Prostate cancer targeting gene oligonucleotide aptamer, delivery carrier, delivery system and preparation method thereof
A technology targeting genes and prostate cancer, applied in other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, gene therapy, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of difficult monoclonal antibody synthesis, high cost, poor stability, etc., and increase transfection efficiency and expression level, improved expression efficiency, and strong stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
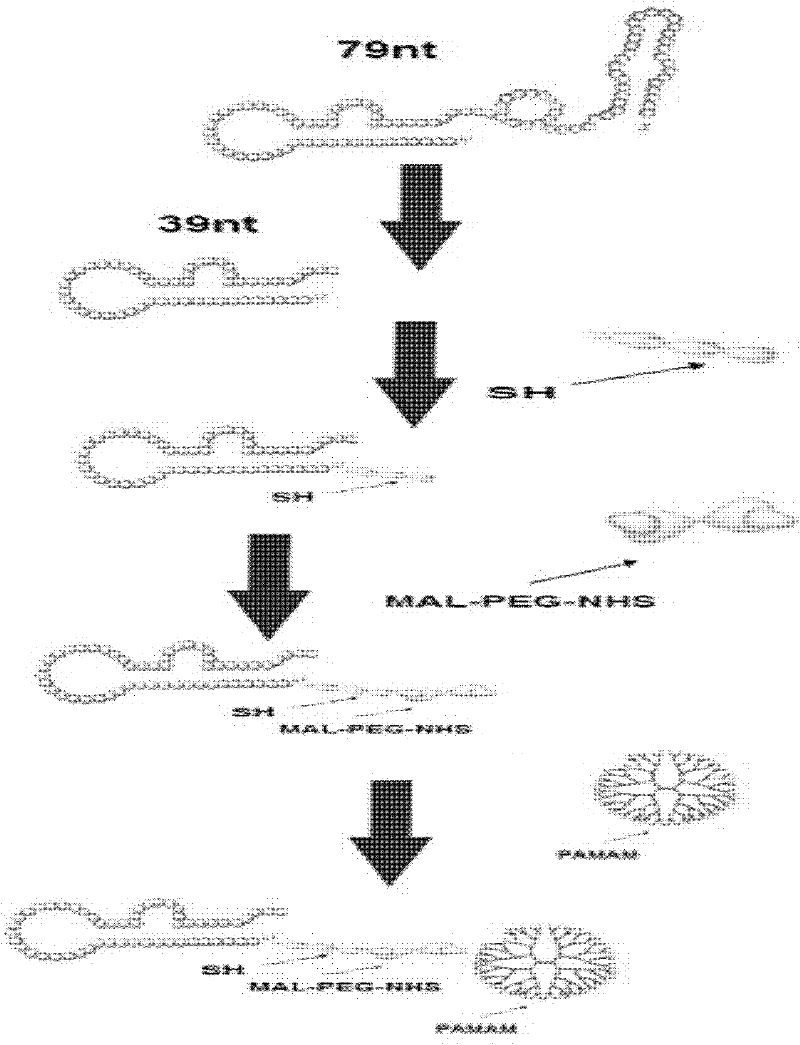
[0040] In the present invention, by modifying the first-generation aptamer A10, the length of 79 nucleotides of the original aptamer A10 is cut to a novel second-generation aptamer A10-3.2 with a length of 39 nucleotides. The prostate cancer targeting gene described in this example uses the A10-3.2 oligonucleotide aptamer as the targeting head group, and the base composition of the A10-3.2 oligonucleotide aptamer is: 5'-GGGAGGACGAUGCGGAUCAGCCAUGUUUACGUCACUCCU(SEQ .ID.NO.1). The specific composition of the oligonucleotide adapter is: 5′-GGGAGGACGAUGCGGAUCAGCCAUGUUUACGUCACUCCU-(CH 2 ) 6 -S-S-(CH 2 ) 6 -OH-3', and has a 2'-fluoro modification, and has a 2'-fluoro modification.
[0041] The prostate cancer-targeted gene delivery carrier described in this example is based on PAMAM, PEG and the above-mentioned A10-3.2 oligonucleotide aptamer, and the three are covalently linked, wherein, PEG and PAMAM The molar ratio is 2:1, and the molar ratio of the A10-3.2 oligonucleotide ap...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The oligonucleotide aptamer of the prostate cancer targeting gene described in this example is as described in Example 1.
[0049] The prostate cancer targeted gene delivery carrier described in this example is based on PLR, PEG and the above-mentioned A10-3.2 oligonucleotide aptamer, and the three are covalently linked to form, wherein, PEG and PLR The molar ratio is 2:1, and the molar ratio of the A10-3.2 oligonucleotide aptamer to the polycation polymer material is 4:1.
[0050] The preparation method of the prostate cancer-targeted gene delivery carrier described in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0051] A. PLR and PEG containing bifunctional groups were dissolved in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) at pH 8.0 according to the molar ratio of 1:2, stirred at room temperature for 2 hours to generate PLR-PEG, and unreacted PEG was removed by ultrafiltration and replaced The buffer is PBS at pH 7.0;
[0052] B. Dissolve the synthesized A10-3.2 oligonucl...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The oligonucleotide aptamer of the prostate cancer targeting gene described in this example is as described in Example 1.
[0057] The prostate cancer targeting gene delivery carrier described in this example is based on PEI, PEG and the above-mentioned A10-3.2 oligonucleotide aptamer, and the three are covalently linked to form, wherein, PEG and PLR The molar ratio is 2:1, and the molar ratio of the A10-3.2 oligonucleotide aptamer to the polycation polymer material is 4:1.
[0058] The preparation method of the prostate cancer-targeted gene delivery carrier described in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0059] A. PEI and PEG containing bifunctional groups were dissolved in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) at pH 8.0 according to the molar ratio of 1:2, stirred and reacted at room temperature for 2 hours to generate PEI-PEG, unreacted PEG was removed by ultrafiltration and replaced The buffer is PBS at pH 7.0;
[0060] B. Dissolve the synthesized A10-3.2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com