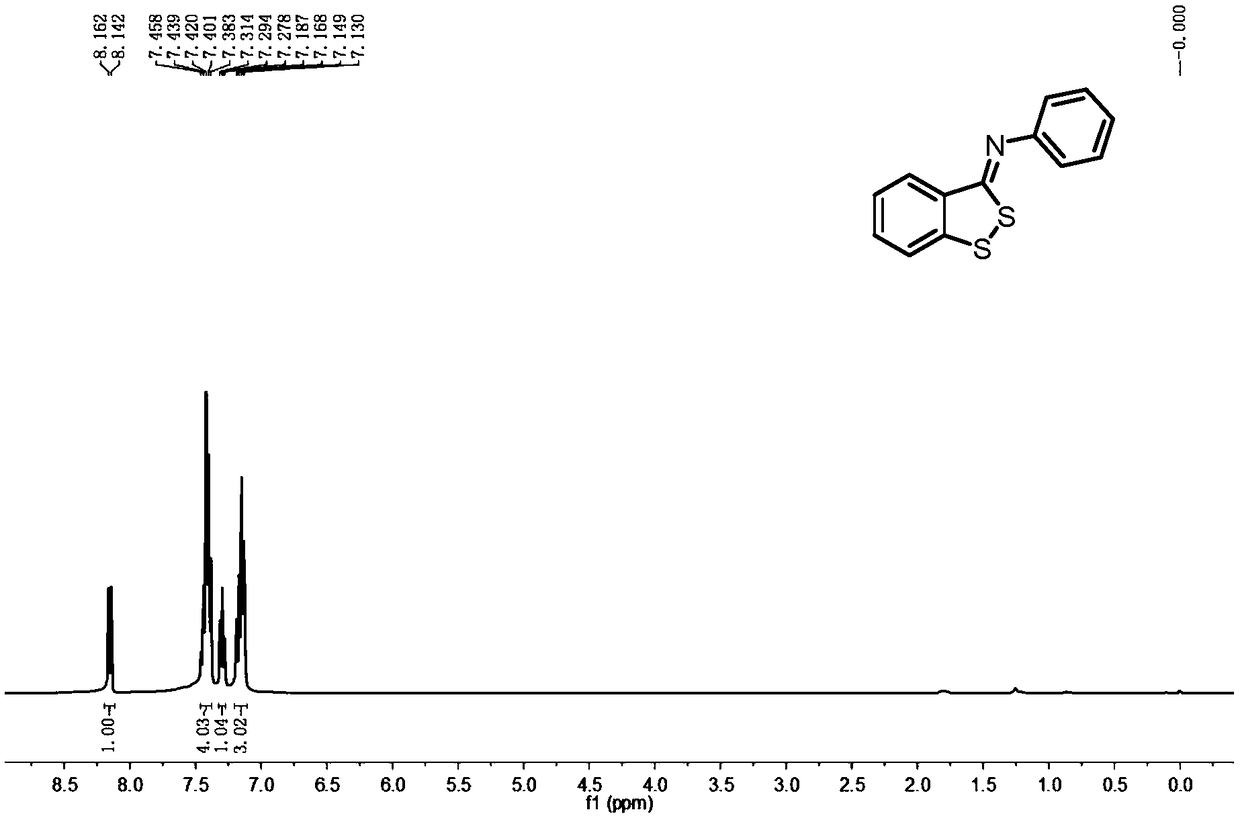
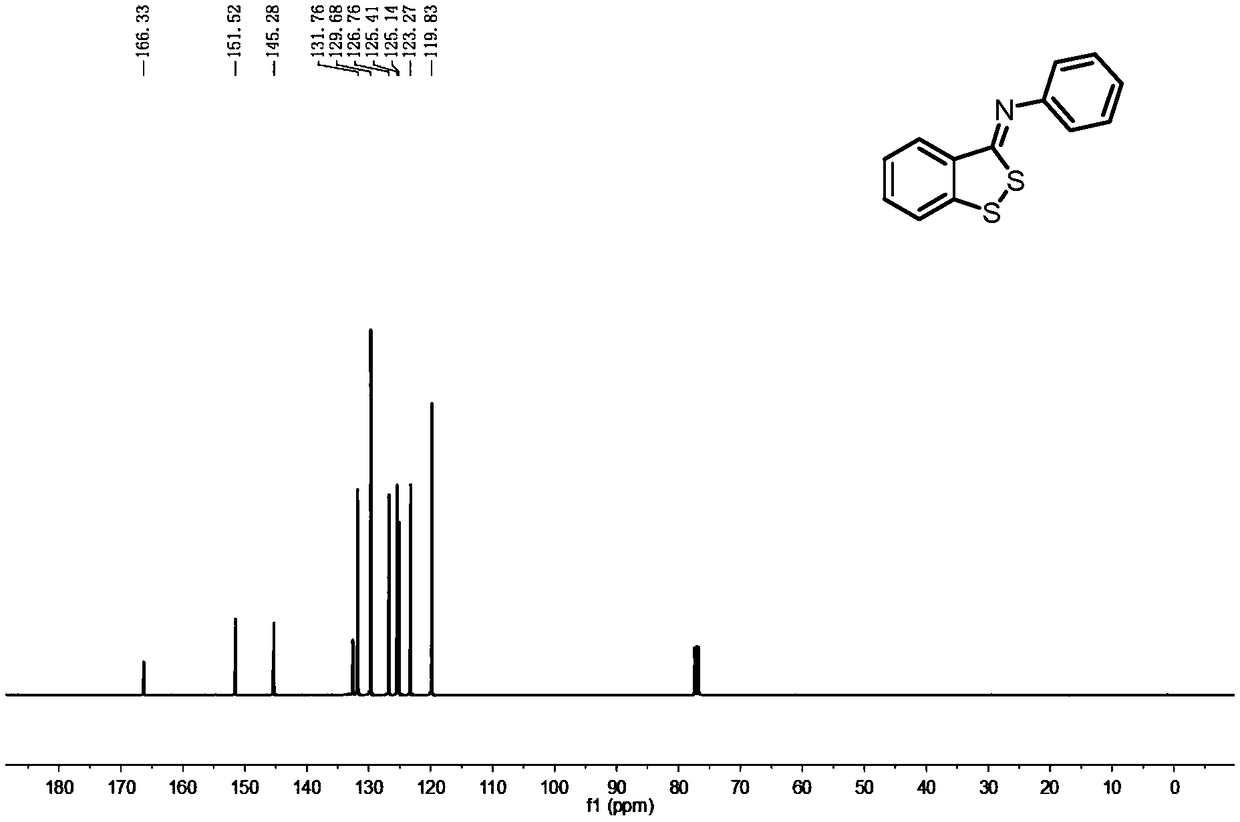
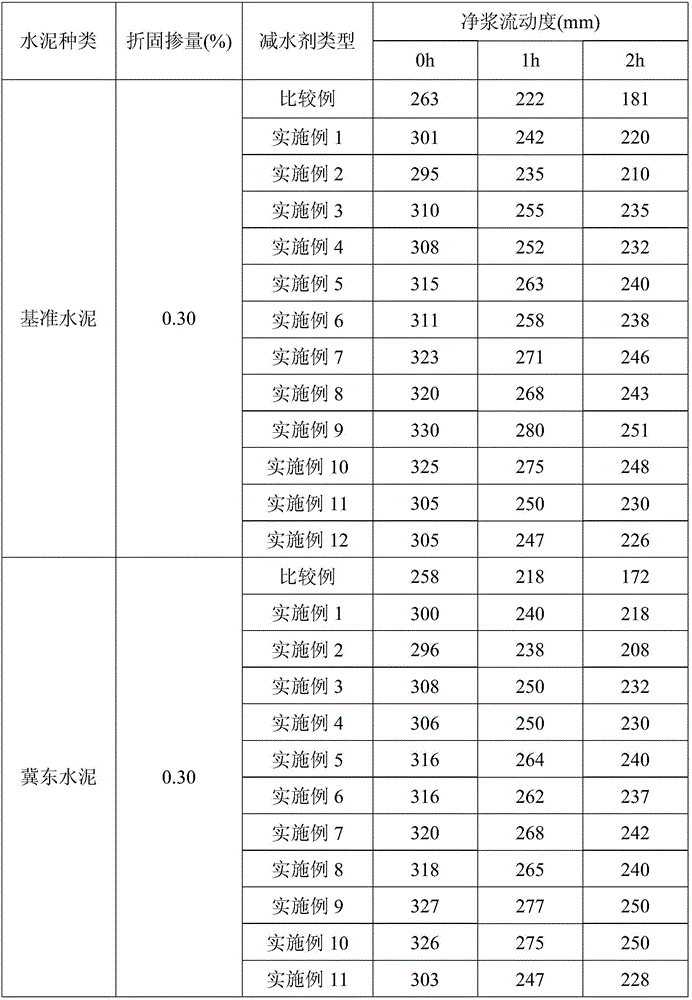
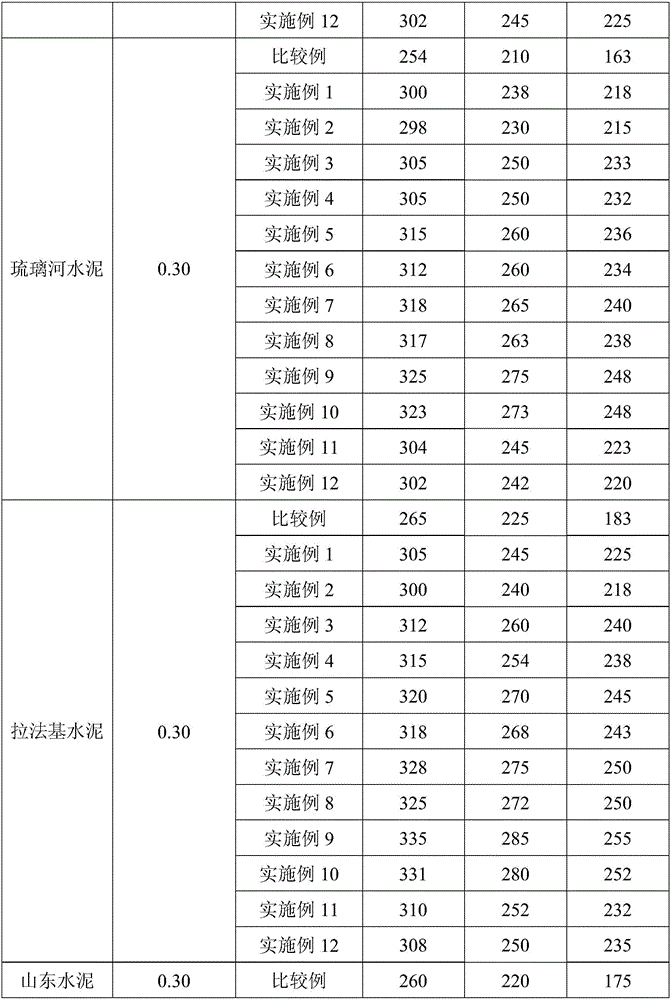
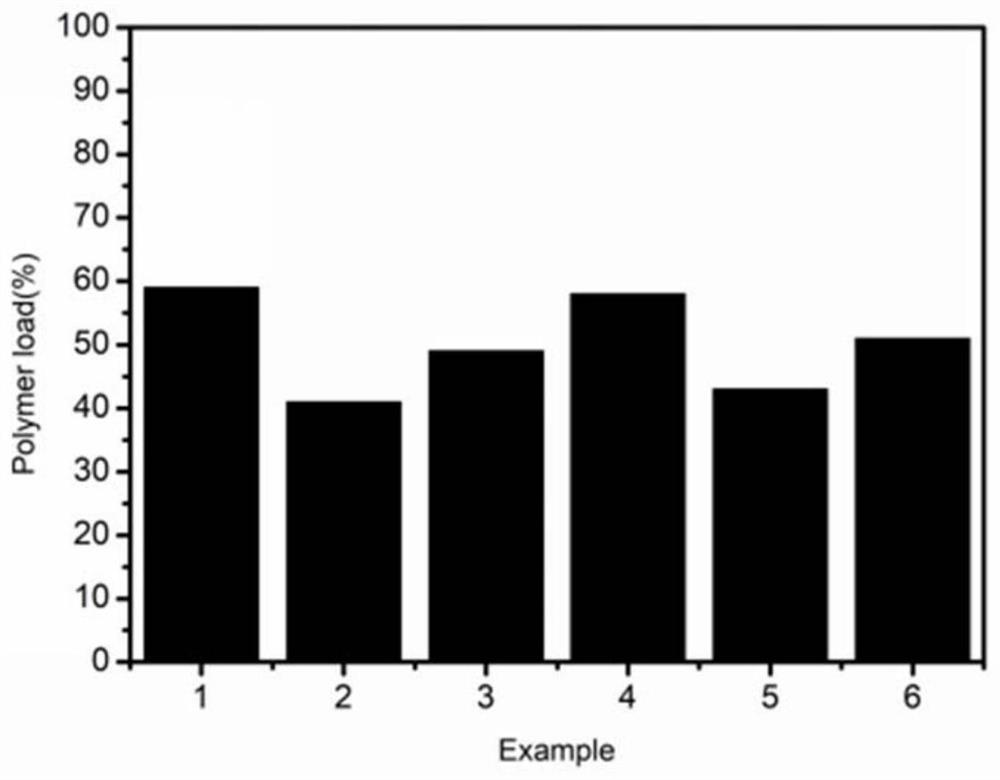
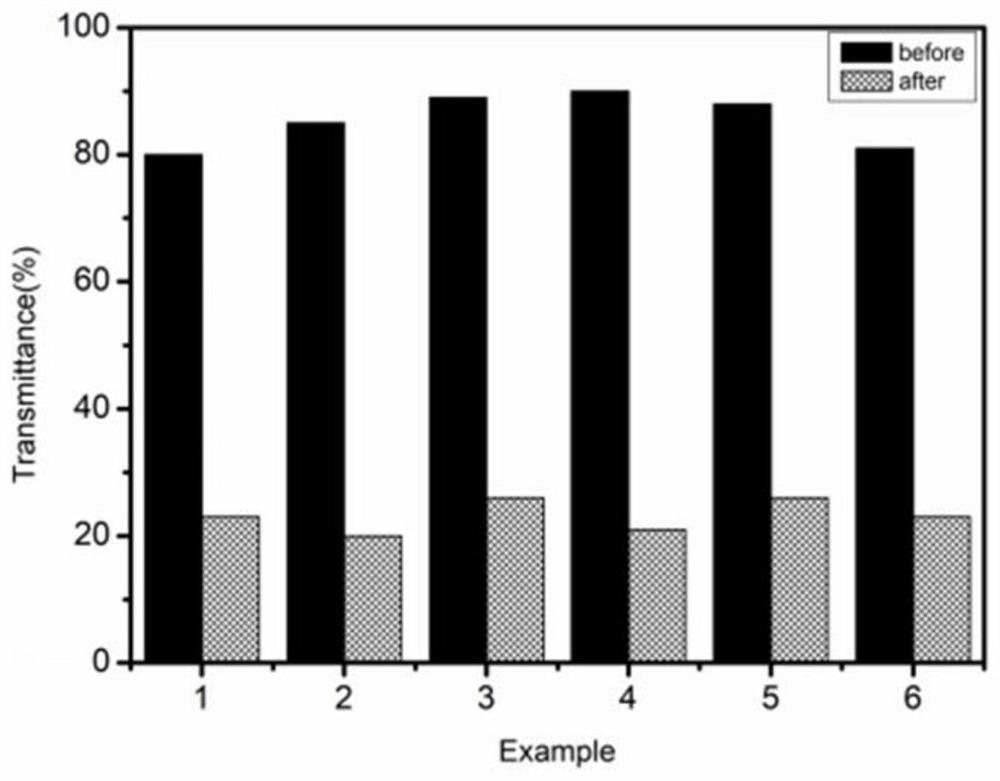
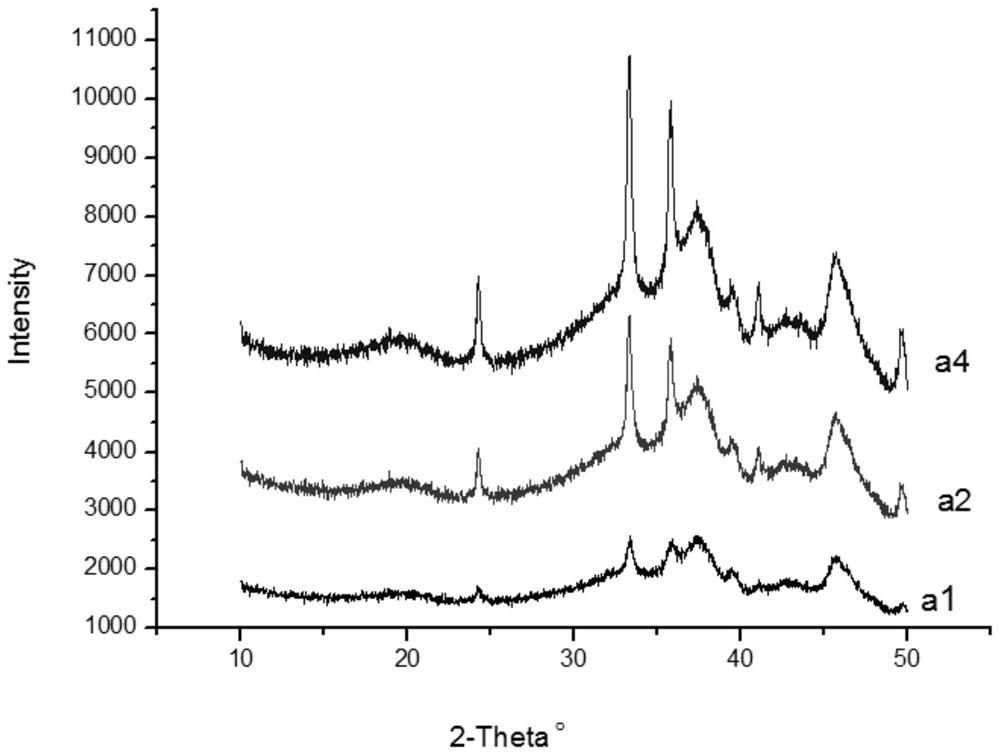
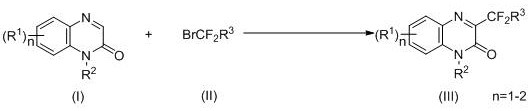Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41results about How to "Rich synthetic methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
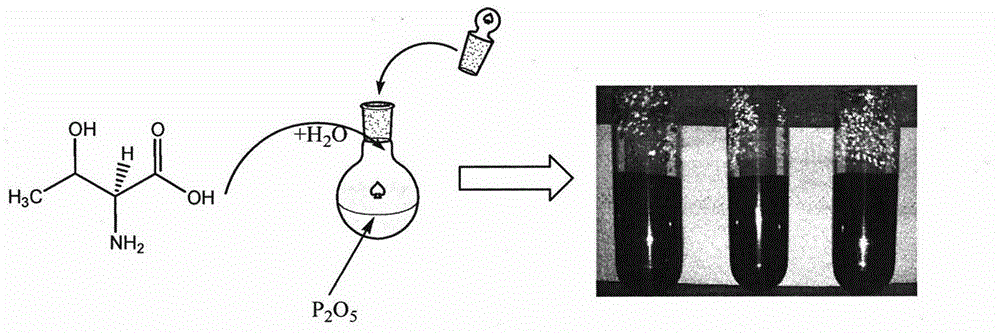
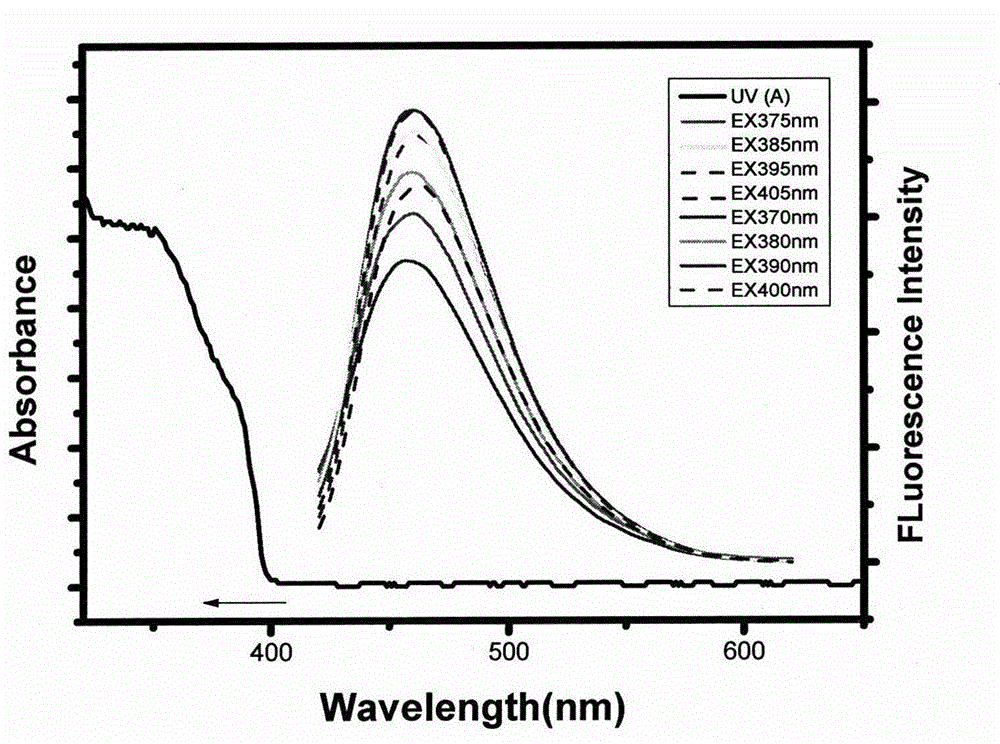
Method for synthesizing carbon quantum dots by using amino acid as precursor and application of carbon quantum dots in detection of metal ion concentration
InactiveCN104787744ALow fluorescence quantum yieldStrong fluorescence quantum yieldNanoopticsFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldSolubility
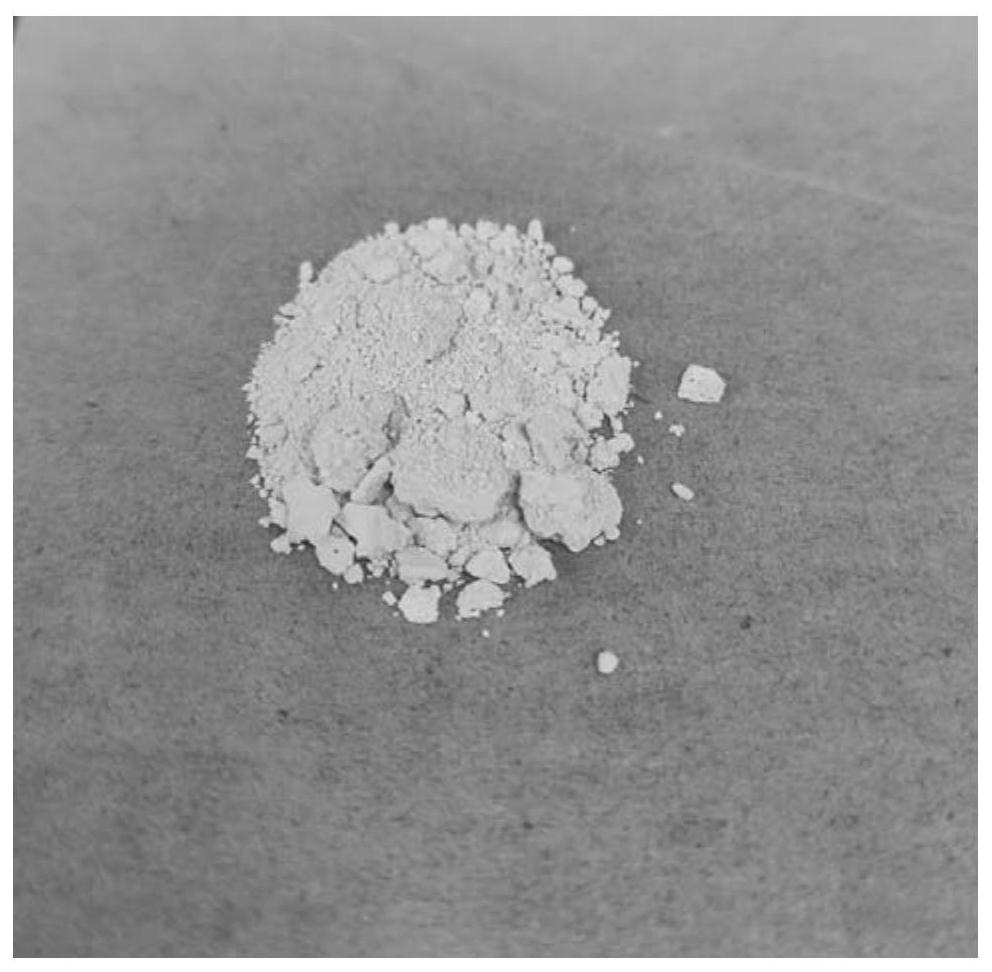
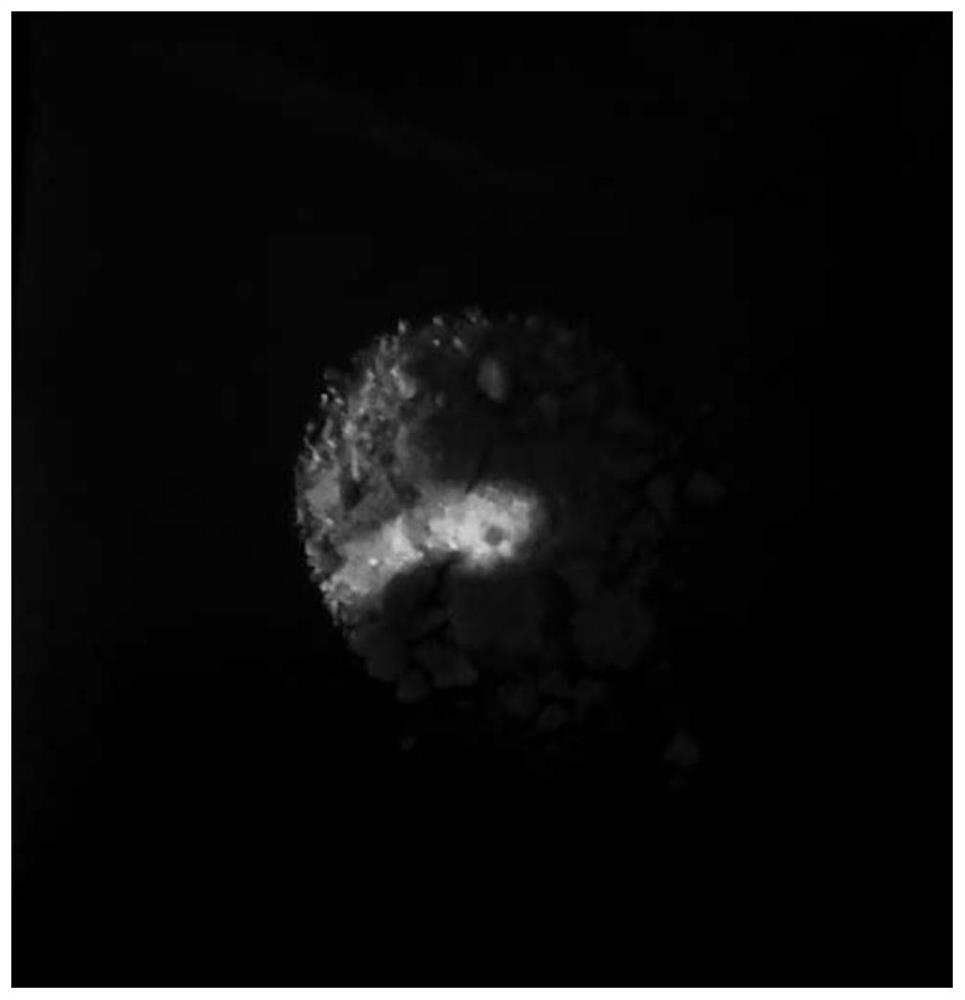
The invention relates to a preparation method of carbon quantum dots based on amino acid and an application of carbon quantum dots in direct detection of metal ion concentration. The method comprises the following specific steps: uniformly mixing amino acid and distilled water, rapidly adding the uniformly-mixed solution (amino acid is dissolved in distilled water) into a round-bottom flask filled with phosphoric pentoxide, rapidly plugging the bottleneck so as to obtain water-soluble carbon quantum dots, and applying the prepared carbon quantum dots in detection of metal ion concentration by a fluorescence quenching method. The synthetic method provided by the invention has a simple process, and reagents and raw materials are green and nontoxic. The prepared carbon quantum dots have characteristics of high quantum yield, strong light stability, good water-solubility and the like. Based on the quantum dots, a simple, rapid and sensitive method for metal ion quantitative detection can be established.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
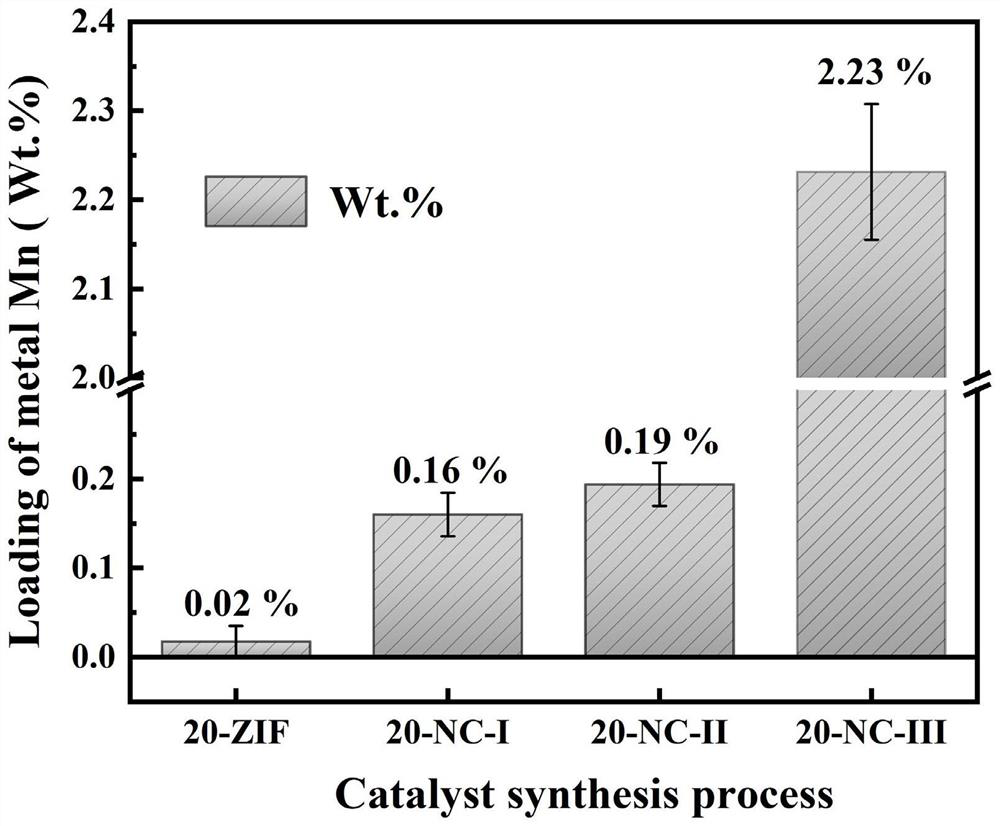
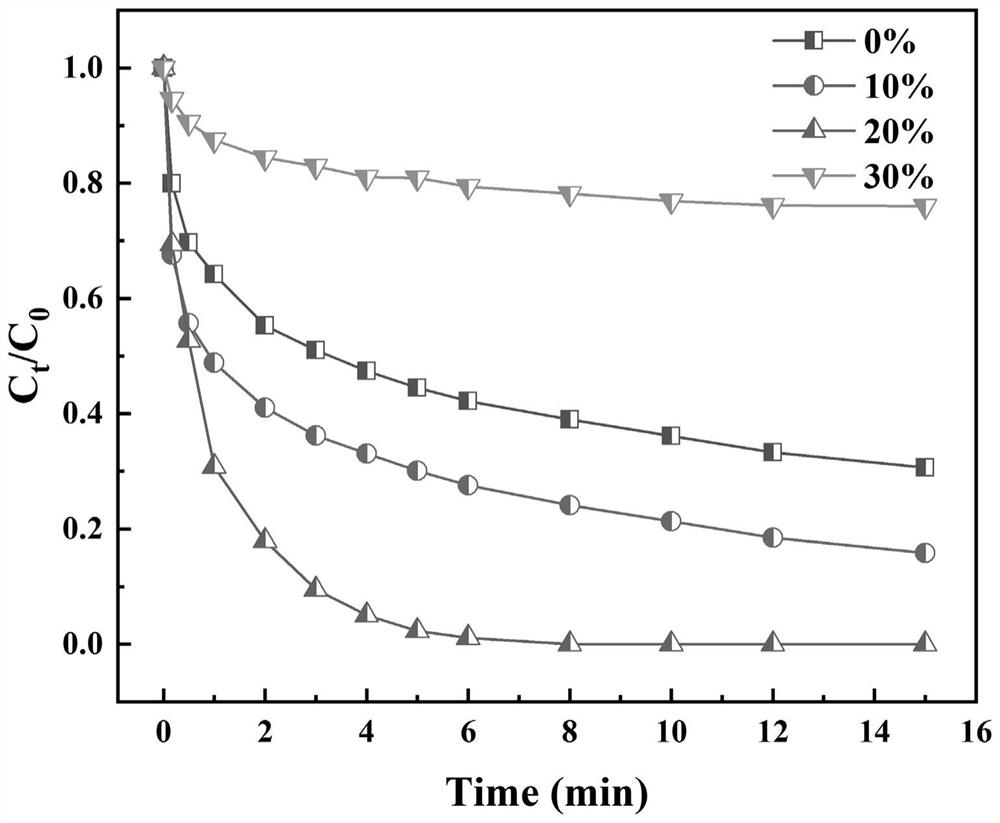
Preparation method of novel carbon-based material loaded transition metal monatomic catalyst
InactiveCN112973754ARich Synthetic MethodsIncrease loadPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater contaminantsPtru catalystHomogeneous catalysis
The invention discloses a preparation method of a novel carbon-based material loaded transition metal monatomic catalyst, and relates to the field of nano material heterogeneous catalysis. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing a DMF solution of a zinc salt and a transition metal salt with a DMF solution of 2-methylimidazole, carrying out heat preservation and centrifugal drying to obtain an M-ZIF-8 precursor, and finally synthesizing the novel carbon-based loaded transition metal monatomic catalyst through synthesis steps of three-step calcination, acid leaching and re-dispersion adsorption. According to the invention, an efficient transition metal monatomic catalyst synthesis method is provided, and the carbon-based material loaded transition metal monatomic catalyst is successfully applied to a reaction system for activating and degrading phenolic compounds by persulfate for the first time; and by taking transition metal Mn as an example, the synthesis method is found to be capable of effectively improving the loading capacity of monatomic metal of the transition metal and efficiently activating persulfate to degrade phenolic compounds, so that a good material basis and a good modification method are provided for application of heterogeneous Fenton-like catalytic reaction in the aspect of wastewater treatment.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of novel zinc monatomic catalyst loaded on carbon-based material
