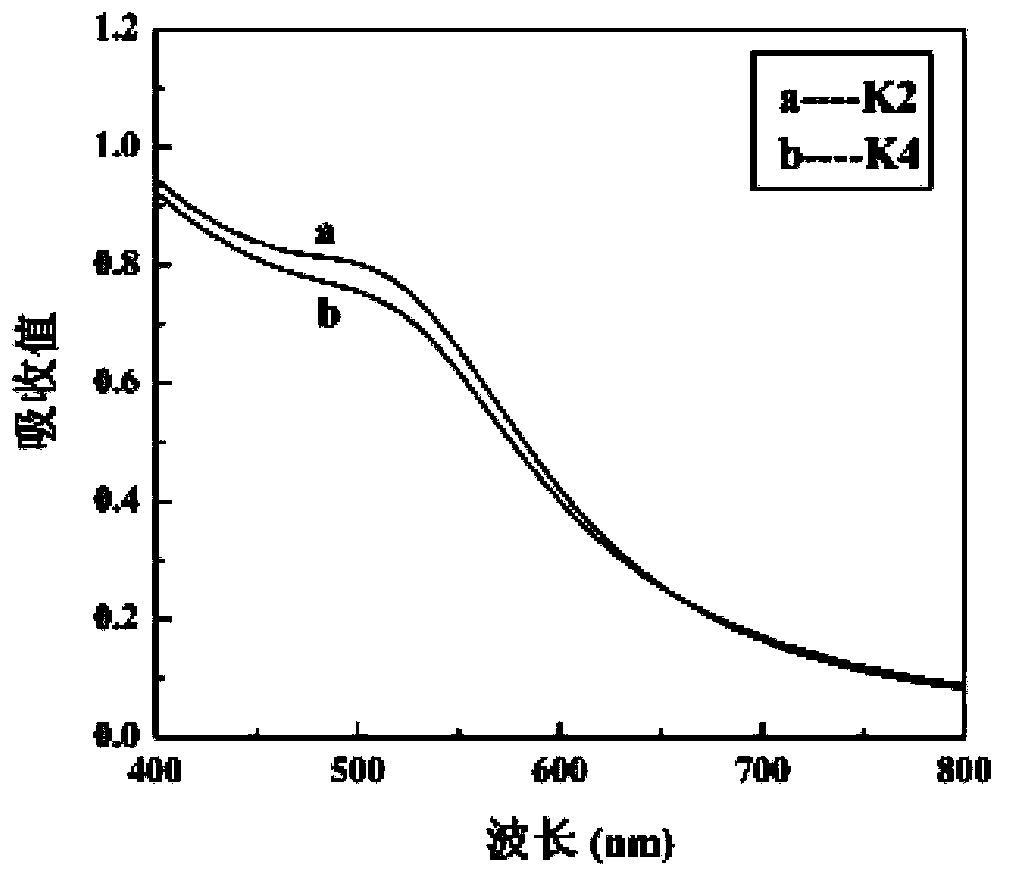
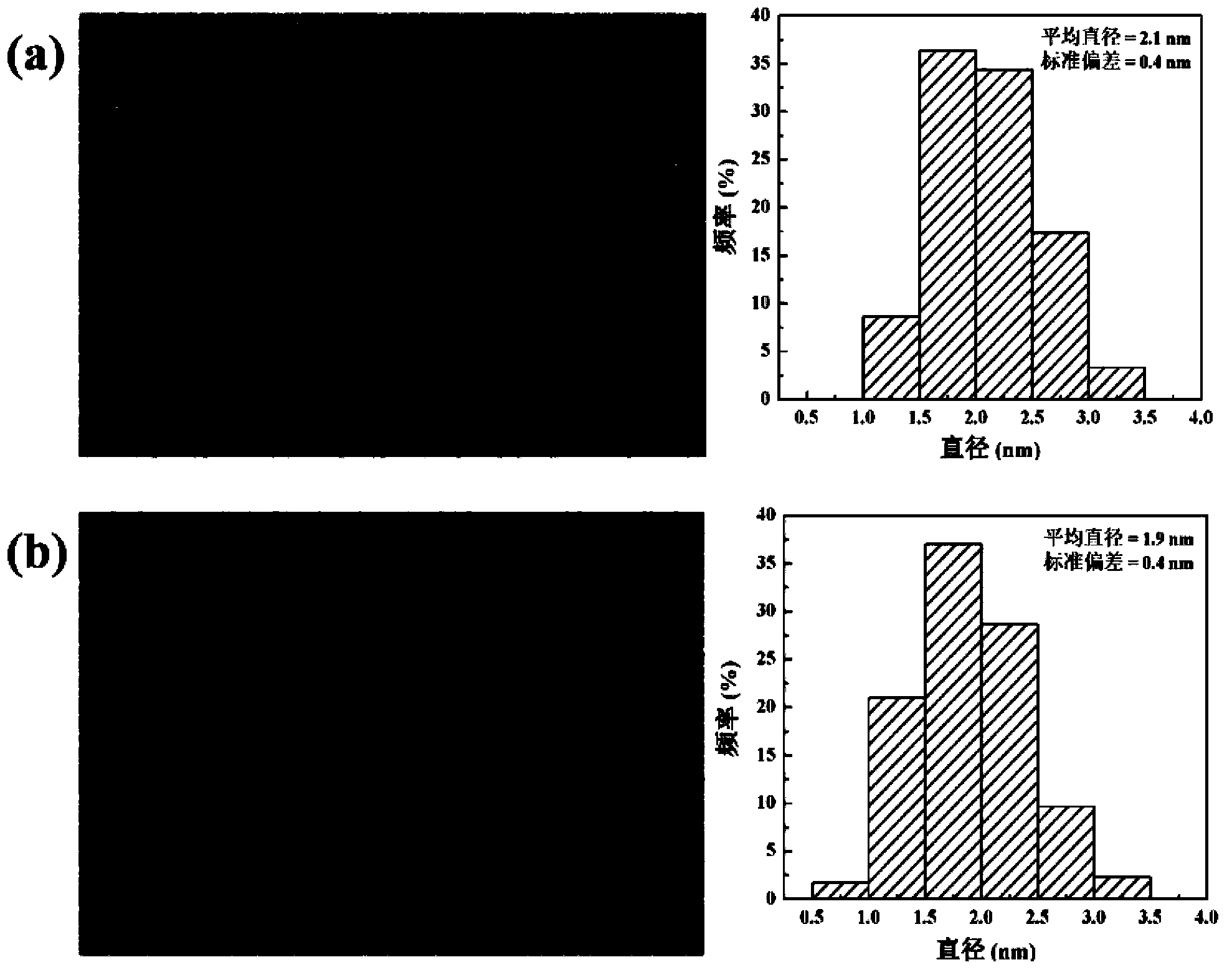
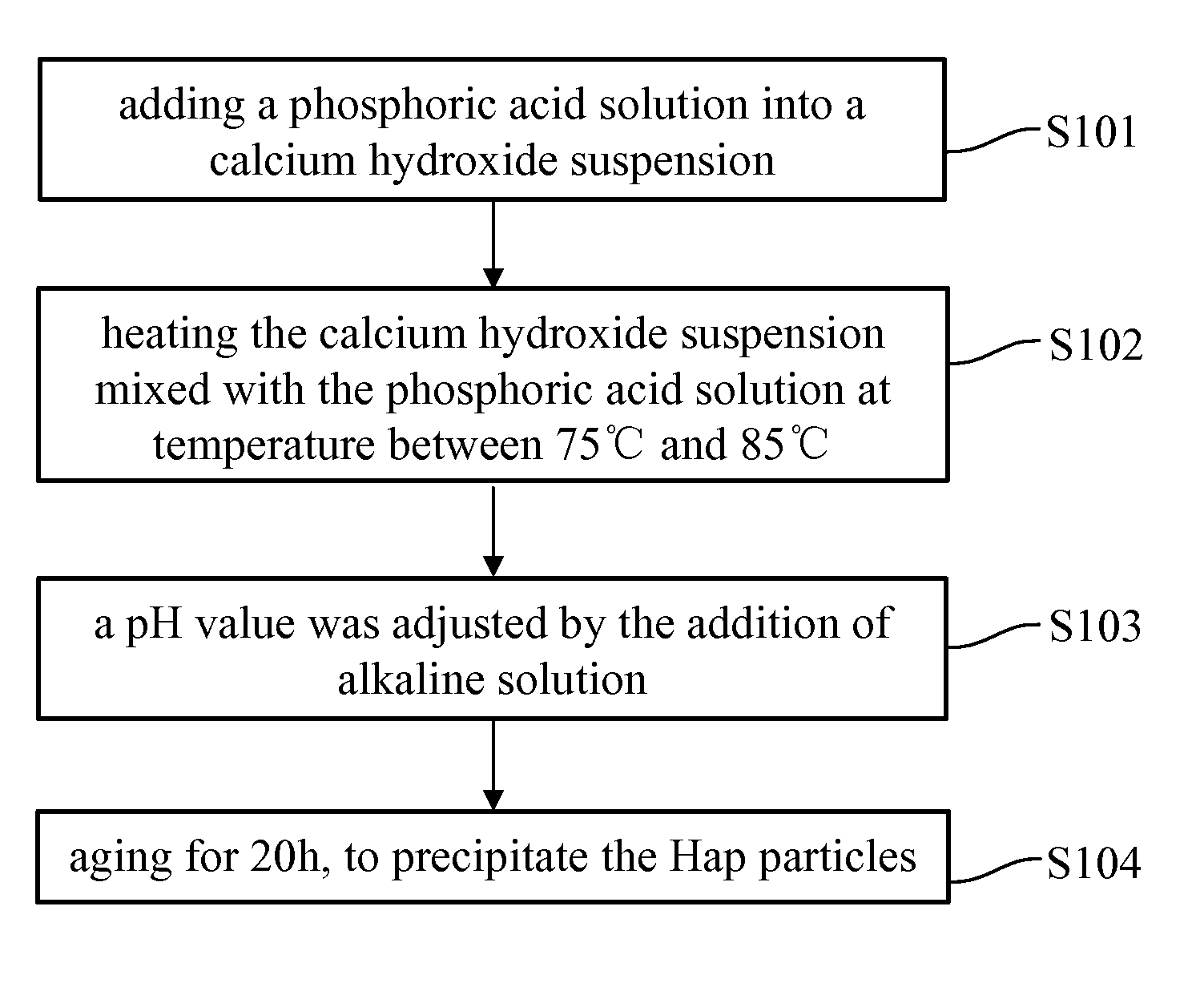
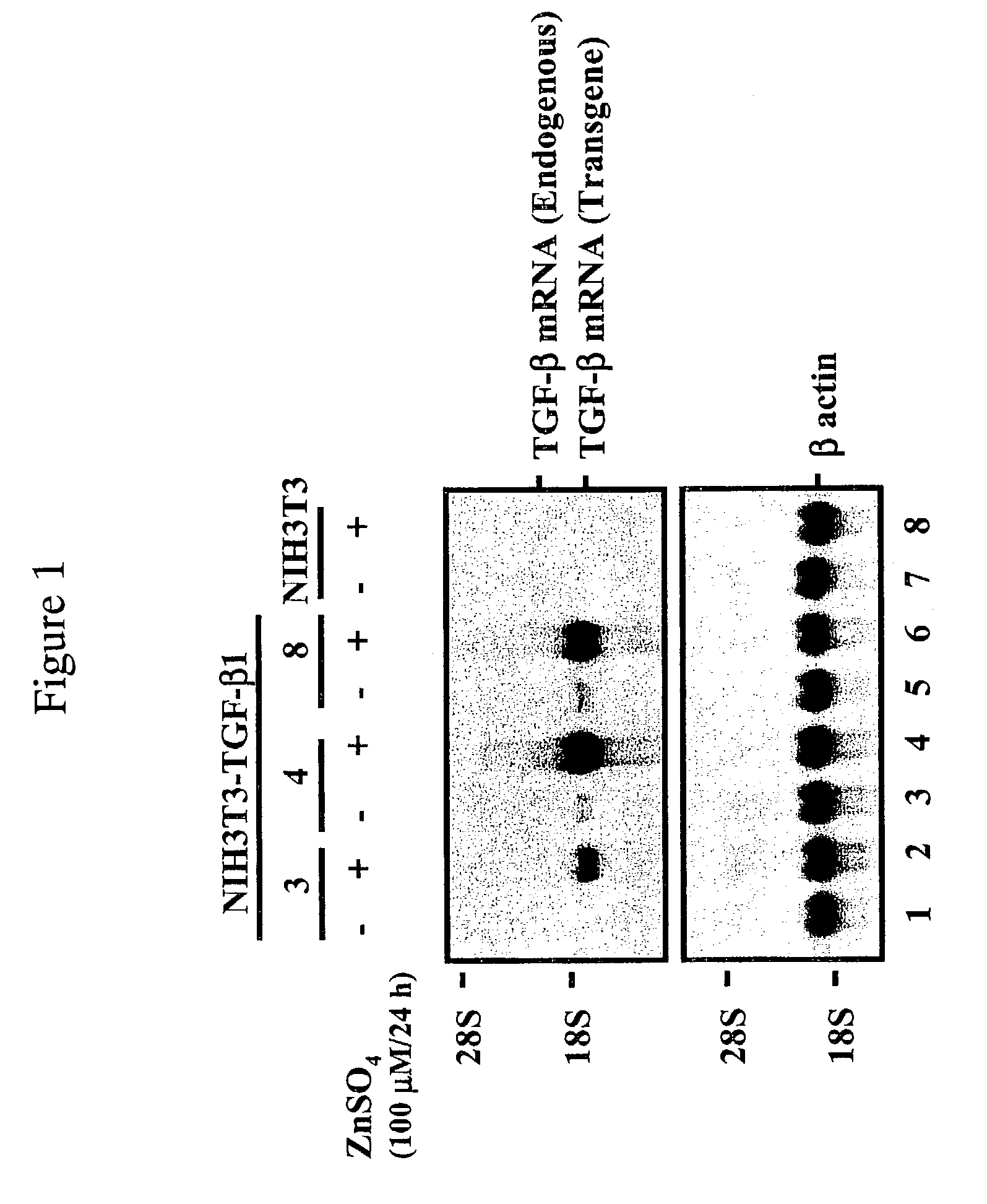
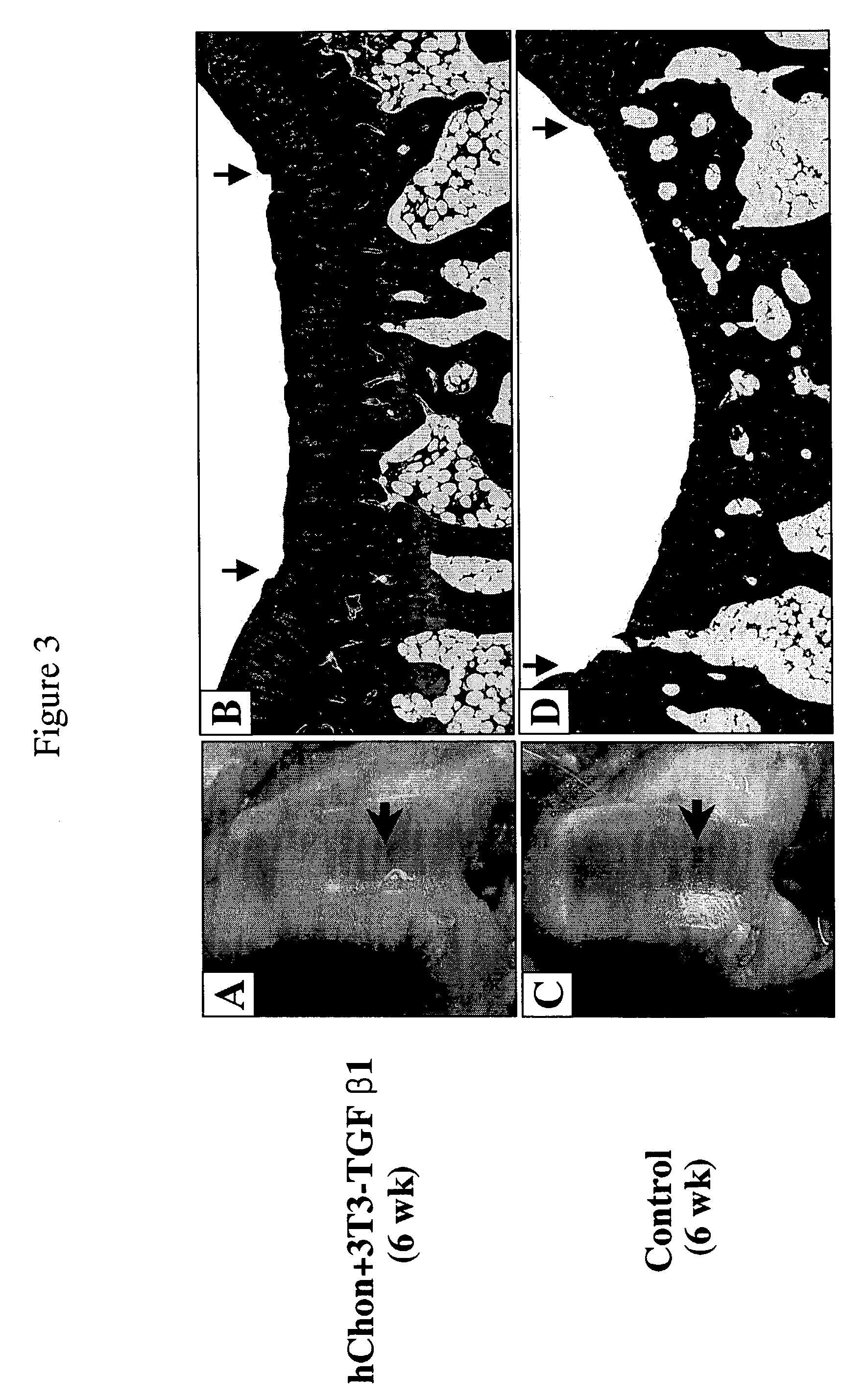
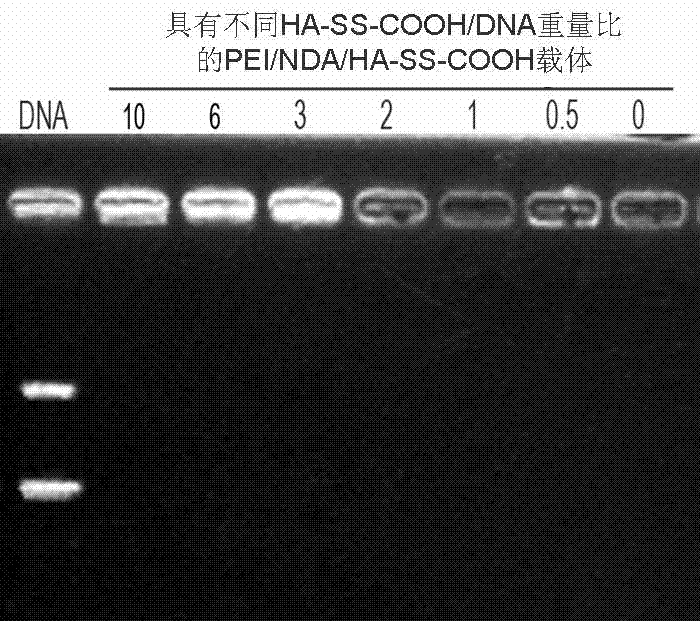
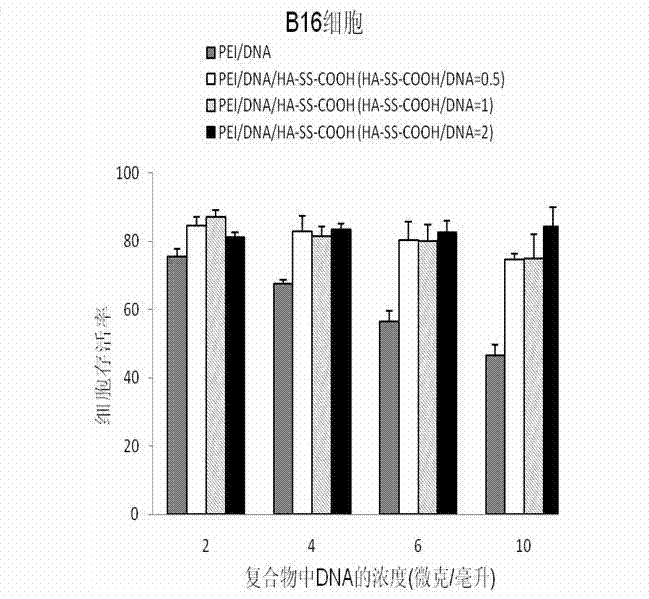
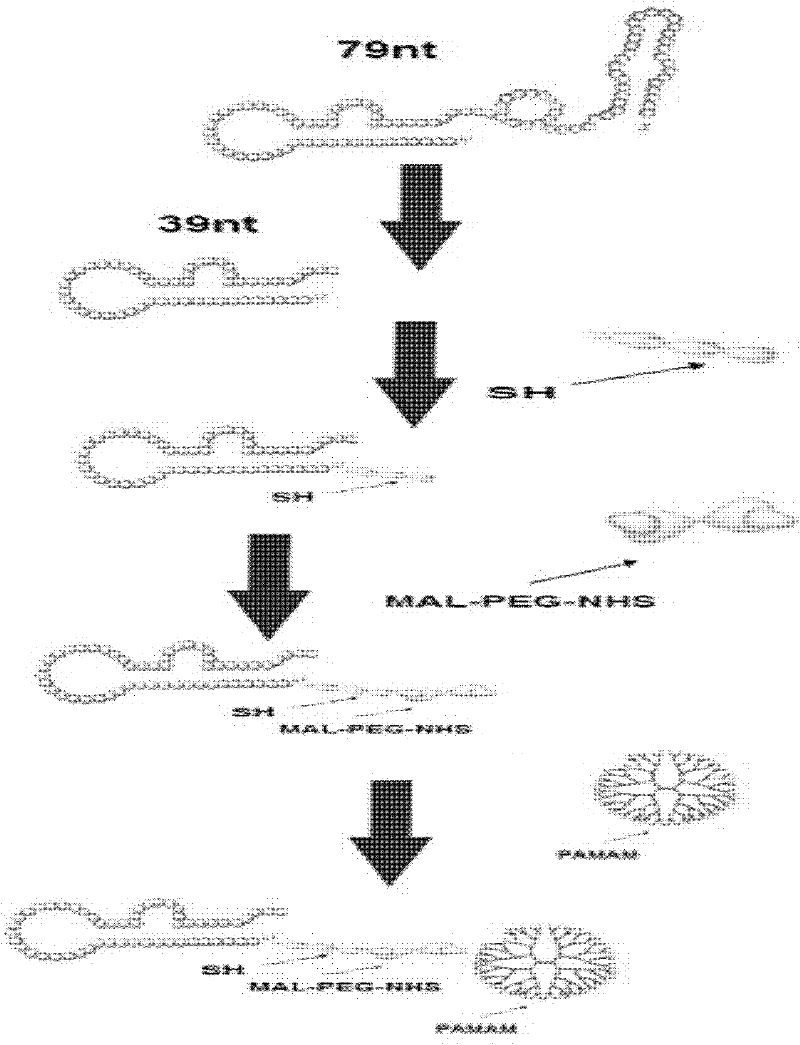
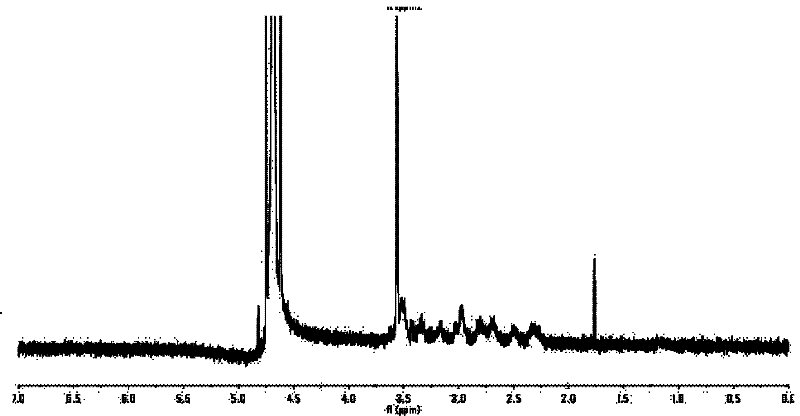
