Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41results about How to "Smooth surface finish" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
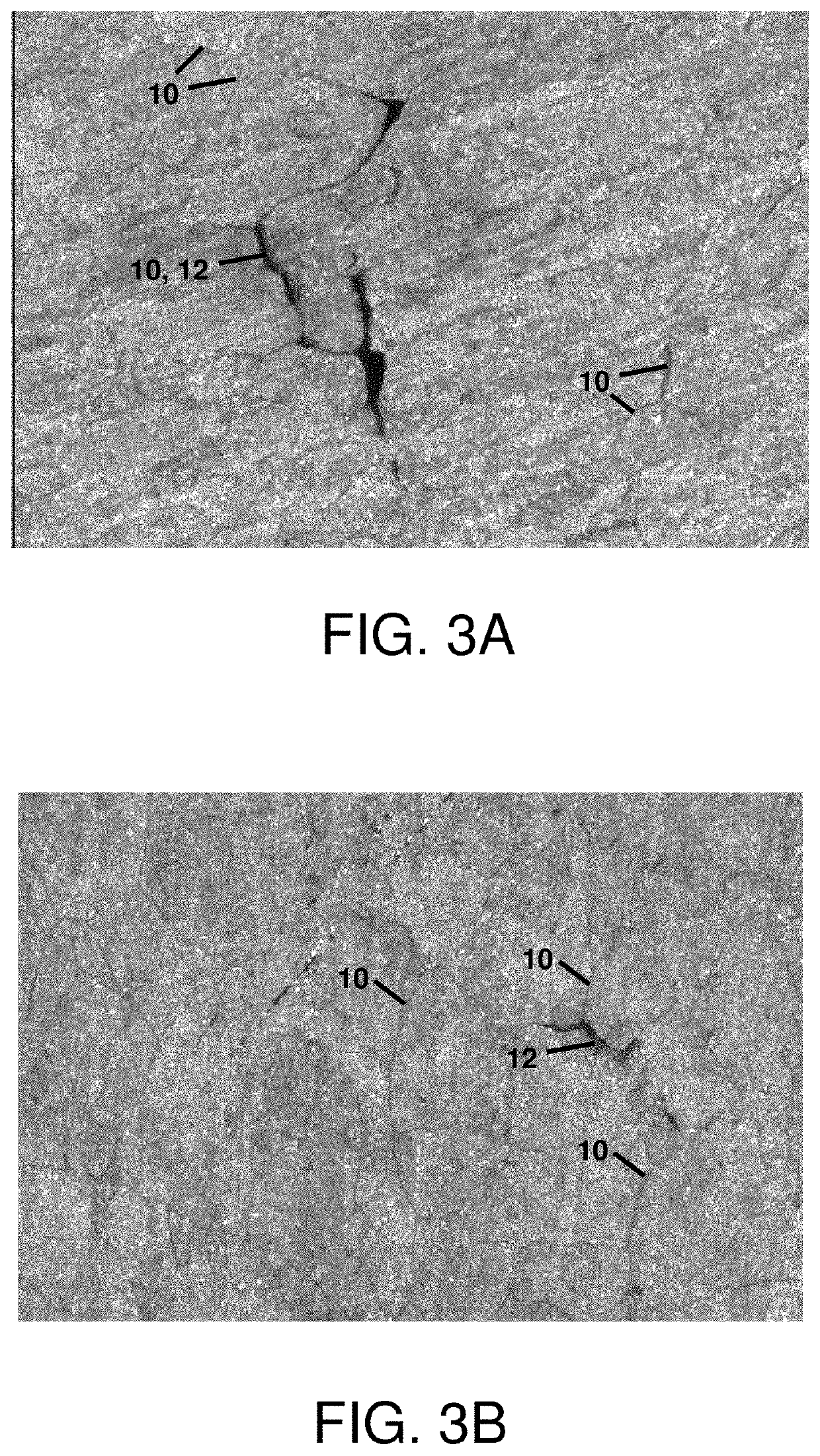
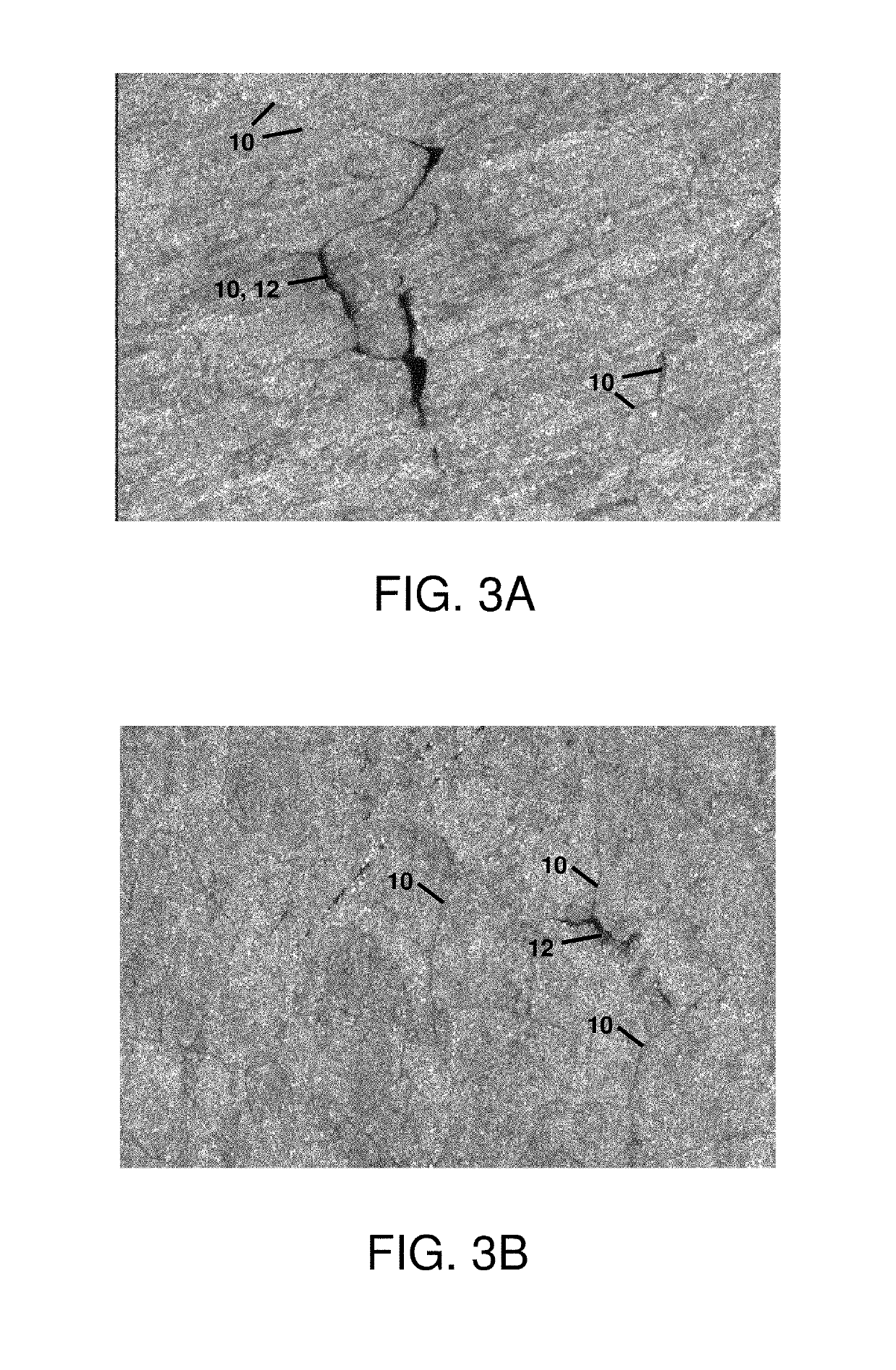
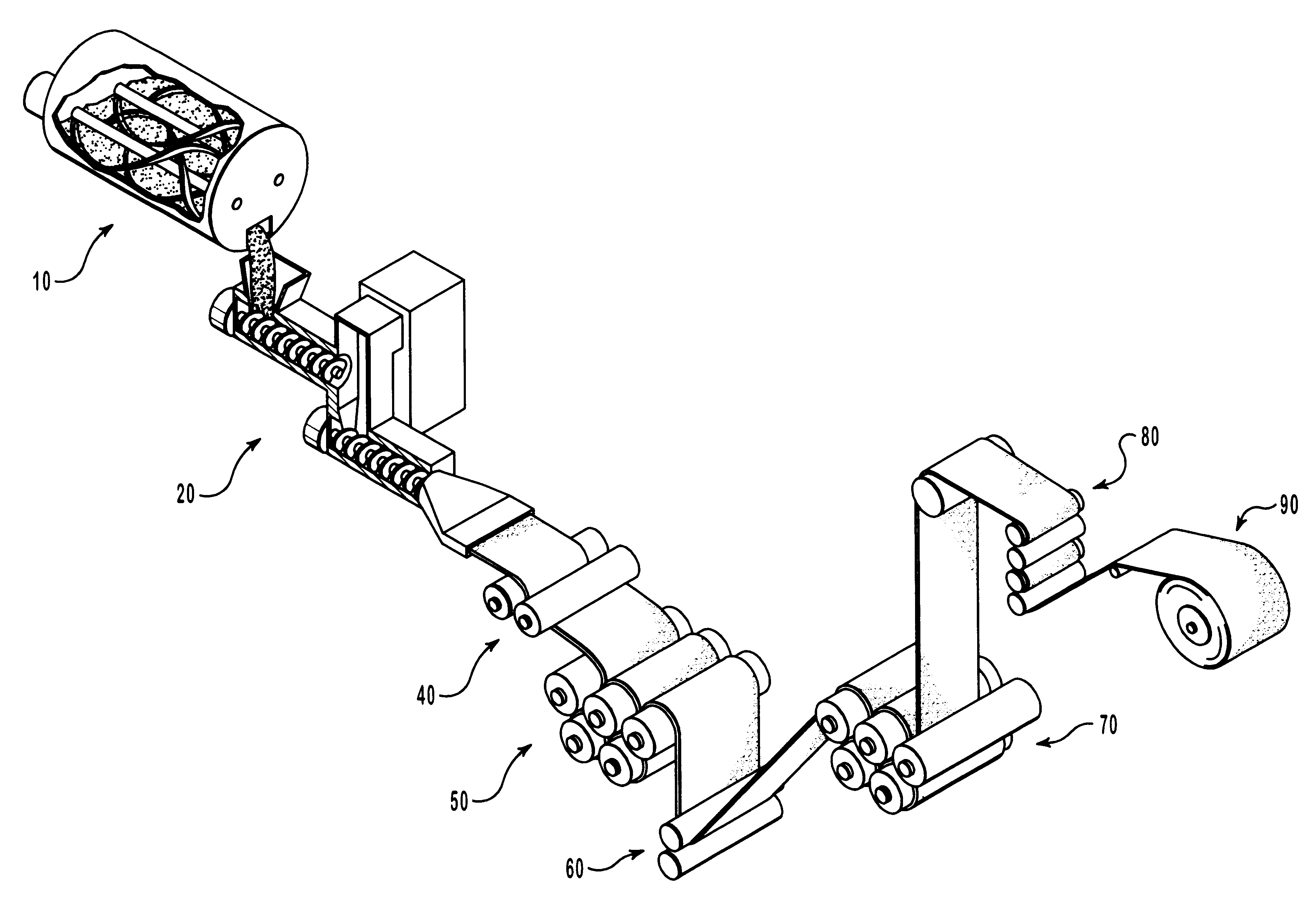
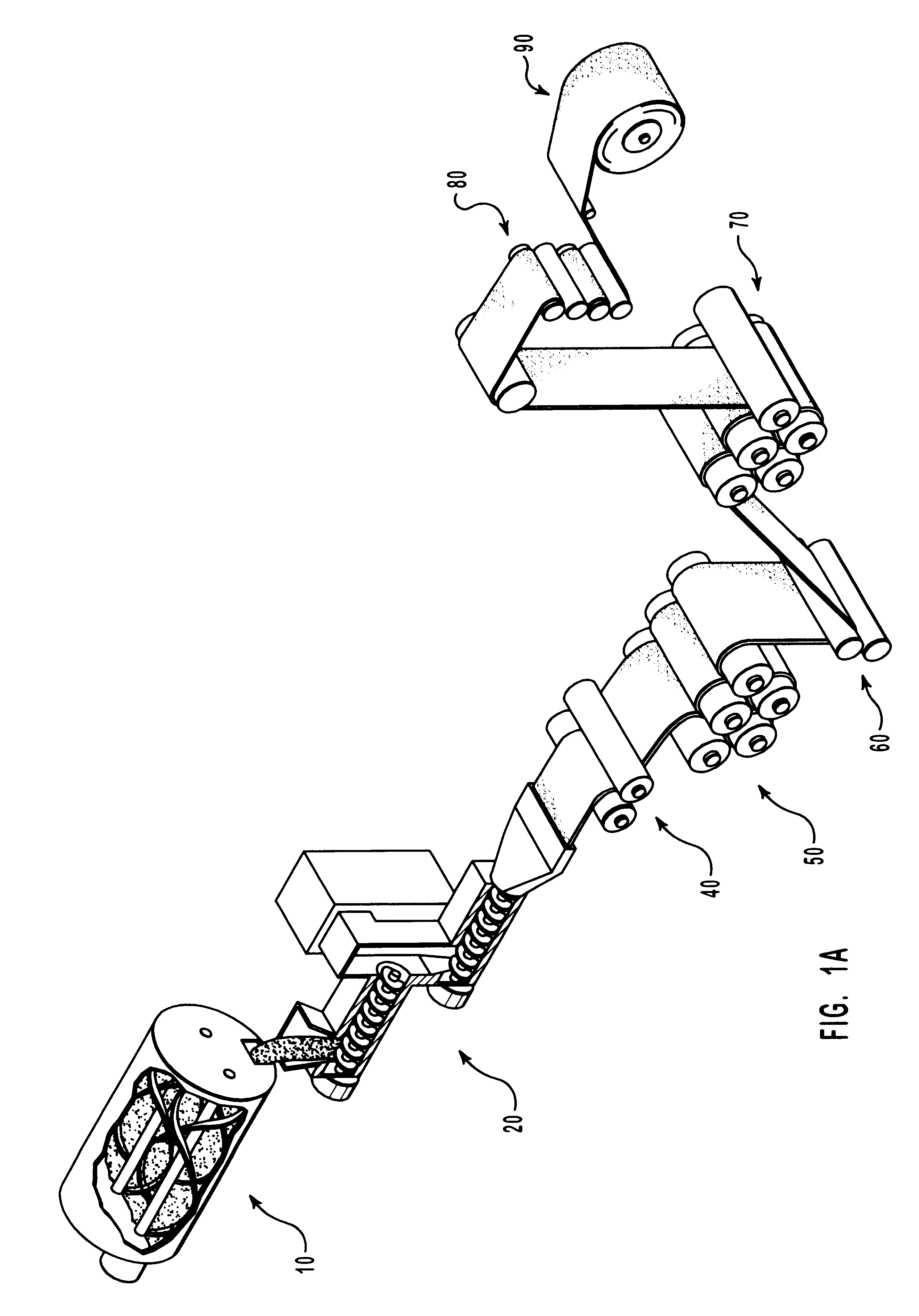
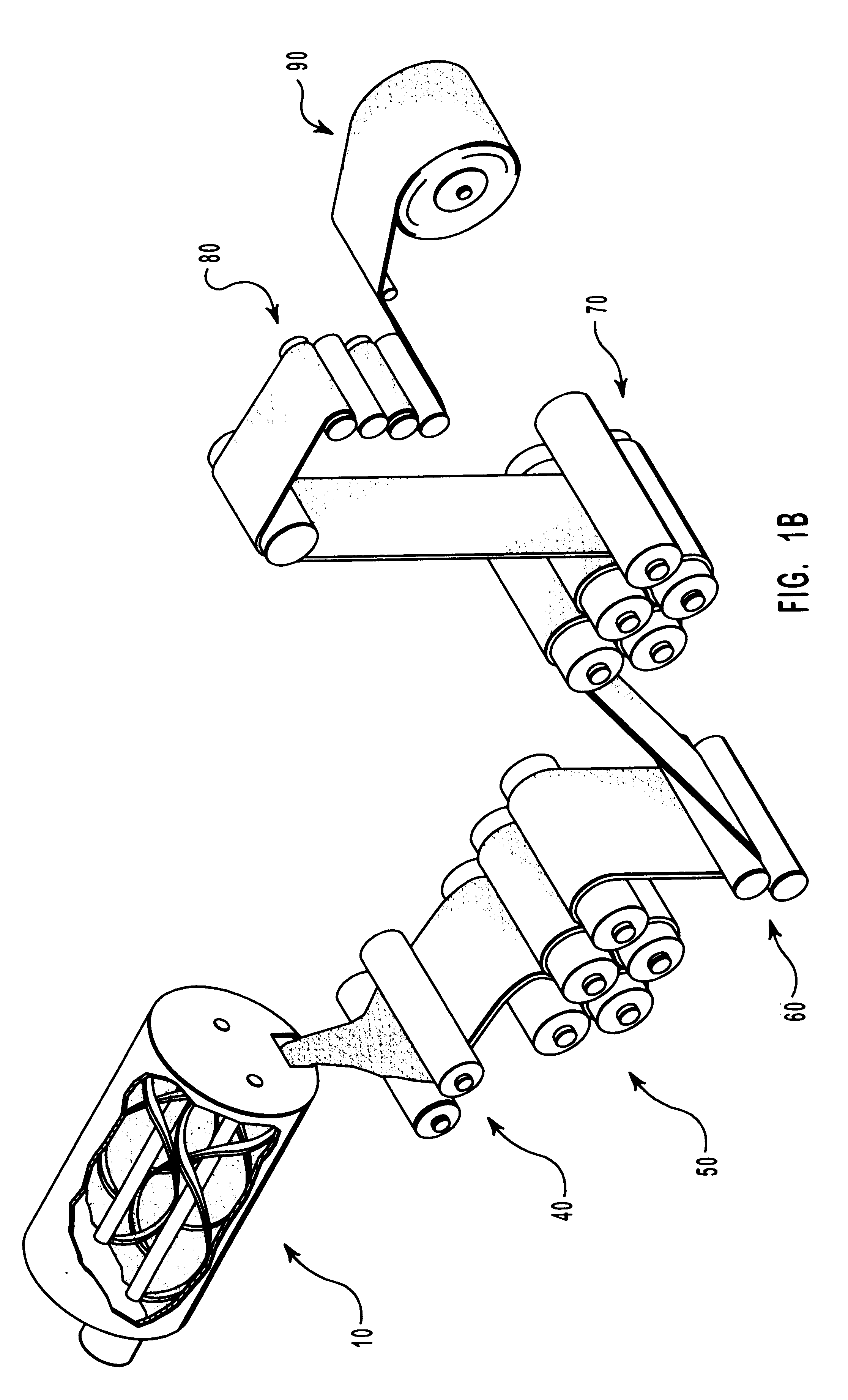
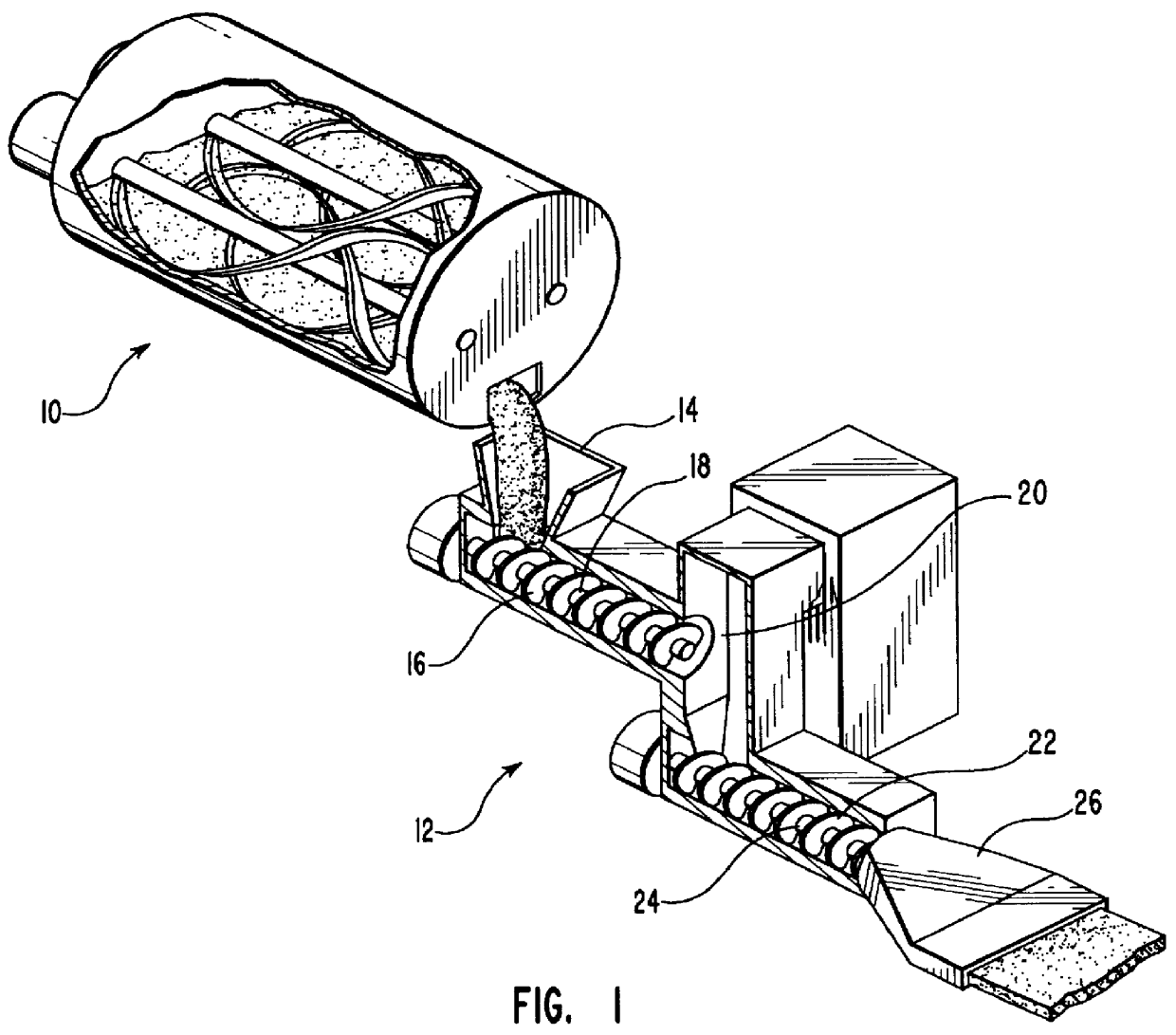
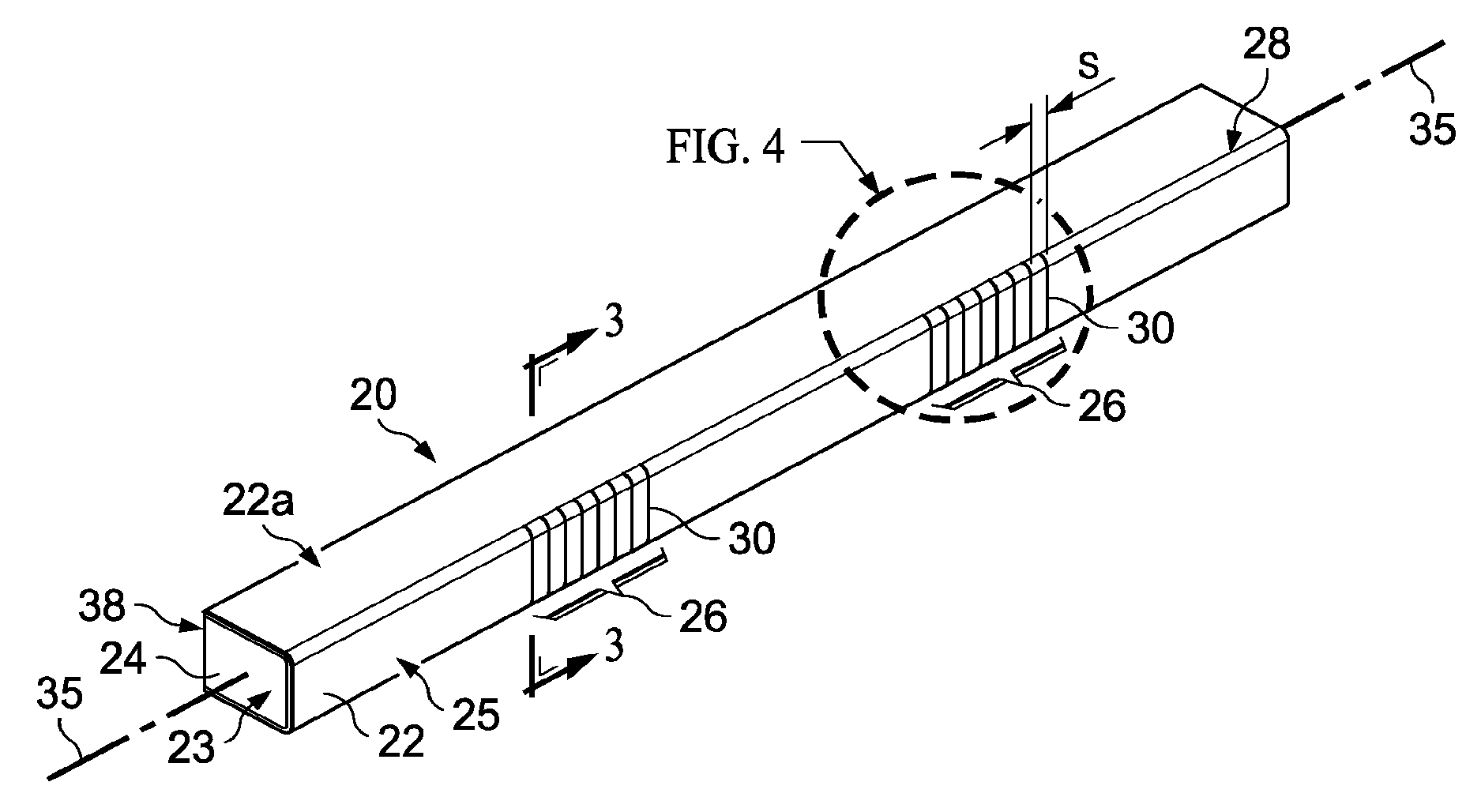
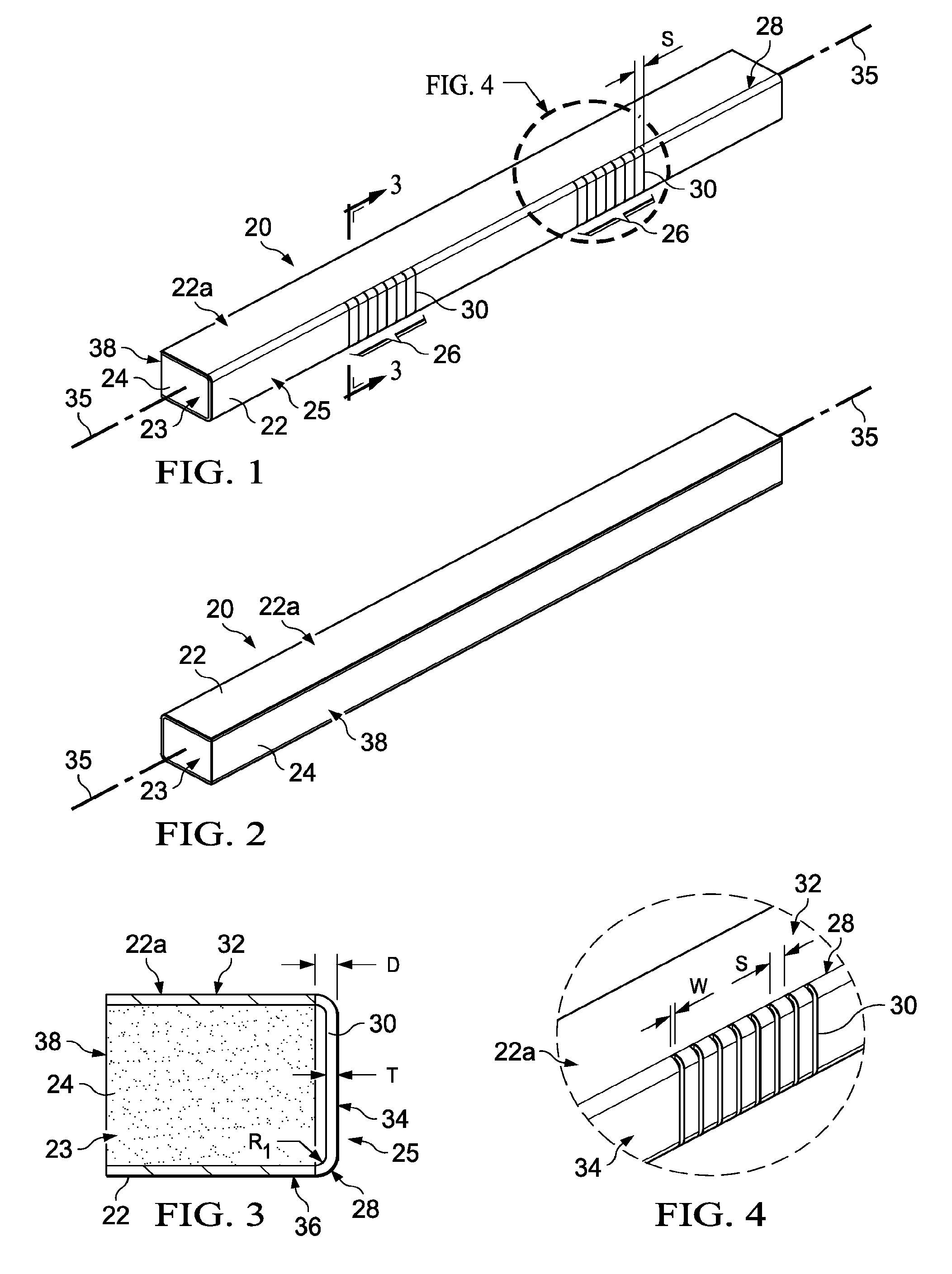
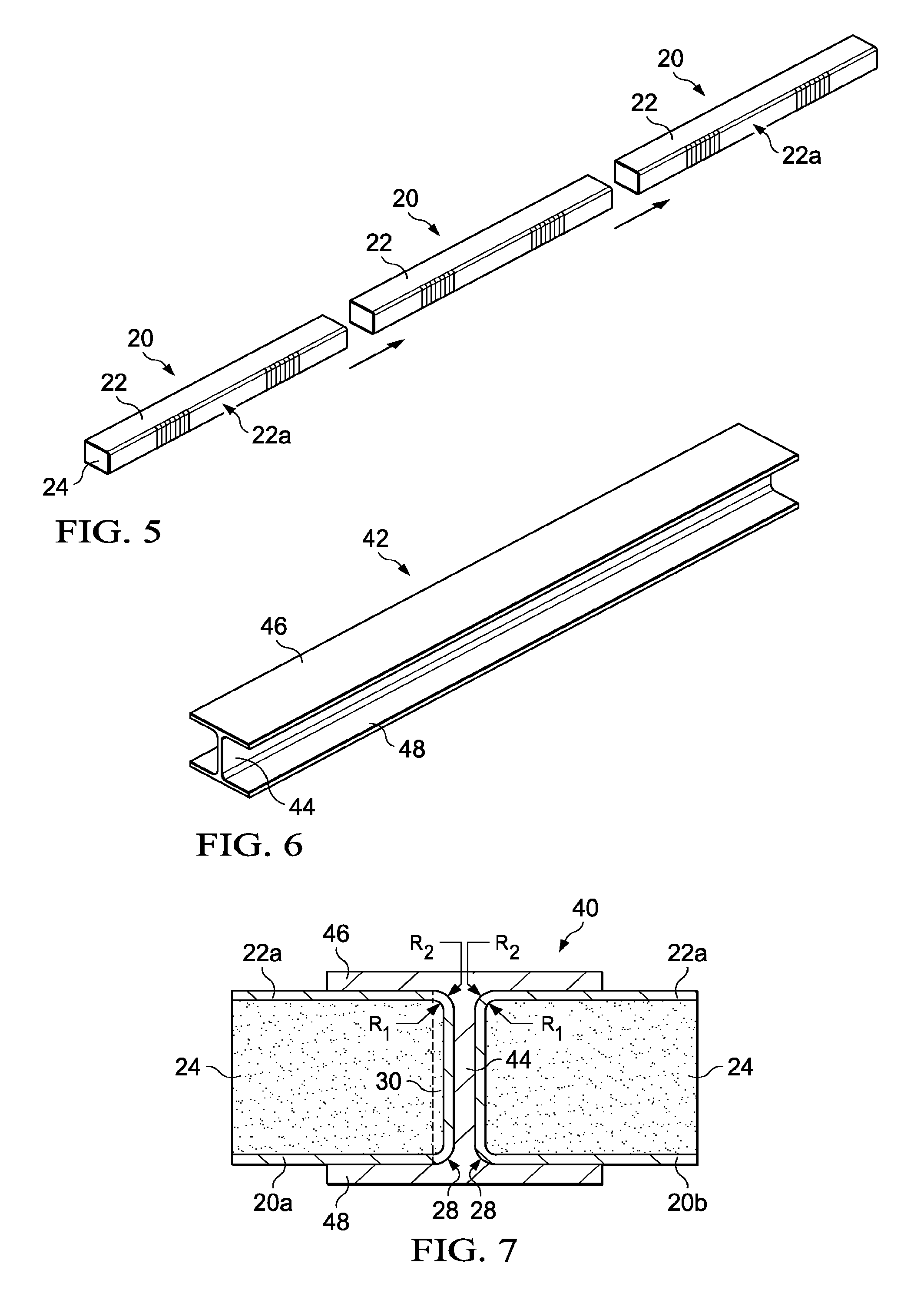
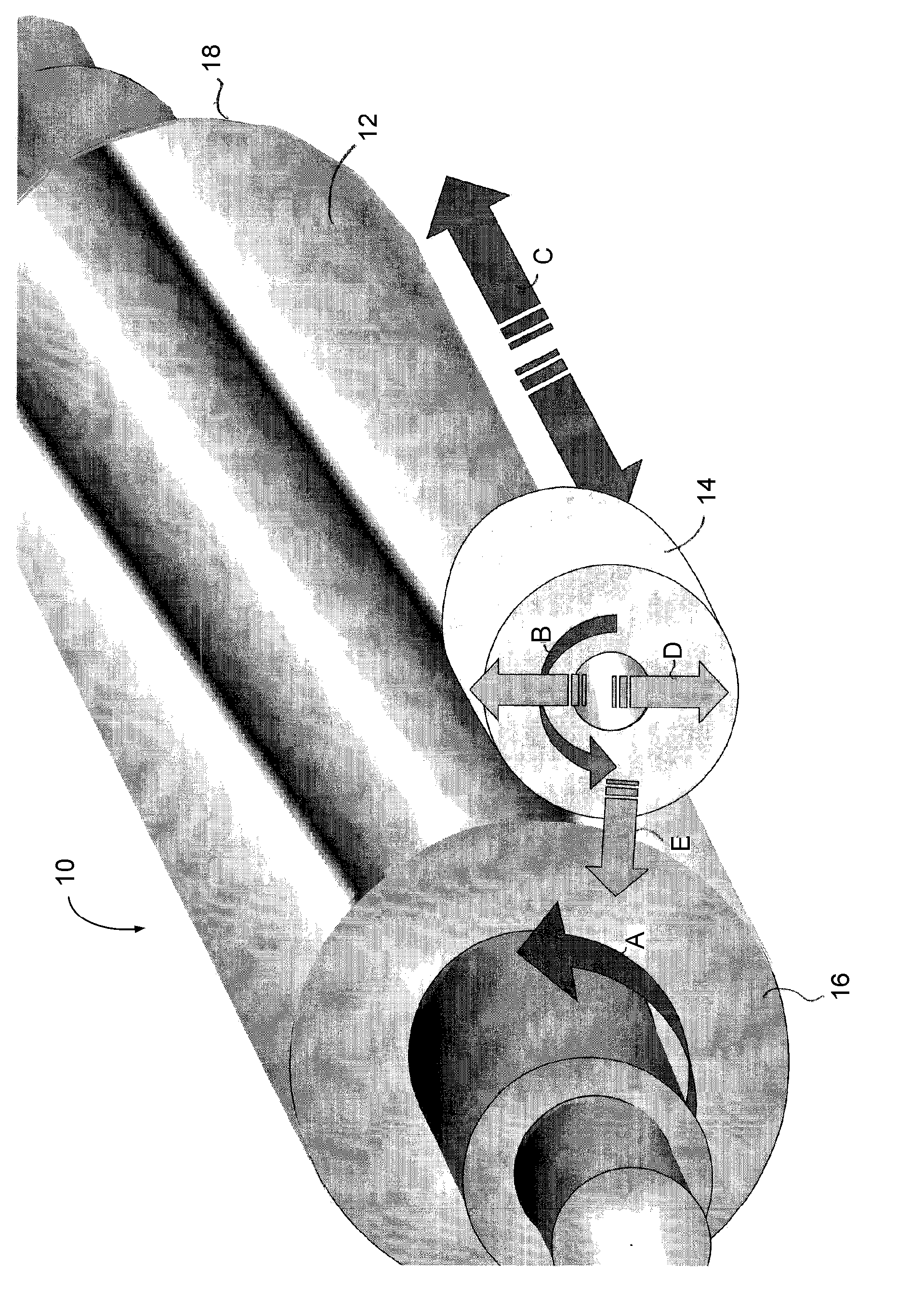
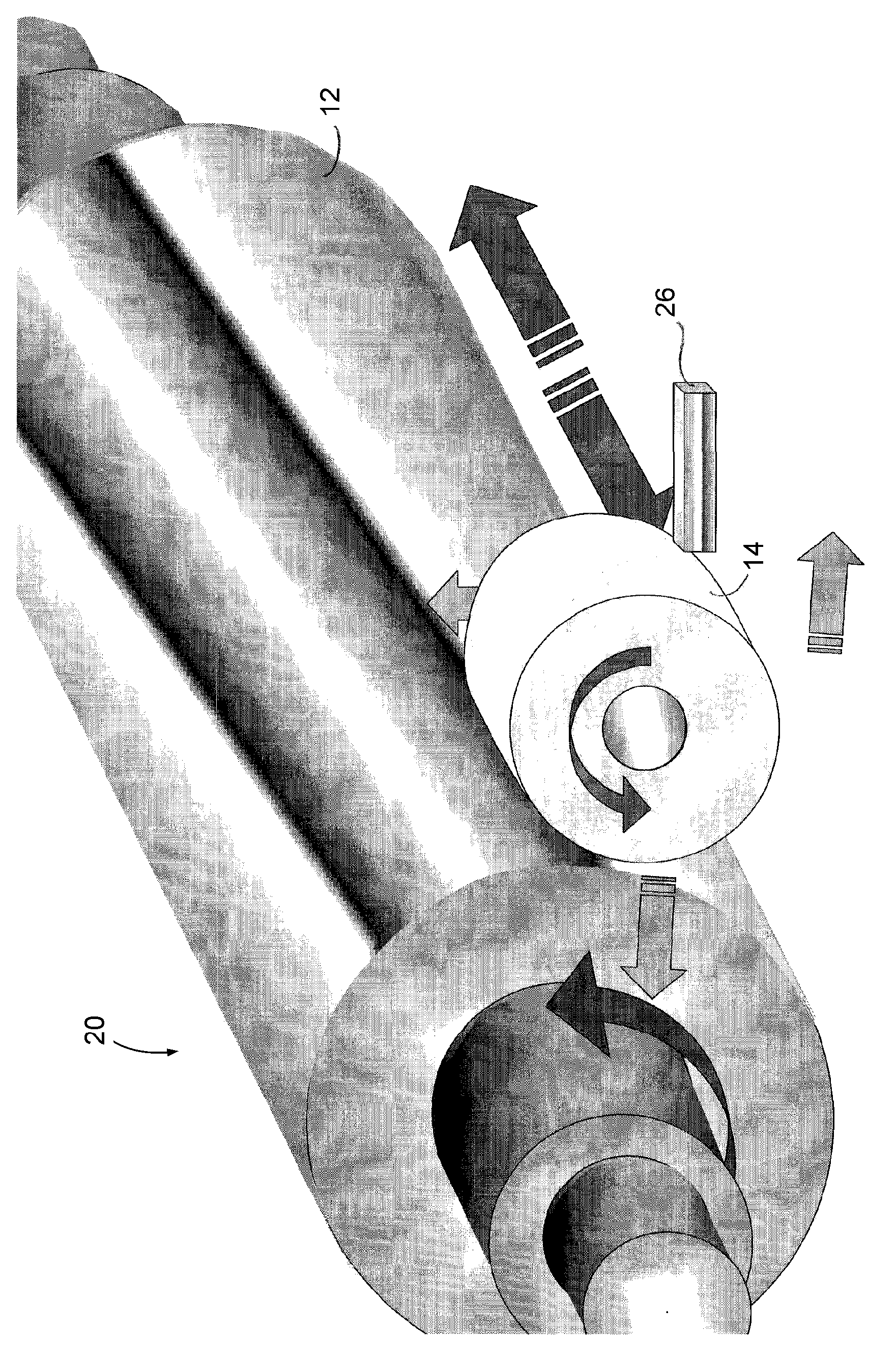
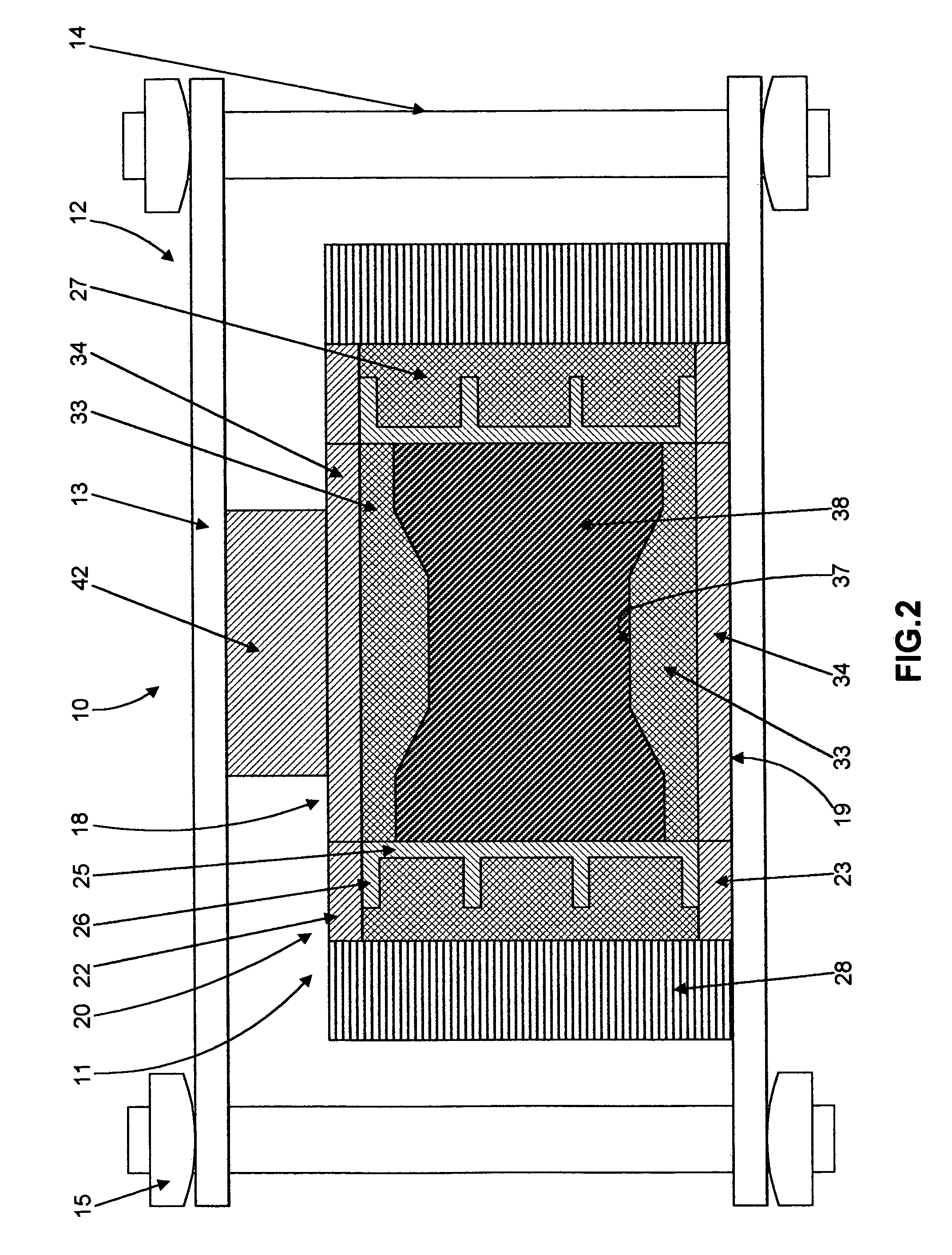
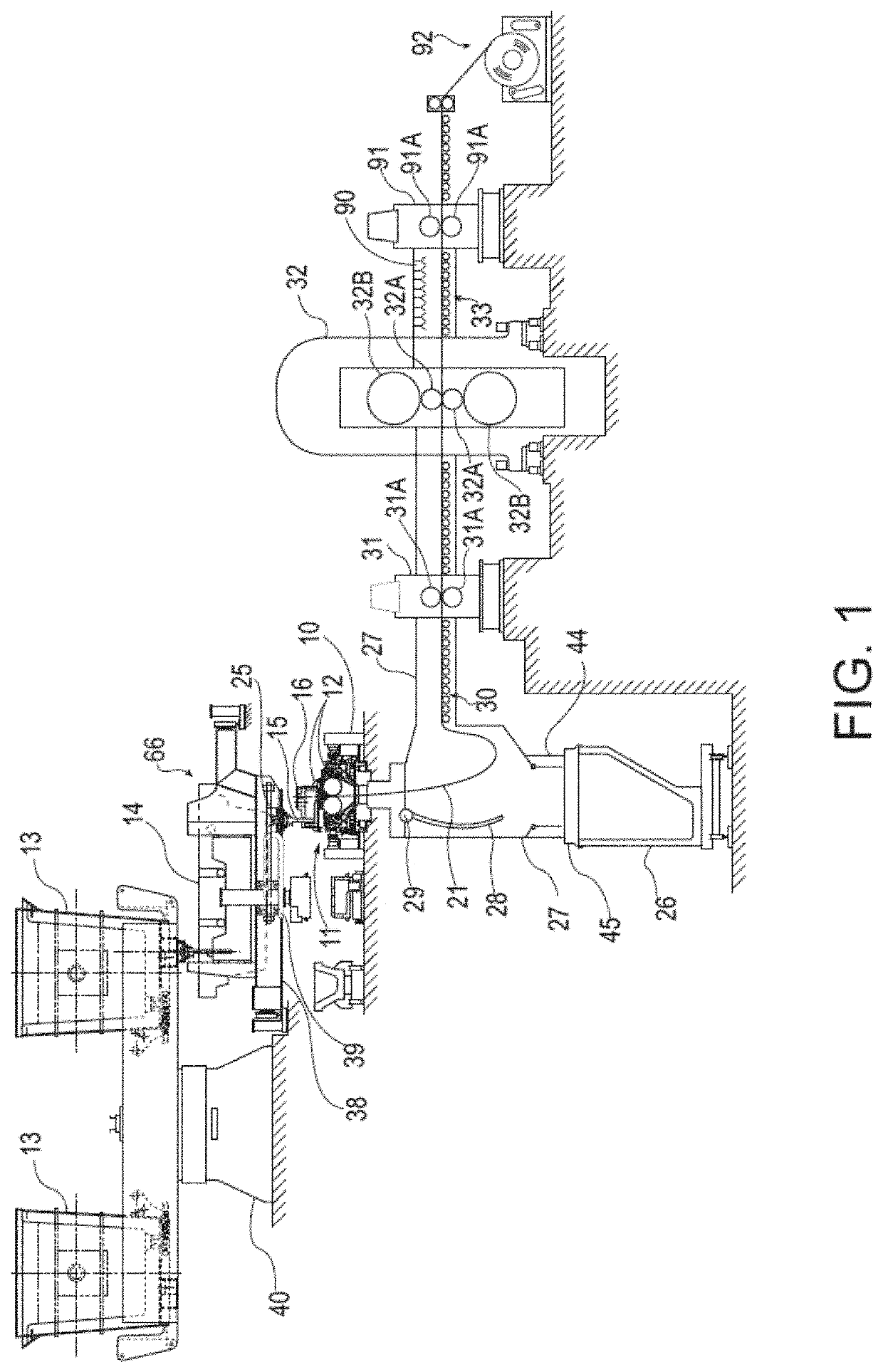
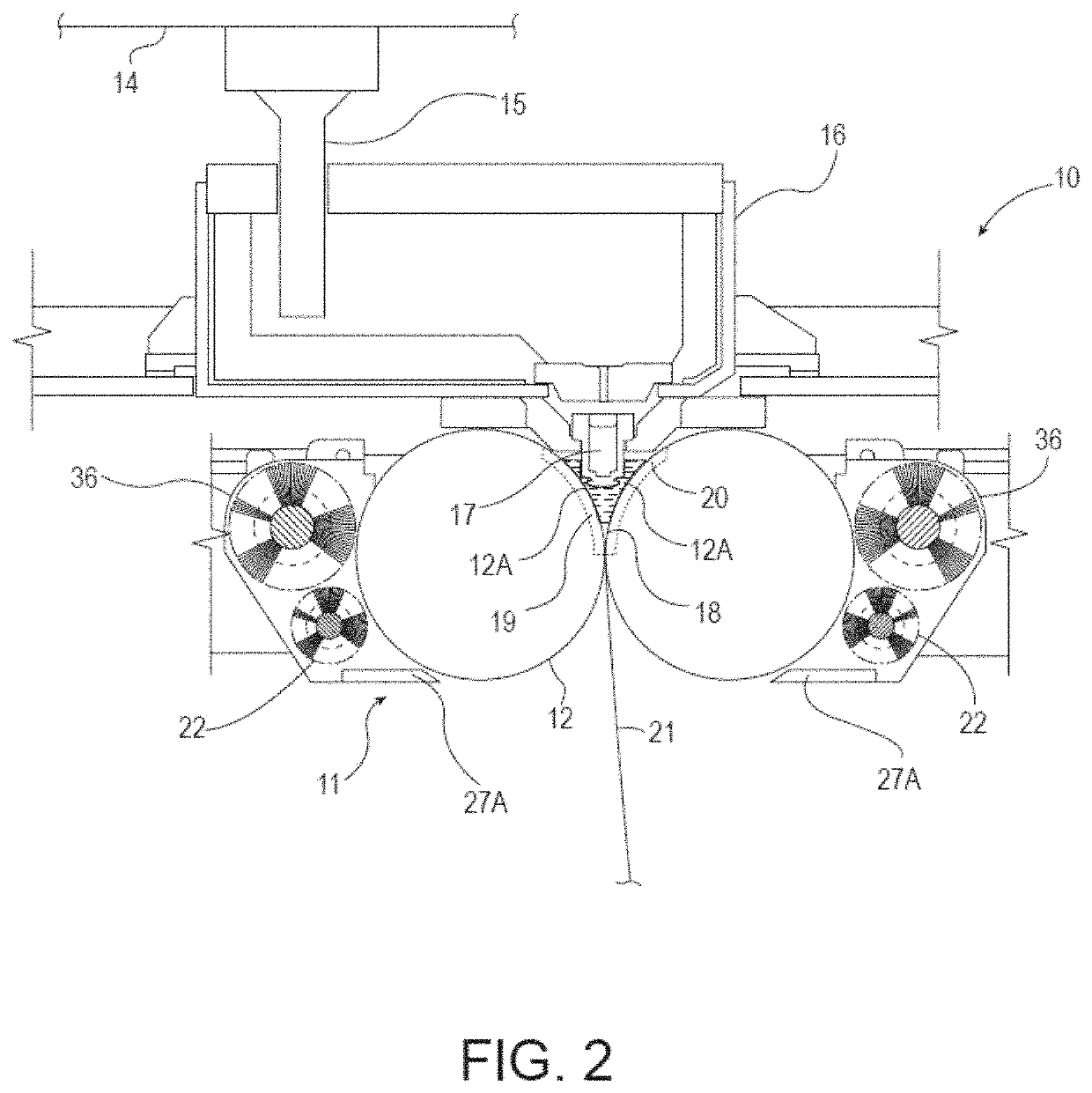
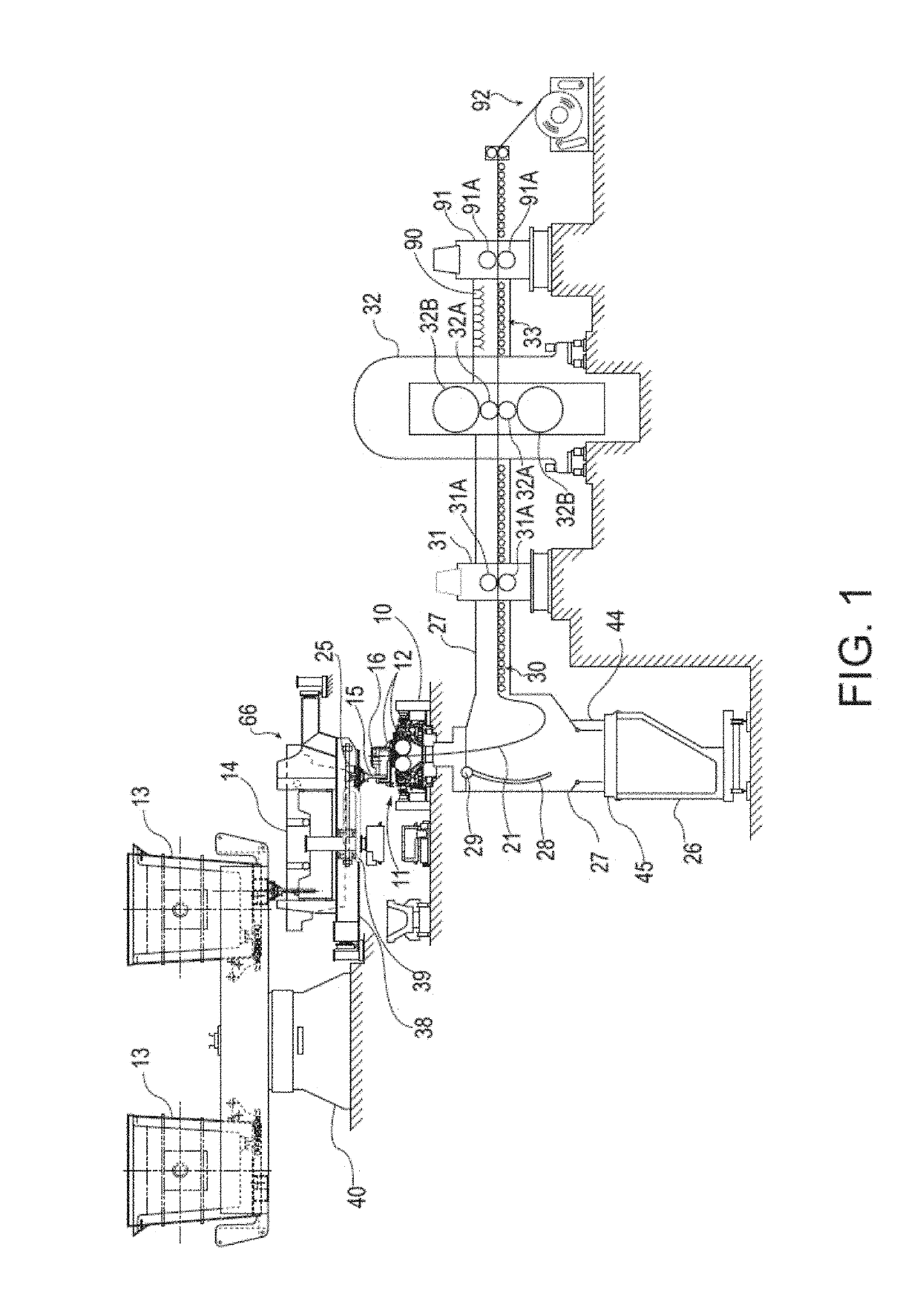
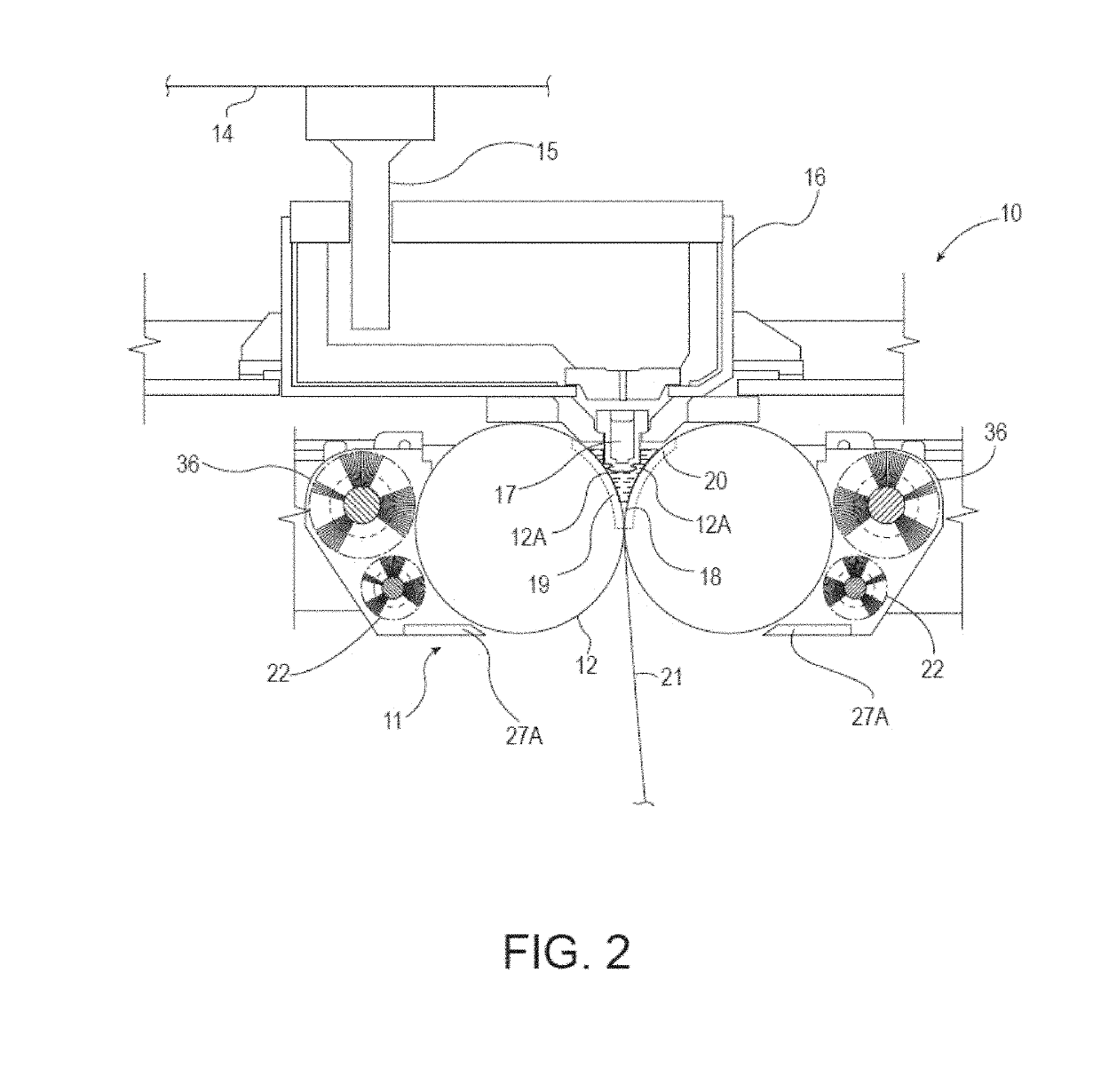
Methods for the manufacture of sheets having a highly inorganically filled organic polymer matrix
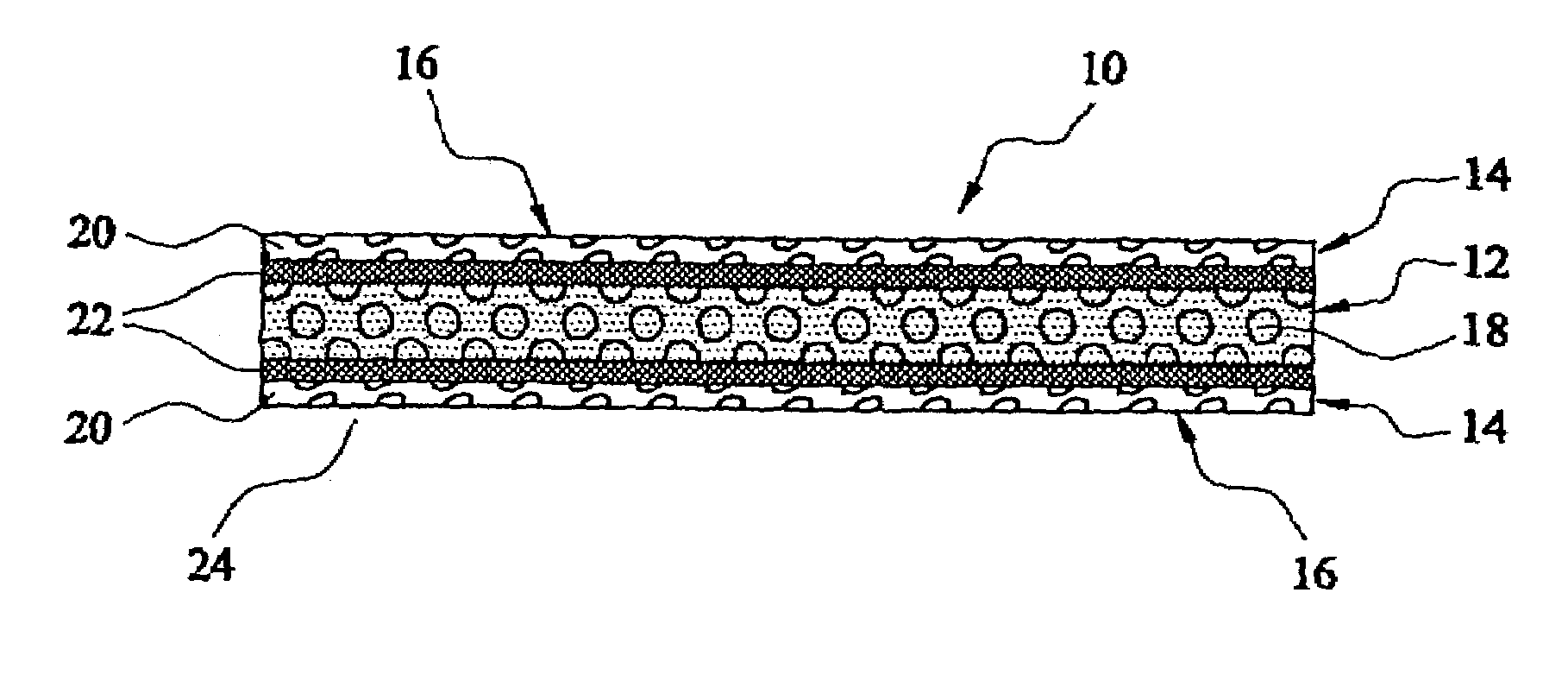
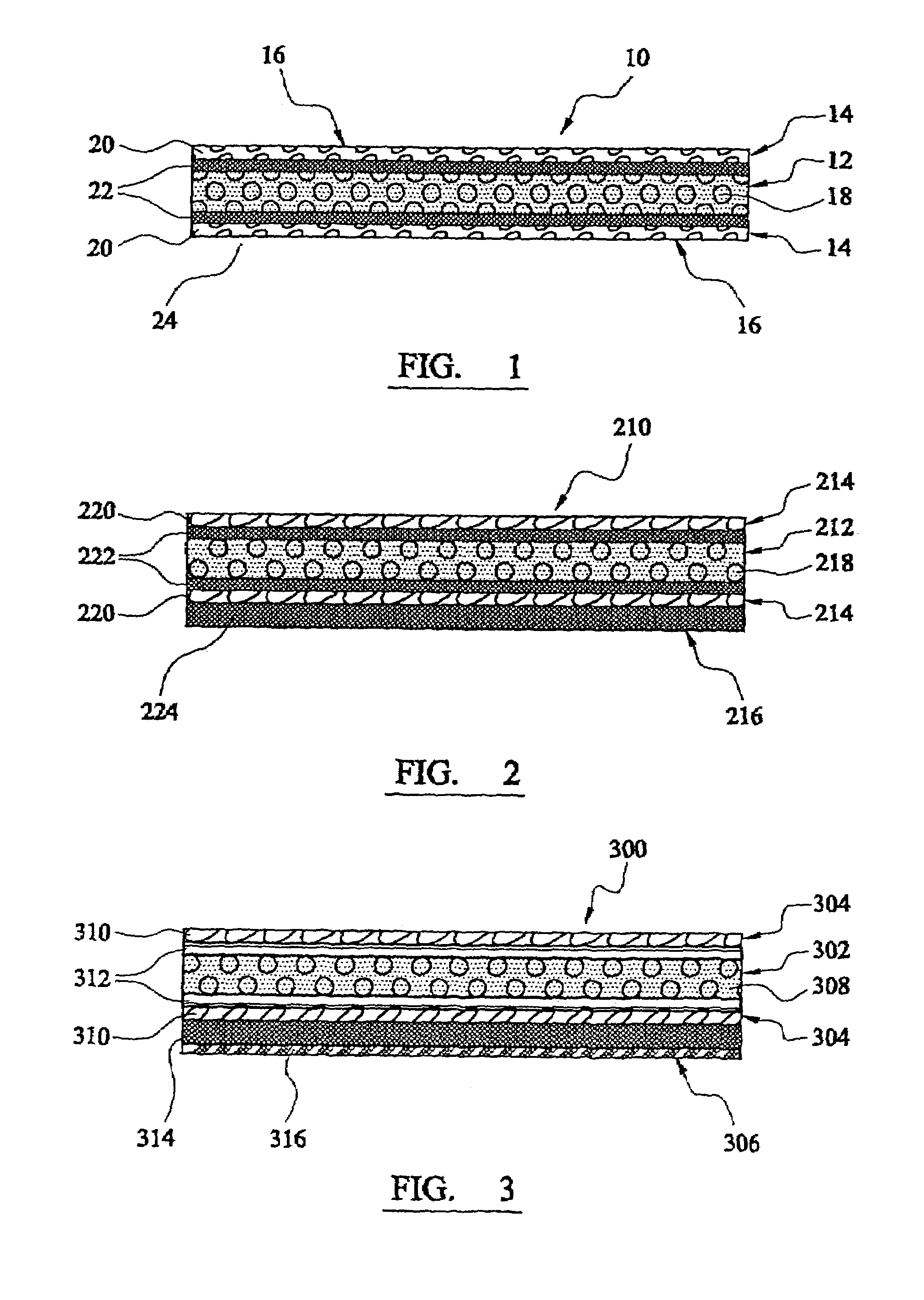
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a highly inorganically filled matrix. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together an organic polymer binder, water, one or more inorganic aggregate materials, fibers, and optional admixtures in the correct proportions in order to form a sheet which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures are formed into sheets by first extruding the mixtures and the passing