InactiveCN111715203ARich Synthetic MethodsIncrease loadWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystHomogeneous catalysis
The invention discloses a preparation method of a novel zinc monatomic catalyst loaded on a carbon-based material, and relates to the field of nano material heterogeneous catalysis. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing a methanol precursor solution composed of cobalt nitrate dissolved by magnetic stirring and 2-methylimidazole, carrying out a magnetic stirring reaction for1 h to obtain a precursor ZIF-8, and subjecting the dried ZIF-8 to calcining and ammoniation to synthesize the zinc monatomic catalyst Zn@NC-1100 DEG C loaded on the carbon-based material. The invention provides a concise zinc monatomic catalyst synthesis method, and a Zn-based material is successfully applied to a persulfate Fenton reaction system for the first time. Meanwhile, the novel zinc monatomic catalyst is high in atom loading capacity and can efficiently catalyze a persulfate Fenton reaction, so that organic pollutants are continuously mineralized. A good material basis and a good modification method are provided for the application of heterogeneous Fenton-like catalytic reaction in the aspect of wastewater treatment.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
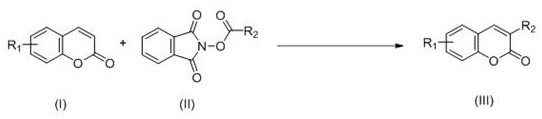
Synthesis method of C-3 alkyl substituted coumarin derivative
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a C-3 alkyl substituted coumarin derivative. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: dissolving a coumarin derivative shown as a formula (I),an N-alkyloxyphthalimide compound shown as a formula (II), a photocatalyst and a proton acid in an organic solvent; reacting under visible light irradiation at a temperature of 20 to 60 DEG C for 3 to36 hours; after the reaction is finished, performing post-treatment on a reaction system to obtain a target product of the C-3 alkyl substituted coumarin derivative shown as a formula (III), whereinthe reaction formulas are shown in the description; in the formulas (I) and the formula (III), the substituent R1 is H, methyl, methoxy, fluorine, chlorine or bromine; in the formula (II) and the formula (III), the substituent R2 is linear alkyl or naphthenic alkyl of with 1 to 8 carbon atoms. The synthesis method realizes the C-3alkylation of coumarin with light as reaction energy, makes the reaction safer, more environmentally friendly and cheaper, expands the application range of the reaction substrate, and enriches the synthesis method of a C-3 substituted coumarin compound.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of nitrogen-modified porous carbon-coated cobalt nanoparticle catalyst
InactiveCN111715254AImprove dispersibility and stabilityImprove transfer efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater contaminantsMeth-Nitrogen gas
