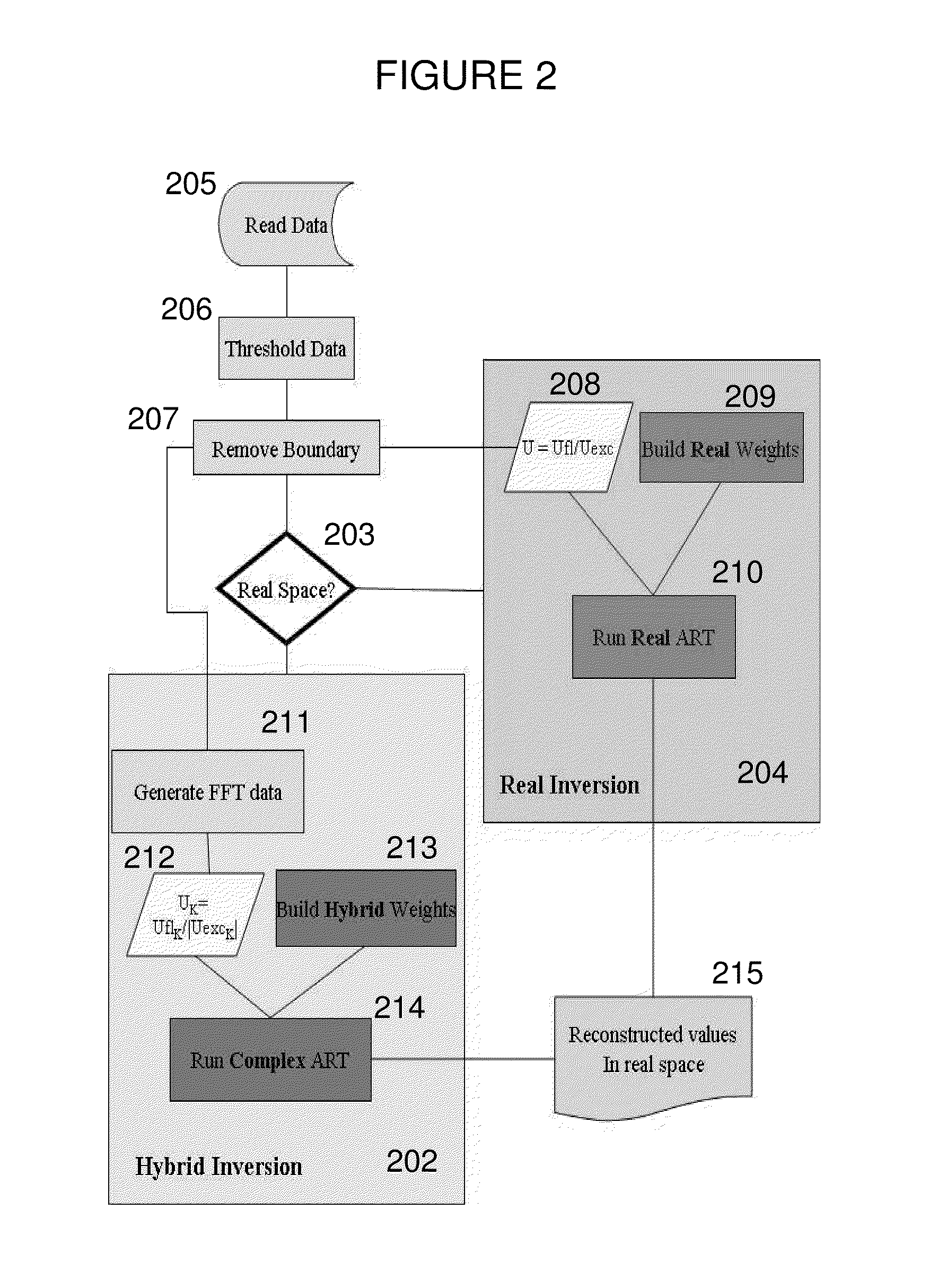
Systems and methods for tomographic imaging in diffuse media using a hybrid inversion technique
ActiveUS20110060211A1Fast rebuildGood tomographic reconstruction performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionTomographic reconstructionFluorophore
The invention relates to systems and methods for tomographic imaging in diffuse media employing a fast reconstruction technique. A hybrid Fourier approach is presented that enables the fast tomographic reconstruction of large datasets. In certain embodiments, the invention features methods of in vivo fluorescence molecular tomographic (FMT) reconstruction of signals, reporters and / or agents (i.e., contrast agents or probes) in a diffusive medium (e.g., a mammalian subject). The method preserves the three-dimensional fluorophore distribution and quantitative nature of the FMT approach while substantially accelerating its computation speed, allowing FMT imaging of larger anatomies.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
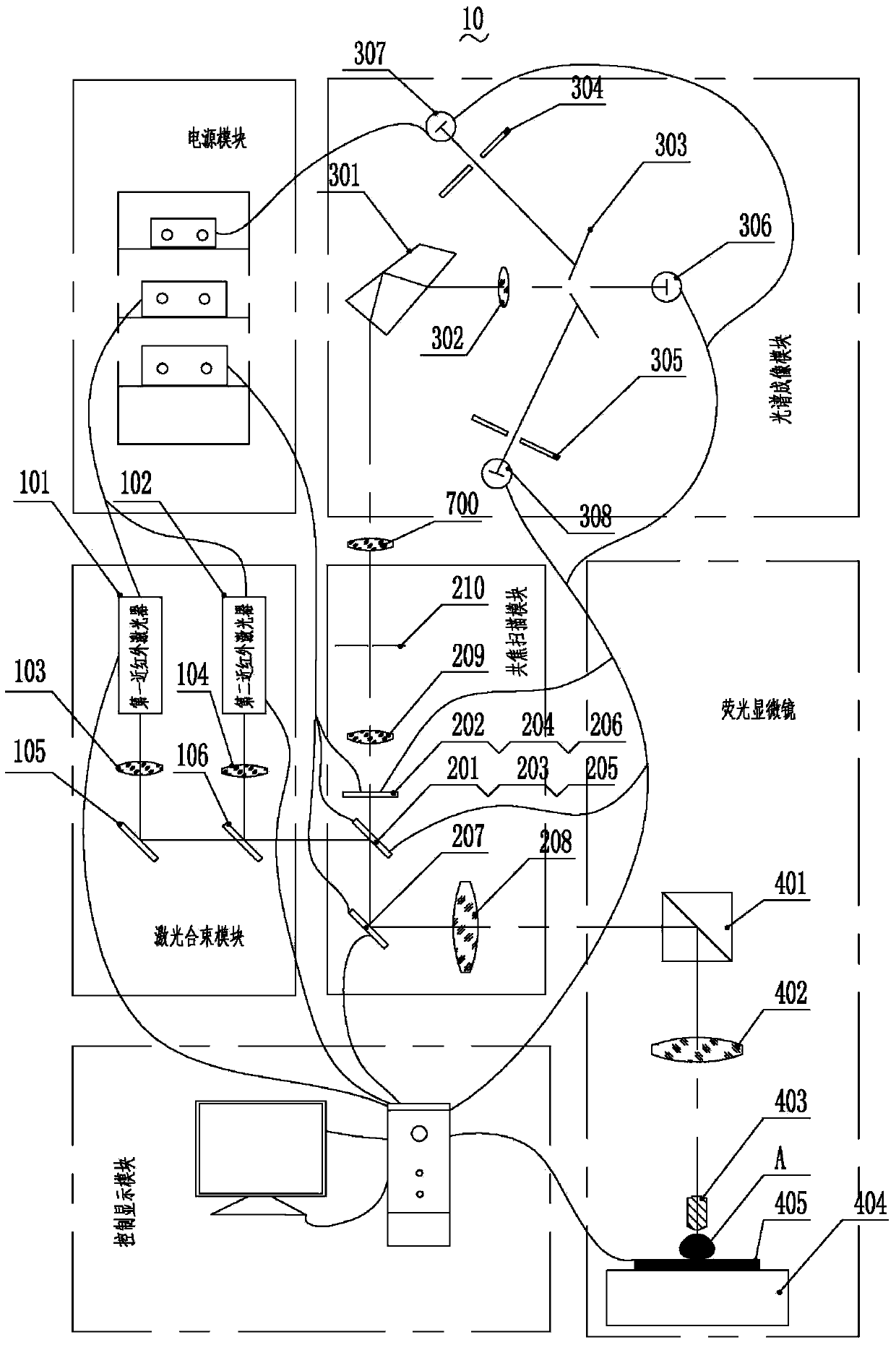
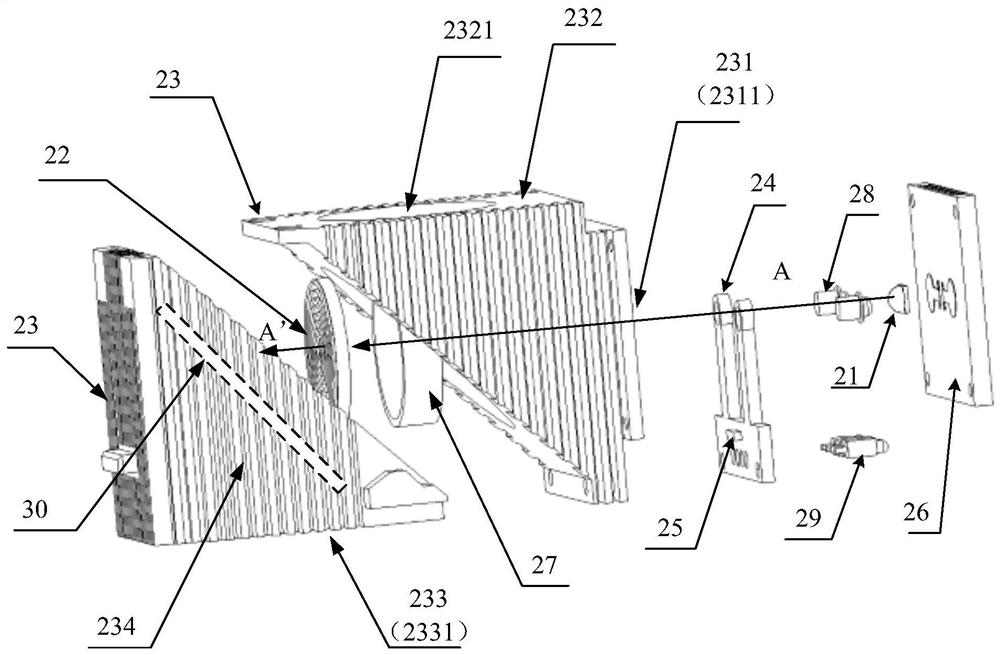
Fluorescence detector
ActiveCN103735249ABreakthrough the shortcomings of low detection depthDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBeam splitterPrism
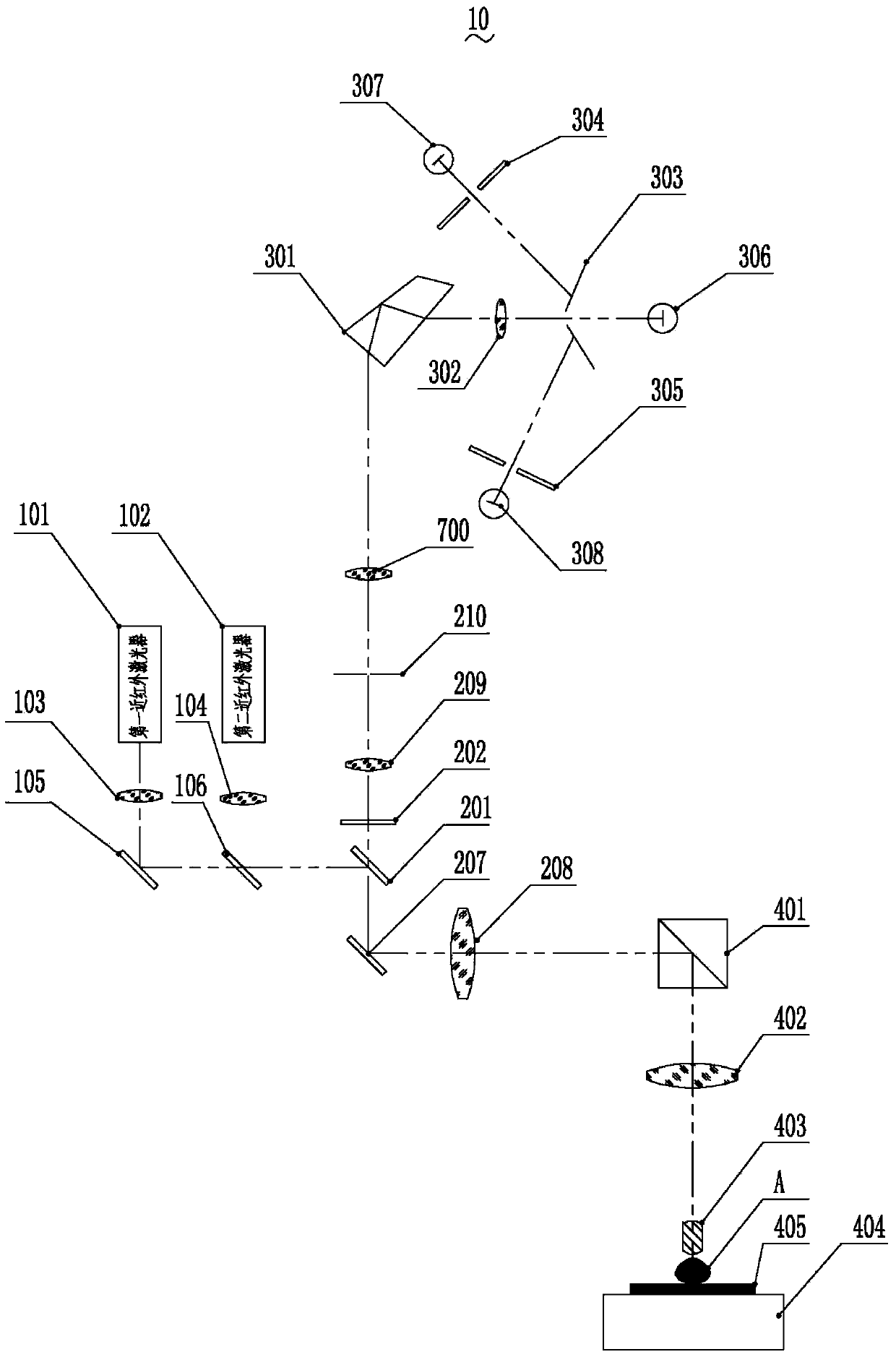
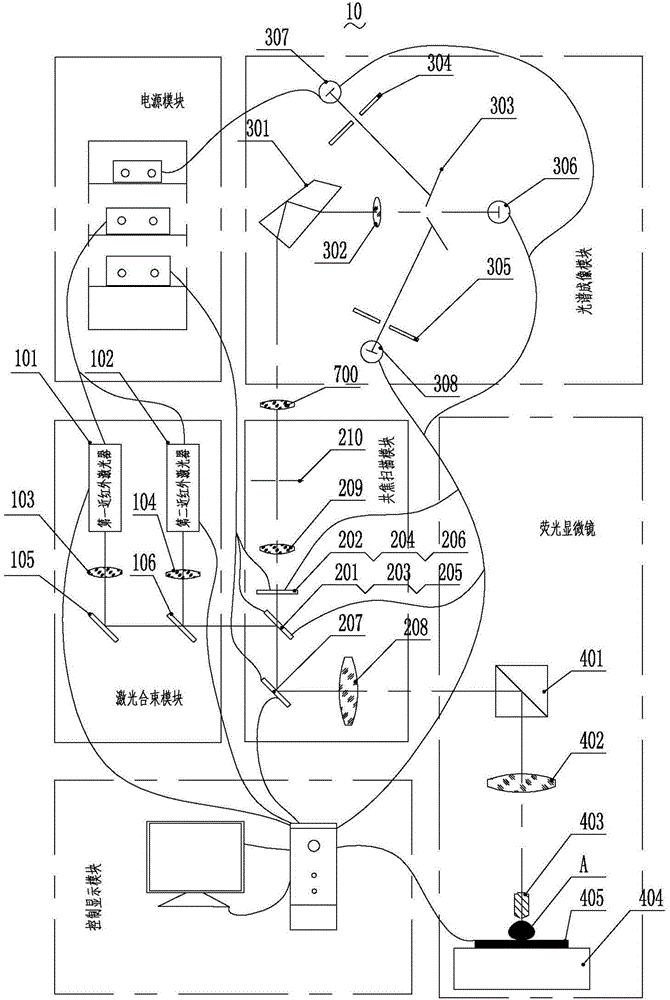
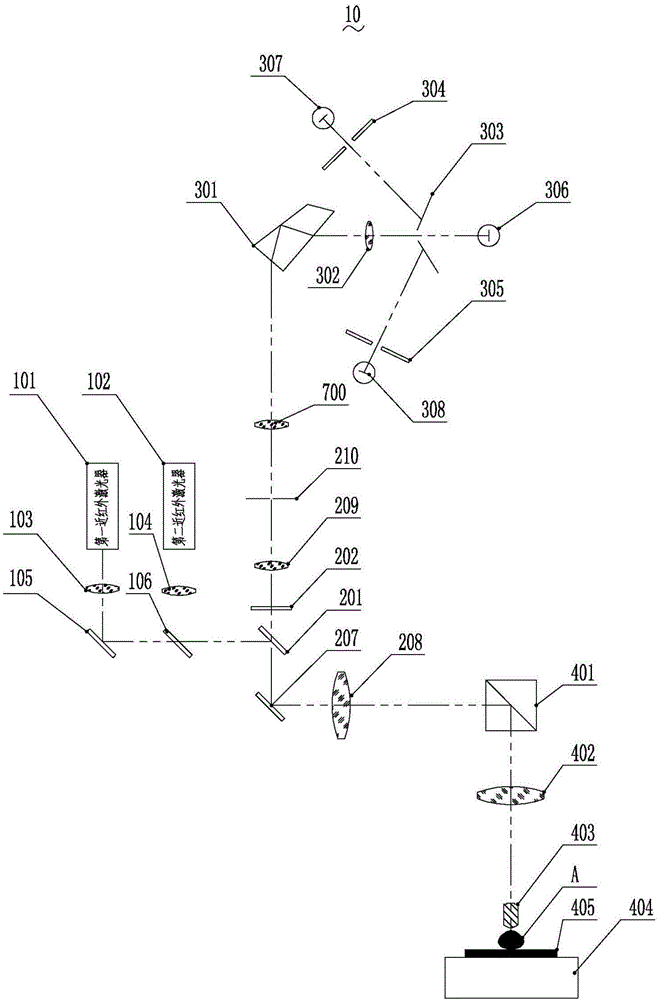
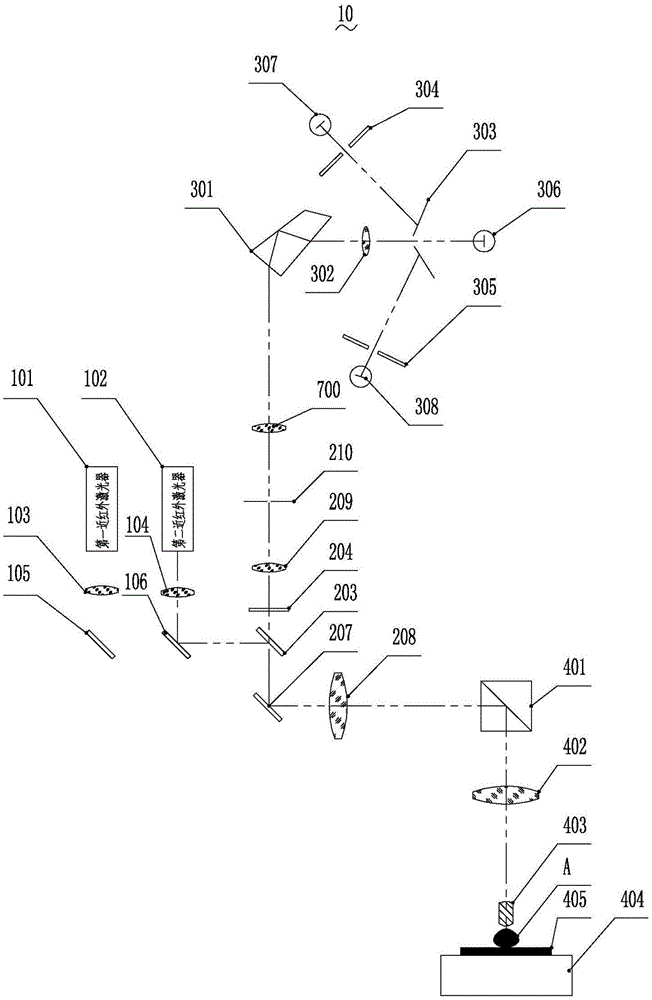
The invention discloses a fluorescence detector. The fluorescence detector comprises a laser beam combining module, a confocal scanning module, a spectral imaging module, a fluorescence microscope and a control display module. The laser beam combining module comprises two near-infrared light continuous lasers, a laser collimating lens, a reflecting mirror and a beam combining lens. The confocal scanning module comprises three switchable dichroic mirrors, three optical filters, a scanning galvanometer, a scanning lens, a pinhole lens and pinholes. The spectral imaging module comprises a beam splitter prism, a focus lens, three slits and three photomultipliers. The fluorescence microscope comprises a total reflection prism, a barrel lens, a micro-objective, a nanometer displacement platform and a sample platform. The control display module is used for controlling the laser, the scanning galvanometer, the micro-objective and the nanometer displacement platform and displaying the image. The fluorescence detector is capable of overcoming the disadvantage of low detection depth of the prior art, realizing the centimeter-level fluorescence detection and simultaneously realizing the fluorescence positioning and component analysis, and the fluorescence detector has broad application prospect in in-vivo fluorescence detection field.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles having near-infrared photothermal and in-vivo fluorescence imaging characteristics as well as preparation method and application of mesoporous silica nanoparticles
ActiveCN105056233AUniform sizeLow cytotoxicityPowder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocompatibility TestingMesoporous silica
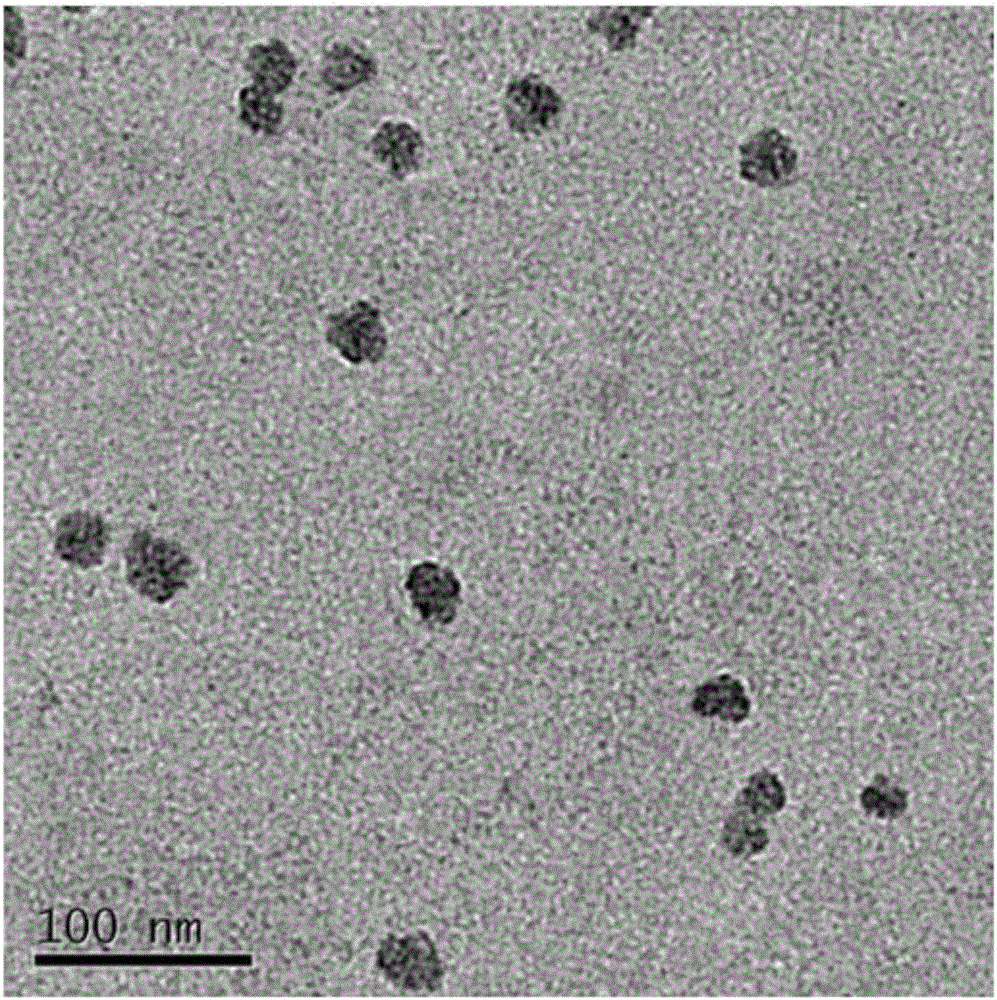
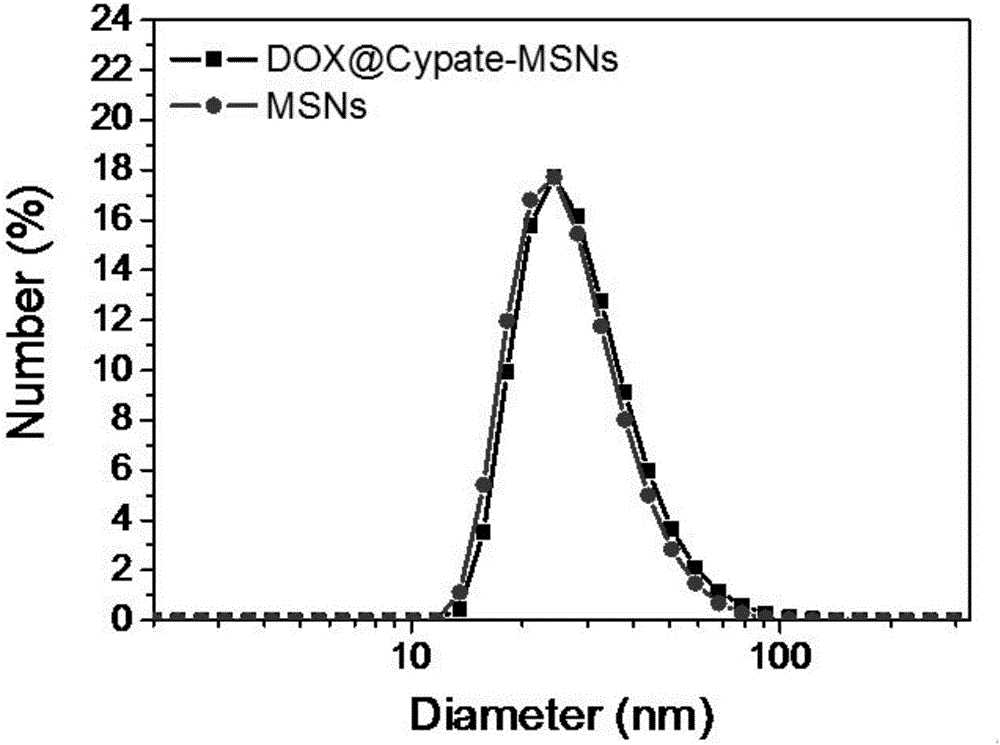
The invention discloses multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles having near-infrared photothermal and in-vivo fluorescence imaging characteristics as well as a preparation method and an application of the mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles subjected to amination are modified by carbocyanine dye Cypate, mesoporous channels are loaded with an antitumor drug, the mesoporous silica nanoparticles subjected to amination are prepared with CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) as a surfactant and are mixed with the antitumor drug in a solution, so that the mesoporous channels are loaded with the drug, an obtained nano-drug carrier is applied to near-infrared photothermal treatment, near-infrared fluorescence imaging and delivery of the antitumor drug, multi-functionalization of the same nano-drug carrier is realized, the mesoporous silica nanoparticles have very good biocompatibility, and produced chemotherapy and photothermal treatment combined effect is better than that produced with single treatment method.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Polyethylene glycol modified magnetic nanoparticle and application thereof