the extruded materials between a set of rollers. The rolled sheets are dried in an accelerated manner to form a substantially hardened sheet, such as by heated rollers and / or a drying chamber. The inorganically filled sheets may have properties substantially similar to sheets presently made from traditional materials like paper, cardboard, polystyrene, plastic, or metal. Such sheets can be rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued. They have especial utility in the mass production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
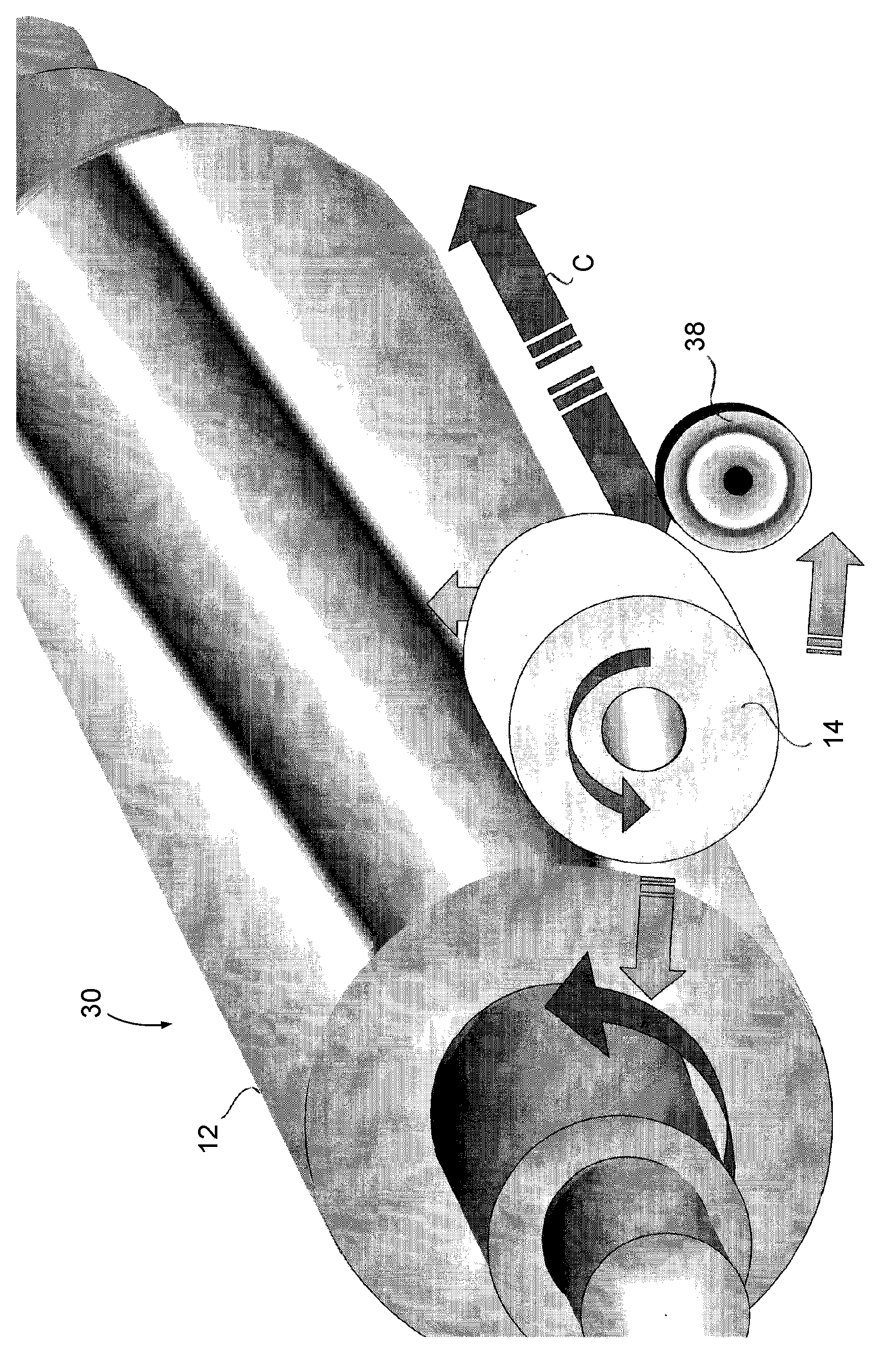
Compositions used in manufacturing articles having an inorganically filled organic polymer matrix
InactiveUS6090195AReadily and inexpensively mass producedHigh strengthClosure lidsWrappersFiberPolymer science
Compositions, methods, and systems for manufacturing articles, particularly containers and packaging materials, having a highly inorganically filled matrix. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together an organic polymer binder, water, one or more aggregate materials, fibers, and optional admixtures in the correct proportions in order to form an article which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures are molded to fashion a portion of the mixture into a form stable shape for the desired article. Once the article has obtained form stability, such as by heating to remove water by evaporation, the