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nitrogen-modified porous carbon-coated cobalt nanoparticle catalyst, and relates to the field of Fenton-like catalysis of nano materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: methanol and a 2-methylimidazole solution dissolved by magnetic stirring and manual oscillation are adopted as precursor solutions, are fully mixed, andare subjected to standing and reaction to generate a ZIF-67 precursor, and the precursor is calcined under the protection of nitrogen to obtain the Co@NC-900 DEG C catalyst. The nitrogen-modified porous carbon-coated cobalt nanoparticle catalyst obtained through ZIF-67 derivation has a better phenol degrading effect than single Co particles and single nitrogen-modified porous carbon activated potassium hydrogen persulfate. Meanwhile, the electrochemical impedance of the novel Co@NC-900 DEG C catalyst is lower, and the TOC removal rate is higher. A good material basis and a good modification method are provided for the application of heterogeneous sulfuric acid free radical heterogeneous catalysis in the aspect of water treatment.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
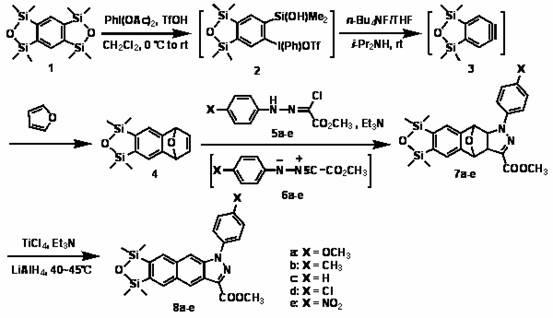
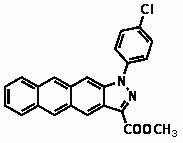
Naphtho-/anthra-pyrazole derivative and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN102603785ARich synthetic methodsHigh quantum yieldSilicon organic compoundsCycloadditionCombinatorial chemistry
The invention relates to a naphtho- / anthra-pyrazole derivative and a synthetic method thereof. The structure of a compound is shown in the specifications, wherein X is OCH3, CH3, H, Cl or NO2. The naphtho- / anthra-pyrazole derivative is synthesized through twice cycloaddition reactions and a deoxygenization reaction, the requirement of an atom economy reaction is met, a brand new thought is provided for the establishment of a naphtho- / anthra-pyrazole framework, and a synthetic method of an organic heterocyclic compound is enriched. The synthetic method of the naphtho- / anthra-pyrazole derivative disclosed by the invention is not reported yet.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
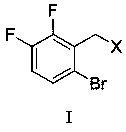
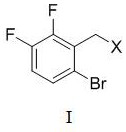
(6-bromo-2, 3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses (6-bromine-2, 3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide and a preparation method thereof. The chemical structural formula of the (6-bromine-2, 3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide is shownin the description; the preparation method of the (6-bromine-2, 3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide comprises the following steps: using 6-bromine-2, 3 difluorobenzyl halogen and phenyl disulfide shown in the first formula as reaction raw materials, using preparing the (6-bromine-2, 3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide according to the first formula, using tetrahydrofuran as a solvent, carrying out nucleophilic substitution reaction under the action of a reducing agent and alkali, and synthesizing to obtain the (6-bromine-2, 3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide; in the first formula, X represents chlorine, bromine or iodine. The (6-bromine-2, 3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide has the advantages of high selectivity, high yield, simple operation and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Synthesis method of alpha-F-beta-OH-carbonyl compound
ActiveCN109734571AReact greenLow costOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationSynthesis methodsSolvent
