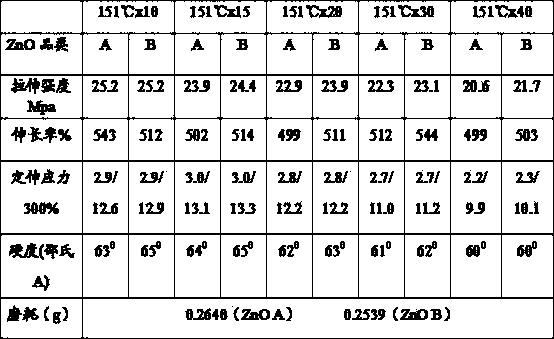
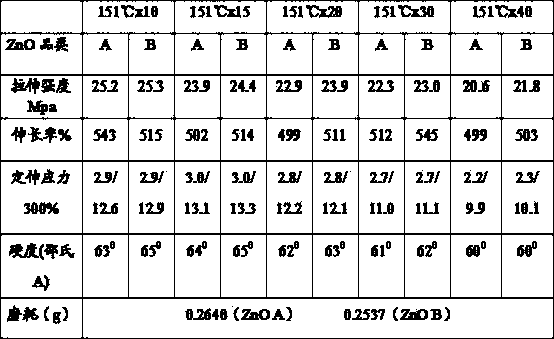
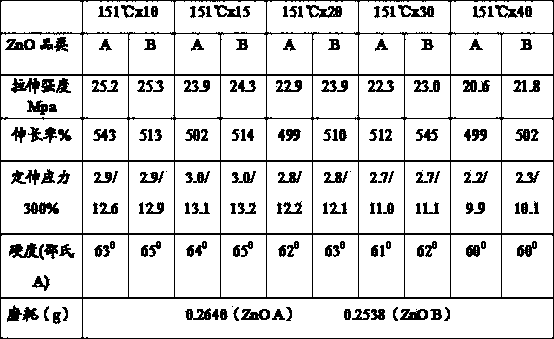
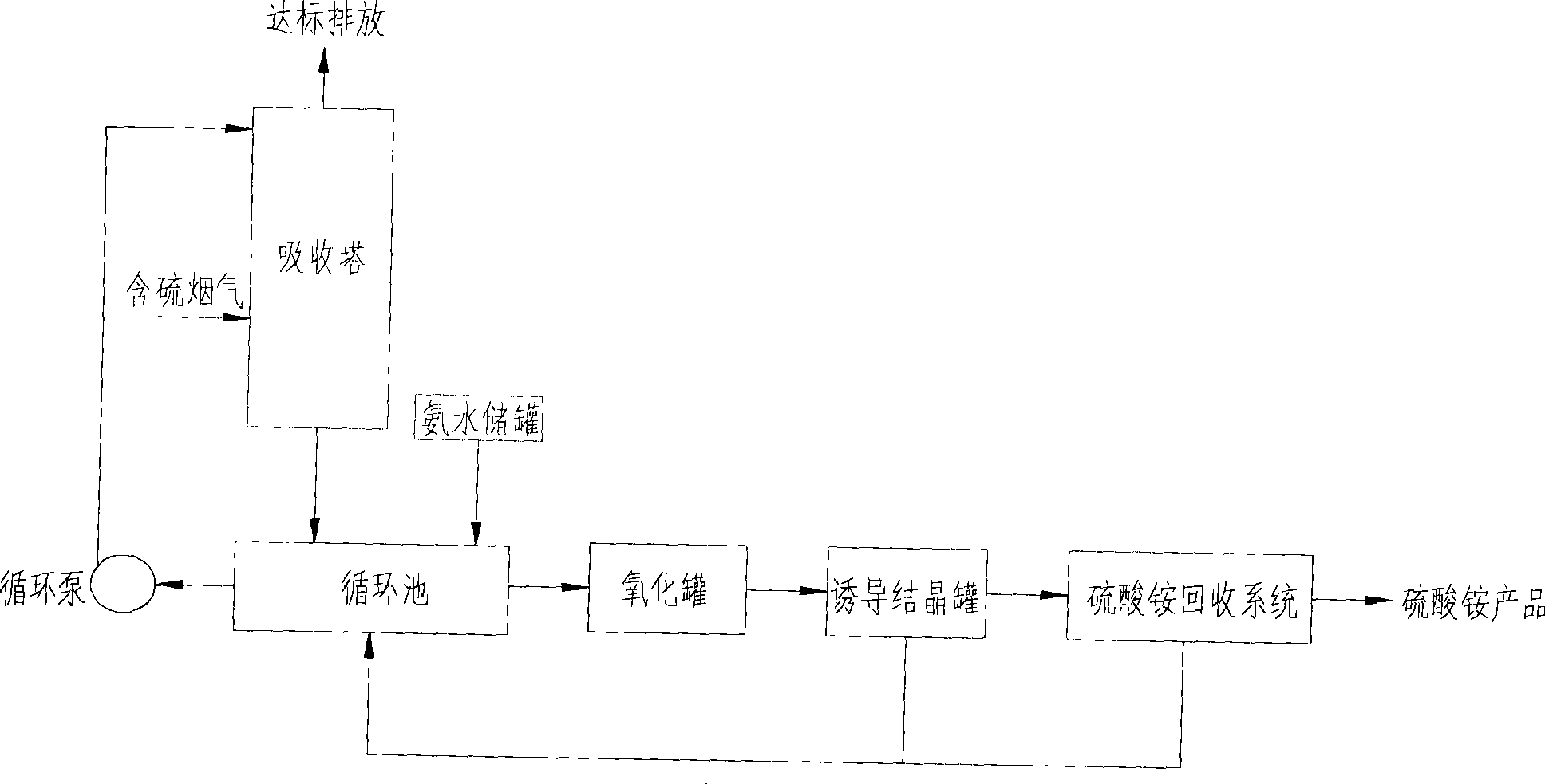Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Ammonia ammonium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ammonia, Ammonium. Ammonium (NH 4 +) — or its uncharged form ammonia (NH 3) — is a form of nitrogen which aquatic plants can absorb and incorporate into proteins, amino acids, and other molecules. High concentrations of ammonium can enhance the growth of algae and aquatic plants.
Method for preparing activated zinc oxide by utilizing high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process
The invention relates to a method for preparing activated zinc oxide by utilizing a high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process, which belongs to the field of inorganic chemical industry and secondary resource recovery. The method comprises the following technical processes in sequence as follows: leaching, purifying, ammonia distillation, washing, dry crushing, calcining and the like. According to the method for preparing the activated zinc oxide by utilizing the high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process, by taking high-arsenic-antimony secondary zinc oxide generated in a lead and zinc smelting process as a raw material, selective leaching is performed by adding ammonia water and ammonium bicarbonate; then, two-stage purification and deeppurification are performed by ferrous salt, hydrogen peroxide, sulfide and zinc powder; and the ammonia water is recycled and valued metal waste residues are comprehensively recovered. The method forpreparing the activated zinc oxide by utilizing the high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process has strong adaptability on zinc-contained materials and is capable of treating various complicated zinc-contained resources. The method for preparing the activated zinc oxide by utilizing the high-arsenic secondary zinc oxide resource ammonia-ammonium process has the advantages of short flow, production process closed cycle, convenience in operation, low energy consumption, excellent product quality, high economic benefits, low pollution, high comprehensive recovery capacityand the like, and is suitable for industrial production and popularization.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
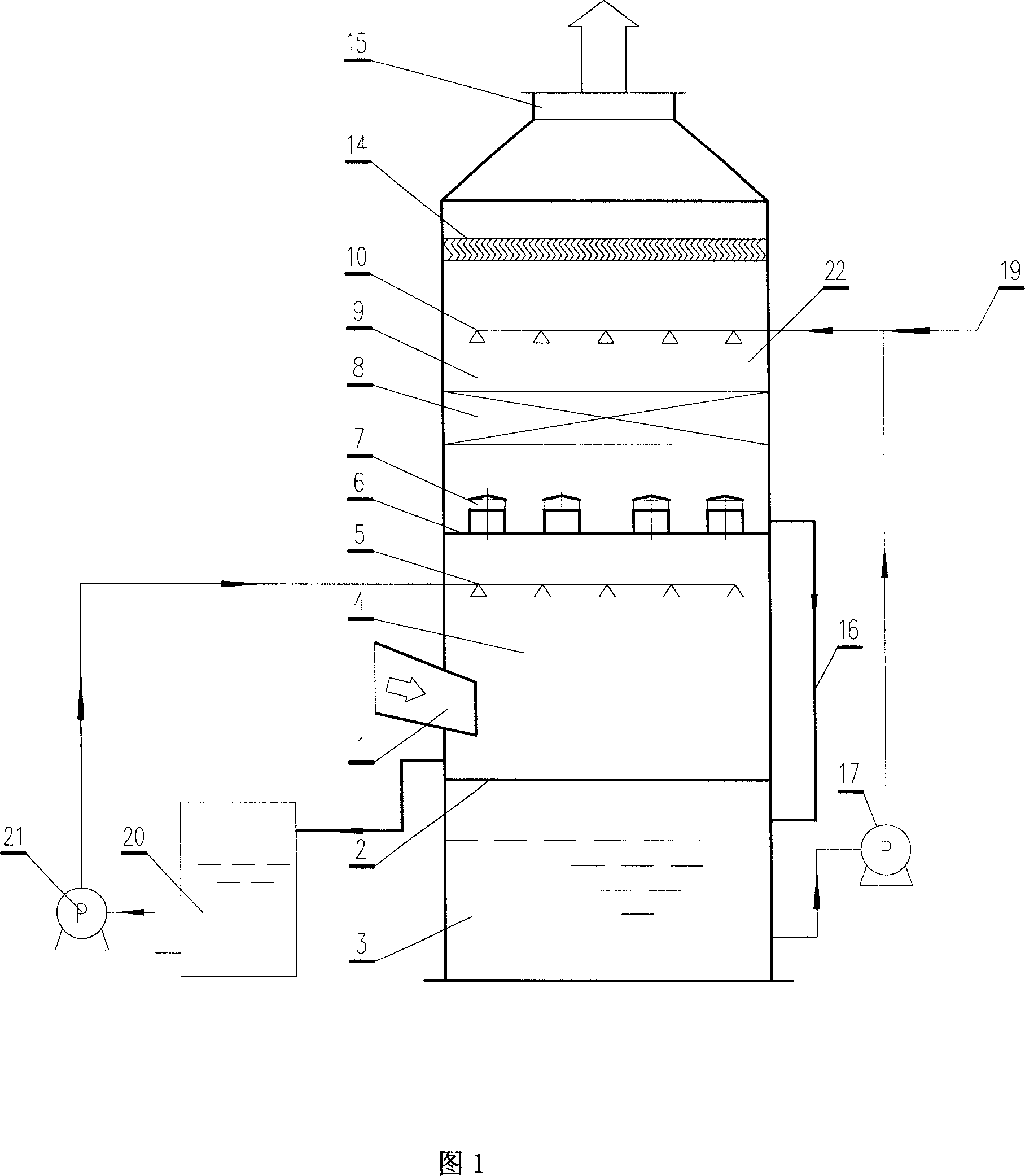
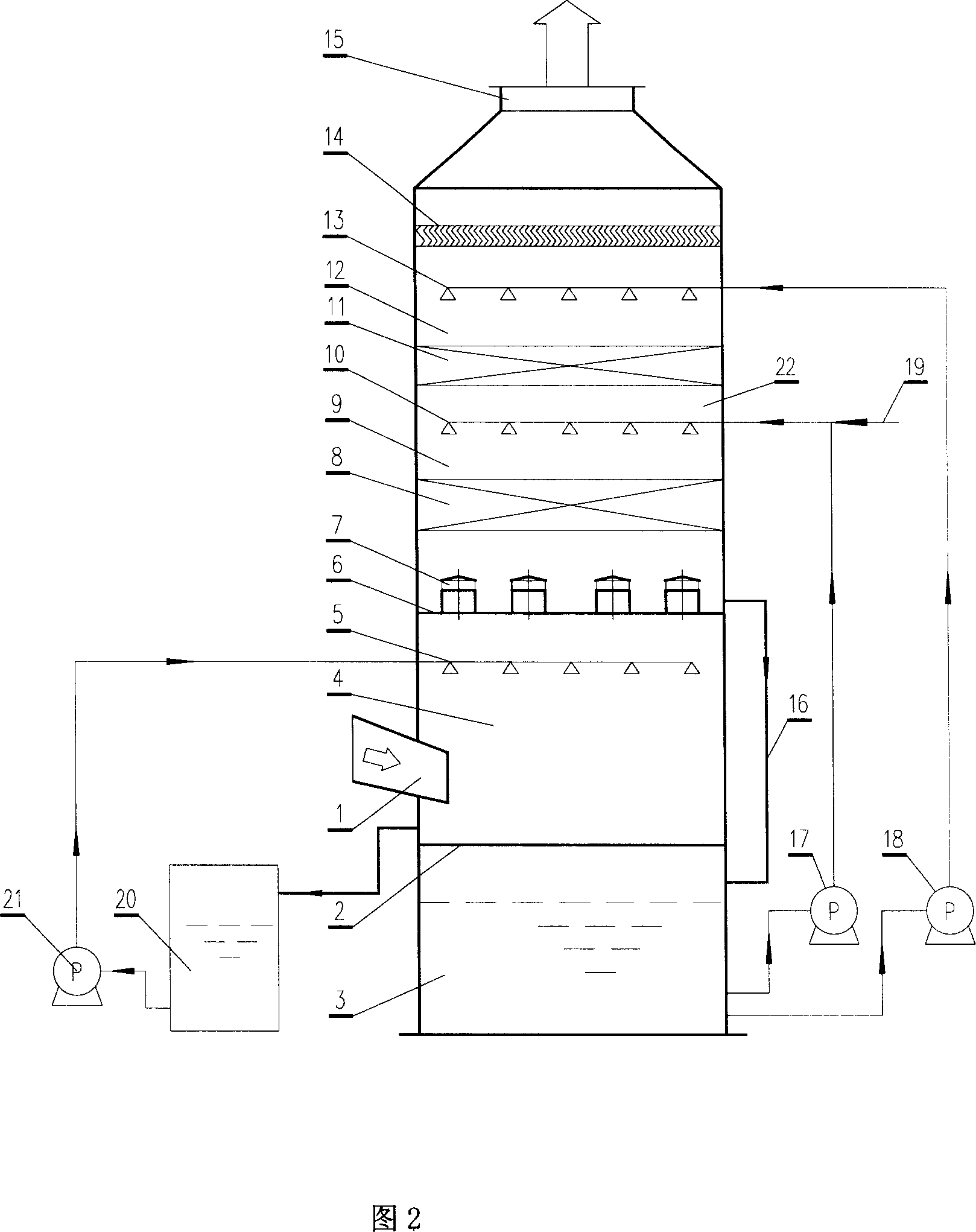
Multi-stage absorbing desulfurizing device by adopting ammonia-ammonium sulfate method
ActiveCN105148712AImprove ammonia utilizationImprove oxidation efficiencyCombination devicesCycloneFlue gas
The invention discloses a multi-stage absorbing desulfurizing device by adopting an ammonia-ammonium sulfate method. The absorbing desulfurizing device comprises a flue gas desulfurizing absorption tower, an absorption liquid circulating tank, a thin slurry circulating tank and a wet-type electric dust remover, wherein the flue gas desulfurizing absorption tower comprises a concentrated slurry circulating tank, a concentration pre-absorption section, an absorption section, a thin slurry washing section and a defogging section that are arranged in a vertical manner; the concentration pre-absorption section comprises at least a layer of concentrated slurry spraying layer; the absorption section comprises an absorption liquid cyclone defogging liquid collector and at least a layer of absorption liquid spraying layer; the thin slurry washing section comprises a thin slurry cyclone defogging liquid collector and a thin slurry spraying layer; the defogging section comprises a defogger and a defogger washing spraying layer. According to the multi-stage absorbing desulfurizing device by adopting the ammonia-ammonium sulfate method, provided by the invention, flue gas cooling, multi-stage defogging absorption and multi-section oxidization are completed in the desulfurizing absorption tower, the utilization rate of ammonia is increased by regulating the ammonia adding positions, and the problems that the concentration of slurry in multiple sections is controlled unsatisfactorily, and the content of aerosol in flue gas after desulfurization is too high are solved, wherein the problems are caused due to the fact that although the conventional desulfurizing absorption tower is divided into multiple sections, slurry in the multiple sections are carried with gases heavily.