article is removed from the mold and allowed to harden to gain strength. The articles may have properties substantially similar to articles presently made from traditional materials like paper, paperboard, polystyrene, plastic, or metal. They have especial utility in the mass production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:EARTHSHELL SPE
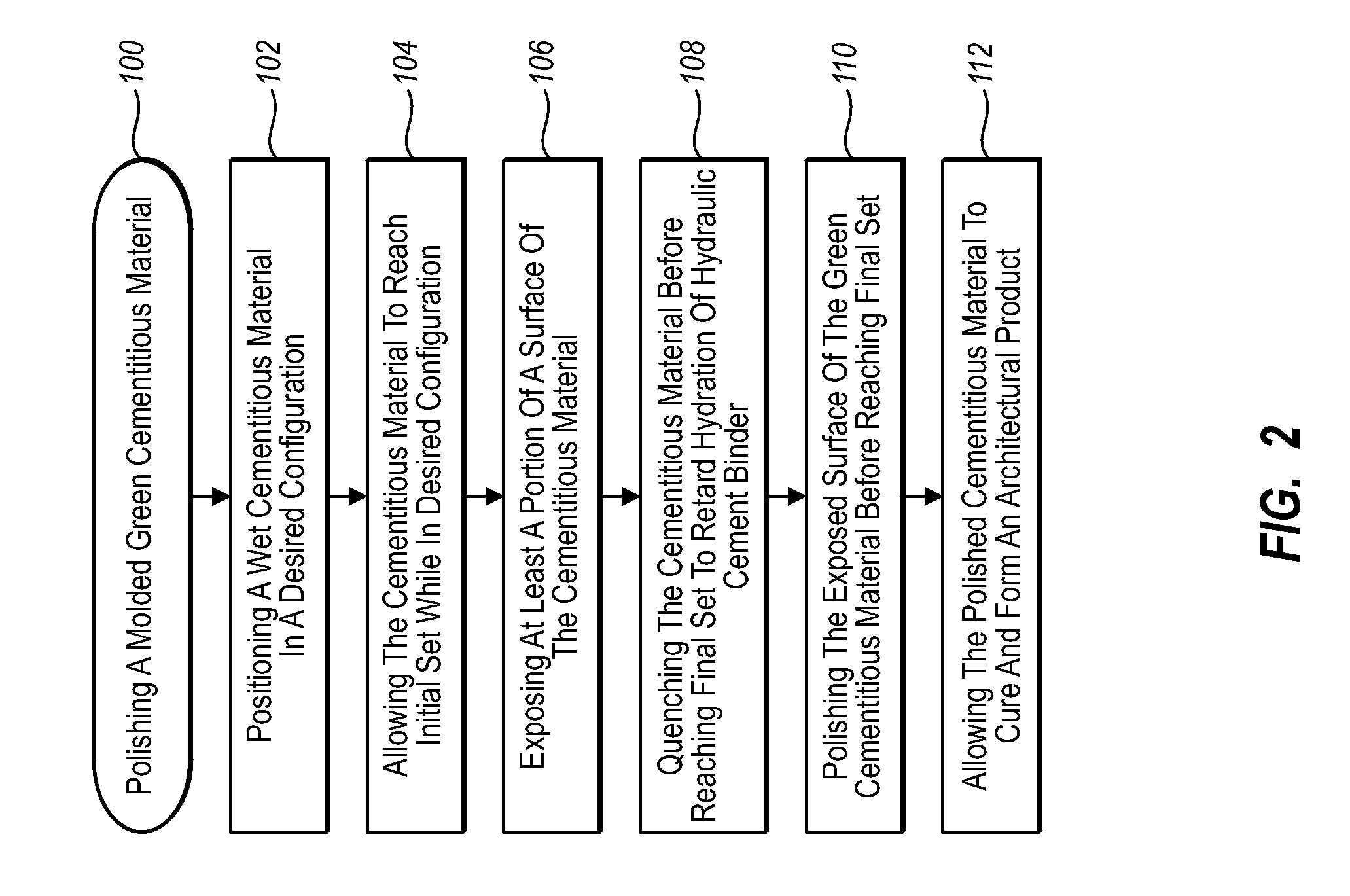
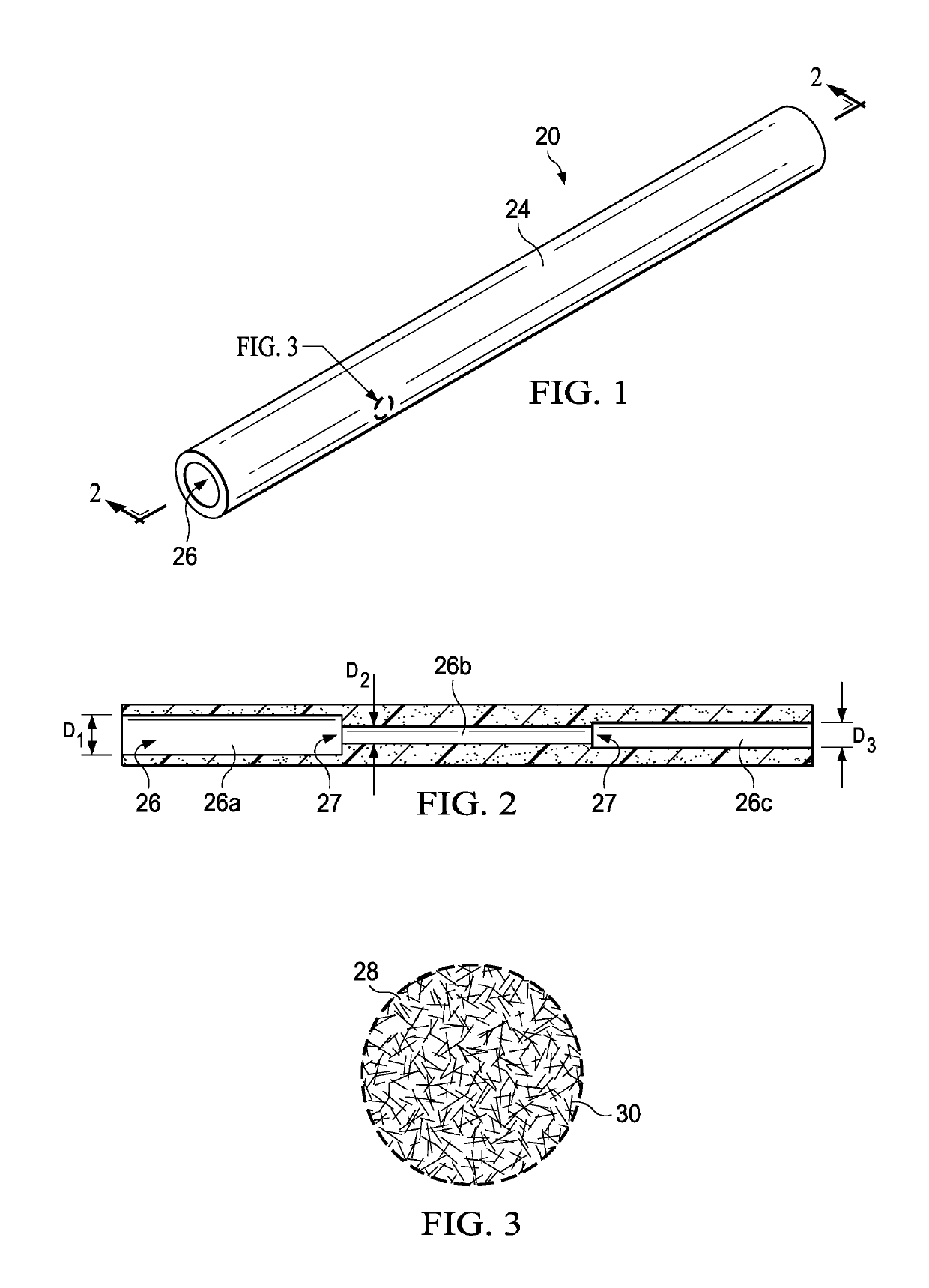
Molded cementitious architectural products having a polished stone-like surface finish
InactiveUS20080286519A1Smooth surface finishMaximized strengthConstruction materialDecorative surface effectsCement particleShell molding
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
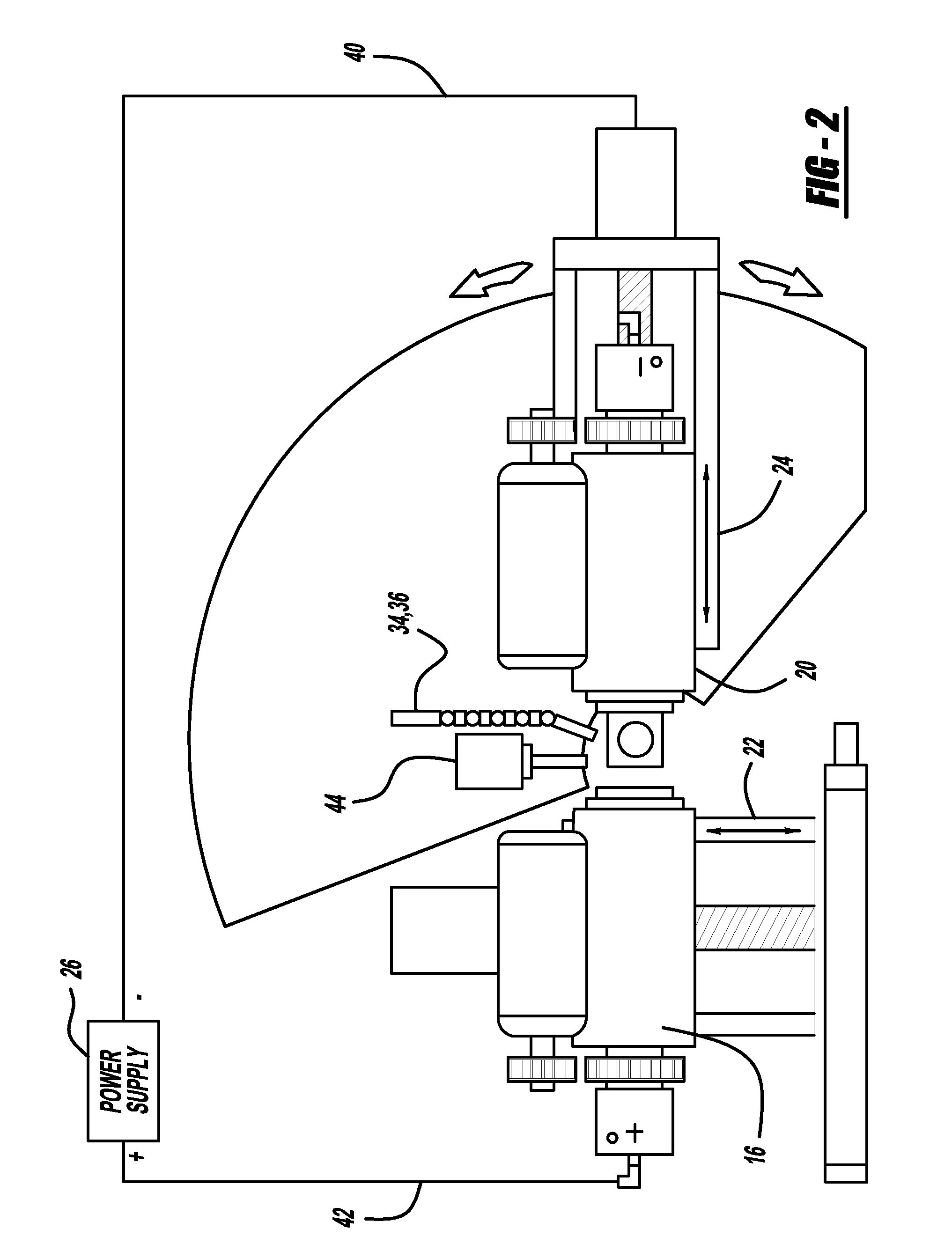
Process for electropolishing a device made from cobalt-chromium
ActiveUS7357854B1Reduce weightHigh densityStentsPolycrystalline material growthElectrolysisBiocompatibility Testing
The invention is directed to an electropolishing solution for products or devices made from at least in part a cobalt-chromium alloy. The invention is particularly suitable for medical devices or intravascular stents made at least in part of cobalt-chromium. More particularly, the electropolishing process of the invention is particularly suited for use on implantable medical devices, such as stents, due to the biocompatibility of cobalt-chromium alloys. The invention is directed to an