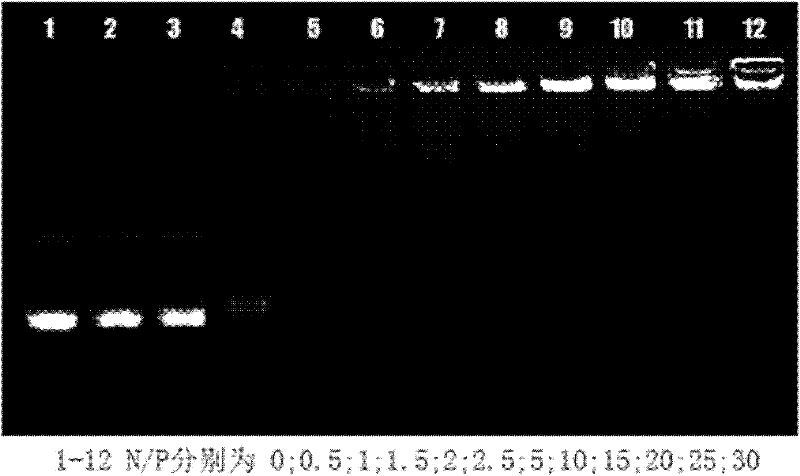
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
286 results about "Genetic transfection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transduction (genetics) Transduction is the process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus. It also refers to the process whereby foreign DNA is introduced into another cell via a viral vector.