The invention discloses a synthesis method of an alpha-F-beta-OH-carbonyl compound. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: dissolving an unsaturated ketone compound shown in formula (I) and an N-F reagent in a reaction solvent, reacting for 5 to 25 hours at the temperature of 30 to 100 DEG C, after the reaction is ended, performing the after-treatment for a reaction solution to obtainan alpha-F-beta-OH-carbonyl compound as shown in formula (II), wherein the reaction formula is shown as follows: (shown in the description) In formula (I) and (II), substituent groups R1 and R2 are respectively independently selected from phenyl, substituted phenyl, thienyl or furyl; and the substituent group of the substituted phenyl is at least one of C1 to C3 alkyl, C1 to C3 alkoxy, nitro, trifluoromethyl, fluorine, chlorine and bromine. The N-F reagent is used as a fluorine source and Lewis acid, no additional catalyst is used, so that the reaction is more environment-friendly, and the cost is lower; and the method for synthesizing the alpha-F-beta-OH-carbonyl compound provided in the invention has the advantages of easy availability of raw materials, mild reaction conditions, no needof other catalysts, good reaction selectivity, simplicity in operation and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of benzodithiocyclopentadiene derivative
The invention discloses a preparation method of a benzodithiocyclopentadiene derivative. Benzodithiocyclopentadiene is synthesized by reacting S8 as a sulfur source with 2-bromothioamide. The synthesis method provides a cheap, easily available and environment-friendly synthesis method for synthesis of benzodithiocyclopentadiene compounds, adopts a green and environment-friendly reaction system, obtains products easy to be separated and purified, is suitable for synthesizing various highly functionalized benzodithiocyclopentadiene compounds, is particularly suitable for large-scale industrial production, and can prepare high-purity benzodithiocyclopentadiene compounds at high efficiency and high yield.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
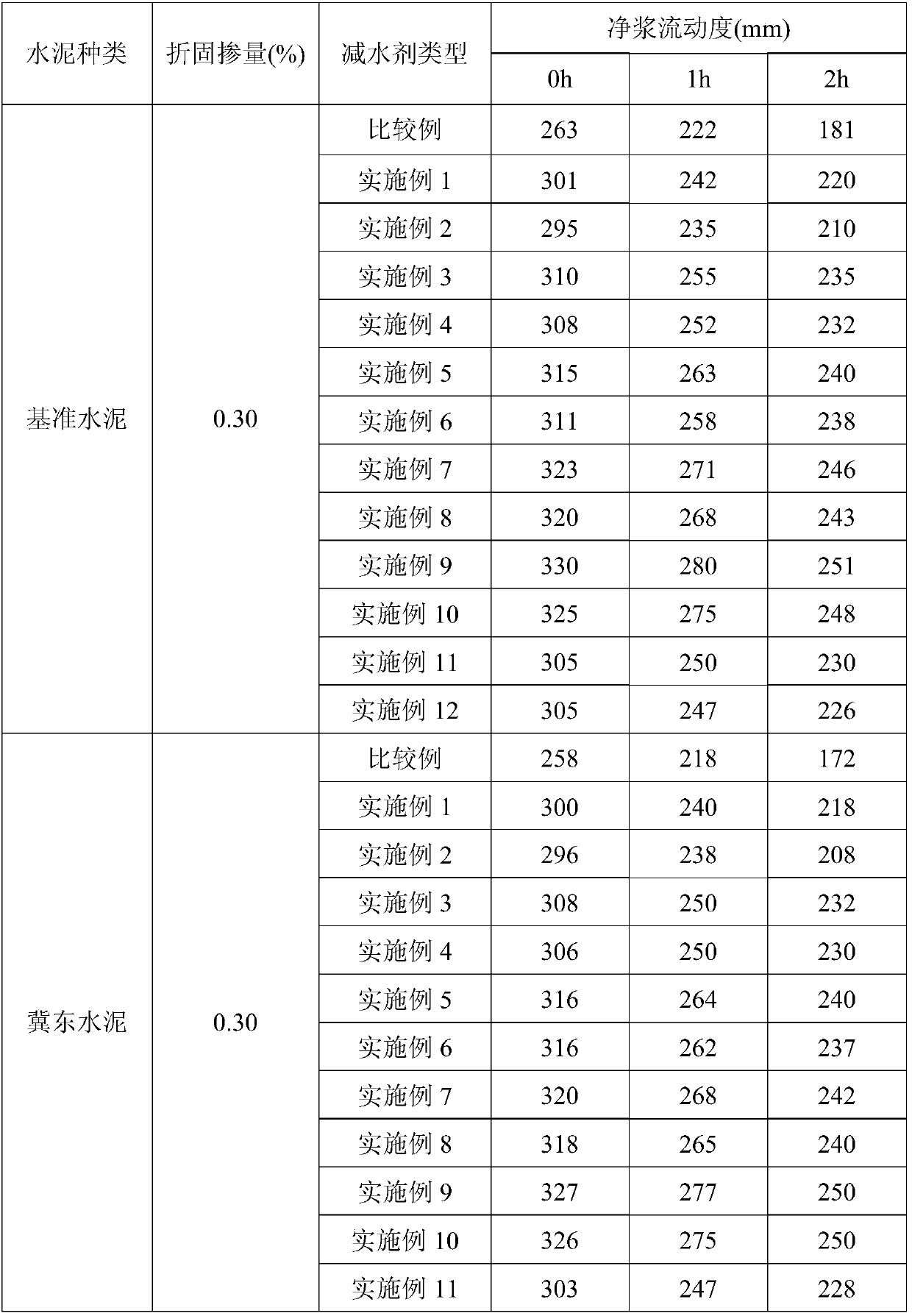
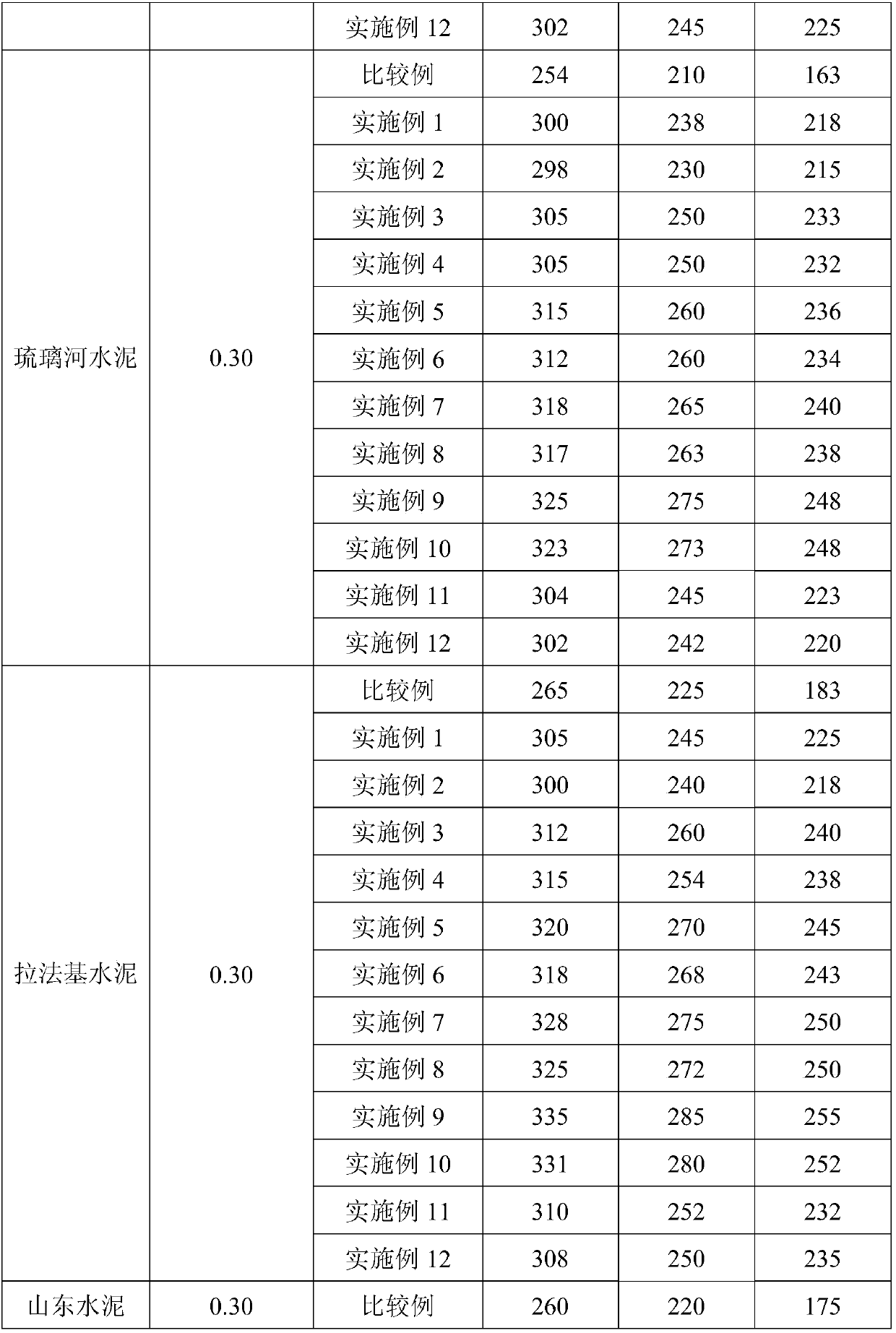
Method for preparing macro-monomer synthesized polycarboxylate water reducer through alcoholysis of alkenyl-acyl chloride
ActiveCN106117461AExpand the theoretical connotationThe polymerization process is mild and stableIonEther
A method for preparing a macro-monomer synthesized polycarboxylate water reducer through alcoholysis of alkenyl-acyl chloride belongs to the field of water reducers. The method comprises the following steps: firstly polymerizing a cationic chain, and then reacting with the alkenyl-acyl chloride, thus obtaining a macro-monomer; then carrying out copolymerization on the macro-monomer and a carboxylic acid micro-monomer, i.e., polymerizing under an oxidization-reduction initiating system formed by high-valence cerate and alcohols by taking an unsaturated cationic quaternary ammonium salt monomer as a reactant, thus obtaining a terminal hydroxyl cationic long chain; then respectively enabling the terminal hydroxyl cationic long chain and polyethylene glycol monomothyl ether to react with the alkenyl-acyl chloride respectively, thus preparing macro-monomers with different structures; then carrying out free radical polymerization on the macro-monomers and unsaturated carboxylic acid micro-monomers, thus obtaining the macro-monomer composite polycarboxylate water reducer. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the macro-monomers with different structures and functions are successfully synthesized through ways of polymerizing the cationic chain and respectively reacting with the alkenyl-acyl chloride by combining polyether, and a novel comb-structure polycarboxylate water reducer which takes a polycarboxyl acid as a main chain and the cationic long chain and the polyether as polybasic side chains can be finally obtained. A reaction technology is simple and easy, and multiple excellent effects of retaining slump through reducing water, resisting clay, and the like are realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