improved stent formed from a cobalt-chromium alloy, that possesses an ultrasmooth shiny surface. This invention is also directed to a method of electropolishing such a stent using an acidic electrolytic solution comprising a mixture of 6 parts of about 98% sulfuric acid (H2SO4), 1 part of about 37% hydrochloric acid (HCl) and 1 part by of about 85% concentrated phosphoric acid (H3PO4) to produce an exceptionally smooth surface.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
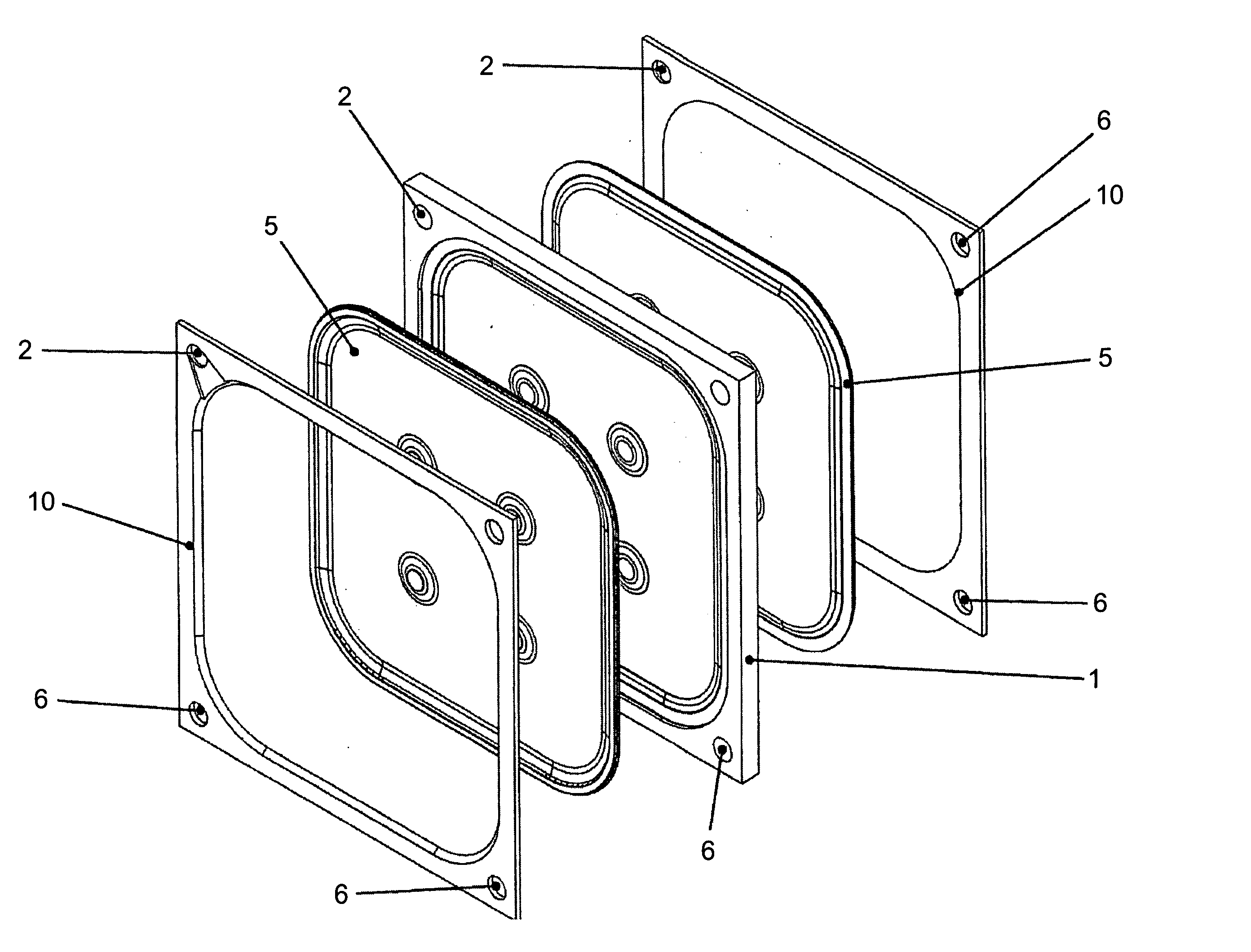
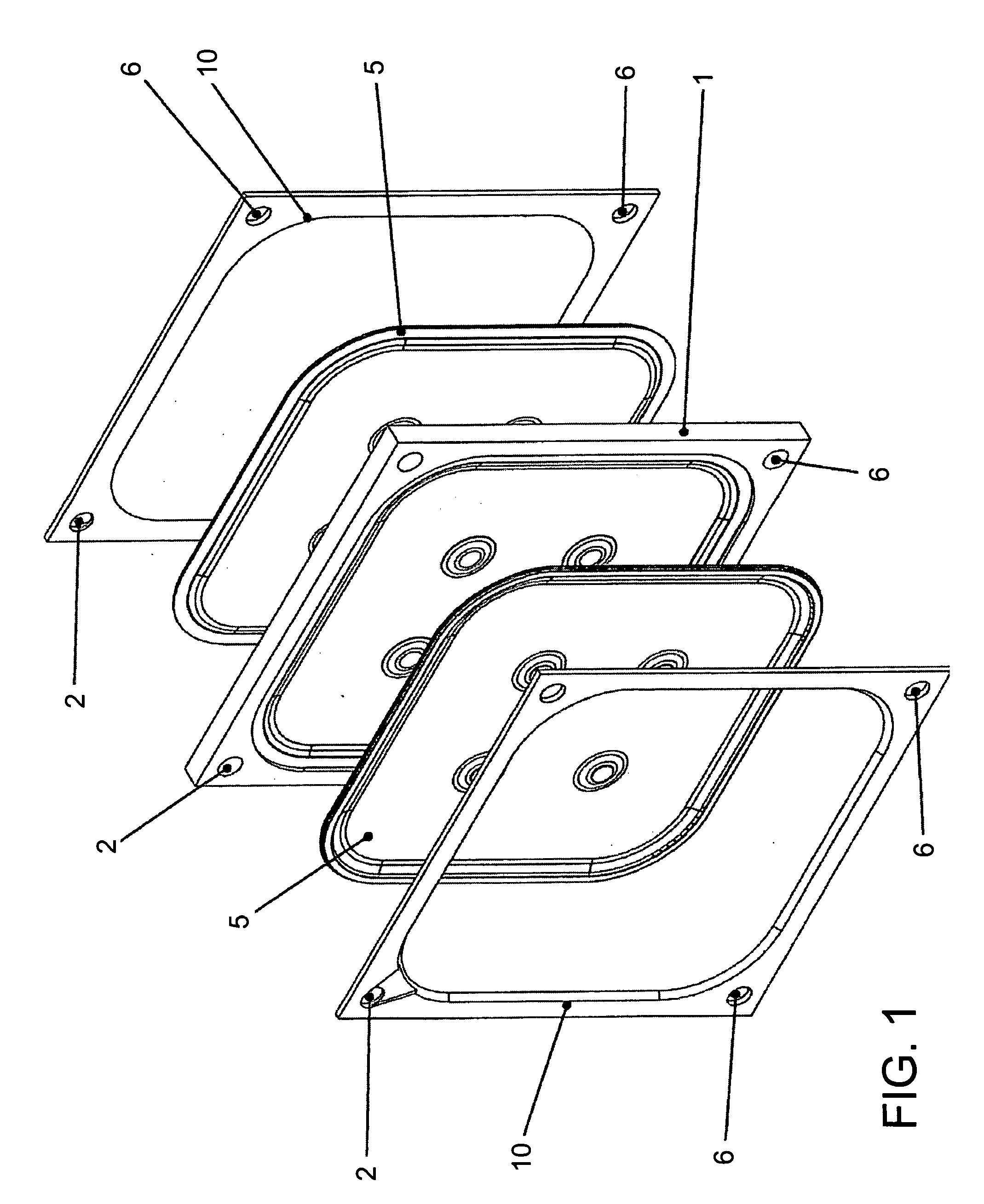
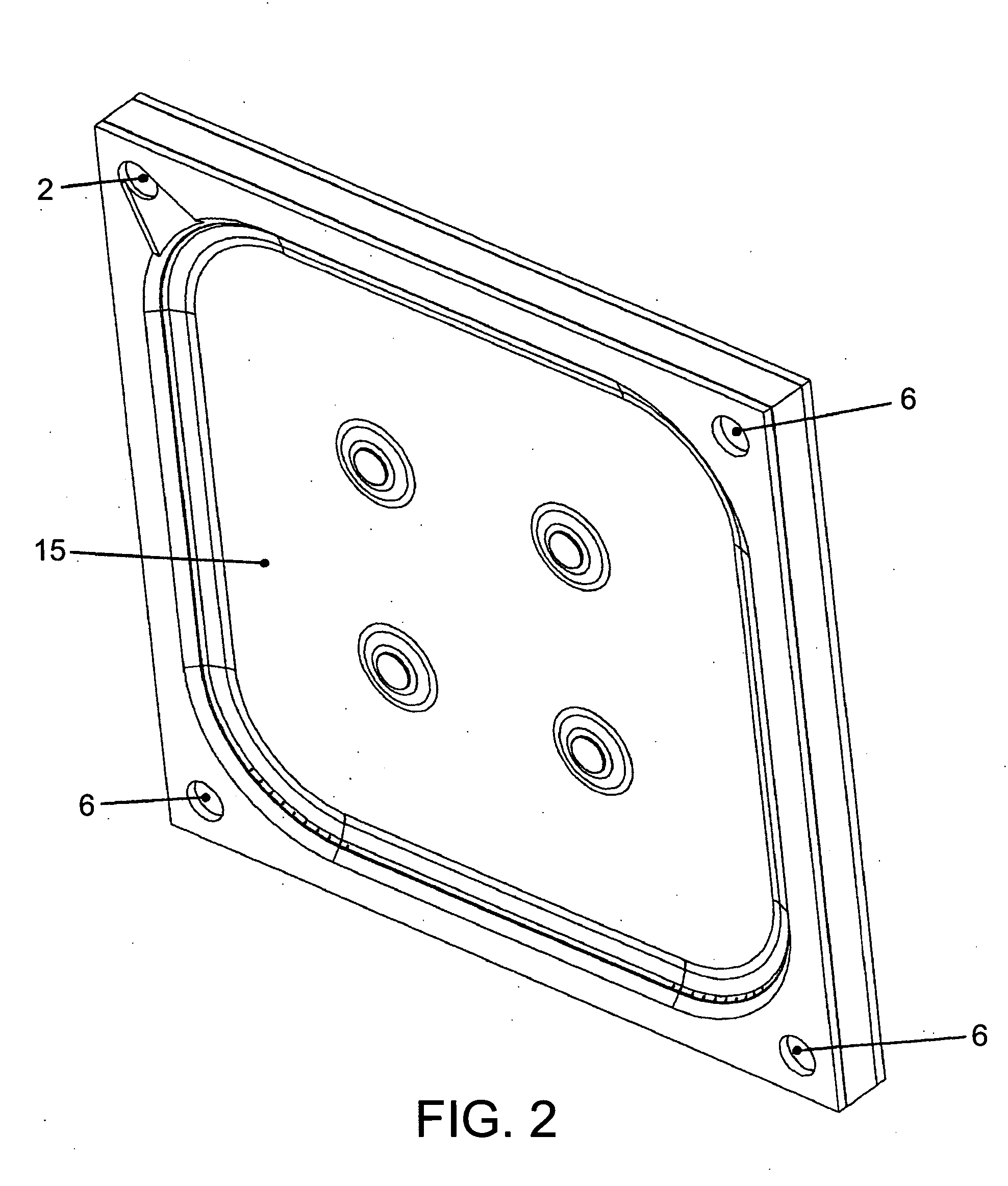
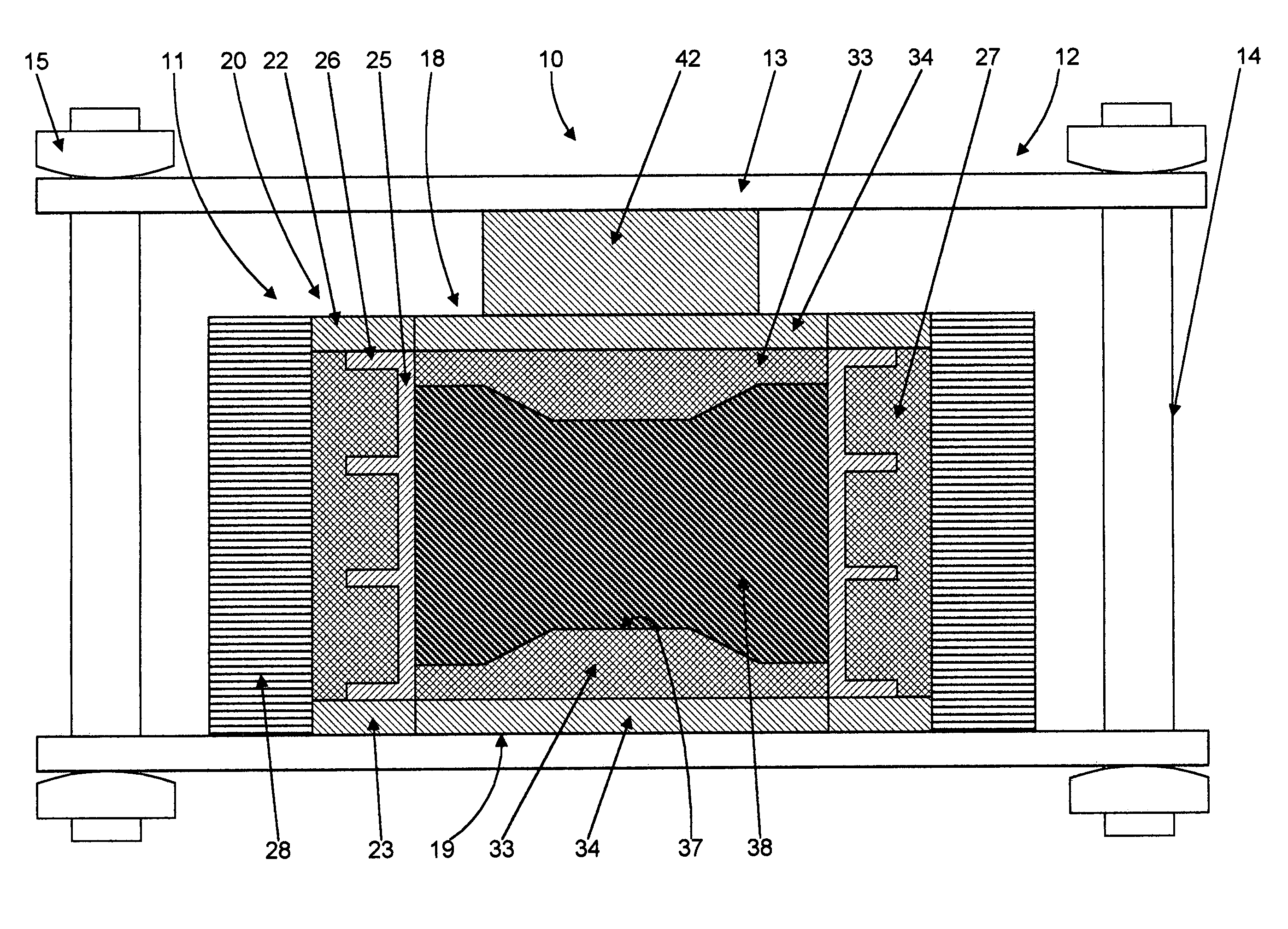
Filter plate assembly
InactiveUS20050218057A1Easy to cleanLong service lifeCartridge filtersStationary filtering element filtersPolyvinyldifluoridePolypropylene
A filter plate assembly includes a base body, a filter media and a frame. The filter plate assembly can be used in a filter press. The filter media is mounted in either side the base body and is held in place by a frame mounted in face to face contact with the filter media. The filter media is a rigid or semi-rigid structure made from sintered material. The filter sintered material can be a polymer, metal, glass, or a ceramic, and the polymer can be polyvinylchloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), polyurethane (PU), polyvinyldifluoride (PVDF), polytetrafluro-ethylene (PTFE), or polypropylene (PP).