Owner:SINOPEC NANJING ENG & CONSTR +1
Method for producing high-purity nano-zinc oxide by ammonia method using electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues
ActiveCN102863007AGrowth inhibitionSmall particle sizeZinc oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyElectrolysisZno nanoparticles
The invention discloses a method for producing high-purity nano-zinc oxide by an ammonia method using electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues. The method comprises the following steps of: adding slaked lime being 1-5% of the mass of electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues before a leaching step to perform activation, then leaching with ammonia-ammonium bicarbonate solution, adding 0.3-0.5kg of sodium fluorosilicate to per cubic meter of ammonia-ammonium bicarbonate solution, and refining after performing purification and impurity removal. According to the method for producing high-purity nano-zinc oxide by ammonia method using electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues, the electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues can be leached efficiently, the high-purity nano-zinc oxide with the purity up to above 99.7% can be obtained, and the high-purity nano-zinc oxide has high practical value and economic value; all the valuable and harmful heavy metals in the electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues are leached and utilized, so that the obtained final leaching residues are converted from electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues as high hazard wastes into ordinary solid wastes, the environment is protected, and the resources are rationally utilized.
Owner:SICHUAN JUHONG TECH
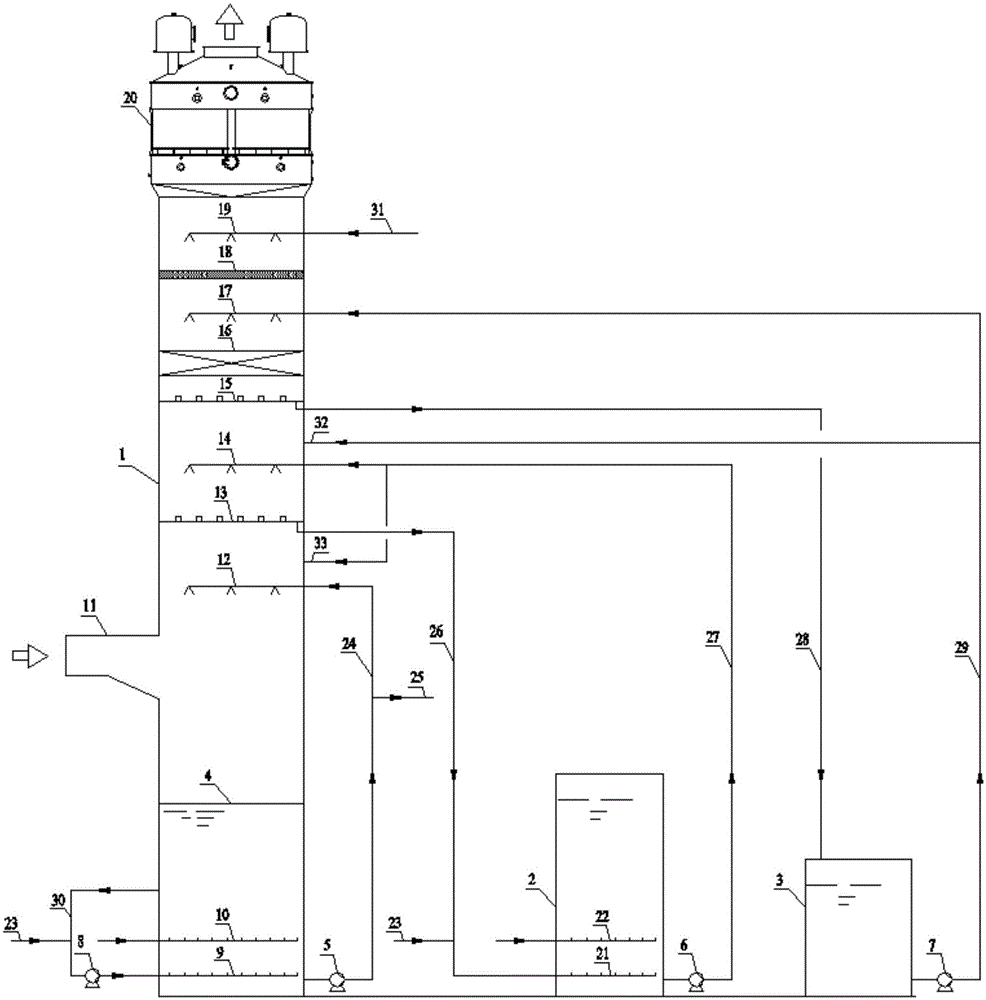
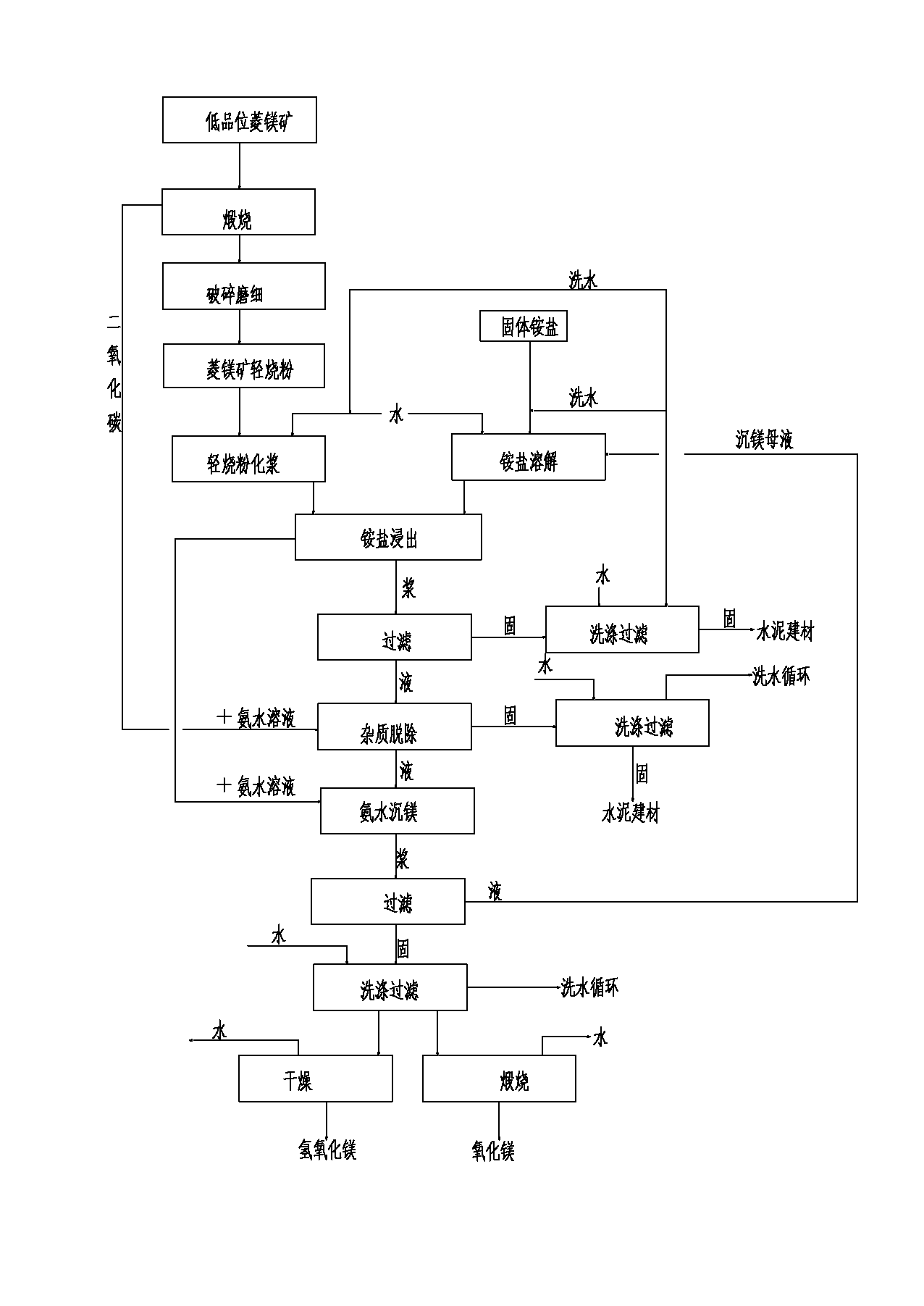
Method of producing high-purity magnesium hydroxide and magnesium oxide by low-grade magnesite
InactiveCN103011630AReduce pollutionTake advantage ofMagnesium hydroxideLime productionStrong acidsMagnesite
The invention relates to the field of mineral resource processing technology, in particular to a method of producing high-purity magnesium hydroxide and magnesium oxide by low-grade magnesite. The method comprises the following steps: calcining low-grade magnesite in a calcining furnace at calcining temperature to obtain light-calcining magnesite ore and carbon dioxide, recovering the carbon dioxide, and crushing the calcined light-calcining magnesite ore. By utilizing a method of realizing leaching, purification and separation coupling of the low-grade magnesite and producing high-pruity magnesium hydroxide and magnesium oxide through recycling of ammonia-ammonium slat, the advantages of preparing high-purity products by adopting the traditional bittern-ammonia process can be fully achieved, the method is of green and cycling clean production technique method, no wastes are emitted in the whole process, resources can be comprehensively utilized, the utilization rate of the magnesite resource can be improved, strong acid is not consumed in the technique process, other constitutions are fully utilized, the pollution to the environment can be reduced, and the method provides a new approach for reasonably developing and utilizing the low-grade magnesite resources.
Owner:新疆蓝天镁业股份有限公司
Ammonia-ammonium sulfate method dual circulation three segments desulfurizing tower
InactiveCN101053759AAvoid formingOptimum Oxidation ConcentrationDispersed particle separationEngineeringDual cycle
The invention relates to the field of wet flue gas desulfurization, especially to a flue gas thionizer of ammonia-ammiaonia sulfate method. The thionizer is divided into three segments, wherein the lower segment of the thionizer is a circulation fluid-absorbing tank, the middle segment of the thionizer is a concentration cooling segment, and the upper segment is an absorbing segment. The concentration cooling segment is separated to the absorbing segment and the circulation fluid-absorbing tank by tower-separating plate at the two end planes upper and lower. The dual cycle three-segment thionizer of ammonia-ammiaonia sulfate method of the invention resolves the design disadvantage of general single-tower and multi-tower. The byproduct that is ammiaonia sulfate is concentrated by high-temperature flue gas to reduce the temperature to a temperature propitious to absorb. The dual cycle design of the thionizer makes the cycle absorbing liquid to be not contacted directly with the high-temperature flue gas to control the cycle absorbing liquid at a low concentration, and is beneficial to the desulfurization clear flue gas to avoid the condition forming aerosol and make the solution sent to the oxidation ditch approaching to the optimal oxidation concentration. The composite cost for flue gas desulfurizing can be reduced, using the quantity of heat of the flue gas in the entrance to cycle concentrate the diluted solution of ammonia-ammiaonia.