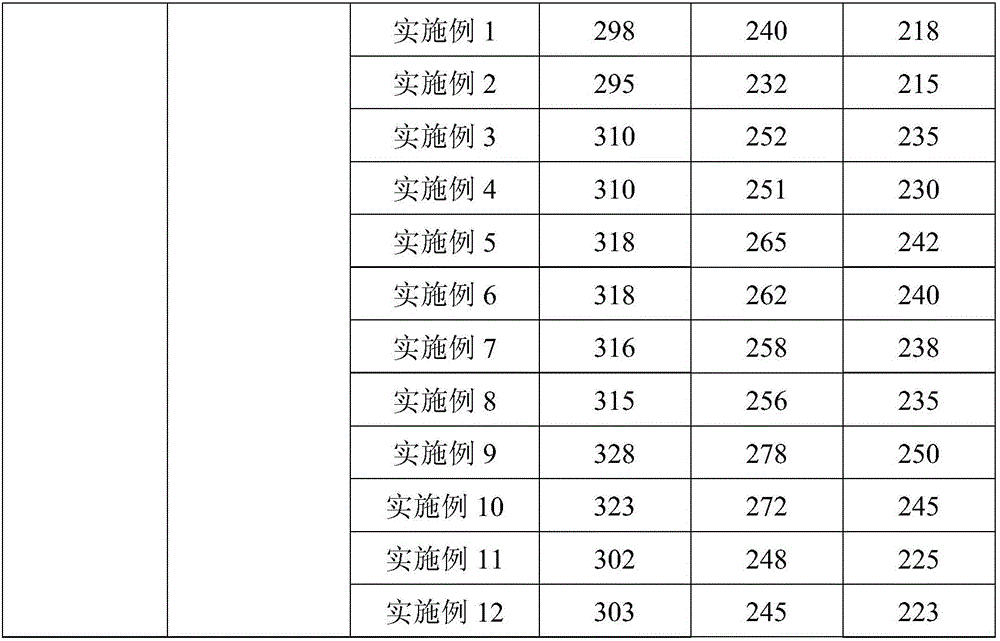
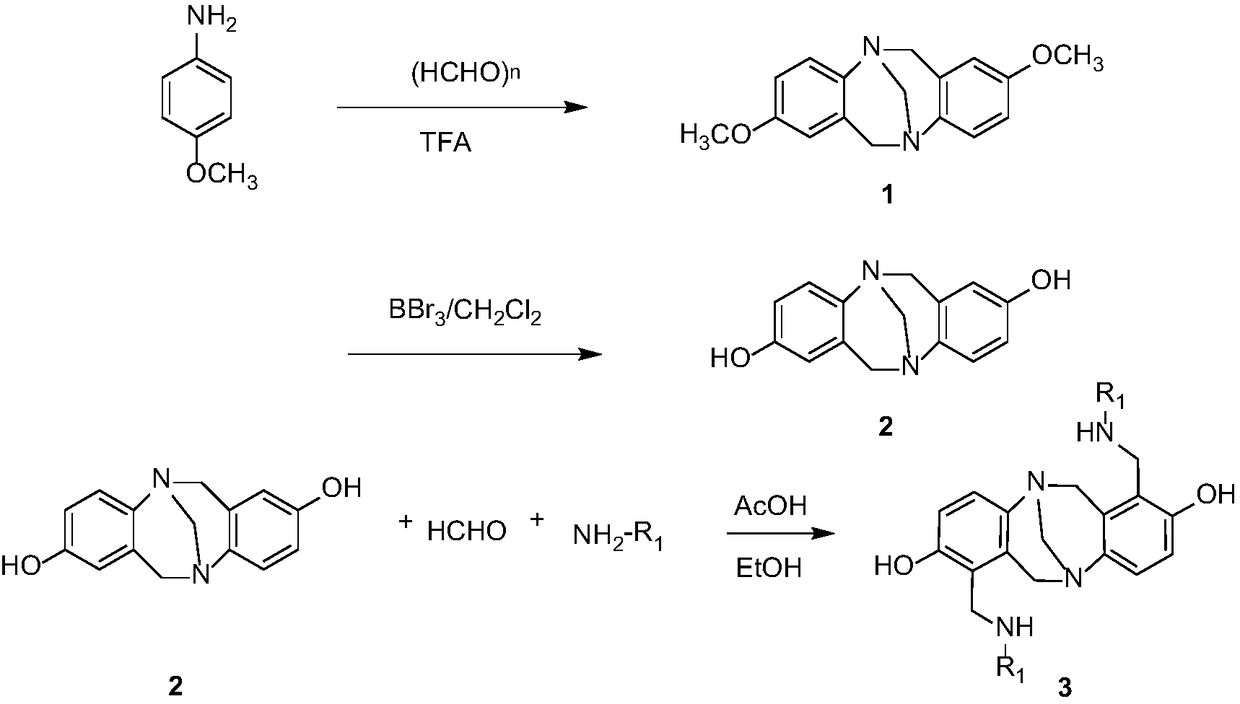
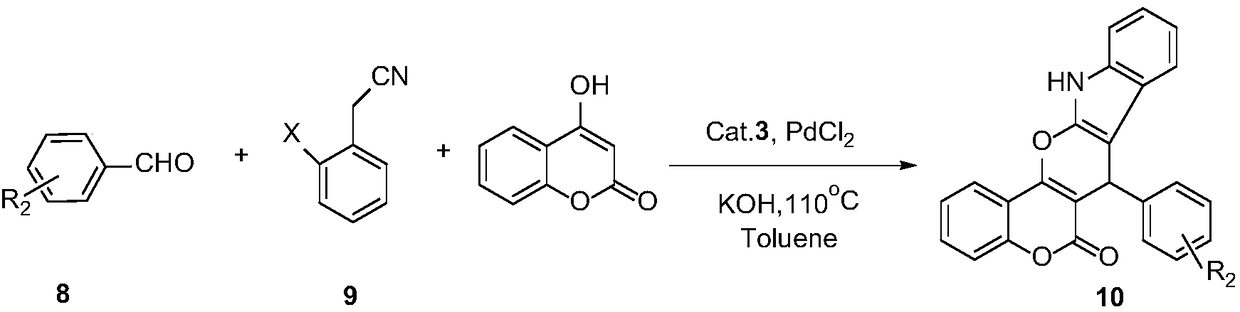
Preparation and application of 1,7-disubstituted aminomethyl-2,8-dyhydroxy-Troger's Base catalyst
ActiveCN109305970ARich synthetic methodsImprove featuresAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryBenzyl cyanideHydrolysis
The invention discloses preparation and application of 1,7-disubstituted aminomethyl-2,8-dyhydroxy-Troger's Base catalyst. P-methoxyaniline and paraformaldehyde are taken as raw materials and are subjected to reaction including hydrolysis, Mannich and the like to synthesize the 1,7-disubstituted aminomethyl-2,8-dyhydroxy-Troger's Base catalyst base derivative; the compound is taken as catalyst tocatalyze addition reaction taking 4-hydroxycoumarin and benzyl cyanide as raw materials, and one series of pyranoid ring derivative is synthesized. According to the invention, the substrate range of the pyranoid ring derivative is widened, and the application range of TB on the aspect of catalysis is widened.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Synthesis method of alpha, alpha-difluoro-gamma-hydroxyacetamide derivative
ActiveCN112574056AReact SafeReact greenOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationOrganic baseAniline
The invention discloses a synthesis method of an alpha, alpha difluoro gamma hydroxyacetamide derivative, which comprises the following steps: dissolving a bromo difluoro acetanilide compound shown ina formula (II), a photocatalyst and an organic alkali in an olefin derivative shown in a formula (I), reacting at room temperature for 5-24 hours under the irradiation of visible light, and after thereaction is finished, filtering to obtain the alpha, alpha difluoro gamma hydroxyacetamide derivative. A reaction system is subjected to post-treatment to obtain the alpha, alpha difluoro gamma hydroxyacetamide derivative shown in the formula (III), and the reaction formula is shown in the specification, in the formula (I) and the formula (III), a substituent group R1 is C2-C11 linear alkyl, arylor substituted aryl; in the formula (II) and the formula (III), the substituent R2 is H, methyl, methoxy, fluorine, chlorine, bromine or aromatic heterocycle. According to the invention, light is used as a reaction energy source to realize hydroxylation of olefin acetamide, so that the reaction is safer and greener, the cost is lower, the substrate application range of the reaction is expanded, and a simpler and more convenient method for preparing the alpha, alpha-difluoro gamma-hydroxyacetamide compound is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing anthraquinone through anthracene oxidation method
ActiveCN108610250AHigh activitySufficient raw materialsQuinone preparation by oxidationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSolid phasesIncipient wetness impregnation