Owner:NGEE LEE CHENG
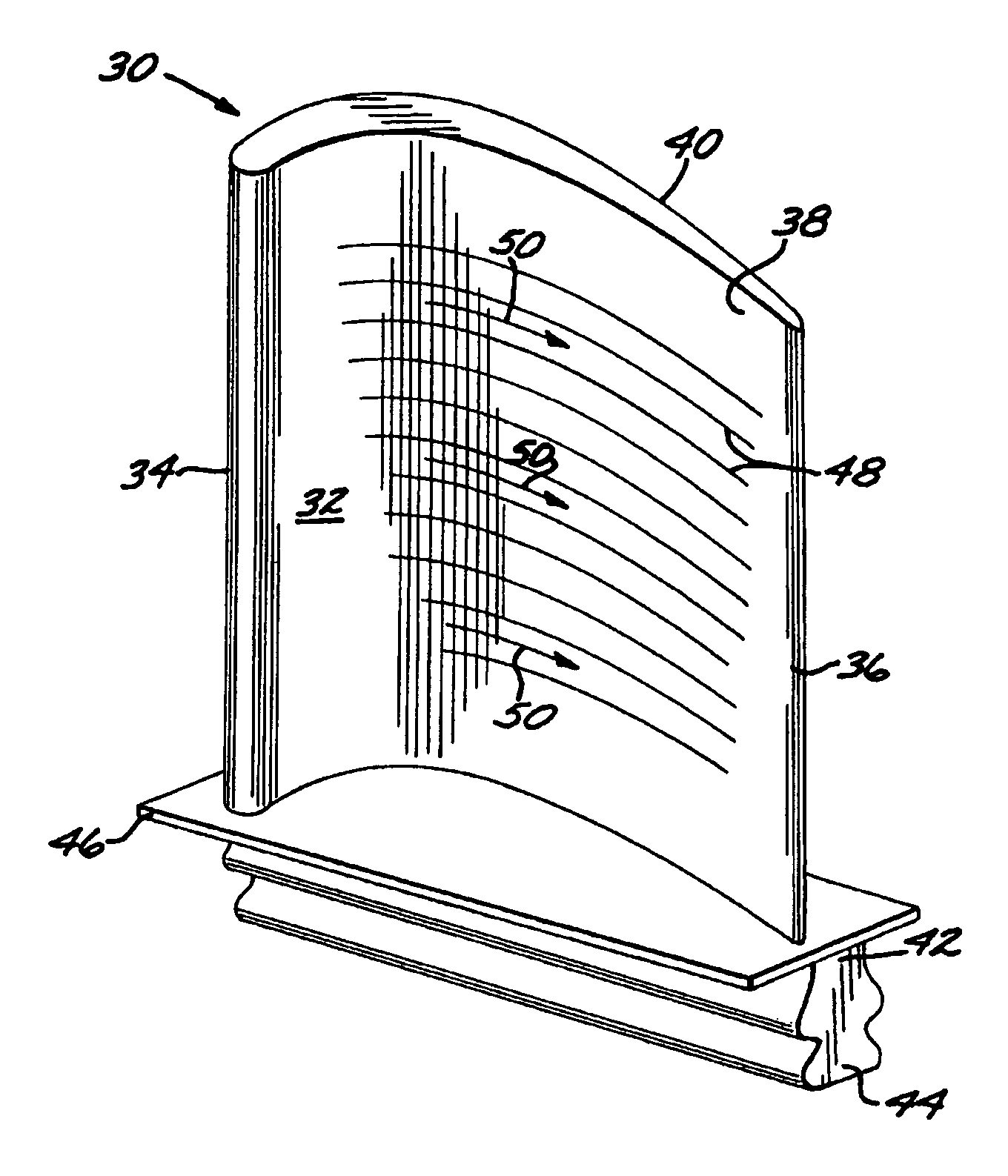
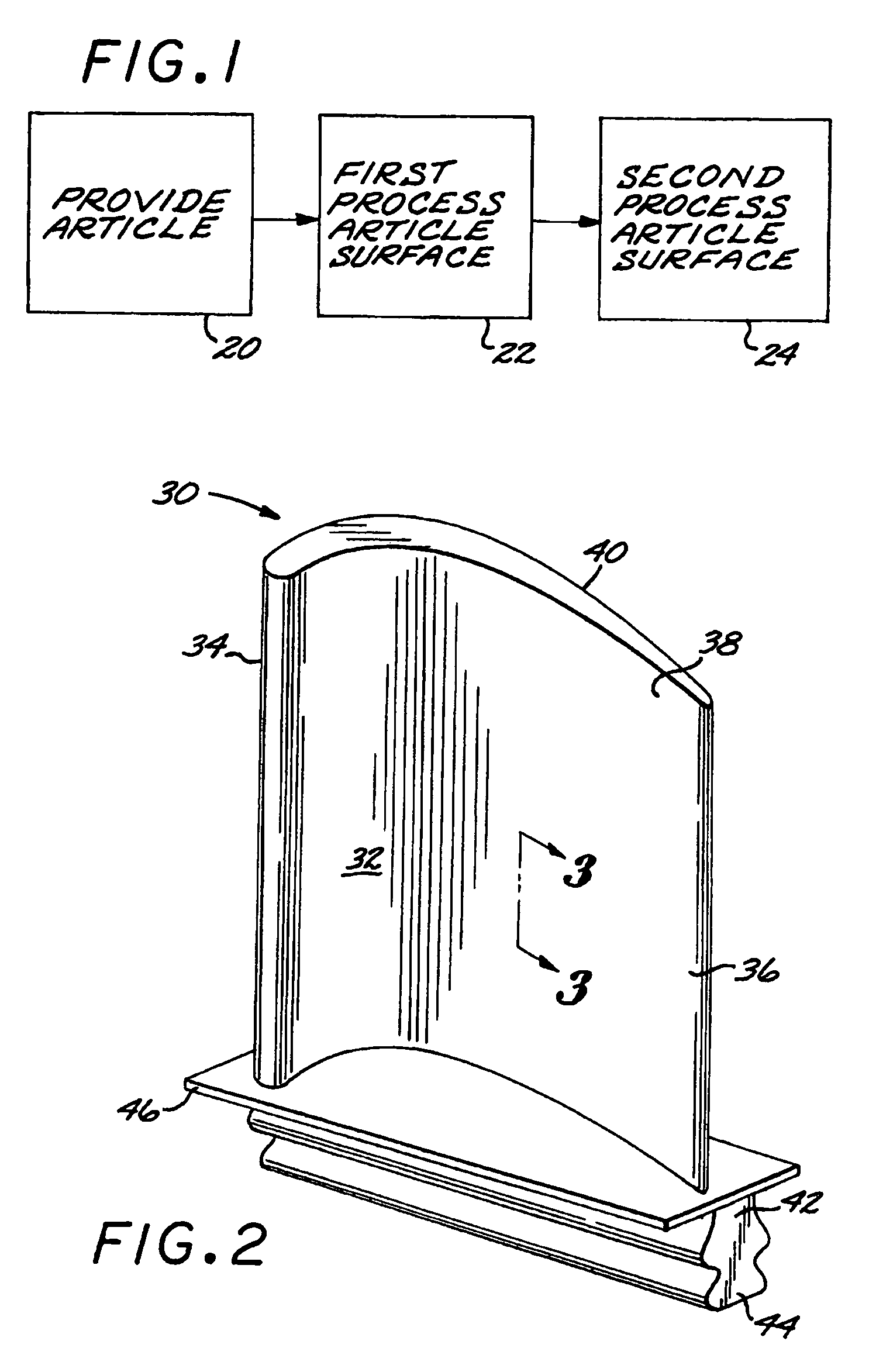
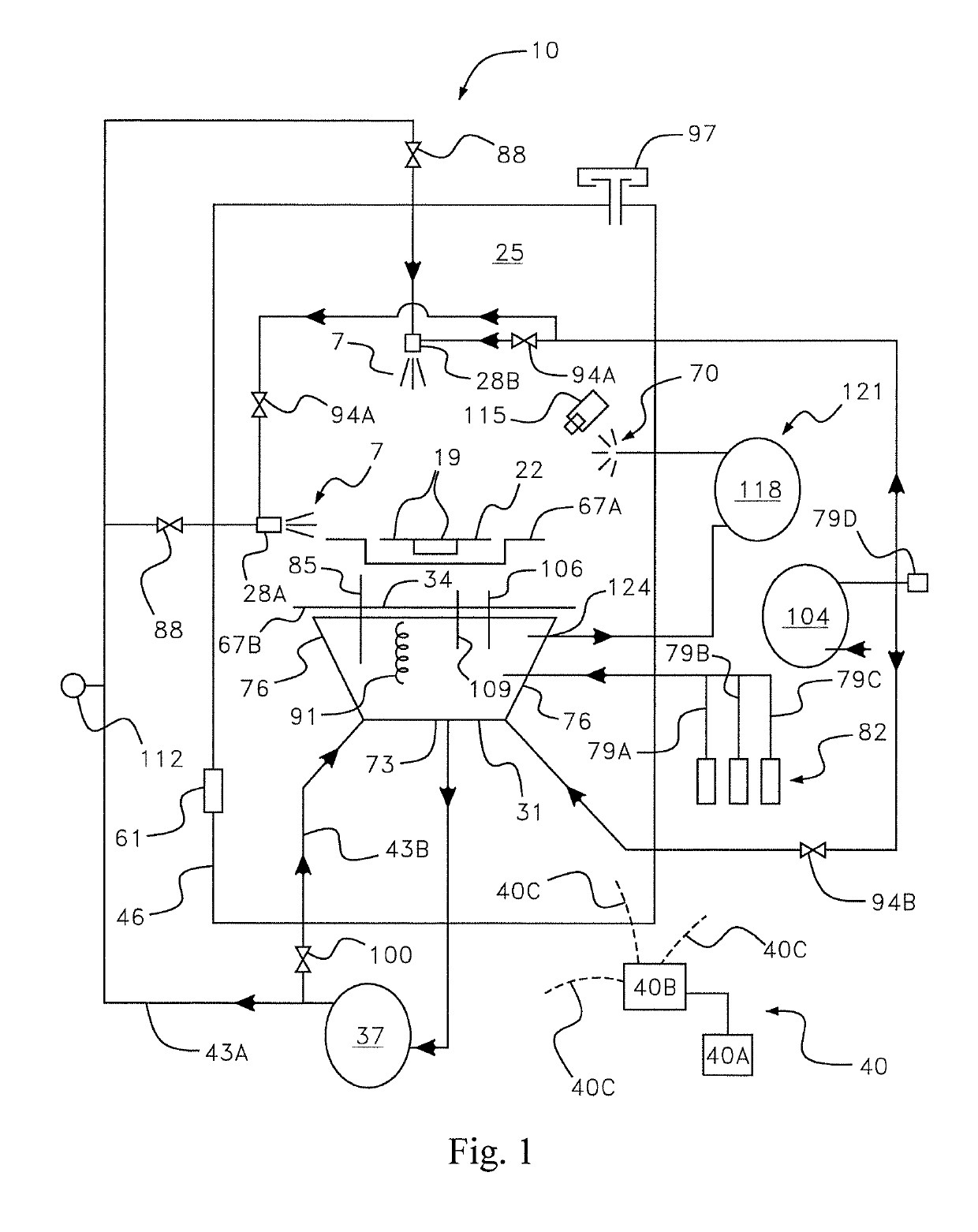
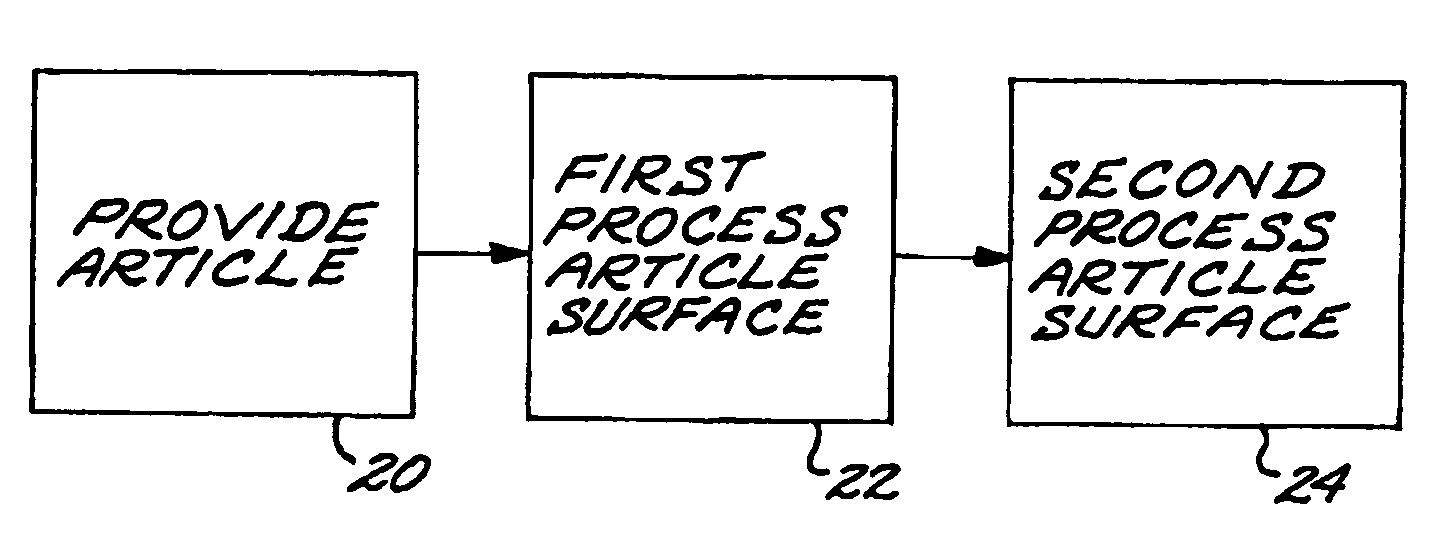
Preparation of an article surface having a surface compressive texture
ActiveUS8024846B2Reduce surface roughnessSmooth surface finishEngine manufactureBlade accessoriesSurface roughnessMaterials science
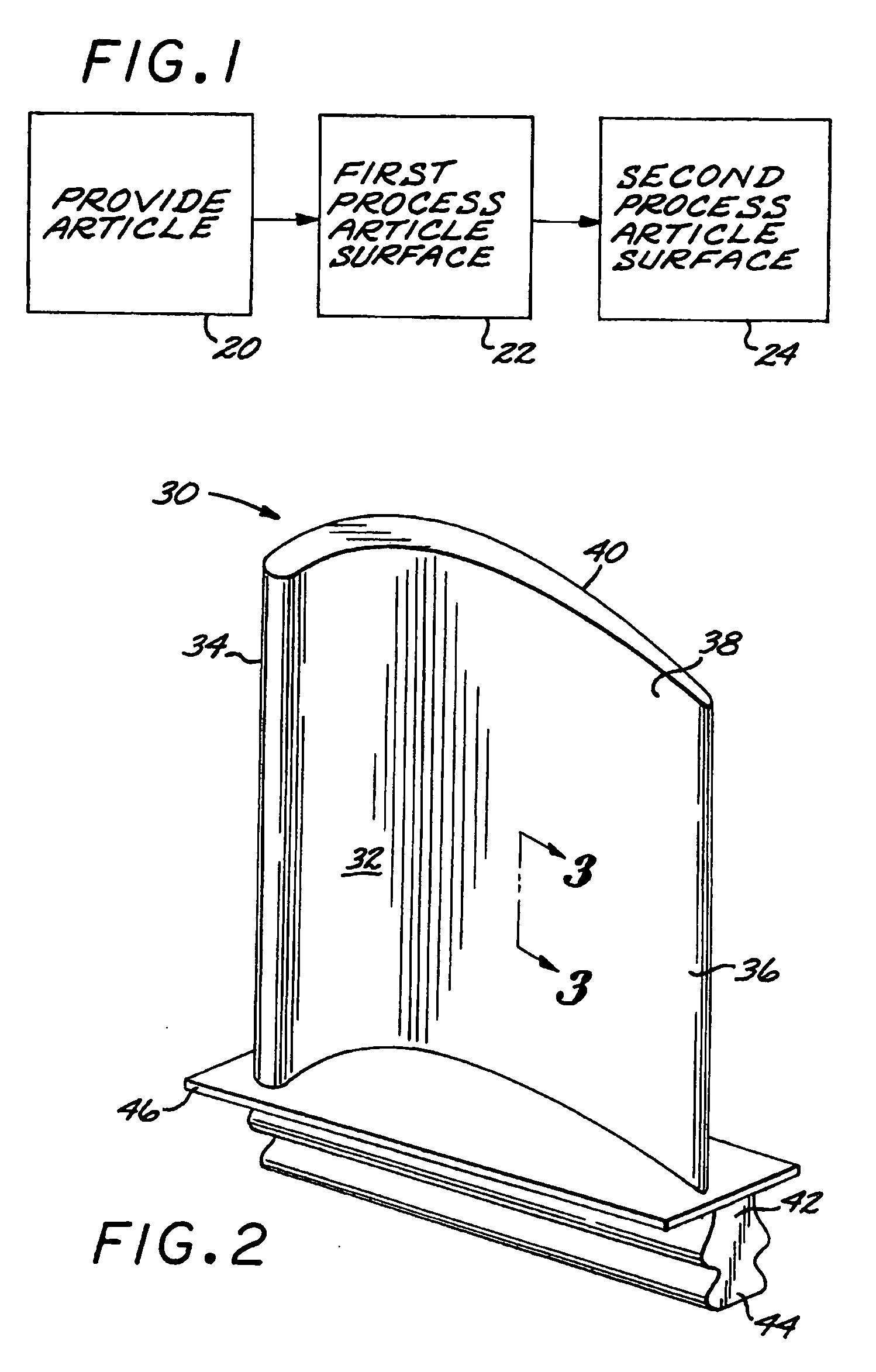
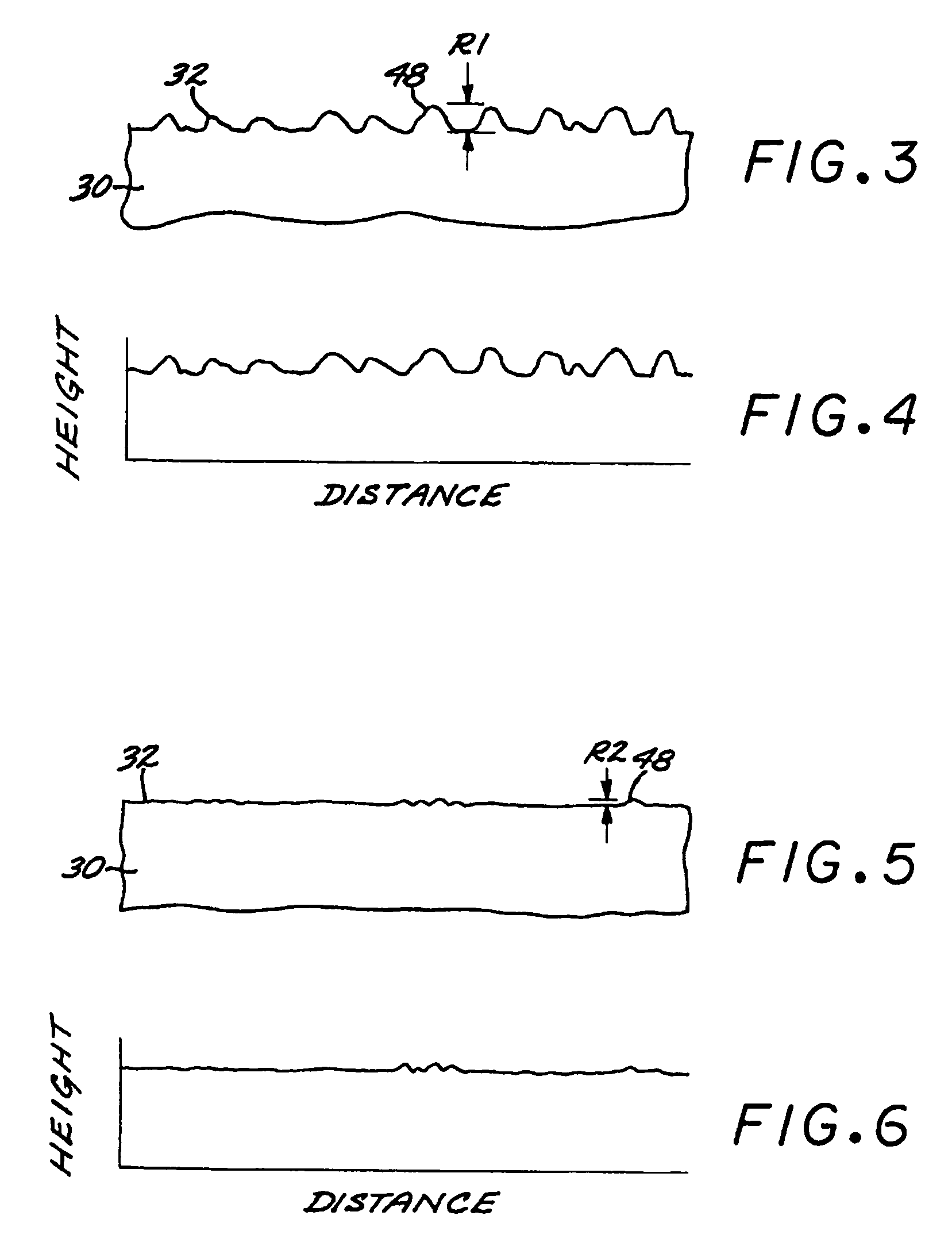
A method for preparing a surface includes providing an article having an article surface, thereafter first processing the article surface to establish a first residual compressive stress state and a first surface roughness in the article surface, and thereafter second processing the article surface by surface compressive texturing to establish a second residual compressive stress state and a second surface roughness in the article surface. The second surface roughness is quantitatively less than the first surface roughness, and substantially no material is removed from the article surface in the step of second processing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
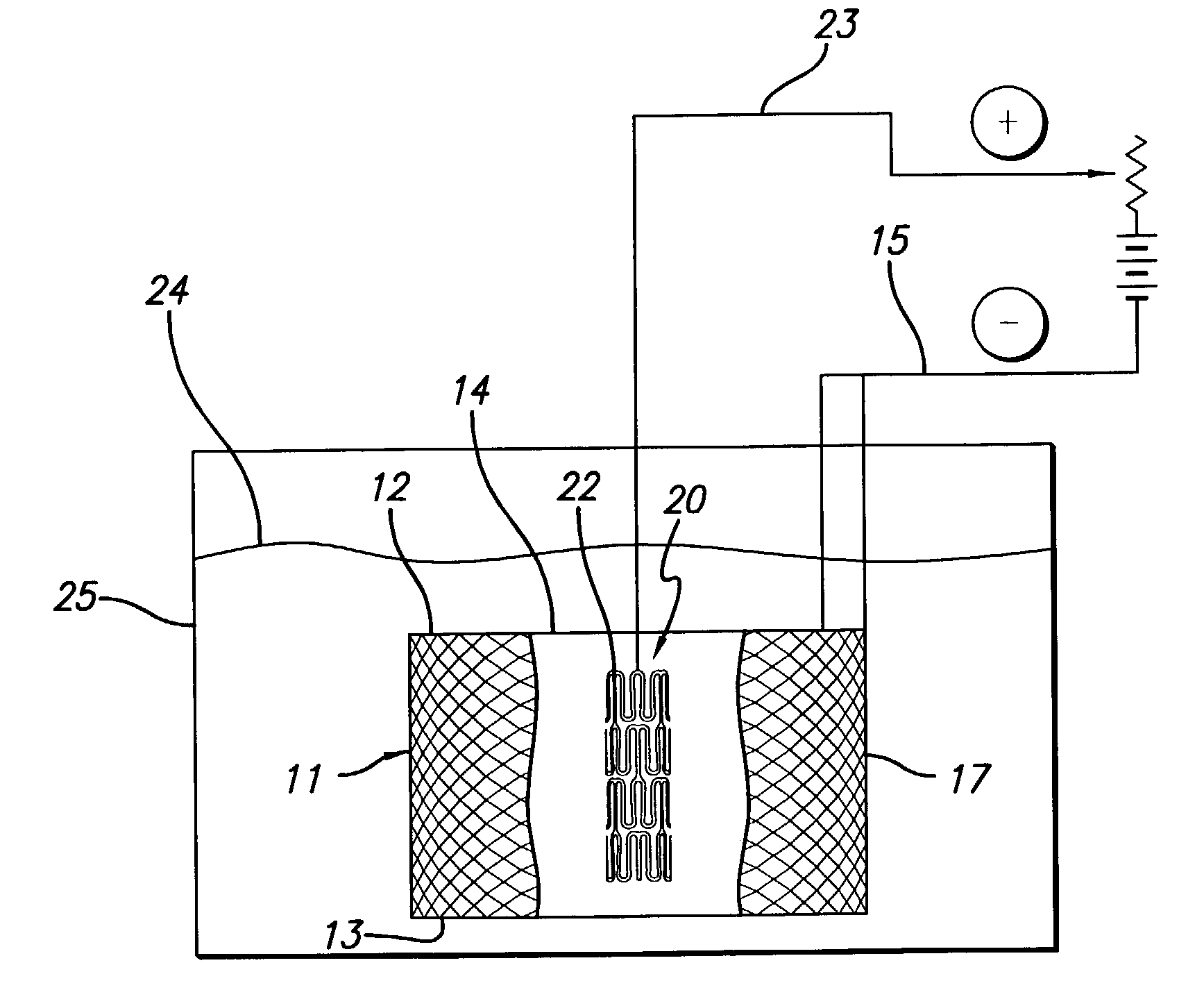
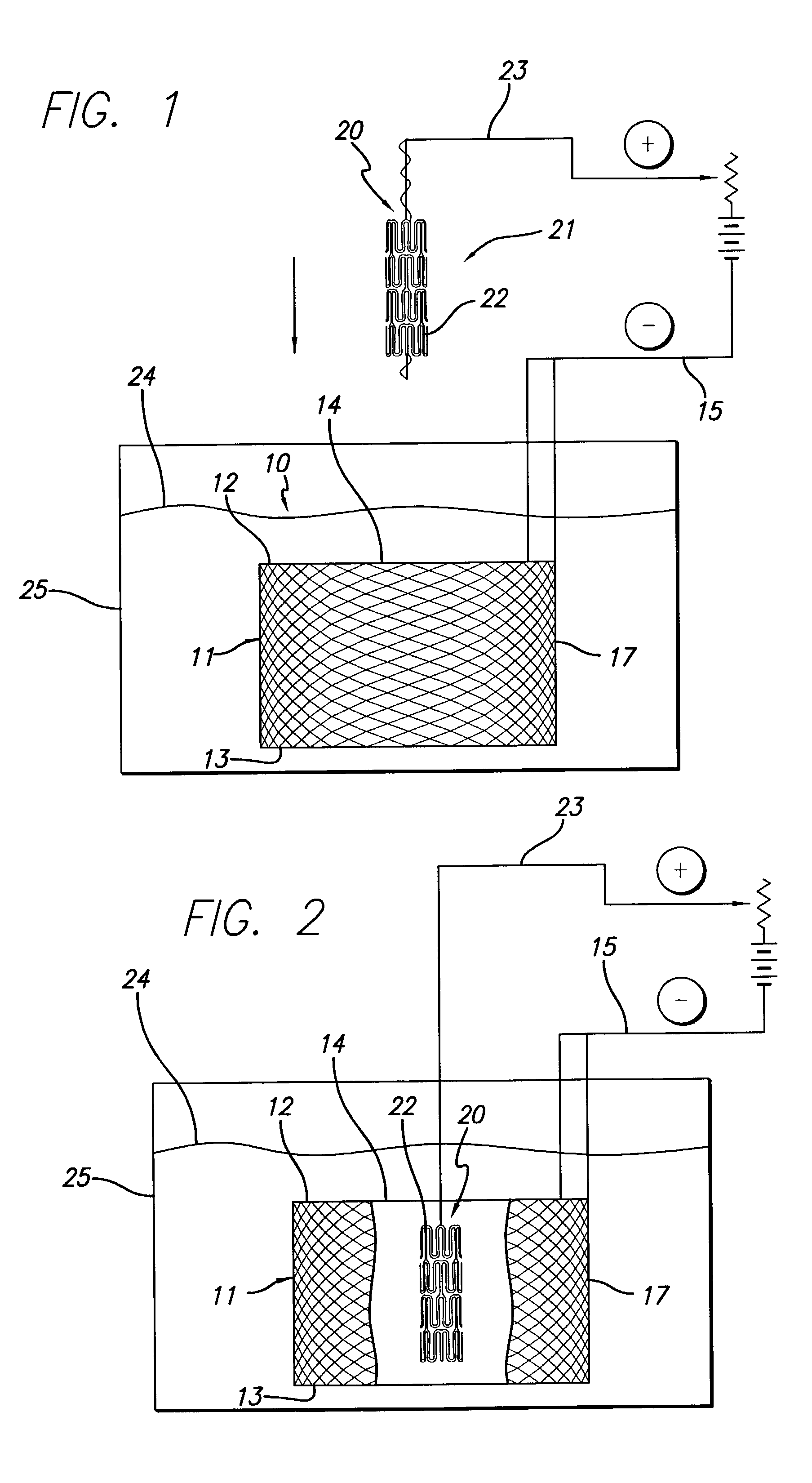
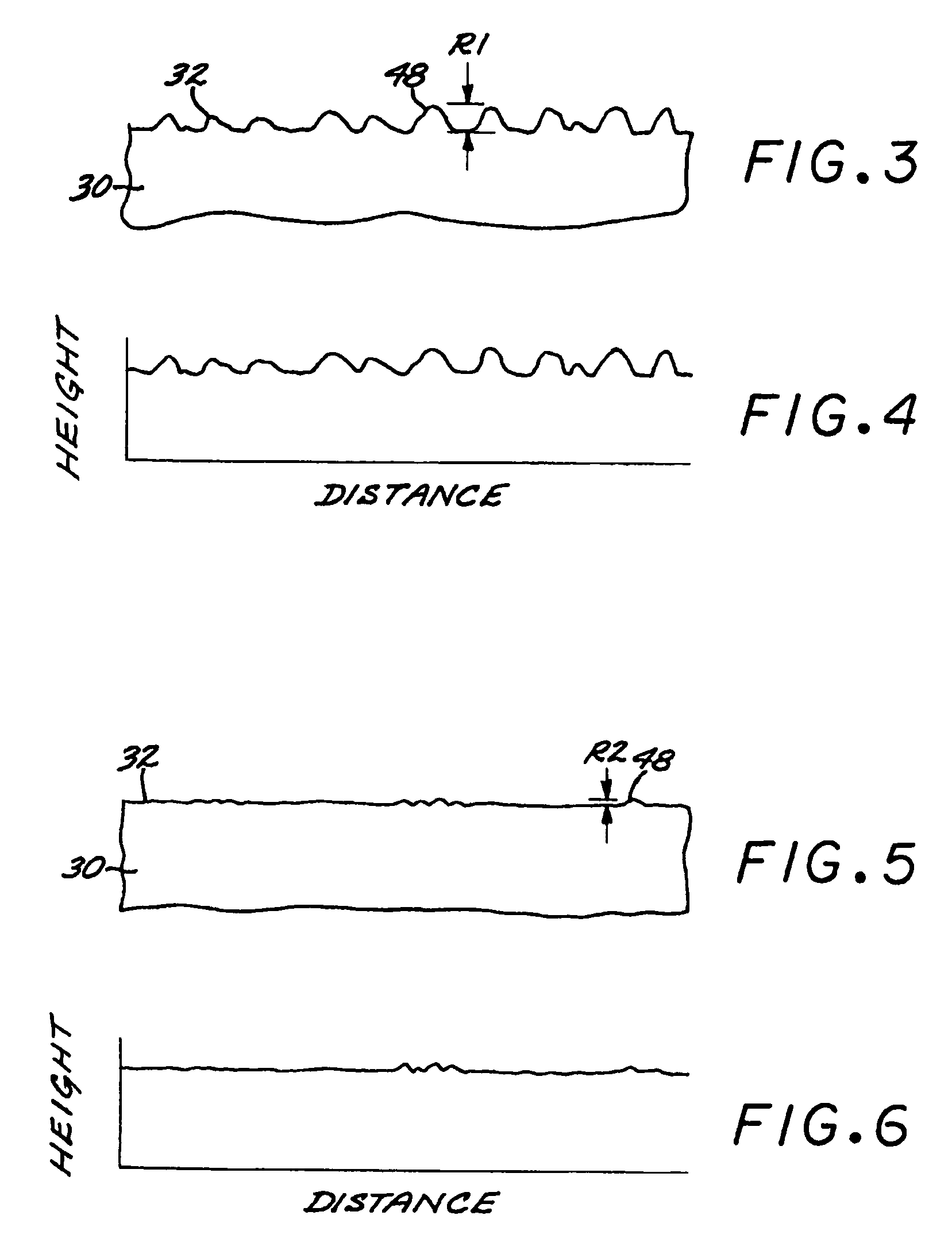