Delivery systems comprising biocompatible and bioerodable membranes
InactiveUS20040120979A1Reduce deliveryHigh expressionGenetic material ingredientsNanomedicineDendrimerIn vivo
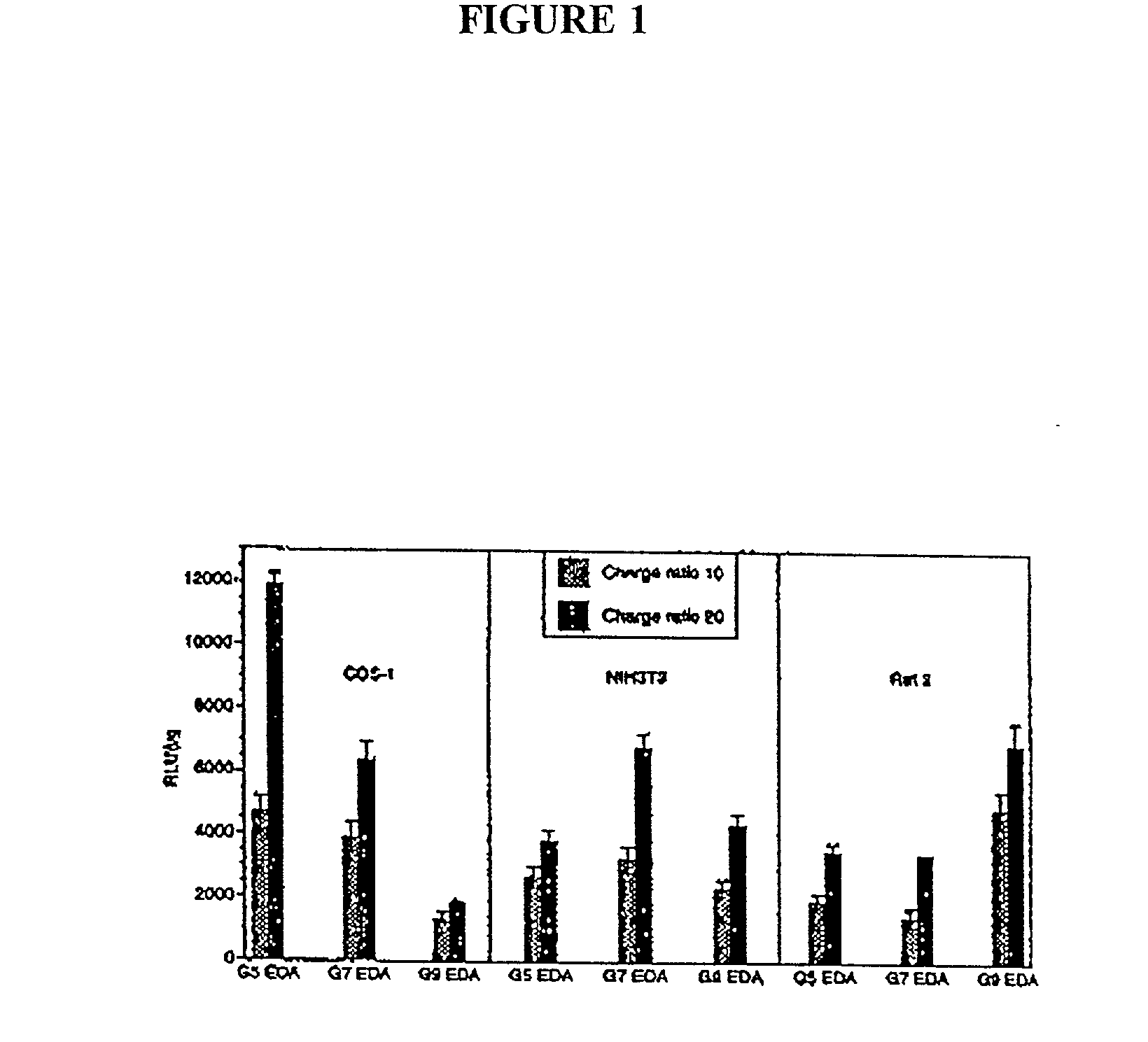
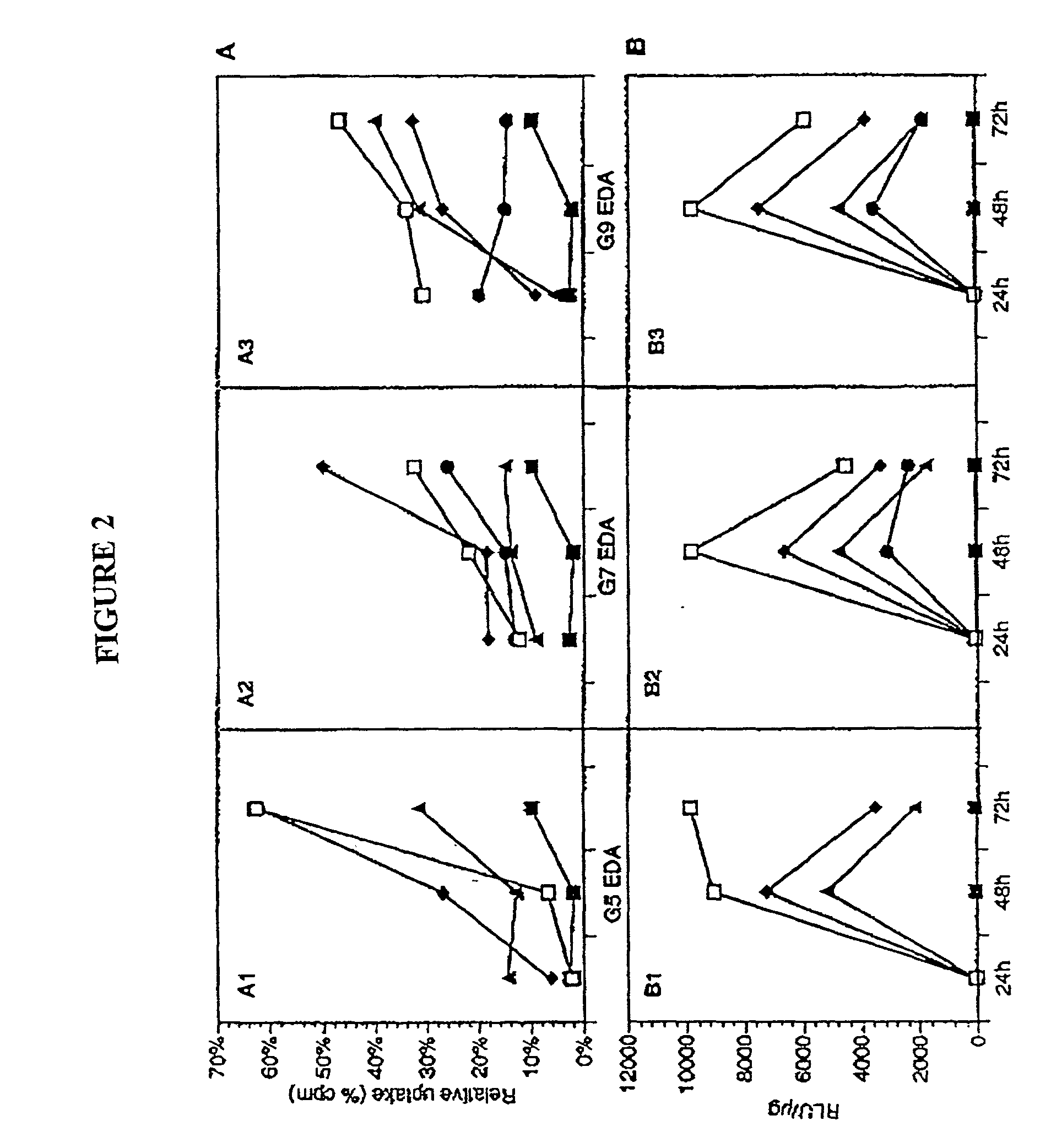
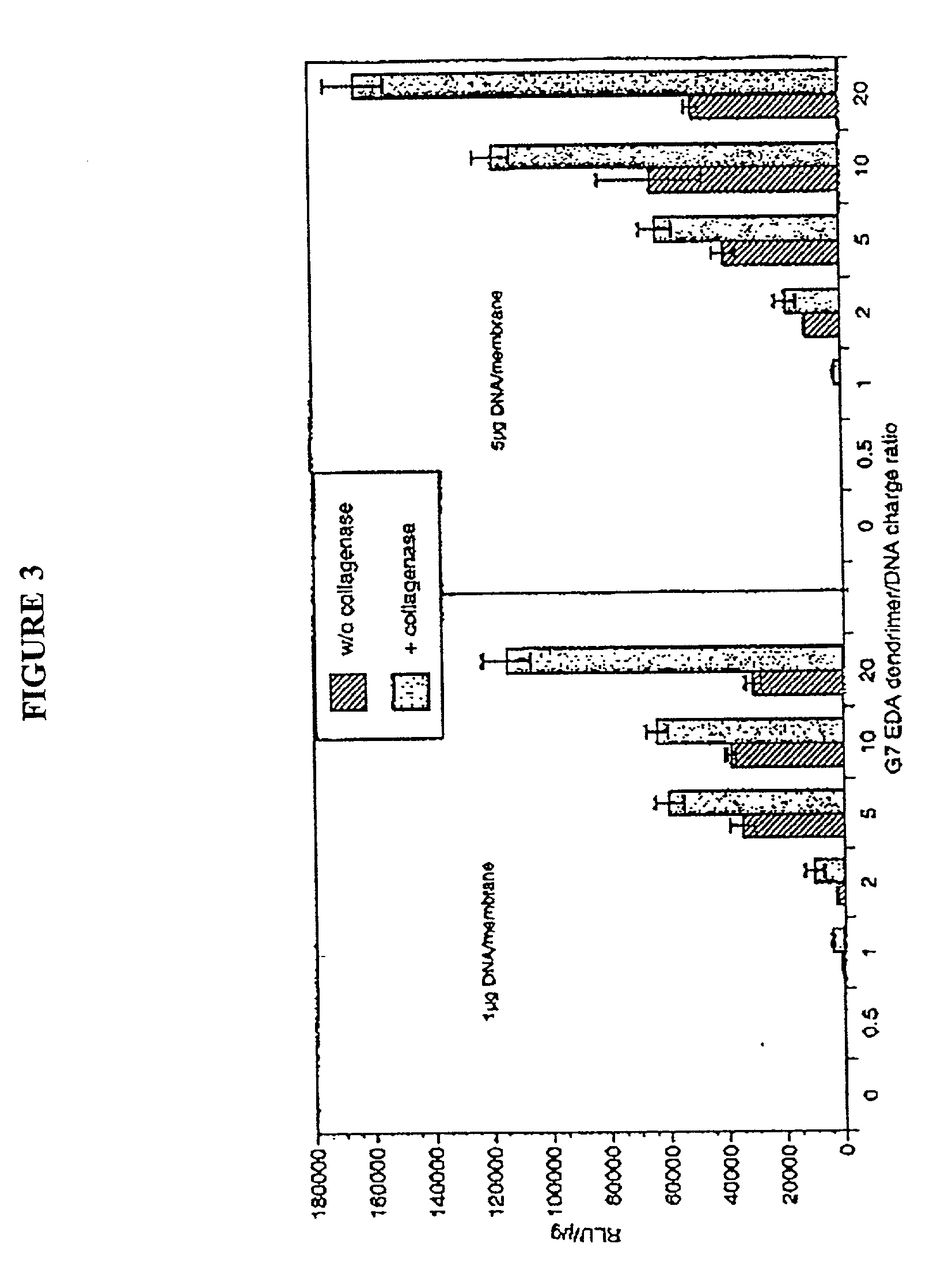
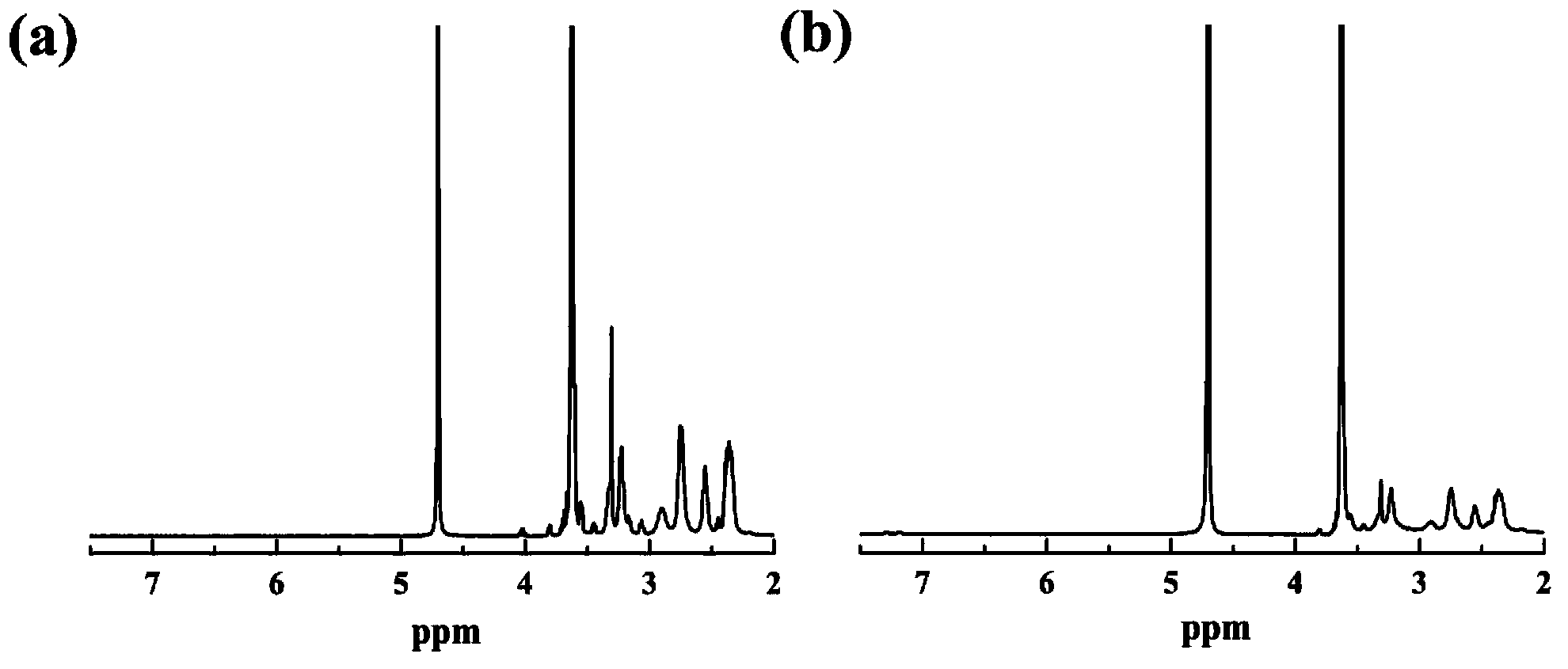
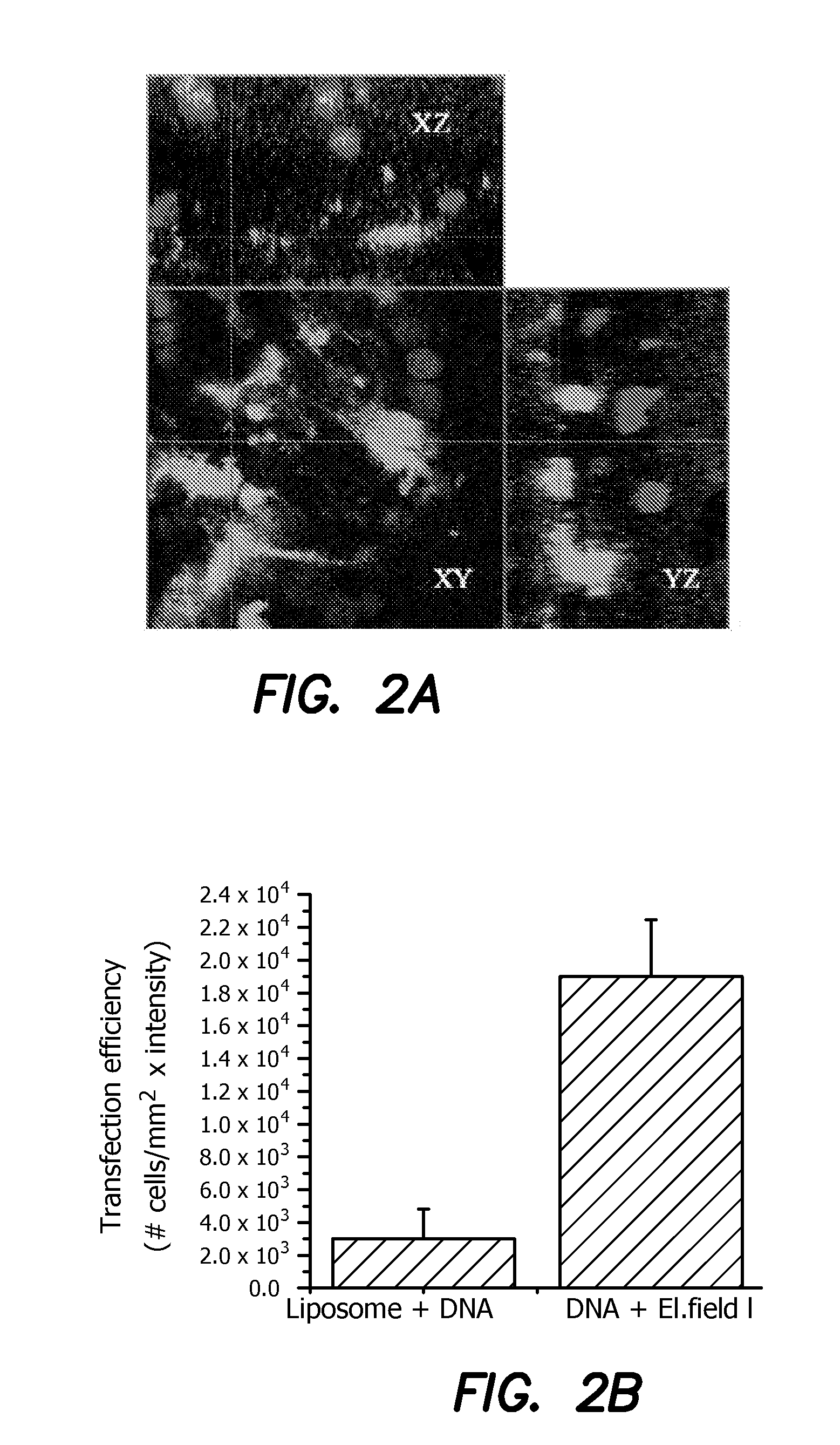
The present invention relates to novel compositions and methods for delivering substances to target tissues and cells by contacting the targets with delivery systems associated with membranes (e.g., biocompatible or bioerodable membranes). More particularly, the present invention is directed to dendrimer-based methods and compositions for use in disease therapies, wound healing, and generally, improved gene transfection and compound delivery to target cells and tissues in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:ROESSLER BLAKE J +2
Method for applying functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and nanometer compound thereof in gene transfection
InactiveCN103435815AImprove transfection abilityGood gene transfection effectGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCompound sBiology
The invention relates to a method for applying a functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and a nanometer compound thereof in gene transfection. The method comprises the following steps: preparation of the functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and the nanometer compound thereof, surface functional modification and characterization; preparation of functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-nanometer compound / pDNA; and research on gene transfection efficiency of the functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-nanometer compound / pDNA. The advantages of easy operation, simple transfection conditions, high transfection efficiency, strong specificity and the like are obtained in application of the functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and the nanometer compound thereof in gene transfection, and the functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and the nanometer compound thereof have good application prospects in aspects like gene therapy of cancers.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Superparamagnetic nanoparticles IN MEDICAL THERAPEUTICS and manufacturing method THEREOF
InactiveUS20110135577A1Safe and effectiveAvoid problemsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDelivery vehicleMagnetite
The successful transfer of therapeutic agents such as genetic materials (e.g. nucleic acid) or drug into living cells is the most important issue depending on the development of the delivery carrier. A method for manufacturing superparamagnetic nanoparticles in medical therapeutics is described to develop nano-sized calcium phosphate (CaP) mineral was rendered magnetic as delivery vehicle. The CaP-based magnetized nanoparticles (NPs) were possessed superparamagnetic property by hetero-epitaxial growth of magnetite on the CaP crystallites and also showed no harm to the cultured cells and elicited no cytotoxicity. The magnetized CaP was demonstrated to have good plasmid DNA binding affinity or drug carrying capacity. It significantly increased the expression of gene transfection and efficiency in delivery to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) under exogenous magnetic field. According to the above facts, this newly-synthesized magnetized CaP NPs has great potential as a novel non-viral targeted delivery vehicle to be applied for medical applications.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
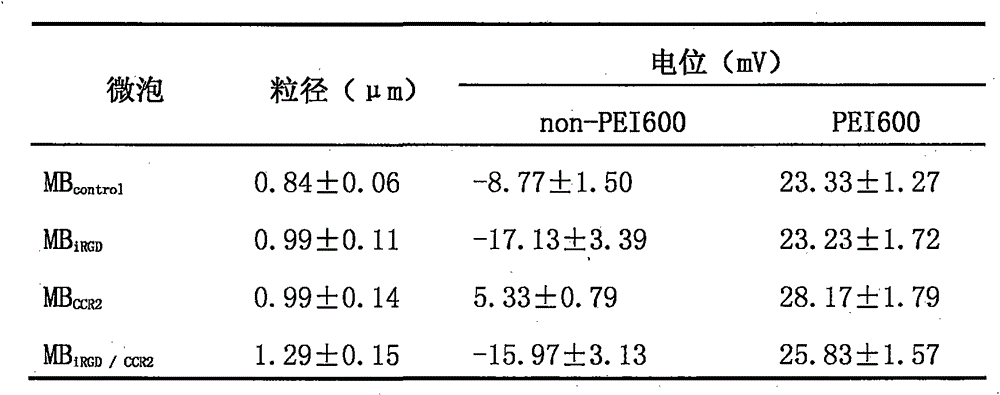
Preparation method of double-targeting cationic ultrasound microbubbles carrying cell-penetrating peptide iRGD
InactiveCN105106977AUniform particle size distributionSpeed up entryEnergy modified materialsGenetic material ingredientsPolyetherimidePlasmid dna
The invention discloses a preparation method of double-targeting cationic ultrasound microbubbles carrying cell-penetrating peptide iRGD and belongs to the field of fundamental research. The preparation method uses materials, including DSPC, DSPE-PEG2000-maleimide, DSPE-PEG2000-Biotin, iRGD peptide, CCR2 antibody, stearic acid, branched-chain polyetherimide-600, N, N'-carbonyldiimidazole, and avidin; by bonding integrin Alpha v Beta3 targeting cell-penetrating peptide iRGD and the CCR2 antibody to surfaces of the microbubbles, double-targeting cationic ultrasonic contrast agent is constructed and has the double functions of carrying plasmid DNA and targeting tumor cells; combining ultrasound-mediated biological effect and iRGD cell-penetrating action, the agent is capable of promoting entry of genes into the tumor cells and improving gene transfection efficiency and is expected to be developed and applied to visual ultrasound-controlled-release genetic treatment of tumors.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Biodegradable crosslinked polyethylenimine and its uses
InactiveCN1970591ASafe Degradation PathwayAddress toxicityGenetic material ingredientsNanomedicineGlycidyl methacrylateActive agent
The invention discloses a decomposable crosslinking polyethylene imine and making method and application under physiological condition, which is characterized by the following: adopting one or more composition of glycidyl ester of each kind diacid, acroleic acid / methacrylic acid glycidyl ester or polyol or polyatomic condensed alcohol / polybasic ester of methyl acroleic acid as crosslinking agent; crosslinking with linear or branched polyethylene imine to form non-virus gene infection-transmitting carrier for each cell and biological tissue.