InactiveCN103585644AEasy to prepareAchieve loadingEnergy modified materialsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
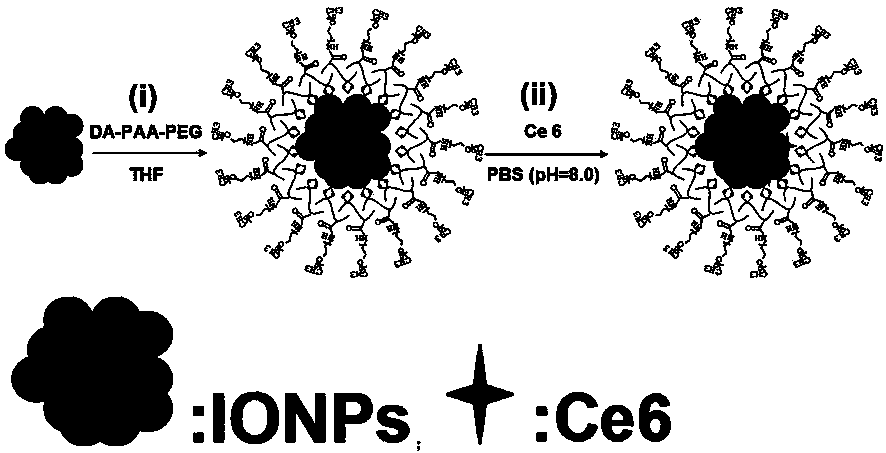
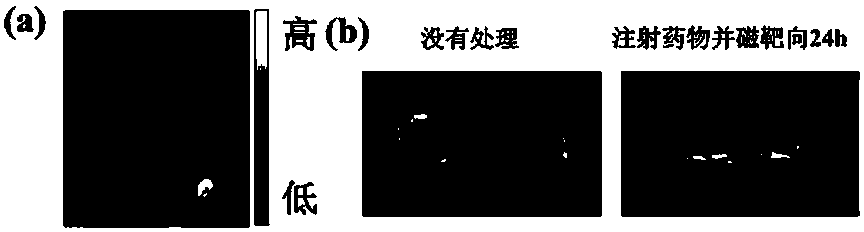
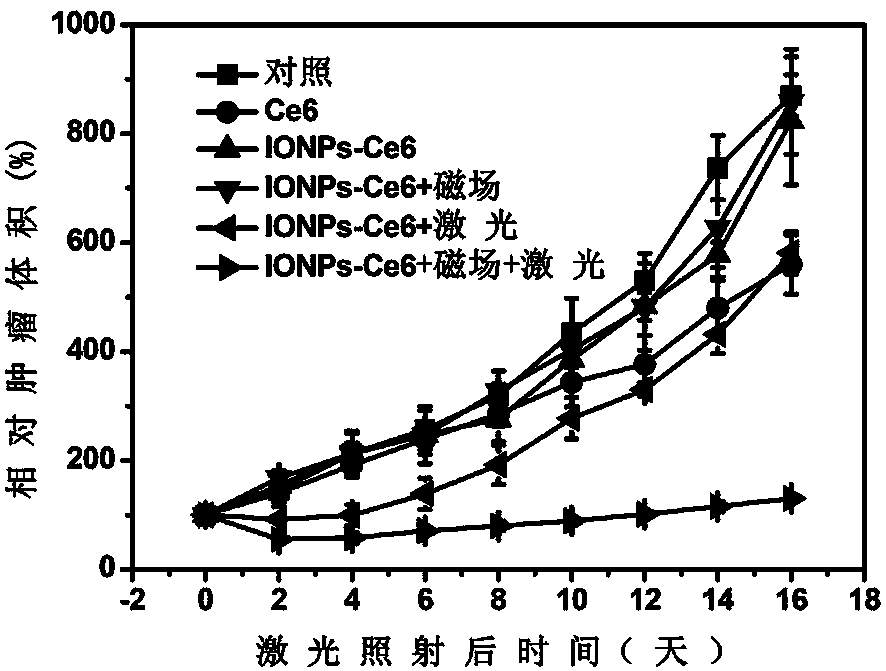
The invention discloses a polyethylene glycol modified magnetic nanoparticle and an application thereof. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, a solvothermal method is adopted to prepare the magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle; then, a layer of grafted copolymer dopamine / polyacrylic acid / polyethylene glycol (DA-PAA-PEG) is decorated on the surface of the magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle through chelation of hydroxide radicals and iron ions on dopamine so as to obtain a polyethylene glycol modified magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle (Fe3O4-DA-PAA-PEG); and finally, photosensitive molecules are loaded through the chelation of hydroxide radicals and iron ions on the photosensitive molecules to obtain the polyethylene glycol modified magnetic nanoparticle. The prepared polyethylene glycol modified magnetic nanoparticle has good water solubility and biocompatibility as well as excellent in-vivo magnetic targeting performance, and can generate singlet oxygen under the laser irradiation, so that cancer cells can be killed efficiently, and accordingly, the a polyethylene glycol modified magnetic nanoparticle can be applied to preparation of an in vivo fluorescence and magnetic resonance bimodal imaging developer and a photo-thermal therapeutic agent for treating cancers.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Cone-beam X-ray luminescence computed tomography method
ActiveCN103239255AOvercome limitationsAccurate reconstructionComputerised tomographsTomographyAnatomical structuresFunction optimization
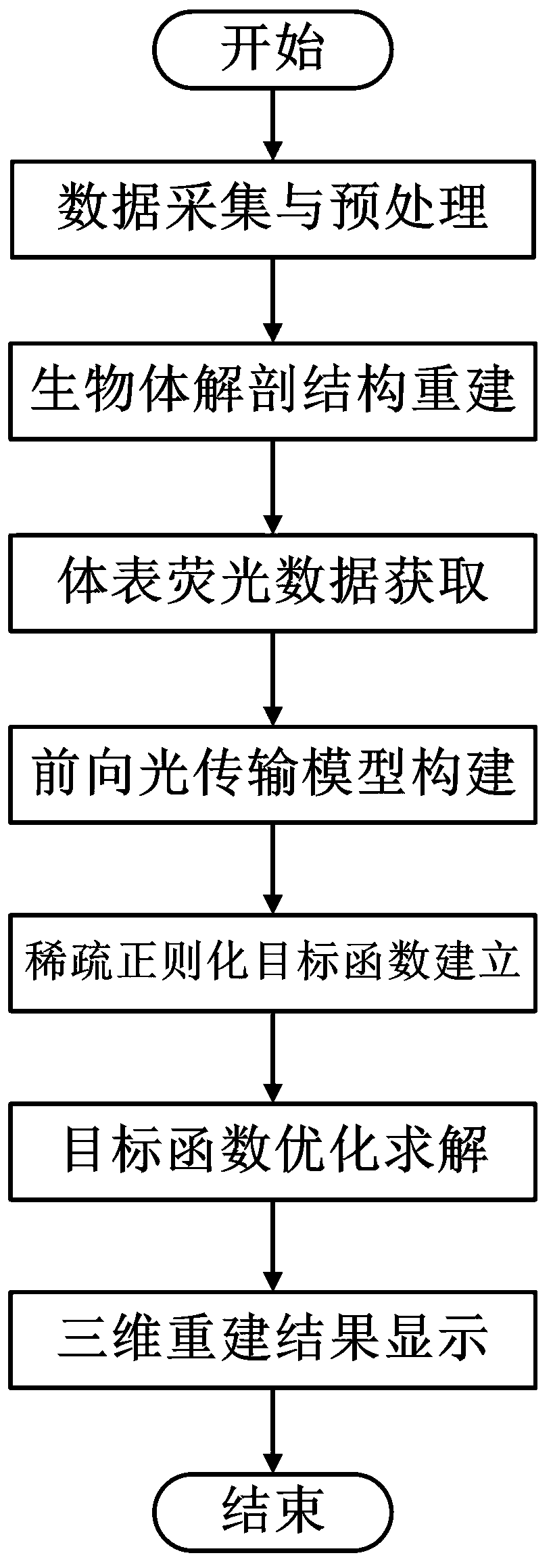
The invention discloses a cone-beam X-ray luminescence computed tomography method based on a simplified ball harmonic wave-diffusion approximation model and solves the problem of fast and accurate imaging for achieving fluorescence image reconstruction based on a diffusion approximation equation or by aid of the traditional X-ray computed tomography technology in the prior art. The cone-beam X-ray luminescence computed tomography method is characterized in that an objective function is constructed on the basis of the simplified ball harmonic wave-diffusion approximation model and a sparse regularization method, and the objective function is solved in a half greedy algorithm to achieve fast and accurate reconstruction of in-vivo fluorescence nano-particle probes. The cone-beam X-ray luminescence computed tomography method specifically includes steps: data collection and preprocessing, living body anatomical structure reconstruction, body surface fluorescence data acquisition, forward light transmission model construction, sparse regularization objective function construction, objective function optimization solution and three-dimensional reconstruction result display. The cone-beam X-ray luminescence computed tomography method has the advantages of being capable of achieving accurate, fast and high-resolution position and concentration distribution reconstruction of the in-vivo fluorescence nano-particle probes, and being capable of being applied to the field of X-ray fluorescence computed tomography.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BLT INSTR & METER
Apparatus and method for quantitative noncontact in vivo fluorescence tomography using a priori information
InactiveUS20130023765A1Accurate recoveryPrecise positioningDiagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic Radiology ModalityOptical tomography
An apparatus for providing an integrated tri-modality system includes a fluorescence tomography subsystem (FT), a diffuse optical tomography subsystem (DOT), and an x-ray tomography subsystem (XCT), where each subsystem is combined in the integrated tri-modality system to perform quantitative fluorescence tomography with the fluorescence tomography subsystem (FT) using multimodality imaging with the x-ray tomography subsystem (XCT) providing XCT anatomical information as structural a priori data to the integrated tri-modality system, while the diffuse optical tomography subsystem (DOT) provides optical background heterogeneity information from DOT measurements to the integrated tri-modality system as functional a priori data. A method includes using FT, DOT, and XCT in an integrated fashion wherein DOT data is acquired to recover the optical property of the whole medium to accurately describe photon propagation in tissue, where structural limitations are derived from XCT, and accurate fluorescence concentration and lifetime parameters are recovered to form an accurate image.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