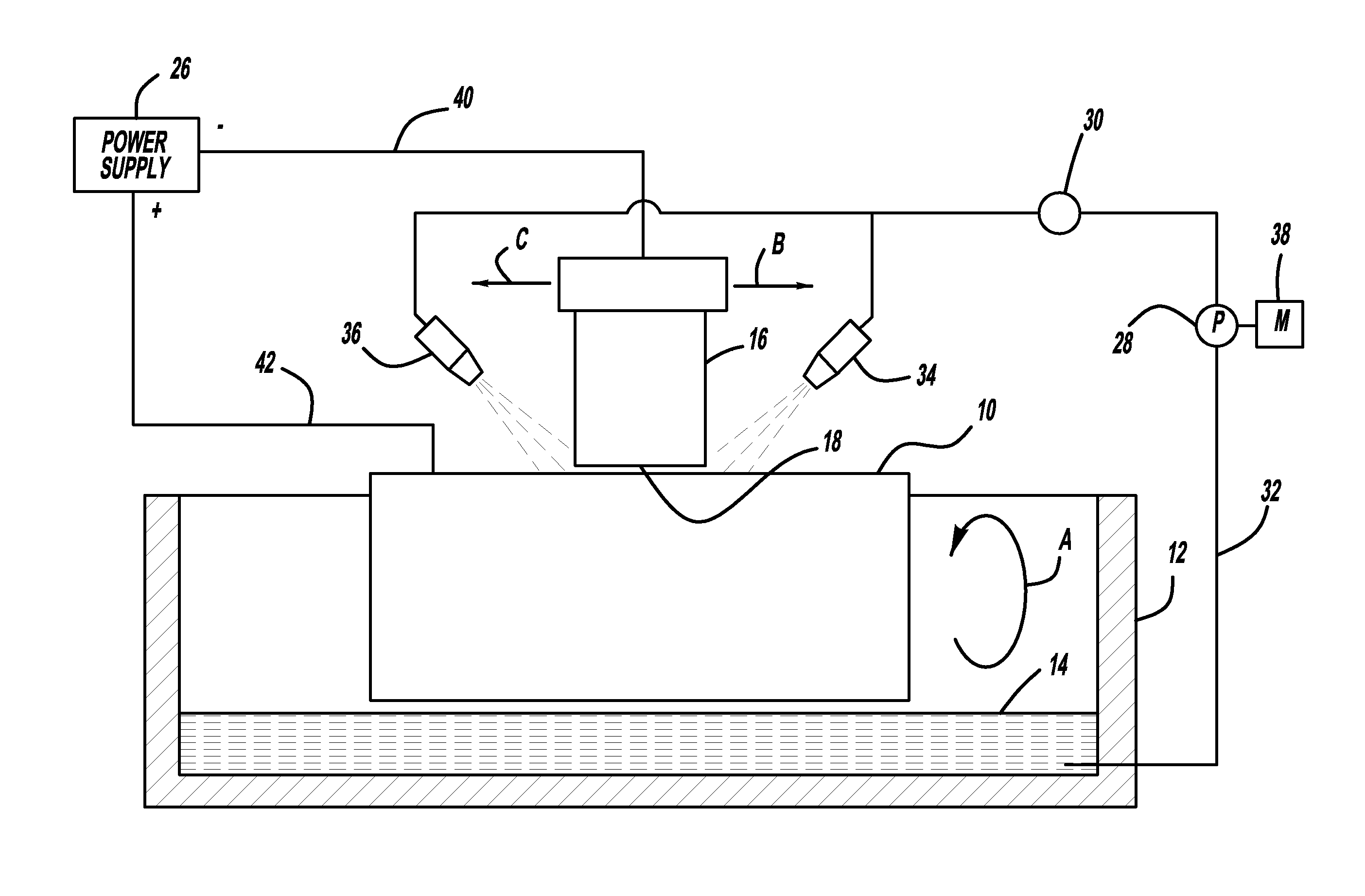
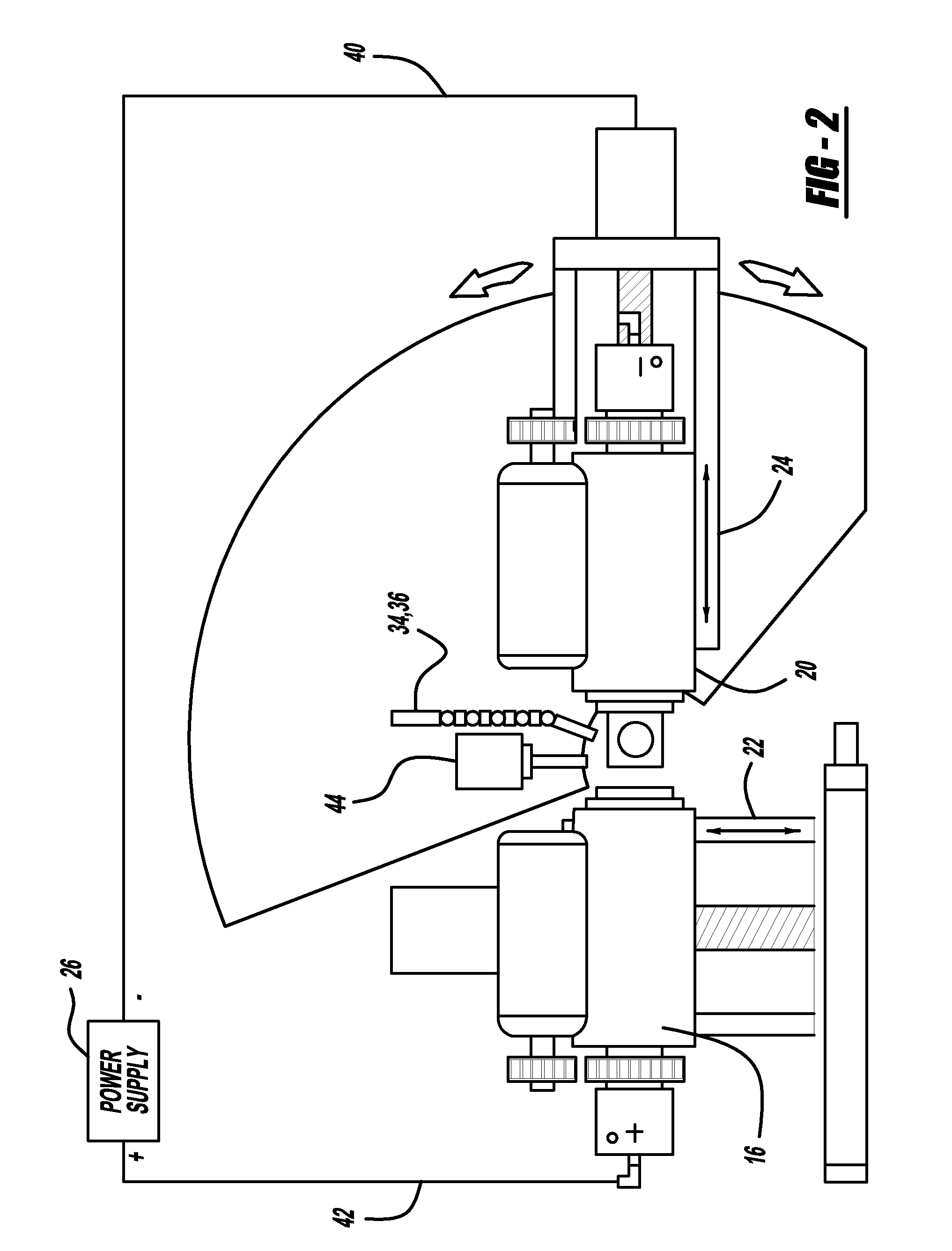
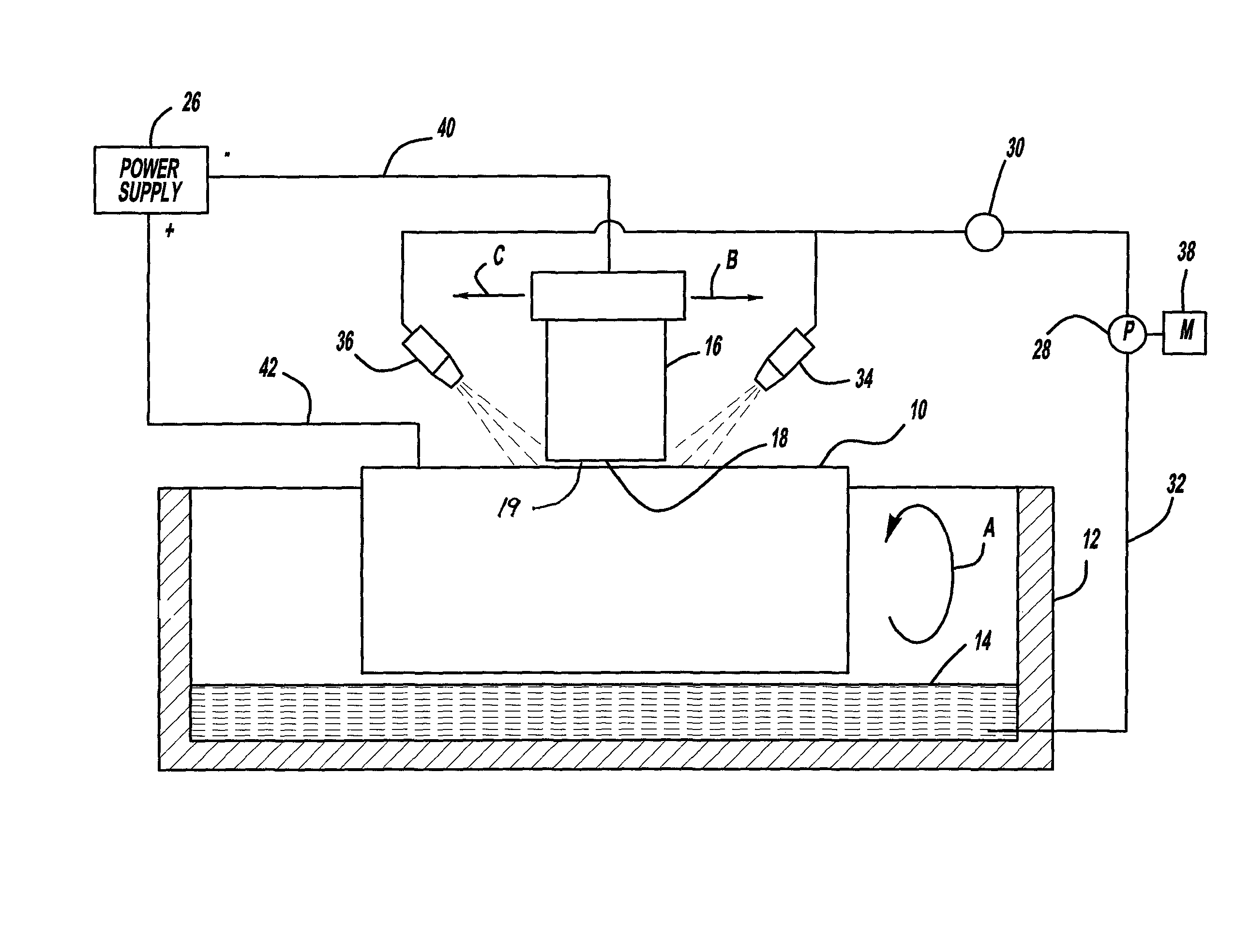
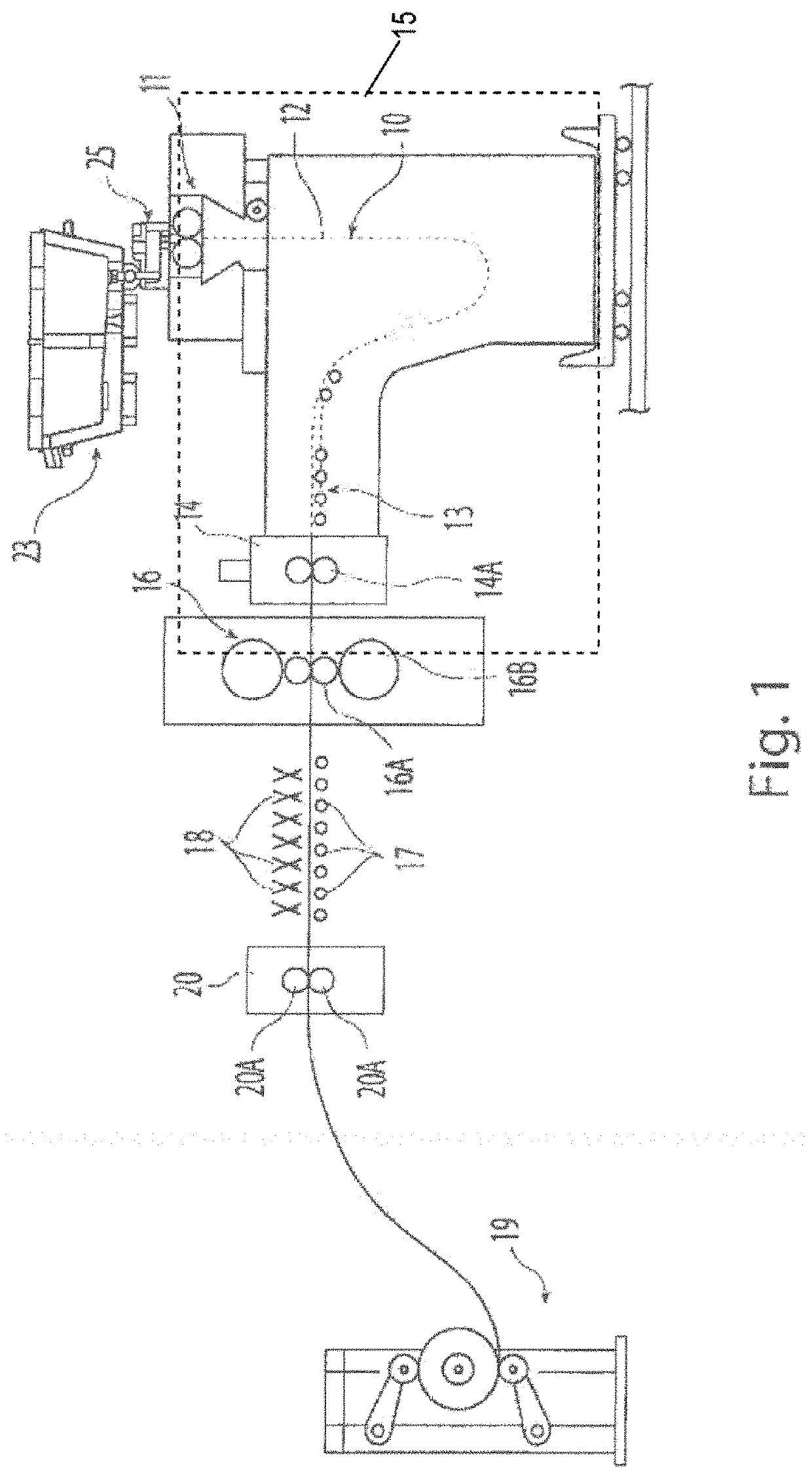
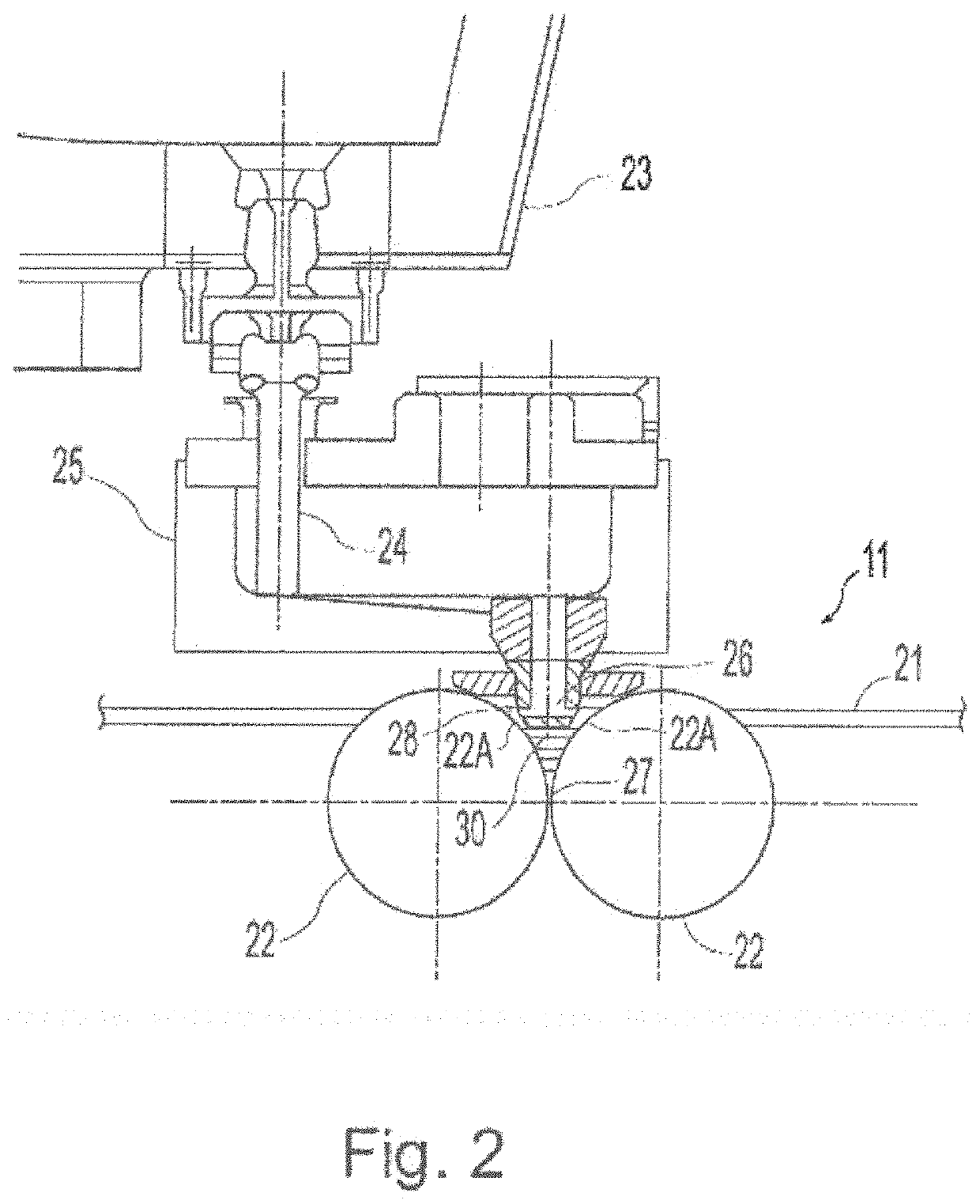
Electrolytic microfinishing of metallic workpieces
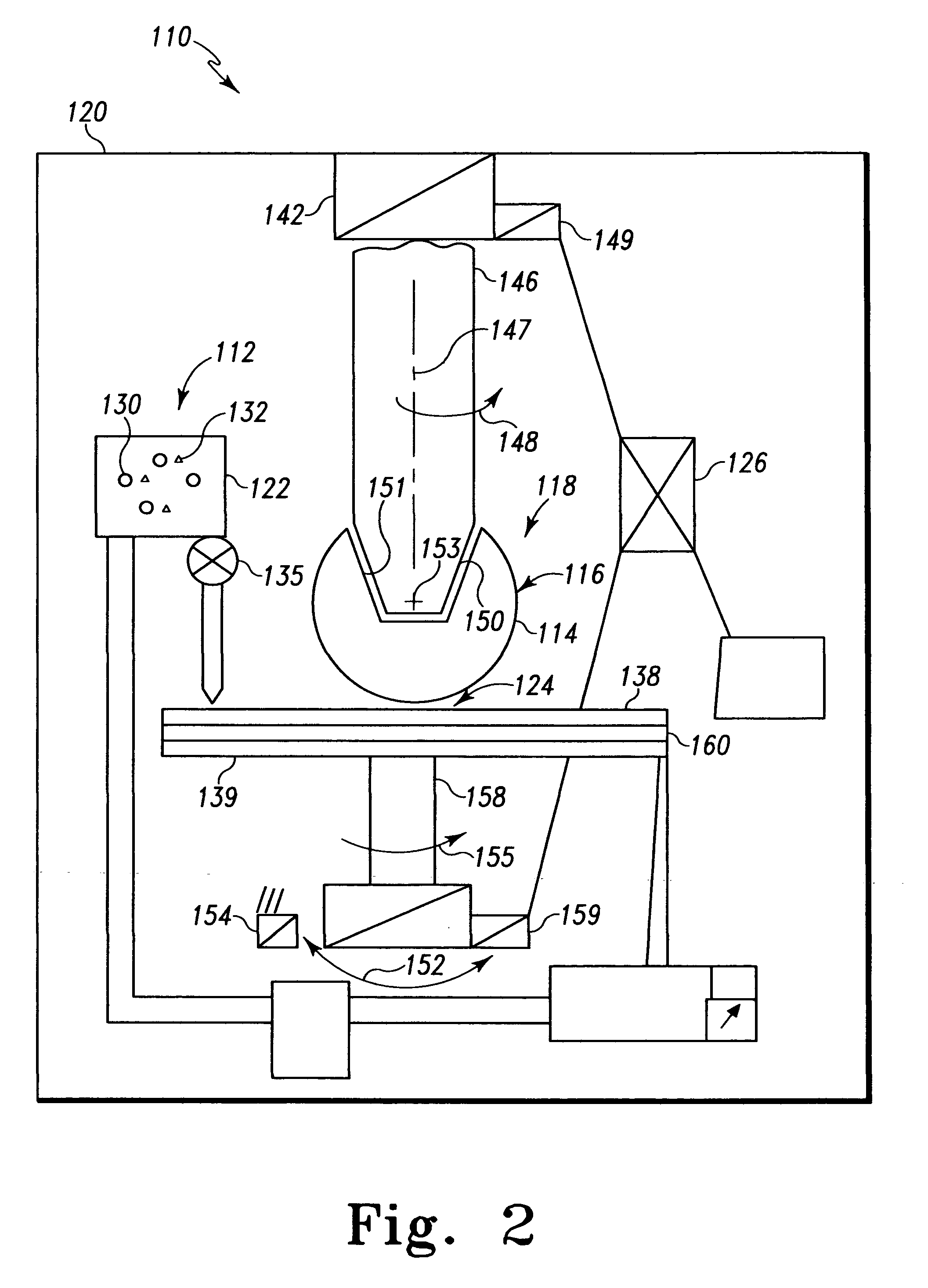
The invention is an electrolytic microfinishing process which utilizes a conductive tool as a cathode and a conductive workpiece as an anode both connected to a power supply. Electrolytic fluid is pumped between the tool and workpiece, creating a decomposition of the workpiece surface allowing the surface of the workpiece to be removed or wiped away by the interaction of the flowing electrolyte and rotation of the tool without generating any heat at a rate significantly faster than any other known machining process. The tool has no contact with the workpiece and accordingly, requires very low clamping loads to hold the workpiece in the spindle during the finishing operation. Due to the low clamping loads, the distortion of the workpiece is completely eliminated. Modulating the power supply during the work cycle allows the use of a single tool for both roughing and finishing as a continuous cycle to significantly provide surface finishes previously unobtainable.