Owner:NANJING WISEGEN BIOTECH
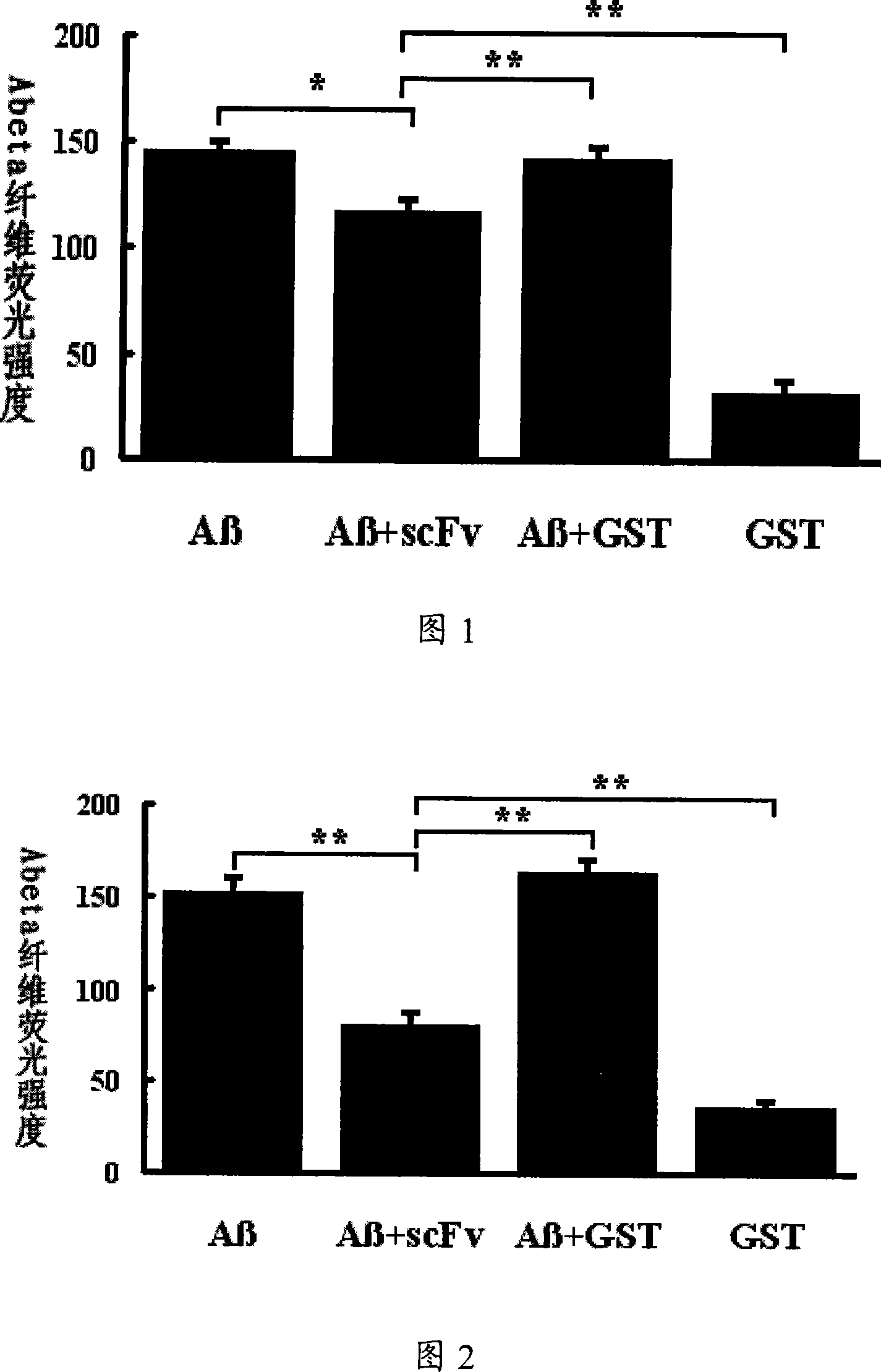
Medicament for preventing and controlling alzheimer's disease
InactiveCN101152576AAvoid repeated dosingLow cost of treatmentNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesSide effect
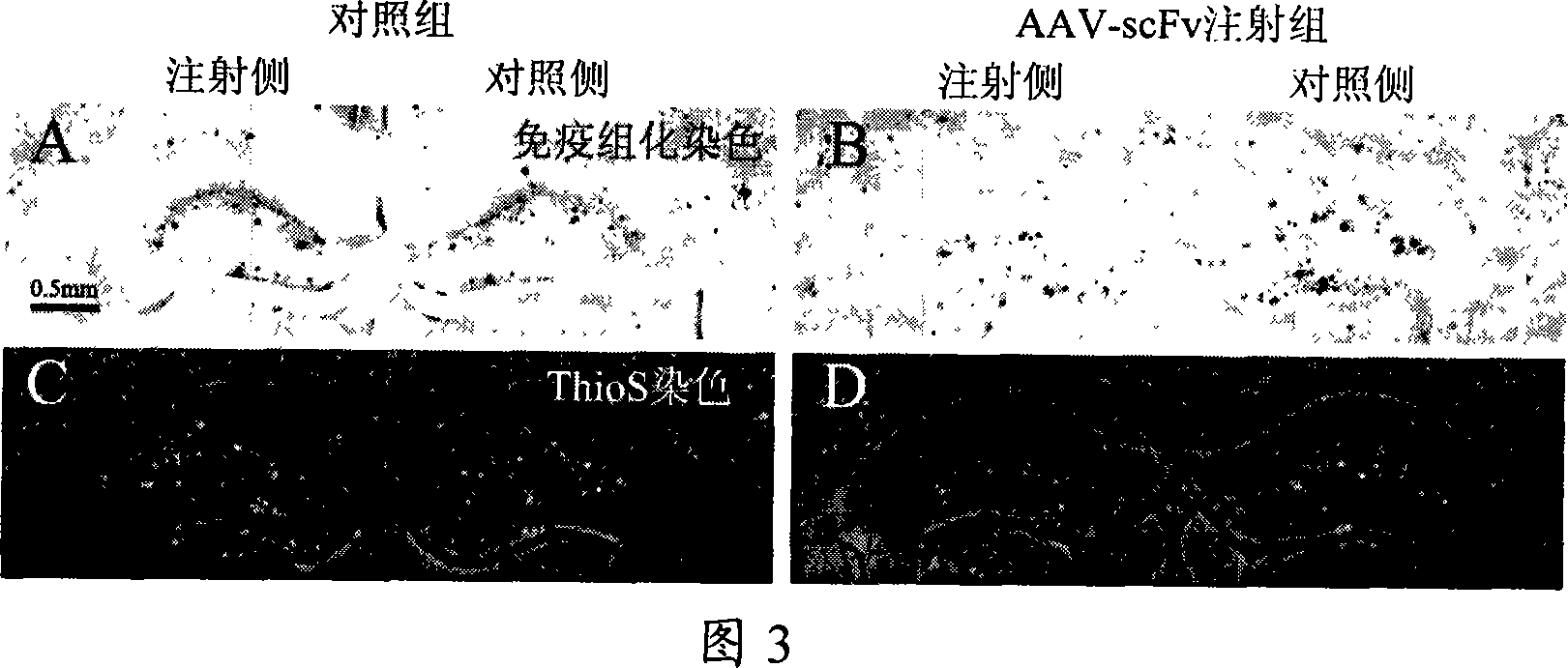
A medicine for curing alzheimer disease is characterized in that a recombinant virus of gene transfection is regarded as a carrier; the front end of one, two or a plurality of anti A beta single-chain antibody genes is respectively connected with a secretion signal peptide dna sequence; and then the anti A beta single-chain antibody genes are inserted into the recombinant virus gene; finally a packaged product is formed through the recombinant virus. The invention can produce anti A beta single-chain antibody in the body by transfecting the anti A beta single-chain antibody genes capable of prohibiting A beta monomer isomerization and promoting A beta polymer depolymerization on the periphery and in the brains, so as to express scFv in the body for a long time, to effectively remove the A beta in the brains with alzheimer disease, prevent inflammatory reaction of the central nervous system and side effect of capillary bleeding produced in the anti A beta immune therapy, avoid repeated feeding of the anti A beta medicine, and reduce the curing cost. The invention provides a safe and effective novel technology of curing alzheimer disease which works for long and has broad clinical application prospect.