The invention discloses a method for preparing anthraquinone through an anthracene oxidation method. The catalyst formula is prepared by the following steps: taking gamma-Al2O3 as a carrier, taking oxides of Fe and Zr as active ingredients, and preparing Fe-gamma-Al2O3 and Zr-gamma-Al2O3 single supported catalysts and a Fe / Zr / gamma-Al2O3 bi-supported catalyst by utilizing an incipient-wetness impregnation method. The product is analyzed by adopting an ultra performance liquid chromatograph, the catalytic performance of the catalyst in a reaction of synthesizing anthraquinone through the anthracene oxidation method is analyzed, and the catalyst is characterized by adopting XRD (X-Ray Diffraction) and other means. The invention tries to develop a solid phase catalyst, and the method is capable of preparing the anthraquinone through catalytic oxidation of anthracene under normal pressure and low-temperature (70 DEG C) conditions, and has the advantages of being low in energy consumption,low in cost, environmental-friendly and the like.
Owner:长沙赢睿知识产权运营有限公司
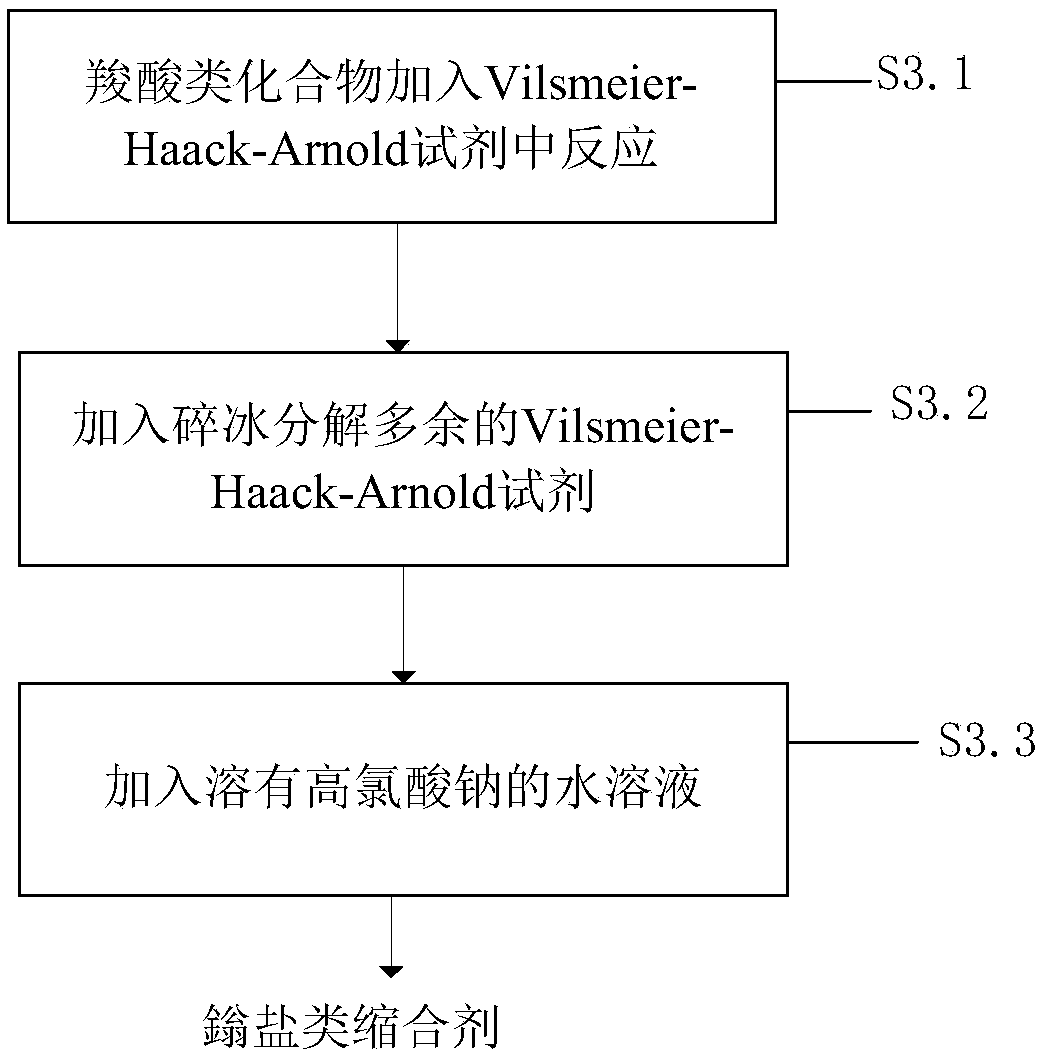
Method for synthesizing pyrazole compound based on WK (Willgerodt-Kindler) reaction and VHA (Vilsmeier-Haack-Arnold) reaction
InactiveCN107556243AReasonable synthetic routeThe method is simple and reliableOrganic chemistryChemistryAldehyde
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a pyrazole compound based on WK (Willgerodt-Kindler) reaction and VHA (Vilsmeier-Haack-Arnold) reaction. The method comprises the steps that an acyl compound is taken as a raw material to synthesize a carboxylic compound through the WK reaction; a VHA reagent is prepared; the carboxylic compound is added into the VHA reagent to synthesize an oniumsalt condensing agent; the onium salt condensing agent is hydrolyzed to obtain an aldehyde compound; the aldehyde compound is reacted with hydrazine hydrate to obtain the pyrazole compound. The methodhas the advantages that the synthetic route is reasonable, the method is stable and reliable, the synthetic efficiency is high, and the carboxylic compound, the onium salt condensing agent, the aldehyde compound and the pyrazole compound can be obtained simultaneously; the method has wide application prospect and huge commercial value, enriches the variety of inorganic and organic compounds as well as the synthetic method in the inorganic and organic field.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
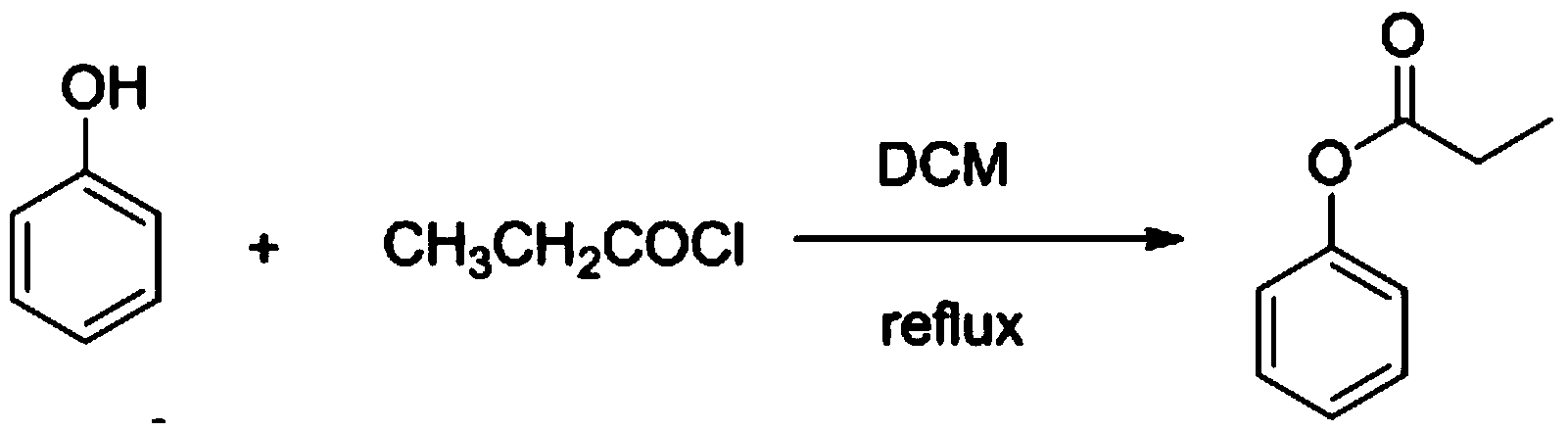
Method for synthesizing p-hydroxypropiophenone
InactiveCN104370727AEasy to operateReaction follow-up processing is easyPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesOrganic compound preparationSolventP-hydroxypropiophenone
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing p-hydroxypropiophenone. The method specifically comprises the following steps: adding phenol and an organic solvent into a reactor, then adding a weak alkali, and adding a propionyl chloride reagent under heating reflux, wherein the reflux reaction time is 4h-6h; pouring into ice water after the reaction, regulating the pH to 6-8 with an alkaline solution, further extracting a reaction solution with the organic solvent for a plurality of times, and drying to evaporate out the solvent to obtain a product, namely propionyl phenol; putting a certain mount of propionyl phenol and methanesulfonic acid in a dry reaction container, wherein the heating temperature is 30-90 DEG C and the reaction time is 0.5-2h; and pouring a reaction solution into a certain amount of ice water, regulating the pH to 6-7 with a weak alkali reagent, further extracting with the organic solvent for a plurality of times, and drying to evaporate out the solvent to obtain a final product. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation, mild reaction conditions and simple post-treatment, and a catalyst is low in price and easy to obtain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