Owner:THIELENHAUS MICROFINISH
Method And Apparatus For Surface Finishing And Support Material Removal (Deci Duo)
ActiveUS20190176403A1Smooth surface finishAvoid damage to partsAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySpray nozzleSolid particle
Apparatuses and methods for removing support material from and / or smoothing surfaces of an additive-manufactured part are disclosed. Apparatuses may include a spraying chamber, a support surface within the spraying chamber, and one or more nozzles having the ability to spray a fluid at the additive-manufactured parts. The fluid may include a liquid and solid particles carried by the liquid. The support surface may have the ability to support the additive manufactured part. The apparatus may include a tank having the ability to hold at least some of the fluid. A heater may be included for heating the fluid to a desired temperature.
Owner:POSTPROCESS TECH INC
Preparation of an article surface having a surface compressive texture
ActiveUS20070175030A1Reduce surface roughnessSmooth surface finishEngine manufactureBlade accessoriesSurface roughnessMaterials science
A method for preparing a surface includes providing an article having an article surface, thereafter first processing the article surface to establish a first residual compressive stress state and a first surface roughness in the article surface, and thereafter second processing the article surface by surface compressive texturing to establish a second residual compressive stress state and a second surface roughness in the article surface. The second surface roughness is quantitatively less than the first surface roughness, and substantially no material is removed from the article surface in the step of second processing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Orthopaedic component manufacturing method and equipment
ActiveUS20080081539A1Reduce break-in wearLong orthopedic implant lifeSurgeryLapping machinesSurface roughnessSlurry
A method of reducing the surface roughness of articulating surfaces of orthopaedic implants is provided. The method includes the steps of providing an abrasive particle providing a chemical including at least one of an oxidant, a corrosion inhibitor, a complexing agent and a surfactant, combining the chemical with the abrasive particle to form a slurry, and polishing the implant with the slurry.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Sheet moulding compound (SMC) with ventilating structure for entrapped gases
InactiveUS7179517B2Promote resultsSmooth surface finishSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationFilling materialsMachining process
Moulding material comprising a core layer, a reinforcement layer provided on each surface of said core layer, and a layer of a surfacing material provided on a reinforcement layer. The core layer comprises a core resin material and a filler material. The reinforcement layer comprises a fibrous reinforcement material and a reinforcement resin material. The reinforcement layer further comprises a conduit to allow gases to pass out of the moulding material via the reinforcement layer during processing of the moulding material whereby the conduit structure is formed by said reinforcement material.
Owner:GURIT (UK) LTD
Lightweight flexible mandrel and method for making the same
ActiveUS8534339B2Easy to useSmooth surface finishArc welding apparatusDough shapingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A mandrel for processing a part comprises an outer sleeve and a generally flexible inner core. The outer sleeve includes at least one flexible portion along its length allowing the sleeve to flex to a desired contour.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method and apparatus for roll grinding
InactiveCN102725102ASolution to short lifeReduce the numberRevolution surface grinding machinesRolling equipment maintainenceEngineeringGrinding wheel
In one aspect, a process for roll grinding employs a grinding wheel that is porous and permeable. In another aspect, a process for grinding mill rolls includes dressing the grinding wheel as the wheel traverses the surface of a mill roll. Other aspects relate to a system, e.g., a mill roll grinding machine, or parts thereof, in which a dressing tool contacts the wheel as the wheel grinds the surface of the mill roll. In specific examples, the wheel and a rotary dressing tool are maintained in contact as the wheel traverses the surface of the mill roll.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIVES INC +1
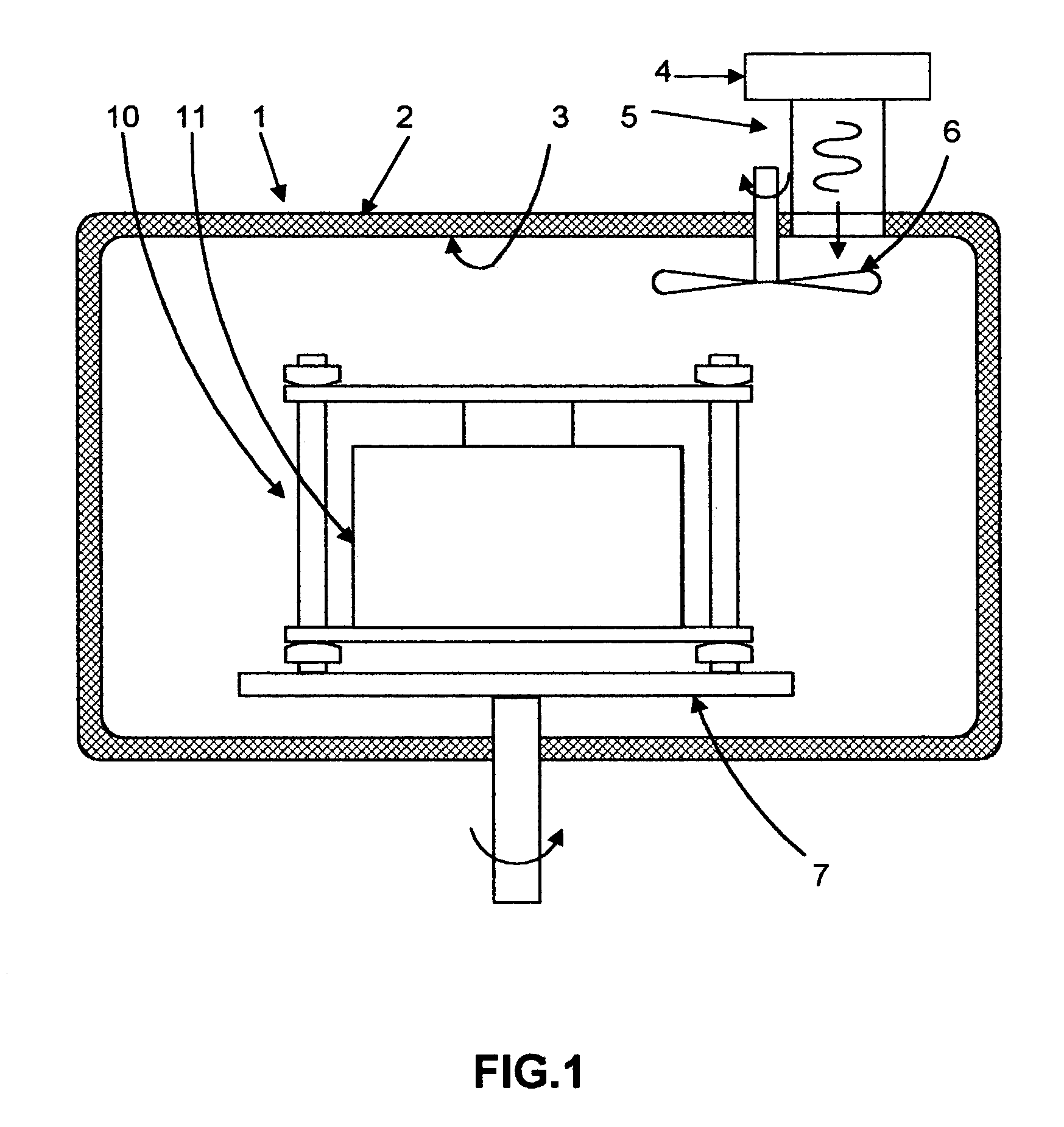
Microwave molding of polymers
InactiveUS7223087B2Efficient heatingEasy to makeAuxillary shaping apparatusCoatingsMicrowave ovenWear resistant
A mold for relatively uniform heating and molding of a work material to form a workpiece using a microwave oven, includes upper and lower mold members and a sidewall mold member. The mold members are formed from materials selected to have an approximately equal effective thermosensitivity. The effective thermosensitivity of work material is its dissipation factor divided by the product of its dielectric constant, density and specific heat. The effective thermosensitivity of the material of mold layer of each mold member is its dissipation factor divided by the product of its dielectric constant, density, and specific heat and multiplied by the fraction of the mass of its mold layer divided by the total mass of this mold member. A metal sleeve is formed on an inner surface of the sidewall mold member with microwave absorbing material formed on the outside thereof and inner surfaces of the end mold members may also be coated with metal or other highly thermally conductive and wear resistant material.
Owner:AKOPYAN RAZMIK
UV Laser Exposure Of Housings And Components Of Door Drives And Door Closers
InactiveUS20130227815A1Easy to wearImprove wear resistanceBuilding braking devicesIncreasing energy efficiencyUv laserEngineering
A door operator or a door closer having at least one housing and at least one piston supported to be movable in a reception of the housing. The surfaces of the reception and / or of the at least one piston have been treated by exposure to electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:DORMA GMBH & CO KG
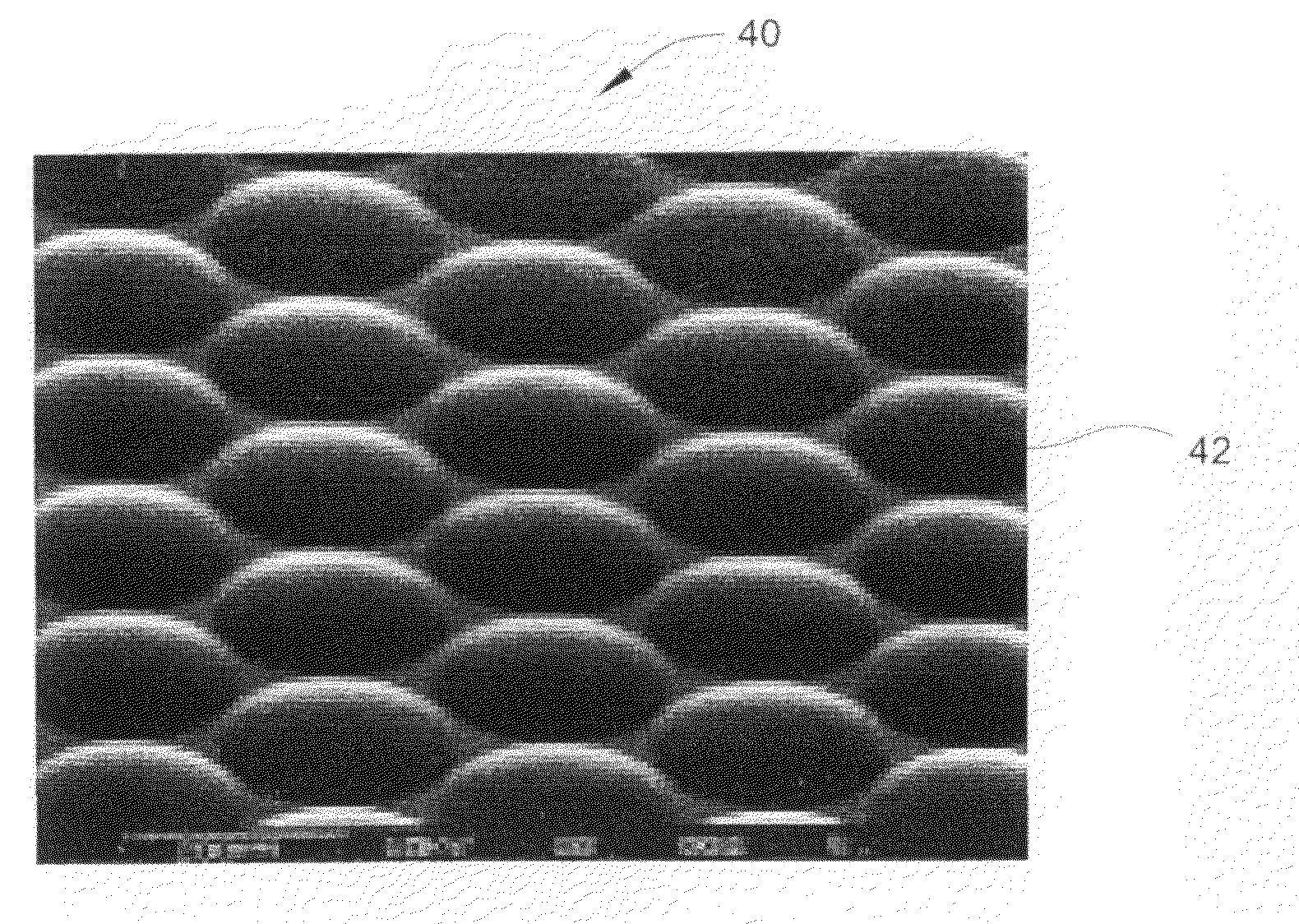
Method of fabricating small dimensioned lens elements and lens arrays using surface tension effects
ActiveUS20090283927A1Superior surface smoothnessAccurate shapeOptical articlesLensLens materialsCurve shape
A method is disclosed of implementing lens elements or lens arrays having dimensions ranging from a few centimeters down to the micro-scale or nano-scale using the surface tension of the lens material in a molten state to allow the curved shape of the lens to be precisely defined. The method has useful application in the fabrication of lens elements and lens arrays out of a large variety of material types, including elemental materials, as well as compound materials and alloys. The method also allows the implementation of lenses having far superior surface smoothness compared to other approaches, as well as very accurate lens shapes. The method allows the making of high quality lenses and lens arrays, wherein the diameter of the lenses are on the order of a few microns or less. Convex, concave, plano-convex, plano-concave, compound lenses, and many other types of lens shapes can be implemented using the method of the present invention.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
Rotary wheel bracket clamp holder device and spinning machining method for large thin-wall curved face product
The invention provides a rotary wheel bracket clamp holder device and a spinning machining method for a large thin-wall curved face product. The rotary wheel bracket clamp holder device comprises a tool rod, a wheel base and a spinning rolling wheel which is in a three-arc combined shape. The spinning machining method for the large thin-wall curved face product comprises the steps that the periphery of a plate-shaped blank with good ductility is fixed to a tool or a die, the whole is put on a large vertical lathe platform, a spinning device is fixed to a lathe saddle, a lathe programs a curved face circular curve, rapidly spins the blank and carries out feeding machining according to an arc track in a layered circular step-by-step manner, and the blank plastically deforms under the action of the rotary wheel and forms a curved face in an accumulation manner. By means of the rotary wheel bracket clamp holder device and the spinning machining method, the product quality and the production benefits are greatly improved, it is ensured that the fracture phenomenon caused by excessive stretching cannot occur during the stretching process, the surface smoothness degree is kept, and no scratches appear on the surface.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROSPACE ELECTROMECHANICAL EQUIP RES INST
Preparing tool surfaces for composites
ActiveUS10118315B1Eliminate porositySmooth surface finishAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsSmooth surfaceMicrostructure
Techniques for producing composites outside of an autoclave that have smooth surface finishes are disclosed. The smooth composite surface, free of porosity, can be fabricated by curing the prepreg in a tool that includes a novel microstructure. In conventional composite manufacturing, some degree of porosity appears to originate from trapped gas bubbles that form during curing. The microstructure can provide a mechanism for the gas bubbles to escape from the tooling, thereby eliminating porosity and yielding a smooth surface finish on the out-of-autoclave composite. The microstructure can be applied to the tool surface using an inkjet process applying an acrylic resin curable with ultraviolet light.
Owner:SURFX TECH
Low-thermal-inertia intake ports for port-injected, spark ignition engines and an associated manufacturing method
ActiveUS7360512B1Low thermal inertia characteristicEasy dischargeAir coolingElectric ignition installationHigh surfaceHydroforming
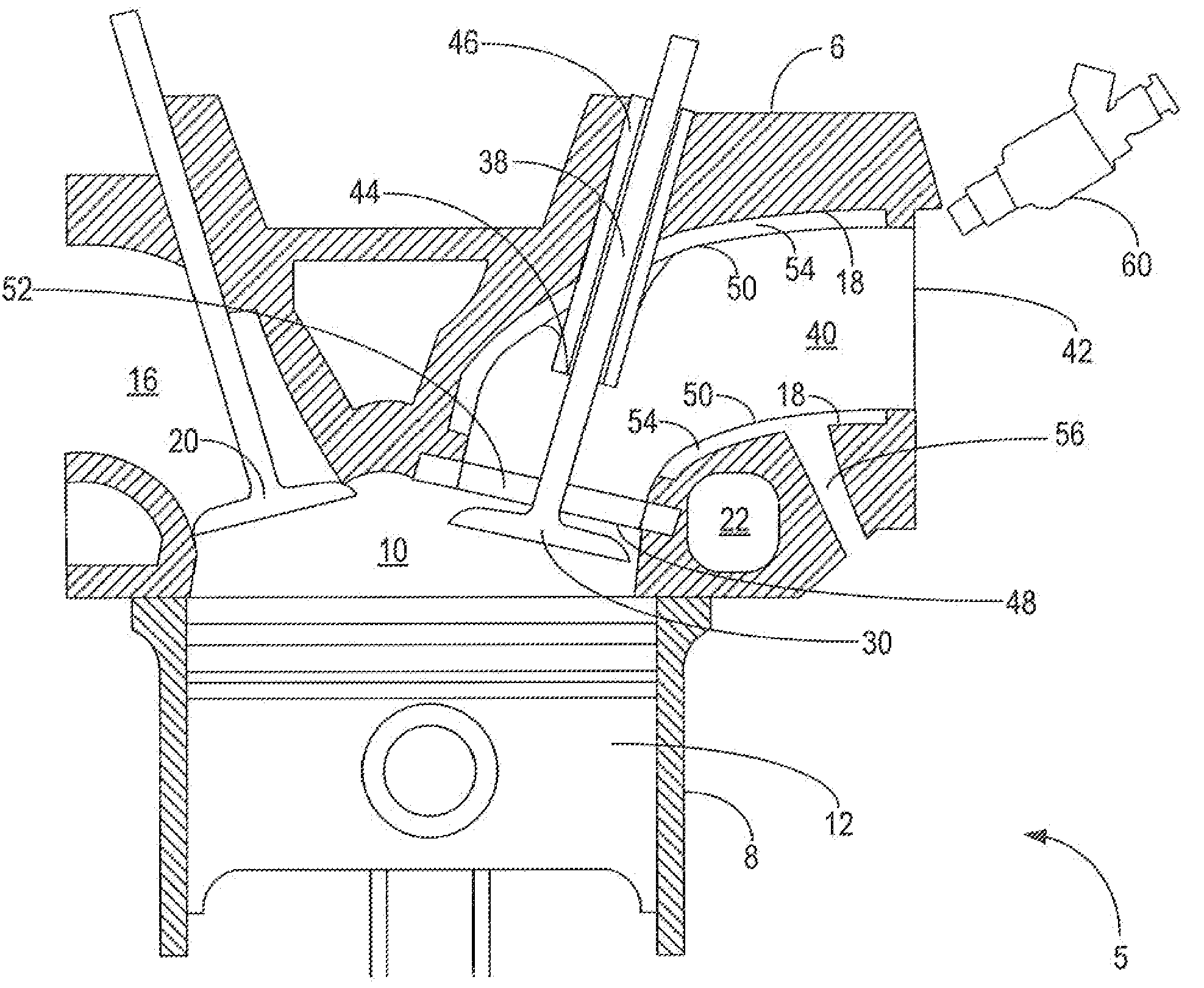
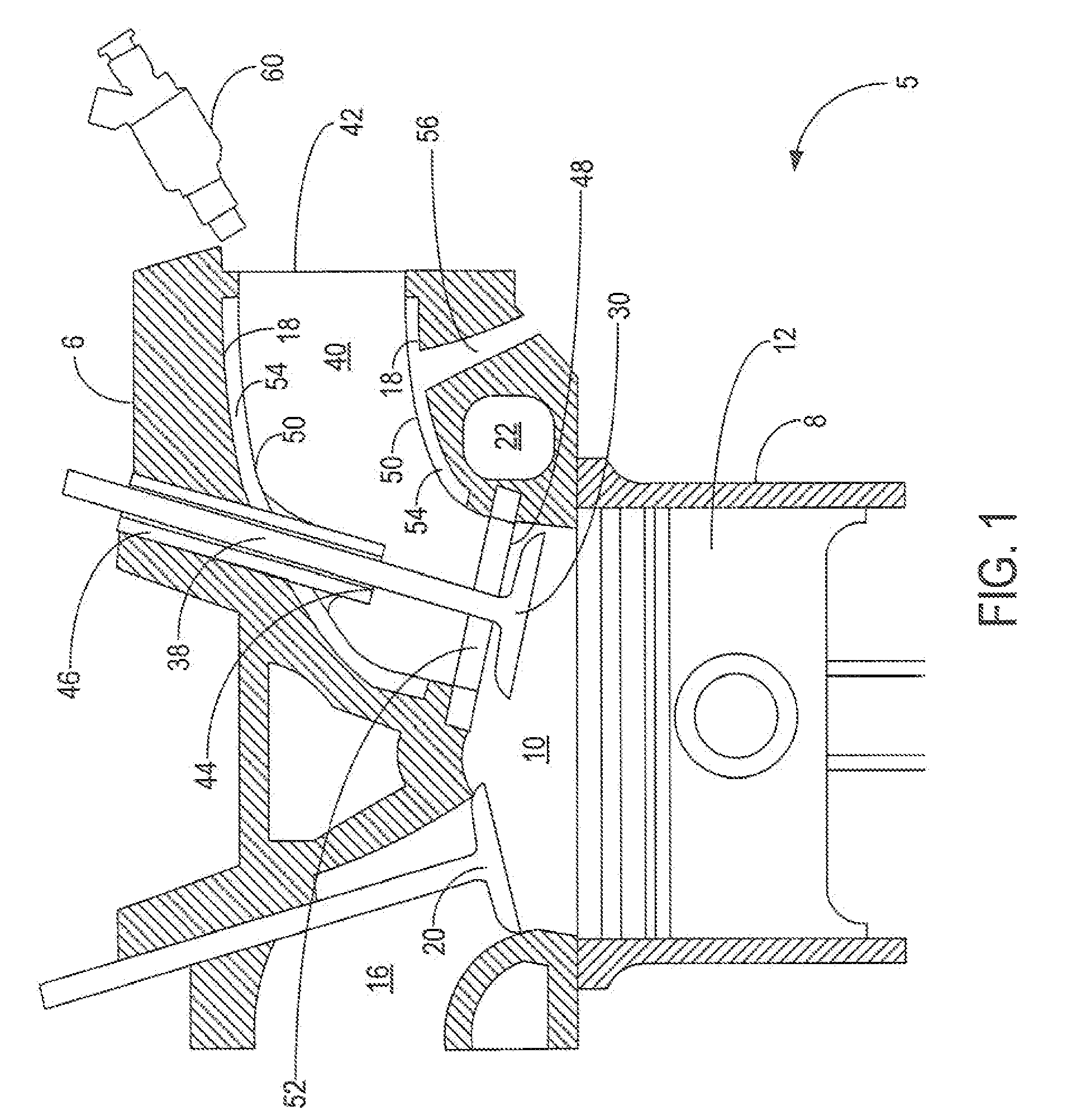
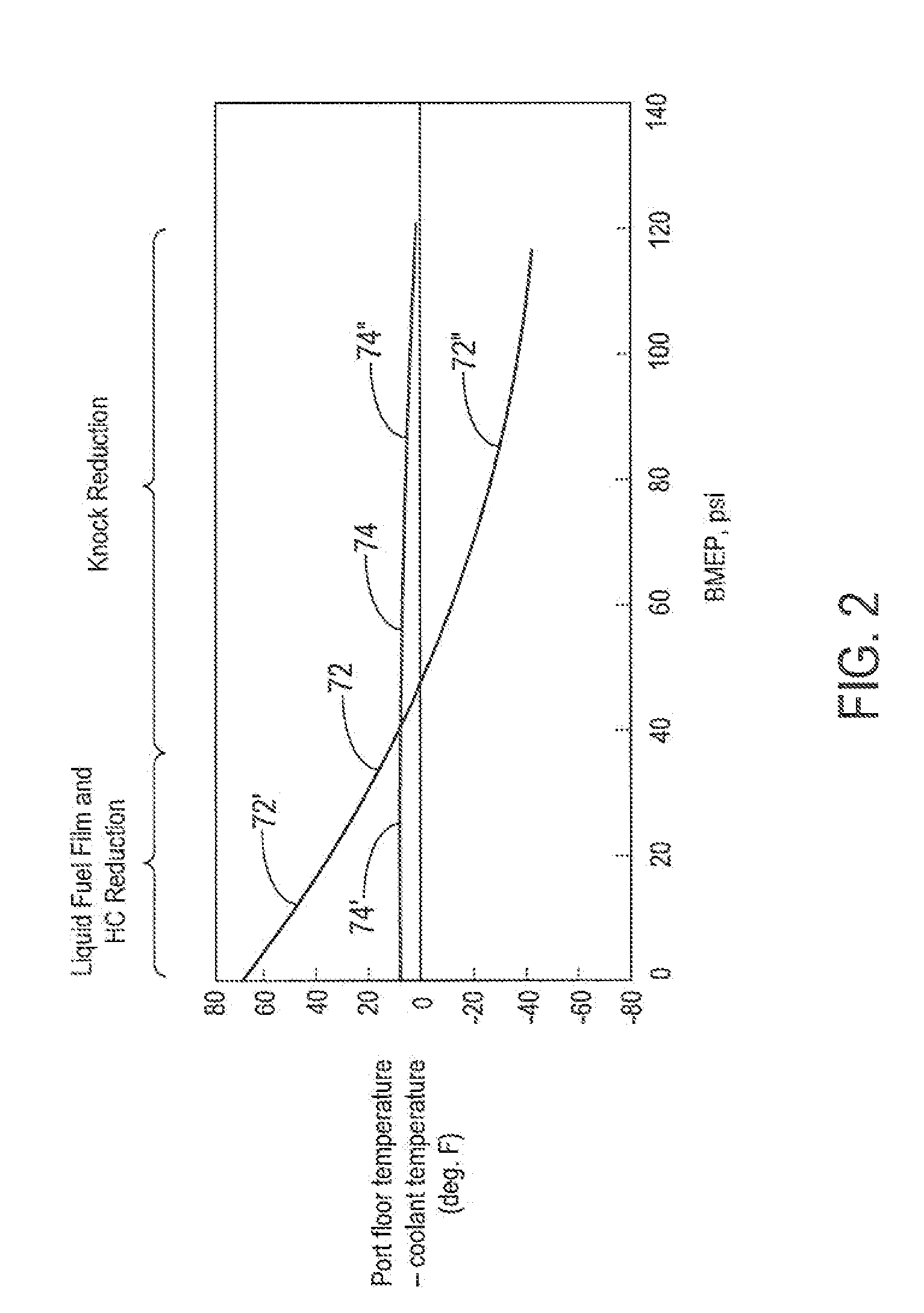
The present invention provides an intake port design that provides a low thermal inertia characteristic, thereby decoupling the surface temperature of the intake port walls from that of the coolant through use of an air gap formed between the intake port and the cylinder head. At idle and part-throttle, the intake port is at a higher surface temperature yielding better cold-start emissions, better mixture preparation, and less dense intake charge (“thermal throttling”) for better fuel economy. At wide-open-throttle, the intake port is at a lower surface temperature yielding better volumetric efficiency for improved torque and reduction in knocking tendency enabling higher compression ratio for improved fuel economy and performance. The intake port design of the present invention can be manufactured with a hydroform manufacturing process resulting in improved dimensional consistency and smooth surface finish. Additionally, the process eliminates some cylinder head machining processes.