Owner:CHINA CITY ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION ENGINEERING LIMITED COMPANY
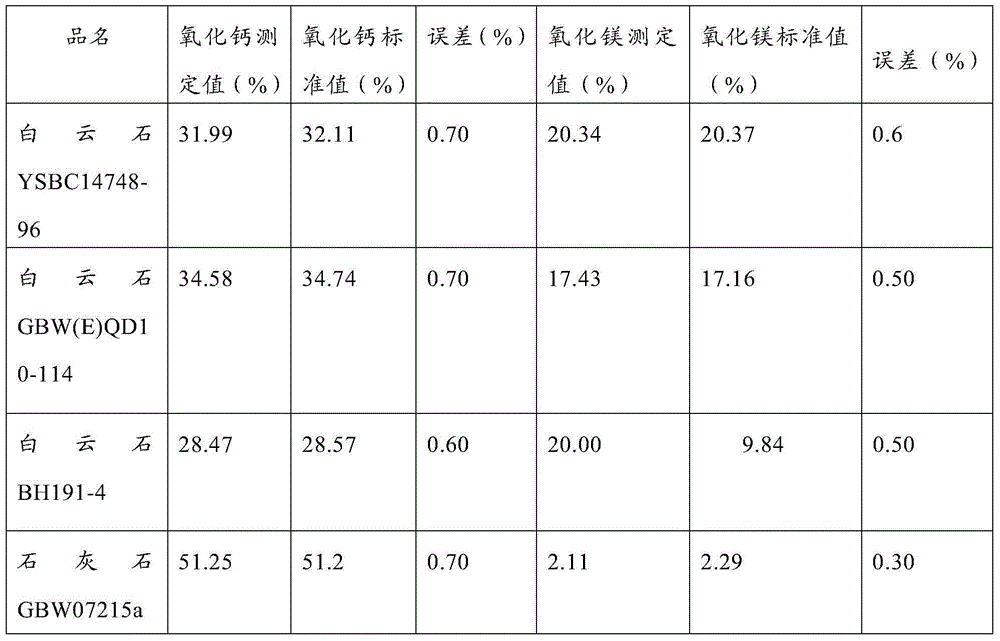
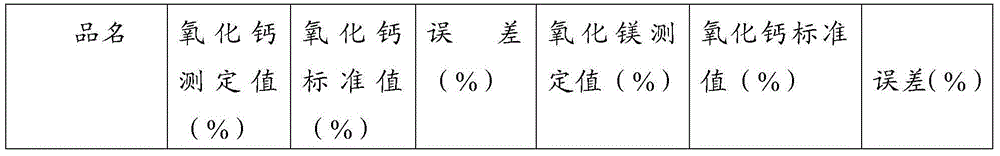
Method for continuous determination of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide content of limestone and dolomite
InactiveCN104977385ALow costReduce operating proceduresChemical analysis using titrationPotassium hydroxideHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
The invention discloses a method for continuous determination of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide content of limestone and dolomite. The method comprises adding a limestone or dolomite sample into a Teflon plastic beaker, preparing a blank contrast without the limestone or dolomite sample, respectively adding hydrochloric acid and nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid into the beakers to dissolve the sample, adding perchloric acid into the beakers to produce smoke, adding hydrochloric acid into the breakers, carrying out salt heating dissolution, transferring the reagents into a big volumetric flask, carrying out dilution until the liquid level reaches to the scale and metered volume is obtained, dividing each solution in the sample and blank contrast into two parts with the same amount, orderly adding appropriate amounts of triethanolamine, water, hydroxylamine hydrochloride, a potassium hydroxide solution and calcein into one part in the sample and blank contrast, carrying out titration by an EDTA standard solution until the fluorescent green color disappears, recording the volume, calculating calcium oxide content, orderly adding appropriate amounts of triethanolamine, water, hydroxylamine hydrochloride, an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer solution and an eriochrome black T indicator into the other part in the sample and blank contrast, carrying out titration by an EDTA standard solution until the prunosus color is changed into a blue color, recording the volume and calculating magnesium oxide content.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of nickel and cobalt by ammoniacal leaching
InactiveUS6524367B1Reduce formationMetal lossSolvent extractionProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgySolvent
The present is a hydrometallurgical procedure for nickel and cobalt recovery, which involves leaching with ammonia-ammonium carbonate solution of the nickel and cobalt bearing mineral material, using a tubular reactors aid mineral material is previously submitted to processes such as selective reduction, cooling, new ammonia leaching, liquid / solid separation and / or nickel and / or cobalt extraction by solvent or ion-exchange resin, allowing the recovery of all the extractable nickel and up to the 130% cobalt extraction reported by the standard ammonia-ammonium leaching.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACIONES PARA LA INDA MINERO METALURGICA CIPIMM
Self catalyzed reduction ammonia soaking process of deep sea polymetallic nodule in ammonia-ammonium chloride system
InactiveCN101020962AAutocatalytic reductionReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgySeawater
The present invention is self catalyzed reduction ammonia soaking process of deep sea polymetallic nodule in ammonia-ammonium chloride system, and relates to method of optionally leaching out Ni, Cu, Co, Mo and other valuable metals from polymetallic nodule. The soaking process includes the following steps: leaching out ground polymetallic nodule in ammonia-ammonium chloride solution containing NH3 in 60-180 g / l, Cl- in 10-60 g / l and Cu+ over 4 g / l; concentrating and separating the leached out ore pulp; returning the supernatant to the leaching process and filtering and washing the underflow; oxidizing the leached liquid with air to eliminate impurity and returning the precipitate to the leaching process; and conventional extraction-electric depositing to recover Ni, Cu, Co, Mo and Zn from the oxidized leached solution. The process has simple leaching system, high metal leaching rate, low power consumption and other advantages.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
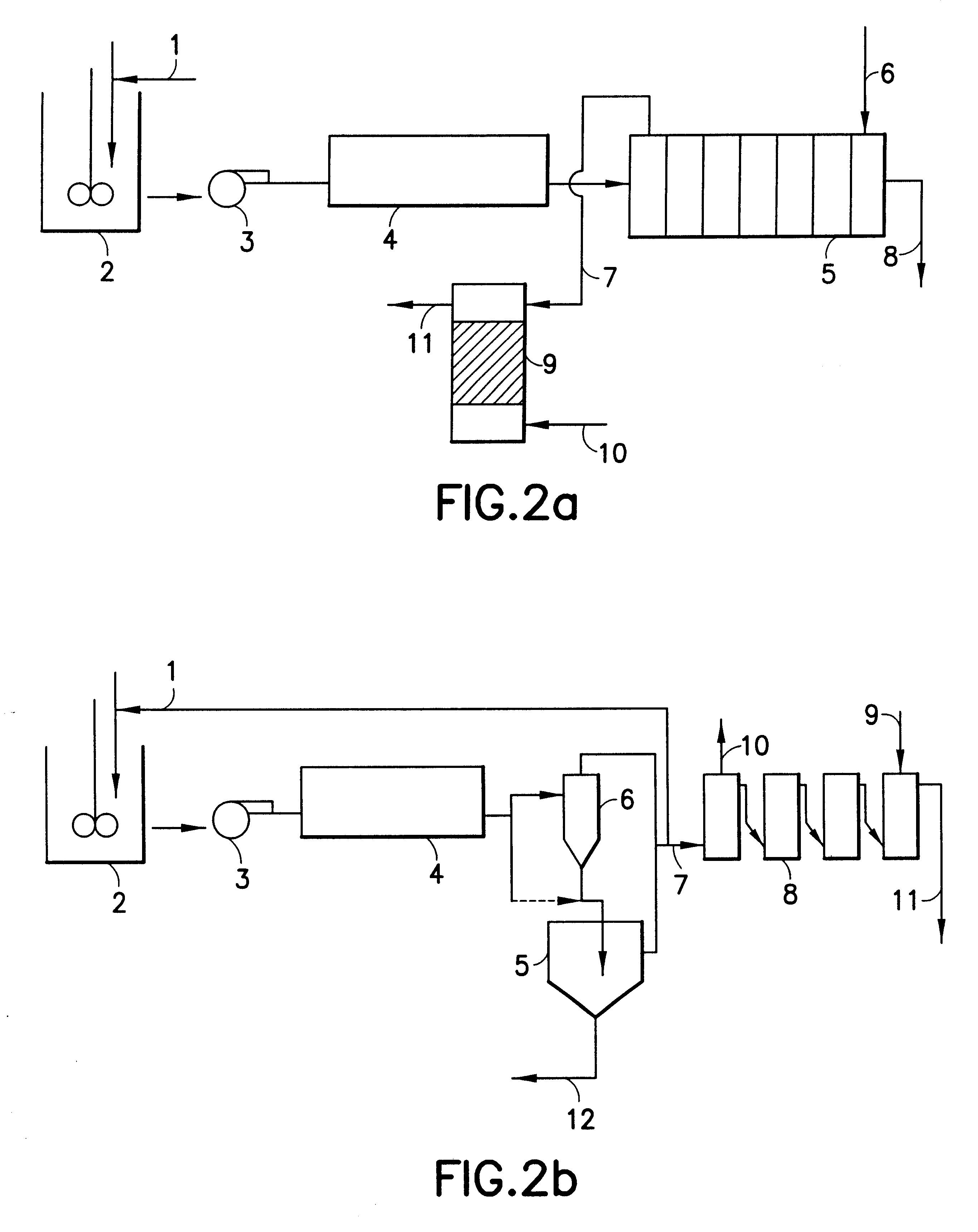
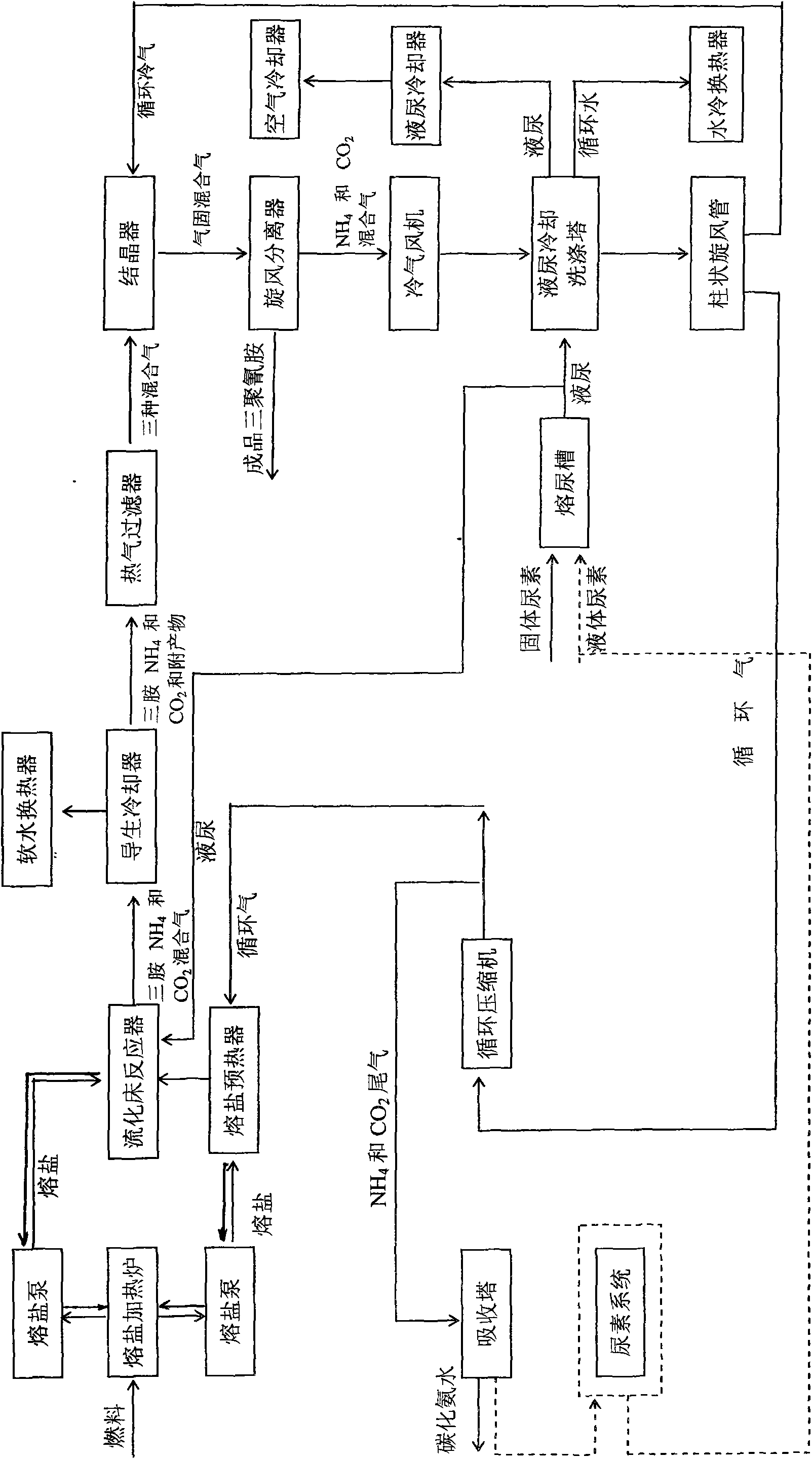
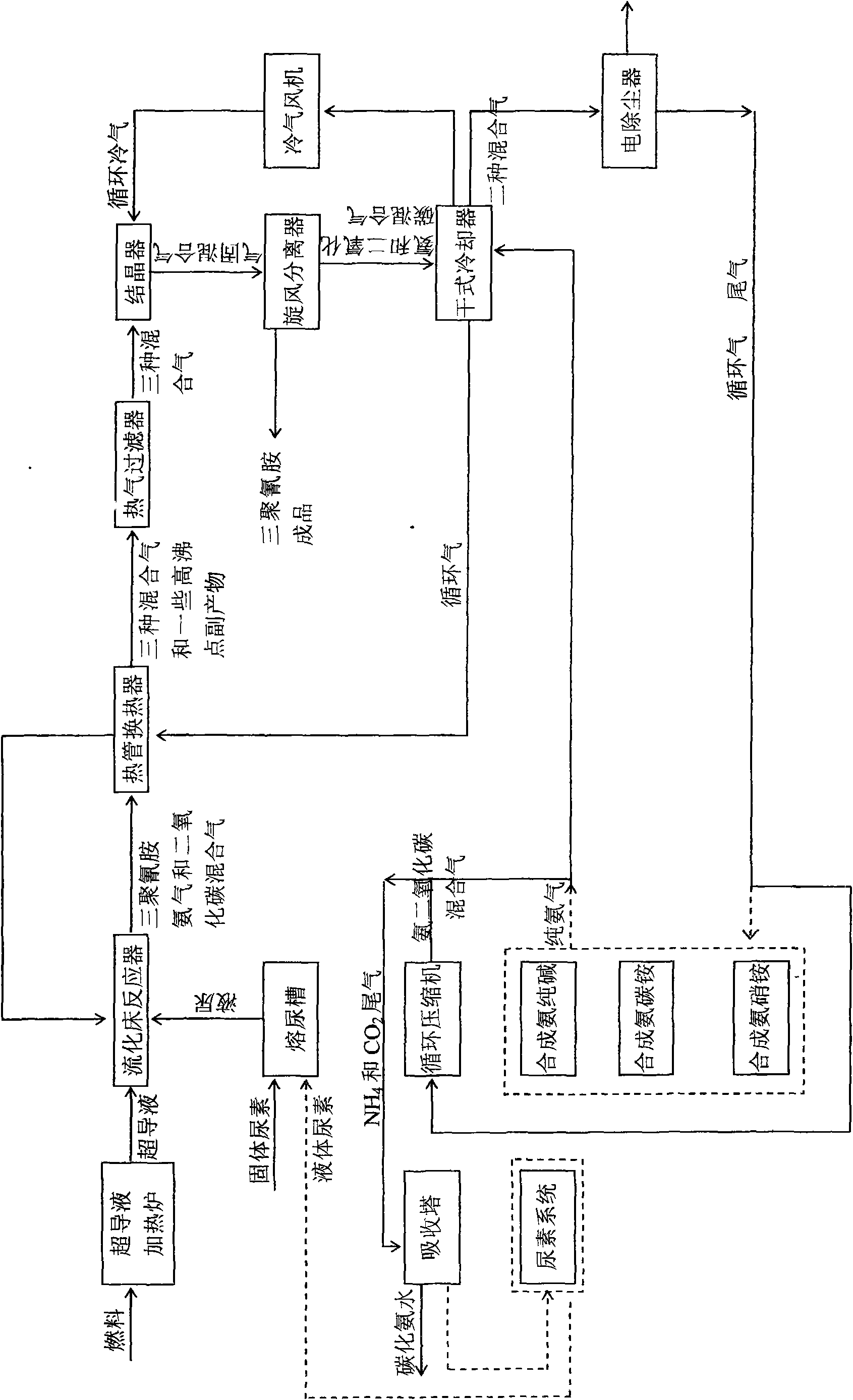
Energy-saving technology for producing melamine by one-step method
InactiveCN101671311AReduce consumptionSave investment costsOrganic chemistryChemical industryFluidized bedHeating furnace
The invention discloses an energy-saving technology for producing melamine by a one-step method, mainly comprising the following steps: supplying heat to a fluidized bed reactor by a superconducting liquid heating furnace or a heat pipe heating furnace; cooling produced gas-state melamine and a high-temperature mixed gas of ammonia and carbon dioxide by a heat pipe exchanger; and then filtering, crystallizing and separating to obtain a finished product solid melamine, wherein the rest mixed gas of the ammonia and the carbon dioxide can be circularly used for supplying a working gas for a system after being purified and can also enter a synthesis ammonia soda ash device or a synthesis ammonia ammonium carbonate device or a synthesis ammonia nitramine device to be used for supplying a raw material for the system. Compared with the traditional one-step method, the energy-saving technology can reduce the fuel consumption by 40 percent and the electric power consumption by 30 percent.