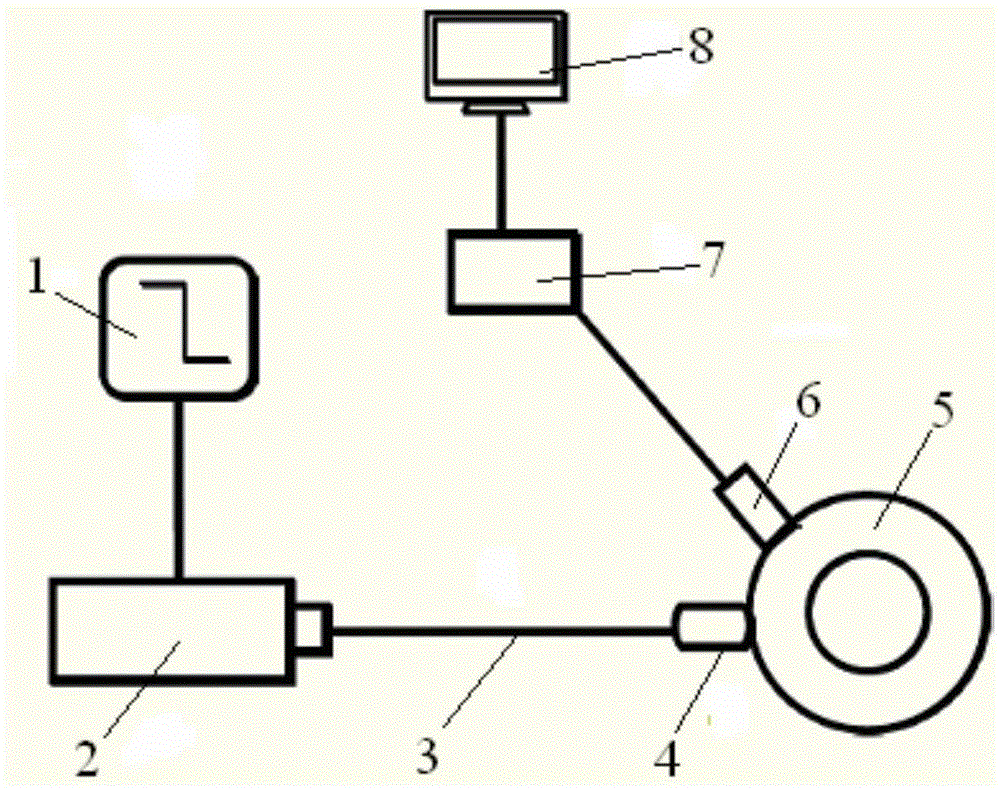
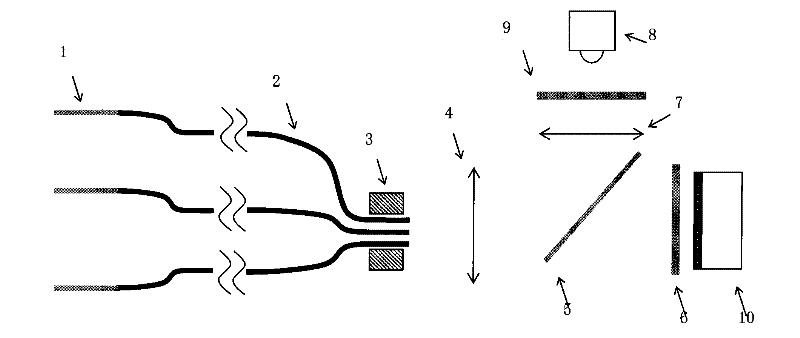
Minimally invasive multiple channel in vivo fluorescence signal real-time detection system and method
InactiveCN101612035AIncrease the number of bundlesUpgrade Simultaneous DetectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFiberImage detection
The invention relates to a minimally invasive multiple channel in vivo fluorescence signal real-time detection system, which belongs to the technical field of in-vivo animal fluorescence detection. The system is characterized in that fiber optic bundles, a fiber optic bundle fixing device, a microscopic objective, a dichroic mirror forming a 45 degree angle with the horizontal plane, a fluorescent filter and an optical detector, which are horizontally arranged in sequence, share an axle to form a fluorescence emission light path; an excitation light source, an excitation light filter and a lens are vertically arranged to form an excitation light path; the excitation light forms a 45 degree angle with the dichroic mirror, and is orthogonal with the fluorescence emission light at the center of the dichroic mirror. The system can detect the concentrations of the fluorescence targets of organs or tissues of in-vivo animals in a minimally invasive, multiple channel, quantitative and continuous way.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
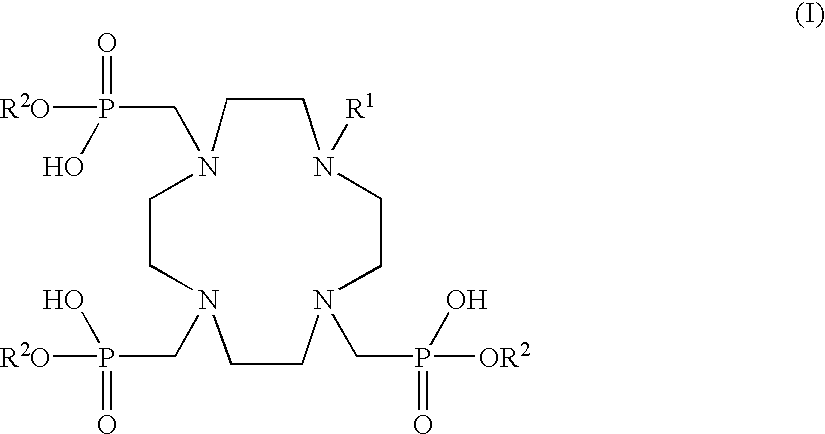
Tissue specific fluorescent chelates possessing long wavelength UV excitation
InactiveUS6962690B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsChemistryTerbium
Fluorescent chelates of lanthanide, terbium, europium and dysprosium with tetraazamacrocyclic compounds are discussed which can be used as fluorescent in vitro or in vivo diagnostic agents. These chelates are tissue specific imaging agents for soft tissue cancers.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY +1
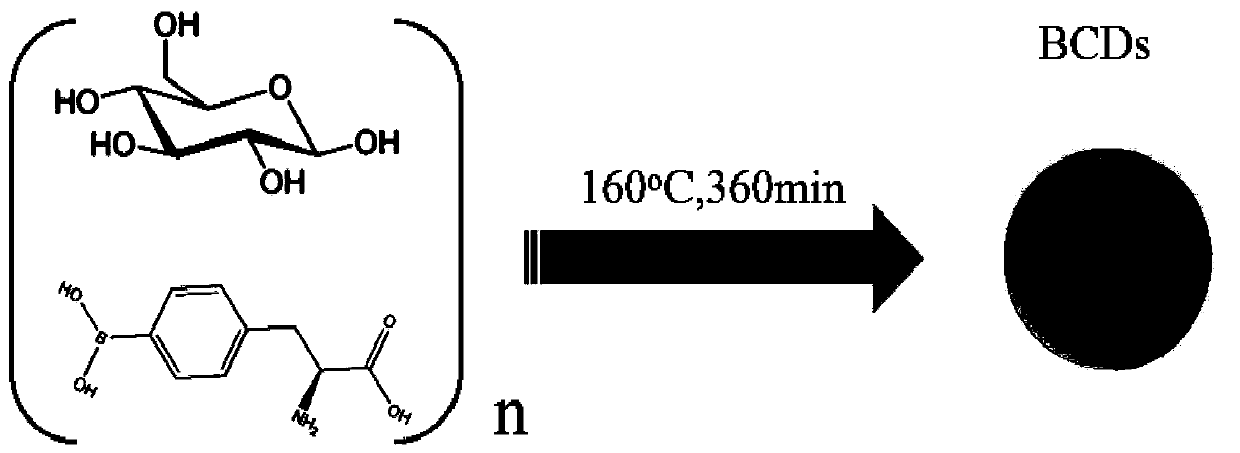
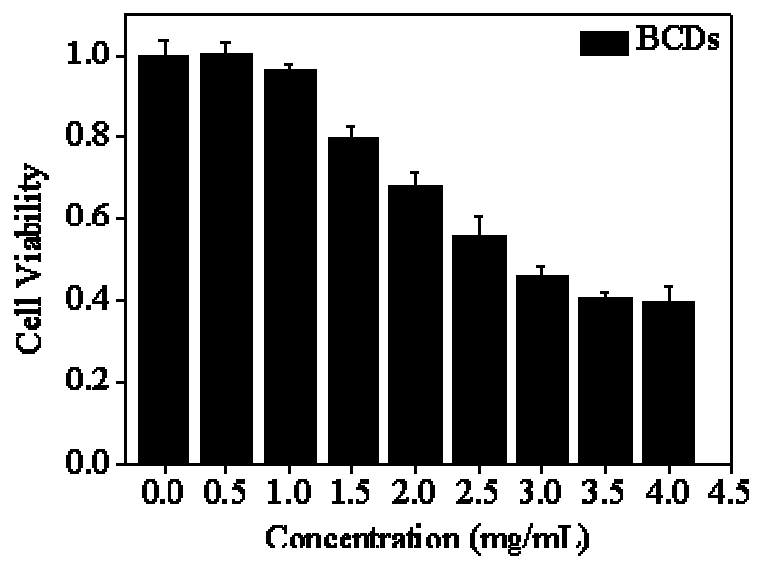
Preparation method of boron-containing carbon quantum dots and application of boron-containing carbon quantum dots in tumor diagnosis and boron neutron capture therapy drugs
ActiveCN111204736AGood treatment effectRealize integrationEnergy modified materialsNano-carbonTumor therapyTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a preparation method of boron-containing carbon quantum dots and an application of the boron-containing carbon quantum dots in tumor diagnosis and boron neutron capture therapydrugs, and relates to the field of chemical and biomedical tumor diagnosis and treatment. Glucose and BPA are used as raw materials to synthesize the boron-containing carbon quantum dots (BCDs), andthe quantum dots have in-vivo and in-vitro fluorescence luminescence properties similar to those of carbon quantum dots. Experiments prove that the BCDs synthesized by taking glucose and BPA can target brain tumors and other tumor tissues and are enriched at tumor parts, and the BCDs in healthy tissues can be quickly metabolized and excreted. The characteristic provides conditions for realizing excellent treatment effect of the BNCT. Therefore, the BCDs can be used as a novel tumor BNCT therapeutic agent, and integration of tumor diagnosis and BNCT treatment can be realized. The boron-containing carbon quantum dots are good in biocompatibility and have an excellent in-vivo fluorescence imaging effect.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for tomographic imaging in diffuse media using a hybrid inversion technique
ActiveUS8401618B2Fast rebuildFast calculation timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionTomographic reconstructionFluorophore
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
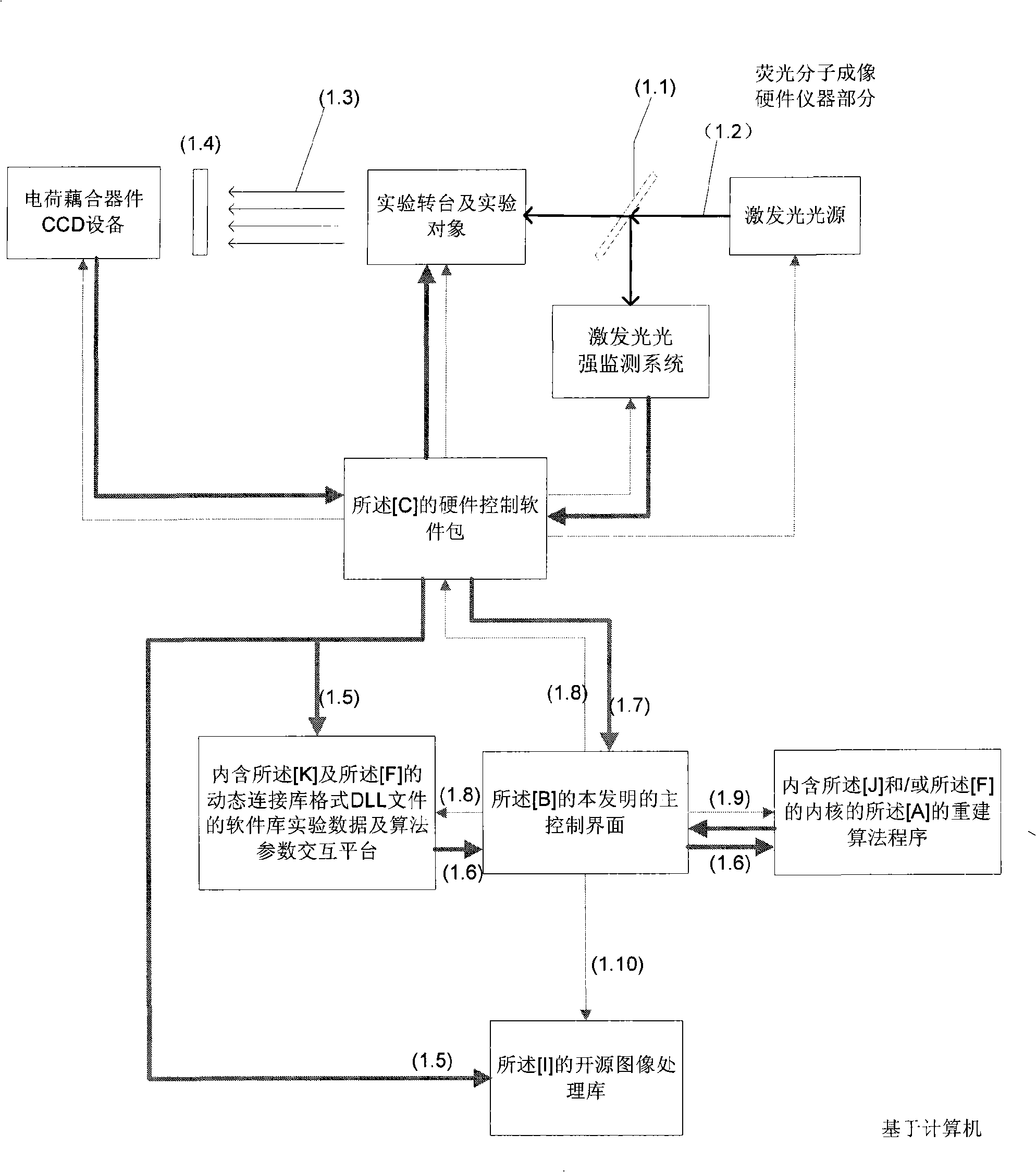
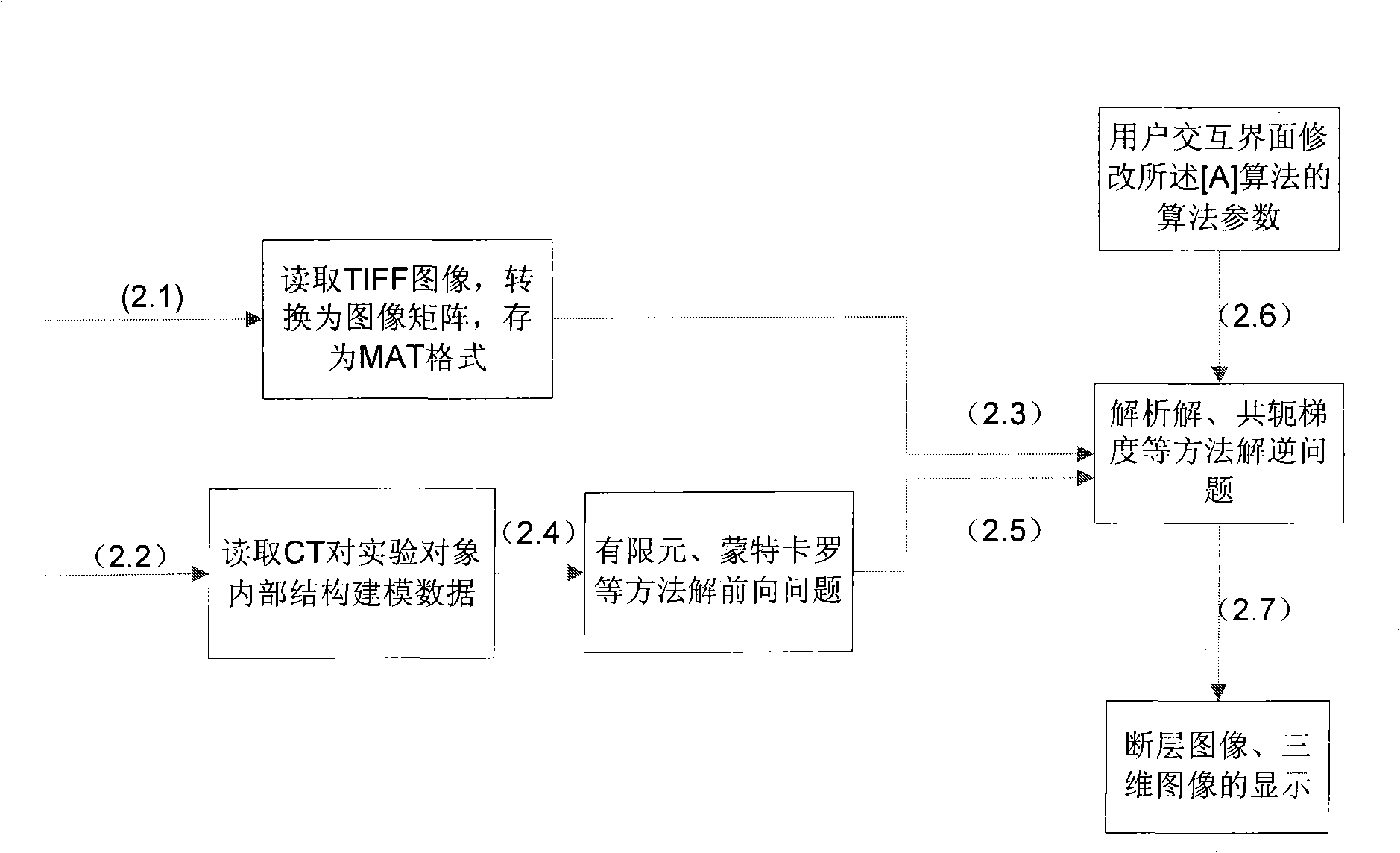
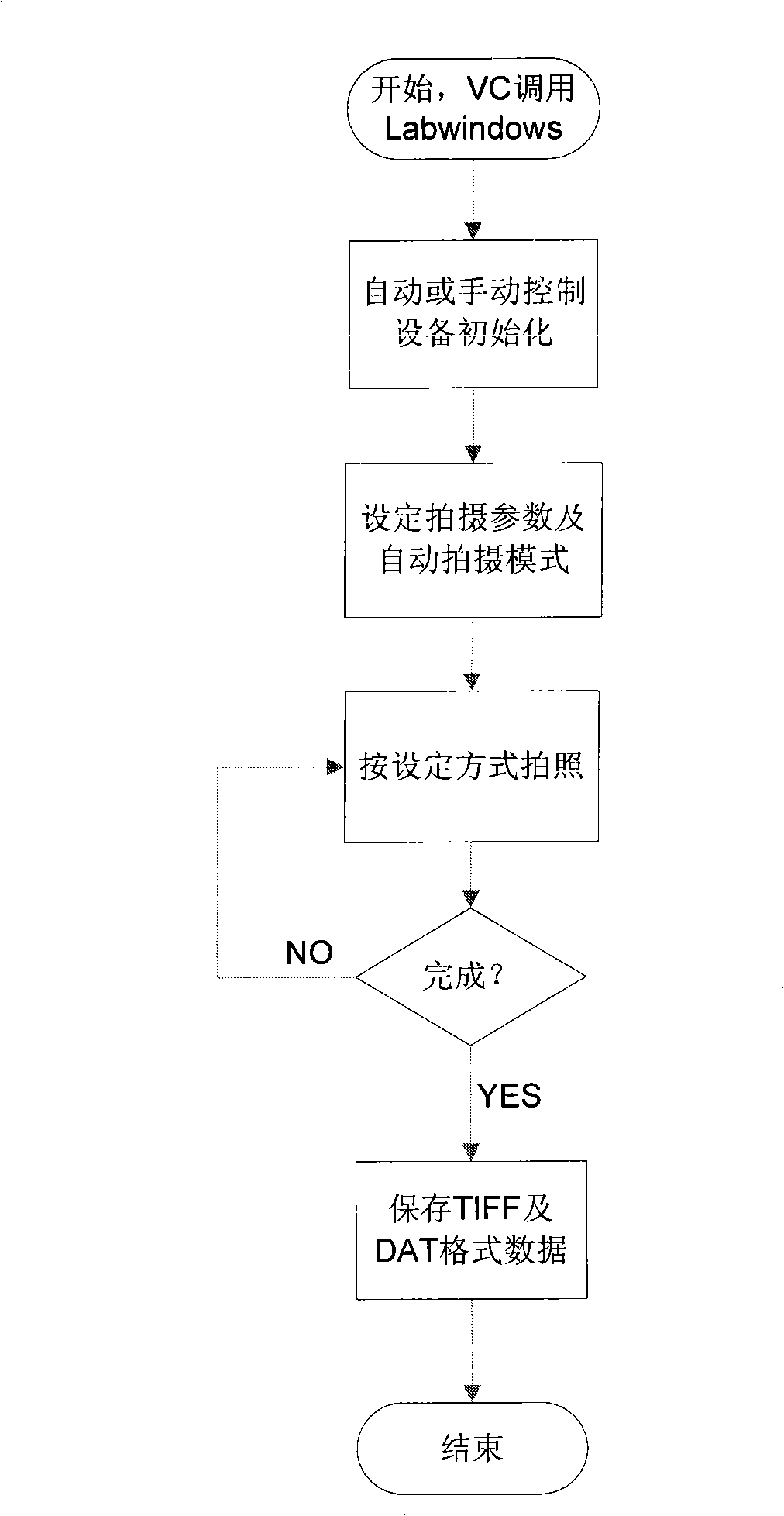
In vivo fluorescence numerator imaging modelling approach capable of calling multiple imaging algorithms
InactiveCN101268935AEasy to updateImplementing Reflection Imaging ExperimentsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsReconstruction algorithmMATLAB