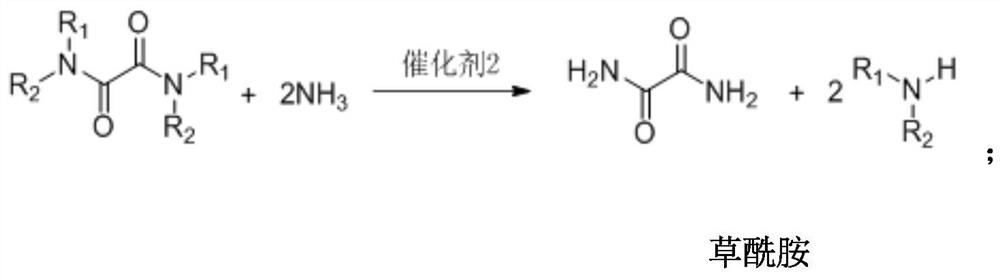
A kind of preparation method of oxamide
ActiveCN110041218BRich synthetic methodsPerfectly compatibleOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationAntifungalPtru catalyst
The present invention provides a kind of preparation method of oxamide, and this preparation method comprises the following steps: with CO, O 2 and amine compounds as raw materials, under the action of catalyst 1, oxidative carbonylation to prepare intermediate oxamide derivatives, and then under the action of catalyst 2, aminolysis of oxamide derivatives to prepare oxamide. The invention uses a brand-new method to co-produce oxamide and oxamide derivatives, which solves the problems of toxic oxalate synthesis raw materials and low catalyst efficiency in the original technology of synthesizing oxamide through aminolysis of oxalate. In addition, the process for synthesizing oxamide derivatives has good substrate applicability and can be used in fields such as medicine, pesticides, synthetic ligands, and food additives.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for preparing anthraquinone by anthracene oxidation using a starch-modified catalyst
ActiveCN108393090BHigh activityLow costQuinone preparation by oxidationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAnthraquinonesAnthracene
Owner:山东金泰淀粉股份有限公司
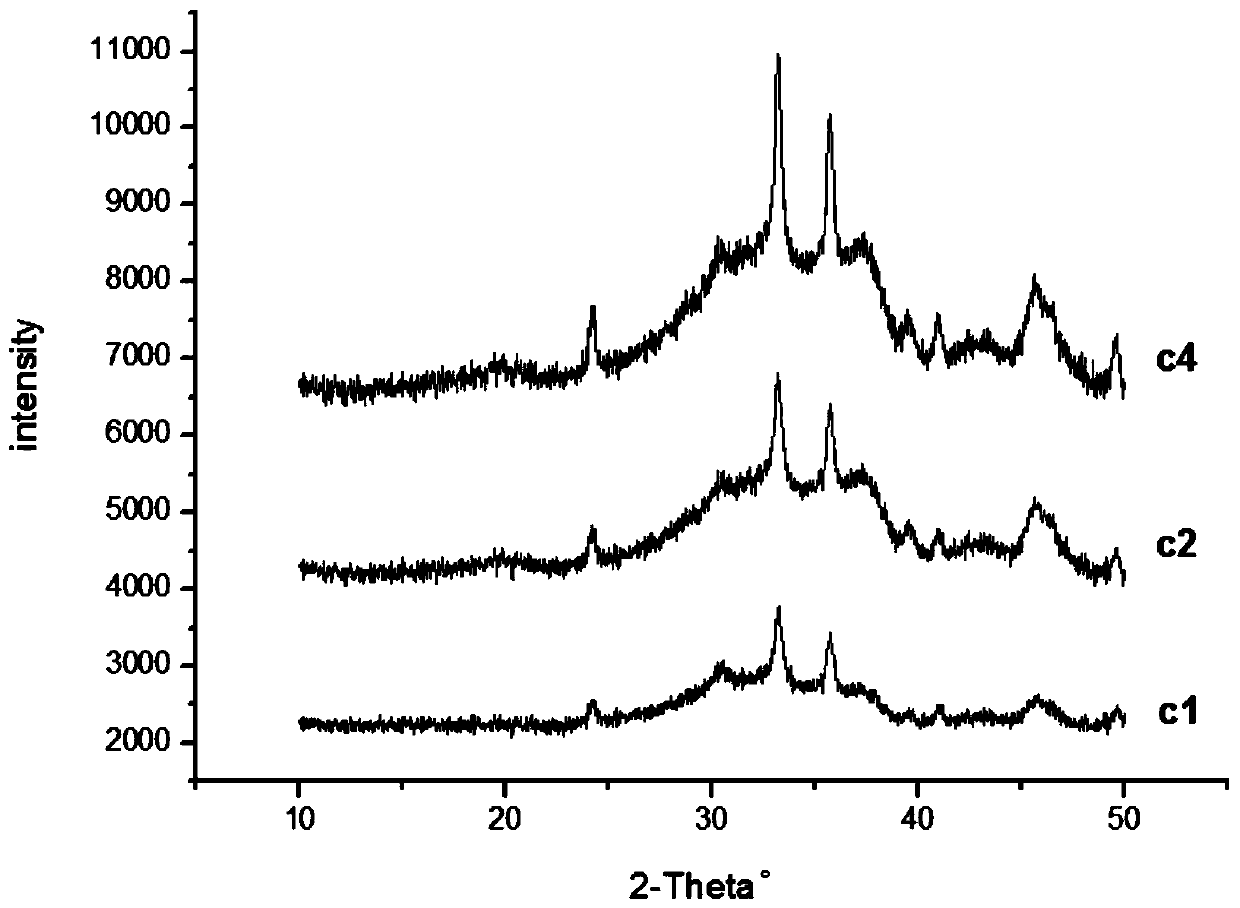
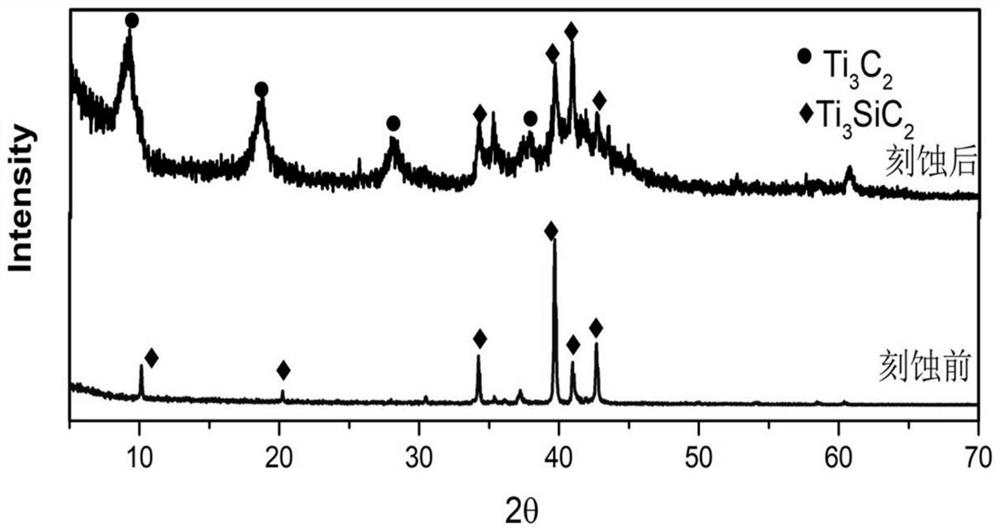
Method for preparing two-dimensional material Ti3C2 by taking Ti3SiC2 as precursor
The invention discloses a method for preparing a two-dimensional material Ti3C2 by taking Ti3SiC2 as a precursor, and the specific scheme is as follows: the precursor material Ti3SiC2 is firstly pre-oxidized at low temperature for a period of time, and then is etched in an HF chemical environment to prepare the two-dimensional material Ti3C2. The method is simple and easy to implement, the synthesis method of the Ti3C2 two-dimensional material is enriched, the cost of the adopted precursor raw material is lower, the preparation process is controllable, and the synthesized material can be applied to the fields of supercapacitors, batteries, catalysis and the like.
Owner:CHUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of benzodithiocyclopentadiene derivatives
ActiveCN109503547BEasy to separate and purifyRich synthetic methodsOrganic chemistryBiochemical engineeringCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
c 3 n 4 Synthesis method, product and application of quantum dot room temperature phosphorescent material
ActiveCN111825068BRich synthetic methodsNanoopticsNitrogen and non-metal compoundsMaterials sciencePhosphorescence
The invention discloses C 3 N 4 The synthesis method, product and application of quantum dot room temperature phosphorescent material. The synthesis method is to use urea or other urea-like small molecules as raw materials, and carry out high-temperature solid-phase reaction in a high-pressure reactor. The obtained product is gray-white powder with solid-phase fluorescence. At the same time, it can continuously emit blue-green phosphorescence visible to the naked eye for 3-6s at room temperature; its preparation method is simple, does not contain harmful metals, and is a new type of room temperature phosphorescent material; it has potential in 3D printing, anti-counterfeiting, decoration, imaging and other fields application value.