Owner:徐建华
Method for producing high-purity nano-zinc oxide by ammonia decarburization of electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues
ActiveCN102838158AExcellent liquidityExcellent dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyZinc oxides/hydroxidesSocial benefitsElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method for producing high-purity nano-zinc oxide by ammonia decarburization of electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues, wherein when leaching, 0.3-0.5kg of sodium fluorosilicate is added to per cubic meter of ammonia-ammonium bicarbonate solution, and then 30-60kg of slaked lime is added to per cubic meter of a leaching agent for performing decarburization and refining treatment; the method can obtain nano-zinc oxide powder with the purity greater than and equal to 99.7%, uniform particle size distribution (wherein the average particle size is 10-30nm), the specific surface area greater than and equal to 105m<2> / g, and excellent fluidity and dispersibility; the treatment method provided by the invention has the characteristics of low energy consumption, high efficiency, and higher economic and social values; all the valuable and harmful heavy metals in the electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues are leached to be rationally used and cleaned with water; and finally, the obtained final leaching residues are turned from the electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues as high-risk wastes into general solid wastes, thereby creating good economic and social benefits.
Owner:SICHUAN JUHONG TECH
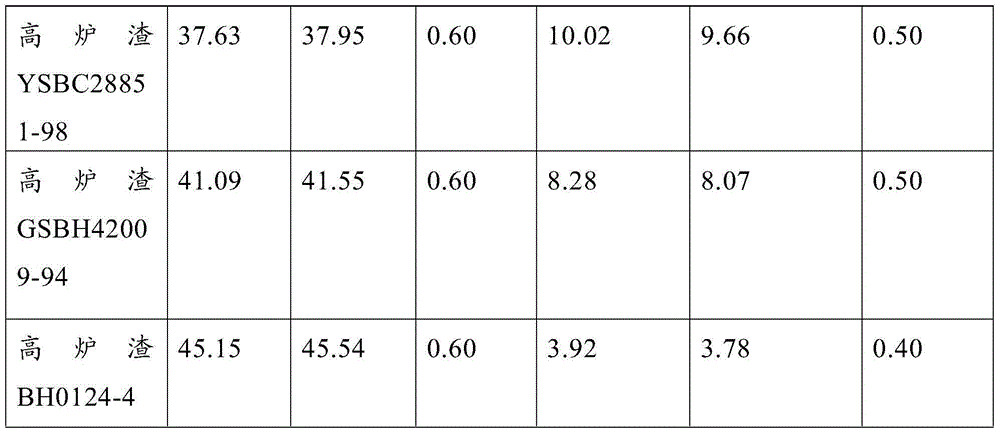
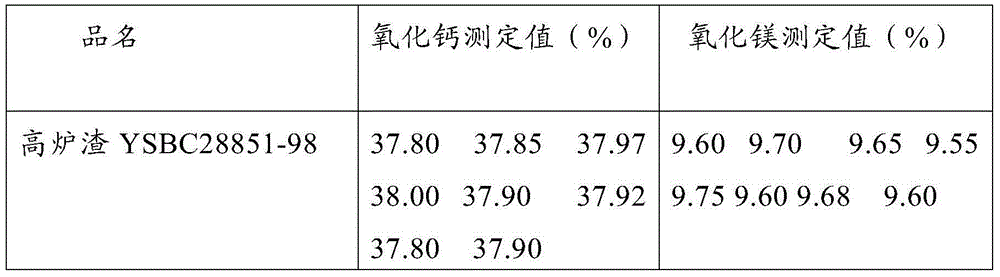
Continuous determination method for content of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide in blast furnace slag
InactiveCN104792784ALow costReduce operating proceduresMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSlagPotassium hydroxide
The invention discloses a continuous determination method for content of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide in blast furnace slag. The continuous determination method comprises the following steps: putting a blast furnace slag test sample into a polyethylene plastic beaker, and taking the other beaker without the test sample as a blank control; then adding hydrochloric acid and nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid respectively to dissolve; adding perchloric acid to form smoke, and adding hydrochloric acid to heat dissolved salts; transferring testing solutions into a high-capacity bottle respectively and diluting to a scale to make the volume constant; taking two parts of the solutions with the same quantity from each solution; sequentially adding triethanolamine, water and hydroxylamine hydrochloride into one part of the test sample and the blank control; adding a potassium hydroxide solution, and adding several drops of magnesium sulfate and a suitable amount of calcein; titrating with an EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) standard solution until fluorescent green disappears and stopping titrating, and recording the volume to calculate the content of calcium oxide; sequentially adding triethanolamine, the water and hydroxylamine hydrochloride into the other part of the test sample and the blank control; adding an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffering solution, and adding a suitable amount of a chrome black T indication agent; and titrating with an EDTA standard solution until purple red becomes blue and stopping titrating, and recording the volume to calculate the content of magnesium oxide.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
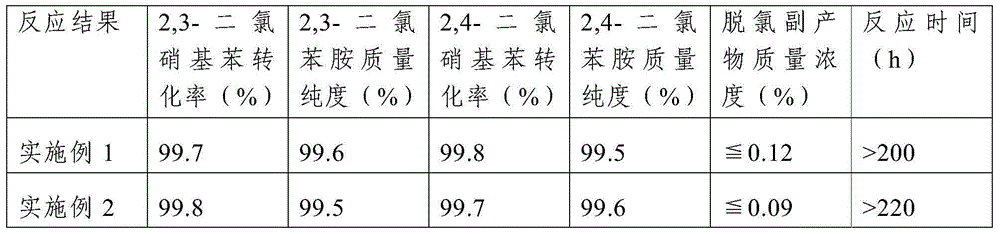
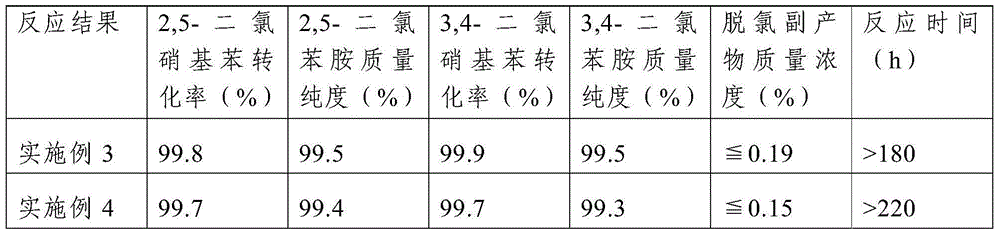
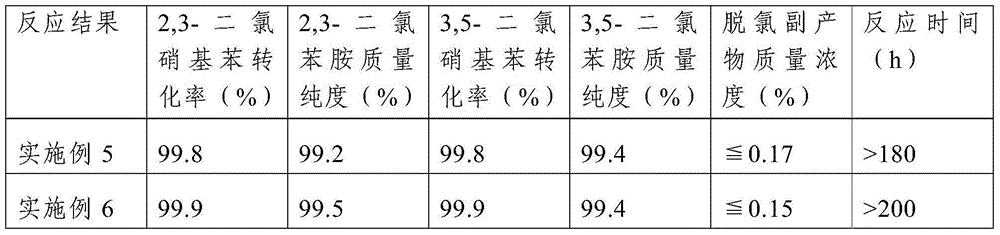
Method for preparing dichloroaniline by continuously catalyzing and hydrogenating dichloronitrobenzene
ActiveCN104672094AImprove performanceHigh catalytic hydrogenation reaction efficiencyOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationFixed bedReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing dichloroaniline by continuously catalyzing and hydrogenating dichloronitrobenzene. The method comprises the following steps: I, filling a fixed bed reactor with catalyst, and introducing reduction gas into the fixed bed reactor to reduce the catalyst; II, lowering the temperature of the fixed bed reactor to a reaction temperature, pumping an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer solution, introducing the molten dichloronitrobenzene, and carrying out the catalytic hydrogenation reaction under the condition of the reaction temperature; and III, separating the material after the catalytic hydrogenation reaction by virtue of an oil-water separator to obtain an organic phase and a water phase, wherein the organic phase is the dichloroaniline. The conversion rate of the raw material dichloronitrobenzene is more than or equal to 99.5 percent, the mass concentration of a dechlorination byproduct is less than 0.2 percent, the mass purity of the dichloroaniline is more than or equal to 99.2 percent, the stability of the catalyst is stable, the catalytic hydrogenation reaction efficiency is high, and the process flow is capable of saving the resource and is environmentally friendly.
Owner:XIAN CATALYST NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
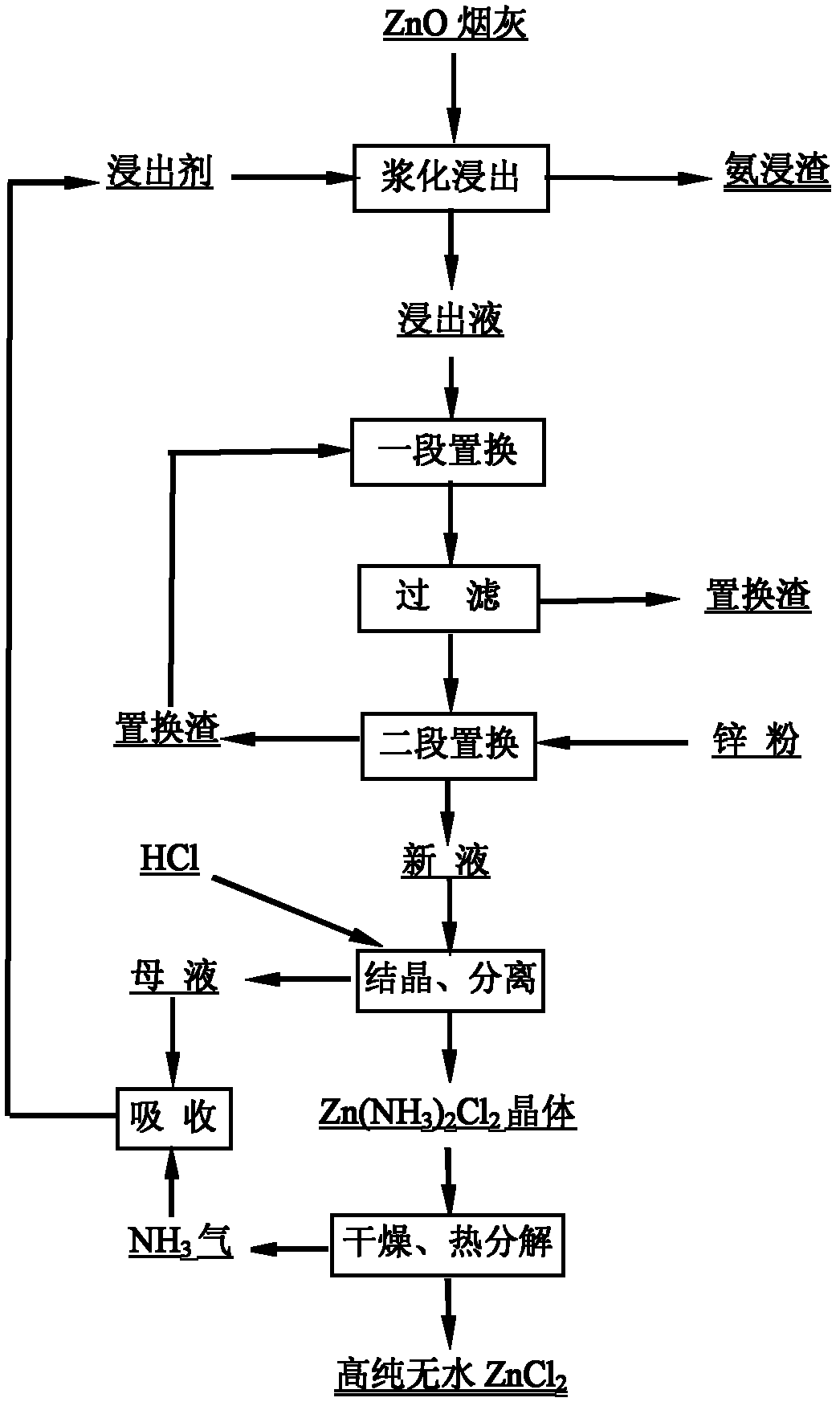
Method for producing high-purity anhydrous zinc chloride
InactiveCN102212700APrevent evaporationReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementRefluxChloride
The invention discloses a method for producing high-purity anhydrous zinc chloride. The method comprises the following steps of: leaching zinc from a zinc oxide-containing material at normal temperature by adopting ammonia-ammonium chloride solution, and removing impurities from the leachate by adopting two-section reflux zinc powder displacement; neutralizing NH3 in the obtained Zn (II)-NH3-NH4Cl solution by using HCl to settle Zn(NH3)2Cl2; and calcining the dried Zn(NH3)2Cl2 at the temperature of between 300 and 550 DEG C to obtain a high-purity anhydrous ZnCl2 product, wherein the NH3 enters the tail gas, and the settled mother solution containing Zn<2+>, NH4Cl and NH3 is used for absorbing the NH3 tail gas generated in the calcining process and returned to next leaching after being prepared. The method is energy-saving, environment-friendly, simple and convenient in operation and good in purifying effect; the product has high purity and high yield; and the method is suitable for industrialized promotion.