The invention relates to an in-vivo fluorescence molecule imaging and modeling method which can invoke a plurality of imaging algorithms and belongs to the technical field of fluorescence molecule imaging. The in-vivo fluorescence molecule imaging and modeling method is characterized in that the method is realized by controlling a florescence molecule imaging apparatus by a computer; a Microsoft main control interface program, a hardware control program package, a software library experimental data conversion and algorithm parameter alternating module, a DLL format DLL document that internally contains a C language library and a MATLAB software, and a rebuilding algorithm program library that internally contains a finite element analysis software and a kernel of the MATLAB software are arranged in the computer; in addition, an open-source image processing library is also contained. The in-vivo fluorescence molecule imaging and modeling method can automatically realize the fluorescence molecule imaging and realize the rebuilding algorithm of the density and the position of the fluorescence group and renovate the algorithm kernel conveniently.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Synthesis and fluorescence detection imaging application of phosphorescence iridium complex
ActiveCN105223171AStrong penetrating powerLight damage is smallColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceIridiumCysteine thiolate
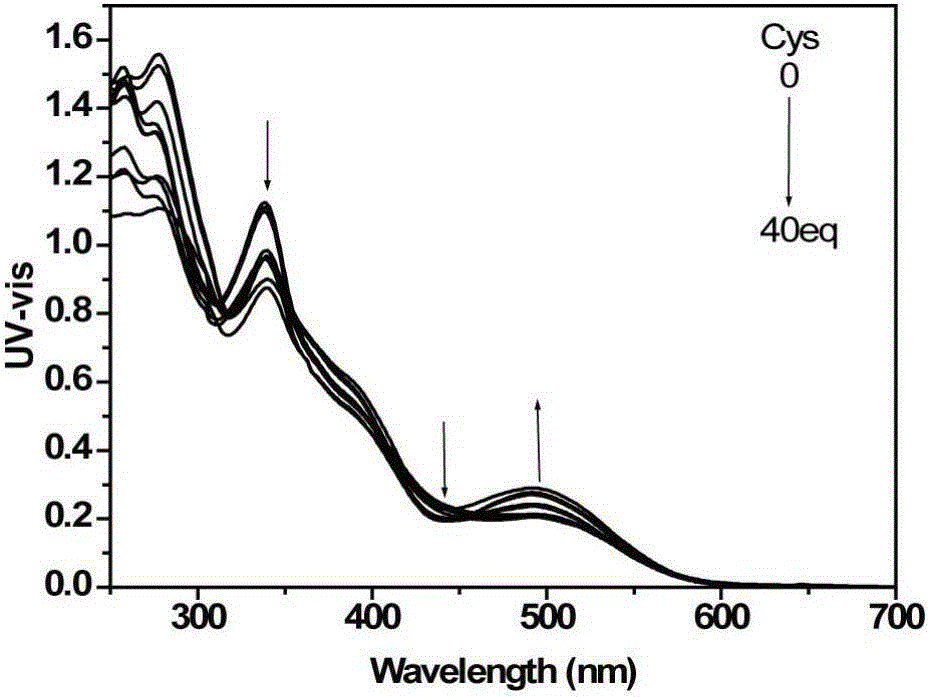
The invention discloses a preparation method and fluorescence detection application of a phosphorescence iridium complex. The phosphorescence complex has a chemical formula [Ir(CHO-btiq)2(bpy)][PF6]. The invention provides the preparation method of the phosphorescence iridium complex, and the application of the phosphorescence iridium complex to the detection of cysteine and homocysteine. The emission spectrum of the phosphorescent iridium complex is in the near-infrared region; biological imaging of the phosphorescent iridium complex has the advantages of little damage small, strong penetrability and little background spontaneous fluorescence; and the phosphorescent iridium complex has good application prospect in small animal in vivo fluorescence imaging. The iridium complex provided by the invention can realize high selectivity detection of cysteine and homocysteine, and provides the possibility for the construction of a simple and high-selectivity fluorescence chemical sensor for determination of cysteine and homocysteine.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
Functional protein and cyanine dye molecule compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110201191AImprove luminous efficiencySmall background scatterPowder deliveryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCyanineMolecular imaging
The invention provides a functional protein and cyanine dye molecule compound and further provides a preparation method of the compound and application of the compound as a fluorescence molecular imaging developer in a second near-infrared region. The functional protein and cyanine dye molecule compound is a compound formed by controllable self-assembly of cyanine dye molecules and functional protein. The outer layer of the compound is provided with the functional protein which wraps the cyanine dye molecules internally. Compared with an existing second near-infrared region probe, the compoundhas advantages that luminescence and in-vivo behaviors are evidently improved, imaging effects in the second near-infrared region are remarkably improved, and the compound can be applied to in-vivo fluorescence imaging and molecular imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI THERANOSTICS BIOTECH CO LTD
Fluorescent probe, fluorescence detection method, and method for using fluorescent probe
InactiveCN109073556AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferBiological body