Owner:王延江 +2
D-configuration polypeptide with brain tumor targeting and tumor tissue penetrating capabilities and gene delivery system thereof
ActiveCN104072581AHigh transfection efficiencyProlong lifeGenetic material ingredientsPeptidesGene deliveryNeuropilins
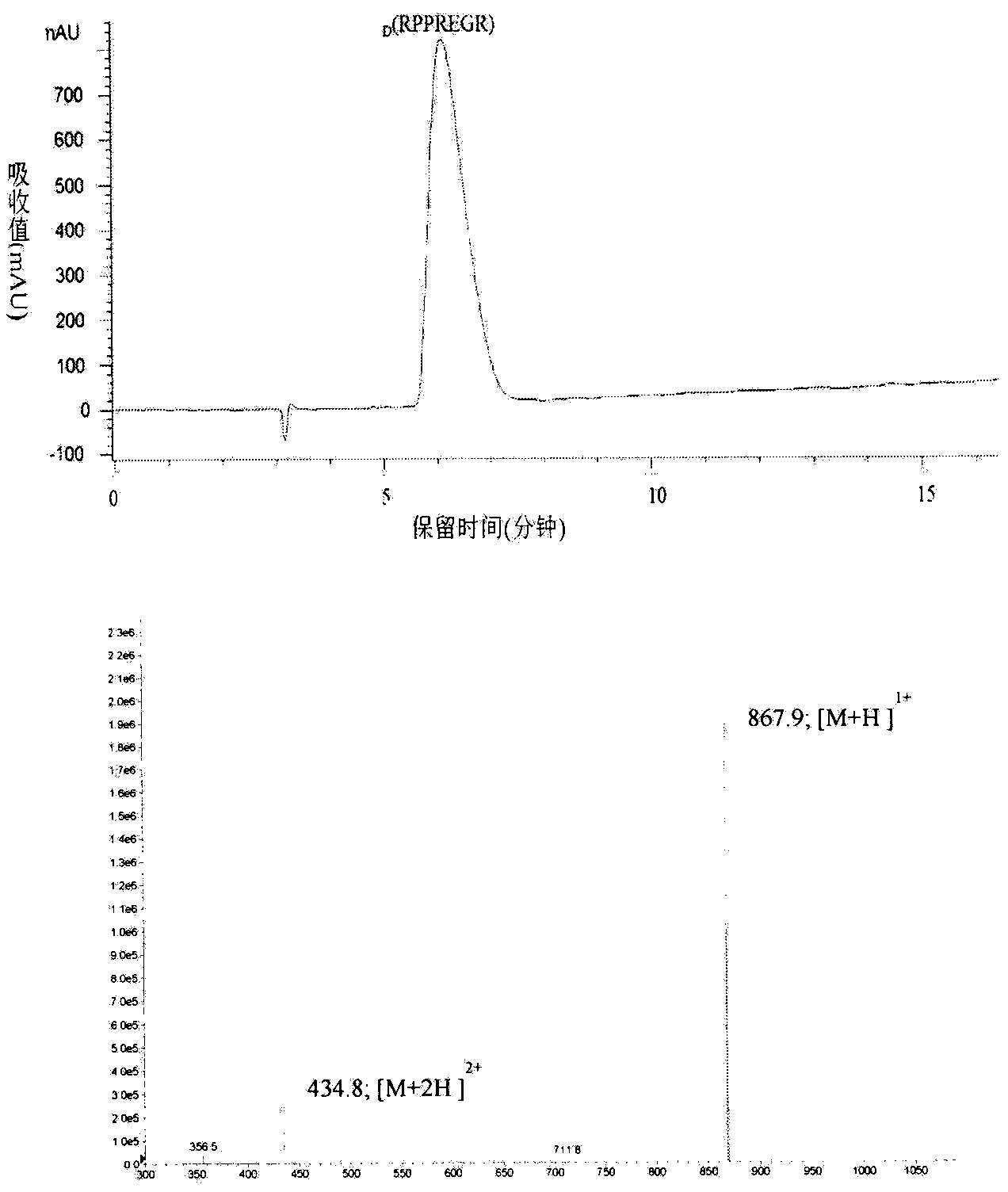
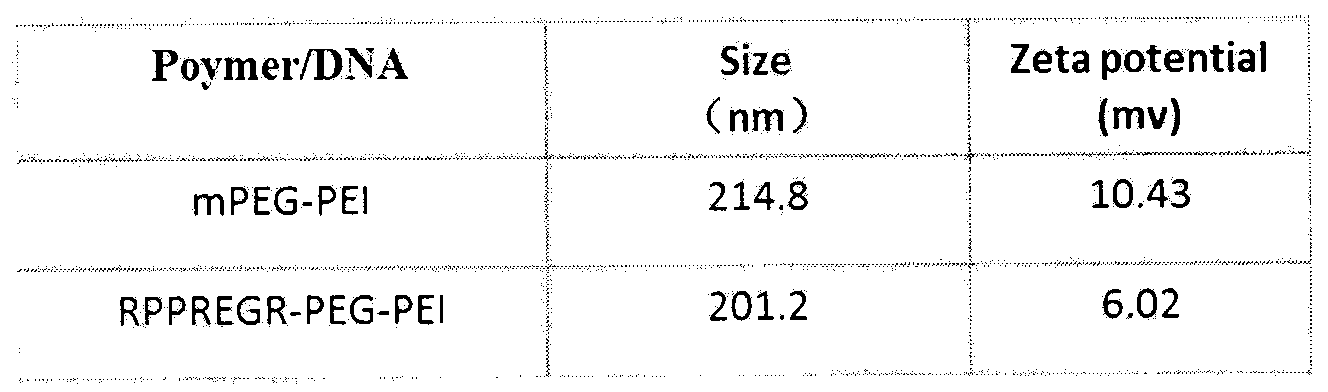
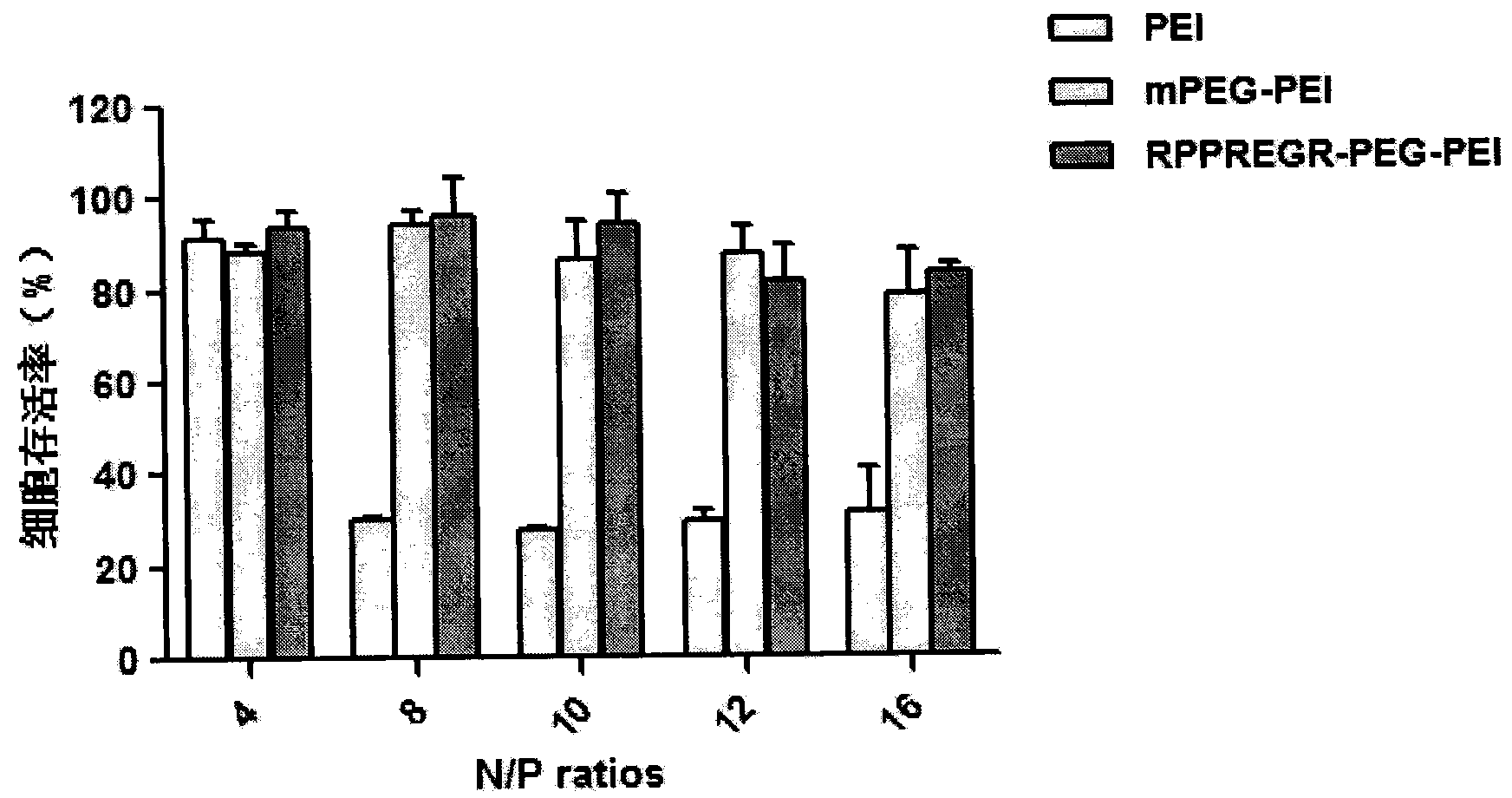
The invention belongs to the field of pharmacy and relates to a D-configuration polypeptide and a gene delivery system of the D-configuration polypeptide and particularly relates to the D-configuration polypeptide which has high combining activity with neuropilin NRP-1 and has the brain tumor targeting and tumor tissue penetrating capabilities. The D-configuration polypeptide provided by the invention can mediate a nano delivery system to deliver drugs to tumors in a targeted manner for realizing targeted treatment of brain in-situ glioma. In vivo and in vitro experiments show that the genetic vector modified by the D-configuration polypeptide can remarkably improve the gene transfection efficiency. The genetic vector entrapping the therapeutic gene pORF-hTRAIL can remarkably prolong the lifetime of a nude mouse of brain glioma in-situ mode.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Mixed-cell gene therapy
The subject invention is directed to a mixed cell composition to generate a therapeutic protein at a target site by providing a first population of mammalian cells transfected or transduced with a gene that is sought to be expressed, and a second population of mammalian cells that have not been transfected or transduced with the gene, wherein endogenously existing forms of the second population of mammalian cells are decreased at the target site, and wherein generation of the therapeutic protein by the first population of mammalian cells at the target site stimulates the second population cells to induce a therapeutic effect.
Owner:KOLON TISSUEGENE INC
Gene vector system, its preparation and application
ActiveCN102899343ADoes not affect compounding abilityImprove binding efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsRespiratory disorderIntracellularGenetic Materials
The invention discloses a gene vector system of a redox sensitive shielding system having targeting function, its preparation and application in the field of gene therapy. The gene vector system disclosed herein comprises a redox sensitive shielding system having targeting function, a cationic high-molecular material and plasmid DNA; wherein the cationic high-molecular material and plasmid DNA form compound particles, the redox sensitive shielding system having targeting function shields the compound surface by electrostatic action, thus the toxicity of the vector can be reduced, the loaded genetic material is transferred into the cell successfully, the expression of the genetic material is realized, the transfection process is completed, the targeting of gene transfection can be raised, and simultaneously the gene transfection efficiency is raised.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Prostate cancer targeting gene oligonucleotide aptamer, delivery carrier, delivery system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102268436AHigh transfection efficiencyImprove expression levelGenetic material ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesProstate cancer cellAntigen
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide aptamer for prostate cancer targeting gene, a delivery carrier, a delivery system and a preparation method thereof. The delivery carrier is made of polycationic polymer material, hydrophilic polymer and Based on the oligonucleotide aptamer, the three are covalently linked, wherein the molar ratio of the hydrophilic polymer to the polycation polymer is 1-25:1, and the oligonucleotide aptamer The molar ratio of the body to the polycation polymer material is 1-5:1; the delivery system is a nanoscale gene delivery system formed by delivery carriers and miRNA, siRNA or plasmid DNA. The delivery carrier and the delivery system of the present invention can effectively improve the gene transfection efficiency and expression efficiency on prostate cancer cells expressing prostate specific membrane antigen, compared with the gene delivery system constructed by targeting the head group used in the prior art , which has the advantages of stronger stability and significantly improved targeting effect.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Genetic vector system of nanoparticle with multiple oxidation-reduction stimulus response as well as preparation method and application of genetic vector system
ActiveCN103305549AExcellent gene transfection efficiencyConvenient Gene TherapyGenetic material ingredientsRespiratory disorderTernary complexVector system
The invention discloses a genetic vector system of a nanoparticle with multiple oxidation-reduction stimulus response as well as a preparation method and application of the genetic vector system. The genetic vector system is composed of a shielding system, a cation material and foreign plasmid DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); and the shielding system and the cation material both have oxidation-reduction stimulus response, so that a ternary complex nanoparticle with multiple oxidation-reduction stimulus response is formed. The genetic vector of the ternary complex nanoparticle is low in cytotoxicity, and capable of well compressing and compounding the plasmid DNA under physiological conditions, successfully transferring a supported genetic substance into a cell and entering the cell; and the reduction environment in the cell can be more rapidly broken to release the supported gene, so that the expression of gene substances is realized, the transfection process is finished, and the gene transfection efficiency can be remarkably increased.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Cholesterol-modified biodegradable polycation carrier as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103110954AEasy to disassembleGood biocompatibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsLysosomeCholesterol
The invention provides a cholesterol-modified biodegradable polycation carrier as well as a preparation method and application of the cholesterol-modified biodegradable polycation carrier. The carrier material is a functionalized linear poly(amide-amine)-cholesterol comb grafting which is formed by connecting functionalized linear poly(amide-amine) with average molecular weight being 2kD20kD and cholesterol through amido bonds or ester bonds; the carrier can be self-assembled in an aqueous phase medium to form nanoparticles, wherein the particle diameter of each nanoparticle is 20-200nm; the surfaces of the nanoparticles are positively charged; and the cholesterol grafting rate is 1-90 percent. The cationic polymer nanoparticles prepared by using the preparation method are low in toxicity, have the functions of rapidly penetrating cell membranes and easily degrading and escaping in lyase and can be used as a gene transfection reagent. In addition, fat-soluble chemicals can be carried by using a lyophobic area in a nanoparticle carrier structure, and therapeutic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) gene medicines or polypeptide protein medicines can be carried by using positive charge characteristics.