Owner:新干县金山化工厂 +1
Method for producing high purity nanometer zinc oxide by using steel plant dust
ActiveCN102826586AGrowth inhibitionAddressing Zinc Loading IssuesZinc oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyZno nanoparticlesSteaming
The invention discloses a method for producing high purity nanometer zinc oxide by using steel plant dust. The method for producing high purity nanometer zinc oxide by using steel plant dust comprises the following steps of: carrying out leaching with an ammonia-ammonium carbonate solution as the leaching agent, adding 0.3-0.5kg of sodium fluosilicate into the leaching agent per cubic meter, sequentially carrying out ammonia pre-steaming and purification and impurity removal, and finally carrying out refining treatment after purification and impurity removal. According to the method, the ammonia process is used for treating steel plant dust, the existing ammonia process is adaptively improved so that zinc in the steel plant dust can be fully recovered, and nanometer zinc oxide with the purity of more than 99.7 percent and the grain diameter of 10-60nm can be obtained by using the method; the method has the advantages of low energy consumption and high efficiency, and thoroughly solves the problem of zinc load of steel plant dust as the leaching agent can be recycled, thereby meeting the requirement of purifying the toxic components including zinc and alkali metals and realizing good production circulation as well as recovering valuable iron and carbon resources of steel plants.
Owner:SICHUAN JUHONG TECH
Method for producing high-purity nanometer zinc oxide by using ammonia process decarburization of steel plant dust
The invention discloses a method for producing high-purity nanometer zinc oxide by using ammonia process decarburization of steel plant dust. The method for producing high-purity nanometer zinc oxide by using ammonia process decarburization of steel plant dust comprises the following steps of: carrying out leaching with an ammonia-ammonium carbonate solution as the leaching agent, adding 0.3-0.5kg of sodium fluosilicate into the leaching agent per cubic meter to obtain a leaching solution, then adding 50-60kg white lime into the leaching solution per cubic meter to carry out heating decarburization, and carrying out purification and impurity removal and then refining treatment. According to the method, the ammonia process is used for treating steel plant dust, and the existing ammonia process is adaptively improved, the leaching speed and the leaching rate of zinc in the dust are improved, and zinc oxide with the purity of more than 99.7 percent can be obtained; the method has the advantages of low energy consumption and high efficiency, and thoroughly solves the problem of zinc load of steel plant dust as the leaching agent can be recycled, thereby meeting the requirement of purifying the toxic components including zinc and alkali metals and realizing good production circulation.
Owner:SICHUAN JUHONG TECH
Ammonia-ammonium sulphate wet-method flue-gas desulfurization and ammonium sulphate recovery technique using induced crystallization
InactiveCN101422688AReduce dosageFast crystallizationDispersed particle separationSulfateEvaporation
The invention discloses a technology of desulfurizing an ammonia-ammonium sulfate wet flue gas and inducing crystallization to recover the ammonium sulfate. The technology comprises the following steps: ammonium sulfate solution is used as an absorbent to contact with the flue gas; sulfate dioxide in the flue gas is dissolved and absorbed; the absorbent absorbing the sulfate dioxide reacts with ammonia to generate ammonium sulfite; after the ammonium sulfate is generated by oxygenization, crystallization is induced; ammonium sulfate crystals are recovered; and the ammonia is not used for desulfurizating the absorbent, which enhances the using efficiency of the ammonia and reduces the escaping of the ammonia. In addition, in the process of the crystallization of the ammonium sulfate, the method for inducing crystallization is used for reducing the evaporation using amount in the traditional technology and accelerating the crystallization speed, which not only saves the operation cost and reduces the energy consumption, but also enhances the stability and reliability of the system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
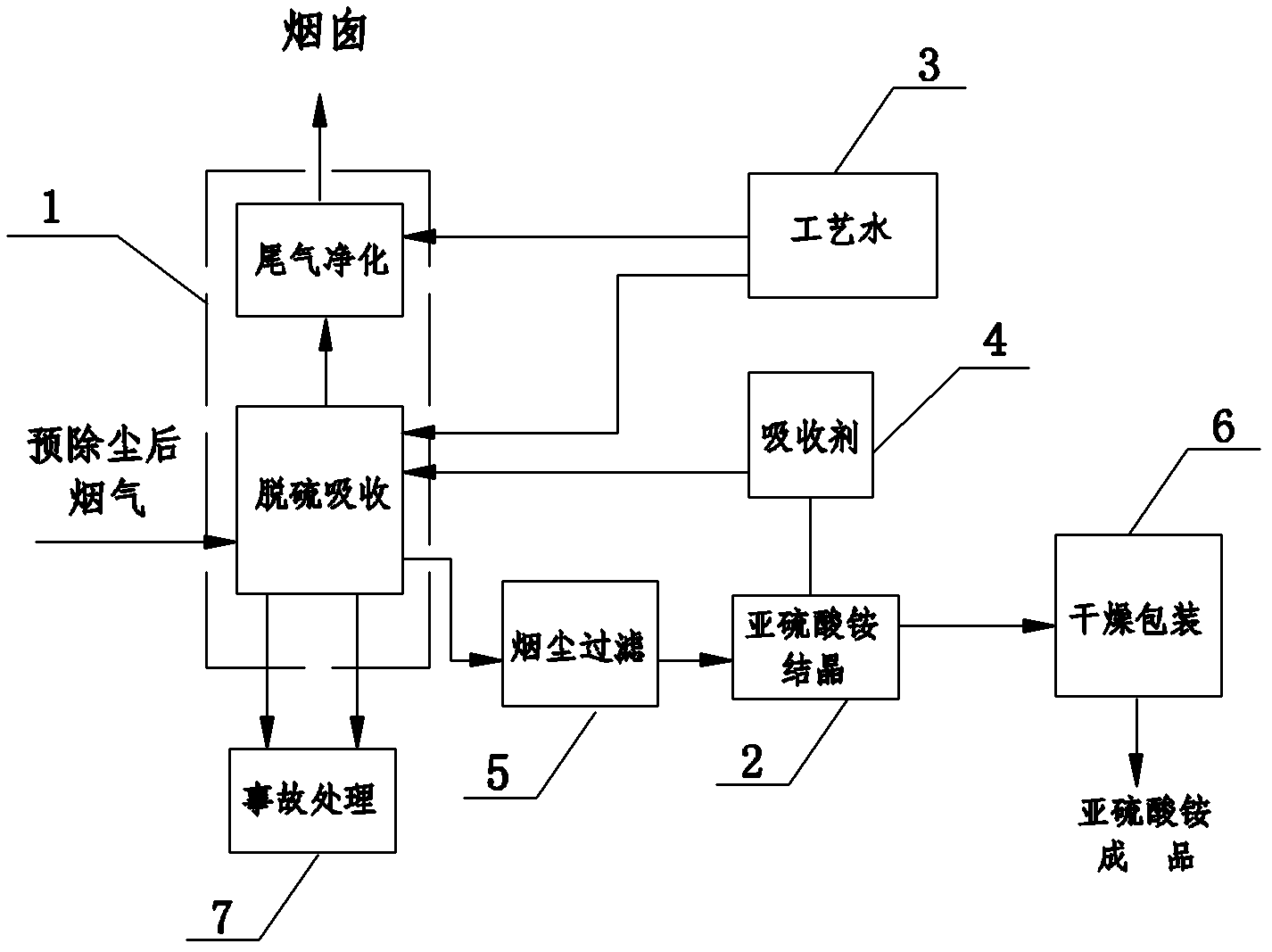
Flue gas desulfurizing device adopting ammonia-ammonium sulfite method
InactiveCN103028317AEfficient removalQuality improvementDispersed particle separationAmmonium sulfitesHandling systemPollution
The invention belongs to the technical field of flue gas desulfurization, and particularly relates to a flue gas desulfurizing device adopting an ammonia-ammonium sulfite method for recycling sulfur resources. The flue gas desulfurizing device comprises a desulfurization absorption system, an ammonium sulfite crystallization system, a process water system, an absorbent system and an emergency treatment system of the desulfurizing device, wherein the ammonium sulfite crystallization system, the process water system and the absorbent system are connected with the desulfurization absorption system. The flue gas desulfurizing device is characterized in that the main body of the desulfurization absorption system is an absorption tower having a double-tower structure or a single-tower double-section structure; a spray device is arranged in the tower; a collision type demister and a desulfurization tail gas purifying device are arranged in sequence above the spray device; an absorption liquid storing groove is formed at the bottom of the tower; the upper section of a single tower is connected with a circulating absorption liquid storing groove arranged outside the tower through a pipeline; and the ammonium sulfite crystallization system comprises a crystallizer provided with a jacket of cooling water. Due to the adoption of the flue gas desulfurizing device, the formation of an aerosol can be suppressed effectively, and secondary pollution is prevented; and compared with the conventional evaporative crystallization, the flue gas desulfurizing device has the advantage that a neutralizing condensation and crystallization way is adopted for ammonium sulfite serving as a side product, so that the energy consumption can be lowered.
Owner:陈有根
Method for continuously determining content of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide in bentonite
InactiveCN105158405ALow costReduce operating proceduresChemical analysis using titrationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSodium BentoniteHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
The invention discloses a method for continuously determining the content of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide in bentonite. According to the method, a bentonite sample is added to a polytetrafluoroethylene plastic beaker, another beaker is not filled with the bentonite sample and serves as a blank control, then hydrochloric acid and nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid are added for dissolution respectively, perchloric acid is added for smoking, then hydrochloric acid is added to heat and dissolve salt, test solutions are transferred to large volumetric flasks respectively and diluted to a constant-volume scale, each solution is split into two parts of solutions with equal quantities; triethanolamine, water and hydroxylamine hydrochloride are added sequentially to one of the sample and the blank control, a potassium hydroxide solution and an appropriate amount of calcein are added, an EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) standard solution is adopted for titration until fluorescent green disappearance, the volume is recorded, and the content of calcium oxide is calculated; triethanolamine, water and hydroxylamine hydrochloride are added sequentially to the other one of the sample and the blank control, an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer solution and an appropriate amount of eriochrome black T indicator are added, the EDTA standard solution is adopted for titration until purple red turns into blue, the volume is recorded, and the content of magnesium oxide is calculated.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Method for producing high purity nanometer zinc oxide by using ammonia process of steel plant dust
ActiveCN102826589AEvenly distributedEfficient leachingZinc oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyBiological activationZinc
The invention discloses a method for producing high purity nanometer zinc oxide by using ammonia process of steel plant dust. According to the method, white lime of 3-5 percent of the mass of steel plant dust is added for activation before leaching, then leaching is carried out with an ammonia-ammonium carbonate solution as the leaching agent, 0.3-0.5kg of sodium fluosilicate is added into the leaching agent per cubic meter, and purification and impurity removal are carried out and then refining treatment is carried out. According to the method, the ammonia process is used for treating steel plant dust, the existing ammonia process is adaptively improved, and high purity nanometer zinc oxide with larger specific surface area can be obtained; and the method has the advantages of low energy consumption and high efficiency, and thoroughly solves the problem of zinc load of steel plant dust as the leaching agent can be recycled, thereby meeting the requirement of purifying the toxic components including zinc and alkali metals and realizing good production circulation.
Owner:SICHUAN JUHONG TECH
Method for producing high-purity zinc oxide through decarbonization on low-grade zinc oxide ore by adopting ammonia process
The invention discloses a method for producing high-purity zinc oxide through decarbonization on low-grade zinc oxide ore by adopting an ammonia process. Ammonia-ammonium bicarbonate is taken as a leaching agent, 0.3-0.5kg of sodium fluosilicate is added into per cubic meter of the leaching agent, and 30-60kg of slaked lime is added into per cubic meter of leaching liquid for heating up and decarbonising; the ammonia process is applied to treatment on the low-grade zinc oxide ore, and adaptability improvement is carried out on the existing ammonia process, thus zinc in the low-grade zinc oxide ore is fully recycled; meanwhile, lower calcination temperature is adopted preferably in the method disclosed by the invention, thus zinc oxide with large specific surface area can be obtained, purity can reach up to more than 99.7%, and higher economic value is realized; and besides, the method disclosed by the invention has low energy consumption and high efficiency, the leaching agent is recycled, final leaching slag subjected to leaching does not destroy the original mineral composition structure and still can be used for making bricks, and dual purposes of being economic and being environment-friendly can be achieved.