The present invention relates to a fluorescent probe which includes: a carrier molecule; and fluorescent dye a and fluorescent dye b which are bonded to the carrier molecule. Fluorescent dye a and fluorescent dye b have different excitation wavelengths. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) does not occur between fluorescent dye a and fluorescent dye b. The present invention also relates to a fluorescence detection method which includes: a step in which target cells are labelled with the fluorescent probe; and a step in which the target cells labelled with the fluorescent probe are irradiated with excitation light, and fluorescence from the fluorescent probe is observed. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a method for using the fluorescent probe, said method including: astep in which cells are fluorescence labelled using the fluorescent probe; a step in which the fluorescence-labelled cells are screened using a flow cytometer or a fluorescence microscope; a step inwhich the screened fluorescence-labelled cells are transplanted into a living organism; and a step in which the fluorescence-labelled cells in the living organism are observed using an in vivo fluorescence imaging device.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +1
Construction method for endophytic fungus efficient genetic system and application thereof
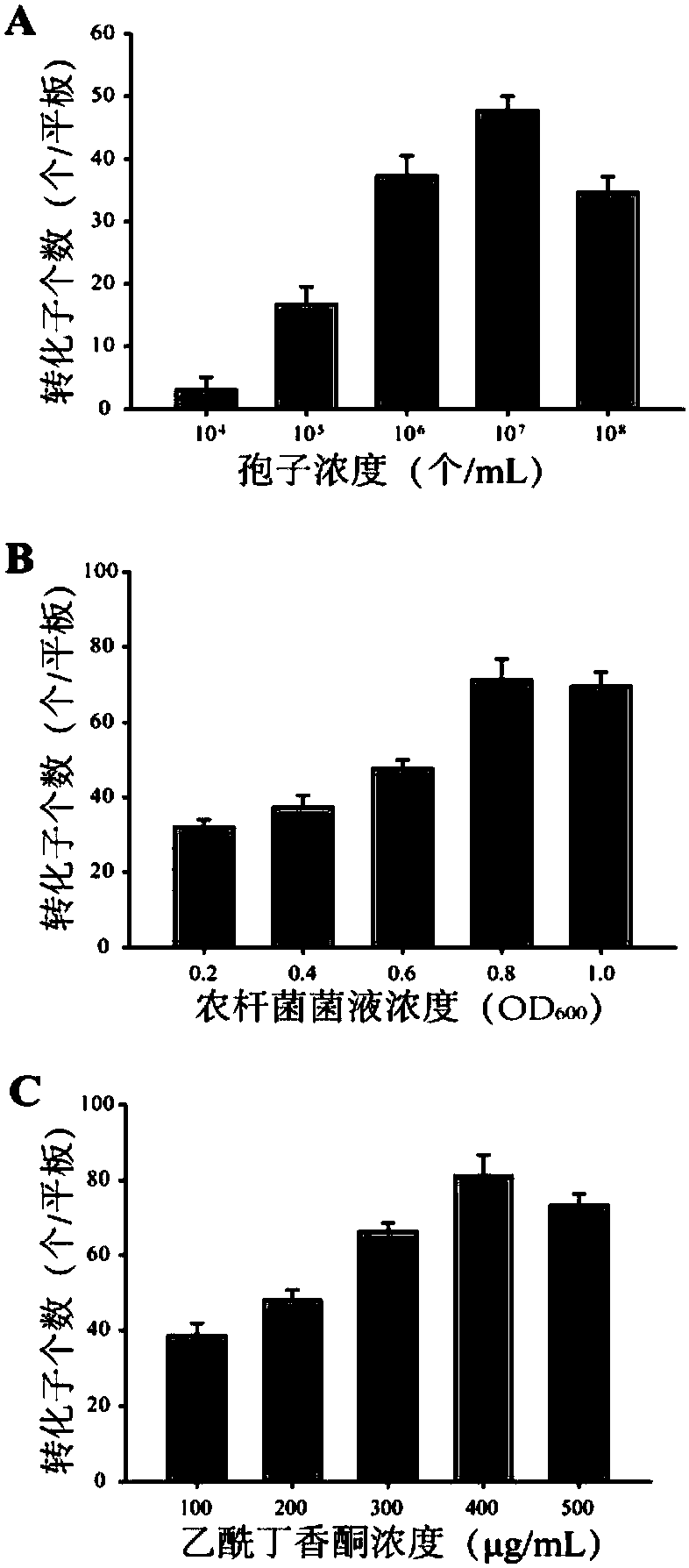
ActiveCN108265074AImprove conversion efficiencyLow costVector-based foreign material introductionCalcarisporium arbusculaGene cluster
The invention provides a construction method for an endophytic fungus efficient genetic system. The method includes: (1) agrobacterium-mediated transformation suitable for calcarisporium arbuscula; (2) establishment of a calcarisporium arbuscula in-vivo high expression system; (3) establishment of a calcarisporium arbuscula in-vivo fluorescence expression system; and (4) establishment of a calcarisporium arbuscula gene directional knockout system. The endophytic fungus is calcarisporium arbuscula. According to the endophytic fungus calcarisporium arbuscula genetic system provided by the invention, the calcarisporium arbuscula in-vivo high expression system is established for the first time, and four strong promoters fitting calcarisporium arbuscula are screened out. The constructed endophytic fungus calcarisporium arbuscula genetic system can be applied to activation of recessive gene clusters, compound biosynthesis mechanisms and enzyme functional study. The method provided by the invention is reasonable in design, and compared with the existing protoplast transformation methods, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of low cost, simple operation, short experiment cycle and high transformation efficiency, and provides materials for genetic engineering research and genetic modification of calcarisporium arbuscula.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fluorescent imaging probe and preparation method and application thereof
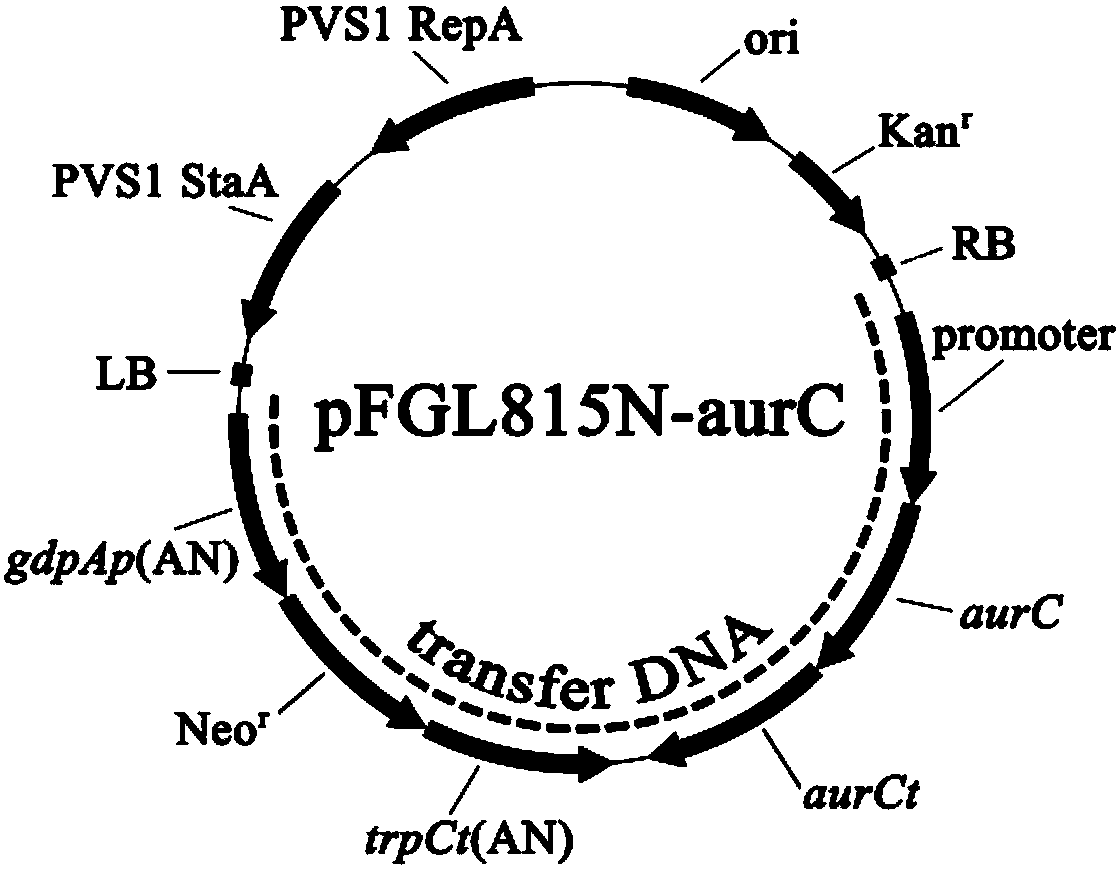
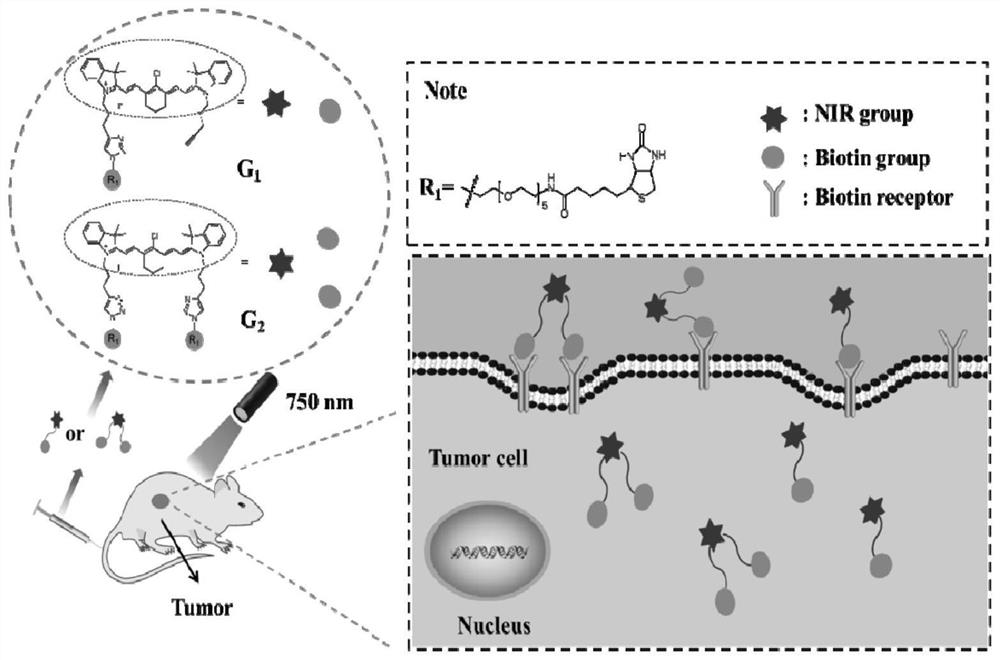
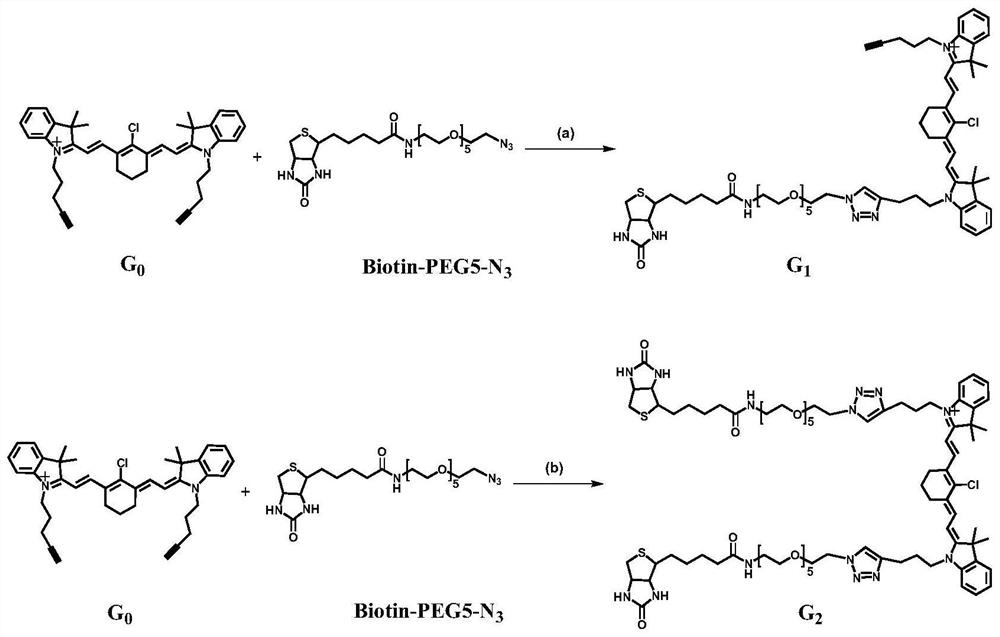
ActiveCN112341474AHigh fluorescence intensityImprove targetingOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceTumor targetTumor targeting
According to the invention, two NIRF probes (G1 and G2) with good water solubility are designed. The PEG structure of the probe improves the hydrophilicity of the probe, and an in vitro spectrum and alipid-water distribution coefficient prove that G1 and G2 have a relatively low aggregation trend. The biotin structure enhances the targeting of the probe to BR positive tumor cells, and G1 and G2 show good fluorescence imaging effects in in-vitro cell experiments and in-vivo fluorescence imaging. Due to the cooperation of a specially selected hydrophilic group-PEG structure and targeting group-biotin, the probe G1 and the probe G2 can be balanced between hydrophilicity and targeting property, so that balance is achieved in multiple aspects such as fluorescence intensity, tumor targeting property, transmembrane transport property, residence time in tumor cells, and the prepared probes G1 and G2 have the advantages of high fluorescence intensity, strong targeting, strong transmembrane transportation and long residence time in tumor cells.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
Separate multimode fusion three-dimensional tomography system and method
ActiveCN103431912AGet quicklyEliminate interactionSurgeryComputerised tomographsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityData acquisition