Owner:FCA US
Insecticidal coils
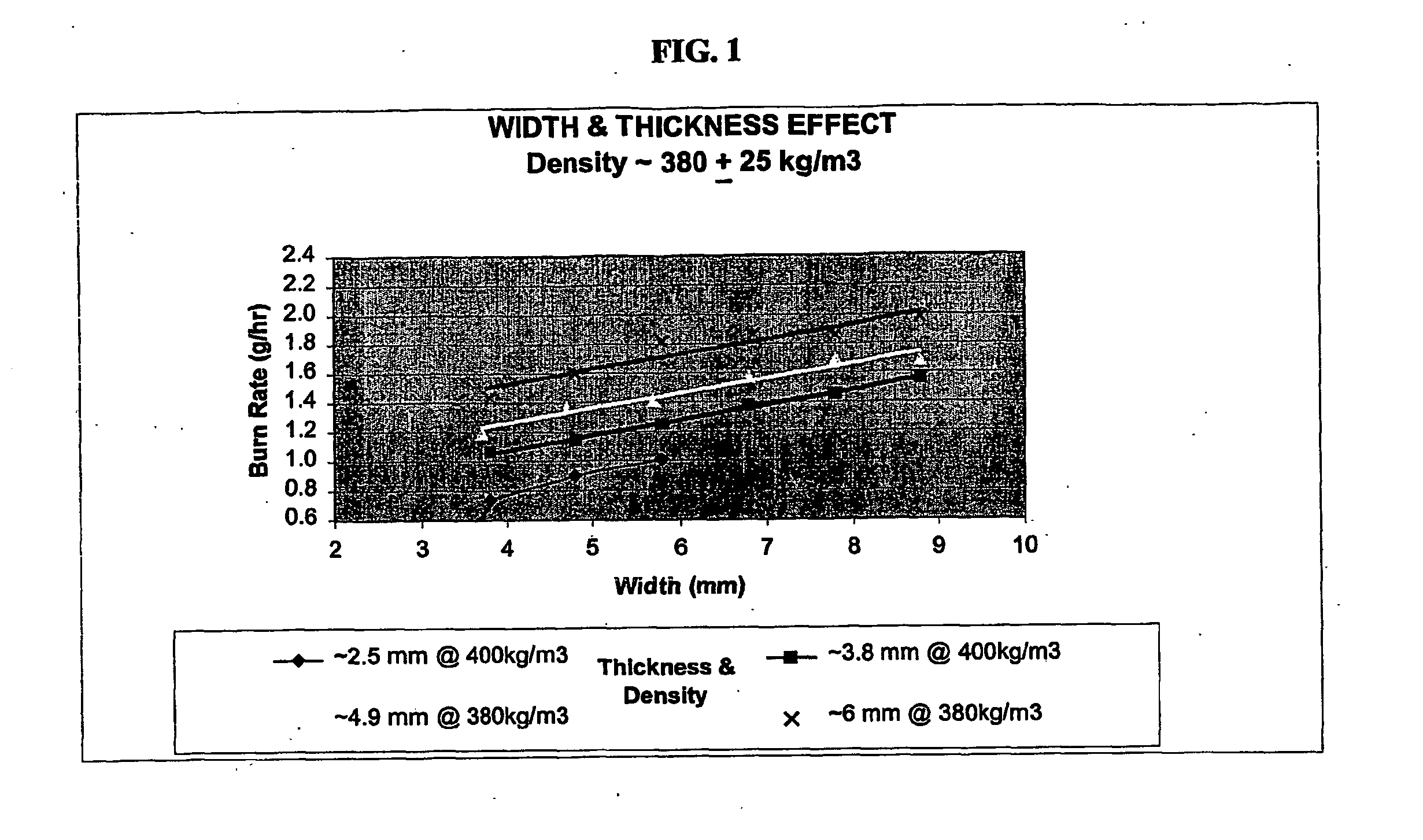
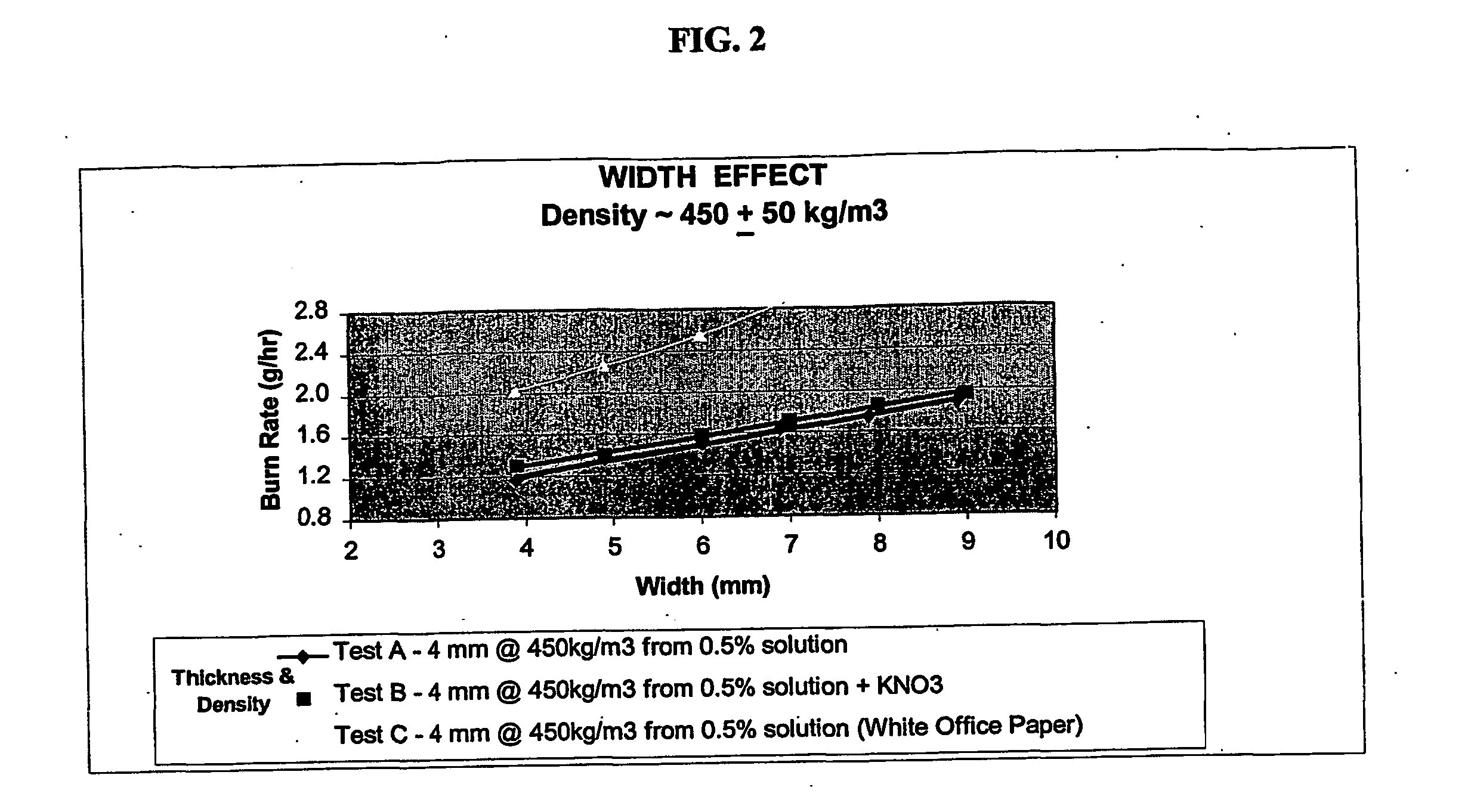
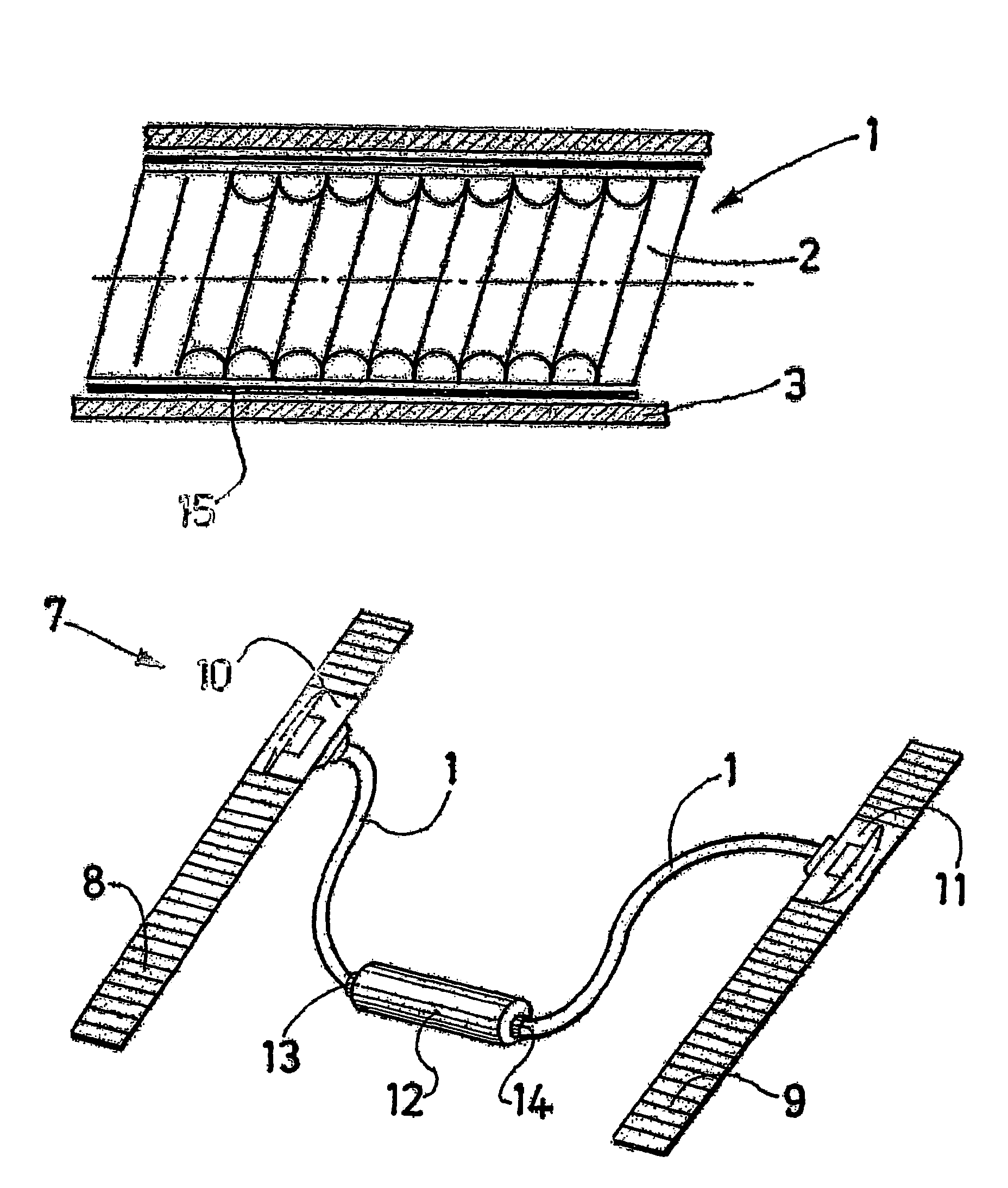
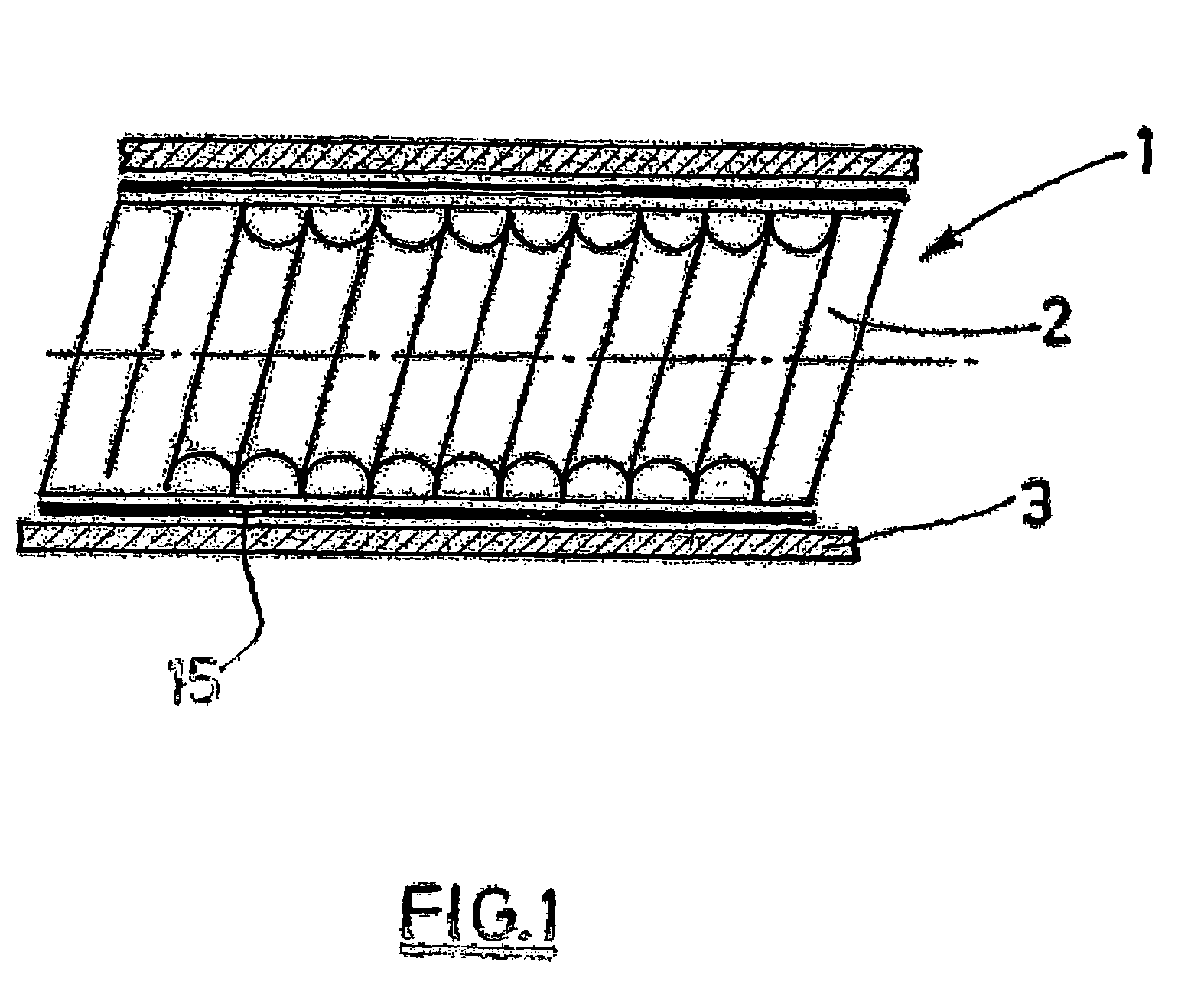
InactiveUS20050249766A1Increase burn rateProvide rigidityBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismChemistryPesticide
A combustible pesticidal product is disclosed which comprises a structural element formed from a pulp of organic fibrous material, cellulose fibres, wood free fibres or mixtures thereof, the product including one or more pesticides which product on combustion emanates the pesticide into the atmosphere. Typically the combustible product will be a mosquito coil which has been impregnated with one or more insecticides effective against mosquitoes. On combustion of the coil, insecticide is emanated into the atmosphere for a period of 7-8 hours.
Owner:RECKITT BENCKISER AUSTRALIA
Device for transmitting a rotational movement by means of a smooth shaft
InactiveUS7472939B2Reduce vibrationEliminate the effects ofYielding couplingShaft for rotary movementSurface finishMobile vehicle
The invention concerns a device for transmitting a rotational movement comprising a flexible shaft and a sheath inside which the flexible shaft is housed, said sheath being arranged in order to allow the rotation of said shaft inside said sheath. The outer surface of the flexible shaft is machined so as to have a substantially smooth surface finish. The invention also concerns an adjustment system for a motor vehicle seat comprising such a device.
Owner:INDERFLEX TECHNOFLEX
Coating Soluble Tooling Inserts
ActiveUS20160339612A1Reduce surface tensionSmooth surface finishLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsCompression moldingPolymer
The surface of a tooling insert is coated with a polymer layer having a low surface energy in order to cover surface irregularities and thereby provide a smooth surface against which a composite part may be compression molded.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
High friction rolling of thin metal strip
Described herein are thin metal strips having hot rolled exterior side surfaces characterized as being primarily or substantially free of all prior austenite grain boundaries, or at least primarily or substantially free of all prior austenite grain boundaries, and including elongated surface structure. As a result, because the prior austenite grain boundaries are not primarily or substantially present, all such prior austenite grain boundaries are not susceptible to grain boundary etching due to acid etching or pickling. In particular examples, the thin metal strips undergo hot rolling performed with a coefficient of friction equal to or greater than 0.20 with or without use of lubrication.
Owner:NUCOR CORP
Electrolytic microfinishing of metallic workpieces
InactiveUS8070933B2Quick cutQuick removalCellsMachining electric circuitsElectrolytic agentSurface finish
The invention is an electrolytic microfinishing process which utilizes a conductive tool as a cathode and a conductive workpiece as an anode both connected to a power supply. Electrolytic fluid is pumped between the tool and workpiece, creating a decomposition of the workpiece surface allowing the surface of the workpiece to be removed or wiped away by the interaction of the flowing electrolyte and rotation of the tool without generating any heat at a rate significantly faster than any other known machining process. The tool has no contact with the workpiece and accordingly, requires very low clamping loads to hold the workpiece in the spindle during the finishing operation. Due to the low clamping loads, the distortion of the workpiece is completely eliminated. Modulating the power supply during the work cycle allows the use of a single tool for both roughing and finishing as a continuous cycle to significantly provide surface finishes previously unobtainable.
Owner:THIELENHAUS MICROFINISH
Ultra-high strength weathering steel for hot-stamping applications
PendingUS20210087650A1Improve formabilityImproved strength propertyFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSteel platesCarbon alloy
Disclosed herein is a light-gauge, ultra-high strength weathering steel sheet with a composition, material properties, and surface characteristics that make it suitable for hot-stamping applications and making hot-stamped products. Also disclosed herein is a high friction rolled carbon alloy steel strip free of prior austenite grain boundary depressions and having a smear pattern. Still further disclosed herein is a high friction rolled carbon alloy steel strip that has been surface homogenized to provide a thin cast steel strip free of a smear pattern.
Owner:NUCOR CORP
High friction rolling of thin metal strip
Described herein are thin metal strips having hot rolled exterior side surfaces characterized as being primarily or substantially free of all prior austenite grain boundaries, or at least primarily or substantially free of all prior austenite grain boundaries, and including elongated surface structure. As a result, because the prior austenite grain boundaries are not primarily or substantially present, all such prior austenite grain boundaries are not susceptible to grain boundary etching due to acid etching or pickling. In particular examples, the thin metal strips undergo hot rolling performed with a coefficient of friction equal to or greater than 0.20 with or without use of lubrication.
Owner:NUCOR CORP
Treated inorganic particulate material for improving performance of construction and assembly compounds
InactiveUS20190055406A1Improve workabilitySmooth surface finishPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsCompound aSurface finish
A composition for use as a construction compound is disclosed. The composition may include an inorganic particulate material treated with at least one surface treatment. The surface treatment may include at least one of a fatty acid, a salt thereof, or an ester thereof, silicone oil, silane, or siloxane. The construction compound may improve the workability and / or surface finish of a construction compound. Methods are also provided, including a method for improving the efficiency of application of a construction compound to a drywall joint.
Owner:IMERYS USA INC
Bird Scooter Amusement Device
InactiveUS20090107416A1Improve usabilitySmooth surface finishOther apparatusTaming and training devicesBeak shapeEngineering
The invention is a low center of gravity animal toy. The toy is a scooter type device that includes a cross bar mounted on a pedestal. The cross bar is knurled for extra grip and enables an animal, usually a large bird, to grip the cross bar with their beak and scooter over a surface. Safe and fun interactive and solo play for parrots or other animals is provided.
Owner:HANDAL PATRICIA M
Method of fabricating small dimensioned lens elements and lens arrays using surface tension effects
ActiveUS8007695B2Smooth surface finishGood optical performanceOptical articlesLensMolten stateMulti material
A method is disclosed of implementing lens elements or lens arrays having dimensions ranging from a few centimeters down to the micro-scale or nano-scale using the surface tension of the lens material in a molten state to allow the curved shape of the lens to be precisely defined. The method has useful application in the fabrication of lens elements and lens arrays out of a large variety of material types, including elemental materials, as well as compound materials and alloys. The method also allows the implementation of lenses having far superior surface smoothness compared to other approaches, as well as very accurate lens shapes. The method allows the making of high quality lenses and lens arrays, wherein the diameter of the lenses are on the order of a few microns or less. Convex, concave, plano-convex, plano-concave, compound lenses, and many other types of lens shapes can be implemented using the method of the present invention.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
Coating soluble tooling inserts
ActiveUS10538019B2Reduce surface tensionSmooth surface finishCoatingsTubular articlesPolymer scienceKnife blades
The surface of a tooling insert is coated with a polymer layer having a low surface energy in order to cover surface irregularities and thereby provide a smooth surface against which a composite part may be compression molded.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com