Owner:SICHUAN JUHONG TECH
Flue gas desulfurization device based on ammonia-ammonium sulfate method
ActiveCN105013313AOptimal chemical conditionsSimple processDispersed particle separationEngineeringAmmonium sulfate
Owner:SINOPEC NANJING ENG & CONSTR +1
Method for preparing high-efficiency zinc oxide complex by using ammonia-ammonium method
ActiveCN103663541ASmall particle sizeHigh activityZinc oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyPhysical chemistryProcess engineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-efficiency zinc oxide complex by using an ammonia-ammonium method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) leaching; (2) primary filtering; (3) impurity removal; (4) secondary filtering; (5) pyrolysis; (6) drying and calcinating. The method is characterized in that in pyrolysis of the step (5), calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide are added when ammonia still process is carried out, so that the coated basic zinc carbonate can be formed by the zinc-ammonia complex. According to the method, in the zinc oxide production process, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide are added in the pyrolysis step to replace the core of high-content zinc oxide, the content of zinc oxide can be reduced, the activity of zinc oxide can be improved, zinc oxide with a content of 60% can have a physical property of 99.7% ordinary zinc oxide, so that not only can the production cost be lowered, but also the quality of the product can be improved.
Owner:LUOYANG LANTIAN CHEM TECH
Method for measuring calcium oxide and magnesium oxide content of tundish covering agent
InactiveCN105738559AReduce consumption costReduce labor costsChemical analysis using titrationFluorescencePotassium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for measuring the calcium oxide and magnesium oxide content of a tundish covering agent. The method has the advantages of being higher in speed, accuracy and efficiency. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a test sample with hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid, adding nitric acid, adding perchloric acid for smoking, adding hydrochloric acid after cooling, and performing heating to dissolve salts; adjusting the pH value to 7 with ammonia water, heating the test solution till the test solution boils, taking down and slightly cooling the test solution, filtering the test solution in a volumetric flask, washing precipitates for 7 to 8 times with a hot ammonium chloride solution, diluting the solution to a scale for volume fixation after cooling, equally dividing the solution into two parts for putting into two beakers; for one of the two breakers, adding small amounts of triethanolamine, water and hydroxylammonium chloride, adding a potassium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH value to 12, adding a proper amount of calcein, and performing titration with an EDTA standard solution until fluorescence green disappears to obtain the amount of calcium; for the other one of the two breakers, adding small amounts of triethanolamine, water and hydroxylammonium chloride, adding an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer solution to adjust the pH value to 10, taking eriochrome black T as an indicator, and performing titration with the EDTA standard solution until the solution is pure blue to obtain the total amount of calcium and magnesium.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Measuring method for content of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide in open-hearth furnace slag, converter slag and electric furnace slag
InactiveCN105606762AReduce consumption costReduce labor costsChemical analysis using titrationSlagHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