The invention discloses a separate multimode fusion three-dimensional tomography system and a separate multimode fusion three-dimensional tomography method. The system comprises a data source transmission module, a data acquisition module, a system control and data transmission module and a data processing module, wherein the data source transmission module is used for transmitting X rays and an exciting light source to irradiate a sample respectively; the data acquisition module is used for detecting the dose of the X rays passing through the sample, and receiving fluorescent information excited from the sample; the system control and data transmission module is used for controlling the ordered operation of each module in the system; the data processing module is used for processing the acquired imaging data of the sample, and three-dimensionally reconstructing the structure information of the sample and light source distribution information. The system and the method can be used for realizing the real-time and nondestructive multimode image acquisition of in vivo fluorescence molecular imaging and X-ray tomography, the biological information of an imaging sample can be rapidly obtained, influence between modes is overcome in terms of physical position, and meanwhile, different mode data of the imaging sample can be well fused in terms of physical position.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescence endoscope imaging device and method
ActiveCN105595947AHigh speedImprove accuracySurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyWide bandBroadband laser
The invention discloses a fluorescence endoscope imaging device and a fluorescence endoscope imaging method. The imaging device comprises an in-vitro spectrum coding unit, an in-vivo fluorescence imaging unit and a light transmission unit, wherein the light transmission unit is connected with the in-vitro spectrum coding unit and the fluorescence imaging unit; the in-vitro spectrum coding unit is used for performing two-dimensional coding on a broadband laser light source spectrum; the light transmission unit is used for transmitting the coded broadband laser light source spectrum to the in-vivo fluorescence imaging unit; the in-vivo fluorescence imaging unit is used for imaging by means of irradiating the coded broadband laser light source spectrum color to in-vivo tissue cells. The fluorescence endoscope imaging device and the fluorescence endoscope imaging method disclosed by the invention have the advantage that the speed and accuracy of fluorescence endoscope imaging can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fluorescence detector
ActiveCN103735249BBreakthrough the shortcomings of low detection depthDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBeam splitterPrism
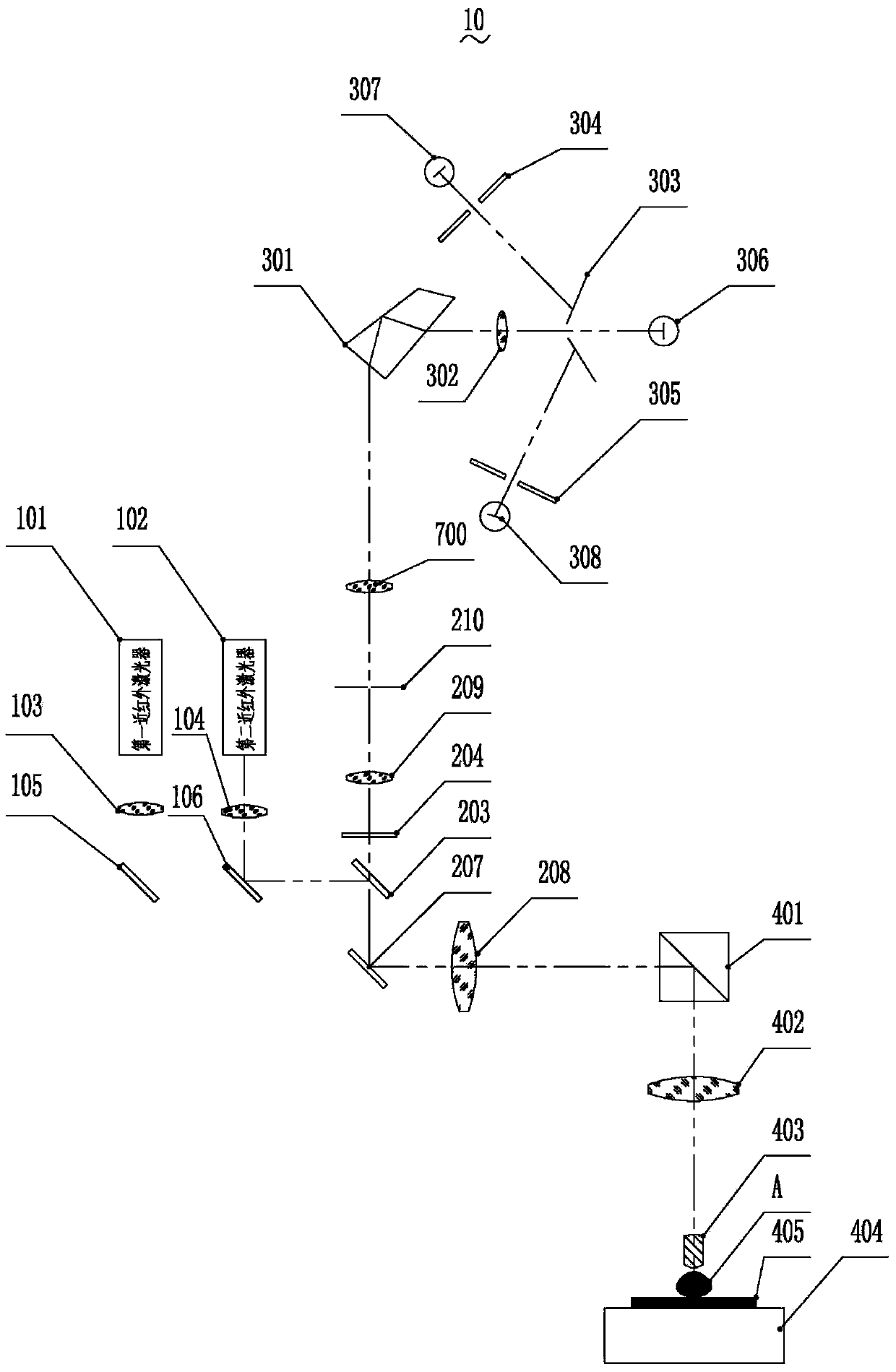
The invention discloses a fluorescence detector. The fluorescence detector comprises a laser beam combining module, a confocal scanning module, a spectral imaging module, a fluorescence microscope and a control display module. The laser beam combining module comprises two near-infrared light continuous lasers, a laser collimating lens, a reflecting mirror and a beam combining lens. The confocal scanning module comprises three switchable dichroic mirrors, three optical filters, a scanning galvanometer, a scanning lens, a pinhole lens and pinholes. The spectral imaging module comprises a beam splitter prism, a focus lens, three slits and three photomultipliers. The fluorescence microscope comprises a total reflection prism, a barrel lens, a micro-objective, a nanometer displacement platform and a sample platform. The control display module is used for controlling the laser, the scanning galvanometer, the micro-objective and the nanometer displacement platform and displaying the image. The fluorescence detector is capable of overcoming the disadvantage of low detection depth of the prior art, realizing the centimeter-level fluorescence detection and simultaneously realizing the fluorescence positioning and component analysis, and the fluorescence detector has broad application prospect in in-vivo fluorescence detection field.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Colorectal cancer peritoneal metastasis model and establishment method thereof
InactiveCN106047933AObserve in timeAvoid building successIn-vivo testing preparationsFermentationDiseaseHCT116 Cell