Owner:广安长明高端产业技术研究院
A kind of synthetic method of C-3 alkyl substituted coumarin derivatives
The invention discloses a synthesis method of C-3 alkyl-substituted coumarin derivatives, which combines the coumarin derivatives represented by the formula (I), the coumarin derivatives represented by the formula (II) N ‑alkanoyloxyphthalimide compound, photocatalyst and protonic acid are dissolved in an organic solvent, and reacted at 20‑60°C for 3‑36 h under visible light irradiation. After the reaction, the reaction system After post-processing, the C-3 alkyl-substituted coumarin derivative target product shown in formula (III) is obtained; the reaction formula is as follows: In formula (I) and formula (III), the substituent R 1 Is H, methyl, methoxy, fluorine, chlorine or bromine; in formula (II) and formula (III), substituent R 2 It is C1-C8 linear alkyl or cycloalkyl. The invention realizes the C-3 alkylation of coumarin by using light as the reaction energy, makes the reaction safer, greener, and lower in cost, expands the scope of application of the substrate of the reaction, and enriches the coumarins substituted by C-3 Compound synthesis method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of synthetic method of c-3 difluoromethyl substituted quinoxalinone derivatives
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a C-3-position difluoromethyl-substituted quinoxalinone derivative. The method comprises the steps of dissolving a quinoxalinone derivative, a bromodifluoromethyl compound, a photocatalyst, an inorganic base and an organic amine in an organic solvent for a reaction for 6-36 hours at the temperature of 20-60 DEG C under the irradiation of visible light;after the reaction is finished, carrying out posttreatment on a reaction system to obtain a target product, namely the C-3-position difluoromethyl-substituted quinoxalinone derivative. According to the method, light is adopted as a reaction energy source to realize C-3 difluoro methylation of quinoxalinone, so that the reaction is safer, environmentally friendly and lower in cost, the applicationrange of reaction substrates is expanded, and synthesis methods of C-3 substituted quinoxalinone compounds are diversified.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
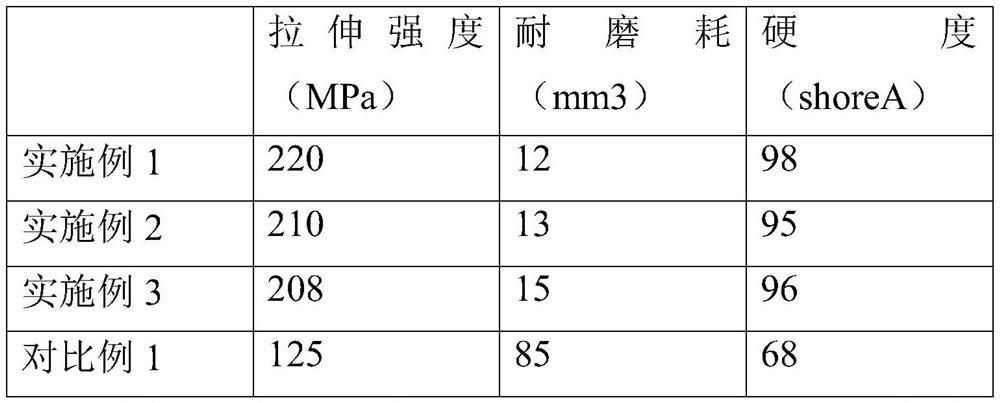
A kind of table edge surround material and preparation method thereof
The present application discloses a table edge surround material, the raw materials of which include by weight: 80-120 parts of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer, 40-50 parts of polyvinyl chloride, 20-60 parts of polytetrafluoroethylene, 5-5 parts of potassium sodium silicate 15 parts, 4-8 parts of blue alum, 3-9 parts of short polyester fiber, 4-8 parts of long glass fiber, 2-8 parts of nano calcium carbonate, 10-20 parts of wear-resistant enhancer, 4-8 parts of chain extender 15-25 parts of modified reinforcing agent A, 16-32 parts of modified reinforcing agent B. The present invention also proposes a preparation method of the above-mentioned table edge surrounding material. The table edge surround material prepared by the invention has excellent wear resistance, strength and toughness.
Owner:HANGZHOU HENGFENG FURNITURE
Alkenyl acid chloride alcoholysis to prepare the method of macromonomer synthesis polycarboxylate water reducing agent
ActiveCN106117461BAchieving a Transformation in Application PerformanceExtended Dionon Design-Structure-PropertySide chainPolyethylene glycol
A method for preparing a macro-monomer synthesized polycarboxylate water reducer through alcoholysis of alkenyl-acyl chloride belongs to the field of water reducers. The method comprises the following steps: firstly polymerizing a cationic chain, and then reacting with the alkenyl-acyl chloride, thus obtaining a macro-monomer; then carrying out copolymerization on the macro-monomer and a carboxylic acid micro-monomer, i.e., polymerizing under an oxidization-reduction initiating system formed by high-valence cerate and alcohols by taking an unsaturated cationic quaternary ammonium salt monomer as a reactant, thus obtaining a terminal hydroxyl cationic long chain; then respectively enabling the terminal hydroxyl cationic long chain and polyethylene glycol monomothyl ether to react with the alkenyl-acyl chloride respectively, thus preparing macro-monomers with different structures; then carrying out free radical polymerization on the macro-monomers and unsaturated carboxylic acid micro-monomers, thus obtaining the macro-monomer composite polycarboxylate water reducer. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the macro-monomers with different structures and functions are successfully synthesized through ways of polymerizing the cationic chain and respectively reacting with the alkenyl-acyl chloride by combining polyether, and a novel comb-structure polycarboxylate water reducer which takes a polycarboxyl acid as a main chain and the cationic long chain and the polyether as polybasic side chains can be finally obtained. A reaction technology is simple and easy, and multiple excellent effects of retaining slump through reducing water, resisting clay, and the like are realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method of synthesizing onium salt type condensation agent on the basis of WK reaction and VHA reaction
InactiveCN107602508AReasonable synthetic routeThe method is simple and reliableOrganic chemistryOrganic compoundRaw material
The invention discloses a method of synthesizing an onium salt type condensation agent on the basis on the basis of a Willgerodt-Kindler reaction and a Vilsmeier-Haack-Arnold reaction. The method includes the steps of synthesizing a carboxylic acid compound through the Willgerodt-Kindler reaction with an acyl compound as a raw material; preparing a Vilsmeier-Haack-Arnold reagent; adding the carboxylic acid compound to the Vilsmeier-Haack-Arnold reagent to synthesize the onium salt type condensation agent. The method has reasonable synthesis route and stable and reliable process, is high in synthesis efficiency, can be used for producing the carboxylic acid compound and the onium salt type condensation agent at the same time, has great application prospect and huge commercial value and enriches types of inorganic and organic compounds and synthesis methods in inorganic and organic fields.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Synthesis method, product and application of C3N4 quantum dot room-temperature phosphorescent material
ActiveCN111825068ARich synthetic methodsNanoopticsNitrogen and non-metal compoundsWhite powderQuantum dot
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a C3N4 quantum dot room-temperature phosphorescent material and a product and application thereof. The synthesis method comprises the following steps of:taking urea or other urea-like small molecules as raw materials and carrying out a high-temperature solid-phase reaction in a high-pressure reaction kettle to obtain a product which is grey white powder, has solid-phase fluorescence and can continuously emit macroscopic blue-green phosphorescence for 3-6 seconds at room temperature. The preparation method is simple, and the product contains no harmful metal and is a novel room-temperature phosphorescent material; and the C3N4 quantum dot room-temperature phosphorescent material has potential application value in the fields of 3D printing, anti-counterfeiting, decoration, imaging and the like.
Owner:广安长明高端产业技术研究院
Method for preparing environment-responsive polymers by composite assembly
ActiveCN112028536BSignificant magnetic intelligent response effectImprove directionPolymer scienceCross linker
The invention relates to a method for preparing an environment-responsive polymer by composite assembly. The present invention uses hydrophobic monomers, polysaccharide derivatives, etc. as the main reaction raw materials, and prepares a magnetic field responsive polymer through the method of first grafting polymerization, cross-linking reaction, and then compound assembly, that is, the hydrophobic monomers are first grafted and polymerized, and then The polysaccharide derivative and ferric iron tetroxide powder are cross-linked under the action of a cross-linking agent to obtain a hydrogel, and finally composite assembled to obtain a magnetic field-responsive polymer. The process of the invention is energy-saving and efficient, and the operation is simple. The magnetic field-responsive polymer is successfully prepared through the method of polysaccharide derivative hydrogel composite assembly of the branch structure polymer, which shows multiple effects such as excellent environmental response and maintaining the stability of the concrete volume, and realizes The goal of self-driven improvement of application performance of concrete materials has very good market competitiveness and application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +2
A kind of method that hydroxylamine sulfate and calcium oxide prepare caprylyl hydroxamic acid
ActiveCN106854166BEfficient preparationEfficient separationOrganic chemistryOctanoic AcidsHydroxamic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing octanohydroxamic acid from hydroxylamine sulfate and calcium oxide and belongs to the field of cosmetic raw material synthesis. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of adding quicklime into a hydroxylamine sulfate solution at a temperature of less than or equal to 10 DEG C, filtering away precipitated calcium sulfate, sequentially adding the quicklime and methyl caprylate, performing hydroxyl oximation reaction at 30-60 DEG C, recovering a solvent after 2-6h, cooling to 0 DEG C, adding 10% hydrochloric acid at the low temperature, regulating a pH (potential of hydrogen) value to 3-4, precipitating octanohydroxamic acid solid, performing filtering, water washing and dryness to form octanohydroxamic acid. The method is mild in reaction condition and high in yield; a product is good in purity; the cheap and readily accessible quicklime is used as alkali, so that the raw material cost is greatly lowered; and the method is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:禹城禹圳生物科技有限公司
(6-bromo-2,3-difluorobenzyl)phenyl sulfide and its preparation method
The invention discloses (6-bromo-2,3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide and a preparation method thereof, the chemical structural formula of (6-bromo-2,3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide As follows:; The preparation method of (6-bromo-2,3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide is: 6-bromo-2,3-difluorobenzyl halide and difluorobenzyl halide shown in formula (I) phenylene disulfide is used as a reaction raw material, tetrahydrofuran is used as a solvent, and under the action of a reducing agent and a base, the (6-bromo-2,3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide is synthesized through a nucleophilic substitution reaction; In formula (I), X represents chlorine, bromine or iodine. The preparation method of (6-bromo-2,3-difluorobenzyl) phenyl sulfide of the present invention has the advantages of high selectivity, high yield, simple operation and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for preparing anthraquinone by anthracene oxidation method
ActiveCN108610250BAchieve transformationHigh activityQuinone preparation by oxidationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAnthraquinonesAnthracene
The invention discloses a method for preparing anthraquinone by an anthracene oxidation method, wherein, the catalyst formula: γ-Al 2 o 3 As the carrier, Fe and Zr oxides are the active components, and the Fe-γ-Al is prepared by the equal volume impregnation method 2 o 3 , Zr‑γ‑Al 2 o 3 Single supported catalyst and Fe‑Zr / γ‑Al 2 o 3 dual-supported catalyst. The product was analyzed by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography, and the catalytic performance of the catalyst in the reaction of anthracene oxidation to anthraquinone was analyzed, and the catalyst was characterized by XRD and other means. The present invention attempts to develop a solid-phase catalyst to realize the catalytic oxidation of anthracene to prepare anthraquinone under normal pressure and low temperature (70° C.) conditions, and has the advantages of low energy consumption, low cost, and environmental friendliness.
Owner:长沙赢睿知识产权运营有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com