The invention discloses a measuring method for the content of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide in open-hearth furnace slag, converter slag and electric furnace slag. The measuring method has the advantages of being rapider, more accurate and more efficient. A sample is dissolved with hydrochloric acid, nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid, perchloric acid is added for smoking, and after taking down and cooling, hydrochloric acid is added to heat and dissolve salt; the pH value of the test solution is adjusted to be 7 with ammonium hydroxide, the test solution is heated to be boiled, taken down, slightly cooled and filtered in a volumetric flask, sediment is washed 7-8 times with a hot ammonium chloride solution, after being cooled, the solution is diluted to scales for volume setting, two parts of equal solutions are taken respectively and put in two flasks, triethanolamine, water and a small amount of hydroxylamine hydrochloride are added to one part, the pH value is adjusted to be 12 after a potassium hydroxide solution is added, a proper amount of calcein is added, and titration is conducted with an EDTA standard solution till an end point that fluorescent green disappears and the amount of calcium is obtained; triethanolamine, water and a small amount of hydroxylamine hydrochloride are added to the other part, the pH value is adjusted to be 10 after an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer solution is added, eriochrome black T serves as an indicator, and titration is conducted with the EDTA standard solution till an end point of pure blue and the resultant amount of calcium and magnesium is obtained.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
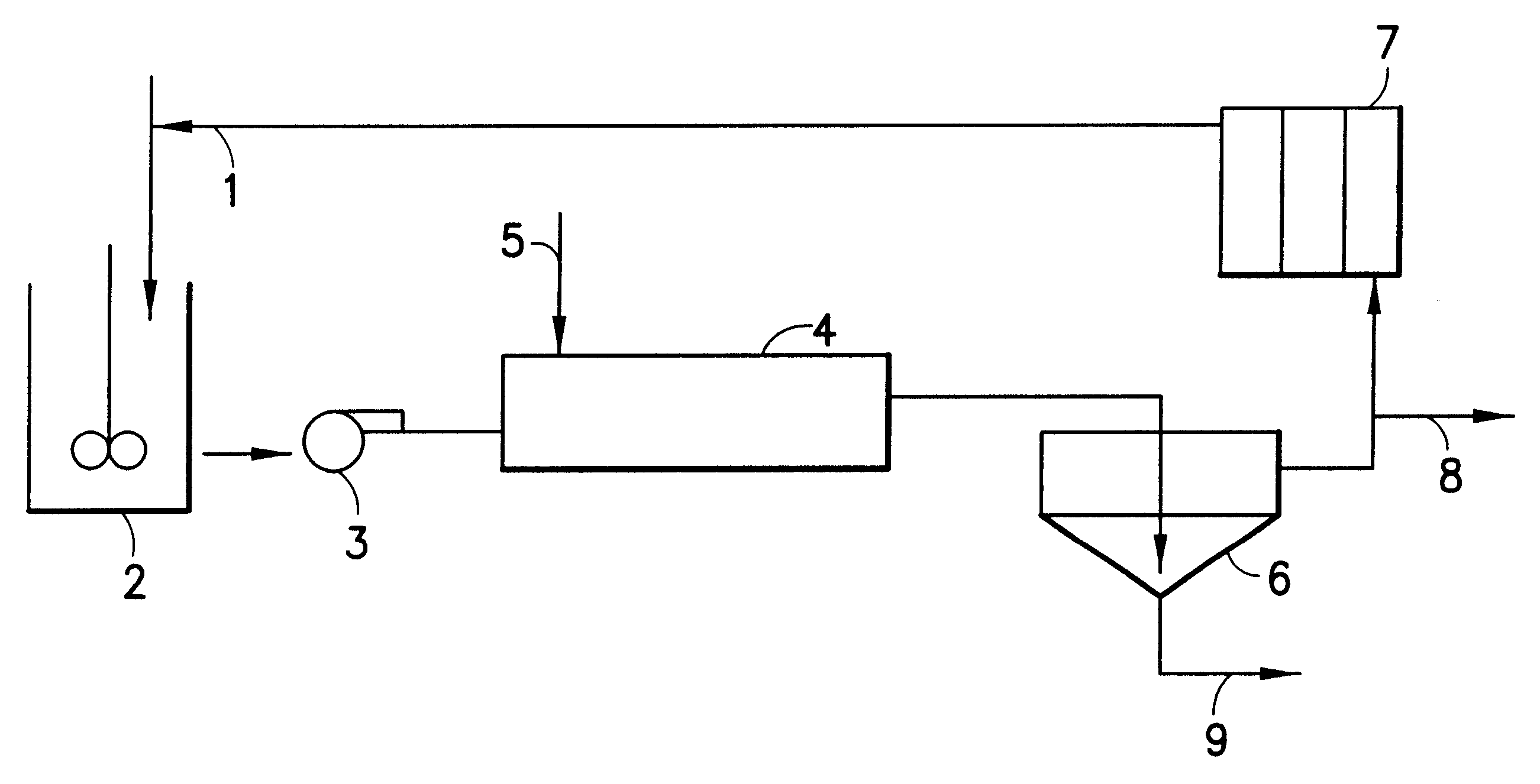
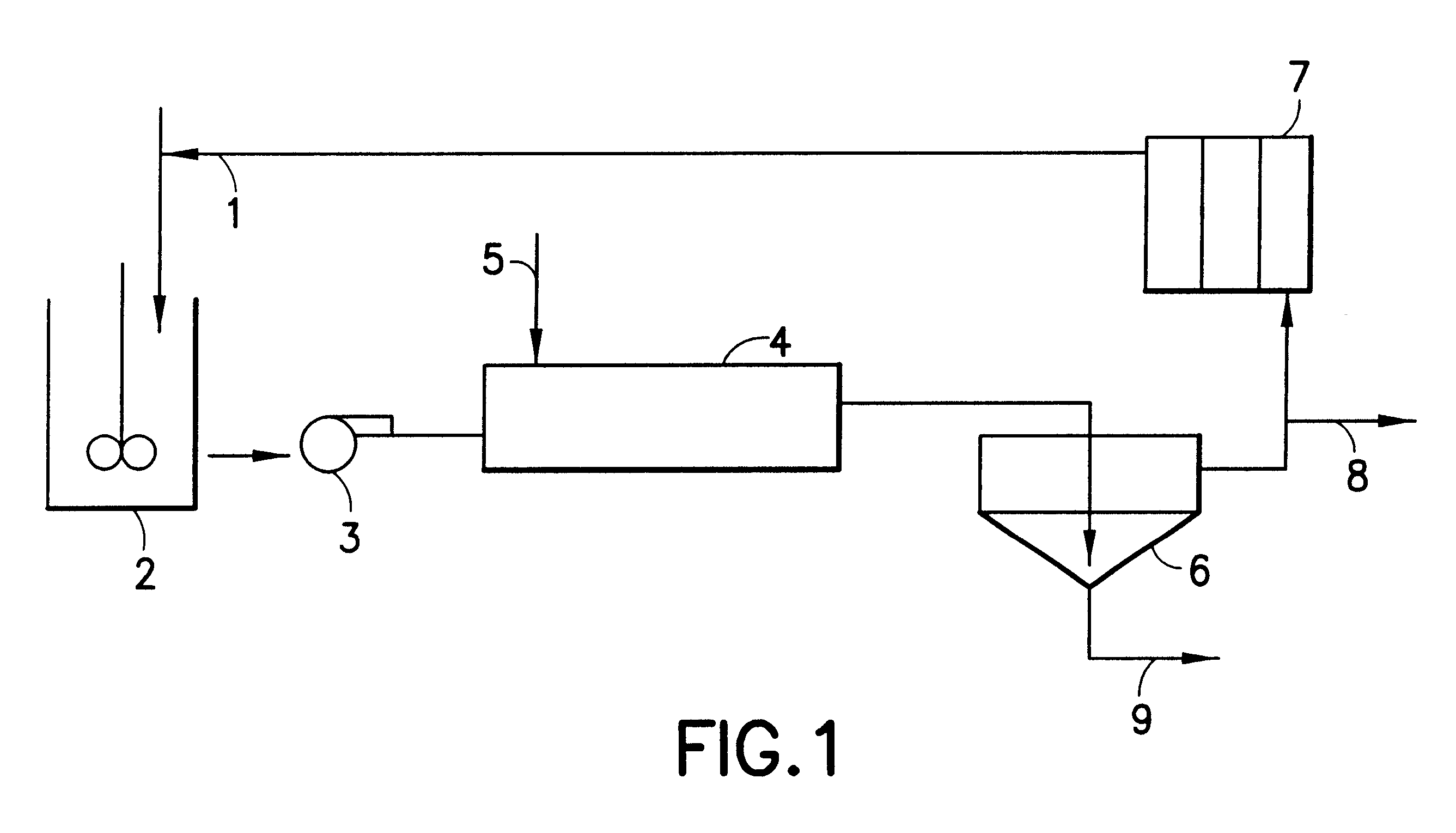
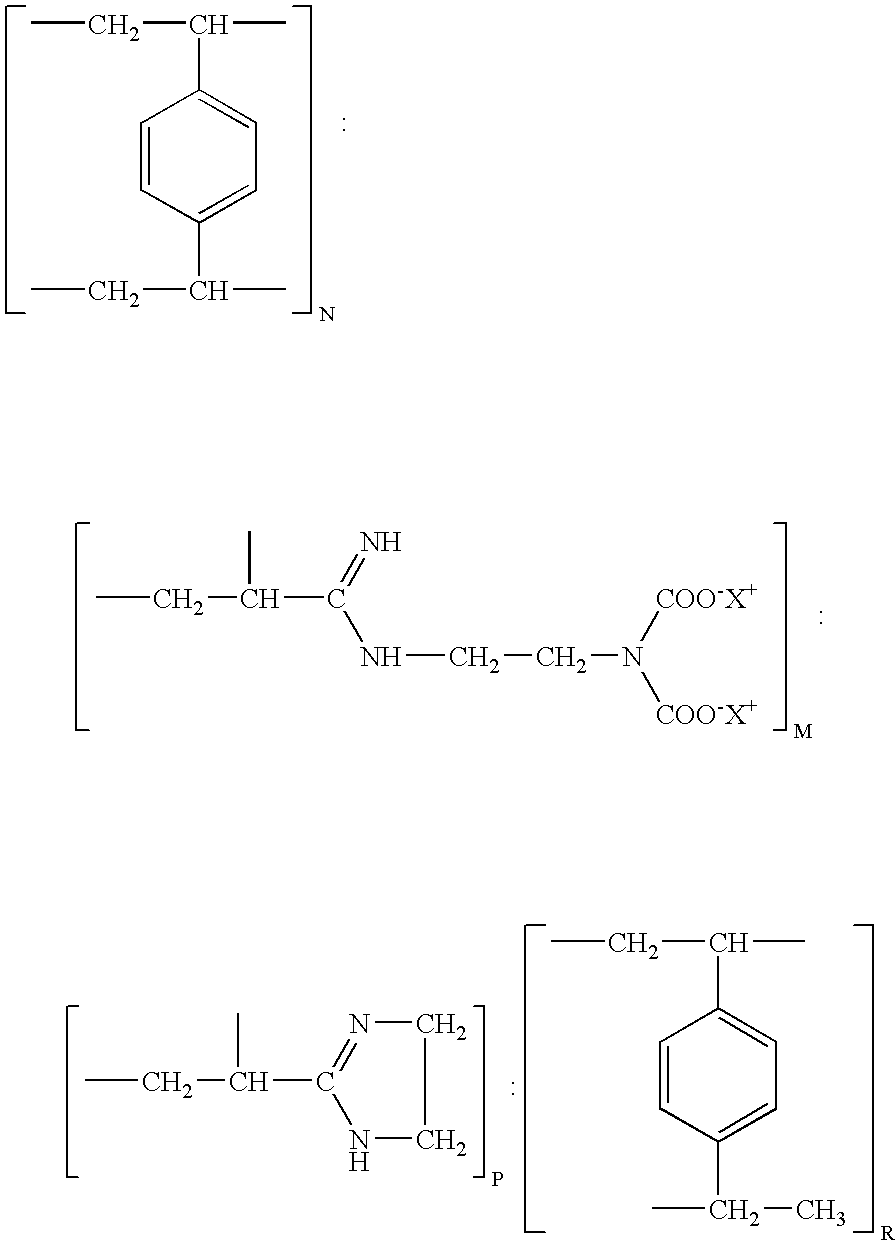
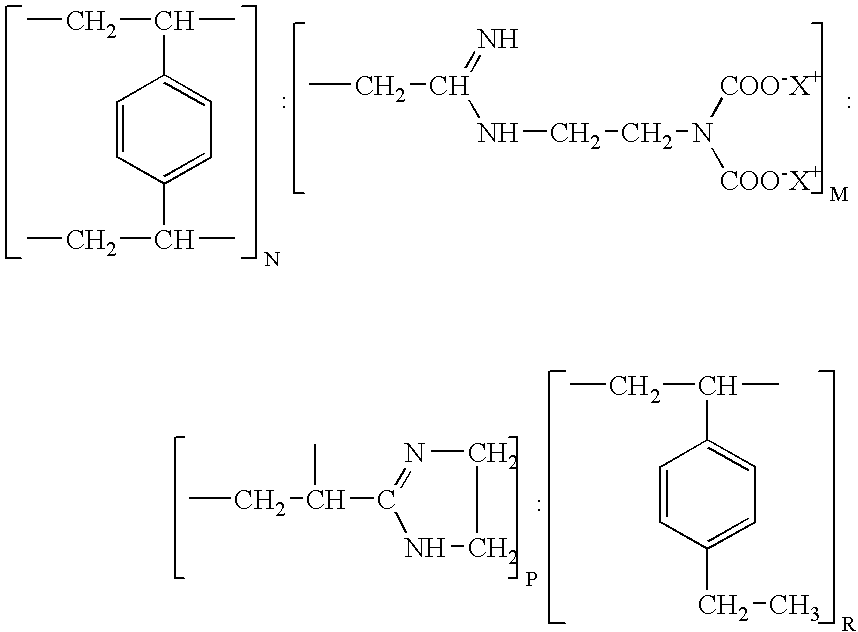
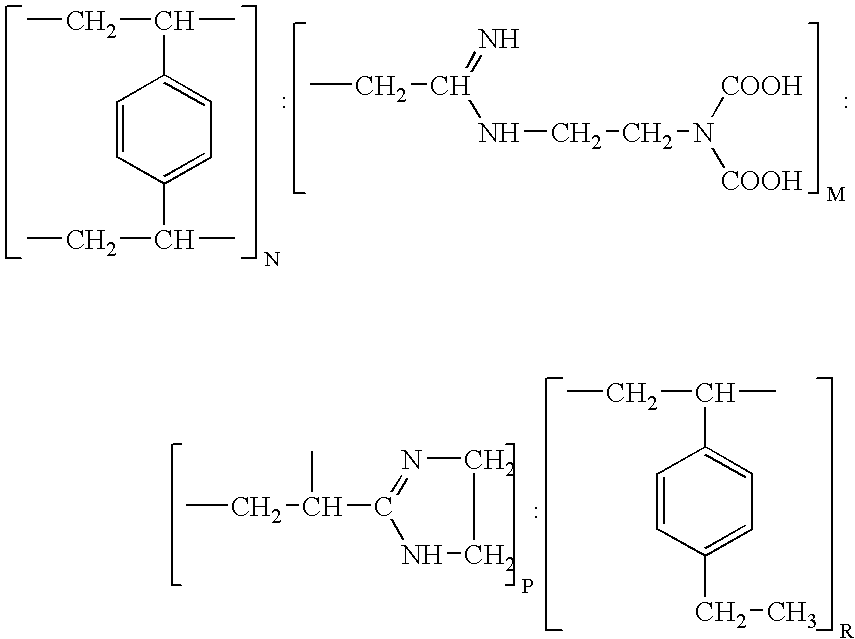
Resin and process for extracting non-ferrous metals
A process is provided for the direct recovery of non-ferrous metals (nickel, cobalt, copper etc) from raw materials such as ores, concentrates, semiproducts and / or solutions by ion exchange. A non-ferrous ore or concentrate is leached with a mineral acid to dissolve the metals. The pH of the resulting leach slurry is adjusted to 1.0-5.0 using some alkaline agents as limestone, sodium hydroxide etc. Non-ferrous metals are absorbed from this leach slurry with ion-exchange resin, which selectively loads the non-ferrous metals and has the structure: wherein the ratio of N : M : P : R is within the ranges of 3-4: 64-70:25-30:2-2.5 The loaded resin is separated from the exhausted leach slurry. The loaded sorbent is stripped with an acidic or ammonia-ammonium carbonate solution. The stripped resin is returned to the loading cycle. The non-ferrous metal can be recovered in substantially pure from the eluate by some known processes. The metal-depleted slurry proceeds to waste treatement and disposal.
Owner:CLEAN TEQ PTY LTD
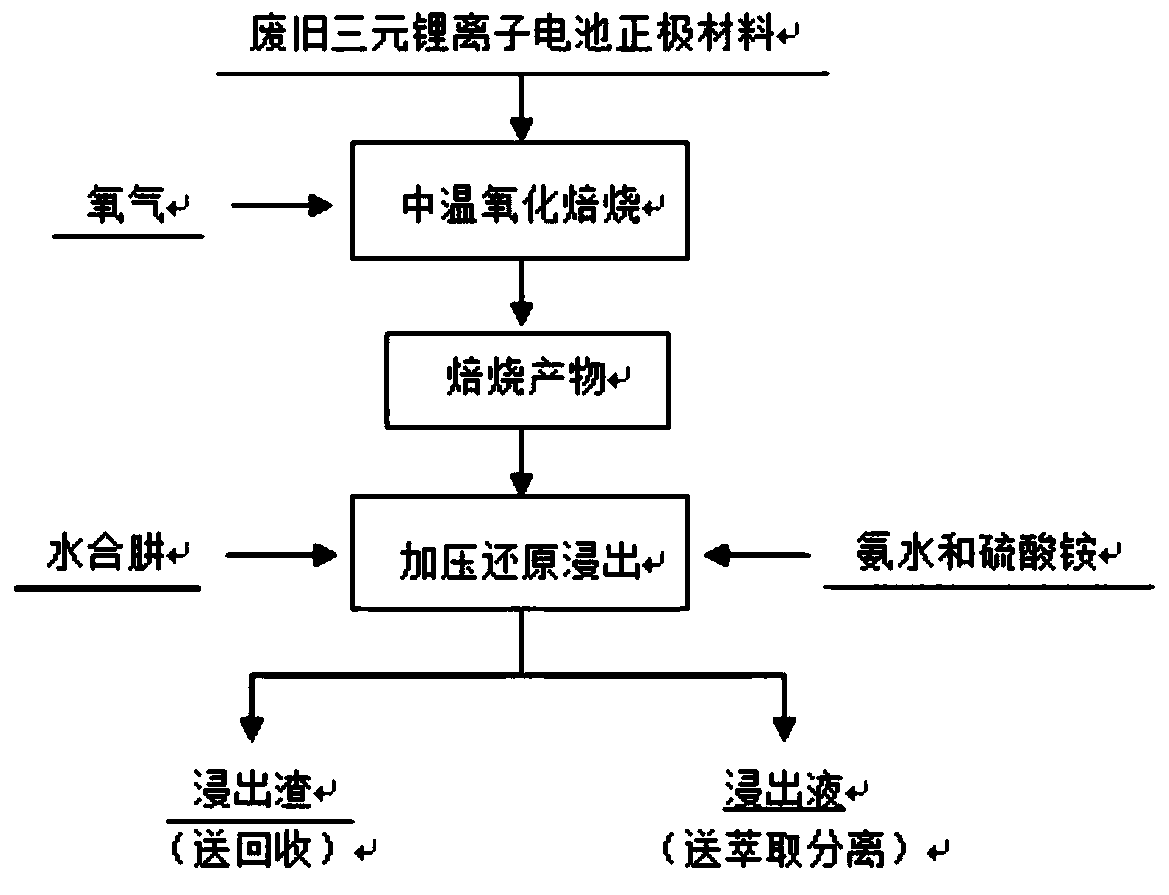
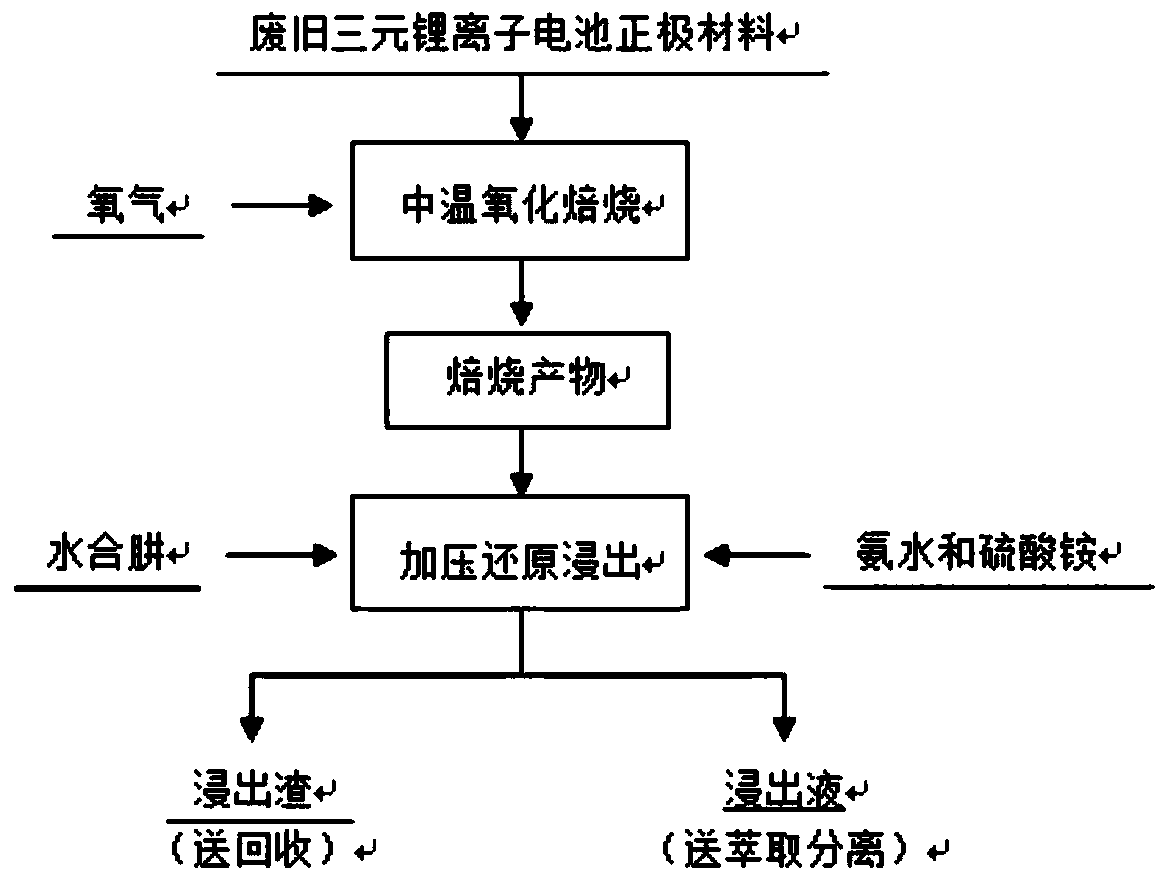
Method for recovering valuable metals in waste ternary lithium ion battery cathode material
ActiveCN110029225AHigh selectivityStrong reductionProcess efficiency improvementCelsius DegreeOxygen
The invention provides a method for recovering valuable metals in waste ternary lithium ion battery cathode material. The method comprises the following steps of putting the raw materials into a tubular furnace fed with oxygen for medium-temperature oxidation roasting, the roasting temperature controlled during medium-temperature oxidation roasting is 700 degrees celsius, and the roasting time is60 min, then a roasted product is obtained, and the content of carbon in the roasted product is reduced by more than 98%; Then, dissolving the roasted product in an ammonia-ammonium salt system with an ammonia concentration of 5mol / L, then putting into a high-pressure kettle, hydrazine hydrate is added to serve as a reducing agent, and reacting for 120min in the high-pressure kettle. According tothe method for recovering valuable metals in waste ternary lithium ion battery cathode material, the equipment used is simple, the investment operation cost is low, the popularization is easy, the process energy consumption is remarkably reduced, the valuable metal recovery rate is high, and the leaching rates of Li, Ni, Co and Mn in the battery powder reach 99.79%, 91.86%, 90.54% and 92.96% respectively.