Owner:NANJING GENELEAP BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Combined use of nucleoside analogues and gene transfection for tissue imaging and therapy
InactiveUS20020025296A1Easily expelledEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsCombined useFhit gene
A method and use of a labelled compound for monitoring the transfer of a foreign gene including selecting the foreign gene which has been isolated from a cell or virus and transferred into a cell population and selecting the labelled compound which will interact selectively with a protein expressed by the foreign gene to produce a labelled product. The labelled compound has a rate of expulsion from the cells which is greater than that of the labelled product. Further, the use and method include administering to the cells an effective dose of the labelled compound such that the labelled compound selectively interacts with the protein to produce the labelled product, waiting a period of time such that a substantial amount of the labelled compound has been expelled from the cells and such that a detectable amount of the labelled product remains and determining the extent and location of the protein by detecting the labelled product.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Application of hydroxyl-containing crosslinked polymer guanidinated product in gene transfer
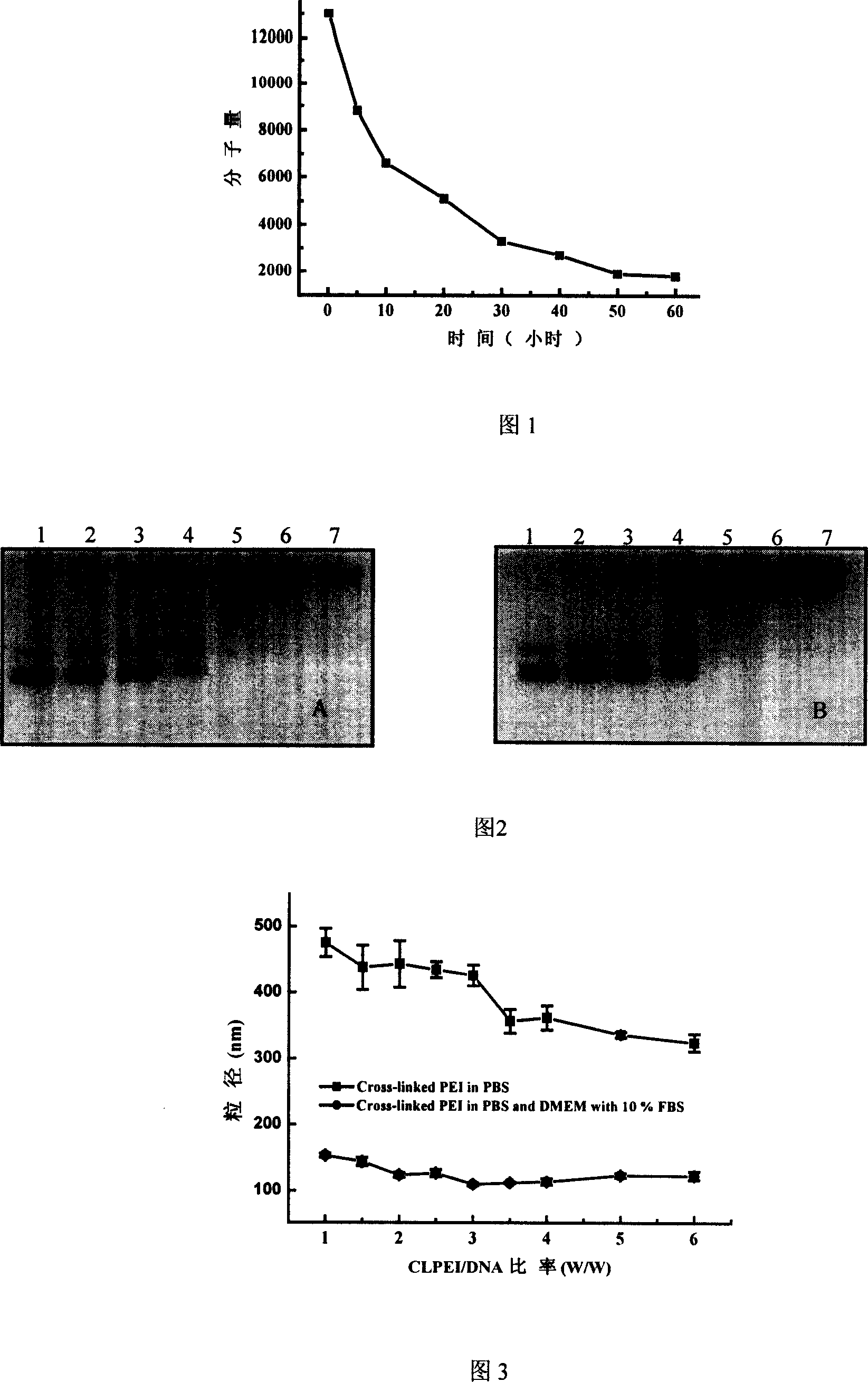
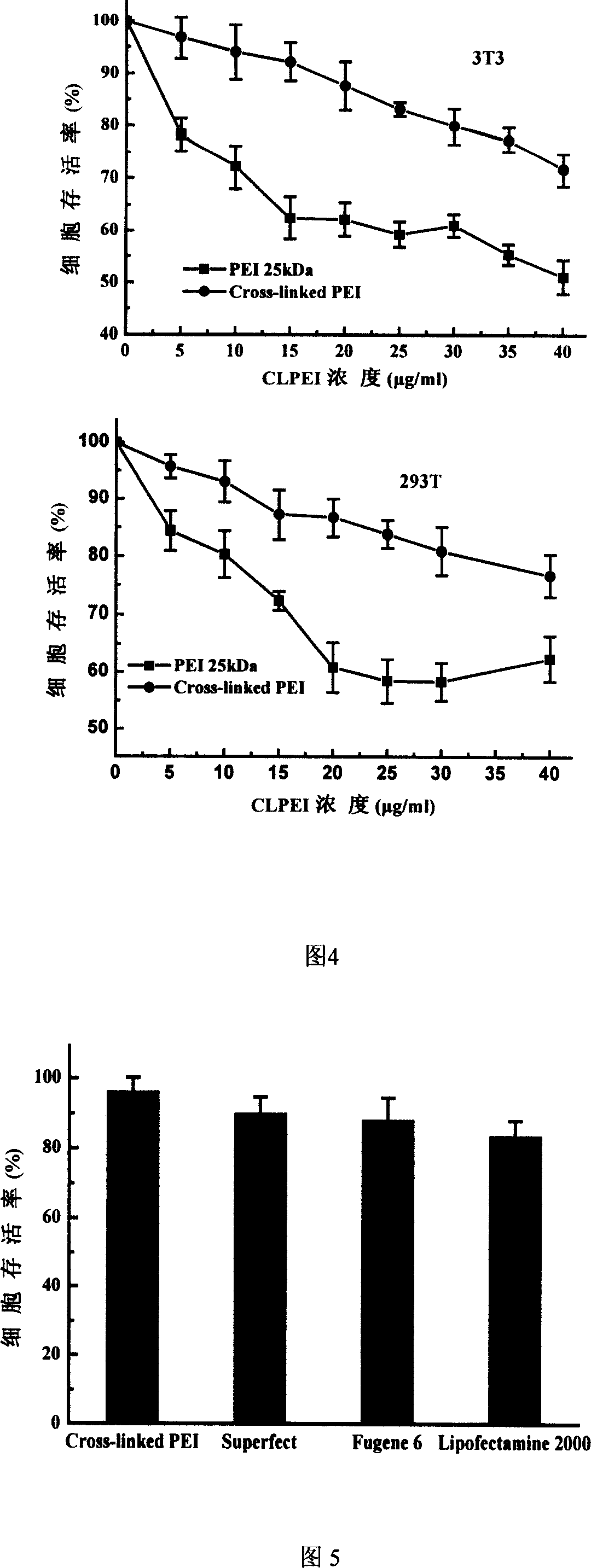
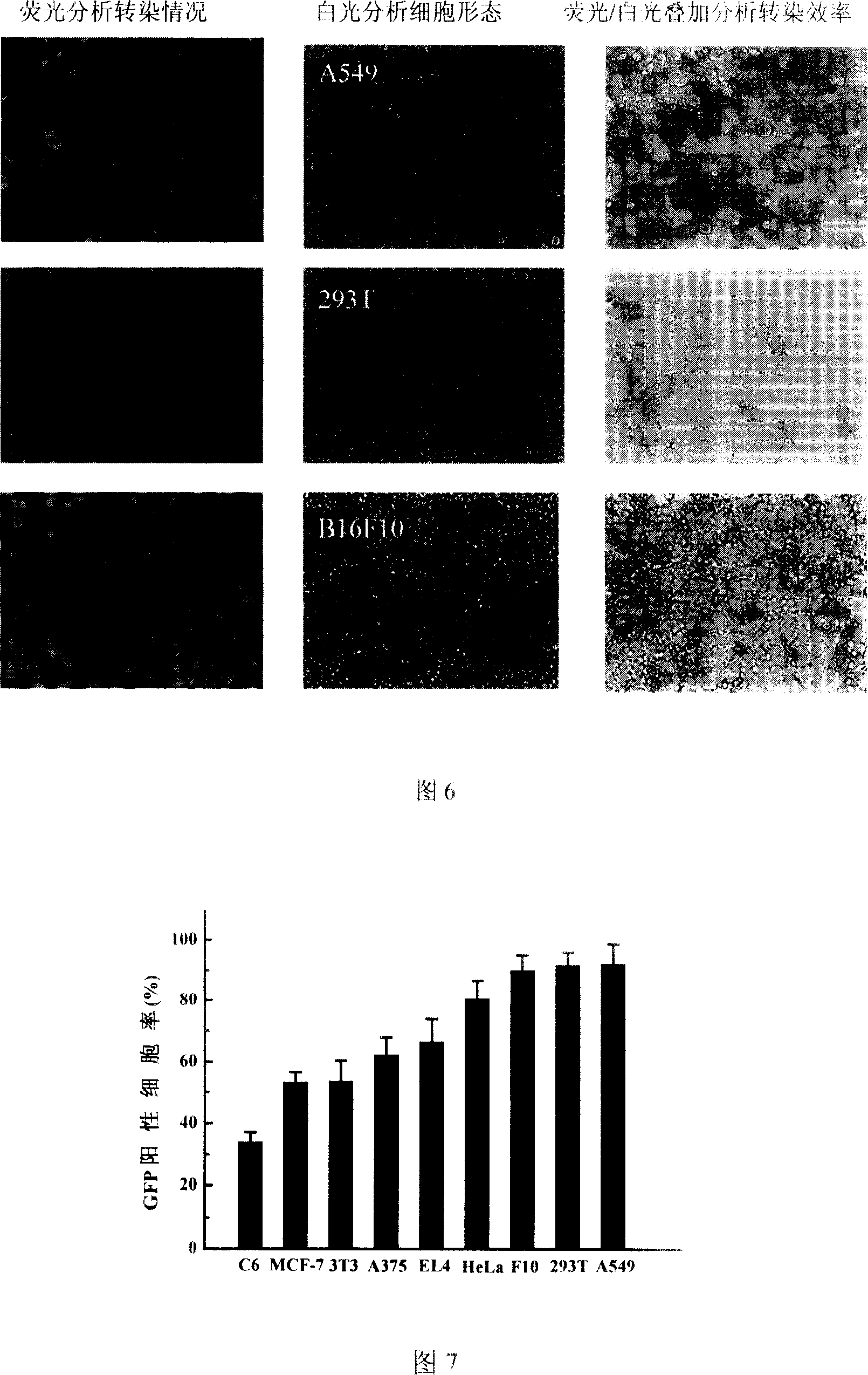
InactiveCN103193979AEfficient transfectionHighly effective topical drug deliveryGenetic material ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesGene deliveryActive agent
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a hydroxyl-containing crosslinked polymer and guanidinated product thereof used for delivering nucleic acid and other bioactive agents. The method comprises the specific steps that: linear or branched polyethyleneimine with a molecular weight of 100-30000Da or various multi-amine compounds are subjected to a compounding reaction with one or more crosslinking agents with a molecular weight of 100-5000Da and containing two or more epoxy groups, such that the hydroxyl-containing crosslinked polymer is prepared. The invention also provides a synthesizing method of a novel guanidination reagent 3-guanidino propanol acrylate or 5-guanidino amyl acrylate. With the guanidination reagent, the hydroxyl-containing crosslinked polymer or other polymers can be guanidinated, such that gene transfection efficiency thereof can be substantially improved, and cytotoxicity can be reduced. The excellent-performance polymers screened by the invention have gene transfection efficiencies in various cell lines such as A549, B16F10, 3T3, and U87 substantially higher than conventional commercialized gene transfection reagents. The polymers are low-toxic high-efficiency non-virus gene transfection vectors. With the vectors provided by the invention, in-vitro high-efficiency and low-toxicity transfection of various cells can be realized, and in-vivo high-efficiency and low-toxicity local administration can be realized. The application has wide application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Modified polyethyleneimin, preparation method of modified polyethyleneimine, gene transfection reagent and application of gene transfection reagent
ActiveCN104419004AAnimal cellsOther foreign material introduction processesGene deliveryCytotoxicity
The invention relates to modified polyethyleneimine, a preparation method of modified polyethyleneimine, a gene transfection reagent and application of the gene transfection reagent. The modified polyethyleneimine comprises polyethyleneimine as a main chain and epsilon-caprolactone grafted onto polyethyleneimine, epsilon-caprolactone and primary amine amino group or secondary amine amino group of polyethyleneimine are subjected to coordination ring-opening grafting reaction and the epsilon-caprolactone is not subjected to coordination ring-opening polymerization reaction. The experiment shows that modified polyethyleneimine with the structure has relatively high gene transfection efficiency which is far higher than those of commercially available products branched polyethylenimine and liposomes 2000, and compared with branched polyethyleneimine having weight-average molecular weight of 25000g / mol, no significant cytotoxicity is observed in modified polyethyleneimine. Therefore, modified polyethyleneimine can be considered as an excellent gene delivery system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multifunctional supramolecular gene delivery system based on polyethyleneimine-cyclodextrin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105463024AStrong transformationDegraded fromOther foreign material introduction processesGene deliveryPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a multifunctional supramolecular gene delivery system based on polyethyleneimine-cyclodextrin and a preparation method thereof. A polyethyleneimine-cyclodextrin polycationic compound serves as a framework, adamantane-disulfide bond-polyethylene glycol having oxidation reduction reactivity and adamantane-polyethylene glycol-targeting peptide having targeting performance serve as modified groups, polyethyleneimine-cyclodextrin is combined with adamantane-disulfide bond-polyethylene glycol and adamantane-polyethylene glycol-targeting peptide through a self-assembling principle, and a subjective body and an objective body act to form a supramolecular gene carrier. The delivery system is multifunctional, has oxidation reduction sensitivity, specificity for targeting liver cancer and excellent gene transfection efficiency, and can carry functional genes to efficiently treat liver malignant tumor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombinant adenovirus carrying rat retinoic acid receptor (RAR) gamma gene and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102168075AShorten the growth cycleEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementViruses/bacteriophagesRetinoic acid receptor betaGene expression level
The invention discloses a recombinant adenovirus carrying a rat retinoic acid receptor (RAR) gamma gene. The gene of the recombinant adenovirus is derived from a rat mesenchymal stem cell and has an SEQID1 sequence. A construction method comprises the following steps: acquiring a target gene RAR gamma; constructing and identifying a recombinant adenovirus plasmid pAd-RAR gamma; and carrying out package, amplification, purification and titer detection on the recombinant adenovirus pAd-RAR gamma in a human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cell. In the invention, the rat mesenchymal stem cell can be efficiently infected and the RAR gamma gene can be efficiently expressed, thereby well solving the problem that a general eukaryotic vector is difficultly led in the RAR gamma cell through transfection of liposome; the physical and chemical properties of the used adenovirus vector are stable, thus preparation and operation are easy; the transfection efficiency of the gene is high, and exogenous gene expression level is high; and the obtained adenovirus is replication-defective, is not combined in a gene group of a host cell, has a high biological safety, and is widely suitable for various in vitro cells and in vivo experiment studies.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Caged ligands and uses thereof
Provided are caged compounds comprising a ligand that specifically reacts with a receptor not naturally present in mammals. The cage is released from the ligand upon illumination of the compound with light. Also provided are cells transfected with a gene of interest and a gene encoding a receptor, the gene of interest operably linked to a genetic element capable of being induced by the receptor when bound to a ligand, and the receptor not naturally present in the species of the cell. The cells also comprise a caged ligand of the receptor. Additionally provided are methods of inducing a gene of interest in the above cells. Also provided are methods of repressing a gene of interest in a cell using caged ligands of receptors. Methods are additionally provided for inducing elimination of a target sequence in a cell of a species, using a caged ligand and a recombinase.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE INC