The invention relates to a colorectal cancer peritoneal metastasis model and an establishment method thereof. The colorectal cancer peritoneal metastasis model comprises a step (1) of adopting lentivirus transfection to construct HCT116 cells with firefly luciferase genes, so that the HCT116 cells can give out near-infrared light with a wavelength of 500-600 nm under substrate excitation; a step (2) of injecting 10*5 cells into the abdominal cavity of one mouse to perform molding; a step (3) of positioning a tumor by means of D-luciferin in vivo, and observing the carcinogenesis process in real time. The colorectal cancer peritoneal metastasis model has the advantages that a sensitive and accurate in vivo fluorescence imaging system is adopted to evaluate in vivo tumor forming and transfer process in real time, the conventional determination of success in model establishment through mouse dissection is avoided, and the disease pathology progress is observed timely better.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
Noninvasive circulating tumor cell detection and diagnosis device and detection and diagnosis method thereof
InactiveCN105286805AAvoid inaccuraciesWide range of usesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringTumor cellsEx vivo
Owner:周辉
Fluorescence excitation block light source and fluorescence microscope
ActiveCN112987273AReduce volumeReduce light lossMicroscopesEnergy saving control techniquesExcitation beamFirst light
The embodiment of the invention discloses a fluorescence excitation block light source and a fluorescence microscope. The light source comprises a light source identification driving module and at least one fluorescence excitation module, the fluorescence excitation module comprises a light-emitting element and a condensing lens, and the light-emitting element is used for emitting an excitation light beam; the condensing lens is used for condensing the excitation light beam to form a condensed light beam; the condensed light beam is used for exciting the to-be-detected sample to generate fluorescence; the fluorescence excitation module further comprises a shell, the light-emitting element is arranged at a first light transmitting opening, and the condensing lens is arranged in the shell. The excitation light beam enters the shell through the first light transmitting opening, the fluorescence condensation light beam enters a to-be-detected sample through a second light transmitting opening, and the fluorescence light beam carrying the characteristics of the to-be-detected sample is emitted through the second light transmitting opening and a third light transmitting opening in sequence; the light source identification driving module is electrically connected with the light-emitting element and used for controlling the light-emitting element to emit excitation light beams. The problems that in the prior art, a fluorescent light source is large in size, high in cost, large in optical loss and inconvenient to adjust optical power are solved.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Minimally invasive multiple channel in vivo fluorescence signal real-time detection system and method
The invention relates to a minimally invasive multiple channel in vivo fluorescence signal real-time detection system, which belongs to the technical field of in-vivo animal fluorescence detection. The system is characterized in that fiber optic bundles, a fiber optic bundle fixing device, a microscopic objective, a dichroic mirror forming a 45 degree angle with the horizontal plane, a fluorescent filter and an optical detector, which are horizontally arranged in sequence, share an axle to form a fluorescence emission light path; an excitation light source, an excitation light filter and a lens are vertically arranged to form an excitation light path; the excitation light forms a 45 degree angle with the dichroic mirror, and is orthogonal with the fluorescence emission light at the centerof the dichroic mirror. The system can detect the concentrations of the fluorescence targets of organs or tissues of in-vivo animals in a minimally invasive, multiple channel, quantitative and continuous way.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Two-photon excitation delay detection fluorescence imaging analysis method and equipment for live animal
ActiveCN109142305ALarge imaging analysis depthImprove reliabilityDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSensorsPhotonFluorescence intensity
The invention discloses a two-photon excitation delay detection fluorescence imaging analysis method and equipment for a live animal. The method is used for analyzing the time-varying kinetic propertyof distribution, fluorescence intensity or a probe concentration of nano fluorescence probes (or fluorescence nano drug carrier simulated probes) in a tissue and an organ in an animal body; the in-vivo fluorescence nano probes are subjected to two-photon excitation by red light or near infrared pulse laser, so as to perform delay detection on the fluorescence intensity and the time-varying kinetic property of an in-vivo specific part by a fluorescence imaging mode; the method has the advantages of large imaging analysis depth, high reliability, high detection sensitivity and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Double-purpose in vivo fluorescence photograph optical filter device for mobile phone and digital camera with replaceable lens
ActiveCN108957913AGuarantee authenticitySolve too strong reflectionCamera body detailsCamera lensDigital imaging
The invention relates to the in vivo fluorescence imaging field, and especially relates to a double-purpose in vivo fluorescence photograph optical filter device for a mobile phone and a digital camera with a replaceable lens; the in vivo fluorescence photograph optical filter device comprises an ear clip type fixed clip, an adjustable aperture, an UV optical filter, and optical filter clasp, a circular polarization film and a switch ring; the ear clip type fixed clip comprises an inner thread interface used for threading the adjustable aperture or the switch ring; the side portion of the inner thread interface is connected with an elastic rod via a telescopic folding extension bar; the other end of the elastic rod is connected with an antiskid block; the camera side of the adjustable aperture, the circular polarization film and the optical filter clasp is respectively provided with an outer thread; the other sides of the adjustable aperture, the circular polarization film and the optical filter clasp are respectively provided with an inner thread; the UV optical filter is embedded in the optical filter clasp. The device can remove the UV excitation light influences on digital imaging in a fluorescence photograph process, thus enabling the digital picture to record and keep the fluorescence color and intensity authenticity.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Corannulene-incorporated AIE nanodots with highly suppressed nonradiative decay for boosted cancer phototheranostics in vivo
ActiveCN111742034APhotodynamic therapyIn-vivo testing preparationsNear infrared absorptionPolyethylene glycol
The present subject matter relates to fluorescent compounds that have aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics and exhibit near infrared absorption. Compositions including the present compounds can include a corannulene-modified polyethylene glycol encapsulation matrix. The compositions can be in nanoparticle form. Encapsulating the AIE compounds within a corannulene matrix provides intraparticle rigidity and restricts intramolecular rotation of the encapsulated AIE compound, which results in enhanced fluorescence and ROS generation capacity of the compositions in vivo. Accordingly,the compositions can be useful in NIR imaging-guided cancer surgery and photodynamic cancer therapy.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fluorescent probe, method for detecting fluorescence, and method for using fluorescent probe
InactiveUS20190137396A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence microscopeIn vivo fluorescence
The present invention relates to a fluorescent probe including a carrier molecule, a fluorescent dye a bound to the carrier molecule, and a fluorescent dye b bound to the carrier molecule in which the excitation wavelengths of the fluorescent dyes a and b are different, and FRET does not occur between the fluorescent dyes a and b. The present invention also relates to a method for detecting fluorescence that includes a step of labeling target cells with the fluorescent probe, and a step of irradiating the target cells labeled with the fluorescent probe with excitation light and observing the fluorescence from the fluorescent probe. The present invention also relates to a method for using a fluorescent probe that includes a step of fluorescently labeling cells with the fluorescent probe, a step of screening the fluorescence-labeled cells using a flow cytometer or a fluorescence microscope, a step of transplanting the screened fluorescence-labeled cells into a living organism, and a step of observing the fluorescence-labeled cells in the living organism using an in vivo fluorescence imaging apparatus.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com