Owner:浙江微通催化新材料有限公司
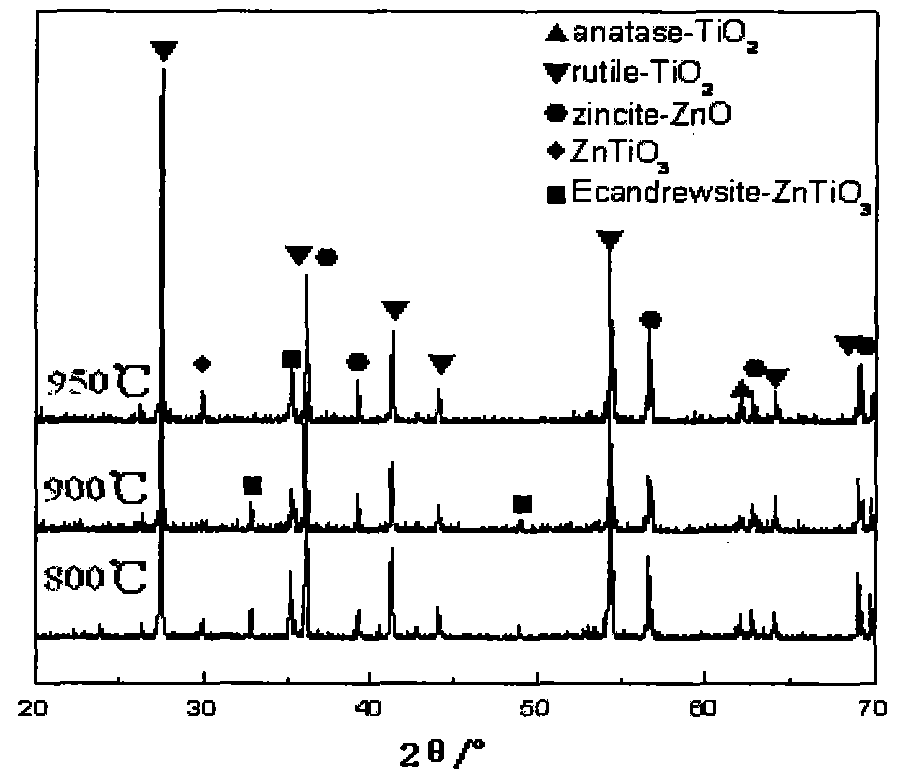
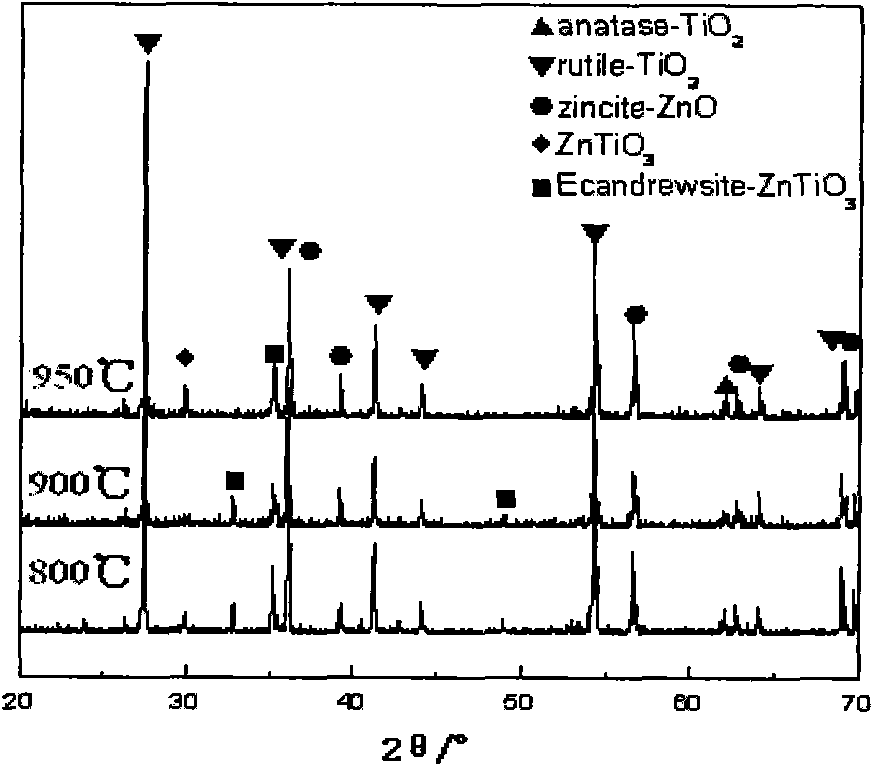
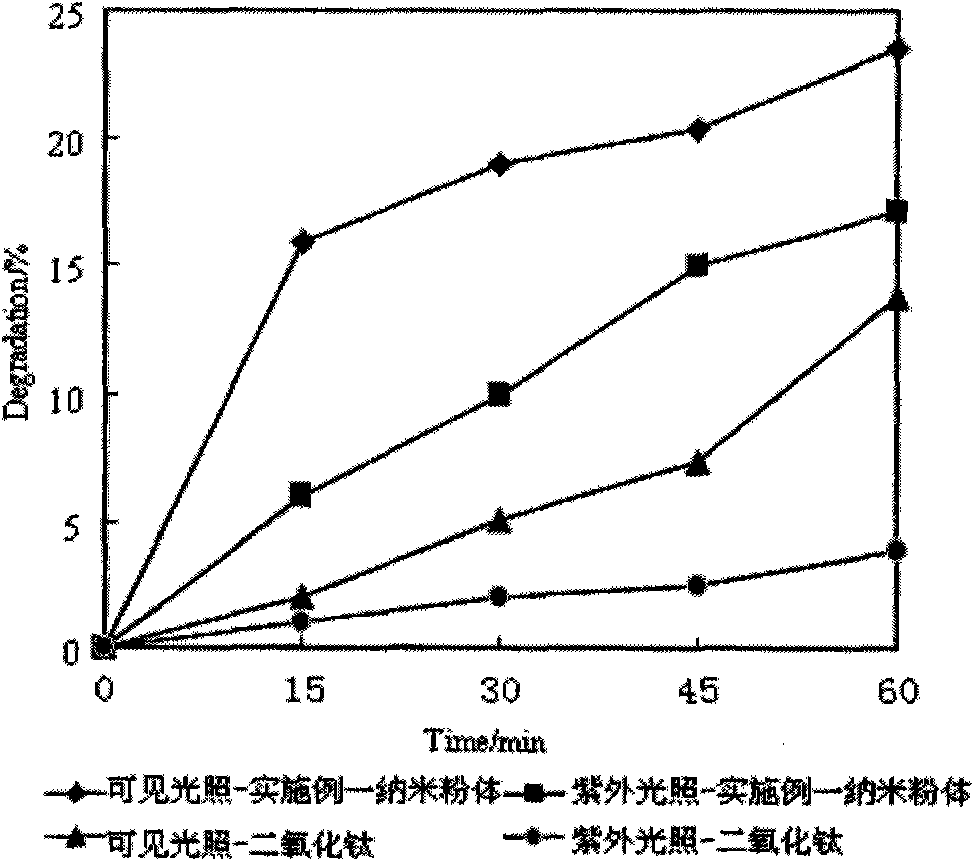
Nanometer powder of titanium oxide coated by zinc oxide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101948318AImprove photocatalytic efficiencyImprove temperature resistanceOxide coatingTitanium oxide
The invention discloses a nanometer powder of titanium oxide coated by zinc oxide and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of the functional material. The nanometer powder contains a zinc oxide coating layer and titanium oxide nanoparticles and also contains a Ti-O-Zn compound phase transition layer, wherein the titanium oxide nanoparticles contain nitrogen with the molar percentage of 0.1-50%; the molar ratio of zinc oxide in the coating layer to titanium oxide in nanoparticles is 0.05-0.3:1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using tetrabutyl titanate as titanium source and urea as nitrogen source to prepare titanium oxide nanoparticles containing nitrogen through the sol-gel method, then using soluble zinc salt as raw material and ammonia-ammonium mixed solution as precipitating agent to prepare zinc oxide through the co-precipitation method, and coating the titanium oxide nanoparticles containing nitrogen. The nanometer powder of the invention overcomes the defects of common titanium oxide nanometer powder, namely poor photocatalytic capability and heat resistance, and is a kind of compound nanometer powder which has good excellent performance and reasonable cost / performance ratio and is advanced and practical.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV
Method for testing constant cadmium and zinc in cadmium zinc telluride crystal
ActiveCN104914093ASolve the problem that titration cannot be carried outSuppress interferenceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTe elementCadmium Cation
The invention provides a method for testing constant cadmium and zinc in cadmium zinc telluride crystal. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: taking a solution obtained by dissolving a proper amount of a sample solution of the cadmium zinc telluride crystal to be tested or a proper amount of a solid sample of the cadmium zinc telluride crystal to be tested, adjusting pH value of the solution to neutral by adding ammoniacal liquor (1+1) to and adjusting pH value of the solution to 10 by adding a proper amount of an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer solution and remaining stable; adding a proper amount of a surfactant into the solution, adding a proper amount of an eriochrome black T indicator, and carrying out complexometric titration by the use of a complexing agent EDTA to turn the solution from purple to pure blue so as to obtain total amount nCd+Zn of cadmium and zinc, wherein molar concentration of the complexing agent EDTA is C1 and the use amount is V1; adding a proper amount of DDTC sodium salt to fully dissolve, selectively precipitate cadmium by DDTC sodium salt and releasing the same amount of EDTA, carrying out titration on EDTA by the use of a magnesium nitrate solution until the solution turns light red so as to obtain cadmium with the amount of nCd and mass of mCd, wherein molar concentration of the magnesium nitrate solution is C2 and use amount is V2; and obtaining zinc with amount of nZn and mass of mZn according to a difference method.
Owner:清远先导材料有限公司
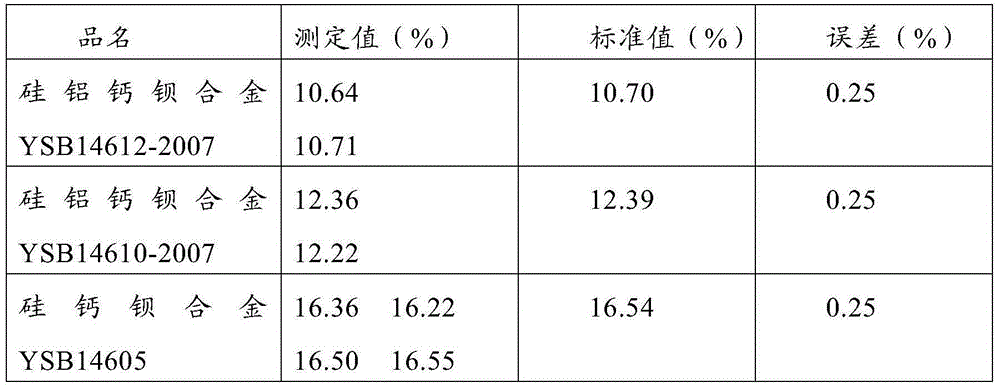
Method for continuous determination of content of Ca, Mg and Ba in Si-Ca-Ba-Mg alloy
InactiveCN105067614ALow costReduce operating proceduresMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHydroxylamine HydrochlorideVolumetric flask
The invention discloses a method for continuous determination of the content of Ca, Mg and Ba in Si-Ca-Ba-Mg alloy. The method includes the steps that a Si-Ca-Ba-Mg alloy sample is added into one beaker, no sample is added in the other breaker which serves as blank control, nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid mixed solutions are added respectively for dissolving the sample, and sulfuric acid is added till smoking happens; afterwards, hydrochloric acid is added for dissolving slats, water and hydroxylamine hydrochloride are added and heated to be boiled till the solutions are changed to be colorless from being yellow, the solutions are filtered into a large volumetric flask, sediments are washed by dilute sulphuric acid and water, and the sediments together with filter paper are placed into a porcelain crucible; ashing, firing and weighing are carried out, and accordingly the content of the Ba is obtained; two groups of quantitative solutions are selected to be put in beakers from the constant volume solution and the blank solution, one group is sequentially added with triethanolamine, water, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and a potassium hydroxide solution, several drips of magnesium sulfate are added, a proper quantity of calcein indicator is added, and EDTA is used for titration till fluorescent green disappears, and accordingly the content of the Ca is obtained; the other group is sequentially added with triethanolamine, water, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffered solution, an eriochrome black T indicator is added, EDTA is used for titration till fuchsia is turned into blue, and accordingly the content of the Mg is obtained.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Electroplating method for assembling nano-micrometre array material in metal aluminium stencil
InactiveCN101319341ASimple preparation processReduce manufacturing costAnodisationNanostructure manufactureSodium acetateNickel salt
The invention relates to an electroplating method for nano-micro array materials assembled in a metallic aluminum template, which is characterized in that: the metallic aluminum template is impregnated into an electroplate liquid, and plating is implemented under certain conditions. Before plating, the metallic aluminum template is not needed to be coated with a layer of conductive metallic film by utilization of the sputtering or evaporation method. During the plating process, the metallic aluminum template is taken as a cathode, and a metal plate to be plated, graphite carbon or metallic platinum is taken as an anode; the pH value of the electroplate liquid is between 4.0 and 12.0; the metallic ion sources can be nickel salt, cupric salt, zinc salt, noble metals and so on; the macromolecular monomers can be aniline, pyrrole, trimethyl thiophene and so on; the pH regulator can use a hydrochloric acid, a sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, ammonia and so on; the pH buffer can use systems such as a boric acid, acetic acid-sodium acetate, potassium hydrogen phosphate-potassium dihydrogen phosphate, ammonia-ammonium salt and so on; the plating temperature is a room temperature of 60 DEG C below zero; and the current density is between 10.0 and 2,000.0 amperes per square meter. After plating is over, the metallic aluminum template is washed by water to remove the residual electroplate liquid on the surface, and then 4.0 to 15.0 percent NaOH solution is used for dissolving the metallic aluminum template; metals or high polymer films obtained are washed by water to remove residual lye on the surface; and then the tubular or cylindrical small-size array materials with different slenderness ratios and different tube wall thicknesses can be obtained after drying. By adoption of the electroplating method to prepare the metallic nano-micro array materials, the technique is simple and the cost is low.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com