Method and apparatus for optogenetic treatment of blindness including retinitis pigmentosa
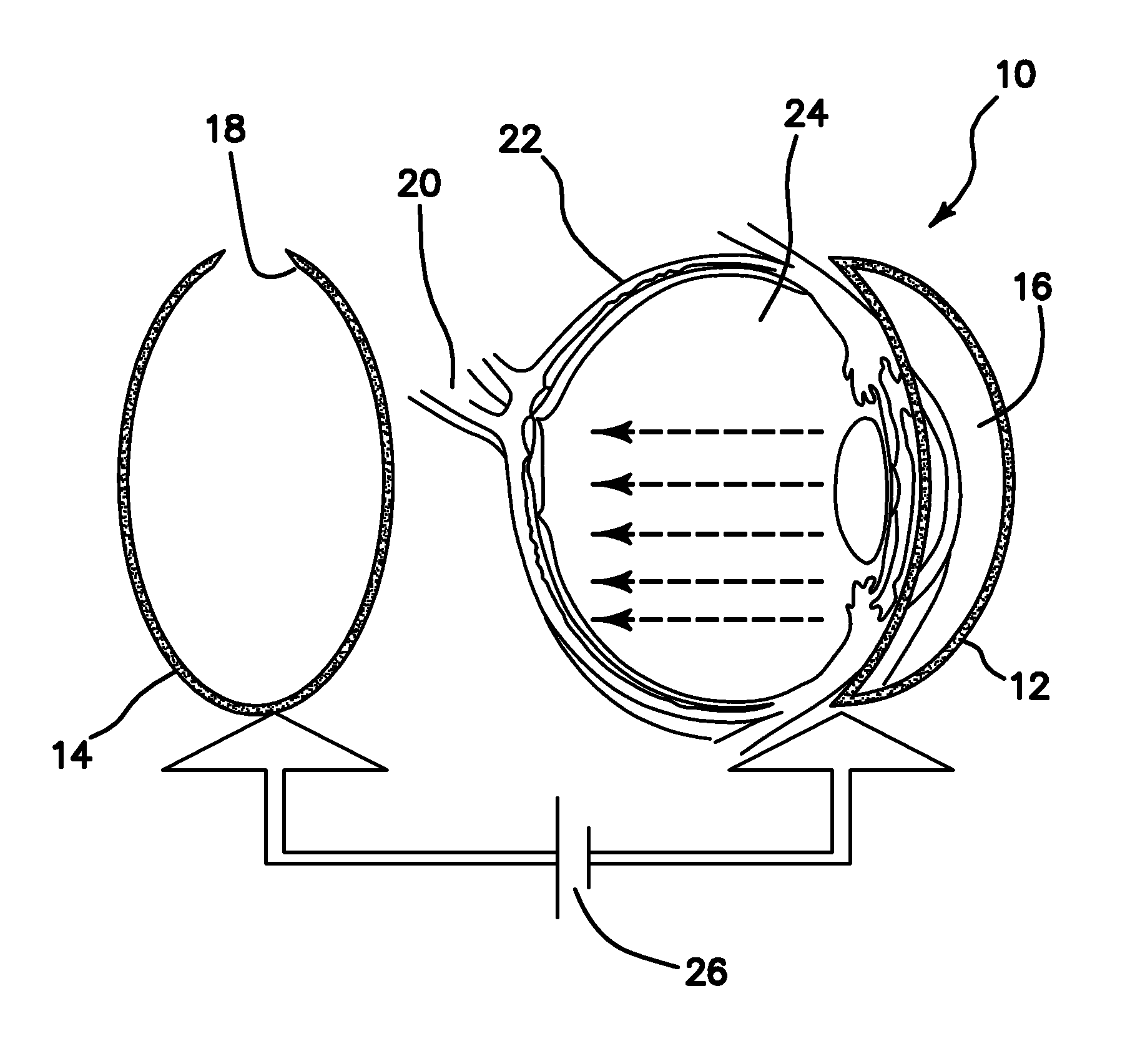
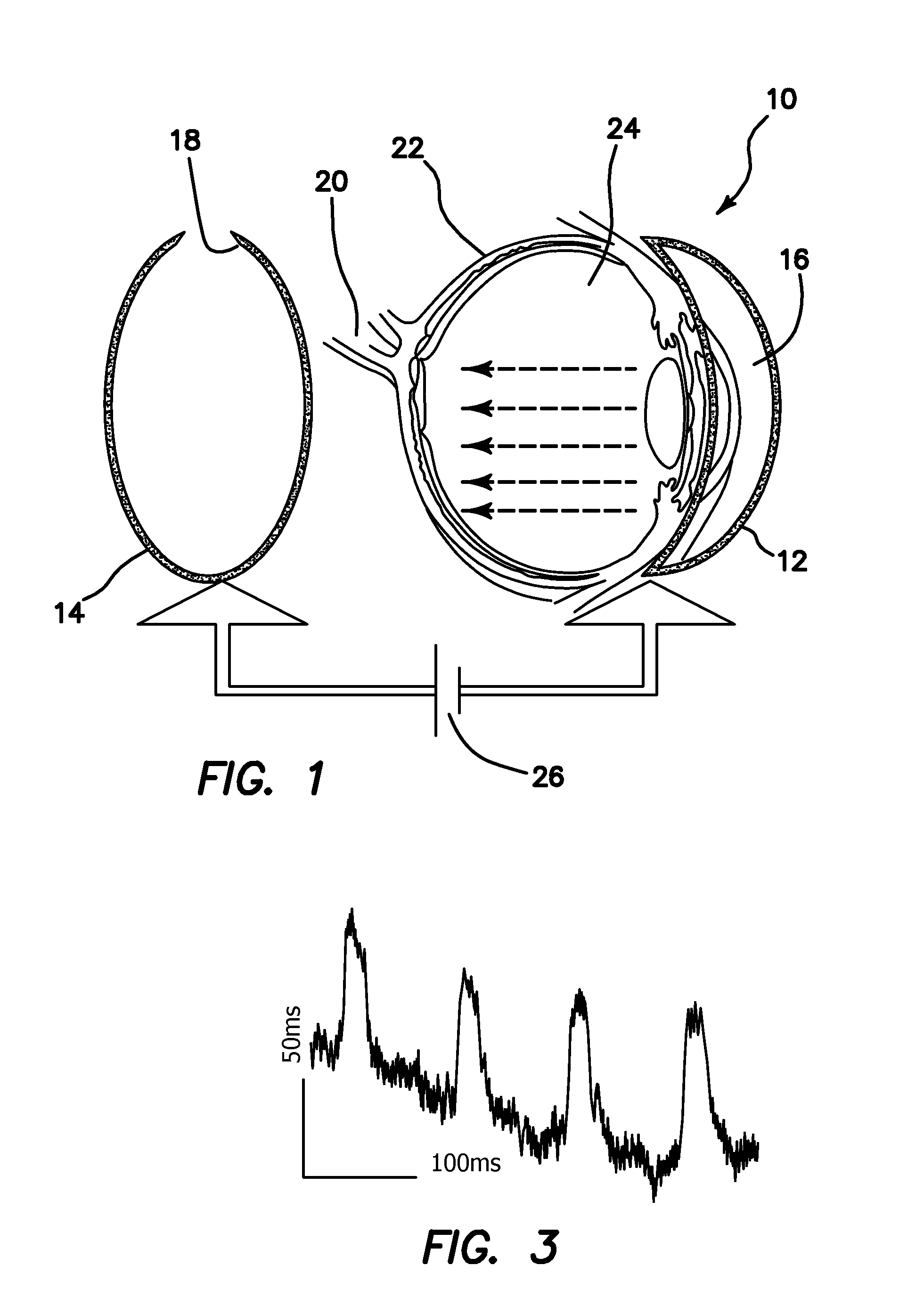
ActiveUS20100268150A1Efficient activationBehavioral improvementElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsOptogeneticsRetinitis pigmentosa
An apparatus for in vivo electroporating a plasmid into a retina of any eye includes a first electrode with a first polarity of voltage placed in contact with a cornea of the eye, a second electrode with an opposite second voltage at least in part behind the retina, and a pulsed voltage source for providing a pulsed DC voltage with an optimized field strength amplitude, frequency, number of pulses, group repetition rate and duration of pulse and group repetition, which are optimized for transfection of the channelrhodospsin-2 (ChR2) gene into the retinal ganglion cells. An in vivo method for treating retinal ganglion cells in an eye without use of viral transfection includes the steps of nonviral in vivo delivering a channelrhodospsin-2 (ChR2) gene to target the specific (retinal ganglion) cells of a retina by intravitreous injection of plasmid DNA, electroporating the plasmid into the retina and use of image intensification device for stimulating the retinal ganglion cells with ambient lighting conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cationic lipid containing peptide dendrimer, transgenic carrier and preparation method and application of transgenic carrier
ActiveCN102911252ALow cytotoxicityStrong wrappingPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionDendrimerTransgene
The invention discloses cationic lipid containing peptide dendrimer, a transgenic carrier, and a preparation method and application of the transgenic carrier. The transgenic carrier has low cell toxicity, can effectively retard and coat pEGFP-N1 plasmid or pGL3 plasmid, and is high in coating capacity. As the average particle size of a compound of the transgenic carrier with the pEGFP-N1 plasmid or pGL3 plasmid ranges from 80 nm to 200 nm, and the Zeta potential is within the range of 5-50mV, the transgenic carrier is quite suitable for gene transfection. When the compound formed of the transgenic carrier and the pEGFP-N1 plasmid or pGL3 plasmid is used for gene transfection of cells HepG2, MCF7 and B16F10, good transfection capacity is achieved, the transfection capacity is higher than that of the commercial product PE125K on the condition of transfection optimization, and the transfection advantage is much superior on the condition with serum existence.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Avian induced pluripotent stem cells and their use
InactiveUS20140363467A1Fast recoveryIncrease the number of cellsSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetically modified cellsGerm layerReprogramming
The present invention relates to the production of avian induced pluripotent stem cells from non-pluripotent somatic cells, including embryonic fibroblasts and adult somatic cells. In this method, avian (including quail or chicken) somatic cells are reprogrammed into a state closely resembling embryonic stem cells including the expression of key stem cell markers alkaline phosphatase, etc. by transfecting / transducing the non-stem cells with genes (preferably using a non-integrating vector as otherwise described herein or alternatively an integrating vector, such a lentiviral vector, retroviral vector or inducible lentiviral vector, among others) which express at least nanog, Lin28 and cMyc. In preferred aspects of the invention, the transfected / transduced vectors express nanog, Lin28, cMyc, Oct 4 (POU5F1 or PouV), SOX2 and KLF4. The induced stem cells which are produced contribute to all 3 germ layers, the trophectoderm and in certain aspects, the gonad in chimeric offspring.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Preparation method for replication and transcription activator (Rta) protein and application of Rta protein to nasopharynx cancer detection reagent
The invention discloses a preparation method for a replication and transcription activator (Rta) protein and the application of the Rta protein to a nasopharynx cancer detection reagent and relates to a medical diagnosis reagent. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: 1, constructing a recombinant expression vector by taking a BRLF1 full-length gene as an exogenous gene; 2, transfecting: transfecting the recombinant expression vector into an eukaryotic expression system to obtain a positive transfected cell; and 3, expressing and purifying: culturing the positive transfected cell so as to enable the positive transfected cell to express an interest protein, and separating and purifying the interest protein, wherein the eukaryotic expression system refers to a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell. The Rta protein prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is used for detecting nasopharynx cancer; the sensitivity of the Rta protein is 96 percent (288 / 300), and the specificity of the Rta protein is 96.7 percent (290 / 300). The sensitivity and the specificity are superior to those of antigens respectively prepared by a prokaryotic expression system and a pichia expression system, and the sensitivity and the specificity on clinical early diagnosis on the nasopharynx cancer are greatly improved.
Owner:同昕生物技术(北京)有限公司
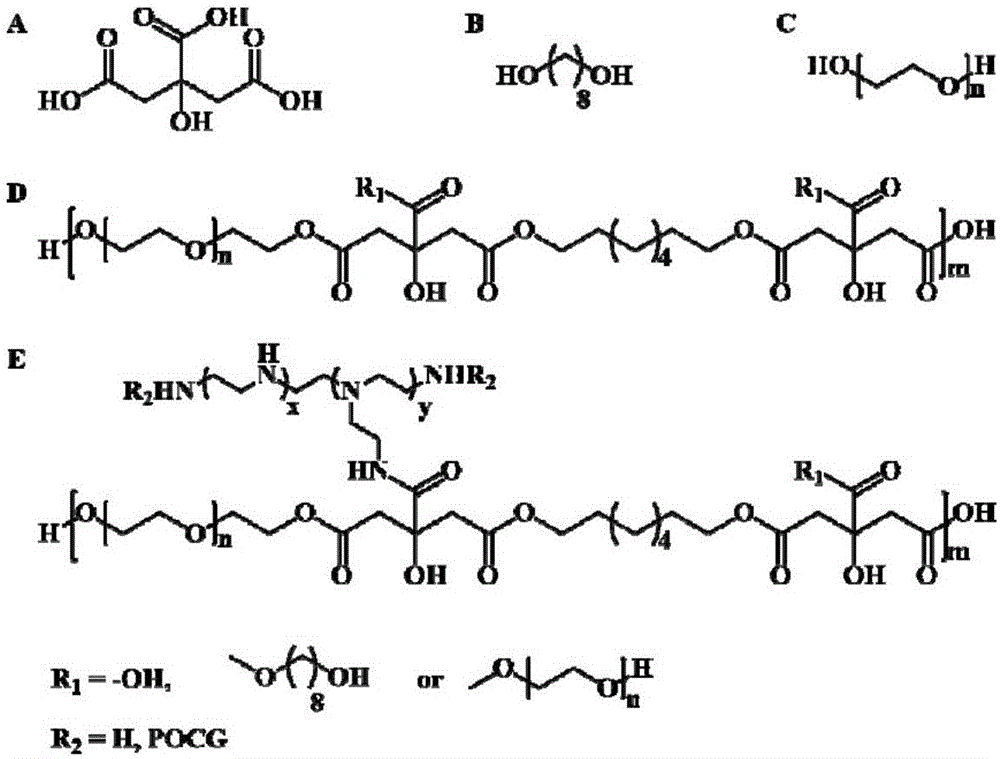
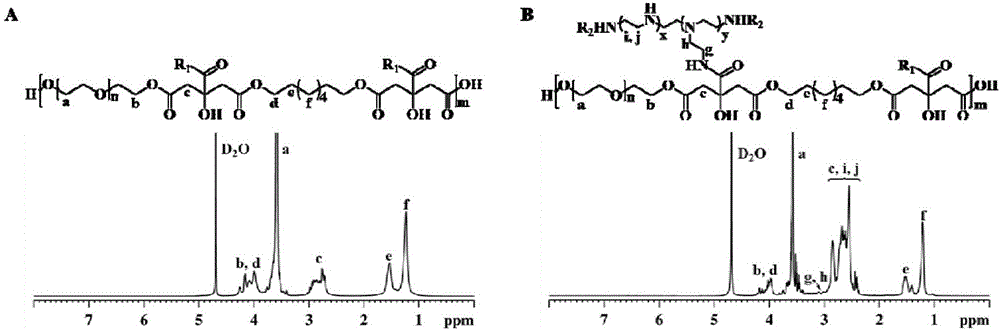
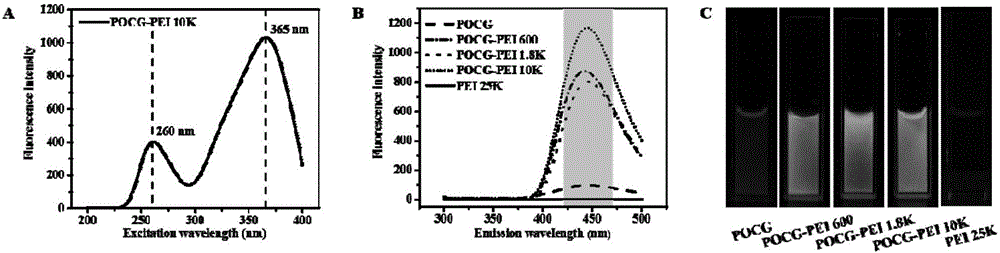
Non-viral gene carrier of autofluorescence degradable poly-citrate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106801068ALow costNo residueOther foreign material introduction processesPolyethylene glycolBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a non-viral gene carrier of autofluorescence degradable poly-citrate and a preparation method thereof. Citric acid, 1,8-octylene glycol and polyethylene glycol are subjected to thermal polymerization to obtain a POCG prepolymer; then, the POCG and PEI (polyethyleneimine) are subjected to catalytic polymerization to obtain a POCG-PEI polymer; the POCG-PEI polymer and various genes (DNA / siRNA / miRNA) can form a stable nanocomposite in HEPES buffer liquid. The used thermal polymerization method has the advantages that the environment is protected; the operation is convenient; the raw material cost is low. The prepared POCG-PEI has good biocompatibility and high gene transfection efficiency; meanwhile, the POCG-PEI also shows certain fluorescence characteristics and optical stability, so that the polymer has good application prospects in the gene treatment process.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
ZnO quantum dot vector/DNA composite-containing collagen-based composite cornea substitute, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101890185AGood biocompatibilityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderFluorescencePolymer network
The invention relates to a ZnO quantum dot vector / DNA composite-containing collagen-based composite cornea substitute, and a preparation method and application thereof. The ZnO quantum dot vector / DNA composite-containing collagen-based composite cornea substitute is prepared by absorbing ZnO quantum dot vectors / DNA composites by using a collagen / MPDSAH IPN cornea substitute, wherein the weight ratio of the cornea substitute to the ZnO quantum dot vectors / DNA composites is 425:1; and the weight ratio of ZnO quantum dot vectors to DNA is 25:1. The ZnO quantum dot vector / DNA composite-containing collagen-based composite cornea substitute has high biocompatibility, can induce and promote the regeneration of a cornea and be biologically decomposed along with the regeneration of the cornea, hasmechanical properties and optical properties the same as those of a human cornea, remarkably improves the stability and mechanical strength of the cornea substitute in collagenase due to the introduction of an MPDSAH polymer network, can effectively compositely compress the DNA, successfully induce the DNA into cells, successfully express the DNA, trace the position of the DNA / vector at any time and determine the intra-cellular distribution of the DNA / vector in a transgenosis process due to ZnO quantum dots, and effectively combines gene transfection, tissue engineering and fluorescent tracing so as to achieve simple manufacturing method, and easy processing and long-term storage and transport.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing non-viral gene vector of amino acid material
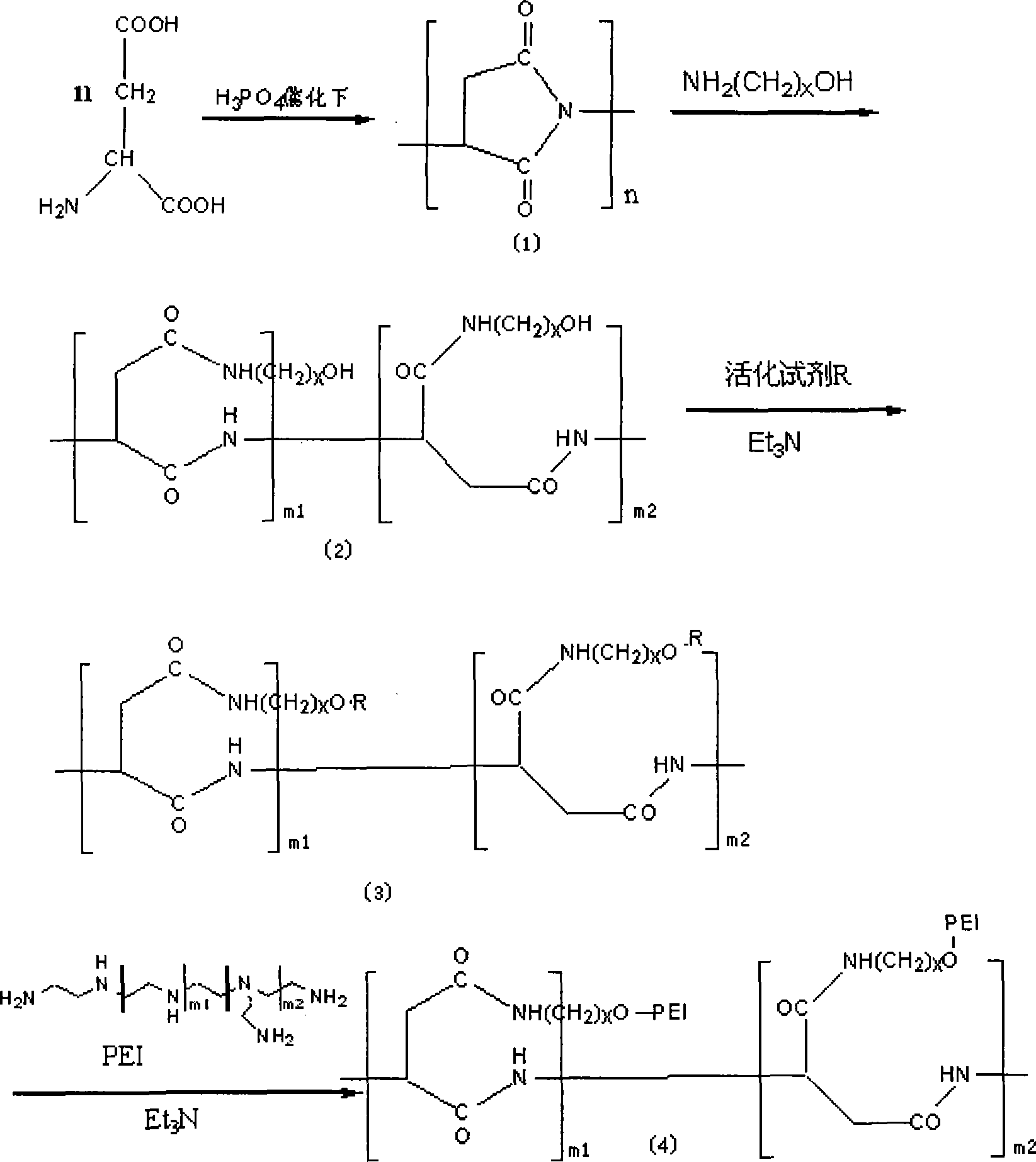
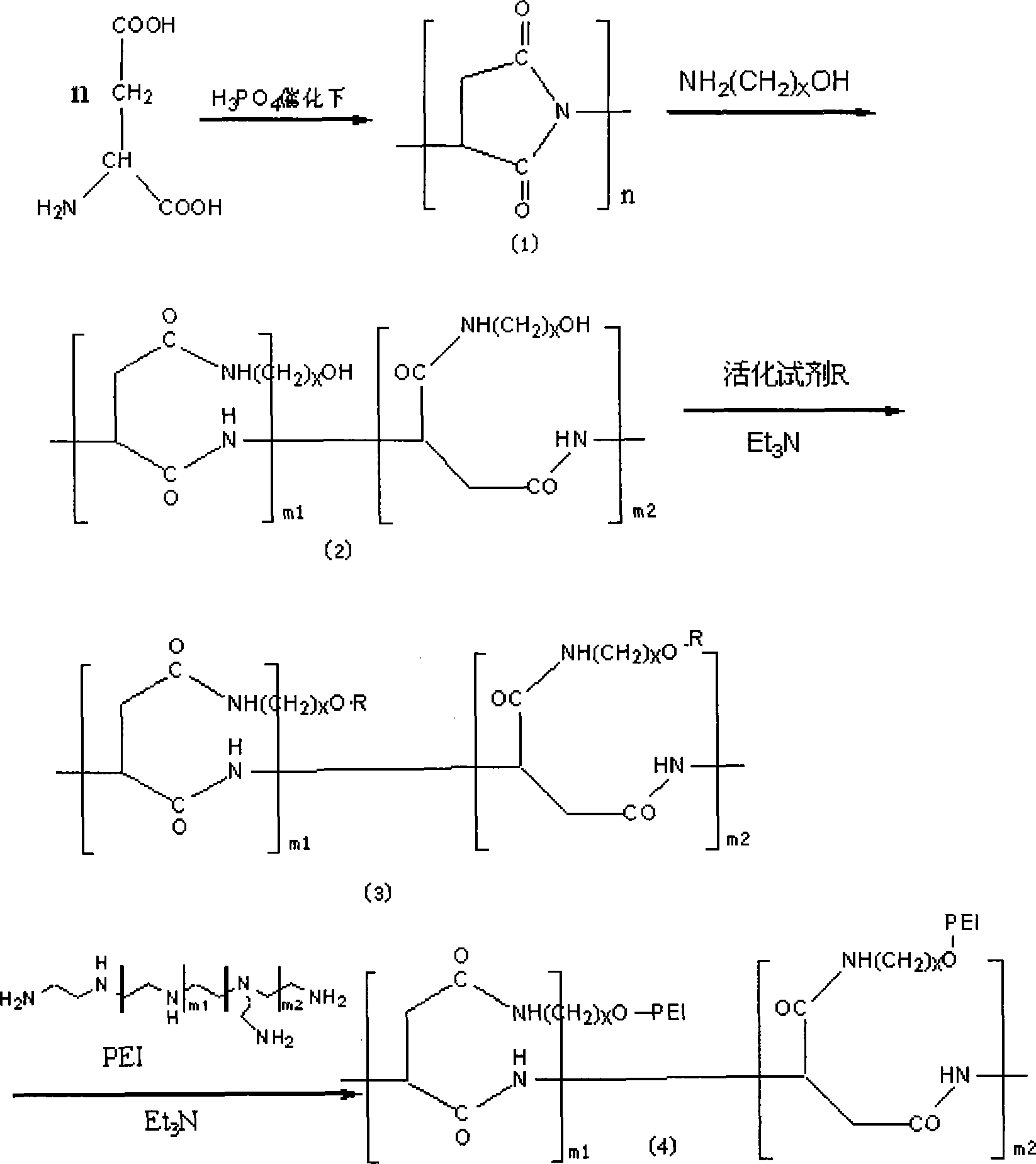
InactiveCN101225399AHigh recovery rateImprove gene transfection efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionMonomerAmino acid
The invention provides a modification method of polymer amino acid, in particular to a macromolecular compound of non-viral gene vector material, which is characterized in that the polymer amino acid is generated by polycondensation of amino acid monomer, the ring-opening of the polymer amino acid side group is processed by amino alcohol reagent, the structure modification is processed by the connection reagent, the polyethyleneimine (PEI) is joined by the activation of active hydroxy on the amino alcohol, and that the functional composite material of polymer amino acid-amino alcohol-polyethyleneimine is generated by dialysis and lyophilization. The modification method of polymer amino acid has the advantages of low mammalian toxicity, high gene transfection efficiency and performance of biodegradation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
New method for gene injection for somatic cell nuclear transfer reconstructed embryo
InactiveCN106520838AMeet biosafety requirementsAvoid screening difficultiesMicroinjection basedFermentationLarge fragmentEmbryo transfer
The invention discloses a new method for gene injection for a somatic cell nuclear transfer reconstructed embryo. The method comprises the following steps: target gene preparation, somatic cell nuclear transfer and a microinjection technology. An expression vector is constructed after a target gene is obtained, the cell nucleus of an oocyte is removed by virtue of micromanipulation, then a somatic cell is injected in the space of the denucleated oocyte, then an exogenous gene is directly injected in the somatic cell, the reconstructed embryo is constructed through one-step electric fusion and activation, and the embryo is transferred to obtain a transgenic progeny. According to the method disclosed by the invention, large-fragment cell gene transfection and screening are avoided, the transgenosis efficiency is increased, the time is saved, and the transgenosis application range is expanded. Importantly, the somatic cell is injected in a transpanent zone during a nuclear transfer operation process, thus microinjection for the exogenous target gene is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Antineoplastic invasion transfer function of snake venom metalloprotease inhibitors BJ46a and uses thereof
InactiveCN101429525AInhibitory activityObvious anti-tumor invasion and metastasis effectPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthIn vivo
The invention discloses a snake venom metal protease inhibitor BJ46a capable of resisting attack and transference of tumor and application thereof, and belongs to the field of medical organism. In the invention, according to the BJ46a gene sequence (AF294836) in GenBank, the BJ46a full gene is designed and synthesized. An expression vector cloned to baculovirus can generate the recombined BJ46a protein capable of inhibiting the activity of the substrate metal protease in Sf9 insect cells, and in vivo and in vitro experiments show that the BJ46a protein has the functions of resisting the attack and transference of melanoma cells B16. The inhibitor adopts the genetic transfection technique, and can establish B16 / pcDNA3.1HisC-BJ46a cell strains with stable transfection, and the in vivo and in vitro experiments prove that the BJ46a can inhibit the attack and transference of B16 cells at the gene level. The inhibitor is applied to preventing and treating the attack and transference of tumor, and has great application prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Multifunctional immune killing transgenic cell as well as preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN102220283AOvercome the defect of low transfection ratePrevent proliferationAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsHigh level expressionCell immunity
The invention relates to a multifunctional immune killing transgenic cell and in particular relates to a multifunctional immune killing transgenic cell which has cell killing toxicity and expressing an antibody containing a human constant region. The gene of the antibody containing the human constant region is transfected into a cell with cell killing toxicity through coding, and is expressed in the cell at a high level so as to realize the double effects of cell immunity and antibody and inhibit multiplication of tumor and virus. The invention also relates to a preparation method and use of the multifunctional immune killing transgenic cell.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY GRP CO LTD
Gene therapy of tumors using non-viral delivery system
InactiveUS20060165773A1Reduce lung cancer mortalityReduction in formation of tumorPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthLipid formation
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition, comprising: (a) cationic lipids, wherein said lipids are a liposomal mixture of a diacyl-ethyl-phosphocholine and 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; and (b) a plasmid cDNA sequence encoding a protein having tumor suppressor or pro-apoptotic activity. This composition has a high gene transfection efficiency at non-toxic doses and is designed to transfect human bronchial premalignant lesions and early endo-bronchial malignancies. Also provided is a method of method of treating a cancerous or pre-cancerous condition of the respiratory tract in an individual in need of such treatment, comprising the step of administering to said individual a pharmacologically effective dose of a pharmaceutical composition, comprising: (a) cationic lipids, wherein said lipids are a liposomal mixture of a diacyl-ethyl-phosphocholine and 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; and (b) a plasmid cDNA sequence encoding a protein having tumor suppressor or pro-apoptotic activity.
Owner:PEREZ SOLER ROMAN +1
Construction and applications of multifunctional graphene gene vector
ActiveCN107805642ALow toxicityHigh transfection efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFluorescenceTreatment field
The invention discloses a multifunctional graphene gene vector construction method, wherein small-size graphene quantum dot with fluorescence is used as a basic vector, and is functionally linked to acationic polymer branched chain polyethyleneimine so as to achieve gene transfection ability, and the non-gene-transfection cationic polymer part can be tracked due to the fluoresce ability. According to the present invention, the synthesis process is simple, the constructed multifunctional graphene gene vector has advantages of low toxicity and high transfection efficiency, the highest transfection efficiency can achieve 80.57%, gene transfection and tracking can be simultaneously achieved, and the constructed multifunctional graphene gene vector can be used for cell biology research and gene therapy field.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com